- 1Department of Engineering, Fujian Jiangxia University, Fuzhou, China
- 2Department of Civil Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
The low water/binder ratio of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) often results in its high autogenous shrinkage. Our study explored the effect of the single or binary addition of a CaO-based expansive agent (CEA) and steel fibers on flowability, compressive strength, flexural strength, microstructure, and autogenous shrinkage of UHPC. X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) were applied to reveal the effects of CEA and steel fibers on hydration products and microstructure characteristics of UHPC. Experimental results show that the autogenous shrinkage of UHPC decreased markedly with the single or binary addition of CEA and steel fibers. Relative to the control group, autogenous shrinkage of UHPC with 2.5% dosage of single steel fibers, 6% dosage of single CEA, and binary addition of 2.5% steel fibers and 6% CEA decreased 17.8%, 10.9%, and 30.8% at 180 days, respectively. Steel fibers could enhance the mechanical performance of UHPC; nevertheless, they would decrease the flowability of UHPC. Meanwhile, the addition of CEA in the UHPC mixture not only maintained the mechanical properties and flowability but also decreased the autogenous shrinkage. Diffraction peak intensity and endothermic peak of Ca(OH)2 and the pore volume of 10–50 nm diminished with the content of CEA; however, that of C-S-H gel and ettringite increased. The prediction accuracy of nine shrinkage models (FHWA model, Lee model, Yoo model, JSCE model, B4 model, JonassonH model, Eurocode 2 model, CEB model, and DilgerW model) is analyzed with RE,
1 Introduction
UHPC is an innovative and promising construction material, which exhibits characteristics of ultra-high mechanical performance, high ductility, and excellent durability (Yang et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2020; Yoo et al., 2018a). Consequently, UHPC could meet the development of civil engineering, such as complex architecture, bridge decks, and long-span curved roofs (Deng et al., 2023). The constituent materials of UHPC contain cement, silica fume, fly ash, superplasticizer, steel fiber, quartz sand, etc. (Zhu et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2022; Du et al., 2021). Owing to a very low water/binder ratio, a substantial amount of binder (800–1,200 kg/m3), high content of active mineral admixtures, and few or no coarse aggregates (Yang et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2022), autogenous shrinkage of UHPC is significantly greater relative to ordinary concrete or high-performance concrete, especially in the early age. Autogenous shrinkage could reach 500–1,500με (Liu et al., 2019), which is one order of magnitude greater than its dry shrinkage. Furthermore, the high autogenous shrinkage means high-risk early cracking. It could tremendously deteriorate the mechanical performance and durability of UHPC. UHPC autogenous shrinkage research has not yet been fully resolved. Hence, it has become a critical factor limiting engineering applications, which is an urgent topic to be solved further.
The variety and dosage of steel fibers have remarkable effects on mechanical performance and UHPC autogenous shrinkage. There were differences among elastic modulus, tensile strength, ultimate elongation, and specific gravity among different types of fibers, while hybrid fibers composed of steel fibers, polyvinyl alcohol fibers, polyoxymethylene fibers, sisal fibers, and other fibers have combined the advantages of diverse fibers to increase the mechanical properties of UHPC (Ren et al., 2022; Moon et al., 2022; Akca and Ipek, 2022; Yu et al., 2022). However, some research studies had the opposite conclusion that steel fibers remain the major reinforcement for UHPC since it has enhanced the mechanical performance of UHPC (Wu et al., 2023). The dosage of steel fibers in UHPC remains generally below 3% because when the steel fiber content exceeds 3%, the increase in mechanical strength and toughness caused by the addition of steel fibers is very slight. However, its economy and flowability will be poor. The content of steel fibers from 2% short straight fibers to 3% hybrid fibers increased the mechanical performance of UHPC by as much as 16% and 48%, respectively (Akca and Ipek, 2022). Steel fibers (Vf = 0.5%) have displayed rational advances of ductility performance and ensured cost performance of UHPC (Nguyen et al., 2023). The size effect of UHPC compressive strength was augmented with the content of short straight fibers, while it was diminished with the augment of the water/binder ratio (Zhang et al., 2022). Steel fibers were dispersed at random in UHPC; furthermore, the distribution and bridging effect of steel fiber has affected the flexural strength and brittleness of UHPC (Lu et al., 2020; Mu et al., 2023).
The calcium sulfoaluminate expansive agent (CSEA), magnesium oxide expansive agent (MEA), and CEA are the most used expansive agents to reduce the shrinkage of UHPC because of their cost-effectiveness (Cui et al., 2023). The content of 6% and 8% of CSEA significantly reduced the shrinkage of UHPC in the first 2 weeks; meanwhile, the additional expansive agents enhanced the bond strength of UHPC (Yoo et al., 2019). Autogenous shrinkage of UHPC diminished with CEA content; however, when the CEA content in UHPC exceeded 60 kg/m3, a crack caused by the increase in the expansion pressures appeared in the late age (Liu et al., 2022); accordingly, the dosage of 40 kg/m3 may be suitable to prevent the delayed expansion of UHPC. CEA could significantly accelerate the hydration process of cement; however, MEA delayed the hydration process of cement (Jia et al., 2023). With the increase of MEA, UHPC had smaller autogenous shrinkage and higher compressive strength (Li et al., 2021). Limited studies have researched the effect of expansive agents on UHPC mechanical strength to date. However, the effect of the microstructure and hydration properties on UHPC mechanical strength and autogenous shrinkage has not been fully studied yet.
This study aims to assess the effect of different additions of steel fibers and expansive agents on the macroscopic properties of UHPC. In this study, X-ray diffraction (XRD), mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP), thermal gravimetric (TG) analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were utilized to explore the characteristics of microstructure and hydration products. Moreover, two round bars under each UHPC shrinkage specimen were used to reduce the influence of bottom constraints on the horizontal measurement of autogenous shrinkage. Several shrinkage models were used to evaluate the difference between predicted shrinkage and experimental shrinkage with statistical parameters RE and
2 Experimental programs
2.1 Materials
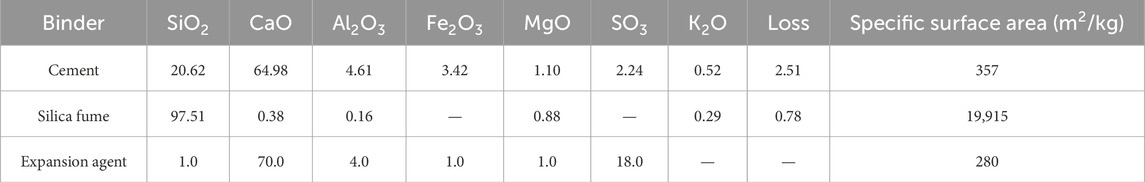
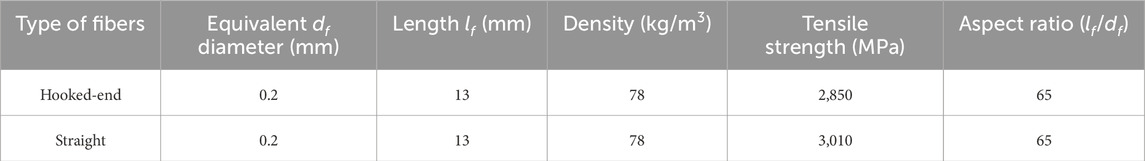
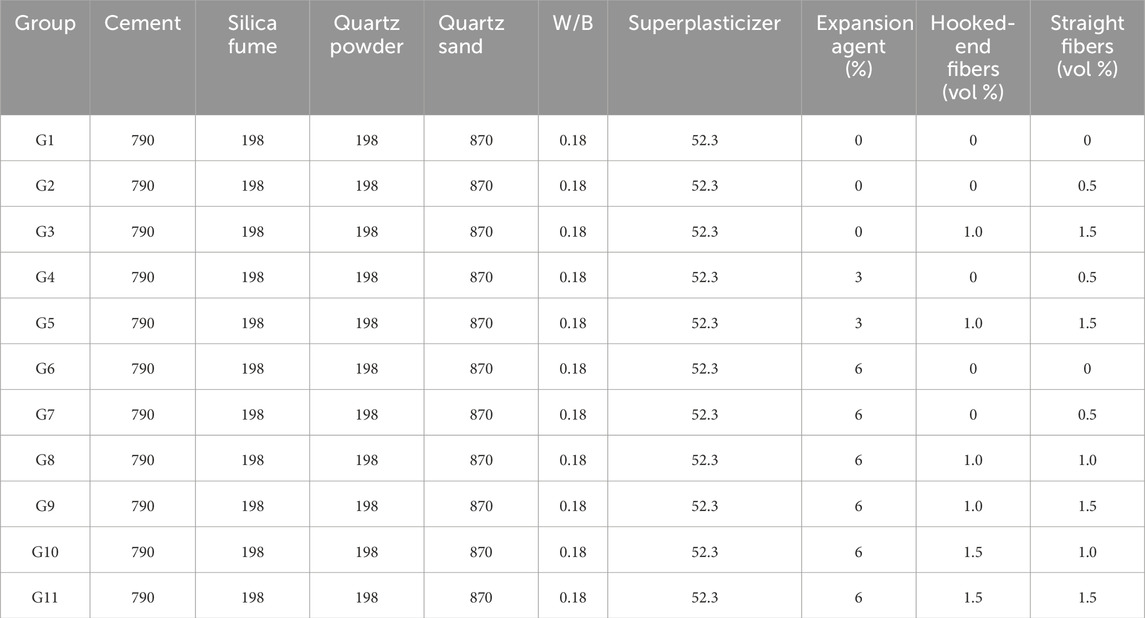
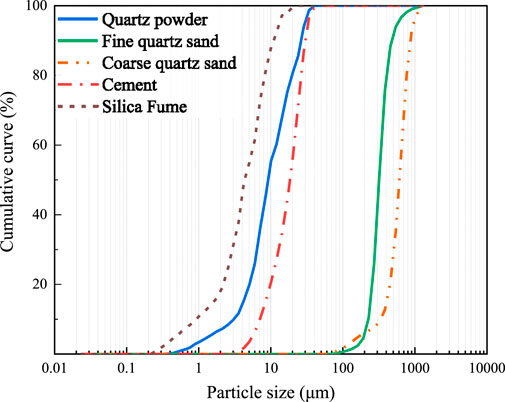
The chemical composition and physical performance of silica fume, cement, and CEA are detailed in Table 1. Type II 52.5R Portland cement for experiments met the Chinese Standard GB 175-2007. Polycarboxylic superplasticizer having a water reduction of more than 30% was used to keep UHPC workability with a low water/binder ratio. The type of fly ash used in the experiment was class F, which met the Chinese Standard GB/T1596-2005. Two kinds of copper-coated steel fibers were used to reinforce the UHPC mixture, which were straight steel fibers and hooked-end steel fibers of 16-mm length. The geometrical and mechanical performance of steel fibers is detailed in Table 2. Volumetric fractions (Vf, 0%–1.5%) of the steel fibers are detailed in Table 3. Two kinds of quartz sand with diverse particle size distributions were utilized in UHPC. The diameter of coarse quartz sand was 26–40 mesh (0.43–0.70 mm) and that of the other one was 40–70 mesh (0.21–0.43 mm). The CEA dosages of the groups by mass of binders are detailed in Table 3. The particle size distribution (PSD) of the major ingredients utilized in UHPC is detailed in Figure 1.
