- Department of Pain Medicine, The Second Affliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
Background: The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) can cause herpes zoster (HZ), which may progress to postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), leading to severe inflammatory responses and pain.
Objective: This study investigates the relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in patients with herpes zoster-related pain, hypothesizing that persistent pain correlates with higher pain intensity compared to intermittent pain.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, China. Data from patients treated for herpes zoster-related pain between January 2019 and February 2024 were analyzed. Pain intensity was measured using the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS-11), and pain duration was categorized as intermittent or persistent. Multivariate regression models were used to assess the association between pain duration and intensity, adjusting for potential confounders.
Results: A total of 840 patients were included. Persistent pain was significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores compared to intermittent pain (β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.50–0.91, p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses showed that persistent pain was associated with higher pain intensity in both acute HZ and PHN patients (HZ: β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.45–0.96, p < 0.001; PHN: β = 0.76, 95% CI 0.40–1.13, p < 0.001). Inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell count, were positively correlated with pain intensity.
Conclusion: Pain duration significantly impacts pain intensity in HZ patients. Considering pain duration is crucial for effective pain management. Further research should explore the mechanisms underlying persistent pain to develop better treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) typically spreads through respiratory droplets and direct contact. When reactivated from its latent state in the dorsal root ganglia, VZV can cause herpes zoster (HZ), leading to immune and inflammatory responses around the nerves, resulting in severe pain (1–3). With an aging population, the health burden associated with VZV is expected to increase, posing a significant global health issue (4). It manifests as a painful rash and can lead to chronic pain conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which is defined as dermatomal pain persisting at least 90 days after the appearance of the acute herpes zoster rash (5). Without vaccination, the lifetime risk of HZ is 30% (6). The burden of pain associated with HZ is substantial, affecting not only physical functioning but also psychological well-being and overall quality of life (7–9). The burden of PHN, however, can be even more severe, as it often becomes chronic and refractory to standard treatments, significantly impairing patients’ quality of life, physical functioning, and psychological well-being, and leading to long-term disability and emotional distress (5). Effective management of herpes zoster-related pain is therefore a critical aspect of patient treatment.
The management of pain duration is a crucial component of pain management. Pain intensity and pain duration have been shown to significantly impair quality of life and mental health (10–13). High pain intensity or prolonged pain duration can negatively impact patients’ muscular function (14), and the duration of neuropathic pain may affect the efficacy of pharmacological treatments (15). Baseline pain duration can also influence patient referrals (16). Despite its clinical importance, the relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in herpes zoster-related pain remains underexplored. Most existing studies focus on the prevalence and risk factors of PHN (17–19), with limited attention to how pain duration affects pain intensity across different stages of HZ.
Understanding the factors that influence pain intensity is crucial for developing targeted and effective pain management strategies. Previous studies have indicated that the relationship between pain intensity and perceived duration is complex, with high-intensity stimuli (high pain) potentially leading to a longer perceived duration (20). Conversely, when the perceived duration of a pain stimulus is misled to be shorter, the perceived pain intensity may decrease (21). In patients with knee osteoarthritis, some studies suggest that intermittent pain is generally associated with lower pain intensity, while persistent pain may correlate with higher pain intensity (22). However, other studies indicate that intermittent pain can be more severe than persistent pain (23). Therefore, larger sample studies are needed to clarify these discrepancies in the literature. Additionally, previous studies have highlighted the need for comprehensive pain assessments that consider not only intensity but also the duration and type of pain (22). Pain duration characteristics are also used in diagnosing chronic pain conditions (24). The pain experience is multifaceted, influenced by factors such as gender, BMI, and comorbidities (22). However, there is a paucity of evidence on the specific impact of pain duration characteristics, such as intermittent versus persistent pain, on pain intensity in HZ and PHN patients. Different diseases and pain management strategies define pain duration characteristics variably, and their impact on pain is not uniformly concluded (25–28).
Given these gaps in the literature, this study aims to investigate the relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in patients with herpes zoster-related pain. We hypothesize that patients experiencing persistent pain will report higher pain intensity, as measured by the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS-11), compared to those with intermittent pain. This study aims to provide valuable insights into the complexity of herpes zoster-related pain, enhancing the understanding of the mechanisms underlying herpes zoster-related pain, and offering strategies to improve pain management, thereby improving treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients affected by this debilitating condition.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and ethical approval
This retrospective study was conducted at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University and received approval from the hospital’s Ethics Committee [2024-KY(0510)]. Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. The study adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines (29).
2.2 Study population
Patients treated for herpes zoster-related pain at the Pain Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University between January 2019 and February 2024 were considered eligible. Each patient was included in the analysis only once. Herpes zoster-related pain includes both acute pain associated with HZ and PHN. HZ is characterized by a painful, unilateral vesicular rash in a dermatomal distribution, occurring during the active phase of varicella-zoster virus reactivation. PHN, on the other hand, is defined as dermatomal pain persisting for at least 90 days after the appearance of the acute herpes zoster rash. Exclusion criteria included patients with mental illnesses affecting accurate pain assessment and those with incomplete or missing records.
2.3 Data collection
Data were extracted from the hospital’s pain virtual ward system, electronic medical records, hospital information system, and laboratory information system. This comprehensive data source ensured data integrity and traceability, jointly managed by the Pain Department and the Information Department.
2.4 Collected variables
2.4.1 Basic patient information
Data collected included body mass index (BMI), gender, age, marital status, smoking history, and alcohol use history.
2.4.2 Pain-related information
Pain location: Specific areas of HZ pain were documented.
Pain intensity: Measured using the NRS-11, where patients rated their pain on a scale from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain) (30).
