- 1The First People’s Hospital of Linping, Hangzhou, China
- 2Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Objective: To investigate the effects of peer-led intervention on knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of stoma care, as well as quality of life in bladder cancer patients post-permanent ostomy.
Methods: A series of 340 eligible bladder cancer patients who underwent permanent ostomy from January 2019 to December 2022 were enrolled in this study. These participants were randomly assigned to the intervention group (peer-led intervention) and the control group (routine health intervention) using random number table, with 170 cases in each group. A 30-item questionnaire was used to evaluate knowledge, healthy attitudes, and healthy practices (KAP) of disease; the WHO Quality of Life-100 (WHOQOL-100) was utilized to assess the quality of life among patients; and the incidence of complications in two groups were also recorded during six-month intervention. For the comparison of continuous variables within and between groups, paired sample and independent t-test were applied. The categorical variables analyzed using x2 test or rank-sum test.
Results: After six-month intervention, 144 participants in the intervention group and 151 participants in the control group were finally retained in this study. The scores of the 20 items in KAP (including basic knowledge of disease, basic knowledge of ostomy, observation of stoma, etc.) in the intervention group were significantly higher than those in the control group (all p < 0.05); the scores of 12 items in WHOQOL-100 (including the positive feelings, thinking, learning, memory and concentration, etc.) in the intervention group were markedly higher than those in the control group, while negative feelings and dependence on medical support in the intervention group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all p < 0.05); the total rate of complications in the intervention group was significantly lower than that in the control group (18.31% vs. 31.13%, p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The peer-led intervention has a positive effect on improving patients’ KAP of stoma care and quality of life and reducing the rate of complications, which enables it to be a favorable intervention approach for patients with permanent ostomy.
1 Introduction
Bladder cancer, as a common urinary cancerous disease, poses a serious threat on personal health and family well-being, as well as social healthcare burden (1). In the United Nations alone, the number of newly diagnosed as bladder cancer has reached 83,730 and 17,200 died from it in 2021 (2). For these bladder cancer patients with muscle invasion or high-risk metastasis, urinary ostomy is a routinely effective procedure after radical cystotomy. Patients with permanent ostomy are prone to experience negative psychological, physiological, and social relationship changes after operation, which may result in subsequent barriers to stoma management and patient’s daily life (3). According to the results of several studies, patients’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) about disease play a vital role in the management of chronic diseases, and their self-care ability and quality of life can be improved through enhanced KAP education and intervention (4–6). Based on these findings mentioned above, we suppose that KAP may have a potential role to ease stoma self-care challenges faced by bladder cancer patients undergoing home care or out-patient intervention after permanent ostomy.
Peer-led intervention is a validated health promotion strategy that involves sharing concepts, experiences, and other information among peers with similar experiences or conditions, and its core lies in effective communication between peer educators and recipients, leading to the improvements in cognitions and behaviors among educators and recipients (7, 8). Over the past decade, peer-led intervention has been widely applied in a variety of settings and populations, and it has been proved to be practical way of promoting individual’s KAP and pursuing health goals in previous literature (9–11). With modern communication methods advancing, including instant messaging, online interviews, and video conferences, peer-led intervention is becoming a convenient, efficient, and popular intervention approach (12). Peer-led intervention has been reported to have a good clinical performance in many studies on the management of chronic diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancerous diseases (13–15). However, it still lacks reports regarding peer-led intervention on KAP of stoma care and quality of life for bladder cancer patients in the present literature, especially for permanent ostomy patients after urinary diversion. In order to fill this knowledge gap, we conducted a case–control study to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of peer-led intervention on KAP and quality of life in bladder cancer patients after permanent ostomy.
