- 1NJSC Kh. Dosmukhamedov Atyrau University, Atyrau, Kazakhstan
- 2Research Institute of New Chemical Technologies, L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan
- 3Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg, Russia
The increase in industrial waste is a significant threat to the environment and economy, as most of it is non-biodegradable. The utilization of waste materials in road construction is effective in terms of recycling, economy, and ecology. The objective of the research is to investigate the potential use of four different industrial wastes – red mud (RM), blast furnace slag (BFS), lime production waste (LPW), and natural loam (NL) – as base materials in road construction. The mechanical and chemical properties of these materials were investigated through X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, atomic absorption spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, and axial compressive strength testing. The structural performance was also conducted for different compositions of the materials by varying ratios of these materials. The results indicate that the combination of 40% RM, 35% BFS, and 8% LPW exhibited the maximum compressive strength of 14.21 MPa after 365 days with lower linear expansion. The mineral composition analysis confirms the absence of heavy metal contaminants and hazardous compounds, which will be environmentally friendly. The findings suggest that a mixture of RM, BFS, LPW, and NL can be considered construction materials in the transportation sector.
1 Introduction
Road construction and maintenance are crucial for social and socioeconomic development, but they impose negative environmental consequences. However, these activities present significant challenges by contributing to environmental degradation through greenhouse gas emissions, material overuse, and waste generation, necessitating innovative solutions to balance infrastructure needs with sustainability goals. Construction often involves substantial material exploration and mass hauling, increasing greenhouse gas emissions (Baabou et al., 2022; Qian et al., 2023a). The soil beneath a road pavement is referred to as subgrade materials. These materials frequently need to be modified or re-engineered to increase their capacity to handle the weight of the road pavement and the traffic loads (Akinwumi et al., 2023). The road pavement structure may break early due to expansive soils generating discomfort. Soil stabilization is a commonly used procedure to improve the physical and geotechnical properties of soil. There are two broad categories of soil improvement approaches: mechanical and chemical stabilization. Reports suggest that chemical soil stabilization methods have been successful in addressing issues related to expansive subgrades (Qian et al., 2023b; Akinwumi et al., 2023). Various industrial wastes can enhance the strength characteristics of clayey soils by inducing pozzolanic reactions, ionic exchanges, and flocculation of treated soil particles (Manso et al., 2013). Cement, commonly used for improving the technical properties of expanding subgrade materials (Finnveden et al., 2016), can be augmented with red mud (RM), an easily accessible and cost-effective industrial by-product (Oguntola and Simske, 2023; Corder et al., 2014). Red mud (RM) is a by-product of the Bayer process for alumina extraction. It is characterized by its high alkalinity and contains key components such as Fe₂O₃, SiO₂, and Al₂O₃. Blast furnace slag (BFS) is a by-product of pig iron production in blast furnaces, containing significant quantities of calcium, silica, and alumina. Lime production waste (LPW) is generated during lime manufacturing and is rich in calcium compounds, making it a potential activator in pozzolanic reactions. Natural loam (NL) is a naturally occurring soil material with a balanced composition of sand, silt, and clay, used as a base material for stabilization in this study.
Researchers have made significant efforts to utilize RM (Giurco et al., 2014) while minimizing its environmental impact. However, the disposal of RM poses substantial challenges due to its high pH (between 10 and 13) and large quantity (Jakab et al., 2023). RM has harmful effects on humans and the environment. Its high alkalinity, fine particles containing heavy metals, and radioactive components such as uranium-238 and thorium-232 are the leading causes of concern (Mayes et al., 2016). These materials, when combined, create a matrix capable of generating essential C-S-H and C-A-S-H gels, enhancing both strength and durability. Each material contributes unique properties: RM introduces high pozzolanic potential, BFS improves hydraulic properties, LPW acts as an activator, and NL provides structural stability.
Extensive research efforts have been devoted to exploring the gelation properties of RM and assessing the potential for fabricating cementitious materials through its amalgamation with blast furnace slag (BFS). This synergistic combination capitalizes on enhanced pozzolanic reactions facilitated by the interaction between RM’s silica and alumina components alongside the calcium oxide found in lime production waste (LPW). The intricate interplay of these elements culminates in the generation of essential C-S-H and C-A-S-H gel formations.
The composition of RM, LPW, BFS, and natural loam (NL) are mainly shaped by its elemental constituents, which prominently include CaO, Fe2O3, SiO2, and Al2O3 as listed in Table 1 with the references to literature sources. Additionally, BFS is a by-product of pig iron manufacturing in blast furnaces, which is often used for soil stabilization purposes. If BFS is used together with RM, then BFS contributes its unique properties to the resulting cementitious matrix (Liu and Poon, 2016).
The optimization of the material composition is a critical aspect of this study, aiming to achieve the desired mechanical properties and environmental sustainability. By carefully selecting and balancing the proportions of RM, BFS, LPW, and NL, this research seeks to enhance the performance of the composite while minimizing its environmental footprint. This approach not only addresses pressing challenges in road construction but also underscores the potential of industrial by-products in sustainable material development.
Previous research has demonstrated the potential benefits of utilizing industrial wastes in construction. For example, Kumar and Kumar (2013) investigated the use of RM in combination with fly ash for soil stabilization, revealing significant improvements in soil strength and reduced environmental impact (Kumar and Kumar, 2013). Similarly, Valcuende et al. (2015) investigated the shrinkage of self-compacting concrete with BFS as fine aggregate, showing reduced shrinkage and increased strength (Valcuende et al., 2015). These findings are corroborated by Ahmad et al. (2022), who explored the mechanical and durability performance of concrete partially substituted with waste glass ащкand recycled concrete aggregate, highlighting the sustainable potential of such materials (Ahmad et al., 2022).
Despite these advances, the combined use of multiple industrial wastes in a single, optimized mixture for road construction remains underexplored. Most studies have focused on individual materials rather than synergistic combinations that could potentially offer superior performance and environmental benefits.
