- 1Genome and Computational Biology Lab, Department of Biotechnology, Mohanlal Sukhadia University, Udaipur, India
- 2Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope, Monrovia, CA, United States
- 3Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 4Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE), Manipal, India
- 5Institute of Bioinformatics, International Technology Park, Bangalore, India
The microbiome of the gut is a complex ecosystem that contains a wide variety of microbial species and functional capabilities. The microbiome has a significant impact on health and disease by affecting endocrinology, physiology, and neurology. It can change the progression of certain diseases and enhance treatment responses and tolerance. The gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in human health, influencing a wide range of physiological processes. Recent advances in computational tools and artificial intelligence (AI) have revolutionized the study of gut microbiota, enabling the identification of biomarkers that are critical for diagnosing and treating various diseases. This review hunts through the cutting-edge computational methodologies that integrate multi-omics data—such as metagenomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics—providing a comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome's composition and function. Additionally, machine learning (ML) approaches, including deep learning and network-based methods, are explored for their ability to uncover complex patterns within microbiome data, offering unprecedented insights into microbial interactions and their link to host health. By highlighting the synergy between traditional bioinformatics tools and advanced AI techniques, this review underscores the potential of these approaches in enhancing biomarker discovery and developing personalized therapeutic strategies. The convergence of computational advancements and microbiome research marks a significant step forward in precision medicine, paving the way for novel diagnostics and treatments tailored to individual microbiome profiles. Investigators have the ability to discover connections between the composition of microorganisms, the expression of genes, and the profiles of metabolites. Individual reactions to medicines that target gut microbes can be predicted by models driven by artificial intelligence. It is possible to obtain personalized and precision medicine by first gaining an understanding of the impact that the gut microbiota has on the development of disease. The application of machine learning allows for the customization of treatments to the specific microbial environment of an individual.
1 Introduction
The gastrointestinal tract, also referred to as the gut, has a large and intricate ecosystem filled with billions of bacteria. The gut microbiome is a complex community consisting of a wide variety of bacteria, archaea, fungus, and viruses (1). Each of these components has an important role in preserving human health. The human microbiome, composed of diverse bacteria, has a vital role in the metabolic processes required for the proper functioning of enzymes in the gut mucosa and liver, as well as the overall metabolism of the host (2). The makeup of this collection of microorganisms is not fixed; it consistently changes over the course of our lives, influenced by several factors such as diet, lifestyle, environment, and even heredity. The gut microbiota influences the host's well-being via altering the biochemical makeup of the diet. A study has been carried out to investigate the functions of various bacteria in metabolic pathways, namely in the breakdown of food components, because of the crucial role of gut microbiota in human immune system (3, 4).
The human microbiome, a diverse collection of microorganisms residing in various anatomical sites, plays a crucial role in health and disease (Table 1). Microorganisms within the human body may engage in commensal, mutualistic, or harmful relationships, influencing host physiology through the production of various metabolites (10). Traditional culture-based methods have historically limited our understanding of these complex microbial communities. However, advancements in metagenomics (MGs) have significantly expanded our ability to identify and characterize previously unknown microbial species and their functions, particularly through whole genome sequencing (WGS) and marker gene sequencing (11). These technologies have been instrumental in large-scale projects like the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) and the American Gut Project, generating extensive datasets that have deepened our understanding of host-microbiome interactions (12).
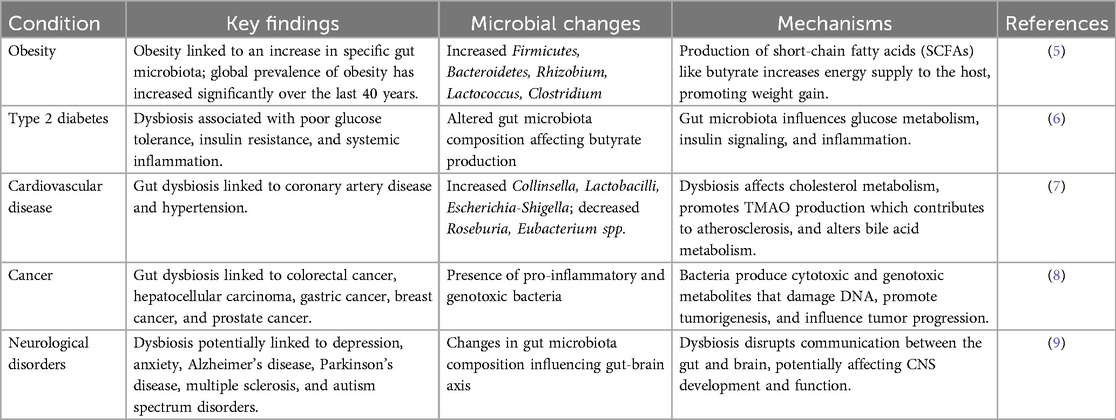
Table 1. Gut microbes and metabolites: systemic manifestations linked to several Gut associated diseases and disorders.
The study of the gut microbiome has seen significant advancements in recent years, with the development of a variety of computational tools and techniques that have revolutionized the field (13). The advent of next-generation sequencing technologies has enabled the comprehensive profiling of microbial communities, allowing researchers to uncover the vast diversity and complexity of the gut microbiome (14). Metagenomics approaches, which involve the sequencing of genetic material extracted directly from environmental samples, have become a cornerstone of gut microbiome research, providing a wealth of information on the taxonomic composition and functional capabilities of these microbial communities (15, 16).
In the past, gut microbiome research has relied heavily on traditional methods such as culture-based techniques and phylogenetic marker gene analysis, notably 16S rRNA sequencing. These approaches have provided foundational knowledge, allowing researchers to identify and classify microbial taxa within complex communities (17). However, traditional methods have significant limitations, particularly in terms of resolution and depth. Culture-based techniques are limited by their inability to grow the vast majority of gut microorganisms, while 16S rRNA sequencing offers limited taxonomic resolution and does not provide functional insights into microbial activities (18).
Advanced computational and multi-omics approaches are transforming gut microbiome research by enabling a deeper exploration of microbial functions beyond traditional taxonomic classifications. These approaches link microbial composition with potential roles in health and disease, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the microbiome's functional capacities (19). Visualization and statistical techniques play a crucial role in interpreting vast datasets, allowing researchers to identify patterns and correlations within microbiome data. By focusing on the small molecules and proteins produced by the microbiome, metabolomics and metaproteomics provide direct insights into microbial activity and its impact on host physiology (20).
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the study of metabolomes and transcriptomes, deepening our understanding of microbial gene expression and function. Network analysis and machine learning further enrich this field by uncovering complex microbial interactions and predicting potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets (21). As the integration of multi-omics data with AI and machine learning continues to evolve, these approaches are poised to unlock new insights into the gut microbiome, paving the way for advancements in personalized medicine and novel therapeutic strategies (22).
In addition to computational tools, the field of gut microbiome research has also benefited from the integration of multi-omics techniques, such as metatranscriptomics, meta-proteomics, and metabolomics (23). These approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome by capturing not only the taxonomic composition, but also the functional activities, metabolic processes, and interactions within the microbial community (24).
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms has opened up new frontiers in gut microbiome research. These advanced analytical techniques have the potential to uncover complex patterns and associations within the gut microbiome, enabling the identification of novel biomarkers and the development of predictive models for various health and disease states (25, 26).
2 Traditional methods for gut microbiome research and their limitation
The study of the gut microbiome has become an increasingly important field in recent years, as researchers have come to recognize the critical role that the diverse community of microorganisms inhabiting the human gastrointestinal tract plays in maintaining overall health and contributing to various disease states (27–29). The advancement of molecular techniques, particularly next-generation sequencing technologies, has revolutionized our ability to characterize the composition, function, and ecology of the gut microbiome in unprecedented detail (30).
2.1 Key molecular techniques for microbiome analysis and their applications
2.1.1 Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)
qPCR is a powerful tool in microbiome analysis that allows for the quantification of specific DNA sequences. It is used to measure the abundance of particular microbial taxa or genes within a sample, providing precise and sensitive data on microbial population dynamics. This technique is especially valuable in monitoring the effects of environmental changes, treatment interventions, or disease conditions on microbial communities (31).
2.1.2 Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE)
DGGE is used to separate DNA fragments based on their sequence-specific melting behaviour. In microbiome analysis, DGGE allows researchers to profile microbial community diversity by comparing the band patterns generated from different samples. This technique is particularly useful for detecting shifts in microbial populations and identifying dominant species or variants in complex communities (32).
2.1.3 Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP)
T-RFLP is a molecular fingerprinting technique used to analyse the diversity of microbial communities. It involves the digestion of amplified DNA with restriction enzymes, followed by the separation of terminal fragments by size. The resulting fragment patterns reflect the community composition, allowing researchers to compare microbial diversity across samples and assess the impact of various factors on community structure (33).
2.1.4 Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
FISH is a technique that uses fluorescent probes to target specific DNA or RNA sequences within microbial cells. In microbiome analysis, FISH enables the visualization and identification of specific microorganisms within their natural environment, often in conjunction with microscopy. This technique is particularly useful for studying the spatial distribution of microbes, understanding microbial interactions, and linking microbial identity to function within a community (34).
2.2 Limitations of molecular microbiome analysis techniques
Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) is highly specific but may not capture the full microbial diversity due to its reliance on primers targeting specific sequences, potentially missing out on less abundant or uncharacterized taxa. Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE) can resolve differences in microbial communities but often lacks sensitivity for detecting subtle variations and may not accurately reflect community composition due to issues with fragment resolution and band intensity interpretation. Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (T-RFLP) provides a fingerprint of microbial diversity but can suffer from inconsistencies in fragment size due to variability in restriction enzyme activity and PCR amplification, which may affect reproducibility. Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) offers detailed spatial information but is limited by the availability of specific probes and the potential for non-specific binding, which can complicate the interpretation of microbial distribution and interactions. Each method's limitations necessitate complementary approaches and careful interpretation to obtain a comprehensive understanding of microbiome dynamics.
2.3 Traditional methods: phylogenetic marker gene analysis and sequencing
One of the primary tools utilized in gut microbiome research is marker-gene analyses, which profile the microbial community by sequencing specific genetic markers, such as the 16S ribosomal RNA gene (35). This approach provides information about the taxonomic composition of the microbiome, allowing researchers to identify the dominant bacterial phyla and track changes in community structure across different populations or conditions. While these surveys offer valuable insights, researchers are now transitioning to integrate other data types, such as metabolite, metaproteome, or metatranscriptome profiles, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome and its functionality (36).
Marker-gene surveys: These approaches profile the microbial community by targeting and sequencing specific marker genes, such as the 16S rRNA gene, which provide varying degrees of taxonomic specificity and phylogenetic information. Disease states (26, 27, 37). The incorporation of these multi-omics approaches has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the gut microbiome and its role in human health and disease (26).
One of the most commonly used marker genes is the 16S rRNA gene, which provides valuable taxonomic specificity and phylogenetic information. The 16S rRNA gene is highly conserved among bacteria but contains variable regions that allow for the identification and classification of bacterial taxa at various levels of resolution. This gene is particularly useful for assessing microbial diversity and community composition in various environments.
Shotgun metagenomics: This approach involves the sequencing of the entire genomic content of the microbial community, providing a deeper understanding of the functional potential of the gut microbiome, including the identification of specific genes and pathways involved in various metabolic processes (38).
Through the use of these diverse tools and techniques, researchers have gained valuable insights into the gut microbiome and its complex interactions with the host, paving the way for the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic interventions for a wide range of health conditions (26, 37, 39).
2.4 Limitations of traditional microbiome analysis techniques
While marker-gene surveys have been widely used in gut microbiome research, they have several limitations. The choice of the specific marker gene, the DNA extraction protocol, and the sequencing platform can all introduce biases that can lead to inconsistencies in the observed microbial community composition. Additionally, marker-gene surveys often lack the resolution to fully capture the functional diversity of the gut microbiome, as they primarily provide information about the taxonomic structure rather than the metabolic and functional capabilities of the microbial community (40).
Previously, gut microbiome analysis relied on 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing. This method targets a specific section of the 16S rRNA gene, a genetic indication found in all bacteria. It determines the identity and percentage of bacterial species in a sample. 16S rRNA sequencing has helped us understand the gut microbiome, but it has limits. First and foremost, this method provides limited gut bacteria functional data. It offers information about gastrointestinal residents but not their activities or behaviours. Due to its focus on bacteria, 16S rRNA sequencing may not capture the whole range of intestinal microbes (41).
To address these limitations, researchers have turned to more comprehensive approaches, such as shotgun metagenomics, which involve the sequencing of the entire genomic content of the microbial community. Shotgun metagenomics can provide a deeper understanding of the functional potential of the gut microbiome, as it allows for the identification of specific genes and pathways involved in various metabolic processes. However, the analysis of shotgun metagenomics data can be computationally intensive and requires specialized bioinformatics expertise (35).