2 Patients and methods
2.1 Patients
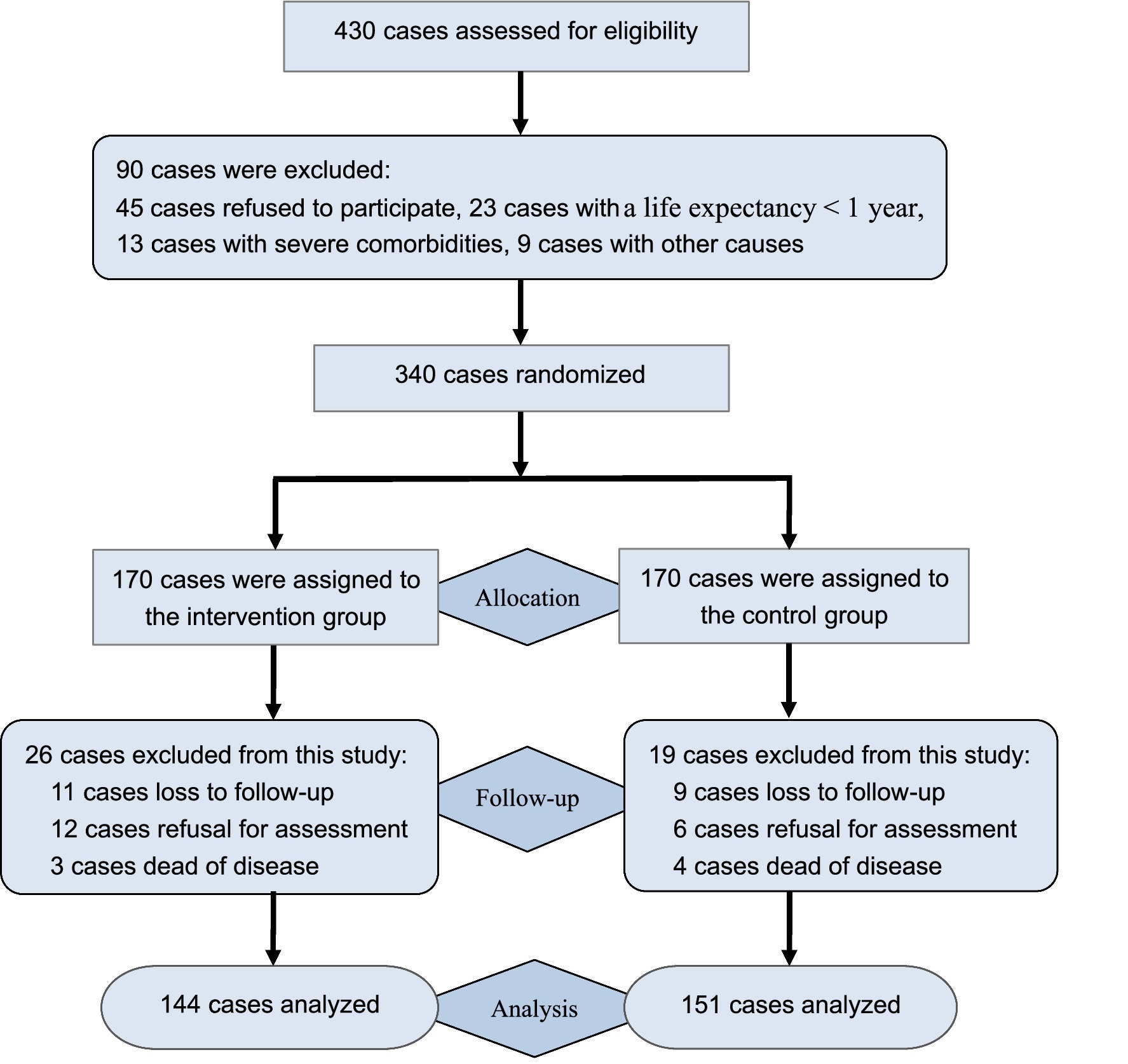
The study participants consisted of bladder cancer patients who underwent permanent ostomy in Hangzhou District from January 2019 to December 2022, and these participants were recruited through posters and snowball methods. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Linping Hospital (Approval no: 2019–015). A preliminary test was used to calculate the sample size referring to the previous study (16). The α value was set at 5% (two-tailed test), the power was set at 80% (1-β), and the effect size was set at 0.15. The σ represents the evaluated value of the standard deviation in quality of life between two groups. It showed that the target sample size should be 236 cases. Given potential dropout or follow-up loss with a 30% attrition rate, the target sample size was set at ≥338 cases. Prior to the inclusion, all patients were screened for study eligibility. Inclusion criteria of this study were set as follows: confirmed bladder cancer and underwent permanent ostomy; healthy condition with a life expectancy of more than 1 year; voluntarily participating in this study and giving informed consent. Exclusion criteria included: patients with temporary ostomy; dropped out or lost to follow-up; severe comorbidities or communication disorders. During the course of recruitment, a total of 430 patients were enrolled to be screened, and 340 patients who met eligible criteria were randomized into the intervention group and the control group. A random number sequence was generated through a random number table with the help of a statistician, and random numbers were distributed to each patient to achieve random grouping in a 1:1 ratio. To avoid allocation bias, randomization was conducted by separate researchers who were not involved in the conception and data analysis of this study. Of them, 170 participants were allocated to the intervention group, receiving peer-led intervention, while another 170 participants were assigned to the control group, receiving routine health intervention. After six-month intervention, 144 participants were included in the intervention group, and 26 participants were excluded from this group due to loss to follow-up, refusal for assessment, or dead of disease; 151 participants retained in the control group, while 19 cases excluded from this group due to the above-mentioned causes. Finally, a total of 295 cases completed the 6-month intervention and were included in data curation. The flowchart of this study was described in Figure 1.
2.2 Methods
Participants in both groups were followed-up for 6 months by WeChat (a social communication medium), telephone, or out-patient visit. During this period, the control group received routine health intervention, including basic disease knowledge, stoma care, postoperative rehabilitation, and other stoma-related concerns. On the basis of the control group, the intervention group received peer-led intervention. Thirty-four volunteers who have full willingness, good communication skills, and stoma care experiences over 1 year were recruited as peer educators through posters. The protocols of training were similar to the previous study (17), consisting of 2 weeks of training sessions to strengthen their knowledge of disease and stoma, diet and exercise, complication observation and management, and other related self-care skills. Furthermore, problem-solving methods and sharing tips are also trained, such as how do you handle pouch leakage; if you handle it well yourself, how do you share your successful experiences with other patients? In brief, the training course focuses on knowledge and skills acquisition related to healthy concept and behavior, effective facilitation, and group management. After the training course 34 educators were assigned to 17 peer teams by random number table. Then, 12 members including 2 educators and 10 participants constituted a peer-led team, and these members were invited to a WeChat communication group. In the initial month, weekly video conferences, online or in-person interviews were conducted to alleviate the sense of unfamiliarity and communicate disease knowledge, self-care skills, and handling experiences. In the subsequent months, educators were responsible for reporting to medical staff regarding the status of stoma care, psychological aspects, and interventing effectiveness of their members. In this study, blinding of participants and study staff failed to apply owing to the nature of the intervention, but the raw data collectors and statistician were blinded to data analysis, making this project an open blinded study.
