- 1School of Civil and Resource Engineering University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
- 2Information Institute of Ministry of Emergency Management, Beijing, China
- 3Jinchuan Group Co. LTD., Jinchuang, Gansu, China
The Jinchuan Nickel Mine is the largest large-scale copper–nickel sulfide deposit in China and the third largest in the world. Due to the deep burial of the ore body, high geostress, and broken ore rock, the downward layered cementing and filling mining method with high cost and low production capacity is adopted. The Jinchuan Nickel Mine uses bar milling sand as the filling aggregate and cement as the cementing material and adopts pipeline autoclave conveying filling mining technology with a high cement-to-sand ratio and high concentration of filling slurry, which results in the high cost of filling mining and poor mining economic benefits. In order to reduce the cost of filling mining, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine has carried out a series of research on low-cost filling mining technology by utilizing solid waste, such as using metallurgical slag instead of cement to develop low-cost filling cementitious material, using waste rock and bar mill sand as the mixed aggregate, using waste rock and tailing sand as the mixed aggregate, mixing fly ash with the mixed aggregate, and mixing copper processing tailing with the mixed aggregate. The strength of the 3d, 7d, and 28d cemented filling body of waste rock and bar mill sand reached 1.5 MPa, 2.6 MPa, and 4.8 MPa, respectively; the strength of the 3d, 7d, and 28d cemented filling body of waste rock tailings reached 4.7 MPa, 6.1 MPa, and 9.0 MPa, respectively; the strength of the 3d, 7d, and 28d cemented filling body of mixed fly ash reached 2.0 MPa, 2.0 MPa, 6.1 MPa, and 9.0 MPa, respectively; the strength of 3d, 7d, and 28d doped fly ash cemented filling body reached 2.0 MPa, 2.7 MPa, and 5.9 MPa, respectively; the strength of the 3d, 7d, and 28d doped copper-selecting tailings cemented filling body reached 1.55 MPa, 3.11 MPa, and 5.10 MPa respectively; and the strength of 3d early-strength type green filling cementitious material increased to 1.73 MPa. The application of cemented filling with solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine has been successful and popularized and applied in the Longshou Mine and the second mine area. Early-strength green filling cementitious materials and mixed aggregate paste filling technology are the research and development direction for utilization in Jinchuan Nickel Mine filling and mining.
1 Introduction
The Jinchuan Nickel Mine is the largest copper–nickel sulfide deposit in China and the third largest in the world. It is located at the foot of Longshou Mountain in Jinchang City, Gansu Province, with a length of 6.5 km and a width of 500 m (Wu et al., 2003). The deposit is divided into four mining areas from east to west: IV, II, I, and III. The proved resource reserves have reached 564 million tons, including nickel–metal reserves of 5.5 million tons. Jinchuan copper–nickel deposit is deeply buried, has high in situ stress, a thick ore body, and broken ore rock, so the stope ground pressure activity is intense. For the sake of safety production, research on stope ground pressure control and safety production management is carried out. Through technical breakthroughs and engineering practice, the downward layered drift cemented filling mining method is explored (Zhao et al., 2006). The mining technology of the high cement–sand ratio and high-concentration slurry pipeline gravity transportation of rod ground aggregate and cement cementitious material is implemented, and the cost of the filling material is as high as 158 yuan/m3. At present, the mining depth of the mine has entered kilometers (Langyan et al., 2023). The “three-high” mining environments of high temperature, high pressure, and high permeability lead to the violent appearance of stope ground pressure, which further improves the cost of controlling the stope. With the gradual reduction in ore grade year by year, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine faces severe economic benefit pressure (Lu et al., 2021). Safe, efficient, and low-cost filling mining technology is an important problem faced by the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
Jinchuan Group Co., Ltd. is the largest nickel–cobalt production base, platinum group metal refining center, and non-ferrous metallurgical and chemical complex supporting mining, beneficiation, and metallurgy in China. A large number of solid wastes such as waste rock, tailings, waste residue, fly ash, and gypsum are discharged every year. Due to the influence of technology and economy and the underdeveloped economy in the West, a large number of low-quality solid wastes are stacked on the surface. It not only occupies a large amount of land but also worsens the regional environment, safety, and environmental protection problems.
Given the poor mining technical conditions and environmental protection problems in the mining area, Jinchuan Enterprises invests a huge amount of money every year to carry out a series of research on the comprehensive utilization of nickel and cobalt resources and practice the concept of circular economy development (Wang et al., 2023a). During the 12th Five-Year Plan period, aiming at the development and utilization of kilometer-deep wells and low-grade refractory lean ores, we carried out deep mining of large deposits and technical research on the utilization of copper–nickel smelting slag and built JINCHUAN COPPER–NICKEL polymetallic ore resources, a comprehensive utilization demonstration base. In terms of the development and utilization of low-grade lean ore resources, safe and low-consumption mining of refractory deposits, and comprehensive utilization of waste, in-depth and extensive research has been carried out, and some research has made breakthrough progress, which not only reduces the discharge of solid waste but also significantly improves the economic, environmental, and social benefits of enterprises and promotes the sustainable development of Jinchuan Enterprises (Wang et al., 2023b). In recent years, with the increasing development of lean ore resources year by year, low cost mining methods and low-cost filling mining technology have been carried out, and some achievements have been industrialized (Figure 1). This paper comprehensively analyzes and summarizes the research progress of solid-waste resources in filling mining, the factors affecting the utilization of solid-waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, and the problems faced at present and puts forward the research and development direction of the utilization of solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine and the direction of the development of the solid-waste filling material paste filling technology.
2 Research progress of solid-waste resources in filling mining
The Jinchuan Nickel Mine is a rare hard-to-mind deposit in the world. Through technical research and engineering practice, a suitable downward layered cemented filling mining method is explored. For safe and efficient filling mining, rod grinding sand is used as the aggregate and cement as the cementitious material, and a high cement–sand ratio and high-concentration cemented filling mining are implemented, resulting in high filling mining costs and poor mining economic benefits. Therefore, the filling mining technology of using slag and fly ash to partially or completely replace cement and waste rock and tailings to replace some bar grinding sand is studied. Its research includes the following aspects.
2.1 Research on mixed-aggregate filling mining technology
The cost of rod grinding is high. Using the waste rock to partially replace rod grinding is one of the ways to reduce the cost of filling mining. Therefore, the original particle size of -3-mm rod grinding sand is increased to -5 mm, the waste rock is used to replace the rod grinding sand, and the cement strength test of the mixed aggregate of waste rock and rod grinding sand is carried out. Given the problem of layered segregation of mixed-aggregate filling slurry, further use of fly ash and copper tailings as a fine aggregate to optimize the particle size gradation of the mixed aggregate and carry out research on the pipeline transportation characteristics and proportion optimization of various mixed-aggregate filling slurry not only improves the fluidity and stability of mixed filling slurry and solves the problem of layered segregation of mixed filling slurry but also for fly ash. We aim to find a way for the resource utilization of solid wastes such as tailings and copper tailings.
