- College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China
NiTi shape memory alloys (SMA) have garnered significant interest owing to their shape memory effect, superior corosion resistance, and biocompatibility. This paper reviewed the current research status of cutting machining for NiTi SMA, focusing on turning, milling, and drilling processes, emphasizing the influence of various cutting parameters, tool materials, and cooling methods on machining performance. The optimal turning effect under dry cutting circumstances is achieved when the cutting speed surpasses 100 m/min. The application of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) in milling, alongside the use of cold air and the optimization of parameters such as feed rate and cutting depth, could diminish cutting force and temperature, thus reducing burr formation. Cemented carbide and high-speed steel covered with TiN are the ideal materials for drilling tools, and the use of substantial cutting fluid yields superior cutting performance compared to MQL. This review concludes that, despite advancements in the study of machining NiTi shape memory alloys, further research is necessary to enhance the efficiency and quality of NiTi SMA machining, particularly with tool material selection and cooling techniques. Finally, based on the current research results, this paper proposes possible future research directions, which provides valuable theoretical guidance for the processing research of NiTi SMA.
1 Introduction
The Chinese government has put forward the goal plan of Made in China 2025, taking aerospace equipment, biomedical and other high-performance devices as the goal of development. Nickel-titanium alloys have attracted wide attention as key materials for development (Committee, 2024). Nickel-titanium alloys are a series of alloys primarily composed of nickel and titanium elements, including nickel alloys, titanium alloys, and NiTi SMA. Nickel alloys are widely utilized in aerospace, petrochemical, turbine, and engine industries due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent high-temperature mechanical properties and corrosion resistance (Marinescu et al., 2011; Shicheng et al., 2024; Thornton et al., 2023; Andrea et al., 2021). Titanium alloy has the characteristics of low density, high specific strength, strong corrosion resistance and superior biocompatibility, so it is widely used in drill pipe, high pressure compressor, aircraft fuselage and medical instruments in petroleum exploration (Shao et al., 2023; Shengchen, 2018; Pasang et al., 2023; Cui et al., 2022; Cui et al., 2021; Minghang, 2021; Guanming, 2019). NiTi SMA is the most widely used type among SMA. They are particularly noted for their unique superelasticity and shape memory effect in addition to their large strength-to-weight ratio, low density, and superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility (Chen et al., 2023; Sehitoglu et al., 2017; Baigonakova et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023; Xie and Xu, 2023). These properties have garnered widespread attention, especially in biomedical applications such as artificial joints and vascular stents (Pelton et al., 2000; Das and Chakraborti, 2018).
There are typically high cutting forces, severe tool wear, and excessive surface roughness when mechanical processing NiTi SMA, making it a typical challenging material to machine. Although non-traditional processing methods, such as electrochemical machining (Singh et al., 2023), water jet machining (Dong-Dong et al., 2023), laser cutting (Sun et al., 2021), and electrical discharge machining (Ao et al., 2020) be able to improve many of the issues associated with cutting machining to a certain extent. However, they could not fully replace cutting machining, thanks to its elevated processing costs and reduced efficiency, and the difficulty in meeting the requirements for complex surface processing. Therefore, mechanical processing remains an indispensable method for processing NiTi SMA.
There are key points regarding current research on the machining of NiTi SMA, including turning, milling, drilling, and the corresponding auxiliary machining methods. Among them, the auxiliary machining methods include flood (Sharif et al., 2017) MQL (Masoudi et al., 2023), liquid nitrogen cooling (Dhananchezian, 2024), CO2-Assisted Cryogenic (Wang et al., 2023), cold air (Khairusshima et al., 2013), pre-treatment (Kim and Lee, 2016; Zhang et al., 2023b) and ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining (Guangxi et al., 2023), which have the ability to improve issues arising from cutting machining, such as tool wear, chip evacuation difficulties and poor surface integrity.
According to the literature, significant advances have been made in the cutting process research of NiTi SMA over the past 2 decades. NiTi SMA often exhibits two distinct crystal structures: martensite and austenite. These two crystal structures have an ability to undergo a transformation between each other. The thermoelastic martensitic transition is the primary cause of the production of SME and superelasticity in NiTi SMA (Abdul, 2016). The distinct physical characteristics of martensite and austenite produce in significant variations in the cutting outcomes of NiTi SMA with varied structures (Davis et al., 2021). This paper provides a review of the machining of NiTi SMA through turning, milling and drilling, exploring the cutting performance of NiTi SMA from three aspects: dry cutting, assisted cutting, and cutting simulation. Meanwhile, the choice of materials for tools will also affect the results of the cutting process. In addition, this paper also looks forward to the potential future development directions in the field of NiTi SMA machining, laying a solid theoretical foundation for subsequent research on NiTi SMA machining.
2 Turning
The most widely used processing technology for rotating parts such as shafts, sleeves, and cones is turning, which is the process completed by rotating the axis of the workpieces. NiTi SMA, as a difficult material, serious tool wear, difficult chip breaking and poor surface roughness are the problems to be solved in turning.
2.1 Dry cutting
2.1.1 Tool wear
Different types of tools could significantly impact the cutting performance and the final machining quality during the turning process. In all metal cutting processes, the main purpose is to use a tool to overcome the shear strength of the workpiece material (Mustafa et al., 2020). The comparison results of tool characteristics of commonly used machined NiTi SMA are shown in Table 1. Weinert et al. used uncoated cemented carbide tools, cemented carbide tools with TiB2 or TiAlN/TiCN coatings, cubic boron nitride (CBN) and composite ceramics for turning machining of NiTi SMA (Weinert et al., 2004b). Ceramic tools are unable to perform turning operations on NiTi SMA, which perhaps owing to its low flexural strength and easily fracture (Du et al., 2023). CBN tools showed better wear resistance in high-speed machining of vc > 100 m/min, but severe notch wear was observed in low-speed machining when vc < 60 m/min, which roughly owing to the formation of BUE on the tool surface (Ociepa et al., 2018).
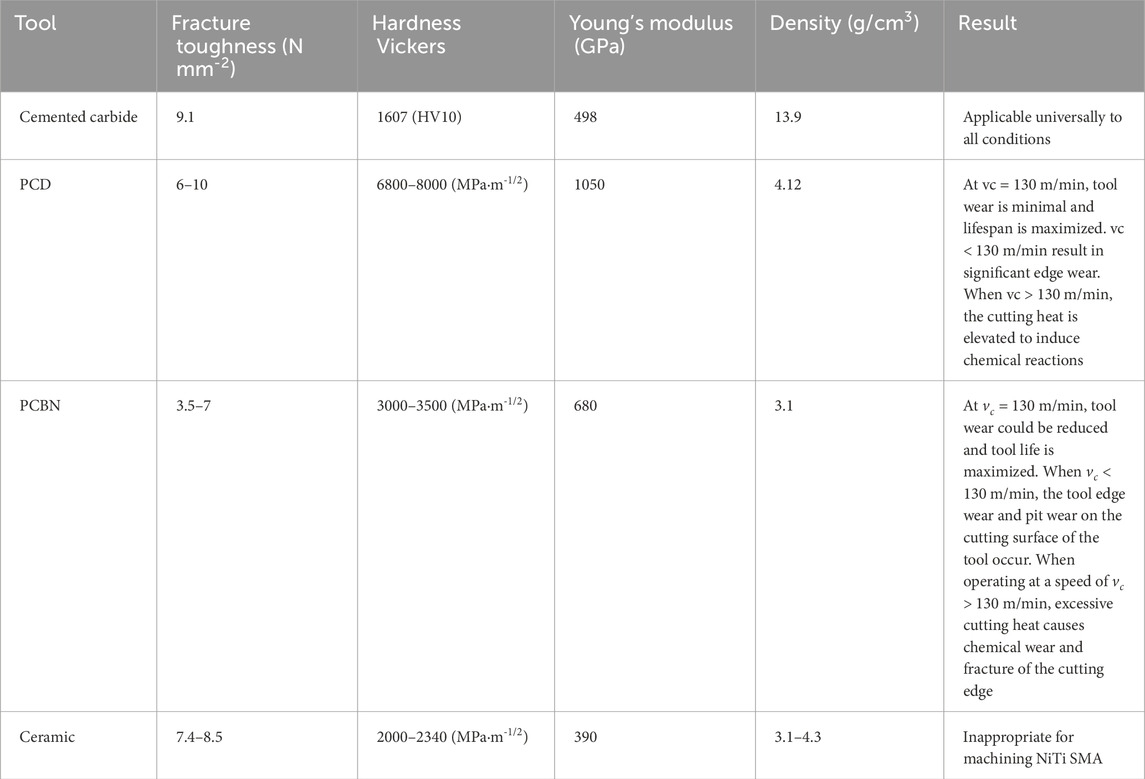
Table 1. Characteristics of three kinds of tools PCD, PCBN and cemented carbide (Wu et al., 2019; Ding et al., 2005; Kaya and Kaya, 2022; Eren and İrfan, 2020; Emmanuel et al., 2006; Ezugwu, 2006; Kaya and Kaya, 2019).
Cemented carbide tools exhibited excellent wear resistance. The uncoated cemented carbide tools suffered from severe notch wear and pitting on the rake face. The TiB2 coating will have a more serious chemical reaction with the workpiece during the machining process, resulting in coating peeling off. Compared to other coatings, it shows more severe flank wear and pitting compared to other coatings. The Cemented carbide tools with TiAlN/TiCN coatings exhibited excellent wear resistance (Weinert and Petzoldt, 2003). Weinert et al. established a feed rate of f = 0.05 mm/rev and a cutting depth of ap = 0.2 mm. When the cutting speed was within the range of vc = 20–60 m/min, the mechanical effects led to larger cutting forces. The maximum measured cutting force of 175 N occurring within this speed range, and serious tool notch wear occurred at the same time. In the range of vc = 60–130 m/min, as the influence of mechanical effected diminished, the cutting forces began to decrease, with a minimum value of 60 N measured within this range, accompanied by a gradual reduction in tool notch wear. There was almost no notch wear observed when vc = 100 m/min. Furthermore, when the cutting speed was in the range of vc = 130–180 m/min, the cutting thermal softening effect was intensified, and the larger friction between the tool and the workpiece led to the increase of cutting temperature, the increase of cutting force and the aggravation of tool wear.
Kaya and Kaya (2022) studied the wear of PCD tools after turning NiTi SMA at different cutting speeds, and compared them with multi-layer PVD coated cemented carbide tools and Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN) tools (Eren and İrfan, 2020) respectively. There are two primary wear types observed in PCD tools: frank wear and notch wear. When vc = 70 m/min, the tool is subjected to relatively serious wear due to the poor thermal conductivity of the workpiece and the influence of strain hardening. Cemented carbide exhibited a property of thermal binder phase thermal softening, resulting in lower cutting temperatures and maximizing tool life when vc = 70 m/min, with slightly less wear compared to PCD. The wear level of PCBN was significantly greater than that on PCD, attributed to the lower strength of PCBN tools, resulting in severe notch wear (VBN) and VBN = 0.355 mm was detected after cutting for 25 m. Additionally, PCBN tools underwent chemical reactions with Ti in the workpiece, generating TiC, which accelerates chemical wear on the tool. The tool is severely worn and may even lead to fracture (Yu et al., 2022). The tool wear of PCD and PCDN reached the minimum when vc = 130 m/min, which might be because of the minimum plastic deformation of the tool itself (Li et al., 2020). Tool wear began to intensify with the increase in tool plastic deformation when vc = 190 m/min. Overall, PCD tool surfaces demonstrated superior performance.
2.1.2 Surface integrity
NiTi SMA belongs to difficult-to-machine materials, with surface integrity being one of the primary criteria for evaluating machining quality. Zhao studied the turning process of austenitic Ti49.6Ni alloy. Figure 1 illustrates the surface topography at various cutting speeds. The cutting temperature was lower when the cutting speed vc < 50 m/min. The mechanical effect dominated the cutting process, there were more dislocations and the latent heat decreased greatly. The deformation of the cross section near the surface was irregular, the grain boundaries were not obvious, and the degree of work hardening was large. The chip shape is continuous, and the chip thickness decreased with increasing cutting speed (Zhao et al., 2020). The workpiece surface exhibited feed marks, metal debris, and long grooves. This was attributed to the built-up edge (BUE) formation on the tool, leading to the detachment of metal fragments and the occurrence of long grooves. In addition, plastic deformation caused by mechanical effects exacerbated the appearance of feed marks.
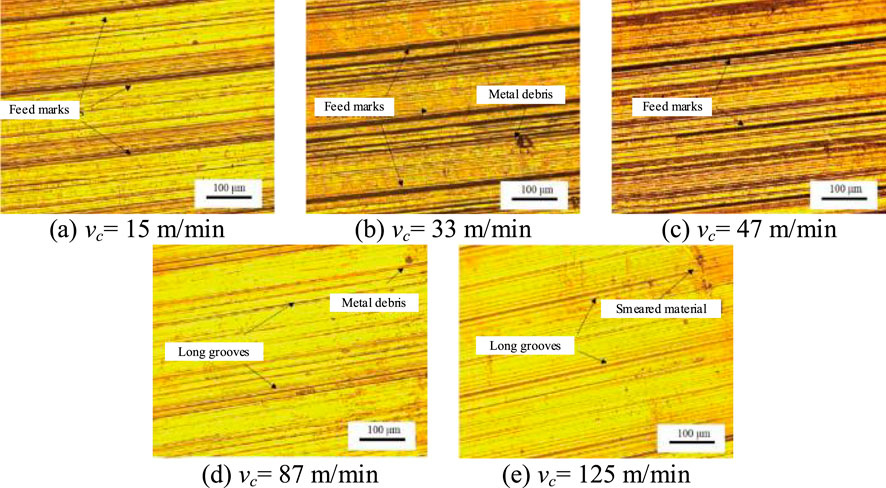
Figure 1. Surface topography images at different cutting speeds: (A) vc = 15 m/min, (B) vc = 33 m/min, (C) vc = 47 m/min, (D) vc = 87 m/min, (E) vc = 125 m/min.
