
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mater., 21 January 2025
Sec. Polymeric and Composite Materials
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2025.1536536
This article is part of the Research TopicRecent Advances in Flame Retardant Polymeric Materials and CompositesView all articles
The combination of aluminum diethylphosphinate (ADP) and melamine pyrophosphate (MPP) has been extensively utilized in flame-retardant polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) composites. However, the hydrophilic nature of ADP and MPP leads to their migration to the surface or separation from the PBT matrix under the influence of heat and moisture, which subsequently results in the degradation of both flame retardancy and mechanical properties. In this study, reactive epoxy groups were introduced onto the surface of the flame retardant (FR) using a simple method. The resulting encapsulated flame retardant (EP@FR) was then incorporated into PBT via a twin-screw extruder. During extrusion process, the reactive epoxy groups interacted with the free terminal hydroxy and carboxy derived from the PBT, forming covalent bonds at the interface of FR and PBT, thereby enhancing flame retardancy and water resistance. With the addition of 16.0 wt% EP@FR, the PBT/EP@FR composites achieved a UL-94 V-0 rating with an LOI value of 28.5%. Notably, the mechanical properties and UL-94 V-0 rating of the PBT/EP@FR composites were maintained even after immersion in water at 70°C for 14 days. It is expected that this work can provide a promising strategy for the development of flame-retardant and water-resistant PBT composites.
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), as one of the most versatile engineering plastics, exhibits excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance and electrical insulation performance. These characteristics have led to its widespread use in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and mechanical engineering (Dobrotă and Lazăr, 2021; Chan et al., 2022). Particularly, due to its superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, the application of PBT is significantly growing, driven by the rapid development of new energy vehicles. However, the flame retardancy of PBT is insufficient for use in electrical devices. The limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of PBT is approximately 22.0%, which is considered as flammable materials (LOI≤22.0%) (Courtat et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2023; Ge et al., 2024). Therefore, it is of significant importance to enhance the flame retardancy of PBT to meet the increasing demands in new energy vehicles application.
The combination of aluminum diethylphosphinate (ADP) and melamine pyrophosphate (MPP) has been demonstrated as an efficient halogen-free flame retardant for PBT (Ding et al., 2018; Hamlaoui et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2017a). However, both ADP and MPP exhibit poor compatibility with PBT, which results in a reduction of the mechanical properties. More importantly, the hydrophilicity of ADP and MPP causes them to easily migrate to the surface or even separate from the PBT matrix when exposed to heat and moisture, thereby adversely affecting both flame retardancy and mechanical properties (Sheng et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2024). Although hygrothermal testing of PBT/ADP/MPP composites is scarce, the water resistance of ADP in other thermoplastic materials has been widely reported. Tan et al. investigated the water resistance of EVA/ADP composites and it was found that ADP was highly sensitive to moisture, easily migrating to the surface of EVA (Tan et al., 2019). Liu et al. found that the flame retardancy of EVA contained Al(OH)3, ADP and melamine cyanurate was seriously deteriorated after hydrothermal aging (Liu et al., 2024). The LOI value of the flame-retardant EVA was decreased from 36.3% to 30.5%. The total heat release and total smoke production were increased by 13.8% and 273.3%, respectively. Given that EVA is widely used in cable applications, and considering the increasing utilization of PBT in electronic devices, similar challenges may arise for PBT.
It has been reported that surface modification is an effective method to improve the hydrophobicity and the compatibility of FR with polymer matrix, thereby improving the water resistance of the materials (Tang et al., 2023a; Jin et al., 2024). Zhou et al. used silicone rubber as a shell to microencapsulate ADP then used it as a flame retardant of ABS (Zhou et al., 2024). The results demonstrated that both of the flame retardancy and mechanical properties were enhanced due to the improved compatibility with ABS. Similarly, Pan et al. encapsulated ADP with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS-ADP). The hydrophobic of ADP was improved and the flame retardancy of PA6/PDMS-ADP was also enhanced (Pan et al., 2020). Nonetheless, most surface modification strategies only formed an organic shell on FR that interacted with polymer matrix physically, resulting in a limited improvement of the compatibility between FR and polymer matrix (Ke et al., 2023; Deng et al., 2024). Furthermore, many studies focused primarily on the improved hydrophobicity of the FR itself, without sufficiently investigating the flame retardancy and water resistance of the entire polymer matrix (Liu et al., 2019; Du et al., 2022).
Recently, reactive extrusion was considered one of the most promising methods for processing thermoplastic materials in the further. Reactive extrusion is a process in which a chemical reaction takes place during the melting and extrusion process, facilitated by heat and shear generated by the equipment. Typically, the reaction between -NH2 groups of nylon and the acetic anhydride was one of the most practical applications of reactive extrusion (Xiao et al., 2021). It was reported that epoxy groups exhibited high reactivity toward the terminalhydroxyl/carboxyl groups of PBT (Choi et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2017; Fang et al., 2024). Poutrel et al. prepared PBT vitrimers through reactive extrusion with commercial PBT and epoxy (Poutrel et al., 2024). Furthermore, Meunier et al. found that aluminum phosphinate (AlPi) acted as a transesterification catalyst during the preparation of PBT vitrimers (Meunier et al., 2024). Fang et al. prepared PBT/ABS copolymer blends by incorporating styrene-acrylonitrile-maleic anhydride (ASMA) copolymers and epoxy (Fang et al., 2024). The results showed that the epoxy functional groups reacted with both the anhydride groups of ASMA and the terminal -OH and -COOH groups of PBT, leading to the formation of ASMA-EP-PBT graft copolymers.