In addition to computational tools, the field of gut microbiome research has also benefited from the integration of multi-omics techniques, such as metatranscriptomics, meta-proteomics, and metabolomics. These approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome by capturing not only the taxonomic composition, but also the functional activities, metabolic processes, and interactions within the microbial community. The integration of these multi-omics techniques has enabled researchers to unravel the complex relationships between the gut microbiome and various health and disease states, leading to the identification of novel biomarkers and the development of predictive models for person. Bioinformatics platforms: Software such as QIIME, Mothur, and DADA2 are used for processing and analysing sequencing data.
3 Computational tools and multi-omics techniques in microbiome analysis
The conventional techniques employed to examine the gut microbiome, however helpful, provide only a limited understanding of this intricate ecology. In order to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex relationship between gut bacteria and their influence on human health, a more comprehensive approach is necessary. This is where the potential of multi-omics is harnessed. Multi-omics involves combining data from many biological fields, including metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics, to provide a thorough comprehension of a biological system (Figure 1). Within the framework of the gut microbiome, this method entails examining different forms of “omic” data, each offering a unique viewpoint on the gut environment.
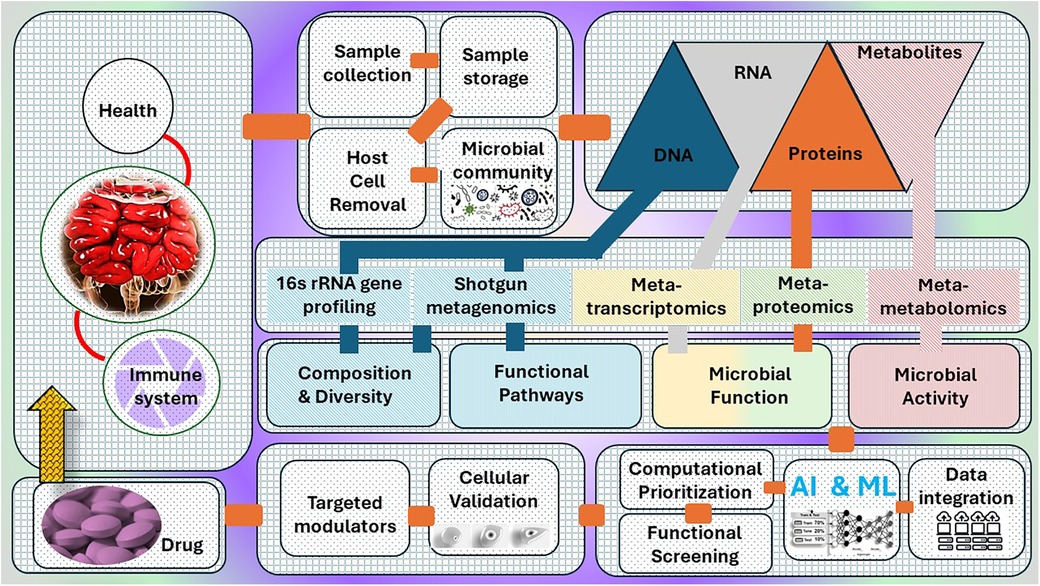
Figure 1. A systematic approach for microbiome data analysis, covering the steps from raw reads to community analyses, incorporating multi-omics techniques and statistical models that allow for more accurate phenotypic and functional profiling.
Computational platforms, such as QIIME, Mothur, and DADA2, are widely used to process and analyse sequencing data in gut microbiome studies (26). These marker-gene surveys target and sequence specific genetic markers, like the 16S rRNA gene, which provide varying degrees of taxonomic resolution and phylogenetic information about the microbial community (27, 37). In contrast, shotgun metagenomics involves sequencing the entire genomic content of the microbial community, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the functional potential of the gut microbiome, including the identification of specific genes and metabolic pathways (42). The integration of multi-omics techniques, including metatranscriptomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics, has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of the gut microbiome and its complex interactions with human health and disease (43).
A key tool in this field is the QIIME 2 platform, an open-source, community-developed software suite that enables reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science (26). QIIME 2 provides a flexible and powerful framework for analysing and visualizing microbiome data, allowing researchers to perform a wide range of analyses, from taxonomic classification to functional profiling, while ensuring the reproducibility and transparency of their research (25, 26). QIIME 2 offers a range of features, including the ability to process and analyse high-throughput sequencing data, perform taxonomic classification, and generate visualizations to aid in the interpretation of results. Additionally, the platform's modular design allows for the integration of various plug-ins, enabling researchers to extend its capabilities to address specific research questions.
The utility of QIIME 2 has been demonstrated in numerous studies, such as the work by Bolyen et al. (26), which described the platform's ability to facilitate reproducible, interactive, and scalable microbiome data analysis (26). Furthermore, the QIIME 2 tutorial by Gonzalez et al. illustrates how the platform can be used for end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome datasets, including the integration of public data through the Qiita platform (26, 44).
Alongside QIIME 2, other computational tools have also emerged as invaluable resources in gut microbiome research. Algorithms for sequence clustering, taxonomic assignment, and functional prediction have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing researchers to gain deeper insights into the structure and function of gut microbial communities (25, 26).
4 Multi-omics techniques in gut microbiome analyses
In addition to computational tools, gut microbiome research has also greatly benefited from the integration of multi-omics approaches, which provide a more comprehensive understanding of the microbial community and its interactions with the host (Figure 2) (20).
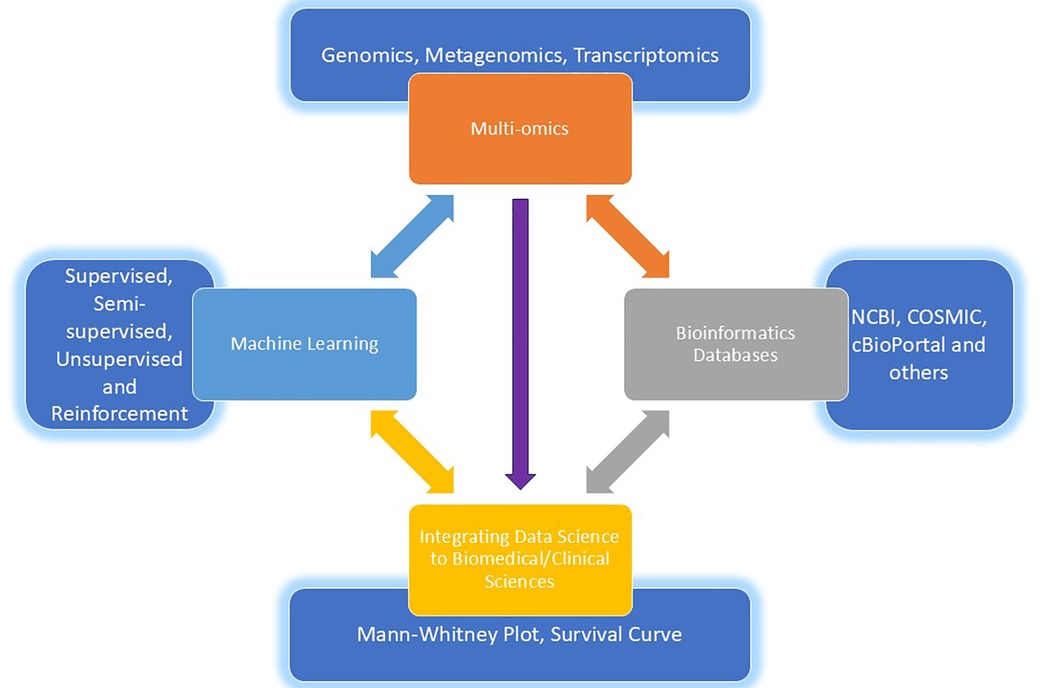
Figure 2. A comprehensive and fascinating intersection of multi-omics, machine learning, databases and the gut microbiota showing evident synergy between multi-omics and machine learning that hold immense promise for advancing our understanding of the gut microbiota and its impact on human health.
One such approach is metatranscriptomics, which involves the sequencing of the RNA molecules expressed by the microbial community. By analysing the metatranscriptome, researchers can gain insights into the functional activities and gene expression patterns of the gut microbiome, revealing how the microbial community responds to changes in the environment or the host's physiology (45).
Another powerful technique is metaproteomics, which focuses on the identification and quantification of the proteins expressed by the gut microbiome (46). This approach can provide valuable information about the metabolic activities and functional capabilities of the microbial community, as well as the interactions between the microbiome and the host (47).
Furthermore, metabolomics, the study of small-molecule metabolites, has emerged as a crucial tool in gut microbiome research. By analysing the metabolic profiles of the gut microbiome, researchers can uncover the complex interplay between the microbial community and the host's physiology, identifying metabolic pathways and biomarkers that are associated with various health and based on the sources provided, this research paper discusses the different tools and techniques used in gut microbiome studies, including marker-gene surveys, shotgun metagenomics, and multi-omics approaches such as metatranscriptomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics (48).
The paper highlights the limitations of traditional marker-gene surveys, which can introduce biases and lack the resolution to fully capture the functional diversity of the gut microbiome. To address these limitations, researchers have turned to more comprehensive approaches, such as shotgun metagenomics, which can provide a deeper understanding of the functional potential of the gut microbiome (49).
The integration of multi-omics techniques, including metatranscriptomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics, has enabled researchers to unravel the complex relationships between the gut microbiome and various health and disease states, leading to the identification of novel biomarkers and the development of predictive models for personalized medicine (50).
4.1 Microbiomics
As discussed earlier, this field focuses on the identification and characterization of the microbial population within a sample. Techniques like 16S rRNA sequencing and shotgun metagenomics are employed to assess the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. Shotgun metagenomics, unlike 16S sequencing, provides a more detailed picture by directly sequencing all the microbial DNA present in a sample, allowing for the identification of not just bacteria but also archaea, fungi, and viruses. Metagenomics refers to the direct examination and analysis of the genetic material present in genomes obtained from diverse sources (51). The term “metabolomics” is often applied incorrectly to 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Sequencing of 16S rRNA is gene-specific and does not examine the entire genome. On the other hand, metagenomics is an approach that utilizes a comprehensive shotgun sequencing methodology to analyze the genetic material of microbes discovered in the environment—without requiring culturing (16, 52). Metagenomics offers an exhaustive enumeration of all microorganisms present in complex environmental samples, including those that are both familiar and unfamiliar and those that are not amenable to laboratory cultivation. In contrast to unimodal phylogenetic studies, which concentrate on the diversity of a solitary gene (e.g., the 16S rRNA gene), metagenomics investigates the multifarious genetic constituents present within microbial communities. Consequently, metagenomics provides a more comprehensive compilation of genomic information and a more precise taxonomic classification (53, 54). The correlation between function and phylogeny is facilitated by genomics, along with the compilation of evolutionary profiles that depict the structure of the microbial community. Significantly, it additionally facilitates the identification of viruses that are challenging to detect through a single-gene approach due to their broad genetic variability and the difficulty in differentiating shared genetic attributes (55). Modern Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) has progressively replaced traditional Sanger sequencing as the predominant technique for shotgun sequencing in metagenomics over the past few years. In numerous contexts, the 454/Roche and Illumina/Solexa technologies were utilized extensively to analyze metagenomics materials (56). Scientists often perform read-based profiling of selected genes (or markers) obtained from unassembled shotgun metagenomics reads to classify taxonomy or annotate genes. They then compare the findings with reference databases. Taxonomic binning can make use of similar DNA compositions or nucleotide patterns, such as k-mer lengths, GC content, or gene homology (57). An example of this is the Kraken algorithm, which utilizes unique k-mer distributions in sequences to assign taxonomy (58). On the other hand, MetaPhlAn2 differentiates between different types of microorganisms and calculates their relative abundance by using particular genes that are unique to each group (59).
Despite recent advancements in computational analysis tools and sequencing methods, various factors can still introduce biases and inaccuracies in metagenomics shotgun assembly. Metagenomics shotgun assemblies can employ a combination of de novo and reference genome-based approaches, each with its own set of challenges (60).
The Overlap, Layout, Consensus assembly method, commonly used in whole genome sequencing, is not feasible for metagenomic shotgun data due to its high processing demands. Consequently, many new assembly algorithms use the de Bruijn graph approach, such as MEGAHIT (61), MetaVelvet (62), IDBAUD (63), and metaSPADES (64, 65). In reference-guided metagenomic assembly, like MetaCompass (66), contigs are reassembled by aligning sequencing reads to reference databases, but the performance is constrained by the quality of the database and the availability of reference genome sequences (67).
The errors and biases in metagenomic shotgun assembly can be classified into two primary categories: computational challenges and experimental issues. From a statistical perspective, the analysis of microbiome data, including shotgun metagenomics, faces the usual challenges of count data analysis, such as skewed distribution, zero inflation, and over-dispersion (68). Additionally, the experimental process and quality control filtering can result in highly variable and noisy data, which requires normalization to ensure comparability of microbiome abundances among different samples.