Pain type: Classified using the DN4 questionnaire and the Chinese version of the Neuropathic Pain Diagnostic and Treatment Assessment Scale, encompassing types like burning, pins and needles, electric shock, tingling, itching, and others (tearing pain, throbbing pain, pulling pain, twitching pain, and aching pain) (31, 32).
Pain duration characteristics: Categorized as intermittent or continuous pain, with continuous pain defined as pain persisting throughout the day and intermittent pain having significant relief periods within a day.
Allodynia: Documented as pain due to a stimulus that does not normally provoke pain (33).
Laboratory data: Collected from fasting peripheral venous blood samples, including globulin, albumin, hemoglobin, C-reactive protein (CRP), cystatin C, platelet count, red blood cell count, urea, and white blood cell count.
Charlson comorbidity index (CCI): Used to assess comorbidities such as myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, moderate/severe renal disease, tumor, leukemia, lymphoma, moderate/severe liver disease, metastatic tumor, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) (34, 35).
2.5 Data usage statement
All data used in this study were sourced from the pain virtual ward system, electronic medical record system, hospital information system, and laboratory information system of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, and were extracted following an information security review and approval. These data will be used for further analyses, including identifying additional risk factors, developing pain prediction models, and analyzing pain trajectories. To ensure academic integrity and data transparency, we declare that subsequent studies may continue to use the same or updated datasets to facilitate comparison and comprehensive analysis of different research outcomes.
2.6 Statistical analysis
All analyses were conducted utilizing R Statistical Software (Version 4.2.2, http://www.R-project.org, The R Foundation) and Free Statistics analysis platform (Version 1.8, Beijing, China). Continuous data were summarized as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR). Categorical variables were represented as frequencies and percentages. Missing values were noted for several variables, with the majority being below 5%. Given the low proportion of missing data and its occurrence primarily in covariates, no special handling was performed for missing values (36).
For continuous data with normal distribution, independent samples t-tests were used for comparisons between two groups; for non-normally distributed continuous data, Mann–Whitney U tests were used. Categorical variables were compared using Pearson chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact tests. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant, and results were presented as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI).
Univariate linear regression models were first used to assess the relationship between baseline variables and NRS-11 scores. Variables with p < 0.05 in the univariate analysis were considered for inclusion in the multivariate model (Model 2). Model 2 adjusted for age, BMI, smoking status, pain type, albumin, hemoglobin, CRP, cystatin C, and white blood cell count. To ensure a comprehensive adjustment for potential confounders, Model 3 included all variables from Model 2 and additional demographic and clinical factors: gender, marital status, alcohol use, CCI, presence of allodynia, and pain location. Subgroup analyses were conducted to examine the association between pain duration characteristics and NRS-11 scores within specific patient subgroups, including those with HZ and PHN.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
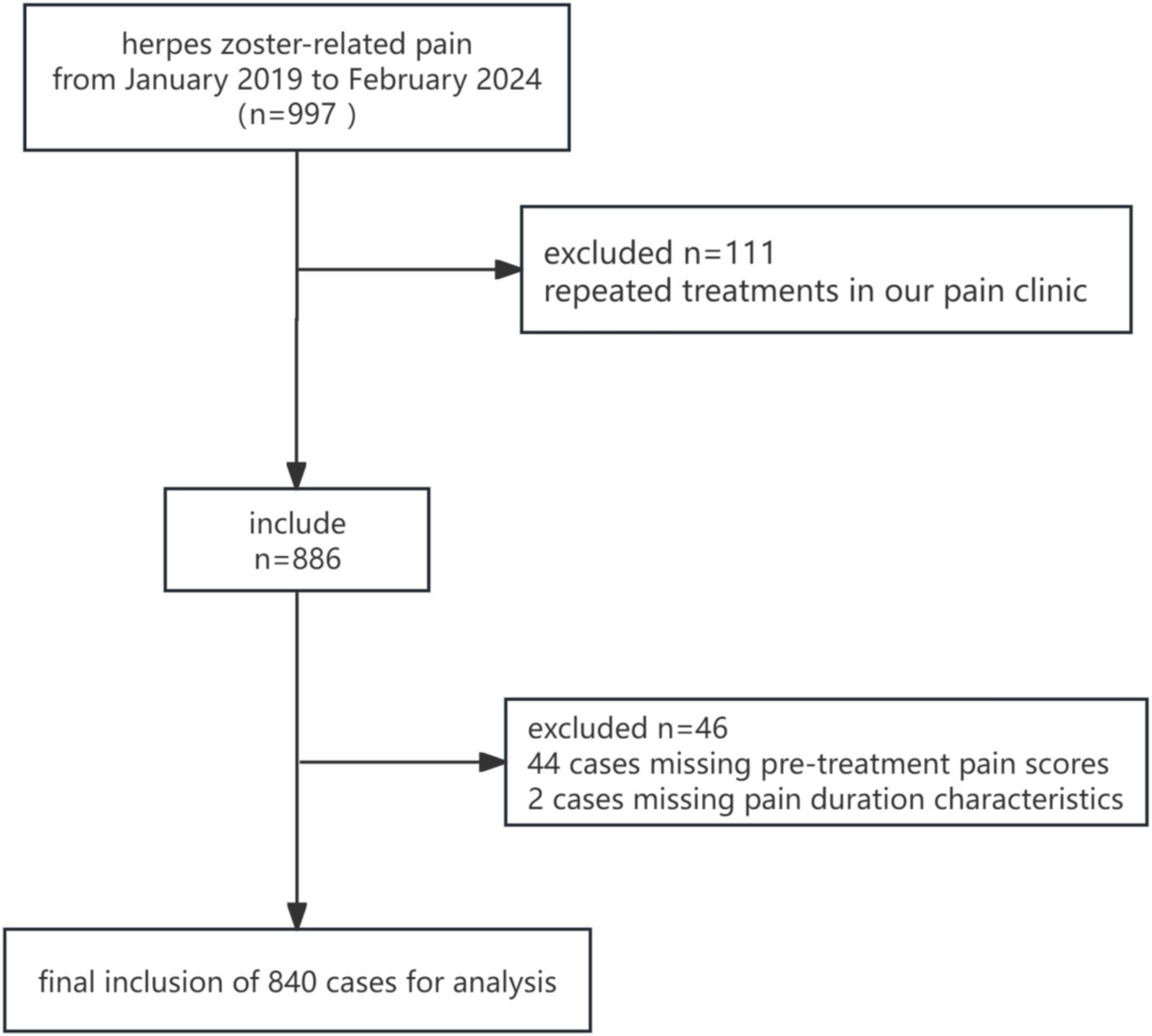
Between January 2019 and February 2024, a total of 997 patients with herpes zoster-related pain were enrolled in this study. After excluding 111 cases due to repeated treatments, 44 cases with missing pre-treatment pain scores, and 2 cases with missing pain duration characteristics, 840 patients were included in the final analysis (Figure 1). The baseline characteristics and pain features of the study population, stratified by pain duration characteristics, are summarized below.
