
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mater., 18 February 2025
Sec. Polymeric and Composite Materials
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2025.1552713
This article is part of the Research TopicDevelopment of High-Performance Resin Matrix Composites - Volume IIView all 4 articles
 Liang Gao1†
Liang Gao1† Hao Wang2†
Hao Wang2† Xuan Yao2
Xuan Yao2 Zhiran Zheng1
Zhiran Zheng1 Liyu Wang2
Liyu Wang2 Zixuan Wang2
Zixuan Wang2 Yonggui Wang2
Yonggui Wang2 Baoyan Zhang1
Baoyan Zhang1 Xianghai Jing3*
Xianghai Jing3* Jianqiao Wu2*
Jianqiao Wu2*Epoxy vitrimer is a kind of recyclable polymer that can reconstruct their network topology through chemical bond exchange reactions, providing an innovative solution for the thermosets recycling dilemma. However, current vitrimers have not yet reached the level of commercial epoxy resins, especially in performance and preparation process. In this study, high-performance epoxy vitrimer has been prepared using a commercial epoxy-anhydride. In the presence of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) as an internal catalyst, both mechanical and thermal properties were improved significantly because of the complete curing reaction facilitated by TBD. With the addition of catalyst TBD, the tensile strength, modulus, elongation at break and the glass transition temperature (Tg) of materials increased from 49.12 to 79.27 MPa, 2080.96 to 2266.19 MPa, 2.78% to 3.86%, and 94°C to 132°C respectively. Meanwhile, the network rearrangement rate improved, in which the stress relaxation time (τ*) of networks declined from 19 min to 10 min at 200°C. Taking advantages of dynamic properties, these vitrimers can be reshaped and chemically degraded. Furthermore, carbon fiber composites are fabricated by using vitrimer as matrix, which can be successfully recycled with chemical degradation process at 160°C within 1 h. This research facilitates the development of recyclable epoxy and composites that exhibits significant potential for commercial applications.
Thermosetting resin is renowned for its high heat resistance and its characteristic of being resistant to deformation under pressure. Apart from being used in the manufacture of reinforced plastics, foams, various types of molded plastics for electrical purposes, and casting products, it has also been widely used in the aerospace industry for manufacturing and repairing aircraft structures due to its superior properties such as high strength, stiffness, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. However, a limitation of thermoset materials lies in their difficulty to alter topology and macroscopic shape once cured, making them non-recyclable and non-degradable at the end of their service life (Oliveux et al., 2015; Ma and Webster, 2018; Faria et al., 2013; An et al., 2022).
Vitrimer, an organic polymer with silica-like properties, presents a viable solution to address this challenge (Montarnal et al., 2011). At a specific temperature, it possesses the ability to rearrange its network topology through chemical bond exchange reactions, demonstrating dynamic characteristics like stress relaxation. Vitrimer combines the plasticity of thermoplastic polymers while maintaining the cross-linking density of thermoset polymers, making it not only recyclable but also exhibiting excellent solvent resistance, with mechanical properties comparable to thermoset polymers (Alabiso and Schlögl, 2020; Long et al., 2013; Denissen et al., 2016). Since Leibler (Montarnal et al., 2011) first introduced the concept of vitrimer in 2011, research in this field has flourished, and the development and application of vitrimers have emerged as a key research focus. This innovative material skillfully integrates the exceptional properties of traditional thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers, thereby demonstrating extensive application potential across multiple cutting-edge fields (Wu et al., 2023), including degradable plastics (Röttger et al., 2017), self-repairing elastomers (Zheng et al., 2023; Luo et al., 2022), reusable adhesives (Wu et al., 2020), shape memory materials (Zheng et al., 2016), liquid crystal elastomers (Pei et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2024), and additive manufacturing technologies (Shi et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2022). Transesterification reactions (TERs)-based epoxy vitrimers have emerged as the most extensively studied vitrimers in recent years. Among these TERs-based vitrimers, the most closely watched focus was how to improve their mechanical, thermal properties as well as their dynamic properties. In the last 5 years, various network regulation strategies have been designed in endlessly, to improve the comprehensive performance of vitrimers, such as increasing the concentration of ester bonds or hydroxyl groups (Hao et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019), constructing dual-dynamic covalent bonds (Gong et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2023), utilizing neighboring group participation effects (Zhao et al., 2022), combination of multiple strategies (Wu et al., 2021). Following the above strategies, comprehensive epoxy vitrimer and its fiber reinforced composites have been fabricated, which exhibited high mechanical and thermal properties as well as capacity of rapid recycling. For example, Yu et al. (2016) first studied the recycling characteristics of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy vitrimer composites by immersing the composites in ethylene glycol (EG) at 180°C. The TERs between EG molecules and the ester bonds in the epoxy occurred to effectively sever the polymer chain segments and dissolve the resin, ultimately achieving complete recycling of the carbon fibers and resin after 10 h. The above pioneer study used 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) as catalysts, while the degradation rates and mechanical properties of materials still had a long way to go. In a study in 2022, catalyst-free high-performance recyclable carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites (Zhao et al., 2022) were prepared, where many parameters such as mechanical, thermal properties, costs had approached commercial epoxy composites. However, the current research vitrimers still encounter obstacles in fulfilling the demands of practical applications. The reversibility of the reactions undermines the network stability at elevated temperatures, thereby hindering the widespread utilization of epoxy vitrimers. In practical applications, vitrimers need to possess good mechanical properties and heat resistance. Furthermore, the necessity for curing in numerous epoxy introduces additional complexity and cost constraints in mass production processes. Moreover, some catalysts may have toxic effects, posing potential risks to the environment and human health (Chrysanthos et al., 2011; Rahimi and García, 2017; Tapper et al., 2020; Sanjay et al., 2018). Overall, the current research vitrimers have not yet reached the level of commercial resins. Therefore, developing a kind of vitrimer with exceptional performance by maneuverable yet effective process undoubtedly poses a formidable challenge.