The increasing presence of environmental contaminants (ECs) due to human activities has created significant ecological and health challenges. As these pollutants accumulate in ecosystems, they threaten human well-being and various organisms. Recent research has focused on the gut microbiota's role in health, given its influence on metabolism, immunity, and the effects of toxins. Advanced computational tools and artificial intelligence (AI) have become crucial in analysing complex microbiome data, aiding in the identification of disease biomarkers and understanding microbiota interactions. This review examines how these technologies enhance microbiome research, offering insights into biomarker discovery, predictive modelling, and strategies to mitigate the health impacts of ECs (69).
The exponential increase in the number of metagenome-assembled genomes, coupled with advancements in assembly and binning tools, has provided invaluable insights into the presence of previously undescribed organisms and their genetic makeup (70, 71). However, the vast majority of the microbiome diversity remains unexplored, highlighting the need for continued research and development in metagenomics analysis methods.
Despite the rapid advancements in computational tools and sequencing technologies, various factors continue to introduce biases and inaccuracies in metagenomics shotgun assembly. The challenges encompass both computational and experimental issues. From a statistical standpoint, the analysis of microbiome data faces common challenges such as skewed distributions, zero inflation, and over-dispersion. Additionally, the experimental process and quality control measures can result in highly variable and noisy data, requiring normalization to ensure comparability across samples. While the exponential increase in metagenome-assembled genomes has provided valuable insights, the vast majority of microbiome diversity remains unexplored, underscoring the need for ongoing research and development in metagenomics analysis methods (72).
4.2 Metabolomics and metaproteomics
This field explores the comprehensive collection of tiny molecules (metabolites) found in a biological system, namely the human stomach. Metabolomics in the field of gut microbiome study is concerned with the identification and quantification of the metabolites generated by both the gut microorganisms and the human host (73). These metabolites are indicative of the metabolic activities of the gut environment and can offer vital information about the functional capabilities of the microbiome. The primary goal of metabolomics analyses is to study the metabolites produced by bacteria and their interactions with the metabolism of both the microbiota and the host (74, 75). These approaches are frequently used to measure small amounts of substances, including as antibiotics, antibiotic metabolites, and products that are produced during the metabolism of bacteria and the host.
Metabolomics and Metaproteomics are crucial techniques in microbiome research that together provide a comprehensive understanding of microbial functionality (76). Metabolomics focuses on analysing the small molecules produced by microbial metabolism, such as amino acids, lipids, and sugars, offering direct insights into the biochemical activities within a microbial community (77). This approach helps reveal active metabolic pathways, detect shifts in microbial processes, and identify biomarkers linked to health or disease. Metaproteomics, on the other hand, examines the proteins actively produced by the microbiome, linking gene expression to protein production and biological functions. By identifying and quantifying these proteins, metaproteomics sheds light on the operational metabolic pathways and microbial responses to environmental stimuli (78). The integration of metabolomics and metaproteomics allows researchers to connect microbial gene expression with functional outcomes, offering a detailed view of the microbiome's role in health, disease, and environmental interactions.
4.3 Metatranscriptomics
It involves the comprehensive analysis of the complete set of RNA transcripts present in a microbiome sample at a given time. This technique provides insights into the active gene expression profiles of microbial communities, revealing which genes are expressed and at what levels. By analyzing mRNA, researchers understand which metabolic pathways and biological processes are active in the microbiome, offering a snapshot of the community's functional capabilities. This approach helps elucidate the functional roles of different microbes and their contributions to overall microbiome activity, which is crucial for understanding how microbial communities respond to environmental changes, disease states, or treatments (79).
This subject is centred on the examination of messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts produced by cells in a given sample. Through the quantification of mRNA levels, we can obtain valuable insights into the genes that are currently undergoing expression by both the gut microorganisms and the host intestinal cells. Metatranscriptomics was first conceived and developed in 2005 as a result of pioneering investigations that sought to identify genes expressed in environmental samples (80, 81).
Metatranscriptomics and metabolomics are complementary approaches in microbiome research, each providing unique insights into the functional dynamics of microbial communities. Metatranscriptomics examines RNA transcripts to identify which genes are actively expressed under various conditions, offering a real-time view of microbial activities and their responses to environmental changes, stressors, or host interactions. Techniques like RNA-Seq are commonly used to capture a comprehensive snapshot of the transcriptome, enabling functional profiling that identifies active metabolic pathways and regulatory networks (82). This is particularly valuable in understanding how microbes adapt to different environmental and host-associated contexts, though the complexity and variability of microbial communities pose challenges in interpreting gene expression data.
5 Technological platforms in multi-omics techniques
5.1 Technological platforms in metaproteomics and metabolomics
Metaproteomics and metabolomics are burgeoning scientific disciplines that have made substantial strides in the investigation of the microbiome. The production of metabolomics data differs significantly from that of metatranscriptomics and metagenomics, as the latter two rely heavily on sequencing. Metabolites are typically detected and measured by employing a mix of chromatography techniques, such as gas chromatography and liquid chromatography, together with detection methods like nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry. NMR provides consistent, quantitative precision, and unambiguous, definitive results for non-destructive, complex structure determination. NMR can target different atom nuclei, such as hydrogen (1H-NMR), carbon (13C-NMR), and phosphorus (31P-NMR), offering further information on specific metabolite types. The utilization of LC-NMR greatly enhances the advantages of NMR-based metabolomics, effectively reducing the complexity of samples. Each analytical platform has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the platform depends on the focus of the study, the nature of the samples, cost, accessibility, and available expertise. Metabolomics contains the downstream products of genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic processes, and the metabolome is sensitive to various genetic and environmental stimuli, requiring careful experimental design to reduce confounders and optimize information recovery (83–87).
Metaproteomics and metabolomics are complementary approaches that provide deep insights into the functional activities of microbial communities. Metaproteomics focuses on identifying and analysing the proteins actively produced by microorganisms, offering a real-time view of their metabolic and regulatory pathways. This method is particularly valuable in complex ecosystems like soil, oceans, and the human gut, where it helps uncover microbial interactions and responses to environmental changes. Metabolomics, on the other hand, studies the small molecules or metabolites produced within these communities, giving a detailed picture of the biochemical processes at play. By linking specific proteins identified through metaproteomics to their corresponding metabolic outputs revealed by metabolomics, researchers can achieve a comprehensive understanding of microbial functions. This integrated approach is especially useful in health-related research, shedding light on the role of the microbiome in conditions like obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases. As these fields continue to advance, the combined use of metaproteomics and metabolomics will be crucial for developing microbiome-based therapies, improving environmental management practices, and driving innovations in biotechnology and personalized medicine.
5.2 Technological platforms in metatranscriptomics
Metatranscriptomic approaches, which collect the RNA transcribed by microbial cells, utilize similar analytical principles as shotgun metagenomics, elucidating the active functional profile of a microbial community through the analysis of all population-expressed genes. A snapshot of gene expression, the metatranscriptome captures the complete mRNA in a given sample at a precise instant and under specific conditions. Shotgun metagenomics and metatranscriptomic techniques mostly rely on Illumina sequencing methods, with the HiSeq or NovaSeq (88) instrument families being the most commonly used due to their cost-effectiveness per base and ability to process large amounts of data. On the other hand, there has been a shift towards using PacBio and Oxford Nanopore sequencing technologies (89) to take advantage of their longer read lengths, which make it easier to map the genetic information of a reference genome and identify genes (17, 90). The usual method for sequencing the microbiome sample involves isolating total RNA, enriching RNA, fragmenting it, synthesizing cDNA, and producing transcriptome libraries.
Until recently, these techniques were limited to a relatively particular assortment of alleles. At this time, shotgun sequencing of complete metatranscriptomics is feasible using metagenomics, and a thorough examination of gene expression across the entirety of the genome provides an elaborate synopsis of the functional attributes and expression patterns of a microbiome. Most of these techniques follow the initial read mapping-based strategy, with de-novo assembly of reads into transcript contigs and supercontigs or mapping of reads to a reference genome constituting a standard metatranscriptomics analysis pathway. Comparable to alignment-based methods in whole-genome sequencing, the initial strategy consists of mapping sequences to reference databases in order to obtain information that can be used to (91–93).
5.3 Metagenomics
Metagenomics has previously been used to evaluate the microbial community within a sample or environment, for example, interrogating the gut microbiome and its association with chronic diseases. Metagenomics is progressively being applied as a novel infectious disease diagnostic assay, with two main approaches: shotgun metagenomics, which attempts to sequence the entire genetic content present in a sample, and targeted-amplicon sequencing, which represents a more biased approach to a particular group of microorganisms (37).
Advances in non-targeted short-read sequencing made during the Human Genome Project, particularly innovations by J. Craig Venter and his team, gave rise to shotgun sequencing, wherein nucleic acid from a sample is fragmented and the entire population of fragments is subjected to unbiased sequencing followed by characterization and assignment of the sequenced fragment. This method serves as a census of organisms in the original sample.
6 Functional classifications in microbiome research
6.1 Metagenomics: leveraging computational tools for microbial insights
Researchers possess the capacity to identify discrepancies in metabolic activity across unique microbial populations, as well as to scrutinize the taxonomic makeup of a microbiome (16). Through the implementation of software applications such as PICRUSt or Tax4Fun (73), it is feasible to predict a functional profile by utilizing 16S sequencing data. By utilizing the relative abundance of taxa in the community and the reference genome for each taxonomic present, these programs are capable of predicting the likely functionality of genes. However, it is important to note that these methods only offer an approximation, as they neglect to consider the true expression levels of proteins and rely significantly on reference genomes and their annotations.
Metatranscriptome and shotgun techniques both facilitate functional analysis. Gene predictions are produced subsequent to the compilation of a metagenome through the utilization of software tools such as Glimmer-MG (94) and MetaGeneMark (95). Functional annotation is executed subsequent to the identification of coding genes through the implementation of computationally intensive searches predicated on protein sequence homology. Typically, databases of orthologues (e.g., EggNOG or COG), and enzymes, or protein domains and families are queried using UBLAST and USEARCH-based queries (96). Software applications such as Pathfinder can be employed to perform pathway enrichment analysis, classification, and scoring purposes. KEGGscape (97) and similar applications may be utilized in a similar fashion to construct a metabolic network (98, 99).
A multitude of publicly accessible automated algorithms has been devised to manage the substantial computational demands and tool sets associated with various tasks, including but not limited to quality filtering, gene calling, functional annotation, and fundamental statistics and visualization using MG-RAST and MEGAN-CE (100). While these approaches have significantly advanced our understanding of microbial communities, it is important to note that culturing of taxa is still essential to determine the ecological significance of function (101). Cheaper sequencing has democratized the application of metagenomics, but has also come at the cost of reduced sequence length, resulting in poor gene annotation and overestimates of bacterial richness and abundance. Recent improvements in sequencing technology are beginning to provide reads of sufficient length for accurate annotation and assembly of whole operons and beyond, that will once again enable experimental testing of gene function and re-capture the early successes of metagenomics investigations (98).
As sequencing projects remain largely biased towards genomes linked to human interests, some serious initiatives are being launched for sequencing organisms that represent all branches of the tree of life. Concomitant with the genomic revolution, unprecedented advances in sequencing technology have also led to the emergence of the field of metagenomics, which offers a novel, revolutionary approach for studying life in different environments (102).
This paper has provided an overview of the current state of functional classifications in metagenomics, highlighting the computational tools and methods available for researchers to gain insights into microbial communities.
6.2 Functional profiling in metatranscriptomics
Metatranscriptomics has emerged as a powerful tool in unravelling the intricate dynamics of the gut microbiome, shedding light on the ongoing biological processes and metabolic pathways that shape this complex ecosystem (103). Through the analysis of RNA sequence data, researchers can categorize and characterize the genes that are actively expressed, providing insights into the functional behaviours of the resident microbial communities (104).
The process typically involves aligning the metatranscriptomic data obtained from microbiome samples to specific pathways and genomes, such as the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (105). Bioinformatics tools like SOAPdenovo have been employed to construct and align these metatranscriptomic datasets (106). Comparative analyses across different health and disease states allow researchers to identify the pathways that experience increased or decreased activity in response to various factors.
The subsequent annotation of these results using databases like Gene Ontology, Clusters of Orthologous Groups, and Swiss-Prot enables a more comprehensive understanding of the metabolic and functional capabilities of the gut microbiome (107).
The applications of functional profiling in metatranscriptomics extend beyond the mere cataloguing of microbial gene expression. Techniques like stable isotope probing have been utilized to isolate the transcriptomes of specific aerobic bacteria found in environmental samples, significantly advancing the field of metabolomics by enabling the targeted investigation of key microbial species (19).
