
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mater., 07 February 2025
Sec. Polymeric and Composite Materials
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2025.1552100
Benzene is a prevalent environmental contaminant, and its effective removal through adsorption is crucial to mitigate both environmental and health impacts. In this study, a series of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/polylactic acid (ZIF-8/PLA) porous microspheres were prepared to adsorb/remove gaseous benzene. The ZIF-8/PLA microspheres were prepared via the double emulsion-solvent evaporation method with ammonium bicarbonate as the foaming agent, and the structures were well adjusted by varying the fabrication parameters of the microspheres. The adsorption of gaseous benzene by these microspheres was evaluated both in flowing benzene vapor and in cigarette smoke. These ZIF-8/PLA microspheres exhibited an interconnected porous network structure with a high surface area, which is beneficial for the fast gas diffusion and effective adsorption, particularly suitable for complex environments with high gas flow rates. The adsorption capacity of gaseous benzene on these ZIF-8/PLA microspheres is as high as 77–238 mg/g and 18%–44% of benzene can be removed from the cigarette smoke by using these ZIF-8/PLA microspheres as absorbents due to the interconnected hierarchical porous network enhancing the fast gas diffusion and the strong π-π stacking interactions of ZIF-8 towards aromatic hydrocarbons, showing the great potential of these ZIF-8/PLA microspheres as adsorbents for efficient removal of gaseous benzene.
Benzene is a prevalent environmental contaminant, commonly present in industrial emissions and natural sources (Zahed et al., 2024). It is also a harmful component in the cigarette smoke with a yield of about 20–100 µg (Chambers et al., 2011). Benzene poses substantial public health risks and has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (IARC, 2024). Prolonged exposure to benzene can result in a variety of health problems, from headaches and eye irritation to more severe conditions such as respiratory diseases, hematopoietic disorders, and cancer (Li et al., 2024; Galbraith et al., 2010). Hence, effective benzene removal is essential to mitigate the environmental and health impacts of benzene.
Currently, there is a rapid development of technologies for the removal of hazardous components, and adsorption is the most commonly used method in this regard (Yue et al., 2021; Scaffaro et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). This can be attributed to its cost-effectiveness, high removal efficiency, and large-scale application (Isinkaralar, 2023; Isinkaralar, 2022). Generally, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), with abundant pores, elevated specific surface area, and π-conjugated motifs are particularly suited to achieve efficient benzene removal (Li et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2024; Lv et al., 2024). Specifically, the zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8), which exhibits zeolite-like structures, has garnered attention due to its exceptional porosity, strong π-π stacking interactions, and gate-opening mechanisms that facilitate the capture of larger molecules, including benzene, toluene, and carbon tetrachloride (Gwardiak et al., 2019; Ueda et al., 2019). Moreover, the integration of MOFs with rich network materials can enhance the adsorption capacity of the composites due to the formation of a hierarchical porous structure and improved handling performance (Wang et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2017). For instance, research conducted by the Wang group introduced a new method to processing MOFs into nanofibrous filters (Zhang et al., 2016). The process employs electrospinning technology, which quickly creates three-dimensional fiber networks with hierarchical structures, allowing the composites to take full advantage of their synergistic properties (Scaffaro and Gammino, 2025; Scaffaro et al., 2023; Huo et al., 2025). Therefore, polymer binders such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), or polystyrene (PS) are mixed with MOF particles like ZIF-8, UiO-66-NH2, or MOF-74, and then spin-coated onto a fiber web substrate (Wang et al., 2019). Furthermore, a method to enhance the gas adsorption efficiency of ZIF-8 nanoparticles has been developed, wherein spherical superparticles are created through emulsion templating. These superparticles exhibit a 30-fold increase in adsorption rate compared to traditional ZIF-8 powder pellets (Fujiwara et al., 2023). The presence of superparticles endows the macroscopic material with a hierarchical pore structure, including large pores between the superparticles, small pores between the ZIF-8 particles, and micropores within the ZIF-8 framework, which facilitates effective mass transfer.
Although MOFs have been reported to exhibit certain advantages in the field of adsorbent materials, their fine powder morphology limits their adsorption capacity when applied inside devices (Cai et al., 2021). In addition, the pure microporous structure is not conducive to the rapid adsorption of target substances, especially in complex smog environments. The cigarette smoke environment is marked by large aerosol particles (0.1–1.0 μm), elevated pollutant concentrations, and an extremely brief 0.01-s exposure window for adsorbents (Yang et al., 2023). This setting necessitates that adsorbent materials rapidly capture and retain gaseous benzene within this minimal contact period. To address this issue, incorporating MOFs with porous materials with good molding properties can endow the composites with a high specific surface area while minimizing diffusion barriers, thereby achieving high benzene removal efficiencies. ZIF-8 composites (including aerogels, microspheres, and mixed matrix membranes, etc.) can gain better adsorption capacity of benzene superior to the individual components (Ali et al., 2021; Marsiezade and Javanbakht, 2020). For example, a ZIF-8/silica aerogel composite has been shown to achieve a benzene adsorption capacity of 337 mg/g at 25°C (Azhagapillai et al., 2021). Additionally, the ZIF-8/agarose composite porous carbon aerogel, with a substantial specific surface area of 1690.4 m2/g and a uniform micropore framework, has been reported to demonstrate exceptional benzene adsorptive performance. At 50% relative humidity, an adsorption capacity of 511.2 mg/g is achieved, surpassing the performance of commercial adsorbents like ZSM-5 and other MOFs such as UiO-66 (Hoffmann et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2019). Moreover, a magnetic nanocomposite of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 has also been reported to attain a benzene adsorption capacity of 129.4 mg/g at 20°C, surpassing the performance of conventional silica aerogels (Kyzas et al., 2022). Although ZIF-8 composites have been shown to be an excellent material for benzene adsorption, their adsorption applications in cigarette smoke environments are still poorly studied. Therefore, the development and structural modulation of ZIF-8 composites for improving benzene trapping capacity in cigarette smoke, along with the examination of the relationship between pore structure and adsorption performance, are necessary.
In this study, multistage porous ZIF-8/PLA composites were fabricated via the double emulsion solvent evaporation method. PLA, derived from renewable resources, is considered cost-effective and environmentally sustainable, making it suitable for large-scale applications (Rajeshkumar et al., 2021; Farah et al., 2016). Its intrinsic plasticity, tunable pore structure, and potential for surface modification enable the efficient adsorption of a wide range of organic and inorganic pollutants (Qin et al., 2022; Lagalante et al., 2020; Palmieri et al., 2020). The impact of various preparation parameters, including the ZIF-8 to PLA ratio, PLA concentration, emulsion water-to-oil ratio, and solvent evaporation temperature, on the microstructure of the resulting ZIF-8/PLA microspheres was systematically investigated. In addition, the benzene removal performance of these functional microspheres, employed as adsorbents in flowing benzene vapor and cigarette smoke, was evaluated.
Polylactic acid (PLA, molecular weight 80,000–100000), NatureWorks. hexavalent zinc nitrate, 2-methylimidazolate, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) were supplied by Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Other reagents were of analytical grade and used without further purification.
1.17 g of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O and 22.70 g of 2-methylimid-azole were dissolved in 8 mL and 80 mL of deionized water, respectively, with a molar ratio of Zn2+: 2-methylimidazole at 1:70. The solution containing Zn(NO3)2·6H2O was poured into the 2-methylimidazole solution, mixed well and stirred magnetically for 24 h. Afterwards, the resulting milky solution was centrifuged three times and washed with water. Finally, the remaining matter was dried in an oven at 100°C for 24 h.
