
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mech. Eng., 01 April 2025
Sec. Vibration Systems
Volume 11 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2025.1560986
This article is part of the Research TopicRecent Advances in Mechanical Design and VibrationView all articles
 Kiran More1*
Kiran More1* Pranoti Honawadajkar2,3
Pranoti Honawadajkar2,3 Sachin Kandharkar4
Sachin Kandharkar4 Bharat Tidke5
Bharat Tidke5 Rahul B. Pawar6
Rahul B. Pawar6 Mangesh Shende7
Mangesh Shende7 Rajesh Kherde8
Rajesh Kherde8 Ganesh Kawade1
Ganesh Kawade1 Sachin Patil9
Sachin Patil9Introduction: Deep-groove ball bearings are widely used in industrial applications due to their ability to support radial and axial loads simultaneously. However, prolonged operation under harsh conditions can lead to localized defects such as inner race, outer race, or rolling element faults. These defects often manifest as distinct vibration patterns, which can be detected and analyzed to diagnose bearing health. This study focuses on the vibrational analysis of faulty deep-groove ball bearings under radial load, aiming to establish a correlation between fault characteristics and vibration signatures.
Methods: A specialized test rig evaluates the vibration responses of deep-groove ball bearings under controlled conditions, capturing data in both time and frequency domains for comprehensive analysis. Vibration signals from healthy and defective bearings are analyzed to ensure precision and reliability. The study identifies characteristic fault frequencies and harmonics caused by localized defects on the inner or outer race, comparing simulated and experimental data. This approach provides insights into how defect types and load conditions influence bearing vibration signatures.
Results: The evaluation of single and multiple defects shows higher velocity amplitudes for multiple defects. Time-domain analysis reveals that a single inner race defect under a 5 kg radial load has a velocity amplitude of 2.00 mm/s, while two defects on the inner race under the same load result in a slightly lower amplitude of 1.88 mm/s.
Discussion: The experimental findings closely match the simulation results, showing a strong correlation between the two methods. Further analysis using orbit analysis is conducted to examine the behavior of deep-groove ball bearings under similar conditions.
Ball bearings are fundamental components in both small and large industrial machines, playing a critical role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Their primary function is to reduce friction between moving parts, support radial and axial loads, and enable precise rotational motion. The performance and reliability of industrial machinery are heavily dependent on the quality and condition of the bearings used. High-quality bearings contribute to enhanced machine efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and extended operational life, while defective or low-quality bearings can lead to increased downtime, higher maintenance costs, and even catastrophic failures. Despite advancements in manufacturing technologies that ensure faultless geometry and precision in ball bearings, vibrations are inherently generated during their operation. These vibrations primarily arise from the dynamic interactions between the rolling elements (balls), the inner race, and the outer race as they move under load. Even in perfectly manufactured bearings, minor imperfections, surface roughness, and variations in load distribution can cause vibrations. These vibrations, though often minimal, can amplify over time due to wear and tear, leading to increased noise, reduced performance, and potential damage to the bearing and surrounding machinery.
A more significant concern is the development of localized defects during operation, such as pit spalls, cracks, or dents on the rolling elements or raceways. These defects typically occur due to factors like excessive loading, inadequate lubrication, contamination, or material fatigue. For instance, pit spalls, which are small surface fractures or craters, can form on the bearing surfaces due to repeated stress cycles or improper lubrication. Once such defects are initiated, they tend to propagate over time, exacerbating the vibration levels and further degrading the bearing’s performance. According to Shah and Patel (2014), these localized defects not only increase vibration amplitudes but also introduce distinct fault frequencies into the vibration spectrum, which can be detected and analyzed for diagnostic purposes.
The development of defects in deep-groove ball bearings is often attributed to improper installation, inadequate maintenance, poor handling practices, and surface fatigue. These issues can result in various types of damage, such as cracks, pits, and spalling. If such defects go unnoticed in their initial stages, they can generate increased noise and vibrations, potentially causing bearing failure, machinery malfunction, and economic setbacks. Consequently, identifying defects in deep-groove ball bearings by analyzing their dynamic behavior and creating precise physical models of rotating parts is crucial to prevent severe damage (More et al., 2025).
Singh and Howard (2015) explored research focused on vibration modeling of rolling element bearings, particularly those with localized and extensive defects. Such imperfections contribute to fatigue, spalling on surfaces and subsurfaces, and reduced bearing longevity (Singh and Howard, 2015). To thoroughly evaluate how defective rolling element bearings affect vibration characteristics, a detailed parametric investigation can be conducted. This involves examining multiple factors, including axial and radial bearing loads, rotational speed, bearing clearance, and the type of defect present.
Shaha and Kulkarni (2015) studied the mechanical dynamics of a rolling bearing system, where the outer ring remains fixed while the rolling elements facilitate motion and transfer the load between the inner and outer raceways. Current research trends emphasize the use of dynamic analysis as a proactive method for early defect prediction, which has proven effective in enhancing system performance. Their study proposes an approach for predicting and confirming the dynamic vibration characteristics in a bearing rotor system (Shaha and Kulkarni, 2015).
The increasing complexity and demand for mechanical designs have highlighted the need to predict component endurance effectively (Patel et al., 2014). One study focused on evaluating the stress distribution and displacement behavior of deep-groove ball bearings using finite element analysis. The research also identified key parameters influencing the bearing’s radial stiffness under axial loads. Findings demonstrated that the bearing had an extended lifespan, ensuring its reliability against static, dynamic radial, and axial loads (Shah and Patel, 2014). Luo et al. (2024) introduced a novel dynamic model for a deep-groove ball bearing (DGBB) that included a localized defect on the outer race. Meanwhile, Manjunath and Girish examined the performance of polymer ball bearings made from polyacetal (POM) material. These bearings are widely utilized in industries ranging from household appliances to aerospace, making their optimal performance critical for preventing severe damage (Manjunath and Girish, 2013). Monitoring bearing conditions and identifying defect severity at an early stage is crucial to avoid significant failures.