This study aims to develop an environmentally sustainable road-based material by replacing a substantial amount of natural resources with industrial solid wastes, specifically LPW, RM, and BFS. The objective is to reduce the dependence on natural resources and promote a more environmentally conscious approach to road construction. Unlike previous studies, this research comprehensively characterizes the mechanical and chemical properties of these materials through advanced analytical techniques and evaluates their performance in various compositions. By identifying the optimal mixture and confirming the absence of hazardous compounds, this study contributes significantly to the fields of waste management and sustainable construction.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Raw materials
Materials were sourced from various locations within Kazakhstan, including blast-furnace slag from the Metallurgical Plant ArcelorMittal Temirtau in Karaganda, RM from the Aluminum Plant in Pavlodar, and refuse from limestone production at the Lime Plant in Maikain of the Pavlodar region. A sample of NL was collected from a quarry near Astana city for the extraction of non-metallic materials.
2.2 Methods
The mineral composition was analyzed using XRD with the Philips PW 1830/40 Powder diffractometer situated in Caerphilly, United Kingdom. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed with the Ultra Plus instrument from Carl Zeiss AG to investigate the surface morphology of the samples. The atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) on a Perkin Elmer 4100 spectrometer (Waltham, MA, United States) was employed to conduct elemental analysis of the solubility and leaching of metals from liquid extracts. For the leaching tests, the following conditions were used: a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 (L/kg), a leaching time of 24 h, and a rotation speed of 10 rpm. These conditions were selected to simulate standard environmental leaching scenarios and ensure consistent and reproducible results. The carbonate content of the developed materials is determined by the calcimeter method. The study of strength changes in the samples during material hydration was conducted by examining the uniaxial compressive strength using an EMIC automatic press with a total capacity of 1, 10, and 100 tons, using a calibrated compression testing machine conforming to relevant standards, such as ASTM C39/C39M for concrete specimens. The specimens were cylindrical with a diameter of 30 mm and a height of 30 mm. Specimens were cured under standard laboratory conditions at an optimal humidity of 10%–12%.
2.3 Experimental procedures
Nine different samples were tested at various time intervals of 3, 7, 14, 28, 60, 90, 180, and 365 days, resulting in a total of approximately 900 samples. These nine samples were created by mixing different ratios of RM, BFS, LPW, and NL components. The proportions of RM, BFS, LPW, and NL were determined based on prior research and an extensive literature review. Several variations of the mixture were prepared to optimize the composition, and 9 samples were selected for further testing. The strength properties of these samples were evaluated, guiding the selection of the final composition. For instance, the first mix (R20-B25-L4) contained 20% RM, 25% BFS, and 4% LPW. The proportions of all mixes are summarized in Table 2. The other eight mixes were labeled similarly (Figure 1).
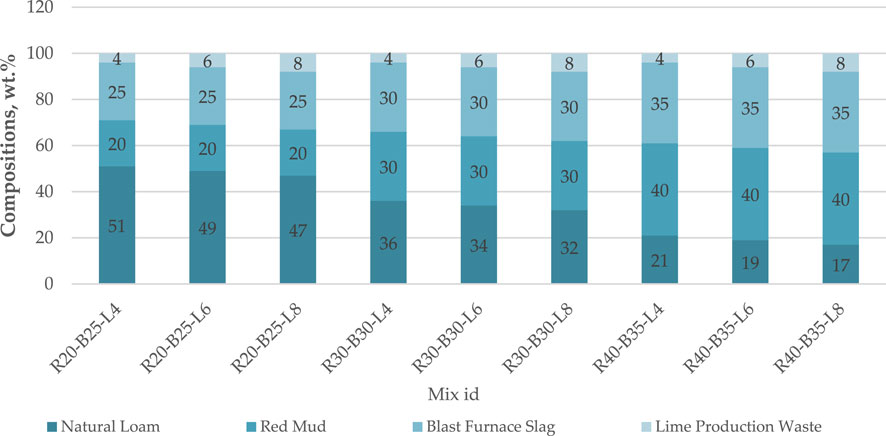
Figure 1. The mixing combination of Natural Loam, Red Mud, Blast Furnace Slag, and Lime Production Waste (wt.%).
3 Results and discussions
This section presents the results of a study of changes in samples’ physical and mechanical properties due to their hydration and curing for 365 days. The mechanical properties of the samples were calculated as the average and standard deviation of nine sample measurements. Raw materials characterization was discussed in the authors’ previous article (Alzhanova et al., 2022). Among the prepared variations, 9 samples were systematically tested for strength and durability. The selected composition demonstrated optimal mechanical properties, aligning with the study’s objectives.
The use of industrial wastes such as RM, BFS, and LPW contributes not only to environmental sustainability but also to enhancing the composite’s mechanical properties. These components play a crucial role in improving strength, durability, and economic feasibility, aligning with the objectives of sustainable material development.
