- Department of Nephrology, Yan’an People’s Hospital, Yan’an, Shaanxi, China
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the most common chronic complications in patients with diabetes and remains a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Despite current treatment strategies focusing primarily on blood glucose control and antihypertensive medications, their efficacy is often limited, failing to halt disease progression effectively. However, Shen-Shuai-Ning (SSN), a traditional Chinese medicine compound, has demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in DN treatment in recent years. SSN exerts multifaceted effects, including immunomodulation, attenuation of oxidative stress, and inhibition of fibrosis, leading to improvements in renal function indices and reductions in proteinuria levels, with favorable tolerability. Furthermore, when combined with conventional treatments, SSN exhibits enhanced therapeutic efficacy, providing a comprehensive and effective treatment strategy for DN patients. Future research endeavors should prioritize large-scale, multicenter clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety across diverse populations, thereby further advancing its integration into clinical practice.
1 Introduction
1.1 Epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy
DN is one of the most common chronic complications in patients with diabetes and is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise globally, the incidence of DN is also increasing. According to the International Diabetes Federation, in 2019, approximately 463 million people worldwide had diabetes, and 30–40% of these patients are expected to develop DN (1, 2). In China, over 120 million people have diabetes, making DN a primary cause of chronic kidney disease in the country (3).
1.2 The hazards and treatment challenges of DN
DN not only significantly reduces patients’ quality of life but also substantially increases healthcare burdens. Clinical features of DN include proteinuria, progressive decline in renal function, and hypertension, eventually leading to renal failure and a high incidence of cardiovascular diseases (4). Current treatment strategies for DN focus on blood glucose control, blood pressure management, and the use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, but their effectiveness is often limited, and they cannot halt disease progression (5). Additionally, existing treatments can have various adverse effects, further restricting their clinical use.
1.3 The potential of Shen-Shuai-Ning as a traditional Chinese medicine formula in treating DN
SSN is a compound formulation composed of several TCM herbs. Recently, it has shown promising clinical efficacy in treating DN. Its main components include Astragalus membranaceus, Salvia miltiorrhiza, and Rehmannia glutinosa, which have the functions of tonifying Qi, nourishing Yin, and promoting Blood circulation (6). Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that SSN exerts significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic effects in the renal glomeruli (7). Numerous clinical studies have confirmed that SSN significantly improves renal function indices, reduces proteinuria, and enhances the quality of life in patients with DN (8). Compared to traditional treatment methods, SSN has fewer adverse effects, and its multi-target, multi-mechanism approach as a TCM compound helps comprehensively control the progression of DN.
Therefore, in-depth research into the mechanisms and clinical application prospects of SSN in treating DN is of great significance for improving treatment outcomes and reducing patient burdens. This study aims to systematically summarize the latest research progress on SSN in the treatment of DN, provide a scientific basis for clinical practice, and explore its future development directions.
2 Components and pharmacological mechanisms of SSN
2.1 Major components of SSN
SSN is a TCM formula comprising several key herbal ingredients. The primary components include Astragalus membranaceus (Huang Qi), Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen), and Rehmannia glutinosa (Di Huang). Each herb has a long history of use in TCM, known for distinct therapeutic properties (6).
2.2 Pharmacological actions of each component
Astragalus membranaceus is known for its immunomodulatory effects, enhancing immune function by stimulating macrophages and natural killer cells (9). Additionally, it possesses strong antioxidant properties, reducing oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals (10). Astragalus also decreases inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines (11).
Salvia miltiorrhiza improves microcirculation, enhancing blood flow and reducing blood stasis, which is beneficial for preventing microvascular complications in diabetes (12). Salvia contains active compounds such as salvianolic acids and tanshinones that offer potent antioxidant effects (13, 14). Furthermore, Salvia modulates inflammatory pathways, reducing inflammatory responses (13, 14).
Rehmannia glutinosa is traditionally used to nourish Yin and support kidney function, making it suitable for chronic kidney disease treatments (6, 11). It mitigates oxidative stress, protecting renal cells from damage (15), and inhibits renal fibrosis, a common pathological process in chronic kidney diseases, including DN (15).
