- 1School of Civil Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 2Department of Structural Engineering, MCE Risalpur Campus, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 3Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia
- 4Division of Research and Development, Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, St.Petersburg, Russia
The research object is concrete with supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as bentonite clay and quarry dust. The impact of incorporating these SCMs on fresh concrete properties, compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths, and acid resistance was investigated. Microstructural analysis using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and X-ray radiography were used. Varying proportions of SCMs (5%–20%) were incorporated into the concrete mix while maintaining a constant water-to-cement ratio. Key findings reveal a 7.31% increase in compressive strength, a significant 19.7% improvement in flexural strength, and enhanced acid resistance. Utilizing Response Surface Methodology (RSM), the optimal mix design for achieving superior mechanical strength was identified. The quadratic model of RSM indicated that a combination of 10.29% bentonite clay, 7.20% quarry dust, and 8.19% fine aggregate replacement yielded the highest strength. Predictive and experimental results demonstrated strong agreement. Compared to the reference concrete, the optimized samples exhibited significant increases of 18.08%, 33.60%, and 11.15% in compressive, flexural, and tensile strengths, respectively. This research demonstrates the potential of locally available SCMs as viable and sustainable alternatives for concrete production, offering improved performance without compromising strength.
1 Introduction
The world rests on concrete, the most prevalent construction material globally, serving as the foundation for both developed and developing economies. It has been quantified that producing one metric ton of cement yields an equivalent carbon dioxide emission, totaling one metric ton, into the Earth’s atmosphere. It is estimated that the production of Portland cement contributes to approximately 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Althoey et al., 2023; da Silva Rego et al., 2023; Soomro et al., 2022; Sousa et al., 2023). Cement production exhibits a growth rate of ten percent annually worldwide. Concrete has three primary constituents: cement, aggregates (fine and coarse materials), and water (Uratani and Griffiths, 2023). In the current production of concrete, there has been a remarkable production in the utilization of locally accessible raw materials such as rice husk ash, fly ash, metakaolin, crushed granulated blast furnace slag, waste glass powder, and foundry sand as Supplementary Cementitious Materials (SCM) over the preceding decades (Isaksson et al., 2023; Manjunatha et al., 2021; Qureshi et al., 2020; Nasiru et al., 2021). Incorporating SCM into concrete is associated with various advantages surrounding its inherent cementitious properties, economical cost, and ready availability within proximity. Throwing away these materials without proper care is not just wasteful. It can also pollute the environment and harm plants, animals, and ourselves (Kolawole et al., 2021; Aprianti S, 2017; Zhang et al., 2023).
Supplementary cementitious materials are not widely available across the globe, the global shift towards green energy has led to the closure of coal power plants in certain regions, resulting in a sharp decrease in fly ash production. The availability of SCMs is uneven across different regions, and their production is considerably lower compared to ordinary Portland cement (OPC). As a result, SCMs cannot fully satisfy the demand for high cement replacement in large-scale construction projects (Arrigoni et al., 2020). Additionally, the production quantity and quality of SCMs are impacted by changes in industrial processes, especially within the steel and coal industries. Therefore, researchers are exploring alternative SCMs, such as bentonite clay and quarry dust, which could serve as partial replacements for cement to address these challenges and promote sustainable construction practices (Duchesne, 2021; Raza et al., 2024; Chengfang et al., 2024). A promising alternative is bentonite clay, which is abundantly available in regions of Asia and Africa (Javed et al., 2020).
Bentonite, a clay mineral rich in montmorillonite (a type of hydrous aluminum silicate), forms layered deposits with varying thicknesses, mainly composed of smectite clays. It is classified into swelling (sodium bentonite) or non-swelling (calcium bentonite) types based on its sodium content (Sun et al., 2022). The choice of bentonite clay dictates the characteristics of the resulting concrete, with swelling bentonite yielding a foamy consistency and non-swelling bentonite resulting in a cracked appearance. Bentonite can bind sand particles in the presence of water, forming a plastic paste that helps create a workable concrete mix. This reaction produces magnesium and potassium oxides, contributing to the strength and setting of the concrete (Ahmad et al., 2022). Some types of bentonite may expand when exposed to water due to the reaction with the montmorillonite content, but calcium-rich bentonite has a lower swelling capacity. Significant bentonite reserves are found in various regions, with estimates of approximately 36 million metric tons. Utilizing bentonite is more cost-effective than cement, with one tonne of bentonite priced at Rs-3600 ($12) versus Rs-24000 ($80). Enhanced concrete mixtures containing bentonite exhibit prolonged strength and resistance to acid attacks, improving durability and reliability, crucial factors in seismic regions (Umair et al., 2023; Ashraf et al., 2022; Masood et al., 2020; Mirza et al., 2009).
Moreover, concrete mixtures enhanced with bentonite have demonstrated the ability to maintain strength over extended periods and resist acid attacks. Bentonite enhances the durability and reliability of structural concrete from an earlier age (Xie et al., 2018), increases mortar creep (Fadaie et al., 2019), and introduces siliceous and aluminous compounds into concrete mixtures, offering a range of benefits (Memon et al., 2012). Seismically active areas have experienced substantial structural damage during previous earthquakes, largely due to the use of substandard materials. The economic challenge wherein a significant portion of the population faces extreme poverty renders them unable to afford high-quality cement (Khan et al., 2019). Additionally, recent research highlights the cement industry as the primary contributor to carbon dioxide emissions. Consequently, advocating for the adoption of locally available construction materials will address economic barriers and align with environmental sustainability goals. Encouraging the use of such materials not only facilitates cost-effective construction but also promotes an eco-friendly approach (Khan et al., 2021; Rehman et al., 2020).
The limited accessibility of conventional SCMs employed for cement substitution presents a significant obstacle for the concrete industry, driving the need to identify and implement alternative cementitious binders (Snellings et al., 2023; Ndahirwa et al., 2022). Quarry dust, a waste product from the crushing process, presents itself as a potential SCM for partial cement substitution in mortar and concrete formulations (Dobiszewska et al., 2023; Sundaralingam et al., 2022). Rock dust, a byproduct generated during the comminution of diverse geological rock formations, exhibits potential for optimizing the particle size distribution (PSD) and packing density within concrete composites. A promising approach to sustainable construction involves partially substituting rock dust for cement. It could lead to less CO2 pollution, a smaller environmental footprint, and a decrease in resource and energy consumption (Zhao et al., 2022; Nasier, 2021; Al-Bakri et al., 2022).
The quarrying and crushing of large rocks into smaller fragments culminate in producing aggregates of varying sizes, serving as the originator for quarry dust. Projections indicate that the global construction aggregates market is composed of growth, with an anticipated Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.7% in the coming years. It was expected to attain an estimated value approaching US$ 393.5 Billion in 2019 (Escavy et al., 2020). This figure alone is compelling evidence of the escalating trajectory within the construction industry. Quarry dust as waste, due to dust fine particle size, has adverse environmental effects (Ali et al., 2023; Shaheen et al., 2023). Quarry dust can be utilized as a filler material (fine aggregate) and as a binding agent, replacing a portion of the customary cement content in concrete mixes (Hemalatha and Sindu, 2020; Kankam et al., 2017; Mugi, 2022).
While there is extensive global research on supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) as sustainable alternatives in concrete production, most studies have predominantly focused on conventional SCMs like fly ash and slag. However, the combined use of waste materials such as bentonite clay and quarry dust as partial cement replacements remains largely unexplored. To the best of our knowledge, no existing research has comprehensively investigated the combined effect of these two materials as concrete binders. This study fills this knowledge gap by evaluating the mechanical properties of concrete (compressive, flexural, and split tensile strength) and its acid resistance when cement is partially replaced with these SCMs. Furthermore, this work advances current knowledge by utilizing Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to optimize the replacement levels, providing a predictive framework for enhancing concrete performance. The novelty lies not only in the use of these unconventional SCMs but also in the validation of RSM as an effective tool in designing sustainable concrete mixes, thus offering a meaningful contribution to both academic research and industry practice.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Material used
Various materials are employed during experimental testing, elucidated in the subsequent subsections.
2.1.1 Cement
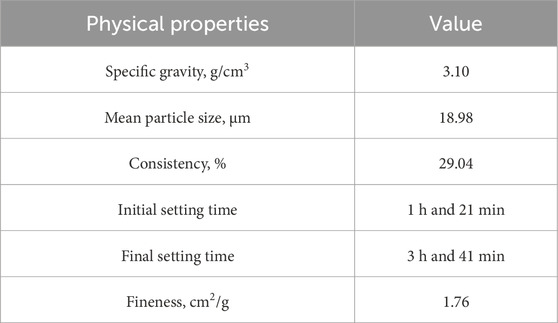
In this research, ASTM Type 1“Fuji Cement,” which was free from clumps and impurities, was utilized. This cement was ordinary Portland cement (OPC) and confirmed to ASTM C150. The cement underwent a physical examination to assess its smoothness and colour. The properties of cement are detailed in Table 1.
2.1.2 Bentonite clay
The Jehangira bentonite deposits are located at 33°59′56″ latitude and 72°12′47″ longitude, as shown in Figure 1 indicated by the Survey of Pakistan topographic sheet 43 C/1 (Karagüzel et al., 2010). The particle size distribution of bentonite clay is shown in Figure 3A and collected from these deposits in small pieces, as depicted in Figures 2A, B. For finer particles, bentonite clay was subjected to grinding in a Los Angeles abrasion machine. Each batch underwent 4,500 revolutions to ensure uniform fineness until fully transformed into powder. The elemental composition of bentonite and quarry dust was determined using an Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) at the Centralized Resource Laboratory (CRL), University of Peshawar, Pakistan.
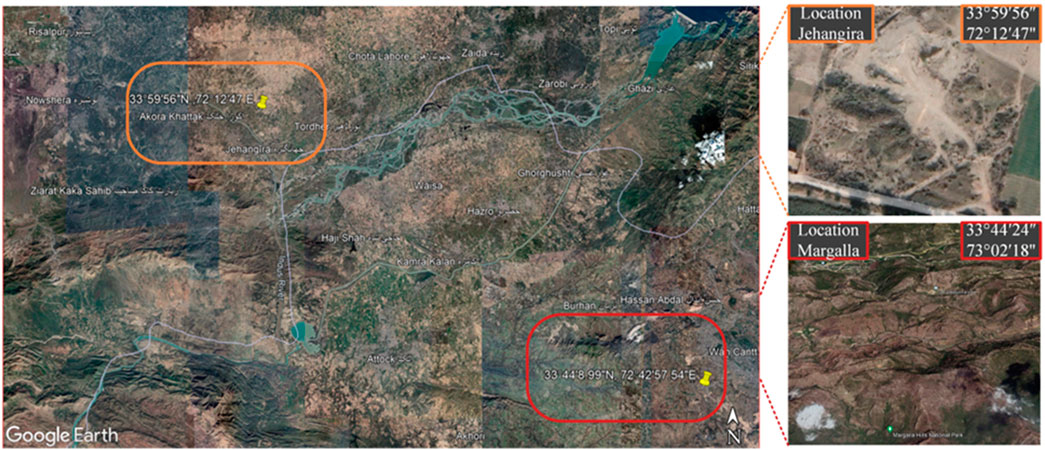
Figure 1. A map of the study area to identify the sampling location. Map data ©2024 Google (Google Earth, 2024).
