- 1Department of Oral-Maxilo-Facial Surgery, “Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- 2Oculens Clinic, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Medicine and Pharmacy Science and Technology University, “George Emil Palade”, Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 4Department of Ophthalmology, Emergency County Hospital, Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 5Department of Pathophysiology, “Iuliu Haţieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- 6Department of Medical Informatics and Biostatistics, “Iuliu Haţieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Purpose: The study aimed to determine the stability of topographic and tomographic indices measured with Pentacam and to evaluate the biomechanical parameters measured with Corvis ST in the diagnosis of subclinical keratoconus (sKCN) and clinical keratoconus (KCN).
Methods: This is a single-center cohort study with a retrospective review of topographic and tomographic indices and biomechanical parameters on adult patients with subclinical keratoconus (sKCN), clinical keratoconus (KCN), and healthy subjects (control group). The area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) was used to identify the cutoff values for evaluated indices able to distinguish between subjects with sKCN and those with KCN.
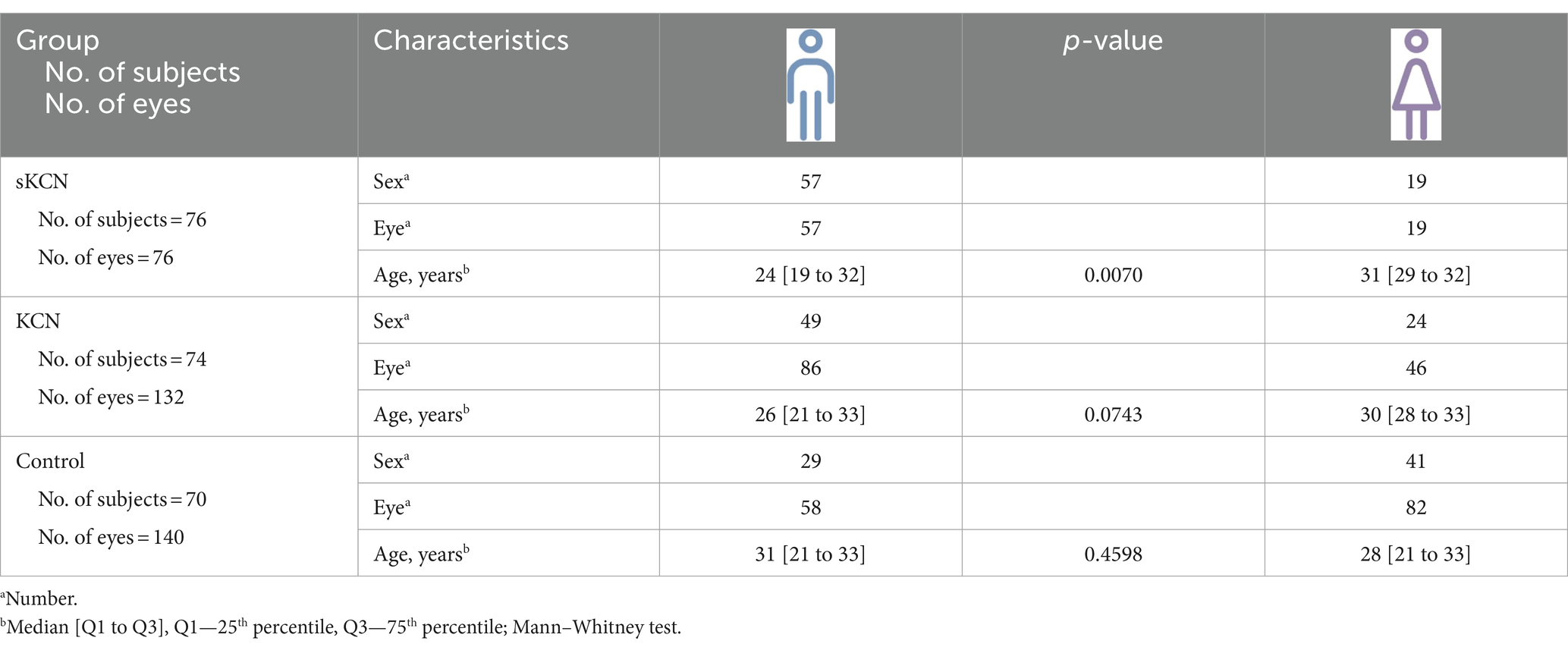
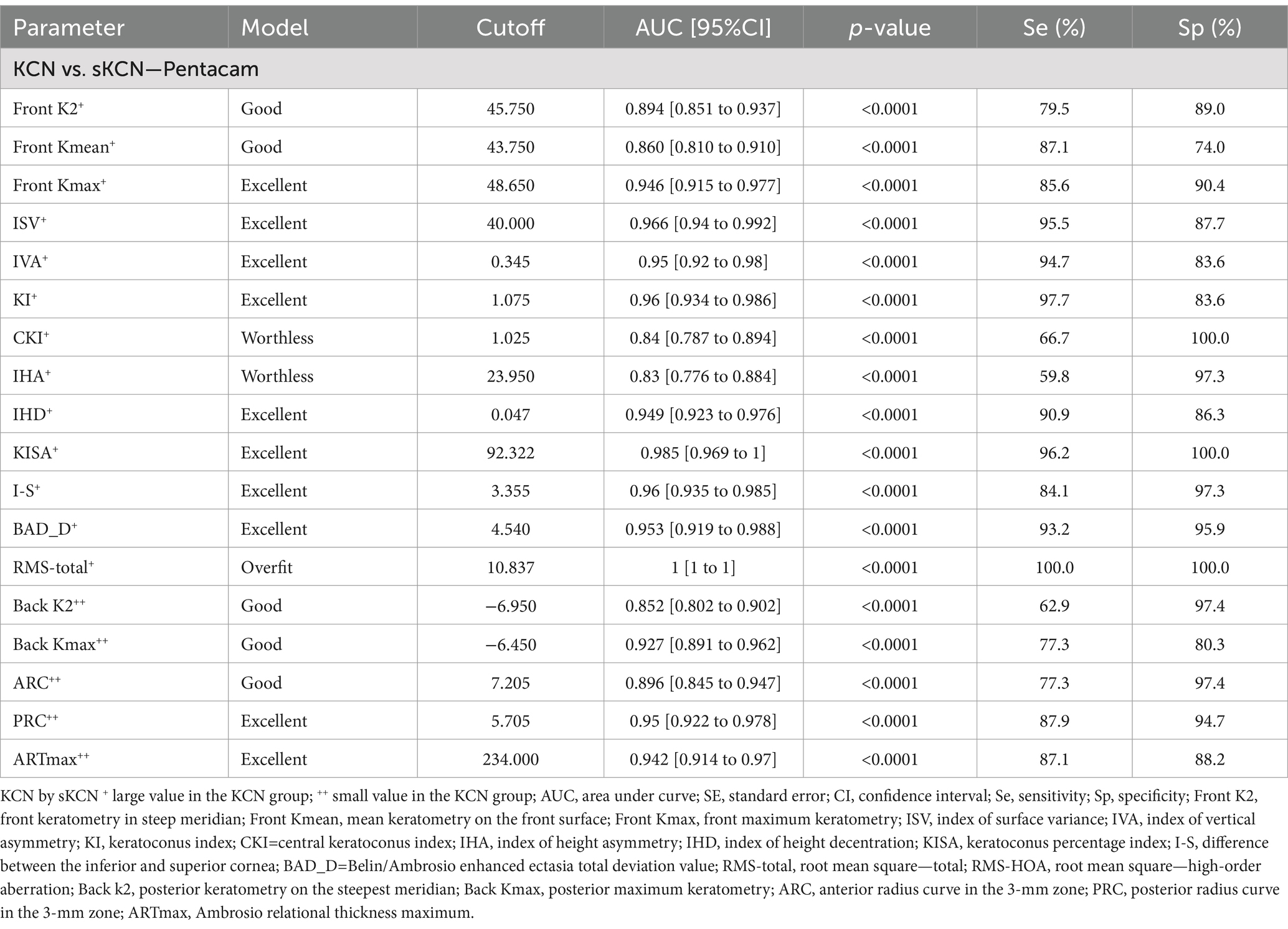
Results: Seventy-six patients (76 eyes) in the sKCN group, 74 patients (132 eyes) in the KCN group, and 70 patients (140 eyes) in the control group were analyzed. Evaluated participants had similar age, but in the sKCN group, men were predominant (p = 0.0070). Significantly higher values in the KCN group of Front Kmax, ISV, IVA, KI, IHD, BAD_D, and lower values of TL and PRC (with excellent accuracy AUC > 0.9) were observed in the differentiation of KCN by controls. Similarly, excellent accuracies were obtained by Front Kmax, ISV, IVA, KI, IHD, KISA, I-S, BAD_D, and RMS-total with higher values in the KCN group and PRC and ARTmax with lower values in patients with KCN as compared to those with sKCN. Only Front Kmean (AUC = 0.946, Se = 85.6%, Sp = 90.4%, p < 0.0001) and I-S Pentacam (AUC = 0.96, Se = 84.1%, Sp = 97.3%, p < 0.0001) proved accurate and not shared with differentiation of sKCN or KCN by normal eyes. Front Kmean Pentacam proved good for case findings (0.806 [0.742 to 0.871]) and screening (0.712 [0.645 to 0.778]). I-S Pentacam performed excellent for case findings (0.826 [0.764 to 0.888]) and good for screening (0.758 [0.700 to 0.817]).
Conclusion: Subclinical and clinical KCN shared common Pentacam parameters with excellent or good accuracy in distinguishing subjects with and without pathology, but Front Kmean and I-S Pentacam proved excellent or good for case finding and screening and are not shared with differentiation of the sKCN or KCN by the normal eyes. Furthermore, differentiation of sKCN by normal eyes could be done with KISA (Pentacam) and CBI (Corvis) parameters, but only CBI is not shared with KCN.