2.1.1 Study on the mixed aggregate of waste rock and bar grinding sand
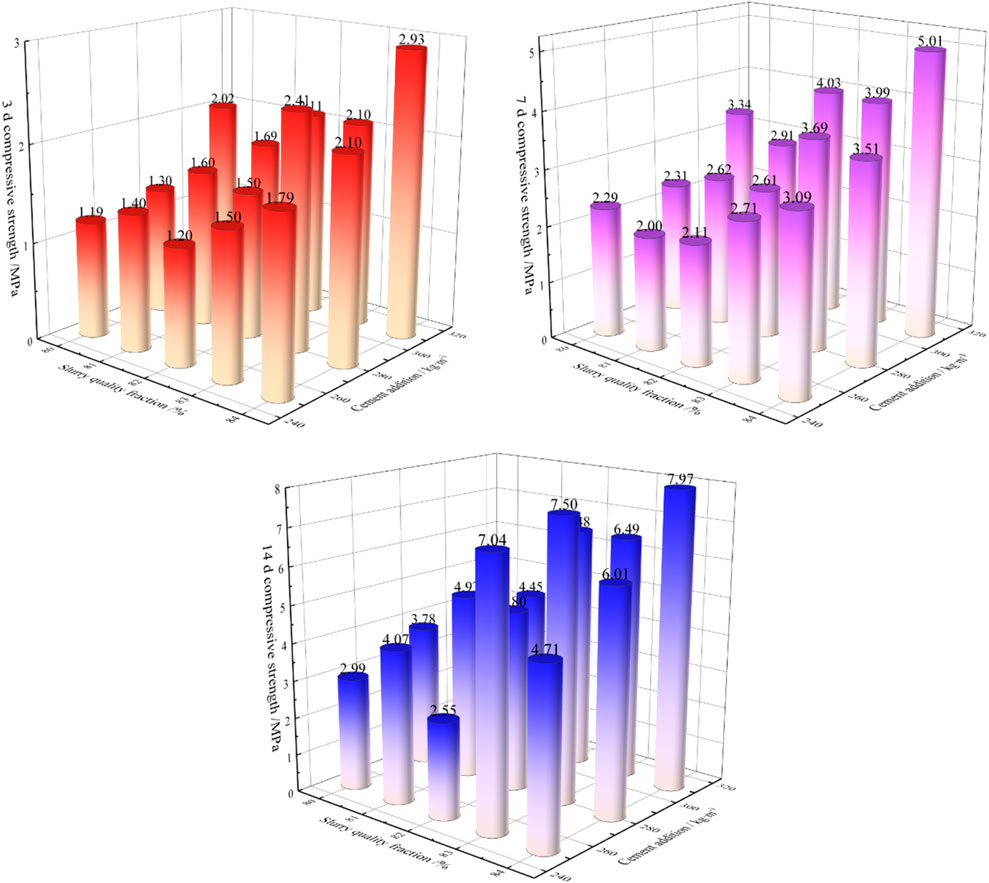
The Jinchuan Nickel Mine first researched the filling technology of waste rock rod frosted mixed aggregate. Wang et al. (2019a) and Yuan et al. (2016a) carried out experimental research on the pipeline transportation characteristics of filling slurry for the mixed aggregate of -5-mm rod frosted sand and waste rock and carried out the strength test of the cemented filling body for the waste rock aggregate with the particle size of -10 mm and -12 mm, respectively. The results show that when the filling slurry concentration of -10-mm waste rock mixed aggregate is 82% and the cement addition is 280 kg/m3, the strength of the cemented backfill can reach 1.5 MPa, 2.6 MPa, and 4.8 MPa, respectively, in 3d, 7d, and 28d, which meets the requirements of cemented backfill mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine (Figure 2). Then, through the stacking compactness test of waste rock and sand mixed aggregate with different ratios, it is determined that the reasonable ratio of mixed-aggregate rod grinding sand and waste rock is 5:5∼6:4. The filling technology has been applied in the Longshou Mine. The filling amount of waste rock has reached 6.073 million tons, and the filling cost has been saved by 14.28 million yuan. Yang Z et al. (2017) and Wen et al. (2019) studied the pipeline transportation characteristics of mixed-aggregate filling slurry for the mixed aggregate of waste rock, Gobi sand, and bar grinding sand, revealed the rheological and pipeline transportation characteristics of filling slurry, and proposed the optimization method of the mixed filling slurry ratio based on RSM-BBD theory (Qian et al., 2019).
2.1.2 Study on the mixed aggregate of waste rock and tailings
The large particle size of waste rock aggregate leads to the layered segregation of slurry, so there is a potential risk of pipe blockage and explosion. Therefore, the filling technology of mixed-bone high-concentration slurry was studied. The results show that the aggregate contains no less than 20% fine aggregate, which is a sufficient and necessary condition for preparing a high-concentration slurry. Therefore, tailings are selected as the fine aggregate to conduct research on filling mining technology of the waste rock tailing mixed aggregate. Yang Zhiqiang, Yang Xiao, He Jianyuan, etc. researched the strength and ratio of the mixed aggregate backfill. The results show that (Yang et al., 2015) when the cement–sand ratio is 1:4, the average particle size of mixed aggregate is ≤1.69 mm, the non-uniformity coefficient is ≥38.4, the slurry concentration is >80.8%, and the density of the 3d test block of the cemented filling body is ≥2.24 g/cm3. When the bar grinding sand:Gobi sand:tailings ratio is 4.5:4.5:1, the strength of the filling body reaches maximum (Wang et al., 2022a; Cao et al., 2022; Yang Xiao et al., 2016). When the tailings:bar grinding sand ratio is 3.95:6.05, the additional amount of cement is 302.8 kg/m3, the additional amount of fly ash is 93.2 kg/m3, and the slurry concentration is 74.9%, it meets the safety filling requirements of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine (Wang et al., 2022b; He et al., 2016). When the waste rock: tailings = 6:4 and 7:3, the particle size distribution curve of the mixed aggregate is close to the fuller ideal grading curve, its stacking compactness reaches the maximum, and the ratio is close to optimal. Therefore, tests on rheological properties and pipeline transportation characteristics of filling slurry (Yang et al., 2014a; Yang et al., 2017b; Wang Aiai et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2017c) and industrial filling tests (Yang et al., 2016b; Yang et al., 2014b) have been carried out to verify the feasibility and reliability of the application of the mixed aggregate in filling mining of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
2.1.3 Study on the mixed aggregate mixed with fly ash
Fly ash is a kind of potentially active pozzolanic solid waste, but its hydration reaction occurs only when it is excited in an alkaline environment due to its low activity. Fly ash is used as a fine aggregate to prepare the filling slurry. Fly ash mainly plays the role of filling pores and compacting in the early stage of hydration. Therefore, with the increase in fly ash content, the early strength decreases. However, under the action of alkali excitation, the potential activity of fly ash is stimulated, and a hydration reaction occurs to improve the later strength of cemented backfill. Therefore, the strength of cemented backfill increases with the increase in fly ash content, and its later strength increases. It can be seen that the fly ash in the mixed aggregate of waste rock and rod frosting plays a dual role in physics and chemistry. At the initial stage of hydration, fly ash is used as a fine aggregate to optimize the particle size gradation of the mixed aggregate and provide the fine aggregate necessary for the mixed aggregate to form a high-concentration slurry. At the later stage, it is excited in the alkali environment to produce a hydration reaction and improve the later strength of the filling body. According to the strength requirements of the filling body in the downward layered filling method of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, the early strength of the mixed-filling aggregate mixed with fly ash is studied. Yang et al. (2014c) and Qu et al. (2018a) carried out a cement strength test and proportion optimization test with fly ash. The test results show that when the ratio of waste rock to bar-grinding sand is 2:8 and the addition of fly ash is 30% of the weight of cement, the strength of the filling body is equivalent to that of bar-grinding sand. However, the fluidity of the filling slurry is improved, and the bleeding rate and shrinkage rate of the filling slurry are also reduced. The test results further prove that fly ash reduces the early strength of the backfill but can promote the later strength. The optimum ratio of mixed-aggregate filling slurry is determined as follows: the amount of cement is 290 kg/m3, the amount of fly ash is 200 kg/m3, and the mass fraction of filling slurry is 82%.