2.2 Mixture proportions and specimen preparation
The mixture proportion of 11 groups of UHPC is detailed in Table 3. It was obtained with diverse dosages of CEA or steel fibers. The manufacturing procedure of the UHPC specimens is detailed in Figure 2. First, quartz sand, silica fume, cement, and quartz powder were poured into the shaft horizontal forced concrete mixer for 4 min mixing slowly. Later, water, polycarboxylic superplasticizer, and CEA were added to the mixer with 3 min of slow mixing and 3 min of fast mixing. Thereafter, steel fibers were evenly scattered into the mixer while it was mixing slowly for 10 min. The fresh UHPC mixtures were poured into prismatic and cubic (100 mm × 100 mm × 100 mm) molds after their flowability test. After curing with a plastic film for 24 h, specimens were placed in the standardized curing room (20°C ± 2°C, >95% RH) after demolding and until the relevant performance tests at the specified age.
2.3 Experiment procedures
2.3.1 Flowability, compressive strength, and flexural strength
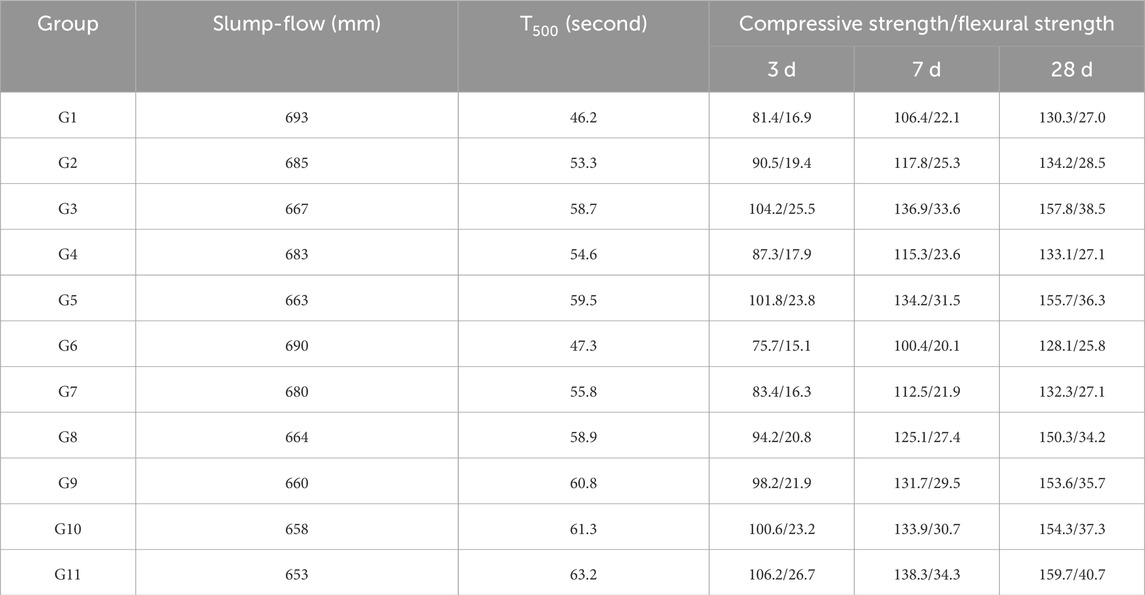
Slump-flow and T500 (spread time of mixtures at the d = 500 mm) of fresh UHPC mixtures were measured via one slump cone; refer to Chinese Standard GB/T 50,080-2016 and Ref (Yoo et al., 2018a). Six cubic specimens were generated for testing the compressive strength of every group in Table 3, tested with the Chinese Standard GB/T50081-2019, at 3 days, 7 days, and 28 days. Cubic specimens were tested at the loading rate range of 1.2–1.4 MPa/s for compressive strength. Three prismatic specimens (100 mm × 100 mm × 515 mm) were generated for testing the flexural strength of every group in Table 3, tested with the Chinese Standard GB/T50081-2019, at 3 days, 7 days, and 28 days. Prismatic specimens were tested at the loading rate range of 0.12–0.14 MPa/s for the flexural strength.
2.3.2 X-ray diffraction
XRD (MiniFlex300) was utilized for mineral phase analysis on CEA in UHPC with Cu–Ka radiation. XRD was conducted on the mineral phase variation in samples with the scanning rate of 10°/min, which was scanned with the range (2θ) from 5° to 80°. Samples of a specified age were immersed within anhydrous ethanol, and later, dried samples were pulverized, followed by an XRD test (Weng and Liao, 2021).
2.3.3 TG analysis
Thermogravimetric (TG, STA 449 F3) analysis was performed to analyze the chemical compositions of samples with CEA (He et al., 2024c). Samples were crushed into particles at the age of 28 days. Before the TG test of the samples, termination of hydration, vacuum, grinding into powder, sieving, and other treatment measures were carried out (He et al., 2024c; He and Lu, 2023a; He et al., 2023b). The tested samples measured 10–15 mg, which were heated at the rate of 10°C/min (the heating temperature ranged from 30°C to 1,000°C) in a nitrogen atmosphere and constant flowing rate of 25 mL/min (Liu et al., 2018). The content of Ca(OH)2 could be calculated according to thermal mass loss (Kim and olek, 2012; He and Lu, 2023a; He et al., 2023b; He et al., 2024c).
2.3.4 Scanning electron microscopy analysis
SEM (JSM-IT100) was conducted for UHPC microstructure observation. First, some typical samples were immersed in the acetone solution for 24 h for terminating further hydration at 28 days. Then, the vacuum drying chamber was used to dry the UHPC samples to constant weight. Polishing, gold coating, and other steps were carried out sequentially before scanning the samples (Liu et al., 2018). The accelerating voltage of the JSM-IT100 was set at 20 kV (Zhu et al., 2017). The microstructure images of these samples were taken at the magnification of 200–10,000 times.
2.3.5 Mercury intrusion porosimetry
MIP (AutoPore V 9600) has been one of the advanced techniques for the analysis of microstructure of cementitious materials (Yoo et al., 2018b; Wu et al., 2021). MIP was carried out to measure porosity and pore size distribution of the samples. Several pieces of approximately 4–6 g samples were obtained from the center of the UHPC specimen. Then, they were soaked within anhydrous ethanol for 48 h for stopping further hydration reactions before experiments (Zhou et al., 2021). The applied pressure from low to high for MIP was approximately 3.45–410 MPa. For our research, pore size distribution was grouped into 0–10 nm, 10–50 nm, 50–10,000 nm, and >10,000 nm (Zhu et al., 2017). For an idealized cylindrical pore, the Washburn equation (Washburn, 1921; He and Lu, 2024a; He and Lu, 2023a) could be used to calculate the applied pressure (P, MPa) and the related pore diameter (d, nm) as follows:
where γ represents the surface tension of mercury (0.485 N/m) and θ is the contact angle between mercury and the pore wall (140°) (He et al., 2023b; He et al., 2024c).
