- School of Basic Education, Beijing Polytechnic College, Beijing, China
Mesoporous carbon materials have great potential in energy storage, catalysis and adsorption separation due to their unique pore size distribution, high specific surface area and excellent stability. This review discusses the synthesis methods of mesoporous carbon materials. The comparative analysis emphasizes the advantages and limitations of different preparation methods, providing a basis for the targeted design of mesoporous carbon materials. The properties of mesoporous carbon (high specific surface area, electrochemical, thermal stability, etc.) are introduced in detail, and the relationship between the physicochemical properties of mesoporous carbon and its electrochemical and adsorption properties is discussed, and the contribution of structural regulation to performance improvement is clarified. In addition, the practical applications of mesoporous carbon materials in supercapacitors, lithium-ion batteries, adsorption and catalysis are discussed. Challenges such as stability, cost-effectiveness and scalability are pointed out, and future research prospects in functional modification, precise structural design and environmentally sustainable synthesis are envisioned.
1 Introduction
Mesoporous carbon materials, characterized by a regular pore structure with pore sizes ranging from 2 to 50 nm, are widely used in molecular adsorption, catalytic reactions, and mass transport due to their high specific surface area, large pore volume, excellent thermal stability, and electrical conductivity (Sriram et al., 2020; Ueda et al., 2015). Their exceptional properties provide significant advantages in energy storage, catalysis, gas separation, and biomedical applications, particularly in supercapacitors, lithium-ion batteries, environmental protection, and drug delivery (Li et al., 2016; Zhang P. et al., 2017). The multifunctionality and outstanding performance of mesoporous carbon materials make them a focal point of both current research and industrial applications.
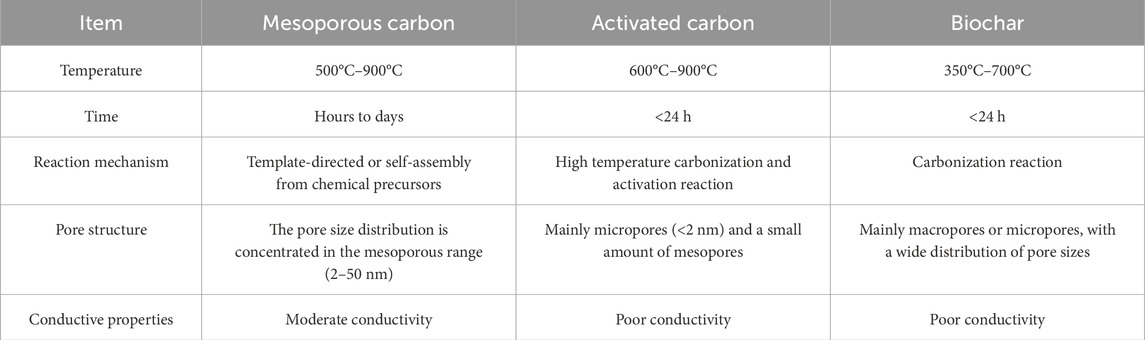
Compared to biochar and activated carbon (Table 1), mesoporous carbon materials exhibit a more ordered and tunable pore structure, which enhances molecular adsorption and catalytic performance (Kumar et al., 2023). While activated carbon has a high specific surface area, its microporous structure leads to relatively low electrical conductivity (Zhang et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2024). Similarly, biochar, commonly applied in environmental protection such as soil remediation, has a rougher pore structure and lower specific surface area. In contrast, mesoporous carbon, with its larger surface area and adjustable pore configuration, demonstrates superior performance in advanced applications like energy storage, catalysis, gas separation, and biomedicine (Zhang et al., 2024; Mehdipour-Ataei and Aram, 2023; Yuan et al., 2022).
The preparation method of mesoporous carbon directly influences its pore structure, specific surface area, pore volume, and surface chemistry, which in turn determines its performance in various applications (Zhang P. et al., 2017; Rahman et al., 2021). Different preparation techniques can lead to variations in pore size distribution, degree of graphitization, and electrical conductivity, thereby affecting its functionality in catalysis, energy storage, and adsorption (Inagaki et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017). For example, the hard template method produces highly ordered pore structures, resulting in materials with high specific surface area and pore volume, making it suitable for applications requiring precise porosity and surface area (Sakina et al., 2019; Soltanali and Darian, 2019). In contrast, the soft template method forms pores through self-assembly, offering simpler operation and better scalability, though with slightly reduced tunability of pore size. The template-free method, which forms pores via self-assembly of precursor molecules, provides advantages such as low cost and environmental friendliness, making it ideal for simplified production processes (Libbrecht et al., 2017; Glatthaar et al., 2023). Regardless of the method used, selecting the appropriate preparation technique is crucial for optimizing the functionalization and application of mesoporous carbon.
The exceptional properties of mesoporous carbon materials have led to their widespread potential applications across various fields (Figure 1). In energy storage, mesoporous carbon, with its high specific surface area and excellent electrical conductivity, is widely used in supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. As an electrode material for supercapacitors, mesoporous carbon significantly enhances both energy and power density, while in lithium-ion batteries, it not only serves as an electrode material but also as a dopant to improve cycling stability and overall performance (Sridhar and Park, 2018; Ubaidullah et al., 2021). Additionally, the superior ion transport properties of mesoporous carbon make it highly valuable in fuel cell applications, effectively increasing fuel cell efficiency and durability (Sadhasivam et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2017). In catalysis, mesoporous carbon serves as a catalyst support, with its pore structure providing abundant active sites that enhance catalyst dispersion and activity. The tunable pore size allows it to accommodate different-sized catalyst particles, optimizing catalytic performance (Ali and Zhao, 2020a; Wang S. et al., 2022). In molecular adsorption and separation, the large pore volume and adjustable pore size of mesoporous carbon make it an efficient adsorbent, capable of selectively adsorbing and separating harmful substances such as heavy metal ions and organic pollutants, playing a crucial role in environmental protection (Libbrecht et al., 2017; Han et al., 2018). Furthermore, in biosensors and drug delivery, the unique pore structure of mesoporous carbon makes it an ideal carrier for immobilizing biomolecules and delivering drugs. Its stable pore structure helps preserve the activity of biomolecules, enhancing sensor sensitivity, while its pore network facilitates controlled release and targeted drug delivery, improving therapeutic efficacy (Zhao et al., 2017; Gisbert-Garzaran et al., 2020).
Figure 1. Potential applications of mesoporous biochar (Zhang et al., 2024; Rahman et al., 2021; Pei et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023).
Despite significant progress in the research of mesoporous carbon materials, the relationship between preparation processes and application performance remains to be further explored, particularly in the areas of green fabrication techniques and functional design, where numerous challenges persist. Moreover, addressing the diverse application needs across different fields and efficiently controlling the preparation processes to develop materials with superior performance remains a key focus for future research. The purpose of this review is to systematically summarize recent advances in the preparation methods of mesoporous carbon materials and their applications in various fields, analyze key progress and existing issues, and provide insights into future development trends. By reviewing the existing literature, this work aims to offer valuable references for related research and lay a theoretical foundation for the further expansion of mesoporous carbon materials in both fundamental research and practical applications.
2 Preparation method of mesoporous carbon material
The synthesis of mesoporous materials involves three key steps: first, the self-assembly of surfactants, which forms ordered nanostructures through intermolecular interactions; second, the interaction between the surfactant and inorganic precursors, which determines the pore structure characteristics of the material; and finally, the hydrolysis and condensation reactions of the inorganic precursors, which result in the formation of a stable inorganic framework. This synthesis process relies on three main factors: the surfactant, which serves as the template to guide the formation of the structure; the inorganic precursor species, which generate the inorganic framework; and the solvent, which acts as the reaction medium (Zhang P. et al., 2017; Rahman et al., 2021). Based on these fundamental principles, the synthesis methods for mesoporous carbon materials can be classified into several categories, including template methods, solvothermal methods, sol-gel methods, and pyrolysis methods (Figure 2).
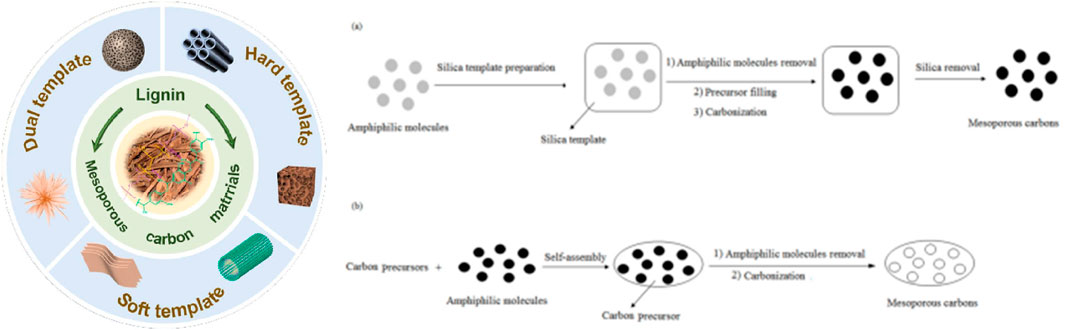
Figure 2. Classification and synthesis methods of mesoporous carbon prepared by template method (Li et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2023).
2.1 Template methods
The template method is a synthesis technique that uses a template agent to guide the formation of specific pore structures, and it has been widely applied in the preparation of mesoporous materials. In this method, the template agent plays a central role, forming pore structures through the synergistic interaction between the template and the precursor, followed by the removal of the template to obtain the desired material. The advantage of the template method lies in its ability to precisely control pore size, structure, and morphology, resulting in materials with high controllability and excellent functional properties (Inagaki et al., 2016; Libbrecht et al., 2017). Depending on the nature and role of the template agent, the template method can be further classified into hard template, soft template, and dual-template methods.
The hard template method uses stable solid materials, such as mesoporous silica or anodized aluminum, as templates. In this process, the precursor is infiltrated into the template’s pores, followed by pyrolysis or chemical etching to remove the template, resulting in a material with a mesoporous structure. Materials synthesized using this method typically have uniform pore sizes and highly ordered pore structures, making it suitable for applications requiring high precision (Sakina et al., 2019; Elma et al., 2020). However, the preparation and removal of the template can be complex, costly, and may lead to environmental concerns. The soft template method relies on the self-assembly of surfactants or block copolymers in solution to form flexible templates. The precursor interacts with the template agent to form the desired structure, followed by heat treatment to remove the template and yield mesoporous materials. This method is relatively simple, cost-effective, and suitable for large-scale production (Glatthaar et al., 2023; Hu et al., 2021). However, the pore order and structural stability of the resulting materials are typically lower than those produced by the hard template method. Nevertheless, by adjusting the type of template agent and reaction conditions, it is still possible to fabricate materials with diverse pore structures. The dual-template method combines the advantages of both hard and soft template methods, enabling the synthesis of materials with hierarchical pore structures. In this approach, the hard template provides support for the macroscopic structure, while the soft template guides the formation of microscopic pores, allowing for the synchronized control of both macro morphology and microstructure. This method can produce materials with both high order and hierarchical structures, but the process is complex and costly, making it particularly suitable for the development of high-performance energy storage materials and catalysts (Melke et al., 2019).
The template method is a key method for preparing mesoporous carbon materials. It uses templates to guide carbon precursors to form regular mesoporous structures. Lee et al. (2002) obtained ordered mesoporous carbon materials with different pore sizes through a template method. The precise pore size control of this material provides an effective way for applications in energy storage and catalysis. Kim TW et al. used a template method to synthesize ordered mesoporous carbon nanoparticles. The potential application of these particles as transmembrane delivery carriers in human cancer cells brings new material options to the biomedical field (Kim et al., 2008). Arif A et al. synthesized ruthenium (Ru) nanoparticles supported on hydrophilic mesoporous carbon for aqueous hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of microalgae oil to alkanes at 140°C. The hydrophilic mesoporous Ru/C catalyst exhibited superior catalytic performance, high activity, sustainability, and recyclability compared to commercial Ru/C (Ali and Zhao, 2020b). Xi et al. synthesized hollow mesoporous carbon spheres (HMCS) using a hard template method and in situ grew NiCo₂S₄ nanoparticles inside them. The material exhibited excellent reversible capacity and cycle stability in half-cells and full-cells, and could be cycled 340 times at 1.0 A g⁻1 with a capacity of 482 mA h g⁻1, and maintained good electrochemical performance at high current density (Xi et al., 2024). Yu et al. (2024a) synthesized nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon material NC-900 by using sucrose and melamine as carbon and nitrogen sources and silica sol as template. In the presence of molecular oxygen, NC-900 showed excellent selectivity and tolerance in the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes and could be reused 5 times. The synergistic effect of graphite N and mesoporous structure improved the catalytic activity (Xi et al., 2024).
The template method has become a key technology for achieving high-performance mesoporous carbon materials due to its excellent tunability. By optimizing synthesis conditions such as carbon source selection, template agent properties, reaction temperature and time, and subsequent treatment steps, researchers can design mesoporous carbon materials that meet specific requirements. These materials are applicable in fields such as supercapacitor electrodes and catalyst supports, offering high specific surface area, conductivity, dispersibility, and active sites. However, the template method also faces several challenges. For instance, the hard template method often requires multiple processing steps, which can lead to environmental pollution and increased costs. While the soft template method is simpler, it typically results in poorer ordering, and the template removal process may involve harmful chemicals. Additionally, the dual-template method increases both the complexity and cost due to the use of two templates. Future research should focus on developing new template systems and optimizing processes to drive breakthroughs in practical applications.