2.1.3 Quarry dust
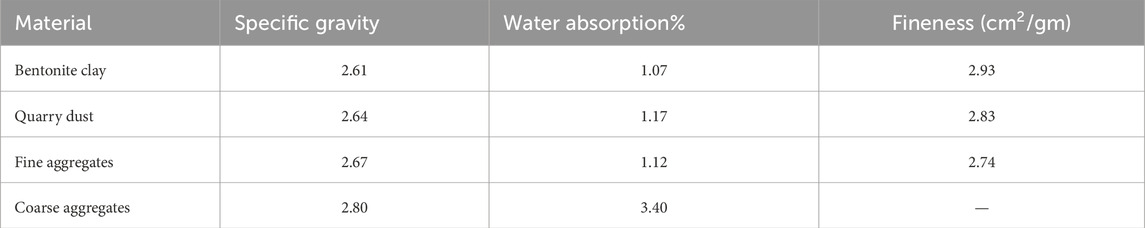
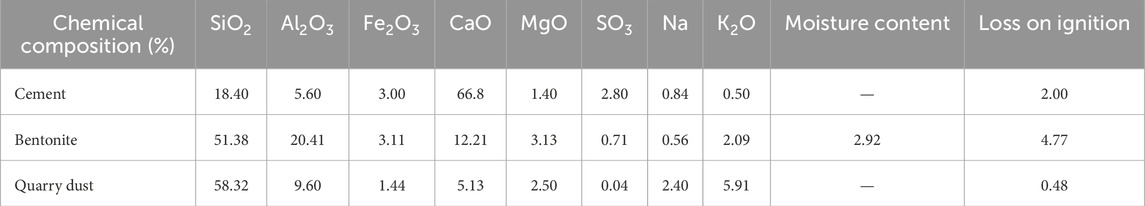
The quarry dust was collected at the crusher facility in Margalla Hills, Islamabad, Pakistan. Large pieces of stone were removed from the location where they were found. The particle sizes ranged from 4.75 mm down to dust sizes of 0.05 mm and smaller; the gradation curve is shown in Figure 2C. Subsequently, the sample was transferred to the laboratory for additional screening and examination. Compared to fine aggregates, Table 2 illustrates that quarry dust has a lower specific gravity and a higher water absorption rate. Table 3 provides information on the chemical characteristics of cement, bentonite, and quarry dust.
The specific gravity and water absorption rates of bentonite clay and quarry dust influence the concrete’s mix design, density, and workability. Their water absorption impacts hydration and particle bonding, improving compressive strength. High SiO2 content in both materials promotes pozzolanic reactions, increasing strength through the formation of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel. The Al2O3 content in bentonite improves acid resistance, while Fe2O3 and MgO enhance binding. The loss on ignition (LOI) values reflect the presence of volatile components that may affect durability. The pozzolanic activity and improved particle packing, driven by these material properties, contribute to the enhanced mechanical properties (compressive, flexural, and tensile strength) of the concrete.
2.1.4 Aggregates
The deposits at Lawrencepur served as the source for collecting fine aggregates. The ASTM C136-04 was employed to determine the fineness modulus. Figure 3A illustrates the gradation curves for fine aggregates of different sizes. Throughout this study, coarse aggregates were sourced from the Margalla hills, widely acknowledged as some of the best in Pakistan (Khan M. I. et al., 2022).
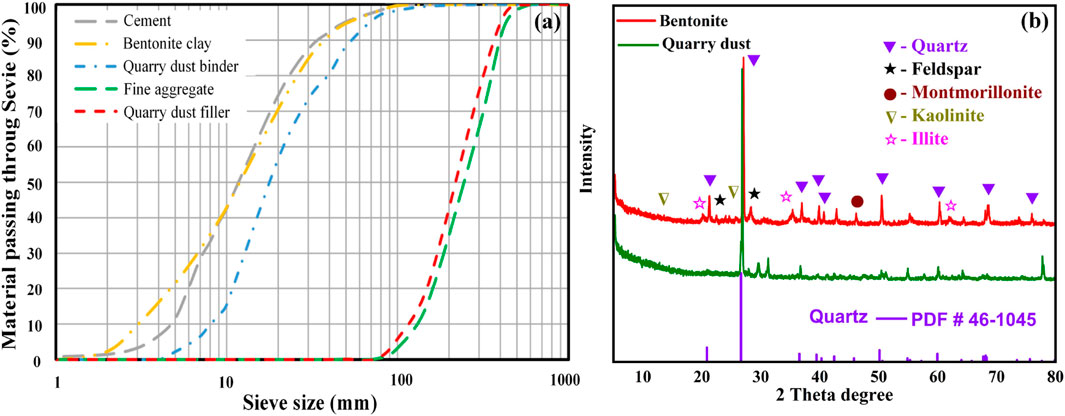
Figure 3. (A) Gradation curve of dry ingredients (B) XRD analysis of bentonite clay and quarry dust.
2.1.5 Characterization of bentonite clay and quarry dust
The XRD analysis was conducted to determine the mineralogical composition of bentonite and quarry dust, which were used as partial replacements for cement in this study as shown in Figure 3B. A Panalytical Empyrean XRD instrument was employed, equipped with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å). The analysis was performed under the following operating conditions: a voltage of 45 kV and a current of 40 mA. The diffraction data were collected over a scanning range of 5°–80° (2θ) with a step size of 0.02° and a scan speed of 2°/minute. For bentonite clay, the XRD pattern reveals a predominance of montmorillonite, which is characterized by its high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties that can impact the water retention and mechanical properties of concrete. Notable peaks of montmorillonite are visible in the diffraction pattern, confirming its significant presence. In addition to montmorillonite, the XRD spectrum of bentonite also shows the presence of other minerals such as illite and kaolinite. Illite, marked by specific peaks in the graph, contributes to the clay’s overall plasticity and strength, while kaolinite, indicated by its distinct peaks, is known for its less expansive nature compared to montmorillonite but adds to the durability when used in cementitious mixes.
Quarry dust, represented in the XRD analysis, primarily comprises quartz, as indicated by the strong peak aligned with the Quartz PDF #46-1045 standard, which is a common phase in many geological materials and significantly impacts the hardness and durability of the resulting concrete. The presence of feldspar and minor traces of kaolinite in quarry dust is also noted, which can influence the chemical durability and workability of the concrete mixes. The identification of these minerals in both bentonite clay and quarry dust is crucial for evaluating their suitability as partial replacements in concrete. The distinct peaks corresponding to quartz, feldspar, montmorillonite, illite, and kaolinite provide insights into the materials’ crystallography and structural characteristics, essential for predicting their behavior in concrete applications. Understanding the composition and distribution of these minerals helps in tailoring the mix designs for enhanced performance and sustainability of the concrete products.
2.2 Casting and mixing proportion
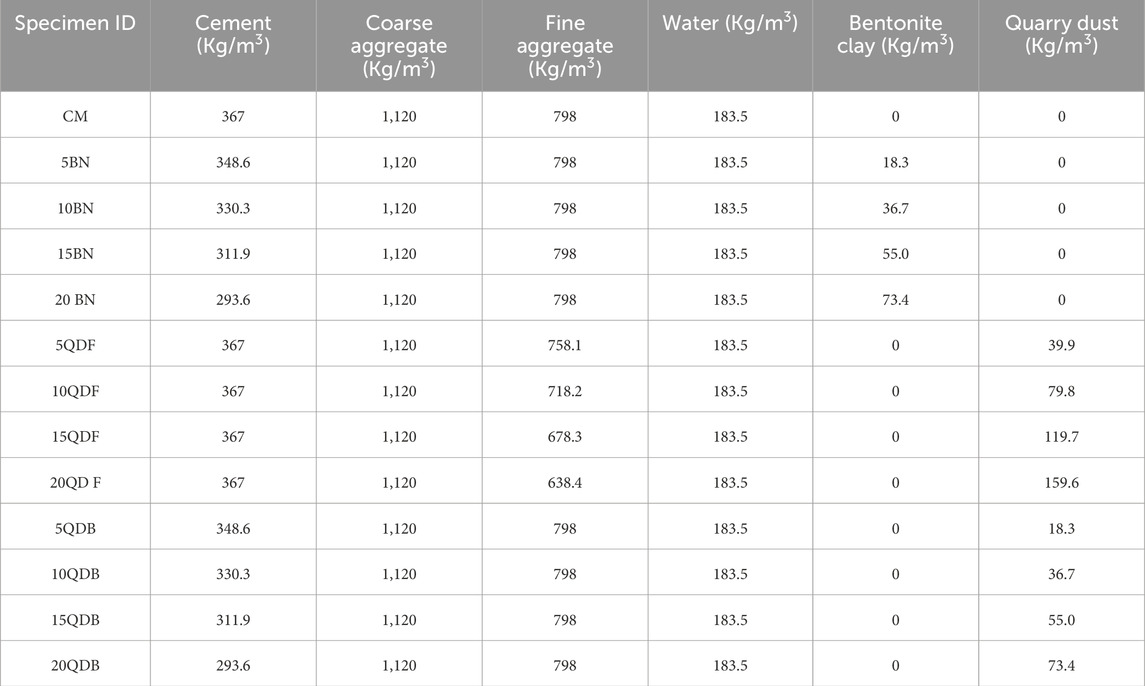
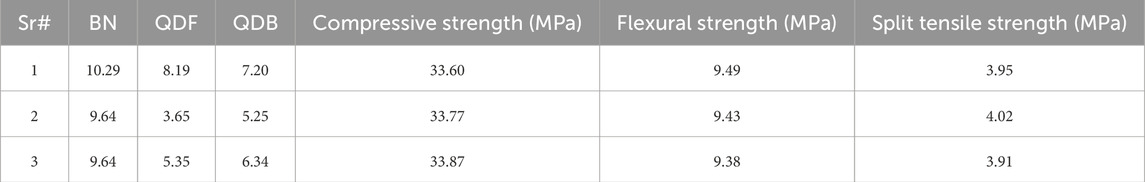
Throughout this research, various percentages of SCM were utilized to achieve maximum strength, improved workability, and long-lasting characteristics; 96 specimens were created, each representing one of 13 possible mix proportions, before RSM was performed. For example, cement was substituted with bentonite clay in proportions of 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%, denoted as 5BN, 10BN, 15BN, and 20BN, respectively. The coarse and fine aggregate proportions were kept constant across all the mixes mentioned above. Quarry dust was categorized into two types as filler, replacing fine aggregates and binder replacing cement. The differentiation between these two groups lies in particle size. The filler group passed through a sieve with a 4.75 mm opening and was retained on a sieve with a 0.3 mm opening. The ‘as binder’ group consisted of particles 0.05 mm or smaller. Mixes falling under the ‘as filler’ category were designated 5QDF, 10QDF, 15QDF, and 20QDF, corresponding to 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% replacement of fine aggregate with quarry dust. Mixes using quarry dust from the ‘as binder’ group were labelled as 5QDB, 10QDB, 15QDB, and 20QDB, indicating 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% replacement of cement with quarry dust. A control mix was also prepared without adding any SCM, and a consistent water-to-cement ratio of 0.5 was maintained for all the mixes. Table 4 outlines the concrete mix proportions required to produce one cubic meter of the final product. To validate the RSM results, nine samples were cast according to the specified ratios generated by the statistical analysis software.