Inspired by previous studies, a highly reactive FR with epoxy groups (EP@FR) was designed and prepared by surface modification of a commercially used FR containing ADP and MPP, using 3-Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (KH560). It is expected that the epoxy functional groups can react with the -OH and -COOH derived from PBT during the extrusion process. In this way, FR was chemically bonded to PBT matrix via covalent bonds. The effects of FR and EP@FR on the flame retardancy, mechanical properties, water resistance and thermal properties of PBT were investigated. A proposed mechanism for the enhanced flame retardancy and water resistance was outlined. It is expected this work can provide valuable insights for the processing of flame-retardant and water-resistant polymer composite materials.
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT, 1100-211S) was supplied by Changchun Plastics Co., Ltd. Aluminum diethylhypophosphate (ADP, OP 1230) was purchased from Clariant (Shanghai, China). Melamine pyrophosphate (MPP) was provided by Sichuan Institute of fine Chemical Industry Research & Desigen Co., Ltd. 3-Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (KH560, ≥97.0%), anhydrous ethanol and acetic acid (≥99.5%) were purchased from aladdin Co., Ltd. All reagents were used without further purification.
The synthesis route of KH560 oligomer was adapted from previous reports with certain modifications (Peng et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). As illustrated in Figure 1, 45.0 g KH560 was dissolved in a mixture solution consisting of 105.0 mL of deionized water and 6.0 mL anhydrous ethanol at ambient temperature. The mixture was stirred at a rate of 500 rpm for 30 min in a beaker. Then, acetic acid was added into the mixture dropwise within 10 min to adjust the PH to 2–4. The solution was stirred continuously for 5 h at 40°C and the transparent KH560 oligomer solution was obtained with a solid content of approximately 28.0 g/mL.
The flame retardants consisted of ADP and MPP in a mass ratio of 2.5:1, which has been identified as the most effective ratio for the flame-retardant PBT. As shown in Figure 1, 200 g of flame retardants (FR) granules were put into a mechanical mixer with a stirring rate of 100 rpm. KH560 oligomer solution was diluted with deionized water to 100.0 mL at varying concentration of 0.08 g/mL, 0.12 g/mL and 0.16 g/mL. Then, the diluted KH560 oligomer solution was sprayed into the mechanical mixer within 10 min and the stirring rate was increased to 500 rpm for 30 min. Subsequently, the mixture of FR and KH560 oligomer solution was transferred to an oven at 120°C to completely evaporate the solvent. Finally, white powders were obtained and named as EP@FR-x, where EP@FR-1, EP@FR-2 and EP@FR-3 corresponded to FR modified with of KH560 oligomer solution at concentration of 0.08 g/mL, 0.12 g/mL and 0.16 g/mL, respectively.
PBT granules, EP@FR-x and other additives were first dried in an oven at 100°C. The dried EP@FR-x was then blended with PBT using a twin-screw extruder (CTE 35, Coperion, Nanjing Machinery Co., ltd, China) with the extrusion temperature at 220, 240, 240, 240, 240, 230, 230, 230, 230, 240°C, respectively. The detailed formulations of the flame-retardant PBT were listed in Table 1. Then the samples for flame-retardant and mechanical performance test were prepared by an injecting molding machine (HTF90W1, Haitian group, China) at temperature ranging from 230 to 250°C.
Detailed information of material characterization is provided in the Supplementary Information.
As shown in Figure 2A, the characteristic peaks of C-O and Si-O were presented in the FTIR spectrums of both EP@FR-2 and KH560 oligomer. The C-O bond was attributed to the epoxy groups from KH560 oligomer and the Si-O structure was also derived from the KH560 oligomers (Feng et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024c). XPS was carried out to investigate the chemical composition of EP@FR-2. As shown in Figure 2B, FR contained C, N, O, P and Al with elemental mass ratio of 60.4 wt%, 5.3 wt%, 23.7 wt%, 7.9 wt% and 2.7 wt%, respectively. In terms of EP@FR-2, compared to the FR, the mass ratio of C, N, P and Al all decreased, while the mass ratio of O increased. Meanwhile, Si appeared with a mass ratio of 2.3 wt%, which was attributed to the KH560 oligomer. As shown in Figure 2D, the XPS Si spectrums revealed that there was only one type of chemical bonding existing for Si. Figure 2C exhibited the thermal stability and char residue of FR and EP@FR. The results indicated that the introduction of KH560 oligomer did not affect the initial decomposition temperature (T5%) or the max decomposition temperature (Tmax) of the FR. However, the char residue was increased from 11.2% to 16.1%, which was attributed to the high char residue of the KH560 oligomer (Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023). Based on the above characterization, it was concluded that KH560 oligomer was successfully coated on the surface of the FR via the condensation reaction between the Si-OH and the -OH on the surface of the FR as well as physical adhesion of the silicon couple agent itself.