3.1 Compressive strength of test specimens
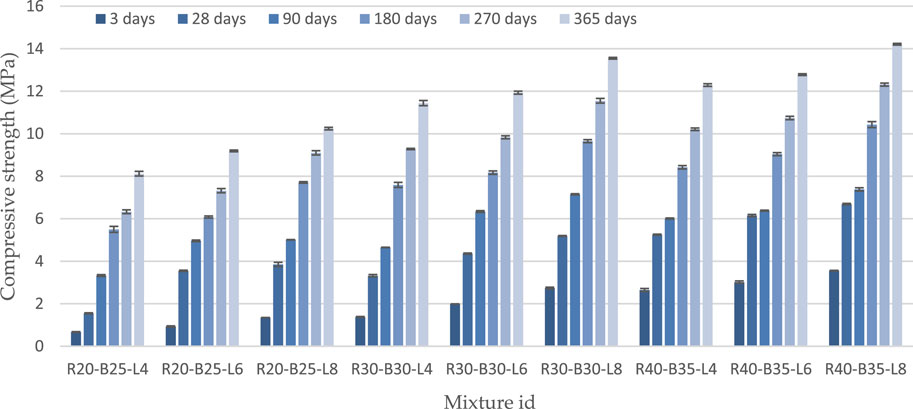
Analysis of the strength testing results of samples from NL, strengthened with RM and BFS, activated by the addition of LPW, show an almost constant increase in the strength of all compositions up to 365 days of age in the samples. Figure 2 shows the changes in the samples’ compressive strength test from 3 to 365 days. The samples’ strength was 0.67–3.56 MPa in 3 days, 3.33–7.38 MPa after 90 days, after 180 days 5.5–10.43 MPa, and 8.12–14.21 MPa after 365 days. The results indicated that the optimum strength was obtained from the samples R30-B30-L8 and R40-B35-L8. The addition of BFS, RM, and LPW improved compressive strength. The strength of composites increases slowly during the year. In the context of mixing soil with RM, BFS, and LPW, chemical reactions occur between these components, significantly improving strength. The alkaline solution acts as an activator of binding on particle surfaces. Increasing LPW, RM, and BFS content in materials invariably increases their strength over time. This increase in strength leads to a decrease in the consumption of alkaline Ca and Mg ions to create and maintain the high alkalinity necessary for the processes of alkaline excitation of surfaces of chemically neutral soil particles and slag particles with the removal of amounts of Ca and Mg ions into the interstitial space. The development of the C–S–H gel was aided by reactive CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 in raw materials. Components react exceedingly slowly with water, resulting in the development of a hardening binder. This slow but steady reaction process is crucial for the long-term strength development of the composites.
The observed trends can be further explained by examining the pozzolanic and hydraulic properties of BFS and RM. The pozzolanic reaction between the silica and alumina in RM and the calcium hydroxide from LPW leads to the formation of additional C-S-H, which is responsible for the strength gain. Similarly, the hydraulic reaction of BFS, which involves the hydration of latent hydraulic components like CaO and SiO2, contributes to the development of a dense microstructure, enhancing compressive strength (Meena et al., 2024).
Moreover, the synergistic effects of these materials result in improved packing density and reduced porosity, which are critical for the mechanical performance of the composites. The fine particles of RM fill the voids between larger particles of BFS and NL, resulting in a denser matrix. This enhanced packing density reduces the pathways for water ingress, thus improving the durabilit and long-term performance of the material.
3.2 Changes in the carbonate content of materials during the hydration of samples
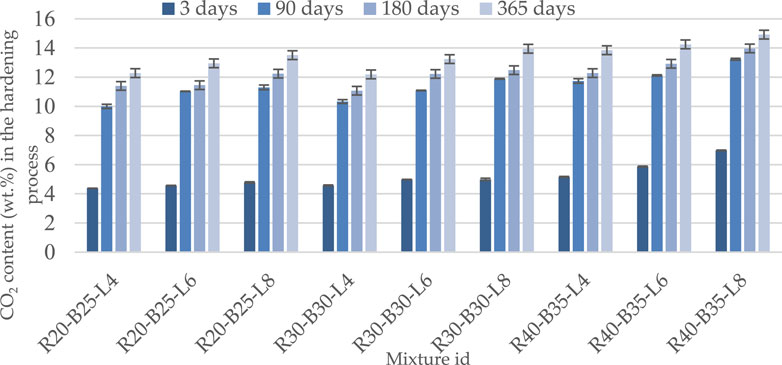
Figure 3 illustrates the carbonatization of the studied compounds after the mixtures are hydrated for up to 365 days. The amount of carbon dioxide absorption from the atmosphere is directly proportional to the amount of calcium oxide injected and the time after hydration begins.
Carbonatization is a crucial phenomenon in the context of cementitious materials, as it influences the long-term durability and mechanical properties of concrete structures. The incorporation of carbon dioxide into the material matrix leads to the formation of carbonate minerals, such as calcite, which can affect the microstructure and overall performance of the material.
Figure 3 shows that the synthesis of crystalline or amorphous calcite cannot provide such increases in the strength of samples. The carbonate content values of the samples ranged from 4.38%–6.98% at 3 days, 10.00%–13.23% at 90 days, 11.4%–13.97% at 180 days, and 12.38%–14.92% at 365 days.
These findings underscore the dynamic nature of carbonatization and its implications for the performance of cementitious materials over extended periods. By elucidating the relationship between carbon dioxide absorption, calcium oxide content, and hydration time, our study contributes to a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying the long-term behavior of materials.
3.3 The morphological structure of the compositions
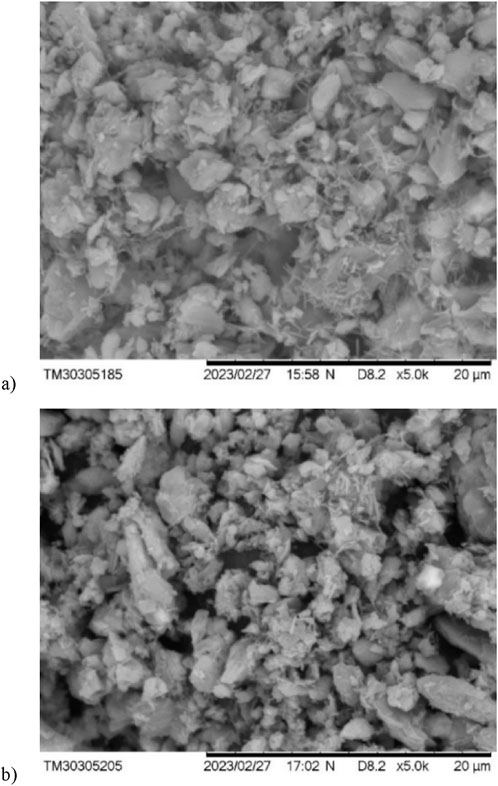
Figure 4 shows the microscopic images of the composition obtained by SEM. Analyzing samples reveals the accumulation of primarily amorphous new forms in the pore space. SEM images of samples R30-B30-L8 and R40-B35-L8 cured for 28 days are shown in Figure 3 (a and b, respectively). As illustrated, an amount of ettringite features filled the interspaces of other particles, followed by some hydrated C-S-H gel. The results of SEM and XRD agree with one another. The strength of samples may be influenced by both ettringite and C-S-H gel. As a result, the structure is more packed, denser, and compacted, with increased strength. Increased curing time will result in more C-S-H gel, which will improve the compressive strength of the mixture.
