- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Medical Genetics of Zhejiang Province, Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine, Ministry of Education, School of Laboratory Medicine and Life Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Laboratory Medicine Center, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital (Affiliated People's Hospital), Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 4Department of Vascular Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Edwardsiella tarda is frequently isolated from aquatic animals and environments. While human infections caused by E. tarda are rare, some extraintestinal infections can be severe. This case report describes a patient with cellulitis of the right upper extremity of unknown origin. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) indicated that the patient was infected with E. tarda. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that the isolate was resistant to quinolones and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. The isolate, positive for four virulence genes (fimA, gadB, mukF, and sodB), was confirmed to be virulent using the Galleria mellonella larvae model. Following early pus drainage and a 9-day course of imipenem, the patient ultimately recovered. This case report aimed to illustrate the presentation, diagnosis, and management of uncommon cellulitis caused by drug-resistant, virulent E. tarda.
Introduction
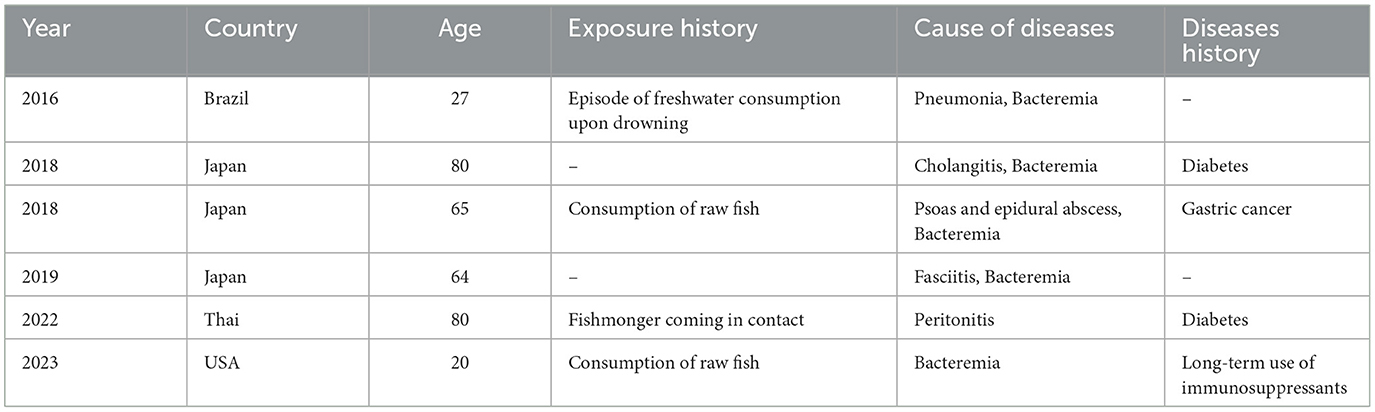
Edwardsiella tarda, a Gram-negative intracellular bacillus within the Enterobacteriaceae family, was first identified by Ewing et al. (1). E. tarda is constantly detected in aquatic environments and aquatic animals, including fish, reptiles, and amphibians (2). Notorious as a pathogen causing edwardsiellosis in fish, which often leads to significant economic losses, E. tarda can also infect humans (3). Approximately 80% of human infections are gastrointestinal (2, 4) and tend to be self-limited. The remaining 20% of cases are extraintestinal infections, including bacteremia, wound infections, liver abscesses, cholecystitis, meningitis, and peritonitis. Previous reports have indicated that E. tarda can cause gastroenteritis in humans through the consumption of contaminated water or seafood, subsequently leading to bacteremia (5, 6). Predisposing factors, such as chronic liver cirrhosis and compromised immune function, increase susceptibility to E. tarda infections in humans (5, 7). In addition, E. tarda can cause extraintestinal infections, such as bacteremia (7), biliary tract infections (8), pneumonia (9), necrotizing fasciitis (10), peritonitis (11), and iliac psoas or epidural abscesses (12) (Table 1). These extraintestinal infections have been increasingly reported in recent years (6, 7, 13–15), with a notable mortality rate of 22.7% for severe cases involving bacteremia (16). These findings underscore the importance of a rapid diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In this study, we present a case of cellulitis caused by E. tarda, which was confirmed by metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS). The use of advanced sequencing technologies such as mNGS has proven critical in the accurate and timely diagnosis of infections caused by rare pathogens.
