- 1College of Physical Education, Chinese Center of Exercise Epidemiology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 2College of Physical Education, Jilin Normal University, Siping, Jilin, China
- 3College of General Education, Guangxi Arts University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 4College of Physical Education, Chinese Center of Exercise Epidemiology, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
Background: The aging population is rapidly increasing, leading to physical decline and higher risks of chronic diseases, including sarcopenia, which adversely affects muscle quality and strength. Yi Jin Jing (YJJ), a traditional Chinese exercise method, can enhance flexibility and strength, but evidence regarding its effectiveness in older adults is conflicting. This meta-analysis aims to systematically evaluate the effects of YJJ on muscle strength and physical performance in this demographic.
Methods: We searched seven electronic databases: China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Data, Sinomed, Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Following PRISMA guidelines, we quantified the effects of YJJ on muscle strength (grip strength, isokinetic strength) and physical performance (chair sit-to-stand, squatting-to-standing, shoulder flexibility, sit-and-reach tests). Treatment effects were calculated using Hedges’g. The Cochrane tool assessed risk of bias, the PEDro scale evaluated methodological quality, and the GRADE method assessed evidence quality. Data analysis was conducted using Stata 17.0 software, utilizing standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: This meta-analysis included 10 RCTs involving 590 participants. The overall risk of bias was assessed to be low. The methodological quality of these studies was generally moderate, and the quality of the main results varied from low to moderate. The findings revealed that YJJ had considerable effects on the chair sit-to-stand test (Hedges’g = 1.06), squatting-to-standing test (Hedges’g = 1.08), and small to moderate effects on handgrip strength (Hedges’g = 0.25), 60°/s extensor peak torque (Hedges’g = 0.47), 60°/s extensor average power (Hedges’g = 0.31), 60°/s extensor total work (Hedges’g = 0.29), 60°/s flexor peak torque (Hedges’g = 0.42), 60°/s flexor average power (Hedges’g = 0.37), and 180°/s extensor peak torque (Hedges’g = 0.29), and left shoulder flexibility (Hedges’g = 0.4). However, there were no significant improvement effects in 180°/s extensor average power (Hedges’g = 0.19), 180°/s extensor total work (Hedges’g = 0.11), 180°/s flexor peak torque (Hedges’g = 0.01), 180°/s flexor average power (Hedges’g = −0.08), right shoulder flexibility (Hedges’g = 0.09), and sit-and-reach test (Hedges’g = 0.15).
Conclusion: YJJ significantly enhances specific aspects of physical performance, particularly chair sit-to-stand and squatting-to-standing tests, while showing small and moderate improvements in handgrip strength and knee muscle strength. However, it had no significant effects on other metrics, including shoulder flexibility and sit-and-reach tests.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42024530487, Registration number: CRD42024530487.
1 Introduction
China’s population is experiencing an accelerated aging process, characterized by a noticeable shift toward older age groups. A national survey conducted in 2021 revealed that the older population in China constitutes 18.7% of the total population, with a continuing upward trend (1). Aging is associated with a decline in physiological ability, rendering individuals highly susceptible to various chronic diseases, including diabetes (2), hypertension (3), and Parkinson’s disease (4). Notably, a recent comprehensive meta-analysis and systematic review reported that the prevalence of sarcopenia in the older Asian population was 21.6%, significantly higher than that in other regions (5). Sarcopenia is defined as a significant loss of muscle mass and strength associated with aging, disease, or other contributing factors (6). This condition adversely affects individual health and increases the risk of falls (7), fractures (8), and mortality (9). Furthermore, these consequences substantially decrease the quality of life and impose a heavy burden on healthcare systems (10).
The implementation of preventive measures is essential to reduce the incidence of age-related diseases. The Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) 2019 introduced the concept of “possible sarcopenia,” which is defined as either low muscle strength or low physical performance only (11). This definition aims to aid early interventions in primary healthcare environments and community initiatives. Therefore, it is imperative to promptly identify and implement effective prevention strategies to halt the progression of sarcopenia in the older individuals.
Yi Jin Jing (YJJ) is a traditional Chinese exercise method that involves slow, controlled movements aimed at improving flexibility, strength, and overall physical performance (12). The traditional YJJ comprises a standardized set of 12 movements, such as stretching, twisting, and squatting, which have gained widespread attention for their potential benefits in enhancing muscle strength and physical performance in older adults (13). Although YJJ is typically practiced in a single, consistent style, the movements emphasize controlled body mechanics and promote gradual improvements in physical capabilities (14). Based on a review of existing studies, there is conflicting evidence regarding the effects of YJJ on muscle strength and physical performance in older individuals (15–23). Although numerous studies have reported significant benefits (15–20), others have not (21–23). We further found that the diversity of research methodologies, participants’ characteristics, and exercise programs among the studies contributed to outcome variability. Additionally, the different definitions of sarcopenia and the measurement methods for physical performance also intensify the uncertainty regarding YJJ’s effectiveness.
Previous meta-analyses have shown that traditional Chinese exercises can improve physical health (24–27). However, these studies often combined various types of traditional Chinese exercises and failed to use Hedges’g statistics to estimate the effect size. The use of Hedges’g is particularly important given the small sample sizes in the analyzed studies, as it provides a more precise estimation, thereby improving the reliability of the findings (28). Therefore, this study aims to accurately calculate the effect size of YJJ on muscle strength and physical performance in older individuals by synthesizing existing studies. It addresses critical gaps in the literature by clarifying the inconsistencies caused by participant characteristics and the diversity of exercise programs. By using Hedges’g statistics, we improve the precision of effect size estimations, thereby improving the reliability of understanding the effectiveness of YJJ. The findings of this study are essential for guiding future research and developing practical interventions to enhance the well-being of the older individuals.
2 Method
The meta-analysis adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (29). This study was registered in the Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO);1 registration number CRD42024530487.
2.1 Search strategy
From November 2023, a systematic search was conducted across seven electronic databases: CNKI, Wanfang Data, Sinomed, Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase. Additionally, manually search the reference list of relevant publications to find the non-indexed studies in these databases. The search terms used to search for relevant literature include the following combinations: (“Qigong” or “Chinese traditional exercise” or “Yijinjing” or “Yi jinjing” or “Yi Jin Jing”) AND (“muscle strength” OR “muscle strength” OR “grip” OR “physical activit*” OR “physical performance” OR “physical fitness” OR “motor function”) AND (“randomized controlled trial*” OR “random*” OR “clinical trial*”). The search strategies for different databases were modified accordingly. The final search date was March 2024.