1 Introduction
Keratoconus (KCN) is a bilateral progressive corneal non-inflammatory ectatic disease, characterized by a conical corneal shape, myopia, irregular astigmatism, corneal thinning, and decreased visual acuity in late stages (1). The disease is diagnosed during puberty and swiftly advances in the range from 10 to 20 years (2). Early detection of the disease and subsequent prevention of risks are crucial factors in its progression (3). During the early stages, the visual acuity may appear normal, but the slit-lamp examination and corneal topography and tomography can detect the subtle alterations in corneal regularity and thickness (4). The lack of classical keratometry and slit-lamp signs is characteristic of subclinical KCN (sKCN), but patients with clinical KCN (5–8) display typical topographic aspects.
One of the most used diagnostic methods is performing corneal topography and tomography with Pentacam HR (OCULUS Optikgeräte GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Pentacam employs a rotating Scheimpflug camera and a monochromatic slit-light source to capture 100 images from 1 to 360 in 2 s. Corneal tomography provides several quantitative indices with high specificity and sensitivity in the diagnosis of KCN (1, 9). Multiple studies indicate that specific Pentacam indices show promise in positively diagnosing subclinical and clinical KCN, yet there is no consensus on the appropriate cutoff values (9–12). Researchers have reported reproducible values for corneal thickness and posterior elevation (13, 14).
Corneal biomechanical parameters showed performances in the diagnosis of KCN (15). Corvis ST (OCULUS Optikgeräte GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany) is a device that combines the Pentacam parameters with the biomechanical data (16) and records corneal deformation responses after the application of a standardized air puff (17). Corvis ST has been reported to detect biomechanical abnormalities in early KCN stages or sKCN (18).
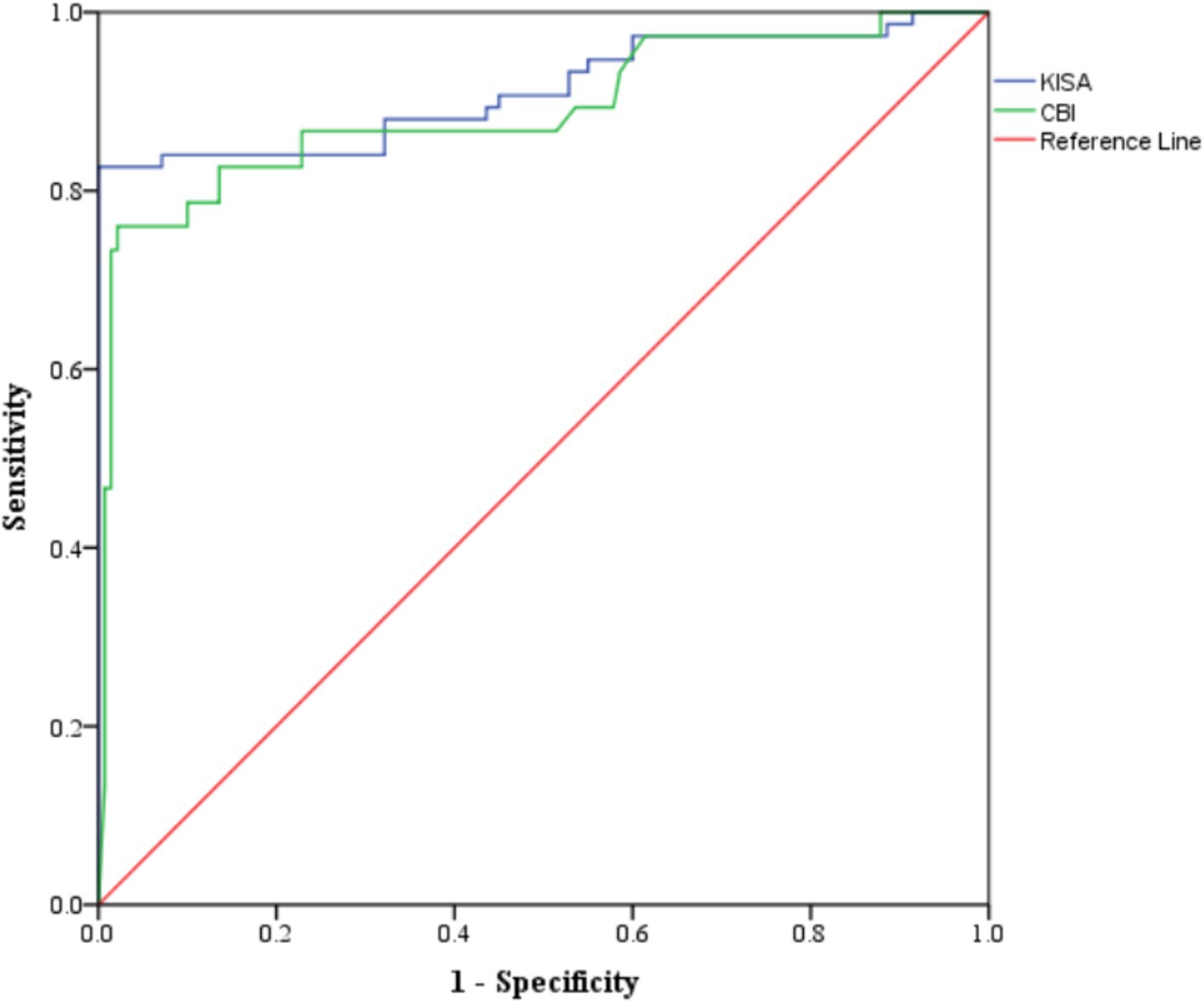
The investigation of Pentacam indices is the primary focus of the limited scientific literature on sKCN and KCN in Romania’s population. Our previous report highlighted the abilities of some Pentacam indices in distinguishing between sKCN and KCN patients, with KISA% (AUC = 0.991, Se = 95.8%, Sp = 98.1% cutoff = 92.322; Se indicates sensibility, and Sp indicates specificity) and PCR (AUC = 0.986, Se = 98.8%, Sp = 96.2%, cutoff = 5.7 mm) as excellent markers both for case finding and screening (19). Our study aimed to determine the stability of reported Pentacam topographic and tomographic indices and to investigate the abilities of Corvis ST biomechanical parameters in distinguishing patients with clinical keratoconus (KCN) from those with subclinical (sKCN).
2 Patients and methods
The research took place at Oculens Clinic in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, and received approval from the clinic’s Ethics Committee (no. 6/2022). The applied procedures were in concordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committee waived the requirement for informed consent.
2.1 Study design and patients
We conducted an observational analytic cohort study with retrospective anonymous data collection. We evaluated subjects who received medical care in the healthcare facility from January 2018 to October 2022 for eligibility. Patients who had abnormal findings in topography and tomography maps but showed no signs of disease on clinical examination were included in the subclinical KCN group (sKCN). The KCN group included patients diagnosed with keratoconus, whereas the control group (C) included subjects without sKCN or KCN who were eligible for refractive surgery. We classified the severity of KCN disease using Belin’s ABCD classification (20). Patients with corneal scars, previous ocular surgery, dry eye syndrome, history of trauma, glaucoma, connective tissue diseases, or those who wear contact lenses in the last month prior to examination were excluded. Pregnant women were also excluded from the study.
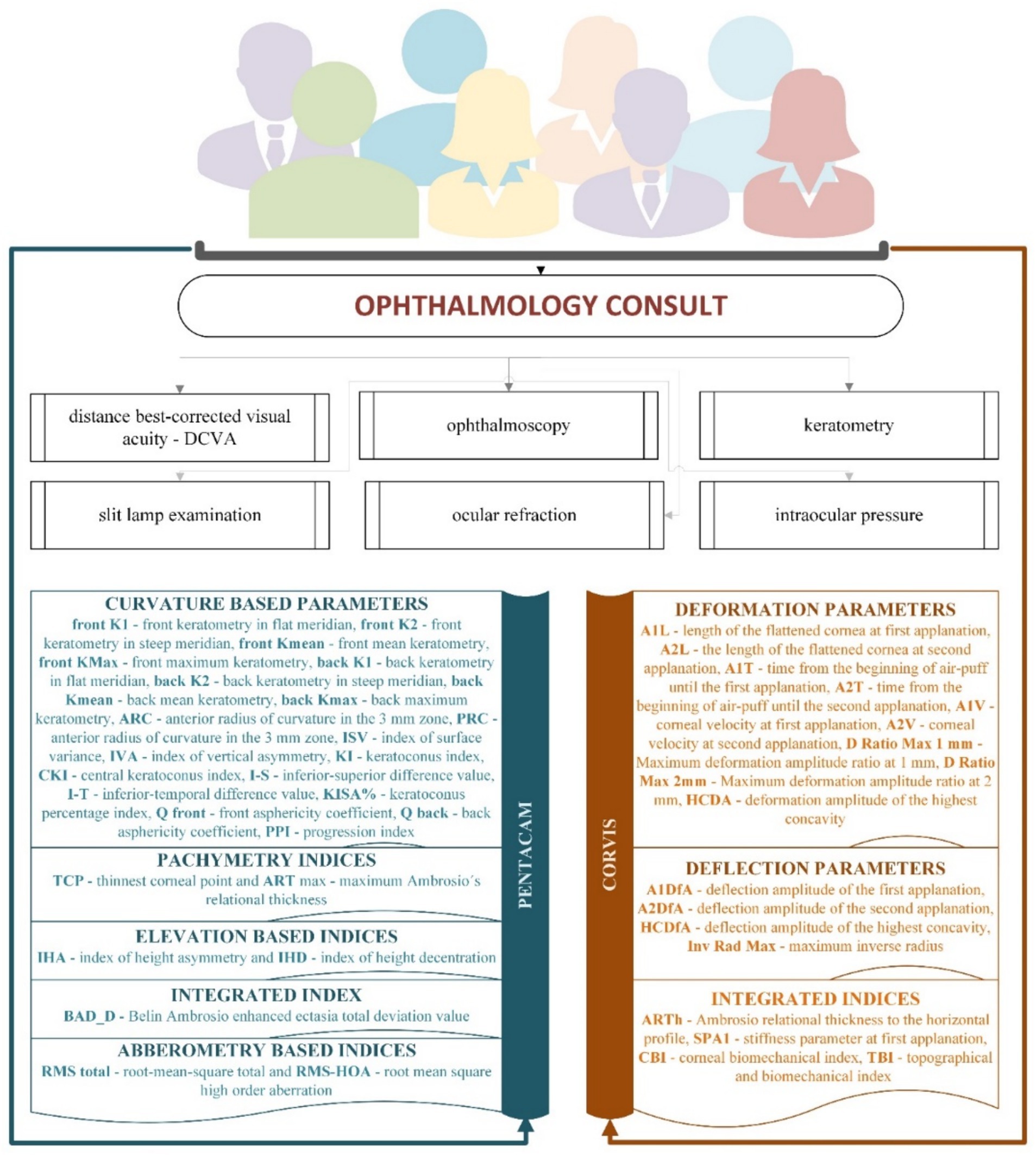
All patients received a complete standard ocular examination and had the imaging performed with the Pentacam (OCULUS Optikgeräte GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany) and Corvis ST (Oculus Optikgeräte GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). The patients were requested not to wear contact lenses for 1 month before the examinations. During the corneal tomography examination, all patients were asked to fixate on the central target and not to blink during the Scheimpflug camera rotation. The researchers assessed corneal biomechanical properties using the Corvis ST device (software version 1.5r1902) with two examinations at a 15-min interval. The same expert assistant performed all imagistic evaluations during one visit, following the same examination protocol, and using the same device for.