Figure 2. (A) FTIR spectrums; (B) XPS full spectrums; (C) thermal stability; (D) XPS Si spectrums of FR and EP@FR-2.
The flame retardancy of the PBT composites was evaluated by the LOI and UL-94 vertical burning test. As shown in Table 2, the LOI value of the control PBT was 22.0%. After the addition of FR, the LOI value was increased to 28.3%, while the introduction of KH560 oligomer did not apparently affect the LOI value. The LOI value of PBT/EP@FR-2 was slightly increased to 28.5%. In the UL-94 vertical burning test, the control PBT completely burned out in the first ignition and did not achieve any UL-94 rating. After the introduction of FR, PBT/FR composites self-extinguished immediately after the first ignition and within 13.0 s after the second ignition, achieving a UL-94 V-1 rating. After being coated with KH560 oligomer, all the PBT/EP@FR composites self-extinguished within 10 s, achieving a UL-94 V-0 rating. There was an optimal core-shell ratio, where the solid mass ratio of KH560 oligomer to FR was 3:50. At this ratio, the self-extinguished time of PBT/EP@FR-2 in the first and second ignition was 0.0 s and 1.3 s respectively, which was the shortest. Therefore, PBT/EP@FR-2 was selected for further testing.
The cone calorimetry test (CCT) was used to investigate the heat and somke release behavior of the flame-retardant PBT composites when exposed to consistant heat flux. The key data of the CCT was listed in Table 3, including time to ignition (TTI), peak heat release rate (PHHR), total heat release (THR), total smoke prodcution (TSP), average CO and CO2 yeild and char residue. As shown in Figures 3A, B. It was found that PBT was very flammable with PHRR and THR of 1772.9 kW/m2 and 92.3 MJ/m2, respectively. The addition of FR slowed down the combustion process, reducing the PHRR and THR of PBT/FR composites to 457.5 kW/m2 and 77.1 MJ/m2, respectively. The introduction of the KH560 oligomer on the surface of FR further decreased the PHRR and THR of PBT. The PHRR and THR of PBT/EP@EP-2 were decreased to 401.6 kW/m2 and 75.7 MJ/m2, respectively.
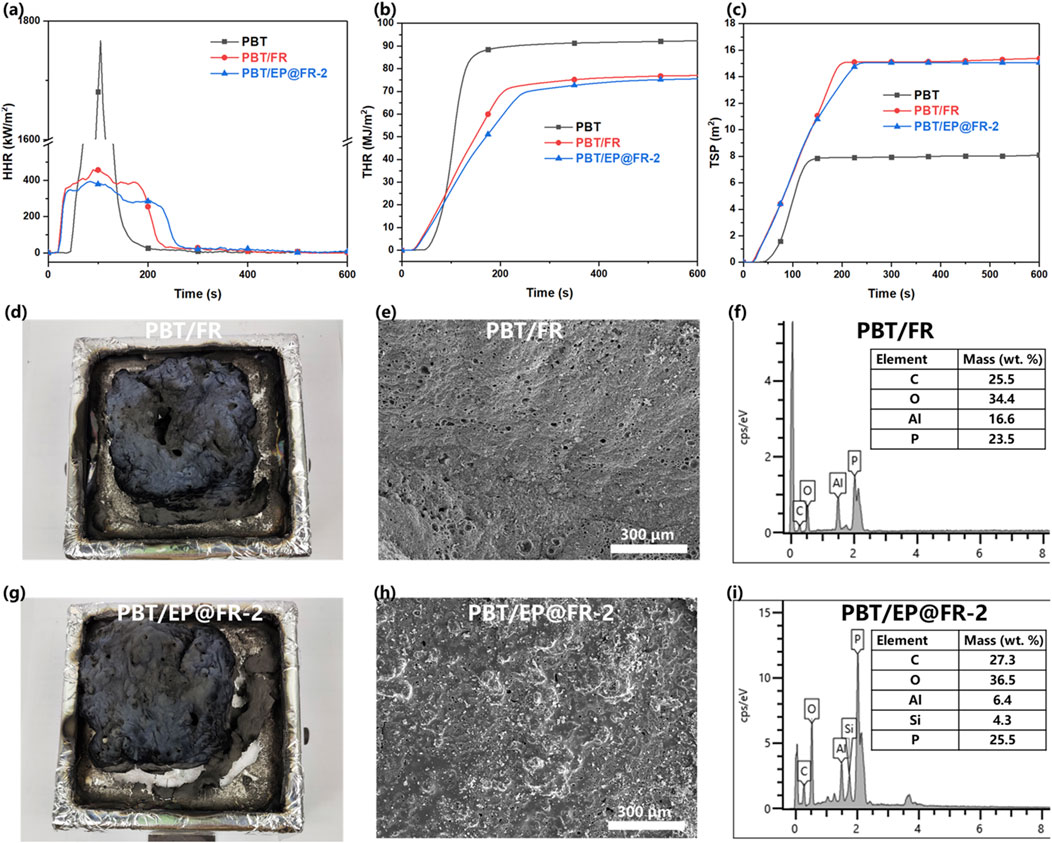
Figure 3. The results of the CCT (A) HHR; (B) THR; (C) TSP; (D) digital image (E) SEM image; (F) element content of the char residue for PBT/FR composites; (G) digital image (H) SEM image; (I) element content of the char residue for PBT/EP@FR-2 composites.