Cylindrical specimens measuring 305 mm in length and 152 mm in diameter were employed to assess the material’s compressive and split tensile strengths, respectively. Compressive strength, following ASTM C39, was measured after curing for 7 and 28 days. Following ASTM C496, split tensile strength was determined after the same curing periods. Flexural strength tests confirming ASTM C78 were conducted on concrete specimens with widths of 101 mm, depths of 101 mm, and lengths of 305 mm after 7 and 28 days of curing. Fresh concrete properties were evaluated using ASTM C 143, incorporating quarry dust and bentonite clay. Additionally, 152 mm cubic concrete specimens were immersed in separate solutions of 5% sulfuric acid and 5% hydrochloric acid. Furthermore, it was observed that the specimens exhibited water observation characteristics. Lastly, the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was employed for statistical analysis to optimize the percentage of partial cement replacement with SCM.
3 Test results and discussion
3.1 Fresh properties
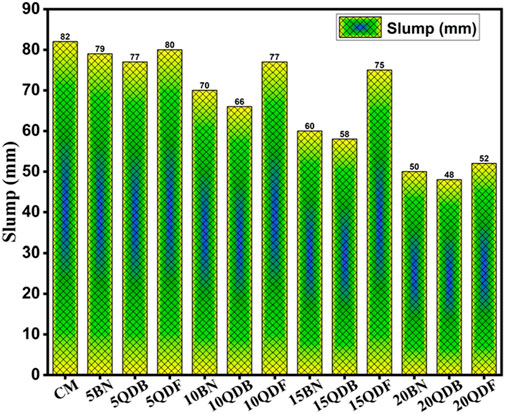
Increasing the quarry dust “as binder” group resulted in a notable decline in the workability of all the mixtures compared to the control mix while maintaining a constant water-cement ratio. The graphical representation in Figure 4 shows that mix 5QDB exhibited the most pronounced slump value among all the mixes categorized under the “as binder group,” surpassing the performance of all other mixes. Conversely, mix 20QDB displayed substantially reduced workability compared to the preceding mixtures. This decrease in workability can likely be attributed to the elevated presence of fine particles within the mix, exceeding the levels found in other mixtures. The amplified surface area of these fine particles in quarry dust, acting as a binder, necessitated a higher demand for water to ensure thorough saturation of the mixtures (Passuello et al., 2015).
For compositions incorporating quarry dust in the capacity of a filler material, the highest observed slump was 72 mm, as recorded in mix 5QDF. Stone dust particles are characterized by their coarse, rough, angular morphology, and the introduction of quarry dust into the concrete mix led to an increased proportion of fine particles, imparting a coarse texture and angular shape to the particles. This augmentation in inter-particle friction and the surface area likely contributed to the unfavorable flow characteristics observed. Furthermore, due to the higher water absorption rate of quarry dust particles, there was a reduction in the available water for lubricating cement particles.
The greater specific surface area of bentonite clay in the mix enhanced the demand for water to adequately wet the particles in the mixture. As the water added to the mix is absorbed by the bentonite clay particles, insufficient water remains available to lubricate the cement and bentonite particles. Consequently, the workability diminishes for a consistent water-cement ratio as the content of bentonite clay increases. In this context, it is important to note that the workability was lower than that of the control mix but higher than the mixes incorporated with quarry dust, as reported by (Xie et al., 2018) and (Nataraja and Nalanda, 2008). While this study focused on maintaining a constant water-cement ratio across all mixes, future research should explore the use of water-reducing admixtures or superplasticizers. These additives could counterbalance the negative impact of fine particles (quarry dust and bentonite clay) on workability without sacrificing the mechanical strength and durability properties of the concrete mix.
3.2 Compressive strength
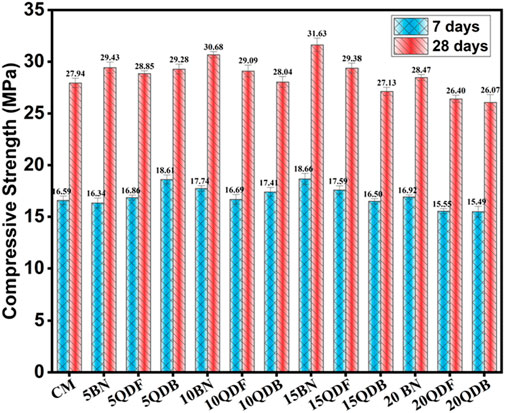
The compressive strength, as measured after 7 days of curing, for the mixes containing different proportions of quarry dust filler, namely 5QDF, 10QDF, 15QDF, and 20QDF, are as follows: 17.38, 18.78, 16.60, and 15.43 MPa, respectively. The control mix (CM) exhibits a compressive strength of 16.77 MPa. As presented in Figure 5, it is evident that the optimal strength performance is achieved at the 10% quarry dust filler ratio (10QDF), resulting in an impressive 11.9% increase in strength when compared to the control mix. Upon extending the curing period to 28 days, the compressive strength values for the quarry dust filler mixes are as follows: 29.13 MPa for 5QDF, 30.11 MPa for 10QDF, 27.95 MPa for 15QDF, and 26.19 MPa for 20QDF. In contrast, the CM maintains a compressive strength of 28.04 MPa. Figure 5 reinforces the observation that the 10% quarry dust filler mix (10QDF) outperforms the CM with a notable 7.38% increase in strength (Ho et al., 2002; Khan, 2023).
The observed trend in the compressive strength of quarry dust mixes, whether used as a binder or filler, exhibited remarkable similarity, except for a slight enhancement in strength. After 7 days of curing, the compressive strengths for mix proportions of 5% QDB, 10% QDB, 15% QDB, and 20% QDB were measured at 16.77, 17.38, 18.78, 16.60, and 15.43 MPa, respectively. These strengths improved to 28.04, 29.13, 30.11, 27.95, and 26.19 MPa at the 28-day mark. A similar growth and reduction pattern emerged when comparing the “as binder” mixes to the “as filler” mixes. Notably, the 10% QDB mixes exhibited the highest strength at all ages compared to control mixes. This enhancement could be attributed to the early acceleration of the hydration reaction, facilitated by the finer particles of quarry dust filling gaps and creating a denser matrix, thus increasing load resistance. However, it is essential to note that increasing the proportion of quarry dust led to reduced workability and poor compaction, resulting in decreased strength (Febin et al., 2019). This decline in strength became more pronounced beyond the 10% replacement threshold, possibly due to limited water availability for dust particles to engage in the hydration process and an increase in the surface area resulting from higher quarry dust concentration.
In contrast, the compressive strength values for mixes containing bentonite (5BD, 10BD, 15BD, and 20BD) showed different trends. After 7 days of curing, these mixtures displayed strengths of 16.59, 16.63, 15.84, and 14.55 MPa, respectively. The decrease in compressive strength in the early stages can be attributed to the slower hydration of bentonite. However, at 28 days, the measured strengths improved to 28.94, 29.42, 25.75, and 24.55 MPa, with 5BD and 10BD mixtures showing increases of 3.15% and 4.91%, respectively, compared to the control sample. The rise in strength is linked to the pozzolanic characteristic of bentonite, which exhibits gradual improvement between 3 and 28 days and further enhancement after 56 days. It is noteworthy that insufficient dust particles are present in specimens with 0% and 5% bentonite content to fill gaps and participate effectively in the hydration process, leading to decreased compressive strength. However, increasing the bentonite clay content beyond 10% tends to reduce the compressive strength of specimens due to the presence of small particles, which increases the total particle surface area (Masood et al., 2020).
3.3 Flexural strength
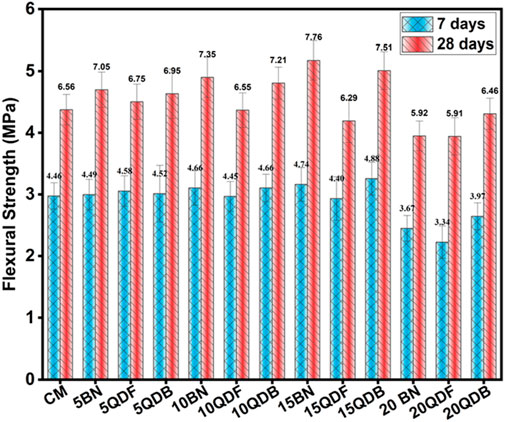
In flexural strength analysis, mixes containing quarry dust and bentonite clay demonstrate a consistent strength pattern similar to that reported for compressive strength when subjected to 7 and 28 days of curing. Specifically, at a 7-day mark, the mixture denoted as “10QD” exhibits a notable increase in strength, registering a rise of 19.7% compared to the control mix. Similarly, at the 28-day juncture, it demonstrates an incremental strength gain of 7.17%. This augmentation in strength can be attributed to the rapid hydration process inherent in the quarry dust mixture, which also acts as a filler (Ramos et al., 2013).