2.3.6 Autogenous shrinkage
As shown in Figure 3, prismatic specimens (100 mm × 100 mm × 515 mm) were used to determine autogenous shrinkage of UHPC with dial gauges at the ends. For every group in Table 3, three UHPC prismatic specimens were generated in an autogenous shrinkage experiment, and the average data were taken. Steel molds would be removed, following the initial setting of the mixture. Later, prismatic specimens of UHPC were sealed with tinfoil after processing the steel fibers on the surface. Two small round rods were placed below each specimen to reduce the impact of bottom constraints on the autogenous shrinkage experimental device. Every specimen was cured in a shrinkage experimental room set at 20°C ± 2°C and 60% ± 5% RH. Autogenous shrinkage was measured until 180 days.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flowability
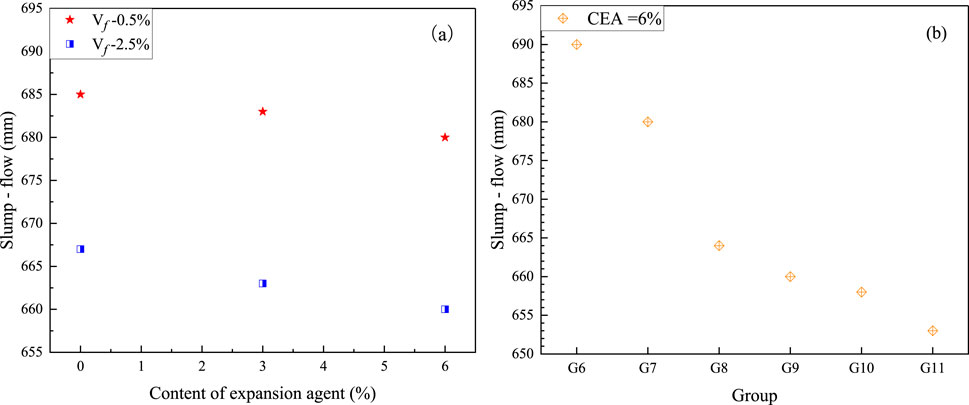
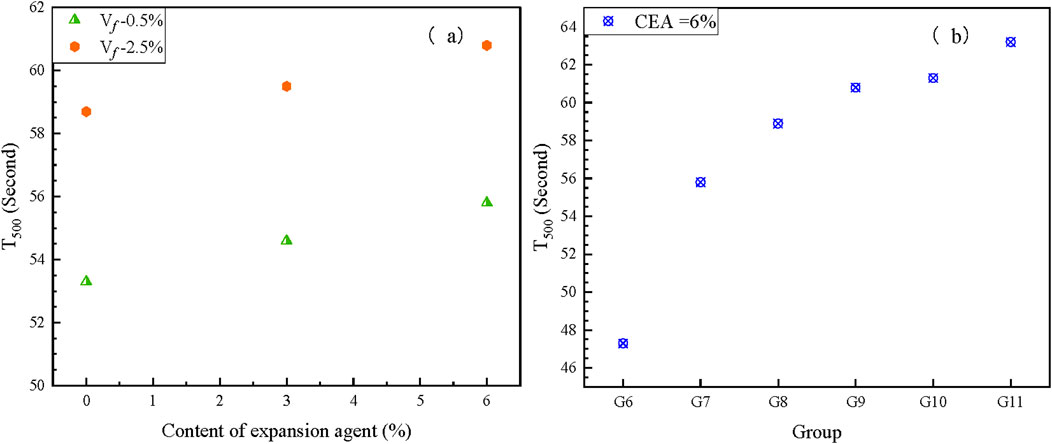
The influence of the CEA content on the T500 and slump-flow of the fresh mixture is shown in Figures 4, 5 and Table 4. Slump-flow of all groups exceeded 650 mm, which indicates that these fresh UHPC mixtures were flowable for concrete construction. The results show that both slump-flow and T500 of the groups were slightly affected by the content of CEA in UHPC. There are two reasons for the decrease of the UHPC flowability. First, with the increased content of CEA, the amount of SO42- ions in the fresh UHPC mixture increased, which worked against the positive influence of the superplasticizer on the flowability of a fresh concrete mixture. Second, CEA also participated in hydration reactions in mixing, leading to a decrease of water for cement hydration, poor flowability, and loss of rheological properties with the age of the fresh UHPC mixture (Ma et al., 2019).
Slump-flow and T500 of fresh UHPC mixtures with different additions of steel fibers are detailed in Figures 4, 5 and Table 4. Flowability experiment results show both slump-flow and T500 of the groups were significantly influenced by the content of steel fibers in UHPC. Relative to group G6, the slump-flow of groups G7, G8, G9, G10, and G11 diminished by 10 mm, 26 mm, 30 mm, 32 mm, and 37 mm, respectively. Similarly, relative to group G6, T500 of groups G7, G8, G9, G10, and G11 increased by 18.0%, 24.5%, 28.5%, 29.6%, and 33.6%, respectively. Furthermore, the slump-flow of UHPC with the incorporation of 3% steel fibers by volume was 653 mm, which approached the lower limit of the technical requirements (650 mm, T/CECS 10107-2020). With the same dosage of steel fibers in UHPC, hooked-end steel fibers caused more reduction in flowability than straight steel fibers. With the same increased content of steel fibers, the decreasing rate of flowability gradually slowed down. The reason for the decrease in flowability could result from the bridging effect, the shape of steel fibers’ ends, the agglomeration phenomenon, and the inter-filament friction of steel fibers in the fresh UHPC mixture (Fang et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2021).
3.2 Compressive strength and flexural strength
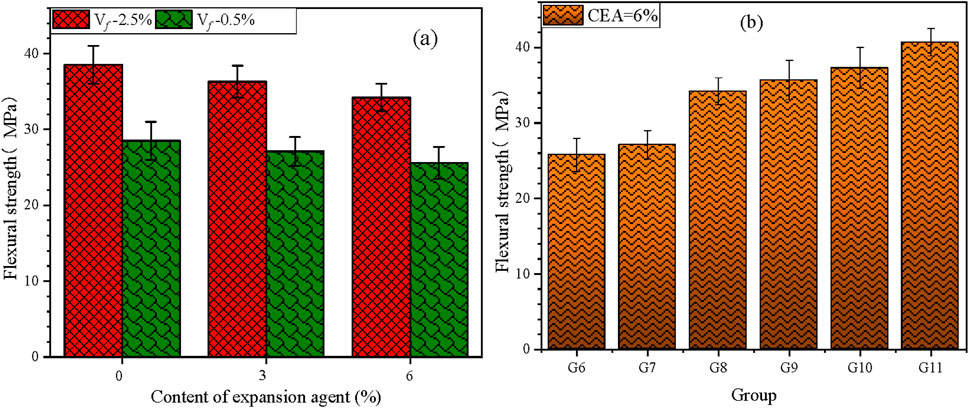
The influence of single or binary addition of CEA and steel fibers on the mechanical performance of UHPC is detailed in Figures 6, 7 and Table 4. All the groups with diverse dosages of CEA or steel fibers demonstrated good mechanical performance. From Figures 6A, 7A and Table 4, the mechanical performance of UHPC slightly diminished with the CEA content at 3 days and 28 days. The study found that 3% and 6% of CEA resulted in a 3.5% (2.1 MPa) and 7.8% (3.9 MPa) compressive strength (fc) reduction of UHPC (Vf = 0.5%) at 3 days. Similarly, the compressive strength of UHPC (Vf = 2.5%) with 3% and 6% of CEA decreased by 1.3% (2.1 MPa) and 2.7% (4.2 MPa) relative to UHPC without CEA. Due to the high compressive strength of UHPC (Vf = 0.5%, fc >130 MPa; Vf = 2.5%, fc >150 MPa), it has little impact on the engineering application of UHPC that 3% and 6% of CEA caused the reduction of compressive strength by 2.1–4.2 MPa. As shown in Figure 7A, 3% and 6% of CEA slightly decreased (1.4 MPa–2.9 MPa) the flexural strength of UHPC. The difference in the mechanical performance of UHPC with different CEA dosages decreased slightly with age. Some possible reasons for the decrease of mechanical properties were the loose microstructure, micro-cracks, and not enough water for cement hydration, which were caused by CEA in UHPC (Jia et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2019; Shen et al., 2020).
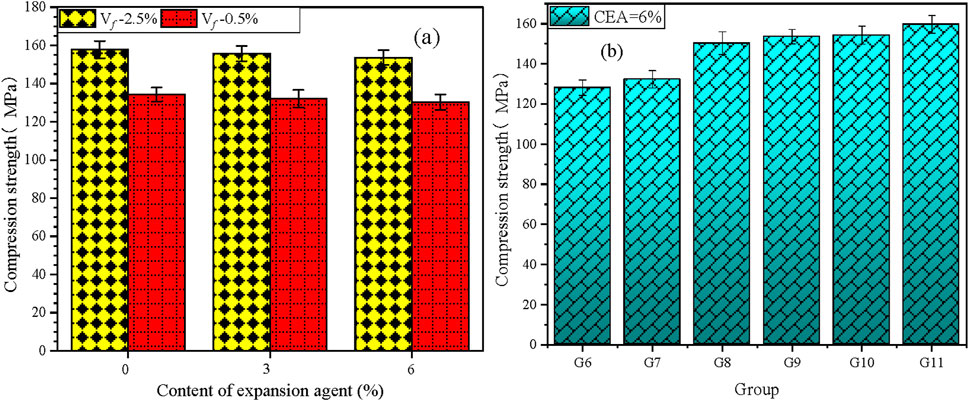
Figure 6. Effects of (A) expansion agent and (B) steel fibers on the compressive strength (28 days).
As presented in Figures 6, 7B and Table 4, UHPC compressive strength was augmented significantly with steel fiber content at 3 days, 7 days, and 28 days. Relative to group G6, compressive strength of groups G7, G8, G9, G10, and G11 increased by 3.3%, 17.3%, 19.9%, 20.5%, and 24.7% at 28 days, respectively. Furthermore, relative to the flexural strength of group G6, that of groups G7, G8, G9, G10, and G11 increased by 5.0%, 32.6%, 38.4%, 44.6%, and 57.8% at the age of 28 days, respectively. Moreover, values of (compressive strength)/(flexural strength) of groups G6, G7, G8, G9, G10, and G11 were 4.97, 4.88, 4.39, 4.30, 4.14, and 3.92, respectively. The ratio of (compressive strength)/(flexural strength) gradually decreased with the increase in the steel fiber content. Mechanical experiments indicated that steel fibers were more beneficial for flexural strength than compressive strength. When steel fiber ratio Vf ≥2%, the compressive strength of the UHPC groups was all beyond 150 MPa. For UHPC with the same Vf = 2.5% of steel fibers, the compressive strength of hooked-end fibers was slightly greater than that of straight fibers. The bond strength of hooked-end fibers contains adhesion and friction along the fiber surface and additional mechanical bonds caused by its deformed ends (Ma et al., 2019).