2.2 Data collection
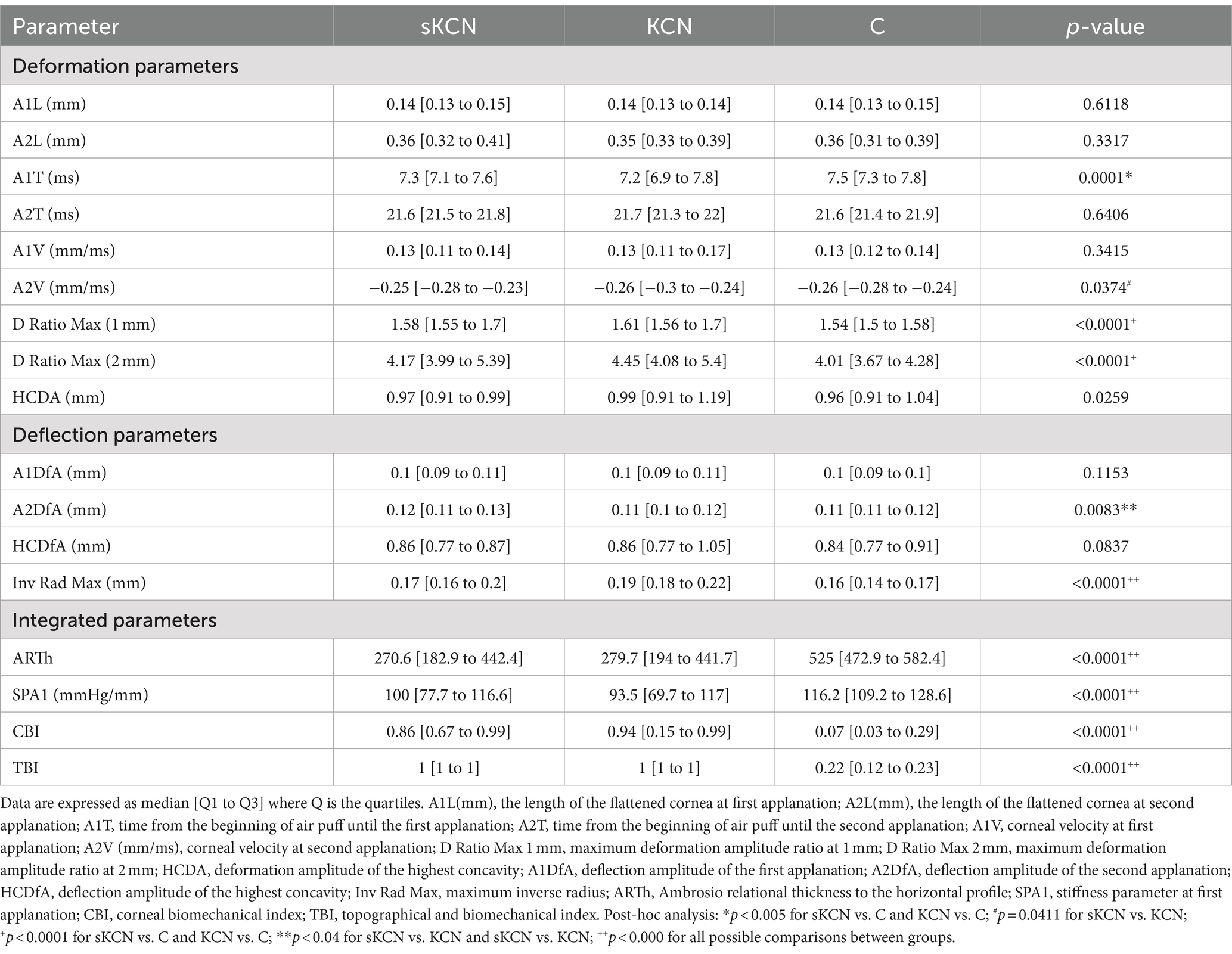
Figure 1 presents the flow of data collection. We evaluated 27 measurements retrieved from Pentacam (20 curvature-based indices, two pachymetry indices, two elevation-based indices, one integrated index, and two aberrometry-based indices) and 17 retrieved from Corvis (nine deformation, four deflection parameters, and four integrated indices).
2.3 Statistical analysis
The eye was the statistical unit in our analysis. The subject’s sex and number of evaluated eyes were summarized as absolute frequencies. Age, Pentacam, and Corvis parameters were first tested to identify the deviation from the theoretical normal distribution (Shapiro–Wilk test). Data were reported as median and [Q1 to Q3], where Q1 is the 25th percentile and Q3 is the 75th percentile, whenever the theoretical normal distribution proved violated. We used the Kruskal–Wallis test to compare the three groups and performed post-hoc analysis whenever we obtained statistical significance. The Mann–Whitney test was used to assess the differences between women and men. The indices measured with Pentacam and Corvis were the input data for receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis whenever significant differences between two groups (e.g., sKCN vs. KCN; sKCN/KCN vs. C) were observed. The performances of Pentacam and Corvis parameters in the classification of subjects were tested and AUC (area under the curve), Se (sensibility), Sp (specificity), for the cutoff values identified by the Youden index. We reported only AUC that indicated a good (>0.8) or an excellent (>0.9) model, considering the lower bound of a 95% confidence interval (21). We reported the clinical utility index for best-performing markers (http://www.clinicalutility.co.uk/, accessed 10 April 2024). Raincloud plots were used to illustrate the distribution of measurements between groups using the JASP program (v. 0.18.3.0). Raw data were analyzed with Statistics (v. 13.5, TIBCO Statistica, OK, USA) considering two-tailed tests and an adjusted significance level of 1.7%.
3 Results
Of 219 patients, 358 eyes were included in the analysis. Participants presented similar age (median values of 26 years for sKCN and 28 years for KCN and C; Kruskal–Wallis test: p = 0.6559) but statistically different distribution of sex (women: 19/76 (25%) in the sKCN group, 24/73 (32.9%) in the KCN group, and 41/70 (58.6%) in the C group; chi-squared test: p < 0.0001). Typically, women were older in the sKCN and KCN groups and younger in the C group (Table 1).
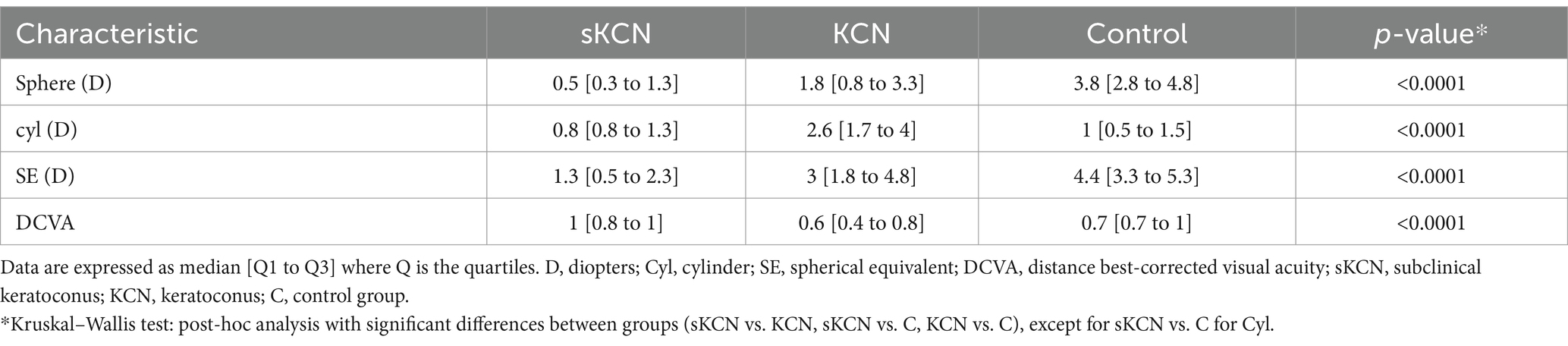
As expected, the participants in our evaluated groups exhibit statistically significant differences in clinical characteristics (sphere (D), cyl (D), SE (D), and DCVA; p-values <0.0001, Table 2).