In Figure 6 the 10BN mixtures containing bentonite clay exhibit different behavior, at 7 days of curing, there is a modest 4.2% increase in strength, whereas at 28 days, a more substantial boost of 11.8% is observed. This disparity can be ascribed to bentonite clay’s relatively sluggish hydration reaction, resulting in lower flexural strength at the 7-day interval. This phenomenon aligns with the observations reported in reference. As mentioned earlier, similar dynamics regarding the increase and subsequent decrease in strength have been discussed in the context of compressive strength.
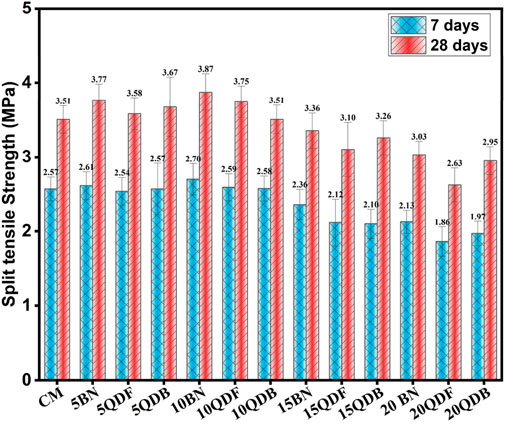
3.4 Split tensile strength
Tensile strength for quarry dust and bentonite clay mixes was observed at 7 days and 28 days of curing. For quarry dust mixes, an increase of 14.6% at 7 days and 9.9% at 28 days of curing was noted, respectively. Various researchers have established that the optimum replacement of cement with quarry dust is 10%–15% to increase split tensile strength. Beyond this replacement, split tensile strength tends to decrease (Abd Elmoaty, 2013; Qian et al., 2024). It is observed in Figure 7 that split tensile strength is affected similarly to compressive strength. The bentonite mix shows a decrease of 6.6% at 7 days and an increase of 3.8% at 28 days of curing compared to the control mix, as reported by. The reduction in early-age strength may be attributed to the slow hydration of bentonite clay at early ages (Mirgozar Langaroudi and Mohammadi, 2022).
3.5 Acid attack
The acid resistance of concrete specimens was evaluated using a constant pH method designed to maintain the pH consistently at 2.0 ± 0.2 throughout the testing period. This analysis was performed using both sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), each diluted to a 5% concentration by volume. Concrete sections were immersed in a solution initially comprising 12 L of water. The necessary volume of each acid at 5% concentration was added to achieve and maintain the solution at a pH of 2.0, with adjustments based on the initial alkalinity of the concrete. An automatic titrator continuously controlled and adjusted the pH in the reservoir. A magnetic stirrer was employed to ensure the even distribution of the acid throughout the reservoir. The acid solution was replaced weekly for the first 28 days to ensure consistent exposure to the acidic environment. After the immersion period, each section was manually brushed in water to remove any loose or deteriorated material, and then dried with adsorbent paper. The degradation of the concrete was quantified by measuring the mass loss after the test period, expressed in kg/m2, to facilitate comparative analysis across different samples.
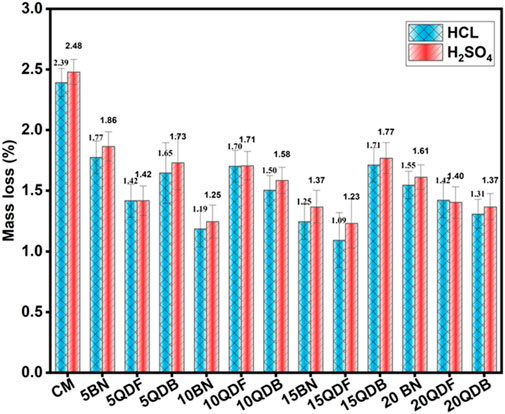
Concrete is susceptible to acid attacks in various industrial facilities, water treatment plants, agricultural operations, transportation infrastructure, swimming pools, battery storage areas, food processing plants, garages, and auto repair shops. Aggressive chemicals like H2SO4 and HCL react highly with the cement paste matrix, consuming Ca(OH)2 and C-S-H (Castillo Lara and Chagas Cordeiro, 2019). Consequently, the formation of CaSO4.2H2HO (gypsum) and ettringite will increase the concrete volume by nearly 2.2 times, leading to internal crack propagation, strength loss, and quick deterioration. Eventually, the degradation of specimens due to acid leads to mass loss. The performance of acid attacks on concrete has been evaluated in terms of mass loss by various researchers (Khan M. et al., 2022). The weight loss absorbed by the quarry dust mix 20QD was found to be the lowest for hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, with the difference in weight loss for both specimens not being significant, i.e., 1.21% and 1.31%. The minimal weight loss may be attributed to the abundance of quarry dust particles, which form a compact mass, thus reducing the permeability of the specimens (Chintalapudi and Pannem, 2022). The mass loss due to acid attack is graphically displayed in Figure 8.
For the bentonite clay mix 20BN, the weight loss in hydrochloric acid was 1.20%, and sulfuric acid was 1.25%. The resistance to acid attack in both mixes is due to the lower production of lime in the mix, resulting from the replacement of cement content, where calcium hydroxide reacts with silica to form silica. Overall, the mass loss decreases with an increase in the proportions of SCM, with minimal variations. The highest weight loss was observed in the control mix for both acid solutions. The presence of free lime in the mixes increases susceptibility to acid attacks, softening the mix, a phenomenon noted by other researchers as well. Additionally, the chemical reaction of cement with the salt solution leads to the disintegration of the specimens (de Siqueira and Cordeiro, 2022; Thomas and Harilal, 2016).
3.6 X-ray radiography analysis and porosity correlation
X-ray radiography, a non-destructive testing (NDT) method, was employed to assess the internal structure and detect defects such as air voids, pockets, and cracks within the concrete specimens. This technique was crucial in evaluating the homogeneity and bonding integrity of the control mix and mixes modified with supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs). Specimens were placed in a high-resolution X-ray cabinet, with the X-ray source adjusted to 150 kV and 5 mA to ensure optimal penetration and contrast. Each specimen was exposed for 10 s, maintaining uniform imaging conditions across all tests. Digital detectors captured the radiographs, facilitating a precise assessment of internal structures at room temperature, and adhering to standardized procedures to ensure consistency in the findings.
Figure 9A, presents an optical photograph of the concrete mix containing 10% bentonite clay after exposure to sulfuric acid. The surface condition shown here complements the X-ray analysis in Figure 9B which highlights areas of reduced porosity indicated by fewer lighter shades. This suggests effective mitigation of acid impact through enhanced matrix density and cohesion, indicative of bentonite clay’s protective role. X-ray radiograph of the same mix further substantiates the visual observations from the optical photograph by showcasing limited acid penetration and damage. The radiograph reveals a denser structure with minimal voids, contrasting sharply with the control mix’s results, pointing to a significant enhancement in acid resistance due to the incorporation of bentonite clay.
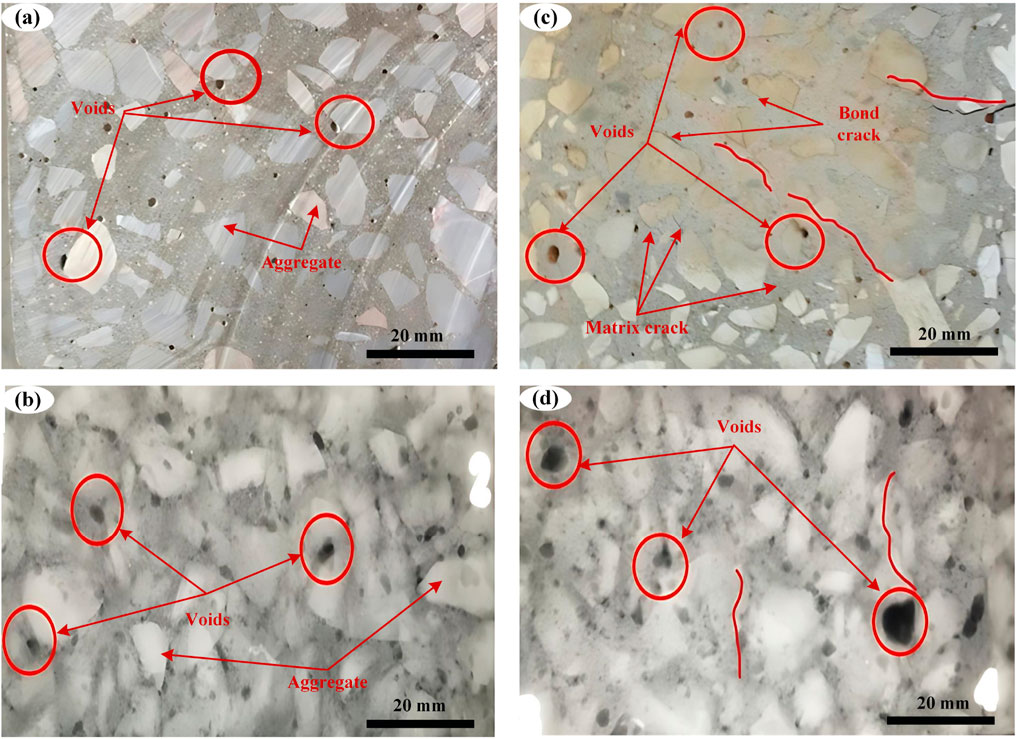
Figure 9. (A) Optical photo of 10BN mix (B) X-ray radiograph of 10BN mix (C) Optical photo of the CM mix (D) X-ray radiograph of CM.
Figure 9C is an optical photograph of the control mix, illustrating pronounced surface damage such as cracks and voids from acid exposure. This damage is visually more severe compared to the bentonite clay mix, reflecting the susceptibility of the standard mix to chemical degradation. Figure 9D provides the X-ray radiograph for the control mix, showing extensive lighter areas that denote high porosity and structural weakening. The comparison of radiographic data between the mixes visually underscores the stark contrast in durability and integrity, highlighting the detrimental effects of acid exposure on the control mix, which exhibits increased material loss and degradation.
3.6.1 Porosity and mechanical strength relationship
The porosity data obtained from the X-ray radiography was cross-referenced with the mechanical strength results to establish a correlation. As expected, mixes with higher porosity, such as the control mix, exhibited a lower compressive strength after acid exposure. In contrast, the modified mix containing bentonite clay demonstrated a lower porosity, which translated to a higher residual strength after acid exposure. This observation aligns with findings from previous research, which have established that porosity is a critical factor influencing the durability and strength of cementitious composites (He et al., 2023; He et al., 2024).