2.3 Mechanisms of renal protection by SSN
SSN exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects, which are critical in the progression of DN. The formula reduces levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are implicated in renal inflammation and damage (16, 17). Additionally, it inhibits the activation of NF-κB, a key regulator of inflammation, thereby reducing inflammatory responses in renal tissues (18).
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of DN, and SSN enhances the body’s antioxidant defenses by upregulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase (7). This enhancement reduces oxidative stress and protects renal cells from damage caused by high glucose levels and other metabolic disturbances (7, 18).
Renal fibrosis, especially tubulointerstitial fibrosis, is a hallmark of advanced DN. SSN helps reduce fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, which is crucial in the development of renal fibrosis (19). This inhibition prevents the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components such as collagen, thereby preserving the normal architecture and function of renal tissue (19, 20).
In summary, SSN’s multi-component and multi-target approach provides a comprehensive therapeutic strategy for DN. Its capabilities to modulate immune responses, reduce oxidative stress, and prevent fibrosis highlight its potential as a valuable treatment option for managing this complex condition.
3 Clinical research on SSN in treating DN
3.1 Overview of clinical research
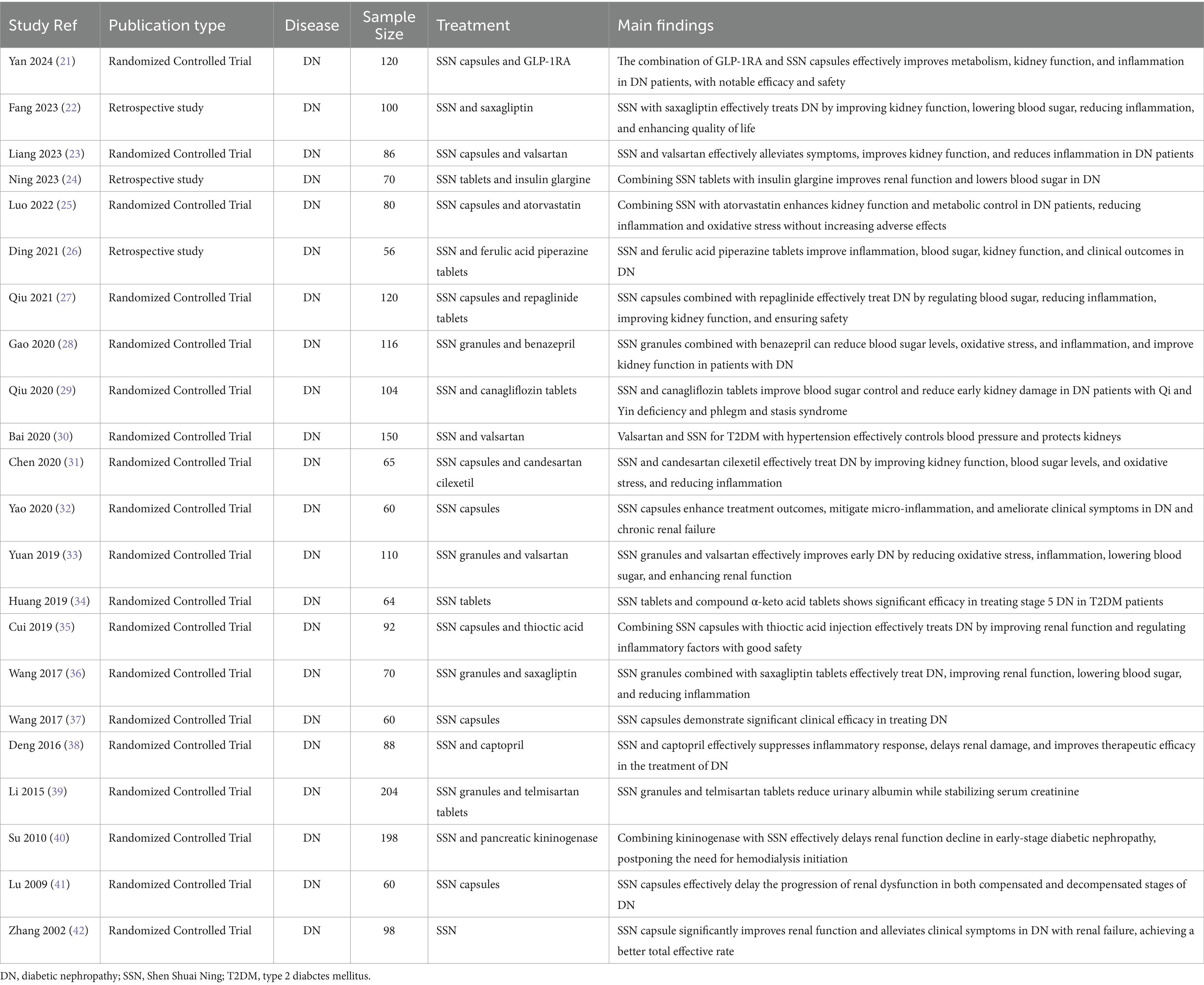
SSN, a TCM formula, has shown promising efficacy in the treatment of DN. Numerous studies have evaluated its efficacy and safety, employing various research designs and methods, including randomized controlled trials, prospective and retrospective analyses (21–42) (Table 1).
3.2 Research design and methods
Several studies utilized random number tables for patient allocation to ensure randomness and reliability (21, 23, 27). Retrospective studies selected patients based on medical records, grouping and analyzing those meeting the criteria (22, 26). Study durations varied from several months to several years, covering different stages and types of DN patients (Table 1).
3.3 Patient selection and grouping
Studies typically selected DN patients meeting specific diagnostic criteria, such as particular renal function indicators and urinary protein levels. Patients were randomly assigned to treatment and control groups, with the treatment group receiving SSN combined with standard therapy, while the control group received only standard therapy or SSN alone (21, 22, 26) (Table 1). Selection criteria generally included age, gender, disease duration, and underlying conditions to ensure the homogeneity and comparability of study subjects (24, 25) (Table 1).