The majority of the patients had intermittent pain (n = 630), while a smaller proportion had persistent pain (n = 210). The overall mean NRS-11 score was 4.9 ± 1.3, with a statistically significant difference observed between the intermittent and persistent pain groups (intermittent: 4.7 ± 1.3, persistent: 5.4 ± 1.3, p < 0.001). Most baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except for BMI, which was significantly different (p = 0.002) (Table 1).
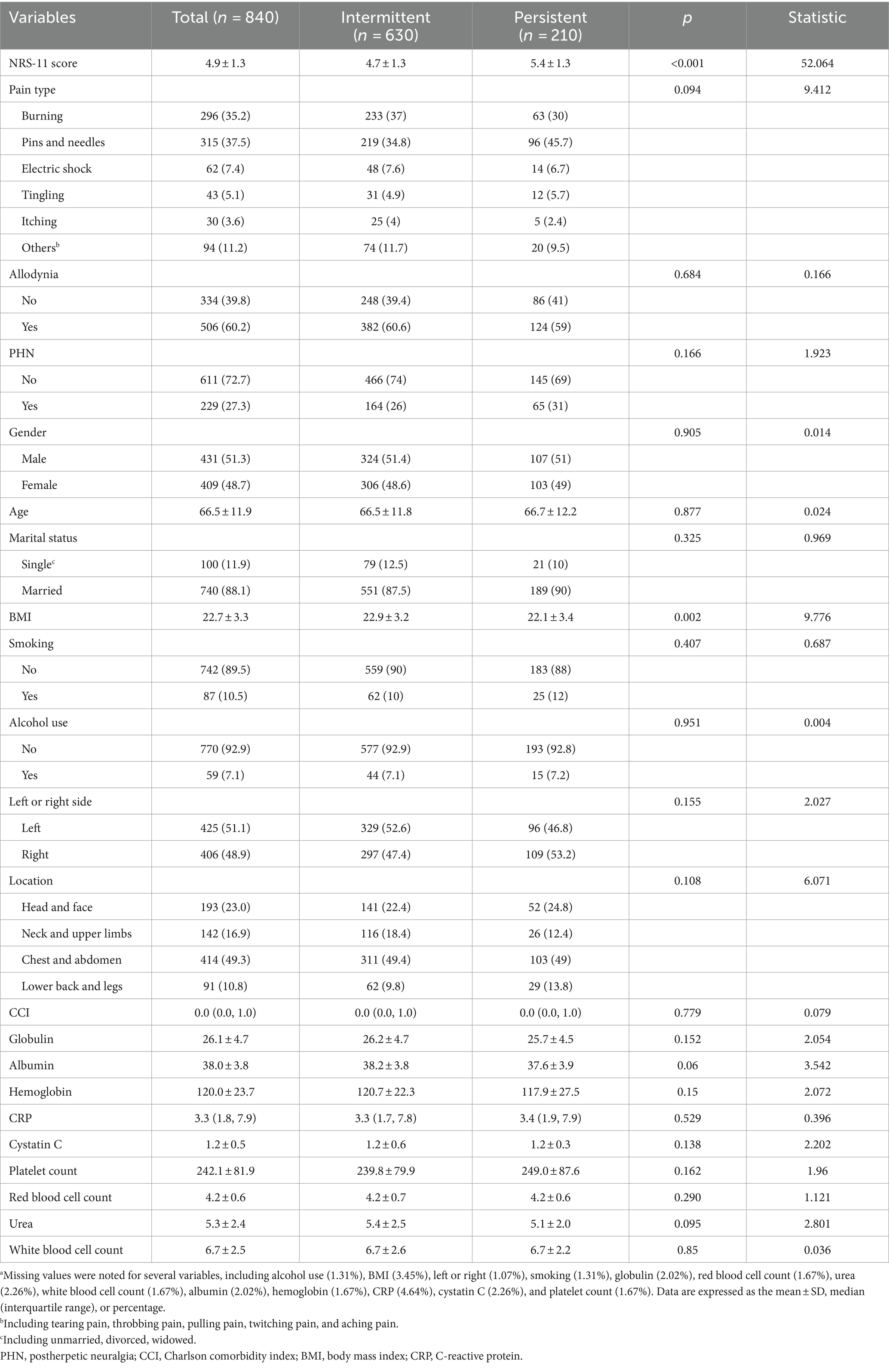
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients with herpes zoster-related pain stratified by pain duration.a
3.2 Correlation analysis
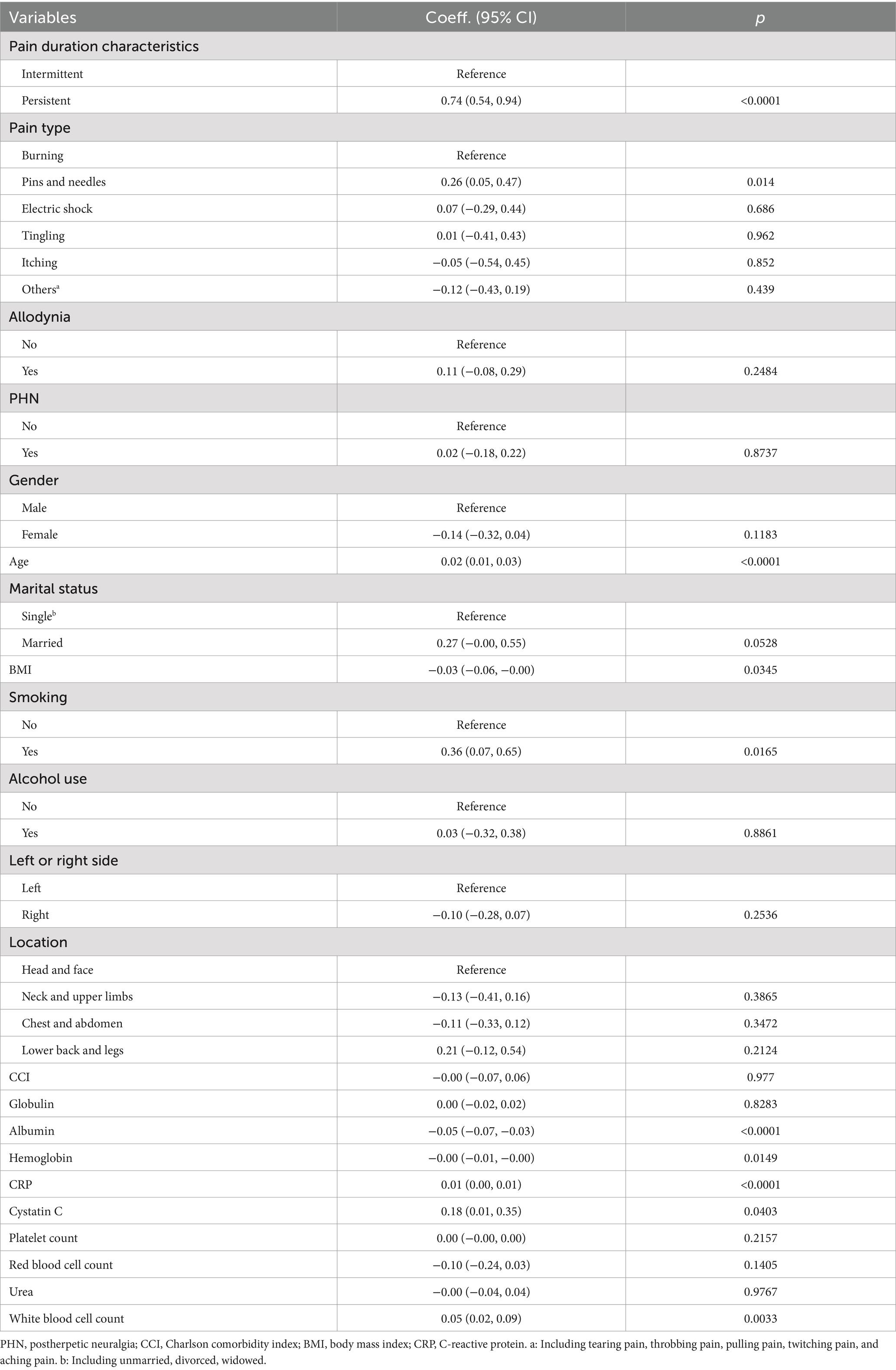
Correlation analysis (Table 2) indicated a significant relationship between pain duration characteristics and NRS-11 scores. In the unadjusted model, patients with persistent pain had significantly higher NRS-11 scores compared to those with intermittent pain (β = 0.74, 95% CI 0.54–0.94, p < 0.0001). Additionally, variables