Cellulitis typically presents as an acute, spreading erythematous area with poorly demarcated borders, exhibiting the cardinal signs of inflammation, such as pain, fever, redness, and swelling. A systematic retrospective study in the United States found that cellulitis in immunocompetent adults is primarily caused by group A Streptococcus, with Staphylococcus aureus being a less frequent pathogen. The significant presence of Gram-negative bacteria might be attributed to patients with compromised immune systems, cirrhosis, aquatic injury exposure, or animal bite injuries (17). In the current study, we established the bacterial diagnosis by aspirating and culturing the patient's exudate, followed by rapid detection using metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS), which confirmed an Edwardsiella tarda infection.
Case description
A 60-year-old female patient was admitted to the Department of Burns and Wound Center, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine on 7 December 2023. The patient, without any evident traumatic cause, was experiencing continuous pain in the right thumb for 4 days, accompanied by edema in the last 2 days. Initially, the patient was treated with intravenous penicillin at a local hospital, but the condition did not improve. Then, localized congestion and necrosis of the thumb were observed, followed by abscess formation and restriction of movement. The patient visited our hospital for medical support and was diagnosed with cellulitis of the right upper extremity. She had no history of immune system disorders but did have chronic hypertension. The patient had no particular travel history to areas known for unique pathogens. The patient informed that she works as a seafood saleswoman with prolonged exposure to freshwater fish.
Upon physical examination, the patient was in good general condition, with no signs of pain or distress in her facial expression. Her breath sounds were clear upon auscultation, with no indication of shortness of breath. However, the skin on the right hand appeared red and swollen. There were localized areas of bruising and necrosis on the right hand, accompanied by limited mobility (Supplementary Figure S1).
Diagnostic assessment and therapeutic intervention
Upon admission (Day 1), the blood tests revealed an elevated leukocyte count of 12.3 × 109/L, a neutrophil count of 10.08 × 109/L, an ultrasensitive C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 98 mg/L, and an interleukin-6 level of 12.27 pg/ml. The patient experienced pain, redness, and swelling localized to the palm of the right hand, particularly around the thumb where an abscess had developed. However, there was no accompanying fever. Since the patient was a seafood retailer with a history of seafood contact, Vibrio infection could not be ruled out. As for infections caused by Vibrio vulnificus, wound infection and primary septicemia are the most common manifestations. Wound infection might lead to necrotizing fasciitis, a severe infection of soft tissue and fascia. The skin could exhibit signs of fever, redness, swelling, ulcers, blisters, or black spots, and patients might experience intense pain, fever, chills, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, or purulent discharge from the infected area. In addition, cellulitis caused by S. aureus or Streptococcus could not be ruled out. Due to clinical suspicion of a bacterial etiology, the patient was started on empirical antibiotic therapy with imipenem (0.5 g every 8 h, intravenously) and amikacin (0.2 g daily, intravenously). Despite this treatment, the patient's response was found to be suboptimal.
On Day 2, to confirm the etiological diagnosis, we performed wound aspiration as part of the initial assessment to identify the bacterial pathogen. The aspirated fluid was submitted for microbiological culture and metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) analysis. The patient's wounds were carefully dressed and managed with regular changes every 3 days. On Day 3, the mNGS analysis detected the presence of E. tarda in the drainage fluid, with a read count of 9,291.
On Day 4, the clinical microbiological laboratory staff reported positive results for E. tarda in the drainage fluid. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing suggested that E. tarda was susceptible to cephalosporin and carbapenem, while resistant to quinolones and sulfamethoxazole (Table 2). Thus, the prescription of imipenem (0.5 g Q8H) continued for 8 days.