2.3 Evaluating variables
Baseline data (age, gender, education level, family income, and others) were collected at the entry of this study. A 30-item questionnaire was used to evaluate participant’s KAP status, including 12 items about stoma knowledge (basic knowledge of disease, basic knowledge of ostomy, observation of stoma, method of pouch replacement, emptying the pouch, etc.), 9 items concerning healthy attitudes (optimistic mentality to disease, optimistic mentality to stoma, trust in medical staff, trust in peer educators, willing to correct bad habits, etc.), and 9 items of healthy practices (maintaining healthy diet, maintaining healthy behaviors, learning relevant books, learning relevant videos, skilled in pouch replacement, etc.) (18). The result of each item was graded on a five-point Likert scale system with indication from very poor to very good. The assessment of quality of life adopted WHO Quality of Life-100 (WHOQOL-100), which involved six domains (physical, psychological, independence, social relationship, environment, and spirituality) and 24 items by using the same Likert scale system (19). Overall, a higher score indicates a better outcome in quality of life. Complications such as dermatitis, stoma infection, local necrosis, mucocutaneous separation, stoma stricture, and others in two groups were recorded during the intervention.
2.4 Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed by SPSS25.0 software. The continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation (x ± s). Normality was assessed using Shapiro–Wilk test. Independent t-test was used to compare the values between the two groups, and paired t-test was utilized to compare the changes between pre-intervention and post-intervention within an individual group. The categorical variables were expressed as frequency and percentages (%), analyzed by x2 test, and the ranked data were analyzed by the rank-sum test. p < 0.05 indicates that the difference was statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of baseline data
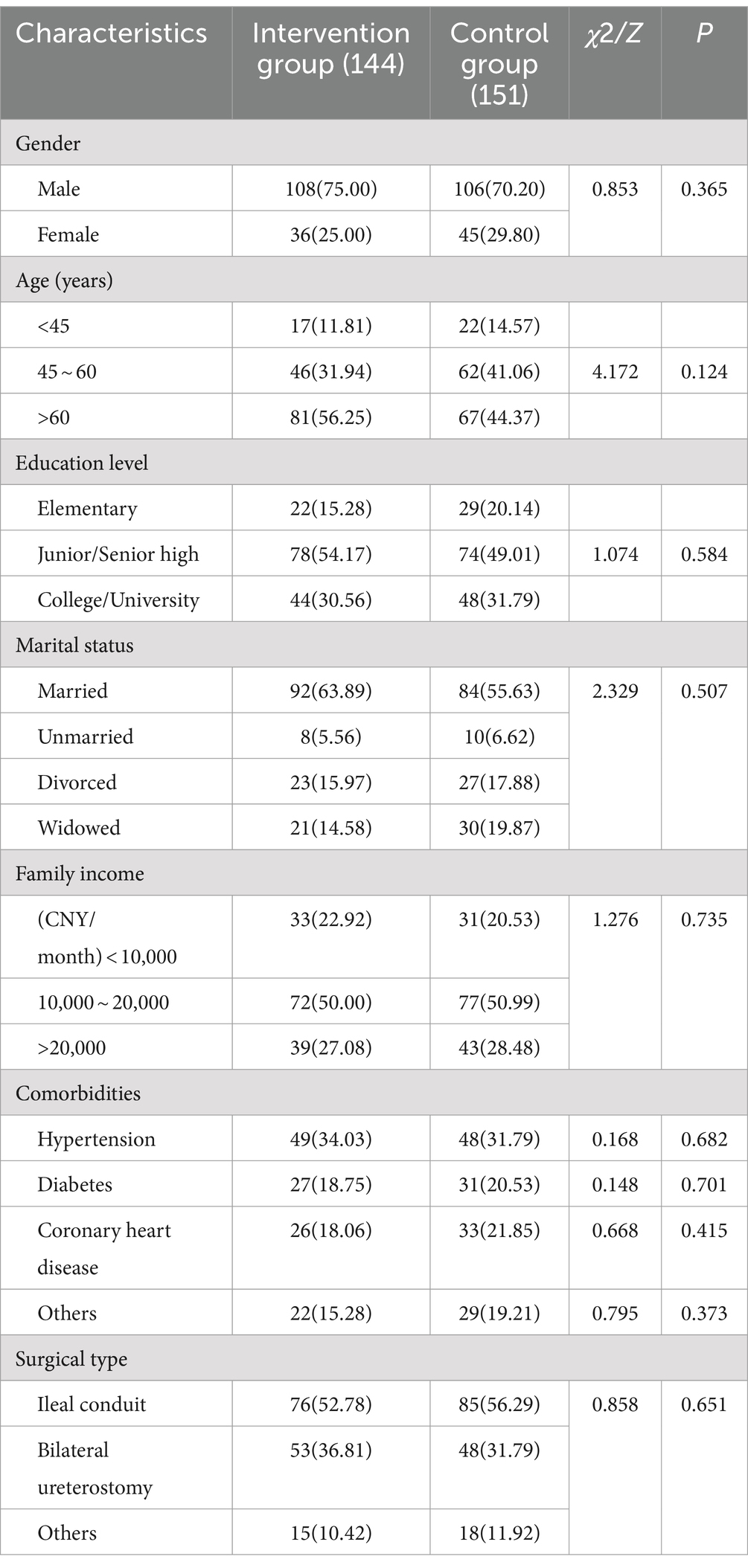
Before the intervention, there was no significant difference in gender, age, education level, marital status, family income, comorbidities, and surgical type between two groups (all p > 0.05). As shown in Table 1.
