
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Med. , 28 July 2022
Sec. Pulmonary Medicine
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.935080
This article is part of the Research Topic Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Value-Based Care View all 14 articles
With the increasing incidence and mortality of pulmonary tuberculosis, in addition to tough and controversial disease management, time-wasting and resource-limited conventional approaches to the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis are still awkward issues, especially in countries with high tuberculosis burden and backwardness. In the meantime, the climbing proportion of drug-resistant tuberculosis poses a significant hazard to public health. Thus, auxiliary diagnostic tools with higher efficiency and accuracy are urgently required. Artificial intelligence (AI), which is not new but has recently grown in popularity, provides researchers with opportunities and technical underpinnings to develop novel, precise, rapid, and automated implements for pulmonary tuberculosis care, including but not limited to tuberculosis detection. In this review, we aimed to introduce representative AI methods, focusing on deep learning and radiomics, followed by definite descriptions of the state-of-the-art AI models developed using medical images and genetic data to detect pulmonary tuberculosis, distinguish the infection from other pulmonary diseases, and identify drug resistance of tuberculosis, with the purpose of assisting physicians in deciding the appropriate therapeutic schedule in the early stage of the disease. We also enumerated the challenges in maximizing the impact of AI in this field such as generalization and clinical utility of the deep learning models.
Among the infectious diseases, tuberculosis (TB) is one of the major causes of mortality worldwide, leading to approximately 1.4 million deaths and 10 million new cases annually, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report 2021 (1). In addition to the threat to public health posed by TB, the incidence of drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) continues to increase, resulting in difficulty in controlling the epidemic (2). Accurate detection methods based on bacteria, such as acid-fast bacilli or bacterial cultures, are time-consuming and condition-limited. Gene testing to identify infection or drug resistance of the pathogen-Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) is inconvenient and restricted by the laboratory environment. Although medical images, such as chest radiographs [also called chest X-ray (CXR)] and computed tomography (CT), are comparatively inexpensive and more available, in certain developing countries or backward areas, there may be no advanced medical equipment or a lack of experienced radiologists to interpret the images, and the growing medical image data may add workload to the physicians. Therefore, automated, precise, efficient, and cost-effective assistance tools devoted to TB management demand prompt exploitation.
Over the past decades, with the vigorous development of computer technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has aroused a whopping level of attention in many fields, especially in image recognition. AI systems based on medical images or other meaningful clinical information have been utilized to screen, diagnose, assess severity, and predict prognosis in multiple diseases, such as brain tumor (3, 4), pneumonia (5), lung cancer (6), cardiovascular disease (7), and even tumor metastasis (8).
In addition, for better implementation of AI in the medical field, particular ethical concerns should also be considered. With the widespread development and utilization of AI, privacy and security during the management and transmission of data, as well as the informed consent of patients are emerging as critical ethical issues. Moreover, specific psychological and legal considerations have also been proposed. For instance, when an error by the automated system leads to a false diagnosis or improper therapeutic schedule resulting in harmful consequences, this may cause a dispute over who should be responsible for that mishap. In medical practice, owing to the opaqueness of the prediction generated by the algorithm, physicians may distrust the model (9). Furthermore, to verify the clinical relevance of the models, clinical trials are required, wherein more intractable issues, such as obtaining informed consent, are present; however, only a few clinical trials involving the use of AI systems have been performed. Collectively, to guide the appropriate adoption of AI systems, the establishment of effective ethical and legal frameworks is of great urgency (10, 11).
We searched the literature in PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using a retrieval search strategy with the following keywords: “tuberculosis” and “artificial intelligence” or “deep learning” or “radiomics” or “machine learning,” selecting quantified studies by the abstracts, and the flow diagram is demonstrated in Supplementary Figure 1. In this review, we mainly focused on approaches based on AI using CXR, CT, positron emission tomography (PET)/CT images, and genetic data associated with TB care. By describing the latest typical AI studies focusing on TB, we aimed to inform physicians and radiologists interested in AI for the precise diagnosis of TB to carry out optimal therapeutic regimens.
We started by briefly introducing AI, with deep learning and radiomics stressed; later, we provided a few definite examples of the application of AI in the medical field, especially in respiratory system. We then narrated the up-and-coming AI techniques in TB from three aspects according to the proposed use, namely, TB detection, discrimination between TB and other pulmonary diseases, and recognition of drug resistance of TB (Figure 1). Finally, we summarized the significance of previous studies, challenges, and prospects of developing more practical and accurate AI tools for TB in the future.
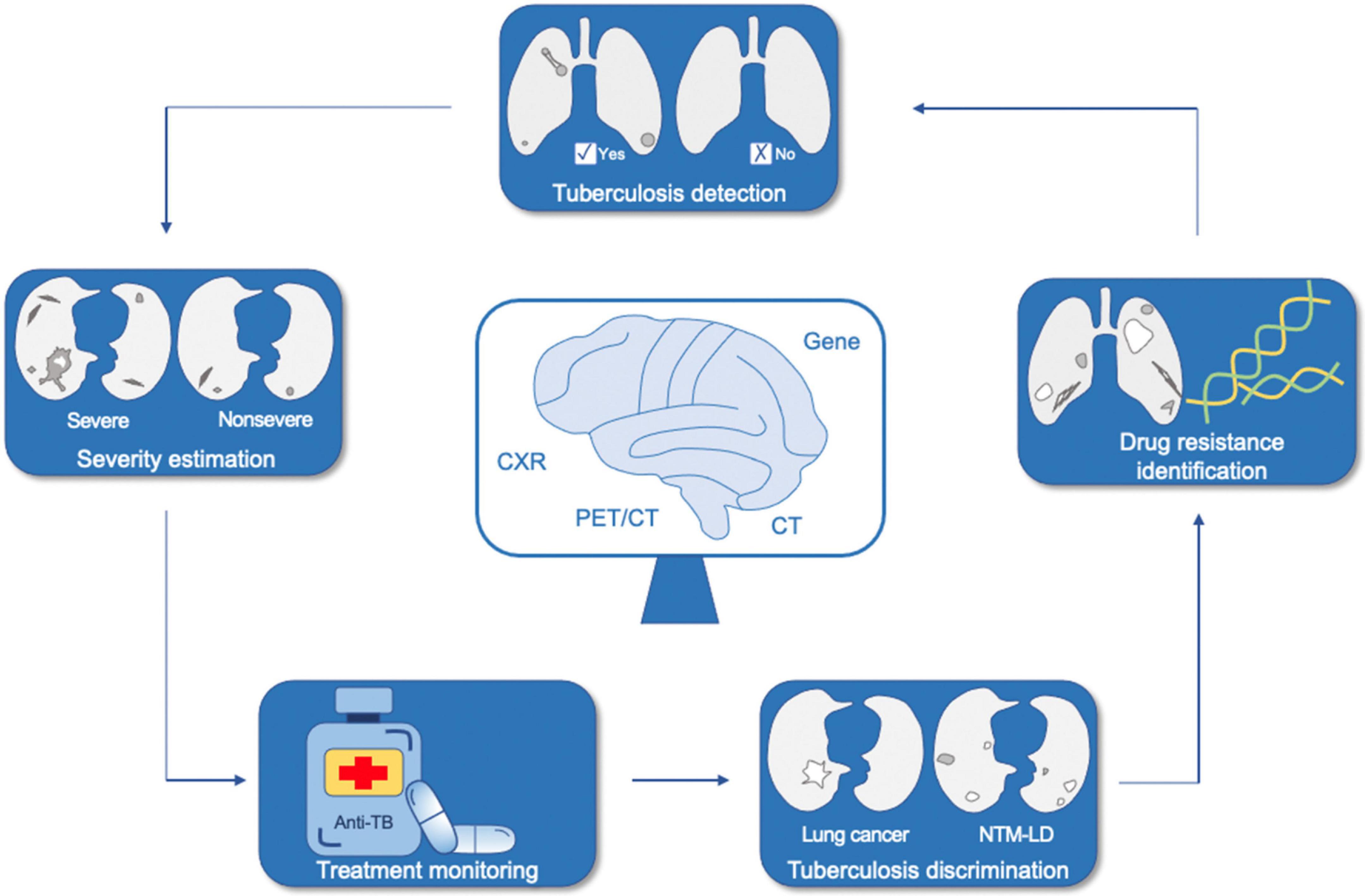
Figure 1. Application of artificial intelligence in tuberculosis. NTM-LD, non-tuberculous mycobacterium lung disease; CXR, chest X-ray; CT, computed tomography; PET/CT, positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