Previous research by Vanhatalo et al. (2018) demonstrated the role of ettringite and C-S-H gel in improving the mechanical properties of cementitious materials, corroborating our findings. Additionally, studies conducted by Johnson et al. (2019) have highlighted the impact of curing time on the formation of C-S-H gel and its subsequent effect on compressive strength.
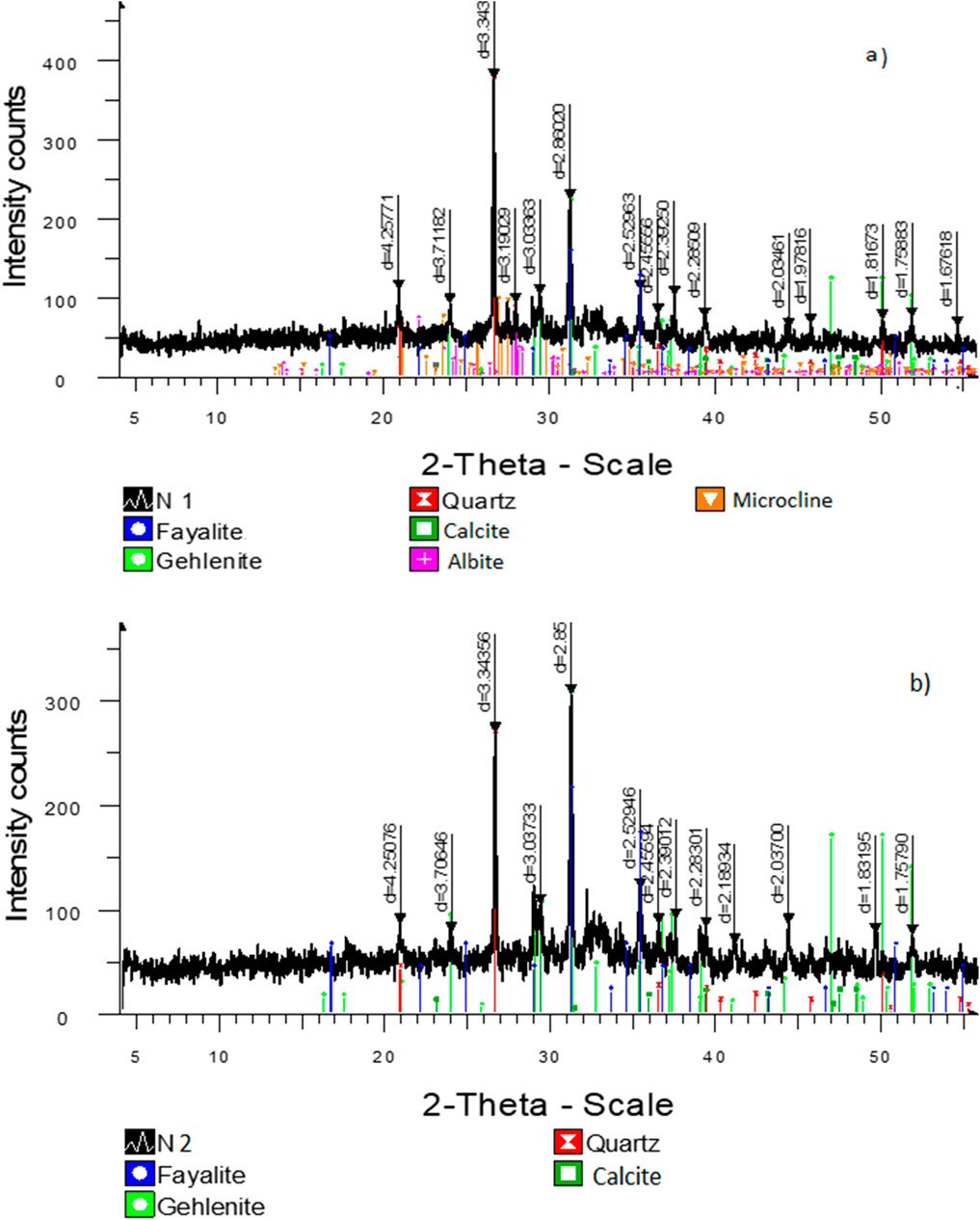
3.4 Change in mineral composition during hydration
On a semi-quantitative basis, X-ray phase analysis was performed on powder using a diffractogram of powder samples using equal attachments and artificial mixtures. A quantitative ratio of crystal phases was determined. Characteristic diffraction reflexes allowing identification of the phases present are noted. The mineral composition of dry mixes for compositions R30-B30-L8 and R40-B35-L8 are presented in Figure 4. In both mixtures, the main components are fayalite, gehlenite, quartz, and calcite. Figure 4A shows the presence of minerals fayalite (33%), gehlenite (29.7%), quartz (22.4%), calcite (6.2%), albite (4.6%), and microcline (4.0%) in a dry mix of composition R30-B30-L8. Figure 4B shows the presence of minerals fayalite (41.7%), gehlenite (37.9%), quartz (14.6%), and calcite (5.7%) in a dry mix of composition R40-B35-L8. The presence of albite and microcline minerals in the dry mixture R30-B30-L8 is related to the amount of NL (34%). CaO is critical in the strength development process; in the presence of moisture, it forms Ca (OH)2, which serves a dual purpose by providing an alkaline environment while also reacting with siliceous and aluminous compounds present in raw materials to form C-S-H and C-A-S-H gels. In an alkaline environment, these siliceous and aluminous compounds react with Ca (OH)2 generated from the hydration of cement to form cementitious materials that will enhance the strength of the road base. The detailed mechanism is explained in the XRD of samples.