Functional Profiling in Metatranscriptomics uses RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to capture gene expression across microbial communities, offering insights into their real-time biochemical activities. Unlike genomics, which identifies potential genetic capabilities, metatranscriptomics reveals the actual molecular processes occurring in microbes within their natural environments. This makes metatranscriptomics essential for understanding microbial behaviour, host-microbe interactions, and identifying biomarkers. Despite challenges like RNA degradation and the need for extensive sequencing, Metatranscriptomics holds significant potential for advancing our knowledge of microbial ecosystems, with broad implications for health, biotechnology, and environmental management (108).
Overall, the integration of metatranscriptomics with functional profiling has opened new avenues for understanding the complex interplay between the gut microbiome and host health, paving the way for more targeted and personalized therapeutic interventions (26, 27, 37, 98).
7 Key bioinformatics tools for phylogenetic and microbiome analysis
7.1 Phenotypic classification
Phylogenetic and microbiome analyses are essential for exploring microbial diversity, structure, and function. Phylogenetic tools elucidate evolutionary relationships and taxonomic classifications of microorganisms. Microbiome analysis tools, including those for 16S rRNA gene sequencing, identify microbial taxa and their functional potential. Multi-omics approaches integrate genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomics data to offer a comprehensive view of microbial interactions. These bioinformatics tools are crucial for advancing our understanding of microbial ecology, health impacts, and therapeutic possibilities (109).
Phyloseq: Phyloseq is an R package designed for the analysis and visualization of microbiome data. It provides tools for importing, analysing, and graphically displaying phylogenetic trees, taxonomic composition, and diversity metrics. Phyloseq integrates well with other R packages, making it a flexible choice for custom analyses and visualizations (110).
USEARCH is a comprehensive software package used for clustering and analysing 16S rRNA gene sequences. It supports a wide range of functionalities, including de novo OTU clustering, chimera detection, and sequence alignment. USEARCH is highly efficient, capable of processing large datasets quickly, which is crucial for handling the vast amounts of data generated in microbiome studies. Although it is a commercial tool, its performance and speed in OTU clustering make it a preferred choice for researchers seeking high throughput and accuracy in sequence analysis (111).
BEAST (Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis Sampling Trees): BEAST is a powerful tool used for Bayesian analysis of molecular sequences. It is particularly well-suited for phylogenetic analysis involving time-stamped sequences, allowing researchers to infer phylogenies and estimate divergence times. BEAST is commonly used in evolutionary biology and can be applied to microbiome studies to explore the evolutionary history of microbial taxa (112).
FastTree: FastTree is an efficient tool for constructing approximately-maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees from large alignments. It is widely used in microbiome studies for its ability to handle large datasets quickly, making it ideal for constructing phylogenetic trees from 16S rRNA gene sequences or other marker genes (113).
RAxML (Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood): RAxML is a popular software tool for maximum-likelihood-based phylogenetic inference. It is used to create phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide or amino acid sequences and is known for its speed and accuracy, making it a valuable tool for large-scale microbiome phylogenetic analyses (114).
MEGA (Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis): MEGA is a comprehensive software suite for conducting a variety of phylogenetic and statistical analyses. It allows users to build phylogenetic trees, estimate evolutionary distances, and conduct hypothesis testing. MEGA is user-friendly and widely used in evolutionary studies, including those involving microbial communities (115).
7.2 Evaluation of microbiome diversity metrics: alpha and beta diversity
The assessment of microbiome variations often involves the comparison of alpha and beta diversity measurements, either individually or in combination (116). Alpha diversity metrics evaluate the level of diversity present within a given sample, enabling comparisons across different groups. For instance, it is common to compare the mean species diversity of samples collected from a cohort of organisms afflicted with a particular ailment to that of a cohort devoid of the ailment (117). Species richness estimators, such as observed OTUs and the Chao1 index, are frequently utilized alpha diversity metrics. Additionally, the Shannon and Inverse Simpson indices are employed to evaluate both species richness and evenness. An alternative approach to quantifying diversity is the utilization of phylogenetic richness estimators, like Faith's phylogenetic diversity (117). Richness and evenness estimators, including Shannon and Inverse Simpson, are regarded as more robust due to their reduced sensitivity to sample sequence count variability. The Shannon index is predominantly impacted by the existence of rare operational taxonomic units, while the Inverse Simpson index is predominantly impacted by the presence of numerous or dominant OTUs (10).
As a diversity metric, beta diversity evaluates the dissimilarity of sample characteristics. The distance matrix is frequently obtained by computing the distance between every pair of samples, which is a common method of deriving it. The Bray-Curtis dissimilarity is a widely employed technique for computing beta diversity. It is a quantitative metric that compares two communities by considering the abundance of various taxa. The Weighted Unifrac distance is a metric that measures dissimilarities between two communities by considering phylogenetic relatedness alongside taxonomic abundances. In contrast, the unweighted Unifrac distance is a qualitative measure that solely considers the existence or absence of taxa (117, 118).
7.3 Visualization and statistical techniques in metagenomics research
Metagenomics research, which involves the study of the collective genetic material of microorganisms within a given environment, has experienced a surge in popularity in recent years. One of the key aspects of such investigations is the application of visualization and statistical methods to analyse and interpret the complex datasets generated.
Microbiome studies often entail the comparison of specific taxa, functional elements, microbial diversity, and control group characteristics between different groups. However, the inherent complexity of these datasets, including high dimensionality and potential zero-inflation, presents challenges when employing standard statistical methods. To address these issues, researchers have developed and refined various visualization and statistical techniques tailored for metagenomics data.
Visual inspection of the data is a common starting point, as it can reveal potential correlations or patterns that may warrant further investigation using more rigorous statistical approaches. Dimension-reduction techniques, such as principal coordinate analysis and principal component analysis, are frequently utilized to convert distance matrices into two- or three-dimensional graphical representations of sample relationships. These visualizations allow for the classification and annotation of samples based on relevant metadata (119) (Thomas et al., 2012). Visual comparison of multiple metagenomes and statistical comparison of two metagenomes at a time have been implemented in tools like MEGAN. These methods provide a means to effectively explore and compare large metagenomics datasets (119). As the field of metagenomics continues to evolve, the development and refinement of computational approaches for data analysis and integration remains an active area of research (119).
The transition from classical microbiology to modern metagenomics has been facilitated by advancements in high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies, which have enabled the direct genetic analysis of complex microbial communities (16). The vast amounts of data generated by these technologies require the integration of various computational methods to collect, process, and extract meaningful biological insights.
7.3.1 Utilizing ordination methods for enhanced visualization and analysis in metagenomics
Ordination techniques are essential tools in metagenomics research for visualizing and interpreting complex microbial community data. These methods help researchers to reduce the dimensionality of large datasets, identify patterns, and explore relationships between microbial communities and environmental factors. Below are some key ordination techniques:
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a technique used in metagenomics to reduce data dimensionality by transforming complex datasets into principal components. This method simplifies data visualization by focusing on the principal axes that capture the most variability, which helps in identifying patterns such as clusters, outliers, and trends across samples. PCA results are typically displayed in scatter plots of the first few principal components (120). In contrast, Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) is designed to preserve the rank order of distances between samples rather than their exact numerical distances. This method is particularly suited for non-parametric data and is used to explore beta diversity by visualizing how microbial communities differ across samples. NMDS provides insights into sample dissimilarities by representing them in two or three dimensions, revealing gradients or clusters without relying on parametric assumptions (121).
Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA), on the other hand, integrates aspects of both principal component and regression analyses to investigate how environmental variables influence microbial community composition. CCA correlates community changes with factors like pH or nutrient levels, offering a way to understand ecological drivers of microbial diversity. The results are often presented in biplots, where microbial taxa and environmental variables are depicted together, highlighting their associations and providing insights into the ecological dynamics of the communities (122).
7.4 Statistical techniques in metagenomics research
Statistical techniques are essential for analysing and interpreting metagenomics data, providing insights into microbial community differences, sample classification, and biomarker discovery (123). PERMANOVA (Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance) is a non-parametric method that tests the significance of differences in microbial community composition across various groups or conditions without assuming a specific data distribution (124). It evaluates whether observed differences among groups exceed what would be expected by chance, with results typically presented in distance-based dissimilarity matrices and permutation test outputs. Random Forests is a machine learning technique that builds multiple decision trees to classify samples or predict outcomes based on microbial compositions. It is robust to overfitting and can handle large datasets, with results visualized through feature importance plots and confusion matrices to assess classification performance. LEfSe (Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size) combines linear discriminant analysis with effect size measurements to identify biomarkers by highlighting features that significantly differ between groups (125). This method is used to discover microbial taxa or functional genes that are discriminatory between conditions, with results often displayed in bar plots or cladograms to illustrate the magnitude of differences and key drivers of microbial community variations.
7.5 Differential abundance analysis
Differential abundance analysis in metagenomics identifies and visualizes changes in microbial taxa between conditions. It helps understand how microbial communities respond to factors like environmental changes, dietary interventions, or diseases. Two key visualization techniques are volcano plots and MA plots.
Volcano Plots display statistical significance vs. fold change, with the x-axis showing the magnitude of change in abundance and the y-axis representing significance [usually -log10 (p-value)]. This plot highlights taxa with substantial changes and significant differences, facilitating the identification of key drivers in microbial shifts (126).
MA Plots visualize the relationship between mean abundance and fold change. The x-axis represents average abundance, while the y-axis shows log-fold change between conditions. This plot reveals how changes in abundance correlate with overall levels and helps identify trends or biases (127).
8 Network analysis and machine learning: connecting the dots
These “omic” data kinds each contribute to the puzzle. However, multi-omics’ true potential lies in its ability to integrate these diverse information. Advanced computational tools and network analysis methods find information layer connections and interactions. We can link chemicals to their microbial creators by combining metabolomics and metagenomics data. Integrating transcriptomic and metabolomics data can reveal how gut bacteria metabolic activities affect host intestinal cell gene expression. Microbiome community connections are often studied using network analysis. In various contexts, correlation networks show community structure disruptions. They can also study interkingdom relationships between environmental elements, metabolites, clinical features, and other bacteria in the microbial community. Graphical networks often compare interactions in ill vs. healthy states or show species co-occurrence or mutual exclusion. Machine learning methods can manage complex data and identify useful properties in microbiome datasets with many attributes, making them appealing for evaluation (128). Machine learning aids in deciphering the intricate relationships within the gut ecology and transforming the varied biological data into useful insights (129).
This method employs various types of networks to reveal complex relationships between microbial taxa or genes, offering insights into community structure, functional relationships, and ecological dynamics. Two primary types of networks used in this analysis are co-occurrence networks and correlation networks.
Co-occurrence Networks are designed to illustrate interactions between microbial taxa within a community. In these networks, nodes represent different taxa, and edges denote the correlations or interactions observed between them. Positive edges suggest that taxa frequently occur together, while negative edges indicate that their presence might be mutually exclusive. By visualizing these relationships, researchers can identify groups of taxa that may influence each other's abundance or activity. For example, co-occurrence networks can help uncover ecological partnerships or competitive interactions, providing insights into the stability and functionality of microbial communities (130).
Correlation Networks focus on identifying potential interactions or co-occurrences between microbial species or genes based on their correlation patterns. In these networks, nodes represent microbial species or genes, and edges represent significant correlations between them. Correlation networks are valuable for exploring how different microbial entities relate to each other in terms of abundance or gene expression. They can reveal patterns of co-expression or co-occurrence that might suggest functional relationships or shared environmental preferences. For instance, identifying highly correlated species can provide clues about cooperative metabolic pathways or shared responses to environmental changes (131).
In the area of gut microbiome research, the integration of network analysis and machine learning (ML) has been greatly enhanced by the development of various computational tools. These tools are designed to analyse complex datasets, identify patterns, and map interactions within microbial communities (132).
In microbiome research, tools for unsupervised learning, such as PCA (Principal Components Analysis) and PCoA (Principal Coordinate Analysis), are essential for simplifying high-dimensional data and revealing the structure of microbial communities (133). These techniques reduce the complexity of large datasets by projecting them onto fewer dimensions while preserving critical information. This approach is vital in studies where datasets may contain vast numbers of microbial species or genes. For instance, a few tools such as
QIIME II, a specialized platform for microbiome analysis, incorporates PCA and PCoA tools to visualize variations in microbial composition across different samples, such as comparing gut microbiota between healthy individuals and those with diseases. This platform enables researchers to track microbial community structures over time and under different conditions, offering valuable insights into the factors influencing microbial diversity (25).
