- 1Graduate School of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
Introduction: Patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) were more vulnerable to and had a higher mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic. As angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine S1 member 2 (TMPRSS2) played crucial roles in viral entry into the human host cells, we therefore investigated in the MHD patients whether their plasma levels were associated with susceptibility to the COVID-19.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from the patients in our then COVID-19 free center immediately upon lifting of the stringent quarantine measures in early December of 2022 and infection situation was observed within the following 2 weeks. Plasma levels of the soluble ACE2 (sACE2), ACE (sACE) and TMPRSS2 (sTMPRSS2) were measured with ELISA method. Data were stepwisely tested for independent effect, relevant role and synergistic action on the susceptibility by multiple logistic regression, receiver operating characteristic curve and multiple dimensionality reduction (MDR) method, respectively.
Results: Among the 174 eligible patients, 95 (54.6%) turned COVID-19 positive with a male to female ratio of 1.57 during the observation period. Comparing with the uninfected, the infected had significantly higher sACE2 and lower sTMPRSS2 levels upon comparable sACE concentration. Besides the sACE2, factors associated with susceptibility were vintage and individual session time of the hemodialysis, smoking and comorbidity of hepatitis, whereas lymphocyte counts showed a tendency (p = 0.052). Patients simultaneously manifesting higher sACE2 level and lower lymphocyte counts had an increased infection risk as confirmed by the MDR method.
Conclusion: By sorting out the susceptible ones expeditiously, this algorithmic approach may help the otherwise vulnerable MHD patients weather over future wave of COVID-19 variants or outbreak of other viral diseases.
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has delivered an almost devastating blow to the world, leaving millions of death in its wake. It is now clear that entry of the virus into host cells depends on two enzymes: angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine S1 member 2 (TMPRSS2) (1). Specifically, the viral spike protein binds to the ACE2 and forms the virus-ACE2 complex. The TMPRSS2, which is expressed by human respiratory, gastrointestinal and urogenital epithelium, then cleaves the spike protein subunits 1 and 2, thus enabling the direct fusion of S2 subunit with the targeted cell membrane and viral entry (2).
Study using primary human airway epithelial cells from German subjects has congruently confirmed the role of ACE2 as receptor and TMPRSS2 as facilitator for cell entry of the SARS-COV-2 (3). Conceivably, natural mutation in and artificial action on the ACE2 may confer resistance to (4) and therapeutic option of the COVID-19 (5), respectively. In this regard, graphene-derived products were suggested to be capable of preventing the COVID-19 infection (6). Detailed discussion of these issues was further available elsewhere (7). Similarly, TMPRSS2 inhibition was suggested as a prophylactic and therapeutic option against the COVID-19 (8). Moreover, lymphocyte dysfunction was also associated with susceptibility to the virus infection (9).
Patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) was a high risk population for COVID-19 and the mortality rate varied between 20 and 35% which was more than twice higher than that in the general population (10). As such, one of the major lessons was the inability to effectively predict who had the higher risk of infection to enable proper risk stratification and early intervention. Consistently, the UK Health Security Agency released a summative study this May of focusing on non-pharmaceutical interventions to reduce COVID-19 transmission (11). This report essentially highlighted the fact that the pandemic but not evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 was over. By nature, the rates of nucleotide substitution of SARS-COV-2 are fast. This higher error rate and the consequent rapidly evolving virus populations, which could lead to the accumulation of amino acid mutations, might affect the transmissibility of the virus, its cell tropism and pathogenicity (12). Indeed, the JN.1-derived KP.2 variant has sprouted out (7) most recently along with the resurgence of highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) virus (13). Thus, finding a way to identify those MHD patients susceptible to virus infections is of great importance, even today.
In the present study, we therefore sought to evaluate levels of both circulating soluble ACE2 (sACE2) and TMPRSS2 (sTMPRSS2) in MHD patients and examine how they could be used with the lymphocyte count in risk prediction. Similar to our previous work of predicting model for pulmonary infection in patients with membranous nephropathy taking the cyclosporin regime (14), an algorithmic approach for risk assessment may arguably increase the preparedness for possible wave of the COVID-19 variants or other global viral disease outbreak.
Methods
Study design
The study was conducted at the hemodialysis center in the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University and the subjects were those on in-center MHD. Generally, the subjects were at least 18-year-old when initiated the MHD and had a dialysis vintage for more than 6 months, without history of prior renal transplantation, free of the virus infection, absent from malignancy and taking no immunosuppressant, as previously described (15). The dialysis prescription was made according to the KDIGO guidelines, with the only exception in duration of each dialysis session. They received either 3 or 4 h in each session as dictated by the requirement of quarantine and availability of dialysis staffs. Otherwise, anemia, hypertension and hyperphosphatemia were managed by standard protocols, whereas low molecular weight heparin was used for anticoagulation. Medical history, medications and lifestyle factors were recorded by the attending dialysis staffs.
Study timing and oversight
The study was launched immediately upon changes in the quarantine measures in early December of 2022 when all the subjects were negative of COVID-19 and infection status was observed within the following 2 weeks. The diagnosis of infection was made once SARS-CoV-2 RNA was confirmed by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay and the remaining COVID-19 negative patients served as control cohort. Prior to the start, the study was approved by our institutional review board and all patients gave written informed consent.
Laboratory tests
Venous blood was collected before the second hemodialysis session of the week after overnight fasting. Data of blood routine was acquired using Beckman Coulter cellular analysis system (Unicel DxH800, CA, United States). Plasma parameters were measured by using Beckman Coulter AU5800 automatic biochemical analyzer. Ferritin and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) were determined by Beckman Coulter automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer (UniCel DxI800). Kt/V of the hemodialysis was derived from the well-established KDOQI equation.