To aid in defect detection, vibration analysis plays a vital role in condition monitoring and quality inspection. One effective method for identifying damage frequencies in ball bearings is the fast Fourier transform (FFT) technique. Research by Mitsuya et al. (1998) found that reduced damping, attributed to the combined effects of tilting mode vibration on the lateral mode and increased clearance, suggested that heightened ball rolling motion rather than slipping motion was the primary cause. In another study, Nonato and Cavalca (2014) proposed a methodology that integrates Elastohydrodynamic (EHD) film effects into a lateral vibration model of a deep-groove ball bearing. This approach involved approximating EHD contacts with a combination of nonlinear springs and viscous dampers, enhancing the model’s accuracy in reflecting real-world conditions.
Researchers conducted a study focusing on both theoretical and experimental analysis of vibrations in deep-groove ball bearings subjected to dynamic loads, specifically those with localized circular defects in the raceways. The mathematical model applied in the research incorporated various components such as the housing, raceways, shafts, and ball masses. A comparison was made between the simulated and experimental results concerning the vibration behavior of the bearing housing (Patel et al., 2012). The findings indicated that as the ball approached the inner race defect, its displacement increased from zero to a peak value, and subsequently decreased from the peak back to zero as it moved past the defect’s center to the opposite end (Utpat, 2013; Safizadeh and Latifi, 2014). Experimental tests were performed using a test rig that captured vibration signals from a sample bearing while external vibrations were applied via an electromechanical shaker. In the envelope analysis, spectral kurtosis was employed to select the optimal center frequency for filters with varying bandwidths, such as 32 and 64 (Patel et al., 2013). The study concluded that the accuracy of defect detection using envelope analysis is highly dependent on the choice of center frequency and bandwidth. Consequently, different center frequencies and bandwidth combinations were tested to enhance detection reliability. Additionally, a bearing joint model was examined using a nonlinear constraint force system that accounted for contact stiffness interactions between the raceways and rolling elements. This model was applied in dynamic simulations involving a planar slider-crank mechanism fitted with a deep-groove ball bearing joint (Xu et al., 2012). The study proposed a technique for dynamic modeling and simulation of multimode systems that include deep-groove ball bearings with clearance. To improve precision, the bearing joint was modeled with a nonlinear constraint force system that considered the elastic deformations occurring at the contact points between the rolling elements and raceways (Muruganatham et al., 2012; Patel et al., 2010). Furthermore, a mathematical model was established to calculate the trajectory of the inner ring’s axis center and the ball center’s motion path by incorporating raceway waviness and ball size variations (Zhang et al., 2018). Lastly, a dynamic model was introduced to predict vibrations in both healthy and defective deep-groove ball bearings. This model accounted for nonlinear force interactions caused by elastic deformations at the contact points between the ball elements and raceways (Shah and Patel, 2019; Xu and Li, 2015).
Researchers have extensively studied the vibration behavior of deep-groove ball bearings under dynamic loads, focusing on the inner and outer races. A dynamic model that incorporates the masses of key components, such as the housing, shaft, races, and balls, was developed (Wang et al., 2024). Comparisons between cases with single and dual race defects showed higher velocity amplitudes in the latter (Shettya et al., 2024). Both theoretical and experimental findings revealed a strong correlation, particularly in identifying characteristic defect frequencies and harmonics (Yang et al., 2023a). An electromechanical-magnetic coupling model was created using the Modified Winding Function Approach (MWFA) to detect fault-induced harmonics in stator currents (Wang et al., 2021). The Dimension Theory using the Matrix Technique (DTMT) was employed to analyze vibration responses (Salunkhe et al., 2021), while an effective impact model successfully replicated real vibration signals from defective bearings (Liu et al., 2023). Research also examined the transition from periodic to chaotic vibration patterns, highlighting the sensitivity of vibration behavior to bearing defects and rotor speed variations (Patra et al., 2020). A mathematical model incorporating raceway waviness and ball size deviations was developed to track the inner ring’s axis and ball center trajectory (Zhang et al., 2018). Nonlinear system dynamics were analyzed using Higuchi’s fractal dimensions (Sharma et al., 2019). A literature review summarized methods for diagnosing bearing faults under nonlinear conditions (Patel et al., 2022). The effectiveness of finite element analysis (FEA) and dimension analysis techniques (DAT) was demonstrated in assessing surface fault depth and slope angle effects on contact characteristics (Salunkhe et al., 2022). Additionally, a bearing test rig was developed to simulate cage damage, with vibration characteristics analyzed in bearings 6,210 and 6,011 (Yang et al., 2023b). Insights into defect-related impulsive forces and vibration patterns were also provided (Singh et al., 2014).
Internationally, extensive research has been conducted on vibration-based fault detection methods for rolling element bearings. Studies from leading research institutions focus on using advanced signal processing techniques, such as Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and envelope analysis, to identify characteristic defect frequencies. These methodologies are widely adopted across industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy for real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance (Shah and Patel, 2014; Luo et al., 2024). Nationally, significant research efforts in India have been dedicated to improving the accuracy of vibration diagnostics through experimental and computational methods. Studies from institutions such as IITs and NITs have pioneered innovative approaches to model dynamic behavior and predict bearing faults under various load conditions, contributing to more efficient maintenance strategies in domestic manufacturing sectors (Patel et al., 2022; Kawade et al., 2024). Building on these national and international advancements, this study bridges a critical gap by providing a comprehensive comparative analysis of time- and frequency-domain vibration responses. Our work enhances the understanding of how defect localization and severity can be detected across varying load conditions, offering practical insights for both academic research and industrial applications.
The literature review highlights key findings on vibration analysis of faulty bearings compared to healthy ones. Researchers have examined single and multiple defects in deep-groove ball bearing races, including the impact of defect angles. Studies have identified fault frequencies in vibrations but fewer investigations have explored impact tests using model hammers or vibration-based data acquisition methods for detecting race defects. Additionally, research on orbit analysis under combined loading conditions and surface contact defects using bond graphs remains limited.