3.1 Pentacam and Corvis characteristics by group
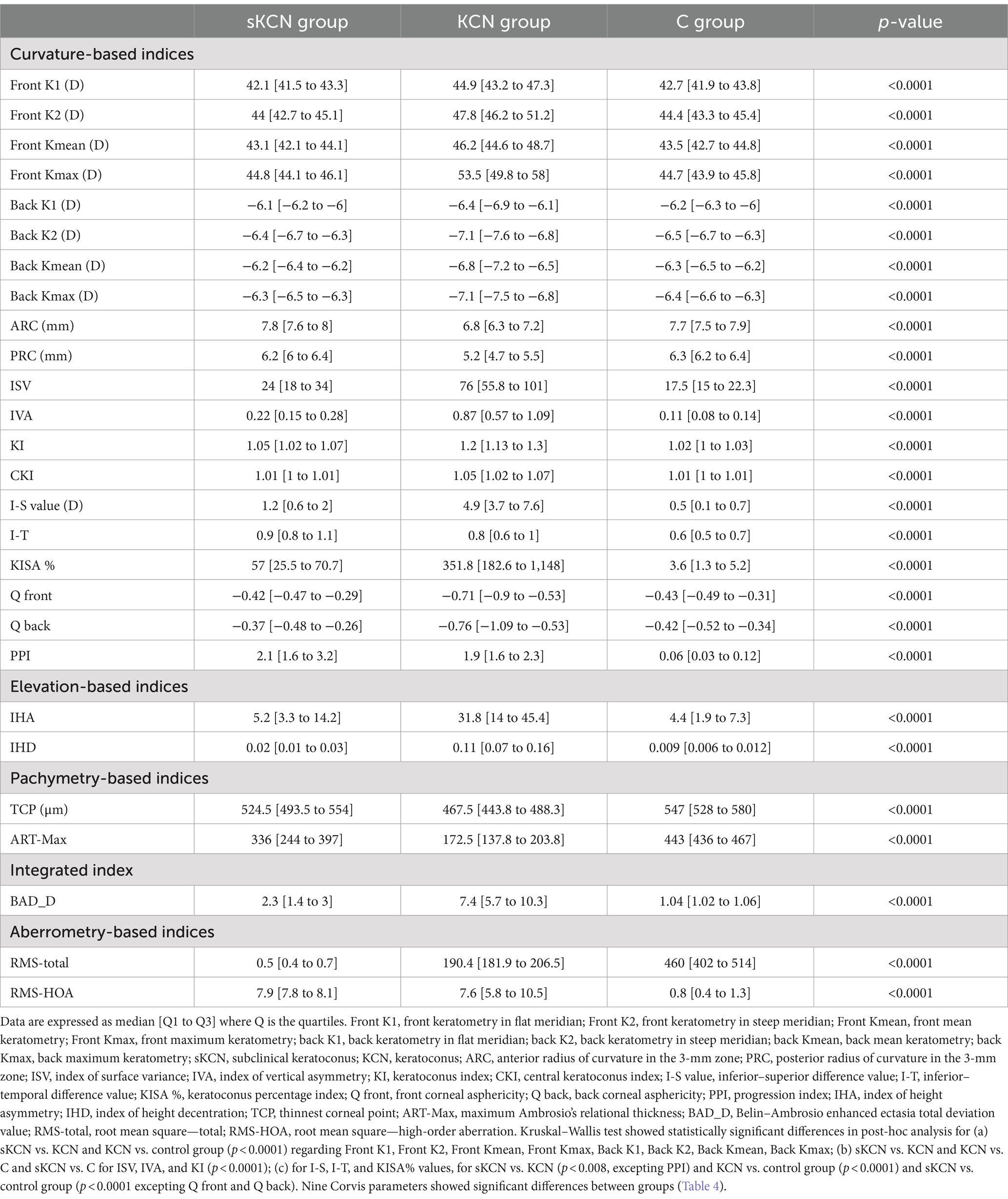
Curvature-based, elevation-based, pachymetry-based, integrated, and aberrometry-based indices measured with Pentacam showed statistically significant values between groups (Table 3).
3.2 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis
Four Pentacam and two Corvis parameters proved performances in the differentiation of sKCN by controls (Table 5; Figures 2, 3), but only the CBI is not shared with KCN. Three Pentacam (RMS-HOA, IP, and MS total) and one Corvis (TBI) parameter proved perfect classifies (AUC = 1; Table 5), showing an overfit and, therefore, the absence of performances on external raw data.
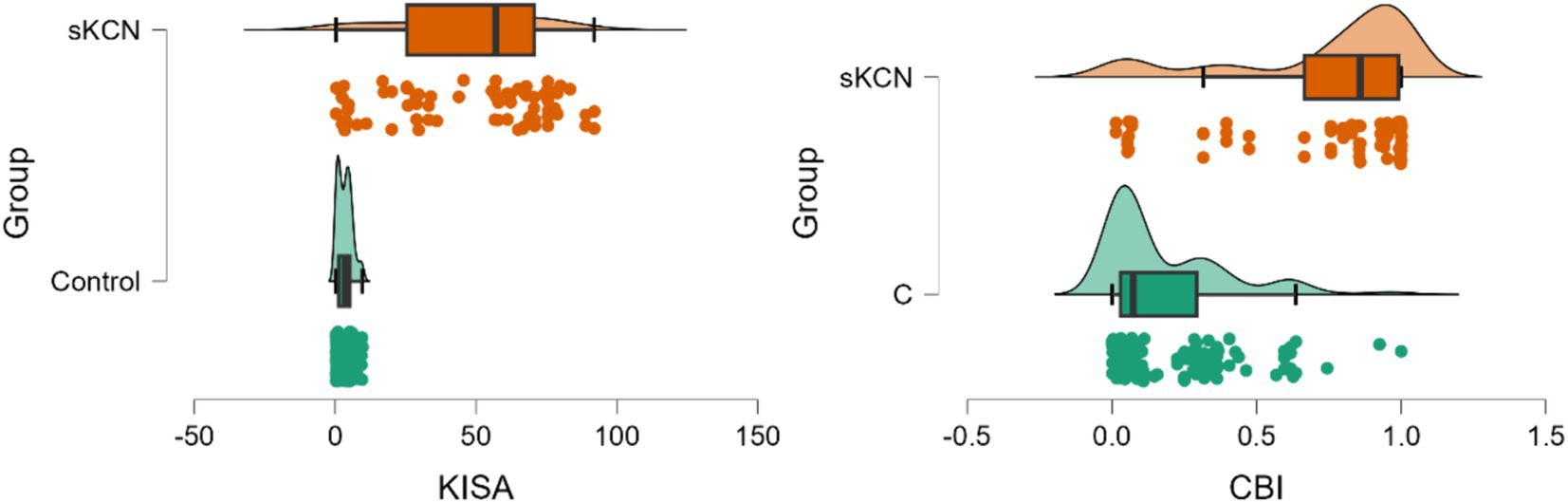
Figure 2. Distribution of KISA% and CBI values on patients with sKCN compared with controls. The dots represent the raw data, the box is determined by the value of the 25th and 75th percentile, and the line in the middle corresponds to the value of the median. The minimum and maximum values give the whiskers. Clinical performances in case finding (+CUI) or screening (−CUI): KISA%—excellent in case findings (0.816 [0.732 to 0.899]) and screening (0.909 [0.880 to 0.938]); CBI—good in case findings (0.726 [0.624 to 0.827]) and excellent in screening (0.865 [0.830 to 0.900]).
Eighteen Pentacam parameters (four overfit) and two Corvis parameters (two overfit) showed performance in the differentiation of KCN by controls, with some overlaps with sKCN (see Tables 5). The distribution of the markers in the KCN group compared to the control group for markers classified as excellent based on AUC is presented in Figure 4. Figure 5 presents the AUC for excellent markers in the differentiation of KCN by controls.
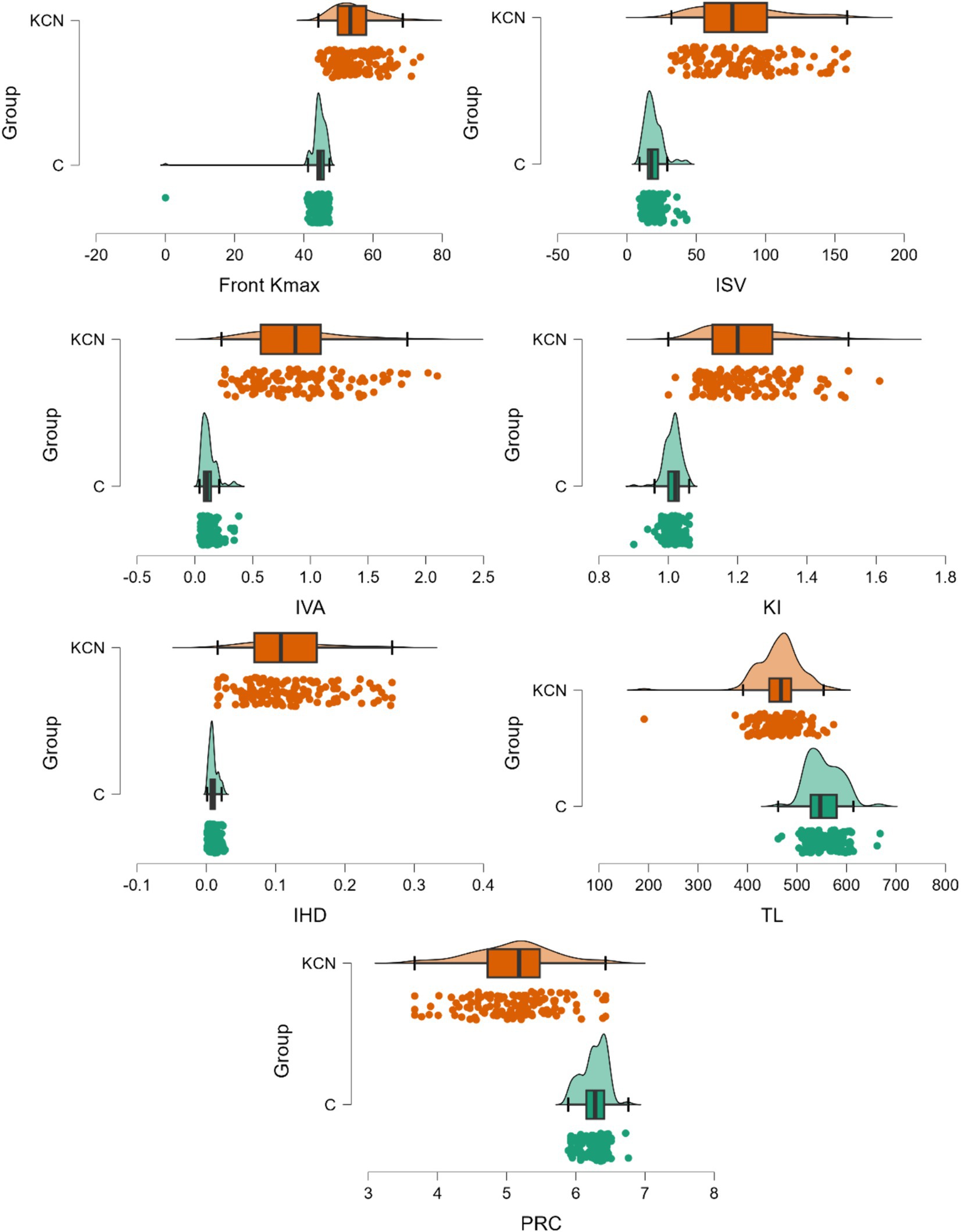
Figure 4. Distribution of markers on the KCN compared to the control group. The dots represent the raw data, the box is determined by the value of the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the line in the middle corresponds to the value of the median. The minimum and maximum values give the whiskers. Front Kmax—excellent in case findings (0.894 [0.846 to 0.942]) and screening (0.909 [0.880 to 0.938]); IVS and IVA—excellent in case findings (0.950 [0.917 to 0.982]) and in screening (0.950 [0.927 to 0.973]); KI—excellent in case findings (0.985 [0.967 to 1]) and screening (0.986 [0.974 to 0.998]); IHD—excellent in case findings (0.939 [0.903 to 0.976]) and screening (0.945 [0.922 to 0.968]); TL—excellent in case findings (0.851 [0.794 to 0.907]) and screening (0.867 [0.831 to 0.902]); PCR—excellent in case findings (0.917 [0.874 to 0.959]) and screening (0.927 [0.901 to 0.953]).