2.2 Solvothermal method
Solvothermal method is an efficient synthesis technique for mesoporous carbon materials, primarily relying on a solvent environment under high temperature and pressure to guide the carbon source in forming ordered pore structures under the direction of a template agent (Shi et al., 2019). The solvothermal process typically involves a series of steps, including solvent impregnation, carbon source dissolution, template agent assembly, filling of the reaction mixture, high-temperature and high-pressure reaction, and post-treatment of the product (Figure 3). First, an appropriate solvent, such as alcohol, acid, water, or a mixture of these, is selected to dissolve the template agent, forming a stable solution. Next, the carbon source, such as phenolic resin (PF), furfural, or urea, is dissolved in the same solvent to create a carbon source solution. These two solutions are then mixed and reacted under high temperature and pressure. The microporous structure of the template agent directs the carbon source molecules to arrange in an orderly fashion, forming the mesoporous structure. After the reaction is complete, the solvent is evaporated by applying reduced pressure and cooling. The template agent is then removed through chemical or physical methods, such as acid washing or thermal treatment, to obtain the mesoporous carbon material (Niu et al., 2018; Mruthunjayappa et al., 2022).
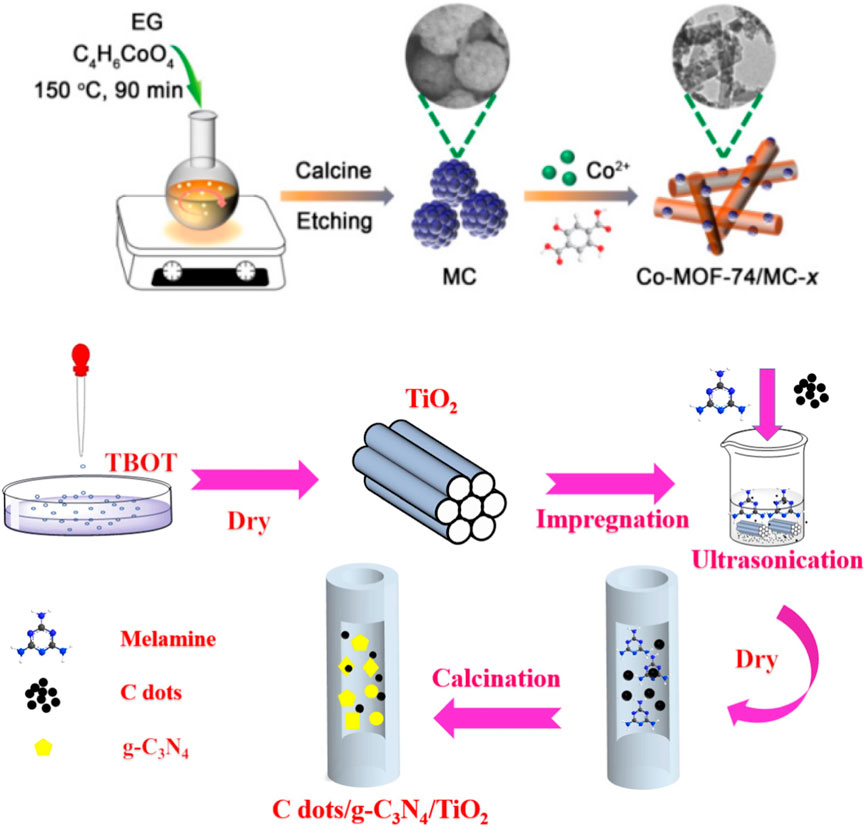
Figure 3. Examples of solution-thermal synthesis of mesoporous carbon materials (Hu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023).
The solvothermal method operates under relatively mild reaction conditions, typically at moderate temperatures and pressures. This not only helps maintain the chemical stability of the reactants but also effectively prevents structural damage from extreme conditions. Furthermore, the adjustability of solvent type, reaction temperature, and reaction time enables precise control over the material’s morphology, size, and dispersibility. The high-temperature, high-pressure environment significantly reduces the energy barrier for nucleation, promoting the directional growth of crystals, which results in materials with high crystallinity and uniform structures. Therefore, the solvothermal method offers an efficient and flexible synthesis route for producing structurally controlled, high-performance functional materials (Olmos-Moya et al., 2022; Peng et al., 2017). For example, Li et al. (2011). used a solvothermal method to prepare mesoporous carbon microspheres (MCM) from glucose as raw materials, which significantly improved the performance of high-specific surface area activated carbon (HSAC) electrodes due to their small particle size, mesoporous structure and high specific surface area. The specific capacitance reaches 230 F/g in 6 mol/L KOH, and has good electrochemical performance at high current density. Chang et al. (2014). prepared a novel organic-inorganic three-dimensional (3D) mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride by solvothermal method and showed excellent performance in the degradation of bisphenol A in heterojunction photocatalysts. The kobs of the catalyst with 10% MCN ratio was 1.6 times that of pure BiOI and 3.4 times that of MCN. The photocurrent intensity was also increased to 1.5 times and 2.0 times, respectively. The main active species was superoxide radicals.
The core of the solvothermal method lies in selecting the appropriate solvent, carbon source, and template agent, while precisely controlling the reaction conditions to achieve fine-tuning of the mesoporous structure. The advantages of this method include the ability to synthesize mesoporous carbon materials with uniform pore size distribution, high mesoporosity, and large specific surface area. Moreover, since the solvent is easily volatilized after the reaction, the post-treatment process is relatively simple and does not introduce additional impurities, thus helping to preserve the integrity of the mesoporous structure (Ibad et al., 2017; Li et al., 2022). In the preparation of mesoporous carbon materials via solvothermal method, reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, time, and the ratio of carbon source to template agent significantly affect the pore size, mesoporosity, and specific surface area. For example, increasing the reaction temperature typically enlarges the pore size, but excessively high temperatures may lead to structural instability. A moderate increase in pressure can enhance mesoporosity, while excessively high pressure may cause pore blockage (Liu et al., 2020; Fang et al., 2025). By precisely adjusting these factors, fine control over the pore structure of mesoporous carbon materials can be achieved to meet the demands of various application fields.
Despite the many advantages of the solvothermal method, it still faces certain limitations, such as stringent reaction conditions, high equipment requirements, and the potential environmental issues associated with solvent use. Therefore, future research should focus on developing eco-friendly solvents, simplifying the reaction process, and optimizing reaction conditions to reduce preparation costs and enhance environmental compatibility. These advancements will help promote the broader application of mesoporous carbon materials across various fields.
2.3 Sol-gel method
The sol-gel method is a commonly used synthesis technique for preparing mesoporous carbon materials, involving several steps including sol preparation, gelation, drying, and heat treatment (Figure 4). In this method, a carbon source (such as sucrose, phenolic resin, etc.) reacts with a metal precursor (such as silanol salts) to form a sol. Through acid or base catalysis, the precursor materials in the sol polymerize and form a gel. The gel then undergoes drying, transforming into a porous solid, and is subjected to heat treatment (carbonization) at high temperatures to produce mesoporous carbon materials (Rivera-Munoz and Huirache-Acuna, 2010; Baccile et al., 2009).
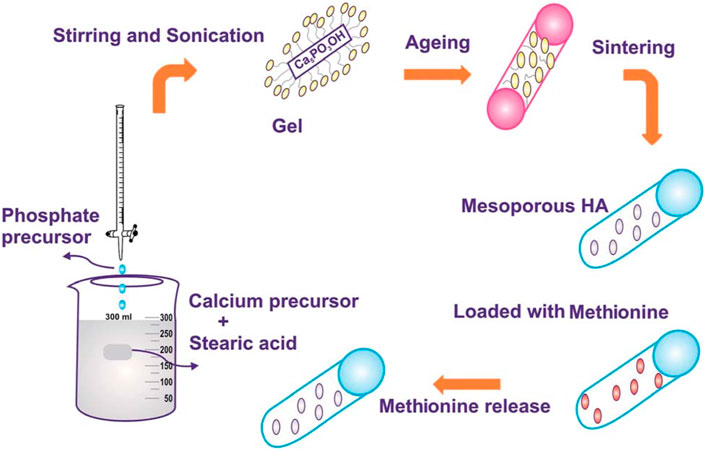
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of preparing mesoporous carbon by sol-gel method (Lett et al., 2019).
The unique advantage of the sol-gel method lies in its ability to precisely control the pore structure, pore size, and porosity of the material. By adjusting the reaction conditions of the sol, such as temperature, pH, and reaction time, mesoporous carbon materials with high specific surface area, uniform pore structures, and good purity can be obtained. The sol-gel method offers significant advantages in its high adjustability and purity. By optimizing synthesis conditions such as reaction temperature, catalyst type, and selection of carbon sources, materials with ideal pore structures and specific surface areas can be obtained. Additionally, the sol-gel process ensures the uniform distribution of metals and carbon sources, resulting in final products with consistent pore distribution and high structural uniformity (Qian et al., 2017). Therefore, the sol-gel method holds substantial potential for the preparation of high-performance mesoporous carbon materials, particularly in fields such as energy storage and catalysis, where it has widespread applications (Ortiz-Martínez et al., 2020).
However, the sol-gel method also has some limitations. First, the synthesis process is relatively complex, involving multiple steps and requiring a long synthesis time. Second, during the heat treatment process, high temperatures are often necessary to achieve complete carbonization, leading to higher energy consumption. Although optimizing the synthesis process can improve material performance, high-temperature carbonization may result in energy waste and cost issues. Lastly, the removal of templates adds additional steps, and in certain complex syntheses, the template removal process can affect the final material properties. Therefore, despite the significant advantages of the sol-gel method, further optimization is needed to overcome these challenges.
2.4 Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a relatively simple and cost-effective method for preparing mesoporous carbon materials. This technique involves the high-temperature decomposition of organic precursors, such as phenolic resin, polymers, or sugars, in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen environment, resulting in the formation of carbon materials (Figure 5). The pyrolysis process typically occurs under specific temperature and time conditions, with the choice of reaction atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon) and pyrolysis temperature significantly influencing the final product’s pore structure, specific surface area, and electrical conductivity (Shen et al., 2014; Saleem et al., 2022; Zhang R. et al., 2021). The pyrolysis method is straightforward, generally requiring no additional templates or complex reaction steps, making it highly economical and efficient for large-scale production of mesoporous carbon materials.
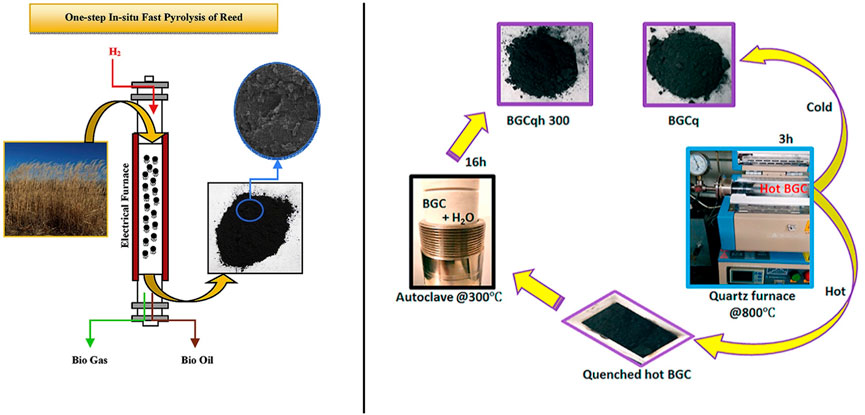
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of preparation of mesoporous carbon by pyrolysis (Rahbar-Shamskar et al., 2020; Okonkwo et al., 2021).
The pyrolysis method offers several advantages, including its simplicity and the absence of complex template systems, making it suitable for large-scale production. By adjusting the temperature, time, and atmospheric conditions during pyrolysis, it is possible to effectively control the porosity, specific surface area, and other physical properties of the carbon material. Additionally, pyrolysis is highly adaptable to various organic precursors, allowing for the production of a wide range of functionalized mesoporous carbon materials (Okonkwo et al., 2021; Du et al., 2019). However, there are also limitations to this method. First, the pore structure generated during pyrolysis may be somewhat disordered, with pore size distribution being difficult to precisely control. Second, the pyrolysis process is often accompanied by the release of harmful gases, which could have negative environmental impacts. Finally, the high-temperature requirements of pyrolysis result in significant energy consumption, and in some cases, may lead to insufficient product uniformity. Therefore, while pyrolysis is economically efficient, further optimization is needed to address these drawbacks and enhance its controllability and environmental sustainability.
2.5 Summary
This chapter systematically summarizes the main preparation methods of mesoporous carbon materials, including the template method, solvothermal method, sol-gel method, and pyrolysis method. The differences in these methods during the synthesis process determine the final material’s pore structure, specific surface area, pore volume, and other key performance indicators. The template method controls the pore structure by introducing an external template, typically achieving well-ordered mesoporous carbon, but its synthesis process is complex and costly. The solvothermal method regulates the pore structure by adjusting factors such as solvent and temperature, offering good operability, although its tunability is somewhat limited. The sol-gel method, due to its simple process and low cost, has certain advantages in large-scale production, but it is challenging to control the uniformity of the pore structure. The pyrolysis method forms mesoporous carbon with a larger pore volume by high-temperature treatment of precursor materials, suitable for low-cost large-scale production; however, the pore structure is often relatively disordered.
In conclusion, the choice of preparation method should be optimized based on the specific application needs of mesoporous carbon materials, such as electrochemical energy storage, catalytic reactions, and environmental purification.