Certain epoxy-anhydride resin has been discovered to possess dynamic covalent bond cross-linking networks, qualifying them as vitrimers. These innovative polymer materials exhibit excellent self-healing capabilities and reprocessing molding characteristics, while also achieving significant degradation. Consequently, they serve as ideal alternatives to non-recyclable traditional thermoset polymer materials. Inspired by this, a commercially viable epoxy resin is committed to developing for such purposes, and continuously refining it through in-depth research on the reactivity of the resin, encompassing key factors such as curing agents and catalysts. The optimal curing time has been successfully determined with expected results obtained. The innovation has been introduced by selecting methyltetrahydrophthalic anhydride (MTHPA) as the curing agent to react with diglycidyl ester of aliphatic cyclo (DGEAC) and TBD as the transesterification catalyst to further enhance the dynamic performance such as stress relaxation. The curing process and network topological rearrangements are illustrated in Figure 1. During the curing process, the anhydride groups in MTHPA attack the epoxy groups on DGEAC, leading to the formation of ester bonds and the generation of new hydroxyl groups. To validate our findings, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Dynamic Mechanical and Thermal Analysis (DMA), and tensile testing were conducted on the vitrimer. The introduction of the catalyst into the conventional epoxy resin successfully induced a transesterification reaction, thereby transforming the vitrimer into a high-performance material that is recyclable and degradable. In fact, the epoxy materials we studied inherently possesses excellent properties and can undergo degradation even without the addition of a catalyst. However, the incorporation of a catalyst does not significantly alter its processing capabilities, instead, it markedly enhances various performance indicators, including the glass transition temperature (Tg) and mechanical strength. Moreover, compared to the scenario without a catalyst, the relaxation process is significantly accelerated, indicating that the inclusion of a catalyst has a positive impact on the materials.
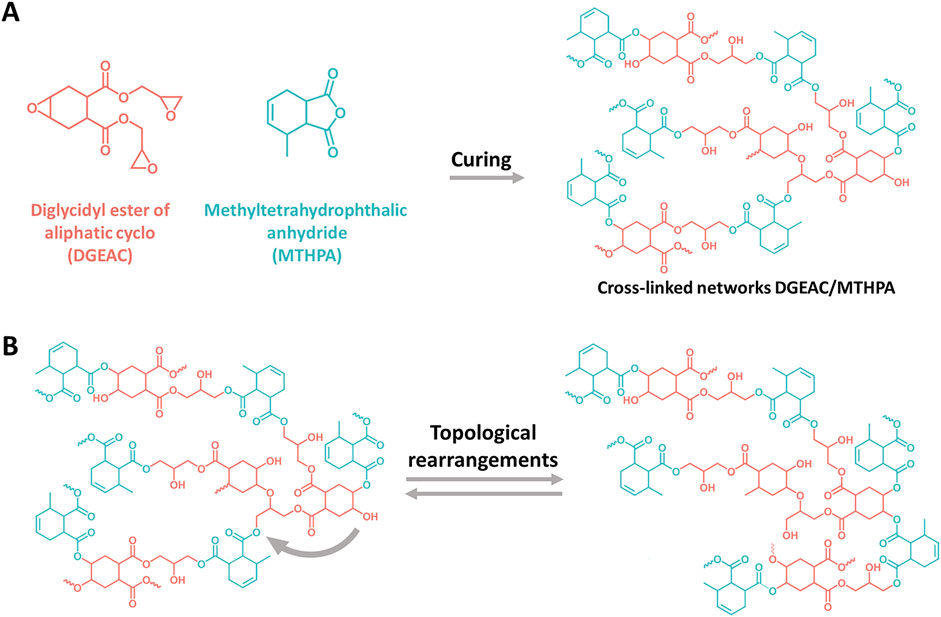
Figure 1. (A) Chemical structures of DGEAC, MTHPA, and DGEAC/MTHPA networks, and curing reaction of DGEAC/MTHPA networks. (B) Topological rearrangements of DGEAC/MTHPA networks.
This research has also overturned our previous concerns about the addition of catalysts. Previously, we feared that incorporating catalysts might degrade the mechanical and thermal properties of materials, thus affecting their processability. Experimental tests have shown that the catalyst facilitates the cross-linking reaction within polymer network, leading to an increase in cross-linking density and enhanced material stiffness. By employing the ester exchange reaction, high-performance vitrimer based on commercial epoxy-anhydride resin has been successfully developed, which is not only reprocessable but also chemically degradable. This achievement provides a solid theoretical foundation and necessary material support for the future commercialization of a new generation of environmentally friendly composites.