2.2 Selection criteria
The selection criteria were as following:
a. Study Type: The studies included were randomized controlled trials (RCTs). These were original, peer-reviewed works with no restrictions on language or publication date.
b. Population: Participants were required to be older than 60 years and inclusion was not limited by sex, race, or country of origin.
c. Intervention: The intervention had to exclusively involve YJJ and could not be combined with other exercise interventions. There were no specified limits on the frequency, intensity, or duration of YJJ.
d. Comparator: The comparator group either received no intervention or was provided health education.
e. Outcome Measures: Muscle strength measures included handgrip strength and isokinetic muscle strength. Physical performance assessments comprised chair sit-to-stand, squatting-to-standing, shoulder flexibility, and sit-and-reach tests.
2.3 Data management and extraction
Data were merged using EndNote, and duplicate entries were removed. Two independent reviewers assessed titles, abstracts, and full texts for eligibility. Any conflicts or ambiguities were resolved through discussion or arbitration with a third reviewer.
The two reviewers extracted relevant data, summarized them in Microsoft Excel spreadsheets, and cross-checked the results. The data extracted from the literature included the first author, publication date, participant age, sample size, sex composition, physical condition, diagnostic criteria, intervention type, intervention frequency and duration, measurement tools, and outcome indicators.
2.4 Quality assessment
The PEDro scale consists of 11 items to assess the methodological quality of the included study (30), with scores downloaded from PEDro (pedro.org.au). The first item (qualification criterion) was excluded from the total score because it did not directly reflect the internal validity of the study. Therefore, the score ranged from 0 (low quality) to 10 (high quality) and was divided into four quality levels: excellent (9–10 points), good (6–8 points), fair (4–5 points), and poor (0–3 points) (31).
The risk of bias for each study was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration tool (32). According to the design and implementation of the original studies, three bias risk levels (high, low, and unclear) were determined for each item. The evaluation was conducted independently by two authors. Any differences were reviewed by a third evaluator and resolved by consensus.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was performed using stata17.0. For continuous results, Hedges’g was used to calculate the between-groups effect sizes, which were classified as small (0.2–0.4), medium (0.5–0.7), or large (≥0.8) (33). The GRADE method was used to determine the certainty of the evidence (34). When there was a high degree of heterogeneity (p < 0.1 or I2 > 50%), a random-effects model was employed for meta-analysis, and the source of heterogeneity was identified through subgroup analysis or a stepwise method (35). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
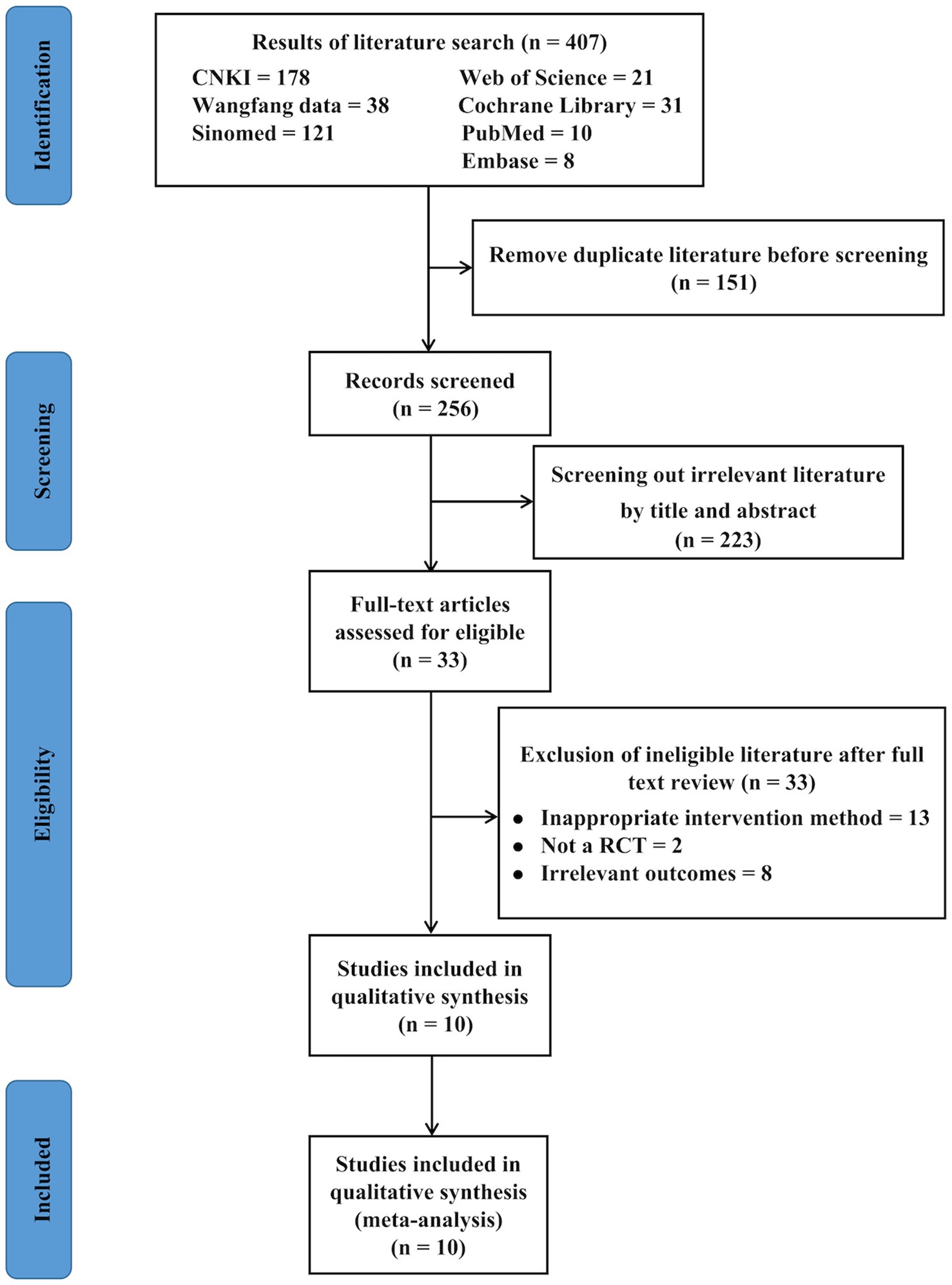
Figure 1 summarizes the screening process. Our initial search yielded 407 articles, of which 151 were duplicates and were excluded. Subsequent screening of titles and abstracts resulted in the exclusion of an additional 223 items. Finally, 33 articles were thoroughly reviewed, 10 of which were included in this meta-analysis (15, 16, 18, 21–23, 36–39).
