- 1Guangxi Transportation Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd., Nanning, China
- 2School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha, China
- 3Guangxi Jiaoke New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., Nanning, China
This study aims to investigate the effect of fine aggregate lithology on the performance of rubberized asphalt mixtures. SEM, XRD, and contact angle tests were used to analyze the microscopic physical and chemical properties of 0–3-mm grain-size diabase and limestone. The performance characteristics of two types of ARAC-13 rubberized asphalt mixtures (with the diabase coarse aggregates and diabase fine aggregates, and diabase coarse aggregates and limestone fine aggregates, respectively) were then compared through conventional high-temperature water stability performance tests, uniaxial penetration tests, and accelerated loading abrasion tests. The results show that the surface roughness, chemical composition, and surface adhesion properties of limestone are better than those of diabase, and the surface roughness of limestone is 13.9% higher than that of diabase, and the surface adhesion energy is 6.4% higher. However, the results show relatively small differences between the asphalt mixtures with the diabase coarse aggregates and diabase fine aggregates and those with diabase coarse aggregates and limestone fine aggregates in the conventional water stability performance test and the high-temperature performance test. Furthermore, the strength reaches 90% when cured for 8 h for limestone and 12 h for diabase, with the curing rate being faster for limestone. The anti-abrasion performance of diabase specimens is superior to that of limestone specimens, but the anti-abrasion decay performance is the opposite. In summary, it can be observed that limestone fine aggregate shows better adhesion performance with asphalt than diabase fine aggregate, and it was recommended that diabase coarse aggregate and limestone fine aggregate be used to improve the asphalt–aggregate interface and enhance the road performance of the asphalt pavement.
1 Introduction
Rubber-modified asphalt is a mature, environmentally friendly pavement material in China, known for its good performance advantages in noise reduction, anti-skid properties, high- and low-temperature resistance, fatigue resistance, and other road performance aspects. Therefore, it has been widely used for decades (Xie et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2024). For example, rubberized asphalt pavement has been applied to more than 2000 km of highways, national and provincial trunk lines, and other projects in Guangxi from 2012 to 2023. Over this period, a mature construction technology system of Guangxi rubberized asphalt pavement was developed after more than 10 years of engineering practice. Aggregate is the most used material in road construction, and it can be classified into coarse and fine aggregates based on the particle size. Therefore, the properties and quantity of fine aggregate have different effects on the performance of asphalt mixtures. However, due to the different raw materials of the aggregates used in some new highways, the time of occurrence, type, and the evolution of damage during the service operation are significantly different (Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Stukhlyak et al., 2015). Some rubberized asphalt pavement construction projects have faced technical problems, such as insufficient adhesion between the asphalt and aggregate and difficulties in compaction of the mixture, resulting in loose pavement, rutting, and other forms of damage shortly after opening to traffic, as shown in Figure 1. Therefore, it is essential to study the effect of fine aggregate on the performance of the rubberized asphalt mixtures to improve the mechanical properties of these mixtures and enhance the road performance of rubberized asphalt pavements.
Many studies show that aggregate affects the properties of asphalt mixtures in multiple dimensions. DelRio-Prat et al. (DelRio-Prat et al., 2010; Ingunza et al., 2013) investigated the effect of aggregate shape characteristics on the modulus of elasticity of asphalt mixtures, and the results showed that asphalt mixes with rounded aggregates are easy to compact, but it will result in a reduction of the modulus of elasticity of the mixture. Jamkar and Rao (Jamkar and Rao, 2004) suggested that the surface texture of the aggregates and the proportion of crushed gravel in the broken surface have a greater effect on the properties of the mixture. Prudêncio et al. (Prudêncio et al., 2013) investigated the correlation between this metric and asphalt mortar based on the metrics of fine aggregate shape characteristics obtained using a simple digital image analysis method and found that the measured metrics have a significant effect on the flowability of asphalt mortar. Ingunza et al. (2013) investigated the effect of aggregate shape characteristics on the modulus of elasticity of asphalt mixtures and found that needle-like particles are detrimental to the compaction of asphalt mixtures, and aggregates with rounded shapes are more conducive to compaction but reduce the modulus of elasticity values. Cheung and Dawson (2002) found that the angularity of the coarse aggregate is the main factor affecting the ultimate shear strength and permanent deformation. Mahboub et al. (2001) used Kentucky limestone with different contents of needle flake for asphalt mixture performance analysis and concluded that the asphalt mixture properties were significantly affected when the needle flake particle content exceeds 40%. Habal and Singh (2017) tested the water stability properties of three types of warm mix asphalt (WMA) using the surface free energy method test with two types of aggregates, namely, granite and limestone. The results showed a correlation between the elemental composition of the asphalt and the surface free energy parameter; the comparison revealed that limestone mixes had better resistance to water damage than granite aggregates. Wang et al. (2011) conducted abrasion tests on mixture specimens prepared from coarse and fine aggregates with different abrasion properties and tested the long-term skid resistance using the Prufstand Wehner/Schulze (PWS) dynamic coefficient of friction tester. It was found that the higher the abrasion value of the aggregate, the better the long-term skid resistance of the mixture and that the fine aggregate had a greater effect on the long-term skid resistance of the pavement compared to the coarse aggregate.
The abovementioned research shows that the various characteristics of the aggregate for asphalt mixture pavement performance need to be addressed. However, in recent construction projects, the traditional 0–5 mm limestone mechanized sand has been used instead of the 0–5-mm diabase mechanized sand. This paper investigates the effect of the different types of mechanized sand on adhesion and compaction properties. The study first focuses on two types of mechanism sand, analyzing their micro-physical properties, the chemical composition of the minerals, and surface adhesion energy. Microscopic adhesion properties are tested for comparison. Additionally, the pavement performance of the mixture is analyzed, including high temperature stability, water stability, strength, and skid resistance. The goal is to provide a theoretical reference basis for the selection of the appropriate sand type.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Mastic-modified asphalt
The pre-prepared finish rubberized asphalt was used in the validation test. The specific performance indicators are shown in Table 1.