AI is a technical science that studies and develops the theory, method, technology, and application of systems used to simulate and extend human intelligence. Deep learning, a hot topic in this field, which has been probed extensively, mostly leverages convolutional neural networks (CNNs) comprised of multiple layers, including input, convolutional, pooling, fully connected, and output layers, through which the specific predictions could derive from primary digitalized inputs, such as images, speech, gene sequences, and clinical text information (12, 13). What’s more, other plentiful sorts of machine learning algorithms, such as logistic regression (LR), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), and decision tree (DT), are valuable components of AI as well (14–18). Radiomics, designed to mine pathophysiological information from medical images, includes a common process involving data collection; identification of the region of interest (ROI); ROI segmentation; feature extraction, selection, and quantification; model establishment; and prediction making in the end (19, 20). The workflow of deep learning and radiomics is displayed in Figure 2.
The prosperity of AI applied to the medical field, especially in respiratory system, has attracted substantial attention with promising results, such as detection of pulmonary nodules (21) and prediction of treatment response or outcome of lung cancer (22, 23). Meanwhile, we have made excellent achievements, including diagnosis and discrimination of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (24), predetermination of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutation status, programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression level, and target therapy effect in patients with lung cancer (25–27).
As a noticeable disease in this system, AI applied to TB is presented as follows and summarized briefly in Table 1.
Since the majority of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) have abnormal chest CXR findings, such as cavities, centrilobular nodules, and consolidations (28), which are suggestive of the diagnosis of PTB, and CXR is comparatively widely available, WHO has recommended TB screening in high-risk populations by chest radiographs (29). Similarly, CT images demonstrate abnormalities when PTB occurs. These representative medical images are commonly utilized to train a deep learning model to detect PTB suffering. As early as 1999, an artificial neural network was exploited to predict active TB, taking advantage of radiographic findings, symptoms, and demographic variables, showing a favorable performance, which gave researchers powerful afflatus (30). Thereafter, abundant studies have been conducted to recognize the contagious disease using radiological images in slightly different forms (Table 2).
Lakhani and Sundaram (31) adopted two deep CNNs to detect PTB on CXR images. Finally, the area under the curve (AUC) achieved a significant level at 0.99 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96–1.00] on account of a method named “resemble,” which indicated that the ultimate PTB probability score was obtained from the two CNNs, with a different weighting of their outputs and choosing the best match. In addition, this study revealed that networks pretrained by daily color images outperformed untrained ones [AUC 0.98 pretrained vs. 0.90 untrained of AlexNet and 0.98 pretrained vs. 0.88 untrained of GoogLeNet (P < 0.001) in the test dataset]. Similarly, Hwang et al. (32) developed an automatic detection algorithm to classify active PTB using chest radiographs from a massive dataset containing 60,989 images which eventually manifested high performance both in lesion localization [area under the alternative free-response receiver operating characteristic curves (AUAFROC) 0.973–1.000] and disease classification (AUC 0.977–1.000), while the observer performance test showed that the algorithm had better behavior than physicians with different degrees of experience (AUC 0.993 vs. 0.664–0.925 in localization and 0.993 vs. 0.746–0.971 in classification). Another study developed an algorithm based on ResNet to detect PTB, and the model reached an accuracy of 96.73% with a heatmap generation for precise lesion location as well (33). Using 20,135 chest radiographs from 19,681 asymptomatic individuals, an out-of-sample test was conducted (34) to validate the screening performance of the deep learning-based automated detection (DLAD) algorithm developed by Hwang et al. (32). Five images from four active PTB cases confirmed by the bacteriological test were properly classified as having abnormal discoveries with specificities of 0.997 and 0.959 at high specificity and high sensitivity thresholds, respectively. Moreover, DLAD showed a decent performance in identifying radiologically relevant abnormalities with an AUC of 0.967 (95% CI 0.93–0.996). Likewise, to verify the performance of deep learning models on the general population, a study assessed five CNNs in two forms, namely, I-CNN (images input only) and D-CNN [images and demographic variables (age, sex, height, and weight) input] to detect PTB by CXR images in 39,677 workers from Korea. Among the five models, VGG19 achieved the highest performance in both the training and test cohorts, regardless of the demographic information input (AUC 0.9075 of I-CNN and 0.9213 of D-CNN in the test set), and the AUCs of the other four systems were all over 0.88 with D-CNN in the test set. Moreover, no statistical significance was observed when only a single demographic variable was included (P > 0.05) (35). Taking advantage of segmentation and augmentation, EfficientNetB3, the CNN structure, demonstrated incredibly high performance in PTB detection with an AUC of 0.999 (36). Moreover, a simplified network was proposed to surmount the trouble of overfitting and difficult deployment in mobile settings owing to the large scale of parameters and hardware requirements of the models, achieving an AUC of 0.925 through 5-fold cross-validation in the diagnosis of PTB on CXRs (37). Uniquely, different from the studies mentioned earlier, Rajaraman et al. blazed new trails to recognize findings consistent with PTB by lateral CXRs through deep learning, with an AUC up to 0.9491 (38).