3 Study on the properties of mesoporous carbon materials
Mesoporous carbon materials are widely used in various fields due to their excellent properties(Figure 6). With high specific surface area and large pore volume, they provide abundant surface active sites and efficient molecular diffusion pathways, making them ideal for applications in adsorption (Kumar et al., 2023; Mehdipour-Ataei and Aram, 2023), energy storage (Zhang et al., 2024; Mehdipour-Ataei and Aram, 2023), and catalysis (Hu et al., 2022; Olmos-Moya et al., 2022). Their outstanding electrochemical performance enables superior performance in supercapacitors, batteries, and electrocatalysis, offering high energy density and cycling stability (Sridhar and Park, 2018; Okonkwo et al., 2021). Additionally, mesoporous carbon materials exhibit excellent thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity even under high-temperature conditions, which makes them suitable for extreme environmental applications (Wang L. et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2013). Furthermore, the surface tunability of mesoporous carbon allows for functionalization, enabling the adjustment of surface chemical properties to further enhance their performance in adsorption, electrochemical, and catalytic processes (Huang et al., 2018).

Figure 6. Properties and potential applications of mesoporous carbon (Ma et al., 2013).
3.1 High specific surface area and large pore volume
The specific surface area and pore volume are critical parameters for evaluating mesoporous carbon materials. Techniques such as nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms, typically analyzed using Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) theory, are widely employed to measure these properties. Additionally, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) are used to visualize the pore structure and confirm the mesoporous nature of the materials. Mercury intrusion porosimetry may also complement these techniques by providing data on pore size distribution.
Mesoporous carbon materials exhibit exceptional adsorption and storage capabilities due to their unique porous structures, with specific surface areas ranging from 500 to 2,000 m2/g and pore volumes between 0.5 and 3 cm³/g. Its SEM image is shown in Figure 7. These characteristics provide abundant active sites for the adsorption of molecules, ions, or gases, making them highly effective in applications such as gas storage, catalysis, and environmental remediation (Kumar et al., 2023; Libbrecht et al., 2017). For instance, Deng et al. (2012). synthesized mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbon (MCN) and nitrogen-carbon composite materials (MCN/C) with partially graphitized structures using mesoporous silica SBA-15 as a hard template, along with ethylenediamine and carbon tetrachloride as precursors. These materials exhibited uniform mesopore sizes (∼6.3 nm) and high specific surface areas (278–338 m2/g), significantly enhancing CO₂ adsorption capacity. Additionally, the large pore volumes of mesoporous carbons are particularly advantageous for storing large molecules or particles, facilitating efficient molecular transport and diffusion, and thereby reducing diffusion resistance to improve reaction efficiency. Liu et al. (Dong et al., 2016). prepared F127-type mesoporous carbon using a solvent evaporation-induced self-assembly method. The functionalized mesoporous carbon exhibited a specific surface area of 393 m2/g, a pore volume of 0.33 cm³/g, and an average pore diameter of 3.7 nm. Zhang J. et al. (2021) used MIL-100(Cr) metal organic framework (MOF) as a template and aminoguanidine hydrochloride (AG) as a high nitrogen content single molecule precursor to synthesize mesoporous carbonitride (MCN) loaded with highly dispersed chromium oxide nanoparticles by single-step carbonization. By adjusting the ratio of AG to template, the amino functional groups of the material and its structural parameters can be controlled. When the ratio of AG to template is 1.5, the specific surface area of MCN reaches 1,294 m2/g, and the highest MCN shows the largest CO₂ adsorption capacity (16.8 mmol/g). The mesoporous carbon-based solid acid effectively catalyzed the condensation reaction between phenol and acetone. The large pore structure of mesoporous carbon facilitates the accommodation of more active components when loading catalysts, while maintaining excellent dispersibility and stability. These properties highlight mesoporous carbon materials as essential functional materials in fields such as catalysis, adsorption-separation, and energy storage, owing to their high specific surface area and large pore volume.
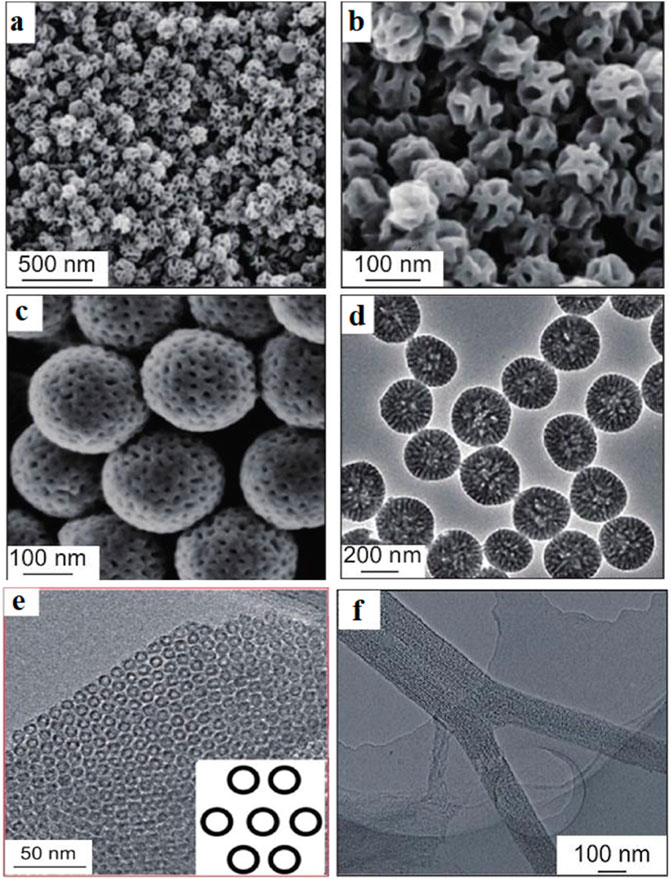
Figure 7. SEM image of mesoporous carbon material (Liang et al., 2022). SEM images of dendritic carbon nanospheres prepared by nanoemulsion method (A,B), SEM images of gradient porous mesoporous carbon nanospheres (C) and (D), TEM image of CMK-5 (E), and SEM image of single mesoporous carbon (F).
3.2 Electrochemical performance
Electrochemical properties, such as capacitance, conductivity, and charge-discharge behavior, are fundamental for evaluating the suitability of mesoporous carbon in energy storage applications. Techniques like cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) are commonly employed. These methods offer insights into the material’s energy storage efficiency, conductivity, and overall electrochemical stability.
Mesoporous carbon materials exhibit outstanding performance in electrochemical applications, primarily due to their unique structural characteristics and tunable chemical properties. Their high specific surface area provides ample active sites for charge storage, while the large pore volume and well-ordered pore structures facilitate rapid transport and diffusion of electrolyte ions, thereby reducing internal resistance (Libbrecht et al., 2017; Lei et al., 2023). Additionally, the excellent electrical conductivity of mesoporous carbon supports efficient electron transfer, enhancing the rate and efficiency of electrochemical reactions (Eftekhari and Fan, 2017). Surface functionalization, such as doping with nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, further improves electrochemical activity and optimizes interfacial reaction performance (Ren et al., 2018). Thanks to these attributes, mesoporous carbon materials demonstrate high energy density, excellent cycling stability, and fast charge-discharge capabilities in applications such as supercapacitors, batteries (e.g., lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries), fuel cells, and electrocatalysis, making them a key material for developing high-performance energy storage devices and electrocatalysts.
In supercapacitors, mesoporous carbon materials significantly enhance capacitance performance due to their high specific surface area, which enables the adsorption of more electrolyte ions(Figure 8) (Mayani et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2016). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is often employed to evaluate the electrochemical activity of materials, and analyzing the CV curve provides the specific capacitance. Specific capacitance, expressed in F/g, is a critical parameter for measuring the energy storage capability of supercapacitors; higher values indicate greater storage capacity (Wang et al., 2024). For instance, mesoporous carbon material C-MOF-T, derived from Co-MOF-74, exhibited a mesoporous structure with a specific surface area of 1,289 m2/g and a mesopore ratio of 96%, as confirmed by nitrogen adsorption-desorption tests. Electrochemical measurements demonstrated a specific capacitance of 187 F/g at a current density of 0.1 A/g, which remained at 117 F/g even at a high current density of 20 A/g, showcasing excellent rate performance. Furthermore, after 4,000 charge-discharge cycles, the specific capacitance retention was 95.7%, indicating exceptional cycling stability. These characteristics highlight the immense potential of C-MOF-T for applications in supercapacitors (Du et al., 2018; Tan et al., 2018).
Figure 8. Examples of electrochemical applications of mesoporous carbon (Wang D. et al., 2022; Kesavan et al., 2020).
In the field of lithium-ion batteries, mesoporous carbon materials have garnered significant attention due to their unique porous structures and excellent electrical conductivity (Yuan et al., 2022; Lei et al., 2023; Azam et al., 2021). As electrode materials, mesoporous carbons facilitate rapid lithium-ion diffusion through their interconnected porous networks, enhancing the charge-discharge rate of the batteries (Zhang et al., 2018; Liu M. et al., 2019). For example Wang et al. (2011) used voltammetry and amperometry as detection methods, and used 4 DNA bases, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), 6 important electroactive compounds and various biomolecules to study their electrochemical responses on ordered mesoporous carbon (OMC) and graphene (GR) modified glassy carbon electrodes (OMC/GCE and GR/GCE). The results showed that OMC/GCE enhanced the apparent electroactive surface area of these compounds (0.0726 cm3) compared with GR/GCE (0,618 cm3).
Additionally, mesoporous carbon can be used as a dopant combined with other electrode materials to improve structural stability and electrochemical performance. From a safety perspective, the porous structure of mesoporous carbon can accommodate lithium ions, effectively suppressing the growth of lithium dendrites. This suppression is crucial for preventing short circuits and thermal runaway in batteries. Furthermore, the porous nature of these materials allows for better penetration of the electrolyte into the electrode, maintaining electrochemical stability within the battery. In practical applications, researchers have assembled lithium-ion batteries using mesoporous carbon materials and conducted performance evaluations (Zhai et al., 2011; Lim et al., 2016). These studies demonstrate that mesoporous carbon electrodes deliver high capacity, excellent rate performance, and long-term cycling stability, underscoring their potential for advanced lithium-ion battery systems. For example, Zhang T. et al. (2017) synthesized a high-performance lithium-ion battery anode material by in-situ growing Fe₂O₃ on an alginate template. This mesoporous carbon material significantly improved the battery’s charge-discharge efficiency and cycling stability due to its superior electrochemical properties. Similarly, Liang et al. (2015) enhanced lithium storage performance by designing a structure with NiO nanosheets anchored on planar carbon hollow particles. This structure not only improved lithium-ion storage but also effectively suppressed the formation of lithium dendrites. Chen et al. (2024) used mesoporous carbon (CMK-3) as a conductive matrix and seven monomers with different solubility and structure to achieve uniform polymerization of monomers through in situ electropolymerization to prepare TDATA/CMK-3 composite electrodes. The results showed that the TDATA/CMK-3 composite electrode exhibited a high specific capacity of 143 mA h g⁻1, an ultra-high rate capability of 25 A g⁻1, and a capacity retention rate of 75% after up to 15,000 cycles.
These studies highlight the enormous potential of mesoporous carbon materials in improving lithium-ion battery performance, particularly in enhancing charge-discharge rates, cycling stability, and safety. With ongoing research, mesoporous carbon materials are expected to find broader applications in lithium-ion batteries. These investigations also reveal critical parameters, such as specific capacity, charge-discharge rates, charge transfer resistance, and ion diffusion rates (Chen et al., 2021; Cao et al., 2016). By optimizing these parameters, researchers can further advance the performance of lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for next-generation energy storage technologies.
With advancements in electrochemical testing technologies such as in-situ Raman spectroscopy and electrochemical mass spectrometry, researchers can now monitor the structural changes of mesoporous carbon materials in real time during electrochemical processes. This capability provides deeper insights into the mechanisms behind their electrochemical performance variations, aiding in the development and synthesis of mesoporous carbon materials with superior electrochemical properties to enhance the efficiency of energy storage devices.
Furthermore, the electrochemical performance of mesoporous carbon materials is closely tied to their pore structure. Pore size control further amplifies the advantages of mesoporous materials by balancing surface area and mass transport. Optimal mesopore sizes ensure rapid ion diffusion and electrolyte penetration, crucial for high-rate applications such as supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. In addition, the incorporation of hierarchical structures, combining mesopores with macropores or micropores, elevates the material’s functionality by enabling multi-scale ion transport. This synergy not only accelerates reaction kinetics but also enhances structural integrity during prolonged electrochemical cycling, outperforming conventional porous materials. Precise tuning of pore size, distribution, and wall characteristics can significantly improve their performance in supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. Future research will delve deeper into methods for controlling the electrochemical properties of mesoporous carbon materials. This includes incorporating functional modifications, such as introducing other elements, to further enhance their electrochemical performance, ultimately driving the practical application of mesoporous carbon materials in the energy storage field.
3.3 Thermal stability
Thermal stability is an essential property for applications under high-temperature conditions. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is commonly used to assess weight changes in the material as a function of temperature, providing information on thermal degradation and decomposition. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is another useful technique for analyzing heat capacity.