2.1.2 Coarse aggregates
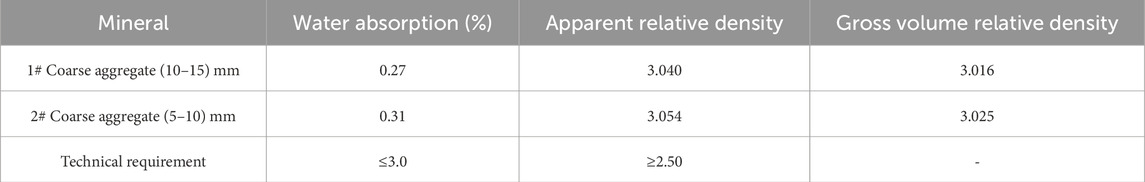
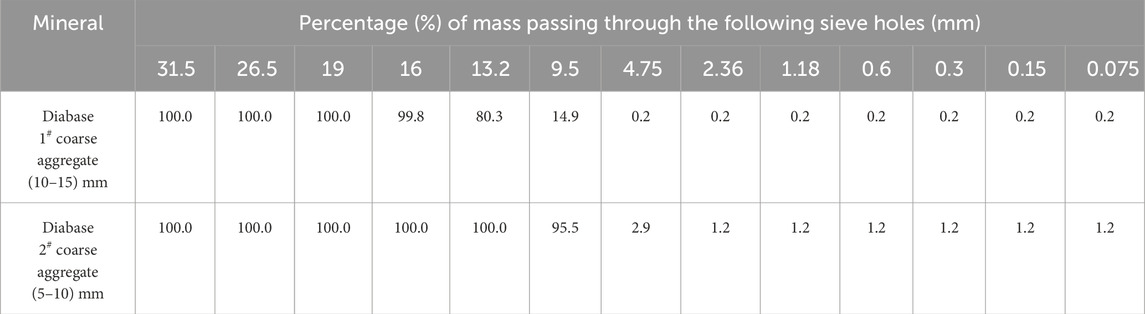
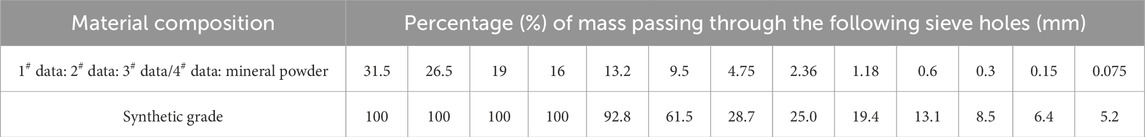
The coarse aggregates used to test the performance of this mixture were all taken from Nanzhan Expressway Division 1–1. The coarse aggregates are 1# (10–15) and 2# (5–10) mm diabase. The performance indexes and sieve test results are shown in Tables 2, 3.
2.1.3 Fine aggregates
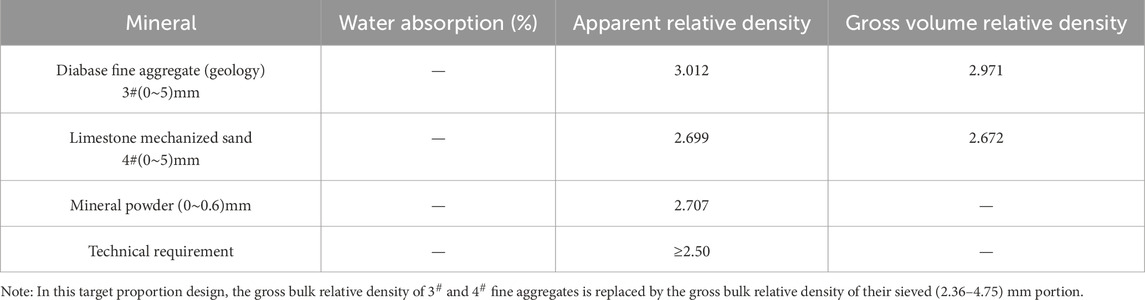
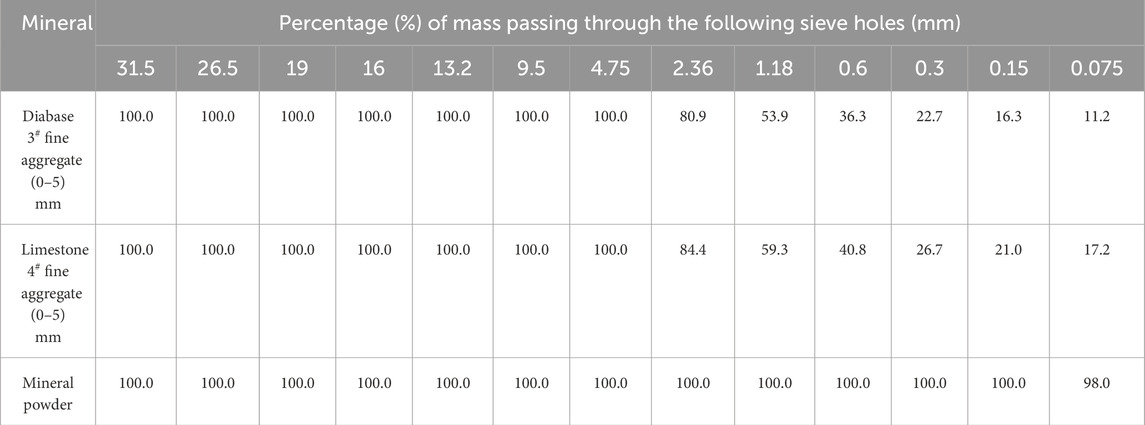
The fine aggregates used in this mix performance test were taken from Nanzhan Expressway Division 1–1 and consisted of 3# (0–5) mm diabase mechanized sand and 4# (0–5) mm limestone mechanized sand. The performance indexes and the results of the sieve test are shown in Tables 4, 5.
2.1.4 Mineral gradation and oil/stone ratio
The synthetic grading of ARAC-13 was determined for this comparative validation based on the characteristics of the aggregate and the grading experience in projects under construction, as shown in Table 6. In this grading, 1# (10–15) mm and 2# (5–10) mm diabase were used as coarse aggregates, as shown in Table 2; and 3# (0–5) mm diabase mechanized sand and 4# (0–5) mm limestone mechanized sand were used as fine aggregates.
The bitumen-aggregate ratio of 5.7% was selected as the optimum asphalt content for all the tests based on engineering experience. Marshall specimens were prepared based on the optimum asphalt content, and volume indexes such as VV, VFA, and VMA were tested.
2.2 Test methods
2.2.1 Fine aggregate adhesion microtest
The physical properties, chemical properties, and texture structure of the surface of fine aggregates were tested to investigate the micro-mechanism of the differences in the adhesion performance of different fine aggregates to asphalt. XRD was then used to determine the mineral composition of the fine aggregates and analyze their chemical composition to evaluate the adhesion performance between aggregates and asphalt. Finally, the surface energy of different aggregates with asphalt was tested using the seated drop method to compare and verify the adhesion properties of different fine aggregates with asphalt.