3.2 Study characteristics
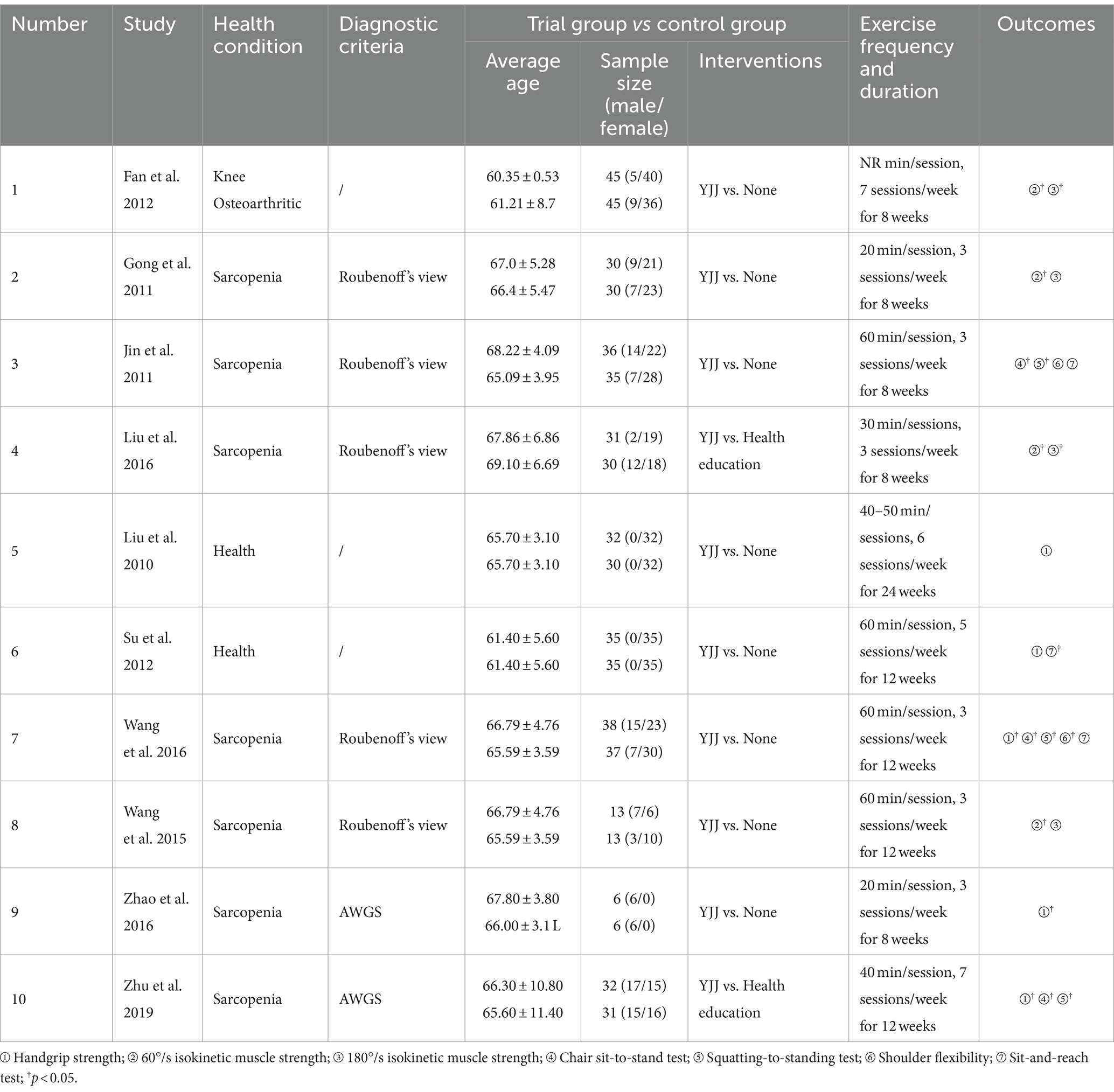
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the studies included in this meta-analysis. However, there were 590 participants, all of whom were over 60 years old, and 75% were female. Two trials included only women (22, 23), one trial included only men (16), and the remaining included a mix of sexes (15, 18, 21, 36–39). Among the participants included in the study, one study focused on patients with knee osteoarthritis (36), two studies identified sarcopenia using the AWGS diagnostic method (15, 16), five studies identified sarcopenia according to Roubenoff’s view (18, 21, 37–39), and the other two studies involved healthy older individuals (22, 23). All experimental groups were treated with YJJ, and the control group received either health education (15, 39) or a blank control (16, 18, 21–23, 36–38). The results of these 10 studies were as follows: handgrip strength (15, 16, 21–23); 60°/s isokinetic muscle strength (18, 36, 38, 39), 180°/s isokinetic muscle strength (18, 36, 38, 39), chair sit-to-stand test (15, 21, 37), squatting-to-standing test (15, 21, 37), shoulder flexibility test (21, 37), and sit-and-reach test (21, 22, 37).
3.3 Quality of the evidence
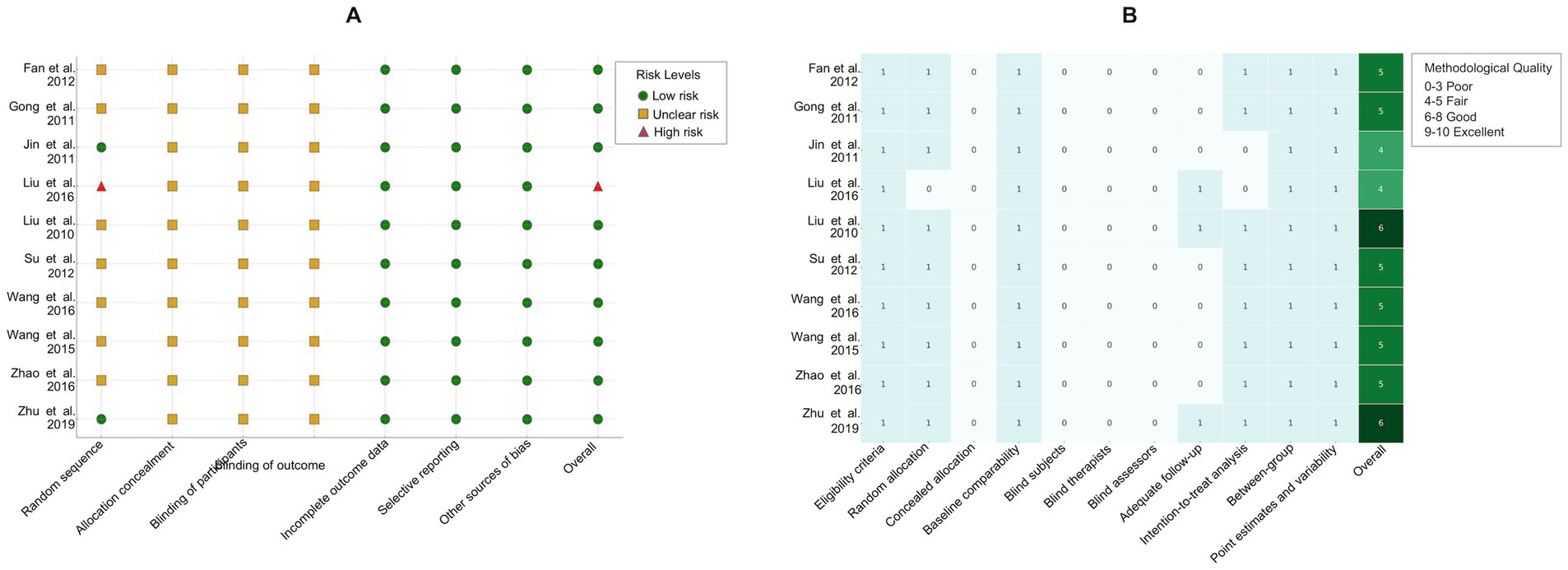
Figure 2A illustrates the results of bias risk assessment for the included studies. In the risk of bias assessment, one study (39) was classified as high risk owing to bias in the randomization process. Two studies (15, 37) used the random number table method for random allocation. None of the studies (15, 16, 18, 21–23, 36–39) did not mention allocation concealment or the use of blinding for evaluating results. Additionally, owing to the nature of the included studies, blinded participants and therapies were not applicable.