such as the type of pain (pins and needles), age, smoking status, BMI, albumin, hemoglobin, CRP, cystatin C, and white blood cell count were significantly correlated with NRS-11 scores (p < 0.05).
3.3 Multivariate regression analysis
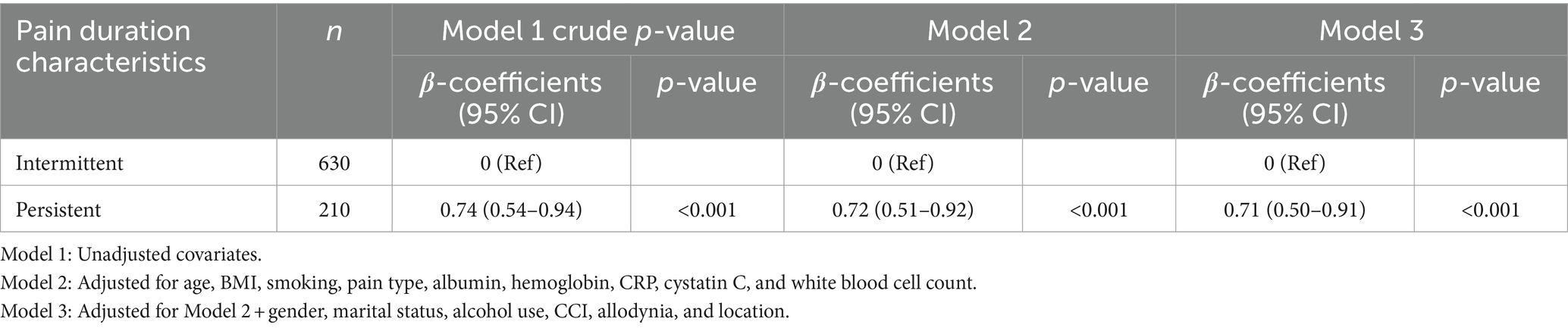
Multivariate regression analysis (Table 3) demonstrated a significant association between pain duration characteristics and NRS-11 scores. In the unadjusted model, persistent pain was significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores (β = 0.74, 95% CI 0.54–0.94, p < 0.001). After adjusting for age, BMI, smoking status, pain type, albumin, hemoglobin, CRP, cystatin C, and white blood cell count, persistent pain remained significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores (β = 0.72, 95% CI 0.51–0.92, p < 0.001). Further adjustment for gender, marital status, alcohol use, and CCI did not alter the significance of the association (β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.51–0.91, p < 0.001).