2.2.1.1 Surface microcharacterization test
The Phenom Pro SEM, manufactured by Phenom-World Company in the Netherlands, was used to scan the surface microscopic characteristics of diabase and limestone fine aggregates with a grain size of 2.36 mm after washing and drying. The SEM scanning magnification was chosen to be ×3,000, and the image unit size was 10 μm because the thickness of the asphalt film of intensively blended mixtures is generally 6∼8 μm. Five parallel experimental specimens were selected and imaged for the quantitative analysis of the degree of roughness of the two types of aggregates. The images were then processed using ImageJ software, which first converted the images to the 8-bit format, calculated the gray value of the images, and then analyzed the variance of the gray value of the images, which was used to characterize the degree of surface roughness of the fine aggregates.
2.2.1.2 Mineral composition analysis test
A D8 advance X-ray diffractometer (Bruker, Germany) was used to analyze the mineral composition of the 2.36-mm grain-size diabase and limestone fine aggregates. The basic principle is that when X-rays are directed at the surface of a mineral crystal, they are scattered by the crystal’s atoms, producing scattered waves emanating from the center of each atom. Because of the periodic arrangement of the atoms within the crystal, a fixed-phase relationship exists between the scattered waves, where certain directions reinforce each other and others cancel out, resulting in diffraction. Given that the arrangement of the atoms within each crystal is unique, the resulting diffraction lines are distinctive in their spatial distribution and intensity. Therefore, the mineral composition of the aggregate can be determined by comparing the XRD results with the established card library.
2.2.1.3 Contact angle test
The SDC-200S Scientific Research Contact Angle Measuring Instrument (China) was used to test the surface energy of limestone, diabase, and rubberized asphalt. The rubber asphalt is first heated and allowed to flow to form a rubber asphalt sheet, which is then compacted with a thick rubber pad to complete the preparation of the asphalt sample. After washing and drying the aggregate, fine aggregates of limestone and diabase with a grain size of 9.5 mm were used to cut and prepare the aggregate specimens. The specimens are 1 cm × 1 cm × 0.5 cm in size, and different mesh coarse, medium, and fine sandpapers were used to polish them smoothly. The two types of test liquids, distilled water and anhydrous ethanol, were used for the seat-drop test to calculate the surface energy parameters of the specimens.
2.2.2 Comparative tests of mixture properties
2.2.2.1 Forming temperature test
The Marshall test is used to prepare specimens of asphalt mixture. The specimen size is Φ101.6 mm, and the diameter is 63.5 ± 1.3 mm. The mixed mixture specimens were placed in a constant-temperature oven set at different temperatures to keep them warm for 1 h. The actual temperature was measured using the inserted temperature sensor. The Marshall compactor was used to compact the mixture, and the void ratio indexes were tested for comparison to evaluate the effect of different fine aggregate lithologies on the mix-forming temperature.
2.2.2.2 Water stability test
The Marshall specimens were prepared using two types of fine aggregates, namely, diabase and limestone. The specimen size is Φ101.6 mm, and the diameter is 63.5 ± 1.3 mm. The water stability performance of the mixture specimens prepared with different fine aggregates was tested, and the effect of different fine aggregate lithologies on the water stability performance of the mixture was evaluated using the residual stability and the freezing–thawing cleavage tensile strength ratio.
2.2.2.3 High-temperature stability test
The rutting specimens were prepared using two types of fine aggregates, namely, diabase and limestone. The specimen size is 300 mm × 300 mm × 50 mm, and the high-temperature performance was tested using a conventional dynamic stability test. The test temperature was set at 60°C ± 1°C, and the ground pressure of the test wheels was set at 0.7 ± 0.05 MPa. Test durations of 45 min and 60 min were used to evaluate the stability of mixes and the effect of different fine aggregate lithologies on the high-temperature stability of the mixture.
2.2.2.4 Curing characteristic test
The diabase and limestone aggregates were used to prepare specimens using the SGC instrument in this paper. The specimens had a diameter of 100 mm ± 2.0 mm and a height of 100 mm ± 2.0 mm, making them cylindrical. The specimens were left at 20°C room temperature for 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 18 h, and 24 h for asphalt mixture curing, according to the “Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture Test Procedures for Highway Engineering.” The uniaxial penetration strength was tested on the SGC specimens using the MTS tester, and the penetration strength index was used to analyze the effect of different fine aggregate lithologies on the curing strength of the asphalt mixture.
2.2.2.5 Anti-slip decay performance test
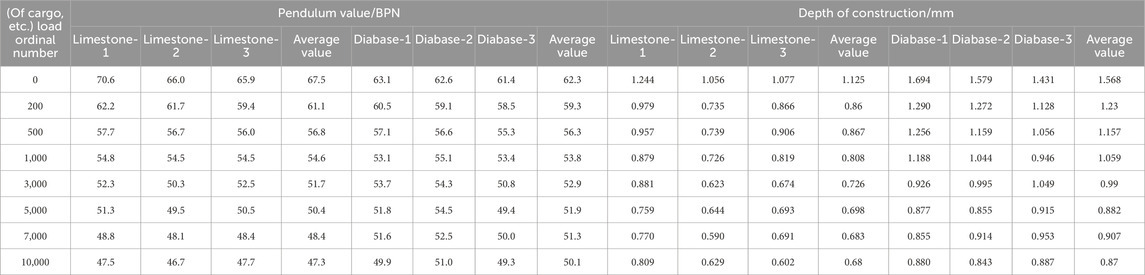
Rutting specimens were prepared with two types of fine aggregates, diabase and limestone, and accelerated abrasion tests were conducted with the skid resistance decay simulation equipment for asphalt pavement studied by the research group, with the loading times of 0, 200, 500, 1,000, 2,000, 5,000, and 10,000 and a test temperature of 30°C. The ground pressure was 0.7 MPa, and the rotation speed was 60 r/min. At the end of each loading cycle, the depth of the structure of the specimen and the pendulum value were measured in the rutted plate track zone, with four measurement points uniformly taken to calculate the average value. Three parallel specimens of two types of fine aggregate were prepared. The depth of the structure and pendulum value index were used to analyze the effect of different fine aggregate lithologies on the skidding decay performance of the rubberized asphalt mixture.