3.4 Treatment protocols and dosages
Treatment protocols included different formulations of SSN (such as capsules, tablets, granules) and dosages, and whether it was combined with other medications (e.g., valsartan, telmisartan) (25, 32, 39) (Table 1). Dosages and treatment durations were adjusted based on disease severity and specific study goals. For instance, some studies used SSN capsules three times daily, four capsules each time, combined with other medications for 2 to 3 months (37, 38) (Table 1).
3.5 Main study results
3.5.1 Improvement in renal function
Most studies reported significant improvements in renal function indicators such as serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and urinary protein excretion rate (34, 35, 37) (Table 1). For example, one study showed that serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels significantly decreased in the treatment group after therapy, and were lower than those in the control group, indicating SSN’s efficacy in enhancing renal function (36) (Table 1).
3.5.2 Changes in urinary protein excretion
Urinary protein excretion is a key indicator for assessing DN treatment efficacy (Table 1). Studies have shown that SSN effectively reduces urinary protein excretion, slowing the progression of DN (28, 36). For instance, in one study, the 24-h urinary protein excretion significantly decreased in the treatment group and was lower than in the control group, demonstrating SSN’s protective effect on the kidneys (33).
3.5.3 Changes in blood glucose and other metabolic indicators
SSN also has a positive effect on blood glucose control in diabetic patients, reducing levels of glycated hemoglobin and fasting blood glucose (26, 30) (Table 1). Additionally, it has been observed to positively impact other metabolic indicators such as blood lipids (Table 1). For example, studies have shown that total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels significantly decreased, while high-density lipoprotein levels increased in patients treated with SSN (25).
3.6 Safety and adverse reactions
3.6.1 Common adverse reactions and management
Reports of adverse reactions to SSN are relatively few and mostly mild to moderate, including gastrointestinal discomfort (33, 38) (Table 1). These reactions are typically self-resolving or can be managed by adjusting the dosage and treatment regimen. Reports of severe adverse reactions are rare, with no significant life-threatening or serious harm events observed (29, 40).