2.1.4 Study on the mixed aggregate mixed with copper tailings
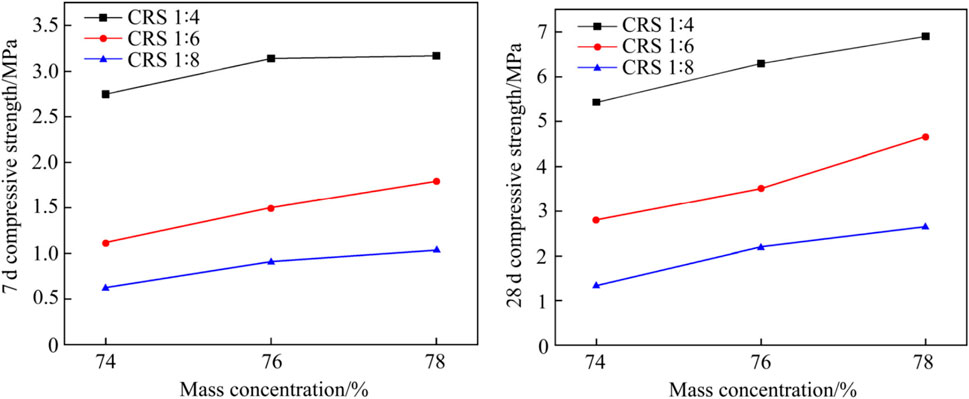
Copper separation tailings are solid wastes discharged from copper–nickel smelting slag after copper separation. They also belong to pozzolanic solid wastes, but their potential activity is very low; hence, they are low-quality solid wastes. To use waste resources of copper tailings in Sichuan, the mining technology of mixed aggregate of waste rock and tailings is studied (Wang et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2015; Dang et al., 2019; Ba et al., 2020). Wang Youtuan et al. researched the influence of adding copper slag tailings on the strength of cemented backfill. The results show that the copper tailings belong to inert solid waste. The fine aggregate as a mixed aggregate has a significant effect on the early strength but has little effect on the later strength. The filling cost of 11.6 yuan/m3 can be saved by using copper tailings to replace the mixed aggregate of 20% rod grinding sand. Chen Jie, Dang Zhiming, Ba Lei, etc. carried out the strength test and proportioning research on the cemented backfill of waste rock mixed aggregate mixed with copper tailings. The results show that with the addition of an early-strength agent and copper slag tailings ≤ L5%, the 3d and 7d strength of cemented backfill can reach more than 1.5 MPa and 2.5 MPa, respectively, which can meet the early-strength requirements of filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. Thus, the optimal ratio of filling slurry is obtained as follows: the additional amount of cement, waste rock, and rod grinding sand is 290 kg/m3, 361.6 kg/m3, and 813.8 kg/m3, respectively, the additional amount of water is 384.8 kg/m3, and the additional amount of copper tailings is 257.6 kg/m3. The filling slurry with 82% concentration is prepared. The strength of the filling body on 3d, 7d, and 28d reaches 1.55 Mpa, 3.11 MPa, and 5.10 MPa, respectively, while the cost of filling slurry is only 112.6 yuan/m3, i.e., 30% lower than the cost of rod frosted filling slurry (156 yuan/m3) (Figure 3).
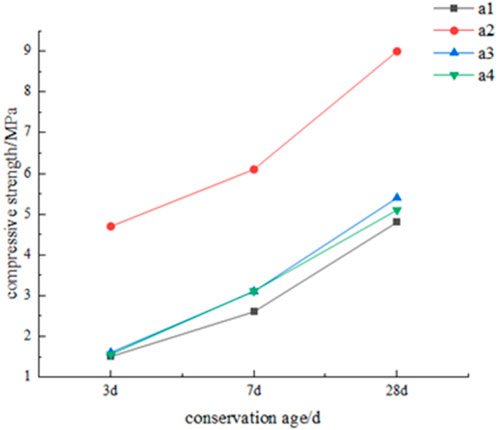
Figure 3. 3d, 7d, and 28d compressive strength of cemented filling with copper selecting tailing slag.
2.2 Research progress of low-cost filling cementitious materials
To reduce the filling mining cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, the development and application of low-cost filling cementitious materials were carried out by using solid wastes such as blast furnace slag, copper–nickel slag, fly ash, and industrial by-product gypsum.
2.2.1 Research on cementitious material filled with rod-frosted sand
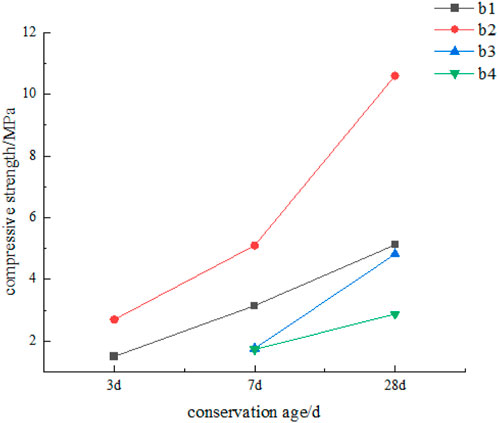
Aiming at the rod ground sand filling aggregate of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, using iron ore slag and desulfurization ash as active materials and NaOH, lime, and mirabilite as alkali activators, Wang et al. (2014), Yang et al. (2014d), and Li et al. (2018) carried out experimental research and showed that the optimal proportion of rod-ground sand aggregate filling cementitious material is slag 4%, desulfurization ash 20%, lime 5%, mirabilite 10%, and NaOH 1%. However, the 3d strength of the filling body is less than 1.5 MPa, which does not meet the early-strength requirements of filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. Yang Zhi-qiang et al. (2014) researched rod-grinding cementitious material with nickel slag and showed that the early strength of the filling body of cementitious material is low and does not meet the early-strength requirements. Further research shows that due to the low activity of desulfurized ash, the early hydration reaction of composite cementitious materials prepared as sulfate activators is very slow and almost anhydrous within 3 days. To solve the problem of early strength of cementitious materials, Xiao et al. (2014) and Yang et al. (2019a) carried out experimental research on new filling cementitious materials by adding fly ash and improving the ratio of the composite activator. The results show that when quick lime is 5%, Glauber’s salt is 3%, sodium sulfite is 1.5%, desulfurization ash is 17.5%, fly ash is 20%, and slag micro-powder is 53%, the 3d, 7d, and 28d strength of the cemented filling body of the rod-grinding aggregate increases to 1.50 MPa, 3.15 MPa, and 5.12 MPa, respectively, which meets the strength requirements of the filling body for downward layered filling mining. When the content of fly ash is increased to 37.5%, the cost of cementitious material is 121 yuan/T. Li et al. (2020a), Li et al. (2016), and Yang et al. (2019b) used gypsum and clinker to prepare composite activators and carried out experimental research on slag-based cementitious materials. The optimal ratio of cementitious materials was obtained as follows: 12% for cement clinker, 3% for desulfurization gypsum, and 85% for slag. The 3d, 7d, and 28d strength of the rod-ground sand cemented backfill can reach 2.7 MPa, 5.1 MPa, and 10.6 MPa, respectively, which meets the strength requirements of cemented backfill in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
2.2.2 Study on the cementitious material filled with the mixed aggregate
The Jinchuan Nickel Mine increased the development of waste rock, tailing coarse aggregate, and the application of mixed aggregate with copper tailings and fly ash as fine aggregates. Therefore, new filling cementitious materials suitable for mixed aggregate were researched. To obtain a filling aggregate mixed with tailings and Gobi aggregate at a ratio of 1:1, Wen Z-j. et al. (2020) carried out experimental research on the new filling cementitious material of the mixed aggregate; determined that the optimal ratio of the new cementitious material is 10% of fly ash, 8% of cement clinker, 14% of desulfurized gypsum, and 68% of slag micro powder; and carried out the cement strength test for the tailings-mixed aggregate. The results show that when the cement–sand ratio is 1:6 and the mass fraction of mixed aggregate filling slurry is 78%, the strength of the cemented filling body can reach 1.76 MPa and 4.82 MPa, respectively, in 7 and 28 days (Figure 4). The bleeding rate and slump of the filling slurry are 5.98% and 23.2 cm, respectively. The cost of filling slurry is only 103 yuan/m3, which is 47% lower than that of rod-frosted aggregate filling slurry.