Early-stage defects in deep-groove ball bearings can increase noise and vibrations, potentially leading to system failure, frequent maintenance, and economic losses. For effective vibration-based diagnosis, understanding defect types, quantities, and orientations is crucial.
This study aims to:
1. Examine vibration responses of a rolling element bearing under varying radial loads with a local defect.
2. Investigate defect impacts on deep-groove ball bearings under different radial load conditions.
3. Analyze time-domain characteristics of solo and multipoint defects using the frequency spectrum.
4. Explore frequency-domain characteristics of these defects.
5. Assess the influence of solo point defect sizes on bearing races using frequency analysis (Pachpute and More, 2024; More and Kumar, 2024; More et al., 2020).
Figure 1 illustrate the experimental setup designed to analyze the vibration responses of defective deep-groove ball bearings. The setup included essential components such as a test bearing, accelerometer, motor, shaft, FFT analyzer, and laptop. This arrangement was specifically configured to study the vibration behavior of rolling element bearings under varying conditions.
The test bearing was the primary component under investigation. It was subjected to different radial loads and defect conditions to study its vibration characteristics. The bearing was mounted on the shaft and supported by the system to simulate real-world operating conditions.
An accelerometer was used to measure the vibrations generated by the test bearing. It was mounted on the bearing housing or a nearby structure to capture the vibration signals accurately. The accelerometer converted mechanical vibrations into electrical signals for further analysis.
A motor was used to drive the shaft and rotate the test bearing at a controlled speed. The rotational speed of the motor was adjustable, allowing the study of vibration responses at different speeds and loads. The motor provided the necessary power for the experimental setup.
The shaft connected the motor to the test bearing, transmitting rotational motion. It ensured proper alignment and stable operation during the experiments. The shaft was designed to maintain minimal imbalance, reducing any additional vibrations unrelated to the bearing defects.
A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analyzer was employed to process the vibration signals acquired by the accelerometer. This transformation from the time domain to the frequency domain facilitates the identification of characteristic frequencies associated with specific bearing defects, thereby enabling precise fault diagnosis.
The laptop was connected to the FFT analyzer to record and analyze the vibration data. Using specialized software, the laptop displayed vibration waveforms, frequency spectra, and other diagnostic information. It facilitated data interpretation and helped identify the effects of defects and varying radial loads on the bearing.
The experimental setup allowed for precise measurement and analysis of bearing vibrations to assess the impact of defects and operating conditions on deep-groove ball bearing performance. Arrows in the diagram indicated the motion direction and data flow, ensuring clarity and reproducibility. The test bearing used was a chrome steel (AISI 52100) deep-groove ball bearing with a 25 mm inner diameter and 52 mm outer diameter. A 250 μm defect was introduced on both the inner and outer races using Electric Discharge Machining (EDM). A piezoelectric accelerometer with ±5% sensitivity was positioned at the load zone on the bearing housing to capture vibrations. Calibration was conducted using a reference vibration source before each test for accuracy. The motor operated at a constant speed of 1,330 rpm, with radial loads of 5 kg, 6 kg, and 7 kg applied to simulate real-world conditions. Data was collected using an FFT analyzer at a 25 kHz sampling rate for detailed frequency analysis. Figures 2, 3 depict the test bearings with a solo defect on the inner and outer races, respectively. Experiments were conducted under three radial load conditions to evaluate the defect’s effects.
Figure 2 shows the vibration signal from a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo inner race defect. The time-domain waveform reveals periodic spikes caused by rolling elements passing over the defect, indicating increased vibration levels. This data was recorded under a 5 kg radial load and a motor speed of 1,330 rpm, with the signal’s periodic nature confirming the presence of the defect.
Figure 3 illustrates the vibration signal for a bearing with a solo outer race defect under identical conditions. While it also shows periodic spikes, the pattern differs slightly due to the stationary outer race. The amplitude of these spikes reflects the energy released as rolling elements strike the defect. Both figures highlight how inner and outer race defects produce distinct vibration patterns, aiding in early fault detection and differentiation based on impact timing and intensity.
Table 1 offers a inclusive outline of the experimental setup. Table 1 provides a detailed summary of the experimental setup used to analyze the vibration characteristics of defective deep-groove ball bearings. The test bearing is made of AISI 52100 steel, known for its high durability and wear resistance, with a 25 mm inner diameter (ID) and a 52 mm outer diameter (OD). Defects measuring 250 μm were introduced on both the inner and outer races using Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) to simulate real-world bearing faults.
The motor was operated at a constant speed of 1,330 rpm across three different radial load conditions (5 kg, 6 kg, and 7 kg) to capture the variation in vibration responses. An accelerometer, mounted on the bearing housing, recorded vibration signals within a frequency range of 10 Hz to 10 kHz with a sensitivity of ±5%, ensuring accurate data collection.
Vibration signals were managed using a FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) analyzer with a sampling rate of 25 kHz to convert time-domain data into frequency-domain information, allowing the identification of characteristic defect frequencies. Calibration was performed before each experiment using a reference vibration source to ensure measurement accuracy. Continuous monitoring during the experiment enabled comprehensive data acquisition for both time- and frequency-domain analysis, providing a robust framework for detecting and analyzing bearing defects.
The experimental test setup was designed to analyze the vibration behavior of deep-groove ball bearings under different conditions. The setup comprised key components such as deep-groove ball bearings, bearing housing, a loading arrangement, accelerometers, and an FFT analyzer.
To control the rotational speed, one end of the shaft was extended and coupled to a motor. The opposite end of the shaft was also extended to connect the loading arrangement, which applied radial loads to simulate real-world conditions. An accelerometer was securely mounted on the bearing housing to capture vibration signals and was linked to the FFT analyzer for data collection and analysis. To study the effect of defects, both single-point and multipoint defects were introduced on the outer surface of the inner race and the inner surface of the outer race of the deep-groove ball bearings. These defects were created using Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) to ensure precision and consistency. Additionally, the impact of angular positioning for multiple defects on the same race was investigated to understand how defect orientation influences vibration behavior. The experiments were conducted by configuring the FFT analyzer for spectrum analysis, which enabled detailed observation of vibration frequencies. Various conditions were applied by altering the load values and defect dimensions in both the inner and outer races. The corresponding vibration responses were recorded for each test scenario. In addition to spectrum analysis, orbit analysis was also performed using the FFT analyzer. This method allowed for visualizing the bearing’s dynamic motion in response to defects and varying loads. Both spectrum and orbit analysis results were carefully compared to assess the influence of defect characteristics and loading conditions on vibration behavior. This comprehensive approach provided valuable insights into the diagnostic capabilities of vibration analysis for identifying defects in deep-groove ball bearings.