3.6.2 Safety evaluation
Based on multiple studies, SSN has demonstrated a high safety profile in treating DN. Most studies did not find significant serious adverse reactions (31, 41) (Table 1). During treatment, patients’ renal function and other biochemical indicators significantly improved without noticeable adverse reactions, indicating its high clinical application value and safety (32, 42) (Table 1).
4 Mechanisms of SSN in treating DN
Understanding the mechanisms underlying SSN’s therapeutic effects in DN entails a comprehensive exploration of its actions at various levels, spanning cellular, animal model, and molecular biology research (6, 16–20). This investigation elucidates how SSN attenuates the progression of DN and offers insights into its clinical application.
4.1 Cellular-level research
4.1.1 Interactions between glomerular and tubular cells
At the cellular level, SSN intervenes in DN by targeting both glomerular and tubular cells within the kidney. These cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of renal damage associated with diabetes (6, 43). SSN’s multi-herbal formulation exhibits protective effects by ameliorating glomerular dysfunction, including podocyte injury and mesangial cell proliferation, while also mitigating tubular cell injury, reducing tubular epithelial cell apoptosis, and promoting tubular cell regeneration (18). By preserving the structural and functional integrity of glomerular and tubular cells, SSN effectively impedes the progression of renal dysfunction in DN.
4.2 Animal model studies
4.2.1 Mechanisms in DN animal models
Animal model studies serve as crucial platforms for elucidating the mechanisms underlying SSN’s therapeutic efficacy in DN. Utilizing various models, such as streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice, researchers have demonstrated SSN’s significant renal protective effects (18). These effects encompass attenuation of renal hypertrophy, reduction in urinary albumin excretion, and amelioration of renal histopathological alterations. Mechanistically, SSN intervenes by suppressing inflammatory responses, ameliorating oxidative stress, and inhibiting renal fibrosis in diabetic animals (43). These findings underscore the multifaceted nature of SSN’s therapeutic action, which involves modulation of diverse pathogenic pathways implicated in DN.
4.3 Molecular biology research
4.3.1 Signaling pathways and gene expression)
Molecular biology investigations provide valuable insights into the signaling pathways underpinning SSN’s therapeutic effects in DN. By targeting key pathways such as the TGF-β/Smad pathway, and NF-κB pathway, SSN orchestrates a comprehensive array of molecular responses (18). It modulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrosis, thereby exerting profound renal protective effects (43). Moreover, the synergistic interactions among SSN’s constituent herbs contribute to its enhanced therapeutic efficacy compared to single-component interventions.
In summary, SSN’s therapeutic mechanisms in DN encompass a multifaceted approach, involving interventions at the cellular, animal model, and molecular levels. By targeting glomerular and tubular cells, suppressing inflammation, ameliorating oxidative stress, and inhibiting renal fibrosis, SSN offers a holistic therapeutic strategy for managing DN. Further elucidation of its mechanisms holds promise for the development of innovative therapeutic interventions aimed at combating this debilitating condition.
5 Comparison of SSN with existing treatment methods
5.1 Conventional medicine treatment regimens
The primary treatment options for DN in Western medicine include Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs) or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) and statins. These medications are widely used due to their proven efficacy in managing DN.
5.1.1 ACEIs/ARBs
ACEIs and ARBs are fundamental in managing DN as they reduce proteinuria and slow kidney disease progression by controlling blood pressure and reducing intraglomerular pressure. Studies indicate these medications significantly decrease the risk of renal failure and delay progression to end-stage renal disease (30, 33). Common ACEIs include enalapril and lisinopril, while losartan and valsartan are frequently prescribed ARBs.
5.1.2 Statins
Statins are primarily prescribed for managing hyperlipidemia, which is common in diabetic patients, and they offer cardiovascular protection. These medications work by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme crucial for cholesterol synthesis. Statins like atorvastatin and rosuvastatin reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol, beneficial in mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation associated with DN (25).