Details of materials, preparation of DGEAC/MTHPA networks, fabrication of CF/DGEAC/MTHPA composite laminates and characterization are shown in Supplementary Material.
The formation of cross-linked networks is accomplished through curing reactions. In order to investigate the impact of incorporating catalysts into diglycidyl ester of aliphatic cyclo/methyl tetrahydrophthalic anhydride (DGEAC/MTHPA) networks on these curing reactions, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was utilized to study the reaction peaks before and after curing process. Catalyst 1,5,7-triazabicyclo [4.4.0] dec-5-ene (TBD) was selected for transesterification reactions (TERs). As depicted in Figure 2A, for pre-curing samples, a broad exothermic peak was observed at 198°C and 115°C for the DGEAC/MTHPA mixtures and the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD mixtures, respectively. The exothermic peak of the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD mixtures shifted to lower temperatures compared to the DGEAC/MTHPA mixtures, indicating that the catalyst TBD accelerates the curing reactions. Concurrently, the glass transition temperature (Tg) was studied by DSC. The Tg of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks appeared at 57°C and 132°C, respectively (Figure 2B). The significant increase in Tg upon incorporating the catalyst TBD into the DGEAC/MTHPA system underscores the effect of the catalyst on enhancing the thermal properties of the networks by promoting the curing reactions.
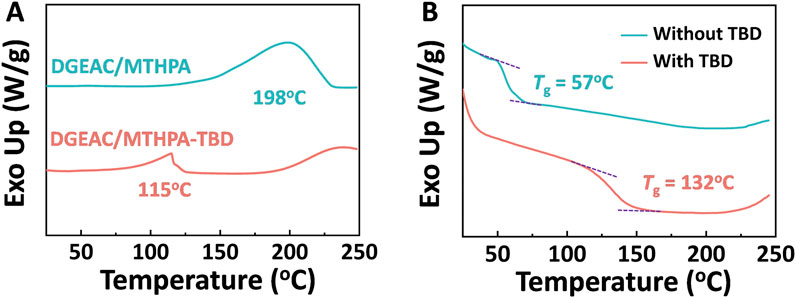
Figure 2. (A) DSC curves of pre-cured DGEAC/MTHPA and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD mixtures at a heating rate of 5°C/min. (B) DSC curves of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at a heating rate of 20°C/min.
Meanwhile, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was served the purpose of confirming the cross-linking structures. As illustrated in Figure 3, the analysis was conducted on monomers, DGEAC/MTHPA networks, and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. The peaks at 1740 and 905/853 cm−1 were attributed to ester bonds and epoxy groups from DGEAC, while the signals at 2935/2856 cm−1 and 1858/1777 cm−1 were assigned to methylene and inner ester bonds from MTHPA (Figure 3A). After cross-linking, a notable change was observed in the FTIR spectrum of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. The epoxy peaks from DGEAC at 905/853 cm−1 completely disappeared for DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks (Figure 3B), indicating the consumption of these groups during the cross-linking process. Furthermore, the prominent ester peak at 1736 cm−1 and the hydroxyl peak at 3514 cm−1 persisted, reflecting the formation of new bonds within the network. FTIR results indicated the complete consumption of epoxy groups and anhydride groups, confirming the successful formation of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD cross-linked networks.
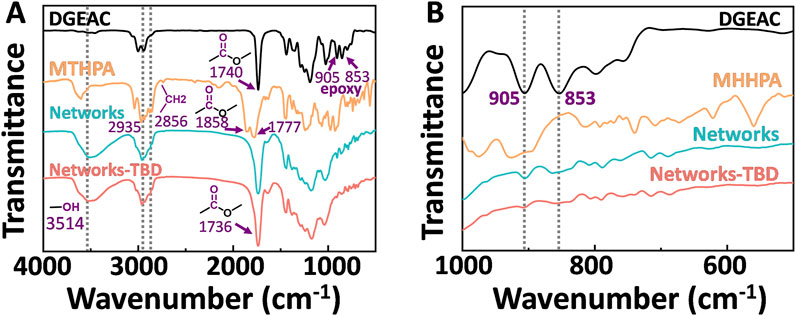
Figure 3. FTIR spectra of DGEAC, MTHPA monomer, cured DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. The wavenumber range of (A, B) were 4000–500 cm−1 and 1000–500 cm−1, respectively.
In addition, gel content tests were performed on DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks to validate effective cross-linking at room temperature. After immersing in acetone, dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate (EA), methanol (MeOH), and ethanol (EtOH) at room temperature for 24 h, the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks exhibited gel contents exceeding 94%, indicating excellent solvent resistance in organic solvents due to the formation of cross-linked networks. Conversely, the gel contents of DGEAC/MTHPA networks only maintained around 87% in DCM (Table 1), indicating that some chains within the DGEAC/MTHPA networks were incompletely cross-linked.