Table 2 presents a detailed comparison of the time-domain analysis for deep-groove ball bearings with solo defects located in the inner race. This analysis evaluates the vibration characteristics resulting from the defect under specific operating conditions. The recorded data highlights key parameters such as peak amplitude, impact intervals, and overall vibration intensity. These indicators provide valuable insights into the behavior of the bearing when a localized defect is present on the inner race. Similarly, Table 3 outlines the time-domain analysis results for deep-groove ball bearings featuring solo defects in the outer race. The comparison emphasizes the differences in vibration response between inner and outer race defects. While both types of defects exhibit periodic impact patterns, their signal characteristics differ due to the movement of the rolling elements and the stationary nature of the outer race. Figures 5, 6 visually represent the time-domain vibration signals for the bearings with inner and outer race defects, respectively. These Figures 5, 6 illustrate the distinct waveform patterns observed during testing at a motor speed of 1,330 rpm and under a radial load of 5 kg. The time-domain waveform for the inner race defect (Figure 5) shows pronounced periodic spikes, corresponding to the rolling elements passing over the defect. These sharp peaks indicate the elevated vibration levels caused by the inner race damage. In contrast, the time-domain waveform for the outer race defect (Figure 6) displays periodic spikes as well, but with a slightly different pattern. Since the outer race remains stationary, the vibration response varies in timing and amplitude compared to the inner race defect. The observed signal differences between the two defect types are critical for distinguishing fault locations based on their unique vibration characteristics. By analyzing these time-domain responses, the study effectively demonstrates how defect location influences vibration behavior in deep-groove ball bearings. This comparison aids in developing reliable diagnostic techniques for early fault detection and improved maintenance strategies.
Time-domain and frequency domain analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing defects in rolling element bearings by examining vibration signals over time. This method helps identify variations in amplitude and periodic impacts caused by defects in the bearing components. The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the significance of time-domain analysis and its application to solo defects in the inner and outer races of a deep-groove ball bearing. Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of the time-domain vibration signals for solo defects in the inner race of a deep-groove ball bearing. When a defect is present in the inner race, the rolling elements impact the defect repeatedly as they pass over it, generating periodic impulses in the vibration signal. These impulses are influenced by factors such as rotational speed, defect size, and applied load.
The vibration signal for an inner race defect typically exhibits high-frequency impacts due to the continuous interaction between the defect and the rolling elements. The amplitude of the impulses depends on the severity of the defect and the operating conditions, such as speed and radial load.
The time between successive impacts is governed by the ball pass frequency of the inner race (BPFI), which is characteristic of inner race defects.
Early Fault Detection: The presence of periodic impulses in the time-domain signal is a key indicator of inner race damage, enabling early fault detection.
Assessment of Defect Severity: The amplitude of the impulses provides insights into the severity of the defect, helping in predictive maintenance.
Machine Reliability: Monitoring time-domain signals allows maintenance teams to take preventive actions before catastrophic bearing failure occurs.
Figure 4 displays the time-domain vibration response of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect on the outer race at a rotational speed of 1,330 rpm under a 5 kg radial load. The waveform exhibits periodic impulses, which occur as the rolling elements repeatedly pass over the fixed defect on the outer race. Compared to inner race defects, these impulses are less frequent because the outer race remains stationary relative to the accelerometer. The figure highlights how the amplitude and periodicity of the signal reflect the presence and severity of the defect. The waveform shows periodic impulses corresponding to the ball pass frequency of the inner race (BPFI), indicative of localized damage.
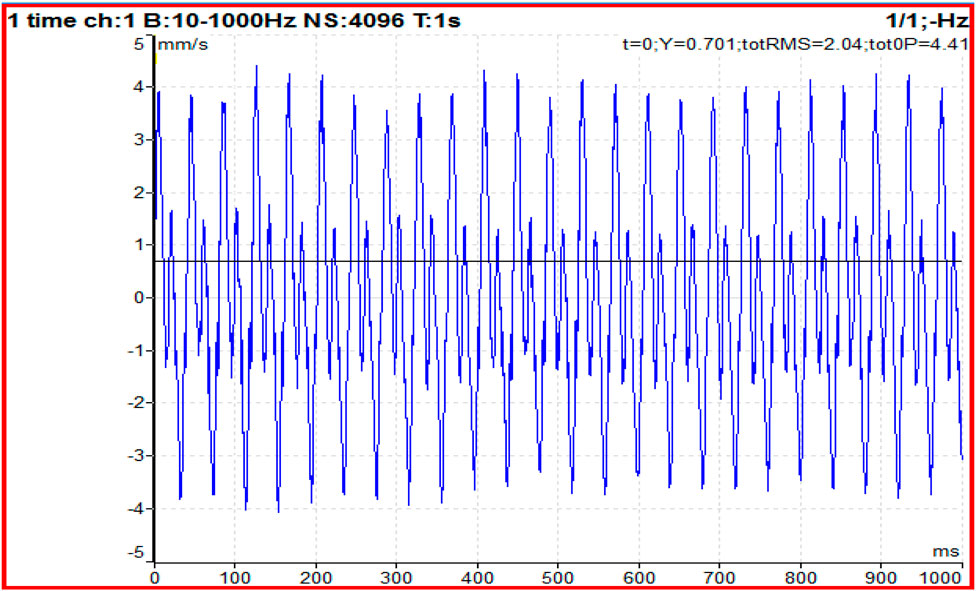
Figure 4. Time domain analysis of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect in the inner race of the bearing at 1,330 rpm, under a 5 kg radial load.