TB is important not only in the general population but also in patients with specific conditions. Due to the high mortality caused by TB in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive patients with the conspicuous incidence and improper treatment, in South Africa, Rajpurkar et al. utilized CXRs, as well as certain clinical covariates, including age, temperature, hemoglobin, and white blood cell counts of 677 HIV-positive patients from two hospitals to establish a deep learning algorithm, named CheXaid, which improved the clinicians’ diagnostic accuracy slightly (0.65 vs. 0.60, P = 0.002). Interestingly, the performance of the algorithm alone was superior to that of clinicians assisted by AI (accuracy 0.79 vs. 0.65, P < 0.001). Moreover, the training strategy of adding clinical variables with CXRs improved the performance of the algorithm (AUC of 0.83 and 0.71 in the combination model and model alone) in this study and suggested the importance of integrating inputs in various modalities to enhance the power of the models (39).
Apart from detecting PTB, deep learning is capable to follow post-treatment changes and estimate the severity of it. Utilizing CXRs, the output of the model developed by Lee and his team elevated by 0.30 when the degree of smear positivity increased (P < 0.001) and decreased gradually during treatment; meanwhile, the model achieved AUCs over 0.82 in the two test sets for PTB diagnosis (40).
Owing to higher resolution and more subtle presentation, CT images provide more nuanced information on the lung region and play an important role in PTB diagnosis as well (28). Thus, Yan et al. (41) developed a model to detect PTB and quantitatively evaluate the disease burden, of which the quantified TB scores were obviously higher in severe patients than in non-severe ones and was well correlated with the CT scores assessed by radiologists. Moreover, the model demonstrated an accuracy of 83.37% for classifying the six pulmonary lesion types, such as consolidation and calcified granulomas in the validation set, while an accuracy of 98.25% was achieved for distinguishing active PTB patients from inactive individuals in the test set.
The two studies are unique as there is a lack of research targeting treatment monitoring and disease burden estimation of TB by AI methods, which inspires us to launch more relevant studies to give rein to their adjuvant role in the clinic.
In addition to the models obtained from the original studies, the computer-aided detection (CAD) systems, such as qXR, CAD4TB, and Lunit INSIGHT CXR (42), which generate a PTB classification when the output is more than a defined threshold score, have been established to facilitate PTB detection using CXR images based on deep learning. Several studies have exclusively assessed the diagnostic ability of the application of various categories and versions in diverse datasets.
To identify the practicalities of qXR version 2.0 (qXRv2) and CAD4TB version 6.0 (CAD4TBv6) in detecting PTB in low- and middle-income countries with a high disease burden, Khan et al. (43) conducted a prospective single-center study with 2,198 individuals at the Indus Hospital, located in Karachi, Pakistan. Finally, qXRv2 attained a sensitivity of 0.93 (95% CI 0.89–0.95) and a specificity of 0.75 (95% CI 0.73–0.77), while CAD4TBv6 showed a specificity of 0.69 (95% CI 0.67–0.71) when matched with the same sensitivity, both reaching the Target Product Profile recommendations defined by WHO (sensitivity ≥ 0.90 and specificity ≥ 0.70). What’s more, the sensitivity decreased obviously in smear-negative patients compared to that in smear-positive patients (0.80 in the negative group vs. 0.96 in the positive cohort of qXRv2 and 0.82 in the negative population vs. 0.97 in positive individuals of CAD4TBv6). This study is worth emphasizing because it is a rare prospective investigation validating CAD approaches.
Qin et al. (44) estimated three commercially available CAD tools, qXRv2, CAD4TBv6, and Lunit INSIGHT CXR, to triage PTB in 1,196 participants from Nepal and Cameroon, with AUCs above 90% [0.94 (95% CI 0.93–0.96) for Lunit INSIGHT CXR, 0.94 (95% CI 0.92–0.97) for qXRv2, and 0.92 (95% CI 0.90–0.95) for CAD4TBv6]. When the purpose was to reduce the Xpert test by 50%, the sensitivities of the three models maintained at 97–99%, with no statistical significance among them. Subsequently, the group assessed five AI algorithms in newer versions, including CAD4TB version 7 (CAD4TBv7), qXR version 3 (qXRv3), Infereread DR version 2, Lunit INSIGHT CXR version 4.9.0, and JF CXR-1 version 2, on a massive dataset comprising CXRs from 23,954 individuals. The performance of all of them surpassed that of three radiologists as a concrete manifestation that AI showed higher specificity and positive predictive values (PPVs) when matched with the same sensitivity (45). Another study evaluated a maximum of 12 CAD solutions to identify PTB in comparison with an experienced radiologist and an intermediate reader. The final results showed that qXRv3, CAD4TBv7, and Lunit INSIGHT CXR version3.1.0.0 achieved the highest AUC of 0.82. Meanwhile, five of them surpassed the intermediate reader in specificity and accuracy when holding at the same sensitivity, while only qXRv3 maintained comparable specificity when sensitivity reached the standard of the experienced reader [95.5% (95% CI 90.4–98.3%)] (46). The three studies mentioned (43, 45, 46) coincidentally discovered that, in groups with previous TB, the performance of AI systems would decline to some extent. In addition, when integrating clinical information with the CAD scores of CXRs generated by CAD4TB, the AUC of the combination framework reached 0.84, improving the performance of CAD4TB alone (47).
Although the verification results seem remarkable as a whole, more prospective validation tests need to be carried out in a real medical environment, after which these mercantile AI systems may be competent enough to supply convenient, efficient, and accurate tools for physicians worldwide, facilitating clinical decision making in the near future.
In addition to detection, effort has been made to differentiate PTB from other pulmonary diseases (Table 3).