Thermal effects began to dominate the cutting process when vc > 50 m/min. There was a decrease in the occurrence of dislocations with increasing cutting speed, and the degree of latent heat reduction gradually diminished. The workpiece began to exhibit adiabatic shear bands, and the chips transition from the continue shape to the serrated shape that was prone to fracture. The surface roughness decreased with the cutting speed increasing. The best result as observed was obtained under the condition of 125 m/min (Zhao et al., 2021a).The BUE on the tool disappeared with the increasing thermal softening effect, reducing the dislocations and defects on the workpiece surface, thereby achieving better surface quality. The surface roughness reached its minimum value of 0.3 μm at vc = 125 m/min.
Scholars also employed the response surface methodology and Box-Behnken design method to establish a mathematical model for the cutting parameters affecting the ratio of surface roughness and remnant depth. The optimal cutting performance parameters were determined to be vc = 126 m/min, f = 0.11 mm/r, ap = 0.14 mm after calculation (2023). To address the uncertainty in the Sa and Sz measurements of the turning surface roughness of NiTi shape memory alloys, the Monte Carlo approach may be employed, while a neural network can enhance the precision of the optimization model development. (Małgorzata and Krzysztof, 2020).
PCD and cemented carbide tools were used by Kaya et al. (Kaya and Kaya, 2022) to machine austenitic NiTi SMA. The stress produced by cutting will induce martensitic transformation and increase the dislocation density. The cutting force decreased with increasing cutting speed, inhibiting the martensitic phase transformation. The phase transformation of the workpiece was influenced by the cutting speed. The latent heat of the NiTi SMA machined with PCD tool and cemented carbide tool compared with the original workpiece decreased by 9.1 j/gr and 11.3 j/gr, respectively, and the phase transformation lags by about 7°C at vc = 70 m/min. The latent heat decreased by 2.18 j/gr and 2.95 j/gr, respectively, and the phase transition lagged by about 1.5°C. The phase transformation temperature delayed between the two types of tools was not significant. Moreover, the paper reported a similar trend between surface roughness variation and tool wear variation at different cutting speeds under the condition of f = 0.05 mm/r and ap = 0.2 mm. This diminished the impact of feed speed and cutting depth on the cutting outcomes. The surface roughness was reduced at vc = 130 m/min.
2.2 Assisted machining
Dry cutting leads to severe tool wear and relatively rough workpiece surfaces in turning of NiTi SMA. Employing appropriate auxiliary machining methods could effectively improve cutting performance.
2.2.1 Assisted processing with liquid
In turning operations, it has become common to use liquid-based substances for assisting cutting machining, including MQL and flood techniques utilizing cutting fluids or lubricants, and LN2 at −196°C for auxiliary machining purposes.
MQL involves spraying the minimum amount of lubricant into the cutting zone, providing sufficient lubrication and convective heat transfer (Balasuadhakar et al., 2022). Kaynak et al. conducted a series of studies on ambient temperature austenitic phase alloys using MQL as an auxiliary machining method. The lubricating fluid was transported to the cutting area, which reduced the cutting temperature, and the protective layer formed with the workpiece reduced friction and cutting force. MQL-assisted machining slowed down the occurrence of notching wear and flank wear on the tool, although the alloy remained in the austenitic state, similar to dry cutting (Kaynak, 2014). MQL-assisted machining reduced the wear rate of notch wear within 5 min when vc = 25 m/min, the average notch wear at the tool tip was half that of dry cutting (Kaynak et al., 2013a), but there was no significant difference in surface roughness between MQL-assisted machining and dry cutting this may be owing to the mechanical effect that dominates the cutting process (Mehta and Gupta, 2019). MQL cooling lubrication had a certain effect when vc = 100 m/min, reducing surface roughness by 60% compared to dry cutting. However, the tool produced more serious notch wear than dry cutting, and the amount of wear was more than 30% of dry cutting (Kaynak et al., 2015b), which may be related to the springback phenomenon caused by the phase transformation of NiTi SMA under the condition of MQL.
The addition of particles to MQL could help improve cutting performance, MQL vortex tube has also been proved to have an excellent auxiliary role in cutting (Sarikaya et al., 2021). Khalil et al. (2019) coupled MQL with vortex tube mixed cooling as an auxiliary machining method. They added Al2O3 nanoparticles to the MQL. The Al2O3 formed a protective layer at the interface between the workpiece and the tool, reducing friction between the tool and the workpiece and consequently lowering cutting forces. This protective layer also exhibited excellent thermal conductivity, reducing cutting temperatures (Khalil et al., 2018). The coupling of MQL vortex lubrication machining with the addition of cold air significantly enhanced cooling and lubrication effects in the cutting zone. The flank wear caused by cutting tools increases with the increase of cutting speed. The wear rate decreased by 4.2%–34.5% compared to dry cutting and Nano MQL when the cutting speed was within the range of 12.5–50 m/min. Coupled auxiliary machining mitigated tool damage, including adhesion, diffusion, and abrasive wear. However, compared with not using vortex tubes, the cutting force of the coupling cooling method was greater when vc = 25 m/min. This might be thanks to the cutting temperature was below the austenite starting temperature, resulting in lower material yield strength, thereby leading to an increase in cutting forces. The reduction in machining friction enhances the surface smoothness of the workpiece due to the coupling effect. It had been reported that coupled machining controlled the formation of chips and burrs. The average surface roughness was reduced by approximately 15%–18% compared to dry cutting and Nano MQL.
LN2 cryogenic cooling is typically achieved by vaporizing liquid nitrogen to absorb heat and cool the cutting zone. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of −196°C, providing excellent cooling effectiveness (Huang et al., 2020). Yu et al. (Jianhang et al., 2022). utilized liquid nitrogen as an auxiliary process to cut both austenitic and martensitic alloys. The surface roughness after machining austenitic alloys was found to be greater than that of martensitic alloys. The difference of the result was 1.24–1.66 times in the range of vc = 40–130 m/min, f = 0.05–0.2 mm/r and ae = 0.2–0.35 mm. Regulating the phase transformation of NiTi shape memory alloy may alter the surface quality of the workpiece. Kaynak observed that the mechanical effect of the machining exceeded the thermal softening effect when vc = 12.5 m/min. This result in significant dislocation on the workpiece surface, leading to stress-induced martensitic phase transformation. The austenite began to transform into twinned martensite (Yanzhe and Jie, 2023). Low-temperature processing promoted the formation of more martensitic phases, reducing cutting forces and tool wear. However, Zhao observed opposite results during low-speed cutting (vc < 33 m/min) (Zhao et al., 2021b). The cutting forces and tool wear were maximal used the cryogenic cooling. The reason for this different result might be that they are cooled in distinct locations. Kaynak et al. applied cooling to both the front and flank of the tool. In contrast, Zhao et al., 2023 only cooled at the tool-chip interface. Martensite tended to adhere to the tool at low speeds, leading to the formation of BUE and resulting in poorer surface quality.
The thermal effect of cutting began to dominate by vc = 25 m/min, the dislocation density decreased, the stress decreased and the martensitic transformation weakened. The stress influence layer decreased gradually and the degree of work hardening decreased (Velmurugan et al., 2018). Zhao found that the stress-induced martensitic transformation disappears when vc > 48 m/min (Yanzhe and Jie, 2023). A greater number of deformation twins exhibiting the (114)B2 mechanism were identified during low-temperature cooling, resulting in an increase in the twins. (Y. et al., 2013), and the residual stress and dislocation density of the workpiece increased significantly. The temperature at the cutting edge increased with the increase of cutting speed, leading to thermal softening of the tool material, which accelerated tool wear. As shown in Figure 2A, low temperature cooling reduces the cutting temperature and reduces the notch wear and adhesion wear of tools in dry cutting (Kaynak et al., 2013b; Kaynak, 2014). Compared to low-speed machining (vc < 100 m/min), the tool shows more severe notch wear when high-speed cutting (vc > 100 m/min) was used. Low-temperature cooling maintained a high density of dislocations and twins, reducing radial forces and resulting in a more pronounced improvement in notch wear. Low-temperature cooling demonstrated a more pronounced improvement in surface morphology during high-speed machining in Figure 2B (Zhao et al., 2021b).
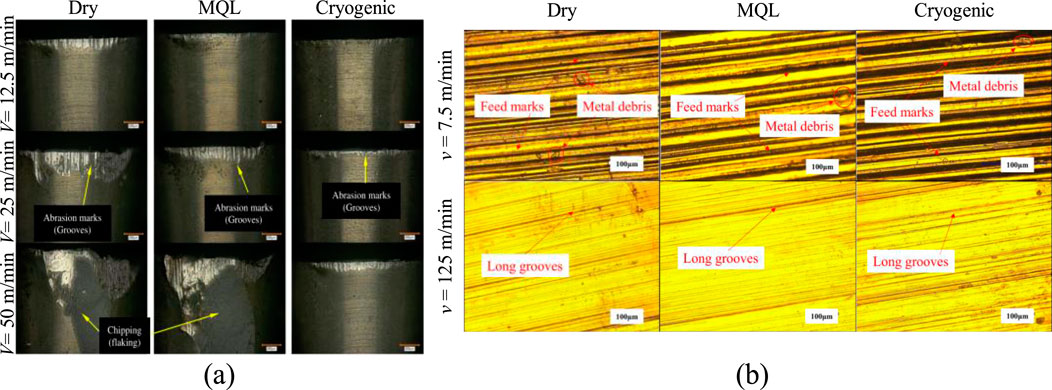
Figure 2. (A) Tool wear in the cutting zone of room-temperature austenitic NiTi SMA. (B) Machined surface morphology under different cutting conditions of vc = 7.5 m/min and vc = 125 m/min (Kaynak, 2014; Zhao et al., 2021b).
Zhao employed flood cooling for turning operations (Zhao et al., 2021b). The mineral oil cutting fluid used in auxiliary machining formed a lubricating film between the tool and the workpiece when vc < 33 m/min, conducted a lot of heat and reduced the cutting force and cutting temperature. Flood cooling has a significant improvement on the flank wear and crater wear of the tool compared to dry cutting. The material surface obtained a more uniform microstructure, and the surface roughness of the material was also better than that of dry cutting. The cutting performance was optimal especially when vc = 15 m/min. Nonetheless, the cutting fluid cannot be delivered promptly, resulting in diminished lubrication efficiency and reduced benefits when vc > 33 m/min. Kitay and Kaynak (Kitay and Kaynak, 2021) found in their study on room temperature austenitic alloy turning that the depth of the affected layer of the workpiece after flood-assisted machining at a cutting speed of 20 m/min was up to 130 μm. The microhardness increased, with an average value of 382 HV, indicating an estimated 29% enhancement compared to the original workpiece. The thermal softening effect in the cutting zone increased, leading to a reduction in the average microhardness to 351 HV as the cutting speed increased.
Kirmacioglu and Kaynak (Kirmacioglu et al., 2019) conducted turning operations on the ternary alloy NiTiHf under flood conditions. It was found that both the cutting tools experienced abrasive wear and adhesive wear after comparing the processing results using the same cutting parameters as machining NiTi SMA (Kaynak et al., 2014). Furthermore, the tools encountered elevated friction and heat production, resulting in intensified tool wear as cutting speed increased. The chips of NiTiHf were more prone to fracture. Continuous and curved chips were produced at cutting speeds ranging from 20 to 45 m/min. Continuous and loose chips were noted when vc = 70, 95, and 120 m/min. The chip thickness decreased with increasing cutting speed, and appropriately raising the cutting speed could alleviate chip breakage difficulties. Considering the comprehensive cutting results, the cutting performance was optimal at vc = 70 m/min. Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of three liquid-assisted machining methods: MQL, LN2 and flood for turning NiTi SMA.
2.2.2 Assisted processing with air
CO2-Assisted has the advantages of low cost, non-toxicity, no pollution, so it has been widely concerned in practical application (Lin et al., 2023). This is a gas-assisted processing method. Kitay and Kaynak (Kitay and Kaynak, 2021) found that after machining an alloy with austenite phase at room temperature was machined by CO2-Assisted, although the cutting temperature still remained above the material’s martensite start temperature, making it difficult for the workpiece to reach the martensite phase. However, there was a significant decrease in cutting temperature compared to dry cutting at all the set cutting speeds. The microhardness value under CO2 circumstances was the highest among all cutting environments, attaining 401 HV at a cutting speed of 20 m/min, attributable to the material in the martensite phase. The paper reported chips accumulated and tangled in the cutting zone. It difficult for CO2 to penetrate the cutting zone, resulting in poor cooling effected at a cutting speed of 70 m/min.
2.2.3 Pre-treatment
Pretreatment is an auxiliary processing method to keep the workpiece at a specific temperature before cutting, including pre-heating treatment and pre-cooling treatment (Dong-Hyeon Kim and Lee, 2014; Zhang et al., 2023a).