3.4 Subgroup analysis
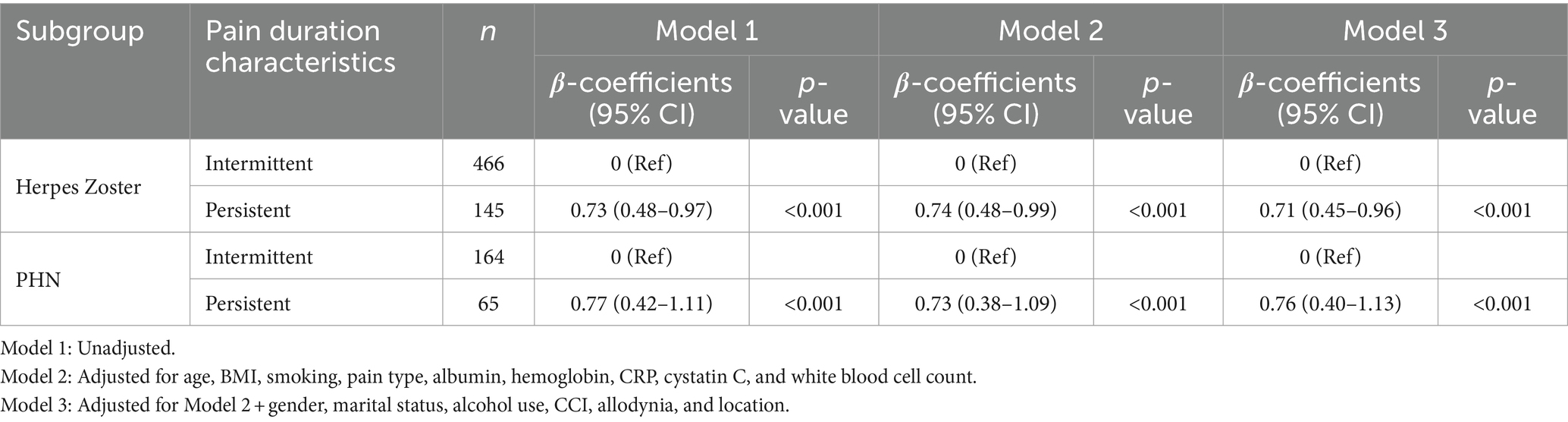
Subgroup analysis (Table 4) results are summarized as follows: persistent pain was significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores in both HZ and PHN patients. In HZ patients, persistent pain was associated with significantly higher NRS-11 scores compared to intermittent pain (adjusted Model 3: β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.45–0.96, p < 0.001). Similarly, in PHN patients, persistent pain was associated with significantly higher NRS-11 scores (adjusted Model 3: β = 0.76, 95% CI 0.40–1.13, p < 0.001).
4 Discussion
This single-center retrospective study systematically explored the relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in patients with herpes zoster-related pain. Different diseases and pain management strategies necessitate varying definitions of pain duration (25–28). Given the typically short disease course in most HZ patients, with some seeking treatment on the first day of pain, we defined continuous pain as pain that persists throughout the entire day regardless of its intensity, and intermittent pain as pain that includes significant periods of relief within the same day. Our multivariate regression analysis revealed that persistent pain is significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores, even after adjusting for various demographic and clinical factors such as age, BMI, smoking status, pain type, albumin, hemoglobin, CRP, cystatin C, white blood cell count, gender, marital status, alcohol use, CCI, presence of allodynia, and pain location (β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.51–0.92, p < 0.001). This finding underscores the critical role of pain duration in influencing pain intensity.
Our study is the first to investigate the relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in a large sample size of HZ patients. The results indicate that intermittent pain (n = 630, 75%) is the predominant type, while persistent pain n = 210, (25%) accounts for only a quarter of the study population. Despite the smaller proportion, patients with persistent pain had significantly higher NRS-11 scores compared to those with intermittent pain, highlighting the critical role of pain duration in influencing pain intensity. Subgroup analysis further revealed that persistent pain was significantly associated with higher NRS-11 scores in both acute HZ (characterized by pain associated with a vesicular rash) and PHN (dermatomal pain persisting for at least 90 days) patients (adjusted Model 3: HZ: β = 0.71, 95% CI 0.45–0.96, p < 0.001; PHN: β = 0.76, 95% CI 0.40–1.13, p < 0.001). These findings underscore the importance of considering pain duration in the management of herpes zoster-related pain across different stages.
Pain intensity is not merely a single instantaneous measure but a complex phenomenon closely linked to the duration of pain (37). The duration of pain is also associated with quality of life and psychological health (38). Previous studies have shown that common symptoms in chronic pain conditions, such as pain intensity and symptoms of depression and anxiety, carry important information for identifying clinically relevant subgroups (39). Our findings suggest that the state of pain on the day of hospital admission is related to pain severity, and the duration of pain should be given high priority in the management of herpes zoster-related pain at different stages.