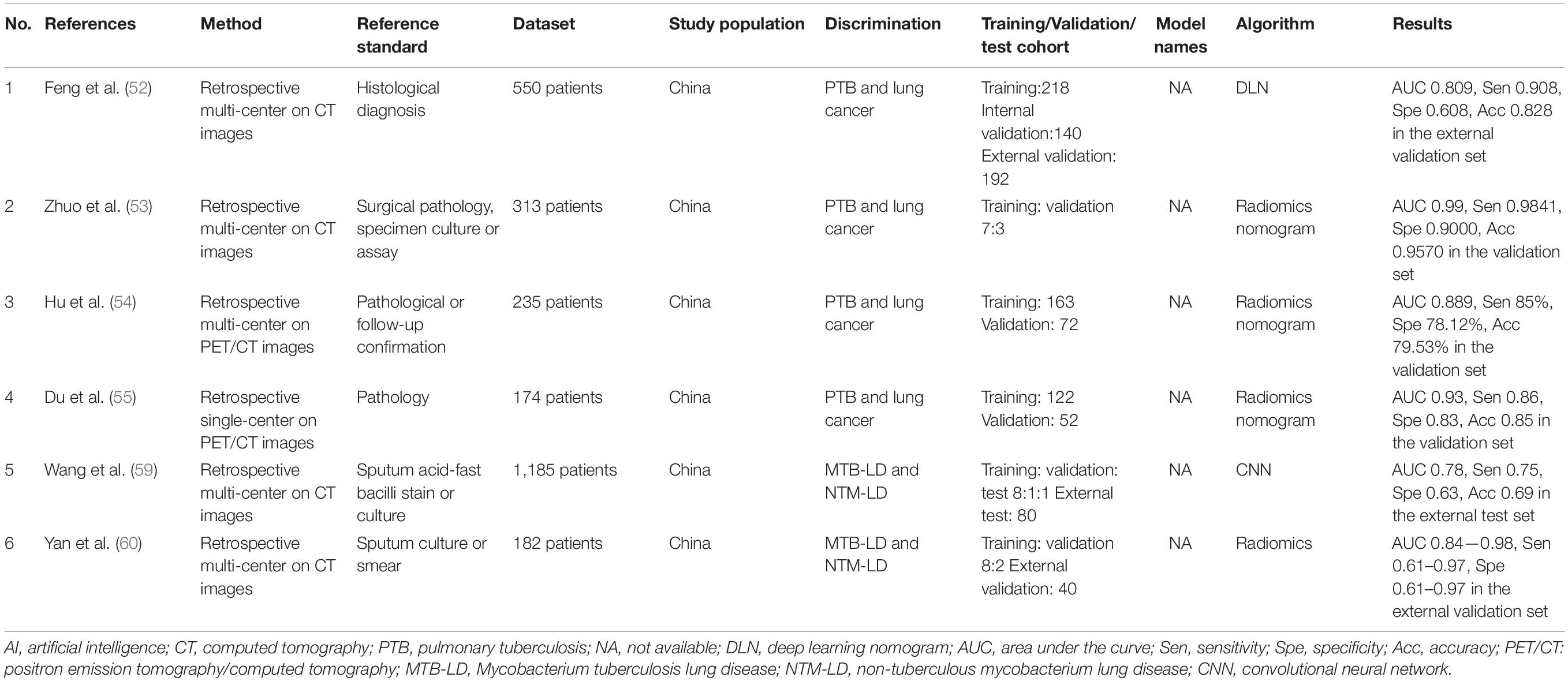
Table 3. Summary of AI applications in discrimination between pulmonary tuberculosis and other lung diseases.
Lung cancer is one of the primary causes of cancer death and is the most common tumor worldwide (48). Moreover, pulmonary tuberculosis granuloma (TBG) may present as lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) with the demonstration of similar solitary pulmonary nodules (49–51), resulting in diagnostic confusion and treatment mistakes. A deep learning-based nomogram (DLN) using CT images was developed and validated to distinguish TBG from LAC (52). The DLN was constituted to compare with a clinical model including age, sex, and subjective findings on CT images, and a deep learning signature (DLS) model, with scores derived from 14 deep learning features constructed in advance, and showed better diagnostic performance than the clinical and DLS models. Comprised by age, sex, lobulated shape, and DLS score, DLN achieved both higher AUC and sensitivity than the other 2 models in the internal validation cohort, meanwhile showing an AUC of 0.809 in the external validation set. A radiomics nomogram based on CT images was proposed by another group, showing an AUC of 0.99 in the validation set to differentiate the two fundamentally different diseases which demonstrated similarities between each other (53). Analogously, to distinguish between solitary LAC and PTB, Hu et al. constructed a radiomic model containing a set of nine fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT (18F-FDG PET/CT) radiomic features, such as Histogram_Skewness and SHAPE_Sphericity (54). While developing a clinical model, they also constructed a complex model, which was a combination of the radiomic and clinical models using multivariate LR. Finally, the radiomic and complex models outperformed the clinical model, as the AUC of the complex model reached 0.909, while the radiomic and clinical models achieved 0.889 and 0.644 in the validation set. Furthermore, a similar study utilized a radiomic nomogram integrating the radiomic score (RAD-score) derived from a weighted linear combination of features selected from 18F-FDG PET/CT images and three semantic features to differentiate the two semblable image phenotypes. The diagnostic performance of the radiomic nomogram slightly surpassed that of the radiomic and semantic models with an AUC of 0.93 in the validation cohort; the decision curve also illustrated the net benefit of the nomogram (55).
Given that non-tuberculous mycobacterium lung disease (NTM-LD) demonstrates an increasing incidence and prevalence in recent years (56, 57), due to similar clinical symptoms and CT imaging characteristics with mycobacterium pulmonary tuberculosis lung disease (MTB-LD) (58), it is crucial to distinguish the different infections as quickly as possible in the early stage to permit appropriate treatment implementation. A deep learning framework was developed by Wang and his colleagues to differentiate between NTM-LD and MTB-LD on chest CT images with an AUC of 0.86 and 0.78 in the internal test set and in the external test cohort, respectively (59). Moreover, the model surpassed three radiologists in almost every metric with higher diagnostic efficiency (1,000 times faster) and output class activation maps identifying abnormal lung areas without manual annotation. To achieve a similar purpose, another study leveraged radiomics by taking advantage of the features of cavities in CT images using six machine learning models (SVM, RF, LR, etc.) (60); 458 ROIs were depicted by two radiologists, with 29 optimal quantified image features, such as gradient and wavelet, selected subsequently. AUCs of the six models were up to over 0.98 in the training and validation sets.
These studies pioneered the application of AI for the discrimination of PTB from lung cancer and NTM-LD, with promising results encouraging investigators to develop more AI models using a variety of original training materials to differentiate PTB from more diseases.
In the context of increasing incidence and intractable management of TB resistance, multiple examination approaches, including drug susceptibility testing (DST), Xpert MTB/RIF, line-probe assays, and whole-genome sequencing (WGS), have been explored to identify DR-TB (2). However, cost and time issues are still remaining. Hence, inexpensive, rapid, and accurate tools for automated detection of the antimicrobial resistance are of great concern (Table 4).