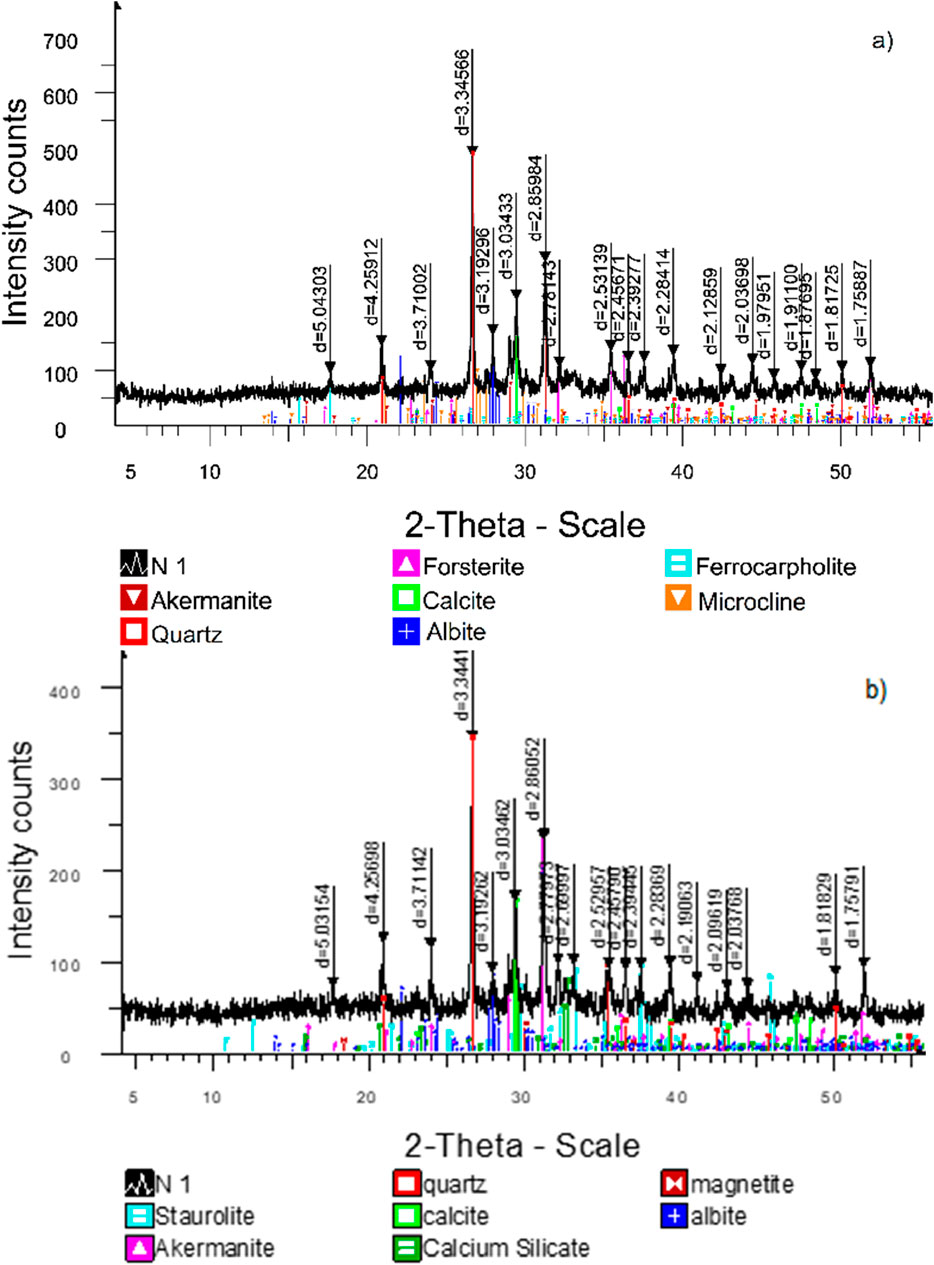
The compositions R30-B30-L8 and R40-B35-L8 were chosen for analysis due to their high physical properties and maximum intensity of the processes that took place, making them more accessible for detection. XRD patterns of composites R30-B30-L8 and R40-B35-L8 after 90 and 180 hydration days (Figures 5, 6) show a rise in intensity in all three mineral peaks - calcite, quartz, and albite. Indeed, materials hydrated with lime and left in open air for 180 days would produce carbonates. However, a more significant amount of crystalline quartz cannot be created under these circumstances as it requires extremely high temperatures and pressures. The only explanation for the rise in quartz peaks is the alkaline corrosion of the sand particles at the surface, which have been mechanically eroded throughout their lengthy geological history.
Figure 6 shows the XRD patterns for composition R30-B30-L8 at 90 and 180 days of curing. The analysis reveals that certain crystalline phases, such as quartz, calcite, and albite, retained their nature even after the alkali activation process. However, there were notable changes in their relative content. The results of semi-quantitative X-ray phase analysis of crystalline phases of composite R30-B30-L8 in 90 days (Figure 5A) show the presence of minerals like akermanite (32.0%), quartz (26.6%), forsterite (16.6%), calcite (8.2%), albite (7.4%), ferrocarpholite (5.5%), and microcline (3.6%). The akermanite peak appears around 27° and has a greater intensity. The results of composite R30-B30-L8 in 180 days (Figure 5A) show the presence of minerals like staurolite (28.1%), akermanite (23.3%), quartz (20.9%), calcite (10.0%), calcium silicate (7.7%), magnetite (5.6%), and albite (4.5%).