Perceived pain stimulus duration may affect perceived pain intensity, with shorter perceived durations leading to reduced perceived intensity (21). Previous research has shown that pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are part of the immune response to the varicella-zoster virus, are associated with pain intensity in chronic pain patients (40). Although our study was based on patients’ self-reported pain over a single day, we observed positive correlations between white blood cell count and CRP with pain intensity in univariate analysis, suggesting that persistent pain may represent more severe neuropathic changes, such as nerve fiber damage and regeneration, and inflammatory damage (41). These changes can lead to hyperalgesia and continuous nociceptive input, thereby increasing pain intensity (42).
Additionally, one study found a higher incidence of intermittent pain compared to persistent pain in chronic knee arthritis (43). Our study similarly found that in herpes zoster-related pain, both HZ and PHN, intermittent pain (n = 630, 75%) patients were nearly three times more common than persistent pain (n = 210, 25%) patients. Despite the lower number of patients with persistent pain, their pain intensity was higher. Another study demonstrated that persistent pain has a greater impact on physical activity, indicating the need to consider pain duration as a key feature for accurately predicting pain intensity and formulating appropriate treatment strategies (23).
Our findings suggest that comprehensive management strategies should be adopted for herpes zoster-related persistent pain, but not be limited to antiviral treatments, immunomodulatory therapies, and anti-inflammatory agents. Previous studies have shown that persistent pain is associated with limitations in daily activities, higher comorbidity rates, and depressive symptoms (44). For patients with persistent pain, long-acting formulations may be needed to achieve more stable and prolonged pain control, or the use of the HZ vaccine in high-risk populations (45, 46). Additionally, integrating non-pharmacological treatments, such as physical therapy and psychological interventions, may help alleviate persistent pain (47–49). For intermittent pain patients, short-acting medications before pain onset may reduce the frequency and intensity of pain episodes, and educating patients on the proper use of analgesics can minimize side effects (50, 51).
Our study has several strengths. Firstly, the large sample size provides high statistical power. Secondly, multivariate regression analysis was used to minimize the impact of confounding factors, enhancing the reliability of the results. Thirdly, subgroup analysis further validated the association between persistent pain and higher NRS-11 scores in both HZ and PHN patients, indicating the robustness of this association.
4.1 Limitations
As a retrospective study, there are inherent limitations in inferring causality. Data collection may have biases, especially with self-reported pain scores influenced by subjective factors (52). Additionally, the pain intensity is related to various physiological and psychological factors. One limitation of this study is the lack of consideration for psychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, and stress, which are known to significantly influence pain perception. Although collecting detailed psychological data from retrospective records is challenging, future studies should explore the interaction between psychological factors and herpes zoster-related pain to better understand their impact on pain intensity and duration. As a single-center study, the generalizability of our results may be limited. Future research should adopt a prospective design to reduce biases associated with retrospective data collection. Exploring more objective tools, such as quantitative sensory testing or biomarkers, to complement or replace self-reported pain scores could enhance the accuracy and consistency of pain assessments. Studies should also include multi-center data and explore the potential impact of antiviral treatments, vaccination, and other factors on pain duration and intensity.
5 Conclusion
Our study systematically reveals a significant association between pain duration and pain intensity in patients with herpes zoster-related pain. The importance of pain duration should be emphasized in clinical assessments and treatment plans. Future studies should further explore the neuropathological and psychological mechanisms underlying persistent pain and develop targeted interventions to improve pain management and patient outcomes. Early identification and intervention for persistent pain patients can help prevent chronic pain and related complications, reducing the progression of PHN and other chronic pain conditions.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: the datasets used in this study are subject to restrictions due to privacy and confidentiality concerns. They are not publicly available and can only be accessed upon reasonable request to the corresponding author, in accordance with the ethical guidelines and data protection regulations of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, and with the approval of the Ethics Committee. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to ZJ, amlhbmd6b25nYmluQHNyLmd4bXUuZWR1LmNu.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethical Review Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University [2024-KY(0510)]. The studies were conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee waived the requirement for written informed consent, as this retrospective study involved only the analysis of pre-existing data without direct patient interaction, thus posing minimal risk to participants’ privacy and well-being.
Author contributions
LW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. XL: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. ZL: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. SX: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. RH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization. ZJ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Guangxi Key R&D Program (Guike AB21220047).
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to the Department of Pain Medicine and Information Department at Guangxi Medical University for their invaluable resources and support. Special thanks go to all the patients who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Peng, Q, Guo, X, Luo, Y, Wang, G, Zhong, L, Zhu, J, et al. Dynamic immune landscape and VZV-specific T cell responses in patients with herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:887892. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.887892
2. Andrei, G, and Snoeck, R. Advances and perspectives in the management of varicella-zoster virus infections. Molecules. (2021) 26:1132. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041132
3. Dworkin, RH, Johnson, RW, Breuer, J, Gnann, JW, Levin, MJ, Backonja, M, et al. Recommendations for the management of herpes zoster. Clin Infect Dis. (2007) 44:S1–S26. doi: 10.1086/510206
4. Kawai, K, Gebremeskel, BG, and Acosta, CJ. Systematic review of incidence and complications of herpes zoster: towards a global perspective. BMJ Open. (2014) 4:e004833. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-004833
5. Johnson, RW, and Rice, AS. Clinical practice. Postherpetic neuralgia. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:1526–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1403062
6. Klein, NP, Bartlett, J, Fireman, B, Marks, MA, Hansen, J, Lewis, E, et al. Effectiveness of the live zoster vaccine during the 10 years following vaccination: real world cohort study using electronic health records. BMJ. (2023) 383:e076321. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076321
7. Mbinta, JF, Nguyen, BP, Awuni, PMA, Paynter, J, and Simpson, CR. Post-licensure zoster vaccine effectiveness against herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. (2022) 3:e263–75. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00039-3
8. Yin, D, van Oorschot, D, Jiang, N, Marijam, A, Saha, D, Wu, Z, et al. A systematic literature review to assess the burden of herpes zoster disease in China. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther. (2021) 19:165–79. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1792290
9. Johnson, RW, Bouhassira, D, Kassianos, G, Leplège, A, Schmader, KE, and Weinke, T. The impact of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia on quality-of-life. BMC Med. (2010) 8:37. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-37
10. Yazdi-Ravandi, S, Taslimi, Z, Jamshidian, N, Saberi, H, Shams, J, and Haghparast, A. Prediction of quality of life by self-efficacy, pain intensity and pain duration in patient with pain disorders. Basic Clin Neurosci. (2013) 4:117–24.