2.2.3 Study on the utilization of low active slag and cementitious material of the consolidated powder
Jinchuan Nickel Mine filling cementitious material development is a new type of filling cementitious material prepared by using slag from Jiuquan Iron and Steel Company and fly ash of a power plant as active materials and activators prepared by lime, cement clinker, and desulfurization gypsum. However, due to the low activity of slag from Jiuquan Iron and Steel Company, the early strength of cemented backfill does not meet the mine strength requirements. Therefore, Yuan et al. (2016b) and Wang Y-d et al. (2019) researched the optimization of the activator ratio and the fineness of slag powder. The results show that the strength of cemented backfill increases with the increase in the fineness of slag powder. When the average particle size of slag powder decreased from 24.3 μm to 12.3 μm, the 3d, 7d, and 28d strength of cemented backfill increased by 33.3%, 30%, and 9.3%, respectively. Through optimization, the optimized proportion of filling cementitious material is as follows: the additional amount of quicklime, desulfurization ash, fly ash, mirabilite, sodium sulfite, and Jiugang slag powder is 3%, 5%, 5%, l%, 2%, and 84%, respectively. The 3d and 7d strength of the backfill reached 1.73 MPa and 2.88 MPa, respectively, meeting the strength requirements of the cemented backfill of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine (Figure 5). Aiming at different filling aggregates of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, a cementitious material filled with consolidation powder has been developed and industrialized in the Longshou Mine (Yang et al., 2016c; Yang et al., 2017d; Wang et al., 2019c; Xiao BL. et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019c).
2.3 Study on the slurry transportation characteristics of the mixed-aggregate filler
The key way to reduce the filling cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine is to use beneficiation tailings, copper tailings, and fly ash as the fine aggregate; mix with waste rock and rod-grinding coarse aggregate; and implement the mixed aggregate filling technology. However, the optimal design of mixed-aggregate filling slurry, pipeline transportation characteristics, and mixing technology and equipment of large capacity and high-concentration slurry are the key technologies for the application of mixed aggregate in filling mining.
2.3.1 Study on characteristics of the mixed aggregate filling slurry
Wu et al. (2020a) researched the segregation characteristics and mathematical model of mixed-aggregate high-concentration filling slurry. According to the stress analysis of coarse aggregate under the initial and critical concentration of filler slurry, the determination coefficient of the segregation characteristics of mixed-aggregate filler slurry is proposed. Selecting the ratio of waste rock to rod grinding sand (waste–rod ratio), the ratio of aggregate to cement (sand–cement ratio), and the concentration of filling slurry as the main factors, using the bleeding rate and rheological properties of filling slurry as the evaluation indexes, a mathematical model of anti-segregation of mixed-aggregate filling slurry is constructed, and the prediction results of the model are tested by the image method. The results show that there is a linear relationship between the determination coefficient and the bleeding rate of the slurry. The determination coefficient of the separation dividing point of the filling slurry is 1, and the bleeding rate is 10%. When the determination coefficient is more than 1 or the bleeding rate is less than 10%, the filling slurry of mixed aggregate has good segregation resistance. Li et al. (2020b) studied the characteristics of mixed-aggregate filling slurry based on the vertical distribution law of mass fraction. Based on the diffusion theory, through the stress analysis of solid particles in the filling slurry, combined with the probability distribution of vertical pulsating velocity in the two-phase flow, the mass fraction distribution formula of the mixed-aggregate filling slurry is deduced, and the distribution law effects of the filling slurry concentration are revealed through the experimental study of the working and rheological properties of the mixed-aggregate filling slurry. The results show that the main factors affecting the vertical distribution of the mass fraction of filling slurry are solid particle size and density, slurry density, initial yield stress, and solid particle shape. When the mass concentration of the filling slurry is less than 80% and the ratio of waste rock:rod frosting is 3:7, the mass fraction distribution of the filling slurry reaches the maximum, and the bleeding rate of the corresponding filling slurry is close to the minimum.
2.3.2 Study on the pipeline transportation characteristics of the mixed aggregate slurry
The rheological characteristics and pipeline transportation resistance of mixed-aggregate filling slurry determine the safety, reliability, and economy of pipeline transportation of filling slurry. Wu et al. (2020b) evaluated the working characteristics of mixed-aggregate filling slurry and the research on the particle size gradation of the mixed aggregate. The mixed aggregate is selected to test the working characteristics of the filling slurry. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to reduce the dimension; two new indexes were extracted to quantitatively evaluate the slurry properties, and the two indexes in the comprehensive evaluation function were transformed into one quantitative evaluation index. Based on PCA and distance discriminant analysis (DDA), a PCA-DDA model for the classification and discrimination of working characteristics of the filling slurry is established. Wen Z et al. (2020) carried out the correlation test between the rheological properties of the filling slurry with different concentrations and the gradation of the mixed aggregate to study the effect of the particle size of the mixed aggregate on the rheological properties of filling slurry. Through the established mechanical model, it is determined that the critical particle size range of the mixed-aggregate filling slurry without delamination is 13.8∼21.6 mm. Yang et al. (2019d), Yang et al. (2016d), Yang et al. (2020a), Wu et al. (2020c), Xiao et al. (2019b), Yang et al. (2020b), and Xiao et al. (2020) researched pipeline transportation characteristics and the hydraulic gradient of mixed-aggregate filling slurry. The results show that the hydraulic gradient of mixed-aggregate filling slurry has a positive correlation with the mass fraction of slurry, a negative correlation with the content of cement and fly ash, and a linear relationship with the flow velocity of slurry. Therefore, it is determined that the reasonable flow rate range of mixed-aggregate filling slurry is 1.91∼2.13 m/s.