3 Test results and analysis
3.1 Fine aggregate adhesion microtest results and analysis
The asphalt/aggregate interface is the main determinant of the adhesion properties between asphalt and aggregate. When the same type of asphalt is used as a binder, the surface microstructure of individual aggregate at the physical level determines the total adhesion area of the asphalt–aggregate interface, while the mineral composition of the aggregates at the chemical level determines the strength of asphalt–aggregate adhesion. Therefore, the physical and chemical characteristics of the aggregate play a key role in the adhesion performance of the asphalt, which directly affects the high-temperature mechanical properties of the mixture.
3.1.1 Fine aggregate surface microcharacterization
The images of the different aggregates after SEM scanning are shown in Figure 4. It can be observed that the microstructure of the 2.36-mm-sized pyrodiabase is mainly in the form of lamellae, with fewer overlying fine particles. The microstructure of 2.36-mm limestone is mainly ellipsoidal, with more overlying fine particles, and the overall intuitive feeling of the roughness of the two aggregates is relatively low. To quantitatively analyze the degree of roughness of the two types of aggregates, each parallel test group was photographed and grayscale-processed, as shown in Figure 2. ImageJ was used to analyze the grayscale matrix value of the image and then seek its variance value; the results are shown in Table 7. From Table 7, the gray scale variance of the limestone image at 2.36-mm particle size is 13.9% higher than that of the diabase image; the reason for this is the larger specific surface area of the ellipsoid-like structure than that of the laminar lamellar structure at the same volume, and it can be intuitively observed in Figure 3 that there are more fine particles in the upper layers of limestone than in the diabase. Therefore, the total adhesion area at the asphalt aggregate interface is greater in limestone than in the diabase. The microstructural roughness of limestone is better than that of diabase, and its overall adhesion area at the asphalt–aggregate interface is greater than that of diabase.
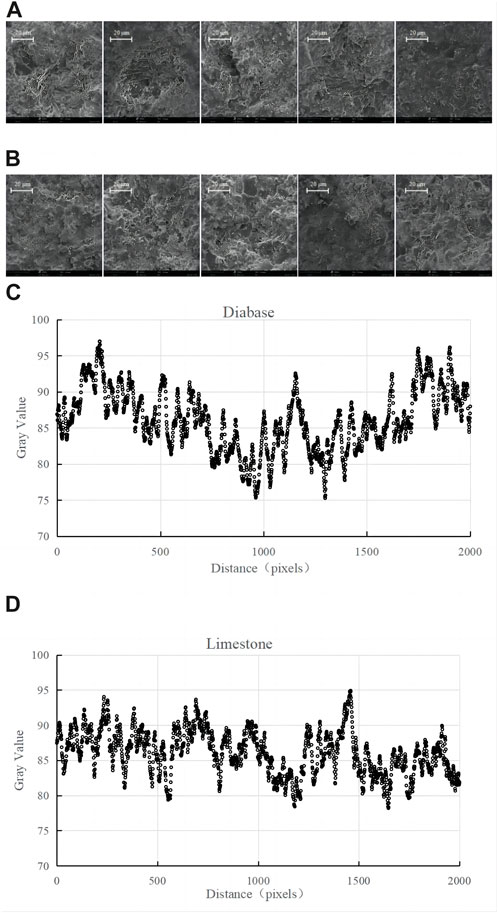
Figure 2. Image gray matrix processing based on “ImageJ” software. (A) SEM scanning of the diabase gray matrix. (B) SEM scanning of the limestone grayness matrix. (C) Diabase after ash treatment. (D) Limestone after ash treatment.
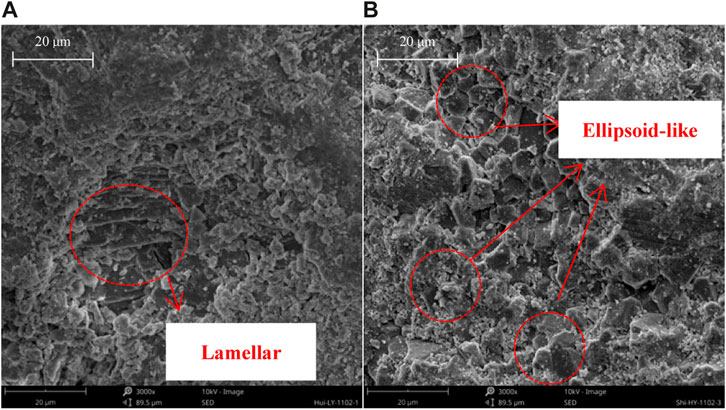

Figure 3. SEM scanning of glow aggregate microscopic properties (magnification 3,000). (A) Diabase. (B) Limestone.
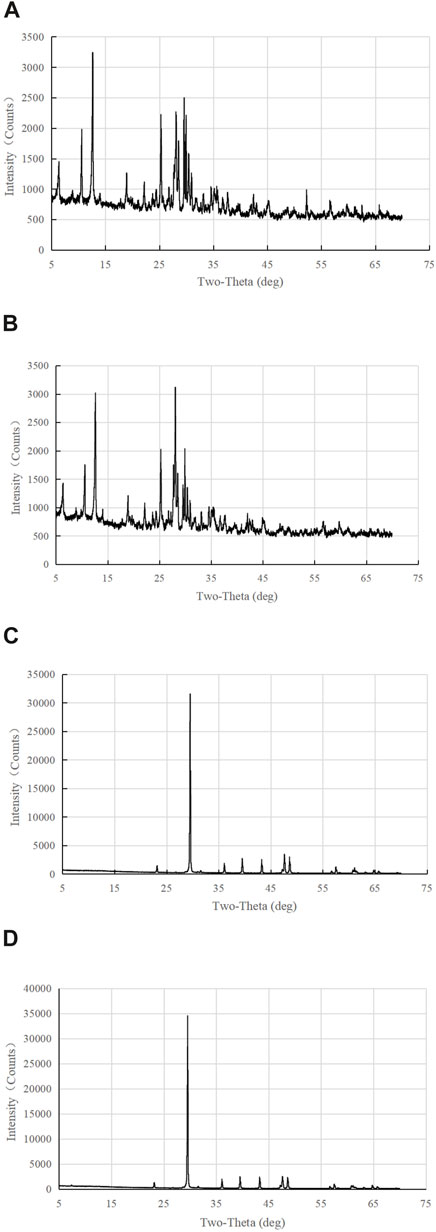
Figure 4. XRD-based mineral content analysis of whole rock of aggregates. (A) Diabase 1. (B) Diabase 2. (C) Limestone 1. (D) Limestone 2.