5.2 Effects of combined treatment with SSN
Combining SSN with conventional Western medications has demonstrated enhanced therapeutic outcomes in DN patients, providing synergistic benefits.
5.2.1 Synergistic effects with Western medications
The combination of SSN with ACEIs or ARBs has shown superior renal protection compared to Western medications alone. Research has demonstrated that combined therapy significantly reduces serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels more effectively than ACEIs or ARBs alone (21, 31). For instance, a study found that combining SSN with valsartan led to greater improvements in renal function and a more substantial reduction in urinary protein excretion than valsartan alone (30). This synergy is likely due to SSN’s ability to enhance blood circulation and reduce inflammation, complementing the renal protective effects of ACEIs and ARBs.
Similarly, combining SSN with statins results in better control of lipid profiles and reduced oxidative stress markers. The antioxidant properties of SSN, combined with the lipid-lowering effects of statins, provide a comprehensive approach to managing DN. Studies have reported that patients receiving this combination therapy showed significant improvements in both renal function and lipid metabolism compared to those receiving only statins (25, 35).
5.2.2 Effects of combination with other Chinese medicines
SSN has also been studied in combination with other TCM, showing promising results. For instance, combining SSN with Ferulic Acid Piperazine has been shown to effectively reduce inflammation and improve renal function markers such as serum creatinine and urinary protein levels (26). Another study highlighted the benefits of combining SSN with other herbal formulations like Astragalus, demonstrating enhanced therapeutic effects in reducing proteinuria and improving overall kidney function (37).
These combinations leverage the multi-targeted approach of TCM, which focus on restoring systemic balance and improving organ function through various mechanisms. This holistic approach often results in better patient outcomes and improved quality of life, as evidenced by several clinical studies (32, 38).
SSN, both as a monotherapy and in combination with conventional Western medicines, offers significant advantages in managing DN. Its integration with ACEIs, ARBs, and statins enhances therapeutic effects, leading to improved renal function and better metabolic control. Additionally, its combination with other TCM provides a comprehensive treatment approach for DN, highlighting its potential as a valuable component of integrated treatment regimens.
6 Prospects for SSN in the treatment of DN
6.1 Future research directions
6.1.1 Large-scale, multicenter clinical trials
Future research on SSN should prioritize large-scale, multicenter clinical trials to thoroughly validate its efficacy and safety (44). These trials would provide robust data across diverse populations and healthcare settings, addressing the limitations of smaller, single-center studies (44). By involving a larger sample size and multiple centers, the generalizability of the results can be enhanced, offering a more accurate assessment of SSN’s therapeutic potential in treating DN.
6.1.2 Long-term efficacy and safety studies
Investigating the long-term efficacy and safety of SSN is crucial. While short-term studies have shown promising results, understanding the long-term effects is essential. This includes evaluating the sustainability of benefits on renal function, glucose metabolism, and overall patient health, as well as monitoring for any long-term adverse effects. Long-term studies would provide valuable insights into the chronic management of DN and the role of SSN, ensuring it remains a safe and effective treatment option over extended periods.
6.2 Challenges in clinical application
6.2.1 Standardization and regulation
A significant challenge in the clinical application of SSN is the standardization and regulation of its production and use. TCM often faces issues related to batch-to-batch consistency and quality control due to variations in raw materials and preparation methods (45, 46). Ensuring that SSN is produced under stringent quality control measures and adheres to standardized protocols is crucial for its widespread clinical adoption (45, 46). Establishing and enforcing regulatory frameworks will ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of SSN, thereby building trust among healthcare providers and patients.
6.2.2 Implementation of personalized treatment
Achieving personalized treatment with SSN presents another challenge. DN patients exhibit significant variability in disease progression, treatment response, and underlying health conditions. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all approach may not be effective. Future research should focus on identifying biomarkers and patient characteristics that predict response to SSN, enabling the development of tailored treatment regimens (47). Personalized medicine approaches, including pharmacogenomics and patient stratification based on genetic, biochemical, and clinical profiles, can optimize treatment outcomes and minimize adverse effects (48).