Imaging manifestations of these two main categories of TB, sensitive or resistant to anti-tuberculosis therapy (ATT), differ depending on the phenotypes, as DR-TB could demonstrate larger lesions and thick-walled cavities on CXR images (61, 62). Jaeger et al. (63) trained an artificial neural network through cross-validation to identify patients with multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) using CXRs, which achieved an AUC of only up to 66%. This unsatisfactory result may be explained by the small dataset containing only 135 cases. However, it is inspiring that the team used a larger dataset of 5,642 CXRs and various CNNs for the same purpose, and finally, a preferable outcome was obtained. With static or dynamic data augmentation, the AUC of InceptionV3 increased to 0.85. For custom CNNs, six-layer CNN expressed the best performance with an AUC of 0.74 (64). After the ImageCLEF2017 competition, a study utilized a small dataset from the match, which comprised CT images from 230 drug-sensitive and MDR-TB patients to implement a combination of a patch-based deep CNN and SVM, with an accuracy of 91.11% in predicting MDR-TB at the patient level and 79.8% at the patch level (65).
To date, the exploitation of using medical images to identify DR-TB has not been investigated thoroughly; hence, these studies are noteworthy because they could give us some instructions for future research orientation.
Besides medical images, genetic information could also serve as a diagnostic tool for TB. As introduced above, various molecular approaches are capable of detecting drug resistance, of which the theoretical proof is that the resistance occurrence in TB is caused by chromosomal mutations, passing along through vertical descent, in present genes. Meanwhile, rapid molecular tests using genomic information are more efficient than culture-based assays so they are adopted widely, and related gene data are available for scientific research (66). Therefore, numerous AI studies based on gene sequences have been explored to identify drug resistance of M. tuberculosis, as follows.
As researched previously, deep learning using genomic data has been applied to reveal antibiotic resistance (67). Thus, with mutations for isolates input and phenotypes of drug resistance output, Yang et al. (68) developed “DeepAMR,” a deep learning model with a deep denoising auto-encoder for multiple tasks to predict co-occurrent drug resistance of M. tuberculosis, comparing the model with conventional machine learning methods, including RF, SVM, and ensemble classification chains (ECC). The co-occurrence of rifampicin (RIF) and isoniazid (INH) resistance accounted for the majority of the dataset (n = 8,388). The results suggested that the model surpassed all other approaches in predicting resistance to the four first-line drugs, MDR-TB, and pan-susceptible tuberculosis (PANS-TB, isolates susceptible to any of the four first-line drugs), showing AUCs from 94.4 to 98.7% (P < 0.05). Later, utilizing a novel method using graphs translated from genetic data of M. tuberculosis, the team developed a graph neural network named “HGAT-AMR” to predict drug resistance in a sample consisting of 13,402 isolates tested for susceptibility to up to 11 drugs (69). HGAT–AMRi-E (HGAT–AMR trained on any available incomplete phenotype specimen for the multi-label learning task) and HGAT–AMRs (HGAT–AMR trained on individual subsets of different drugs for the single-label learning task) performed best in INH and RIF, respectively, with AUCs of 98.53 and 99.10%. Meanwhile, HGAT–AMRi-E demonstrated the highest sensitivity for INH, ethambutol (EMB), and pyrazinamide (PZA) at 94.91, 96.60, and 90.63%, respectively, and HGAT-AMR outperformed SVM and LR, unless in a condition of highly imbalanced data when an isolate had only been tested by INH and EMB, but not by other drugs. Favorable performance was yielded in machine learning models constructed by the group as well, with higher sensitivity compared to the previous rule-based method (P < 0.01) (70). Collecting 16,688 isolates of which the WGS and DST data are available to predict drug resistance, another study developed the gradient boosted tree, a machine learning method, reaching an accuracy of 95.5% in MDR-TB identification (71).
Similarly, to determine the drug resistance of M. tuberculosis strains by inputting gene sequences, Chen et al. compared the performance of three deep learning models (72). The wide and deep neural network (WDNN), constructed in the study, incorporating LR and deep multilayer perceptron, was presented in four forms, namely, kSD-WDNN (detecting preselected mutations), SD-WDNN (detecting single resistance), and 2 MD-WDNNs (detecting common mutations and for all mutations in multiple resistance), in which the most complex model MD-WDNN surpassed others in both first-line and second-line drugs, with average AUCs of 0.937 and 0.891 in the validation set. Subsequently, a correlative study developed a user-friendly online tool named GenTB based on genome sequencing to predict the antibiotic resistance (73), involving the WDNN and an RF algorithm constituted by Farhat et al. (74). After testing on 20,408 isolates, both GenTB-RF and GenTB-WDNN demonstrated satisfactory performance in first-line drugs with AUCs of more than 87% and with a slightly lower performance in second-line drugs. In particular, GenTB-RF reached the highest prediction for RIF [AUC 96% (95% CI 95–96%)]. Based on 1D CNN, using large and diverse M. tuberculosis isolates from six continents to verify the accuracy and steadiness of deep learning, another study developed a model which outperformed the advanced Mykrobe classifier which utilizes a De Bruijn graph to identify resistance profiles in antimicrobial-resistant prediction with higher F1 scores (75). Concurrently, it is worth mentioning that an innovative hierarchical attentive neural network has been constructed to predict the drug resistance of M. tuberculosis through genome-wide variants recently, discovering a potential gene related to drug resistance besides achieving supernal AUC and sensitivity in resistance recognition (76).
As described earlier, in terms of TB detection, discrimination, and drug resistance identification, AI showed a great potential, with performance approximate to or even better than that of physicians. Yet, there are still lots of challenges remaining, with the concurrence of prospects, as described below.
First, DR-TB remains a critical issue worldwide, with an increasing incidence and tough management. Developing dependable AI systems using sufficient radiology-based data, which is more convenient than gene sequences to rapidly recognize patients with DR-TB to assist physicians in executing correct clinical decisions, is of great imperative.
Then, up till now, only a few studies have adopted deep learning or other AI approaches to predict TB relapse or treatment response to anti-tuberculosis drugs. An algorithm based on CNN was proposed to predict the persistence time needed to achieve culture negative in TB individuals with an unsatisfactory accuracy, regrettably (77). In addition, it has been revealed that the minimum inhibitory concentration grew higher with an increasing risk of relapse (78) and aggressive regimens may reduce the recurrence of MDR-TB after successful treatment (79). Thus, if a prediction of relapse can be made in advance, more precise and positive treatment could be carried out to reduce the hazard of returning.
Third, the generalization of these models in a broader population remains to be seen, since not all of those studies contain external tests, and research samples are not abundant or variable enough. However, studies, including external validation sets, demonstrated diminishing performance from training to external cohorts which gives us a hint of sustaining the reproducibility of the models to suit various individuals. Perhaps, multicenter studies in an enormous study population are capable of solving this problem, but the subsequent issues of data transmission efficiency and security in the process of data sharing deserve to be highlighted.