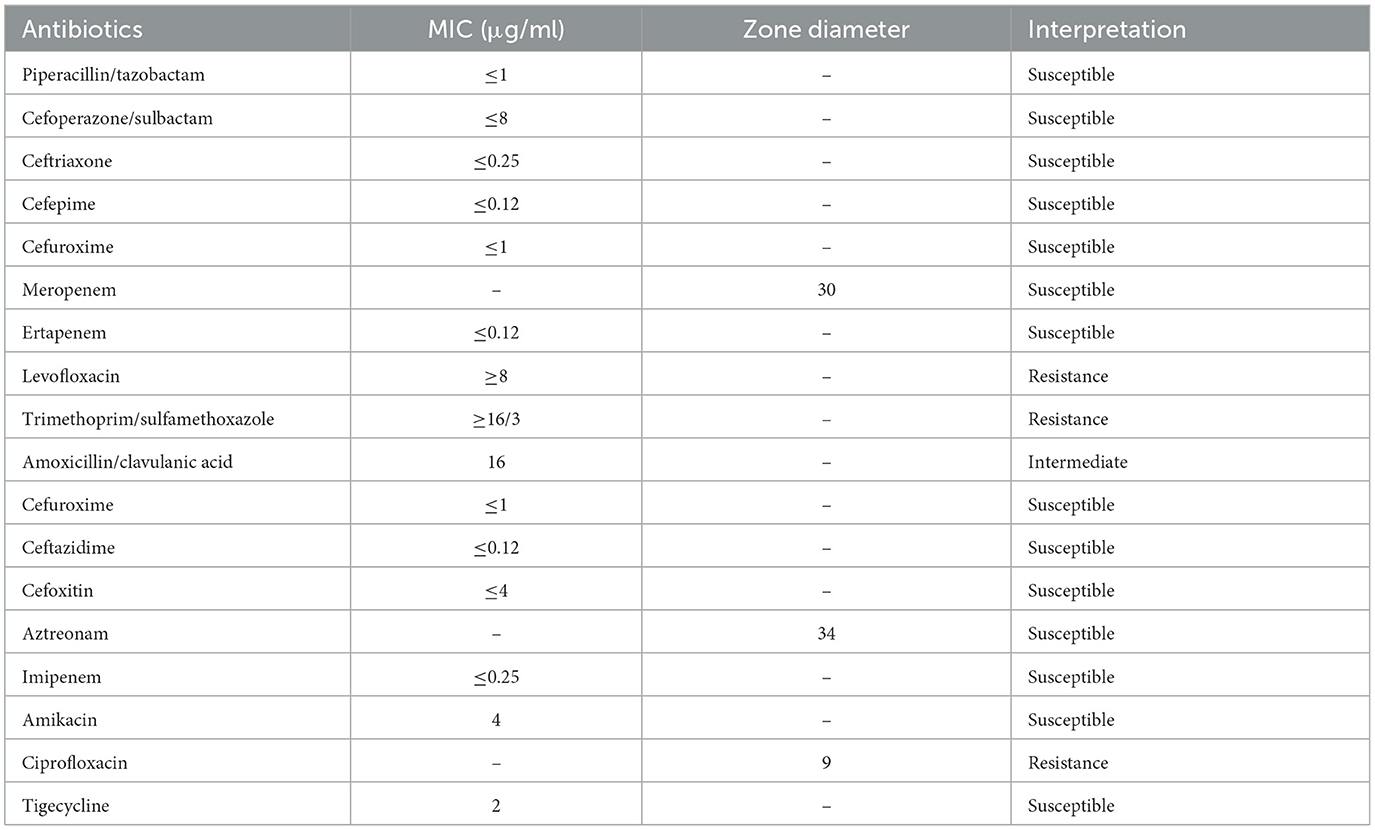
Table 2. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of the Edwardsiella tarda isolate from the wound exudate.
On Day 9, the patient was prescribed topical mucopolysaccharide polysulfate cream and underwent infrared radiation therapy. The wound showed gradual signs of healing, and subsequent cultures of the wound swabs consistently yielded negative results. The inflammatory markers mostly returned to the normal values (Figure 1). The patient was discharged on Day 12. A schematic of the patient's treatment course is provided in Figure 1.
Characteristics of E. tarda from the drainage fluid
Phenotypic characterization
The purulent exudate was streaked onto Columbia Blood Agar plates (Autobio, Zhengzhou, China) and incubated anaerobically at 37°C for hours. The isolates were confirmed as E. tarda using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), a technology provided by Bruker Daltonik GmbH (Bremen, Germany), known for its high-resolution microbiological identification capabilities.