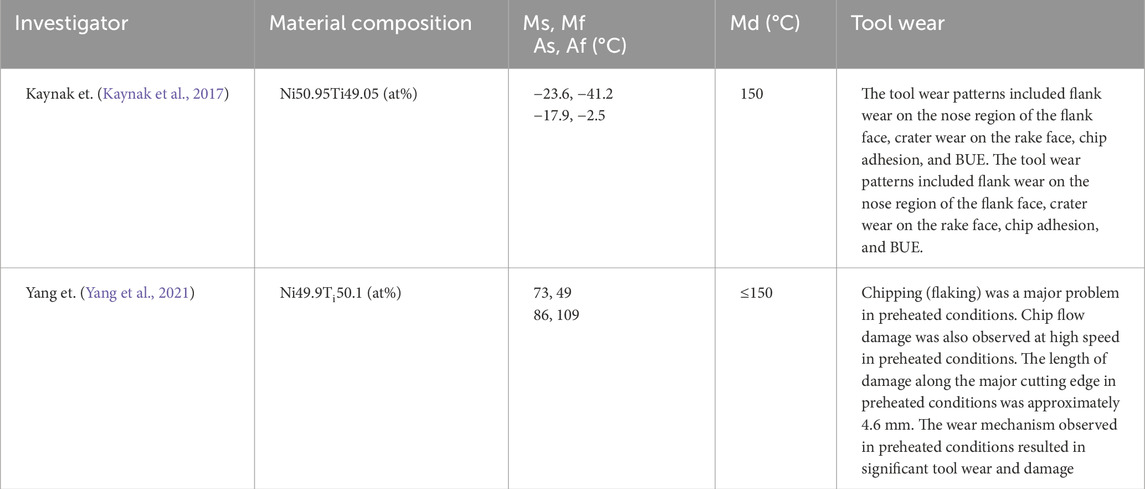
Kaynak et al. conducted preheating treatment on the Ni49.9Ti50.1, which was in the martensitic phase at room temperature. The preheating temperature was set at 175°C, at which the material fully austenitized. The appearance of the austenitic phase, compared to the martensitic phase, results in reduced surface dislocations, with higher latent heat after preheating (Kaynak et al., 2017). The tool suffered from severed notch wear, which increased gradually with the rise in cutting speed under preheating conditions (Kaynak et al., 2013c; Kaynak et al., 2015b). Similarly, Yang subjected the Ni50.95Ti49.05, which was in the austenitic phase at room temperature, to preheating at 175°C (Yang et al., 2021). The heating temperature exceeded the martensite desist temperature (Md) of 150°C, keeping the material in the austenitic phase during processing. The workpiece underwent martensitic transformation during cutting on the surface without preheating, resulting in springback phenomena and exhibiting characteristics of superelasticity, the workpiece accuracy was inferior (Davis et al., 2021). The tool exhibited severe wear under non-preheating conditions in Figure 3A, which contrasted with the results presented in Kaynak’s study depicted in Figure 3B. The materials undergo different phase transformations after preheating at the same temperature. Table 3 summarizes the results of tool wear after two preheating processes. Consequently, the alloy exhibits different superelastic behavior, thereby affecting the result of tool wear.
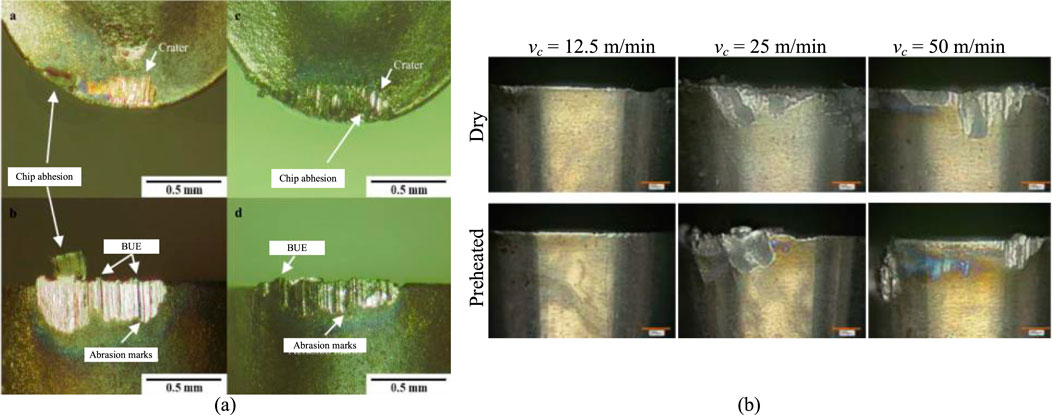
Figure 3. (A) Tool wear patterns at vc = 25 m/min after machining under a and b non-preheating condition, c and d preheating condition (Yang et al., 2021). (B) Tool wear patterns under different cutting speeds and cooling/preheating conditions (Kaynak et al., 2013a).
Kaynak turned the workpieces, which was in the austenitic phase at room temperature, to cryogenic treatment before machining. The workpiece was cooled to −185°C using liquid nitrogen, resulting in the workpiece being in the martensitic phase after cryogenic treatment (Kaynak et al., 2015b). The alloy in the martensitic state exhibited more twinning and a higher dislocation density compared to the original workpiece (Kaynak et al., 2014). The workpiece exhibited greater plastic deformation and deeper machining affected layers after cutting (Kaynak et al., 2015a). The workpiece in the martensitic phase was softer compared to the austenitic phase, which contributed positively to reducing the cutting force on the tool. The workpiece after pre-cooling becomes more brittle when vc = 100 m/min, eliminating the formation of debris, and the workpiece surface has a smoother appearance.
2.3 Simulation
There are few simulation experiments on the machining of NiTi SMAs owing to the lack of constitutive equations and failure models describing stress, strain, temperature, and other material state variables and their temporal relationships. Kaynak et al. (Kaynak et al., 2020; Kaynak et al., 2015c) employed the DEFORM 2D finite element analysis software, based on a modified Helmholtz free energy phase transformation model, to simulate the volume fraction of mechanically induced martensitic transformation in the cutting process. The accuracy of the model was verified by the experiments done by the model.
Mehrpouya et al. (2017) conducted finite element simulations of NiTi SMA machining using ANSYS/LS-DYNA R15. The plasticity and damage parameters of the material were derived from those of titanium alloy processing. Cutting parameters were selected from turning experiments conducted by Weinert and Petzoldt (2003), Weinert et al. (2004b). The Mises stress and shear stress of the material after cutting were obtained through finite element calculations. A coupled relationship was established, yielding a new equation after obtaining the influence functions of the two stresses with respect to cutting speed. The optimal solution was determined for a cutting speed of 109 m/min, with an error of 9% compared to the experimental value of 100 m/min.
Johnson-Cook (JC) material model is commonly used to predict the strength limit and failure process of metal materials under large strain, high strain rate, and high temperature conditions (Jomaa et al., 2017). Zhao conducted dynamic compression experiments on Ni50.8Ti SMA using a Hopkinson pressure bar apparatus (Yanzhe, 2021). The Scholar applied the ABAQUS finite element analysis software to establish a two-dimensional orthogonal cutting model to simulate turning processes. The simulation results for cutting force, cutting morphology, and chip geometry compared to experimental parameters had errors within 25% at a lower cutting parameter setting with a cutting speed vc = 50 m/min and a feed rate f = 0.05 mm/r. Figure 4 illustrated the comparison between experimental and simulated chip morphology. The simulation results exhibited higher errors with increasing cutting settings, occasionally surpassing 25% due to the failure to account for the influence of airflow on workpiece temperature fluctuations in thermal-coupled analysis. Although the parameters of JC constitutive equation could be used effectively at this stage, the cutting damage parameters of JC are uncertain. Fracture energy is used as the failure criterion for Ni50.8Ti SMA in the damage evolution stage in this model (Hillerborg et al., 1976).
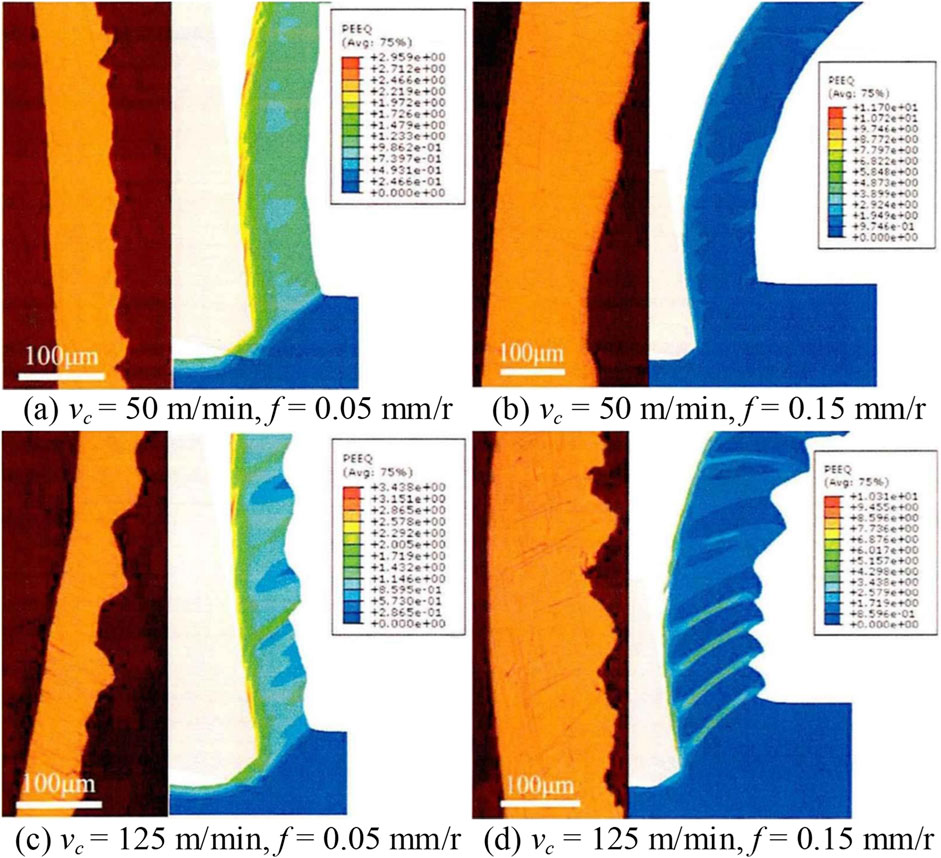
Figure 4. Comparison of chip morphology between experiment and simulation under different machining parameters: (A) vc = 50 m/min, f = 0.05 mm/r, (B) vc = 50 m/min, f = 0.15 mm/r, (C) vc = 125 m/min, f = 0.05 mm/r, (D) vc = 0.15 mm/r.
2.4 Summary
The turning machining of dry cutting often leads to significant tool wear. Coated carbide tools, especially those with TiAlN/TiCN coatings, offer better wear resistance and PCD tools also demonstrated excellent wear resistance. The cutting speed is critical; reduced speeds result in increased wear from DUE, whereas elevated speeds exacerbate heat effects, contributing to tool wear and inferior surface roughness. Assisted machining methods like Assisted processing with liquid, CO2-Assisted and Pre-treatment help improve tool life and surface quality, but each has limitations depending on the cutting conditions. Simulating the machining of NiTi SMAs is challenging due to the lack of accurate constitutive equations and failure models.
3 Milling
The workpiece might be milled into complex surface shapes in a short amount of time, as milling processing utilizes multi-axis machining techniques to achieve this. Its intermittent processing characteristics also lead to Severe work hardening and more burr when machining NiTi SMA.
3.1 Dry cutting
3.1.1 Tool wear
Huang (Huang, 2004) observed all the features of tool wear shown in Figure 5 after milling NiTi SMA with cemented carbide. The tool generated BUE as a result of the adhesion on the rake face. Researchers assessed tool wear by examining the wear state on the flank face. The tool wear on the rake face decreased with the increased of the cutting speed when vc > 200 m/min. This could be attributed to the reduction in cutting force and chip thickness at higher cutting speeds. The chip cross-sectional area decreased as the cutting speed increases, resulting in a reduced cutting force. Reducing cutting force led to less tool wear on the rake face. Additionally, the decrease in chip thickness at higher cutting speeds diminished the contact area between the chip and the tool, further reducing tool wear. The thermal softening effect and plastic deformation of the material increase when vc > 200 m/min, resulting in shorter and thinner chips, which will aggravate the adhesion wear of the tool.
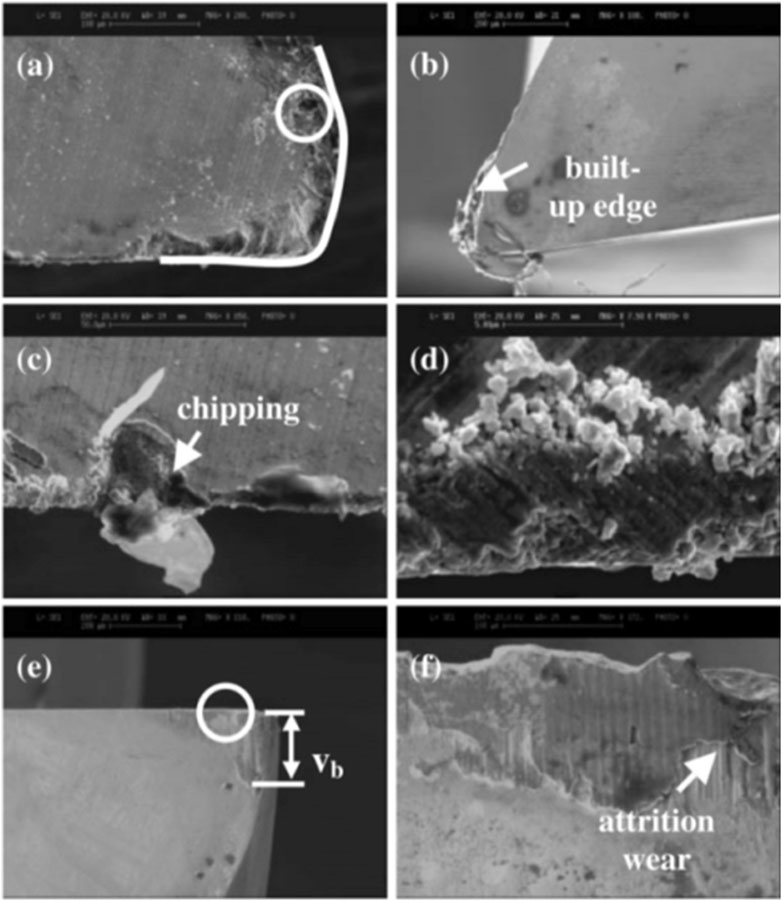

Figure 5. SEM micrographs showing tool wear characteristics. (A) Fracture and wear on the cutting edge. (B) BUE. (C) Chipping. (D) Tool adhesion. (E) Flank wear. (F) Cutting edge wear due to flank adhesion wear (Huang, 2004).