As for model modalities, since Lu et al. developed a fusion CNN integrated with images and basic clinical information to predict lung cancer (80) and the model CheXaid utilized CXRs with clinical variables to detect TB in HIV patients (39), it is being probed prevalently in the construction of a fusion neural network, which is composed of several modules dealing with data at multiple scales. Thus, there is an incredible amount of untapped potential to develop AI models with the capacity to handle multimodal inputs. Furthermore, primary inputs, including images or data in other forms, are supposed to be standardized, while diversiform data obtained from different apparatuses may be at an uneven quality level.
Finally, to achieve the purpose of directing clinical practice, the practicality of these novel models should be tested in a real medical environment and seamlessly integrated into the routine workflow, especially in countries with high TB burden and a lack of advanced medical equipment and professional physicians. Owing to the prospective real-world clinical setting, the superior performance of retrospectively developed AI compared with that of human should be regarded with some care.
Following tremendous progress in computational power and advanced techniques, AI is blooming increasingly in countless fields. In radiology, AI demonstrates remarkable performance in the detection, treatment monitoring, and prognosis prediction of multiple diseases, especially in oncology. With regard to TB, saving labor and time costs, AI is capable of improving detection efficiency and precision; therefore, medical institutions worldwide could benefit from these novel assistance tools. In the coming decades, after better integration with clinical workflow, AI will exert a brilliant influence on the entire duration of TB from screening, diagnosis, and treatment following to outcome prediction, meanwhile saving medical resources, avoiding inappropriate management, and improving the quality of life of patients.
AI-based approaches, including deep learning, radiomics, and other conventional machine learning methods applied to TB, provide a self-driven, convenient, and time-saving strategy to improve diagnostic efficiency and accuracy, outperforming radiologists. Nonetheless, the clinical utility of them remains to be verified, while pitfalls, such as reproducibility of the model and data standardization, need to be addressed as well. To summarize, in this review, we listed several studies focusing on AI-based assistance methods applied to TB detection, discrimination, and drug resistance identification using CXR, CT, PET/CT images, and genome data. Although most of these studies developed AI models with favorable performance, quite a few hurdles must be overcome along the way to maximize the potential of AI. Although TB is especially emphasized in this study, application of AI in other diseases is worth equivalent attention.
WL and CW contributed to supervision and conceptualization. SL, GW, JS, and JL designed the search strategy, performed the literature retrieval, and contributed to the original draft of the manuscript. CW, HD, JM, and SL reviewed and revised the final version of the manuscript. WL contributed to the funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82100119, 91859203, and 81871890), the Science and Technology Project of Sichuan (2020YFG0473 and 2022ZDZX0018), the Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M692309), and the Postdoctoral Program of Sichuan University (2021SCU12018).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.935080/full#supplementary-material
2. Lange C, Dheda K, Chesov D, Mandalakas AM, Udwadia Z, Horsburgh CR Jr. Management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet. (2019) 394:953–66. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31882-3
3. Hollon TC, Pandian B, Adapa AR, Urias E, Save AV, Khalsa SSS, et al. Near real-time intraoperative brain tumor diagnosis using stimulated Raman histology and deep neural networks. Nat Med. (2020) 26:52–8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0715-9
4. Martini ML, Oermann EK. Intraoperative brain tumour identification with deep learning. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:200–1. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0343-9
5. Zhang K, Liu X, Shen J, Li Z, Sang Y, Wu X, et al. Clinically applicable AI system for accurate diagnosis, quantitative measurements, and prognosis of COVID-19 pneumonia using computed tomography. Cell. (2020) 182:1360. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.029
6. Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, Choi B, Reicher JJ, Peng L, et al. End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med. (2019) 25:954–61. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0447-x
7. Gal R, van Velzen SGM, Hooning MJ, Emaus MJ, van der Leij F, Gregorowitsch ML, et al. Identification of risk of cardiovascular disease by automatic quantification of coronary artery calcifications on radiotherapy planning CT scans in patients with breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:1024–32. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1144
8. Pan C, Schoppe O, Parra-Damas A, Cai R, Todorov MI, Gondi G, et al. Deep learning reveals cancer metastasis and therapeutic antibody targeting in the entire body. Cell. (2019) 179:1661–76.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.013
9. Rajpurkar P, Chen E, Banerjee O, Topol EJ. AI in health and medicine. Nat Med. (2022) 28:31–8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01614-0
10. Pesapane F, Volonté C, Codari M, Sardanelli F. Artificial intelligence as a medical device in radiology: ethical and. regulatory issues in Europe and the United States. Insights Imaging. (2018) 9:745–53. doi: 10.1007/s13244-018-0645-y
11. Coppola F, Faggioni L, Gabelloni M, De Vietro F, Mendola V, Cattabriga A, et al. Human, all too human? An all-around appraisal of the “artificial intelligence revolution” in medical imaging. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:710982. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.710982
13. Schmidhuber J. Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw. (2015) 61:85–117. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
14. Erickson BJ, Korfiatis P, Akkus Z, Kline TL. Machine learning for medical imaging. Radiographics. (2017) 37:505–15. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160130
15. Stoltzfus JC. Logistic regression: a brief primer. Acad Emerg Med. (2011) 18:1099–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01185.x
17. Huang S, Cai N, Pacheco PP, Narrandes S, Wang Y, Xu W. Applications of support vector machine (SVM) learning in cancer genomics. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. (2018) 15:41–51. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20063
19. Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology. (2016) 278:563–77. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169
20. Zhou Y, Xu X, Song L, Wang C, Guo J, Zhang Y, et al. The application of artificial intelligence and radiomics in lung cancer. Precis Clin Med. (2020) 3:214–27. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa028
21. Hua KL, Hsu CH, Hidayati SC, Cheng WH, Chen YJ. Computer-aided classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images via deep learning technique. Onco Targets Ther. (2015) 8:2015–22. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S80733
22. Bera K, Braman N, Gupta A, Velcheti V, Madabhushi A. Predicting cancer outcomes with radiomics and artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:132–46. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00560-7
23. Vaidya P, Bera K, Gupta A, Wang X, Corredor G, Fu P, et al. CT derived radiomic score for predicting the added benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery in stage I, II resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective multicohort study for outcome prediction. Lancet Digit Health. (2020) 2:e116–28. doi: 10.1016/s2589-7500(20)30002-9