3.2 Comparison of KAP
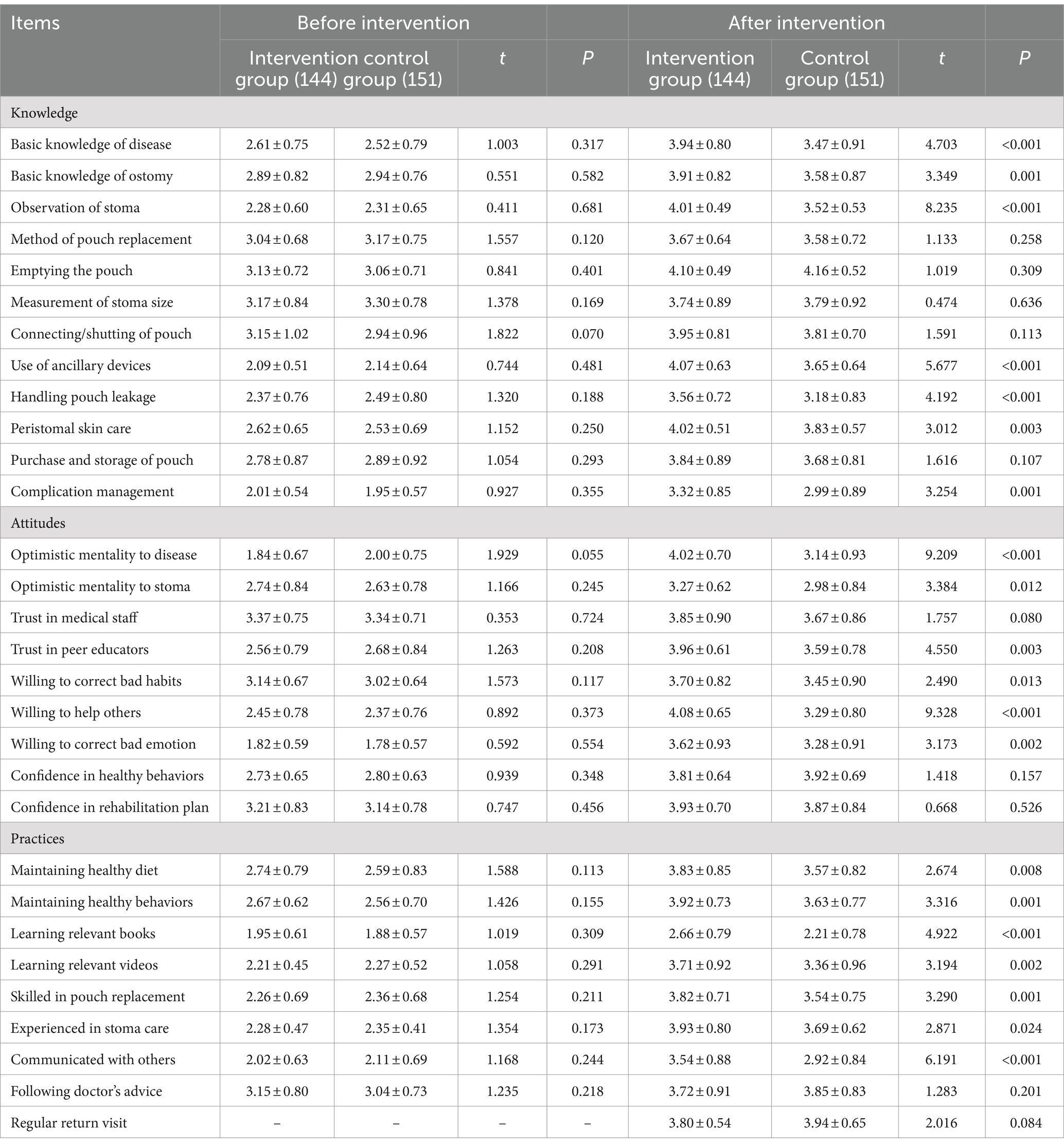
There was no statistically significant difference in the score of each item of KAP between two groups before intervention (p > 0.05). At 6 months after intervention, the scores of 7 items in knowledge dimension such as basic knowledge of disease, basic knowledge of ostomy, observation of stoma, use of ancillary devices, handling pouch leakage, peristomal skin care, and complication management of the intervention group were significantly higher than those of the control group; the scores of 6 items in attitudes dimension including optimistic mentality to disease, optimistic mentality to stoma, trust in peer educators, willing to correct bad habits, willing to help others, and willing to correct bad emotion were significantly higher than those of the control group; the scores of 7 items in practices dimension including maintaining healthy diet, maintaining healthy behaviors, learning relevant books, learning relevant videos, skilled in pouch replacement, experienced in stoma care, and communicated with others of the intervention group were markedly superior to the control group. These differences of aforementioned 20 items were statistically significant (all p < 0.05). As shown in Table 2.