As for the smoke production shown in Figure 3C, the presence of P/N elements in the FR increased the TSP of the FR-contained PBT composites. Compared to the control PBT, the Av-COY of the FR-contained PBT was increased, while the Av-CO2Y was decreased. This suggested that the addition of the FR resulted in the incomplete combustion of the substrate, which accounted for the increased TSP (Li et al., 2024a; Tang et al., 2023b).
It was found that KH560 oligomer was able to further improve the flame-retardant effeciency of the FR and the contribution of the KH560 was furthre investigated. As it shown in Figures 3D–F, the char residue of PBT/FR composites was porous and consisted of C (25.5 wt%), O (34.4 wt%), Al (16.6 wt%) and P (23.5 wt%) elements. While that of the PBT/EP@FR-2 composites shown in Figures 3G–I was dense with few voids observed. The proportion of Si element in the char residue was 4.3 wt%, which indicated that Si participanted in the char forming and enhanced the density of the char residue. Therefore, the transfer of the oxygen and heat was slowed down (Feng et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024b).
The thermal stability of the flame-retardant PBT composites was presented in Figure 4; Table 4. The T5% and Tmax of the control PBT was 389.3°C and 418.8°C, respectively, with a char residue of 5.4%. Due to the catalytic effects of the phosphorus flame retardants, the T5% and Tmax of the FR-contained PBT composites were both lower and the char residue increased. The introduction of the KH560 oligomer did not apparently affect the thermal decomposition behavior of the PBT. The T5%, Tmax and char residue did not show any change, compared to the PBT/FR composites. However, notable changes were observed in the maximum decomposition rate (DTGmax). The DTGmax of PBT composites was 2.6%/oC, while that of the PBT/FR composites was 2.4%/oC. With the introduction of KH560 oligomer, the DTGmax further decreased to 2.3%/oC, indicating that FR was able to reduce the thermal decomposition rate of PBT, and the KH560 oligomer further slowed down the decomposition of the substrate (Jin et al., 2017b; Tang et al., 2022).
The mechanical properties of the flame-retardant PBT were comprehensively evaluated and the results were shown in Figure 5. As shown in Figure 5A, The tensile and bending strength of the control PBT were 50.0 MPa and 76.0 MPa, respectively. It was noticed that the addition of both the FR and EP@FR slightly reduced the tensile strength while maintaining the bending strength. Specifically, the tensile and bending strength of PBT/EP@FR-2 were 46.8 MPa and 76.4 MPa, respectively. As shown in Figure 5B, the elongation at break and notched impact strength of PBT were 143.6% and 5.1 kJ/m2 respectively. The addition of FR reduced the toughness of PBT with both of the elongation at break and notched impact strength decreasing. Compared with PBT/FR composites, the elongation at break of PBT/EP@FR was decreased but the notched impact strength was increased. This phenomenon was attributed to the reaction between epoxy groups and -OH and -COOH groups during reactive extrusion. As a result, the compatibility of EP@FR with PBT was better than that of FR, leading to fewer interface defects and gaps between EP@FR and PBT substrate, which resulted in a higher notched impact strength. SEM images of the fracture surface further proved it. As shown in Figure 5C, on the fracture surface of PBT/FR, FR was exposed on the outside of the substrate, while that of the PBT/EP@FR was different. As shown in Figure 5D, EP@FR was embedded within the substrate, demonstrating good compatibility with PBT. However, due to the formation of covalent bonding at the interface of PBT and EP@FR, the mobility of the molecular chains was restricted, which led to a decreased in the elongation at break.
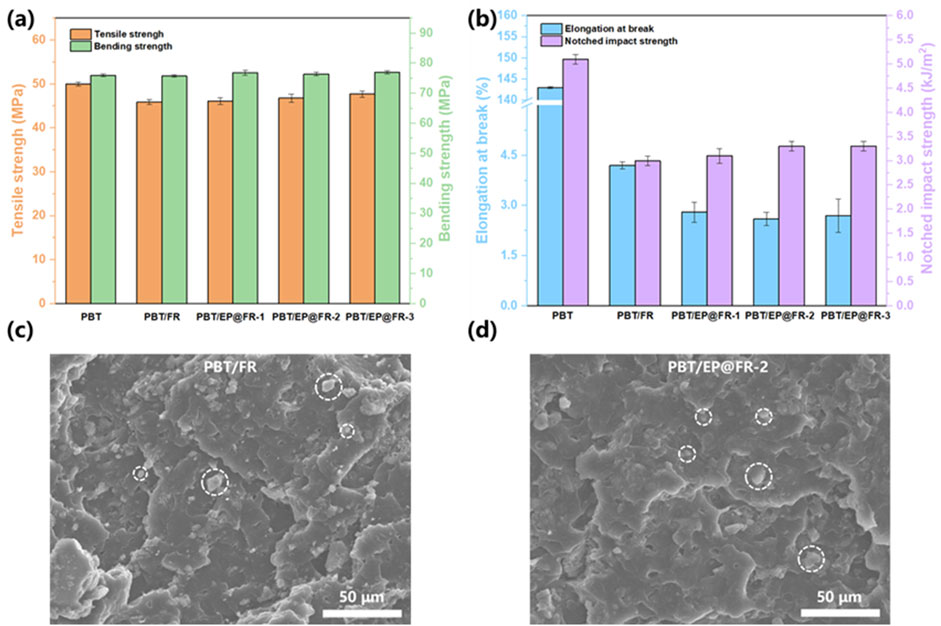
Figure 5. (A) Tensile and bending strength; (B) elongation at break and notched impact strength of the flame-retardant PBT composites; SEM images of the fracture surface for (C) PBT/FR and (D) PBT/EP@FR-2.