24. Wang G, Liu X, Shen J, Wang C, Li Z, Ye L, et al. A deep-learning pipeline for the diagnosis and discrimination of viral, non-viral and COVID-19 pneumonia from chest X-ray images. Nat Biomed Eng. (2021) 5:509–21. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00704-1
25. Wang S, Yu H, Gan Y, Wu Z, Li E, Li X, et al. Mining whole-lung information by artificial intelligence for predicting EGFR genotype and targeted therapy response in lung cancer: a multicohort study. Lancet Digit Health. (2022) 4:e309–19. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(22)00024-3
26. Wang C, Ma J, Shao J, Zhang S, Liu Z, Yu Y, et al. Predicting EGFR and PD-L1 status in NSCLC patients using multitask AI system based on CT images. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:813072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.813072
27. Wang C, Ma J, Shao J, Zhang S, Li J, Yan J, et al. Non-invasive measurement using deep learning algorithm based on multi-source features fusion to predict PD-L1 expression and survival in NSCLC. Front Immunol. (2022) 3:828560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.828560
28. Nachiappan AC, Rahbar K, Shi X, Guy ES, Mortani Barbosa EJ Jr, Shroff GS, et al. Pulmonary tuberculosis: role of radiology in diagnosis and management. Radiographics. (2017) 37:52–72. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160032
30. El-Solh AA, Hsiao CB, Goodnough S, Serghani J, Grant BJ. Predicting active pulmonary tuberculosis using an artificial neural network. Chest. (1999) 116:968–73. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.4.968
31. Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep Learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. (2017) 284:574–82. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017162326
32. Hwang EJ, Park S, Jin KN, Kim JI, Choi SY, Lee JH, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning-based automatic detection algorithm for active pulmonary tuberculosis on chest radiographs. Clin Infect Dis. (2019) 69:739–47. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy967
33. Nijiati M, Ma J, Hu C, Tuersun A, Abulizi A, Kelimu A, et al. Artificial intelligence assisting the early detection of active pulmonary tuberculosis from chest X-rays: a population-based study. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:874475. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.874475
34. Lee JH, Park S, Hwang EJ, Goo JM, Lee WY, Lee S, et al. Deep learning-based automated detection algorithm for active pulmonary tuberculosis on chest radiographs: diagnostic performance in systematic screening of asymptomatic individuals. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:1069–80. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07219-4
35. Heo SJ, Kim Y, Yun S, Lim SS, Kim J, Nam CM, et al. Deep learning algorithms with demographic information help to detect tuberculosis in chest radiographs in annual workers’ health examination data. Int J Res Public Health. (2019) 16:250. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16020250
36. Nafisah SI, Muhammad G. Tuberculosis detection in chest radiograph using convolutional neural network architecture and explainable artificial intelligence. Neural Comput Appl. (2022) 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07258-6 [Epub ahead of print].
37. Pasa F, Golkov V, Pfeiffer F, Cremers D, Pfeiffer D. Efficient deep network architectures for fast chest X-ray tuberculosis screening and visualization. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:6268. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42557-4
38. Rajaraman S, Zamzmi G, Folio LR, Antani S. Detecting tuberculosis-consistent findings in lateral chest X-rays using an ensemble of CNNs and vision transformers. Front Genet. (2022) 13:864724. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.864724
39. Rajpurkar P, O’Connell C, Schechter A, Asnani N, Li J, Kiani A, et al. CheXaid: deep learning assistance for physician diagnosis of tuberculosis using chest x-rays in patients with HIV. NPJ Digit Med. (2020) 3:115. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00322-2
40. Lee S, Yim JJ, Kwak N, Lee YL, Lee JK, Lee JY, et al. Deep learning to determine the activity of pulmonary tuberculosis on chest radiographs. Radiology. (2021) 301:435–42. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210063
41. Yan C, Wang L, Lin J, Xu J, Zhang T, Qi J, et al. A fully automatic artificial intelligence-based CT image analysis system for accurate detection, diagnosis, and quantitative severity evaluation of pulmonary tuberculosis. Eur Radiol. (2021) 32:2188–99. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08365-z
42. The Stop Tb Partnership.FIND. Resource Center on Computer-Aided Detection Products for the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. (2020). Available online at: https://www.ai4hlth.org/ (accessed September 10, 2020).
43. Khan FA, Majidulla A, Tavaziva G, Nazish A, Abidi SK, Benedetti A, et al. Chest x-ray analysis with deep learning-based software as a triage test for pulmonary tuberculosis: a prospective study of diagnostic accuracy for culture-confirmed disease. Lancet Digit Health. (2020) 2:e573–81. doi: 10.1016/s2589-7500(20)30221-1
44. Qin ZZ, Sander MS, Rai B, Titahong CN, Sudrungrot S, Laah SN, et al. Using artificial intelligence to read chest radiographs for tuberculosis detection: a multi-site evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of three deep learning systems. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:15000. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51503-3
45. Qin ZZ, Ahmed S, Sarker MS, Paul K, Adel ASS, Naheyan T, et al. Tuberculosis detection from chest x-rays for triaging in a high tuberculosis-burden setting: an evaluation of five artificial intelligence algorithms. Lancet Digit Health. (2021) 3:e543–54. doi: 10.1016/s2589-7500(21)00116-3
46. Codlin AJ, Dao TP, Vo LNQ, Forse RJ, Van Truong V, Dang HM, et al. Independent evaluation of 12 artificial intelligence solutions for the detection of tuberculosis. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:23895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03265-0
47. Melendez J, Sanchez CI, Philipsen RHHM, Maduskar P, Dawson R, Theron G, et al. An automated tuberculosis screening strategy combining X-ray-based computer-aided detection and clinical information. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:25265. doi: 10.1038/srep25265
48. Mao Y, Yang D, He J, Krasna MJ. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surgl Oncol Clin N Am. (2016) 25:439–45. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2016.02.001
49. Starnes SL, Reed MF, Meyer CA, Shipley RT, Jazieh AR, Pina EM, et al. Can lung cancer screening by computed tomography be effective in areas with endemic histoplasmosis? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2011) 141:688–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.045
50. MacMahon H, Naidich DP, Goo JM, Lee KS, Leung ANC, Mayo JR, et al. Guidelines for management of incidental pulmonary nodules detected on CT images: from the Fleischner society 2017. Radiology. (2017) 284:228–43. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017161659
51. Patel VK, Naik SK, Naidich DP, Travis WD, Weingarten JA, Lazzaro R, et al. A practical algorithmic approach to the diagnosis and management of solitary pulmonary nodules: part 2: pretest probability and algorithm. Chest. (2013) 143:840–6. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-1487
52. Feng B, Chen X, Chen Y, Lu S, Liu K, Li K, et al. Solitary solid pulmonary nodules: a CT-based deep learning nomogram helps differentiate tuberculosis granulomas from lung adenocarcinomas. Eur Radiol. (2020) 30:6497–507. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07024-z
53. Zhuo Y, Zhan Y, Zhang Z, Shan F, Shen J, Wang D, et al. Clinical and CT radiomics nomogram for preoperative differentiation of pulmonary adenocarcinoma from tuberculoma in solitary solid sodule. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:701598. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.701598