3.1.2 Fine aggregate mineral composition
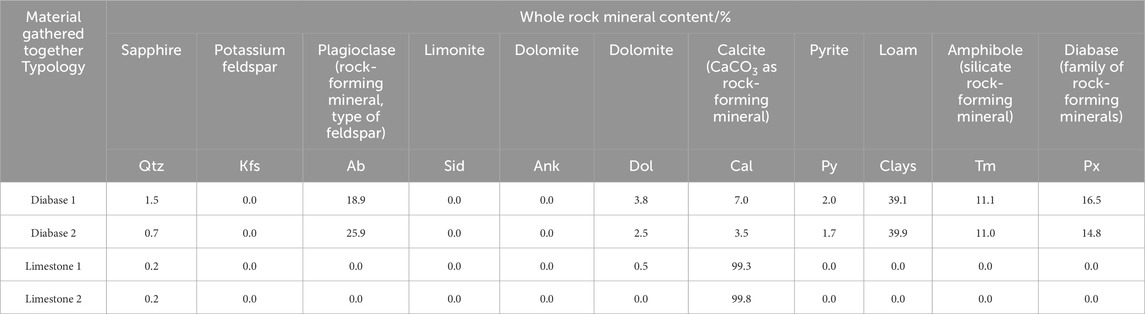
The XRD test results of the two groups of materials are shown in Figure 4; it can be observed that the shape of the diffraction pattern remains the same for the same type of aggregate. In contrast, the intensity of the diffraction peaks is slightly different, indicating that the constituent minerals are similar within the same aggregate lithology. However, their proportions are slightly different because the sources are different. In addition, there is a large difference between the two when the aggregate lithologies are different. For further quantitative analysis, the mineral composition of the aggregates can be obtained by analyzing Figure 4, as shown in Table 8.
1) Diabase is mainly composed of eight mineral components, including clay, plagioclase, and diabase; among these, the clay component accounts for the highest proportion of approximately 40%, followed by plagioclase, diabase, amphibole, calcite, dolomite, pyrite, and quartz, accounting for a total of approximately 60%.
2) The main mineral composition of limestone is calcite, accounting for more than 99%, with trace amounts of other components such as dolomite and quartz.
3) According to the existing literature, it is confirmed that the oxides that affect the adhesion between aggregate and asphalt mainly include four types, namely, SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, and CaO. Among these, CaO and MgO exhibit stronger adhesion to asphalt, whereas SiO2 and Al2O3 show weaker adhesion. Although the main chemical composition of calcite is CaO, the main chemical compositions of clay and plagioclase are SiO2 and Al2O3, respectively, and the main chemical composition of diabase is SiO2. Therefore, the XRD test results confirm that the adhesion of limestone to asphalt, analyzed in terms of its chemical composition, is significantly better than that of diabase.
3.1.3 Fine aggregate surface energy properties
Adhesion of asphalt–aggregate refers to the process of solid and liquid surfaces being replaced by solid–liquid interfaces, and the change in Gibbs free energy of the system before and after the process can characterize the tendency of the system state change. Equations 1, 2 were used to calculate the adhesion energy.
where
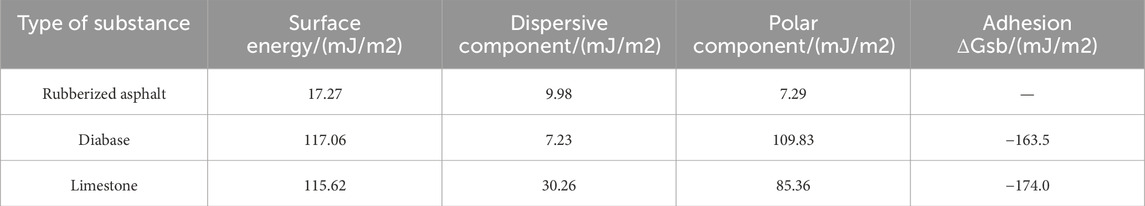
The various aggregate and asphalt surface energy parameters were calculated, as shown in Table 9.
1) The adhesion of limestone rubberized asphalt is better than that of diabase-rubberized asphalt. As shown in Table 9, the adhesion energy of limestone and rubberized asphalt is −174.0 mJ/m2. It is 6.4% lower than that of diabase and rubberized asphalt (−163.2 mJ/m2), which means that the adhesion between the limestone and rubberized asphalt releases more energy, the whole solid–liquid interface is more stable, and the adhesion is better.
2) The polarity component of diabase is significantly higher than that of limestone. From Table 9, the difference in surface energy between diabase and limestone is relatively small. However, the polarity component of diabase is 109.83 mJ/m2, which is 28.7% higher than that of limestone (85.36 mJ/m2), indicating that diabase is more hydrophilic than limestone. It shows that when diabase is used as a fine aggregate in an asphalt mixture, it is more susceptible to water-induced damage; capillary water can more easily penetrate the interface between asphalt and aggregate, leading to asphalt film detachment, reduced adhesion, and early-stage deterioration.
3.2 Comparative test results and analysis of mix performance
3.2.1 Comparison of molding temperatures
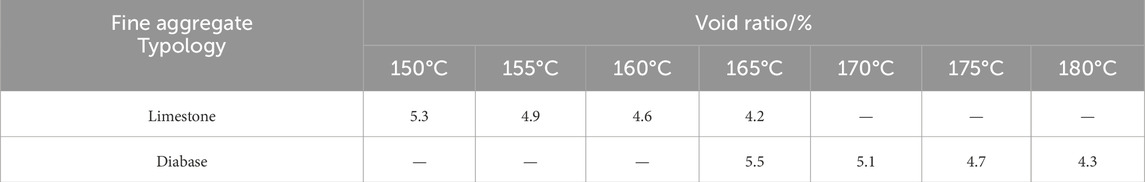
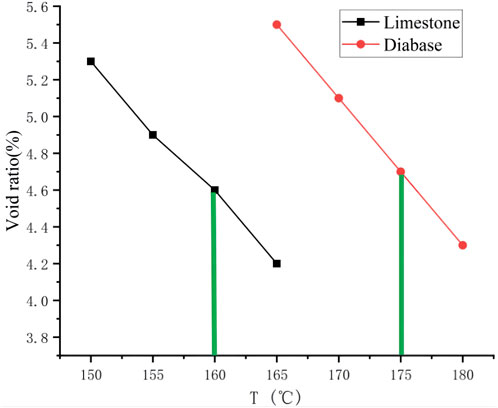
After comparing the test results of the previous trial compaction, it was found that for the same grading and bitumen–aggregate ratio, it is difficult to achieve the same mixture filling state under the same compaction conditions when molding the mixture. This is due to the differences in the surface microstructure and lithology of diabase and limestone fine aggregates. To investigate the compaction conditions of different specimens, specimens were prepared at different compaction temperatures. Specific results are shown in Table 10.