The thermal stability of mesoporous carbon materials is crucial in various applications, particularly in high-temperature or heat-demanding environments. This thermal resistance not only affects the material’s lifespan but also determines its stability in catalytic and energy storage processes, as these processes typically involve heat generation and transfer (Shin et al., 2007; Yan et al., 2007). By studying the thermal stability of mesoporous carbon materials in depth, researchers can optimize their structure, thereby enhancing their performance under extreme conditions. Due to their excellent thermal properties, mesoporous carbon materials play a vital role in numerous high-temperature applications (Wang et al., 2005; Jin et al., 2016). In catalysis, they serve as catalysts or catalyst supports that maintain structural integrity under high-temperature reaction conditions, thereby improving catalytic efficiency (Roggenbuck and Tiemann, 2005; Krawiec and Kaskel, 2006). In energy storage and conversion technologies, such as fuel cells and water electrolysis for hydrogen production, they function as electrodes or catalyst supports, contributing to improved device performance and longevity. Moreover, the high thermal conductivity and stability of mesoporous carbon materials make them ideal for use in electronic device cooling and thermal interface materials.
In environmental protection, they are used as adsorbents for high-temperature industrial emissions, effectively removing harmful chemicals (Liu et al., 2018). In aerospace, the thermal resistance and mechanical strength of mesoporous carbon materials make them ideal for manufacturing aircraft components and spacecraft thermal protection systems (Guo et al., 2015). Even in lithium-ion batteries, their thermal stability contributes to better performance and safety in high-temperature environments (Kim et al., 2020). Through precise control of pore size and wall characteristics, the application potential of mesoporous carbon materials in these fields is continuously being explored and utilized, showing vast prospects for future development.
Thermal stability is primarily evaluated using Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) (Barra et al., 2023). TGA records the change in mass of a material during heating, allowing for the analysis of weight loss rate and decomposition temperature. This helps to reveal the thermal decomposition patterns of mesoporous carbon materials and the composition of their residues. On the other hand, DSC focuses on the changes in thermal effects, such as heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and phase transition enthalpy, during heating or cooling, aiding in the understanding of the physical and chemical mechanisms behind the material’s thermal stability (Gu and Schuth, 2014; Cui et al., 2019). For example, a mesoporous carbon material synthesized from phenolic resin as a precursor showed significant results in TGA tests. The analysis indicated that mass loss began at approximately 400°C, which was attributed to the initial pyrolysis of the phenolic resin. As the temperature continued to rise, the mass loss rate increased, likely due to the further decomposition of the carbon structure. When the temperature reached around 800°C, the rate of mass loss slowed down, suggesting that most of the carbon structure had stabilized (Wang et al., 2008). DSC analysis further revealed a distinct endothermic peak around 250°C, which could correspond to the dehydration of the phenolic resin. A series of peaks between 400°C and 600°C were attributed to the pyrolysis of the carbon structure. These data suggest that the mesoporous carbon material has good thermal stability below 800°C, making it potentially suitable for applications in moderate-temperature environments. This combination of TGA and DSC provides a comprehensive understanding of the thermal stability and behavior of mesoporous carbon materials, which is essential for optimizing their performance in various high-temperature applications (Gao et al., 2008).
However, the thermal stability of mesoporous carbon materials is not fixed and can be influenced by factors such as pore size, mesoporosity, surface area, and pore wall structure. For example, smaller pore sizes and higher mesoporosity may lead to reduced thermal stability because smaller pores can accelerate heat transfer during the thermal decomposition process, while higher mesoporosity may expand the area subject to thermal degradation (Xu and Zhao, 2024). Therefore, by optimizing the pore structure, such as controlling pore size and distribution using template methods or adjusting mesoporosity by altering synthesis conditions, the thermal stability of mesoporous carbon materials can be significantly enhanced. Introducing heat-resistant elements such as N, Si, or Al into mesoporous carbon materials, or combining them with other heat-resistant materials, can greatly improve their stability under high-temperature conditions (Luo et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2014). This modification not only enhances thermal stability but may also endow the material with additional functions, such as electrical conductivity or catalytic activity, thus broadening its range of applications. Research into the thermal stability of mesoporous carbon materials is crucial for understanding and optimizing their use in high-temperature environments (Jang and Kim, 2024). Researchers can conduct precise structural characterization and thermal analysis to explore the relationship between thermal stability, pore size, and mesoporosity. Based on these studies, more stable and practically applicable mesoporous carbon materials can be developed. With ongoing research and improvement, the potential for mesoporous carbon materials in energy storage, catalysis, and other fields will continue to grow.
3.4 Surface adjustability
Surface adjustability involves the functionalization and chemical modification of mesoporous carbon. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is frequently used to analyze surface chemical composition and functional groups. Additionally, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is applied to identify specific functional groups introduced during modification. Raman spectroscopy and zeta potential measurements can also provide insights into the surface characteristics and stability of modified materials.
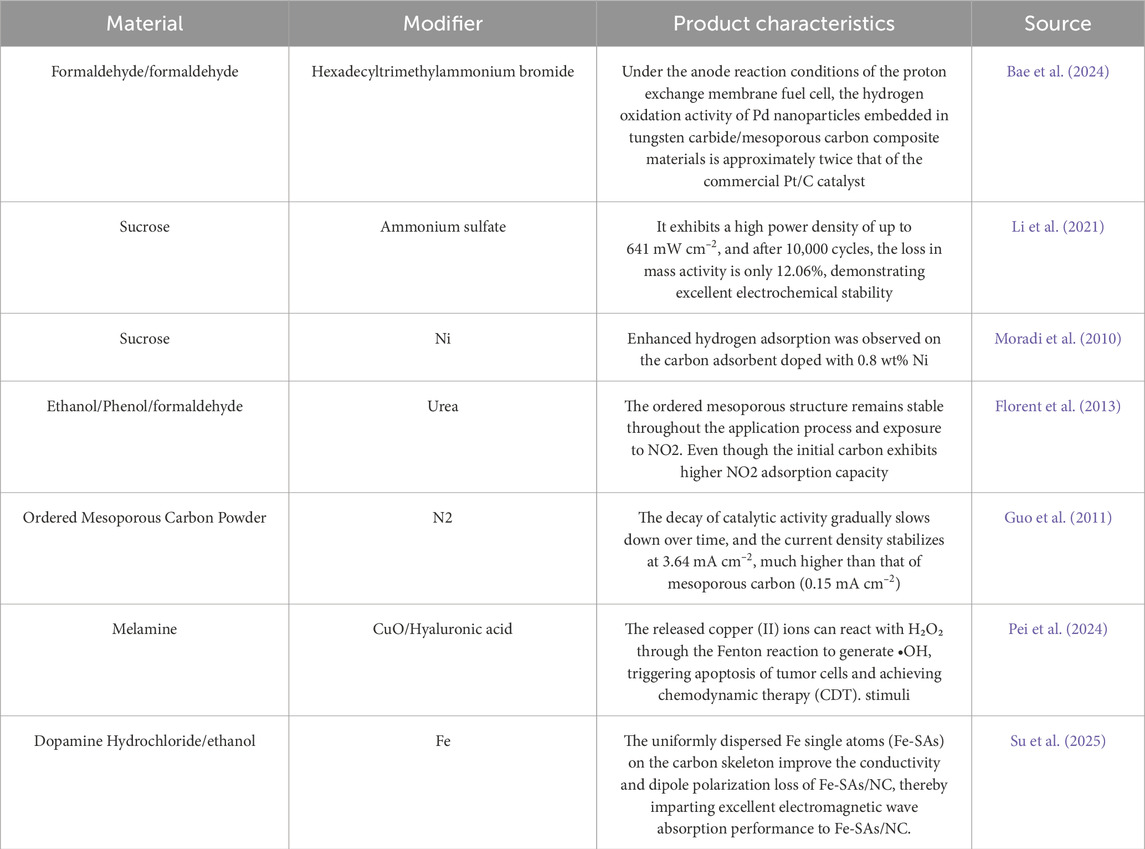
Mesoporous carbon materials possess flexible and tunable surface chemistry, which stems from their rich carbon framework and a variety of modification methods. By introducing functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or carbonyl groups, or by doping heteroatoms like N, S, P, or O, the surface properties of mesoporous carbon can be significantly altered, granting it specific functionalities (Table 2).
For example, in energy storage applications, particularly in supercapacitors, nitrogen doping enhances the carbon’s electronic conductivity and introduces active sites that promote charge storage. This results in improved energy and power densities, as the combination of high surface area from the mesoporosity and the presence of heteroatoms provides more sites for ion adsorption, thereby enhancing the efficiency and longevity of charge-discharge cycles. This functionalization leads to more efficient energy storage systems with greater cycle stability.N doping not only improves hydrophilicity but also enhances electrochemical activity, making it excellent for supercapacitors and redox reactions (Li et al., 2013).
In the field of catalysis and electrocatalysis, the incorporation of heteroatoms significantly alters the electronic structure of mesoporous carbon, increasing its catalytic activity. Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbons, for instance, have been extensively studied for their ability to catalyze key reactions such as oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution. The presence of nitrogen atoms introduces basic sites that facilitate electron transfer, making these materials suitable for platinum-free catalysts in fuel cells. Furthermore, the functionalization of mesoporous carbon with heteroatoms can improve the selectivity and reactivity of the material in various catalytic processes.
In environmental remediation, mesoporous carbons doped with heteroatoms such as sulfur and oxygen show enhanced adsorption properties for pollutants such as heavy metals, organic contaminants, and CO₂. These modifications generate functional groups like hydroxyl, carbonyl, and thiol, which enhance the material’s ability to bind and remove pollutants. For example, sulfur-doped mesoporous carbon has demonstrated superior adsorption capacity for heavy metals, such as mercury, making it highly effective for water treatment and air purification applications. Sulfur doping effectively increases its selectivity for metal ion adsorption, useful in wastewater treatment or as a catalyst support (Zhang J. et al., 2021; Xie and Guo, 2022).
In gas storage and separation, the doping of heteroatoms alters the pore structure and surface chemistry of mesoporous carbon, improving gas adsorption and selectivity. Nitrogen doping, in particular, has been found to enhance the uptake of CO₂, with the nitrogen atoms interacting with CO₂ molecules. The increased surface area and tailored pore structure also enable more efficient hydrogen storage and natural gas separation, making heteroatom-doped mesoporous carbons attractive for energy applications requiring specific molecule discrimination (Singh et al., 2017; Liu X. et al., 2019).
The functionalization of mesoporous carbon with heteroatoms has also shown promise in sensor and biosensor applications. The introduction of heteroatoms improves the electrochemical properties of mesoporous carbon, which leads to higher sensitivity and specificity in detecting a range of analytes. For instance, nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon exhibits enhanced performance in glucose sensing and the detection of toxic gases, owing to the increased number of active sites and improved surface reactivity. This functionalization also improves the response time and sensitivity of sensors, making them more reliable for real-time monitoring (Yang et al., 2021; Kochana et al., 2016).
In biomedical applications, heteroatom doping in mesoporous carbon enhances its potential for drug delivery and bioimaging. The incorporation of nitrogen, for example, improves the material’s surface chemistry, which facilitates the adsorption and controlled release of therapeutic agents. Additionally, heteroatom doping can influence the material’s surface charge and biocompatibility, making it more suitable for use in medical and therapeutic applications (Sivarasan et al., 2023).
Additionally, the surface functional groups of mesoporous carbon can be further optimized through heat treatment, chemical modification (such as oxidation or reduction), or plasma treatment. For instance, increasing oxygen-containing groups via oxidation can enhance adsorption capacity for polar molecules, making it suitable for environmental pollutant removal (Liu et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2011). Surface modification can also regulate the interfacial interactions between mesoporous carbon and other materials, such as enhancing bonding with polymers or metals, enabling the development of composite materials or highly efficient catalysts (Li et al., 2013; Li et al., 2021).
This controllable surface modification ability allows mesoporous carbon materials to exhibit high functionalization and specificity in various fields, including catalytic reactions, adsorption separation, energy storage devices, and biomedicine. Its design flexibility and tunability give it tremendous potential for future material development.
3.5 Summary
This chapter reviews the preparation process of mesoporous carbon materials and their application fields. Mesoporous carbon materials are widely used in gas storage, catalysis, electrochemical energy storage and other fields due to their unique pore structure, high specific surface area and good thermal stability. By regulating the synthesis conditions, the pore size distribution, specific surface area and surface chemical properties of mesoporous carbon materials can be effectively adjusted, which makes them show great application potential in environmental protection, energy storage and catalytic reactions. In addition, with the deepening of research, the progress in the functionalization of mesoporous carbon materials has provided new possibilities for their application in a wider range of fields. Future research should focus on the optimization of the preparation technology of mesoporous carbon materials and their application in high-efficiency environmental protection and new energy technologies.
4 Applications of mesoporous carbon materials
4.1 Supercapacitors
The application of mesoporous carbon materials in supercapacitors is mainly due to their excellent electrochemical properties and structural advantages. Due to its large specific surface area, this material is able to absorb a large number of electrolyte ions, thereby significantly enhancing the energy density of the capacitor (Lim et al., 2016). In addition, its excellent conductivity and adjustable pore structure make the charge transfer and ion diffusion process more efficient, which helps to improve the power density of the capacitor. In supercapacitor electrode materials, it is particularly important to optimize the pore size, porosity and specific surface area of mesoporous carbon, which directly affect the specific capacitance and conductivity of the material (Sridhar and Park, 2018; Wang et al., 2016).