Colonies from the culture plate were isolated and resuspended in 0.45% sterile saline to prepare a 0.5 McFarland standard bacterial suspension. A 145 μl aliquot was further diluted with 3 ml of the 0.45% sterile saline. The VITEK 2 Gram-negative AST card was selected, and antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using the VITEK 2 Compact system (bioMérieux, France). Disk diffusion was also performed for meropenem, aztreonam, and ciprofloxacin. The results were interpreted following the guidelines in the M100 document from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (34th Edition).
An E. tarda strain (named 80236) was isolated from the drainage fluid, and an assessment of its virulence was performed using the Galleria mellonella larvae model. Overnight cultures of E. tarda 80236 were adjusted with saline to concentrations of 1 × 107 CFU/ml and 1 × 108 CFU/ml. A 10 μl of the bacterial suspension was injected into each larva. The larvae were randomly divided into groups of eight larvae each and incubated at 37°C for 48 h. The survival rate of the larvae was recorded at 18, 24, 42, and 48 h after the injection. HvKP4, an ST11 hypervirulent K. pneumoniae strain, and FJ8, a K. pneumoniae strain of low-virulence, were used as hypervirulent and low-virulent controls (18), respectively. We analyzed the data using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test on GraphPad Prism version 9.0. Then, we found that the 1 × 107 CFU/ml E.tarda concentration resulted in reduced larval survival, with almost 100% of the larvae dying within 18 h, as well as the E. tarda concentration of 1 × 108 CFU/ml (Figure 2). Notably, E. tarda 80236 was more virulent than ST11 K. pneumoniae HvKP4 and FJ8.
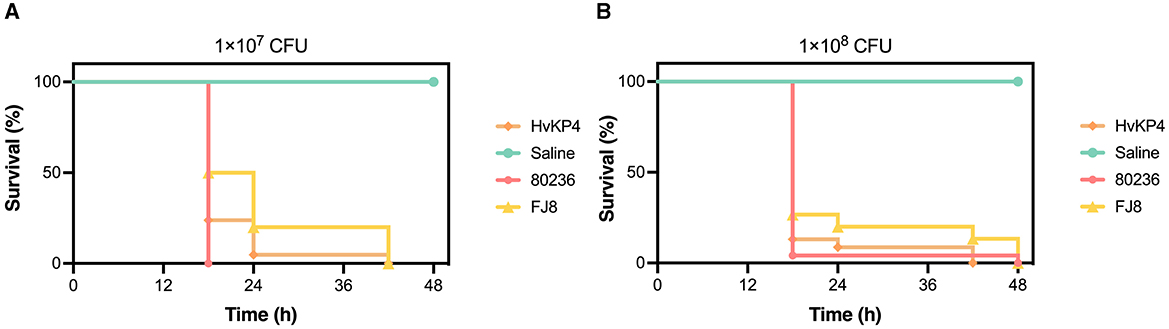
Figure 2. The virulence evaluation of Edwardsiella tarda 80236. (A) Survival graph of the wax moth larvae that were challenged by a dose of the E. tarda strain 80236 (108 CFU/ml). (B) Survival graph of the wax moth larvae that were challenged by a dose of the E. tarda strain 80236 (107 CFU/ml). The graphs are representative of the three independent experiments.
Genomic characterization
For the mNGS analysis, we followed the protocol provided by BGI Genomics Co., Ltd., which included nucleic acid extraction, enzymatic digestion, DNA library construction, and circularization amplification. Subsequently, the sequencing was conducted using the MGISEQ-2000 genetic sequencer with the respective universal sequencing reagent kit, employing the probe-anchored polymerization sequencing method. After ~16 h of sequencing, the data were analyzed and compared using PMseq, infection pathogen nucleic acid detection software (19).