3.3 Comparison of quality of life
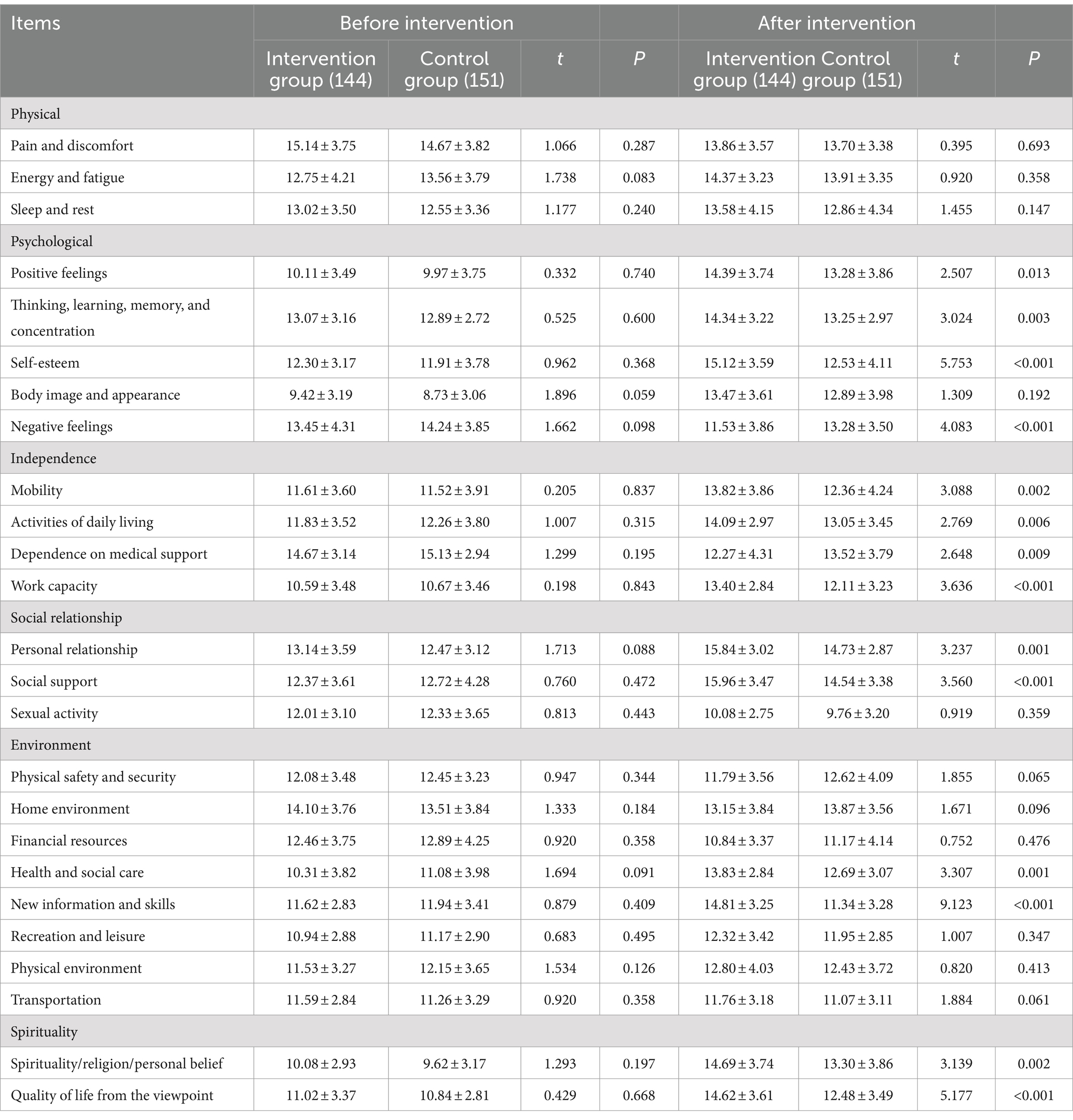
There was no significant difference in WHOQOL-100 score between two groups before intervention (p > 0.05). After six-month intervention, significant differences in the scores of 14 items of WHOQOL-100 were observed between two groups. Among these items, scores of the positive feelings, thinking, learning, memory and concentration, self-esteem, mobility, activities of daily living, work capacity, personal relationship, social support, healthy and social care, new information and skills, spirituality/religion/personal belief, quality of life from the viewpoint in the intervention group were significantly higher than those in the control group, while scores of negative feelings and dependence on medical support in the intervention group were markedly lower than those in the control group. All differences mentioned above were statistically significant (all p < 0.05). As shown in Table 3.
3.4 Comparison of complications
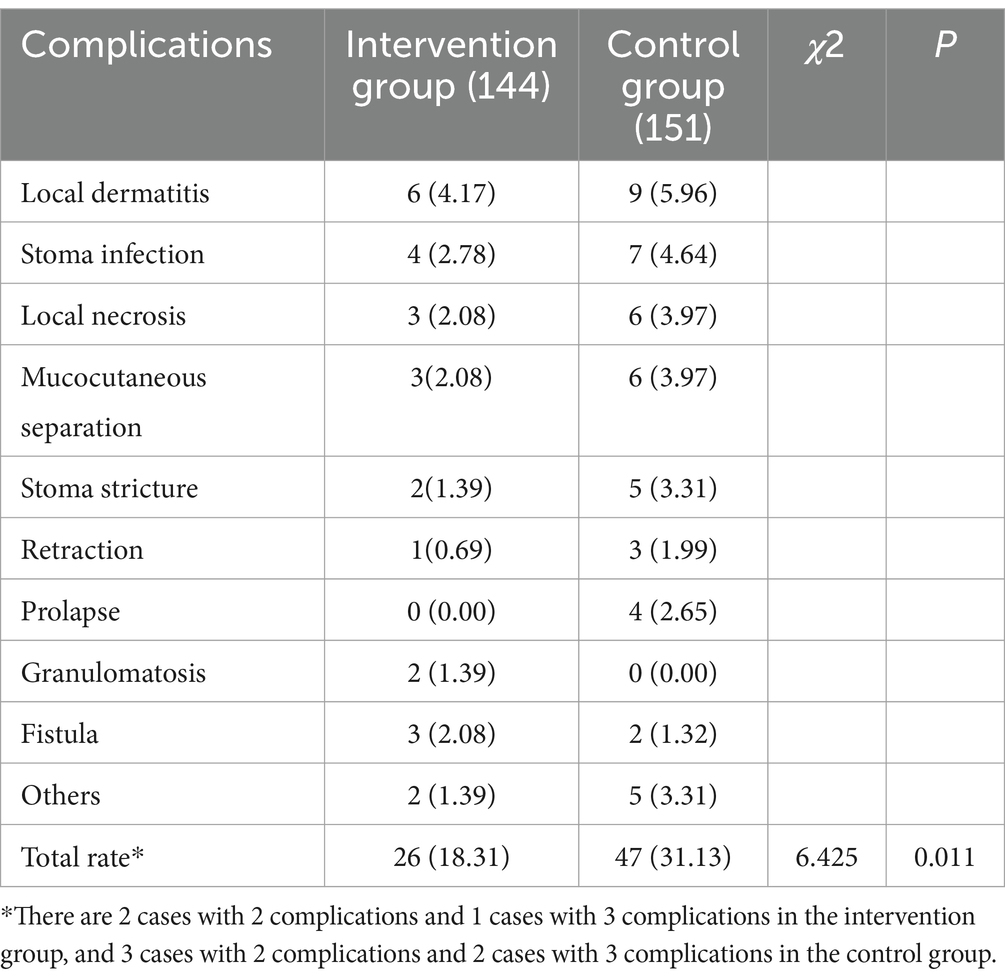
During the 6-month intervention, 26 complications occurred in 22 participants of the intervention group, accounting for 18.31% (26/144) in participants, while 47 complications occurred in 42 participants of the control group, accounting for 31.13% (47/151) in participants. The total rate of complication in the intervention group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and differences were statistically significant (x2 = 6.425, p = 0.011). As shown in Table 4.