Figure 2B shows the methodological quality of the included studies assessed using the PEDro scale (31). Two studies (15, 23) were rated as “good” because they provided detailed records of dropout during the testing process or conducted measurements at multiple time points, while the remaining studies (16, 18, 21, 22, 36–39) were rated as “fair.”
3.4 Outcome measures
3.4.1 Muscle strength in the older individuals
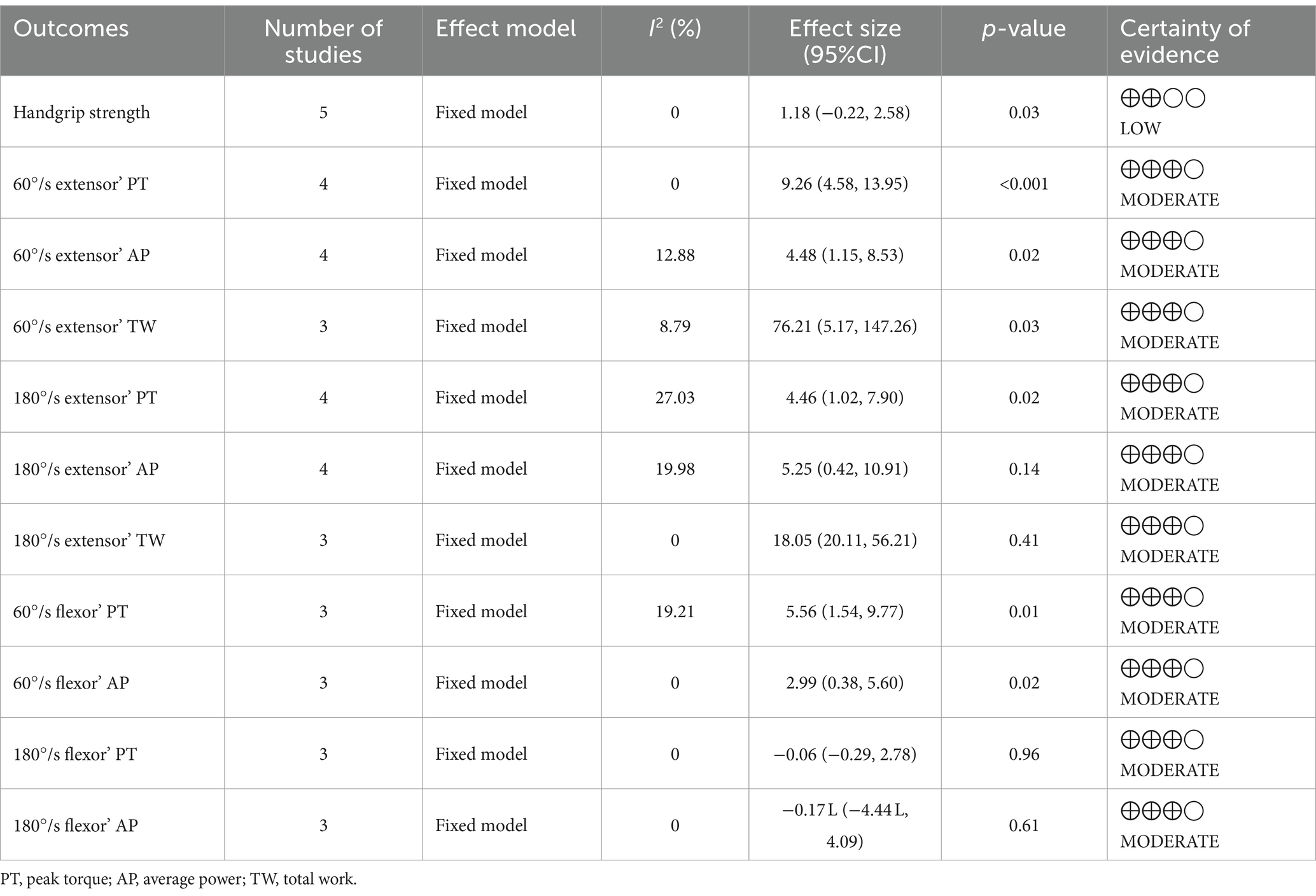
Table 2 and Figure 3 summaries the evidence for the effect of YJJ on muscle strength in the older population. Forest plots and specific grade ratings are provided in Supplementary material.