2.3.3 Development of a large-capacity and high-concentration slurry mixing system
Mixed-aggregate filling slurry usually adopts a high concentration or paste-like body and is transported by pipeline gravity or pump pressure. Therefore, the mixing equipment and process of large-capacity and high-concentration mixed slurry not only affect the mixing quality of filling slurry but also determine the production capacity of the filling mine. Therefore, to prepare the filling slurry of the mixed aggregate, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine has developed the design and research on large-capacity and high-concentration filling slurry mixing equipment (Yang X et al., 2017) and industrial filling test (Yang et al., 2016e). Aiming at the mixed aggregate of rod grinding and waste rock in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, the design and process research on high-concentration and large-capacity mixing equipment with a production capacity of 150∼180 m3/h was carried out. Therefore, first, the pipeline transportation characteristics and mixing mechanism of the high-concentration slurry of the mixed aggregate are analyzed. Then, based on the research on small-capacity mixing equipment with a production capacity of 80∼100 m3/h, scale-up theoretical research is carried out, and the design parameters and technical indexes of large-capacity mixing equipment are obtained. Finally, research on the supporting feeding equipment and production process is carried out, the high-capacity filling slurry mixing equipment and filling process of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine are developed, and the semi-industrial and industrial filling tests are passed, which lays a foundation for the Jinchuan Nickel Mine to improve the filling production capacity of the mixed aggregate and safe production.
3 Research and exploration of the influencing factors and utilization of solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine
The goal of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine Research Institute is to use solid waste to carry out filling mining costs and improve the economic and environmental benefits of filling mining. Since the establishment of the Jinchuan Mine, a large number of scientific and technical studies have been carried out. Using pozzolanic solid wastes such as fly ash and slag to research the partial replacement of cement and filling technology of rod grinding sand, waste rock, and tailings mixed aggregate has been successful and has been applied in mines, thus reducing the filling and mining costs. In recent years, the development of green filling cementitious materials using metallurgical slag and industrial by-products not only further reduces the filling cost but also explores a way for the resource utilization of solid waste. However, due to the inherent complexity and variability of solid waste, there are still difficulties and problems in the current research, mainly reflected in the following two aspects.
3.1 Research progress on the early strength of green cementitious materials
Usually, new filling cementitious materials use lime, cement clinker, and admixture to prepare an activator, which can stimulate the potential activity of blast furnace slag and produce a hydration reaction to form a stone body. At present, slag-based cementitious materials, such as cementitious powder, have consolidation agents, and consolidation powders have been developed. In recent years, with the strict management of China’s environmental protection and the restriction of the production and energy reduction of iron, steel, and cement enterprises, the output of blast furnace slag has decreased, and its application in building materials has increased. Not only is the utilization cost of blast furnace slag increasing year by year but the demand is also in short supply in some areas. Therefore, with the increase in the cost of slag-based cementitious materials, it is close to ordinary Portland 42.5 cement. On the other hand, the metallurgical industry discharges a large number of low-quality solid wastes, such as steel slag, white slag, magnesium slag, and industrial by-product gypsum every year. Due to their poor quality, low activity, and adverse mineral components, such as toxic and harmful substances, the utilization of low-quality solid wastes is difficult, has a high cost, and has a low utilization rate. In 2016, the output of steel slag in China was approximately 65–120 million tons, while the utilization rate was only about 20% and the storage volume of steel slag was as high as 1 billion tons. The main chemical components of steel slag are CaO, MgO, SiO2, Fe2O3, MnO, Al2O3, and a small amount of TiO2 and P2O5. The main mineral composition comprises tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium magnesium olivine, calcium merwinite, dicalcium ferrite, RO (oxide of magnesium, iron, and manganese), free lime (f–CaO), etc. Therefore, steel slag has certain potential activities. With the gradual increase in filling mines in China, the demand for filling cementitious materials is increasing year by year. According to the characteristics of filling cementitious materials, research on green filling cementitious materials using low-quality solid waste can not only significantly reduce filling mining costs and alleviate the shortage of high-quality slag resources but also explore a method for the modeling of low-quality solid waste and the utilization of high added value. The research results show that the main problem faced by the application of solid waste in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine in filling mining is the low early strength of cemented backfill of green cementitious material. There are three main influencing factors: first, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine adopts the downward layered filling method, and the operators work under the top plate of the backfill, so the strength of cemented backfill is very important for safe production. Therefore, the early strength of cemented backfill is required to be high. Second, the basic characteristics of developing cementitious materials with metallurgical slag are hydration reaction, low early strength, and high late strength. Third, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine nearby uses blast furnace slag of Jiuquan Iron and Steel Company with poor quality and low activity, which makes the development and application of green cementitious materials face severe technical and economic problems.
Research has been carried out on the problems existing in the utilization of solid waste from the Jinchuan Nickel Mine in filling mining. Wang et al. (2016) studied the effect of powder fineness on the early strength of cemented backfill for low-activity acid slag. The results show that the specific surface area of undisturbed slag powder is increased from 405 m2/kg to 521 m2/kg and 577 m2/kg by the indoor small mill for 1 h and 1.5 h, respectively. The 3d strength of cemented backfill increased by 33.3% and 22.2%, respectively. Liu et al. (2015) and Wang et al. (2018) researched the early-strength activator of fly ash slag composite cementitious material. The proportion test of the early-strength activator for composite cementitious material is carried out by using fly ash instead of 20% slag micro-powder. From this, the optimized proportion of the composite activator is obtained as follows: quicklime is 5%, desulfurization ash is 17.5%, industrial mirabilite is 3%, and sodium sulfite is 1.5%. The 3d strength of the cemented filling body reaches 2.19 MPa, which meets the requirements of the early strength of the filling body of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. Yang et al. (2020a); Wu et al. (2020c), Xiao et al. (2019b), Yang et al. (2020b); Xiao et al. (2020); Yang Xiaobing et al. (2017); Yang et al. (2016e), Wang et al. (2016), Liu et al. (2015), Wang et al. (2018), Qu et al. (2018b), and Wen Zhenjiang et al. (2018) carried out experimental research on green filling cementitious material of bar grinding sand, waste rock, and Gobi aggregate. For the mixed aggregate of bar grinding sand:waste rock:Gobi aggregate = 0.63:0.23:0.14, the optimal formula of green filling cementitious material is as follows: clinker is 2%, desulfurization gypsum is 2%, limestone powder is 2%, and slag powder is 94%. When the mass fraction of slurry is 80% and the cement–sand ratio is 1:5, the strength of cemented backfill can meet the requirements of the early strength of cemented backfill in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
The existing research results show that improving the fineness of slag powder, exploring high-efficiency early strength agents, and optimizing low-cost production processes are the key technologies to improve the early strength of green filling cementitious materials, and these are the urgent research topics for the utilization of solid waste resources in filling mining of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
3.2 Current problems in the application of solid waste in filling mining
The filling mining design of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine adopts rod-grinding cement filling technology, so the filling cost is high, and the economic benefit is poor. Through scientific research and technical breakthroughs, development of low-cost filling cementitious materials, and application of waste rock tailings mixed aggregate, the filling cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine has been significantly reduced. However, due to the low early strength of cemented backfill and the layered segregation of mixed aggregate filling slurry, the application of solid waste still faces many difficulties and is difficult to realize the large-scale industrial application. Rod-ground aggregate and cement cementitious material are still the main materials for filling and mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. Therefore, high filling costs and poor economic benefits are the current problems faced by the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. With the reduction in rich nickel ore in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine year by year, it faces more lean ore development, and the mining depth extends to the deep, so the pressure faced by filling mining will also increase. To improve the economic benefits of deep lean ore mining, the mine has set up a project to research low-cost caving mining technology and has entered the experimental stage of industrialization. To increase the additional amount of waste rock in the mixed aggregate, Xiao et al. (2019c), Du et al. (2020), and Xiao et al. (2018) started with the research on the coarse aggregate particle size gradation and model, and explored the optimization of the coarse aggregate particle size gradation and the control technology of layered segregation of coarse aggregate filling slurry to expand the utilization scale of the waste rock aggregate in filling mining and reduce the filling mining cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. However, the large-scale application of research results in the industry needs large-scale industrial tests.