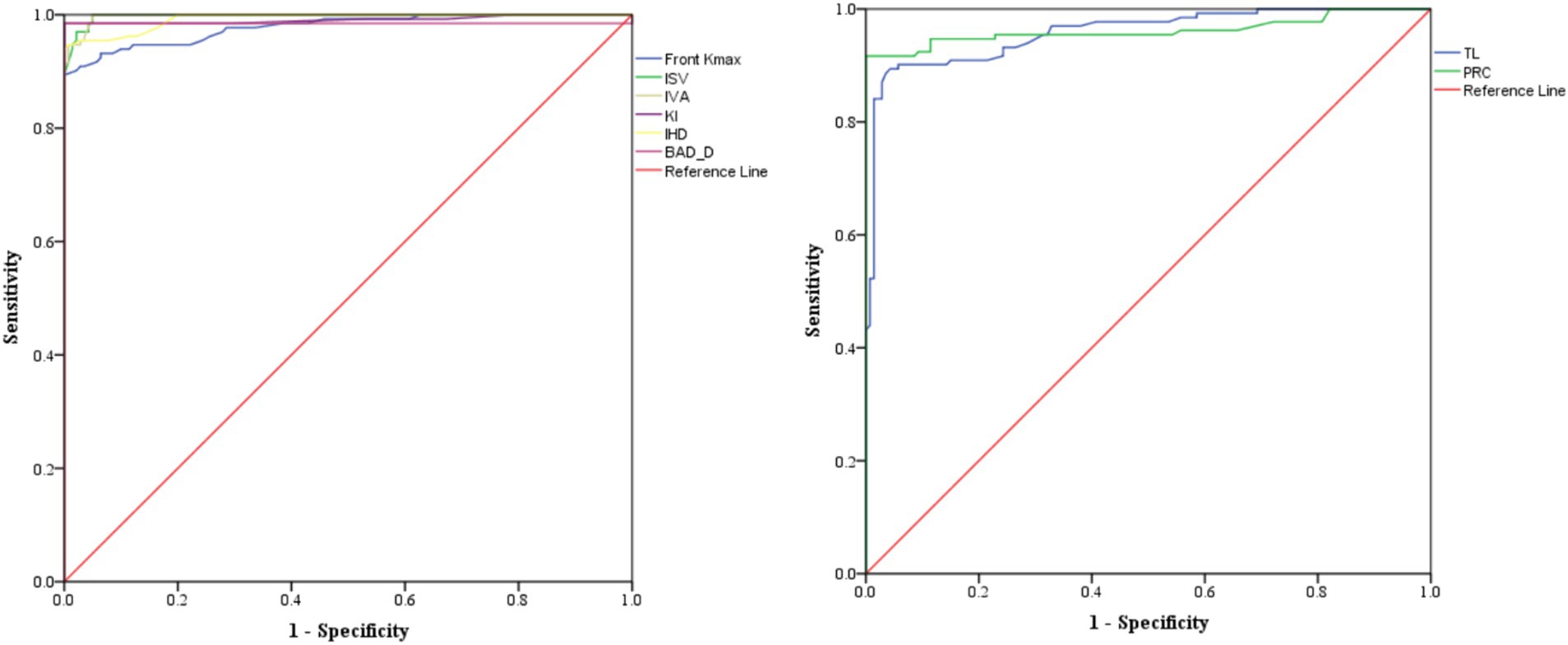
Figure 5. AUC for performing markers classified as excellent in the differentiation of KCN by controls. The graph on the left includes the markers with higher values in the KCN group, while the one on the right includes the markers with smaller values in the KCN group.
Eighteen parameters showed performances in discrimination between the KCN and sKCN groups (Table 6). Two markers, Front Kmean and I-S, are the only ones not shared with KCN vs. controls or sKCN vs. controls (Table 6).
The Front Kmean and I-S raw data exhibit higher values on patients with KCN than those with sKCN (Figure 6) and showed excellent performances in the differentiation of KCN by sKCN (Figure 7).
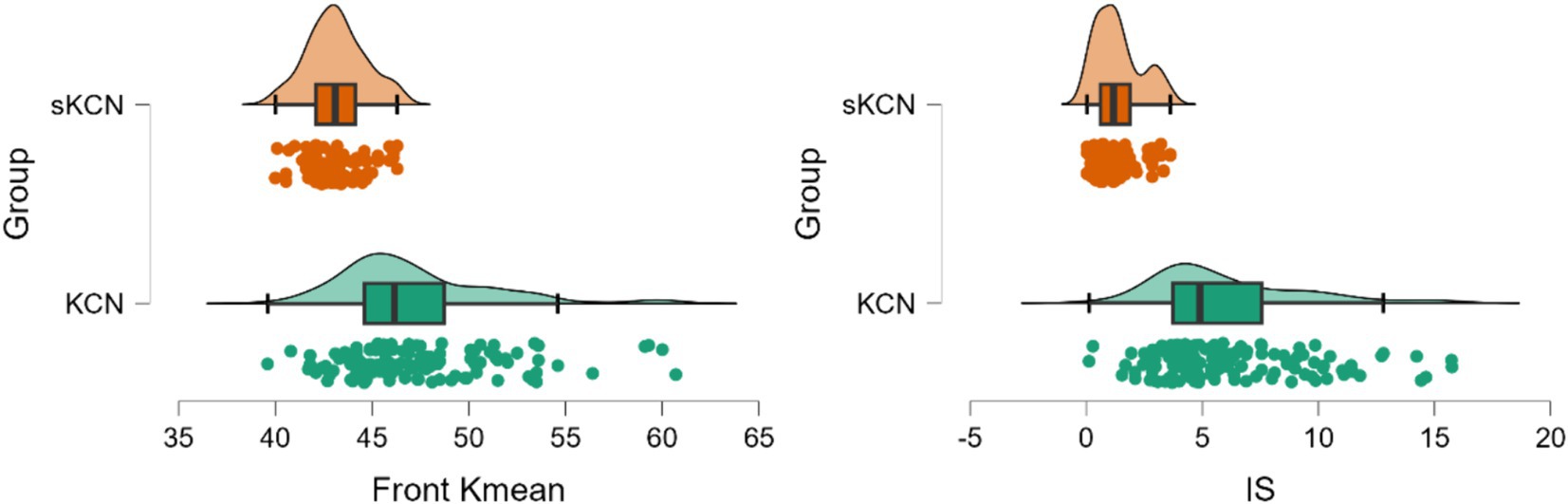
Figure 6. Distribution of performing measured markers in the KCN and sKCN groups. The dots represent the raw data, the box is determined by the value of the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the line in the middle corresponds to the value of the median. The minimum and maximum values give the whiskers. Clinical performances in case finding (+CUI) or screening (-CUI): Front Kmean—good for case findings (0.806 [0.742 to 0.871]) and screening (0.712 [0.645 to 0.778]) and I-S—excellent for case findings (0.826 [0.764 to 0.888]) and good for screening (0.758 [0.700 to 0.817]).