Another widely used tool is Emperor, an interactive visualization software that works seamlessly with outputs from QIIME 2 and other microbiome analysis pipelines. Emperor allows researchers to explore and interpret the results of PCA and PCoA in a dynamic, three-dimensional environment, facilitating the identification of patterns and relationships within microbial communities (134). Using the application of these tools, researchers can acquire a deeper understanding of the ways in which microbial communities assemble or separate, ultimately assisting in the recognition of significant microbial taxa and advancing the creation of targeted measures or treatments. These unsupervised learning tools are crucial for transforming complex, high-dimensional data into interpretable visualizations, driving forward the field of microbiome research (135).
9 Key functional annotation tools for microbial genomics
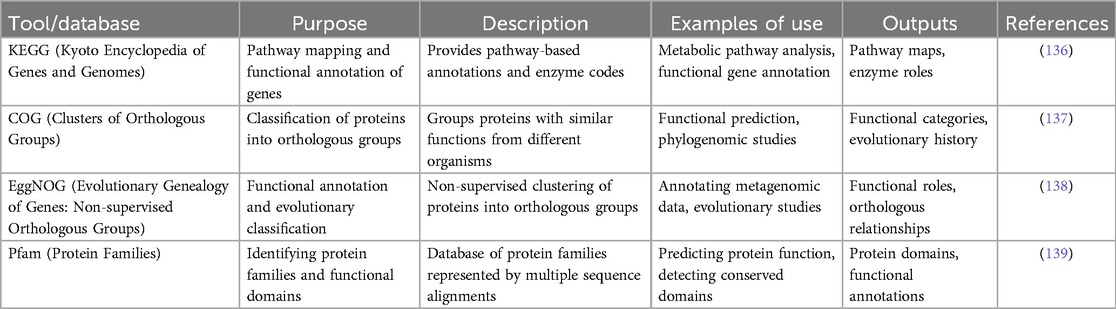
Key functional annotation tools for microbial genomics, such as KEGG, COG, EggNOG, and Pfam, provide critical insights into metabolic pathways, protein functions, and evolutionary relationships, enabling comprehensive analysis of microbial genomes and their functional roles (Table 2).
KEGG offers valuable insights into metabolic pathways and enzyme functions, essential for understanding the biochemical processes within microbial communities. It provides detailed pathway maps and enzyme roles that facilitate the analysis of microbial metabolism and functional capacities (24). COG classifies proteins into orthologous groups, enabling researchers to predict protein functions based on evolutionary conservation across different organisms. This classification supports functional prediction and elucidates the evolutionary history of microbial proteins (140). EggNOG complements COG by employing non-supervised clustering methods to group proteins into orthologous categories, aiding in the annotation of metagenomic data and evolutionary studies. It provides crucial information on functional roles and orthologous relationships, which are vital for interpreting the functional potential of microbial genomes (141). Pfam focuses on identifying protein families and functional domains through multiple sequence alignments, crucial for predicting protein functions and detecting conserved domains, thus enhancing our understanding of protein functionality and evolutionary conservation in microbial species (142).
10 Inferring microbial interaction networks from microbiome data: a comparative analysis of SparCC, CCLasso, and SPEIC-EASI
The study of microbial communities and their interactions within complex ecosystems, such as the human gut, has become a crucial area of research in the field of microbiome science. Researchers have developed several computational methods to infer these intricate networks of microbial interactions from high-throughput sequencing data.
One common approach is to examine pairwise associations between microbial taxa, where networks are established by measuring the similarity or correlation coefficients between pairs of variables. Three commonly used software programs for this purpose are SparCC, CCLasso, and SPEIC-EASI (143, 144).
SparCC and CCLasso are two popular methods that account for the inherent compositional nature of microbiome data, which can lead to spurious correlations if not properly addressed. However, the SPEIC-EASI model is currently the most commonly utilized approach due to its strong ability to estimate interactions using techniques for both sparse neighbourhood and inverse covariance selection, following the initial CLR transformation of the count data (144).
Regression-based techniques, such as sparse regression, Dirichlet-multinomial regression, and generalized boosted linear models, can also be employed to forecast the abundance of a particular species based on the abundance of various combinations of other species (145). Another strategy relies on the presence-absence patterns of taxa in relation to distinct phenotypes or outcomes, which is often referred to as association rule mining.
These complex network analyses, together with machine-learning approaches, provide a more comprehensive understanding of the intricate relationships within the gut ecosystem. They enable researchers to not only identify the microbial players, but also understand their functional roles and how they interact with each other and with the human host.
11 Comparing the interpretability and performance of machine-learning, random forest and decision tree models in clinical predictive modelling
Machine learning is a field within artificial intelligence that enables independent knowledge acquisition and operational improvement through the utilization of input data, without the need for explicit programming (146). Random Forest, an ensemble machine learning technique, is commonly employed for classification and regression tasks. It is often utilized to uncover significant taxonomic and clinical variables that can differentiate various phenotypes or classifications, or predict specific outcomes (147).
Despite being less precise and reliable, techniques like CART analyses are more interpretable and, consequently, more therapeutically actionable. Decision trees allow researchers to gain insights into the significance of variables, their cutoff points, and their order of importance. It is crucial to note that these models should always undergo cross-validation, either through sample and replacement, or by using independent cohorts for training, testing, and validation (148).
The goal of this comparative study is to assess the effectiveness of decision trees, such as those used in CART analyses, and Random Forest models in the analysis of biomedical data. Specifically, we aim to evaluate the trade-offs between model interpretability and predictive performance, as these factors are crucial considerations for clinical decision-making.
Random Forest is an ensemble machine learning technique that constructs multiple decision trees and aggregates their predictions to improve the overall accuracy and stability of the model. This method has been shown to be effective in uncovering significant variables that can differentiate various phenotypes or classifications, or predict specific outcomes in a wide range of scientific fields (149).
On the other hand, decision tree-based models, such as CART, are more interpretable, enabling researchers to gain insights into the significance of variables, their cutoff points, and their order of importance. These insights can be more readily translated into actionable clinical decisions (150).
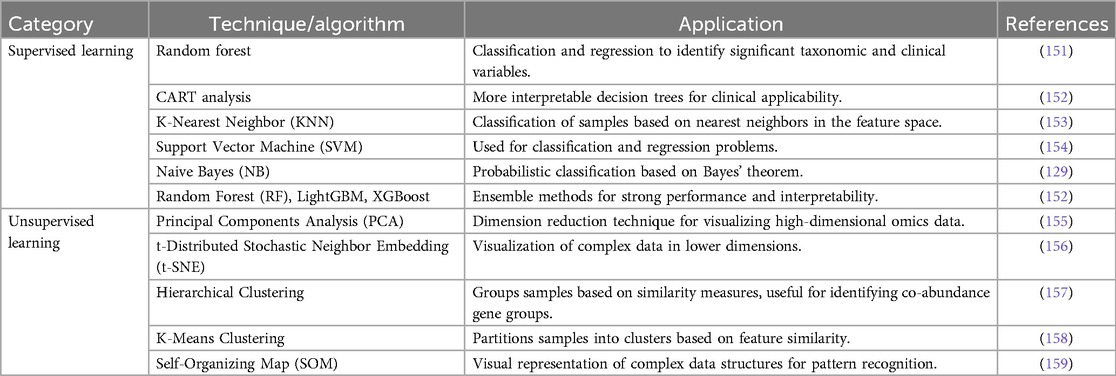
11.1 Unsupervised and supervised machine-learning in gut microbiome analysis
Machine learning algorithms can be broadly classified as either unsupervised learning or supervised learning, and they have been extensively applied in the study of intestinal microbiota (Table 3). Unsupervised learning methodologies obtain and classify novel hidden patterns uniquely from given datasets in which the dependent variables are unknown, and they are frequently described as predictions that are driven by data (160). Dimension reduction and clustering analysis are two main categories of unsupervised learning techniques. For the visualization of omics data, principal components analysis, principal coordinate analysis, and t-distributed stochastic neighbour embedding (t-SNE) (156) are typical dimension reduction techniques that extract a subset of crucial variables from the high-dimensional feature space. Clustering techniques, such as hierarchical clustering, k-means clustering, and self-organizing map, are frequently employed to partition a collection of entities into multiple clusters according to their similarities or dissimilarities. In the study of intestinal microbiota, clustering analysis has been used to discern novel patterns, such as the identification of co-abundance gene groups and enterotypes of the human microbiota.
Unsupervised machine learning algorithms not only derive insights directly from the data and group the data, but also use these insights for data-driven decision making. Supervised learning, on the other hand, utilizes labelled data to train a model that can then make predictions on new, unseen data.
11.2 Supervised and supervised machine-learning in gut microbiome analysis
In contrast, supervised learning methods obtain information and infer a function from input data that includes dependent variables for all samples and independent variables (also known as features). Supervised learning is the process of using known dependent variables from a training dataset to create a machine learning model that can predict the outcomes of new samples. ML models can be used to perform classification problems when the dependent variables are categorical. Because the dependent variables are continuous, they can also be used for regression problems.
The application of both unsupervised and supervised learning techniques has been crucial in the study of gut microbiome, enabling researchers to uncover novel patterns, identify enterotypes, and develop predictive models for various health and disease states (118, 161).
12 Challenges in current applications
The gut microbiota, a complex and dynamic ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms, plays a pivotal role in human health and disease. Understanding the intricate interactions within this microbial community and their impact on the host requires advanced computational tools and cutting-edge machine learning (ML) approaches. These technologies have revolutionized the field of microbiome research, enabling the identification of novel biomarkers for disease diagnosis, treatment, and personalized medicine (162).
One of the primary challenges in gut microbiota research is the vast complexity and diversity of microbial communities. The gut microbiome consists of a host of bacterial, viral, fungal, and archaeal species, each contributing to the overall ecosystem. Traditional sequencing methods, such as 16S rRNA gene sequencing, provide a restricted view of microbial diversity, often missing rare or less abundant species (163). To overcome this, advanced computational tools like metagenomics and metatranscriptomics have been developed to capture a more comprehensive concept of microbial diversity and function. However, these approaches generate massive amounts of data, creating a need for sophisticated data processing and analysis pipelines (164).
Machine learning has emerged as a powerful approach to handle the complexity of microbiome data. By leveraging algorithms capable of detecting patterns and making predictions based on large datasets, ML can identify key microbial features associated with specific health outcomes (165). In case, ML models can be trained to distinguish between healthy and diseased microbiomes, potentially leading to the discovery of biomarkers for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), obesity, and colorectal cancer. Despite these advancements, several challenges persist, including the need for large, well-annotated datasets and the risk of overfitting models to specific cohorts, which can limit the generalizability of findings (129).
Another significant challenge in the application of ML to gut microbiota research is the integration of multi-omics data. The gut microbiome interacts with various host systems, influencing metabolic, immune, and neural processes. To capture this complexity, researchers are increasingly turning to multi-omics approaches, integrating data from genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and more. Tools like Multi-Omics Factor Analysis (MOFA) and Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) have been developed to facilitate this integration, enabling a more holistic understanding of microbiome-host interactions. However, the integration of such diverse data types requires advanced computational frameworks and careful consideration of data harmonization and normalization techniques (166).
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in microbiome analysis face significant challenges, particularly regarding reproducibility, replicability, robustness, and generalizability. These challenges are exacerbated by the complex, interdisciplinary nature of microbiome research, where slight variations in methods, data processing, and analytical frameworks can lead to divergent results (152). Reproducibility issues are not merely technical but are deeply rooted in the lack of standardized methods, the complexity of biological data, and the evolving nature of computational tools. The historical example of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's struggle to have his microbial observations accepted illustrates the enduring difficulty of ensuring that scientific work can be precisely replicated by others. Modern examples, like the challenge posed by Philip Bourne's group to reproduce their computational analysis, underscore the immense effort required to replicate complex bioinformatics research, even when transparency is prioritized. These challenges highlight the need for greater methodological transparency, standardization, and collaborative efforts to enhance the robustness and generalizability of AI and ML approaches in microbiome research (167).
Furthermore, ethical and privacy concerns associated with microbiome research pose additional challenges. As the field moves towards personalized medicine, where individual microbiome profiles guide treatment decisions, issues related to data privacy, consent, and ownership become increasingly important. Researchers must navigate these challenges carefully, ensuring that the benefits of microbiome-based interventions are realized without compromising patient privacy or autonomy (168).
Despite these challenges, the potential of advanced computational tools and ML in gut microbiota research is immense (Figure 3). The integration of these approaches holds promise for the discovery of novel biomarkers that can revolutionize disease diagnosis and treatment. For instance, biomarkers identified through ML could lead to the development of non-invasive diagnostic tests for gastrointestinal disorders or the creation of personalized probiotics tailored to an individual's unique microbiome composition.