Measurements of the plasma level of sACE, sACE2 and sTMPRSS2
Circulating levels of ACE2, ACE and TMPRSS2 from plasma samples were quantified using the Abcam Human SimpleStep ELISA® Kit (Cambridge, MA, United States) (16), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Major technical parameters for the ACE2 kit (ab235649) are: range of detection 3.98–255 ng/mL, sensitivity 1,052 pg./mL, intra-assay CV 2.3% and inter-assay CV 3.2%. In the same order, corresponding values for the ACE kit (ab263889) are 0.625–40 ng/mL, 0.15 ng/mL, 3.4 and 3.0%. For the TMPRSS2 kit (ab283552), they were 15.625–1,000 pg./mL, 4.266 pg./mL, 4.9 and 5.8%. The OD at 450 nm was determined on a multiskan MK3 reader (Thermo Scientific, CA, United States). Each measurement was performed in duplicate and average value was used.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 19.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, United States). All data used in the analysis were normally distributed as the significantly skewed ones were log-transformed. Student’s t-test and the chi-square test were used for comparing continuous and categorical variables between groups, respectively. Multiple logistic regression analysis was then used to examine the independent effect of sACE/sACE2/sTMPRSS2, if any, on the susceptibility with adjustment of potential confounding factors. The selection of confounding factors was previously described in details (17), which mainly depended on clinical relevance and results of preceding t-test. The identified risk factors were further evaluated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, which generated paired sensitivity/specificity ranking and the optimal one (cutoff value) was selected according to the Youden’s index (18). Finally, interaction between risk factors that may influence the susceptibility was examined by the multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) method. Subjects are divided into high-and low-risk groups, using the individual cutoff value of risk factors, and the MDR method is able to detect significant inter-group difference through cross-validation and permutation testing, as we have previously described (19). Two-sided p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
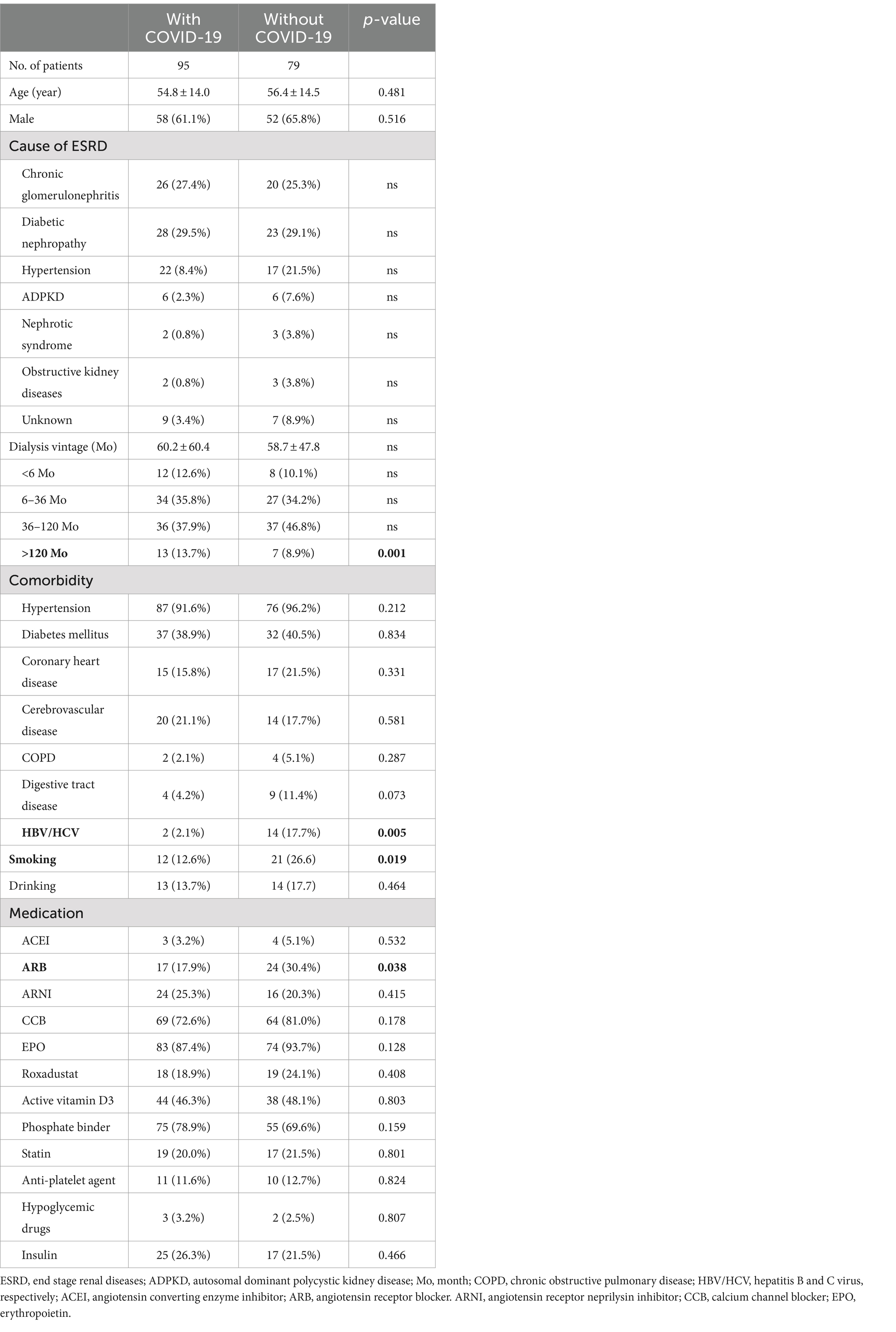
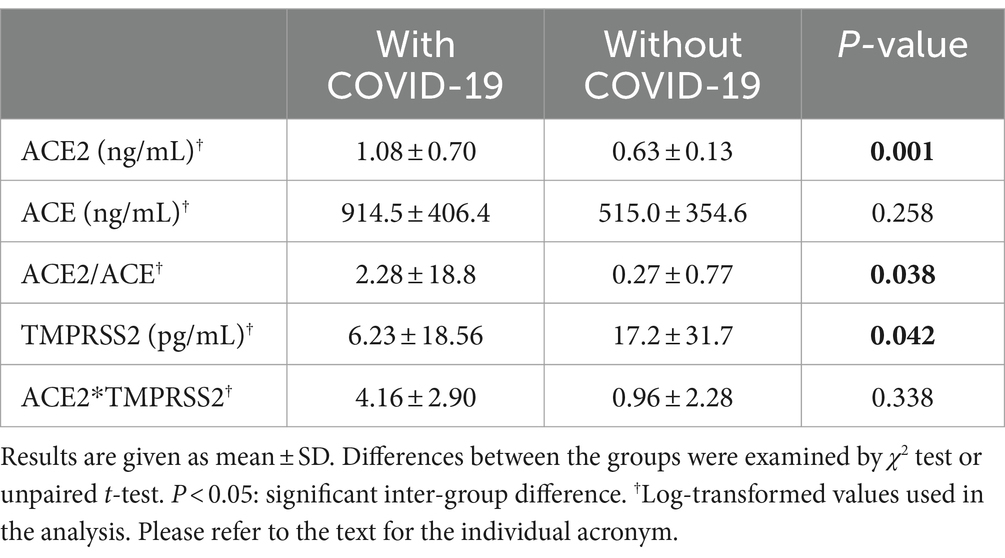
After the observation period of 2 weeks, we had 95 patients turned COVID-19 positive and 79 remained negative among our MHD cohorts. The symptoms included fever (60.0%), upper respiratory manifestations (70.5%), digestive tract disturbance (56.8%) and dysgeusia (39.7%). As shown in Table 1, age, gender composition and cause of their ESRD between the two groups were comparable. In terms of dialysis duration, comorbidities, and medication, however, there was significant inter-group difference in hemodialysis vintage of more than 120 months, concurrent HBV/HCV infection, smoking and the use of angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). Clinical features of the two groups were further listed in Table 2 and the significantly different ones were interdialysis weight gain, lymphocyte count, C-reaction protein, plasma uremic acid, ferritin, dialysis session time and ultrafiltration. Otherwise, there was no difference in the pre-dialysis blood pressure, blood routine, hepatic and renal function, lipid profiles and Kt/V. Moreover, sACE2 but not sACE level was significantly higher in the infection group, whereas the sTMPRSS2 level showed reverse pattern (Table 3).