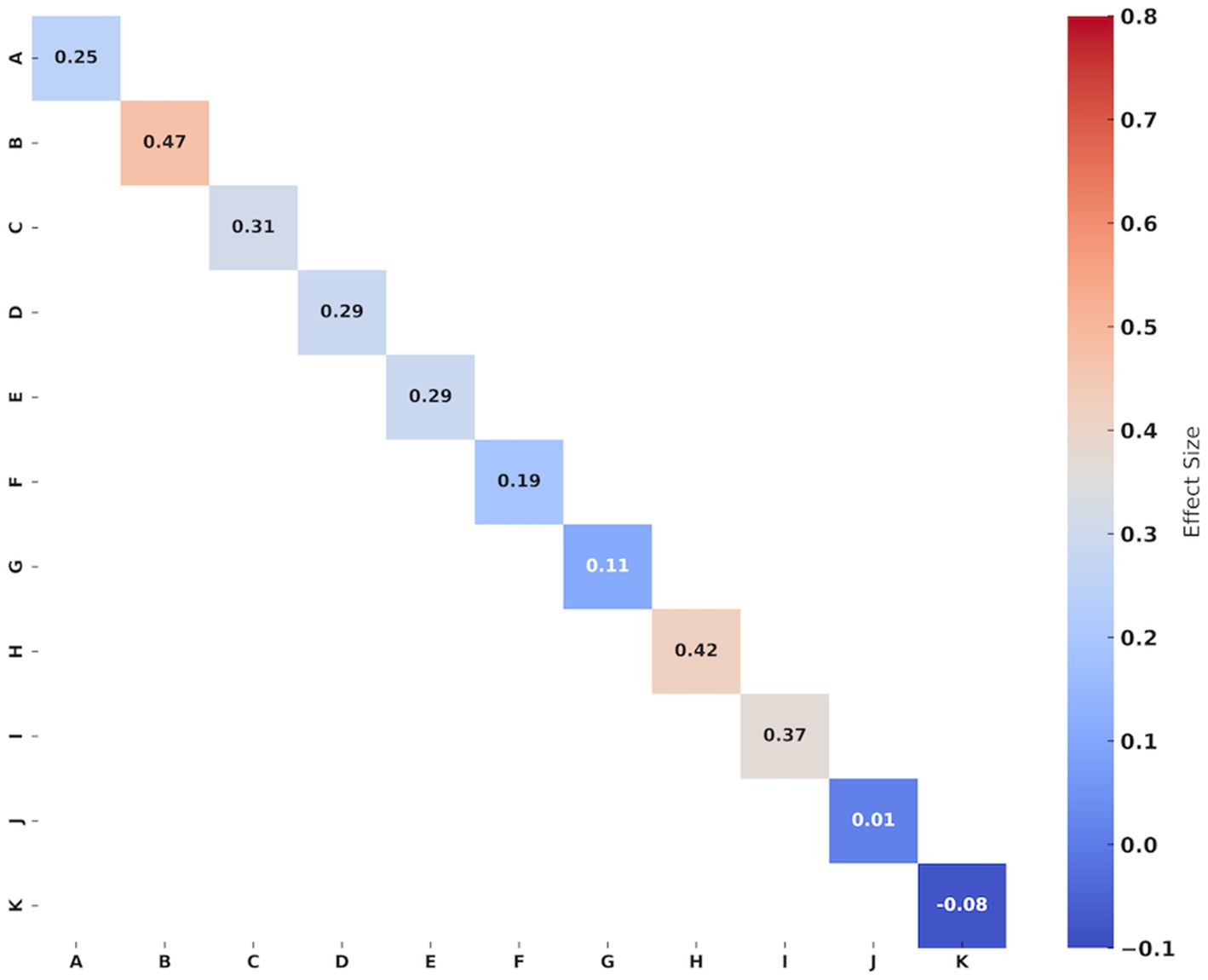
Figure 3. Effect size of Yi Jin Jing on muscle strength in the older individuals. A: Handgrip strength; B: 60°/s extensor’ PT; C: 60°/s extensor’ AP; D: 60°/s extensor’ TW; E: 180°/s extensor’ PT; F: 180°/s extensor’ AP; G: 180°/s extensor’ TW; H: 60°/s flexor’ PT; I: 60°/s flexor’ AP; J: 180°/s flexor’ PT; K: 180°/s flexor’ AP. Hedges’g values of 0.2–0.4 indicating small, 0.5–0.7 signifying medium, and ≥0.8 representing large effect sizes, respectively.
Five studies (15, 16, 21–23) reported handgrip strength outcomes. The synthesized data indicated that compared to the control group, the effect of YJJ on enhancing handgrip strength in the older individuals was statistically significant (I2 = 0%, p = 0.03, certainty of evidence = low), with a small improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.25).
In the assessment of lower limb strength, four studies (18, 36, 38, 39) evaluated the peak torque and average power of the extensor muscles of the participants, and three of them (36, 38, 39) evaluated the total work of the extensor muscles. The synthesized data indicated that in the 60°/s isokinetic muscle strength of extensors, YJJ significantly enhanced extensor peak torque (I2 = 0%, p < 0.001, certainty of evidence = moderate), with a moderate improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.47); extensor average power (I2 = 12.88%, p = 0.02, evidence certainty = moderate), with a small improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.31); and extensor total work (I2 = 8.79%, p = 0.03, certainty of evidence = moderate), with a small improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.29). However, in the 180°/s isokinetic muscle strength of extensors, YJJ only marginally improved extensor peak torque (I2 = 27.03%, p = 0.02, evidence certainty = moderate), with a small improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.29); there was no significant improvement effect observed for extensor average power (I2 = 19.98%, p = 0.14, evidence certainty = moderate) (Hedges’g = 0.19) and extensor total work (I2 = 0%, p = 0.41, certainty of evidence = moderate) (Hedges’g = 0.11).
Three studies (18, 38, 39) assessed the peak torque and average power of the participants’ flexor muscles. The synthesized data showed that at 60°/s isokinetic muscle strength of the flexors, YJJ significantly increased flexor peak torque (I2 = 19.21%, p = 0.02, evidence certainty = moderate), with a moderate improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.42); as well as flexor average power (I2 = 0%, p = 0.01, evidence certainty = moderate), with a moderate improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.37). However, in the 180°/s isokinetic muscle strength of the flexors, YJJ did not demonstrate any improvement in flexor peak torque (I2 = 0%, p = 0.96, evidence certainty = moderate) (Hedges’g = 0.01) or flexor average power (I2 = 0%, p = 0.61, evidence certainty = moderate) (Hedges’g = −0.08).
3.4.2 Physical performance in the older individuals
Table 3 and Figure 4 summarize the evidence of the effect of YJJ on physical performance in the older population. Forest plots and specific grade ratings are provided in Supplementary material.