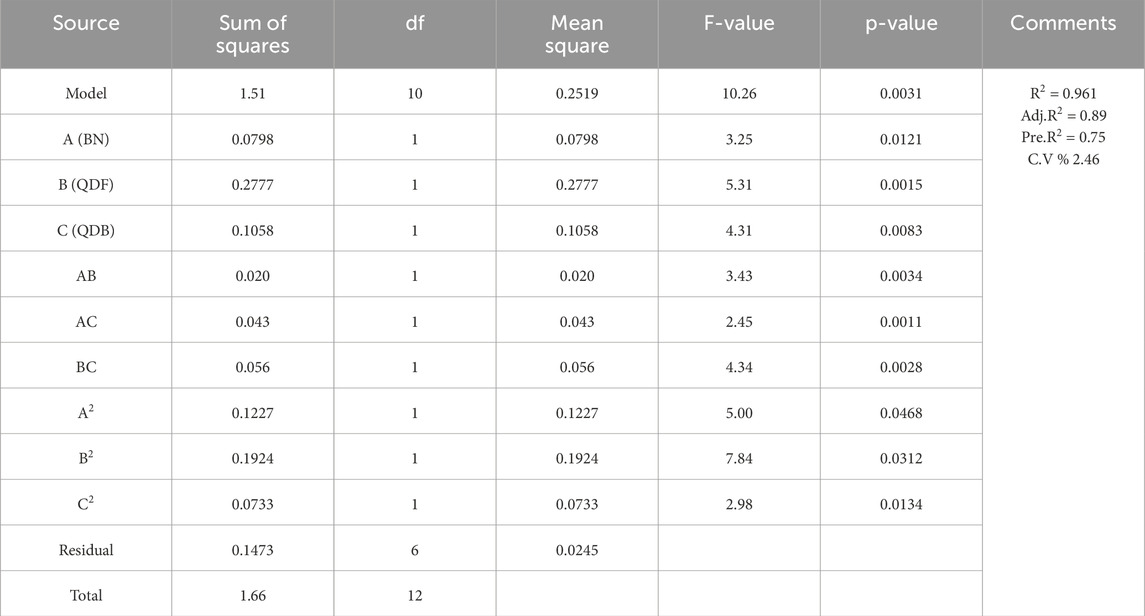
4 Response surface methodology (RSM) analysis
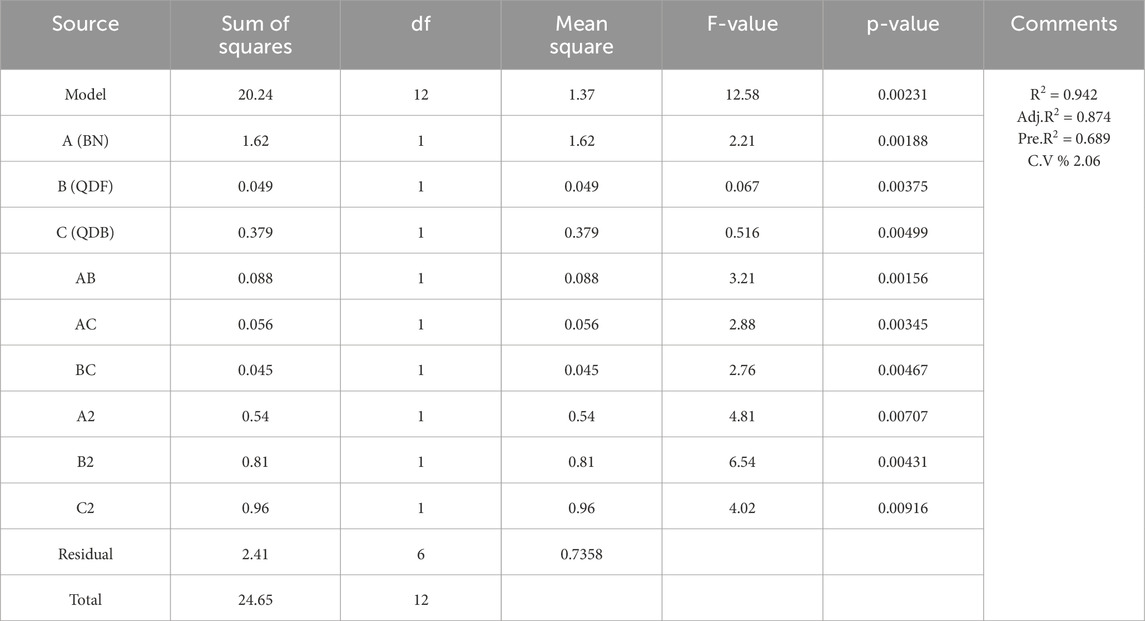
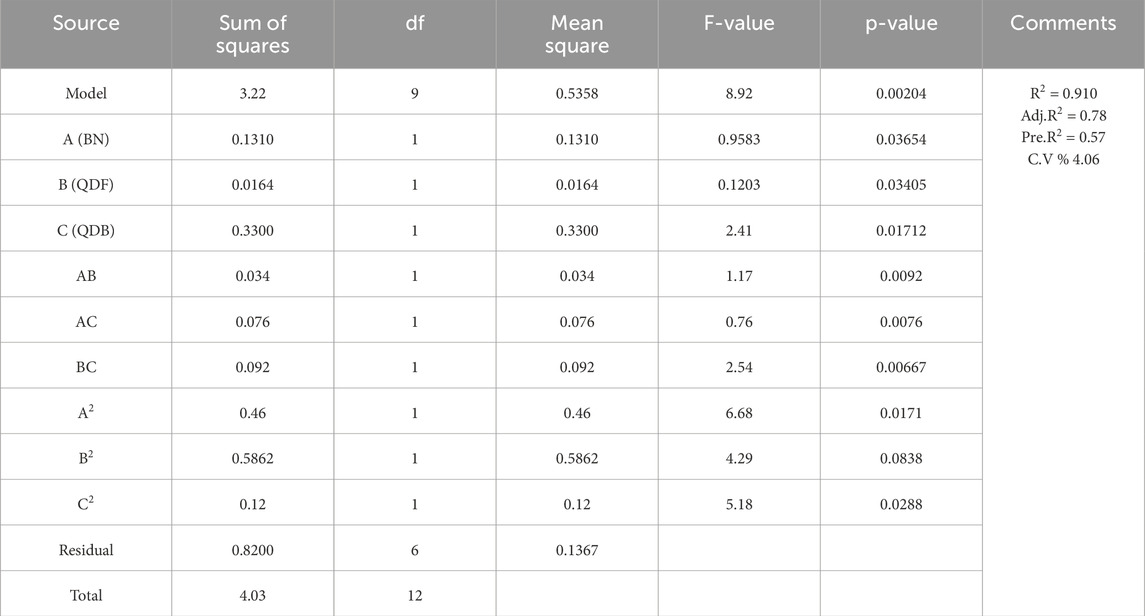
The response surface approach is a statistical technique that maximizes an output or response affected by several input variables or factors. A contour plot or graphical representation of the response or output in three dimensions can be used (Ma et al., 2022; Kursuncu et al., 2022). The response surface provides the matrix for the ideal strength value in concrete at different percentages of SCM. The results of the ANOVA analysis for the measured parameters, including compressive strength (
In this study, the optimization of compressive strength (
Equations 1–3 represent the refined models.
4.1 Contour plots and 3D surface response
The adequacy of the model was assessed through diagnostic plots, depicted in Figure 10, which are crucial for validating the model. In the normal residual plot Figures 10A–C the data points follow a normal distribution, with residuals parallel to an inclined straight line. The residuals vs. expected diagram reveals a random and consistent distribution of residuals above and below the reference line, indicating uniform data variation. Moreover, the plot comparing predicted and actual compressive, flexural, and split tensile strength Figures 10D–F demonstrates that the values closely align along the inclined straight line. The suggested optimized model accurately predicts these values.
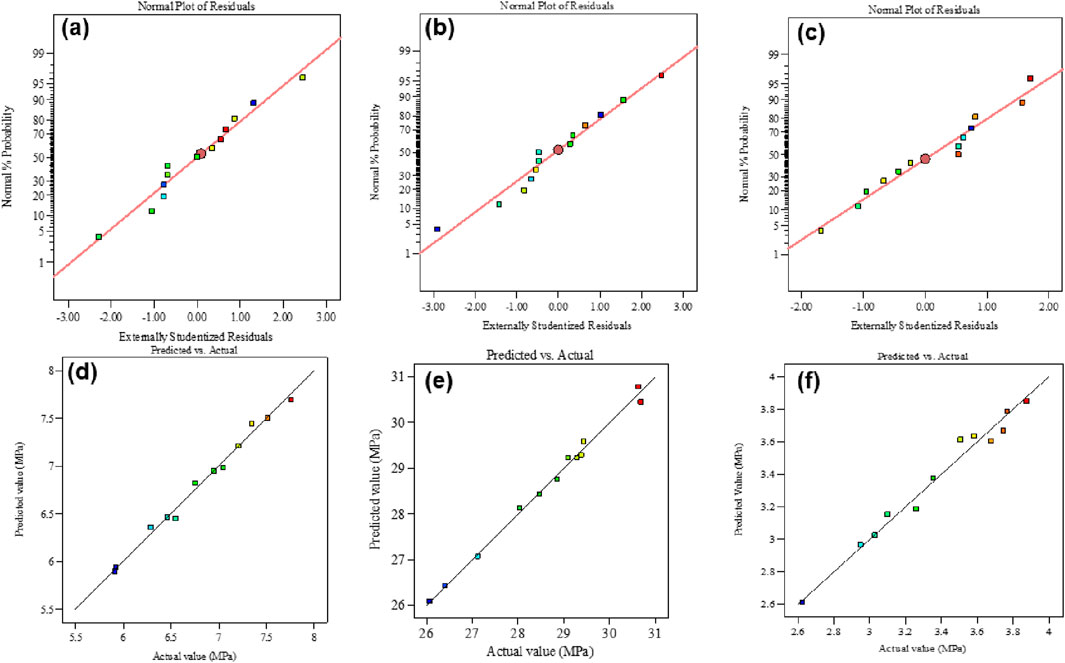
Figure 10. The normal plot of residual (A) compressive strength, (B) flexural strength, (C) tensile strength Predicted vs. actual plot (D) compressive strength (E) flexural strength (F) tensile strength.
Figures 11A–C display contour plots illustrating the compressive, flexural, and split tensile strength of concrete. These plots demonstrate that different combinations of input factors, such as Bentonite clay, quarry dust binder, and filler, result in a range of compressive, flexural, and split tensile strength values. Typically, contour plots in the literature emphasize the optimal response area and variable combinations. According to the figure, optimal 28-day compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths within the range of 33, 9.5, and 3.5 MPa, respectively, can be attained by incorporating 10%–15% substitution of cement with bentonite clay and 8%–12% substitution of sand and quarry dust as a binder.