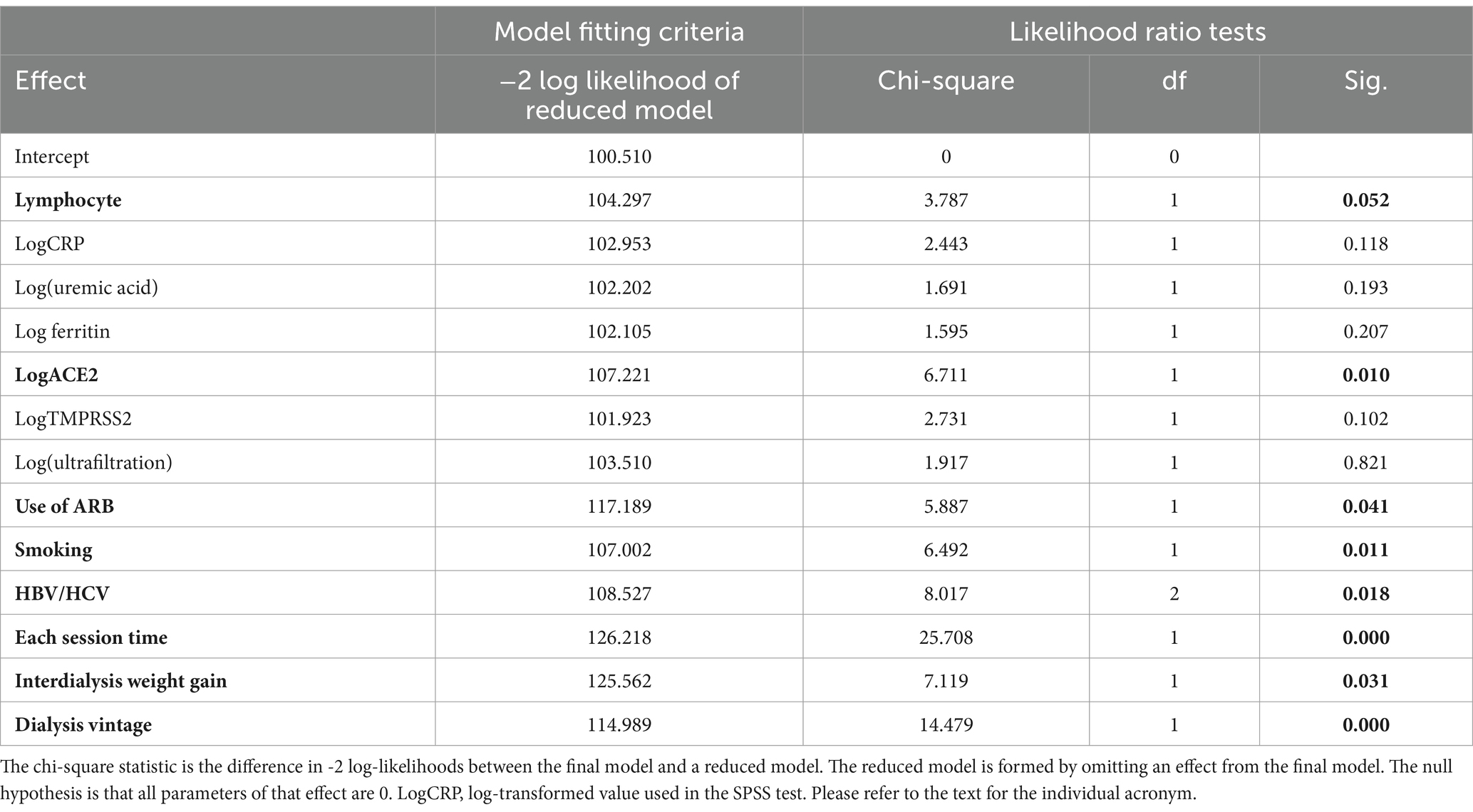
Independent effect of the sACE2 and sTMPRSS2 level on the susceptibility was given in Table 4, as tested by the multiple logistic regression analysis. Clearly, effect of the sACE2 remained significant and that of sTMPRSS2 disappeared. In addition, contributory factors were lymphocyte count, the use of ARB, smoking, concurrent infection of HBV/HCV, dialysis session time, interdialysis weight gain and dialysis duration.
Next, we examined the usefulness of sACE2 and lymphocyte count in predicting susceptibility to COVID-19. For this purpose, these two indexes were processed by the ROC curve (Supplementary Figure S1). Accordingly, area under curve was 0.753 for sACE2 with a significance of 0.001 and the corresponding values for lymphocyte count were 0.730 and 0.003. Subsequently, cutoff values for sACE2 and lymphocyte count that yielded the most optimal paired sensitivity/specificity ranking were deduced as 0.90 ng/mL and 0.60 × 109/L, respectively, using the Youden’s index. Eventually, the MDR method confirmed that patients with sACE2 level higher than 0.90 ng/mL and lymphocyte count lower than 0.60 × 109/L were exposed to increased risk of infection (Figure 1).
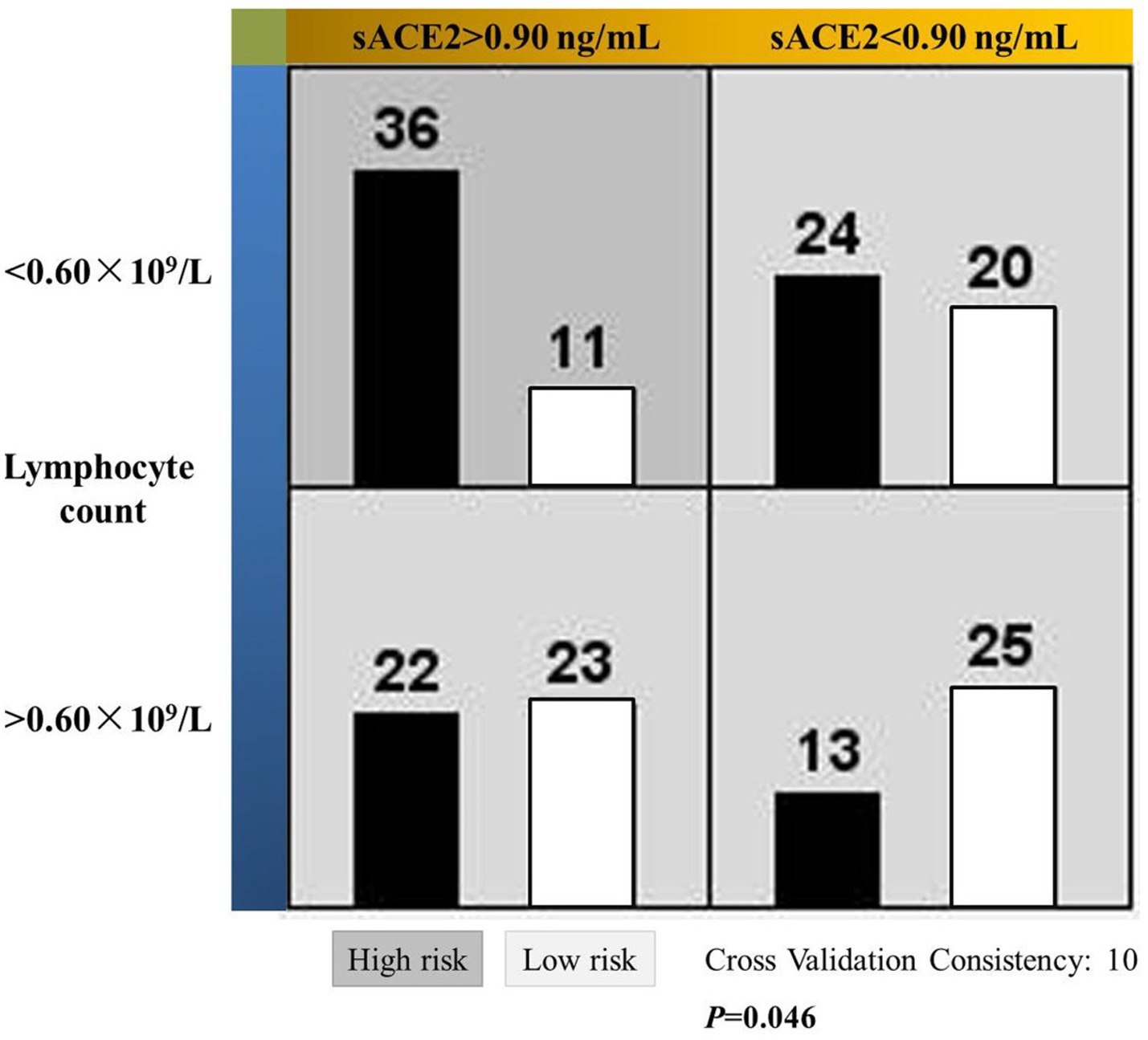
Figure 1. Significant interactive actions of the soluble ACE2 level and lymphocyte count on the susceptibility to COVID-19 in MHD patients. Left and right bars in each cell represent patients with and without the viral infection, respectively. Dark cell indicates higher risk of infection and the light ones for lower risk.