To further characterize the E. tarda isolate, the virulence genes and drug resistance genes were analyzed. We sequenced genomes using the NextSeq 500 sequencing platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). We trimmed or filtered raw reads to remove low-quality sequences and adaptors and assembled them de novo with the SPAdes Genome Assembler version 3.11.1 (20). Given the clinical importance of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and the virulence of E. tarda, a targeted analysis of the acquired AMR genes and virulence-factor-associated genes was performed using ABRicate (https://github.com/tseemann/abricate) against the ResFinderFG v2.0 (21) database, PlasmidFinder (22) database, and the virulence factor database (VFDB) (http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs/; >90% identity and >75% coverage) (23). The genome assemblies of E. tarda 80236 have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology information (NCBI) and are registered under BioProject accession no. PRJNA1153709. All data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
The presence of seven virulence genes, which include those associated with invasion (fimA and esrB), survival (katB, sodB, citC, and gadB), and proliferation (mukF), was assessed using BLAST analysis (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). Based on relevant reviews (24), the fimA-encoded fimbrial protein plays a critical role in the adherence of E. tarda to the host's tissues, facilitating bacterial colonization and the initiation of infection. The esrB gene controls the type III secretion system (T3SS), which is vital for the injection of effector proteins into the host's cells. This mechanism enables the bacteria to manipulate the host's cellular functions, promoting infection and evading the immune responses. In addition, the katB gene encodes catalase, which protects the bacteria from oxidative stress by neutralizing the reactive oxygen species produced by the host. Furthermore, the gadB gene, encoding glutamate decarboxylase, helps the bacteria survive in acidic environments, such as the host's gastrointestinal tract, during infection. In summary, these genes collectively contribute to E. tarda's ability to adhere, invade, and survive within the host, playing key roles in its pathogenicity and immune evasion.
Discussion and conclusion
Humans are rarely infected by E. tarda, given its primary status as a fish pathogen. However, exposure to aquatic environments or consumption of improperly cooked aquatic animals remains the primary cause of infection for humans (2). E. tarda typically induces gastrointestinal inflammation; while extra-intestinal infections are uncommon, and they may result in potentially life-threatening conditions, with mortality rates reaching up to 50% (6).
Aquatic injuries, exposure to infected animals, certain dietary habits, and chronic underlying diseases are established risk factors for E. tarda infections (12). Soft tissue infections caused by E. tarda can facilitate the bacterium's entry into the bloodstream, especially in immunocompromised patients. Such infections can rapidly progress to life-threatening systemic sepsis. In severe cases, this poses a critical risk. A case report documented an instance of rare E. tarda-induced sepsis resulting from fishbone injury cellulitis in an Indian patient with an underlying hematological malignancy (25). According to a previous review, patients with soft tissue infections who developed bacteremia faced a significantly higher mortality rate, which reached 61.1% (6). In our case, the patient, a fishmonger by occupation, handles aquatic products on a daily basis. The cellulitis was likely caused by consistent contact with fish carrying E. tarda. Fortunately, an early diagnosis using metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and prompt drainage of the abscess allowed for the timely administration of appropriate antibiotics, leading to a favorable patient outcome. Clearly, mNGS offers significant advantages in terms of timeliness and sensitivity, proving to be an invaluable diagnostic tool for identifying infections caused by rare and opportunistic pathogens.
E. tarda isolates are susceptible to most clinically administered antibiotics (26); however, they are resistant to benzylpenicillin, colistin, and polymyxin B (27). Empiric treatment options against E. tarda infections include beta-lactams, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, and oxyquinolones (2). Alarmingly, multi-drug resistant E. tarda isolates are being increasingly reported among fishes (28, 29). However, there have been few reports of drug-resistant isolates in human infections. In 2011, Kawai et al. (4), reported the recovery of a trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole-resistant E. tarda isolate from a pediatric patient in Japan with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease who was experiencing osteomyelitis. In this study, the E. tarda strain 80236 exhibited resistance to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and quinolones, while showing intermediate susceptibility to amoxicillin-clavulanate. The emergence of drug-resistant E. tarda isolates in human infections warrants attention and raises concerns regarding antimicrobial resistance.
E. tarda has evolved through multiple mechanisms to cause infections in both humans and aquatic animals (30). Some studies revealed that the production of dermatotoxins and hemolysins, along with the ability to invade epithelial cells, resist phagocytosis, and evade serum-mediated killing, contributes to the pathogenesis of E. tarda (31). E. tarda 80236, possessing four virulence genes, demonstrated a significantly high level of virulence, as was confirmed by the G. mellonella larvae model. Notably, E. tarda 80236 was even more virulent than the hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate HVKP4 (18).