Porous ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres were synthesised by the double emulsion-solvent evaporation technique with ammonium bicarbonate as the foaming agent (Figure 1). Firstly, the primary emulsion (W1/O) was prepared by mixing 20 mL of the internal aqueous phase (W1) containing 5 wt% ammonium bicarbonate and ZIF-8 powder with 100 mL of a dichloromethane solution containing 5 wt% PLA. Emulsification was carried out using a homogeniser (T25, IKA, Staufen, Germany) at 10,000 rpm. Subsequently, 1000 mL of 0.2 wt% PVA solution (W2) was added under continuous stirring to form a secondary emulsion (W1/O/W2). The stirring process was continued for at least 4 h to promote evaporation of the solvent. The resulting ZIF-8/PLA microspheres were then collected, thoroughly washed with deionised water and ethanol and separated by a standard sieve. Finally, the microspheres were dried at 60°C.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was performed with an IRTracer 100 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan) using the KBr method in the range of 4000–400 cm-1. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained by the SmartLab SE X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku, Japan) with a scanning range of 5°–90° and a scanning speed of 5°/min. The surface and inner structure of the microspheres were characterized with a Sigma 300 (ZEISS, Germany) field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM). The samples were attached to the SEM sample holder with double-sided tape and gold-plated in a vacuum prior to measurement. To characterise the internal structure, the microspheres were brittle fractured in liquid nitrogen and then subjected to SEM examination. Nitrogen adsorption/desorption analysis was measured on a Tristar II 3020 surface area and porosity analyzer (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, United States) with the sample maintained at −196°C using liquid nitrogen. Before the determination, the samples were degassed under vacuum at 60°C for 8 h. The surface area was calculated by the standard Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (BET) method, and the pore size distribution was determined from nonlocal density functional theory (NLDFT) model. Mercury intrusion porosimetry was performed on an AutoPore IV 9520 system (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, United States). The pore volume was calculated from measuring the total amount of mercury entering the pores under pressures ranging from 0.5 to 33,000 psi and the pore size distribution was obtained using the Washburn equation. The thermal stability was investigated by thermal gravimetric (TG) analysis using Discovery TGA 550 thermogravimetric analyzer under the operation condition of a heating rate of 10°C/min from 30°C to 1000°C under N2 atmosphere (60 mL/min).
A mass spectrometer gas analyzer (BSD-MAB, Beishide Instrument Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) was used to evaluate the adsorption performance of the material for benzene. The test conditions were set with an inlet concentration of benzene at 1500 ppm in N2, a test temperature of 25°C, and a vapor flow rate of 100 mL/min. Firstly, prior to adsorption, the samples were degassed at 60°C for 120 min. Secondly, the prepared gas was passed through the sample in the breakthrough column, where the column’s inner diameter was 5.0 mm and the sample length was 50.0 mm. The outlet concentration change was then monitored using a mass spectrometer (MS) for benzene. Finally, the adsorption capacity was calculated from the breakthrough curves according to the equation in the literature (Qi et al., 2018). To assess the regeneration and reusability of the microspheres, ZIF-8/PLA microspheres were subjected to a regeneration process, which involved washing with methanol and then vacuum drying at 60°C. The regenerated microspheres were tested for dynamic adsorption performance in flowing benzene vapor.
The removal of benzene from cigarette smoke using these ZIF-8/PLA microspheres as adsorbents was evaluated on a homemade device linked to the smoking machine (Figure 2). To measure the smoke benzene yield in the main stream, the ISO standard smoking regime was adopted with a puff volume of 35 mL, a puff duration of 2 s and a puff interval of 60 s on a linear smoker SM-450 (Cerulean, Milton Keynes, UK). The test cigarettes had a circumference of 24.4 mm and were selected from a 59 mm long tobacco rod and a 25 mm long unvented CA filter with a mass of 975 ± 15 mg and a draw resistance of 1030 ± 30 Pa and equilibrated under a constant temperature of 22°C and a relative humidity of 60% for 48 h. The amounts of adsorbents added were 10 mg/cig. Cigarette smoke was generated from the combustion cone in the main stream and passed through the adsorbents packing area for adsorption. Benzene in the gas phase of the cigarette smoke was collected by passing the entire bulk stream of smoke through a methanol-filled absorption flask in the cold trap. The yield of captured benzene was determined by Agilent 5977A GC-MS. The tests were performed on three replicates, and the data was further statistical analyzed by using ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis method.
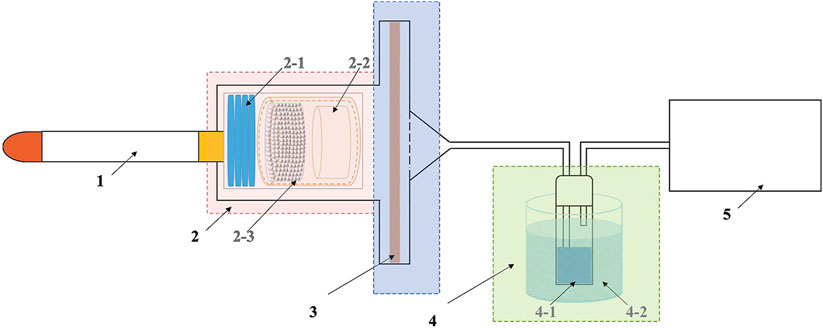
Figure 2. Illustration for cigarette smoke adsorption (1: Cigarettes; 2: Cigarette holding device and material filling chamber; 3: Particulate phase trap; 4: Gaseous phase trap; 5: Smoking machine; 2–1: Cigarette holding ring; 2–2: 120-mesh baffle; 2–3: Adsorbent material; 4-1 Methanol absorption flask; 4-2: Cold trap).
ZIF-8 nanoparticles were synthesized in an aqueous system using Zn(NO3)2·6H2O and 2-methylimidazole as precursors. As shown in the SEM image (Figure 3A), the particles exhibited a distinct dodecahedral morphology, which is the characteristic morphology of ZIF-8. The XRD pattern illustrated in Figure 3B revealed principal diffraction peaks at 2θ = 7.35°, 10.40°, 12.75°, 18.07°, 26.73°, and 29.72°, which closely matched simulated ZIF-8 structural data from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), thereby confirming the formation of phase-pure ZIF-8 crystals (Morris et al., 2012). From the nitrogen adsorption isotherm shown in Figure 3C, a sharp uptake is observed at low relative pressures, which is consistent with a Type I isotherm, indicating the presence of microporosity (Gholampour et al., 2017). Furthermore, the pore size distribution (Figure 3D), which aligned well with prior reports (Chen and Tang, 2019), indicated a peak pore size of 1.2 nm. Together, these results validated the successful synthesis of ZIF-8 with expected structural and morphological features.
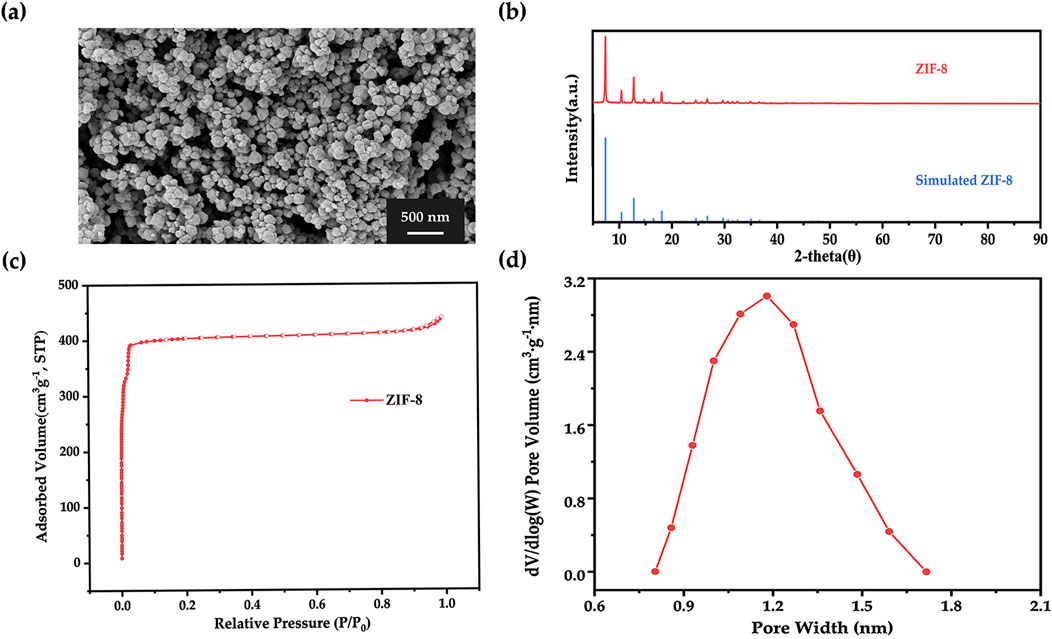
Figure 3. (A) SEM image, (B) X-ray diffraction pattern, (C) nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherm, and (D) corresponding DFT pore size distribution of ZIF-8.