11. Salazar-Méndez, J, Núñez-Cortés, R, Suso-Martí, L, Ribeiro, IL, Garrido-Castillo, M, Gacitúa, J, et al. Dosage matters: uncovering the optimal duration of pain neuroscience education to improve psychosocial variables in chronic musculoskeletal pain. A systematic review and meta-analysis with moderator analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2023) 153:105328. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105328
12. Bouhassira, D, Chassany, O, Gaillat, J, Hanslik, T, Launay, O, Mann, C, et al. Patient perspective on herpes zoster and its complications: an observational prospective study in patients aged over 50 years in general practice. Pain. (2012) 153:342–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.10.026
13. Guerriero, F, and Reid, MC. Linking persistent pain and frailty in older adults. Pain Med. (2020) 21:61–6. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnz174
14. Kim, S, and Park, J. Influence of severity and duration of anterior knee pain on quadriceps function and self-reported function. J Athl Train. (2022) 57:771–9. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0647.21
15. Sindrup, SH, Holbech, J, Demant, D, Finnerup, NB, Bach, FW, and Jensen, TS. Impact of etiology and duration of pain on pharmacological treatment effects in painful polyneuropathy. Eur J Pain. (2017) 21:1443–50. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1048
16. Jess, MA, Ryan, C, Wellburn, S, Atkinson, G, Greenough, C, Peat, G, et al. Does pain duration and other variables measured at baseline predict re-referral of low back pain patients managed on an evidence-based pathway? A cohort study. Physiotherapy. (2023) 121:5–12. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2023.07.006
17. Cadogan, SL, Mindell, JS, Breuer, J, Hayward, A, and Warren-Gash, C. Prevalence of and factors associated with herpes zoster in England: a cross-sectional analysis of the Health Survey for England. BMC Infect Dis. (2022) 22:513. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07479-z
18. Patil, A, Goldust, M, and Wollina, U. Herpes zoster: a review of clinical manifestations and management. Viruses. (2022) 14:192. doi: 10.3390/v14020192
19. Steinmann, M, Lampe, D, Grosser, J, Schmidt, J, Hohoff, ML, Fischer, A, et al. Risk factors for herpes zoster infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis unveiling common trends and heterogeneity patterns. Infection. (2024) 52:1009–26. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-02156-y
20. Piovesan, A, Mirams, L, Poole, H, Moore, D, and Ogden, R. The relationship between pain-induced autonomic arousal and perceived duration. Emotion. (2019) 19:1148–61. doi: 10.1037/emo0000512
21. Pomares, FB, Creac'h, C, Faillenot, I, Convers, P, and Peyron, R. How a clock can change your pain? The illusion of duration and pain perception. Pain. (2011) 152:230–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.10.047
22. Hoteit, F, Erhmann Feldman, D, and Carlesso, LC. Factors associated with intermittent, constant, and mixed pain in people with knee osteoarthritis. Physiother Can. (2022) 74:267–75. doi: 10.3138/ptc-2020-0093
23. Song, J, Chang, AH, Chang, RW, Lee, J, Pinto, D, Hawker, G, et al. Relationship of knee pain to time in moderate and light physical activities: data from osteoarthritis initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2018) 47:683–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.10.005
24. Von Korff, M, and Dunn, KM. Chronic pain reconsidered. Pain. (2008) 138:267–76. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.12.010
25. Ritchie, CS, Patel, K, Boscardin, J, Miaskowski, C, Vranceanu, AM, Whitlock, E, et al. Impact of persistent pain on function, cognition, and well-being of older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2023) 71:26–35. doi: 10.1111/jgs.18125
26. Rong, W, Zhang, C, Zheng, F, Xiao, S, Yang, Z, and Xie, W. Persistent moderate to severe pain and long-term cognitive decline. Eur J Pain. (2021) 25:2065–74. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1826
27. Sellevold, VB, Steindal, SA, Lindberg, MF, Småstuen, MC, Aamodt, A, Lerdal, A, et al. Many patients with persistent pain 1 year after TKA report improvement by 5 to 7 years: a mixed-methods study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2022) 480:2075–88. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002183
28. Hunnicutt, JN, Ulbricht, CM, Tjia, J, and Lapane, KL. Pain and pharmacologic pain management in long-stay nursing home residents. Pain. (2017) 158:1091–9. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000887
29. Vandenbroucke, JP, von Elm, E, Altman, DG, Gøtzsche, PC, Mulrow, CD, Pocock, SJ, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. (2007) 4:e297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040297
30. Ferreira-Valente, MA, Pais-Ribeiro, JL, and Jensen, MP. Validity of four pain intensity rating scales. Pain. (2011) 152:2399–404. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.07.005
31. Truini, A, Aleksovska, K, Anderson, CC, Attal, N, Baron, R, Bennett, DL, et al. Joint European Academy of Neurology-European Pain Federation-Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment. Eur J Neurol. (2023) 30:2177–96. doi: 10.1111/ene.15831
32. Jiang, Z, Zhao, P, Lü, J, Li, Q, Xu, S, Zhou, Z, et al. The design and practice of Chinese scale for the diagnosis and assessment of neuropathic pain. Chin J Painol. (2022) 466–475. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101658-20220705-00106
33. Jensen, TS, and Finnerup, NB. Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. (2014) 13:924–35. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70102-4