Table 3 provides a comprehensive comparison of the time-domain analysis for solo defects in the outer race of deep-groove ball bearings. Unlike inner race defects, outer race defects exhibit distinct vibration signal characteristics due to their stationary position relative to the bearing housing. Since the outer race remains fixed, the rolling elements periodically strike the defect as they rotate, producing vibration impulses at specific intervals. These impulses occur at the ball pass frequency of the outer race (BPFO), a characteristic frequency that corresponds to the rate at which rolling elements pass over a stationary defect on the outer race. The BPFO is generally lower than the ball pass frequency of the inner race (BPFI) since the outer race does not rotate. Consequently, the periodic impacts caused by outer race defects are less frequent but can still generate considerable vibration amplitudes, particularly when the defect is located within the load-bearing zone. The vibration signal’s intensity and pattern are closely linked to the defect’s position in relation to the load zone. Defects located in the load-bearing area experience greater force from the rolling elements, producing stronger and more prominent impact spikes in the time-domain waveform. Conversely, defects outside the load zone tend to generate weaker vibration responses due to reduced contact pressure. This variation underscores the significance of load distribution when analyzing vibration signals for defect detection. A key aspect of differentiating between inner and outer race defects lies in their respective impulse frequencies. Inner race defects, associated with the BPFI, result in higher-frequency vibration impulses because the defect moves relative to both the rolling elements and the stationary outer race. In contrast, outer race defects produce lower-frequency impulses aligned with the BPFO. This distinction in impulse frequency serves as a vital diagnostic tool for identifying defect locations within the bearing assembly. Early detection of outer race defects is crucial for effective condition monitoring, as undetected faults can lead to severe bearing damage, equipment seizure, and unexpected downtime in rotating machinery. By analyzing time-domain vibration signals and understanding the influence of load conditions on defect behavior, maintenance strategies can be optimized to ensure timely interventions, improving the reliability and longevity of mechanical systems.
Figure 5 illustrates the frequency-domain analysis (FFT) of a deep-groove ball bearing featuring a solo defect on the inner race, recorded under identical operating conditions (1,330 rpm and 5 kg radial load). The spectrum distinctly displays prominent peaks at the Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race (BPFI) at 106.4 Hz, along with successive harmonics at 212.8 Hz (2×BPFI) and 319.2 Hz (3×BPFI). These frequency components are key indicators of the defect’s presence, location, and severity. The detection of higher harmonics highlights a nonlinear response resulting from the defect, further confirming localized damage on the inner race. The rotational speed directly influences the frequency of defect-induced impacts in the time-domain signal, while the applied radial load affects the vibration intensity—greater loads amplify the interaction forces between the rolling elements and the defect. Additionally, the waveforms presented in Figures 4, 5 exhibit distinct impact signatures corresponding to the defect’s position, aiding in defect identification. These distinct patterns arise from the stationary nature of the outer race defect relative to the moving rolling elements, further supporting accurate defect classification.
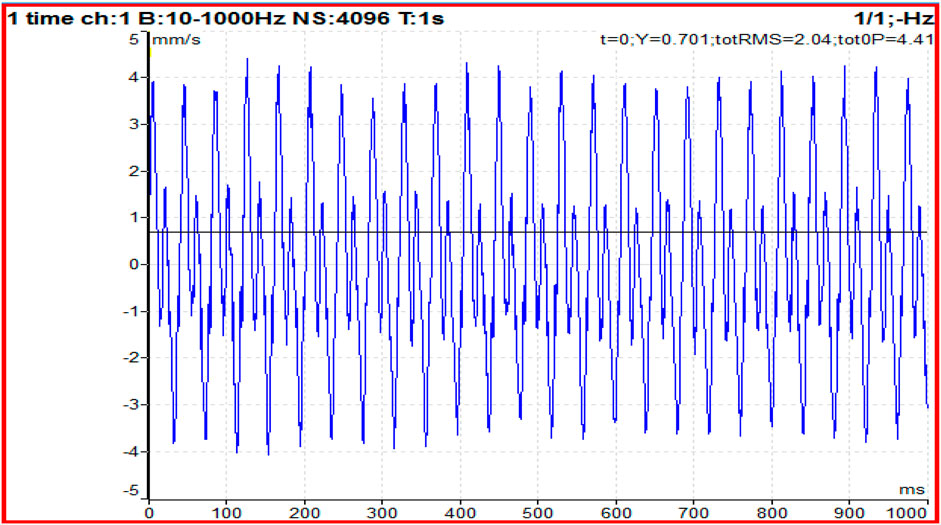
Figure 5. Time domain analysis of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect in the outer race of the bearing at 1,330 rpm, under a 5 kg radial load.
Figure 6 presents the FFT spectrum for the vibration response of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect on the inner race, recorded under operating conditions of 1,330 rpm and a 5 kg radial load. The spectrum reveals key frequency peaks, including the Rotational Frequency (fr) at 22.17 Hz (marked by a red dashed line), the Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race (BPFI) at 106.4 Hz (marked by a green dashed line), and successive harmonics at 212.8 Hz (2×BPFI) and 319.2 Hz (3×BPFI). The dominant peak at 106.4 Hz corresponds to the BPFI, indicating periodic impacts caused by rolling elements passing over the defect. The presence of harmonic peaks at 212.8 Hz and 319.2 Hz suggests repeated interactions with the defect, which are characteristic of localized damage. The occurrence of higher-order harmonics further implies either an increase in defect severity or the presence of nonlinear system behavior.