From Figure 5, it can be observed that the compaction temperature required for the diabase specimens is approximately 15°C higher than that for the limestone specimen when the same compaction effort is proposed to achieve the target void ratio. To comparatively analyze the pavement performance of the mix specimens prepared with different fine aggregates, two types of ARAC-13 mixes were prepared for the water immersion Marshall test, the freeze-thaw splitting test, and the rutting test based on the selected gradation, bitumen-aggregate ratio, and molding temperature (160°C for limestone and 175°C for diabase), using the same gradation of SGC to prepare the specimens. The uniaxial penetration method was used to compare the cure time-strength, and finally, the accelerated loading abrasion test was used to compare the skidding decay resistance.
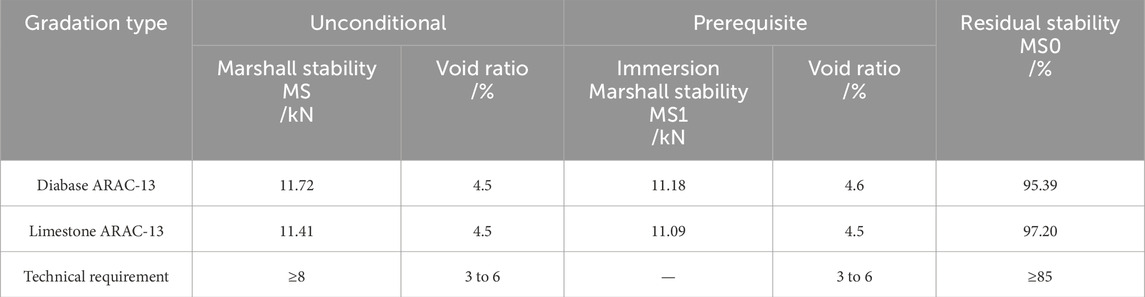
3.2.2 Comparison of water and high-temperature stability
The results of water stability tests are shown in Tables 11, 12, and the results of high-temperature stability tests are shown in Table 13. From Tables 11–13, the water stability performance and high-temperature stability performance of the mix specimens prepared at different molding temperatures (160°C for limestone and 175°C for diabase) are much higher than the specification requirements, and there is no significant difference between them.
3.2.3 Effect of curing time on strength
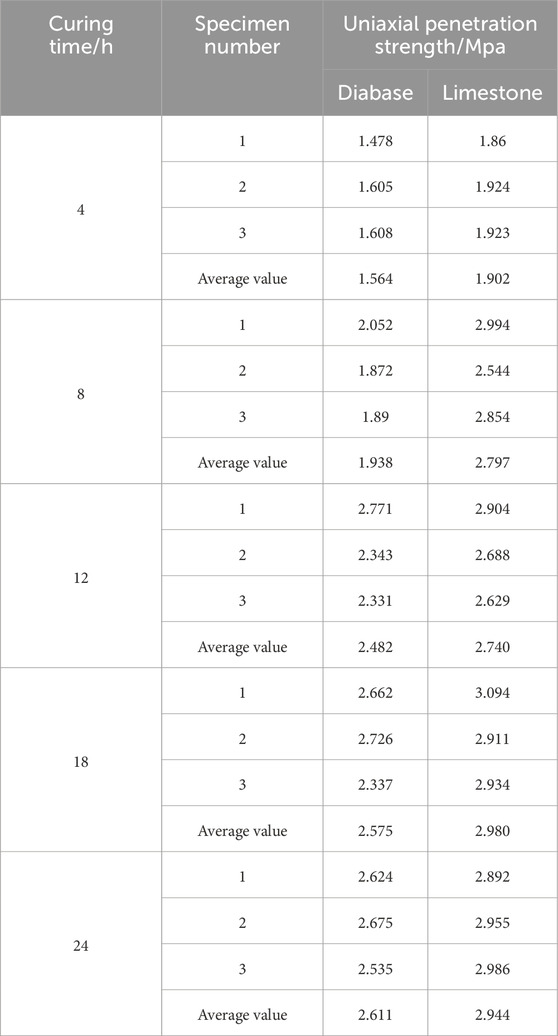
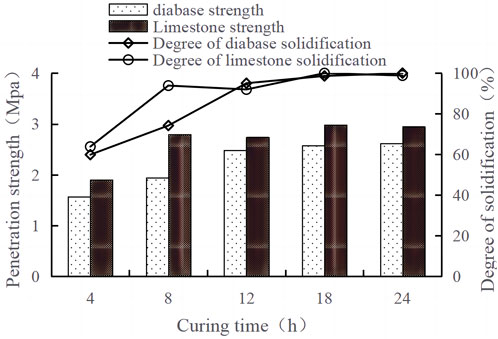
The results of uniaxial penetration tests at different curing times are shown in Table 14; Figure 6.
1) The cured strength of the limestone specimens is significantly higher than that of diabase specimens, and the penetration strength is 10%–20% higher under different curing times. The cured strength of the two types of rubberized asphalt mixtures under curing for 4 h is 1.563 MPa and 1.902 MPa, respectively. The limestone specimens are 21.7% higher than the diabase specimen, and its cured strength under a curing time of 24 h is elevated to 2.944 MPa and 2.611 MPa. The limestone specimens are still 12.7% higher than the diabase specimen.
2) The curing rate of limestone specimens is significantly higher than that of diabase specimens, and the curing time is more than 4 h faster than that of diabase specimens. Figure 6 illustrates that the degree of curing of the two rubberized asphalt mixtures is approximately 60% when the curing time is 4 h. The degree of curing of the limestone asphalt mixture curing strength has reached 90% when the curing time is 8 h. At the same time, the curing strength of the diabase asphalt mixture is only 74% when the curing time is extended to 12 h, but the curing strength of the limestone asphalt mixture is more than 90%.
3.2.4 Anti-slip decay properties
The location of the two specimens’ measuring points and the effects after abrasion are shown in Figure 7. The test data, after taking the mean values, are shown in Table 15. When plotted, these data (provided in Table 15) reveal the trend shown in Figure 8.
1) As the number of abrasions increases, the anti-skid performance of two types of specimens gradually decreases. However, the declining trend gradually tends to level off, as shown in Figure 8. After 10,000 cycles of abrasion, the anti-skid performance index tends to stabilize for all six specimens. This phenomenon is primarily attributed to the abrasion wheel aggregating the surface of the asphalt, leading to significant initial decreases in anti-skid performance. Over time, the abrasion mainly relies on wear resistance, hardness, and other properties of the aggregate, resulting in a slower rate of decrease in anti-skid performance.