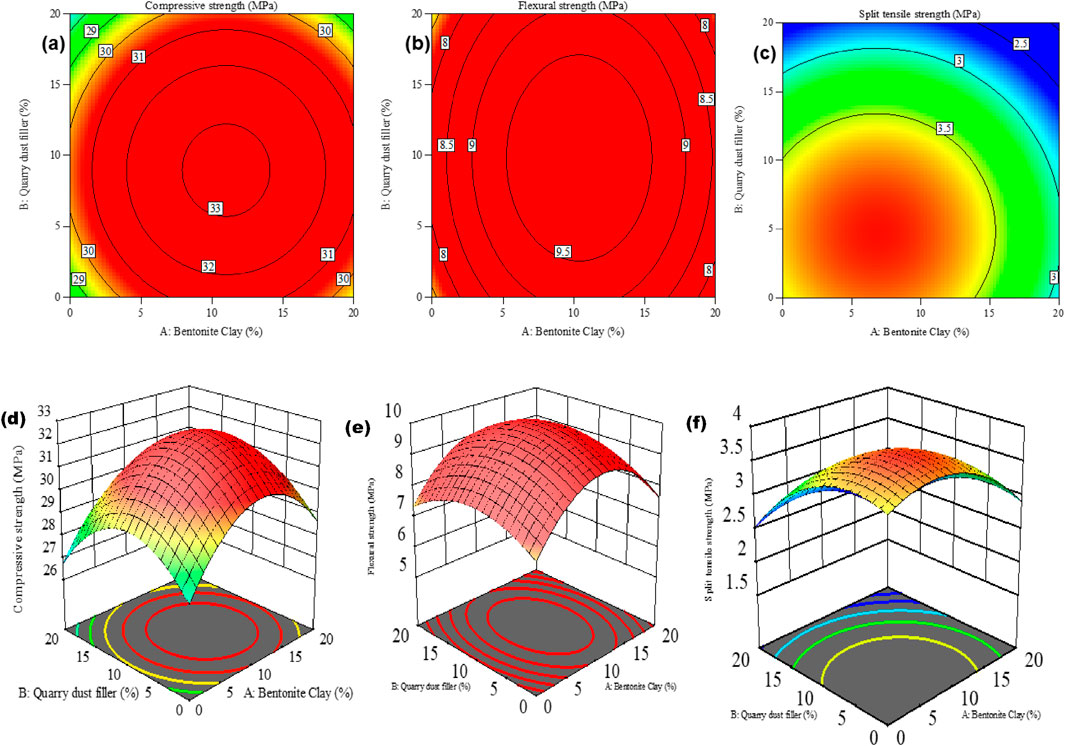
Figure 11. Response spectrum plot (A) contour compressive (B) contour flexural (C) contour tensile strength (D) 3D surface compressive (E) 3D surface flexural (F) 3D surface tensile strength.
In Figures 11D, E, it can be observed that substituting cement by over 15% leads to a reduction in strength due to increased proportions of bentonite clay and quarry dust. Concrete with high levels of bentonite clay, especially at a 15% replacement level with cement, exhibits decreased strength. Figure 11F shows that replacing cement by over 10% with quarry dust binder reduces strength. This outcome is attributed to non-uniform distribution and unequal dispersion of additives, which weaken matrix bonds. Additionally, a higher fraction of supplementary cementitious material (SCM) leads to increased alkali-silicate reaction due to excess content not undergoing pozzolanic reaction. This heightened reaction raises the risk of alkaline-silica response (ASR), detrimental to compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths.
4.2 Optimization combination
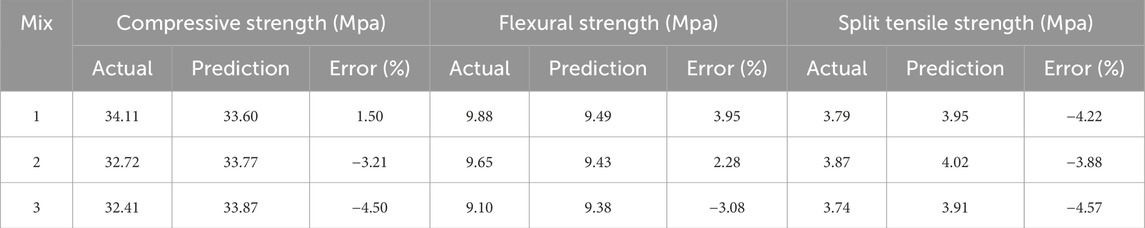
Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was employed as a numerical optimization tool to identify the ideal mix design for maximizing the compressive strength of concrete after 28 days of curing. The optimal combination, predicted by the model and presented cubic Figure 12 representation of the optimized combinations of bentonite clay, quarry dust as a binder, and quarry dust as a filler, predicting their effects on compressive strength, flexural strength, and split tensile strength. The figure visualizes how different proportions of these materials influence the mechanical properties of the cementitious composite. It highlights the optimal mix designs that maximize the desired strengths, demonstrating the interaction between the three components and their combined effects on performance. The cubic figure shows that 13.92% of cement with bentonite clay, 10.418% with quarry dust, and 12.196% of fine aggregate with quarry dust. This optimized mix was predicted to achieve compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths of 34.031, 10.232, and 3.458 MPa, respectively as shown in Table 8. It highlights the optimal mix designs that maximize the desired strengths, demonstrating the interaction between the three components and their combined effects on performance.
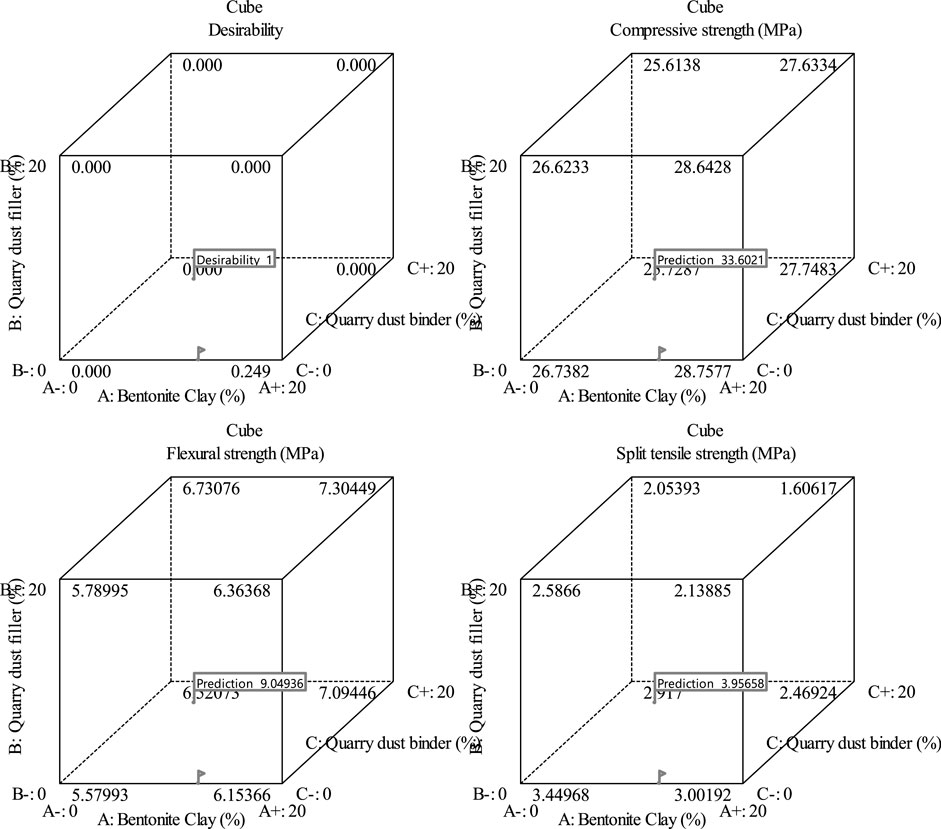
Figure 12. Optimization combination prediction of compressive, flexural, and split tensile strength.
4.3 Validation of model
The optimal mix design was determined using response surface methodology, resulting in a composition of 10.29% bentonite clay and 7.20% quarry dust as cement replacements, along with 8.19% quarry dust replacing fine aggregate. This mix was experimentally validated over a 28-day curing period, with three samples tested per mix. The average compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths achieved were 33.60, 9.49, and 3.95 MPa, respectively. The differences between the predicted and experimental values were consistently below 5%, highlighting the accuracy of the model. This validation confirms the optimal effectiveness of the mix in achieving maximum strength. Furthermore, the developed models reliably predicted strength values under experimental conditions. Compared to reference concrete, the optimized samples demonstrated notable strength improvements of 18.08%, 33.60%, and 11.15% in compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths, respectively as shown in Table 9. The table also illustrates the minimal discrepancies below 5% between the model predictions and actual experimental results across all curing periods, further affirming the models’ effectiveness in accurately predicting compressive strength with a 95% confidence level.
5 Cost-benefit analysis
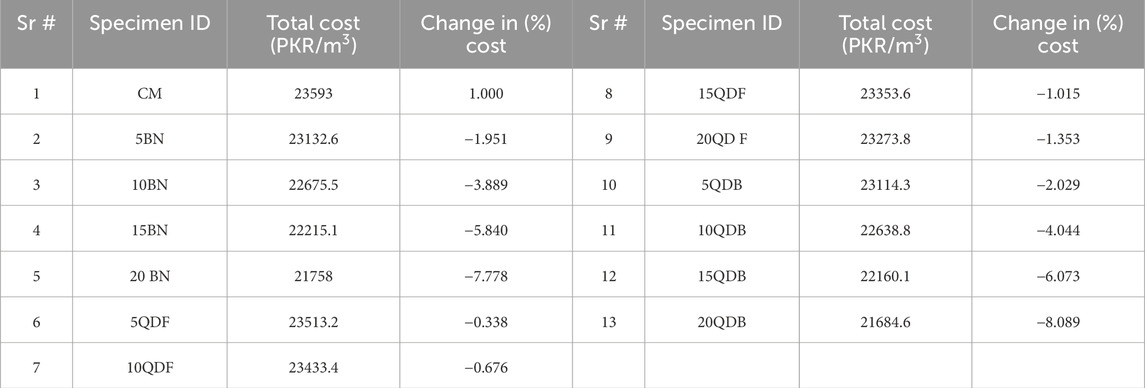
It is well established that using supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like bentonite (BN) and quarry dust (QD) as substitutes for ordinary Portland cement (OPC) can effectively reduce pressure on natural resources and lower production costs. Additionally, such alternative concrete mixes can exhibit enhanced strength and durability. Consequently, it is essential to explore cost-reducing methods. In this study, bentonite and quarry dust were combined as OPC replacements to lower the overall expenses of the concrete mix. Table 10 summarizes the unit costs in Pakistani Rupees (PKR) for the raw materials used. The cost analysis for 1 m³ of various concrete mixes with different percentages of BN, QDB, and QDF is presented in Table 11. The cost of the control mix with only OPC is PKR 23,593. However, as the bentonite content increases, the cost decreases; for example, mixes with 1.95% and 3.88% BN cost 5.84 and 7.77 times less than the control mix, respectively. When the bentonite content exceeds 20%, the cost is over 7% lower compared to the control mix, offering a cost-effective solution for the construction industry.