SSN holds significant promise in treating DN, but its future success depends on overcoming current challenges through rigorous research and standardization. Large-scale, multicenter trials and long-term studies are necessary to establish its efficacy and safety comprehensively. Addressing standardization issues and advancing personalized treatment approaches will be crucial for its effective integration into clinical practice. With these efforts, SSN can potentially become a cornerstone in the holistic management of DN, combining the strengths of TCM with modern medical practices.
7 Summary
7.1 Summary of research progress
SSN has demonstrated significant potential in treating DN, with clinical studies showing improvements in renal function, reduced urinary protein excretion, and enhanced metabolic control. Combining SSN with conventional treatments like ACEIs, ARBs, and statins has provided synergistic benefits, leading to better clinical outcomes. Its favorable safety profile, with few reported adverse effects, supports its use as a therapeutic option for DN.
7.2 Outlook for future research and clinical application
Future research should focus on large-scale, multicenter clinical trials to validate SSN’s efficacy and safety across diverse populations. Long-term studies are needed to assess the sustainability of its benefits and monitor for chronic adverse effects. Standardizing production and regulatory practices will ensure consistency and quality, fostering greater trust among healthcare providers and patients. Advancing personalized treatment approaches by identifying biomarkers that predict response to SSN will optimize outcomes and minimize adverse effects. Overcoming these challenges will enable SSN to become a cornerstone in managing DN, integrating TCM with modern healthcare practices.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
NG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. X-jZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Alicic, RZ, Rooney, MT, and Tuttle, KR. Diabetic kidney disease: challenges, Progress, and possibilities. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 12:2032–45. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11491116
2. Saeedi, P, Petersohn, I, Salpea, P, Malanda, B, Karuranga, S, Unwin, N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international Diabetes federation Diabetes atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
3. Zhang, L, Long, J, Jiang, W, Shi, Y, He, X, Zhou, Z, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:905–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1602469
4. ElSayed, NA, Aleppo, G, Aroda, VR, Bannuru, RR, Brown, FM, Bruemmer, D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and risk management: standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:S191–202. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S011
5. Tuttle, KR, Bakris, GL, Bilous, RW, Chiang, JL, de Boer, IH, Goldstein-Fuchs, J, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA consensus conference. Diabetes Care. (2014) 37:2864–83. doi: 10.2337/dc14-1296
6. Zhang, J, Yue, YL, and Zhang, YN. Application and pharmacological mechanism analysis of Shen Shuai Ning capsules in the treatment of chronic renal failure patients. J Pract Tradit Chin Internal Med. (2022) 36:110–2. doi: 10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.Z20221774
7. Chen, Y, Xiao, W, Ma, Y, and Hou, LB. Effect of shenshuaining dispersible tablets on the levels of NO, NOS, SOD and MDA in kidney of chronic renal failure rats. Zhong Yao Cai. (2008) 31:1190–3. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2008.08.037
8. Cui, RZ, Xie, YM, Liao, X, and Wang, JD. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the adjuvant treatment of chronic renal failure with Shenqi Ning capsule. Chin J Chin Materia Medica. (2016) 41:2149–61. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20161128
9. Dai, YJ, Guo, MF, Jiang, L, and Gao, JR. Network pharmacology-based identification of mi RNA expression of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Medicine (Baltimore). (2022) 101:e28747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028747
10. Wu, Q, Guan, YB, Zhang, KJ, Li, L, and Zhou, Y. Tanshinone IIA mediates protection from diabetes kidney disease by inhibiting oxidative stress induced pyroptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 316:116667. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116667
11. Yokozawa, T, Kim, HY, and Yamabe, N. Amelioration of diabetic nephropathy by dried Rehmanniae Radix (Di Huang) extract. Am J Chin Med. (2004) 32:829–39. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X04002442
12. Chen, X, Guo, J, Bao, J, Lu, J, and Wang, Y. The anticancer properties of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen): a systematic review. Med Res Rev. (2014) 34:768–94. doi: 10.1002/med.21304