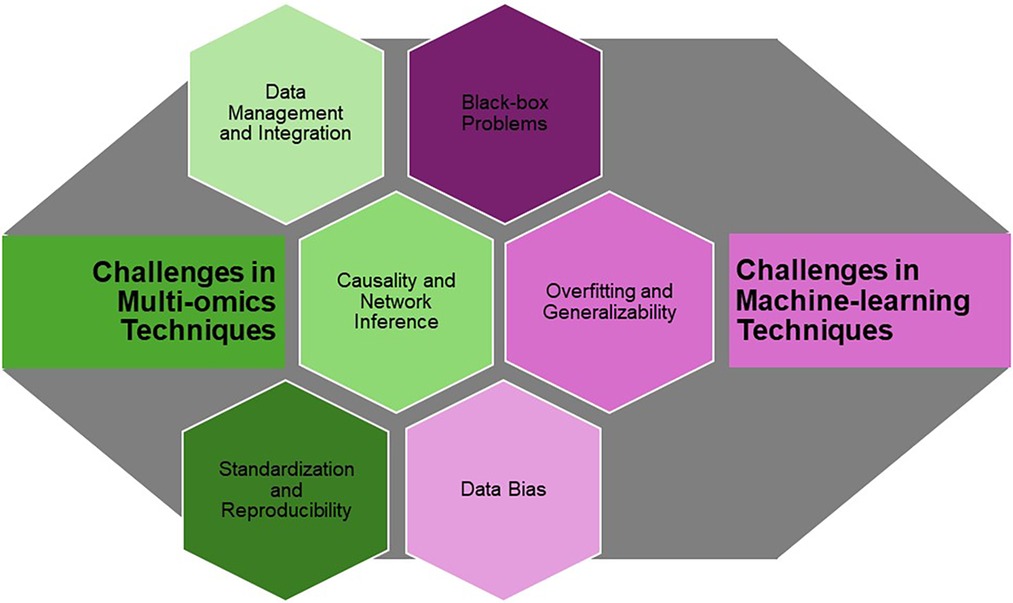
Figure 3. Potential challenges and considerations in multi-omics and machine learning for advancing gut microbiome research.
To fully realize these opportunities, ongoing collaboration between microbiologists, data scientists, clinicians, and ethicists is essential. Interdisciplinary teams are needed to develop and refine computational tools, address the challenges of data integration and interpretability, and ensure that microbiome research is conducted ethically and responsibly. Additionally, the development of standardized protocols for data collection, analysis, and reporting will be crucial in advancing the field and enabling the translation of research findings into clinical practice.
13 Conclusion
The analysis of the gut microbiome has undergone a transformative shift, driven by the integration of advanced computational tools, multi-omics techniques, and the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning (169). This convergence of technologies is enabling researchers to gain unprecedented insights into the complex dynamics and interactions within the gut microbial ecosystem.
One of the key elements fuelling this progress is the availability of high-throughput sequencing technologies that generate vast datasets across various omics levels, including genomics, transcriptomic, proteomics, and metabolomics. These data-rich studies are in turn supported by a suite of powerful bioinformatics software, such as QIIME and Mothur, which facilitate the processing and analysis of the microbiome data (26, 170).
The multi-omics approach, which combines data from different biological layers, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome. By integrating genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomics information, researchers can uncover intricate relationships between microbial composition, gene expression, protein function, and metabolic profiles. Artificial intelligence and machine learning play a pivotal role in the interpretation of this complex multi-omics data. These computational techniques excel at pattern recognition, enabling the identification of correlations and associations within large datasets. Furthermore, AI and ML models can be leveraged for predictive modelling, helping to forecast disease outcomes or responses to treatments based on microbiome profiles. This, in turn, has led to advancements in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of personalized medicine approaches. The integration of these cutting-edge tools and techniques has opened up new frontiers in gut microbiome research. Researchers can now explore the intricate interactions between the microbiome and the host, uncover biomarkers for disease, and develop more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions (Figure 4). As this field continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more transformative breakthroughs in our understanding and management of various health conditions. The integration of multi-omics techniques, including metatranscriptomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics, has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of the gut microbiome and its complex interactions with human health and disease. These approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiome by capturing not only the taxonomic composition, but also the functional activities, metabolic processes, and interactions within the microbial community. Metatranscriptomics examines the RNA molecules expressed by the microbial community, revealing insights into their functional activities and gene expression patterns. Metaproteomics focuses on identifying and quantifying the proteins expressed by the gut microbiome, providing valuable information about their metabolic activities and functional capabilities, as well as the interactions between the microbiome and the host. Furthermore, metabolomics, the study of small-molecule metabolites, can uncover the complex interplay between the microbial community and the host's physiology, identifying metabolic pathways and biomarkers associated with various health and disease states. The integration of these multi-omics approaches has enabled researchers to unravel the complex relationships between the gut microbiome and human health, leading to the identification of novel biomarkers and the development of predictive models for personalized medicine.
Figure 4. Different computational, bioinformatics, AI & ML approaches in gut microbiome analysis and biomarker discovery for achieving D3 (diagnostics, discovery and decision) and goals of precision medicine.
Author contributions
TD: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Conceptualization. CX: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. AK: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. (2017) 474(11):1823–36. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160510
2. Chen M, Yao C, Qin Y, Cui X, Li P, Ji Z, et al. Mutations of Msh5 in nonobstructive azoospermia (noa) and rescued via in vivo gene editing. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00710-4
3. Afzaal M, Saeed F, Shah YA, Hussain M, Rabail R, Socol CT, et al. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: unveiling the relationship. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:999001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.999001
4. Cardona D, Roman P. New perspectives in health: gut microbiota. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19(10):1–3. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19105828
5. Sze MA, Schloss PD. Looking for a signal in the noise: revisiting obesity and the microbiome. mBio. (2016) 7(4):e01018–16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01018-16
6. Slouha E, Rezazadah A, Farahbod K, Gerts A, Clunes LA, Kollias TF. Type-2 diabetes Mellitus and the gut microbiota: systematic review. Cureus. (2023) 15(11):e49740. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49740
7. Nesci A, Carnuccio C, Ruggieri V, D'Alessandro A, Di Giorgio A, Santoro L, et al. Gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease: evidence on the metabolic and inflammatory background of a complex relationship. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(10):1–3. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109087
8. Asseri AH, Bakhsh T, Abuzahrah SS, Ali S, Rather IA. The gut dysbiosis-cancer axis: illuminating novel insights and implications for clinical practice. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1208044. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1208044
9. Tiwari P, Dwivedi R, Bansal M, Tripathi M, Dada R. Role of gut microbiota in neurological disorders and its therapeutic significance. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(4):1650. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041650
10. Gevers D, Knight R, Petrosino JF, Huang K, McGuire AL, Birren BW, et al. The human microbiome project: a community resource for the healthy human microbiome. PLoS Biol. (2012) 10(8):e1001377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001377
11. Shi Y, Wang G, Lau HC, Yu J. Metagenomic sequencing for microbial DNA in human samples: emerging technological advances. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(4):2181. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042181
12. Zhang L, Chen F, Zeng Z, Xu M, Sun F, Yang L, et al. Advances in metagenomics and its application in environmental microorganisms. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:766364. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.766364
13. Berg G, Rybakova D, Fischer D, Cernava T, Verges MC, Charles T, et al. Microbiome definition Re-visited: old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome. (2020) 8(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00875-0
14. Wensel CR, Pluznick JL, Salzberg SL, Sears CL. Next-generation sequencing: insights to advance clinical investigations of the microbiome. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(7):1–3. doi: 10.1172/JCI154944
15. Perez-Cobas AE, Gomez-Valero L, Buchrieser C. Metagenomic approaches in microbial ecology: an update on whole-genome and marker gene sequencing analyses. Microb Genom. (2020) 6(8):mgen000409. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000409
16. Escobar-Zepeda A, Vera-Ponce de Leon A, Sanchez-Flores A. The road to metagenomics: from microbiology to DNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics. Front Genet. (2015) 6:348. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00348
17. Yen S, Johnson JS. Metagenomics: a path to understanding the gut microbiome. Mamm Genome. (2021) 32(4):282–96. doi: 10.1007/s00335-021-09889-x
18. Fuks G, Elgart M, Amir A, Zeisel A, Turnbaugh PJ, Soen Y, et al. Combining 16s rrna gene Variable regions enables high-resolution microbial community profiling. Microbiome. (2018) 6(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0396-x
19. Zampieri G, Campanaro S, Angione C, Treu L. Metatranscriptomics-guided genome-scale metabolic modeling of microbial communities. Cell Rep Methods. (2023) 3(1):100383. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100383
20. Wu J, Singleton SS, Bhuiyan U, Krammer L, Mazumder R. Multi-omics approaches to studying gastrointestinal microbiome in the context of precision medicine and machine learning. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1337373. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1337373
21. Aguiar-Pulido V, Huang W, Suarez-Ulloa V, Cickovski T, Mathee K, Narasimhan G. Metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics approaches for microbiome analysis. Evol Bioinform Online. (2016) 12(Suppl 1):5–16. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S36436
22. Pammi M, Aghaeepour N, Neu J. Multiomics, artificial intelligence, and precision medicine in perinatology. Pediatr Res. (2023) 93(2):308–15. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02181-x
23. Puig-Castellví F, Pacheco-Tapia R, Deslande M, Jia M, Andrikopoulos P, Chechi K, et al. Advances in the integration of metabolomics and metagenomics for human gut microbiome and their clinical applications. TrAC Trends Analytic Chem. (2023) 167:117248. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117248
24. Zhou Z, Tran PQ, Breister AM, Liu Y, Kieft K, Cowley ES, et al. Metabolic: high-throughput profiling of microbial genomes for functional traits, metabolism, biogeochemistry, and community-scale functional networks. Microbiome. (2022) 10(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01213-8
25. Estaki M, Jiang L, Bokulich NA, McDonald D, Gonzalez A, Kosciolek T, et al. Qiime 2 enables comprehensive end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome data and comparative studies with publicly available data. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. (2020) 70(1):e100. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.100
26. Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using qiime 2. Nat Biotechnol. (2019) 37(8):852–7. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
27. Ehrlich SD. The human gut microbiome impacts health and disease. Comptes Rendus Biologies. (2016) 339(7-8):319–23. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2016.04.008
28. Fouhy F, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C, Cotter PD. Composition of the early intestinal Microbiota: knowledge, knowledge gaps and the use of high-throughput sequencing to address these gaps. Gut Microbes. (2012) 3(3):203–20. doi: 10.4161/gmic.20169
29. Guinane CM, Cotter PD. Role of the gut Microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. (2013) 6(4):295–308. doi: 10.1177/1756283X13482996
30. Satam H, Joshi K, Mangrolia U, Waghoo S, Zaidi G, Rawool S, et al. Next-Generation sequencing technology: current trends and advancements. Biology (Basel). (2023) 12(7):997. doi: 10.3390/biology12070997
31. Jian C, Luukkonen P, Yki-Jarvinen H, Salonen A, Korpela K. Quantitative pcr provides a simple and accessible method for quantitative microbiota profiling. PLoS One. (2020) 15(1):e0227285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227285
32. Fujimoto C, Maeda H, Kokeguchi S, Takashiba S, Nishimura F, Arai H, et al. Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (Dgge) to the analysis of microbial communities of subgingival plaque. J Periodontal Res. (2003) 38(4):440–5. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0765.2003.02607.x
33. Schutte UM, Abdo Z, Bent SJ, Shyu C, Williams CJ, Pierson JD, et al. Advances in the use of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-rflp) analysis of 16s rrna genes to characterize microbial communities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. (2008) 80(3):365–80. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1565-4
34. Nguyen T-Q, Bomberg M, Nuppunen-Puputti M, Ratia-Hanby V, Sohlberg E, Rajala P. Integrating double-labeling hcr-fish into a multidisciplinary pipeline for biofouling assessment on austenitic stainless steel in brackish seawater circuit. Environ Technol Innov. (2024) 36:103782. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2024.103782
35. Yang M-Q, Wang Z-J, Zhai C-B, Chen L-Q. Research progress on the application of 16s rrna gene sequencing and machine learning in forensic microbiome individual identification. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1360457. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1360457
36. Van Den Bossche T, Arntzen MØ, Becher D, Benndorf D, Eijsink VG, Henry C, et al. The metaproteomics initiative: a coordinated approach for propelling the functional characterization of microbiomes. Microbiome. (2021) 9(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01176-w
37. Forbes BA, Hall GS, Miller MB, Novak SM, Rowlinson M-C, Salfinger M, et al. Practical guidance for clinical microbiology laboratories: mycobacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2018) 31(2):e00038-17. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00038-17
38. Nam NN, Do HDK, Loan Trinh KT, Lee NY. Metagenomics: an effective approach for exploring microbial diversity and functions. Foods. (2023) 12(11):2140. doi: 10.3390/foods12112140
39. Chaudhari DS, Jain S, Yata VK, Mishra SP, Kumar A, Fraser A, et al. Unique trans-kingdom microbiome structural and functional signatures predict cognitive decline in older adults. Geroscience. (2023) 45(5):2819–34. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00799-1