PBT/FR and PBT/EP@FR-2 were soaked in water at 70°C for 14 days to investigate their water resistance. Figure 6A illustrated the appearance of the PBT and PBT/EP@FR composites before and after soaking in water. It was observed that the water was clear prior to soaking. However, after soaking, white precipitate appeared in water of the PBT/FR composites, which was attributed to the FR leaching out of the PBT matrix. In contrast, the water of the PBT/EP@FR composites remained clear, indicating better water resistance. The white precipitate was filtered out and dried in an oven. The FTIR spectrums of the white precipitate was shown in Figure 6B. It was found that the spectrums of the white precipitate were similar to that of FR, indicating that both ADP and MPP separated out from the PBT matrix.

Figure 6. (A)The digital photos of the PBT and PBT/EP@FR-2 before and after soaked in water; (B) FTIR spectrums of ADP, MPP, FR and the white precipitate.
The flame retardancy of the PBT and PBT/EP@FR-2 composites after soaked was evaluated by LOI and UL-94 vertical burning test. As shown in Table 5, after soaked in water, the flame retardancy of the PBT/FR composites decreased. The LOI value decreased from 28.3% to 26.2% and the UL-94 rating shifted from V-1 to V-2. However, the PBT/EP@FR composites maintained its flame retardancy. The LOI value slightly decreased from 28.5% to 27.9% and the UL-94 vertical burning rating remained at V-0.
The mechanical properties of the flame-retardant PBT composites after soaked was also characterized and the results were shown in Table 6. After soaking, the mechanical properties of PBT/FR and PBT/EP@FR-2 composites both decreased. The tensile strength, elongation at break and notched impact strength of PBT/FR composites decreased by 13.0%, 21.4% and 16.7%, respectively. These of PBT/EP@FR-2 decreased by 12.8%, 0% and 6.0%, respectively. Meanwhile, the tensile strength and notched impact strength of PBT/EP@FR-2 were both higher than those of PBT/FR after soaking.
Totally, both the flame retardancy and mechanical properties of PBT/EP@FR-2 were superior to those of the PBT/FR composites after soaking. Under humid and heat conditions, the hydrophilic nature of the FR caused it to migrate to the surface of the substrate or even separate from the substrate inducing by water. This led to mass loss and uneven distribution of the FR, which in turn resulted in a deterioration of mechanical properties and reduced flame retardancy. The loss of FR further promoted the deterioration of the flame retardancy. However, the introduction of the KH560 oligomer alleviated this issue, helping to maintain both the mechanical properties and flame retardancy of the composites.
It was hypothesized that during reactive extruding, under heat and shear, a reaction took place between the EP@FR and PBT. The epoxy groups on the surface of EP@FR reacted with the terminal -OH and -COOH of PBT, forming a C-O-C structure at the interface between PBT and FR (Figure 7) (Fu et al., 2017; Jubinville et al., 2019; Jiang et al., 2020). In this manner, the FR was covalently bonded to the substrate. As a result, the FR was effectively fixed within the PBT matrix, making it difficult for water to induce its separation. Consequently, the FR remained stably distributed in the substrate.
The torque-time curve was used to characterize the viscosity change during the melting blend to reflect the reactive extrusion and the results was shown in Figure 8A. The torques of PBT and PBT/FR showed a trend of increasing, then decreasing, and finally stabilizing, corresponding to the melting and mixing process, respectively. The max torque of PBT was 15.9 Nm at around 30 s. The addition of FR increased the max torque to 19.9 Nm at 48 s, which was attributed to the friction between PBT molecular chains and FR. It was worthy noticed that EP@FR-2 altered the viscosity during processing. Two peaks showed up in the torque curve of the PBT/EP@FR-2: the first peak, similar to PBT/FR, corresponding to the melting process. However, instead of gradually decreasing, the torque increased again, reaching a max value of 23.2 Nm at 66 s. This phenomenon indicated that the reaction between epoxy groups and terminal -OH and -COOH of PBT occurred at this moment. After most of the reactive epoxy groups were consumed, the torque started to decease and eventually equalized (Himmelsbach et al., 2023).