3.3 X-ray diffraction
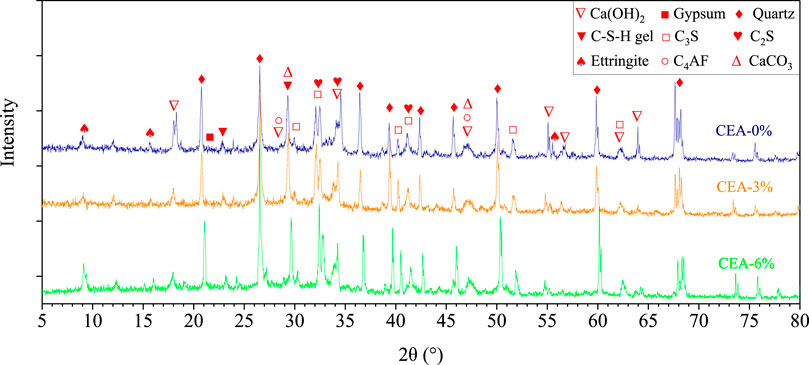
XRD patterns of UHPC pastes having diverse dosages of CEA at 28 days are detailed in Figure 8. Diffraction peaks of C3S, C2S, quartz, C-S-H gel, and Ca(OH)2 could be observed clearly by XRD (Weng and Liao, 2021; Shen et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2014); however, the diffraction peak of gypsum was unclear, as shown in Figure 8 (Zhu et al., 2018; Xiong et al., 2022). The variation in the intensity peak of C-S-H gel, CaCO3, ettringite, and Ca(OH)2 could indicate the hydration reaction of UHPC with CEA (Weng and Liao, 2021; Zhu et al., 2018; Puertas and Torres-Carrasco, 2014). The diffraction peak of Ca(OH)2 at approximately 2θ = 18°, 34°, and 55° diminished significantly with the content of CEA at 28 days (Xu et al., 2022). Meanwhile, the intensity of the ettringite peak at approximately 2θ = 9°, the C-S-H gel peak at approximately 2θ = 30°, and the CaCO3 peak at approximately 2θ = 29° increased slightly with the content of CEA at 28 days. Within a range of 2θ = 30°–63°, some diffraction peaks about the unhydrated C3S, C2S, and C4AF could be observed in XRD patterns because of the low water/binder ratio of UHPC pastes. C-S-H gel is beneficial for enhancing the mechanical properties of UHPC (Geng et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021). A decrease of calcium hydroxide and an augment of ettringite were helpful in compensating autogenous shrinkage of UHPC (Shen et al., 2020).
3.4 Thermogravimetric analysis
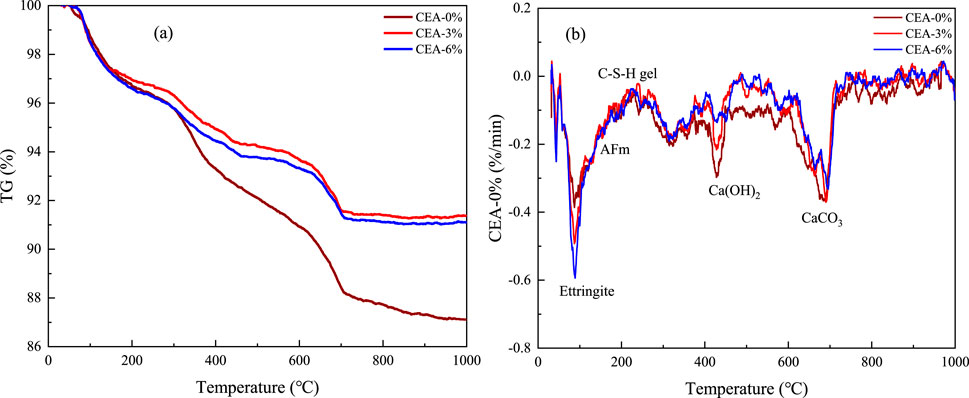
TG analysis and DTG analysis of the UHPC pastes with 0%, 3%, and 6% content of CEA at 28 days are detailed in Figure 9. The three major endothermic peaks in the DTG figure correspond to the thermal mass loss process of ettringite, Ca(OH)2, and CaCO3 separately (Wu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). The temperature range of the first peak was below 200°C; meanwhile, this was the sharpest and broadest endothermic peak, as shown in Figure 9B. The first endothermic peak might result from the dehydration of several hydrates like ettringite, C-S-H gel, and AFM (Wu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). It follows that more ettringite was generated in the UHPC mixture with an increased content of CEA. Furthermore, increasing CEA content could promote the hydration degree of UHPC (Jia et al., 2023).
The second endothermic peak in Figure 9B, approximately 370°C–470°C, might be because of Ca(OH)2 decomposition. The endothermic peak of calcium hydroxide without the CEA group remained the highest (Wang et al., 2023); furthermore, the peak corresponding to calcium hydroxide consistently decreased with CEA contents. As shown in Figure 9B, the generated calcium hydroxide of the UHPC sample diminished with CEA content. The possible reason was that the secondary hydration reaction of CEA and calcium hydroxide consumed a part of calcium hydroxide and generated more C-S-H gel. In Figure 9, mass loss of approximately 500°C–700°C might refer to the decomposition of CaCO3 in the UHPC samples. As illustrated in Figure 9B, the endothermic peak of CaCO3 in UHPC with 0% and 3% CEA was roughly equivalent, while the endothermic peak of CaCO3 in UHPC with 6% CEA slightly decreased. The analysis of TG and DTG images shows that the increase in the CEA content would increase ettringite and C-S-H gel quantity and decrease the calcium hydroxide quantity. Alterations in these hydration products would be beneficial for improving the mechanical performance and reducing autogenous shrinkage of UHPC.
3.5 Scanning electron microscopy
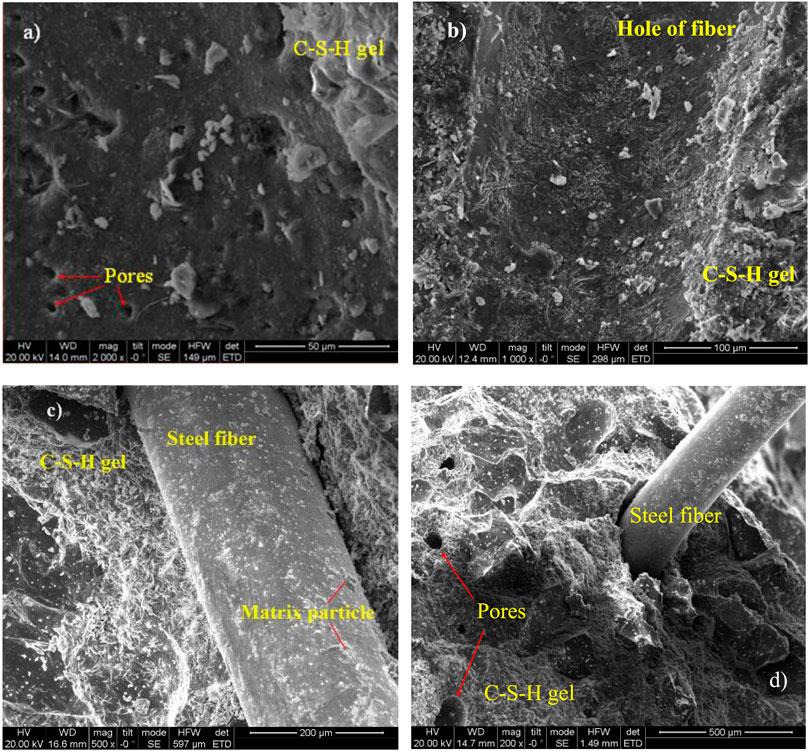
As shown in Figure 10, steel fibers, C-S-H gel, pores, and fiber–matrix interface of the UHPC samples were observed in the SEM images of the UHPC samples at 28 days. C-S-H gel was found on the steel fibers’ surface and the steel fibers’ hole, which could make the steel fibers’ surface rougher. Furthermore, it could enhance the bonded adhesion between steel fibers and matrix. Because of the finer particle size of the mixture proportions, UHPC had a denser matrix and higher interfacial stiffness than ordinary concrete. Both Ca(OH)2 crystals and the transition interface were not obvious in Figure 10. With the increased content of CEA, the UHPC matrix had been looser and more porous due to the expansion effect. There was no obvious interfacial transition zone between the matrix and aggregate and between the matrix and steel fiber. It was mainly due to the low water/binder ratio, small-sized aggregate, and high binder content of UHPC (Wu et al., 2023). There was no needle-like ettringite crystal to find because the microstructure of the matrix could wrap and cover ettringite. It was observed that matrix particles (C-S-H gel) were adhered on the steel fibers’ surface in Figure 10C. The reason for improving the UHPC mechanical strength by steel fibers is as follows: 1) the bridging effect and high elastic modulus of steel fibers; 2) the combined effect is beneficial for steel fiber–matrix bond (Wu et al., 2021). The effect of CEA and steel fibers on the mechanical performance of UHPC was compatible with its SEM images.