4 Discussion
Adapting to carrying an ostomy pouch for life is often an additional burden for bladder cancer patients after permanent ostomy. Most of patients will struggle to maintain long-term self-management under the enormous stress and anxiety caused by disease and ostomy. Therefore, seeking an appropriate educational intervention plays an important role in the improvements of postoperative rehabilitation, stoma management, and quality of life, especially for those patients with home care or lacking professional care from medical institutions. Peer-led intervention has been proven to be an effective intervention program for health promotion in various fields since it was proposed in 1987 (20). Poudel et al. (21) considered that peer-led cancer education program was a beneficial way to encourage participants in active learning and participate in problem-solving and self-reflection sustainably. Yip et al. (22) concluded that peer-led nutrition education had a positive effect on the dietary health of school-age adolescent. Furthermore, there was an agreement that patients’ knowledge can directly link to their practices while the impacts of knowledge on practices can also be enhanced or jeopardized by their attitudes, and the educational intervention based on the KAP model has also been demonstrated as an effective way to long-term self-management of patients with chronic disease (23–25). In this study, we tested this viewpoint and confirmed the effectiveness of peer-led intervention on KAP of stoma care, quality of life, and stoma complications in patients with permanent ostomy.
In the assessment of patients’ KAP, we found that the scores of 7 items in knowledge, 6 items in attitudes, and 7 items in practices of the intervention group were notably higher than those of the control group. This implies that the peer-led intervention can shift patients’ KAP on stoma care from negative to positive more effectively compared with the routine health intervention. The main reasons of which probably includes (26, 27): First, the educators have a physiological and psychological situations as same/similar as the patients’, easier to develop a good connection and effective communication with peers, give them better social support, and further alleviate patients’ alienation, frustration, and other negative emotions; Second, each educator shares his/her experience of stoma care with the rest members of peer-led team by sharing and demonstrating detail skills, so as to help patients to improve their self-care ability; Third, knowledge and attitudes are the foundation of practices while the improvement of cognition and attitudes can further promote healthy behaviors. For example, when a participant has learned the relevant knowledge with others’ help, he/she successfully handles a problem related to stoma care, and the participant possibly has an optimistic attitude toward the disease and stoma care. After that, he/she is more likely to help others in peer-led team, thereby constituting a mutual optimistic influence on each other (28). It will offer a further facilitation to promote the level of practices in some way.
The WHOQOL-100 is an international scale developed by the World Health Organization to measure individuals’ health-related quality of life, and it has been widely used in different countries with multiple language versions over the past decades, making the outcomes of quality of life more comparable across different cultural backgrounds (29, 30). This scale has good properties such as reliability, validity and responsiveness with multidimensional perspectives, including the aspects of physical health, psychological health, level of independence, state of social relationship, environmental factors, and personal beliefs for life (31). Also, the use of WHOQOL-100 may serve as a reliable feedback on the effectiveness of peer-led intervention in the assessment of quality of life. In this study, our results showed that 14 items of WHOQOL-100 in the intervention group were significantly higher than those of the control group, suggesting that the peer-led intervention can obviously improve the quality of life of participants. However, most of items were seen in physical, psychological, independence and social relationship domains, and only two items were found in the environment domain, indicating that the peer-led intervention had a greater impact on participants’ physical, psychological, and social aspects while less on environment domain. The reason may be that environment factors are difficult to make a noticeable improvement in a few months. Based on the findings of previous studies, postoperative improvement or reduction of quality of life can reflect patients’ adaption to their life with ostomy (32, 33). In this study, our results revealed that the peer-led intervention presented a substantial improvement of patients’ adaption to stoma, which was also consistent with other’s study (34).
A previous report on ostomy patients pointed out that the educational intervention can decrease the rate of complications (35), which was also found in our study. During six-month intervention, the total rate of complications in the intervention group was obviously lower than that in the control group (18.31% vs. 31.13%). As others’ reports, most of stoma patients sought for help from professional guidance in stoma care, especially for patients with permanent ostomy, and those patients can benefit from more educational intervention and reduce the rate of complications through mutual support (35–37). By considering the above viewpoints and our findings, the conclusion can be drawn that peer-led intervention is a feasible and effective approach for bladder cancer patients after permanent ostomy. Peer support is understood as a form of mutual support between individuals and educators with similar experiences, which is distinct from professional support (38). As previously reported, the promotion of patients’ KAP may be the fundamental mechanism by which peer-led education improves the outcomes of individuals in various diseases (9, 39). In our opinion, by setting an example, patients’ desire for well-being can be motivated and enhanced. With the help of experienced educators, gaps in medical services outside of healthcare institutions have been filled, thereby improving patients’ KAP and quality of life, and reducing the rate of complications.