Porous ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres were then synthesized using a double emulsion-solvent evaporation method. In this process, an ammonium bicarbonate aqueous solution was first emulsified in a PLA-dichloromethane solution containing ZIF-8, followed by further emulsification in a PVA solution to form microspheres. The ammonium bicarbonate stabilized the emulsion during solvent evaporation, preserving microsphere porosity, and generated pores through gas release upon decomposition (Wang et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2006). Apparently, as can be seen from the FT-IR spectroscopy data (Figure 4A), the presence of both ZIF-8 and PLA was confirmed, with characteristic peaks for ZIF-8 at Zn–N (419 cm-1), C=N (1583 cm-1), and N–H (1301 cm-1), and for PLA at C–H (2997 and 2937 cm-1) and C=O (1760 cm-1) (Tsai and Langner, 2016; Moazzen et al., 2019). Moreover, the appearance of characteristic ZIF-8 diffraction peaks in the XRD pattern (Figure 4B) further validated the composite formation. A decrease in peak intensity suggested reduced crystallinity, possibly resulting from interactions between ZIF-8 and the PLA matrix. Figure 4C presents nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms with a marked uptake at low relative pressures, confirming the existence of micropores, and the pore size distribution is shown in Figure 4D. The upward trend near P/P₀ = 1 in the nitrogen adsorption isotherms indicated that there would be macropore structure in the microspheres. To confirm the hierarchical porous structure of the ZIF-8/PLA microspheres, mercury intrusion was used to characterize the macro and super-macro pore structure, which is shown in Figure 4E. Mercury intrusion curves (Figure 4E) showed a significant increase in mercury intrusion at about 0.8–10 MPa, which indicated the existence of macropore structure in the ZIF-8/PLA microspheres. Figure 4F shows the pore size distribution calculated from the mercury intrusion curves. A high peak at 553 nm were observed for the ZIF-8/PLA microspheres, further confirming the presence of interconnected hierarchical porous network structure. SEM was used to characterize the surface and cross-sectional morphologies of the resultant microspheres (Figure 4G). The surface images (Figure 4g1, g2) exhibit rough textures with prominent large pores. Cross-sectional images (Figure 4g3, g4) revealed an internal network of interconnected extra-large pores, with ZIF particles deposited on the pore walls. This structure probably facilitated benzene adsorption, with macropores promoting gas diffusion and ZIF-8 particles providing specific adsorption sites that interact with aromatic hydrocarbons. Collectively, these analyses confirm the successful synthesis of microspheres with a high surface area and well-defined, interconnected porous architecture. Figure 4H shows the thermodynamic properties of the ZIF-8/PLA porous microspheres. The ZIF-8/PLA microspheres are stable below 150°C, suitable for most adsorbent applications, such as in cigarette filters. Specifically, the microspheres combine the distinct properties of both PLA and ZIF-8, exhibiting two separate thermal degradation stages, as observed in previous studies (Misran et al., 2018; Kervran et al., 2022). The first stage, occurring between 200°C and 400°C, is associated with the degradation of PLA, characterized by a rapid loss in mass. The second stage, between 500°C and 700°C, corresponds to ZIF-8, where a more gradual mass loss is observed, attributed to the breakdown of organic ligands in ZIF-8.
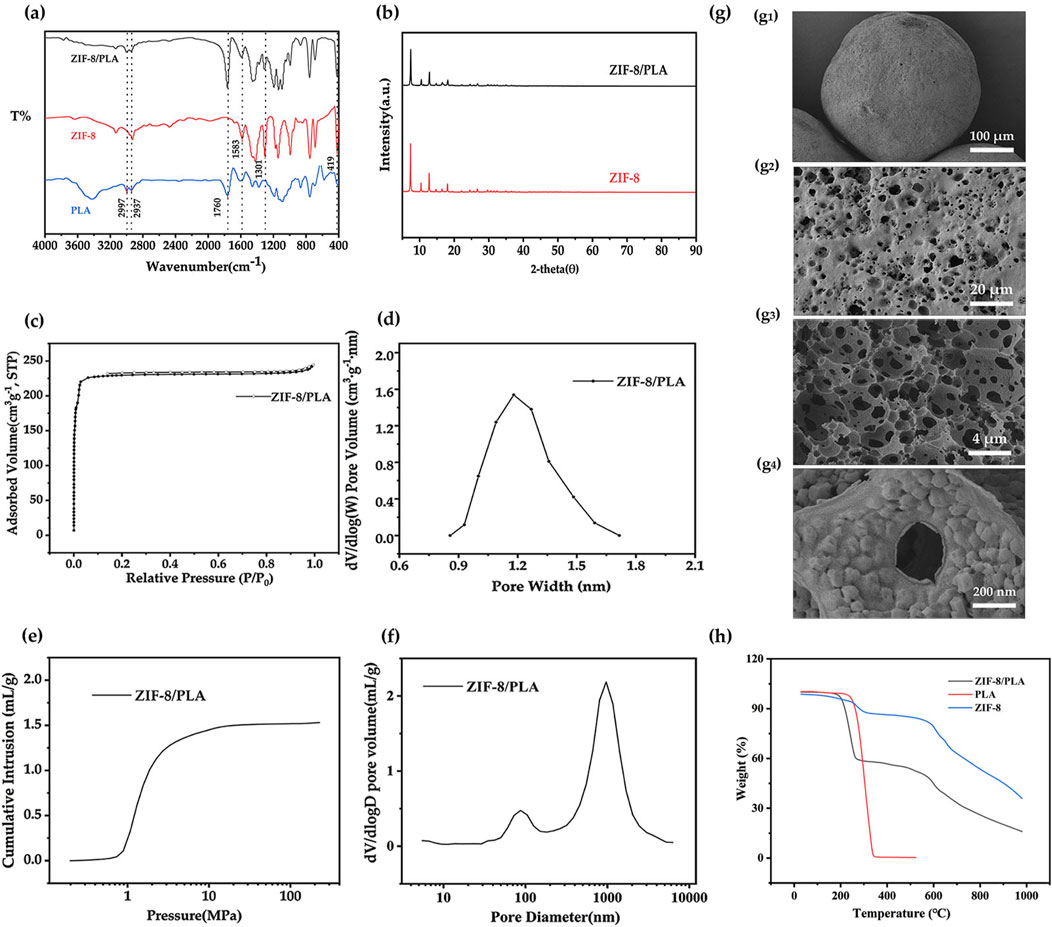
Figure 4. (A) FTIR spectrum, (B) X-ray diffraction pattern, (C, D) Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms curves and pore size distribution, (E, F) Cumulative mercury intrusion curves and pore size distribution, (G) SEM images of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres, displaying surface (g1, g2) and cross-sectional (g3, g4) views, and (H) TG curves for ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres, PLA and ZIF-8.
The impact of formulation and processing conditions on the microsphere structure was investigated by preparing multiple batches with systematic variations in the ZIF-8 to PLA ratio, PLA concentration, emulsion water-to-oil ratio (W1/O), and solvent evaporation temperature, as summarized in Table 1. The optimization of microsphere architecture depends on these factors, which control the uniformity of morphology, pore structure, and overall structural integrity.
Porous microspheres were prepared with varying PLA concentrations (3 wt%, 4 wt%, 5 wt%, 6 wt%, 7 wt%). As can be seen from the nitrogen adsorption curve (Figure 5A) and micro/mesopore characterization in Table 1, as PLA concentration increased, the BET specific surface area initially rose from 281 to 839 m2/g, then decreased sharply to 139 m2/g. A moderate increase in PLA concentration (and thus viscosity) can aid in achieving uniform nanoparticle distribution; however, excessive PLA concentrations resulted in a highly viscous oil phase, which induced polymer/particle aggregation driven by intramolecular force (Ibadat et al., 2021). Besides, mercury intrusion curves (Figure 5B) and macropore characterization (Table 1) revealed that increasing PLA concentrations led to a gradual reduction in pore volume and pore size. This further indicated that excessive PLA might hinder droplet dispersion and reduce emulsion stability. In Figure 6, the SEM images revealed that as the solution concentration increased, the microsphere diameter enlarged, while the size of surface and internal macropores decreased, consistent with the observed reduction in pore volume.