Altas et al. (Emre et al., 2020) employed the L18 orthogonal Taguchi method to investigate the influence of tool nose radius (rε) and cutting parameters on the extent of flank wear (Vb). Tungsten carbide steel is the tool material used in this experiment. There were three mainly kinds of wear of the tool: Vb, BUE and mechanical fatigue fracture. The increase in cutting speed and feed per tooth (fz) elevated the cutting temperature in low-speed machining (vc < 50 m/min), exacerbating flank wear of the tool. The greater the rε, the greater the tool stiffness and wear resistance. It was found that the most important factor affecting tool side wear was fz by using analysis of variance, followed by rε. This may be due to the fact that, on one hand, as the fz, the heat and pressure generated during the cutting process also increase (Zhang and Xu, 2020). NiTi SMA has a lower thermal conductivity, so this heat could not be efficiently removed. On the other hand, tools with reduced rε values exhibit diminished strength (Caliskan et al., 2017). This ultimately leads to an increase in Vb value on the tool, and accelerated tool wear.
3.1.2 Surface integrity
Huang et al. (Huang, 2004) investigated the surface roughness and microhardness of milled NiTi SMA under different cutting parameters. The cutting speed had the greatest impact on surface integrity results. Twins and dislocations appear on the machined surface due to the mechanical effect that dominates the whole cutting process when vc was in the range of 5–50 m/min, resulting in the maximum value of 360 HV for microhardness, and the worst result of surface roughness was Ra = 0.8 μm. The thermal effect began to dominate the cutting process when the cutting speed was within the range of 50–200 m/min. The minimum result of 310 HV was obtained for microhardness at vc = 150 m/min. The best result was that the surface roughness was reduced to 0.1 μm in vc = 200 m/min, which may be related to the reduced chip thickness. When the cutting speed was in the range of 200–500 m/min, all cutting results showed a slight increase, but generally tended to stabilize. Both increasing the feed rate and cutting depth will lead to an elevation in cutting force, which in turn will result in heightened surface roughness and microhardness, albeit with a relatively little effect.
Enhancing the hardening degree of NiTi SMA impacts the material’s phase change, augments plastic deformation, and diminishes the shape memory effect (SME) (Wang et al., 2019b). Wang et al. utilized the L9 orthogonal array Taguchi method to examine the impact of cutting settings on work hardening (Wang et al., 2018). There was a positive correlation between the magnitude of microhardness and the induced work layer during machining as shown in Figure 6. The plastic deformation exhibited a positive correlation with the rise in cutting speed when vc < 200 m/min. However, the shear slip zone would become narrower and the material’s yield limit will increase, which weakens the degree of plastic deformation, the dislocation density decreased and the grain size decreased. The depth of the machining-induced layer and the degree of work hardening decreased with increasing cutting speed. The amount of plastic deformation surpasses the degree of weakening when vc > 200 m/min. This leads to a rise in lattice distortion and the density of metal dislocations. Additionally, the depth of the induced layer started to expand, resulting in a higher degree of hardening. The larger feed rates and cutting widths resulted in increased friction between the material and the tool, leading to a larger area of plastic deformation and higher cutting temperatures. The alloy experienced a partial martensitic transformation, resulting in the development of tougher austenite, which increases the hardening of the workpiece. Ultimately, the paper reported that the parameters with the least degree of hardening and the strongest SME were vc = 200 m/min, f = 0.08 mm/r and ae = 0.3 mm.
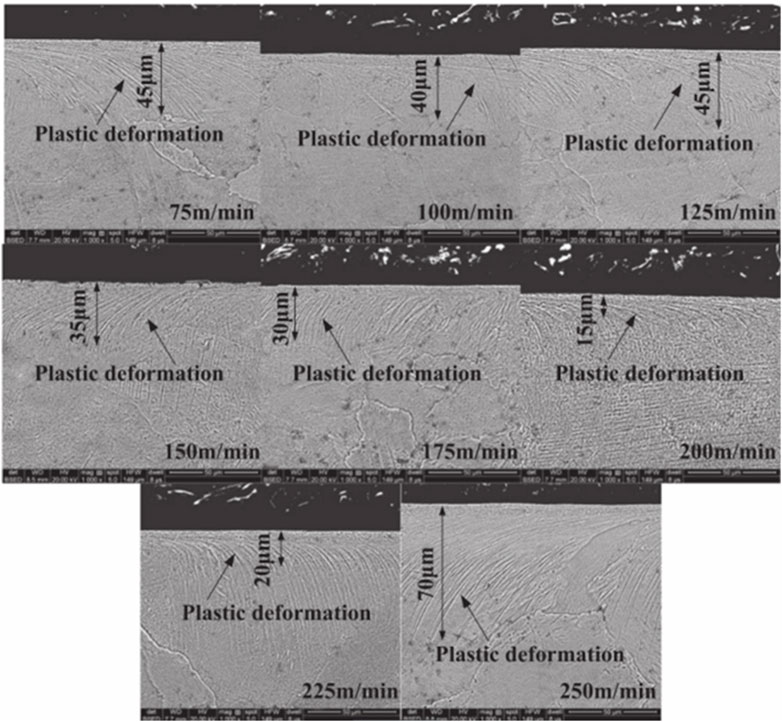
Figure 6. Microstructure of NiTi SMA at different milling speed (Wang et al., 2019b).
Wang et al. investigated the trend of the influence of cutting parameters on surface roughness through orthogonal array experiments (Wang et al., 2019a). By increasing the cutting speed in milling operations, the cutting temperature could be raised, while simultaneously reducing the friction coefficient and cutting forces. This, in turn, led to a decrease in the plastic deformation of the workpiece material and ultimately implied a drop in surface roughness. The feed rate also affected surface roughness. Increasing the feed speed led to a thicker undeformed chip, which in turn caused a higher cutting force and wear on the rake face, resulting in a more uneven surface. The variation in cutting width has minimal impact on the level of surface roughness.
Altas et al. explored the impact of the rε and cutting parameters on surface roughness using an L18 orthogonal Taguchi method (Emre et al., 2020). The value of Ra decreased as rε increased. This is because that larger cutting tools possess more rigidity, leading to a decrease in the thickness of the uncut chip as the cutting tool size increases. Consequently, this reduced tool wear and minimizes surface roughness. The tool suffered severe flank wear, which had a negative impact on the surface roughness as the cutting speed increased from vc = 20 m/min to 35 m/min. The tool tended to form BUE, increasing rε and reducing the uncut chip thickness at lower cutting speeds, thus lowering the surface roughness. With the increase in fz, the temperature in the cutting zone increases and the resulting heat was concentrated at the tool-chip interfaces, which would also lead to the increase of surface roughness.
Dry milling of NiTi SMAs presents challenges such as tool wear and surface integrity. Tool wear, including BUE formation, microchipping, and flank wear, is influenced by cutting speed and tool nose radius. Higher speeds reduce wear on the rake face due to decreased cutting force, but excessive speeds could increase adhesive wear. Surface integrity, including roughness and microhardness, is significantly affected by cutting parameters. Optimal conditions (vc = 200 m/min, f = 0.08 mm/r, ae = 0.3 mm) minimize work hardening while enhancing surface quality and maintaining the SME.
3.2 Assisted machining
3.2.1 Assisted processing with liquid
The application of MQL in milling not only reduces the amount of cutting fluid used but also enhances the ability of cutting fluid to penetrate the cutting zone (Li et al., 2019). Weinert and Petzoldt (2006) investigated the effects of different cutting parameters on burr formation and tool adhesion during milling of NiTi SMA. Efficient reduction of the contact area between the tool and workpiece could be achieved by decreasing the ap. Consequently, this aids in reducing the formation of burrs, decreasing cutting pressures, and minimizing tool deterioration. Expanding the cutting width has the effect of increasing the size of the chips, which makes it easier for the chips to form and reduces the creation of burrs and the incidence of adhesive wear on the tool. Increasing the feed rates and cutting speeds resulted in a decrease in cutting time, an increase in cutting depth, a reduction in the passive component of cutting forces, which in turn made it easier to remove chips and reduced the wear on the tool. MQL-assisted machining could alleviate adhesive buildup on the tool surface and reduce tool wear. There was almost no adhesion after milling six continuous grooves with the same tool with the cutting parameters (vc = 33 m/min, fz = 12 μm/tooth, ap = 10 μm, ae = 40 μm) selected in Figure 7, the quality of the workpiece was maintained at a high level, and the burr formation was minimized.
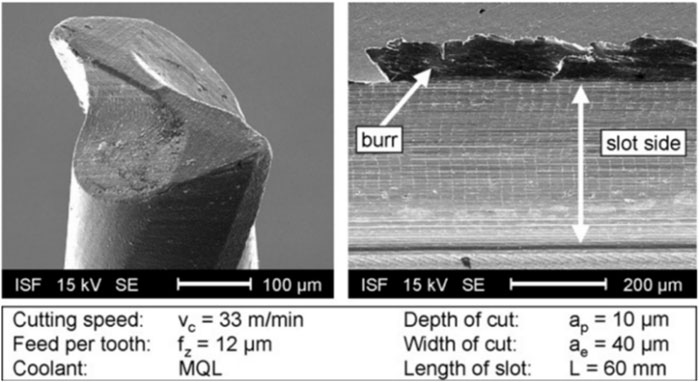
Figure 7. Tool condition and workpiece quality after milling six slots using optimal cutting parameters (Weinert and Petzoldt, 2006).
Kuppuswamy and Yui (2017) used the L9 orthogonal array method to investigate the effects of cutting parameters on cutting force and burr size during microend milled slots. Cutting force and burr size were most significantly influenced by cutting speed. The cutting force gradually increased with the increase of cutting speed when vc > 15 m/min. Hardness was maximum at vc = 15 m/min, attributed to stress-induced martensitic phase transformation in the material, which exhibited higher hardness compared to the austenitic phase material and was more prone to strain hardening. The high ductility of the material that led to tool deflection during low-speed machining (vc < 35 m/min), resulting in incomplete milling, albeit with fewer burrs. The burrs also increased with the increase in cutting speed as the material’s elastic deformation increases. There was also a situation where the milling was incomplete at vc = 30.15 m/min. Taking into account both the cutting force and the burr situation, the optimal result for slot milling was achieved at vc = 15 m/min. Piquard et al. (2014) explored the influence of different cutting parameters, up-milling and down-milling on the size of burr in two kinds of NiTi SMA of austenitic phase and martensitic phase at room temperature with MQL. It was found that the height and width of the burrs were most influenced by fz and ae, and decreased with increasing fz and decreasing ae through mathematical analysis using variance analysis. The thickness of the burrs was most influenced by the material, with burrs being thicker in martensitic phase alloys. The second was the machining strategy, with burrs being thinner after down-milling compared to up-milling, resulting in a curly shape.
Biermann et al. (Biermann et al., 2009) conducted milling operations on martensitic Ni49.7Ti50.3 and austenitic Ni49.9Ti50.1 alloys using a ball-end mill at various tool inclination angles. Different inclination angles result in different time-discrete chip cross-sections, thereby generating varying gradients in chip thickness, cutting force, and cutting speed distribution, which subsequently affected tool wear. The tool wear was minimized, and the surface quality of the workpiece was optimal when the inclination angle was 50°, as shown in Figure 8. The tool wear of cutting martensitic alloy was more severe, resulting in more burrs along the milling path because of the higher fracture elongation of 15.8% and the higher tensile strength of 174 MPa in the martensitic phase compared to the austenitic phase.
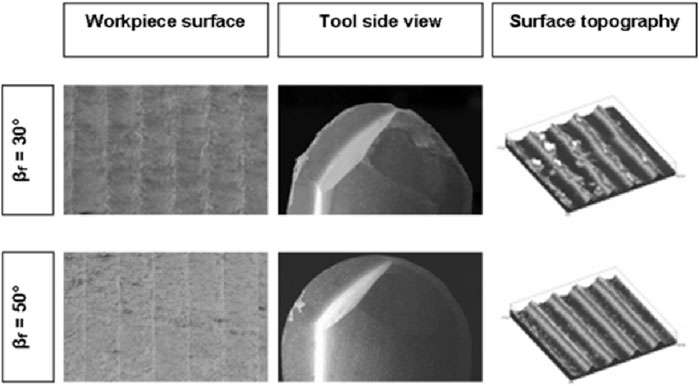
Figure 8. The effect of inclination angle variation on surface quality and tool wear (Biermann et al., 2009).
Davis et al. (2023). primarily investigated the impact of several cooling methods (flood coolant (WME), cryogenic liquid nitrogen (CME), and a hybrid technique (HME)) on the surface roughness and micro-hardness of Ni55.6Ti44.4 alloy during milling. By employing the L27 Taguchi technique, Shapiro-Wilk normality test, and Breusch-Pagan variance test analysis, it has been shown that the optimal cutting conditions involve milling with low-temperature treated tools using the HME method. The recommended cutting parameters are vc = 55 m/min, fz = 0.075 mm/tooth, and ap = 1 mm. Cryogenically treated tools could increase the grain size of the tool material, enhance the grain structure, and enhance the thermal conductivity of the tool, thus minimizing heat-induced damage to the tool. Research in the literature has shown that cutting tools treated with cryogenic treatment exhibit improved performance in HME. This could be attributed to the fact that cryogenically not only refines the grains of the tools, but also causes strain hardening due to rapid cooling. As a result, cutting temperatures were reduced and thermal softening was minimized. Conversely, the WME might lead to the softening of the region owing to the relatively high temperature of the cooling environment, which could have an impact on the quality of the surface. By combining cutting fluid and LN2, the cooling and lubricating requirements of the cutting area could be fulfilled, resulting in improved machining outcomes.
The demand for the conversion of biomaterials into high-quality, industrially produced medical implants has surged significantly (Rahul et al., 2022). Researchers studied the functional markers of NiTi SMA following machining and investigated its capacity for use in biological contexts. By utilizing HME, the surface properties of Ni55.6Ti44.4 alloy have been greatly enhanced to fulfill the requirements of biomedical implants, such as cardiac stents. The altered surface is tuned with regards to roughness, morphology, and wettability, hence enhancing the adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of cells on the material surface. The cell culture situation is shown in Figure 9. Furthermore, surface modification also diminishes the emission of detrimental elements like Ni, enhances the biocompatibility of materials, and facilitates prolonged cell cultivation and the execution of tissue engineering. The research findings have substantial implications for the development and production of biomedical implants, since they could enhance the efficacy of implants and minimize problems.