Inevitably, there were several limitations in our study that should be pointed out. First, we only obtained study data within 6 months of follow-up, and the results of quality of life and changes in KAP beyond 6 months still need further exploration. Therefore, the mid- and long-term outcomes should be further explored in future studies with a longer follow-up. In addition, our study was conducted using a small-scale sample size, with all participants coming from Hangzhou District. This will inevitably lead to some statistical and regional biases in our findings, which to some extent limit the generalizability of our findings across all populations and different regions. Moreover, despite a random number table used in this study, the results of this study are not derived from the triple-blind design. The main reason may be that patients have the right to know the content of this project and decide whether to participate in this study. Finally, some potential unmeasured variables, such as type of insurance, patient adherence, and subgroup differences among different age, gender, and personal income, were not analyzed in this study. This requires more rigorous design and subgroup analysis of potential influencing factors in the future, so as to obtain more detailed and objective results. All in all, in view of the shortcomings mentioned above, more studies should be performed to eliminate the effects of confounding bias and confirm our conclusion in well-designed multi-center randomized controlled trials.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the peer-led intervention can enhance patients’ understanding of healthy knowledge, improve healthy attitudes and practices, reduce the rate of stoma complications, and eventually promote quality of life of patients with permanent ostomy. These advantages enable peer-led intervention to be a favorable approach for bladder cancer patients after permanent ostomy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Linping Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
J-YD: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. T-TP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. X-JL: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. X-MY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. J-XQ: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks are extended to all collaborating doctors and nurses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lobo, N, Afferi, L, Moschini, M, Mostafid, H, Porten, S, Psutka, SP, et al. Epidemiology, screening, and prevention of bladder Cancer. Eur Urol Oncol. (2022) 5:628–39. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2022.10.003
2. Siegel, RL, Miller, KD, Fuchs, HE, and Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654
3. Stavropoulou, A, Vlamakis, D, Kaba, E, Kalemikerakis, I, Polikandrioti, M, Fasoi, G, et al. “Living with a stoma”: exploring the lived experience of patients with permanent colostomy. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:8512. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168512
4. Sadanandan, SA, Shreedevi, AU, and Padmanabha, H. Parental KAP and its relation with the quality of life in children with epilepsy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. (2023) 26:419–23. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_199_23
5. Wong, FMF. Factors associated with knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to oral care among the elderly in Hong Kong community. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:1–15. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218088
6. Stellefson, M, Paige, SR, Alber, JM, Chaney, BH, Chaney, D, Apperson, A, et al. Association between health literacy, electronic health literacy, disease-specific knowledge, and health-related quality of life among adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12165. doi: 10.2196/12165
7. Kiemen, A, Czornik, M, and Weis, J. How effective is peer-to-peer support in cancer patients and survivors? A systematic review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:9461–85. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04753-8
8. Addanki, S, Macedo, L, MacDermid, J, and Moll, S. Becoming peer educators in workplace mental health: qualitative exploration of challenges and opportunities. Work. (2022) 72:157–69. doi: 10.3233/WOR-205084
9. Xia, W, Li, HCW, Liang, T, Luo, Y, Ho, LLK, Cheung, AT, et al. Structured online training for university students to deliver peer-led addiction counselling for young drug abusers in China: effect on improving knowledge, attitude, confidence, and skills. Patient Educ Couns. (2022) 105:1009–17. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2021.07.038
10. Warren, KR, Parker, EA, Ganjavi, M, Watkins-Lewis, K, Clark, S, Randolph Cunningham, S, et al. Peer-led focus groups identify barriers to healthy lifestyle in African American Adolescents from Baltimore City. Ethn Dis. (2024) 33:163–9. doi: 10.18865/ed.33.4.163
11. Anderson, E, Dvorin, K, Etingen, B, Barker, AM, Rai, Z, Herbst, AN, et al. ‘It makes you sit Back and think where you Wanna Go’: veteran experiences in virtual whole health peer-led groups. Health Expect. (2022) 25:2548–56. doi: 10.1111/hex.13581
12. Wong, WC, Sun, WH, Chia, SMC, Tucker, JD, Mak, WP, Song, L, et al. Effectiveness of a peer-led web-based intervention to improve general self-efficacy in using dating apps among Young adults: randomized clustered trial. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e16378. doi: 10.2196/16378
13. Verma, I, Gopaldasani, V, Jain, V, Chauhan, S, Chawla, R, Verma, PK, et al. The impact of peer coach-led type 2 diabetes mellitus interventions on glycaemic control and self-management outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. (2022) 16:719–35. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2022.10.007
14. Beauvais, C, Rodère, M, Pereira, B, Legoupil, N, Piperno, M, Pallot Prades, B, et al. Essential knowledge for patients with rheumatoid arthritis or spondyloarthritis: results of a multicentric survey in France among health professionals and patients. Joint Bone Spine. (2019) 86:747–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2019.06.006
15. Thurston, C, Deleemans, JM, Gisser, J, Piercell, E, Ramasamy, V, and Tutelman, PR. The development and impact of AYA can-Canadian Cancer advocacy: a peer-led advocacy Organization for Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer in Canada. Curr Oncol. (2024) 31:2582–8. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31050193
16. Furukawa, C, and Morioka, I. Health-related quality of life and sleep disorders in patients with a Urostomy: is there a relationship? J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. (2017) 44:358–62. doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000334