To further improve the performance of mesoporous carbon in supercapacitors, researchers are optimizing its electrochemical properties through functional modification. For example, the incorporation of elements such as sulfur (S) or nitrogen (N) can enhance the conductivity and stability of electrode materials and improve charge storage efficiency (Du et al., 2019; Liu M. et al., 2019). For example, the sulfur-doped mesoporous carbon material S-OMC-900 has a specific surface area of 1,230 m2/g, a pore diameter of 4.6 nm, and a pore volume of 2.03 cm³/g, showing significant improvement in electrochemical performance (Maluta et al., 2018). By adjusting the pore size and the concentration of doped elements, the charge storage and transfer capacity of mesoporous carbon can be effectively adjusted to meet the needs of different supercapacitor designs. The structural design of mesoporous carbon is also crucial. By adjusting the reaction parameters in the solvothermal method, such as the ratio of carbon source to template, the temperature and duration of the reaction, researchers can finely adjust the pore size distribution of the material, thereby improving the charging and discharging speed and energy storage efficiency of the supercapacitor (Zhang et al., 2018). Xing et al. prepared nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon (N-MCs) using aniline as the precursor and Pluronic F127 as a template through oxidative polymerization in a nitrogen atmosphere at 850°C, followed by activation in KOH solution. The results showed that the specific surface areas of N-MCs and nitrogen-doped carbons (N-Cs) were 721 m2/g and 394 m2/g, respectively. At a current density of 0.2 A/g, the specific capacitances of N-MCs and N-Cs reached 318 F/g and 106 F/g, respectively. Moreover, after 5,000 charge-discharge cycles at various current densities, N-MCs retained over 96% of their initial capacitance, demonstrating excellent cycling stability (Xin et al., 2017).
Recent studies demonstrate the industrial potential of converting waste plastics into advanced mesoporous carbon materials for supercapacitors, offering sustainable solutions for energy storage and environmental challenges. One notable example involves the production of porous carbon nanosheets (PCNSs) through catalytic carbonization of mixed waste plastics on organically-modified montmorillonite (OMMT) followed by KOH activation. The resulting PCNSs featured hierarchically micro-/mesoporous structures with pore sizes centered at 0.57, 1.42, and 3.63 nm, a high specific surface area of 2,198 m2/g, and a large pore volume of 3.026 cm³/g. These properties enabled PCNSs to achieve outstanding supercapacitor performance, with specific capacitances of 207 F/g and 120 F/g at 0.2 A/g in aqueous and organic electrolytes, respectively, maintaining excellent rate capability even at high current densities (Wen et al., 2019). In addition, Lian et al. (2019) developed a greener, cost-effective method to produce graphene/mesoporous carbon (G@PE40-MC700) by low-temperature carbonization of polyethylene plastic waste combined with graphene oxide and flame retardants, without the need for activating agents. This material exhibited a surface area of 1,175 m2/g and mesopore volume of 2.3 m³/g, delivering an energy density of 63.3 Wh/kg and retaining 89.3% cycling stability over 5,000 cycles in high-voltage (4.0 V) symmetric supercapacitors using EMIMBF4 electrolyte. Together, these studies demonstrate the potential of waste plastics as a resource for scalable, low-cost production of advanced materials for energy storage applications.
Mesoporous carbon materials, with their unique pore structure and tunability, exhibit excellent performance in supercapacitors, particularly in terms of high specific surface area, high conductivity, and good cycling stability. Through continuous structural optimization and functionalization improvements, the application of mesoporous carbon materials in supercapacitors is expected to become increasingly widespread, driving innovation in this technology and providing more efficient and reliable energy solutions for portable electronic devices and electric vehicles.
4.2 Lithium-ion battery
The application of mesoporous carbon materials in lithium-ion batteries is mainly due to their excellent electrical conductivity, stable pore structure and ability to efficiently capture and release lithium ions (Eftekhari, 2017; Shahsavarifar et al., 2024). As an electrode material, mesoporous carbon can provide a large number of active sites to accelerate the diffusion of lithium ions, thereby improving the energy density and power density of the battery. Its high specific surface area and porosity are conducive to the rapid insertion and extraction of lithium ions, which helps to improve the rate performance of the battery. In addition, the pore structure of mesoporous carbon facilitates the penetration of electrolytes, thereby maintaining the electrochemical stability inside the battery. In lithium-ion battery negative electrode materials, the pore size and distribution of mesoporous carbon have a decisive influence on the diffusion path of lithium ions. The ideal mesopore size should match the size of lithium ions, thereby reducing the diffusion resistance and increasing the diffusion rate of lithium ions (Wang et al., 2019). For example, mesoporous carbon materials with pore sizes between 0.5 and 2 nm can significantly promote the deintercalation process of lithium ions, thereby enhancing the charge and discharge efficiency of the battery. In the hard template method, by selecting an appropriate mesoporous silica template, a mesoporous structure of this size can be obtained, further optimizing the negative electrode performance (Huang et al., 2021). In cathode materials, mesoporous carbon is often used as a basic carrier or doping component for lithium ion embedding, which improves the Coulombic efficiency and cycle stability of cathode materials by enhancing the conductivity of active materials and improving the efficiency of charge transfer (Xue et al., 2022). For example, by compounding active lithium compounds such as LiCoO2 or LiFePO4 with mesoporous carbon, it is possible to achieve uniform distribution of active materials, reduce the formation of lithium dendrites, and avoid internal short circuits in the battery, thus significantly improving the cycle performance of lithium-ion batteries (Nanaji et al., 2017).
Functional modification is a key application strategy for mesoporous carbon in lithium-ion batteries. By introducing elements such as nitrogen and sulfur, the conductivity and structural stability of mesoporous carbon can be enhanced, the interfacial resistance of electrode materials can be reduced, and the overall performance of the battery can be improved (Wang et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2021). For example, nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon materials improve the electron conductivity of the electrode by generating nitrogen heterocycles, while the strong interaction between nitrogen atoms and lithium ions helps to maintain the structural stability of the electrode and extend the service life of the battery (Tan et al., 2017). Mesoporous carbon materials have significant application potential in lithium-sulfur batteries and lithium metal batteries. In lithium-sulfur batteries, mesoporous carbon serves as a carrier of sulfur, which can improve the uniformity of sulfur distribution and control the volume expansion of sulfur, thus improving the utilization efficiency of sulfur (Moreno et al., 2015). In lithium metal batteries, the porous structure of mesoporous carbon helps to alleviate the volume change of lithium metal during charging and discharging, inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites, and thus enhance the safety performance of the battery.
Mesoporous carbon materials have garnered significant attention in the field of lithium-ion batteries due to their unique pore structure and excellent electrochemical performance. By optimizing pore size, doping modifications, and structural design, mesoporous carbon is expected to become a key material for the next-generation of high-performance lithium-ion batteries, driving innovation in battery technology. However, despite its potential in lithium-ion batteries, the application of mesoporous carbon is still constrained by several challenges, such as insufficient structural stability under long-term cycling and high-rate charge-discharge conditions, as well as high preparation costs. To address these challenges, future research will focus on exploring more environmentally friendly preparation techniques, such as using green solvents and alternative templates, and further improving the performance of mesoporous carbon in lithium-ion batteries through precise structural design, such as adjusting pore size, doping with heteroatoms, and composite with other materials.
4.3 Application of mesoporous carbon in adsorption field
Mesoporous carbon materials, due to their unique pore structure and high specific surface area, have shown strong potential in the field of adsorption. Whether for water purification, gas purification, or pollutant removal, mesoporous carbon has become an ideal solution owing to its excellent adsorption performance (Rahman et al., 2021; Libbrecht et al., 2017). In water treatment, the tunable pore size and surface chemistry of mesoporous carbon can be precisely engineered, enabling it to effectively adsorb heavy metal ions, organic pollutants, microorganisms, and oils, thereby significantly improving water quality. For instance, by appropriately doping with nitrogen or sulfur, the electronic structure and hydrophilicity of mesoporous carbon are optimized, enhancing its adsorption capacity for heavy metal ions and organic pollutants (Zhu et al., 2024).
For gas adsorption, mesoporous carbon is an excellent material for gas separation and storage. Its pore size and distribution can be precisely controlled to accommodate different gas molecules, enabling efficient gas adsorption and separation. For example, in carbon dioxide capture and storage, the pore structure of mesoporous carbon helps reduce interactions between gas molecules, thereby enhancing the capture efficiency (Sriram et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2018). In addition, the high specific surface area and rapid diffusion pathways of mesoporous carbon contribute to improving the adsorption and desorption rates of gases, which is crucial for achieving fast gas response and efficient recycling (Guo et al., 2015).
In environmental remediation, mesoporous carbon materials, as efficient adsorbents, can be applied to atmospheric pollution control. By optimizing the pore structure and surface properties of mesoporous carbon, efficient adsorption of atmospheric pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) can be achieved (Zhang et al., 2019; Yu C. et al., 2024). Furthermore, the multifunctionality of mesoporous carbon is also reflected in its ability to serve as a catalyst support, enabling synergistic adsorption and catalysis to simultaneously remove pollutants and enhance remediation efficiency (Sun et al., 2023).
The application of mesoporous carbon in sewage treatment has attracted wide attention due to its excellent specific surface area, regular pore structure and good surface chemical properties. The following describes its application from the perspective of its adsorption and removal of pollutants and functional modification. Da Silva et al. (2024) study explores green composites for removing emerging water contaminants, using mesoporous carbons derived from glucosamine or a sucrose-cyanamide mixture, green iron nanoparticles synthesized from water hyacinth waste, and proanthocyanidins as natural crosslinkers. Detailed studies on malachite green and crystal violet revealed maximum adsorption capacities of 713.26 mg g⁻1 and 606.79 mg g⁻1, respectively, fitting the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Notably, the presence of malachite green enhanced atenolol and sodium diclofenac adsorption rates by 57% and 404%, respectively. The composite achieved 91%–98% dye removal from river water, demonstrating resistance to interference from salts and organic matter, and maintained up to 70% efficiency over seven reuse cycles.
In industrial production processes, the adsorption properties of mesoporous carbon have also found wide applications. For example, in chemical production, mesoporous carbon can adsorb and remove by-products from reactions, thereby improving product purity. In chemical waste gas treatment, mesoporous carbon can effectively adsorb organic solvents and harmful gases, reducing emissions. It is noteworthy that the application of mesoporous carbon in adsorption is not without challenges. A key issue for researchers is how to maintain high adsorption capacity while ensuring the material’s stability, renewability, and cost-effectiveness. Through modification strategies such as doping, compositing, or functionalization, the adsorption performance and selectivity of mesoporous carbon are expected to be further enhanced, enabling it to adapt to broader and more challenging adsorption applications, and making a greater contribution to environmental protection and industrial sustainability.
4.4 Application of mesoporous carbon in catalysis
Mesoporous carbon has demonstrated significant application value in the field of catalysis. Its unique pore structure, high specific surface area, and tunable surface properties make it an ideal catalyst support and active catalytic material. During catalytic processes, the pore size and shape of mesoporous carbon can be precisely tailored to match and guide reactant molecules, thereby facilitating the reaction and improving catalytic efficiency (Eftekhari-Sis, 2024; Ji et al., 2009). Moreover, its large surface area and rapid diffusion pathways promote the fast diffusion of reactants and products, shortening reaction times and enhancing reaction activity.
In chemical transformations, mesoporous carbon, as a catalyst support, can load active species such as transition metals, metal oxides, or metal sulfides, and is applied in reactions like oxidation, reduction, isomerization, and dehydrogenation. These catalysts, supported on the pore walls of mesoporous carbon, not only increase the number of active sites but also, due to the diffusion limitations within the pore channels, extend the residence time of reactant molecules on the catalyst surface. This helps control the reaction kinetics and enables selective catalysis (Chen et al., 2022; Ren et al., 2013).
The catalytic applications of mesoporous carbon in energy conversion are also noteworthy, especially in processes such as fuel cells and water electrolysis. In fuel cells, mesoporous carbon loaded with catalysts like platinum and nickel can enhance the performance of oxygen reduction reactions (ORR) in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) and methanol oxidation reactions in direct methanol fuel cells (DMFC). In water electrolysis for hydrogen production, mesoporous carbon loaded with catalysts such as titanium nitride and cobalt oxide can effectively catalyze water splitting, thereby improving hydrogen production efficiency (Tang et al., 2013; Ding et al., 2019).
In environmental catalysis, mesoporous carbon, as a catalyst support, can effectively treat pollutants in both the atmosphere and water bodies. For example, palladium-loaded mesoporous carbon catalysts can efficiently catalyze the oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing air pollution. Mesoporous carbon catalysts loaded with iron or copper can enhance the oxidation rates of ammonia nitrogen and sulfides in wastewater, enabling efficient wastewater treatment (Yang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2020).
Mesoporous carbon can also serve as the active phase in heterogeneous catalytic systems. By embedding or growing metal nanoparticles within the carbon pores to form “core-shell” or “layered” structures, the catalytic activity and stability can be further enhanced, while enabling the directed transport of reactants and the rapid removal of products (Savateev et al., 2018).
Mesoporous carbon has extensive applications in catalysis, both as a catalyst support and as the active phase, demonstrating great potential. However, its application in catalysis also faces challenges, such as the aggregation or leaching of loaded active species, leading to a decrease in catalytic activity, as well as the need to optimize the surface chemistry of mesoporous carbon to improve the selectivity of the catalyst. Through precise pore channel design, functional modification, and catalyst loading strategies, the catalytic performance and stability of mesoporous carbon can be significantly enhanced to meet the higher demands of practical applications. With advancements in catalyst design and loading technologies, mesoporous carbon is expected to play an even more critical role in areas such as energy conversion, environmental protection, and fine chemicals, offering new solutions to global energy and environmental challenges.