Discussion
In this study, we determined the plasma levels of sACE2 and sTMPRSS2 in the MHD patients, and confirmed the role of sACE2 in susceptibility to the COVID-19 infection. Next, a de novo predicting algorithm was configured using the sACE2 level and lymphocyte count. Then, contributory role of the use of ARB, smoking, concurrent HBV/HCV infection and single dialysis session time was defined. Arguably, an important link between the susceptible individual and COVID-19 was established, which can be useful in the cross-disciplinary prophylaxis of this zoonotic disease and the like.
The observation period was carefully selected for 2 weeks, considering the highly contagious nature of the COVID-19 and closely congregated setting of the in-center hemodialysis. Not surprisingly, the infected had a higher sACE2 level comparing with that of the non-infected, which was consistent with report confirming the role of sACE2 in promoting cell entry of the virus (20). This difference further led to higher sACE2/sACE ratio in the infection group and its association with disease severity was found in a recent study (21). Nonetheless, this ratio was not tested in the regression analysis because of possible co-linearity.
Less expected, sTMPRSS2 was significantly lower in the infection group, but the association was lost in multivariate analysis. In this regard, sACE2 was increased and sTMPRSS2 decreased in patients with eosinophilic asthma (22), whereas the same pattern of change in tissue expression was also observed in rats with decompensated chronic heart failure (23). We therefore speculated that soluble level and tissue expression of sACE2/sTMPRSS2 may be inversely related in some disease settings, as they are co-expressed ubiquitously in human cells (24). Supporting this speculation, we have previously found that NADPH oxidase, which was distributed in perivascular sympathetic nerve fibers, was functionally down-regulated during β2-adrenoceptor over-activity to help maintain renal function (25). Nonetheless, disassociation of the sTMPRSS2 with predilection to COVID-19 in our study may reflect the fact that ACE2 is also cleaved by other proteolytic enzymes such as a disintegrin and metalloproteinase-17 (ADAM-17) (26). Indeed, sACE2 but not sTMPRSS2 may predict disease severity (27).
Lymphopenia and reduced peripheral T cell levels was another major feature of the COVID-19, otherwise a normal immune response was supposed to be capable of resolving the infection (9). Compromised immune function may potentiate the virus’ power of infection for a given ACE2 level and vice versa. Therefore, COVID-19 infection was believed to be the result of close interaction between the virus and the immune system of an individual (28). Precisely, the near-significant association between lymphocyte counts and susceptibility (p = 0.052) in our work suggested that lymphocyte counts are de facto clinically relevant. Following these lines of evidence, we made the risk stratification by simultaneously using the sACE2 level and lymphocyte counts, which in turn produce a higher dimension of prediction than using either value alone. In this way, the risk of infection is considered as a binary function of cell entry and immune status. Our work thus offered new insights to uncover, in a broader sense, the pathogen-host interaction in the MHD patients.
It is noteworthy that the MDR method was used for this investigative purpose. It is basically a non-parametric method that facilitates the simultaneous detection and characterization of multiple genetic loci associated with a discrete clinical end-point. In our current work, different data partitions were achieved by the cutoff values of sACE2 and lymphocyte count (Figure 1), then assigned as presumed ‘genotypes’ and eventually tested for possible high-order interaction between these two variables. Using relatively small sample sizes, this method made it possible for data analysis in situations where traditional methods cannot be applied as we have previously described (25). In fact, performance of the MDR method was outstanding for skewed distributions over several current methods (29), including the principle component analysis which is the basic algorithm of dimensionality reduction in SPSS (30). Briefly, the MDR method is a useful multivariate non-parametric approach that can be used regardless of the factor distribution, the correlations between factors, and sample size. The related technical details are beyond the scope of our work and could be found elsewhere (29).
The risk factors also included the use of ARB, smoking, concurrent infection of HBV/HCV, each individual dialysis session time, interdialysis weight gain and duration on hemodialysis. In line with our findings, ARB was associated with a lower incidence of COVID-19 infection in both European MHD patients (10) and a mega-large population-based study (31). Possible explanations were attributed to the amelioration of inflammation and direct protection of the lung from the SARS-CoV-2 infection, despite the up-regulation of pulmonary ACE2 expression by ARB (32). As for the smoking, we had a somehow a counterintuitive finding. However, it was in agreement with data from United Kingdom, United States and France (31). The investigators believed that this may reflect a general immunomodulatory effect of smoking (31) or there may be a direct protective effect of nicotinic receptor stimulation (33).