4 Research and development direction of resource utilization of solid waste in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine
Given the problems faced by filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, the research and development direction of solid-waste utilization in filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine is put forward.
4.1 Research and development direction of early-strength green filling cementitious material
The cost of filling cementitious material accounts for an important part of the whole filling cost. The filling cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine is high due to the high ash–sand ratio, which is rare at home and abroad. Due to the low early strength of the developed green-filling cementitious material, it is still difficult to popularize and apply on a large scale. Therefore, it is imperative to tackle the technical problems of early-strength filling cementitious materials. At the same time, with China’s increasing requirements for environmental protection and strict management and implementation year by year, the utilization cost of blast furnace slag, cement clinker, quicklime, and other materials will increase, and the supply is still in short supply in some areas. Therefore, the application of low-quality solid wastes such as steel slag, calcium carbide slag, phosphogypsum, and desulfurization gypsum in the filling mining of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine is the research and development direction to reduce the filling mining cost of the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
Li et al. (2019); Yang and Gao (2015), Zhang et al. (2015), and Wen Kai et al. (2018) carried out exploratory research on cementitious materials filled with all solid wastes. Using phosphogypsum from Gansu Wengfu Chemical Company, the experimental study of phosphogypsum-based solid-waste cementitious material was carried out. The test results show that when the proportion of quicklime, phosphogypsum, mirabilite, and slag powder is 6%, 30%, 3%, and 61%, respectively, the strength of the filling body can reach 0.62 MPa, 3.36 MPa, and 10.81 MPa in 3d, 7d, and 28d, respectively. When the early-strength agent is added, the 3d strength is increased to 1.73 MPa, which meets the early-strength requirements of filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. It can be seen that the development and utilization of all solid-waste green-filling cementitious materials are not only feasible but also imperative for the development and utilization of Jinchuan Nickel Mine resources. Therefore, it is one of the development directions of Jinchuan Nickel Mine filling mining and filling technology.
4.2 Development direction of paste-filling technology of mixed-aggregate filling materials
The cost of filling aggregate is an important part of the cost of filling mining. To reduce the mining cost of rod-grinding aggregate filling, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine researched the filling technology of waste rock, tailings, and rod-grinding aggregate and realized industrial application in the Longshou Mine and No. 2 mining area. However, the layered segregation of mixed-aggregate filling slurry and pipeline wear are the key problems for the large-scale popularization and application of mixed-aggregate filling technology. Therefore, the development of mixed-aggregate paste filling technology is another development direction of filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
The key to the large-scale application of the mixed aggregate in filling mining lies in the separation control technology of the filling slurry. It is necessary to increase the slurry concentration of mixed filler and realize high-concentration, paste-like or paste filling. Using tailings as the fine aggregate to optimize the particle size gradation of the mixed aggregate is a sufficient condition for the preparation of high-concentration paste. Therefore, for the research on the sufficient and necessary conditions and proportion optimization of the high concentration of mixed aggregate or paste filling, indoor experimental research has been carried out. It is necessary to further carry out the transformation and experimental research of the paste-filling system to lay the foundation for the implementation of paste-filling technology. The mixed aggregate of waste rock and tailings contains some fine-grained aggregate, and the cement has poor adaptability to the fine-grained aggregate, which reduces the strength of cemented backfill. It is the development direction of filling mining technology development and research in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine to meet the conditions for preparing paste by adding the fine aggregate of tailings and using the adaptability of green filling cementitious material to fine tailings to research low-cost filling technology of mixed aggregate and green cementitious material.
5 Conclusion
In order to reduce the cost of filling mining and increase the utilization rate of solid waste, the Jinchuan Nickel Mine has carried out a large number of experimental studies and on-site industrial applications using solid waste. This paper reviews the progress of research on the utilization of solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine and summarizes the factors affecting the utilization of solid-waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine and the direction of development of research on the utilization of solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine.
(1) The utilization of solid waste resources in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine mainly includes a mixed aggregate of waste rock and bar mill sand, the mixed aggregate of waste rock and tailing sand, mixed aggregate mixed with fly ash, and the mixed aggregate mixed with the tailing slag of copper processing.
(2) In order to reduce the cost of filling mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine, research on the development and application of low-cost filling cementitious materials has been carried out by utilizing solid wastes such as blast furnace slag, copper–nickel slag, fly ash, and industrial by-product gypsum for the purpose of filling aggregate at different periods of the mine.
(3) The main problem in the application of filling mining is the green cementitious materials. The early strength of the cemented filling body is low, mainly due to the downward filling mining requirements of cementing, and the slag quality is poor.
(4) Steel slag, calcium carbide slag, phosphogypsum, desulfurization gypsum, and other low-quality solid waste are the research and development direction to reduce the cost of Jinchuan Nickel Mine fill mining, while mixed aggregate and green cementitious materials research is the direction of Jinchuan Nickel Mine filling mining technology development.
Author contributions
CH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition. WA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–original draft. XL: Data curation, Supervision, Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition. ZX-Z: Writing–review and editing, Supervision. WY-D: Writing–review and editing, Supervision. GQ: Writing–review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundationof China (No. U21A20106) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 06500229).
Conflict of interest
Authors ZX-Z and WY-D were employed by Jinchuan Group Co. LTD.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ba, L., Wei, H., Wen, Z., Gao, Q., and Wang, Y. (2020). Optimization proportioning test on mixed aggregate of waste rock and copper slag tailings. Min. R&D 40 (2), 31–37. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2020.02.006
Cao, H., Gao, Q., Zhang, X., and Guo, B. (2022). Research progress and development direction of filling cementing materials for filling mining in iron mines of China. Gels 8, 192. doi:10.3390/gels8030192
Chen, J., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., and Chen, D. (2015). Experimental study on cement-sand ratio of copper slag-rod-mill tailings backfilling materials. Nonferrous Met. Min. Sect. 67 (1), 54–58. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2015.01.013
Dang, M., Wen, Z., Gao, Q., and Tian, W. (2019). Experiment on proportion and strength of mixed aggregates with cooper slag tailings. Min. R&D 39 (1), 32–35. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2019.01.008
Du, X., Yang, X., Wang, Y., and Gao, Q. (2020). AQH packing model for improved aggregate gradation. Min. R&D 40 (1), 54–59. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2020.01.011
He, J., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Yao, W., and Guo, H. (2016). Analysis on particle size grading of mixed aggregate with waste rock and whole tailings and its proportion decision. Min. R&D 36 (11), 22–27. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2016.11.005
Langyan, W., Zhao, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Optimization of filling ratio in Jinchuan II mine. Min. Res. Dev. 43 (11), 18–22.