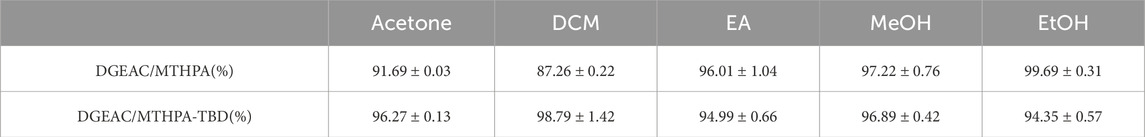
Table 1. Gel content of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks in acetone, DCM, EA, EtOH and MeOH.
To ascertain that the catalyst in the DGEAC/MTHPA system remained intact at elevated temperatures that did not adversely affect the thermal stability of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was utilized under a nitrogen atmosphere. Notably, the TBD monomer typically initiates degradation at 150°C. As shown in Figure 4A, the temperature at which 5% weight loss (Td5) occurred was 250°C for DGEAC/MTHPA networks and 246°C for DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. This suggests that the TBD catalyst did not undergo decomposition, and both DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks exhibited commendable thermal stability.
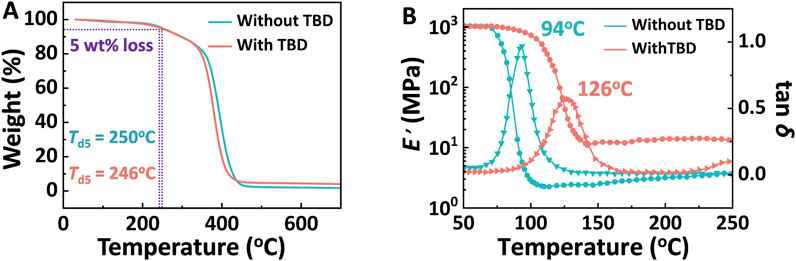
Figure 4. (A) The TGA curves of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at a heating rate of 10°C min−1. (B) Storage modulus (circle) and tan δ (triangle) of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks by using three-point bending mode.
To gain a deeper understanding of the viscoelastic properties of these networks, dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMA) was performed by using three-point bending mode. As depicted in Figure 4B, a distinct transition from the glass plateau to the rubbery plateau was evident for each network (circle in Figure 4B). The storage modulus (E′) of each network at the glass plateau was approximately 1000 MPa at 50°C. The peaks of tan δ (triangle in Figure 4B) observed at 94°C and 126°C were identified as the glass transition temperatures (Tg) for DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks, respectively. The increase in Tg aligned with the DSC results presented in Figure 2B. Leveraging the rubber elasticity theory, the cross-linking density (νe) of cross-linked networks was calculated using Equation 1:
where E′ is the elastic modulus in rubbery plateau region at temperature T (Tg + 40°C), T denotes the absolute temperature and R is the universal gas constant (8.315 J mol−1 K−1). The calculated cross-linking densities were determined to be 265 and 1358 mol m−3 for DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks, respectively. The increase in cross-linking density aligns with the findings from DSC, FTIR, and gel content analyses, further substantiating that the internal catalyst TBD facilitates more thorough cross-linking of the DGEAC/MTHPA networks. Consequently, this enhances the rigidity of the network chains and elevates the thermal properties of the material.
The mechanical characteristics of materials are often governed by the rigid structure of their network chains. Consequently, an investigation into the mechanical properties of both DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks was conducted using tensile testing (Figure 5). The results revealed that the tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and elongation at break increased from 49.12 to 79.27 MPa, from 2080.96 to 2266.19 MPa, and from 2.78% to 3.86%, respectively. This enhancement can be ascribed to the improvement of cross-linking density.
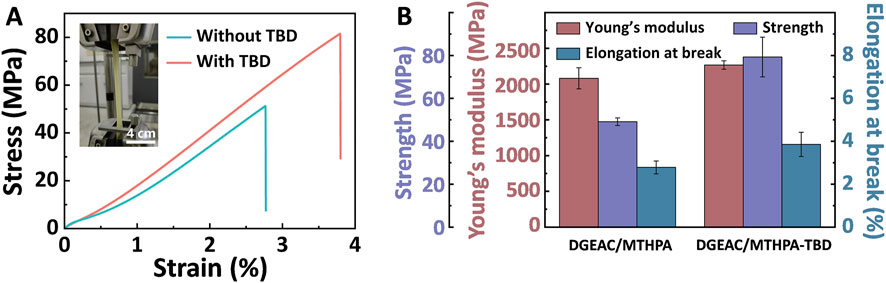
Figure 5. (A) Tensile stress–strain curves of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. (B) Values of tensile strength, Young’s modulus and elongation at break of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks.
Stress relaxation analysis was performed to explore the rearrangement of the DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks. At elevated temperatures, the cross-linked networks underwent topological rearrangement due to transesterification reactions (TERs). Specifically, the hydroxyl groups interacted with the ester bonds, resulting in the formation of new hydroxyl groups and ester bonds, leading to the rearrangement of the cross-linked networks (Figure 1B). The investigation focused on examining the changes in the relaxation modulus of both the DGEAC/MTHPA networks and the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at temperature of 200°C (Figure 6A). The relaxation time (τ*) was determined as the duration required for the material to relax to 1/e of the initial modulus (G/G0 = 1/e). The relaxation times were calculated to be 1128 s (19 min) and 598 s (10 min) for the DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at 200°C, respectively. The decrease in relaxation time observed for the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks indicates that the TERs were accelerated with the addition of the internal catalyst TBD (Capelot et al., 2012). Furthermore, the τ* of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD was 2405 s (40 min) at 180°C, 1412 s (23 min) at 190°C, 598 s (10 min) at 200°C, and 175 s at 210°C (Figure 6B). The decrease in relaxation time with increasing temperature further confirms that the TERs were accelerated with higher temperatures.