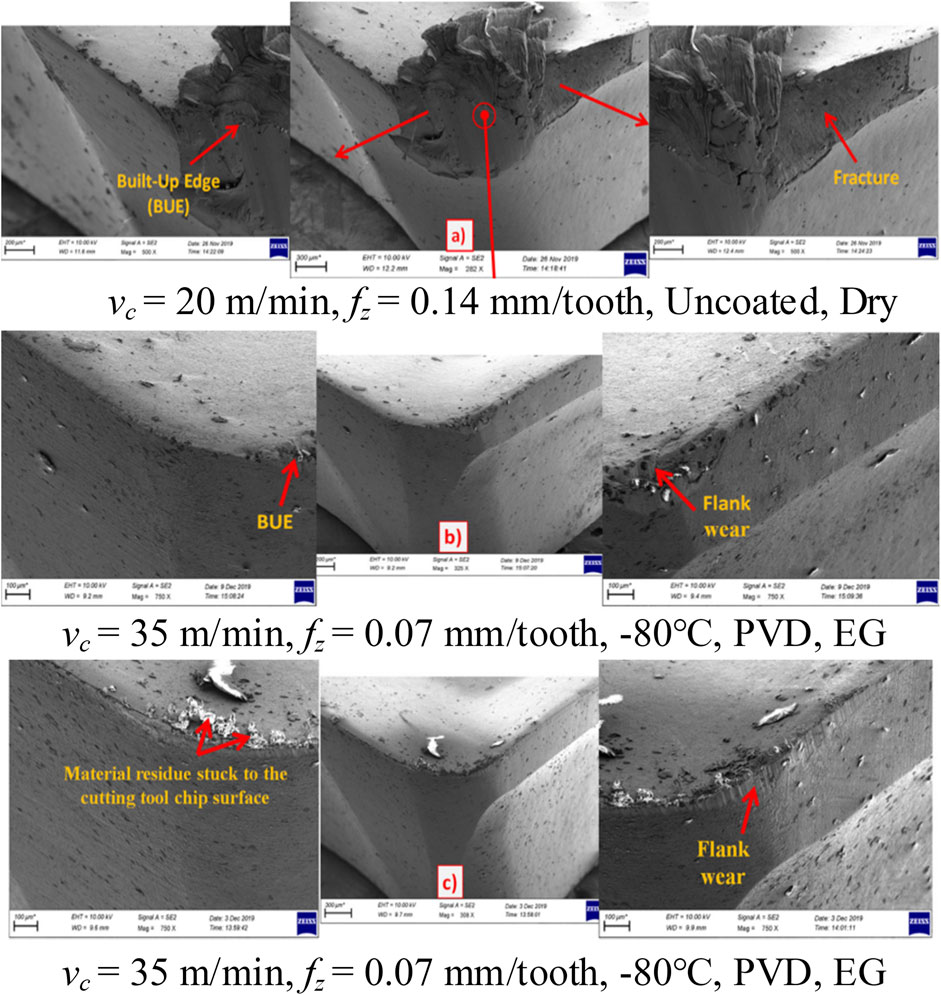

Figure 9. SEM images showing tool wear of NiTi SMA face milling cutters under different cutting parameters (Altas et al., 2021).
3.2.2 Assisted processing with air
Cold air-assisted machining helps reduce cutting force, eliminate chips, and reduce tool wear in milling (Jozić et al., 2015). Zailani et al. used an auxiliary machining method that combines chilled air with MQL (Zailani and Mativenga, 2016). The workpiece selected was Ni45Ti55 (wt%), which was in the martensitic phase at room temperature. The use of chilled air in this material promoted the transformation of martensite to austenite (Abidin and Tarisai, 2023). Simultaneous use of chilled air and MQL results in minimal changed in grain size of the workpiece and did not generate significant dislocations compared to dry cutting. The application of a cold air vortex can efficiently eliminate debris from the workpiece surface, while the use of MQL reduces the likelihood of debris adhering to the tool. The flank wear of the tool was significantly reduced after combined auxiliary processing (Zainal Abidin et al., 2020). The burrs were softer and easier to remove because of the lower hardness of the material processed with cold air.
3.2.3 Pre-treatment
Altas utilized three various kinds of tungsten carbide tools milling cutters for milling operations: uncoated, PVD coated, and CVD coated. The tools were given two types of cryogenic treatments at temperatures of −80°C and −196°C. Figure 10 depicts the wear and tear of the cutter after milling NiTi SMA under different cutting conditions. On one hand, the CVD-coated tool exhibited less wear compared to the PVD-coated tool, as it formed eta carbides after undergoing low-temperature treatment at −196°C, thereby enhancing tool hardness and wear resistance. The low-temperature pre-treatment of the tools improved their thermal conductivity, reducing the temperature between the tool and chip interface, which in turn mitigates the degree of tool flank wear (Altas et al., 2021). On the other hand, using ethylene glycol (EG) and borax decahydrate (BX) cutting fluid assisted in forming a protective film on the surface, effectively improving the tool wear. Similar to dry cutting, opting for a higher cutting speed minimizes tool degradation. Higher fz leads to a greater material removal rate, accompanied by an increase in cutting force and cutting heat, which in turn leads to reduced tool hardness and higher side wear (Emre et al., 2022).
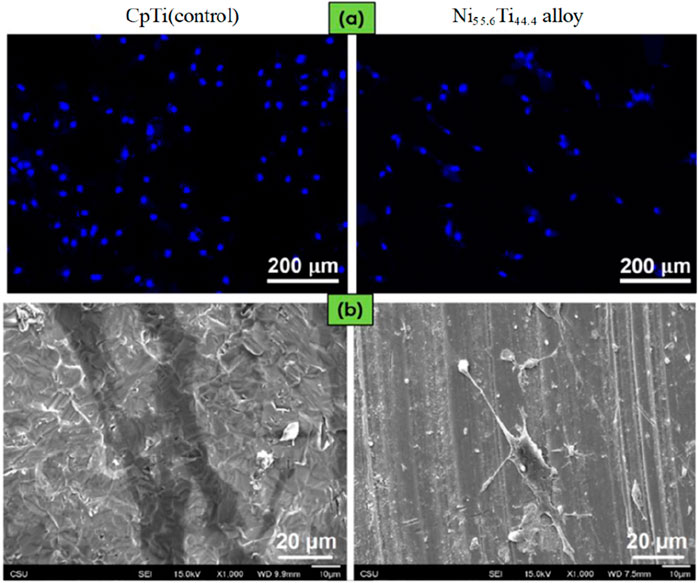
Figure 10. (A) Fluorescence microscopic images demonstrating ADSCs stained with DAPI (blue) after 4 days of cell culture on both surfaces, (B) SEM images of ADSCs on both surfaces after 4 days of cell culture (Davis et al., 2023).
Altas explored the influence on the workpiece surface roughness under the same machining conditions (Altas et al., 2021). There was a reduction in cutting temperature when, EG + BX combined lubricant was used, and there were particles that decreased the friction between the tool and workpiece. Milling cutters subjected to cryogenic treatment at a temperature of −196°C demonstrate enhanced thermal conductivity and increased toughness. The friction coefficient of CVD-coated tools is lower than that of PVD-coated tools. The average Ra of the workpiece after machining, CVD coating is 2% lower than that of PVD-coated tools and 17% lower than that of uncoated tools (Altas et al., 2021). The tool exhibited a tendency to create BUE at lower cutting speeds, leading to a surface roughness that was roughly 15% lower at a cutting speed of 50 m/min compared to a cutting speed of 20 m/min. The chip removal rate and thickness were raised by increasing the feed rate, which in turn increased the cutting temperature and resulted in an increase in Ra. Specifically, at fz = 0.03 mm/tooth, Ra was approximately 27% lower compared to fz = 0.14 mm/tooth. Finally, the authors determined the importance of factors affecting surface roughness through the orthogonal array method and variance analysis, ranking them as follows: feed rate, tool coating, cutting fluid, cutting speed, and cryogenic heat treatment of the tool (Emre et al., 2022).
3.3 Summary
Currently, research on milling NiTi SMA mainly discusses the effects of factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, cutting depth, cutting strategy, cooling conditions, tool material and geometry on the milling process. Milling is intricate, with burr development being the primary issue, associated with the high ductility and superelasticity of NiTi SMA. Employing MQL or cold air in machining helps mitigate burr formation to some degree. An elevation in fz and ae will result in an augmentation in burr height and width, but an increase in ap will cause a reduction in burr height. Proper cooling methods enable the alloy to maintain a more homogeneous austenite structure, hence diminishing cutting forces and enhancing surface finish. In dry cutting, a cutting speed of vc = 200 m/min could decrease work hardening and enhance surface quality.
4 Drilling
Drilling is an indispensable machining method when manufacturing hole type parts such as shaft holes or threaded holes components. Its characteristics lead to issues such as surface stress concentration, significant work hardening, chip evacuation difficulties, and severe tool wear in NiTi SMA.
Selecting cutting tools is particularly important, which has a significant impact on the surface integrity of the workpiece in drilling (Karpat et al., 2014). Lin et al. (2000) conducted drilling experiments on SMA Ni50Ti50 in martensitic phase and Ni51Ti49 in austenitic phase. They used uncoated high-speed steel (HSS), HSS coated with TiN and twist drill of cemented carbide steel for the drilling tests. Applying coatings to HSS tools enhances their surface hardness and reduces wear. The HSS drill with TiN coating exhibited lower cutting forces compared to the uncoated tool. Additionally, the maximum cutting depth increased from 11.8 mm to 22.9 mm. The cemented carbide tool head features high hardness and strength, with superior wear resistance compared to high-speed steel (Faria et al., 2009), its maximum cutting depth was 39.596 mm. A significant amount of plastic deformation was observed after machining the austenitic Ni51Ti49, with hardness values near the bore reaching up to 370 HV, higher than the 310 HV of the martensitic Ni50Ti50. The optimal cutting results were reported at a cutting speed of n = 163 rpm and a feed rate of f = 0.07 mm/rev in the experiment.
Biermann et al. (2011) conducted micro deep-hole drilling experiments on Ni50.2Ti49.8 using uncoated, TiN-coated, and TiAlN-coated single-lip drills and twist drills. The cutting edges of the single-lip drills were designed asymmetrically, resulting in the generation of more radial force components during the cutting process, which led to adhesion of the drill to the guide pad. There was an improvement in the adhesion phenomenon with the application of coatings. There was a risk of tool edge chipping when using low cutting speeds with single-edge tools due to the higher work hardening of the alloy, while higher cutting speeds could exacerbate adhesion. Therefore, using single-edge tools at vc = 30 m/min yielded favorable cutting results, with a maximum cutting depth of 420 mm. There was minimal occurrence of adhesion on the tool after machining when using twist drills due to the symmetric design of the blade reducing radial forces. Twist drills achieved a maximum cutting depth of 1,200 mm at vc = 50 m/min, Twist drills had a significant advantage over single-edge tools.
Weinert et al. investigated the effects of different cutting parameters on drilling of both martensitic Ni50.3Ti49.7 and austenitic Ni50.9Ti49.1. The tool chosen was a solid carbide twist drill with a diameter of 5 mm and TiCN/TiN coating. The feed rate and drilling depth were kept at a constant value of f = 0.1 mm/rev and l = 5 mm, respectively (Weinert and Petzoldt, 2003). The torque for both metals remained nearly constant at 3 Nm, resulting in high cutting forces when vc = 40–80 m/min. The thick chip thickness and material-induced mechanical effects lead to high cutting forces caused by dislocation motion during low-speed cutting. The increase in cutting temperature caused a thermal softening effect in the material, leading to increased plastic deformation and reduced chip thickness during high-speed machining, resulting in decreased cutting force. The author also found that there was no obvious relationship between the surface roughness and the cutting speed of the martensitic alloy (Weinert et al., 2004a). The best surface roughness of austenitic alloy at vc = 100 m/min was Rz = 1 μm.
The increase in feed rate led to a linear growth in feed force and drilling torque due to the increase in chip thickness. The feed rate varied in the range of f = 0.05–0.2 mm/rev when the cutting speed remained constant at vc = 60 m/min. Increased feed forces were noted in the austenitic alloy due to the superior tensile strength of the martensitic phase relative to the austenitic phase. The feed rate had little effect on surface roughness. There is a decrease in microhardness, and the effect of workpiece work hardening could also be reduced by decreasing feed speed With the increase of cutting speed. (Weinert and Petzoldt, 2003). Martensitic alloys exhibited more pronounced hardening due to their twin martensitic phase having a lower plateau strain compared to austenitic alloys.
The drilling process of NiTi SMA is significantly influenced by different cooling conditions (Perçin et al., 2016). Rosnan et al. (Rosnan et al., 2019; Rosnan et al., 2018) investigated the impact of two types of cemented carbide twist drill bits, one with TiAlN coating and one without, on the drilling performance of NiTi SMA at various cutting speeds. The experiment utilized the MQL-assisted machining process, where MQL was infused with Al2O3 particles with a diameter measuring less than 50 nm. The incorporation of nanoparticles into MQL could significantly enhance the thermal conductivity of the lubricant and provide a thin protective layer between the alloy and the tool, thereby diminishing the drilling thrust. Tools with TiAlN coating exhibited better wear resistance. With a cutting speed of 20 m/min, under the premise of VBmax ≤ 0.2 mm, the processing time for uncoated drills was less than 180 s, whereas under the conditions of coated tools, this time extended to 785 s. Tool wear exacerbated with increasing cutting speed, and traced amounts of nanolubricant showed significant anti-wear effects only at cutting speeds of vc = 10–20 m/min. The flank wear of the tool appeared earlier in the cutting process when vc = 30 m/min because the difficulty of the cutting fluid to effectively penetrate the cutting zone. The researchers discovered that the minimal lubrication strategy had subpar performance in terms of enhancing the surface morphology and aperture accuracy, as depicted in Figure 11.