4.5 Summary
Mesoporous carbon materials have demonstrated significant potential in various energy storage and environmental applications. Their high specific surface area, tunable pore structure, and excellent conductivity make them ideal candidates for supercapacitors, lithium-ion batteries, and adsorption processes. Through functionalization and structural optimization, mesoporous carbons can be tailored to enhance charge storage, ion diffusion, and cycling stability in energy devices, as well as improve adsorption efficiency for pollutants in water and air. Moreover, their versatility as catalyst supports in energy conversion and environmental catalysis further broadens their application scope.
Although mesoporous carbon has shown excellent performance in supercapacitors, catalysis, adsorption and other fields, its limitations in practical applications cannot be ignored. For example, the production costs are significantly impacted by the choice of activation method, with chemical activation requiring costly reagents and physical activation demanding high energy input. These factors collectively drive up the overall cost of production, making large-scale manufacturing economically challenging. Furthermore, the availability of raw materials is often limited by the inconsistent supply of suitable biomass, which is highly dependent on seasonal variations and geographical factors. In addition, competition for biomass with other industries can exacerbate supply chain uncertainties. On the environmental front, conventional activation processes generate harmful by-products and exhibit high energy consumption, contributing to substantial carbon emissions. Therefore, to make mesoporous carbon production more viable, it is essential to develop more cost-effective and environmentally sustainable methods, including exploring alternative raw materials and optimizing activation processes to reduce energy demands and waste generation.
5 Conclusion and outlook
Mesoporous carbon materials are promising nanomaterials with broad applications in energy storage, catalysis, and adsorption due to their unique structure, high surface area, and stability. This paper reviews their preparation methods, including templating (hard and soft), solvothermal, and electrochemical approaches, discussing the mechanisms, impact of operating conditions, and optimization strategies. A comparative analysis identifies the strengths and weaknesses of each method, offering insights for targeted design.
The paper also examines the relationship between microstructure and performance, particularly in electrochemical and adsorption applications. Despite their potential, challenges such as stability, cost, and large-scale production remain. Future research will focus on improving stability through surface modifications, using sustainable raw materials, reducing production costs, and developing efficient, environmentally friendly synthesis methods. Expanding applications to fields like flexible electronics and biomedicine will also broaden their market potential.
In the future, mesoporous carbon materials are anticipated to drive groundbreaking advancements in energy storage, catalysis, and environmental protection. Innovations in material design and preparation technologies, particularly those leveraging nanotechnology, are expected to enable more sustainable and efficient applications across diverse fields. The integration of mesoporous carbon with other materials, such as polymers, metals, or metal oxides, could result in composite systems with enhanced functionalities. Such synergies may lead to breakthroughs in energy density for storage devices, higher catalytic efficiency in industrial processes, and more effective environmental remediation strategies.
Author contributions
ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZY: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WJ: Data curation, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program (2022YFC3701904), 2024 School Key Project (BGY2024 KY-27Z); 2022 Beijing Vocational Education Reform Project (CG2022006; CG2022003); 2023 Beijing Education Science “14th Five-Year Plan” Project (CDDB23232).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ali, A., and Zhao, C. (2020a). Ru nanoparticles supported on hydrophilic mesoporous carbon catalyzed low-temperature hydrodeoxygenation of microalgae oil to alkanes at aqueous-phase. Chin. J. Catal. 41, 1174–1185. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63539-2
Ali, A., and Zhao, C. (2020b). Ru nanoparticles supported on hydrophilic mesoporous carbon catalyzed low-temperature hydrodeoxygenation of microalgae oil to alkanes at aqueous-phase. Chin. J. Catal. 41, 1174–1185. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63539-2
Azam, M. A., Ramli, N. S. N., Nor, NANM, and Nawi, T. I. T. (2021). Recent advances in biomass-derived carbon, mesoporous materials, and transition metal nitrides as new electrode materials for supercapacitor: a short review. Int. J. Energy Res. 45, 8335–8346. doi:10.1002/er.6377
Baccile, N., Babonneau, F., Thomas, B., and Coradin, T. (2009). Introducing Ecodesign in silica sol-gel materials. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 8537–8559. doi:10.1039/b911123a
Bae, G., Byun, W. J., Lee, J. H., Lee, M. H., Choi, Y., Kim, J. Y., et al. (2024). Phosphorus-modified palladium and tungsten carbide/mesoporous carbon composite for hydrogen oxidation reaction of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nanomaterials 14, 1024. doi:10.3390/nano14121024
Barra, G., Guadagno, L., Raimondo, M., Santonicola, M. G., Toto, E., and Vecchio, C. S. (2023). A comprehensive review on the thermal stability assessment of polymers and composites for aeronautics and space applications. Polymers 15, 3786. doi:10.3390/polym15183786
Cao, B., Liu, H., Xu, B., Lei, Y., Chen, X., and Song, H. (2016). Mesoporous soft carbon as an anode material for sodium ion batteries with superior rate and cycling performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 6472–6478. doi:10.1039/C6TA00950F
Chang, C., Zhu, L., Wang, S., Chu, X., and Yue, L. (2014). Novel mesoporous graphite carbon nitride/BiOI heterojunction for enhancing photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 6, 5083–5093. doi:10.1021/am5002597
Chen, T., Fu, C., Liu, Y., Pan, F., Wu, F., You, Z., et al. (2021). Adsorption of volatile organic compounds by mesoporous graphitized carbon: enhanced organophilicity, humidity resistance, and mass transfer, Sep. Purif. Technol., 264: 118464. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118464
Chen, Y., Dai, X., Zhang, W., Wu, T., Chen, L., and Peng, X. (2022). Carboxylation of sodium arylsulfinates with CO2 over mesoporous K-Cu-20TiO2. RSC Adv. 12, 772–776. doi:10.1039/d1ra05228d
Chen, Z., Wang, Z., Yang, J., and Xu, Y. (2024). In situ electropolymerization in mesoporous carbon: a universal method for improving the electrochemical performance of polymer electrode materials. ACS Appl. Energ Mater 7, 7584–7591. doi:10.1021/acsaem.3c01766
Cui, Y., Lian, X., Xu, L., Chen, M., Yang, B., Wu, C., et al. (2019). Designing and fabricating ordered mesoporous metal oxides for CO2 catalytic conversion: a review and prospect. Materials. 12, 276. doi:10.3390/ma12020276
Da Silva, P. M. M., Camparotto, N. G., Neves, T. D. F., Carrara, A. S., Mastelaro, V. R., Oliveira, R. L., et al. (2024). Green composites based on magnetic N-doped carbons: synergetic effect on the simultaneous adsorption of emerging contaminants from water. J. Water Process Eng. 58, 104832. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.104832
Deng, Q., Liu, L., Lin, X., Du, G., Liu, Y., and Yuan, Z. (2012). Synthesis and CO2 capture properties of mesoporous carbon nitride materials. Chem. Eng. J. 203, 63–70. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.124
Ding, J., Ji, S., Wang, H., Gai, H., Liu, F., Linkov, V., et al. (2019). Mesoporous nickel-sulfide/nickel/N-doped carbon as HER and OER bifunctional electrocatalyst for water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 2832–2840. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.031
Dong, X., Jiang, Y., Shan, W., and Zhang, M. (2016). A novel highly ordered mesoporous carbon-based solid acid for synthesis of bisphenol-a. RSC Adv. 6, 17118–17124. doi:10.1039/c5ra24966j
Du, J., Liu, L., Hu, Z., Yu, Y., Qin, Y., and Chen, A. (2018). Order mesoporous carbon spheres with precise tunable large pore size by encapsulated self-activation strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater 28 (23). doi:10.1002/adfm.201802332
Du, J., Liu, L., Yu, Y., Zhang, Y., Lv, H., and Chen, A. (2019). N-doped ordered mesoporous carbon spheres derived by confined pyrolysis for high supercapacitor performance. J. Mater Sci. Technol. 35, 2178–2186. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2019.05.029
Eftekhari, A. (2017). Ordered mesoporous materials for lithium-ion batteries. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 243, 355–369. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.02.055
Eftekhari, A., and Fan, Z. (2017). Ordered mesoporous carbon and its applications for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Mater Chem. Front. 1, 1001–1027. doi:10.1039/c9qm90060h
Eftekhari-Sis, B. (2024). Biomass derived n-doped ordered mesoporous carbon: efficient support for metals nanoparticles and heterogeneous catalyst for organic transformations. Process Petrochem Oil Refin., 65. doi:10.62972/1726-4685.si2024.1.65
Elma, M., Rampun, E. L. A., Rahma, A., Assyaifi, Z. L., Sumardi, A., Lestari, A. E., et al. (2020). Carbon templated strategies of mesoporous silica applied for water desalination: a review. J. Water Process Eng. 38, 101520. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101520
Fang, J., Wang, W., Fan, Y., Guan, H., Wang, Q., Liu, D., et al. (2025). Tin oxide nanoparticles anchored on ordered mesoporous carbon for efficient acetone sensing. Sensors Actuators. B, Chem. 425, 136957. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2024.136957
Florent, M., Tocci, M., and Bandosz, T. J. (2013). NO2 adsorption at ambient temperature on urea-modified ordered mesoporous carbon. Carbon 63, 283–293. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.06.081
Gao, P., Wang, A., Wang, X., and Zhang, T. (2008). Synthesis of highly ordered Ir-containing mesoporous carbon materials by organic–organic self-assembly. Chem. Mater 20, 1881–1888. doi:10.1021/cm702815e
Gisbert-Garzaran, M., Berkmann, J. C., Giasafaki, D., Lozano, D., Spyrou, K., Manzano, M., et al. (2020). Engineered pH-responsive mesoporous carbon nanoparticles for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 12, 14946–14957. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c01786
Glatthaar, C., Wang, M., Wagner, L. Q., Breckwoldt, F., Guo, Z., Zheng, K., et al. (2023). Lignin-derived mesoporous carbon for sodium-ion batteries: block copolymer soft templating and carbon microstructure analysis. Chem. Mater 35, 10416–10433. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c01520
Gu, D., and Schuth, F. (2014). Synthesis of non-siliceous mesoporous oxides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 313–344. doi:10.1039/c3cs60155b
Guo, Y., He, J., Wang, T., Xue, H., Hu, Y., Li, G., et al. (2011). Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of platinum supported on nitrogen modified ordered mesoporous carbon. J. Power Sources 196, 9299–9307. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.07.073
Guo, Y., Zhao, C., Li, C., and Wu, Y. (2015). CO2 sorption and reaction kinetic performance of K2CO3/AC in low temperature and CO2 concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 260, 596–604. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.052
Han, X., Chang, Q., Li, N., Wang, H., Yang, J., and Hu, S. (2018). In-situ incorporation of carbon dots into mesoporous nickel boride for regulating photocatalytic activities. Carbon 137, 484–492. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.05.066
Hu, F., Lin, Y., Qiu, Y., Wen, B., Zheng, Y., and Yang, H. (2021). Synthesis of mesoporous hollow carbon microcages by combining hard and soft template method for high performance supercapacitors. Ceram. Int. 47, 5968–5976. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.170
Hu, Z., Shi, D., Wang, G., Gao, T., Wang, J., Lu, L., et al. (2022). Carbon dots incorporated in hierarchical macro/mesoporous g-C3N4/TiO2 as an all-solid-state Z-scheme heterojunction for enhancement of photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 601, 154167. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154167
Huang, S., Yang, D., Zhang, W., Qiu, X., Li, Q., and Li, C. (2021). Dual-templated synthesis of mesoporous lignin-derived honeycomb-like porous carbon/SiO2 composites for high-performance Li-ion battery. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 317, 111004. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111004
Huang, W., Xie, H., Tian, Y., and Wang, X. (2018). Controlled growth of N-doped and large mesoporous carbon spheres with adjustable litchi-like surface and particle size as a giant guest molecule carrier. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 10, 20073–20084. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b02040
Ibad, M. F., Kosslick, H., Tomm, J. W., Frank, M., and Schulz, A. (2017). Impact of the crystallinity of mesoporous polymeric graphitic carbon nitride on the photocatalytic performance under UV and visible light. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 254, 136–145. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.04.052
Inagaki, M., Toyoda, M., Soneda, Y., Tsujimura, S., and Morishita, T. (2016). Templated mesoporous carbons: synthesis and applications. Carbon 107, 448–473. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2016.06.003
Jang, J., and Kim, J. (2024). Recent advances in the development of nickel catalysts for carbon dioxide methanation. Appl. Chem. Eng. 35, 361–371. doi:10.14478/ace.2024.1043
Ji, Z., Liang, S., Jiang, Y., Li, H., Liu, Z., and Zhao, T. (2009). Synthesis and characterization of ruthenium-containing ordered mesoporous carbon with high specific surface area. Carbon 47, 2194–2199. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2009.04.001
Jin, L., Zhang, M., Li, H., Li, M., Shang, L., Xiao, L., et al. (2016). Improvement of interfacial strength and thermal stability of carbon fiber composites by directly grafting unique particles: functionalized mesoporous silicas. RSC Adv. 6, 80485–80492. doi:10.1039/c6ra13669a