17. Abadi, MH, Drake, C, Richard, BO, Schweinhart, A, Rychener, D, Shamblen, SR, et al. An evaluation of the facilitator training to implement 'Taking charge of my life and health', a peer-led group program to promote self-care and patient empowerment in veteran participants. Patient Educ Couns. (2020) 21:S0738. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2020.06.014
18. Goumei, Q, Xiaoli, Z, Yangmin, W, and Lingzhi, X. Study on construction of health education evaluation criteria for urinary stoma patients. Chin Nurs Res. (2014) 28:2775–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.10096493.2014.22.041
19. da Silva, JP, and Amadei, JL. Influence of medical care in the quality of life (WHOQOL-100) of women living with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed. (2016) 56:198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.rbr.2015.01.010
20. Mehdipour-Rabori, R, Nematollahi, M, and Bagherian, B. Effect of classmate as peer-led education on clinical performance: a mixed-method study. J Educ Health Promot. (2021) 10:58–6. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_761_20
21. Poudel, K, Sumi, N, and Yano, R. Impact of peer-led cancer education program on knowledge, health beliefs, practice, and self-esteem among pairs of nepalese high-school students and their knowledge-sharing partners. Healthcare. (2021) 9:64. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9010064
22. Yip, C, Gates, M, Gates, A, and Hanning, RM. Peer-led nutrition education programs for school-aged youth: a systematic review of the literature. Health Educ Res. (2016) 31:82–97. doi: 10.1093/her/cyv063
23. Liu, C, Liu, C, Wang, D, and Zhang, X. Knowledge, attitudes and intentions to prescribe antibiotics: a structural equation modeling study of primary care institutions in Hubei, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:2385. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16132385
24. Mohammed, AH, Ying, LH, Boon Hong, ML, Sze Nee, AW, Ying, LS, Ramachandram, DS, et al. Development and validation of a knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) questionnaire for skin cancer in the general public: KAP-SC-Q. Res Social Adm Pharm. (2024) 20:124–36. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2023.10.009
25. HB, ALB, and Alali, NM. Evaluation of knowledge, attitude, and practices toward the outbreak pandemic (COVID-19) virus disease among ophthalmologists: a cross-sectional study. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. (2020) 27:164–71. doi: 10.4103/meajo.MEAJO_219_20
26. Davis, S, Keep, S, Edie, A, Couzens, S, and Pereira, K. A peer-led diabetes education program in a homeless community to improve diabetes knowledge and empowerment. J Community Health Nurs. (2016) 33:71–80. doi: 10.1080/07370016.2016.1159435
27. Krishnamoorthy, Y, Sakthivel, M, Sarveswaran, G, and Eliyas, SK. Effectiveness of peer led intervention in improvement of clinical outcomes among diabetes mellitus and hypertension patients-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. (2019) 13:158–69. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.11.007
28. van der Storm, SL, Bemelman, WA, van Dieren, S, and Schijven, MPthe Stoma APPtimize Collaborative Study Group. A personalized app to improve quality of life of patients with a stoma: a protocol for a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Color Dis. (2023) 25:2071–7. doi: 10.1111/codi.16694
29. Attafuah, PYA, Everink, IHJ, Halfens, RJG, Lohrmann, C, Abuosi, A, and Schols, JMGA. Instruments used to assess quality of life of older adults in African countries: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr. (2021) 21:344–55. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02262-2
30. Mao, Z, Ahmed, S, Graham, C, Kind, P, Sun, YN, and Yu, CH. Similarities and differences in health-related quality-of-life concepts between the east and the west: a qualitative analysis of the content of health-related quality-of-life measures. Value Health Reg Issues. (2021) 24:96–106. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2020.11.007
31. Li, L, Young, D, Xiao, S, Zhou, X, and Zhou, L. Psychometric properties of the WHO quality of life questionnaire (WHOQOL-100) in patients with chronic diseases and their caregivers in China. Bull World Health Organ. (2004) 82:493–502.
32. Cengiz, B, and Bahar, Z. Perceived barriers and home care needs when adapting to a fecal ostomy: a phenomenological study. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. (2017) 44:63–8. doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000271
33. Lin, CY, Lee, TY, Sun, ZJ, Yang, YC, Wu, JS, and Ou, HT. Development of diabetes-specific quality of life module to be in conjunction with the World Health Organization quality of life scale brief version (WHOQOL-BREF). Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2017) 15:167–87. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0744-3
34. Wulff-Burchfield, EM, Potts, M, Glavin, K, and Mirza, M. A qualitative evaluation of a nurse-led pre-operative stoma education program for bladder cancer patients. Support Care Cancer. (2021) 29:5711–9. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06093-0
35. Liao, JJ, Meng, YX, Li, JR, Su, XX, and Chen, L. Evaluation of effect of health education pathway intervention on quality of life, health belief and health behaviors among urostomy patients. Chin J Heal Educ. (2017) 33:749–55. doi: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2017.08.018
36. Maydick-Youngberg, D. A descriptive study to explore the effect of peristomal skin complications on quality of life of adults with a permanent ostomy. Ostomy Wound Manage. (2017) 63:10–23.
37. Khalilzadeh Ganjalikhani, M, Tirgari, B, Roudi Rashtabadi, O, and Shahesmaeili, A. Studying the effect of structured ostomy care training on quality of life and anxiety of patients with permanent ostomy. Int Wound J. (2019) 16:1383–90. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13201
38. Higgins, A, Hybholt, L, Meuser, OA, Eustace Cook, J, Downes, C, and Morrissey, J. Scoping review of peer-led support for people bereaved by suicide. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:3485. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063485
Keywords: bladder cancer, ostomy, stoma care, peer-led intervention, knowledge, attitudes, and practices, quality of life
Citation: Ding J-Y, Pan T-T, Lu X-J, You X-M and Qi J-X (2024) Effects of peer-led education on knowledge, attitudes, practices of stoma care, and quality of life in bladder cancer patients after permanent ostomy. Front. Med. 11:1431373. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1431373
Edited by:
Francesco Ferrara, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Nicola Pavan, University of Palermo, ItalyGeraldo Magela Salomé, Universidade do Vale do Sapucaí, Brazil
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Pan, Lu, You and Qi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan-Ying Ding, ZGluZ2p5Nzg2OUAxNjMuY29t
 Juan-Ying Ding
Juan-Ying Ding Ting-Ting Pan1
Ting-Ting Pan1