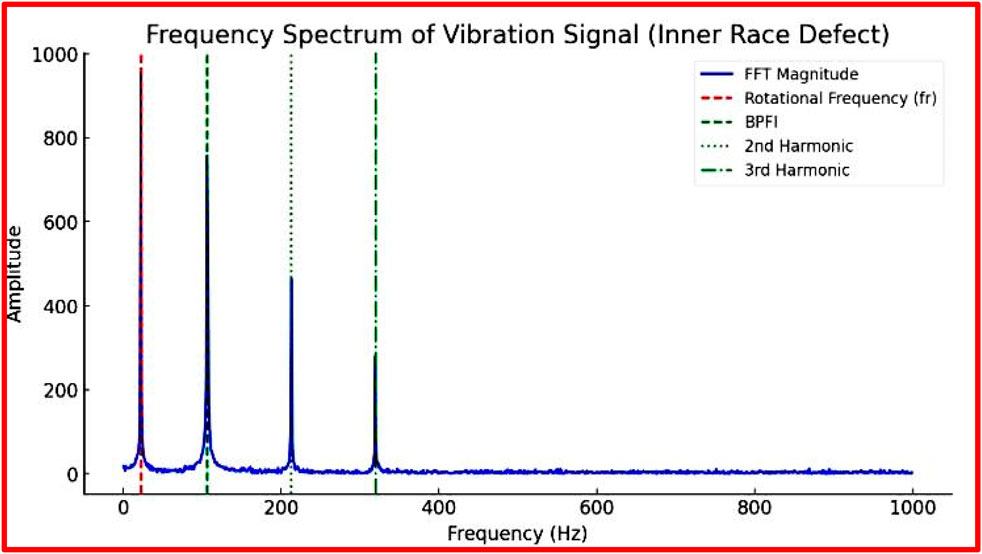
Figure 6. Frequency domain analysis of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect in the inner race of the bearing at 1,330 rpm, under a 5 kg radial load.
Figure 7 presents the FFT spectrum for the vibration response of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect on the outer race, recorded under identical conditions (1,330 rpm and a 5 kg radial load). Key frequency peaks include the Rotational Frequency (fr) at 22.17 Hz (indicated by a red dashed line), the Ball Pass Frequency of the Outer Race (BPFO) at 70.9 Hz (indicated by a green dashed line), and its harmonics at 141.8 Hz (2×BPFO) and 212.7 Hz (3×BPFO). The strong peak at BPFO (70.9 Hz) confirms the presence of an outer race defect, distinguishing it from an inner race defect, which would typically present a dominant peak at the Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race (BPFI) at 106.4 Hz. The absence of a prominent BPFI peak further supports the diagnosis of an outer race defect.
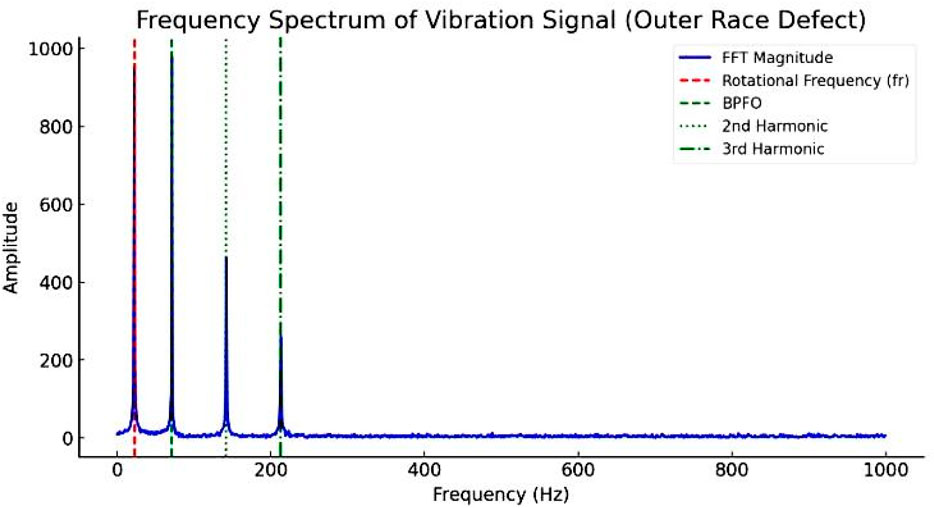
Figure 7. Time domain analysis of a deep-groove ball bearing with a solo defect in the outer race of the bearing at 1,330 rpm, under a 5 kg radial load.
The presence of rotational frequency (22.17 Hz) indicates minor machine imbalance but is not indicative of an inner race fault. The appearance of higher-order harmonics, such as 2×BPFO (141.8 Hz) and 3×BPFO (212.7 Hz), suggests a significant nonlinear vibration response, which often correlates with defect progression and increased severity. The amplitude of these peaks reflects the intensity of impact forces generated as rolling elements interact with the defect, with higher amplitudes indicating greater defect severity.
This study proposed an intelligent reconfiguration and optimization method for a modular process under customization. However, the results do not guarantee absolute accuracy or error-free outcomes. The inherent characteristics of the intelligent optimization algorithm indicate that data accuracy may decrease if errors occur in integer optimization, reorganization, or prediction beyond the sample limit. The analysis revealed that the velocity amplitudes at faulty frequencies were higher for solo defects on the inner race under a 5 kg radial load, measuring 0.383 mm/s, compared to 0.248 mm/s for two defects on the inner race under identical load conditions. The strong correlation observed between simulated and experimental results validates the reliability of this faulty ball bearing model for analyzing and predicting vibrations in both healthy and defective deep-groove ball bearings. Furthermore, time-domain vibration analysis showed that the velocity amplitude was greater for a solo defect on the inner race, recorded at 2.00 mm/s under a 5 kg radial load, compared to 1.88 mm/s for two defects on the inner race under the same load conditions.
The clear identification of characteristic defect frequencies provides actionable insights for condition monitoring systems. Implementing these findings in industrial setups can enhance real-time fault detection, allowing operators to track bearing health continuously. This methodology supports condition-based maintenance (CBM) strategies, reducing unexpected failures and optimizing machinery lifecycle. While the experimental findings offer a robust framework for fault detection, practical implementation faces challenges such as noise contamination in complex industrial environments and the need for advanced computational tools. Further research should focus on improving signal processing techniques to isolate defect-specific frequencies and enhancing cost-effective deployment of sensors in large-scale operations. These findings hold significant potential across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and energy sectors, where precision monitoring of rotating machinery is crucial. The methodology can be adapted to monitor turbines, compressors, and other high-speed components, thereby improving operational reliability and safety.