Similarly, increasing the quarry dust content also reduces costs. For instance, mixes with 2.02% and 4.0% QDB cost 6 and 8 times less than the control mix, respectively. When quarry dust content exceeds 20%, the mix cost is more than 8% lower than the control mix, making it a cost-efficient option for construction.
Moreover, a mix with a synergistic combination of 10% bentonite, 8% quarry dust as a filler, and 7% quarry dust as a binder costs approximately 8.4% less than the control mix. Given its enhanced strength and durability, this mix is well-suited for various structural applications. These benefits could be particularly significant for large-scale projects like dams and multi-story buildings, where concrete production constitutes a substantial portion of the costs (Ashraf et al., 2022; Memon et al., 2012).
6 Conclusion
This research investigated the effectiveness of locally available supplementary cementitious materials (bentonite clay and quarry dust) in enhancing concrete properties. The study investigated compressive strength, flexural strength, and acid resistance at 7 and 28 days of curing. Moreover, experimental results were compared using statistical analysis through the Response Surface Method. The summary of the key findings are:
1. Incorporating bentonite clay and quarry dust tends to lower the workability of mixes compared to reference mixes. Due to smaller and coarser particles, mixes contained with quarry dust exhibited the lowest workability. This observation is crucial for practical applications, as adjustments in water content or admixtures may be required to maintain workability in field applications.
2. Quarry dust (10%) significantly improved compressive strength, with increases of 11.9% and 7.38% at 7 and 28 days of curing, respectively, compared to reference concrete. Bentonite clay (10%) initially reduced strength by 1.3% at 7 days but compensated with a 4.91% increase by 28 days of curing. The later age strength improvement is attributed to the late hydration reaction of bentonite clay that produces C2S, which creates extra C-S-H. This delayed strength gain suggests that bentonite clay can be effectively used in applications where long-term strength development is desired, making it suitable for structures with extended curing periods.
3. Incorporating 10% bentonite clay and 10% quarry dust increased flexural strength. Bentonite clay showed a 4.2% increase at 7 days but improved to 11.9% at 28 days of curing. Quarry dust initially showed higher strength, 19.7%, but it was reduced to a 7.17% improvement. However, the strength gain for quarry dust decreased over time, whereas bentonite clay showed a consistent improvement. This suggests that while quarry dust offers significant early-age strength benefits, bentonite clay contributes to longer-term strength development, which is valuable for designing concrete that performs well over its service life.
4. The same trend was observed for the split tensile strength test. The highest split strength for bentonite clay bentonite clay was noted at 28 days of curing, whereas the highest strength for quarry dust was noted for mixes containing 10% quarry dust at 7 days of curing.
5. Mixtures containing 20% bentonite clay and 20% quarry dust demonstrated superior resistance to chemical attack compared to the control mix. The quarry dust filled the voids and concrete gaps, making acid ingress difficult—similarly, the formation of calcium hydrate due to bentonite clay made it difficult for acid ingress. The SEM analysis confirmed the capillaries produced after exposure to acids. The acids react with cement, lowering the C-S-H composition leading to voids and capillary formation, which is ideal for the formation of etrringite. This makes the SCM-modified concrete highly suitable for aggressive environments, such as chemical plants and coastal areas.
6. Statistical analysis revealed that a combination of 10.29% bentonite clay, 7.20% quarry dust replacing cement, and 8.19% replacing fine aggregate produced concrete with excellent strength matching theoretical predictions. This optimal mix provides a sustainable approach to concrete production, balancing performance and resource utilization effectively.
6.1 Significance and implications
This study underscores the potential of using bentonite clay and quarry dust as sustainable SCMs, offering both environmental and performance benefits. The findings highlight the practical advantages of these materials in improving concrete properties while contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation. Future research should explore the rheological behavior of these SCMs under varying conditions, such as elevated temperatures, to further validate their applicability in diverse construction scenarios.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MU: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HQ: Writing–review and editing, Supervision. MK: Writing–original draft. MS: Software, Writing–original draft. HA: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing–review and editing. AA: Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. MB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NV: Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Taif University, Saudi Arabia, Project No. (TU-DSPP-2024-33). The research is also partially funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation as part of the World-class Research Center program Advanced Digital Technologies (contract No. 075-15-2022-311 dated 20.04.2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to Taif University, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through project number (TU-DSPP-2024-33).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd Elmoaty, A. E. M. (2013). Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of concrete modified with granite dust. Constr. Build. Mater. 47, 743–752. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.05.054
Ahmad, J., Kontoleon, K. J., Al-Mulali, M. Z., Shaik, S., El Ouni, M. H., and El-Shorbagy, M. A. (2022). Partial substitution of binding material by bentonite clay (BC) in concrete: a review. A Rev. Build. 12, 634. doi:10.3390/buildings12050634
Al-Bakri, A. Y., Ahmed, H. M., and Hefni, M. A. (2022). Cement kiln dust (CKD): potential beneficial applications and eco-sustainable solutions. Sustain 14, 7022. doi:10.3390/su14127022
Ali, S., Khan, S. M., Ahmad, Z., Abdullah, A., Kazi, N., Nawaz, I., et al. (2023). Relative humidity, soil phosphorus, and stand structure diversity determine aboveground biomass along the elevation gradient in various forest ecosystems of Pakistan. Sustain 15, 7523. doi:10.3390/su15097523
Althoey, F., Ansari, W. S., Sufian, M., and Deifalla, A. F. (2023). Advancements in low-carbon concrete as a construction material for the sustainable built environment. Dev. Built Environ. 16, 100284. doi:10.1016/j.dibe.2023.100284
Aprianti S, E. (2017). A huge number of artificial waste material can be supplementary cementitious material (SCM) for concrete production – a review part II. J. Clean. Prod. 142, 4178–4194. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.115
Arrigoni, A., Panesar, D. K., Duhamel, M., Opher, T., Saxe, S., Posen, I. D., et al. (2020). Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of concrete containing supplementary cementitious materials: cut-off vs. substitution. J. Clean. Prod. 263, 121465. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121465
Ashraf, M., Iqbal, M. F., Rauf, M., Ashraf, M. U., Ulhaq, A., Muhammad, H., et al. (2022). Developing a sustainable concrete incorporating bentonite clay and silica fume: mechanical and durability performance. J. Clean. Prod. 337, 130315. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130315
Castillo Lara, R., and Chagas Cordeiro, G. (2019). Effect of rice husk ash as supplementary cementitious material on the performance of cement-based pastes continuously exposed to organic acid solution (vinasse). J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 31. doi:10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0002739
Chengfang, Y., Raza, A., Manan, A., Ahmad, S., Chao, W., and Umar, M. (2024). “Experimental and FEM analysis on the impact of yellow river sand replacement rate on engineered cementitious composite (ECC),” in Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Sustain. (England: Emerald Publishing Limited), 1–18.
Chintalapudi, K., and Pannem, R. M. R. (2022). Enhanced chemical resistance to sulphuric acid attack by reinforcing Graphene Oxide in Ordinary and Portland Pozzolana cement mortars. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 17, e01452. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01452
da Silva Rego, J. H., Sanjuán, M. Á., Mora, P., Zaragoza, A., and Visedo, G. (2023). Carbon dioxide uptake by Brazilian cement-based materials. Appl. Sci. 13, 10386. doi:10.3390/app131810386
de Siqueira, A.A., and Cordeiro, G. C. (2022). Sustainable cements containing sugarcane bagasse ash and limestone: effects on compressive strength and acid attack of mortar. Sustain 14, 5683. doi:10.3390/su14095683
Dobiszewska, M., Bagcal, O., Beycioğlu, A., Goulias, D., Köksal, F., Płomiński, B., et al. (2023). Utilization of rock dust as cement replacement in cement composites: an alternative approach to sustainable mortar and concrete productions. J. Build. Eng. 69, 106180. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106180
Duchesne, J. (2021). Alternative supplementary cementitious materials for sustainable concrete structures: a review on characterization and properties. Waste Biomass Valorization 12, 1219–1236. doi:10.1007/s12649-020-01068-4
Escavy, J. I., Herrero, M. J., Trigos, L., and Sanz-Pérez, E. (2020). Demographic vs economic variables in the modelling and forecasting of the demand of aggregates: the case of the Spanish market (1995–2016). Resour. Policy. 65, 101537. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101537
Fadaie, M. A., Nekooei, M., and Javadi, P. (2019). Effect of dry and saturated bentonite on plastic concrete. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 23, 3431–3442. doi:10.1007/s12205-019-0835-2
Febin, G. K., Abhirami, A., Vineetha, A. K., Manisha, V., Ramkrishnan, R., Sathyan, D., et al. (2019). Strength and durability properties of quarry dust powder incorporated concrete blocks. Constr. Build. Mater. 228, 116793. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116793
Google Earth (2024). Google Earth. Available at: https://earth.google.com/web/search/33°44’24”,+73°02’18”/@33.74,73.0383333,806.57842694a,860.84456841d,35y,257.91465127h,45t,0r/data=CiwiJgokCbO2O9GGAEFAES9Opevw_UBAGQzQfO_4DVJAIS3xTcB8DFJAQgIIAUoNCP___________wEQAA.