2) Limestone and diabase specimens have advantages and disadvantages with respect to abrasion slip resistance performance indexes. The pendulum values of the limestone and diabase specimens were 67.5 BPN and 62.3 BPN, respectively, with the limestone specimens slightly higher by 8.34%. The structural depths were 1.125 mm and 1.568 mm, with the diabase specimens displaying a 39.3% greater depth.
3) The anti-abrasion performance of the limestone specimen is slightly worse than that of the diabase specimen. As shown in Table 14, the BPN value is 47.3 and 50.1, and tectonic depth is 0.68 mm and 0.87 mm for limestone specimens and diabase specimens, respectively, after 10,000 cycles of abrasion.
4) Limestone specimens have slightly better anti-slip properties than diabase. From Table 14, it is observed that the initial pendulum value and the average value of the tectonic depth of the limestone specimens are 67.5 BPN and 1.125 mm, respectively. With the number of abrasions increasing from 0 to 200 cycles, these values decreased by 9.48% and 23.55%, respectively. However, between 7,000 and 10,000 cycles, the values decreased by 2.27% and 0.44%, respectively. In contrast, the initial pendulum value and tectonic depth of the diabase specimens are 62.3 BPN and 1.568 mm, respectively. As the number of abrasion cycles increased from 0 to 200, these values decreased by 4.81% and 21.55%, respectively. Between 7,000 and 10,000 cycles, the values decreased by 2.53% and 4.07%, respectively. These results indicate that limestone specimens exhibit better resistance to abrasion decay compared to diabase specimens, and the anti-slip properties of both may converge as the number of abrasion cycles continues to increase.
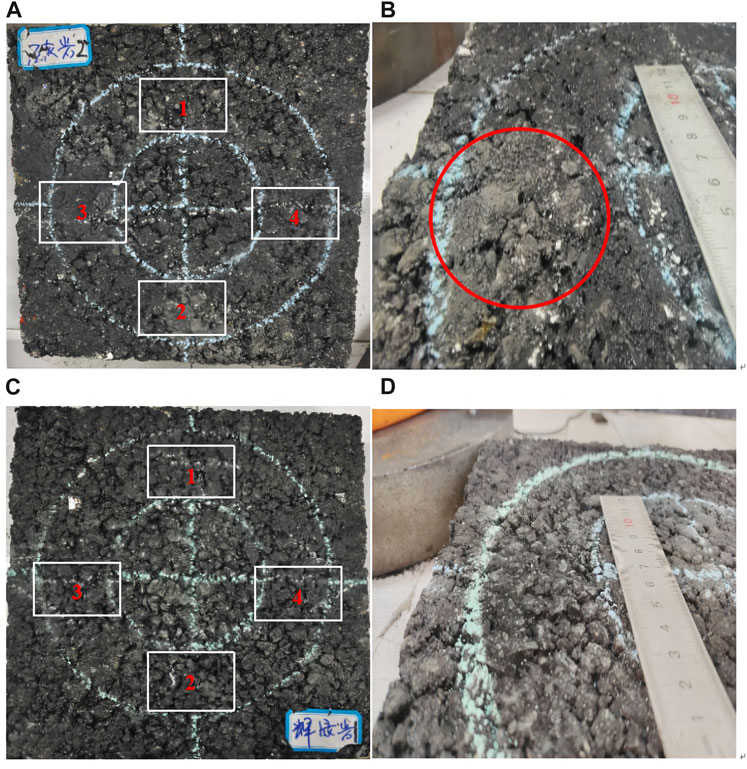
Figure 7. Different specimens’ measuring point positions and the effect after abrasion. (A) Measurement points of limestone specimens. (B) Surface structure of limestone specimens after 10,000 cycles of abrasion. (C) Measurement points of diabase specimens. (D) Surface structure of diabase specimens after 10,000 cycles of abrasion.
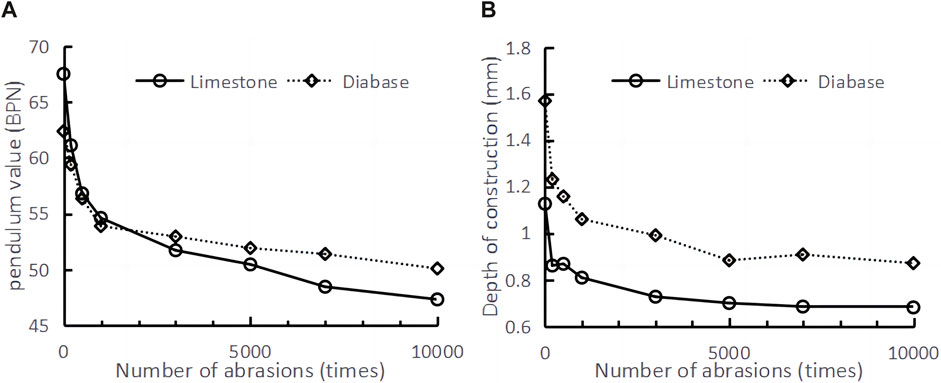
Figure 8. Trend of skidding decay of specimens with a different number of abrasions. (A) Pendulum value. (B) Depth of construction.
4 Conclusion
This paper presents comparative tests on the microphysical characteristics, mineral chemical composition, and surface adhesion energy of two types of manufactured sands (diabase and limestone). It then compares and analyzes the compaction characteristics, high temperature, water stability, strength, skid resistance, and other road properties of the two types of mixtures. The conclusions obtained are as follows.
1) Based on the microscopic test results, it is shown that the adhesion of limestone to asphalt is significantly better than that of diabase. SEM image analysis shows that the surface roughness of limestone is 13.9% higher than that of diabase. XRD analysis reveals that the mineral composition of the limestone, consisting of 99% CaO system alkaline components, exhibits excellent adhesion to asphalt. In contrast, the chemical composition of diabase, which comprises 60% SiO2 and an Al2O3-based acidic and neutral system, shows poor adhesion to asphalt. According to surface energy theory, the adhesion energy at the limestone–asphalt interface is 6.4% higher than that at the diabase–asphalt interface.
2) Based on the test of compaction characteristics of the mixture, it is shown that the compaction performance of the limestone sand specimens is significantly better than that of the diabase specimens. To achieve the target void ratio under the same compaction work, the compaction temperature of the diabase specimens needs to be approximately 15°C higher than that of the limestone specimens.