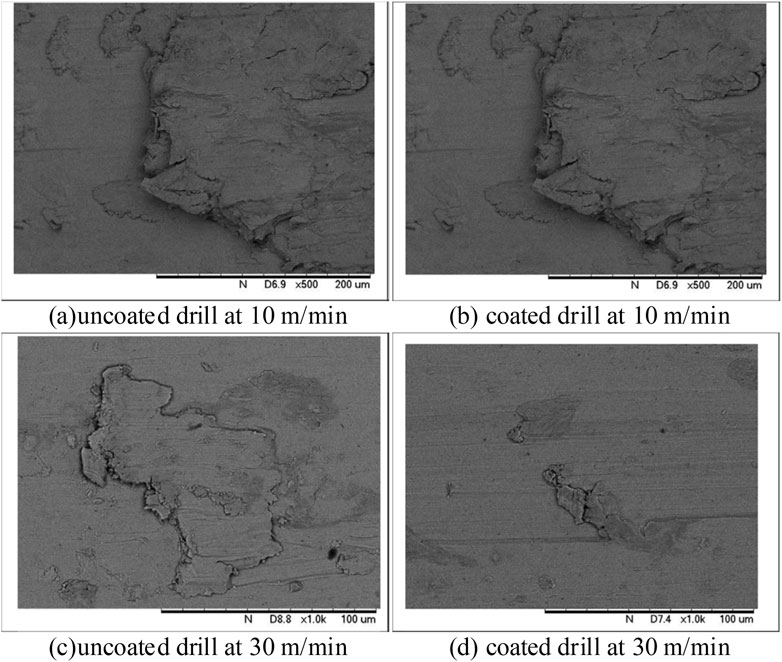
Figure 11. Comparison of chip morphology between experiment and simulation under different machining parameters: (A) uncoated drill at 10 m/min, (B) coated drill at 10 m/min, (C) uncoated drill at 30 m/min, (D) coated drill at 30 m/min.
Namlu et al. (Hakkı et al., 2023) studied four different machining/cooling combinations as conventional drilling with flood cooling (CD-Wet) and with MQL (CD-MQL), ultrasonic-assisted drilling with flood cooling (UAD-Wet) and with MQL (UAD-MQL), on deep hole drilling of Ni55.8Ti. The lubricant could not effectively penetrate in conventional machining and the penetration capability of MQL compared to wet machining in deep drilling was weaker. The periodic cutting process of ultrasonic-assisted machining resulted in gaps between the workpiece and the tool. These gaps helped in removing chips and enabling coolant to penetrate, which in turn reduced friction forces, decreased feed forces, and lowers heat in the cutting area. The integration of UAD-WET drilling yielded the minimal variance in hole diameter and the greatest precision, with a minimal error of only 0.1%. Tool wear was shown in Figure 12, where it could be observed that in CD-MQL, the tool wear mainly manifests as edge chipping; The CD-Wet drilling mode exhibits a conjunction of BUE creation and flank wear, attributable to erratic BUE development and material degradation of the tool during separation.; UAD-MQL exhibited excessive wear due to incomplete chip evacuation and hammering effect; UAD-WET forms stable BUE on the cutting edge, protecting it from rapid wear.
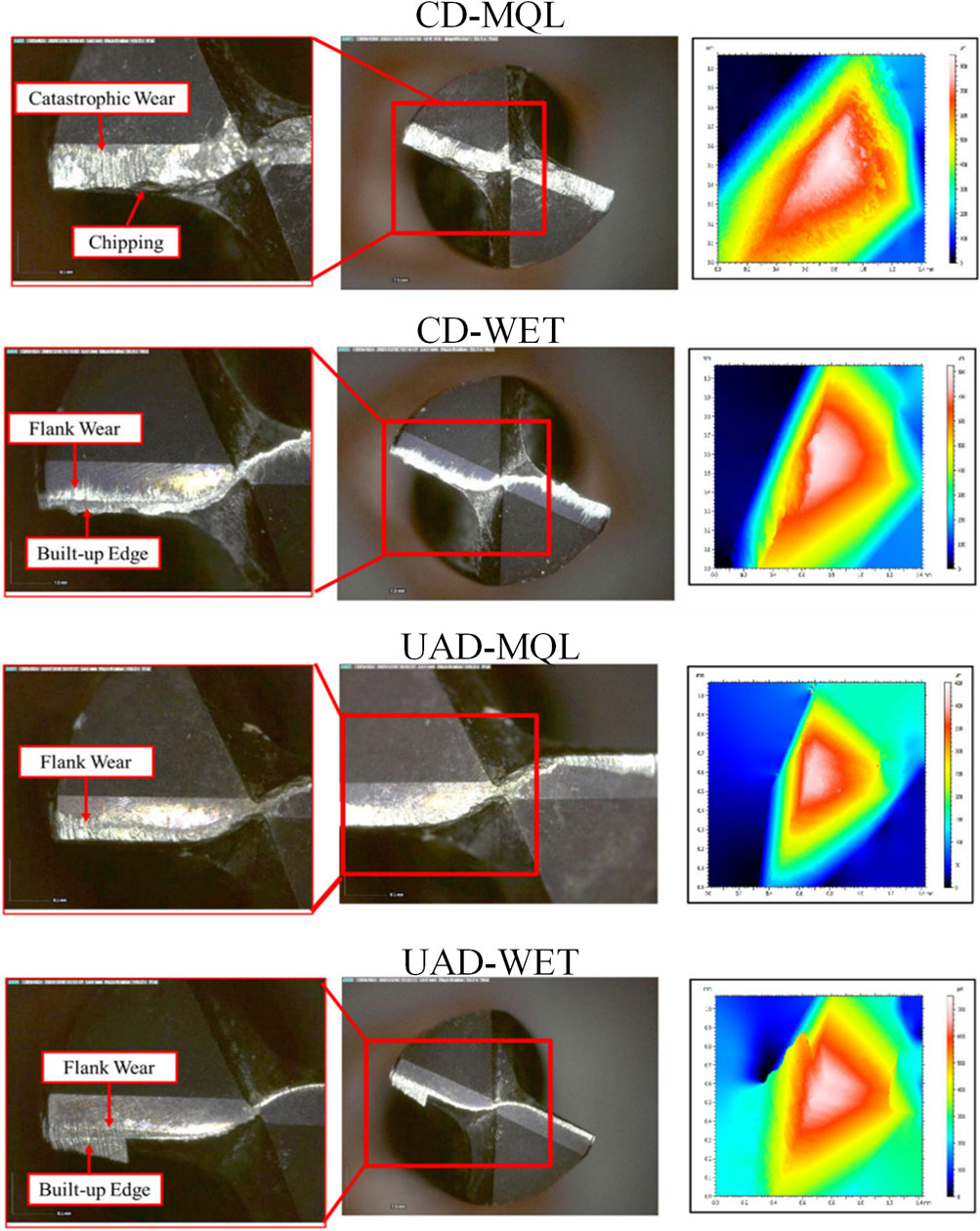

Figure 12. Tool wear under different conditions (Hakkı et al., 2023).
5 Summary
The selection of tool material significantly impacts the drilling outcomes in NiTi SMA research. Carbide steel tools demonstrate superior performance and maximize the effective cutting depth. HSS with TiN coating has advantages over HSS without coating in reducing cutting force and improving tool wear. HSS + TiN drill bits exhibit superior hardness and exceptional wear resistance, resulting in enhanced drilling performance. Drilling and cutting generate large cutting forces, so the surface hardness of the workpiece is considerable. Some academics had examined the tool wear conditions associated with micro-drilling, revealing that twist drills exhibit the least wear. In auxiliary machining, the lubrication and cooling provided by MQL are inferior to that of flood, and ultrasonic vibration significantly contributes to the reduction of tool wear and cutting force.
6 Discussion
The NiTi SMA, a shape memory material known for its growing range of applications, remains to rely on cutting machining such as turning, milling, and drilling as the primary method of machining. While NiTi SMA shares similarities with Ni alloys and Ti alloys in terms of being challenging to machine, the presence of its shape memory effect and superelasticity makes it more difficult the process of machining NiTi SMA.
6.1 Turning processing: tool material
There are the most research on turning processing at present. The research on the selection of turning tool materials is also relatively comprehensive. Cemented carbide is commonly employed for cutting NiTi SMA in the current study. Widely utilized coatings comprise of CVD, TiB2, TiAlN and TiCN, which significantly enhance the wear resistance of cemented carbide steel tools (Xie, 2010). PCD tools have superior hardness and thermal conductivity compared to cemented carbide, resulting in a longer lifespan (Li et al., 2016). PCD tools may achieve a maximum turning distance of 1725 m for NiTi SMA, exceeding the maximum turning distance of 475 m for PCBN tools when vc = 130 m/min. It demonstrated excellent cutting performance when turning the NiTi SMA. However, PCD tools might undergo chemical reactions with the Ti element in the alloy, hence accelerating the wear of the PCD tool, even potentially encounter blade breakage or fracture (Eren and İrfan, 2020). Hence, PCD tools exhibit more sensitivity to cutting conditions. Ceramic tools are unsuitable for milling NiTi SMA due to their high toughness and poor thermal conductivity, which makes them prone to breakage during processing.
6.2 Turning processing: assisted machining method
The predominant auxiliary machining techniques employed in turning operations include Assisted processing with liquid, Assisted processing with air and Pre-treatment at present. The use of cryogenic cooling yields optimal results in auxiliary machining. The reduced boiling point of LN2 could sustain the NiTi SMA in the austenite phase. This helps to minimize material phase transformation resulting from cutting heat, thereby reducing the depth of the hardened layer caused by processing. It improves the surface quality of the workpiece and also reduces tool wear, thereby increasing the service life. The tool side wear for low-temperature machining, MQL machining when vc = 25 m per minute, and dry machining is approximately 72 μm, 140 μm, and 250 μm, respectively. Nevertheless, the impact of cryogenic cooling during low-speed machining is limited, potentially attributable to the low cutting temperature and the tendency of the coolant to stick to the tool, resulting in adhesive wear. Preheating is typically regarded as negative to cutting outcomes due to the risk for excessive heat buildup in the cutting zone. However, Recent studies have demonstrated that when the NiTi SMA is heated above the Md, the martensite phase undergoes a transformation into the austenite phase. This transformation results in a decline of superelastic properties, nevertheless it additionally contributes to improved tool wear and reduced work hardening caused by the phase change. While the cutting results of NiTi SMA using the dry cutting process may not be as optimal as those achieved through auxiliary processing, dry cutting offers the advantages of cost reduction and environmental pollution reduction. At present, the most efficient method to enhance the unsatisfactory cutting results caused by dry cutting is to change the cutting parameters. The cutting speed is the cutting parameter that has the most significant influence on cutting performance. In turning machining, the optimal cutting outcome occurs when the cutting speed exceeds 100 m/min marginally.
6.3 Milling processing: comprehensive analysis
Milling processing entails complexity. Besides tool wear and poor surface roughness in milling NiTi SMA, burr formation is prevalent issues in this process. Optimizing cutting parameters and employing suitable cooling techniques might mitigate burr formation to some degree. MQL diminishes the coefficient of friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece material by delivering minimal quantities of lubricant to the cutting zone, hence decreasing cutting force and temperature. Chilled air disperses chips in the cutting zone and diminishes the BUE produced by the tool. The cutting temperature is concurrently lowered to achieve superior surface quality. Reduced cutting temperatures mitigate the heat influence on the material, thereby decreasing the occurrence of burrs resulting from its plastic deformation. Experimental verification indicates that the burr thickness could be diminished by employing down-milling while decreasing fz and ae. The same as turning, alloys containing the martensite phase exhibit inferior cutting performance in milling compared to austenitic alloys. The burrs in martensitic phase alloys are thicker than austenitic. LN2 at −196°C positively contributes to mitigating cutting overheating and suppressing martensitic transformation during milling. In dry cutting, fz significantly enhances cutting outcomes. Employing a reduced fz diminishes cutting force, hence enhancing tool longevity and refining surface topology. During the milling of NiTi shape memory alloys, a cutting speed of 200 m/min results in minimal plastic deformation and work hardening, yielding optimal surface quality. There has been certain progress in the research on ball milling NiTi SMA. Current experiments show that when the cutting angle is 50°, the ball-end milling cutter is subjected to less impact load to avoid tool fracture.
6.4 Drilling processing: comprehensive analysis
Research on NiTi shape memory alloy drilling is progressively expanding. The predominant material utilized for drilling tools remains cemented carbide steel. High-speed steel with a TiN coating has demonstrated exceptional performance in drilling. The rapid drilling speed typically results in substantial cutting force and significant tool wear. Presently employed cutting fluid-assisted machining techniques encompass MQL and flood. The drilling area is relatively closed, resulting in MQL being unable to deliver cutting fluid to the cutting area in time during the drilling process, leading to issues such as ineffective chip removal and overheating of the cutting tool. This results in significant tool wear and pronounced surface hardening of the workpiece. The application of substantial cutting fluid may remove some chips, lower the cutting temperature, and diminish friction between the tool and the workpiece. Ultrasonic vibration minimizes contact between the tool and the workpiece, enhancing the efficient use of cutting fluid.
6.5 Simulated machining
Over the past 20 years, there has been a scarcity of research on simulating the cutting process of NiTi SMA. The establishment of the J-C constitutive equation for NiTi SMA, utilized to forecast the strength limit and failure mechanisms of metallic materials under situations of significant strain, elevated strain rates, and high temperatures, marks a substantial advancement in the research of NiTi simulation machining. The cutting damage characteristics of J-C remain ambiguous. If pertinent parameters could be acquired by experimentation, the J-C material model of NiTi SMA could be utilized to do cutting simulations utilizing ABAQUS or ANSYS software in the future. These simulations could accurately anticipate cutting outcomes and minimize wastage.