Li, L., Chen, D., and Gao, Q. (2020b). Characterization of coarse aggregate filling slurry based on vertical distribution of mass fraction. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 51 (1), 176–183. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.01.020
Li, L., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Wu, F. (2020a). Effect of gypsum-clinker mass ratios on properties of slag filling cementitious material and its application. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 51 (2), 489–498. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.02.022
Li, L., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2016). Experimental research on new filling cementitious material about compound of desulfurization ash and slag, IM& P 45 (4), 60–64. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2016.04.016
Li, L.-t., Yang, X.-b., Gao, Q., and Chen, D.-x. (2019). Preparation of cementitious backfill material with full solid waste based on uniform test and intelligent algorithms. Min. METALLURGICAL Eng. (6), 15–19. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2016.04.016
Li, M., Chen, Z., and Gao, Q. (2018). Optimized decision for the development of new backfill cementing materials based on the rod milling sand. Metal. Mine (2), 64–69. doi:10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.201802012
Liu, R., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2015). Study on activation of early strength for slag powder adding fly ash as a new cementitious material. NONFERROUS Met. Min. Sect. 67 (2), 49–53. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2015.02.011
Lu, B., Li, Y., Fang, S., Lin, H., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Cemented backfilling mining technology for gently inclined coal seams using a continuous mining and continuous backfilling method. Shock Vib. 2021. doi:10.1155/2021/6652309
Qian, G. A. O., Yang, X., Wen, Z., Chen, D., and He, J. (2019). Optimization of proportioning of mixed aggregate filling slurry based on BBD response surface method. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 46 (6), 47–55. doi:10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.06.007
Qu, L., Wang, Y.-d., Gao, Q., and He, J. (2018a). Study on strength of cemented backfill for mixed aggregate with fly ash. IM& P 47 (9), 33–36. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2018.09.009
Qu, L., Wang, Y.-q., Gao, Q., and Wang, Y.-d. (2018b). Strength test of low cost early strength filling material for cementing material in Jinchuan Mine. IM&. P 47 (8), 24–27. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2018.08.006
Wang, A., Cao, S., and Erol, Y. (2022a). Effect of height to diameter ratio on dynamic characteristics of cemented tailings backfills with fiber reinforcement through impact loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 322, 126448. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126448
Wang, A., Cao, S., and Erol, Y. (2022b). Influence of types and contents of nano cellulose materials as reinforcement on stability performance of cementitious tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 344, 128179. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128179
Wang, A., Cao, S., and Erol, Y. (2023c). Quantitative analysis of pore characteristics of nanocellulose reinforced cementitious tailings fills using 3D reconstruction of CT images. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 26, 1428–1444. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.08.004
Wang, G., Zhao, B., Wu, B., Zhang, C., and Liu, W. (2023b). Intelligent prediction of slope stability based on visual exploratory data analysis of 77 in situ cases. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 33 (1), 47–59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.07.002
Wang, G., Zhao, B., Zhao, K., Wu, B., Zhong, W., and Liu, W. (2023a). Piping-seepage mechanism of tailings with different fine particle contents. Int. J. Geomechanics 23 (11). doi:10.1061/ijgnai.gmeng-8657
Wang, Q., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2016). Influence of fineness of acidic slag powders with low activity on early stage strength of cemented backfill. China Powder Sci. Technol. 22 (2), 27–31. doi:10.13732/j.issn.1008-5548.2016.02.007
Wang, Y., He, J., and Gao, Q. (2019a). Application study on self-flow hilling technology in pipeline filling with waste coarse aggregate. J. Xuzhou Inst. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 34 (2), 86–92. doi:10.15873/j.cnki.jxit.000295
Wang, Y., Wen, Z., Yang, X., and Gao, Q. (2019c). Study on development and ratio optimization of cementing material of fly ash-slag based consolidated powder. Min. R&D 39 (5), 88–94. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2019.05.018
Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Li, M., Gao, Q., and Wang, Y. (2015). Effect of Jinchuan copper slag on filling body strength. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 46 (12), 4391–4397. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.12.001
Wang, Y., Yang, Z., and Wang, Y. (2014). GAO qian orthogonal experimental studies of new cementing material with rod milling sand of jinchuan mine. Min. R&D 34 (4), 27–31. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2014.04.009
Wang, Y.-d., Qu, L., Gao, Q., and Chen, D. (2018). Test on early strong filling cementitious material with slag and fly ash base in Jinchuan Mine. IM&. P 47 (6), 45–51. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2018.06.012
Wang, Y.-d., Wen, Z.-j., Yang, Z.-q., and Gao, Q. (2019b). Influence of slag fineness on the strength of cemented backfill. J. Guangxi Univ. (Nat Sci Ed) 44 (4), 1149–1155. doi:10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2019.1149
Wen, K., Gao, Q., Chen, D.-x., and Wang, Y.-ding (2018b). Orthogonal-BP neural network model for strength of phosphogypsum-based cementitious material backfill. IM&. P 47 (10), 60–64. doi:10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2018.10.017
Wen, Z., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Wang, Y. (2019). Effect of mixed aggregate gradation on segregation of filling slurry. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 50 (09), 2264–2272. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.09.023
Wen, Z., Gao, Q., Wang, Y.-d., and He, J.-yuan (2020b). Experiment on correlation between rheological properties of filling slurry with different mass concentration and mixed aggregate gradation. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 41 (5), 642–648. doi:10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2020.05.006
Wen, Z., Yang, Z.-q., Gao, Q., and Yuan, G.-b. (2018a). Proportioning and optimization test for backfill cementing material with faster strengthening property in jinchuan mine. Min. METALLURGICAL Eng. 38 (6), 29–32. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2018.06.006
Wen, Z.-j., Gao, Q., Wang, Y.-d., and Yang, X.-b. (2020a). Development of composite cementitious material and optimization of lurry proportion based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Chin. J. Nonferrous Metals 30 (3), 698–707. doi:10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37561
Wu, A., Han, B., and Liu, T. (2003). Study on deformation and support of roadways in weak rockmass in Jin chuan nickel mine. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. (S2), 2595–2600. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.z2.014
Wu, F., Yang, Z.-q., and Gao, Q. (2020b). Quantitative evaluation and classification discrimination of working characteristics of coarse aggregate filling slurry. J. China Coal Soc. doi:10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.1345
Wu, F., Yang, X., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2020a). Anti-segregation property and its mathematical model of high concentration filling slurry with coarse aggregate. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 51 (5), 1309–1316. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.05.015
Wu, F., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2020c). Experimental study on pipeline transport characteristics of high concentration and mixed aggregate filling slurry. J. Southwest Jiaot. Univ. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200264
Xiao, B., Mamadou, F., and Anis, R. (2020). Towards understanding the rheological properties of slag-cemented paste backfill. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 35, 268–290. doi:10.1080/17480930.2020.1807667
Xiao, B., Wen, Z., Wu, F., Li, L., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2019b). A simple L-shape pipe flow test for practical rheological properties of backfill slurry: a case study. Powder Technol., 3561008–3561015. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.012
Xiao, B., Yang, Z., Chen, D., and Gao, Q. (2019c). Evaluation of the quantifying methods for shape characteristics of filling aggregate. J. Tian Jin Univ. Sci. Technol. 52 (5), 545–553. doi:10.11784/tdxbz201808031