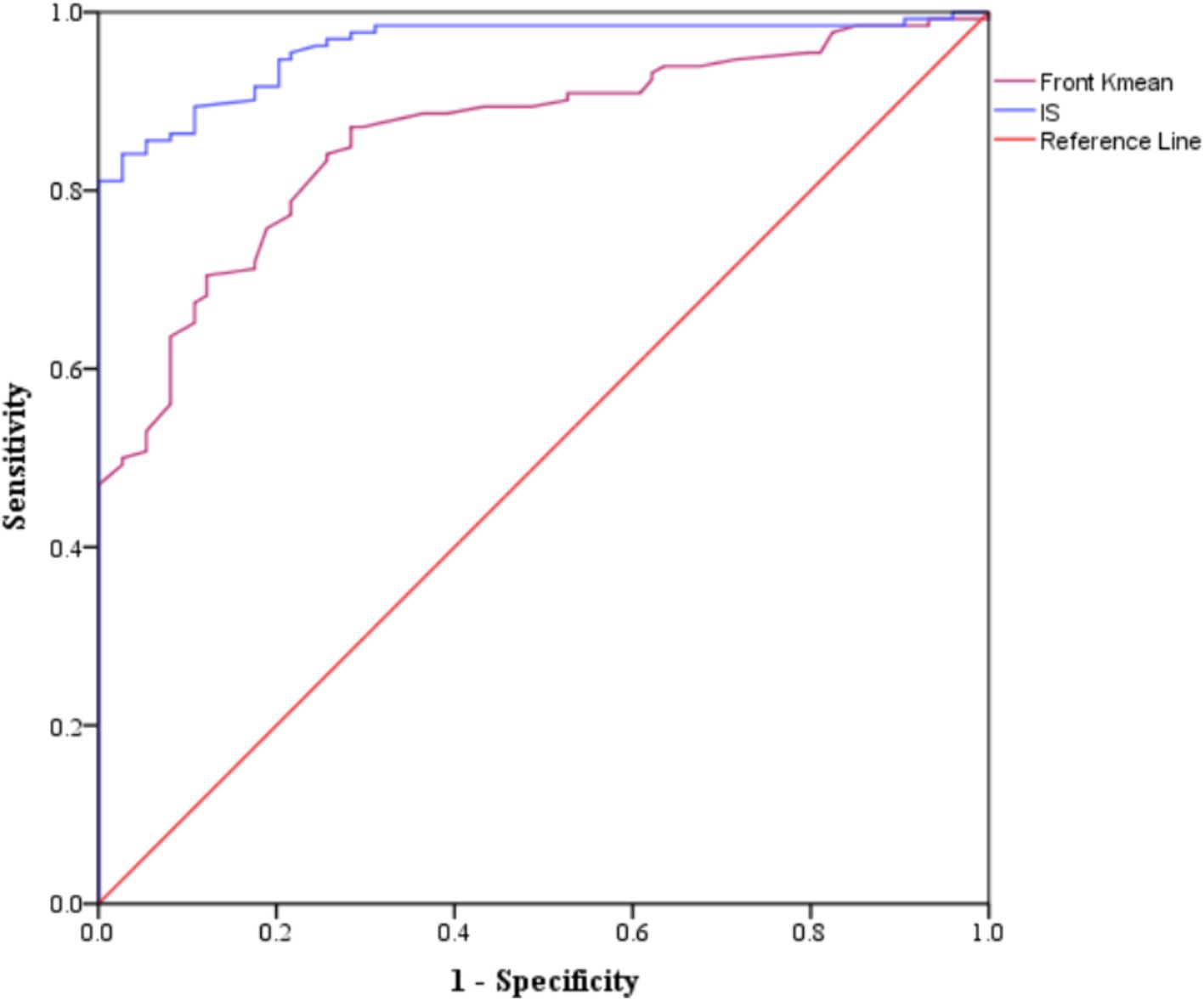
Figure 7. Areas under the curve for performing markers classified as good or excellent in the differentiation of KCN by sKCN.
4 Discussion
In the evaluated cohort, Pentacam indices, and Corvis parameters demonstrated statistically significant differences between the investigated groups. Several Pentacam indices exhibit significant differences between pairs of groups, but most of the observed significant differences are shared by comparisons of pairs groups (Table 3) according to our post-hoc analysis. Only a limited number of indices exhibited excellent or good performance in distinguishing KCN or sKCN by controls or KCN by sKCN in ROC analysis (Tables 5, 6; Figures 2–7). The results of our study confirm that reported Pentacam indices are valid for diagnosing KCN and sKCN in a Romanian cohort, showing comparable performance in terms of AUC and cutoff values (19).
The anterior corneal curvature, pachymetry, and refractive status can predict the central posterior corneal curvature, excluding the corneal shape factor (22, 23). Keratoconus-suspect eyes showed discrepancies in corneal thickness and posterior corneal elevation values (24, 25). The biomechanical weakening of the cornea can help predict changes in the posterior corneal curvature (18). Consequently, the analysis of corneal biomechanics is critical for the early detection of KCN and other ectatic corneal diseases (26).
The Pentacam indices Front Kmax, ISV, IVA, KI, IHD, and BAD_D were identified in our study as excellent markers for differentiating KCN from normal corneas, with the KCN group exhibiting higher values and TL and PRC showing lower values (Table 5). According to Sedaghat et al. (27), I-S can distinguish between KCN and normal corneas. In contrast to our finding where KISA(%) proved overfit, Heidari et al. (15) reported KISA index is sufficiently strong for the differentiation of KCN compared to normal eyes (AUC > 0.8).
The results of our study indicate that IHA and IHD distinguished KCN from normal corneas, with good and excellent performances (Table 5; Figure 4). In previous reports, the IHD showed excellent performance in diagnosing KCN, with AUC values of 0.999 and 0.979 (15, 28). The study conducted by Tian et al. (16) revealed that IHD has a high discriminatory power (AUC = 0.999) and recommend to monitor patients with IHD higher than 0.008 and highlighted that IHD > 0.018 could indicate an increased risk of KCN. The Kmax, ISV, IVA, KI, IHA, and IHD previously demonstrated adequate strength to differentiate between KCN and sKCN eyes (AUC range: 0.83 to 0.981) (16). Kovács et al. (29) found that IHD was better at distinguishing KCN from normal corneas than BAD_D, which aligns with our findings of the study (Table 5). Hashemi et al. (30) found that IVA had good performances in diagnosis (AUC = 0.952), results also obtained in our study but with higher AUC and a different cut-off value (Table 5). The top three performing indices to differentiate KCN from normal corneas identified in our study are ISV, IVA, and BAD_D (Table 5; Figure 4). The utility of ARTmax has been reported as a valid diagnostic index for differentiating keratoconic eyes from normal corneas (31), without consistent value for determining the fruste form of KCN (32), while this index proved overfit in our study (Table 5). Tian et al. (16) demonstrated a low power for CBI Corvis index (AUC = 0.624) in differentiating KCN from normal corneas while other previously reported research evaluated the TBI (15, 33). In our study, only two Corvis indices proved significant differences in KCN and controls and were investigated, TBI that overfit and ARTh that exhibited only good performance (Table 5), so not necessarily recommended for clinical use.
Ren et al. (34) found that CBI had high diagnostic efficiency in differentiating KCN from sKCN and control eyes. The use of CBI is efficient in differentiating KCN from normal corneas (35) with clinical utility in screening. Sedaghat et al. (27) and Herber et al. (36) also found similar results, validating the clinical usefulness of CBI parameters to distinguish KCN from normal corneas. Francis et al. (37) found evidence suggesting that a parameter linked to corneal stiffness could be a valid measure for distinguishing KCN from normal eyes.
In our study, the CBI (Corvis) and KISA (Pentacam) showed good potential to diagnose sKCN when compared to normal eyes (Table 5). Our results are similar to those reported by Heidari et al. (15) with regard to KISA. Tian et al. (16) demonstrated a limited applicability of CBI to distinguish sKCN or KCN when corneas are ≤ 500 μm. Ambrósio et al. (38) found a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 96% for a CBI (cutoff value of 0.29). Like Ambrósio et al. (38), Steinberg et al. reported CBI as a valid marker in the diagnosis of sKCN (35). Our findings showed that the Corvis TBI (Table 5) had an AUC equal with 1 showing on overfit and thus a parameter with possible external instability. Koc et al. (33) reported lower diagnostic accuracy for sKCN when the TBI Corvis index with a cutoff value equal to 0.29, with sensitivity at 67% and specificity at 86%.
The differentiation of KCN by sKCN was achieved in our cohort using 11 Pentacam parameters (Table 6; Figures 6, 7), with no Corvis parameters performing at a good or excellent level. Tian et al. (16) reported that ARTh and CBI provided moderate strength (AUC = 0.762, cutoff ≤ 338.03; AUC = 0.738, cutoff > 0.766) to distinguish KCN from sKCN.
In our cohort, the KCN group exhibited notable differences in A1T and D Ratio Max (1 mm) and D Ratio Max (2 mm) compared to the control group, as did the sKCN group (Table 4). Tian et al. (16) found A1T to be the predictor (AUC = 0.719) for sKCN, but the performance is limited. Our study also demonstrated significant differences (p < 0.0001) in all possible group comparisons for ARTh and SP-A1 (Table 4). Ren et al. (34) found that sKCN eyes have higher values for Max Inverse Radius (Inv Rad Max), D Ratio Max (2 mm), D Ratio Max (1 mm), Integrated Radius, and CBI than normal corneas, but lower than KCN eyes. The authors also suggested that SPA1 could be useful in distinguishing sKCN from normal corneas (34). Catalán-López et al. (39) found that combining A2L and corneal central thickness differentiated sKCN from normal corneas. In sKCN, the values of A1T, A1L SPA1, and HCR were reported to be lower than in the normal cornea (18, 40), while KCN exhibited higher values of A1V, A2T, A2V, and HCDA (16). Wu et al. demonstrated that HCR could differentiate between KCN, sKCN, and normal corneas (41). Our study revealed significant differences in A2DfA (mm) between sKCN and KCN, sKCN and control group, and a significant difference in Inv Rad Max for all group comparisons (Table 4). However, the observed differences do not show good or excellent discriminatory performances. Chan et al. (42) found that ART and Inv Rad Max had acceptable abilities to differentiate sKCN from control eyes, with AUC values of 0.836 and 0.754 (21), showing limited classification performance. Heber et al. (36) showed using regression analysis that the thinnest corneal thickness was accompanied by Max Inverse Radius, D Ratio Max (2 mm), D Ratio Max (1 mm), Integrated Radius, and SPA1 in normal and KCN eyes.