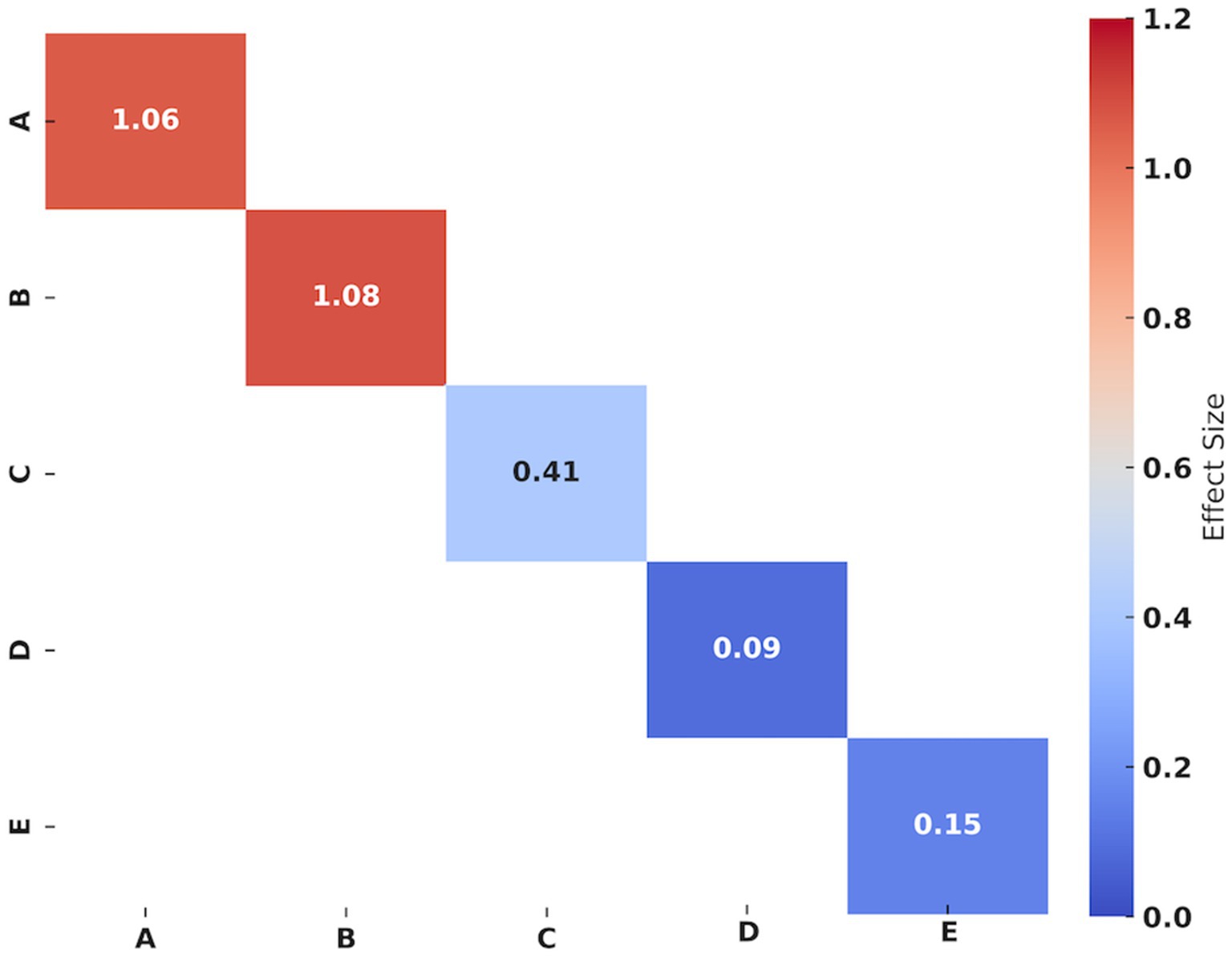
Figure 4. Effect size of Yi Jin Jing on physical performance in the older individuals. A: Chair sit-to-stand test; B: Squatting-to-standing test; C: Shoulder flexibility (left); D: Shoulder flexibility (right); E: Sit-and-reach test. Hedges’g values of 0.2–0.4 indicating small, 0.5–0.7 signifying medium, and ≥0.8 representing large effect sizes, respectively.
Three studies (15, 21, 37) assessed chair sit-to-stand test results in older individuals. The synthesized data indicated that the effect of YJJ on the chair sit-to-stand test was statistically significant (I2 = 69.30%, p < 0.001, certainty of evidence = low), with a large improvement effect (Hedges’g = 1.06). Sensitivity analysis showed that the heterogeneity of the chair sit-to-stand test decreased from 69.30 to 29.75% when one study was removed (15).
Three studies (15, 21, 37) reported the outcomes of the squatting-to-standing tests in older individuals. The synthetic data showed that the effect of YJJ on the chair sit-to-stand test was statistically significant (I2 = 90.91%, p < 0.001, certainty of evidence = low), with a large improvement effect (Hedges’g = 1.08). Sensitivity analysis revealed that the heterogeneity of the squatting-to-standing test decreased from 90.91 to 76.05% when one study was removed (15).
Two studies (21, 37) reported the outcomes of shoulder flexibility in older individuals. The synthetic data revealed that YJJ significantly increased left shoulder flexibility (I2 = 0%, p = 0.01, certainty of evidence = moderate), with a slight improvement effect (Hedges’g = 0.41); however, no effect was observed on right shoulder flexibility (I2 = 0%, p = 0.06, certainty of evidence = moderate) (Hedges’g = 0.09).
Three studies (21, 22, 37) investigated the outcomes of the sit-and-reach test in the older individuals. The synthetic data suggested that YJJ did not affect the sit-and-reach test (I2 = 0%, p = 0.25, the certainty of evidence = moderate) (Hedges’g = 0.15).
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis included 10 RCTs involving 590 patients. The overall risk of bias was assessed to be low. The methodological quality of these studies was generally moderate, and the quality of the main results ranging from low to moderate. The results of the meta-analysis showed that compared with the control group, YJJ significantly improved both muscle strength and physical performance in the older individuals.
Previous studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of traditional Chinese exercises on muscle strength and overall physical function in older individuals (16, 17, 20). However, these studies have certain limitations. First, they often combined various traditional Chinese exercises without conducting subgroup analyses of the YJJ. For example, Wang et al. categorized exercise types into Tai Chi, Baduanjin, and other Qigong and found that traditional Chinese exercises significantly improved balance, physical performance, and muscle strength in older adults (24). Similarly, Wan et al.’s study, which included Tai Chi and Baduanjin, revealed that both exercises were beneficial for alleviating frailty and enhancing physical function in pre-frail and frail older adults, although Tai Chi did not improve handgrip strength in frail individuals (25). Additionally, two studies referenced sarcopenia, Niu et al. combined Tai Chi, Baduanjin, and YJJ, demonstrating the significant benefits of traditional Chinese exercises for lower limb muscle strength and physical function, but no improvement in handgrip strength (26). Guo et al.’s study on traditional Chinese medicine, including herbal medicine, acupuncture, and traditional Chinese exercises (including Tai Chi, Baduanjin, and YJJ), demonstrated the effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine in treating sarcopenia as indicated by improvements in grip strength, chair stand test, timed up and go test, 6-m walking speed, and sit and reach (27). Second, these studies (24–27) did not calculate the effect size, which is a useful indicator in meta-analyses because it can statistically correct the variance caused by small sample sizes and synthesize data measured on different scales (28). Notably, a recent network meta-analysis reported that YJJ was the most effective method for enhancing balance and reducing their fear of falling in older individuals compared to Tai Chi, Baduanjin, and Wuqinxi (40). To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to explore the specific effect sizes of YJJ on muscle strength and physical performance in an older population.
Although our study revealed a low heterogeneity in muscle strength, the results should be interpreted with caution because of the limited number of studies included. YJJ’s movement framework involves a series of complex motions, including rotation, bending, and extension of the forearm, as well as intricate finger and grip movements (41). This comprehensive exercise targets the muscles of the shoulders, arms, and hands, potentially improving handgrip strength and flexibility (12). Furthermore, YJJ plays a key role in knee joint stabilization through closed-chain exercises (17, 42, 43). It emphasizes isotonic contractions in lower-limb movements, particularly through extensive squatting, enhancing muscle coordination and strength around the joints (13). This meta-analysis suggests that YJJ substantially enhanced the peak torque, average power, and total work of both the extensor and flexor muscles during the 60°/s isokinetic muscle strength test. However, the gentle and progressive movement nature of YJJ may not be well suited for the 180°/s test, which depends on rapid strength and explosive muscular force. This indicates that YJJ is more appropriate for improving endurance and controlled strength than for high-speed activities.