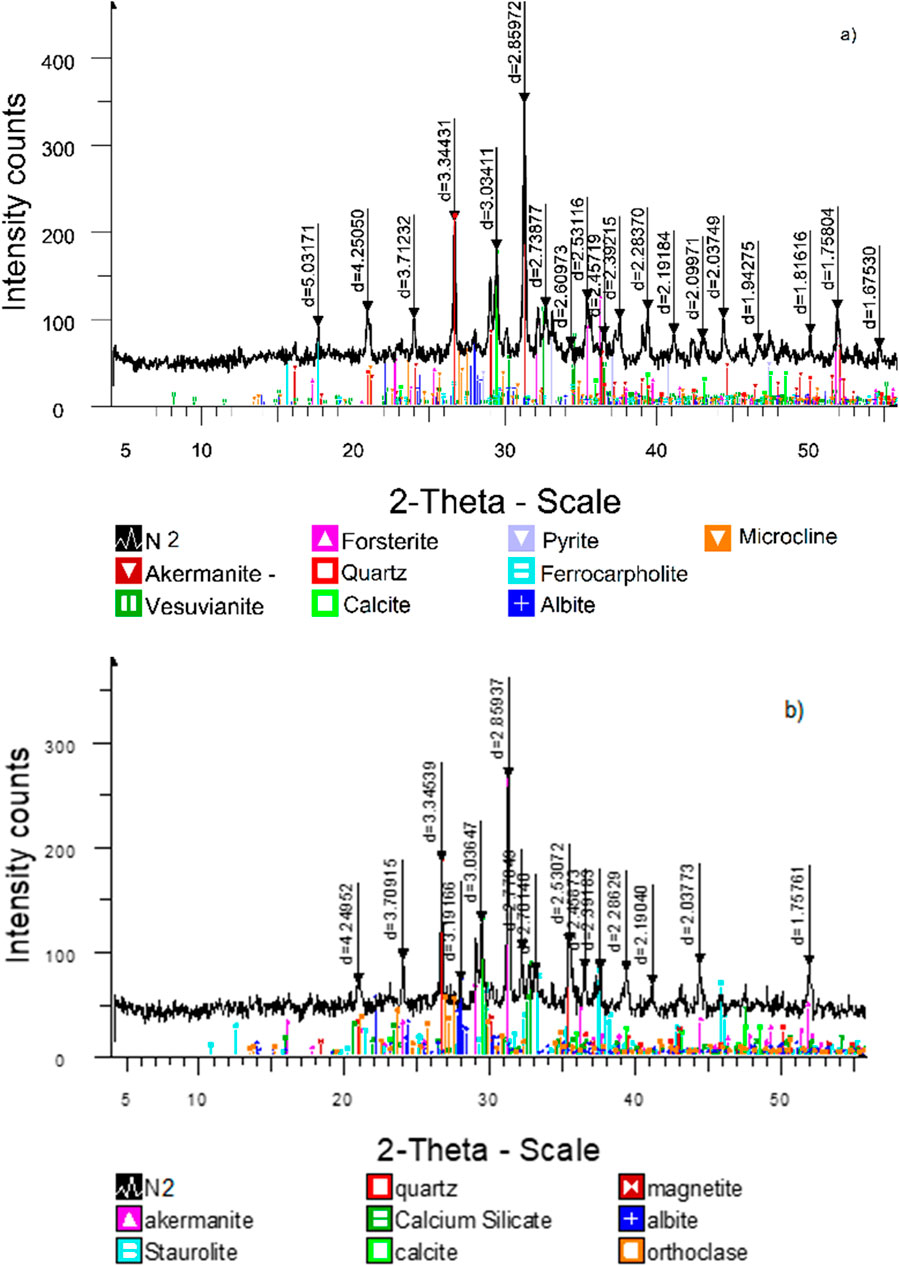
The recorded XRD data plotted in Figure 7 shows the mineralogical composition change of R40-B35-L8 during the 90 and 180 days of cure. According to the graph at 90 days of age (Figure 6A), the sample reflects the peaks of new minerals, such as akermanite (28.8%), vesuvianite (27.5%), forsterite (12.4%), pyrite (6.2%), ferrocarpholite (4.8%). The akermanite peak appears around 31° and has a greater intensity. The presence of vesuvianite mineral corresponds to the diffraction peak at 34.5°. Vesuvianite [Ca10Al4(MgFe)2Si9O34(OH)4] is a mineral of complex composition crystallizing in the tetragonal system due to isomorphic impurities. The mineral is a product of contact metamorphism involving clay, limestone, dolomite, and marl. Additionally, it is conceivable that the mineral might have been pre-existing within the raw materials. Forsterite is found in dolomitic marble, formed by the metamorphism of high-magnesium limestones and dolomites.
The XRD patterns of the R40-B35-L8 composite at 180 days (Figure 6A) reveal the presence of various minerals, with the following relative percentages: staurolite (28.1%), akermanite (23.3%), quartz (20.9%), calcite (10.0%), calcium silicate (7.7%), magnetite (5.6%), and albite (4.5%).
3.5 Mechanism of hydration product formation
The synergy of all raw components results in the formation of hydration products. According to the following equations, Ca3SiO5 and Ca2SiO4 from RM and BFS are hydrated to produce Ca2SiO4·4H2O, CaSiO3·H2O and Ca(OH)2, respectively as Equations 1, 2:
The production of Ca (OH)2 helps to create an alkaline environment that is beneficial for the formation of hydration products. This process also contributes to the pozzolanic reactions. As the curing ages increase, the reaction between BFS and lime begins, leading to the formation of hydration products, as shown in Equations 3, 4.
During pozzolanic reactions, it is continually consumed to produce ettringite, C-A-S-H, and N-A-S-H gels from raw materials and reactive aluminous and siliceous compounds. The resulting reactions can be expressed as Equations 5–9.