13. Fang, Y, Liu, J, Xin, L, Jiang, H, Guo, J, Li, X, et al. Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza for ankylosing spondylitis: determining potential inflammatory molecular targets and mechanism using network pharmacology. Biomed Res Int. (2022) 2022:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2022/3816258
14. Zhou, L, Zuo, Z, and Chow, MSS. Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. (2005) 45:1345–59. doi: 10.1177/0091270005282630
15. Zhang, RX, Li, MX, and Jia, ZP. Rehmannia glutinosa: review of botany, chemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. (2008) 117:199–214. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.02.018
16. Guo, HJ, and Huang, ZC. Clinical observation on the efficacy of Shen Shuai Ning combined with compound α-keto acid in the treatment of chronic renal insufficiency. Zhejiang Med J. (2023) 45:22–1827. doi: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2023.45.2.2022-1827
17. Liu, B, Wang, J, and Liu, HY. Clinical study on the treatment of chronic renal insufficiency with Shen Shuai Ning tablets combined with compound α-keto acid tablets. New Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 54:120–4. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2022.11.026
18. Jiang, LL, Mao, LM, Hu, SJ, and Peng, Y. Effect of Shen Shuai Ning granules on the expression of NF-κB and PPAR-γ in renal tissues of diabetic nephropathy rats. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Therapeut. (2018) 23:132–7. doi: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2018.02.003
19. Chen, YX, Jiang, XX, Zhang, QY, Xu, CQ, Hu, YM, Jin, CY, et al. Role of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway in diabetic kidney disease and research progress of traditional Chinese medicine intervention. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2023) 48:2630–8. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20221114.401
20. Wang, XL, Sun, YM, and Chen, L. The effect and mechanism of Shen Shuai Ning pills on the outcome of patients with stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease. Chin J Experiment Tradit Med Formulae. (2017) 23:159–64. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017030159
21. Yan, JJ, Wei, H, Li, LP, Hu, Y, Cheng, MZ, Cheng, L, et al. Observing the efficacy of GLP-1RA combined with Shenshuaining capsule in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Modern J Integrated Chin Western Med. (2024) 33:258–62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2024.02.021
22. Fang, SJ. Clinical efficacy of Shenshuaining combined with saxagliptin in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy and its effects on blood sugar and kidney function. Rational Clin Drug Use. (2023) 16:91–4. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2023.12.028
23. Liang, Y, Li, W, and Wu, MX. Clinical effect of Shenshuaining capsule combined with valsartan in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Pract Clin Med. (2023) 24:6–8. doi: 10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2023.02.002
24. Ning, C. Clinical efficacy of Shenshuaining tablets combined with insulin glargine in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy and its effects on blood sugar and kidney function indicators. J Neuro-Oncol. (2023) 13:21–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1396.2023.01.004
25. Luo, X, Wei, SH, and Wei, ZH. Clinical effect of Shenshuaining capsule combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Guangxi Med J. (2022) 44:1462–6. doi: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2022.13.05
26. Ding, PP, and Li, Y. Clinical study on Shenshuaining tablets combined with ferulic acid piperazine tablets in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. New Chin Med. (2021) 53:130–3. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2021.21.031
27. Qiu, FP, and Zhu, HY. Clinical study on Shenshuaining capsule combined with repaglinide tablets in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. New Chin Med. (2021) 53:81–4. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2021.14.022
28. Gao, XT, and Yang, HH. Effects of Shenshuaining granules combined with benazepril on blood sugar and oxidative stress indicators in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Hainan Med. (2020) 31:3039–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2020.23.012
29. Qiu, JF, and Su, Z. Clinical study on Shenshuaining tablets combined with canagliflozin tablets in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. New Chin Med. (2020) 52:38–40. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2020.21.012