This meta-analysis further demonstrated that YJJ exerted a significant positive effect on chair sit-to-stand and squatting-to-standing tests, which are key indices of lower limb strength and overall physical performance. The marked reduction in heterogeneity observed in these two tests likely stems from different participant selection criteria. Specifically, Zhu’s research focused on patients with sarcopenia diagnosed according to the AWGS criteria (11), whereas Wang and Jin’s study applied Roubenoff’s view to identify sarcopenia in individuals aged 60 and over (44). Therefore, YJJ can be considered an effective intervention to enhance lower limb strength and physical performance in the older individuals.
Aging is associated with decreased skeletal muscle quality and functionality, leading to diminished joint mobility and muscle flexibility (45). This deterioration affects the performance of older individuals in flexibility assessments, such as sit-and-reach performance (46). Conversely, YJJ, which includes arm rotations and lifts, may improve the range of motion and coordination of the shoulder joint, potentially leading to increased shoulder flexibility. Studies have shown that asymmetric use of the dominant hand in daily activities affects muscle and joint functions (47). Considering that the left shoulder is less involved in high-intensity activities in daily life, it may be more responsive to YJJ, resulting in a significant improvement in flexibility.
5 Conclusion
In summary, our findings indicate that YJJ significantly enhances specific aspects of physical performance, notably the chair sit-to-stand test and squatting-to-standing test. Additionally, moderate improvements were observed in handgrip strength and various measures of knee flexor and extensor strength. In contrast, YJJ had no significant effects on certain metrics, including extensor and flexor average power at 180°/s, extensor total work at 180°/s, flexor peak torque at 180°/s, right shoulder flexibility, and the sit-and-reach test.
6 Limitations and directions for future research
This study has several limitations. First, it did not include high-quality studies, which may have affected the robustness of our conclusions. Second, the reliance on expert opinions for sarcopenia diagnosis in earlier studies may introduce a potential risk of bias and uncertainty. Third, the limited number of eligible studies and their small sample sizes are constraints. Future studies should adopt rigorous research designs, including clear selection criteria, sample size calculations, randomization, allocation concealment, and blinding. Additionally, it is crucial to adjust exercise parameters, such as frequency, duration, and intensity, to match the physiological characteristics of the older individuals and meticulously record any adverse events and reasons for dropout. Importantly, our findings revealed that Yi Jin Jing had a small but significant effect on handgrip strength in older individuals, suggesting that combining it with resistance exercises could achieve better outcomes.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: the data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Software, Methodology, Formal analysis. WJ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis. ZC: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Conceptualization. GY: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. ZR: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the authors, researchers and participants who participated in this study. Thanks to their efforts and contributions, this research can be carried out smoothly.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1441858/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. China NBS. Bulletin of the seventh national census. (2021). Available at: https://www.gov.cn/guoqing/2021-05/13/content_5606149.htm?eqid=d8d59db4000a192000000004645e543b (Accessed May 11, 2021).
2. Demircan, K, Hybsier, S, Chillon, TS, Vetter, VM, Rijntjes, E, Demuth, I, et al. Sex-specific associations of serum selenium and selenoprotein P with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension in the Berlin aging study II. Redox Biol. (2023) 65:102823. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102823
3. Arnold, AC, Gallagher, PE, and Diz, DI. Brain renin-angiotensin system in the nexus of hypertension and aging. Hypertens Res. (2013) 36:5–13. doi: 10.1038/hr.2012.161
4. Rodriguez, M, Rodriguez-Sabate, C, Morales, I, Sanchez, A, and Sabate, M. Parkinson's disease as a result of aging. Aging Cell. (2015) 14:293–308. doi: 10.1111/acel.12312
5. Chen, S, Xu, X, Gong, H, Chen, R, Guan, L, Yan, X, et al. Global epidemiological features and impact of osteosarcopenia: a comprehensive meta-analysis and systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:8–20. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13392
6. Cruz-Jentoft, AJ, Bahat, G, Bauer, J, Boirie, Y, Bruyère, O, Cederholm, T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. (2019) 48:601. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afz046
7. Gadelha, AB, Vainshelboim, B, Ferreira, AP, Neri, SGR, Bottaro, M, and Lima, RM. Stages of sarcopenia and the incidence of falls in older women: a prospective study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2018) 79:151–7. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.07.014
8. Yeung, SSY, Reijnierse, EM, Pham, VK, Trappenburg, MC, Lim, WK, Meskers, CGM, et al. Sarcopenia and its association with falls and fractures in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2019) 10:485–500. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12411
9. Kitamura, A, Seino, S, Abe, T, Nofuji, Y, Yokoyama, Y, Amano, H, et al. Sarcopenia: prevalence, associated factors, and the risk of mortality and disability in Japanese older adults. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2021) 12:30–8. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12651
10. Lim, WS, Cheong, CY, Lim, JP, Tan, MMY, Chia, JQ, Malik, NA, et al. Singapore clinical practice guidelines for sarcopenia: screening, diagnosis, management and prevention. J Frailty Aging. (2022) 11:348–69. doi: 10.14283/jfa.2022.59
11. Chen, L, Woo, J, Assantachai, P, Auyeung, T, Chou, M, Iijima, K, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–307.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
12. Yufan, C, and Min, W. Research on the use of "classics of tendon changing" in improving physical capacity of the aged. Sports Sci. (1998) 19 33–35, 48. doi: 10.13598/j.issn1004-4590.1998.03.009
13. Tundeworld. Yi Jin Jing (strengthen the muscle and build energy within exercises). (n.d.). Available at: https://tundeworld.com/YiJinJing.Health.Preserving.Qigong
14. Guo, C, Cheng, Y, Kong, L, Bu, J, and Xiuaocun, Y. On Gongfa and Gongli of Yi Jin jing from the perspective of biomechanics. J Changchun Univ Tradit Chinese Med. (2014) 30:262–4. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2014.02.027
15. Zhu, G, Luo, K, Shen, Z, Gao, F, Fu, Y, and Shen, Q. Effect of Yijinjing on muscle strength of senile patients with sarcopenia. Chinese J Gen Pract. (2019) 17:1388–91. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000951
16. Zhao, Y, Zhang, Y, and Guo, Y. Effects of Chinese massage and resistance exercise on ADL in elderly Chinese sarcopenic men. Chinese J Rehabil Med. (2016) 31:989–94.
17. Zhang, S, Zhu, Q, Cheng, Y, and Fang, M. Yijinjing exercise on gait biomechanics in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. China J Tradit Chinese Med Pharm. (2023) 38:5081–6.
18. Bing Wang, SM, and Ying, H. Delaying effect of Yijinjing qigong exercise on senile skeletal muscle weakness. Chin J Gerontol. (2015) 35:28–30.