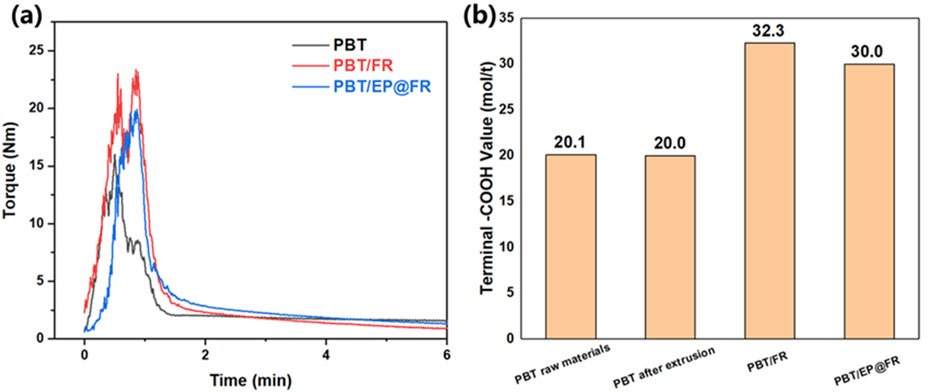
Figure 8. (A)The torque-time curve; (B)The terminal carboxyl values of PBT and flame-retardant PBT composites.
To further investigate this reactive extruding process, the terminal carboxyl values of the flame-retardant PBT was carried out and the results were shown in Figure 8B. For both the raw PBT materials and PBT after extrusion, the terminal -COOH value was around 20.00 mol/t. After the addition of the FR, the acid catalysis effect of the FR broke the ester bonds of PBT, leading to an increase in terminal -COOH groups. As a results, the terminal -COOH of PBT/FR increased to 32.33 mol/t. In contrast, the terminal -COOH value of PBT/EP@FR-2 decreased with the introduction of reactive epoxy groups, which was attributed to the consumption of terminal -COOH reacted with epoxy groups.
In this study, flame-retardant and water-resistant PBT composites were prepared via reactive extrusion. The reactive epoxy groups were able to form C-O-C bonds with the terminal hydroxy and carboxyl groups of PBT during extrusion. The results showed that PBT/EP@FR-2 composites achieved a UL-94 V-0 rating (3.2 mm) with an LOI value of 28.5%. Compared to the control PBT composites, the PHRR and THR were reduced by 77.4% and 18.0%, respectively. Furthermore, the PBT/EP@FR-2 composites exhibited superior water resistance compared to the PBT/FR composites. The PBT/EP@FR-2 composites maintained a UL-94 V-0 rating and an LOI value of 27.9% after soaked in water at 70°C for 14 days, while those of PBT/FR decreased to V-2 and 26.2%, respectively. Meanwhile, the mechanical properties of PBT/EP@FR-2 maintained at above 85%. The prepared flame-retardant and water-resistant PBT composites had bright prospects for the application in the electronic devices and new energy vehicles.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
GR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. YY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. HX: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. TL: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. XL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YC: Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Thanks to the financial support provided by China Bluestar Chengrand (Grant No. E-20245290D05).
Authors GR, JZ, YY, HX, TL, XL, and YC were employed by China Bluestar Chengrand Co., Ltd.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2025.1536536/full#supplementary-material
Chan, J. X., Wong, J. F., Hassan, A., Othman, N., Razak, J. A., Nirmal, U., et al. (2022). Synthetic wollastonite nanofiber for polybutylene terephthalate nanocomposite: mechanical, thermal, tribological and flammability properties. Polymer 256, 125259. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125259
Choi, E. Y., Kim, S. W., and Kim, C. K. (2016). In situ grafting of polybutylene terephthalate onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes by melt extrusion, and characteristics of their composites with polybutylene terephthalate. Compos. Sci. Technol. 132, 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.07.003
Courtat, J., Mélis, F., Taulemesse, J.-M., Bounor-Legaré, V., Sonnier, R., Ferry, L., et al. (2017). Effect of phosphorous-modified silica on the flame retardancy of polybutylene terephthalate based nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 143, 74–84. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.06.014
Deng, M., Zhang, Z., Sun, J., Liu, X., Li, H., Gu, X., et al. (2024). Improving the flame retardancy and water resistance of polypropylene by introducing microcapsule flame retardant system and modified zinc oxide. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 221, 110668. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.110668
Ding, Y., Stoliarov, S., and Kraemer, R. (2018). Development of a semiglobal reaction mechanism for the thermal decomposition of a polymer containing reactive flame retardants: application to glass-fiber-reinforced polybutylene terephthalate blended with aluminum diethyl phosphinate and melamine polyphosphate. Polymers 10 (10), 1137. doi:10.3390/polym10101137
Dobrotă, D., and Lazăr, S. V. (2021). Ultrasonic welding of PBT-GF30 (70% polybutylene terephthalate + 30% fiber glass) and expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (e-PTFE). Polymers 13 (2), 298. doi:10.3390/polym13020298
Du, H., Ren, J., Fu, X., Zhang, W., and Yang, R. (2022). Simultaneous improvements of the fire safety, mechanical properties and water resistance of vinyl ester resin composites by introducing microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate by polytriazole. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 238, 109908. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109908
Fang, Y.-G., Lin, J.-Y., Zhang, Y.-C., Qiu, Q.-W., Zeng, Y., Li, W.-X., et al. (2024). A reactive compatibilization with the compound containing four epoxy groups for polylactic acid/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/thermoplastic starch ternary bio-composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 262, 129998. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129998
Feng, H., Li, D., Cheng, B., Song, T., and Yang, R. (2022). A cross-linked charring strategy for mitigating the hazards of smoke and heat of aluminum diethylphosphonate/polyamide 6 by caged octaphenyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. J. Hazard. Mater. 424, 127420. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127420