30. Bai, JQ, Qin, ZH, and Bai, XH. Observation on the efficacy of valsartan combined with Shenshuaining in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with hypertension. Chin Med Engineering. (2020) 28:75–8. doi: 10.19338/j.issn.1672-2019.2020.08.023
31. Chen, SS, Cheng, HR, Yan, HB, and Liu, XX. Clinical study on Shenshuaining capsule combined with candesartan in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Modern Drugs Clinics. (2020) 35:1609–12. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.08.023
32. Yao, J, Lu, ML, Zhou, DL, and Chen, Y. Efficacy of Shenshuaining capsule in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy chronic renal failure and its effect on patients' micro-inflammatory state. Guangming Tradit Chin Med. (2020) 35:686–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2020.05.022
33. Yuan, JF, Liu, LJ, Suo, XF, and Wang, X. Clinical study on Shenshuaining granules combined with valsartan in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. Modern Drugs Clinics. (2019) 34:1784–8. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2019.06.039
34. Huang, MZ, Huo, SY, Liu, YH, and Yuan, MH. Efficacy of Shenshuaining tablets combined in the treatment of type 2 diabetic nephropathy stage 5. Shenzhen J Integrated Tradit Chin Western Med. (2019) 29:50–1. doi: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2019.06.024
35. Cui, JP, and Wu, YX. Clinical study on Shenshuaining capsule combined with alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Modern Drugs Clinics. (2019) 34:781–5. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2019.03.044
36. Wang, X. Clinical study on Shenshuaining granules combined with saxagliptin in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Modern Drugs Clinics. (2017) 32:884–7. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.05.031
37. Wang, XQ, Shan, DW, and Zhang, D. Observation on the efficacy of Shenshuaining capsule in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Integrated Tradit Western Med Nephropathy. (2017) 18:55–6.
38. Deng, SY. Clinical observation of Shenshuaining combined with captopril in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. Inner Mongolia Tradit Chines Med. (2016) 35:42–3. doi: 10.16040/j.cnki.cn15-1101.2016.12.038
39. Li, BY, Peng, H, Xiong, DL, Yi, J, and Chen, H. Observation on the efficacy of Shenshuaining granules combined with telmisartan tablets in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Integrated Tradit Western Med. (2015) 35:142–6. doi: 10.7661/CJIM.2015.02.0142
40. Su, R. Clinical observation of the combined treatment of 2 type diabetic nephropathy renal failure with kininogenase and Shenshuaining. Modern J Integrated Chin Western Med. (2010) 19:3714–5.
41. Lu, SZ, and Wen, YW. Observation on the efficacy of Shenshuaining capsule in the treatment of diabetic renal insufficiency. Chin Med Herald. (2009) 6:216–7.
42. Zhang, RG, Kong, YQ, Chen, HP, and Zhou, HQ. Clinical analysis of 42 cases of Shenshuaining in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Integrated Tradit Western Med Nephropathy. (2002) 11:670–1.
43. Fan, L, Gao, J, Liu, MJ, Zhen, JH, Jiang, H, and Hu, Z. Protective effect of Shen Shuai Ning on renal injury in diabetic rats. J Shandong Univ (Medical Edition). (2011) 49:48–52.
44. Bhatt, DL, and Mehta, C. Adaptive designs for clinical trials. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:65–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1510061
45. Liu, EH, Qi, LW, Li, K, Chu, C, and Li, P. Recent advances in quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. (2010) 13:869–84. doi: 10.2174/138620710793360301
46. van Beek, TA, and Xie, PS. Quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. Foreword J Chromatogr A. (2009) 1216:1931–2. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.027
47. Limonte, CP, Kretzler, M, Pennathur, S, Pop-Busui, R, and de Boer, IH. Present and future directions in diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Complicat. (2022) 36:108357. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108357
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, Shen-Shuai-Ning, herbal medicine, treatment, perspective
Citation: Gao N and Zhang X-j (2024) Perspectives of clinical research on Shen-Shuai-Ning in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Front. Med. 11:1438266. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1438266
Edited by:
Gulali Aktas, Abant Izzet Baysal University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Satilmis Bilgin, Abant Izzet Baysal University, TürkiyeIbrahim Karagoz, University of Health Sciences, Türkiye
Copyright © 2024 Gao and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xi-jun Zhang, eGlqdW56aGFuZ19kckBvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
 Na Gao
Na Gao Xi-jun Zhang
Xi-jun Zhang