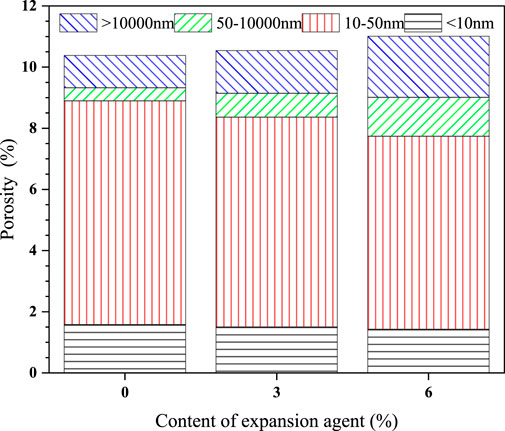
3.6 Pore size distribution
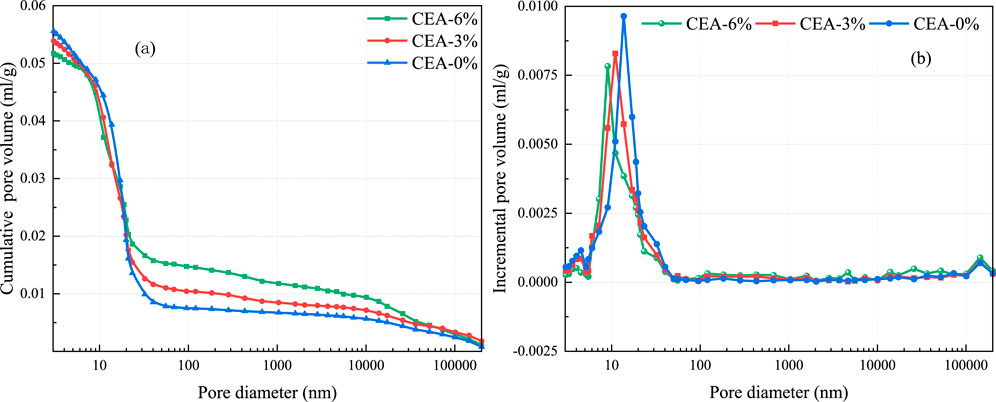
As shown in Figures 11, 12, the pore structure of samples could be investigated with MIP. The pore diameters of the highest peak in Figure 11B were approximately 10 nm. As shown in Figure 11, the incremental pore volume of UHPC decreased tremendously in 3–50 nm with the CEA content. However, with the increase of CEA, the cumulative pore volume increased markedly in Figure 11A of pore diameter ≥30 nm. As shown in Figure 12, the porosity of 10–50 nm accounts for the largest proportion. Furthermore, with the increase of CEA, the pore volume of 10–50 nm in UHPC decreased dramatically. The above variations in the pore structure were helpful for the reduction of UHPC autogenous shrinkage with CEA because autogenous shrinkage was primarily related to the pore size of 5–50 nm (Shen et al., 2020). However, because the expansion effect of the CEA could increase the volume of micropores, the total porosity and the pore volume of 50–10,000 nm and >10,000 nm in UHPC increased significantly with the increase of CEA. The total porosity of UHPC with CEA 0%, 3%, and 6% were 10.38%, 10.54%, and 11.01% at 28 days, respectively. With the increase of CEA, the pore structure of the UHPC samples would be looser, and the compressive strength of UHPC samples also decreased accordingly. It follows that CEA could increase the average pore size, which would decrease the mechanical properties of UHPC (Nagataki and Gomi, 1998; Zhou et al., 2023; Liao et al., 2023).
3.7 Autogenous shrinkage
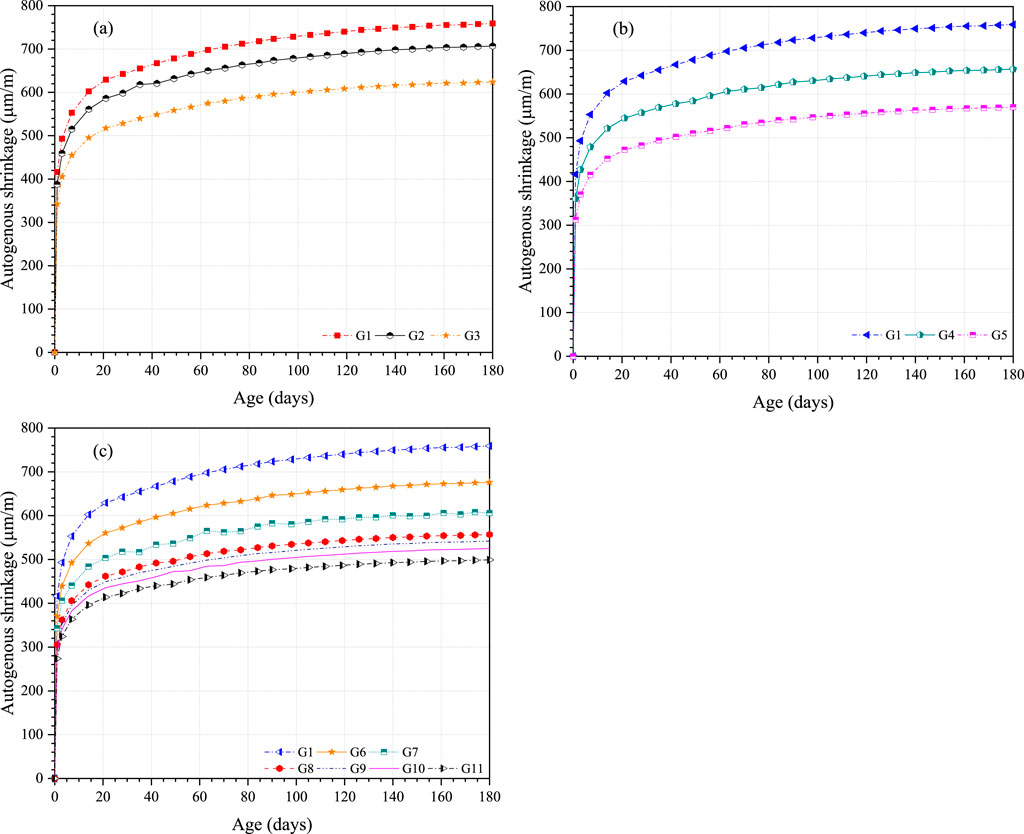
UHPC autogenous shrinkage having a diverse content of steel fibers or CEA is detailed in Figures 13, 14. Curves of autogenous shrinkage show a steep increase at an early age (Li et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2019), and then, those autogenous shrinkage curves became flat after approximately 1 week. Due to the rapid development of autogenous shrinkage in an early age, the difference in autogenous shrinkage between different groups of UHPC mainly occurs in an early age. The free water affecting autogenous shrinkage in the cement paste gradually decreased with age, and the expansion effect of MEA also decreased (Zhou et al., 2023). From Figure 13, UHPC autogenous shrinkage diminished significantly with the content of steel fibers. Autogenous shrinkage of G2 (707 × 10−6) and G3 (624 × 10−6) decreased by approximately 6.9% and 17.8% relative to that of G1 (759 × 10−6) at 180 days. Similarly, autogenous shrinkage of G4 (657 × 10−6) and G5 (570 × 10−6) diminished by approximately 13.4% and 24.9% relative to that of G1 at 180 days. Steel fibers in UHPC are vital for promoting mechanical performance and toughness and limiting shrinkage (Wu et al., 2019). Due to the high stiffness of steel fibers and bonded adhesion of steel fibers and matrix, UHPC autogenous shrinkage decreased. The steel fibers could balance the inner relative humidity with absorbed water, which helped diminish autogenous shrinkage (Ma et al., 2019). Because of the low elastic modulus of the paste at an early age, steel fibers could partially restrict UHPC autogenous shrinkage (Yang et al., 2019).
UHPC autogenous shrinkage with binary steel fibers and CEA was less than that with single steel fibers or CEA. The autogenous shrinkage of G7 (606 × 10−6), G8 (557 × 10−6), G9 (542 × 10−6), G10 (525 × 10−6), and G11 (499 × 10−6) decreased by approximately 10.4%, 17.6%, 19.8%, 22.3%, and 26.2% compared with that of G6 (676 × 10−6) at the age of 180 days, respectively. Consistent with UHPC with single steel fibers or CEA, the autogenous shrinkage diminished tremendously with CEA content. Due to the crystallization pressure and expansion effect of CEA, autogenous shrinkage of UHPC could be partially compensated (Yang et al., 2019). The randomly distributed steel fibers helped reduce pore pressure in UHPC, which was able to decrease autogenous shrinkage (Afroughsabet et al., 2018). For UHPC groups with a 2.5% dosage of binary steel fibers, the mixture containing 1.5% hooked-end fibers (G10) could reduce the autogenous shrinkage by 3% more than that with 1.5% straight fibers (G9). Because the bonded adhesion between hooked-end fibers and the matrix was more enhanced, hooked-end steel fibers could more efficiently limit autogenous shrinkage of UHPC relative to straight steel fibers (Fang et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2019).
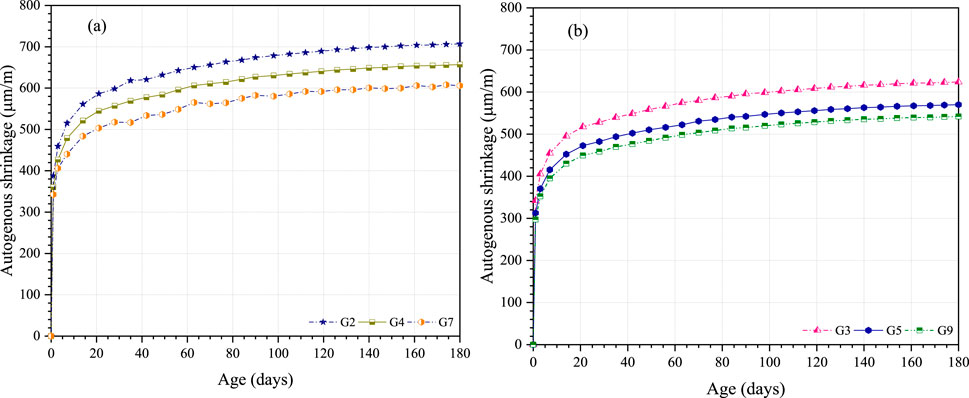
As shown in Figure 14, UHPC autogenous shrinkage diminished tremendously with CEA content. The autogenous shrinkage of G2 at 180 days was approximately 707 × 10−6, and the autogenous shrinkage of G4 and G7 with the same 0.5% steel fiber content was 657 × 10−6 and 606 × 10−6 (decreased by 7.1% and 14.3%, respectively). Similarly, autogenous shrinkage of G5 and G9 with 2.5% steel fiber content was 570 × 10−6 and 542 × 10−6, which was 8.7% and 13.1% lower than that of G3 (624 × 10−6), respectively. The content of 3% and 6% CEA in UHPC resulted in a decrease of compressive strength (28 days) by 0.8% and 1.4% (Vf = 0.5%); and 1.3% and 2.7%. Meanwhile, the autogenous shrinkage (180 days) of UHPC decreased by 7.1% and 14.3% (Vf = 0.5%); and 8.7% and 13.1% (Vf = 2.5%). It was indicated that the addition of CEA could effectively decrease the autogenous shrinkage of UHPC (7.1%–14.3%) with a slight reduction of its compressive strength (<2.7%).