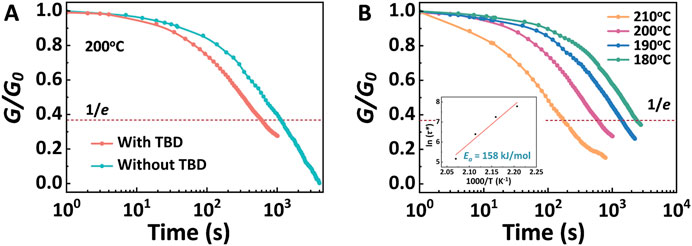
Figure 6. (A) Stress relaxation of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at 200°C. (B) Stress relaxation of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks at 180°C, 190°C, 200°C and 210°C. The inset is the fitting of experimental values of relaxation times (τ*) to an Arrhenius-type equation.
The relaxation of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks followed a Maxwell model fitted by an Arrhenius-type Equation 2:
where τ* is the relaxation time defined as the time needed to achieve a particular G/G0 value (1/e) at a given temperature, Ea is the activation energy of the bond exchange, T is the experimental temperature, and R is the universal gas constant. As shown in the inset in Figure 6B, the nearly perfect fitting was obtained with an Ea of 158 kJ mol−1, which was comparable with the values of vitrimers reported by Leibler et al. (Montarnal et al., 2011), therefor exhibiting viscosity properties of typical transesterification vitrimers.
The remodeling of materials was vividly captured in Figure 7A. Both preheated DGEAC/MTHPA sample and the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD sample were bent and secured onto a mold, subsequently heated at 200°C for 2 h in a vacuum oven. Upon cooling to room temperature, curved samples emerged due to the stress relief facilitated by topological network rearrangements. Following this, the samples were reheated at 200°C for an additional 10 min in a conventional oven. It was noticed that DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD sample failed to revert to its original shape (Figure 7B), whereas the curvature of the DGEAC/MTHPA sample decreased compared to the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD sample. This indicated that a portion of the stored entropic energy in the DGEAC/MTHPA sample was released, facilitated by the acceleration of the TERs due to the presence of the internal catalyst TBD during the 2-h heating at 200°C. These results underscore the plasticity attributes of the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks.
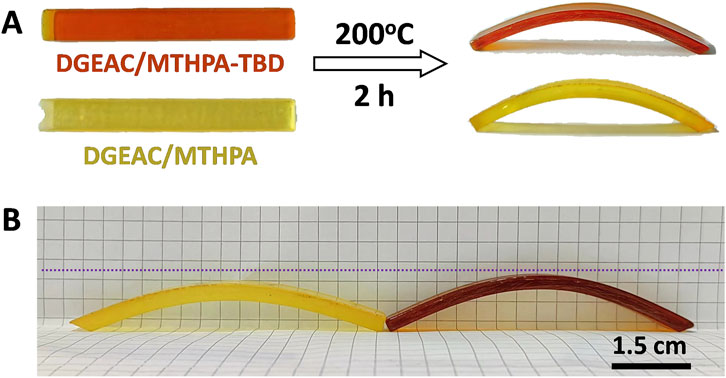
Figure 7. (A) Remodeling testing of DGEAC/MTHPA networks: The DGEAC/MTHPA sample (light yellow color) and the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD sample (brownish yellow color) were remodeled into an arc shape by heating them at 200°C for 2 h and this shape maintained after cooling to room temperature. (B) Comparison photo of arc shape of DGEAC/MTHPA (light yellow color) and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD (brownish yellow color) from (A) after heating at 200°C for 10 min.