Simultaneous presence of two pathogens is known to modulate, exacerbate or ameliorate, the effects of either or both. Reportedly, underlying HBV alone and HBV/HCV may decrease susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection in a Korean nationwide survey and one Spanish study, respectively (34, 35). The use of antiviral agents including tenofovir was presumably accounted for these findings. Interestingly, HCV shared major similarities with the SARS-CoV-2, including utilization of the homoeomorphic ion channels (36). It is thus likely that the viruses may competitively seek utilization of the ion channels, which are diminished in the uremic state (37). The remaining three risk factors are all dialysis-specific and reduced individual hemodialysis session time may underlie the increased interdialysis weight gain. The latter in MHD patients is known to result in fluid overload or even edema of the lungs, both of which confer higher risk of pulmonary infection in ANCA-associated vasculitis (38) and acute brain injury (39). Evidently, patients undergoing long-term dialysis are at increased risk of the COVID-19 infection (40).
Age and gender has no effect on the circulating levels of sACE2/sACE/sTMPRSS2 in our MHD cohorts as a whole or divided into infection group and otherwise. Further, they were unrelated to the susceptibility to COVID-19. Reportedly, sACE was comparable between boys and girls up to 12-year and showed a boy predominance from age 15 (41). In an Arabian cohort, sACE2 was higher in male healthy individuals compared to female controls and this was reversed in those with type 2 diabetes (42). And there was a weak negative association with age but not gender in Japanese MHD patients (43). As the susceptibility to COVID-19 is concerned, age (>70) but not gender was a risk factors in the study including 38,236 MHD patients (10), whereas absence of age as risk factor was found in the French national dialysis registry (44) and a Chinese study observed a higher infection risk for patients aged 65-year or above (45). Taken together, the effects of these two demographic figures appeared to be maturation-dependent, epigenetics-specific (43) and hemodialysis-regulatory (46).
Our work is an essentially nested case–control study with strengths and inherent limitations. On the positive side, it was time-sensitive and marker-innovative, especially with definition of plasma levels of sACE2 and sTMPRSS2 in the MHD patients. Most recently, it was observed that ACE2-mediated pathway played an important role in the increased cardiovascular events during the ‘long COVID’ era (47) and a better understanding of such a role among MHD patients in particular may greatly ameliorate their risk of cardiovascular disease (48). Therefore, our work may definitely both warrant and facilitate further study on this critical issue in the MHD population. Admittedly, it by essence was a single-center study conducted in Chinese MHD patients, which requires caution when applied to other ethnic groups or general population. Further, there was non-availability of age-matched healthy controls in our study. By reality, recruitment of healthy controls was still impossible when the current work was initiated prior to the lifting of stringent quarantine policy, whereas age-matched ‘healthy controls’ without history of infection and vaccination of SARS-COV-2 after the open-up were scarce. Another setback was no free access to research facility having HPLC-MS instrument then. Likewise, enzyme inactive sACE2 was not considered in methodology. By practice, nonetheless, we did confirm that sACE2 could mediate cell entry of the SARS-CoV-2 (20) and its level may reflect membrane-bound mACE2 content (41), in addition to all the 16 publications validating the reliability of the Abcam Human SimpleStep ELISA® Kit studying the pathogenesis of ACE2 in COVID-19 (49). Taken together, these limitations in methodology appeared to have no discernible effect on the outcome of the study and, in any case, close attention will be paid to them in our future work.
Conclusion
Our model was able to pre-emptively predict the group of MHD patients with higher risk of SARS-COV-2 infection. Obviously, what counts is the methodology of configuring clinical parameters for prediction of viral diseases rather than the parameters per se. As such, this algorithmic approach may contribute to infection control in dialysis facilities after further validation in larger cohorts or randomized controlled trials. With no less certainty, such a screening model is needed as COVID-19 is not the first pandemic of this kind, nor is it the last.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SY: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. FM: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources. SZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation. XYL: Writing – original draft, Data curation. XML: Writing – original draft, Investigation. LZ: Writing – original draft, Project administration. TW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Key Science & Technology Project of Hebei Province (20277737D).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1444719/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Jackson, CB, Farzan, M, Chen, B, and Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:3–20. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
2. Baughn, LB, Sharma, N, Elhaik, E, Sekulic, A, Bryce, AH, and Fonseca, R. Targeting TMPRSS2 in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mayo Clin Proc. (2020) 95:1989–99. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.018
3. Hoffmann, M, Kleine-Weber, H, Schroeder, S, Krüger, N, Herrler, T, Erichsen, S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. (2020) 181:271–80.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
4. Raghav, PK, Raghav, A, Lathwal, A, Saxena, A, Mann, Z, Sengar, M, et al. Experimental and clinical data analysis for identification of COVID-19 resistant ACE2 mutations. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:2351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20773-9
5. Raghav, PK, Kalyanaraman, K, and Kumar, D. Human cell receptors: potential drug targets to combat COVID-19. Amino Acids. (2021) 53:813–42. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02991-z