A higher steel fiber content could benefit the internal curing effect (Shen et al., 2020). Furthermore, the higher the internal humidity is in UHPC, the more significant the reduction of autogenous shrinkage would be. Moreover, UHPC autogenous shrinkage was efficiently mitigated because of the expansion effect of CEA (Wei et al., 2023). As shown in Table 1, the main ingredient of the expansion agent was CaO, which could generate Ca(OH)2 and ettringite crystals in the hydration reaction. The micro-expansion effect of ettringite crystals benefits filling the pores of the cement paste. These favorable factors could decrease UHPC autogenous shrinkage.
4 Prediction models of the autogenous shrinkage of UHPC
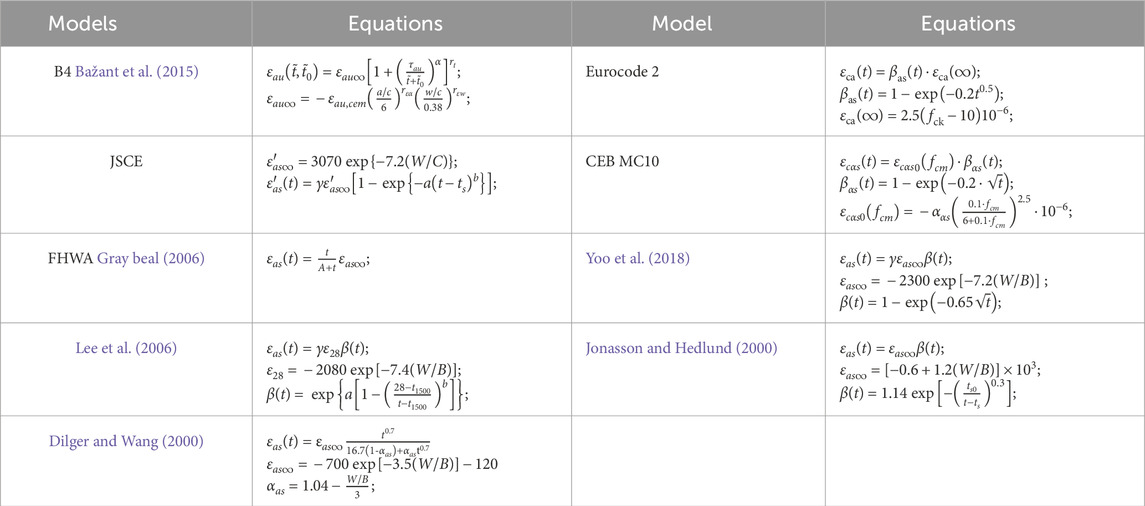
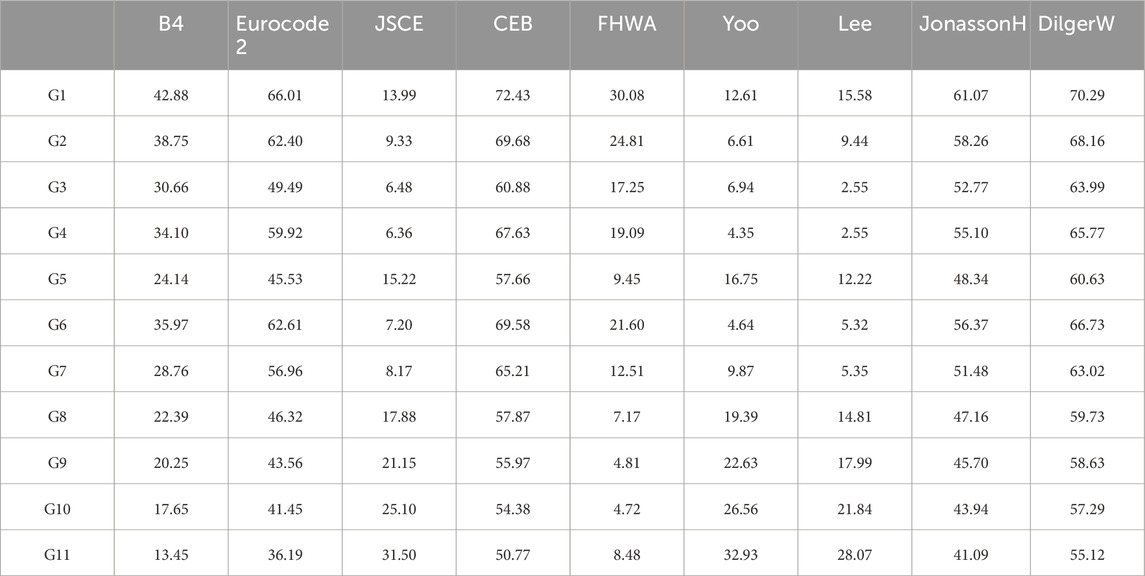
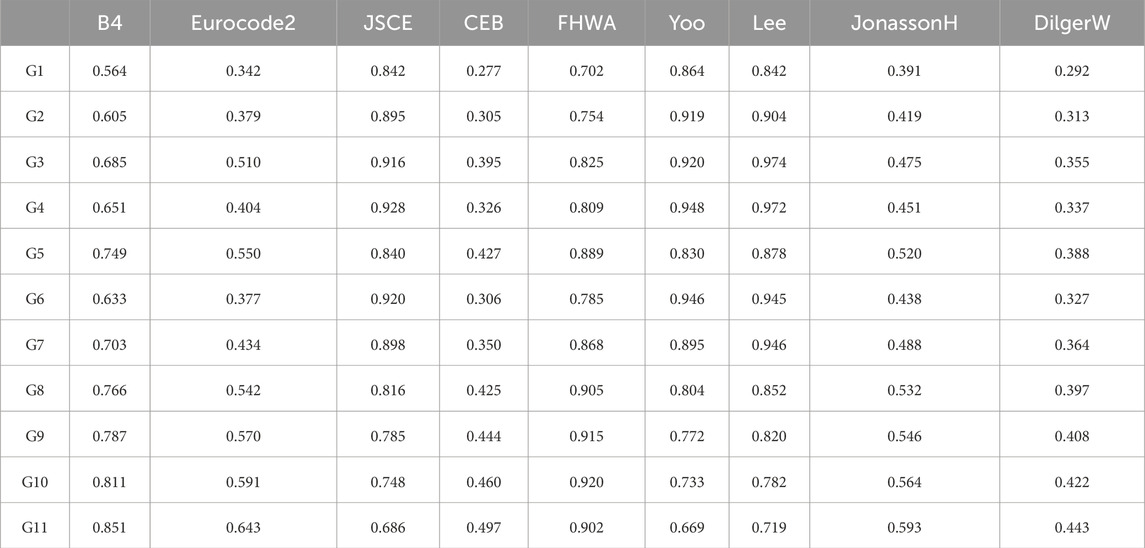
As shown in Table 5, there are nine prediction models that could be used to predict the autogenous shrinkage of UHPC.
As shown in Figure 15, the predicted autogenous shrinkage of all the 11 groups of UHPC with the B4 model was the same. Furthermore, the JSCE model, Yoo model, Lee model, JonassonH model, and DilgerW model prediction models also had no discrimination for predicting the autogenous shrinkage of these groups of UHPC. The reason was that w/c (water/cement), w/b (water/binder), a/c (aggregate/cement), and
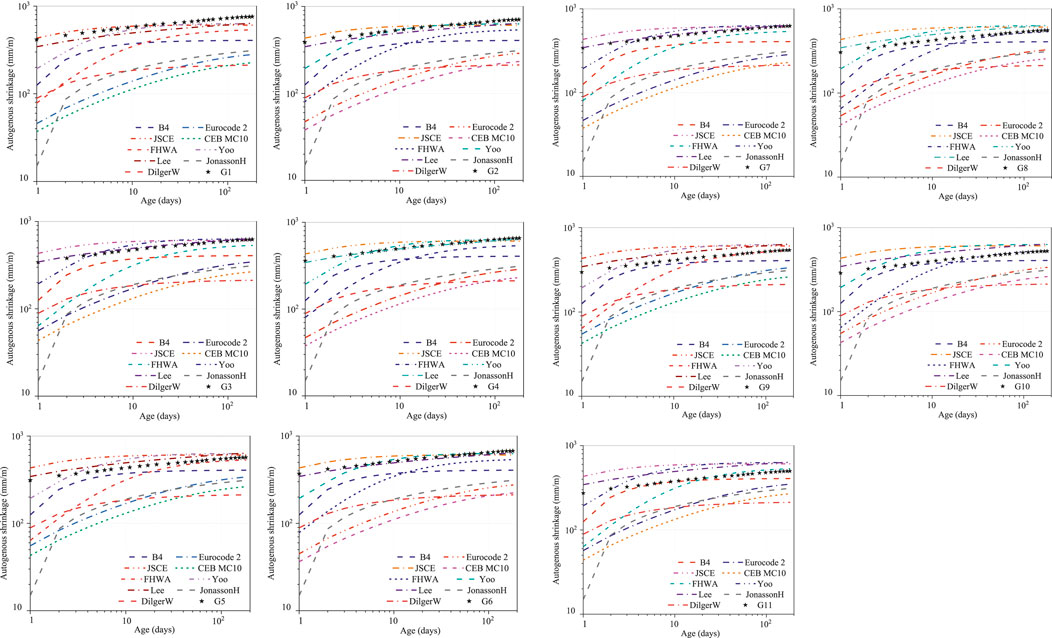
Figure 15. Predicted shrinkage of models and experimental shrinkage of UHPC with CEA and steel fibers.