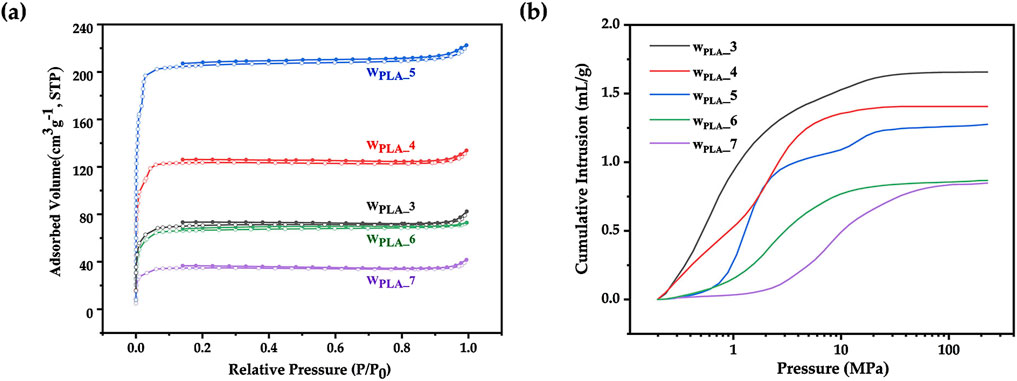
Figure 5. (A) Nitrogen adsorption curves and (B) Mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres with different PLA concentrations (3 wt%, 4 wt%, 5 wt%, 6 wt%, 7 wt%).

Figure 6. SEM images of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres fabricated with different PLA concentrations. (A) 3 wt%, (B) 4 wt%, (C) 5 wt%, (D) 6 wt%, and (E) 7 wt%. The images with subscript of 1 and 2 are the surface views while subscript of 3 demonstrated the cross-sectional view.
Porous microspheres were fabricated at different W1/O ratios, specifically 1:3, 1:5, 1:7, and 1:10. As illustrated in nitrogen adsorption curve (Figure 7A) and micro/mesopore characterization (Table 1), as the W1/O ratio decreased from 1:3 to 1:10, the BET specific surface area of the microspheres increased markedly from 432 to 943 m2/g. This increase was potentially due to the hydrophobic nature of ZIF-8, which enhanced its uniform dispersion in dichloromethane and stabilized the emulsion. Additionally, mercury intrusion curves (Figure 7B) and macropore characterization (Table 1) revealed that a lower W1/O ratio resulted in a decrease in pore volume from 1.28 to 0.73 mL/g. This reduction likely stemmed from decreased emulsion stability at lower W1/O ratios, as a diminished oil-water interface encouraged polymer solidification. The resulting variability in oil droplet sizes further promoted coalescence, leading to emulsion separation. SEM images shown in Figure 8 further reveal that as the W1/O ratio decreased, the internal pore volume of the microspheres also decreased, which was consistent with the reduced pore volume. It is noteworthy that when the W1/O ratio was 3, although the pore diameter was larger, the pore volume was smaller, which may have been due to the formation of fewer interconnected pores.
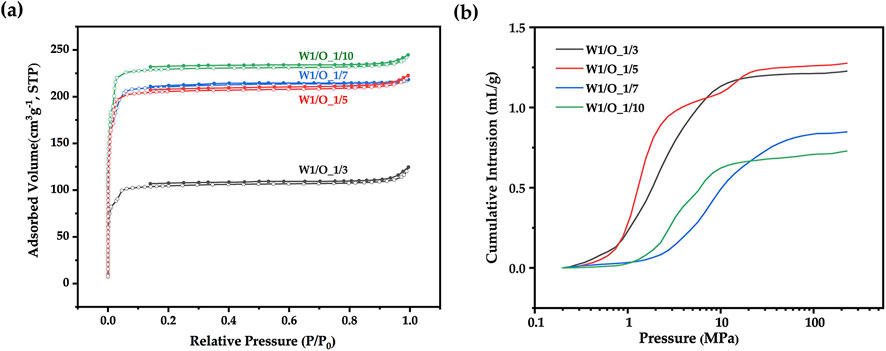
Figure 7. (A) Nitrogen adsorption curves and (B) Mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres at different W1/O ratios (1:3, 1:5, 1:7, 1:10).
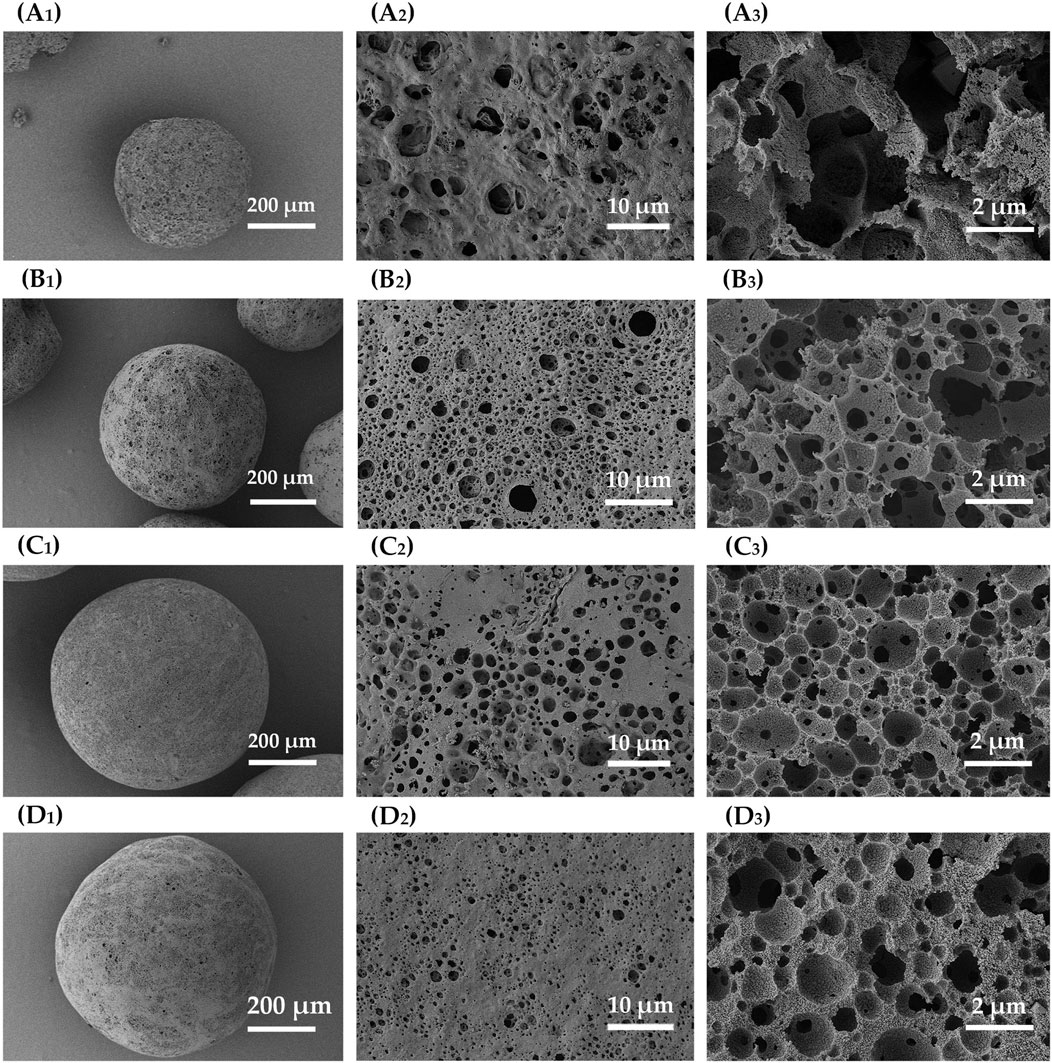
Figure 8. SEM images of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres fabricated with different W1/O ratios. (A) 1:3, (B) 1:5, (C) 1:7, and (D) 1:10. The images with subscript of 1 and 2 are the surface views while subscript of 3 demonstrated the cross-sectional view.
The solvent evaporation temperature was adjusted by varying the temperature of the external aqueous phase (W2) in the range of 25°C–45°C, which would affect the formation of the composite microsphere. Figures 9A, B shows the nitrogen adsorption curve and the mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres prepared at different solvent evaporation temperature. The pore volume and pore size were summarized in Table 1. With the solvent evaporation temperature increased from 25°C to 45°C, the BET specific surface area determined by nitrogen adsorption decreased from 839 to 218 m2/g, and the pore volume determined by mercury intrusion method decreased from 1.28 to 1.00 mL/g. The phenomenon was probably attributed to the accelerated curing of PLA at higher temperatures, which caused the microsphere structure to contract, tightly encapsulating the ZIF-8 particles and reducing their surface exposure. As exhibited in Figure 10, SEM images further revealed that with an increase in temperature, the surface pores became fewer, while the internal porosity of the microspheres increased. The interior pore size enlarged, yet the total pore volume decreased, potentially due to a reduced number of interconnected pores.