40. Schnorr SL. Meanings, measurements, and musings on the significance of patterns in human microbiome variation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2018) 53:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2018.06.014
41. Peterson D, Bonham KS, Rowland S, Pattanayak CW, Consortium R, Klepac-Ceraj V. Comparative analysis of 16s rrna gene and metagenome sequencing in pediatric gut microbiomes. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:670336. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.670336
42. Jovel J, Patterson J, Wang W, Hotte N, O'Keefe S, Mitchel T, et al. Characterization of the gut microbiome using 16s or shotgun metagenomics. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:459. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00459
43. Afshinnekoo E, Chou C, Alexander N, Ahsanuddin S, Schuetz AN, Mason CE. Precision metagenomics: rapid metagenomic analyses for infectious disease diagnostics and public health surveillance. J Biomol Tech. (2017) 28(1):40–5. doi: 10.7171/jbt.17-2801-007
44. Gonzalez A, Navas-Molina JA, Kosciolek T, McDonald D, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Ackermann G, et al. Qiita: rapid, web-enabled microbiome meta-analysis. Nat Methods. (2018) 15(10):796–8. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0141-9
45. Jiang Y, Xiong X, Danska J, Parkinson J. Metatranscriptomic analysis of diverse microbial communities reveals core metabolic pathways and microbiome-specific functionality. Microbiome. (2016) 4(2):2. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0146-x
46. Issa Isaac N, Philippe D, Nicholas A, Raoult D, Eric C. Metaproteomics of the human gut Microbiota: challenges and contributions to other omics. Clin Mass Spectrom. (2019) 14 Pt A:18–30. doi: 10.1016/j.clinms.2019.06.001
47. Armengaud J. Metaproteomics to understand how microbiota function: the crystal ball predicts a promising future. Environ Microbiol. (2023) 25(1):115–25. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16238
48. Wang J, Dong P, Zheng S, Mai Y, Ding J, Pan P, et al. Advances in gut microbiome in metabonomics perspective: based on bibliometrics methods and visualization analysis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1196967. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1196967
49. Bokulich NA, Ziemski M, Robeson MS 2nd, Kaehler BD. Measuring the microbiome: best practices for developing and benchmarking microbiomics methods. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2020) 18:4048–62. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.049
50. Matchado MS, Ruhlemann M, Reitmeier S, Kacprowski T, Frost F, Haller D, et al. On the limits of 16s rRNA gene-based metagenome prediction and functional profiling. Microb Genom. (2024) 10(2):001203. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001203
51. Handelsman J. Metagenomics: application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. (2004) 68(4):669–85. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.4.669-685.2004
52. Gilbert JA, Dupont CL. Microbial metagenomics: beyond the genome. Ann Rev Mar Sci. (2011) 3:347–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142811
53. Quince C, Walker AW, Simpson JT, Loman NJ, Segata N. Shotgun metagenomics, from sampling to analysis. Nat Biotechnol. (2017) 35(9):833–44. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3935
54. Riesenfeld CS, Schloss PD, Handelsman J. Metagenomics: genomic analysis of microbial communities. Annu Rev Genet. (2004) 38:525–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.091216
55. Kristensen DM, Mushegian AR, Dolja VV, Koonin EV. New dimensions of the virus world discovered through metagenomics. Trends Microbiol. (2010) 18(1):11–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.11.003
56. Luo C, Tsementzi D, Kyrpides N, Read T, Konstantinidis KT. Direct comparisons of illumina vs. Roche 454 sequencing technologies on the same microbial community DNA sample. PLoS One. (2012) 7(2):e30087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030087
57. Claesson MJ, Clooney AG, O'Toole PW. A clinician’s guide to microbiome analysis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14(10):585–95. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.97
58. Wood DE, Salzberg SL. Kraken: ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. (2014) 15(3):R46. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-3-r46
59. Truong DT, Franzosa EA, Tickle TL, Scholz M, Weingart G, Pasolli E, et al. Metaphlan2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nat Methods. (2015) 12(10):902–3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3589
60. Purushothaman S, Meola M, Egli A. Combination of whole genome sequencing and metagenomics for microbiological diagnostics. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(17):9834. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179834
61. Li D, Liu CM, Luo R, Sadakane K, Lam TW. Megahit: an ultra-fast single-node solution for large and Complex metagenomics assembly via Succinct De Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics. (2015) 31(10):1674–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv033
62. Namiki T, Hachiya T, Tanaka H, Sakakibara Y. Metavelvet: an extension of velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40(20):e155. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks678
63. Peng Y, Leung HC, Yiu SM, Chin FY. Idba-Ud: a de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics. (2012) 28(11):1420–8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts174
64. Nurk S, Meleshko D, Korobeynikov A, Pevzner PA. Metaspades: a new Versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. (2017) 27(5):824–34. doi: 10.1101/gr.213959.116
65. Abdul-Aziz MA, Cooper A, Weyrich LS. Exploring relationships between host genome and microbiome: new insights from genome-wide association studies. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:1611. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01611
66. Cepeda V, Liu B, Almeida M, Hill CM, Koren S, Treangen TJ, et al. Metacompass: reference-guided assembly of metagenomes. bioRxiv. (2017):212506. doi: 10.1101/212506
67. Ayling M, Clark MD, Leggett RM. New approaches for metagenome assembly with short reads. Brief Bioinform. (2020) 21(2):584–94. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz020
68. Calle ML, Pujolassos M, Susin A. Coda4microbiome: compositional data analysis for microbiome cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. BMC Bioinformatics. (2023) 24(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05205-3
69. Wang F, Xiang L, Sze-Yin Leung K, Elsner M, Zhang Y, Guo Y, et al. Emerging contaminants: a one health perspective. Innovation (Camb). (2024) 5(4):100612. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100612
70. Pavlopoulos GA, Baltoumas FA, Liu S, Selvitopi O, Camargo AP, Nayfach S, et al. Unraveling the functional dark matter through global metagenomics. Nature. (2023) 622(7983):594–602. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06583-7
71. Pasolli E, Asnicar F, Manara S, Zolfo M, Karcher N, Armanini F, et al. Extensive unexplored human microbiome diversity revealed by over 150,000 genomes from metagenomes spanning age, geography, and lifestyle. Cell. (2019) 176(3):649–62 e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.001
72. Kumar B, Lorusso E, Fosso B, Pesole G. A comprehensive overview of microbiome data in the light of machine learning applications: categorization, accessibility, and future directions. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1343572. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1343572
73. Agus A, Clement K, Sokol H. Gut Microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut. (2021) 70(6):1174–82. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323071
74. Lamichhane S, Sen P, Dickens AM, Oresic M, Bertram HC. Gut metabolome meets microbiome: a methodological perspective to understand the relationship between host and microbe. Methods. (2018) 149:3–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.04.029
75. Zierer J, Jackson MA, Kastenmuller G, Mangino M, Long T, Telenti A, et al. The fecal metabolome as a functional readout of the gut microbiome. Nat Genet. (2018) 50(6):790–5. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0135-7
76. Peters DL, Wang W, Zhang X, Ning Z, Mayne J, Figeys D. Metaproteomic and metabolomic approaches for characterizing the gut microbiome. Proteomics. (2019) 19(16):e1800363. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800363
77. Chen Y, Li EM, Xu LY. Guide to metabolomics analysis: a bioinformatics workflow. Metabolites. (2022) 12(4):357. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040357
78. Van Den Bossche T, Arntzen MØ, Becher D, Benndorf D, Eijsink VGH, Henry C, et al. The metaproteomics initiative: a coordinated approach for propelling the functional characterization of microbiomes. Microbiome. (2021) 9(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01176-w
79. Bashiardes S, Zilberman-Schapira G, Elinav E. Use of metatranscriptomics in microbiome research. Bioinform Biol Insights. (2016) 10:19–25. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S34610
80. Poretsky RS, Bano N, Buchan A, LeCleir G, Kleikemper J, Pickering M, et al. Analysis of microbial gene transcripts in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2005) 71(7):4121–6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.4121-4126.2005
81. Botero LM, D'Imperio S, Burr M, McDermott TR, Young M, Hassett DJ. Poly(a) polymerase modification and reverse transcriptase pcr amplification of environmental rna. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2005) 71(3):1267–75. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1267-1275.2005
82. Sharuddin SS, Ramli N, Yusoff MZM, Muhammad NAN, Ho LS, Maeda T. Advancement of metatranscriptomics towards productive agriculture and sustainable environment: a review. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(7):3737. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073737
83. Alonso A, Marsal S, Julia A. Analytical methods in untargeted metabolomics: state of the art in 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2015) 3:23. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00023
84. Emwas AH, Roy R, McKay RT, Tenori L, Saccenti E, Gowda GAN, et al. Nmr spectroscopy for metabolomics research. Metabolites. (2019) 9(7):1–15. doi: 10.3390/metabo9070123
85. Castro-Puyana M, Herrero M. Metabolomics approaches based on mass spectrometry for food safety, quality and traceability. TrAC Trends Analytic Chem. (2013) 52:74–87. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.05.016
86. Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, et al. The gencode V7 catalog of human long noncoding rnas: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. (2012) 22(9):1775–89. doi: 10.1101/gr.132159.111
87. Johnson CH, Patterson AD, Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ. Xenobiotic metabolomics: major impact on the metabolome. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2012) 52:37–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134748
88. Stoler N, Nekrutenko A. Sequencing error profiles of illumina sequencing instruments. NAR Genom Bioinform. (2021) 3(1):lqab019. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqab019
89. Weirather JL, de Cesare M, Wang Y, Piazza P, Sebastiano V, Wang XJ, et al. Comprehensive comparison of pacific biosciences and Oxford Nanopore technologies and their applications to transcriptome analysis. F1000Res. (2017) 6:100. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10571.2
90. Loeffler T, Schilcher I, Flunkert S, Hutter-Paier B. Neurofilament-light chain as biomarker of neurodegenerative and rare diseases with high translational value. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:579. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00579
91. Armstrong J, Fiddes IT, Diekhans M, Paten B. Whole-genome alignment and comparative annotation. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. (2019) 7:41–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-020518-115005
92. Jovel J, Nimaga A, Jordan T, O'Keefe S, Patterson J, Thiesen A, et al. Metagenomics versus metatranscriptomics of the murine gut microbiome for assessing microbial metabolism during inflammation. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:829378. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.829378
93. Shakya M, Lo CC, Chain PSG. Advances and challenges in metatranscriptomic analysis. Front Genet. (2019) 10:904. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00904
94. Kelley DR, Liu B, Delcher AL, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Gene prediction with glimmer for metagenomic sequences augmented by classification and clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40(1):e9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1067
95. Gemayel K, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M. Metagenemark-2: improved gene prediction in metagenomes. bioRxiv. (2022):2022.07.25.500264. doi: 10.1101/2022.07.25.500264
96. Saripella GV, Sonnhammer EL, Forslund K. Benchmarking the next generation of homology inference tools. Bioinformatics. (2016) 32(17):2636–41. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw305
97. Kozo N, Keiichiro O, Shigehiko K, Takahashi K. Keggscape: a cytoscape app for pathway data integration. F1000Res. (2014) 3:144. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.4524.1
98. Temperton B, Giovannoni SJ. Metagenomics: microbial diversity through a scratched lens. Curr Opin Microbiol. (2012) 15(5):605–12. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.07.001
99. D’Argenio V, Salvatore F. The role of the gut microbiome in the healthy adult status. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2015) 451:97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.01.003
100. Wani AK, Dhanjal DS, Akhtar N, Chopra C, Goyal A, Singh R. Role of genomics, metagenomics, and other meta-omics approaches for expunging the environmental contaminants by bioremediation. In: Kumar V, Garg VK, Kumar S, Biswas JK, editors. Omics for Environmental Engineering and Microbiology Systems. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press (2022). p. 19–51.