6. Kumar Raghav, P, and Mohanty, S. Are graphene and graphene-derived products capable of preventing COVID-19 infection? Med Hypotheses. (2020) 144:110031. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110031
7. Raghav, PK, Mann, Z, Ahluwalia, SK, and Rajalingam, R. Potential treatments of COVID-19: drug repurposing and therapeutic interventions. J Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 152:1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2023.02.004
8. Shapira, T, Monreal, IA, Dion, SP, Buchholz, DW, Imbiakha, B, Olmstead, AD, et al. A TMPRSS2 inhibitor acts as a pan-SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic and therapeutic. Nature. (2022) 605:340–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04661-w
9. Tay, MZ, Poh, CM, Rénia, L, MacAry, PA, and Ng, LFP. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:363–74. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
10. Haarhaus, M, Santos, C, Haase, M, Mota Veiga, P, Lucas, C, and Macario, F. Risk prediction of COVID-19 incidence and mortality in a large multi-national hemodialysis cohort: implications for management of the pandemic in outpatient hemodialysis settings. Clin Kidney J. (2021) 14:805–13. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab037
11. Duval, D, Evans, B, Sanders, A, Hill, J, Simbo, A, Kavoi, T, et al. Non-pharmaceutical interventions to reduce COVID-19 transmission in the UK: a rapid mapping review and interactive evidence gap map. J Public Health. (2024) 46:e279–93. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdae025
12. Giovanetti, M, Benedetti, F, Campisi, G, Ciccozzi, A, Fabris, S, Ceccarelli, G, et al. Evolution patterns of SARS-CoV-2: snapshot on its genome variants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 538:88–91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.102
13. Uyeki, TM, Milton, S, Abdul Hamid, C, Reinoso Webb, C, Presley, SM, Shetty, V, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza a (H5N1) virus infection in a dairy farm worker. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:2028–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2405371
14. Wang, T, Zhang, Y, Ping, F, Zhao, H, Yan, L, Lin, Q, et al. Predicting risk of pulmonary infection in patients with primary membranous nephropathy on immunosuppressive therapy: the AIM-7C score. Nephrology. (2019) 24:1009–16. doi: 10.1111/nep.13544
15. Wang, T, Li, Y, Wu, H, Chen, H, Zhang, Y, Zhou, HM, et al. Optimal blood pressure for the minimum all-cause mortality in Chinese ESRD patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20200858. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200858
16. Maza, MDC, Úbeda, M, Delgado, P, Horndler, L, Llamas, MA, van Santen, HM, et al. ACE2 serum levels as predictor of infectability and outcome in COVID-19. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:836516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.836516
17. Kaku, Y, Uriu, K, Kosugi, Y, Okumura, K, Yamasoba, D, Uwamino, Y, et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 KP.2 variant. Lancet Infect Dis. (2024). doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00298-6
18. Ivanes, F, Isorni, MA, Halimi, JM, Fauchier, L, Saint Etienne, C, Babuty, D, et al. Predictive factors of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing primary coronary angioplasty. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. (2014) 107:424–32. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2014.05.008
19. Wang, T, Zhang, Y, Wang, N, Liu, Q, Wang, Z, Liu, B, et al. Synergistical action of the β2 adrenoceptor and fatty acid binding protein 2 polymorphisms on the loss of glomerular filtration rate in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Int Urol Nephrol. (2018) 50:715–23. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-1812-2
20. Yeung, ML, Teng, JLL, Jia, L, Zhang, C, Huang, C, Cai, JP, et al. Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system. Cell. (2021) 184:2212–2228.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053
21. Neves, RL, Branquinho, J, Arata, JG, Bittencourt, CA, Gomes, CP, Riguetti, M, et al. ACE2, ACE, DPPIV, PREP and CAT L enzymatic activities in COVID-19: imbalance of ACE2/ACE ratio and potential RAAS dysregulation in severe cases. Inflamm Res. (2023) 72:1719–31. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01775-3
22. Lee, JH, Lee, CE, Yoo, Y, Shin, E, An, J, Park, SY, et al. Soluble ACE2 and TMPRSS2 levels in the serum of asthmatic patients. J Korean Med Sci. (2022) 37:e65. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e65
23. Khoury, EE, Knaney, Y, Fokra, A, Kinaneh, S, Azzam, Z, Heyman, SN, et al. Pulmonary, cardiac and renal distribution of ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 in rats with heart failure: potential implication for COVID-19 disease. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:3840–55. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16310
24. Glowacka, I, Bertram, S, Müller, MA, Allen, P, Soilleux, E, Pfefferle, S, et al. Evidence that TMPRSS2 activates the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein for membrane fusion and reduces viral control by the humoral immune response. J Virol. (2011) 85:4122–34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02232-10
25. Wang, T, Zhang, Y, Ma, JT, Feng, Z, Niu, K, and Liu, B. Additive effect of polymorphisms in the β2-adrenoceptor and NADPH oxidase p 22 phox genes contributes to the loss of estimated glomerular filtration rate in Chinese. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2014) 41:657–62. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12268
26. Patel, VB, Clarke, N, Wang, Z, Fan, D, Parajuli, N, Basu, R, et al. Angiotensin II induced proteolytic cleavage of myocardial ACE2 is mediated by TACE/ADAM-17: a positive feedback mechanism in the RAS. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 66:167–76. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.017
27. Kassif Lerner, R, Stein Yeshurun, M, Hemi, R, Zada, N, Asraf, K, Doolman, R, et al. The predictive value of serum ACE2 and TMPRSS2 concentrations in patients with COVID-19-a prospective pilot study. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:622. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040622