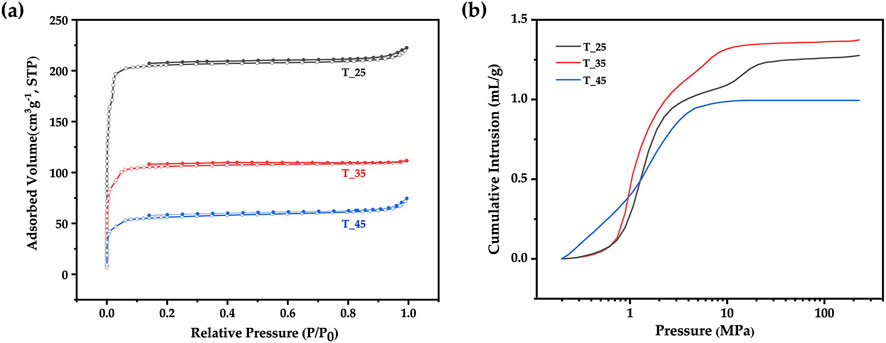
Figure 9. (A) Nitrogen adsorption curves and (B) Mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres prepared at different solvent evaporation temperature (25°C, 35°C, 45°C).
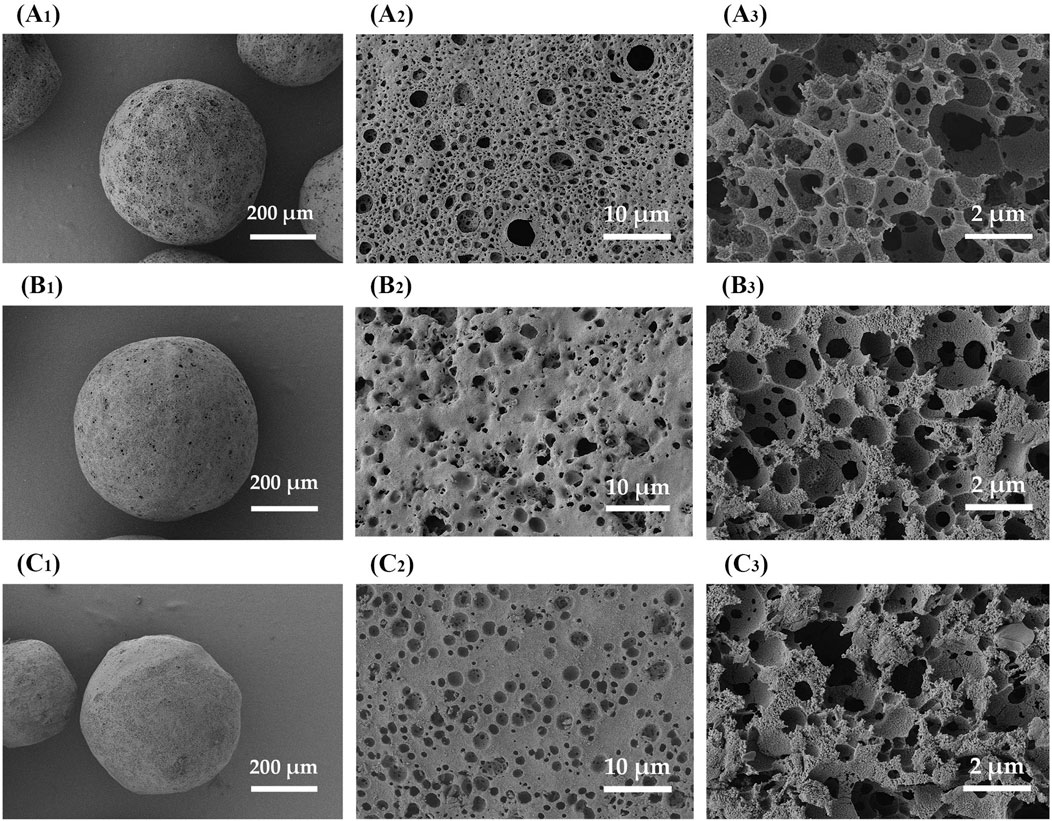
Figure 10. SEM images of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres fabricated with different solvent evaporation temperatures. (A) 25°C, (B) 35°C, (C) 45°C. The images with subscript of 1 and 2 are the surface views while subscript of 3 demonstrated the cross-sectional view.
Porous microspheres were synthesized by varying the ZIF-8/PLA ratio at 3:7, 4:6, 6:4, and 7:3. Figures 11A, B shows the nitrogen adsorption curve and the mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres prepared at different ZIF-8 to PLA ratio. The pore volume and pore size were summarized in Table 1. As the ZIF-8/PLA ratio increased, the BET specific surface area of the microspheres generally rose from 246 to 839 m2/g. However, when the ratio became too high, the specific surface area slightly decreased to 653 m2/g, which could be due to the increased solid content in the oil phase, complicating the stabilization of the primary emulsion. Meanwhile, the pore volume decreased from 1.86 to 0.92 mL/g as the ZIF-8/PLA ratio increased. This reduction may be attributed to the excessive ZIF-8 particles occupying certain pore channels within the PLA matrix, thereby limiting the overall pore size and volume of the microspheres. SEM images shown in Figure 12 further illustrated the impact of the ratio on the porous structure of the microspheres. As the ratio increased, the diameter of surface macropores enlarged, and the number of pores notably escalated. Concurrently, an increase in internal ZIF-8 particles and a more uniform distribution were observed. As the ZIF-8 to PLA ratio increased, the distribution of ZIF-8 particles within the PLA matrix became denser, significantly enhancing the surface exposure of ZIF-8 micropores. However, an excessively high ratio led to the overly compact aggregation of ZIF-8 particles, which affected emulsion stability, resulting in a reduced number of interconnected pore structures.
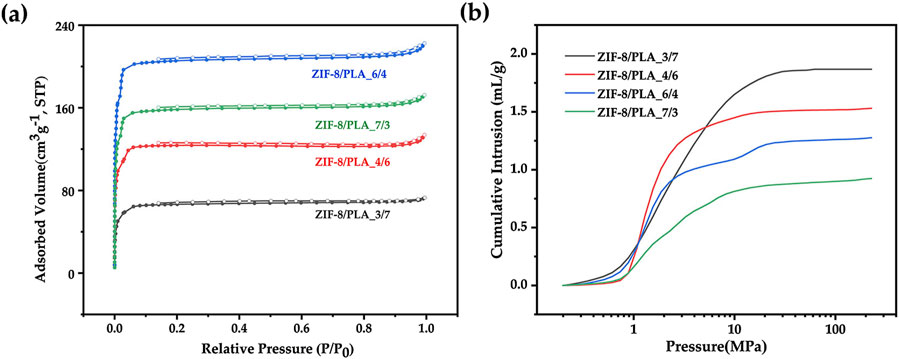
Figure 11. (A) Nitrogen adsorption curves and (B) Mercury intrusion curves of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres with different ZIF-8/PLA ratios (3:7, 4:6, 6:4, 7:3).