The hypervirulence of the isolate likely contributed to the rapid progression of cellulitis. Without the timely drainage and early administration of imipenem (0.5 g every 8 h intravenously), the patient's outcome might not have been as favorable. Clinicians should remain vigilant about the pathogenic potential of E. tarda. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and microbiological identification are recommended for facilitating an early diagnosis. This should be swiftly followed by drainage and targeted antibiotic therapy to optimize favorable patient outcomes.
In summary, this report detailed a case of cellulitis caused by a quinolone-resistant and virulent strain of E. tarda. The patient was successfully managed with a combination of surgical drainage and antibiotic therapy. To mitigate the risk of E. tarda infection, it is advisable to avoid exposing wounds to aquatic environments and to ensure the consumption of only thoroughly cooked fish. Advanced microbiological techniques such as mNGS facilitate the early detection of pathogens, thereby enhancing clinical decision-making and treatment outcomes.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Ethics statement
Ethical permission for this study was agreed by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine (2023-0280). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by- product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
XW: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DG: Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – original draft. YW: Investigation, Writing – original draft. RZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. KL: Writing – review & editing. HR: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Number: 2022YFD1800400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 82272392).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1413561/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Localized bruising and necrosis presented in the right hand of the patient.
References
1. Ewing WH, McWhorter AC, Escobar MR, Lubin AH. Edwardsiella, a new genus of Enterobacteriaceae based on a new species, E. tarda. Int Bull Bacteriol Nomencl Taxon. (1965) 15:33–8. doi: 10.1099/00207713-15-1-33
2. Janda JM, Abbott SL. Infections associated with the genus Edwardsiella- the role of Edwardsiella tarda in human-disease. Clin Infect Dis. (1993) 17:742–8. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.4.742
3. Xu T, Zhang X-H. Edwardsiella tarda: an intriguing problem in aquaculture. Aquaculture. (2014) 431:129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.12.001
4. Kawai T, Kusakabe H, Seki A, Kobayashi S, Onodera M. Osteomyelitis due to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole-resistant Edwardsiella tarda infection in a patient with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Infection. (2011) 39:171–3. doi: 10.1007/s15010-011-0080-1
5. Healey KD, Rifai SM, Rifai AO, Edmond M, Baker DS, Rifai K, et al. Edwardsiella tarda: a classic presentation of a rare fatal infection, with possible new background risk factors. Am J Case Rep Dec. (2021) 7:22. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.934347
6. Hirai Y, Asahata-Tago S, Ainoda Y, Fujita T, Kikuchi K. Edwardsiella tarda bacteremia. A rare but fatal water- and foodborne infection: review of the literature and clinical cases from a single centre. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. (2015) 26:313–8. doi: 10.1155/2015/702615
7. An L, Chan JL, Nguyen M, Yang S, Deville JG. Case report: disseminated Edwardsiella tarda infection in an immunocompromised patient. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1292768
8. Miyajima S, Yamakawa G, Ohana M. Edwardsiella tarda-associated cholangitis associated with Lemmel syndrome. IDCases. (2018) 11:94–6. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2018.01.009
9. Zambon LS, Marta GN, Chehter N, Del Nero LG, Cavallaro MC. Near-drowning-associated pneumonia with bacteremia caused by coinfection with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and Edwardsiella tarda in a healthy white man: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2016) 10:197–197. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0975-7
10. Yamamuro T, Fukuhara A, Kang J, Takamatsu J. A case of necrotizing fasciitis following Edwardsiella tarda septicemia with gastroenteritis. J Infect Chemother. (2019) 25:1053–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.05.017
11. Chieochanthanakij R, Manuprasert W, Udomsantisuk N, Pearson LJ, Kanjanabuch T. Genetically confirmed Edwardsiella tarda peritonitis was associated with improper caregiver's hand hygiene during peritoneal dialysis bag exchange. Case Rep Nephrol Dial. (2022) 12:11–5. doi: 10.1159/000521351
12. Suzuki K, Yanai M, Hayashi Y, Otsuka H, Kato K, Soma M, et al. Edwardsiella tarda bacteremia with psoas and epidural abscess as a food-borne infection: a case report and literature review Intern Med. (2018) 57:893–7. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9314-17
13. Ding Y, Men W. A case report and review of acute cholangitis with septic shock induced by Edwardsiella tarda. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. (2022) 4:21. doi: 10.1186/s12941-022-00524-4
14. Hara C, Tanaka T, Nishiwada S, Kirihataya Y, Yoshimura A. Acute cholecystitis with sepsis due to Edwardsiella tarda: a case report. Surg Case Rep. (2023) 9:184–184. doi: 10.1186/s40792-023-01763-z
15. Tonosaki K, Yonenaga K, Mikami T, Mizuno T, Oyama S. Acute cholecystitis, sepsis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation caused by Edwardsiella tarda in an elderly woman. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. (2021) 46:51–3.