19. Hu, W, Gong, L, Qian, Y, and Hu, H. Tuina Yijinjing Gong practice improves the knee muscle strength of the elderly. Chinese J Sports Med. (2013) 32:775–9.
20. He, S, Wei, M, Meng, D, Wang, Z, Yang, G, and Wang, Z. Self-determined sequence exercise program for elderly with sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial with clinical assistance from explainable artificial intelligence. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2024):119. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105317
21. Wang, B, Ma, S, and Hu, Y. Influence of fitness Yijinjing Qigong on the rehabilitation effect of patients with osteopenia. Chin J Gerontol. (2016) 36:898–9.
22. Su, Y, and Liu, X. The effect of health qigong (Yijinjing) on physical function and blood lipids in the elderly. J Nanjing Inst Phys Educ (Nat Sci). (2012) 11:27–9. doi: 10.15877/j.cnki.nsin.2012.02.021
23. Liu, X, Jin, H, and Gu, Y. The effect of health Qigong (Yijinjing) on physical quality of elderly women. Contemp Med. (2010) 16:3–4.
24. Wang, C, Liang, J, Si, Y, Li, Z, and Lu, A. The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine-based exercise on physical performance, balance and muscle strength among older adults: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2022) 34:725–40. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-01964-2
25. Wan, X, Shen, J, and He, G. Effects of traditional Chinese exercises on frailty, quality of life, and physical function on frail and pre-frail older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Frailty Aging. (2022) 11:407–15. doi: 10.14283/jfa.2022.52
26. Niu, K, Liu, Y-L, Yang, F, Wang, Y, Zhou, X-Z, and Qu, Q. Efficacy of traditional Chinese exercise for sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Neurosci. (2022) 16:1094054. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1094054
27. Guo, C-Y, Ma, Y-J, Liu, S-T, Zhu, R-R, Xu, X-T, Li, Z-R, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine and sarcopenia: a systematic review. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:872233. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.872233
28. Hedges, LV, and Olkin, I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. San Diego, CA: Academic Press (2014).
29. Moher, D, Shamseer, L, Clarke, M, Ghersi, D, Liberati, A, Petticrew, M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. (2015) 4:1. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
30. Maher, CG, Sherrington, C, Herbert, RD, Moseley, AM, and Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. (2003) 83:713–21. doi: 10.1093/ptj/83.8.713
31. Cashin, AG, and McAuley, JH. Clinimetrics: physiotherapy evidence database (PEDro) scale. J Physiother. (2020) 66:59. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2019.08.005
32. Higgins, J, Savović, J, Page, M, Elbers, R, and Sterne, J. Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. Cochrane Handb Syst Rev Intervent. (2019):205–28. doi: 10.1002/9781119536604.ch8
33. Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York, NY: Routledge (2013).
34. Guyatt, G, Oxman, AD, Sultan, S, Brozek, J, Glasziou, P, Alonso-Coello, P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. (2013) 66:151–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006
35. Patsopoulos, NA, Evangelou, E, and Ioannidis, JPA. Sensitivity of between-study heterogeneity in meta-analysis: proposed metrics and empirical evaluation. Int J Epidemiol. (2008) 37:1148–57. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn065
36. Fan, Z, Wu, Y, Wang, J, Zhang, J, and Han, C. Effect of Tuina exercise on quadriceps Femoris muscle strength of patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. (2012) 10:321–8. doi: 10.1007/s11726-012-0629-2
37. Jin, D, Xu, J, Zhao, J, Hu, Y, and Wang, D. Effect of Yijinjing on daily activity ability and physique of patients with osteopenia. Chinese J Inf TCM. (2011) 18:14–6.
38. Li, G, Yan, J, Liu, Y, Fang, L, Zhang, H, Xu, J, et al. Effect of Yijinjing on isokinetic muscle strength in elderly patients with osteopenia. J Shanghai Univ Trad Chinese Med. (2011) 25:55–8. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2011.03.014
39. Liu, Y, Yan, J, Wang, Z, Zhu, Q, Fang, M, Zhang, H, et al. Effect of Yijinjing on skeletal muscle contractile function in elderly patients with osteopenia. J Shanghai Univ Trad Chinese Med. (2016) 30:42–5. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2016.05.011
40. Cheng, M, Wang, Y, Wang, S, Cao, W, and Wang, X. Network meta-analysis of the efficacy of four traditional Chinese physical exercise therapies on the prevention of falls in the elderly. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1096599. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1096599
41. Association BHQ. A scientific interpretation of the “Meridian musculature” system. Health Qigong in the UK & Europe with the BHQA. (n.d.). Available at: https://healthqigong.org.uk/info/?page_alias=yi_jin_jing_article_15_meridian_musculature
42. Jing, L, Huang, L, Wang, Y, and Gao, M. Effects of Yi Jin Jing training on lower limb kinetics and muscle contribution in older adults. J Shandong Sport Univ. (2019) 35 82–89+102. doi: 10.14104/j.cnki.1006-2076.2019.02.012
43. Li, Y, Ye, Y, Niu, X, Qiu, Z, and Zhong, W. Effects of Yi Jin Jing exercise on the coordination activation ability of lower limb muscles of knee osteoarthritis. China J Trad Chinese Med Pharm. (2022) 37:2380–5.
44. Roubenoff, R. Origins and clinical relevance of sarcopenia. Can J Appl Physiol. (2001) 26:78–89. doi: 10.1139/h01-006
45. Larsson, L, Degens, H, Li, M, Salviati, L, Lee, YI, Thompson, W, et al. Sarcopenia: aging-related loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol Rev. (2019) 99:427–511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00061.2017
46. Wilke, J, Macchi, V, De Caro, R, and Stecco, C. Fascia thickness, aging and flexibility: is there an association? J Anat. (2019) 234:43–9. doi: 10.1111/joa.12902
Keywords: Yi Jin Jing, traditional Chinese exercise, older individuals, muscle strength, physical performance
Citation: Zhang X, Jiang W, Chen Z, Yang G and Ren Z (2024) Effects of Yi Jin Jing on enhancing muscle strength and physical performance in older individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 11:1441858. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1441858
Edited by:
Diogo Luís Marques, University of Beira Interior, PortugalReviewed by:
Catarina Rondão, University of Beira Interior, PortugalTiago Sousa, University of Beira Interior, Portugal
Mafalda Pamplona Pinto, University of Beira Interior, Portugal
Mário C. Marques, University of Beira Interior, Portugal
Tiago Sousa and Mafalda Pamplona Pinto, University of Beira Interior, Portugal, in collaboration with reviewer MM
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Jiang, Chen, Yang and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenqi Chen, MjAwMzAwMjhAZ3hhdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaoping Zhang
Xiaoping Zhang Wenda Jiang2†
Wenda Jiang2† Zhenqi Chen
Zhenqi Chen Zhongyu Ren
Zhongyu Ren