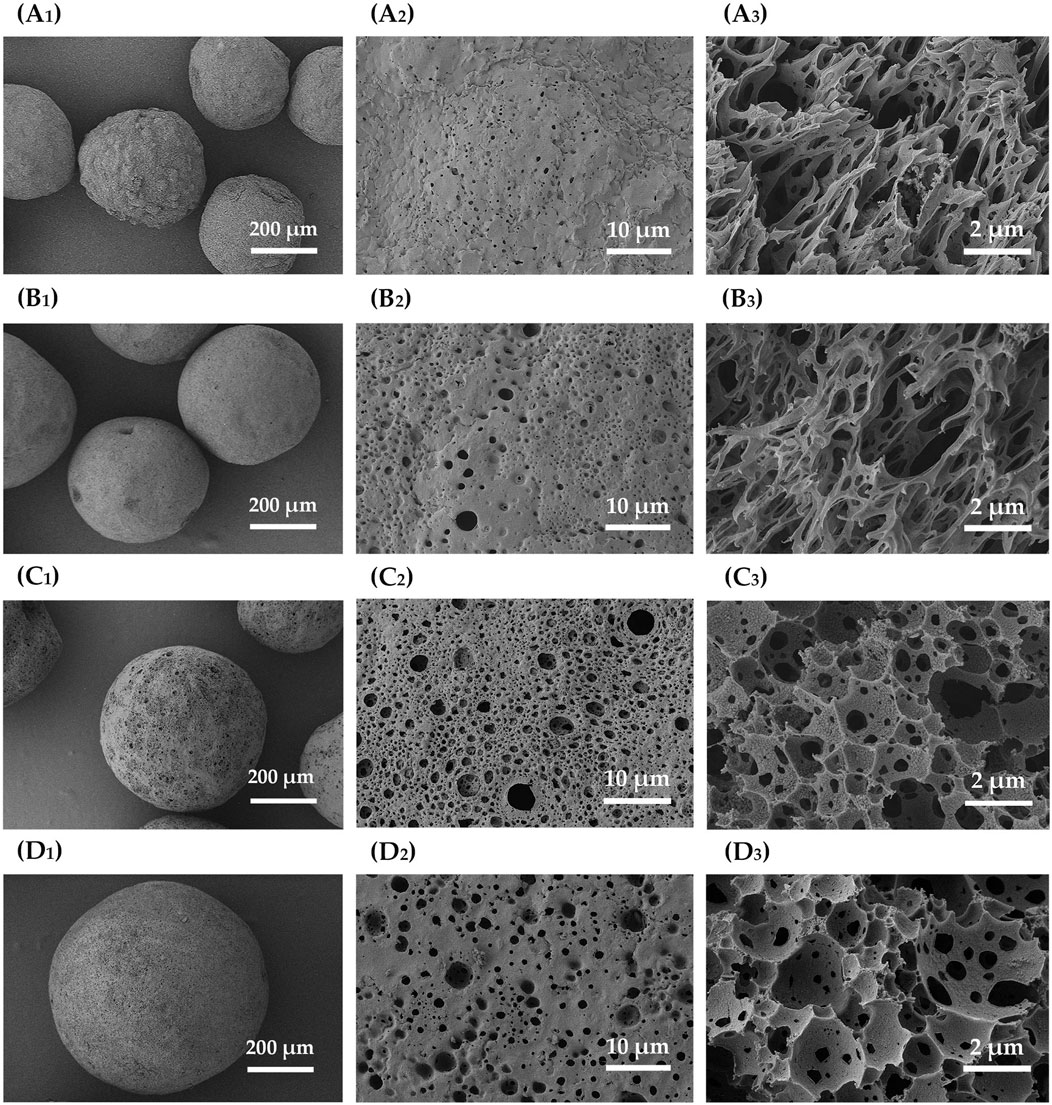

Figure 12. SEM images of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres fabricated with ZIF-8/PLA ratios. (A) 3:7, (B) 4:6, (C) 6:4, (D) 7:3. The images with subscript of 1 and 2 are the surface views while subscript of 3 demonstrated the cross-sectional view.
To assess the dynamic adsorption capacity of ZIF-8/PLA microspheres for benzene vapor, the BSD MAB mass spectrometer gas analyzer was utilized. The experiment was conducted with benzene at an inlet concentration of 1500 ppm in N2, a temperature of 25°C, and a vapor flow rate of 100 mL/min. The results in Table 2 showed that the ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres had a saturated adsorption capacity of up to 238.3 mg/g, higher than that of ZIF-8 powder (144.3 mg/g) and PLA microspheres (23.3 mg/g), indicating high adsorption performance. This can be attributed to the composite’s interconnected hierarchical porous network that facilitates fast gas diffusion, as well as the strong π-π stacking interactions between ZIF-8 and aromatic hydrocarbons.
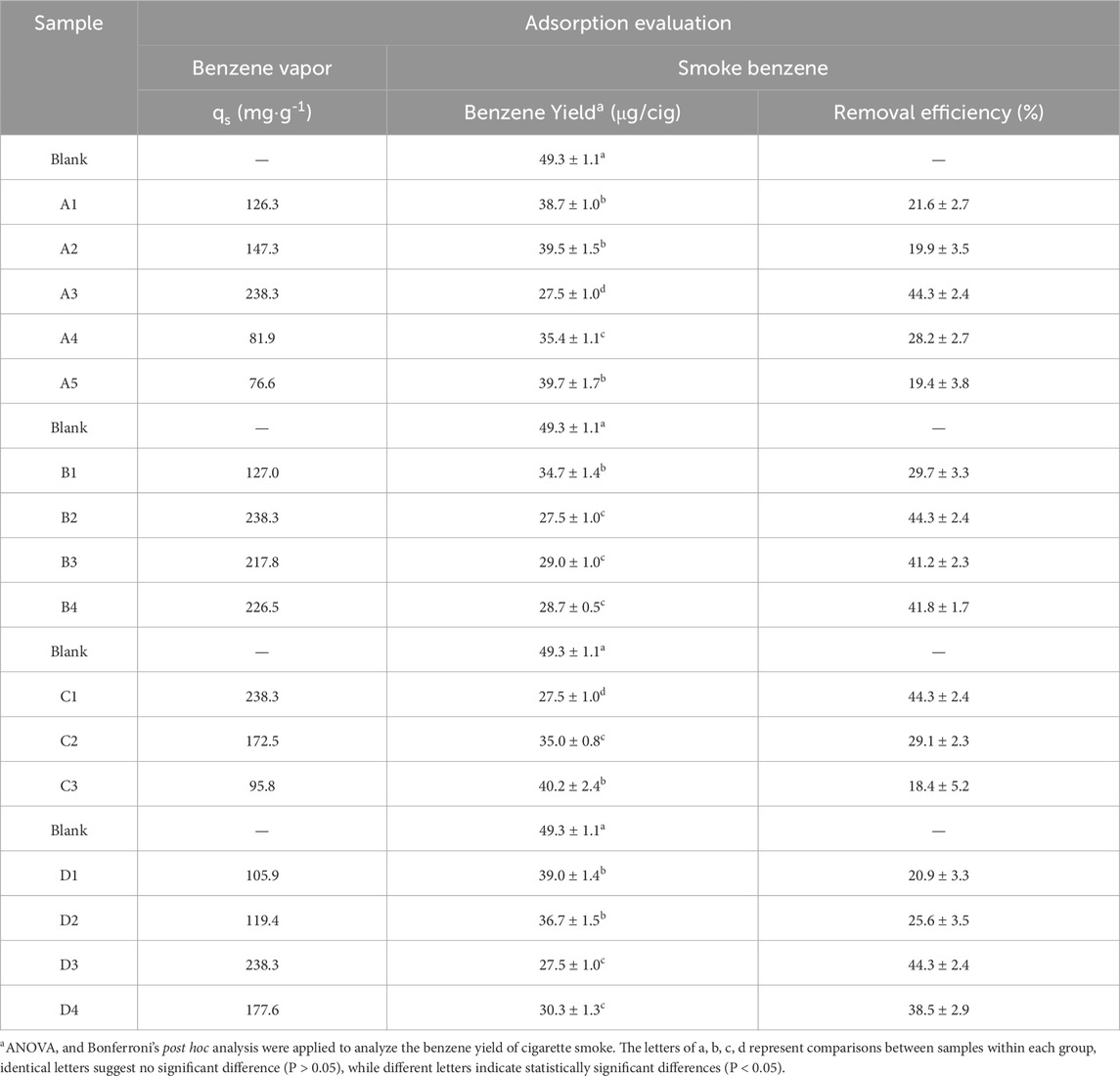
Table 2. Adsorption performance of ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres in benzene vapor and cigarette smoke.
Optimization of the preparation parameters significantly influenced the structure of the composite microspheres, thereby affecting the benzene saturation adsorption capacity. For instance, the maximum adsorption capacity of 238.3 mg/g was achieved at a 5 wt% PLA concentration, which can result from the abundance of micropores and the interconnected porosity brought about by the moderate PLA concentration. Moreover, as the W1/O decreased, the adsorption capacity increased to 217.8–238.3 mg/g, suggesting that a lower W1/O ratio enhanced ZIF-8 dispersion and micropore exposure, thereby improving adsorption performance. Conversely, an increase in the solvent evaporation temperature led to a significant reduction in adsorption capacity, decreasing from 238.3 to 95.8 mg/g. This decline is likely ascribed to the rapid evaporation of the solvent at elevated temperatures, which may induce reduced micropore exposure and the formation of interconnected pores, both resulting from the contraction of the microspheres. Lastly, higher ZIF-8 ratios of 6/4 and 7/3 resulted in adsorption capacities of 238.3 mg/g and 177.6 mg/g, respectively. This can be attributed to the higher ZIF-8 ratios facilitating stable emulsion conditions, which in turn provided more micropores and interconnected pores. The data consistently demonstrated that the interconnected hierarchical pores was crucial for the enhanced adsorption of benzene.