Xiao, B., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., and Guo, X. (2018). Discussion on packing density models of combined aggregate and a new solution. Mater. Rep. 32 (14), 2400–2406. doi:10.11784/tdxbz201808031
Xiao, B., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., and Wang, Y. (2014). Development of new cementitious materials based on fly ash water quenched slag in a mine in Gansu Province. NONFERROUS Met. Eng. 4 (5), 61–64. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2014.05.014
Xiao, B. L., Yang, Z. O., Chen, D. X., and Gao, Q. (2019a). Impacts of slag-based-binder fineness on strength in mining backfill. Sci. Sin. Tech. 49, 402–410. doi:10.1360/n092018-00109
Yang, X., Bolin, X., and Qian, G. (2019b). Validating the use of slag binder with 91 percent blast furnace slag for mine back filling. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020. doi:10.1155/2020/2525831
Yang, X., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., and He, J. (2019c). Optimization on the fineness of consolidation powder cementing materials and the proportioning of filling slurry in jinchuan Longshou mine. Min. R&D 39 (12), 22–27. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2019.12.005
Yang, X., Wang, Y., Gao, Q., He, J., and Qu, L. (2019a). Research on a new cementitious materials based on desulphurization ash and fly ash and its application in jinchuan mine. Multipurp. Util. Mineral Resour. 0 (4), 130–134. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.028
Yang, X., Wu, F., Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2019d). Pipeline hydraulic gradient model and its application for coarse aggregate filling with high mass fraction of slurry. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 50 (11), 2851–2858. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.11.024
Yang, X., Xiao, B., Qian, G., and He, J. (2020b). Determining the pressure drop of cemented Gobi sand and tailings paste backfill in a pipe flow. Constr. Build. Mater. 255, 119371. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119371
Yang, X., Xiao, B., and Gao, Q. (2020a). Prediction of friction pressure for non-Newtonian backfilling pipe-flow slurry. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. 47 (6), 125–131. doi:10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2020.06.016
Yang, X., Yang, Z., Chen, Z., and Gao, Q. (2017e). Design on large-capacity mixing equipment for high-density rod-milled sand aggregate slurry in Jinchuan. M and PE (8), 66–71. doi:10.16816/j.cnki.ksjx.2017.08.016
Yang, X., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., and Chen, D. (2016a). Research on the influence of mixed filling aggregate distribution based on the RRB model on filling body strength. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. 39 (7), 965–969. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2016.07.020
Yang, Z., Chen, D., Gao, Q., and Chen, Z. (2014c). Experimental research on proportioning of filling material mixed with rod milled sand-river sand-fly ash. COAL ASH 5, 1–4. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-046X.2014.05.001
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Wang, H. (2014b). Industrial filling experiment on full tailings-rod milled sands as mixed filling materials in jinchuan nickel mine. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. Sci. 33 (2), 40–47. doi:10.16452/j.cnki.sdkjzk.2014.02.011
Yang, Z., and Gao, Q. (2015). Development of new filling cementitious material of phosphogypsum in jinchuan mine. Min. R&D 35 (1), 21–24. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2015.01.005
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Chen, D., Wang, Y., and He, J. (2017d). Development of consolidation powder cementing material and strength test of cemented filling body. J. Hohai Univ. Nat. Sci. 45 (1), 69–76. doi:10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2017.01.010
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Wu, S. (2016b). Backfilled starting modes and pipeline resistance of mixed slurry prepared with waste rocks and tailings. J. Wuhan Inst. Technol. 38 (4), 369–375. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2016.04.011
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., Chen, D., and Ba, D. (2014a). Research on filuing body strengthand rheological properties of mixed filling mortar with unclassieied tailingsand rod milling sand in jinchuan mine. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 33 (z2), 3985–3991. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.s2.075
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., and Wang, H. (2017b). Test study on rheological characteristics for mixed filling slurry including waste rock and tailings and its liquidity in the stope. J. Xiamen Univ. Nat. Sci. 56 (2), 294–299. doi:10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201603048
Yang, Z., Gao, Q., Yao, W., and Liu, Z. (2017a). Experiment on pipeline characteristics of filling slurry of Gobi sand and rod-mill sand aggregates. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. Sci. 36 (01), 38–45. doi:10.16452/j.cnki.sdkjzk.2017.01.001
Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Yao, W. (2015). Test research on cemented filling body strength of mixed filling aggregate in Jinchuan Nickel mine. J. HENAN Polytech. Univ. Nat. Sci. 34 (2), 171–178. doi:10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2015.02.007
Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Gao, Q., and Chen, Z. (2017c). Research on pressure loss in pipe by conveying mix slurry with waste rock and full tailings based on round pipe test. J. HEFEI Univ. Technol. 40 (8), 1092–1098. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2017.08.017
Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Gao, Q., Zhao, C., and Chen, Z. (2016e). Industrial test on large-capacity mixing equipment for high-density sand slurry from rod mill. M and PE (10), 66–71. doi:10.16816/j.cnki.ksjx.2016.10.015
Yang, Z., Xiao, B., Gao, Q., and Li, M. (2014d). Experimental study on development of a new cementitious material based on Rod Grinding in Jinchuan Nickel Mine. NONFERROUS Met. Min. Sect. 66 (5), 65–68. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2014.05.015
Yang, Z.-q., Chen, D.-x., Gao, Q., Ma, L., and Zou, L. (2016d). Key technologies in long-distance pipeline transportation of filling slurry of coarse aggregate. J. Guangxi Univ. (Nat Sci Ed) 41 (4), 1306–1312. doi:10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2016.1306
Yang, Z.-q., Gao, Q., Wang, Y.-q., Ma, L., and Wang, Y.-d. (2016c). Strength test on consolidation powder cementing filling body and comparison analysis for different aggregates. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 56 (5), 466–473. doi:10.7511/dllgxb201605005
Yang, Z.-q., Gao, Q., Wang, Y.-q., Ni, W., and Chen, D.-x. (2014e). Experimental study on new filling cementing material using water-hardening nickel slag tailings of Jinchuan Mine. Chin. J. Geotechnical Eng. 0 (8), 1498–1506. doi:10.11779/CJGE201408016
Yuan, G., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., and Ba, D. (2016b). Optimization of the formula of low activity slag cementitious materials using BP neural network. J. HEFEI Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. 39 (9), 1189–1195.
Yuan, G., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., He, J., Zhang, Z., and Wang, Q. (2016a). Strength test on cemented filling body for combined aggregate of waste rock and rod-mill sand. Min. R and D 36 (08), 16–20. doi:10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2016.08.005
Yang, C., Yang, L. J., Wang, S. G., Wang, Q., Gao, F. Q., Wang, , et al. (2023). Strength design of filling body and optimization of slurry ratio based on energy matching. Metal. MINE (2), 38–42. doi:10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202302006
Zhang, G., Yang, Z., Gao, Q., and Wang, Y. (2015). Development of early strength filling cementing material with phosphogypsum as substitute of traditional cement. Metal. MINE (3), 194–198.
Keywords: Jinchuan Nickel Mine, backfill mining, solid waste utilization, research progress, high-sulfur tailings
Citation: Hui C, Aiai W, Lianku X, Xi-Zhi Z, Yong-Ding W and Qian G (2024) Research progress of solid waste resource utilization backfill mining for Jinchuan Nickel Mine, China. Front. Mater. 11:1442564. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1442564
Received: 02 June 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Xiaming Feng, Chongqing University, ChinaReviewed by:
Erol Yilmaz, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan University, TürkiyeGuangjin Wang, Kunming University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Hui, Aiai, Lianku, Xi-Zhi, Yong-Ding and Qian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xie Lianku, eGllbGtAaWllbS5hYy5jbg==
 Cao Hui1
Cao Hui1 Wang Aiai
Wang Aiai