54. Hu Y, Zhao X, Zhang J, Han J, Dai M. Value of F-FDG PET/CT radiomic features to distinguish solitary lung adenocarcinoma from tuberculosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:231–40. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04924-6
55. Du D, Gu J, Chen X, Lv W, Feng Q, Rahmim A, et al. Integration of PET/CT radiomics and semantic features for differentiation between active pulmonary tuberculosis and lung cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. (2021) 23:287–98. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01550-4
56. Lee H, Myung W, Koh WJ, Moon SM, Jhun BW. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacterial infection, South Korea, 2007-2016. Emerg Infect Dis. (2019) 25:569–72. doi: 10.3201/eid2503.181597
57. Kendall BA, Winthrop KL. Update on the epidemiology of pulmonary nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2013) 34:87–94. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1333567
58. Kwak N, Lee CH, Lee HJ, Kang YA, Lee JH, Han SK, et al. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease: diagnosis based on computed tomography of the chest. Eur Radiol. (2016) 26:4449–56. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4286-6
59. Wang L, Ding W, Mo Y, Shi D, Zhang S, Zhong L, et al. Distinguishing nontuberculous mycobacteria from Mycobacterium tuberculosis lung disease from CT images using a deep learning framework. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:4293–306. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05432-x
60. Yan Q, Wang W, Zhao W, Zuo L, Wang D, Chai X, et al. Differentiating nontuberculous mycobacterium pulmonary disease from pulmonary tuberculosis through the analysis of the cavity features in CT images using radiomics. BMC Pulm Med. (2022) 22:4. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01766-2
61. Icksan AG, Napitupulu MRS, Nawas MA, Nurwidya F. Chest X-ray findings comparison between multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis and drug-sensitive tuberculosis. J Nat Sci Biol Med. (2018) 9:42–6. doi: 10.4103/jnsbm.JNSBM_79_17
62. Wang YXJ, Chung MJ, Skrahin A, Rosenthal A, Gabrielian A, Tartakovsky M. Radiological signs associated with pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: an analysis of published evidences. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2018) 8:161–73. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.03.06
63. Jaeger S, Juarez-Espinosa OH, Candemir S, Poostchi M, Yang F, Kim L, et al. Detecting drug-resistant tuberculosis in chest radiographs. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. (2018) 13:1915–25. doi: 10.1007/s11548-018-1857-9
64. Karki M, Kantipudi K, Yu H, Yang F, Kassim YM, Yaniv Z, et al. Identifying drug-resistant tuberculosis in chest radiographs: evaluation of CNN architectures and training strategies. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). Mexico (2021) 2964–7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630189
65. Gao XW, Qian Y. Prediction of multidrug-resistant TB from CT pulmonary images based on deep learning techniques. Mol Pharm. (2018) 15:4326–35. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00875
66. Cohen KA, Manson AL, Desjardins CA, Abeel T, Earl AM. Deciphering drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using whole-genome sequencing: progress, promise, and challenges. Genome Med. (2019) 11:45. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0660-8
67. Arango-Argoty G, Garner E, Pruden A, Heath LS, Vikesland P, Zhang L. DeepARG: a deep learning approach for predicting antibiotic resistance genes from metagenomic data. Microbiome. (2018) 6:23. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0401-z
68. Yang Y, Walker TM, Walker AS, Wilson DJ, Peto TEA, Crook DW, et al. DeepAMR for predicting co-occurrent resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bioinformatics. (2019) 35:3240–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz067
69. Yang Y, Walker TM, Kouchaki S, Wang C, Peto TEA, Crook DW, et al. An end-to-end heterogeneous graph attention network for Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistance prediction. Brief Bioinform. (2021) 22:bbab299. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab299
70. Yang Y, Niehaus KE, Walker TM, Iqbal Z, Walker AS, Wilson DJ, et al. Machine learning for classifying tuberculosis drug-resistance from DNA sequencing data. Bioinformatics. (2018) 34:1666–71. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx801
71. Deelder W, Christakoudi S, Phelan J, Benavente ED, Campino S, McNerney R, et al. Machine learning predicts accurately Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug resistance from whole genome sequencing data. Front Genet. (2019) 10:992. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00922
72. Chen ML, Doddi A, Royer J, Freschi L, Schito M, Ezewudo M, et al. Beyond multidrug resistance: leveraging rare variants with machine and statistical learning models in Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance prediction. EBioMedicine. (2019) 43:356–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.04.016
73. Gröschel MI, Owens M, Freschi L, Vargas R Jr, Marin MG, Phelan J, et al. GenTB: a user-friendly genome-based predictor for tuberculosis resistance powered by machine learning. Genome Med. (2021) 13:138. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00953-4
74. Farhat MR, Sultana R, Iartchouk O, Bozeman S, Galagan J, Sisk P, et al. Genetic determinants of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their diagnostic value. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 194:621–30. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201510-2091OC
75. Kuang X, Wang F, Hernandez KM, Zhang Z, Grossman RL. Accurate and rapid prediction of tuberculosis drug resistance from genome sequence data using traditional machine learning algorithms and CNN. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:2427. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06449-4
76. Jiang Z, Lu Y, Liu Z, Wu W, Xu X, Dinnyés A, et al. Drug resistance prediction and resistance genes identification in Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on a hierarchical attentive neural network utilizing genome-wide variants. Brief Bioinform. (2022) 23:bbac041. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac041
77. Higashiguchi M, Nishioka K, Kimura H, Matsumoto T. Prediction of the duration needed to achieve culture negativity in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis using convolutional neural networks and chest radiography. Respir Investig. (2021) 59:421–7. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2021.01.004
78. Colangeli R, Jedrey H, Kim S, Connell R, Ma S, Chippada Venkata UD, et al. Bacterial factors that predict relapse after tuberculosis therapy. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:823–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715849
79. Ahmad Khan F, Gelmanova I, Franke M, Atwood S, Zemlyanaya N, Unakova I, et al. Aggressive regimens reduce risk of recurrence after successful treatment of MDR-TB. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 63:214–20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw276
Keywords: pulmonary tuberculosis, artificial intelligence, deep learning, radiomics, machine learning
Citation: Liang S, Ma J, Wang G, Shao J, Li J, Deng H, Wang C and Li W (2022) The Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Drug Resistance Prediction of Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Front. Med. 9:935080. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.935080
Received: 03 May 2022; Accepted: 13 June 2022;
Published: 28 July 2022.
Edited by:
Mohaimenul Islam, Aesop Technology, TaiwanReviewed by:
Michela Gabelloni, University of Pisa, ItalyCopyright © 2022 Liang, Ma, Wang, Shao, Li, Deng, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Deng, aHVpZGVuZzA5MjNAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=; Chengdi Wang, Y2hlbmdkaV93YW5nQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=; Weimin Li, d2VpbWkwMDNAc2N1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.