The reusability of the adsorbents is an important factor to evaluate the practical application value of the materials. The ZIF-8/PLA microspheres were regenerated by washing with methanol, followed by vacuum drying at 60°C. As shown in Figure 13, after three successive adsorption and desorption cycles, the adsorption capacity could remain 90% of its initial level, verifying the good benzene adsorption cycling performance of these microspheres.
To evaluate the removal efficiency of ZIF-8/PLA microspheres, cigarettes containing 10 mg/cig of microspheres and control cigarettes with an empty cavity were smoked on a homemade device linked to the smoking machine under the ISO smoking regime. The benzene removal efficiency was evaluated, with comparative results presented in Table 2. The mainstream yield of benzene in cigarette smoke was measured at 49.3 μg/cig. In contrast, cigarettes with ZIF-8/PLA microspheres as filter additives exhibited a significantly reduced benzene yield of 40.2–27.5 μg/cig. When used to remove benzene from cigarette smoke, 18.4%–44.3% of benzene could be removed, while benzene removal efficiency was 11.0% and 3.4% for ZIF-8 and PLA, respectively. Consistent with these findings, prior research demonstrated that powdered MOF adsorbents like UIO-66 exhibited limited efficacy in smoke filtration, with a maximum benzene adsorption capacity of only 9% [ = 25]. The improved benzene adsorption of the composite microspheres in cigarette smoke is due to several key interactions: i) d-π interactions between zinc ions and the benzene rings, ii) hydrophobic interactions between the methyl groups of 2-methylimidazole and the benzene rings, iii) π-π stacking interactions between the imidazole rings and the benzene rings, and iv) the hierarchical porous structure, comprising micropores and interconnected macropores, which facilitated smoke contact and transport. Moreover, precise tuning of the pore structure in PLA microspheres, achieved by optimizing preparation parameters, was essential for facilitating smoke flow and enhancing interaction with active adsorption sites, thereby significantly impacting the reduction rate of benzene in cigarette smoke. Firstly, the benzene removal efficiency increased before decreasing with rising PLA concentration. Microspheres prepared with a PLA concentration of 5 wt% achieved the highest benzene reduction rate (44.3%) due to the most stable emulsion status, forming an optimal structure rich in micropores and interconnected pores. Secondly, the substantial increase in benzene removal efficiency to 41.2%–44.3% was associated with a decrease in the W1/O ratio. Microspheres prepared with a lower W1/O ratio facilitated uniform dispersion of ZIF-8 particles, and resulting in a structure with sufficient interconnected pores. Thirdly, the significant reduction in benzene removal efficiency to 18.4% was linked to the rising temperature of the external aqueous phase. This decrease was most likely caused by rapid solvent evaporation, leading to microsphere contraction and a subsequent decrease in both micropore exposure and pore interconnectivity. Finally, the benzene removal efficiency increased significantly to 38.5%–44.3% with the rising proportion of ZIF-8, particularly at ratios of 6/4 and 7/3, which exhibited comparable adsorption capacities. This improvement was attributed to the distribution of ZIF-8 and the affected emulsion stability.
In general, both the π conjugation and hierarchical porous structure played pivotal roles in removing benzene from cigarette smoke. The π conjugation and micropores were crucial for benzene adsorption, while mesopores/macropores facilitated the passage of smoke. The ZIF-8/PLA composite microspheres were easily fabricated from commercially available polylactic acid, offering a green and economical solution and demonstrating significant potential as benzene adsorbents in cigarette filters.
In conclusion, porous composite microspheres composed of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) and polylactic acid (PLA) were successfully synthesized using the double emulsion-solvent evaporation method, with ammonium bicarbonate as the foaming agent. These microspheres featured an interconnected hierarchical porous structure, with abundant active adsorption sites, facilitating efficient gas diffusion and adsorption. Key fabrication parameters, including the ZIF-8/PLA ratio, PLA concentration, water-to-oil (W1/O) ratio, and solvent evaporation temperature, were systematically optimized to achieve an enhanced microsphere structure. The adsorption capacity of ZIF-8/PLA microspheres for gaseous benzene ranged from 77 to 238 mg g⁻1, with a benzene removal efficiency of 18%–44% from cigarette smoke. These findings suggest that the microspheres hold significant promise as adsorbents for benzene in air purification.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
JL: Writing–original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. PS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. YW: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. XS: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. BP: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. WX: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. ML: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CN: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project (Grant No. 232102230023).
Author ML was employed by China Tobacco Jiangsu Industrial Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ali, H. R., Mohamed, R. S., Mubarak, M. F., and El Shahawy, A. (2021). A novel synthesis of quaternary nanocomposite as a potential adsorbent for removal organic pollutants (benzene and toluene) from produced water. Desalination Water Treat. 227, 42–57. doi:10.5004/dwt.2021.27273
Azhagapillai, P., Al Shoaibi, A., and Srinivasakannan, C. (2021). A facile synthesis of highly porous silica aerogel hybrid materials for BTX adsorption. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 94, 1609–1615. doi:10.1246/bcsj.20200405
Cai, G., Yan, P., Zhang, L., Zhou, H. C., and Jiang, H. L. (2021). Metal–organic framework-based hierarchically porous materials: synthesis and applications. Chem. Rev. 121, 12278–12326. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00243
Chambers, D. M., Ocariz, J. M., McGuirk, M. F., and Blount, B. C. (2011). Impact of cigarette smoking on Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) blood levels in the U.S. Population: NHANES 2003–2004. Environ. Int. 37 (8), 1321–1328. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.05.016
Chen, Y., and Tang, S. (2019). Solvothermal synthesis of porous hydrangea-like zeolitic i-midazole framework-8 (ZIF-8) crystals. J. Solid State Chem. 276, 68–74. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2019.04.034
Chen, Y., Zhang, S., Cao, S., Li, S., Chen, F., Yuan, S., et al. (2017). Roll-to-roll production of metal-organic framework coatin-gs for particulate matter removal. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606221. doi:10.1002/adma.201606221
Farah, S., Anderson, D. G., and Langer, R. (2016). Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications-A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 107, 367–392. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.06.012
Fujiwara, A., Wang, J., Hiraide, S., Götz, A., Miyahara, M. T., Hartmann, M., et al. (2023). Fast gas-adsorption kinetics in supraparticle-based MOF packings with hierarchical porosity. Adv. Mater. 35, 2305980. doi:10.1002/adma.202305980
Galbraith, D., Gross, S. A., and Paustenbach, D. (2010). Benzene and human health: a h-istorical review and appraisal of associations with various diseases. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 40 (Suppl. 2), 1–46. doi:10.3109/10408444.2010.508162
Gholampour, N., Chaemchuen, S., Hu, Z. Y., Mousavi, B., Van Tendeloo, G., and Verpoort, F. (2017). Simultaneous creation of metal nanoparticles in metal-organic frameworks via spray drying technique. Chem. Eng. J. 322, 702–709. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.085
Gwardiak, S., Szczęśniak, B., Choma, J., and Jaroniec, M. (2019). Benzene adsorption on synthesi-zed and commercial metal–organic frameworks. J. Porous Mater. 26, 775–783. doi:10.1007/s10934-018-0678-0
Hoffmann, F., Cornelius, M., Morell, J., and Fröba, M. (2006). Silica-Based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 3216–3251. doi:10.1002/anie.200503075
Hu, L., Wu, W., Hu, M., Jiang, L., Lin, D., Wu, J., et al. (2024). Double-walle-d Al-based MOF with large microporous specific surface area for trace benzene adsorpt-ion. Nat. Commun. 15, 3204. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47612-x
Huo, X., Chen, W., and Gu, H. (2025). Electrospun coarse modified polystyrene/carbon aerogel nanofibrous composite membrane for effective PM2.5 air filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 354, 128793. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.128793
IARC (2024). IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/.