Figure 8A demonstrates that DGEAC/MTHPA networks undergo degradation in monoethanolamine (MEA), primarily due to the large amount of ester bonds reacted with hydroxyl groups and amino groups at high temperature. To delve deeper into this process, the degradation kinetics of DGEAC/MTHPA networks were examined by measuring their relative weights at various stages of degradation. As illustrated in Figure 8B, during the degradation of DGEAC/MTHPA networks at 160°C over a period of 45 min, the weight dropped to 42% within the first 15 min, further declined to 4% at 30 min, and ultimately reached 0 at 45 min. The degradation kinetics equation was determined to be:
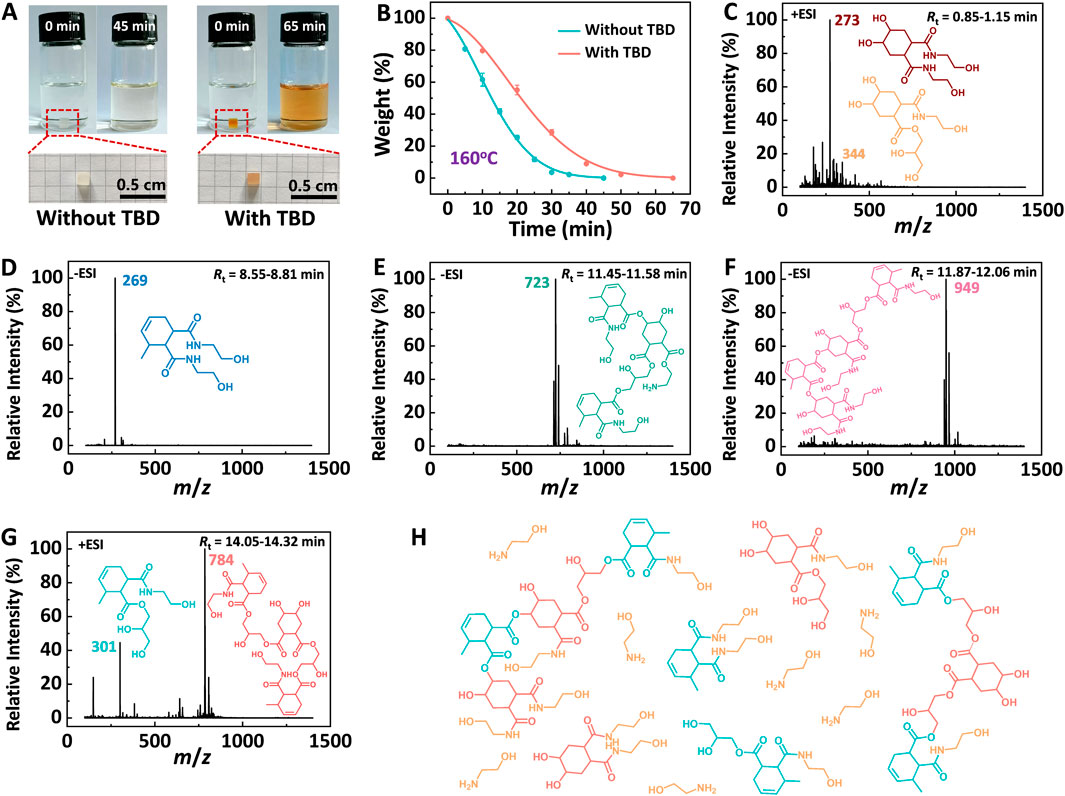
Figure 8. (A) Photos of DGEAC/MTHPA networks degradation experiment in MEA (left). Photos of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks degradation experiment in MEA (right). (B) Degradation kinetics of DGEAC/MTHPA networks and DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks in MEA at 160°C. (C–G) HPLC-MS chromatogram of degradation products of DGEAC/MTHPA networks. Retention time of degradation products was 0.85–1.15, 8.55–8.81, 11.45–11.58, 11.87–12.06 and 14.05–14.32 min. Products at 0.85–1.15 min showed [M+Na]+ at 344 m/z. Products at 8.55–8.81 min showed [M−H]− at 269 m/z. (H) Mechanism of chemical degradation of DGEAC/MTHPA networks at 160 °C in the presence of MEA.
The structures of products obtained at various retention times were identified through the analysis of mass spectrometry cleavage features (Figures 8C–G). The mass spectrometry analysis revealed the following: at 0.85–1.15 min, a [M+Na]+ peak was observed at 344 m/z (Figure 8C); at 8.55–8.81 min, a [M−H]− peak appeared at 269 m/z (Figure 8D); and at 14.05–14.32 min, a [M] peak was detected at 301 m/z (Figure 8G). The derived molecular structures, presented in Figures 8C–G, validate the occurrence of TERs during the degradation process. Following this, the proposed degradation mechanism is illustrated in Figure 8H.
As depicted in Figure 9A, it was clear that as the degradation time increased, the color of the degradation solution intensified, and the carbon fiber (CF) layers started to separate from each other. After a degradation period of 60 min, the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD matrix fully detached from the CFs. Subsequently, the CFs were extracted from the degradation solution and rinsed with acetone. To investigate the chemical structure of the virgin and recycled CFs, their Raman spectra were acquired, as shown in Figure 9B. Obviously, no discernible differences were observed between the virgin and recycled CFs, indicating that the degradation process had minimal impact on the graphitization structure of the CFs. Thereby, these recycled CFs could be reused.
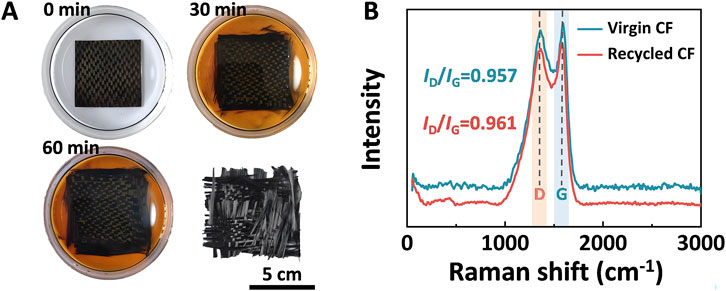
Figure 9. (A) Photos of the recycling process of DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD composites in MEA at 160°C. (B) Raman spectra of virgin and recycled CFs.