A comparative assessment of time-domain and frequency-domain results offers a comprehensive understanding of how bearing defects influence vibration signals. Time-domain analysis effectively captures vibration amplitude and periodic impulses, while frequency-domain analysis identifies characteristic fault frequencies and their harmonics, providing valuable diagnostic insights. For a solo defect on the inner race (refer to Figures 4, 6), time-domain analysis indicates elevated vibration amplitudes, measured at 2.00 mm/s under a 5 kg radial load. In contrast, the frequency-domain analysis reveals a distinct peak at 106.4 Hz (Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race, BPFI) along with its harmonics, confirming both the defect’s presence and its location. Similarly, for an outer race defect (Figures 5, 7), the presence of a peak at 70.9 Hz (Ball Pass Frequency of the Outer Race, BPFO) distinctly identifies the defect’s position—information that cannot be solely inferred from the time-domain waveform. Integrating both time-domain and frequency-domain analyses significantly enhances the accuracy of defect detection. Time-domain analysis provides quick insights into vibration severity, while frequency-domain analysis enables precise fault localization and monitoring of defect progression. This combined approach is essential for developing reliable condition monitoring systems in industrial applications.
An experimental test rig was developed to analyze the vibration characteristics of deep-groove ball bearings with single and multiple defects under various radial load conditions. Utilizing both time-domain and frequency-domain analyses, distinct fault signatures were identified. In healthy bearings, vibration peaks corresponded to the shaft rotational frequency and cage frequencies, along with their harmonics. Conversely, defective bearings exhibited prominent peaks at the Ball Pass Frequency of the Outer Race (BPFO) and Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race (BPFI), including their harmonics. Notably, the velocity amplitude at fault frequencies was higher for a single inner race defect (0.383 mm/s) compared to two defects (0.248 mm/s) under a 5 kg radial load. The strong correlation between experimental and simulated results validates the efficacy of this approach. This study underscores that vibration-based analysis is a reliable method for detecting and classifying bearing faults, offering valuable insights for condition monitoring and maintenance strategies.
This study establishes a comprehensive framework for diagnosing bearing defects by correlating experimental and simulated vibration data. By identifying characteristic fault frequencies—specifically, the Ball Pass Frequency of the Inner Race (BPFI) and the Ball Pass Frequency of the Outer Race (BPFO)—and their harmonics under varying load conditions, the accuracy of defect detection is significantly enhanced. This research contributes to the development of diagnostic methodologies capable of distinguishing between inner and outer race defects, providing a practical foundation for future condition monitoring systems. The findings have direct implications for industrial applications, particularly in enhancing predictive maintenance systems across sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, and energy. By offering a clearer understanding of vibration signatures, this research aids in optimizing maintenance schedules, reducing downtime, and extending the lifespan of critical machinery.
Future research could focus on integrating the proposed diagnostic approach into real-time monitoring systems, utilizing advanced machine learning algorithms for automated fault detection and prediction. Exploring alternative optimization techniques, such as deep learning models and hybrid algorithms, may further improve the accuracy and efficiency of defect identification in complex environments. Additionally, expanding the analysis to include multi-axis vibration measurements could provide a more comprehensive assessment of bearing health.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: NA.
KM: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SK: Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. BT: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RP: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Project administration, Validation. MS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RK: Project administration, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. GK: Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SP: Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that no acknowledgments are required for this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Kawade, G., Karanjkar, A., and More, K. C. (2024). Performance optimization of compression ignition (C.I.) engine powered by recycled plastic oil using advanced optimization algorithms. SSRG Int. J. Mech. Eng. 11 (5), 87–98. doi:10.14445/23488360/IJME-V11I5P108
Liu, J., Xue, L., Wang, L., Shi, Z., and Xia, M. (2023). A new impact model for vibration features of a defective ball bearing. ISA Trans. 142, 465–477. doi:10.1016/j.isatra.2023.08.014
Luo, M., Hugo, A., Yu, G., and Yunhao, P. (2024). Analysis of contact behaviors and vibrations in a defective deep groove ball bearing. J. Sound. Vib. 570, 118104. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2023.118104
Manjunath, A., and Girish, D. V. (2013). Defect detection in deep-groove polymer ball-bearing using vibration analysis. Ij. Mech. 2 (3), 45–52. Available online at: http://13.232.72.61:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/443.