28. Paces, J, Strizova, Z, Smrz, D, and Cerny, J. COVID-19 and the immune system. Physiol Res. (2020) 69:379–88. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934492
29. Park, M, Jeong, HB, Lee, JH, and Park, T. Spatial rank-based multifactor dimensionality reduction to detect gene-gene interactions for multivariate phenotypes. BMC Bioinformat. (2021) 22:480. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04395-y
30. Liu, RX, Kuang, J, Gong, Q, and Hou, XL. Principal component regression analysis with SPSS. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. (2003) 71:141–7. doi: 10.1016/s0169-2607(02)00058-5
31. Hippisley-Cox, J, Young, D, Coupland, C, Channon, KM, Tan, PS, Harrison, DA, et al. Risk of severe COVID-19 disease with ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: cohort study including 8.3 million people. Heart. (2020) 106:1503–11. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317393
32. Elkahloun, AG, and Saavedra, JM. Candesartan could ameliorate the COVID-19 cytokine storm. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 131:110653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110653
33. Changeux, JP, Amoura, Z, Rey, FA, and Miyara, M. A nicotinic hypothesis for Covid-19 with preventive and therapeutic implications. C R Biol. (2020) 343:33–9. doi: 10.5802/crbiol.8
34. Kang, SH, Cho, DH, Choi, J, Baik, SK, Gwon, JG, and Kim, MY. Association between chronic hepatitis B infection and COVID-19 outcomes: a Korean nationwide cohort study. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0258229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258229
35. Lens, S, Miquel, M, Mateos-Muñoz, B, García-Samaniego, J, and Forns, X. SARS-CoV-2 in patients on antiviral HBV and HCV therapy in Spain. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:1262–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.007
36. Alothaid, H, Aldughaim, MSK, El Bakkouri, K, AlMashhadi, S, and Al-Qahtani, AA. Similarities between the effect of SARS-CoV-2 and HCV on the cellular level, and the possible role of ion channels in COVID19 progression: a review of potential targets for diagnosis and treatment. Channels. (2020) 14:403–12. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2020.1837439
37. Staruschenko, A, Ma, R, Palygin, O, and Dryer, SE. Ion channels and channelopathies in glomeruli. Physiol Rev. (2023) 103:787–854. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2022
38. Kronbichler, A, Jayne, DR, and Mayer, G. Frequency, risk factors and prophylaxis of infection in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Eur J Clin Investig. (2015) 45:346–68. doi: 10.1111/eci.12410
39. Ziaka, M, and Exadaktylos, A. Brain-lung interactions and mechanical ventilation in patients with isolated brain injury. Crit Care. (2021) 25:358. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03778-0
40. Taji, L, Thomas, D, Oliver, MJ, Ip, J, Tang, Y, Yeung, A, et al. COVID-19 in patients undergoing long-term dialysis in Ontario. CMAJ. (2021) 193:E278–84. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.202601
41. Swärd, P, Edsfeldt, A, Reepalu, A, Jehpsson, L, Rosengren, BE, and Karlsson, MK. Age and sex differences in soluble ACE2 may give insights for COVID-19. Crit Care. (2020) 24:221. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02942-2
42. Elemam, NM, Hasswan, H, Aljaibeji, H, and Sulaiman, N. Circulating soluble ACE2 and upstream micro RNA expressions in serum of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:5263. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105263
43. Kawabe, M, Nakashima, A, Yamamoto, I, Ohkido, I, Yokoo, T, and Urashima, M. Higher soluble ACE2 levels and increased risk of infection-related hospitalization in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Front Med. (2022) 9:791284. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.791284
44. Couchoud, C, Bayer, F, Ayav, C, Béchade, C, Brunet, P, Chantrel, F, et al. Low incidence of SARS-CoV-2, risk factors of mortality and the course of illness in the French national cohort of dialysis patients. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:1519–29. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.07.042
45. Xu, X, Nie, S, Sun, J, Kong, Y, Liang, M, Li, D, et al. The cumulative rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Chinese hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int Rep. (2020) 5:1416–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.07.010
46. Yang, CW, Lu, LC, Chang, CC, Cho, CC, Hsieh, WY, Tsai, C, et al. Imbalanced plasma ACE and ACE2 level in the uremic patients with cardiovascular diseases and its change during a single hemodialysis session. Ren Fail. (2017) 39:719–28. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1398665
47. Philip, B, Mukherjee, P, Khare, Y, Ramesh, P, Zaidi, S, Sabry, H, et al. COVID-19 and its long-term impact on the cardiovascular system. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. (2023) 21:211–8. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2023.2184800
48. Malik, U, and Raizada, V. Some aspects of the renin-angiotensin-system in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. (2015) 40:614–22. doi: 10.1159/000368537
49. Publications: in overview of Abcam Human ACE2 ELISA Kit (ab 235649). Available at: https://www.abcam.com/en-us/products/elisa-kits/human-ace2-elisa-kit-ab235649
Keywords: COVID-19, maintenance hemodialysis, ACE2, TMPRSS2, lymphocyte count
Citation: Yuan S, Meng F, Zhou S, Liu X, Liu X, Zhang L and Wang T (2024) Predicting susceptibility to COVID-19 infection in patients on maintenance hemodialysis by cross-coupling soluble ACE2 concentration with lymphocyte count: an algorithmic approach. Front. Med. 11:1444719. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1444719
Edited by:
Diego Ripamonti, Papa Giovanni XXIII Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Jitender Sharma, University of Delhi, IndiaRan Wang, Anhui Medical University, China
Pawan Kumar Raghav, University of California, San Francisco, United States
Copyright © 2024 Yuan, Meng, Zhou, Liu, Liu, Zhang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Wang, d2FuZ3Rhby1QSUBoZWJtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Tao Wang, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7370-7299
 Shuang Yuan1†
Shuang Yuan1† Tao Wang
Tao Wang