The advancement of vitrimer materials has addressed the limitations associated with traditional thermosetting resins, which are notoriously difficult to recycle or degrade. This work focused on designing and enhancing a commercially available epoxy-anhydride resin, in which diglycidyl ester of aliphatic cyclo (DGEAC) and methyl tetrahydrophthalic anhydride (MTHPA) were applied to create a high-performance epoxy vitrimer. The characterization results demonstrated that the incorporation of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo [4.4.0] dec-5-ene (TBD) facilitated cross-linking reactions, leading to an increase in cross-linking density from 265 to 1358 mol m−3 and improvement in glass transition temperature (Tg) from 94°C to 132°C. Meanwhile, the tensile strength increased from 49.12 to 79.27 MPa, Young’s modulus improved from 2.08 to 2.27 GPa, while elongation at break enhanced from 2.78% to 3.86%. Furthermore, stress relaxation tests showed that the addition of TBD expedited the topological rearrangements within the vitrimer networks. The stress relaxation time (τ*) was 2405 s (40 min) at 180°C, 1412 s (23 min) at 190°C, 598 s (10 min) at 200°C, and 175 s at 210°C, which followed by Arrhenius-type equation with their Ea at 158 kJ/mol. The remodeling tests confirmed the plastic properties of the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks, as the networks retained their permanent arc shape even after being subjected to heating. Furthermore, the DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD networks could completely degrade in monoethanolamine (MEA) at 160°C for 65 min, revealing their favorable chemical recycling properties. Based on the chemical recycling properties, carbon fiber composites (CF/DGEAC/MTHPA-TBD) were prepared, where the matrices could be completely removed from the carbon fibers in MEA after 60 min, thereby recycling carbon fibers. In summary, this work provided valuable insights into the development of environmentally friendly composites that possess recyclable and degradable properties. These epoxy vitrimers exhibited tremendous potential for high-performance epoxy and fiber reinforced composites. Further investigations and optimizations of these vitrimer materials will pave the way for their commercialization and broader adoption within the industry.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
LG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. HW: Investigation, Writing–original draft. XY: Investigation, Writing–original draft. ZZ: Writing–review and editing. LW: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. ZW: Writing–review and editing. YW: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. BZ: Writing–review and editing. XJ: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Supervision. JW: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is supported from NSFC (22205029), Key Research Program of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (2023AH052840, 2023AH051585), Project for Cultivating Excellent Young Teachers Program in Higher Education of Anhui Province (YQZD2024047). This work is also supported by the National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Key Areas Research, apply in Chuzhou University, 202410377001). We also acknowledge Anhui Province Liquid Crystal Display Panel Recycling Research Engineering Center for supporting.
Author XJ was employed by Lianyungang Lianxin FRP Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2025.1552713/full#supplementary-material
Alabiso, W., and Schlögl, S. (2020). The Impact of Vitrimers on the industry of the future: chemistry, properties and sustainable forward-looking applications. Polymers 12, 1660. doi:10.3390/polym12081660
An, W., Wang, X., Liu, X., Wu, S., and Wang, Y. (2022). Chemical recovery of thermosetting unsaturated polyester resins. Green Chem. 24, 701–712. doi:10.1039/d1gc03724b
Capelot, M., Unterlass, M. M., Tournilhac, F., and Leibler, L. (2012). Catalytic control of the vitrimer glass transition. ACS Macro. Lett. 1, 789–792. doi:10.1021/mz300239f
Chen, J., Wen, Y., Zeng, L., Wang, X., Chen, H., Huang, W., et al. (2022). Room-temperature solid-state UV cross-linkable vitrimer-like polymers for additive manufacturing. Polymers. 14, 2203. doi:10.3390/polym14112203
Chrysanthos, M., Galy, J., and Pascault, J.-P. (2011). Preparation and properties of bio-based epoxy networks derived from isosorbide diglycidyl ether. Polymer 52, 3611–3620. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2011.06.001
Denissen, W., Winne, J. M., and Du Prez, F. E. (2016). Vitrimers: permanent organic networks with glass-like fluidity. Chem. Sci. 7, 30–38. doi:10.1039/c5sc02223a
Faria, H., Pereira, C. M. C., Andrade Pires, F. M., and Marques, A. T. (2013). Kinetic models for the SR1500 and LY556 epoxies under manufacturer’s recommended cure cycles. Eur. Polym. J. 49, 3328–3336. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.06.040
Gong, H., Wu, J., Zhao, Z., Guo, Z., Gao, L., Zhang, B., et al. (2022). Recyclable high-performance glass-fiber/epoxy composites with UV-shielding and intrinsic damage self-reporting properties. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 137392. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.137392
Guo, Z., Jiao, X., Wei, K., Wu, J., and Hu, J. (2023). Comprehensive itaconic acid-based vitrimers via one-pot inverse vulcanization. Green Chem. 25, 4544–4552. doi:10.1039/d3gc00899a
Hao, C., Liu, T., Zhang, S., Brown, L., Li, R., Xin, J., et al. (2019). A high-lignin-content, removable, and glycol-assisted repairable coating based on dynamic covalent bonds. ChemSusChem 12, 1049–1058. doi:10.1002/cssc.201802615