101. Dantas G, Sommer MO, Degnan PH, Goodman AL. Experimental approaches for defining functional roles of microbes in the human gut. Ann Rev Microbiol. (2013) 67(1):459–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155642
102. Aziz RK, Breitbart M, Edwards RA. Transposases are the most abundant, most ubiquitous genes in nature. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38(13):4207–17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq140
103. Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. (2020) 30(6):492–506. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7
104. Noecker C, McNally CP, Eng A, Borenstein E. High-resolution characterization of the human microbiome. Transl Res. (2017) 179:7–23. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.012
105. Bikel S, Valdez-Lara A, Cornejo-Granados F, Rico K, Canizales-Quinteros S, Soberon X, et al. Combining metagenomics, metatranscriptomics and viromics to explore novel microbial interactions: towards a systems-level understanding of human microbiome. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2015) 13:390–401. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2015.06.001
106. Galloway-Pena J, Hanson B. Tools for analysis of the microbiome. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65(3):674–85. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06091-y
107. Maranga M, Szczerbiak P, Bezshapkin V, Gligorijevic V, Chandler C, Bonneau R, et al. Comprehensive functional annotation of metagenomes and microbial genomes using a deep learning-based method. mSystems. (2023) 8(2):e0117822. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01178-22
108. Wang L, Li F, Gu B, Qu P, Liu Q, Wang J, et al. Metaomics in clinical laboratory: potential driving force for innovative disease diagnosis. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:883734. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.883734
109. Hassler HB, Probert B, Moore C, Lawson E, Jackson RW, Russell BT, et al. Phylogenies of the 16s rrna gene and its hypervariable regions lack concordance with core genome phylogenies. Microbiome. (2022) 10(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01295-y
110. McMurdie PJ, Holmes S. Phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One. (2013) 8(4):e61217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061217
111. Prodan A, Tremaroli V, Brolin H, Zwinderman AH, Nieuwdorp M, Levin E. Comparing bioinformatic pipelines for microbial 16s rrna amplicon sequencing. PLoS One. (2020) 15(1):e0227434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227434
112. Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. Beast: bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol. (2007) 7:214. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-214
113. Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. Fasttree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One. (2010) 5(3):e9490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009490
114. Stamatakis A. Raxml version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. (2014) 30(9):1312–3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
115. Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. Mega5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. (2011) 28(10):2731–9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121
116. Human Microbiome Project C. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature. (2012) 486(7402):207–14. doi: 10.1038/nature11234
117. Finotello F, Mayer C, Plattner C, Laschober G, Rieder D, Hackl H, et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-Seq data. Genome Med. (2019) 11(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0638-6
118. Hu H, Lin A, Kong M, Yao X, Yin M, Xia H, et al. Intestinal microbiome and Nafld: molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J Gastroenterol. (2020) 55(2):142–58. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01649-8
119. Mitra S, Forster-Fromme K, Damms-Machado A, Scheurenbrand T, Biskup S, Huson DH, et al. Analysis of the intestinal microbiota using solid 16s rrna gene sequencing and solid shotgun sequencing. BMC Genomics. (2013) 14 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S5-S16
120. Alshawaqfeh M, Bashaireh A, Serpedin E, Suchodolski J. Consistent metagenomic biomarker detection via robust pca. Biol Direct. (2017) 12(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13062-017-0175-4
121. Rajput V, Yadav R, Dharne MS. Metagenomic exploration reveals a differential patterning of antibiotic resistance genes in urban and peri-urban stretches of a riverine system. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2021) 28(46):66477–84. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16910-y
122. Rafiq T, Stearns JC, Shanmuganathan M, Azab SM, Anand SS, Thabane L, et al. Integrative multiomics analysis of infant gut microbiome and serum metabolome reveals key molecular biomarkers of early onset childhood obesity. Heliyon. (2023) 9(6):e16651. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16651
123. Navgire GS, Goel N, Sawhney G, Sharma M, Kaushik P, Mohanta YK, et al. Analysis and interpretation of metagenomics data: an approach. Biol Proced Online. (2022) 24(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12575-022-00179-7
124. Garrido-Martin D, Calvo M, Reverter F, Guigo R. A fast non-parametric test of association for multiple traits. Genome Biol. (2023) 24(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03076-8
125. Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, et al. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. (2011) 12(6):R60. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
126. Perez-Prieto I, Vargas E, Salas-Espejo E, Lull K, Canha-Gouveia A, Perez LA, et al. Gut microbiome in endometriosis: a cohort study on 1000 individuals. BMC Med. (2024) 22(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03503-y
127. Fernandes AD, Reid JN, Macklaim JM, McMurrough TA, Edgell DR, Gloor GB. Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: characterizing RNA-Seq, 16s rrna gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis. Microbiome. (2014) 2:15. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-2-15
128. Knight R, Vrbanac A, Taylor BC, Aksenov A, Callewaert C, Debelius J, et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2018) 16(7):410–22. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0029-9
129. Marcos-Zambrano LJ, Karaduzovic-Hadziabdic K, Loncar Turukalo T, Przymus P, Trajkovik V, Aasmets O, et al. Applications of machine learning in human microbiome studies: a review on feature selection, biomarker identification, disease prediction and treatment. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:634511. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.634511
130. Pan Z, Chen Y, Zhou M, McAllister TA, Guan LL. Microbial interaction-driven community differences as revealed by network analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2021) 19:6000–8. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.10.035
131. Matchado MS, Lauber M, Reitmeier S, Kacprowski T, Baumbach J, Haller D, et al. Network analysis methods for studying microbial communities: a Mini review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2021) 19:2687–98. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.001
132. Rajkomar A, Dean J, Kohane I. Machine learning in medicine. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380(14):1347–58. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1814259
133. Hernandez Medina R, Kutuzova S, Nielsen KN, Johansen J, Hansen LH, Nielsen M, et al. Machine learning and deep learning applications in microbiome research. ISME Commun. (2022) 2(1):98. doi: 10.1038/s43705-022-00182-9
134. Vazquez-Baeza Y, Pirrung M, Gonzalez A, Knight R. Emperor: a tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience. (2013) 2(1):16. doi: 10.1186/2047-217X-2-16
135. Jiang Y, Luo J, Huang D, Liu Y, Li DD. Machine learning advances in microbiology: a review of methods and applications. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:925454. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.925454
136. Kanehisa M, Goto S. Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. (2000) 28(1):27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27
137. Kurokawa K, Itoh T, Kuwahara T, Oshima K, Toh H, Toyoda A, et al. Comparative metagenomics revealed commonly enriched gene sets in human gut microbiomes. DNA Res. (2007) 14(4):169–81. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsm018
138. Dias CK, Starke R, Pylro VS, Morais DK. Database limitations for studying the human gut microbiome. PeerJ Comput Sci. (2020) 6:e289. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.289
139. Yang P, Zheng W, Ning K, Zhang Y. Decoding the link of microbiome niches with homologous sequences enables accurately targeted protein structure prediction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2021) 118(49):e2110828118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2110828118
140. Mendler K. Large-Scale Phylogenomic Visualization and Analysis of Functional Traits in Bacteria. Waterloo, ON: University of Waterloo (2019).
141. Muller J, Szklarczyk D, Julien P, Letunic I, Roth A, Kuhn M, et al. Eggnog V2.0: extending the evolutionary genealogy of genes with enhanced non-supervised orthologous groups, species and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38(Database issue):D190–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp951
142. Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, et al. Pfam: the protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49(D1):D412–D9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa913
143. Kurtz ZD, Muller CL, Miraldi ER, Littman DR, Blaser MJ, Bonneau RA. Sparse and compositionally robust inference of microbial ecological networks. PLoS Comput Biol. (2015) 11(5):e1004226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004226
144. Fang H, Huang C, Zhao H, Deng M. Cclasso: correlation inference for compositional data through lasso. Bioinformatics. (2015) 31(19):3172–80. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv349
145. Maurice CF, Haiser HJ, Turnbaugh PJ. Xenobiotics shape the physiology and gene expression of the active human gut microbiome. Cell. (2013) 152(1-2):39–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.052
146. Li Z, Yoon J, Zhang R, Rajabipour F, Srubar WV III, Dabo I, et al. Machine learning in concrete science: applicatioa. NPJ Computational Materials. (2022) 8(1):127. doi: 10.1038/s41524-022-00810-x
147. Simon HY, Siddle KJ, Park DJ, Sabeti PC. Benchmarking metagenomics tools for taxonomic classification. Cell. (2019) 178(4):779–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.010
148. Song Y-Y, Ying L. Decision tree methods: applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch Psychiatr. (2015) 27(2):130. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.215044
149. Palimkar P, Shaw RN, Ghosh A. Machine Learning Technique to Prognosis Diabetes Disease: Random Forest Classifier Approach. Advanced Computing and Intelligent Technologies: Proceedings of ICACIT 2021. Springer (2022).
150. Banerjee M, Reynolds E, Andersson HB, Nallamothu BK. Tree-Based analysis: a practical approach to create clinical decision-making tools. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. (2019) 12(5):e004879. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004879
151. Wilhelm RC, van Es HM, Buckley DH. Predicting measures of soil health using the microbiome and supervised machine learning. Soil Biol Biochem. (2022) 164:108472. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108472
152. Li P, Luo H, Ji B, Nielsen J. Machine learning for data integration in human gut microbiome. Microbial Cell Factor. (2022) 21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01973-4
153. Wu S, Chen Y, Li Z, Li J, Zhao F, Su X. Towards multi-label classification: next step of machine learning for microbiome research. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2021) 19:2742–9. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.054
154. Nakano Y, Takeshita T, Kamio N, Shiota S, Shibata Y, Suzuki N, et al. Supervised machine learning-based classification of oral malodor based on the microbiota in saliva samples. Artif Intell Med. (2014) 60(2):97–101. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2013.12.001
155. Namkung J. Machine learning methods for microbiome studies. J Microbiol. (2020) 58(3):206–16. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0066-8
156. Xu X, Xie Z, Yang Z, Li D, Xu X. A T-sne based classification approach to compositional microbiome data. Front Genet. (2020) 11:620143. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.620143
157. Shi Y, Zhang L, Peterson CB, Do KA, Jenq RR. Performance determinants of unsupervised clustering methods for microbiome data. Microbiome. (2022) 10(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01199-3
158. Taie WS, Omar Y, Badr A. Clustering of Human Intestine Microbiomes with K-Means. 2018 21st Saudi Computer Society National Computer Conference (NCC). IEEE (2018).
159. Nakao R, Abe T, Nijhof AM, Yamamoto S, Jongejan F, Ikemura T, et al. A novel approach, based on blsoms (batch learning self-organizing maps), to the microbiome analysis of ticks. The ISME Journal. (2013) 7(5):1003–15. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.171
161. Panch T, Szolovits P, Atun R. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and health systems. J Glob Health. (2018) 8(2):020303. doi: 10.7189/jogh.08.020303
162. Bianchetti G, De Maio F, Abeltino A, Serantoni C, Riente A, Santarelli G, et al. Unraveling the gut microbiome-diet connection: exploring the impact of digital precision and personalized nutrition on microbiota composition and host physiology. Nutrients. (2023) 15(18):3931. doi: 10.3390/nu15183931
163. Matijasic M, Mestrovic T, Paljetak HC, Peric M, Baresic A, Verbanac D. Gut Microbiota beyond Bacteria-mycobiome, virome, archaeome, and eukaryotic parasites in Ibd. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(8):2668. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082668
164. Terron-Camero LC, Gordillo-Gonzalez F, Salas-Espejo E, Andres-Leon E. Comparison of metagenomics and metatranscriptomics tools: a guide to making the right choice. Genes (Basel. (2022) 13(12):2280. doi: 10.3390/genes13122280
165. Marcos-Zambrano LJ, Lopez-Molina VM, Bakir-Gungor B, Frohme M, Karaduzovic-Hadziabdic K, Klammsteiner T, et al. A toolbox of machine learning software to support microbiome analysis. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1250806. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1250806
166. Papoutsoglou G, Tarazona S, Lopes MB, Klammsteiner T, Ibrahimi E, Eckenberger J, et al. Machine learning approaches in microbiome research: challenges and best practices. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1261889. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1261889
167. Schloss PD. Identifying and overcoming threats to reproducibility, replicability, robustness, and generalizability in microbiome research. mBio. (2018) 9(3):e00525-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00525-18
168. Rhodes R. Ethical issues in microbiome research and medicine. BMC Med. (2016) 14(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0702-7
169. Jiang D, Armour CR, Hu C, Mei M, Tian C, Sharpton TJ, et al. Microbiome multi-omics network analysis: statistical considerations, limitations, and opportunities. Front Genet. (2019) 10:995. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00995
Keywords: gut microbiome, gut microbiota, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), network-based methods, biomarker discovery, precision medicine, personalized treatment
Citation: Dakal TC, Xu C and Kumar A (2025) Advanced computational tools, artificial intelligence and machine-learning approaches in gut microbiota and biomarker identification. Front. Med. Technol. 6:1434799. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2024.1434799
Received: 23 July 2024; Accepted: 16 October 2024;
Published: 15 April 2025.
Edited by:
Ali Asger Bhojiya, Mohanlal Sukhadia University, IndiaReviewed by:
Atif Khurshid Wani, Lovely Professional University, IndiaParijat Hazarika, Assam Down Town University, India
Nar Singh Chauhan, Maharshi Dayanand University, India
Copyright: © 2025 Dakal, Xu and Kumar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abhishek Kumar, YWJoaXNoZWsuYWJoaXNoZWtrdW1hckBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Tikam Chand Dakal, dGlrYW0yNjA3MEBnbWFpbC5jb20=; dGMuZGFrYWxAbWxzdS5hYy5pbg==
 Tikam Chand Dakal
Tikam Chand Dakal Caiming Xu
Caiming Xu Abhishek Kumar
Abhishek Kumar