16. Wang IK, Kuo HL, Chen YM, Lin CL, Chang HY, Chuang FR, et al. Extraintestinal manifestations of Edwardsiella tarda infection. Int J Clin Pract. (2005) 59:917–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00527.x
17. Raff AB, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis a review. JAMA. (2016) 316:325–37. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.8825
18. Gu D, Dong N, Zheng Z, Lin D, Huang M, Wang L, et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: a molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. (2018) 18:37–46. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30489-9
19. Chiu CY, Miller SA. Clinical metagenomics. Nat Rev Genet. (2019) 20:341–55. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0113-7
20. Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. (2012) 19:455–77. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
21. Gschwind R, Ugarcina Perovic S, Weiss M, Petitjean M, Lao J, Coelho LP, et al. ResFinderFG v2.0: a database of antibiotic resistance genes obtained by functional metagenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:W493–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad384
22. Carattoli A, Zankari E, Garcia-Fernandez A, Larsen MV, Lund O, Villa L, et al. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using plasmidfinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2014) 58:3895–903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14
23. Liu B, Zheng D, Zhou S, Chen L, Yang J. VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. (2022) 50:D912–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107
24. Janda JM, Duman M. Expanding the spectrum of diseases and disease associations caused by Edwardsiella tarda and related species. Microorganisms. (2024) 12. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051031
25. Sarathi S, Brahma A, Das PK, Mahapatra A, Behera B. Edwardsiella tarda causing fishbone injury cellulitis leading to sepsis in a case of hematological malignancy-a rare report and review of literature. J Lab Physicians. (2023) 15:602–7. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1770930
26. Clark RB, Lister PD, Janda JM. In vitro susceptibilities of Edwardsiella tarda to 22 antibiotics and antibiotic-beta-lactamase-inhibitor agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. (1991) 14:173–5. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90054-J
27. Stock I, Wiedemann B. Natural antibiotic susceptibilities of Edwardsiella tarda, E. ictaluri, and E. hoshinae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2001) 45:2245–55. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2245-2255.2001
28. Hua Y, Hui W, Bo YU, Shengmou H, Yunjie LI, Jinju WU, et al. Isolation of pathogenic Edwardsiella tarda strain CA26 from Silurus asotus and its effect on immune factors. J Henan Agric Sci. (2018).
29. Xiao J, Wang Q, Liu QQ, Wang X, Zhang Y. Isolation and identification of fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda from mariculture in China. Aquacult Res. (2010) 40:13–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02101.x
30. Leung KY, Siame BA, Tenkink BJ, Noort RJ, Mok YK. Edwardsiella tarda - virulence mechanisms of an emerging gastroenteritis pathogen. Microbes Infect. (2012) 14:26–34. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.08.005
Keywords: Edwardsiella tarda, cellulitis, virulence, resistant, metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS)
Citation: Wang X, Gu D, Zhang L, Wu Y, Zhang R, Li K and Ren H (2024) mNGS-identified cellulitis due to quinolone-resistant Edwardsiella tarda: a case report. Front. Med. 11:1413561. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1413561
Received: 13 June 2024; Accepted: 13 September 2024;
Published: 16 October 2024.
Edited by:
Daniele Roberto Giacobbe, University of Genoa, ItalyReviewed by:
Seto Charles Ogunleye, Mississippi State University, United StatesLuigi Principe, Azienda Sanitaria Provinciale di Crotone, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Gu, Zhang, Wu, Zhang, Li and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haitao Ren, cmh0QHpqdS5lZHUuY24=; Kewei Li, Y3Vyd2F5bGVlQHdtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Xuejin Wang
Xuejin Wang Danxia Gu
Danxia Gu Liwei Zhang
Liwei Zhang Yuchen Wu1
Yuchen Wu1 Rong Zhang
Rong Zhang