Feng, Y., Wang, W., and Wang, S. (2024). Multiscale analysis of recycled coarse aggregate concrete under the synergistic action of KH560 and PVA fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 419, 135433. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135433
Fu, Z., Wang, H., Zhao, X., Horiuchi, S., and Li, Y. (2017). Immiscible polymer blends compatibilized with reactive hybrid nanoparticles: morphologies and properties. Polymer 132, 353–361. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2017.11.004
Ge, B., Ma, M., Bai, L., Liu, Z., Chen, S., Shi, Y., et al. (2024). Synergistic effects of organosilicon flame retardant and DOPO-based reactive compatibilizer for high performance PC/PBT composites. Polymer 299, 126948. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2024.126948
Hamlaoui, O., Klinkova, O., Elleuch, R., and Tawfiq, I. (2021). Effect of the glass fiber content of a polybutylene terephthalate reinforced composite structure on physical and mechanical characteristics. Polymers 14 (1), 17. doi:10.3390/polym14010017
Himmelsbach, A., Standau, T., Kuhnigk, J., Bubmann, T., Akdevelioglu, Y., Nofar, M., et al. (2023). Investigation of the reaction kinetics of poly(butylene terephthalate) and epoxide chain extender. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 308 (7). doi:10.1002/mame.202200683
Jiang, L., Huang, Z., Wang, X., Lai, M., Zhang, Y., and Zhou, H. (2020). Influence of reactive compatibilization on the mechanical, thermal and rheological properties of highly filled PBT/Al2O3 composites. Mater. Des. 196, 109175. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109175
Jin, X.-D., Gu, X.-Y., Chen, C., Tang, W.-F., Li, H.-F., Liu, X.-D., et al. (2017b). The fire performance of polylactic acid containing a novel intumescent flame retardant and intercalated layered double hydroxides. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 12235–12250. doi:10.1007/s10853-017-1354-5
Jin, X.-D., Sun, J., Jessica, S. Z., Gu, X.-Y., Serge, B., Li, H.-F., et al. (2017a). Preparation of a novel intumescent flame retardant based on supramolecular interactions and its application in polyamide 11. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 24964–24975. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b06250
Jin, X.-D., Wu, X.-Y., Tang, W.-F., Tan, Z.-N., Wang, W.-F., and Sun, S.-B. (2024). Self-assembled coatings with durable flame retardancy for EPS foam. Chem. Eng. J. 494, 153285. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.153285
Jubinville, D., Chang, B. P., Pin, J.-M., Mohanty, A. K., and Misra, M. (2019). Synergistic thermo-oxidative maleation of PA11 as compatibilization strategy for PA6 and PBT blend. Polymer 179, 121594. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121594
Ke, Q., Bai, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, J., and Yang, M. (2023). Simultaneously enhancing the flame retardancy, water resistance, and mechanical properties of flame-retardant polypropylene via a linear vinyl polysiloxane-coated ammonium polyphosphate. Polymers 15 (9), 2074. doi:10.3390/polym15092074
Li, H., Liu, C., Zhu, J., Huan, X., Xu, K., Geng, H., et al. (2024a). Intrinsically reactive hyperbranched interface governs graphene oxide dispersion and crosslinking in epoxy for enhanced flame retardancy. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 672, 465–476. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2024.06.005
Li, J., Qin, Z., Zhai, C., and Yang, R. (2024b). Study on the synergistic flame-retardancy of phenyl/vinyl siliconesquioxane and aluminum diethyl phosphinate on polyethylene terephthalate. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 220, 110660. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.110660
Li, X., Guan, J., Zeng, W., Li, H., Shi, J., Wen, N., et al. (2022). Effects of a symmetrical inorganic-organic monomer on the flame retardancy and mechanical properties of polyethylene terephthalate copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 171, 111174. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111174
Li, Y.-M., Zhu, D.-P., Hu, S.-L., Jiao, Y.-H., Xu, J.-Z., and Wang, D.-Y. (2024c). The fabrication of organic-inorganic hybrid structure towards high mechanical property and improved flame retardancy. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 225, 110818. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.110818
Liu, H., Wang, W., Yan, L., and Xu, Z. (2024). Flammability degradation behavior and ageing mechanism of flame-retardant cable sheath under different ageing conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 230, 111019. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.111019
Liu, L., Xu, Y., He, Y., Xu, M., Shi, Z., Hu, H., et al. (2019). An effective mono-component intumescent flame retardant for the enhancement of water resistance and fire safety of thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 167, 146–156. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.07.006
Meunier, L., Montarnal, D., Fournier, D., Gaucher, V., Duquesne, S., and Samyn, F. (2024). Effect of addition of aluminum phosphinate as fire retardant in a PBT vitrimer. Polymer 290, 126559. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2023.126559
Pan, Y., Song, L., Wang, W., and Zhao, H. (2020). Polydimethylsiloxane wrapped aluminum diethylphosphinate for enhancing the flame retardancy of polyamide 6. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137 (35). doi:10.1002/app.49027