Kesavan, T., Partheeban, T., Vivekanantha, M., Prabu, N., Kundu, M., Selvarajan, P., et al. (2020). Design of P-doped mesoporous carbon nitrides as high-performance anode materials for Li-ion battery. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 12, 24007–24018. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c05123
Kim, S. J., Ahn, M., Park, J., Jeoun, Y., Yu, S. H., Min, D. H., et al. (2020). Enhancing the of performance of lithium-sulfur batteries through electrochemical impregnation of sulfur in hierarchical mesoporous carbon nanoparticles. ChemElectroChem 7, 3653–3655. doi:10.1002/celc.202001022
Kim, T., Chung, P., Slowing, I. I., Tsunoda, M., Yeung, E. S., and Lin, V. S. Y. (2008). Structurally ordered mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as transmembrane delivery vehicle in human cancer cells. Nano Lett. 8, 3724–3727. doi:10.1021/nl801976m
Kochana, J., Wapiennik, K., Knihnicki, P., Pollap, A., Janus, P., Oszajca, M., et al. (2016). Mesoporous carbon-containing voltammetric biosensor for determination of tyramine in food products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408, 5199–5210. doi:10.1007/s00216-016-9612-y
Krawiec, P., and Kaskel, S. (2006). Thermal stability of high surface area silicon carbide materials. J. Solid State Chem. 179, 2281–2289. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2006.02.034
Kumar, N., Pandey, A., and Rosy, S. Y. C. (2023). A review on sustainable mesoporous activated carbon as adsorbent for efficient removal of hazardous dyes from industrial wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 54, 104054. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104054
Lee, J., Joo, S. H., and Ryoo, R. (2002). Synthesis of mesoporous silicas of controlled pore wall thickness and their replication to ordered nanoporous carbons with various pore diameters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 1156–1157. doi:10.1021/ja012333h
Lei, J., Hu, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, H., and Li, K. (2023). A review of the advancements in the synthesis and modification of mesoporous carbon and its application to electrochemistry. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 101, 6417–6445. doi:10.1002/cjce.24921
Lett, J. A., Sundareswari, M., Ravichandran, K., Latha, M. B., Sagadevan, S., and Bin Johan, M. R. (2019). Tailoring the morphological features of sol-gel synthesized mesoporous hydroxyapatite using fatty acids as an organic modifier. RSC Adv. 9, 6228–6240. doi:10.1039/c9ra00051h
Li, Q., Mao, H., Li, J., and Xu, Q. (2013). Effect of nitric acid on modified mesoporous carbon as catalyst support of direct methanol fuel cell. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 10, 51006. doi:10.1115/1.4024835
Li, T., Liang, Z., Yang, G., Yang, J., Wang, Y., Qiao, W., et al. (2011). Preparation of mesoporous carbon microsphere/activated carbon composite for electric double-layer capacitors. New Carbon Mater. 26, 237–240. doi:10.1016/s1872-5805(11)60079-6
Li, W., Liu, J., and Zhao, D. (2016). Mesoporous materials for energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16023. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2016.23
Li, X., Deng, D., He, L., and Xu, Y. (2023). A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on a mesoporous carbon sphere immobilized Co-MOF-74 nanocomposite. Dalton Trans. 52, 15447–15455. doi:10.1039/d3dt01544k
Li, X., Yan, Y., Lin, Y., Jiao, J., Wang, D., Di, D., et al. (2017). Hollow mesoporous carbon as a near-infrared absorbing carrier compared with mesoporous carbon nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 494, 159–169. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.090
Li, Y., Gui, F., Wang, F., Liu, J., and Zhu, H. (2021). Synthesis of modified, ordered mesoporous carbon-supported Pt3Cu catalyst for enhancing the oxygen reduction activity and durability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46, 37802–37813. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.042
Li, Y., Shan, L., Wang, R., Lian, X., and Zhou, Q. (2022). Enhanced n-butanol sensing performance of SnO2/ZnO nanoflowers fabricated via a facile solvothermal method. Ceram. Int. 48, 22426–22434. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.256
Lian, Y. M., Utetiwabo, W., Zhou, Y., Huang, Z. H., Zhou, L., Faheem, M., et al. (2019). From upcycled waste polyethylene plastic to graphene/mesoporous carbon for high-voltage supercapacitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 557, 55–64. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.003
Liang, J., Hu, H., Park, H., Xiao, C., Ding, S., Paik, U., et al. (2015). Construction of hybrid bowl-like structures by anchoring NiO nanosheets on flat carbon hollow particles with enhanced lithium storage properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 8 (8), 1707–1711. doi:10.1039/c5ee01125f
Liang, Z., Hong, Z., Xie, M., and Gu, D. (2022). Recent progress of mesoporous carbons applied in electrochemical catalysis. New Carbon Mater. 37, 152–179. doi:10.1016/S1872-5805(22)60575-4
Libbrecht, W., Verberckmoes, A., Thybaut, J. W., Van Der Voort, P., and De Clercq, J. (2017). Soft templated mesoporous carbons: tuning the porosity for the adsorption of large organic pollutants. Carbon 116, 528–546. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2017.02.016
Lim, E., Jo, C., and Lee, J. (2016). A mini review of designed mesoporous materials for energy-storage applications: from electric double-layer capacitors to hybrid supercapacitors. Nanoscale 8, 7827–7833. doi:10.1039/c6nr00796a
Liu, C., Pei, W., Li, J., Yang, J., and Ma, J. (2020). Calix[4]arene-based [Co4] complex/ordered mesoporous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for efficient detection of baicalein. Sensors Actuators. B, Chem. 308, 127677. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2020.127677
Liu, L., Zou, G., Yang, B., Luo, X., and Xu, S. (2018). Amine-functionalized mesoporous silica@ reduced graphene sandwichlike structure composites for CO2 adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 1, 4695–4702. doi:10.1021/acsanm.8b00943
Liu, M., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Yu, Y., and Chen, A. (2019a). Synthesis of n-doped mesoporous carbon by silica assistance as electrode for supercapacitor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 3214–3221. doi:10.1007/s10854-019-00695-5
Liu, S., Li, C., and Liu, D. (2021). Modified separator based on mesoporous carbon/TiO2 composites as advanced polysulfide adsorber for high electrochemical performance Li-S batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 862, 158381. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158381
Liu, X., Sun, C., Liu, H., Tan, W. H., Wang, W., and Snape, C. (2019b). Developing hierarchically ultra-micro/mesoporous biocarbons for highly selective carbon dioxide adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 199–208. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.062
Lu, Y., Zhu, N., Yin, F., Yang, T., Wu, P., Dang, Z., et al. (2017). Biomass-derived heteroatoms-doped mesoporous carbon for efficient oxygen reduction in microbial fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 98, 350–356. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.006
Luo, H., Yu, F., Wu, H., Wang, C., and Wang, M. (2023). High-performance heat storage phase change composite by highly aligned N-doped mesoporous carbon for efficient battery thermal management. ACS Appl. Energ Mater. 6, 950–959. doi:10.1021/acsaem.2c03383
Ma, T., Liu, L., and Yuan, Z. (2013). Direct synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbons. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 3977–4003. doi:10.1039/c2cs35301f
Maluta, J. R., Machado, S. A., Chaudhary, U., Manzano, J. S., Kubota, L. T., and Slowing, I. I. (2018). Development of a semigraphitic sulfur-doped ordered mesoporous carbon material for electroanalytical applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 257, 347–353. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.164
Mayani, S. V., Mayani, V. J., Park, S. K., and Kim, S. W. (2012). Synthesis and characterization of metal incorporated composite carbon materials from pyrolysis fuel oil. Mater Lett. 82, 120–123. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2012.05.078
Mehdipour-Ataei, S., and Aram, E. (2023). Mesoporous carbon-based materials: a review of synthesis, modification, and applications. Catalysts 13, 2. doi:10.3390/catal13010002
Melke, J., Schuster, R., Möbus, S., Jurzinsky, T., Elsässer, P., Heilemann, A., et al. (2019). Electrochemical stability of silica-templated polyaniline-derived mesoporous N-doped carbons for the design of Pt-based oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. Carbon 146, 44–59. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.057
Moradi, S. E., Amirmahmoodi, S., and Baniamerian, M. J. (2010). Hydrogen adsorption in metal-doped highly ordered mesoporous carbon molecular sieve. J. Alloys Compd. 498, 168–171. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.03.144
Moreno, N., Agostini, M., Caballero, A., Morales, J., and Hassoun, J. (2015). A long-life lithium ion sulfur battery exploiting high performance electrodes. Chem. Commun. 51, 14540–14542. doi:10.1039/c5cc05162b
Mruthunjayappa, M. H., Kotrappanavar, N. S., and Mondal, D. (2022). New prospects on solvothermal carbonisation assisted by organic solvents, ionic liquids and eutectic mixtures – a critical review. Prog. Mater Sci. 126, 100932. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100932
Nanaji, K., Jyothirmayi, A., Varadaraju, U., Rao, T. N., and Anandan, S. (2017). Facile synthesis of mesoporous carbon from furfuryl alcohol-butanol system by EISA process for supercapacitors with enhanced rate capability. J. Alloys Compd. 723, 488–497. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.231
Niu, B., Wang, X., Wu, K., He, X., and Zhang, R. (2018). Mesoporous titanium dioxide: synthesis and applications in photocatalysis, energy and biology. Materials 11, 1910. doi:10.3390/ma11101910
Okonkwo, C. A., Menkiti, M. C., Obiora-Okafo, I. A., and Ezenwa, O. N. (2021). Controlled pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse enhanced mesoporous carbon for improving capacitance of supercapacitor electrode. Biomass Bioenergy 146, 105996. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.105996
Olmos-Moya, P. M., Velazquez-Martinez, S., Pineda-Arellano, C., Rangel-Mendez, J. R., and Chazaro-Ruiz, L. F. (2022). High added value functionalized carbon quantum dots synthetized from orange peels by assisted microwave solvothermal method and their performance as photosensitizer of mesoporous TiO2 photoelectrodes. Carbon 187, 216–229. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2021.11.003
Ortiz-Martínez, V. M., Gómez-Coma, L., Ortiz, A., and Ortiz, I. (2020). Overview on the use of surfactants for the preparation of porous carbon materials by the sol-gel method: applications in energy systems. Rev. Chem. Eng. 36, 771–787. doi:10.1515/revce-2018-0056
Pei, Y., Liu, M., He, C., Chen, H., Li, J., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Application of pH and hyaluronidase dual-responsive mesoporous carbon nitride nano-drug delivery system for chemodynamic therapy and chemotherapy combination therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Appl. Mater Today 41, 102469. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2024.102469
Peng, Y., Le, Z., Wen, M., Zhang, D., Chen, Z., Wu, H. B., et al. (2017). Mesoporous single-crystal-like TiO2 mesocages threaded with carbon nanotubes for high-performance electrochemical energy storage. Nano Energy 35, 44–51. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.03.003
Qian, M., Xu, F., Bi, H., Lin, T., and Huang, F. (2017). Facile sol-gel method combined with chemical vapor deposition for mesoporous few-layer carbon. Carbon 112, 47–52. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.093
Rahbar-Shamskar, K., Aberoomand Azar, P., Rashidi, A., Baniyaghoob, S., and Yousefi, M. (2020). Synthesis of micro/mesoporous carbon adsorbents by in-situ fast pyrolysis of reed for recovering gasoline vapor. J. Clean. Prod. 259, 120832. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120832
Rahman, M. M., Ara, M. G., Alim, M. A., Uddin, M. S., Najda, A., Albadrani, G. M., et al. (2021). Mesoporous carbon: a versatile material for scientific applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4498. doi:10.3390/ijms22094498
Ren, Q., Wang, H., Lu, X. F., Tong, Y. X., and Li, G. R. (2018). Recent progress on MOF-derived heteroatom-doped carbon-based electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Sci. 5, 1700515. doi:10.1002/advs.201700515
Ren, T., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., and Yuan, Z. (2013). Nitric acid oxidation of ordered mesoporous carbons for use in electrochemical supercapacitors. J. Solid State Electrochem 17, 2223–2233. doi:10.1007/s10008-013-2088-1
Rivera-Munoz, E. M., and Huirache-Acuna, R. (2010). Sol gel-derived SBA-16 mesoporous material. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11, 3069–3086. doi:10.3390/ijms11093069
Roggenbuck, J., and Tiemann, M. (2005). Ordered mesoporous magnesium oxide with high thermal stability synthesized by exotemplating using CMK-3 carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 1096–1097. doi:10.1021/ja043605u
Sadhasivam, T., Roh, S., Kim, T., Park, K., and Jung, H. (2016). Graphitized carbon as an efficient mesoporous layer for unitized regenerative fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 18226–18230. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.092
Sakina, F., Munoz-Ocana, J. M., Bouziane, A., Lopez-Haro, M., and Baker, R. T. (2019). Synthesis of mesoporous ceria using metal- and halogen-free ordered mesoporous carbon as a hard template. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 4772–4782. doi:10.1039/c9na00482c
Saleem, A., Zhang, Y., Usman, M., Haris, M., and Li, P. (2022). Tailored architectures of mesoporous carbon nanostructures: from synthesis to applications. Nano Today 46, 101607. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101607
Savateev, A., Ghosh, I., König, B., and Antonietti, M. (2018). Photoredox catalytic organic transformations using heterogeneous carbon nitrides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 15936–15947. doi:10.1002/anie.201802472
Shahsavarifar, S., Rezapour, M., Mehrpooya, M., Ehrlich, H., Jesionowski, T., Ganjali, M. R., et al. (2024). Review—advances in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries utilizing polyoxometalate-functionalized nanocarbon materials. J. Electrochem Soc. 171, 080536. doi:10.1149/1945-7111/ad6b46