Mitsuya, Y., Sawai, H., Shimizu, M., and Aono, Y. (1998). Damping in vibration transfer through deep-groove ball bearings. J. Tribol. 120 (3), 413–420. doi:10.1115/1.2834564
More, K. C., Dongre, S., and Deshmukh, G. P. (2020). Experimental and numerical analysis of vibrations in impeller of centrifugal blower. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 82. doi:10.1007/s42452-019-1853-x
More, K. C., and Kumar, A. (2024). An approach for narrowing the method of selection of profile shift coefficient for A given helical gear pair. SSRG Int. J. Mech. Eng. 15 (5), 37–47. doi:10.14445/23488360/IJME-V11I5P105
More, K. C., Kumar, A., Honawadajkar, P., Shende, M., and Kherde, R. (2025). Resolution of micropitting in case-carburized helical gear pairs through tooth profile modification. Int. J. Sci. Tech. 13 (2), 1030. doi:10.62110/sciencein.jist.2025.v13.1030
Muruganatham, B., Sanjith, M. A., Krishnakumar, B., and SatyaMurty, S. A. V. (2012). Roller element bearing fault diagnosis using singular spectrum analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 35 (1-2), 150–166. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.08.019
Nonato, F., and Cavalca, K. L. (2014). An approach for including the stiffness and damping of elastohydrodynamic point contacts in deep groove ball bearing equilibrium models. J. Sound. Vib. 333, 6960–6978. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2014.08.011
Pachpute, S. L., and More, K. C. (2024). Design optimization of plate-fin heat exchanger with metaheuristic hybrid algorithm. Heat. Trans., 1–10. doi:10.1002/htj.23213
Patel, N., Tandon, N., and Pandey, R. K. (2012). Defect detection in deep-groove ball-bearing in presence of external vibration using envelope analysis and duffing oscillator. Meas. 45 (5), 960–970. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2012.01.047
Patel, N., Tandon, N., and Pandey, R. K. (2013). Vibration studies of dynamically loaded deep-groove ball bearings in presence of local defects on races. Procedia Eng. 64, 1582–1591. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2013.09.240
Patel, N., Tandon, N., and Pandey, R. K. (2014). Experimental study for vibration behaviors of locally defective deep-groove ball bearings under dynamic radial load. Adv. Acoust. Vib. 2014 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1155/2014/271346
Patel, S., Shah, U., Khatri, B., and Patel, U. (2022). Research progress on bearing fault diagnosis with localized defects and distributed defects for rolling element bearings. Noise and Vib. Worldw. 53 (7-8), 352–365. doi:10.1177/09574565221114661
Patel, V. N., Tandon, N., and Pandey, R. K. (2010). A dynamic model for vibration studies of deep groove ball bearings considering single and multiple defects in races. J. Tribol. 132 (4), 1–10. doi:10.1115/1.4002333
Patra, P., Huzur Saran, V., and Harsha, S. P. (2020). Chaotic dynamics of cylindrical roller bearing supported by unbalanced rotor due to localized defects. J. Vib. Control 26 (21–22), 1898–1908. doi:10.1177/1077546320912109
Safizadeh, M. S., and Latifi, S. K. (2014). Using multi-sensor data fusion for vibration fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings by accelerometer and load cell. Inf. Fusion 18, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2013.10.002
Salunkhe, V. G., Desavale, R. G., and Jagadeesha, T. (2021). A numerical model for fault diagnosis in deep groove ball bearing using dimension theory. Mater. Today Proc. 47 (11), 3077–3081. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.072
Salunkhe, V. G., Desavale, R. G., and Kumbhar, S. G. (2022). Vibration analysis of deep groove ball bearing using finite element analysis and dimension analysis. ASME J. Tribol. 144 (8), 081202. doi:10.1115/1.4053262
Shah, D. S., and Patel, V. N. (2014). A review of dynamic modeling and fault identifications methods for rolling element bearing. Procedia Tech. 14, 447–456. doi:10.1016/j.protcy.2014.08.057
Shah, D. S., and Patel, V. N. (2019). A dynamic model for vibration studies of dry and lubricated deep groove ball bearings considering local defects on races. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 137, 535–555. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2019.01.097
Shaha, R. D., and Kulkarni, S. S. (2015). Vibration analysis of deep-groove ball-bearing using finite element analysis. Int. J. Eng. Rese Appl. 5 (5), 44–50.
Sharma, A., Amarnath, M., and Kankar, P. K. (2019). Nonlinear dynamic analysis of defective rolling element bearing using Higuchi’s fractal dimension. Sadhana - Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 44 (4), 76. doi:10.1007/s12046-019-1060-x
Shettya, P., Meijera, R. J., Osaraa, J. A., Pasaribub, R., and Lugt, P. M. (2024). Effect of bearing size on film thickness in grease-lubricated axially loaded deep groove ball bearings. Tribol. Int. 197, 109748. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2024.109748
Singh, S., and Howard, C. (2015). An extensive review of vibration modeling of rolling element bearings with localized and extended defects. J. Sound. Vib. 132, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2015.04.037
Singh, S., Kopke, U. G., Howard, C. Q., and Petersen, D. (2014). Analyses of contact forces and vibration response for a defective rolling element bearing using an explicit dynamics finite element model. J. Sound. Vib. 333 (21), 5356–5377. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2014.05.011
Utpat, A. (2013). Vibration signature analysis of defective deep-groove ball bearings by numerical and experimental approach. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Rese 4 (6), 592–598.
Wang, C., Wang, M., Yang, B., Song, K., Zhang, Y., and Liu, L. (2021). A novel methodology for fault sizeestimation of ball bearings using stator current signal. Meas 171, 108723. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108723
Wang, Z., Li, G., Zhou, X., Zhang, H., Lin, Z., and Jia, S. (2024). Dynamic analysis of deep groove ball bearing with localized defects and misalignment. J. Sound. Vib. 568, 118071. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2023.118071
Xu, L., Yang, Y., Li, Y., Li, C. n., and Wang, S. y. (2012). Modeling and analysis of planar multibody systems containing deep-groove ball-bearing with clearance. Mech. Mach. Theory 56, 69–88. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2012.05.009
Xu, L. X., and Li, Y. G. (2015). Modeling of a deep-groove ball bearing with waviness defects in planar multi-body system. Multi-body Syst. Dyn. 33, 229–258. doi:10.1007/s11044-014-9413-z
Yang, Y., Hui, L. B., Hui, M., Wang, P., Han, Q., Liaoning, S., et al. (2023a). Experimental study on vibration characteristics due to cage damage of deep groove ball bearing. Tribol. Int. 185, 108555. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108555
Yang, Y., Liu, H., Ma, H., Wang, P., Han, Q., and Wen, B. (2023b). Experimental study on vibration characteristics due to cage damage of deep groove ball bearing. Tribol. Int. 185, 108555. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108555
Keywords: solo defect, several defects, frequency domain time domain, vibration, orbit analysis, deep-groove ball bearing
Citation: More K, Honawadajkar P, Kandharkar S, Tidke B, Pawar RB, Shende M, Kherde R, Kawade G and Patil S (2025) Vibrational analysis of faulty deep-groove ball bearing under radial load. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1560986. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2025.1560986
Received: 15 January 2025; Accepted: 17 March 2025;
Published: 01 April 2025.
Edited by:
Shravan H. Gawande, Modern Education Society’s College of Engineering Pune India, IndiaReviewed by:
Lagouge Tartibu, University of Johannesburg, South AfricaCopyright © 2025 More, Honawadajkar, Kandharkar, Tidke, Pawar, Shende, Kherde, Kawade and Patil. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kiran More, a2lyYW4uaW1hZ2luZTY3QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.