This study measured the prediction deviation of 9 shrinkage models to 11 groups of UHPC with RE (relative error) or
As shown in Figure 15 and Table 6, 7, the prediction accuracy of the autogenous shrinkage of 11 groups of UHPC with the FHWA model, Lee model, Yoo model, and JSCE model was better than that of the other prediction models overall. For the G5, G8–G11 groups of UHPC, the prediction accuracy of the FHWA model in autogenous shrinkage was better than that of other shrinkage prediction models. According to the FHWA model (Graybeal, 2006), the ultimate shrinkage in the untreated curing regime
The prediction accuracy (RE > 50% and
The JonassonH model, Eurocode 2 model, CEB MC10 model, and DilgerW model had significantly underestimated the autogenous shrinkage of all 11 groups of UHPC at all ages; the JSCE, model, Yoo model, and Lee model had overestimated more or less the autogenous shrinkage of UHPC with high-content steel fibers and CEA (G5, G8–G11), but there was a little deviation in the prediction of the autogenous shrinkage of other groups of UHPC.
The prediction accuracy of shrinkage models varied from early age to late age. The shape of the prediction autogenous shrinkage curves of the Lee model was similar to the corresponding UHPC autogenous shrinkage experimental curves. The prediction deviation of the Lee model and experimental autogenous shrinkage in G2–G7 UHPC is relatively small in all ages. The deviation between the prediction autogenous shrinkage curves of the Lee model, JSCE model, and Yoo model and the autogenous shrinkage experimental curves of G2–G7 UHPC was relatively small from mid-age to late-age (after 20–30 days). The prediction deviation between the Lee model, JSCE model, and Yoo model and the autogenous shrinkage experimental curves of G1, G8–G11 UHPC were significant.
There are significant differences in the time function and the ultimate shrinkage among the nine shrinkage prediction models, which also determines that each shrinkage prediction model has different prediction errors for concrete shrinkage. There were some limitations to these shrinkage models in the prediction of UHPC autogenous shrinkage. First, these models did not consider the influence of UHPC compressive strength. Second, these models did not consider the difference in the water/cement ratio or water/binder ratio between UHPC and ordinary concrete. Third, the difference in material composition between UHPC and ordinary concrete was not reflected in these shrinkage models.
5 Conclusion
The study researched the microstructure, autogenous shrinkage, and mechanical performance of UHPC with CEA and steel fibers. Advanced materials characterization technology like XRD, TG, SEM, and MIP were carried out to explore the autogenous shrinkage characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical performance of UHPC. With experiments presented in our research, the results are summarized below:
1. Slump-flow and T500 of fresh UHPC mixture diminished significantly with steel fiber content, which could result from the bridging effect and agglomeration phenomenon of steel fibers. Meanwhile, slump-flow and T500 of fresh UHPC mixture decreased slightly with the CEA content.
2. UHPC mechanical performance increased dramatically with steel fiber content; however, it slightly diminished with CEA content. Losses of compressive strength and flexural strength relate to differences in microstructures, hydration products, and bonded adhesion of UHPC, as confirmed by SEM observations.
3. Diffraction peak intensity, the endothermic peak of Ca(OH)2, and pore volume of 10–50 nm diminished with the CEA content in UHPC. However, diffraction peak intensity, the endothermic peak of ettringite and C-S-H gel, and pore volume of above 50 nm augmented with the CEA content in UHPC. The results of XRD, TG, and MIP matched the results of the macroscopic experiment.
4. Autogenous shrinkage decreased markedly with single or binary addition of CEA and steel fibers. Relative to control group G2, group G11 binary addition of 3% steel fibers and 6% CEA could diminish autogenous shrinkage of UHPC at 180 days by 29.4%. It was due to the expansion effect of CEA and the relatively large stiffness and bridging effect of steel fibers. Constriction of hooked-end steel fibers on UHPC autogenous shrinkage was better than that of straight steel fibers.
5. Predicted autogenous shrinkage of nine prediction models and experimental autogenous shrinkage of 11 groups of UHPC were evaluated with RE,
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available; please see the paper. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Jia-rui Weng, MzQzMDk4MTQ3QHFxLmNvbQ==.
Author contributions
JW: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, validation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. WL: supervision and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation Project of Fujian Province (2023J011107) and the Scientific Research Project of Fujian Jiangxia University (JXZ2021008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Afroughsabet, V., Biolzi, L., and Monteiro, P. (2018). The effect of steel and polypropylene fibers on the chloride diffusivity and drying shrinkage of high-strength concrete. Compos. Part B Eng. 139, 84–96. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.047
Akca, K., and Ipek, M. (2022). Effect of different fiber combinations and optimisation of an ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) mix applicable in structural elements. Constr. Build. Mater. 315, 125777. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125777
Bažant, Z., Hubler, M., and Wendner, R., (2015). RILEM draft recommendation: TC-242-MDC multi-decade creep and shrinkage of concrete: material model and structural analysis*: model B4 for creep, drying shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage of normal and high-strength concretes with multi-decade applicability autogenous shrinkage of normal and high-strength concretes with multi-decade applicability. Mater. Struct., 48, 753–770. doi:10.1617/s11527-014-0485-2
Cui, Y., L, Y., and Wang, Q. (2023). Engineering performance and expansion mechanism of MgO expansion agent in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). J. Build. Eng. 68, 106079. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106079
Deng, Y., Zhang, Z., Shi, C., Wu, Z., and Zhang, C. (2023). Steel fiber-matrix interfacial bond in ultra-high performance concrete: a review. Eng. 22, 215–232. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2021.11.019
Dilger, W., and Wang, C. (2000). Creep and shrinkage of high-performance concrete, 194. ACI. Spec. Publ., 361–380.
Du, J., Meng, W., Khayat, K., Bao, Y., Guo, P., Lyu, Z., et al. (2021). New development of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Compos. Part B Eng. 224, 109220. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109220
European Committee for Standardization (2004). “EN 1992-1-1:2004. Design of concrete structures,” in General rules and rules for buildings.
Fang, C., Ali, M., Xie, T., Visintin, P., and Sheikh, A. (2020). The influence of steel fibre properties on the shrinkage of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 242, 117993. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117993
Geng, Z., Tang, S., Wang, Y., A, H., He, Z., Wu, K., et al. (2024). Stress relaxation properties of calcium silicate hydrate: a molecular dynamics study. J. Zhejiang Univ-Sc A 25, 97–115. doi:10.1631/jzus.A2300476
He, R., and Lu, N. (2023a). Unveiling the dielectric property change of concrete during hardening process by ground penetrating radar with the antenna frequency of 1.6 GHz and 2.6 GHz by ground penetrating radar with the antenna frequency of 1.6 GHz and 2.6 GHz. Cem. Concr. Compos. 144,105279. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.105279
He, R., and Lu, N. (2024a). Air void system and freezing-thawing resistance of concrete composite with the incorporation of thermo-expansive polymeric microspheres the incorporation of thermo-expansive polymeric microspheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 419, 135535. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135535
He, R., and Lu, N. (2024b). Hydration, fresh, mechanical, and freeze-thaw properties of cement mortar incorporated with polymeric microspheres incorporated with polymeric microspheres. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 7, 92. doi:10.1007/s42114-024-00899-2
He, R., Nantung, T., and Lu, N. (2024c). Unraveling microstructural evolution in air-entrained mortar and paste: insights from MIP and micro-CT tomography amid cyclic freezing-thawing damage paste: insights from MIP and micro-CT tomography amid cyclic freezing-thawing damage. J. Build. Eng. 94, 109922. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109922
He, R., Nantung, T., Olek, J., and Lu, N. (2023b). Field study of the dielectric constant of concrete: a parameter less sensitive to environmental variations than electrical resistivity. J. Build. Eng. 74, 106938. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106938
Japan Society of Civil Engineers. (2007). JSCE guidelines for concrete No.15. English version of standard specifications for concrete structures. Tokyo, Japan.
Jia, Z., Zhang, Z., Jia, L., Cao, R., Yu, C., Yu, J., et al. (2023). Effect of different expansive agents on the early age structural build-up process of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 144, 105282. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.105282
Jonasson, J., and Hedlund, H. (2000). “An engineering model for creep and shrinkage in high performance concrete,” in Proceedings of the international RILEM workshop on shrinkage of concrete, shrinkage (Paris, Bagneux, France: RILEM), 173–178.