Shen, Y., Zhao, P., and Shao, Q. (2014). Porous silica and carbon derived materials from rice husk pyrolysis char. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 188, 46–76. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.01.005
Shi, Z., Ma, M., and Zhu, J. (2019). Recent development of photocatalysts containing carbon species: a review. Catalysts 9, 20. doi:10.3390/catal9010020
Shin, Y., Fryxell, G. E., Um, W., Parker, K., Mattigod, S. V., and Skaggs, R. (2007). Sulfur-functionalized mesoporous carbon. Adv. Funct. Mater 17, 2897–2901. doi:10.1002/adfm.200601230
Singh, G., Lakhi, K. S., Kim, I. Y., Kim, S., Srivastava, P., Naidu, R., et al. (2017). Highly efficient method for the synthesis of activated mesoporous biocarbons with extremely high surface area for high-pressure CO2 adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 9, 29782–29793. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b08797
Sivarasan, G., Manikandan, V., Periyasamy, S., AlSalhi, M. S., Devanesan, S., Murphin, K. P., et al. (2023). Iron-engineered mesoporous biocarbon composite and its adsorption, activation, and regeneration approach for removal of paracetamol in water. Environ. Res. 227, 115723. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.115723
Soltanali, S., and Darian, J. T. (2019). Synthesis of mesoporous beta catalysts in the presence of carbon nanostructures as hard templates in MTO process. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 286, 169–175. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.05.013
Sridhar, V., and Park, H. (2018). Carbon nanofiber linked FeS2 mesoporous nano-alloys as high capacity anodes for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 732, 799–805. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.252
Sriram, G., Kurkuri, M., and Hegde, G. (2020). Efficient CO2 adsorption using mesoporous carbons from biowastes. Mater Res. Express 7, 015605. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/ab5f2c
Su, Y., Jiang, B., Shen, H., Yang, N., Tantai, X., Xiao, X., et al. (2025). Mesoporous carbon spheres modified with atomically dispersed iron sites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon N. Y. 231, 119699. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119699
Sun, L., Bao, X., Li, Y., Zhao, J., Chen, P., Liu, H., et al. (2023). CoS2 and FeS2 nanoparticles embedded in carbon polyhedrons for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 6, 11095–11103. doi:10.1021/acsanm.3c00777
Tan, H., Tang, J., Zhou, X., Golberg, D., Bhatia, S. K., Sugahara, Y., et al. (2018). Preparation of 3D open ordered mesoporous carbon single-crystals and their structural evolution during ammonia activation. Chem. Commun. 54, 9494–9497. doi:10.1039/c8cc05318a
Tan, X., Cui, C., Wu, S., Qiu, B., Wang, L., and Zhang, J. (2017). Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon-encapsulated MoO(2) nanobelts as a high-capacity and stable host for lithium-ion storage. Chem. Asian J. 12, 36–40. doi:10.1002/asia.201601521
Tang, J., Wang, T., Sun, X., Guo, Y., Xue, H., Guo, H., et al. (2013). Effect of transition metal on catalytic graphitization of ordered mesoporous carbon and Pt/metal oxide synergistic electrocatalytic performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 177, 105–112. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.04.027
Ubaidullah, M., Al-Enizi, A. M., Ahamad, T., Shaikh, S. F., Al-Abdrabalnabi, M. A., Samdani, M. S., et al. (2021). Fabrication of highly porous N-doped mesoporous carbon using waste polyethylene terephthalate bottle-based MOF-5 for high performance supercapacitor. J. Energy Storage 33, 102125. doi:10.1016/j.est.2020.102125
Ueda, Y., Takeda, H., Yui, T., Koike, K., Goto, Y., Inagaki, S., et al. (2015). A visible-light harvesting system for CO2 reduction using a Ru(II) -Re(I) photocatalyst adsorbed in mesoporous organosilica. ChemSusChem 8, 439–442. doi:10.1002/cssc.201403194
Wang, D., Liu, J., Bao, X., Qing, C., Zhu, T., and Wang, H. (2022c). Macro/mesoporous carbon/defective TiO2 composite as a functional host for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Energ Mater 5, 2573–2579. doi:10.1021/acsaem.2c00033
Wang, H., Qi, B., Lu, B., Bo, X., and Guo, L. (2011). Comparative study on the electrocatalytic activities of ordered mesoporous carbons and graphene. Electrochim Acta 56, 3042–3048. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.099
Wang, J., Xia, Y., Liu, Y., Li, W., and Zhao, D. (2019). Mass production of large-pore phosphorus-doped mesoporous carbon for fast-rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 22, 147–153. doi:10.1016/j.ensm.2019.01.008
Wang, L., Seah, G. L., Li, Y., Tu, W. H., Manalastas, W., Reavley, M. J. H., et al. (2022b). Ultrafast crystallization of ordered mesoporous metal oxides and carbon from block copolymer self-assembly and joule heating. Adv. Mater Interfaces 9 (19), 9. doi:10.1002/admi.202200151
Wang, S., Eberhardt, T. L., Guo, D., Feng, J., and Pan, H. (2022a). Efficient conversion of glucose into 5-HMF catalyzed by lignin-derived mesoporous carbon solid acid in a biphasic system. Renew. Energy 190, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.021
Wang, X., Liang, C., and Dai, S. (2008). Facile synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbons with high thermal stability by self-assembly of resorcinol-formaldehyde and block copolymers under highly acidic conditions. Langmuir 24, 7500–7505. doi:10.1021/la800529v
Wang, X. Q., Ge, H. L., Jin, H. X., and Cui, Y. J. (2005). Influence of Fe on the thermal stability and catalysis of SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 86, 335–340. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.07.038
Wang, Y., Wang, H., Ji, J., You, T., Lu, C., Liu, C., et al. (2024). Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of Sn-based peanut shell biochar electrode materials. RSC Adv. 14, 6298–6309. doi:10.1039/d3ra08655k
Wang, Z., Sun, L., Xu, F., Peng, X., Zou, Y., Chu, H., et al. (2016). Synthesis of N-doped hierarchical carbon spheres for CO2 capture and supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 6, 1422–1427. doi:10.1039/c5ra20484d
Wen, Y., Kierzek, K., Chen, X., Gong, J., Liu, J., Niu, R., et al. (2019). Mass production of hierarchically porous carbon nanosheets by carbonizing “real-world” mixed waste plastics toward excellent-performance supercapacitors. Waste Manage 87, 691–700. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.006
Xi, J. C., Yuan, Y. F., Yang, J. L., Chen, Y. B., Shen, S. H., Guo, S. Y., et al. (2024). NiCo2S4 nanoparticles encapsulated within hollow mesoporous carbon spheres enabling rapid and stable sodium storage. J. Energy Storage 102, 114216. doi:10.1016/j.est.2024.114216
Xie, Y., and Guo, Q. (2022). Improved electrochemical performance of mesoporous carbon via N/S doping. J. Solid State Electrochem 26, 1013–1020. doi:10.1007/s10008-022-05145-7
Xin, G., Wang, Y., Jia, S., Tian, P., Zhou, S., and Zang, J. (2017). Synthesis of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon from polyaniline with an F127 template for high-performance supercapacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 422, 654–660. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.084
Xu, L., Miao, Z., Song, H., and Chou, L. (2014). CO2 reforming of CH4 over rare earth elements functionalized mesoporous Ni–Ln (Ln = Ce, La, Sm, Pr)–Al–O composite oxides. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 39, 3253–3268. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.077
Xu, Y. X., and Zhao, C. Y. (2024). Structure-activity relationship between pore morphology and thermochemical energy storage properties based on MgCO3/MgO. Sol. Energy Mater Sol. Cells 275, 113027. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2024.113027
Xue, S., Wang, J., Xia, Y., Wang, Y., Jiang, W., Dong, A., et al. (2022). Mesoporous carbon as conductive additive to improve the high-rate charge/discharge capacity of lithium-ion batteries. Energy Technol. 10 (8). doi:10.1002/ente.202200472
Yan, J., Wang, A., and Kim, D. (2007). Preparation of ordered mesoporous SiCN ceramics with large surface area and high thermal stability. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 100, 128–133. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.10.027
Yang, C., Li, Y., Wang, X., Zheng, L., and Liang, H. (2023). Oxygen reduction catalyzed by Pt nanoparticles confined in mesoporous carbon supports doped with single Fe atoms. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 6, 16016–16023. doi:10.1021/acsanm.3c03016
Yang, P., Zuo, S., Zhang, F., Yu, B., Guo, S., Yu, X., et al. (2020). Carbon nitride-based single-atom Cu catalysts for highly efficient carboxylation of alkynes with atmospheric CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59, 7327–7335. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.0c00547
Yang, X., Qiu, P., Yang, J., Fan, Y., Wang, L., Jiang, W., et al. (2021). Mesoporous materials–based electrochemical biosensors from enzymatic to nonenzymatic. Small 17, e1904022. doi:10.1002/smll.201904022
Yu, C., Dan, J., Liu, Z., Wang, J., Wang, J., Fang, H., et al. (2024b). A facile, green strategy to synthesize N/P self-doped, biomass-derived, hierarchical porous carbon from water hyacinth for efficient VOCs adsorption. Fuel 358, 130136. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130136
Yu, X., Ni, L., Bai, E., Miao, M., Tang, X., and Wang, L. (2024a). Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon as metal-free catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Mol. Catal. 569, 114526. doi:10.1016/j.mcat.2024.114526
Yuan, S., Gao, Q., Ke, C., Zuo, T., Hou, J., and Zhang, J. (2022). Mesoporous carbon materials for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. ChemElectroChem 9 (6). doi:10.1002/celc.202101182
Zhai, Y., Dou, Y., Zhao, D., Fulvio, P. F., Mayes, R. T., and Dai, S. (2011). Carbon materials for chemical capacitive energy storage. Adv. Mater. 23, 4828–4850. doi:10.1002/adma.201100984
Zhang, J., Zhang, N., Tack, F., Sato, S., Alessi, D. S., Oleszczuk, P., et al. (2021b). Modification of ordered mesoporous carbon for removal of environmental contaminants from aqueous phase: a review. J. Hazard Mater 418, 126266. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126266
Zhang, J., Zhang, P., Li, M., Shan, Z., Wang, J., Deng, Q., et al. (2019). Facile preparation of biomass-derived mesoporous carbons for highly efficient and selective so2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58, 14929–14937. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01938
Zhang, M., He, L., Shi, T., and Zha, R. (2018). Nanocasting and direct synthesis strategies for mesoporous carbons as supercapacitor electrodes. Chem. Mater 30, 7391–7412. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03345
Zhang, P., Zhang, J., and Dai, S. (2017a). Mesoporous carbon materials with functional compositions. Chemistry 23, 1986–1998. doi:10.1002/chem.201602199
Zhang, R., Li, W., Hao, G., and Lu, A. (2021a). Confined nanospace pyrolysis: a versatile strategy to create hollow structured porous carbons. Nano Res. 14, 3159–3173. doi:10.1007/s12274-021-3425-9
Zhang, T., Zhu, C., Shi, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, S., and Zhang, D. (2017b). Synthesis of Fe2O3 in situ on the surface of mesoporous carbon from alginate as a high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Lett. 205, 10–14. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2017.06.020
Zhang, X., Gao, Z., Fan, X., Tan, L., Jiang, Y., Zheng, W., et al. (2022). A comparative study on adsorption of cadmium and lead by hydrochars and biochars derived from rice husk and Zizania latifolia straw. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 29, 63768–63781. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20263-5
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, Z., Li, Y., Liu, Z., and Sun, S. (2023). Mesoporous carbon in biomedicine: modification strategies and biocompatibility. Carbon 212, 118121. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118121
Zhang, Z., Zhai, Y., Zhao, D., and Li, W. (2024). Monomicelle-directed synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion. Adv. Mater Interfaces. doi:10.1002/admi.202400358
Zhao, B., Li, H., Yang, X., Xiao, J., and Chen, G. (2024). Hydrochar derived from willow using in phytoremediation: hydrochar properties, metals behavior and potential applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 339, 126697. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126697
Zhao, Q., Lin, Y., Han, N., Li, X., Geng, H., Wang, X., et al. (2017). Mesoporous carbon nanomaterials in drug delivery and biomedical application. Drug Deliv. 24, 94–107. doi:10.1080/10717544.2017.1399300
Zhao, X., Gao, P., Shen, B., Wang, X., Yue, T., and Han, Z. (2023). Recent advances in lignin-derived mesoporous carbon based-on template methods. Renew. Sustain Energy Rev. 188, 113808. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113808
Zhao, X. Y., Tu, J. P., Lu, Y., Cai, J. B., Zhang, Y. J., Wang, X. L., et al. (2013). Graphene-coated mesoporous carbon/sulfur cathode with enhanced cycling stability. Electrochim Acta 113, 256–262. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.078
Zheng, S., Luo, Y., Zhang, K., Liu, H., Hu, G., and Qin, A. (2021). Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped mesoporous carbon nanosheets derived from bagasse for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Lett. 290, 129459. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129459
Zhou, Y., Tao, Y. F., Yang, J., Lin, W. G., Wan, M. M., Wang, Y., et al. (2011). Novel phenol capturer derived from the as-synthesized MCM-41. J. Hazard Mater 190, 87–93. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.089
Keywords: mesoporous carbon materials, preparation process, properties, application research, preparation method
Citation: Wei Z, Yanfei Z and Jiao W (2025) Mesoporous carbon materials: synthesis methods, properties, and advanced applications . Front. Mater. 12:1548671. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1548671
Received: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 03 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Wang, Zhengzhou University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wei, Yanfei and Jiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhou Wei, emhvdXdlaTE4MDEyNkAxNjMuY29t
 Zhou Wei
Zhou Wei Zhi Yanfei
Zhi Yanfei