Peng, C., Huang, A., Ma, X., Zhong, J., Chen, G., Luo, W., et al. (2023). Transparent and flame-retardant hybrid protective coating with high surface hardness, yet foldability. Prog. Org. Coat. 175, 107346. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2022.107346
Poutrel, Q. A., Kmo, R., Cohadon, A., Boisse, J., Rouzière, S., André, S., et al. (2024). Effect of processing conditions on the properties of vitrimerized polybutylene terephthalate prepared by reactive extrusion. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 225, 110820. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.110820
Sheng, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, B., Yu, B., Shi, Y., Song, L., et al. (2017). Effect of electron beam irradiation and microencapsulation on the flame retardancy of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer materials during hot water ageing test. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 133, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.11.018
Sun, J., Zhang, D., Shang, X., Tan, F., Bao, D., and Qin, S. (2022). Flame-retardant properties and mechanism of LGF/PBT/DOPO-HQ-conjugated flame-retardant composites. Front. Chem. 10, 981579. doi:10.3389/fchem.2022.981579
Tan, Y., Wachtendorf, V., Klack, P., Kukofka, T., Ruder, J., and Schartel, B. (2019). Durability of the flame retardance of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer cables: comparing different flame retardants exposed to different weathering conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137 (1). doi:10.1002/app.47548
Tang, W.-F., Liang, G.-Q., Wang, L., Yuan, Y., Wubliker, D., Liu, F., et al. (2023a). Multi-functional flame retardant coatings comprising chitosan/gelatin and sodium phytate for rigid polyurethane foams. J. Clean. Prod. 394, 136371. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136371
Tang, W.-F., Song, L.-X., Liu, F., Wubliker, D., Qin, Z.-D., Zhang, S., et al. (2022). Improving the flame retardancy and thermal stability of polypropylene composites via introducing glycine intercalated kaolinite compounds. Appl. Clay. Sci. 217, 106411. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2022.106411
Tang, W.-F., Zhang, A.-Z., Cheng, Y.-W., Wubliker, D., Liao, Y.-H., Chen, H.-F., et al. (2023b). Fabrication and application of chitosan-based biomass composites with fire safety, water treatment and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 225, 266–276. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.261
Wang, W., Liu, Y., and Wang, Q. (2023). Adjustable boron nitride segregated framework in epoxy resin for high performance thermal management and flame retardant applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 242, 110161. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.110161
Xiao, Y., Mu, X., Wang, B., Hu, W., Wang, J., Zhou, F., et al. (2021). A novel phosphorous-containing polymeric compatibilizer: effective reinforcement and flame retardancy in glass fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 205, 108536. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108536
Yan, C., Xu, B., Shan, D., Zhang, W., Xu, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2023). Fabrication and mechanism research of high-efficiency water-resistant flame retardant, transparent and mechanically reinforced polycarbonate composites. Polym. Test. 119, 107937. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2023.107937
Yang, Z., Xiao, G., Chen, C., Chen, C., Zhong, F., Wang, M., et al. (2021). Mussel inspired polydopamine@KH560-linked hexagonal boron nitride and CNTs nanoflame retardants improve fire performance of composite coatings. Colloid. Surf. A 631, 127717. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127717
Zhang, J., Liu, Z., Qi, P., Liu, J., Sun, J., Gu, X., et al. (2024). Rapid-curing imidazole-based highly transparent protective coating for polycarbonate films with good hardness and flame retardancy. Prog. Org. Coat. 189, 108289. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2024.108289
Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Cao, W., Guo, Z., Fang, Z., Li, J., et al. (2023). Ultra-high flame-retardant efficiency of phosphorous-silicon hybrid microsphere in poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate). Compos. Part. B-Eng. 263, 110861. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110861
Zhou, F., Tang, W., Xi, W., Qian, L., Wang, J., Qiu, Y., et al. (2024). Improving the fracture toughness, flame retardancy and smoke suppression of ABS by core-shell elastic flame retardant particles with P/Si synergistic effect. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 228, 110893. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2024.110893
Keywords: polybutylene terephthalate, reactive extrusion, flame retardancy, water resistance, mechanical properties
Citation: Ran G, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Xie H, Li T, Lan X and Cao Y (2025) Construction of flame-retardant and water-resistant polybutylene terephthalate composites by reactive extrusion. Front. Mater. 12:1536536. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1536536
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 21 January 2025.
Edited by:
Jun Sun, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiaodong Jin, Beijing University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Ran, Zhang, Yuan, Xie, Li, Lan and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanxiao Cao, Y2FveWFueGlhb0BzaW5vY2hlbS5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.