7 Future prospectives
The following avenues are recognized as potential research directions in the realm of NiTi SMA machining:
1. PCD tools could be utilized to conduct cutting experiments with a wider range of cutting parameters in order to investigate the cutting performance of PCD tools on NiTi SMA.
2. Future experiments could involve doing tests on NiTi SMA with varying martensite termination temperatures to better understand the impact of preheating on the turning process of NiTi SMA.
3. The exploration of finite element machining simulation for NiTi SMA materials could be gradually undertaken as the parameters are improved. Simulation processing could optimize cutting settings, direct actual machining processes, and improve actual production efficiency while avoiding wasteful resource waste.
4. The cutting-affected layer of NiTi SMA after a single-step machining process could exceed 100 μm. It is often difficult to complete workpiece shaping in a single step, typically requiring two or even multiple steps in practical machining processes. The changes in surface integrity of NiTi SMA after the first step of machining and their impact on the second step present a new direction for current research.
5. Tools required for cutting NiTi SMA typically experience significant wear. In future research, we may examine the impact of various tool textures on the tool wear. The microstructure and surface texture of the tool could enhance lubrication conditions, minimize the contact area between the tool and the workpiece, and thereby decrease tool wear.
6. The application of NiTi SMA have its particularity. Functional indicators such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and chemical composition distribution of machined surfaces are key areas to consider in future research. Establishing the mapping relationship between surface integrity and functional indicators after alloy machining is a crucial step towards the practical application of NiTi SMA.
Author contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LY: Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. GW: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CG: Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FY: Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52105463), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (Nos ZR2022QE015 and ZR2023QE200), Development Plan for Youth Innovation Teams in Colleges and Universities in Shandong Province (Science and Technology) (No. SKDZK20240107) and Qingdao Postdoctoral Program (No. SKDZK20240117).
Acknowledgments
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work presented in this review paper. Their collective efforts have been instrumental in the conceptualization, research, analysis, and writing of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdul, W. (2016). Brief overview on nitinol as biomaterial. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2016/4173138
Abidin, Z. Z., and Tarisai, M. P. (2023). Machinability of nickel-titanium shape memory alloys under dry and chilled air cutting conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 126, 4675–4684. doi:10.1007/s00170-023-11373-6
Altas, EMRE, Karatas, A., Meltem, GOKKAYA, and Hasan, AKINAYYUKSEL (2021). Surface integrity of NiTi shape memory alloy in milling with cryogenic heat treated cutting tools under different cutting conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 9426–9439. doi:10.1007/s11665-021-06095-3
Andrea, D., Dirk, B., Alborz, S., Biermann, D., and Shokrani, A. (2021). Future research directions in the machining of Inconel 718. J. Mater. Process. Tech 297, 117260. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117260
Ao, S., Li, K., Liu, W., Qin, X., Wang, T., Dai, Y., et al. (2020). Electrochemical micromachining of NiTi shape memory alloy with ethylene glycol-NaCl electrolyte containing ethanol. J. Manuf. Process. 53, 223–228. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.02.019
Baigonakova, G., Marchenko, E., Kovaleva, M., and Vorozhtsov, A. (2022). Influence of wire geometry on the mechanical behavior of the TiNi design. Metals 12, 1131. doi:10.3390/met12071131
Balasuadhakar, A., Kumaran, S. T., Kurniawan, R., and Ahmed, F. (2022). A comprehensive review on minimum quantity lubrication in turning process. Surf. Rev. and Lett. 1. doi:10.1142/s0218625x22300088
Biermann, D., Kahleyss, F., Krebs, E., and Upmeier, T. (2011). A study on micro-machining technology for the machining of NiTi: five-Axis micro-milling and micro deep-hole drilling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 20, 745–751. doi:10.1007/s11665-010-9796-9
Biermann, D., Kahleyss, F., and Surmann, T. (2009). Micromilling of NiTi shape-memory alloys with ball nose cutters. Mater. Manuf. Process. 24, 1266–1273. doi:10.1080/10426910903129935
Caliskan, H., Altas, E., and Panjan, P. (2017). Study of nanolayer AlTiN/TiN coating deposition on cemented carbide and its performance as a cutting tool. J. Nano Res. 47, 1–10. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/jnanor.47.1
Chen, F., Lu, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., and Shen, Q. (2023). Microstructure and mechanical properties of NiTi shape memory alloys by laser engineered net shaping. Adv. Eng. Mater. 25, 2200504. doi:10.1002/adem.202200504
Committee, N. (2024). Made in China 2025 blue book. Beijing, China: Publishing House of Electronics Industry.
Cui, Y.-W., Chen, L.-Y., and Liu, X.-X. (2021). Pitting corrosion of biomedical titanium and titanium alloys: a brief review. Curr. Nanosci. 17, 241–256. doi:10.2174/15734137mtexdodu13
Cui, Z., Zhu, J., Jiang, H., Wu, S., and Zhu, S. (2022). Research progress of the surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical application. Jinshu Xuebao/Acta Metall. Sin. 58, 837–856. doi:10.2174/1573413716999201125221211
Das, S. S., and Chakraborti, P. (2018). Development of biomaterial for total hip joint replacement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 377, 012177. doi:10.1088/1757-899x/377/1/012177
Davis, R., Singh, A., Debnath, K., Sabino, R. M., Popat, K., Da Silva, L. R. R., et al. (2021). Surface modification of medical-grade Ni55.6Ti44.4 alloy via enhanced machining characteristics of Zn powder mixed-μ-EDM. Surf. and Coatings Technol. 425, 127725. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127725
Davis, R., Singh, A., Pereira, R. B. D., Sabino, R. M., Popat, K., Soares, P., et al. (2023). Collaborative impact of cryo-treated cutting tool and hybrid milling environment towards improved sustainable milling of ASTM F2063 Ni55.6Ti44.4 alloy. Int. J. Of Precis. Eng. And Manufacturing-Green Technol. 10, 1485–1509. doi:10.1007/s40684-023-00520-9
Dhananchezian, M. (2024). A review on performance evaluation of liquid nitrogen as coolant in turning Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 26, 701–857. doi:10.1080/10910344.2023.2180749
Ding, X., Liew, W. Y. H., and Liu, X. D. (2005). Evaluation of machining performance of MMC with PCBN and PCD tools. Wear 259, 1225–1234. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.02.094
Dong-Dong, Z., Shu-Hao, Z., Hai-Xia, L., and Jie, C. (2023). Cavitation erosion behavior and anti-cavitation erosion mechanism of NiTi alloys impacted by water jet. Wear, 518–519. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2023.204631
Dong-Hyeon Kim, C.-M. L., and Lee, C. M. (2014). A study of cutting force and preheating-temperature prediction for laser-assisted milling of Inconel 718 and AISI 1045 steel. Int. J. Heat and Mass Transf. 71, 264–274. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.12.021
DU, C., Huang, C., Li, S., and Liu, H. (2023). Research progress of laminated composite ceramic cutting tools. Adv. Eng. Mater. 25, 2300564. doi:10.1002/adem.202300564
Emre, A., Hasan, G., Altin, K. M., and Dervis, O. (2020). Analysis of surface roughness and flank wear using the Taguchi method in milling of NiTi shape memory alloy with uncoated tools. Coatings 10, 1259. doi:10.3390/coatings10121259
Emre, A., Omer, E., Dervis, O., and Hasan, G. (2022). Optimization of cutting conditions, parameters, and cryogenic heat treatment for surface roughness in milling of NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 31, 7315–7327. doi:10.1007/s11665-022-06769-6
Eren, K., and İrfan, K. (2020). Tool wear progression of PCD and PCBN cutting tools in high speed machining of NiTi shape memory alloy under various cutting speeds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 105, 107810. doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107810
Ezugwu, E. O., Bonney, J., Silva, R. B. D., and çakir, O. (2006). Surface integrity of finished turned Ti–6Al–4V alloy with PCD tools using conventional and high pressure coolant supplies. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 47, 884–891. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.08.005
Faria, P. E., Abrao, A. M., Rubio, J. C. C., and Davim, J. P. (2009). The influence of tool wear on delamination when drilling glass fibre reinforced epoxy composite with high speed steel and cemented carbide tools. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 37, 129–139. doi:10.1504/ijmpt.2010.029464
Guangxi, L., Hongtao., W., Yongbo, C., Shaolin, Z., Liquan, Y., and Yang, L. (2023). Optimizing processing parameters and surface quality of TC18 via ultrasonic-assisted milling (UAM): an experimental study. Micromachines 14, 1111. doi:10.3390/mi14061111
Hakkı, N. R., Bahram, L., Engin, K. S., Deniz, Y. O., and Samet, A. (2023). Combined use of ultrasonic-assisted drilling and minimum quantity lubrication for drilling of NiTi shape memory alloy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 27, 325–349. doi:10.1080/10910344.2023.2224860
Hillerborg, A., ModéER, M., and Petersson, P.-E. (1976). Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements. Cem. Concr. Res. 6, 773–781. doi:10.1016/0008-8846(76)90007-7
Huang, H. (2004). A study of high-speed milling characteristics of nitinol. Mater. Manuf. Process. 19, 159–175. doi:10.1081/amp-120029849
Huang, Z., Zhang, S., Yang, R., Wu, X., Li, R., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). A review of liquid nitrogen fracturing technology. Fuel 266, 117040. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117040
Jianhang, Y., Pei, Y., Lei, F., Huiqing, G., Li, J., Tianyang, Q., et al. (2022). Effects of phase states on clean cutting performance and surface integrity of NiTi alloys. CHINA Mech. Eng. 33, 569–576. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2022.05.005
Jomaa, W., Mechri, O., LéVESQUE, J., Songmene, V., Bocher, P., and Gakwaya, A. (2017). Finite element simulation and analysis of serrated chip formation during high–speed machining of AA7075–T651 alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 26, 446–458. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.02.015
Jozić, S., Bajić, D., and Celent, L. (2015). Application of compressed cold air cooling: achieving multiple performance characteristics in end milling process. J. Clean. Prod. 100, 325–332. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.095
Karpat, Y., Değer, B., and Bahtiyar, O. (2014). Experimental evaluation of polycrystalline diamond tool geometries while drilling carbon fiber-reinforced plastics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 71, 1295–1307. doi:10.1007/s00170-013-5592-7
Kaya, E. E. A. E. T. K., and Kaya, İ. (2019). A review on machining of NiTi shape memory alloys: the process and post process perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 100, 2045–2087. doi:10.1007/s00170-018-2818-8
Kaya, E., and Kaya, I. (2022). Investigation of high speed cutting performance and phase transformation behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 119, 489–502. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-08254-1
Kaynak, Y., Tobe, H., Noebe, R. D., Karaca, H. E., and Jawahir, I. S. (2013c). The effects of machining on the microstructure and transformation behavior of NiTi Alloy. Scr. Mater. 74, 60–63. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.10.023
Kaynak, Y. (2014). Machining and phase transformation response of room-temperature austenitic NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 3354–3360. doi:10.1007/s11665-014-1058-9
Kaynak, Y., Huang, B., Karaca, H. E., and Jawahir, I. S. (2017). Surface characteristics of machined NiTi shape memory alloy: the effects of cryogenic cooling and preheating conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 3597–3606. doi:10.1007/s11665-017-2791-7
Kaynak, Y., Karaca, H. E., and Jawahir, I. S. (2014). Surface integrity characteristics of NiTi shape memory alloys resulting from dry and cryogenic machining. Procedia CIRP 13, 393–398. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2014.04.067
Kaynak, Y., Karaca, H. E., and Jawahir, I. S. (2015a). Cutting speed dependent microstructure and transformation behavior of NiTi alloy in dry and cryogenic machining. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 452–460. doi:10.1007/s11665-014-1247-6
Kaynak, Y., Karaca, H. E., Noebe, R. D., and Jawahir, I. S. (2013a). Analysis of tool-wear and cutting force components in dry, preheated, and cryogenic machining of NiTi shape memory alloys. Procedia CIRP 8, 498–503. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2013.06.140
Kaynak, Y., Karaca, H. E., Noebe, R. D., and Jawahir, I. S. (2013b). Tool-wear analysis in cryogenic machining of NiTi shape memory alloys: a comparison of tool-wear performance with dry and MQL machining. Wear 306, 51–63. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2013.05.011
Kaynak, Y., Karaca, H. E., Noebe, R. D., and Jawahir, I. S. (2015b). The effect of active phase of the work material on machining performance of a NiTi shape memory alloy. Metallurgical Mater. Trans. 46, 2625–2636. doi:10.1007/s11661-015-2828-1
Kaynak, Y., Manchiraju, S., and Jawahir, I. S. (2015c). Modeling and simulation of machining-induced surface integrity characteristicsof NiTi alloy. Procedia CIRP 31, 557–562. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2015.03.071
Kaynak, Y., Manchiraju, S., Jawahir, I. S., and Biermann, D. (2020). Chip formation and phase transformation in orthogonal machining of NiTi shape memory alloy: microstructure-based modelling and experimental validation. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol. 69, 85–88. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2020.04.025
Khairusshima, M. K. N., Hassan, C. H. C., Jaharah, A. G., Amin, A., and Md Idriss, A. (2013). Effect of chilled air on tool wear and workpiece quality during milling of carbon fibre-reinforced plastic. WEAR 302, 1113–1123. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2013.01.043
Khalil, A. N. M., Azmi, A. I., Murad, M. N., and Ali, M. A. M. (2018). The effect of cutting parameters on cutting force and tool wear in machining Nickel Titanium Shape Memory Alloy ASTM F2063 under Minimum Quantity Nanolubricant. Procedia CIRP 77, 227–230. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2018.09.002
Khalil, A. N. M., Azmi, A. I., Murad, M. N., Annuar, A. F., and Ali, M. A. M. (2019). Coupled effects of vortex tube hybrid cooling with minimal quantity reinforced nanoparticle lubricants in turning NiTi alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105, 3007–3015. doi:10.1007/s00170-019-04507-2
Kim, D.-H., and Lee, C.-M. (2016). A study on the laser-assisted ball-end milling of difficult-to-cut materials using a new back-and-forth preheating method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 85, 1825–1834. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-8014-1
Kirmacioglu, K. E., Kaynak, Y., and Benafan, O. (2019). Machinability of Ni-rich NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Smart Mater. Struct. 28, 055008. doi:10.1088/1361-665x/ab02a2
Kitay, O., and Kaynak, Y. (2021). The effect of flood, high-pressure cooling, and CO 2 -assisted cryogenic machining on microhardness, microstructure, and X-ray diffraction patterns of NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 5799–5810. doi:10.1007/s11665-021-05854-6
Kuppuswamy, R., and Yui, A. (2017). High-speed micromachining characteristics for the NiTi shape memory alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 93, 11–21. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7598-9
Li, G. X., Rahim, M. Z., Ding, S. L., and Sun, S. J. (2016). Performance and wear analysis of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools manufactured with different methods in turning titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Of Adv. Manuf. Technol. 85, 825–841. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7949-6
Li, G. X., Rahim, M. Z., Pan, W. C., Wen, C., and Ding, S. L. (2020). The manufacturing and the application of polycrystalline diamond tools - a comprehensive review. J. Of Manuf. Process. 56, 400–416. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.05.010
Li, M., Yu, T., Yang, L., Li, H., Zhang, R., and Wang, W. (2019). Parameter optimization during minimum quantity lubrication milling of TC4 alloy with graphene-dispersed vegetable-oil-based cutting fluid. J. Clean. Prod. 209, 1508–1522. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.147
Lin, H. C., Lin, K. M., and Chen, Y. C. (2000). A study on the machining characteristics of TiNi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Process. Tech 105, 327–332. doi:10.1016/s0924-0136(00)00656-7
Lin, C., Tian, Q., Shizhan, H., Hong, X., Chao, L., Yousheng, L., et al. (2023). Study on tool wear mechanism under cryogenic CO2-assisted minimum quantity lubrication technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 126, 543–559. doi:10.1007/s00170-023-11122-9
Liu, T., Wu, Z., Zhou, W., Zhong, M., Lin, J., and Yang, Y. (2023). Quasilinear pseudoelasticity and small hysteresis in SLM-fabricated NiTi. J. Alloys and Compd. 933, 167694. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167694
Lu, H. Z., Liu, L. H., Luo, X., Ma, H. W., Cai, W. S., Lupoi, R., et al. (2023). Formation mechanism of heterogeneous microstructures and shape memory effect in NiTi shape memory alloy fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. Mater. and Des. 232, 112107. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112107
Małgorzata, K., and Krzysztof, T. (2020). Procedure for determining the uncertainties in the modeling of surface roughness in the turning of NiTi alloys using the Monte Carlo method. Mater. Basel, Switz. 13, 4338. doi:10.3390/ma13194338
Marinescu, I., Axinte, D., Herbert, C., Mcgourlay, J., and Withers, P. J. (2011). Assessment of thread-cutting strategies to enable damage-tolerant surfaces on an advanced Ni-based aerospace superalloy. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 225, 12–24. doi:10.1243/09544054jem2045
Masoudi, S., Esfahani, M. J., Jafarian, F., and Mirsoleimani, S. A. (2023). Comparison the effect of MQL, wet and dry turning on surface topography, cylindricity tolerance and sustainability. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manufacturing-Green Technol. 10, 9–21. doi:10.1007/s40684-019-00042-3
Mehrpouya, M., Shahedin, A. M., Dawood, S. D. S., and Ariffin, A. K. (2017). An investigation on the optimum machinability of NiTi based shape memory alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 1497–1504. doi:10.1080/10426914.2017.1279290
Mehta, K., and Gupta, K. (2019). Machining of shape memory alloys. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology, 9–37. Book Chapter).