34. Cho, SI, Lee, DH, and Park, YM. Identification of herpes zoster high-risk group using Charlson comorbidity index: a nationwide retrospective cohort study. J Dermatol. (2020) 47:47–53. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15115
35. Charlson, ME, Pompei, P, Ales, KL, and MacKenzie, CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. (1987) 40:373–83. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
36. Jakobsen, JC, Gluud, C, Wetterslev, J, and Winkel, P. When and how should multiple imputation be used for handling missing data in randomised clinical trials—a practical guide with flowcharts. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2017) 17:162. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0442-1
37. Qian, MP, Dong, MR, Li, J, and Kang, F. The duration of chronic low back pain is associated with acute postoperative pain intensity in lumbar fusion surgery: a prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. (2022) 22:129. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01674-w
38. Maxwell Watts, J, Blackwell, SE, and Daniels, J. Intrusive mental imagery in chronic pain: prevalence and associations with common comorbidities. Cogn Ther Res. (2024) 48:910–22. doi: 10.1007/s10608-024-10480-2
39. Bromley Milton, M, Börsbo, B, Rovner, G, Lundgren-Nilsson, Å, Stibrant-Sunnerhagen, K, and Gerdle, B. Is pain intensity really that important to assess in chronic pain patients? A study based on the Swedish Quality Registry for Pain Rehabilitation (SQRP). PLoS One. (2013) 8:e65483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065483
40. Koch, A, Zacharowski, K, Boehm, O, Stevens, M, Lipfert, P, von Giesen, HJ, et al. Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines correlate with pain intensity in chronic pain patients. Inflamm Res. (2007) 56:32–7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-007-6088-4
41. Vanini, G . Sleep deprivation and recovery sleep prior to a noxious inflammatory insult influence characteristics and duration of pain. Sleep. (2016) 39:133–42. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5334
42. Gulur, P, and Nelli, A. Persistent postoperative pain: mechanisms and modulators. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. (2019) 32:668–73. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000770
43. Soni, A, Kiran, A, Hart, DJ, Leyland, KM, Goulston, L, Cooper, C, et al. Prevalence of reported knee pain over twelve years in a community-based cohort. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:1145–52. doi: 10.1002/art.33434
44. Hoteit, F, Feldman, DE, Pollice, J, and Carlesso, LC. Scoping review of pain and patient characteristics and physical function associated with intermittent and constant pain in people with knee osteoarthritis. Physiother Can. (2021) 73:118–28. doi: 10.3138/ptc-2019-0049
45. Södergren, E, Mårdberg, K, Nishimwe, M, Bhavsar, A, Marijam, A, Bergström, T, et al. Incidence and burden of herpes zoster in Sweden: a regional population-based register study. Infect Dis Ther. (2024) 13:121–40. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00902-1
46. Kim, JH, Johnson, R, Kovac, M, Cunningham, AL, Amakrane, M, Sullivan, KM, et al. Adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine decreases herpes zoster-associated pain and the use of pain medication across 3 randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Pain. (2023) 164:741–8. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002760
47. Moisset, X, Bouhassira, D, Avez Couturier, J, Alchaar, H, Conradi, S, Delmotte, MH, et al. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments for neuropathic pain: systematic review and French recommendations. Rev Neurol. (2020) 176:325–52. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2020.01.361
48. Shi, Y, and Wu, W. Multimodal non-invasive non-pharmacological therapies for chronic pain: mechanisms and progress. BMC Med. (2023) 21:372. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03076-2
49. Paroli, M, and Galdino, G. Editorial: psychological therapies for the management of chronic pain. Front Pain Res. (2023) 4:1219971. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1219971
50. Kosugi, T, Hamada, S, Takigawa, C, Shinozaki, K, Kunikane, H, Goto, F, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of fentanyl buccal tablets for breakthrough pain: efficacy and safety in Japanese cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manag. (2014) 47:990–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.07.006
51. Manchikanti, L, Kaye, AM, Knezevic, NN, McAnally, H, Slavin, K, Trescot, AM, et al. Responsible, safe, and effective prescription of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) guidelines. Pain Physician. (2017) 2:S3–s92. doi: 10.36076/ppj.2017.s92
Keywords: herpes zoster, postherpetic neuralgia, pain duration characteristics, pain intensity, inflammation
Citation: Wang L, Lan X, Lan Z, Xu S, He R and Jiang Z (2024) The relationship between pain duration characteristics and pain intensity in herpes zoster-related pain: a single-center retrospective study. Front. Med. 11:1466214. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1466214
Edited by:
Trine Andresen, Aalborg University, DenmarkReviewed by:
Mohammed Abu El-Hamd, Sohag University, EgyptSara Dochnal, University of California, San Diego, United States
Bing Huang, Zhejiang University, China
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Lan, Lan, Xu, He and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruilin He, NDIwMzM0QHNyLmd4bXUuZWR1LmNu; Zongbin Jiang, amlhbmd6b25nYmluQHNyLmd4bXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liu Wang
Liu Wang Xiaoxiao Lan
Xiaoxiao Lan Zhixuan Lan
Zhixuan Lan Ruilin He
Ruilin He Zongbin Jiang
Zongbin Jiang