These reactions are known as cementitious and pozzolanic reactions because they result in the formation of cementitious gels. The resulting C-S-H or C-A-S-H gels bind the solid particles together, leading to a more robust soil matrix. The early strength development of road base materials made from RM, BFS, LPW, and NL is due to the predominance of hydration products of C-S-H, C-A-S-H, and N-A-S-H gels, as well as ettringite. Ettringite is a hexacalcium aluminate trisulfate hydrate with the general formula 6CaO·Al2O3·3SO3·32H2O or 3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4·32H2O when expressed as oxides. Since the chemical composition of BFS is similar to cement, subjecting it to conditions similar to the initial stages of hydration produces ettringite from BFS.
3.6 Environmental performance of road base materials
Particular solid wastes may contain hazardous substances, including radioactive elements and heavy metals, raising concerns about potential contamination of ground and surface water systems. It is essential to assess their environmental impact by comparing them to the maximum permissible quantities of hazardous or radioactive elements allowed in building materials to avoid secondary pollution during use. RM contains traces of radioactive elements, which are known to be harmful even at low concentrations. Studies have shown that RM concentrations of various toxic metals are between 0.01% and 1% of the total weight (Qi et al., 2018).
The atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) method was employed to conduct elemental analysis of the solubility and leaching of metals from liquid extracts. This analysis served a dual purpose: first, it characterized the elements present in the material; second, it identified the elements that are leachable after compliance with standard leaching tests. Leaching tests were performed to evaluate the materials under controlled conditions, ensuring thorough analysis of their potential for use in road construction. The AAS method detected the presence of heavy metals such as As (0.47%), Pb (0.17%), Zn (0.10%), and Cu (0.05%), highlighting both their inherent presence in the material and their potential to leach into the environment.
Radioactive elements such as isotopes of potassium, radium, and thorium can be present in the composition of iron slag. Many studies have observed that large amounts of deposited slag can leach toxic elements such as Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn, contaminating soils and groundwater (Wang et al., 2024). Therefore, evaluating the environmental performance of road base materials necessitates a comprehensive assessment of both the chemical composition and leaching potential of these materials to mitigate the risks of secondary pollution effectively.
4 Conclusion
The combination of RM, BFS, and LPW exhibited positive outcomes in enhancing the strength and durability of NL, both in dry and wet conditions. The study confirms the potential of developing road construction materials using various industrial wastes: RM, BFS, LPW, and NL. Based on the experiments, it is suggested that the optimal proportions of samples are R30-B30-L8 (32% NL, 30% RM, 30% BFS, 8% LPW) and R40-B35-L8 (17% NL, 40% RM, 35% BFS, 8% LPW) to achieve maximum strength. These proportions offer a balanced combination of materials, leading to enhanced performance characteristics.
The utilization of industrial waste materials in construction offers significant environmental benefits. By diverting these materials from landfills and extending the lifespan of industrial waste disposal sites, we contribute to reducing environmental impact. Additionally, reducing reliance on natural raw materials through the use of industrial waste helps mitigate the ecological damage associated with their extraction.
Moreover, the economic feasibility of utilizing industrial waste materials in construction is noteworthy. Not only do these materials often come at a lower cost compared to traditional natural raw materials, but their potential for large-scale utilization makes them economically viable alternatives. This lower cost not only benefits construction projects economically but also contributes to sustainable resource management practices.
In summary, the integration of RM, BFS, and LPW into NL for road construction presents a win-win solution, offering both environmental and economic advantages. By embracing the use of industrial waste materials, we move closer to sustainable and responsible construction practices while simultaneously improving the performance and longevity of infrastructure projects.
This research highlights the importance of utilizing industrial by-products in innovative ways to address both environmental and engineering challenges. Future studies could focus on evaluating the long-term performance of these materials under various climatic and load conditions to further validate their practical application. Additionally, exploring the potential of other industrial by-products or optimizing curing processes could further enhance the properties of the proposed composite materials.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. GZA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZI: Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. GGA: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. MO: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. AG: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. KV: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research is funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. AP13067712 «Chemical study of the structure of innovative composites obtained through the interaction of natural raw materials and waste of enterprises»).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Laboratory of Self-Healing Structural Materials of the Center for the National Technological Initiative «New Manufacturing Technologies» (Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg 195251, Russia) for recommendations and advice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
RM, Red mud; BFS, Blast furnace slag; SS, Steel slag; NL, Natural loam; LPW, Lime production waste; SEM, Scanning electron microscope; XRD, X-Ray Diffraction; AAS, Atomic absorption spectroscopy; XRF, X-ray fluorescence; EDS, Energy dispersive spectroscopy; LAMMA, Laser micro-mass analysis.
References
Ahmad, J., Martínez-García, R., De-Prado-gil, J., Irshad, K., El-Shorbagy, M. A., Fediuk, R., et al. (2022). Concrete with partial substitution of waste glass and recycled concrete aggregate. Materials 15 (2), 430. doi:10.3390/ma15020430
Akinwumi, I., Onyeiwu, M., Epelle, P., and Ajayi, V. (2023). Soil improvement using blends of coal ash and plantain peel ash as road pavement layer materials. Resources 12 (3), 41. doi:10.3390/resources12030041
Alzhanova, G. Z., Aibuldinov, Y. K., Iskakova, Z. B., Khabidolda, S. M., Abdiyussupov, G. G., Omirzak, M. T., et al. (2022). Development of environmentally clean construction materials using industrial waste. Materials 15 (16), 5726. doi:10.3390/ma15165726
Anik Hasan, M., Abul Hashem, M., and Payel, S. (2022). Stabilization of liming sludge in brick production: a way to reduce pollution in tannery, Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 314, 125702. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125702
Baabou, W., Bjørn, A., and Bulle, C. (2022). Absolute environmental sustainability of materials dissipation: application for construction sector. Resources 11 (8), 76. doi:10.3390/RESOURCES11080076Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9276/11/8/76/htm (Accessed May 26, 2024)
Corder, G. D., Golev, A., Fyfe, J., and King, S. (2014). The status of industrial ecology in Australia: barriers and enablers. Resources 3 (2), 340–361. doi:10.3390/resources3020340
Farage, R. M. P., Silva, C. M., Passos Rezende, A. A., Lelis Leal de Souza, J. J., Teixeira de Matos, A., and Vinha Zanuncio, A. J. (2019). Intermediate covering of municipal solid waste landfills with alkaline grits, dregs and lime mud by-products of kraft pulp production. J. Clean. Prod. 239 (1), 117985. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117985
Finnveden, G., Arushanyan, Y., and Brandão, M. (2016). Exergy as a measure of resource use in life cycle assessment and other sustainability assessment tools. Resources 5 (3), 23. doi:10.3390/resources5030023
Giurco, D., Littleboy, A., Boyle, T., Fyfe, J., and White, S. (2014). Circular economy: questions for responsible minerals, additive manufacturing and recycling of metals. Resources 3 (2), 432–453. doi:10.3390/resources3020432
Hamid Abed, M., Hamid Abed, F., Alireza Zareei, S., Sabbar Abbas, I., Canakci, H., Kurdi, N. H., et al. (2024). Experimental feasibility study of using eco- and user-friendly mechanochemically activated slag/fly ash geopolymer for soil stabilization. Clean. Mater. 11, 100226. doi:10.1016/j.clema.2024.100226Available at: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2772397624000108.