Minghang, L. (2021). Multi-scale and multi-physics evolution mechanism in two-step machining deformation of titanium alloy. 硕士.
Mustafa, K., Abdullah, A., Yurievich, P. D., Ali, U. Ü., Emin, S., Kumar, G. M., et al. (2020). A review of indirect tool condition monitoring systems and decision-making methods in turning: critical analysis and trends. Sensors Basel, Switz. 21, 108. doi:10.3390/s21010108
Ociepa, M., Jenek, M., and Feldshtein, E. (2018). On the wear comparative analysis of cutting tools made of composite materials based on polycrystalline cubic boron nitride when finish turning of AISI D2 (EN X153CrMoV12) steel. J. Superhard Mater. 40, 396–401. doi:10.3103/s1063457618060059
Pasang, T., Budiman, A. S., Wang, J. C., Jiang, C. P., Boyer, R., Williams, J., et al. (2023). Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys – enabling re-manufacturing of aerospace and biomedical components. Microelectron. Eng. 270, 111935. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2022.111935
Pelton, A. R., Stockel, D., and Duering, T. W. (2000). Medical uses of nitinol. Mater. Sci. Forum 327-328, 63–70. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.327-328.63
PerçIN, M., Aslantas, K., Ucun, İ., Kaynak, Y., and Çicek, A. (2016). Micro-drilling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy: the effects of cooling/lubricating. Precis. Eng. 45, 450–462. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.02.015
Piquard, R., D’Acunto, A., Laheurte, P., and Dudzinski, D. (2014). Micro-end milling of NiTi biomedical alloys, burr formation and phase transformation. Precis. Eng. 38, 356–364. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2013.11.006
Rahul, D., Abhishek, S., James, J. M., Teixeira, C. R., Divya, P., Panayiotou, C. C., et al. (2022). A comprehensive review on metallic implant biomaterials and their subtractive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 120, 1473–1530. doi:10.1007/s00170-022-08770-8
Rosnan, R., Azmi, A. I., and Murad, M. N. (2018). Effects of cutting parameters on tool wear and thrust force in drilling nickel-titanium (NiTi) alloys using coated and uncoated carbide tools. Key Eng. Mater. 4813. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.791.111
Rosnan, R., Murad, M. N., Azmi, A. I., and Shyha, I. (2019). Effects of minimal quantity lubricants reinforced with nano-particles on the performance of carbide drills for drilling nickel-titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 136, 58–66. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2019.03.029
Sarikaya, M., Gupta, M. K., Tomaz, Í. V., Danish, M., Mia, M., Rubaiee, S., et al. (2021). Cooling techniques to improve the machinability and sustainability of light-weight alloys: a state-of-the-art review. J. Manuf. Process. 62, 179–201. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.12.013
Sehitoglu, H., Wu, Y., Patriarca, L., Li, G., Ojha, A., Zhang, S., et al. (2017). Superelasticity and shape memory behavior of NiTiHf alloys. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 3, 168–187. doi:10.1007/s40830-017-0108-1
Shao, L., Li, W., Li, D., Xie, G., Zhang, C., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). A review on combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti alloys for advanced aero-engine. J. Alloys Compd. 960, 170584. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170584
Sharif, M. N., Pervaiz, S., and Deiab, I. (2017). Potential of alternative lubrication strategies for metal cutting processes: a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 89, 2447–2479. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9298-5
Shengchen, Y. (2018). Research on performance of TC27 titanium alloy drill pipe based on deep sea drilling. 硕士.
Shicheng, Z., Rong, J., Haoxiang, G., Lu, Z., Xuping, L., Haiyong, Z., et al. (2024). Effect of film cooling holes on creep properties of a nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Acta Aeronautica Astronautica Sinica 1-13. doi:10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.29737
Singh, T., Kumar, J., and Misra, J. P. (2023). Surface integrity analysis of machined surface of Ni-Ti shape memory alloy during wire spark erosion machining. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 95, 225–236. doi:10.1108/aeat-01-2022-0014
Sun, X., Wei, X., Li, Z., Lou, D., Wang, Y., and Liu, H. (2021). Investigating the influences of wet fiber laser cutting upon the surface integrity of nitinol cardiovascular stents. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 22, 1237–1248. doi:10.1007/s12541-021-00522-0
Thornton, E.-L., Zannoun, H., Vomero, C., Caudill, D., and Schoop, J. (2023). A review of constitutive models and thermal properties for nickel-based superalloys across machining-specific regimes. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 145, 080801. doi:10.1115/1.4056749
Velmurugan, C., Senthilkumar, V., Dinesh, S., and Arulkirubakaran, D. (2018). Machining of NiTi-shape memory alloys-A review. Mach. Sci. And Technol. 22, 355–401. doi:10.1080/10910344.2017.1365894
Wang, G., Liu, Z., Ai, X., Huang, W., and Niu, J. (2018). Effect of cutting parameters on strain hardening of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy. Smart Mater. Struct. 27, 075027. doi:10.1088/1361-665x/aac43d
Wang, G., Liu, Z., Huang, W., Wang, B., and Niu, J. (2019a). Influence of cutting parameters on surface roughness and strain hardening during milling NiTi shape memory alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 2211–2221. doi:10.1007/s00170-019-03342-9
Wang, G., Liu, Z., Niu, J., Huang, W., and Xu, Q. (2019b). Work hardening influencing on shape memory effect of NiTi alloy by varying milling speeds. Smart Mater. Struct. 28, 105034. doi:10.1088/1361-665x/ab3de2
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Peng, R., Zhao, X., Zhao, G., Chen, N., et al. (2023). Research on cutting parameters of low-temperature liquid CO2 assisted PCD tool turning bearing ring. J. Manuf. Process. 87, 199–208. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.01.009
Weinert, K., and Petzoldt, V. (2003). Machining of NiTi based shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. and Eng. A 378, 180–184. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.344
Weinert, K., and Petzoldt, V. (2006). Machining NiTi micro-parts by micro-milling. Mater. Sci. and Eng. A 481. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.10.220
Weinert, K., Petzoldt, V., Koetter, D., and Buschka, M. (2004a). Drilling of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Werkst. 35, 338–341. doi:10.1002/mawe.200400752
Weinert, K., Petzoldt, V., and KöTTER, D. (2004b). Turning and drilling of NiTi shape memory alloys. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol. 53, 65–68. doi:10.1016/s0007-8506(07)60646-5
Wu, X., Li, L., He, N., Zhao, G., and Shen, J. (2019). Investigation on the surface formation mechanism in micro milling of cemented carbide. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 78, 61–67. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.09.001
Xie, C. Q. (2010). Research on the microstructure and properties of multilayer cvd coated cemented carbides.
Xie, X., and Xu, B. (2023). Achieving tunable graded functional properties of NiTi shape memory alloy: a phase field study. J. Mater. Sci. 58, 14860–14878. doi:10.1007/s10853-023-08931-4
Yang, H., Sakai, K., Shizuka, H., Kurebayashi, Y., Hayakawa, K., and Nagare, T. (2021). Experimental investigation of the effects of super-elasticity on the machinability of NiTi alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 115, 581–593. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-07166-4
Yanzhe, Z. (2021). Investigation on machined surface integrity and zero phase transformation cutting optimization for Ni50.8Ti shape memory alloy. 博士.
Yanzhe, Z., and Jie, S. (2023). Study on the characteristics of phase in turning NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 98, 277–284. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.05.009
Yu, P. D., Andres, B., Szymon, W., Gupta, M. K., Mustafa, K., and Kuntoğlu, M. (2022). Artificial intelligence systems for tool condition monitoring in machining: analysis and critical review. J. Intelligent Manuf. 34, 2079–2121. doi:10.1007/s10845-022-01923-2
Zailani, Z. A., and Mativenga, P. T. (2016). Effects of chilled air on machinability of NiTi shape memory alloy. Procedia CIRP 45, 207–210. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.156
Zainal Abidin, Z., Tarisai Mativenga, P., and Harrison, G. (2020). Chilled air system and size effect in micro-milling of nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manufacturing-Green Technol. 7, 283–297. doi:10.1007/s40684-019-00040-5
Zhang, P., Liu, Z., Liu, J., Yu, J., Mai, Q., and Yue, X. (2023a). Effect of aging plus cryogenic treatment on the machinability of 7075 aluminum alloy. Vacuum 208, 111692. doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2022.111692
Zhang, P., Wang, S., Lin, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, J., Mai, Q., et al. (2023b). Corrosion mechanism and machinability of 7075-T6 aluminum alloy in high-speed cutting: with and without cryogenic treatment. Mater. and Corros./Werkstoffe und Korrosion 74, 872–886. doi:10.1002/maco.202213515
Zhang, Y., and Xu, X. (2020). Transformation temperature predictions through computational intelligence for NiTi-based shape memory alloys. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 6, 374–386. doi:10.1007/s40830-020-00303-0
Zhao, Y., Cui, L., Sivalingam, V., and Sun, J. (2023). Understanding machining process parameters and optimization of high-speed turning of NiTi SMA using response surface method (rsm) and genetic algorithm (ga). Materials, 16.
Zhao, Y.-Z., Guo, K., Sivalingam, V., Li, J.-F., Sun, Q.-D., Zhu, Z.-J., et al. (2021a). Surface integrity evolution of machined NiTi shape memory alloys after turning process. Adv. Manuf. 9, 446–456. doi:10.1007/s40436-020-00330-1
Zhao, Y., Guo, K., Li, J., and Sun, J. (2021b). Investigation on machinability of NiTi shape memory alloys under different cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116, 1913–1923. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-07563-9
Keywords: NiTi SMA, tool wear, surface integrity, dry cutting, assisted machining, cutting simulation
Citation: Wei J, Yang L, Wang G, Gong C and Yang F (2024) Research status of cutting machining NiTi shape memory alloys: a comprehensive review. Front. Mater. 11:1431992. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1431992
Received: 13 May 2024; Accepted: 29 October 2024;
Published: 27 November 2024.
Edited by:
Weihua Li, University of Wollongong, AustraliaReviewed by:
Rahul Davis, Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences, IndiaMustafa Kuntoğlu, Selcuk University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2024 Wei, Yang, Wang, Gong and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guijie Wang, bmloYW93YW5nZ3VpamllQDE2My5jb20=
 Junying Wei
Junying Wei Lei Yang
Lei Yang Guijie Wang
Guijie Wang Feiyang Yang
Feiyang Yang