Ibadat, N. F., Ongkudon, C. M., Saallah, S., and Misson, M. (2021). Synthesis and cha-racterization of polymeric microspheres template for a homogeneous and porous Mon-olith. Polymers 13 (21), 3639. doi:10.3390/polym13213639
Isinkaralar, K. (2022). High-efficiency removal of benzene vapor using activated carbon from Althaea officinalis L. biomass as a lignocellulosic precursor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 66728–66740. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20579-2
Isinkaralar, K. (2023). A study on the gaseous benzene removal based on adsorption onto the cost-effective and environmentally friendly adsorbent. Molecules 28 (8), 3453. doi:10.3390/molecules28083453
Kervran, M., Vagner, C., Cochez, M., Ponçot, M., Saeb, M. R., and Vahabi, H. (2022). Thermal degradation of polylactic acid (PLA)/polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) blends: a sy-stematic review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 201, 109995. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109995
Kim, K. H., Szulejko, J. E., Raza, N., Kumar, V., Vikrant, K., Tsang, D. C. W., et al. (2019). Identifying the best materials for the removal of airborne toluene based on performance metrics-A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 241, 118408. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118408
Kim, T. K., Yoon, J. J., Lee, D. S., and Park, T. G. (2006). Gas foamed open porous b-iodegradable polymeric microspheres. Biomaterials 27, 152–159. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.05.081
Kyzas, G. Z., McKay, G., AlMusawi, T. J., Salehi, S., and Balarak, D. (2022). Removal of benzene and toluene from synthetic wastewater by adsorption onto magnetic zeolitic imidazole framework nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 12, 3049. doi:10.3390/nano12173049
Lagalante, L. A., Lagalante, A. J., and Lagalante, A. F. (2020). 3D printed solid-phase e-xtraction sorbents for removal of volatile organic compounds from water. J. Water Process Eng. 35, 101194. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101194
Li, H., Sun, Q., Li, F., Wang, B., and Zhu, B. (2024). Metabolomics of benzene exposu-re and development of biomarkers for exposure hazard assessment. Metabolites 14 (7), 377. doi:10.3390/metabo14070377
Li, X., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Wang, P., Yan, Y., and Ran, J. (2020). Adsorption materia-ls for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption pr-ocess: a review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 235 (18), 116213. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116213
Lv, J. A., Tang, Z. L., Liu, Y. H., Zhao, R. C., Xie, L. H., Liu, X. M., et al. (2024). Interior and exterior surface modification of Zr-based metal-organic frameworks for trace benzene removal. Inorg. Chem. 63, 4249–4259. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c04389
Marsiezade, N., and Javanbakht, V. (2020). Novel hollow beads of carboxymethyl cellul-ose/ZSM-5/ZIF-8 for dye removal from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 162, 1140–1152. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.229
Misran, H., Mahadi, N., Othman, S. Z., Lockman, Z., Amin, N., and Matsumoto, A. (2018). Room temperature synthesis and characterizations of ZIF-8 formation at water-F-atty alcohols interface. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1082, 012046. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1082/1/012046
Moazzen, N., Khanmohammadi, M., Garmarudi, A. B., Kazemipour, M., and Ansari Dogaheh, M. (2019). Optimization and infrared spectrometric evaluation of the mechanical p-roperties of PLA-based biocomposites. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 56 (1), 17–25. doi:10.1080/10601325.2018.1477478
Morris, W., Stevens, C. J., Taylor, R. E., Dybowski, C., Yaghi, O. M., and Garcia-Garibay, M. A. (2012). NMR and X-ray study revealing the rigidity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 13307–13312. doi:10.1021/jp303907p
Palmieri, S., Pierpaoli, M., Riderelli, L., Qi, S., and Ruello, M. L. (2020). Preparation a-nd characterization of an electrospun PLA-cyclodextrins composite for simultaneous H-igh-Efficiency PM and VOC removal. J. Compos. Sci. 4, 79. doi:10.3390/jcs4020079
Qi, J., Wei, G., Li, Y., Li, J., Sun, X., Shen, J., et al. (2018). Porous carbon spheres for simultaneous removal of benzene and H2S. Chem. Eng. J. 339, 499–508. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.157
Qin, Q., Yang, Y., Yang, C., Zhang, L., Yin, H., Yu, F., et al. (2022). Degradatio-n and adsorption behavior of biodegradable plastic PLA under conventional weathering conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 842, 156775. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156775
Rajeshkumar, G., Arvindh Seshadri, S., Devnani, G. L., Sanjay, M. R., Siengchin, S., Maran, J. P., et al. (2021). Environment friendly, renewable and sustainable poly lactic acid (PLA) based natural fiber reinforced composites-A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 310, 127483. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127483
Scaffaro, R., and Gammino, M. (2025). 3D wet-electrospun “branch leaf” graphene oxide polycaprolactone fibers structure for enhancing oil-water separation treatment performanc-e in a multi-scale design. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 43, e01200. doi:10.1016/j.susmat.2024.e01200
Scaffaro, R., Gammino, M., and Maio, A. (2022). Wet electrospinning-aided self-assembly of multifunctional GO-CNT@PCL core-shell nanocomposites with spider leg bioinspired hierarchical architectures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 221, 109363. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109363
Scaffaro, R., Gammino, M., and Maio, A. (2023). Hierarchically structured hybrid membranes for continuous wastewater treatment via the integration of adsorption and membrane ultrafiltration mechanisms. Polymers 15 (1), 156. doi:10.3390/polym15010156
Tsai, C. W., and Langner, E. H. G. (2016). The effect of synthesis temperature on the p-article size of nano-ZIF-8. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 221, 8–13. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.08.041
Ueda, T., Yamatani, T., and Okumura, M. (2019). Dynamic gate opening of ZIF-8 for bulky molecule adsorption as studied by vapor adsorption measurements and computational approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 27542–27553. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b07239
Wang, H., Zhao, S., Liu, Y., Yao, R., Wang, X., Cao, Y., et al. (2019). Membrane adsorbers with ultrahigh metal-organic framework loading for high flux separations. Nat. Commun. 10, 4204. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12114-8
Wang, Q., Zhu, S., Xi, C., and Zhang, F. (2022). A review: adsorption and removal o-f heavy metals based on polyamide-amines composites. Front. Chem. 10, 814643. doi:10.3389/FCHEM.2022.814643
Wang, S., Shi, X., Gan, Z., and Wang, F. (2015). Preparation of PLGA microspheres wi-th different porous morphologies. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 33, 128–136. doi:10.1007/s10118-014-1507-9
Wang, Z., Fu, Q., Xie, D., Wang, F., Zhang, G., and Shan, H. (2024). Facile fabrication of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8@regenerated cellulose nanofibrous membranes for e-ffective adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride. Molecules 29, 4146. doi:10.3390/molecules29174146
Yang, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Qian, J., Yang, S., Liao, H., et al. (2023). Preparation of functionalized Zr-based MOFs and MOFs/GO for e-fficient removal of 1,3-butadiene from cigarette smoke. Materials 16, 684. doi:10.3390/ma16020684
Yue, X., Ma, N. L., Sonne, C., Guan, R., Lam, S. S., Le, Q. V., et al. (2021). Mitigation of indoor air pollution: a review of recent advances in adsorption materials and catalytic oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 405, 124138. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124138
Zahed, M. A., Saligh, S., Akbarzadeh-Khoi, M., Esmaili, P., and Mohajeri, L. (2024). G-lobal atmospheric risk assessment of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX): a review. Toxicol. Vitro 98, 105825. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2024.105825
Zhang, X., Lv, X., Shi, X., Yang, Y., and Yang, Y. (2019). Enhanced hydrophobic UiO-66 (University of Oslo 66) metal-organic framework with high capacity and selectivity f-or toluene capture from high humid air. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 539, 152–160. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.12.056
Keywords: metal-organic frameworks, zeolitic imidazolate framework-8, poly lactic acid, composite microspheres, porous material, adsorbents, benzene removal
Citation: Li J, Sun P, Wang Y, Sun X, Peng B, Xu W, Liu M and Nie C (2025) ZIF-8/PLA porous composite microspheres: preparation, characterization, and effective removal of gaseous benzene. Front. Mater. 12:1552100. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1552100
Received: 27 December 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Nafisa Gull, University of the Punjab, PakistanReviewed by:
Sathickbasha K., B. S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Li, Sun, Wang, Sun, Peng, Xu, Liu and Nie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mengmeng Liu, bG1tODc4MjI3NjRAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Cong Nie, bmllY0B6dHJpLmNvbS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.