3) Based on the mixture curing characteristics, the test shows that the curing rate and strength of limestone specimens are significantly better than those of the diabase specimens. Under the same conditions, the curing strength of limestone specimens reaches more than 90% in just 8 h, whereas diabase specimens need 12 h. Additionally, the final curing strength of limestone specimens is 7.8% higher compared to diabase specimens.
4) The anti-abrasion performance of limestone specimens is slightly inferior to that of diabase specimens. After 10,000 cycles of abrasion, the BPN values for limestone and diabase specimens were 47.3 and 50.1, respectively, with structural depths of 0.68 mm and 0.87 mm. The decrease in the anti-slip index for diabase specimens is smaller than that of the limestone specimens.
5) The limestone specimens are slightly better than the diabase specimens in wear decay resistance. When the number of abrasions increased from 7,000 to 10,000 cycles, the BPN and tectonic depth of the limestone specimens decreased by 2.27% and 0.44%, respectively, whereas the BPN and tectonic depth of the diabase specimens decreased by 2.53% and 4.07%, respectively. As the number of abrasions continues to increase, the slip resistance properties of the two materials may gradually converge.
In summary, for asphalt pavement construction, limestone sand should be used as a fine aggregate due to its superior asphalt adhesion and strength characteristics. If diabase sand is utilized as a fine aggregate, the open traffic time must be strictly controlled. It is recommended that traffic be opened after 5 days of traffic restriction, especially during high summer temperatures, following milling.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LZ: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. HZ: writing–original draft and writing–review and editing. SJ: writing–original draft and writing–review and editing. HH: data curation and writing–review and editing. BX: writing–review and editing. HY: writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors LZ, HZ, and HH were employed by Guangxi Transportation Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd. Authors BX and HY were employed by Guangxi Jiaoke New Materials Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cheung, L. W., and Dawson, A. R. (2002). Effects of particle and mix characteristics on performance of some granular materials. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1787, 90–98. doi:10.3141/1787-10
Delrio-Prat, M., Vega-Zamanillo, A., Castro-Fresno, D., and Calzada-Pérez, M. Á. (2010). Energy consumption during compaction with a gyratory intensive compactor tester. Estimation models. Constr. Build. Mater. 25, 979–986. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.06.083
Habal, A., and Singh, D. (2017). Moisture damage resistance of gtr-modified asphalt binders containing wma additives using the surface free energy approach. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 31. doi:10.1061/(asce)cf.1943-5509.0000995
Huang, Z. G., Liu, B. Q., and Gong, W. J. (2022). Discussion on the quality engineering construction mode of wide highway pavement under the hot and humid mountain environment in Guangxi Province. West. China Commun. Sci. and Technol., 16–18. doi:10.13282/j.cnki.wccst.2022.10.005
Ingunza, M. D. P. D., Júnior, O. F. D. S., and Medeiros, S. A. (2013). Sewage sludge as raw-material in asphalt mixtures. Adv. Mater. Res. 664, 638–643. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.664.638
Jamkar, S. S., and Rao, C. B. K. (2004). Index of aggregate particle shape and texture of coarse aggregate as a parameter for concrete mix proportioning. Cem. Concr. Res. 34, 2021–2027. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.03.010
Li, S. C., Bai, W., and Chen, N. (2020). Comparative study on performance of rubber asphalt pavement and SBS modified asphalt pavement of yihe Expressway in Guangxi. Subgr. Eng., 89–93. doi:10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.201911001
Mahboub, K. C., Oduroh, P. K., and Anderson, R. M. (2001). Hot mix asphalt with flat and elongated aggregates. Constr. Mater. Issues 2001, 183–192. doi:10.1061/40591(269)19
Peng, W., Li, P., Gao, J., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Long-term skid resistance evolution and influence mechanism of asphalt pavement based on self-developed wear equipment. Constr. Build. Mater. 453, 139085. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.139085
Prudêncio, L. R., Weidmann, D. F., de Oliveira, A. L., and Damo, G. F. (2013). Particle shape analysis of fine aggregate using a simplified digital image processing method. Mag. Concr. Res. 65, 27–36. doi:10.1680/macr.11.00199
Stukhlyak, P. D., Buketov, A. V., Panin, S. V., Maruschak, P. O., Moroz, K. M., Poltaranin, M. A., et al. (2015). Structural fracture scales in shock-loaded epoxy composites. Phys. Mesomech. 18, 58–74. doi:10.1134/S1029959915010075
Wang, D., Steinauer, B., and Yin, C. (2011). “Optimization of long-term skid resistance on asphalt concrete pavement,” in Paper presented at 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, 24-26 June 2011, 4246–4248. doi:10.1109/rsete.2011.5965267
Wang, Y., Yan, J. C., and Yuan, H. T. (2022). Study on the high temperature storage performance of rubber composite modified asphalt on wulong Expressway. West. China Commun. Sci. and Technol., 96–98. doi:10.13282/j.cnki.wccst.2022.05.030
Xie, C., Luo, J., Zeng, L., Ren, T., Liu, H., and Chen, J. (2022). Research on evaluation index of high temperature performance of rubberized asphalt binder. Front. Mater. 9. doi:10.3389/fmats.2022.904087
Zhang, H. G., Tan, H., Wang, B., Xiong, J. P., Kuang, D. L., and Liu, W. C. (2021). Performance evaluation, modification mechanism and application research progress of rubber asphalt. Appl. Chem. Ind. 50, 299–303. doi:10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2021.s2.059
Keywords: asphalt mixtures, fine aggregates, physical and chemical properties, curing properties, anti-slip decay properties
Citation: Zeng L, Zhang H, Jiang S, Huang H, Xiong B and Yuan H (2025) Research on the effect of lithology of fine aggregates on the performance of rubberized asphalt mixtures. Front. Mater. 12:1495219. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1495219
Received: 12 September 2024; Accepted: 15 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Nicholas Thom, University of Nottingham, United KingdomReviewed by:
Pavlo Maruschak, Ternopil Ivan Pului National Technical University, UkraineJue Li, Chongqing Jiaotong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zeng, Zhang, Jiang, Huang, Xiong and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lihao Zeng, Mjg5NzgxMzg4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Honggang Zhang, Mjg2NjAxNjc2QHFxLmNvbQ==; Shuo Jiang, MTIxOTEwNDAzNEBxcS5jb20=
 Lihao Zeng
Lihao Zeng Honggang Zhang1*
Honggang Zhang1* Shuo Jiang
Shuo Jiang