Liu, T., Zhang, S., Hao, C., Verdi, C., Liu, W., Liu, H., et al. (2019). Glycerol induced catalyst-free curing of epoxy and vitrimer preparation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 40, 1800889. doi:10.1002/marc.201800889
Long, R., Qi, H. J., and Dunn, M. L. (2013). Modeling the mechanics of covalently adaptable polymer networks with temperature-dependent bond exchange reactions. Soft Matter 9, 4083–4096. doi:10.1039/c3sm27945f
Luo, J., Demchuk, Z., Zhao, X., Saito, T., Tian, M., Sokolov, A. P., et al. (2022). Elastic vitrimers: beyond thermoplastic and thermoset elastomers. Matter 5, 1391–1422. doi:10.1016/j.matt.2022.04.007
Ma, S., and Webster, D. C. (2018). Degradable thermosets based on labile bonds or linkages: a review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 76, 65–110. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.07.008
Montarnal, D., Capelot, M., Tournilhac, F., and Leibler, L. (2011). Silica-like malleable materials from permanent organic networks. Science 334, 965–968. doi:10.1126/science.1212648
Oliveux, G., Dandy, L. O., and Leeke, G. A. (2015). Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 72, 61–99. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.004
Pei, Z., Yang, Y., Chen, Q., Terentjev, E. M., Wei, Y., and Ji, Y. (2014). Mouldable liquid-crystalline elastomer actuators with exchangeable covalent bonds. Nat. Mater. 13, 36–41. doi:10.1038/nmat3812
Rahimi, A. R., and García, J. M. (2017). Chemical recycling of waste plastics for new materials production. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1, 0046–111. doi:10.1038/s41570-017-0046
Röttger, M., Domenech, van der Weegen, T. R., Breuillac, A., Nicolaÿ, R., and Leibler, L. (2017). High-performance vitrimers from commodity thermoplastics through dioxaborolane metathesis. Science 356, 62–65. doi:10.1126/science.aah5281
Sanjay, M. R., Madhu, P., Jawaid, M., Senthamaraikannan, P., Senthil, S., and Pradeep, S. (2018). Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: a comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 172, 566–581. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.101
Shi, Q., Yu, K., Kuang, X., Mu, X., Dunn, C. K., Dunn, M. L., et al. (2017). Recyclable 3D printing of vitrimer epoxy. Mater. Horiz. 4, 598–607. doi:10.1039/c7mh00043j
Tapper, R. J., Longana, M. L., Norton, A., Potter, K. D., and Hamerton, I. (2020). An evaluation of life cycle assessment and its application to the closed-loop recycling of carbon fibre reinforced polymers. Compos. B. Eng. 184, 107665. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107665
Wu, J., Gao, L., Guo, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, B., Hu, J., et al. (2021). Natural glycyrrhizic acid: improving stress relaxation rate and glass transition temperature simultaneously in epoxy vitrimers. Green Chem. 23, 5647–5655. doi:10.1039/d1gc01274f
Wu, J., Pan, Y., Ruan, Z., Zhao, Z., Ai, J., Ban, J., et al. (2022). Carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy with 100% fiber recycling by transesterification reactions. Front. Mater. 9, 1045372. doi:10.3389/fmats.2022.1045372
Wu, J., Yu, X., Zhang, H., Guo, J., Hu, J., and Li, M.-H. (2020). Fully biobased vitrimers from glycyrrhizic acid and soybean oil for self-healing, shape memory, weldable, and recyclable materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8, 6479–6487. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01047
Wu, Y., Wei, Y., and Ji, Y. (2023). Carbon material/vitrimer composites: towards sustainable, functional, and high-performance crosslinked polymeric materials. Giant 13, 100136. doi:10.1016/j.giant.2022.100136
Yu, K., Shi, Q., Dunn, M. L., Wang, T., and Qi, H. (2016). Carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composite with near 100% recyclability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 6098–6106. doi:10.1002/adfm.201602056
Zhao, Z., Wu, J., Gao, L., Gong, H., Guo, Z., Zhang, B., et al. (2022). Auto-catalytic high-performance recyclable carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites mediated by neighboring group participation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 162, 107160. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107160
Zheng, N., Fang, Z., Zou, W., Zhao, Q., and Xie, T. (2016). Thermoset shape-memory polyurethane with intrinsic plasticity enabled by transcarbamoylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 11421–11425. doi:10.1002/anie.201602847
Zheng, Z., Li, J., Wei, K., Tang, N., and Hu, J. (2023). Bioinspired integrated auxetic elastomers constructed by a dual dynamic interfacial healing strategy. Adv. Mater. 35, 2304631. doi:10.1002/adma.202304631
Keywords: epoxy, vitrimer, transesterification reactions, reprocessable, carbon fiber composites
Citation: Gao L, Wang H, Yao X, Zheng Z, Wang L, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang B, Jing X and Wu J (2025) High-performance epoxy vitrimer from commercial epoxy-anhydride with reprocessable and chemical degradable properties. Front. Mater. 12:1552713. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1552713
Received: 29 December 2024; Accepted: 03 February 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Wenliang Li, Jilin Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Gao, Wang, Yao, Zheng, Wang, Wang, Wang, Zhang, Jing and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianqiao Wu, d3VqaWFucWlhbzEwMTJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Xianghai Jing, YWVyb3N1bkBhbGl5dW4uY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.