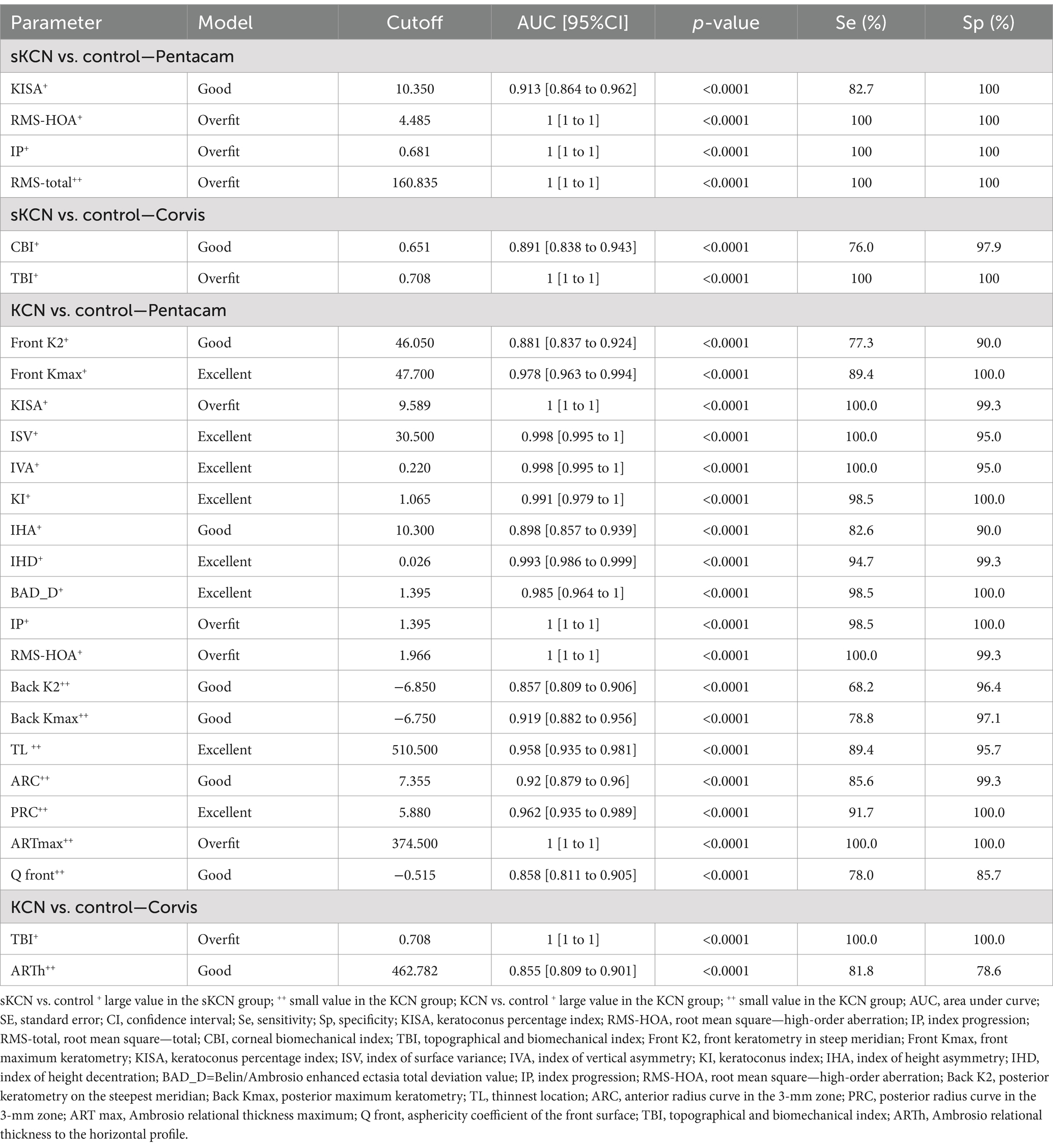
Table 5. Performant Pentacam and Corvis parameters in the differentiation of sKCN by controls and KCN by controls.
The strengths of our study are represented by the applied rigorous methodology and the existence of a control group, to compare the measured indices and to identify those markers with diagnostic potential. The evaluated number of patients was higher than our previous study (21), and the slight changes in the cutoff values for Pentacam indices indicate the robustness of our findings. Our findings show the potential of Pentacam and Corvis indices in differentiating patients with sKCN or KCN by controls, respectively, KCN by sKCN. However, their potential to become current practice need validation on external cohorts. While our study has strengths, we cannot overlook its limitations. The small number of participants in each group guarantees that our results directly reflect the evaluated cohort, but they must be interpreted with caution. To support generalizability, our results must undergo external validation. The study was done at one location, which may introduce institutional biases and limit the generalizability of the results. Multi-center studies would help to mitigate institutional biases and enhance the generalizability of the results. The retrospective nature of data collection hinders our ability to infer causality or track the development of sKCN or KCN over time. Long-term studies can effectively measure the changes in Pentacam and Corvis parameters during the disease progression. We concentrated on the Pentacam and Corvis parameters in our study, without considering additional diagnostic tests. Including a broader range of diagnostic tools (e.g., genetic, environmental, and behavioral) could provide a more comprehensive assessment. Furthermore, emerging technologies or a combination of different tools that increase the costs of diagnosis showed diagnostic performances (43–46), but validity and reliability assessment must provide evidence to support current practice implementation.
Lack of agreement is common in scientific literature regarding tomography and topography findings (43), potentially caused by variations in devices used (47, 48), genetic characteristics of the evaluated patients (49), and individual intrinsic biologic diversity. Consideration of all potential factors and confounders is crucial when determining cutoff values for diagnosing sKCN and KCN.
In conclusion, our findings showed that KISA (Pentacam) and CBI (Corvis) metrics are effective in differentiating sKCN from normal eyes in our evaluated cohort. To distinguish KCN from normal eyes, the most effective approach is to analyze ISV, IVA, IHD, KI, and BAD_D Pentacam measurements. Only two Pentacam indices, Front Kmean and I-S, have shown performances on the differentiation of KCN by sKCN not shared with distinguish between KCN and sKCN from normal eyes. Among the Corvis parameters, only ARTh showed performances in distinguishing KCN from normal eyes and CBI for distinguish sKCN from the normal eyes, but they did not reach the good or excellent thresholds for case findings or screening are not achieved.
Data availability statement
The data used to support the results of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Ethics statement
The Ethical Committee of the Oculens clinic approved the study (no. 6/2022) and waived the need of written informed consent due to reyrospective analysis of routine healthcare data. The study adhered to the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CN: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. KH: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AN: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AB: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SB: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DN: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rabinowitz, YS. Videokeratographic indices to aid in screening for keratoconus. J Refract Surg. (1995) 11:371–406. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-19950901-14
2. Chopra, I, and Jain, AK. Between-eye asymmetry in keratoconus in an Indian population. Clin Exp Optom. (2005) 88:146–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2005.tb06687.x
3. Ferdi, AC, Nguyen, V, Gore, DM, Allan, BD, Rozema, JJ, and Watson, SL. Keratoconus natural progression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of11 529 eyes. Ophthalmology. (2019) 126:935–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.02.029
4. Mohammadpour, M, Heidari, Z, and Hashemi, H. Updates on managements for keratoconus. J Curr Ophthalmol. (2018) 30:110–24. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2017.11.002
5. Maguire, L, and Bourne, W. Corneal topography of early keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. (1989) 108:107–12. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90001-9
6. Rabinowitz, Y, Garbus, J, and McDonnell, PJ. Computer-assisted corneal topography in family members of patients with keratoconus. Arch Ophthalmol. (1990) 108:365–71. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070050063032
7. Rabinowitz, Y, Nesburn, AB, and McDonnell, PJ. Videokeratography of the fellow eye in unilateral keratoconus. Ophthalmology. (1993) 100:181–6. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(93)31673-8
8. Li, X, Rabinowitz, Y, Rasheed, K, and Yang, H. Longitudinal study of the normal eyes in unilateral keratoconus patients. Ophthalmology. (2004) 111:440–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2003.06.020
9. Rabinowitz, YS, and Rasheed, K. KISA% index: a quantitative videokeratography algorithm embodying minimal topographic criteria for diagnosing keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. (1999) 25:1327–35. doi: 10.1016/S0886-3350(99)00195-9
10. Shetty, R, Rao, H, Khamar, P, Sainani, K, Vuanava, K, Jayadev, C, et al. Keratoconus screening indices and their diagnostic ability to distinguish normal from ectatic corneas. Am J Ophthalmol. (2017) 181:140–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2017.06.031
11. Heydarian, S, Hashemi, H, Yekta, A, Ostadimoghaddam, H, Derakhshan, A, Aghamirsalim, M, et al. Heritability of corneal curvature and Pentacam Topometric indices: a population-based study. Eye Contact Lens. (2019) 45:365–71. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000589
12. Ferreira-Mendes, J, Lopes, BT, Faria-Correia, F, Salomão, MQ, Rodrigues-Barros, S, and Ambrósio, R Jr. Enhanced ectasia detection using corneal tomography and biomechanics. Am J Ophthalmol. (2019) 197:7–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2018.08.054
13. de Sanctis, U, Missolungi, A, Mutani, B, Richiardi, L, and Grignolo, FM. Reproducibility and repeatability of central corneal thickness measurement in keratoconus using the rotating Scheimpflug camera and ultrasound pachymetry. Am J Ophthalmol. (2007) 144:712–718.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2007.07.021
14. Chen, D, and Lam, AK. Intrasession and intersession repeatability of the Pentacam system on posterior corneal assesment in the normal human eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2007) 33:448–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.11.008
15. Heidari, Z, Hashemi, H, Mohammadpour, M, Amanzadeh, K, and Fotouhi, A. Evaluation of corneal topographic, tomographic and biomechanical indices for detecting clinical and subclinical keratoconus: a comprehensive three-device study. Int J Ophthalmol. (2021) 14:228–39. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.02.08
16. Tian, L, Zhang, D, Guo, L, Qin, X, Zhang, H, Zhang, H, et al. Comparisons of corneal biomechanical and tomographic parameters among thin normal cornea, forme fruste keratoconus, and mild keratoconus. Eye Vis (Lond). (2021) 8:44. doi: 10.1186/s40662-021-00266-y
17. Vinciguerra, R, Ambrósio, R Jr, Elsheikh, A, Roberts, CJ, Lopes, B, Morenghi, E, et al. Detection of keratoconus with a new biomechanical index. J Refract Surg. (2016) 32:803–10. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20160629-01
18. Elham, R, Jafarzadehpur, E, Hashemi, H, Amanzadeh, K, Shokrollahzadeh, F, Yekta, A, et al. Keratoconus diagnosis using Corvis ST measured biomechanical parameter. J Current Ophthalmol. (2017) 29:175–81. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2017.05.002
19. Nicula, CA, Bulboacă, AE, Nicula, D, Nicula, AP, Horvath, KU, and Bolboacă, SD. Performances of corneal topography and tomography in the diagnosis of subclinical and clinical keratoconus. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:904604. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.904604
20. Belin, MW, Kundu, G, Shetty, N, Gupta, K, Mullick, R, and Thakur, P. ABCD: a new classification for keratoconus. Indian J Ophthalmol. (2020) 68:2831–4. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2078_20