He, R., Nantung, T., and Lu, N. L. (2024). Unraveling microstructural evolution in air-entrained mortar and paste: insights from MIP and micro-CT tomography amid cyclic freezing-thawing damage. J. Build. Eng. 94, 109922. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109922
He, R., Nantung, T., Olek, J., and Lu, N. (2023). Field study of the dielectric constant of concrete: a parameter less sensitive to environmental variations than electrical resistivity. J. Build. Eng. 74, 106938. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106938
Hemalatha, T., and Sindu, B. S. (2020). Experimental studies to investigate efficacies of slag as fine aggregate substitute. ACI Mater. J. doi:10.14359/51725981
Ho, D. W. S., Sheinn, A. M. M., Ng, C. C., and Tam, C. T. (2002). The use of quarry dust for SCC applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 32, 505–511. doi:10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00726-8
Isaksson, R., Rosvall, M., Babaahmadi, A., Buregyeya, A., Hazarika, A., Marangu, J. M., et al. (2023). Supplementary cementitious materials in building blocks—diagnosing opportunities in sub-saharan Africa. Sustain 15, 5822. doi:10.3390/su15075822
Javed, U., Khushnood, R. A., Memon, S. A., Jalal, F. E., and Zafar, M. S. (2020). Sustainable incorporation of lime-bentonite clay composite for production of ecofriendly bricks. J. Clean. Prod. 263, 121469. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121469
Kankam, C. K., Meisuh, B. K., Sossou, G., and Buabin, T. K. (2017). Stress-strain characteristics of concrete containing quarry rock dust as partial replacement of sand. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 7, 66–72. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2017.06.004
Karagüzel, C., Çetinel, T., Boylu, F., Çinku, K., and Çelik, M.S. (2010). Activation of (Na, Ca)-bentonites with soda and MgO and their utilization as drilling mud. Appl. Clay Sci. 48, 398–404. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2010.01.013
Khan, I. U. (2023). Utilizing bentonite clay as a pozzolanic material to reduce cement consumption and cost in construction industry. Juniper Online J. Mater. Sci. 7. doi:10.19080/jojms.2023.07.555722
Khan, M., Cao, M., Chu, S. H., and Ali, M. (2022b). Properties of hybrid steel-basalt fiber reinforced concrete exposed to different surrounding conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 322, 126340. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126340
Khan, M. I., Shah, M. U., and Usman, M. (2022a). Experimental investigation of concrete properties using locally available coarse aggregates in Punjab, Pakistan. NUST J. Eng. Sci. 15, 26–29. doi:10.24949/njes.v15i1.655
Khan, M. Y., Turab, S. A., Riaz, M. S., Atekwana, E. A., Muhammad, S., Butt, N. A., et al. (2021). Investigation of coseismic liquefaction-induced ground deformation associated with the 2019 Mw 5.8 Mirpur, Pakistan, earthquake using near-surface electrical resistivity tomography and geological data. Near Surf. Geophys 19, 169–182. doi:10.1002/nsg.12148
Khan, S. U., Qureshi, M. I., Rana, I. A., and Maqsoom, A. (2019). An empirical relationship between seismic risk perception and physical vulnerability: a case study of Malakand, Pakistan. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 41, 101317. doi:10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101317
Kolawole, J. T., Babafemi, A. J., Fanijo, E., Chandra Paul, S., and Combrinck, R. (2021). State-of-the-art review on the use of sugarcane bagasse ash in cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 118, 103975. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.103975
Kursuncu, B., Gencel, O., Bayraktar, O. Y., Shi, J., Nematzadeh, M., and Kaplan, G. (2022). Optimization of foam concrete characteristics using response surface methodology and artificial neural networks. Constr. Build. Mater. 337, 127575. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127575
Ma, H., Sun, Z., and Ma, G. (2022). Research on compressive strength of manufactured sand concrete based on response surface methodology (RSM). Appl. Sci. 12, 3506. doi:10.3390/app12073506
Manjunatha, M., Preethi, S., Malingaraya, , Mounika, H. G., Niveditha, K. N., and Ravi, (2021). Life cycle assessment (LCA) of concrete prepared with sustainable cement-based materials. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 3637–3644. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.248
Masood, B., Elahi, A., Barbhuiya, S., and Ali, B. (2020). Mechanical and durability performance of recycled aggregate concrete incorporating low calcium bentonite. Constr. Build. Mater. 237, 117760. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117760
Memon, S. A., Arsalan, R., Khan, S., and Lo, T. Y. (2012). Utilization of Pakistani bentonite as partial replacement of cement in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 30, 237–242. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.11.021
Mirgozar Langaroudi, M. A., and Mohammadi, Y. (2022). Effect of nano-clay on the freeze–thaw resistance of self-compacting concrete containing mineral admixtures. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 26, 481–500. doi:10.1080/19648189.2019.1665107
Mirza, J., Riaz, M., Naseer, A., Rehman, F., Khan, A. N., and Ali, Q. (2009). Pakistani bentonite in mortars and concrete as low cost construction material. Appl. Clay Sci. 45, 220–226. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2009.06.011
Mugi, K. (2022). Comparative study on the effects of quarry dust and natural fines on performance of concrete blocks. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Soc. Sci. 1. doi:10.58506/ajstss.v1i1.50
Nasier, S. (2021). Utilization of recycled form of concrete, E-wastes, glass, quarry rock dust and waste marble powder as reliable construction materials. Mater. Today Proc. 45, 3231–3234. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.381
Nasiru, S., Jiang, L., Yu, L., Chu, H., Huang, Y., Pei, C., et al. (2021). Properties of cement mortar containing recycled glass and rice husk ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 299, 123900. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123900
Nataraja, M. C., and Nalanda, Y. (2008). Performance of industrial by-products in controlled low-strength materials (CLSM). Waste Manag. 28, 1168–1181. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.03.030
Ndahirwa, D., Zmamou, H., Lenormand, H., and Leblanc, N. (2022). The role of supplementary cementitious materials in hydration, durability and shrinkage of cement-based materials, their environmental and economic benefits: a review. Clean. Mater. 5, 100123. doi:10.1016/j.clema.2022.100123
Passuello, A., Rodríguez, E. D., Hirt, E., Longhi, M., Bernal, S. A., Provis, J. L., et al. (2015). Deflection analysis of flexible pavements-materials and test division report. Constr. Build. Mater.
Qian, H., Umar, M., Khan, M. N. A., Shi, Y., Manan, A., Raza, A., et al. (2024). A state-of-the-art review on shape memory alloys (SMA) in concrete: mechanical properties, self-healing capabilities, and hybrid composite fabrication. Mater. Today Commun. 40, 109738. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.109738
Qureshi, L. A., Ali, B., and Ali, A. (2020). Combined effects of supplementary cementitious materials (silica fume, GGBS, fly ash and rice husk ash) and steel fiber on the hardened properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 263, 120636. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120636
Ramos, T., Matos, A. M., Schmidt, B., Rio, J., and Sousa-Coutinho, J. (2013). Granitic quarry sludge waste in mortar: effect on strength and durability. Constr. Build. Mater. 47, 1001–1009. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.05.098
Raza, A., Junjie, Z., Shiwen, X., Umar, M., and Chengfang, Y. (2024). Experimental analysis of frost resistance and failure models in engineered cementitious composites with the integration of Yellow River sand. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 31, 20240017. doi:10.1515/secm-2024-0017
Rehman, S. U., Kiani, U. A., Yaqub, M., and Ali, T. (2020). Controlling natural resources depletion through Montmorillonite replacement for cement-low cost construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 232, 117188. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117188
Shaheen, A. ul H., Ahmed, K. S., Sarfraz, Y., Riaz, M. T., and Shahzad, A. (2023). Physico-mechanical characterization of cement concrete using quarry waste as fine aggregate replacement of natural sand. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48, 13807–13821. doi:10.1007/s13369-023-07981-9
Snellings, R., Suraneni, P., and Skibsted, J. (2023). Future and emerging supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 171, 107199. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2023.107199
Soomro, M., Tam, V. W. Y., and Jorge Evangelista, A. C. (2022). Production of cement and its environmental impact. Recycl. Concr. Technol. Perform., 11–46. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-85210-4.00010-2
Sousa, V., Bogas, J. A., Real, S., and Meireles, I. (2023). Industrial production of recycled cement: energy consumption and carbon dioxide emission estimation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 8778–8789. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20887-7
Sun, Z., gui Chen, Y., and min Ye, W. (2022). A systematic review of bentonite/concrete interaction system in HLW disposal repositories: theoretical, experimental and geochemical modelling analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 353, 129075. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129075
Sundaralingam, K., Peiris, A., Anburuvel, A., and Sathiparan, N. (2022). Quarry dust as river sand replacement in cement masonry blocks: effect on mechanical and durability characteristics. Materialia 21, 101324. doi:10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101324
Thomas, J., and Harilal, B. (2016). Mechanical properties of cold bonded quarry dust aggregate concrete subjected to elevated temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 125, 724–730. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.08.093
Umair, M., Mehmood, A., Rukh, S., Khan, A., Ahmad, Z., Rafique, M., et al. (2023). Controlling arsenic contamination through bentonite clays: a batch sorption study. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 23, 2381–2391. doi:10.1007/s42729-023-01191-w
Uratani, J. M., and Griffiths, S. (2023). A forward looking perspective on the cement and concrete industry: implications of growth and development in the Global South. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 97, 102972. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2023.102972
Xie, Y., Li, J., Lu, Z., Jiang, J., and Niu, Y. (2018). Effects of bentonite slurry on air-void structure and properties of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 179, 207–219. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.226
Zhang, Y., Raza, A., Umar, M., Chen, Y., and Yuan, C. (2023). Study on frost resistance and interface bonding performance through the integration of recycled brick powder in ultra-high-performance concrete for structural reinforcement. Mater. (Basel) 16, 6999. doi:10.3390/ma16216999
Keywords: bentonite clay, quarry dust, compressive strength, cement, response surface
Citation: Umar M, Qian H, Khan MNA, Siddique MS, Almujibah H, A. Elshekh AE, Bashir MO and Vatin NI (2025) Strength and durability of concrete with bentonite clay and quarry dust. Front. Mater. 11:1458836. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1458836
Received: 03 July 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Biao Hu, Shenzhen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Amir Ali Shahmansouri, Washington State University, United StatesChuanqing Fu, Zhejiang University of Technology, China
Paolo Di Re, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Umar, Qian, Khan, Siddique, Almujibah, A. Elshekh, Bashir and Vatin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Qian, cWlhbmh1aUB6enUuZWR1LmNu; M. Nasir Ayaz Khan, ZW5nci5raGFubmFzaXJAZ21haWwuY29t
 Muhammad Umar
Muhammad Umar Hui Qian1*
Hui Qian1* M. Nasir Ayaz Khan
M. Nasir Ayaz Khan Muhammad Shahid Siddique
Muhammad Shahid Siddique Hamad Almujibah
Hamad Almujibah Nikolai Ivanovich Vatin
Nikolai Ivanovich Vatin