Kim, T., and Olek, J. (2012). Effects of sample preparation and interpretation of thermogravimetric curves on calcium hydroxide in hydrated pastes and mortars. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2290, 10–18. doi:10.3141/2290-02
Lee, K., Lee, H., Lee, S., and Kim, G. (2006). Autogenous shrinkage of concrete containing granulated blast-furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 36, 1279–1285. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.01.005
Lee, N., Jang, J., and Lee, H. (2014). Shrinkage characteristics of alkali-activated fly ash/slag paste and mortar at early ages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 53, 239–248. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.07.007
Li, S., Mo, L., Deng, M., and Cheng, S. (2021). Mitigation on the autogenous shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete via using MgO expansive agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 312, 125422. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125422
Liao, Y., Wang, S., Wang, K., Qunaynah, S., Wan, S., Yuan, Z., et al. (2023). A study on the hydration of calcium aluminate cement pastes containing silica fume using non-contact electrical resistivity measurement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 24, 8135–8149. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.080
Liu, G., Kan, D., Cao, S., Chen, Z., and Lyu, Q. (2022). Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotube on reactive powder concrete (RPC) performance in sulfate dry-wet cycling environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 342, 128075. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128075
Liu, K., Yu, R., Shui, Z., Li, X., Guo, C., Yu, B., et al. (2019). Optimization of autogenous shrinkage and microstructure for Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) based on appropriate application of porous pumice. Constr. Build. Mater. 214, 369–381. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.089
Liu, L., Fang, Z., Huang, Z., and Wu, Y. (2022). Solving shrinkage problem of ultra-high-performance concrete by a combined use of expansive agent, super absorbent polymer, and shrinkage-reducing agent. Compos. Part B Eng. 230, 109503. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109503
Lu, Y., Han, J., Wang, P., Wu, X., Hwang, H., Zhou, J., et al. (2020). Flexural strengthening of reinforced concrete beams or slabs using ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): a state of the art review. Eng. Struct. 205, 110035. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.110035
Ma, R., Guo, L., Ye, S., Sun, W., and Liu, J. (2019). Influence of Hybrid Fiber Reinforcement on mechanical properties and autogenous shrinkage of an ecological UHPFRCC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 31 (5), 04019032. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002650
Moon, J., Youm, K., Lee, J., and Yun, T. (2022). Flowability and mechanical characteristics of self-consolidating steel fiber reinforced ultra-high performance concrete. Steel. compos. Struct. 43 (3), 389–401. doi:10.12989/scs.2022.43.3.389
Mu, Ru., Chen, J., Chen, X., Diao, C., Wang, X., and Qing, L. (2023). Effect of the orientation of steel fiber on the strength of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Constr. Build. Mater. 406, 133431. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133431
Nagataki, S., and Gomi, H. (1998). Expansive admixtures (mainly ettringite). Cem. Concr. Compos. 20 (2–3), 163–170. doi:10.1016/S0958-9465(97)00064-4
Nguyen, T., Thai, H., and Ngo, T. (2023). Effect of steel fibers on the performance of an economical ultra-high strength concrete. Struct. Concr. 24 (2), 2327–2341. doi:10.1002/suco.202200326
Puertas, F., and Torres-Carrasco, M. (2014). Use of glass waste as an activator in the preparation of alkali-activated slag. Mechanical strength and paste characterisation. Cem. Concr. Res. 57, 95–104. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.12.005
Ren, G., Gao, X., and Zhang, H. (2022). Utilization of hybrid sisal and steel fibers to improve elevated temperature resistance of ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 130, 104555. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104555
Shen, P., Lu, L., He, Y., Wang, F., Lu, J., Zheng, H., et al. (2020). Investigation on expansion effect of the expansive agents in ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 105, 103425. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103425
Tang, S., Wang, Y., Geng, Z., Xu, X., Yu, W., A, H., et al. (2021). Structure, fractality, mechanics and durability of calcium silicate hydrates. Fractal. Fract. 5, 47. doi:10.3390/fractalfract5020047
Wang, J., Wang, X., Ding, S., Ashour, A., Yu, F., Lv, X., et al. (2023). Micro-nano scale pore structure and fractal dimension of ultra-high performance cementitious composites modified with nanofillers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 141, 105129. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.105129
Wang, L., Guo, F., Lin, Y., Yang, H., and Tang, S. (2020). Comparison between the effects of phosphorous slag and fly ash on the C-S-H structure, long-term hydration heat and volume deformation of cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 250, 118807. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118807
Wang, L., Jin, M., Zhou, S., Tang, S., and Lu, X. (2021). Investigation of microstructure of C-S-H and micro-mechanics of cement pastes under NH4NO3 dissolution by 29Si MAS NMR and microhardness. Measurement 185, 110019. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110019
Wang, X., Wu, D., Geng, Q., Hou, D., Wang, M., Li, L., et al. (2021). Characterization of sustainable ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) including expanded perlite. Constr. Build. Mater. 303, 124245. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124245
Washburn, E. (1921). Note on a method of determining the distribution of pore sizes in a porous material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 7, 115–116. doi:10.1073/pnas.7.4.115
Wei, K., Xu, G., Yang, J., Zhao, Y., and Sun, Y. (2023). Study on mechanical and shrinkage properties of ES-UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 377, 131137. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131137
Weng, J., and Liao, W. (2021). Microstructure and shrinkage behavior of high-performance concrete containing supplementary cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 308, 125045. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125045
Wu, H., Shen, A., Cai, Y., Ma, Q., Ren, G., Deng, S., et al. (2023). Interfacial bond properties and pullout behaviors of steel fibers embedded in ultra-high-performance concrete: a review. Mater. tod. Comm. 35, 106081. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106081
Wu, N., Ji, T., Huang, P., Fu, T., Zheng, X., and Xu, Q. (2022). Use of sugar cane bagasse ash in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) as cement replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 317, 125881. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125881
Wu, Z., Khayat, K., Shi, C., Tutikian, B., and Chen, Q. (2021). Mechanisms underlying the strength enhancement of UHPC modified with nano-SiO2 and nano-CaCO3. Cem. Concr. Compos. 119, 103992. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.103992
Wu, Z., Shi, C., and Khayat, K. (2019). Investigation of mechanical properties and shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete: influence of steel fiber content and shape. Compos. Part B Eng. 174, 107021. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107021
Xiong, X., Wu, M., Shen, W., Li, J., Zhao, D., Li, P., et al. (2022). Performance and microstructure of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) with silica fume replaced by inert mineral powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 327, 126996. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126996
Xu, S., Yuan, P., Liu, J., Pan, Z., Liu, Z., Su, Y., et al. (2022). Development and preliminary mix design of ultra-high-performance concrete based on geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 308, 125110. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125110
Yan, P., Chen, B., Afgan, S., Haque, M., Wu, M., and Han, J. (2021). Experimental research on ductility enhancement of ultra-high performance concrete incorporation with basalt fibre, polypropylene fibre and glass fibre. Constr. Build. Mater. 279, 122489. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122489
Yang, L., Shi, C., and Wu, Z. (2019). Mitigation techniques for autogenous shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete – a review. Compos. Part B Eng. 178, 107456. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107456
Yoo, D., Kim, J., and Chun, B. (2019). Dynamic pullout behavior of half-hooked and twisted steel fibers in ultra-high-performance concrete containing expansive agents. Compos. Part B Eng. 167, 517–532. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.022
Yoo, D., Kim, M., Kim, S., Ryu, G., and Koh, K. (2018a). Effects of mix proportion and curing condition on shrinkage behavior of HPFRCCs with silica fume and blast furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 166, 241–256. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.126
Yoo, D., Kim, S., and Kim, M. (2018b). Comparative shrinkage behavior of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete under ambient and heat curing conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 162, 406–419. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.029
Yu, R., Liu, K., Yin, T., Tang, L., Ding, M., and Shui, Z. (2022). Comparative study on the effect of steel and polyoxymethylene fibers on the characteristics of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC). Cem. Concr. Compos. 127, 104418. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104418
Zhang, C., Wu, Z., Luo, C., Hu, X., Li, K., Shi, C., et al. (2022). Size effect of ultra-high-performance concrete under compression: effects of steel fiber characteristics and water-to-binder ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 330, 127170. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127170
Zhou, X., Hou, D., Chen, T., Dong, Y., and Wang, X. (2023). The development of concrete filled steel tube with enhanced performance via the use of expansive ultra high performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 79, 107793. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107793
Zhou, Y., Huang, J., Yang, X., Dong, Y., Feng, T., and Liu, J. (2021). Enhancing the PVA fiber-matrix interface properties in ultra high performance concrete: an experimental and molecular dynamics study. Constr. Build. Mater. 285, 122862. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122862
Zhou, Y., Li, W., Peng, Y., Tang, S., Wang, L., Shi, Y., et al. (2023). Hydration and fractal analysis on low-heat Portland cement pastes using thermodynamics-based methods. Fractal. Fract. 7, 606. doi:10.3390/fractalfract7080606
Zhu, X., Kang, X., Yang, K., and Yang, C. (2017). Effect of graphene oxide on the mechanical properties and the formation of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) in alkali-activated slag cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 132, 290–295. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.059
Zhu, X., Tang, D., Yang, K., Zhang, Z., Li, Q., Pan, Q., et al. (2018). Effect of Ca(OH)2 on shrinkage characteristics and microstructures of alkali-activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 175, 467–482. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.180
Keywords: shrinkage prediction model, autogenous shrinkage, UHPC, microstructure, expansive agent
Citation: Weng J and Liao W (2024) Autogenous shrinkage prediction models and microstructure of UHPC with single or binary addition of an expansive agent and steel fibers. Front. Mater. 11:1427230. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1427230
Received: 03 May 2024; Accepted: 04 September 2024;
Published: 25 September 2024.
Edited by:
Syed Minhaj Saleem Kazmi, RMIT University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Shengwen Tang, Wuhan University, ChinaChuanqing Fu, Zhejiang University of Technology, China
Mingzhi Wang, Harbin Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Weng and Liao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: WenCheng Liao, d2NsaWFvQG50dS5lZHUudHc=
 JiaRui Weng
JiaRui Weng WenCheng Liao2*
WenCheng Liao2*