21. Bolboacă, SD. Medical diagnostic tests: a review of test anatomy, phases, and statistical treatment of data. Comput Math Methods Med. (2019) 2019:1891569–22. doi: 10.1155/2019/1891569
22. Montalbán, R, Piñero, DP, Javaloy, J, and Alió, JL. Scheimpflug photography-based clinical characterization of the correlation of the corneal shape between the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces in the normal human eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2012) 38:1925–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.06.050
23. Montalbán, R, Alio, JL, Javaloy, J, and Piñero, DP. Correlation of anterior and posterior corneal shape in keratoconus. Cornea. (2013) 32:916–21. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3182904950
24. Schlegel, Z, Hoang-Xuan, T, and Gatinel, D. Comparison of and correlation between anterior and posterior corneal elevation maps in normal eyes and keratoconus-suspect eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2008) 34:789–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2007.12.036
25. Tomidokoro, A, Oshika, T, Amano, S, Higaki, S, Maeda, N, and Miyata, K. Changes in anterior and posterior corneal curvatures in keratoconus. Ophthalmology. (2000) 107:1328–32. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00159-7
26. Yang, K, Xu, L, Fan, Q, Gu, Y, Song, P, Zhang, B, et al. Evaluation of new Corvis ST parameters in normal, post-LASIK, post-LASIK keratectasia and keratoconus eyes. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:5676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62825-y
27. Sedaghat, MR, Momeni-Moghaddam, H, Ambrosio, R Jr, Heidari, HR, Maddah, N, Danesh, Z, et al. Diagnostic ability of corneal shape and biomechanical parameters for detecting krank keratoconus. Cornea. (2018) 37:1025–34. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001639
28. Huseynli, S, and Abdulaliyeva, F. Evaluation of Scheimpflug tomography parameters in subclinical keratoconus, clinical keratoconus and normal caucasian eyes. Turk J Ophthalmol. (2018) 48:99–108. doi: 10.4274/tjo.89587
29. Kovács, I, Miháltz, K, Kránitz, K, Juhász, É, Takács, Á, Dienes, L, et al. Accuracy of machine learning classifiers using bilateral data from a Scheimpflug camera for identifying eyes with preclinical signs of keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2016) 42:275–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2015.09.020
30. Hashemi, H, Khabazkhoob, M, Pakzad, R, Bakhshi, S, Ostadimoghaddam, H, Asaharlous, A, et al. Pentacam accuracy in discriminating keratoconus from Normal corneas: a diagnostic evaluation study. Eye Contact Lens. (2019) 45:46–50. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000531
31. Motlagh, MN, Moshirfar, M, Murri, MS, Skanchy, DF, Momeni-Moghaddam, H, Ronquillo, YC, et al. Pentacam® corneal tomography for screening of refractive surgery candidates: a review of the literature, part I. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. (2019) 8:177–203. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-0169-7
32. Bae, GH, Kim, JR, Kim, CH, Lim, DH, Chung, ES, and Chung, TY. Corneal topographic and tomographic analysis of fellow eyes in unilateral keratoconus patients using Pentacam. Am J Ophthalmol. (2014) 157:103–109e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.08.014
33. Koc, M, Aydemir, E, Tekin, K, Inane, M, Kosekahya, P, and Kiziltoprak, H. Biomechanical analysis of subclinical keratoconus with normal topographic, topometric and tomographic findings. J Refract Surg. (2019) 35:247–52. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20190226-01
34. Ren, S, Xu, L, Fan, Q, Gu, Y, and Yang, K. Accuracy of new Corvis ST parameters for detecting subclinical and clinical keratoconus eyes in a Chinese population. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:4962. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84370-y
35. Steinberg, J, Amirabadi, NE, Frings, A, Mehlan, J, Katz, T, and Linke, SJ. Keratoconus screening with dynamic biomechanical in vivo Scheimpfug analyses: a proof-of-concept study. J Refract Surg. (2017) 33:773–8. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20170807-02
36. Herber, R, Ramm, L, Spoerl, E, Raiskup, F, Pillunat, L, and Terai, N. Assessment of corneal biomechanical parameters in healthy and keratoconic eyes using dynamic bidirectional applanation device and dynamic Scheimpfug analyzer. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2019) 45:778–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.12.015
37. Francis, M, Pahuja, N, Shroff, R, Gowda, R, Matalia, H, Shetty, R, et al. Waveform analysis of deformation amplitude and deflection amplitude in normal, suspect, and keratoconic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. (2017) 43:1271–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2017.10.012
38. Ambrósio, R Jr, Lopes, BT, Faria-Correia, F, Salomão, MQ, Bühren, J, Roberts, CJ, et al. Integration of Scheimpflug-based corneal tomography and biomechanical assessments for enhancing ectasia detection. J Refract Surg. (2017) 33:434–43. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20170426-02
39. Catalán-López, S, Cadarso-Suárez, L, López-Ratón, M, and Cadarso-Suárez, C. Corneal biomechanics in unilateral keratoconus and fellow eyes with a Scheimpflug-based tonometer. Optom Vis Sci. (2018) 95:608–15. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001241
40. Zemova, E, Eppig, T, Seitz, B, Toropygin, S, Arnold, S, Langenbucher, A, et al. Interaction between topographic/tomographic parameters and dry eye disease in keratoconus patients. Curr Eye Res. (2014) 39:1–8. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2013.798667
41. Wu, Y, Li, XL, Yang, SL, Yan, XM, and Li, HL. Examination and discriminant analysis of corneal biomechanics with CorVis ST in keratoconus and subclinical keratoconus. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. (2019) 51:881–6. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.015
42. Chan, TCY, Wang, YM, Yu, M, and Jhanji, V. Comparison of corneal tomography and a new combined tomographic biomechanical index in subclinical keratoconus. J Refract Surg. (2018) 34:616–21. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20180705-02
43. Al Bdour, M, Sabbagh, HM, and Jammal, HM. Multi-modal imaging for the detection of early keratoconus: a narrative review. Eye Vis. (2024) 11:18. doi: 10.1186/s40662-024-00386-1
44. Zhang, X, Munir, SZ, Sami Karim, SA, and Munir, WM. A review of imaging modalities for detecting early keratoconus. Eye (Lond). (2021) 35:173–87. doi: 10.1038/s41433-020-1039-1
45. Heidari, Z, Mohammadpour, M, Hajizadeh, F, Fotouhi, A, and Hashemi, H. Corneal layer thickness in keratoconus using optical coherence tomography. Clin Exp Optom. (2024) 107:32–9. doi: 10.1080/08164622.2023.2201369
46. Kuo, AN, Cortina, MS, Greiner, MA, Li, JY, Miller, DD, Shtein, RM, et al. Advanced corneal imaging in keratoconus. A report by the American Academy of ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. (2024) 131:107–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2023.07.030
47. Angelo, L, Gokul, A, McGhee, C, and Ziaei, M. Comparing repeatability and agreement between commonly used corneal imaging devices in keratoconus. Optom Vis Sci. (2023) 100:761–9. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000002079
48. Seiler, TG, Mueller, M, and Mendes, BT. Repeatability and comparison of corneal tomography in mild to severe keratoconus between the anterior segment OCT MS-39 and Pentacam HR. J Refract Surg. (2022) 38:250–5. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20220114-02
49. AvaGen test for keratoconus risk factors and corneal dystrophies-clinical test-NIH genetic testing registry (GTR)-NCBI. (2021). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/tests/569033/ (Accessed February 2024).
Keywords: keratoconus, subclinical keratoconus, topographic indices, tomographic indices, biomechanical parameters
Citation: Nicula CA, Horvath KU, Nicula AP, Bulboacă AE, Bolboacă SD and Nicula D (2024) Distinguishing subclinical from clinical keratoconus by corneal measurements. Front. Med. 11:1427666. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1427666
Edited by:
Yan Li, Oregon Health and Science University, United StatesReviewed by:
Katarzyna Krysik, Wojewódzki Szpital Specjalistyczny nr 5 Sosnowiec, PolandMukharram M. Bikbov, Ufa Eye Research Institute, Russia
Yi Dong, Tianjin Eye Hospital, China
Copyright © 2024 Nicula, Horvath, Nicula, Bulboacă, Bolboacă and Nicula. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sorana D. Bolboacă, c2JvbGJvYWNhQHVtZmNsdWoucm8=
 Cristina Ariadna Nicula
Cristina Ariadna Nicula Karin Ursula Horvath3,4
Karin Ursula Horvath3,4 Sorana D. Bolboacă
Sorana D. Bolboacă