Hu, X., Jarnerud, T., Karasev, A., Jönsson, P. G., and Wang, C. (2020). Utilization of fly ash and waste lime from pulp and paper mills in the argon oxygen decarburization process. J. Clean. Prod. 261 (July 10), 121182. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121182
Jakab, M., Patthy, G. B., Korim, T., and Makó, É. (2023). Investigation of the usability of reduced alkalinity red mud in the building material industry. Resources 12 (7), 79. doi:10.3390/resources12070079
Johnson, K. A., Busdieker-Jesse, N., McClain, W. E., and Lancaster, P. A. (2019). Feeding strategies and shade type for growing cattle grazing endophyte-infected tall fescue. Livest. Sci. 230, 103829. doi:10.1016/J.LIVSCI.2019.103829
Kumar, A., and Kumar, S. (2013). Development of paving blocks from synergistic use of red mud and fly ash using geopolymerization. Constr. Build. Mater. 38, 865–871. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.013Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950061812006757.
Li, S., Zhang, J., Li, Z., Gao, Y., and Liu, C. (2021). Feasibility study of red mud-blast furnace slag based geopolymeric grouting material: effect of superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 267, 120910. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120910
Liu, R. X., and Poon, C. S. (2016). Utilization of red mud derived from bauxite in self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 112, 384–391. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.049
Luo, Z., Zhi, T., Liu, L., Mi, J., Zhang, M., Tian, C., et al. (2022). Solidification/stabilization of chromium slag in red mud-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 316 (2021), 125813. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125813
Mandal, S., Singh, J. P., and General, A. (2016). Stabilization of expansive soil using ground granulated blast furnace slag. Int. J. Mod. Trends Eng. and Res. 3 (9), 102–106. doi:10.21884/ijmter.2016.3049.fvhb2
Manso, J. M., Ortega-López, V., Polanco, J. A., and Setién, J. (2013). The use of ladle furnace slag in soil stabilization. Constr. Build. Mater. 40, 126–134. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.079
Mayes, W. M., Burke, I. T., Gomes, H. I., Anton, D., Molnár, M., Feigl, V., et al. (2016). Advances in understanding environmental risks of red mud after the ajka spill, Hungary. J. Sustain. Metallurgy 2 (4), 332–343. doi:10.1007/s40831-016-0050-z
Meena, A., Singh, N., and Singh, S. P. (2024). Shear strength and microstructural investigation on high-volume fly ash self-compacting concrete containing recycled concrete aggregates and coal bottom ash. Mater. Construccion 74 (353), e333. doi:10.3989/mc.2024.354623
Mukiza, E., Liu, X., Zhang, L., and Zhang, N. (2019). Preparation and characterization of a red mud-based road base material: strength formation mechanism and leaching characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 220, 297–307. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.027
Mymrin, V., Aibuldinov, E. K., Alekseev, K., Petukhov, V., Avanci, M. A., Kholodov, A., et al. (2019). Efficient road base material from Kazakhstan’s natural loam strengthened by ground cooled ferrous slag activated by lime production waste. J. Clean. Prod. 231, 1428–1436. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.250
Mymrin, V., Scremim, C. B., Stella, J. C., Pan, R. C. Y., Avanci, M. A., Bosco, J. C., et al. (2021). Environmentally clean materials from contaminated marine dredged sludge, wood ashes and lime production wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 307, 127074. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127074
Oguntola, O., and Simske, S. (2023). Continuous assessment of the environmental impact and economic viability of decarbonization improvements in cement production. Resources 12 (8), 95. doi:10.3390/resources12080095
Qi, X., Wang, H., Huang, C., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., Xu, B., et al. (2018). Analysis of bauxite residue components responsible for copper removal and related reaction products. Chemosphere 207, 209–217. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.041
Qian, L. P., Ahmad, M. R., Lao, J. C., and Dai, J. G. (2023a). Recycling of red mud and flue gas residues in geopolymer aggregates (GPA) for sustainable concrete. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 191, 106893. doi:10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2023.106893
Qian, L. P., Ahmad, M. R., Lao, J. C., and Dai, J. G. (2023b). Recycling of red mud and flue gas residues in geopolymer aggregates (GPA) for sustainable concrete. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 191 (April 1), 106893. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.106893
Sas, Z., Sha, W., Soutsos, M., Doherty, R., Bondar, D., Gijbels, K., et al. (2019). Radiological characterisation of alkali-activated construction materials containing red mud, fly ash and ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Sci. Total Environ. 659, 1496–1504. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.006
Valcuende, M., Benito, F. J., Parra, C., and Miñano, I. (2015). Shrinkage of self-compacting concrete made with blast furnace slag as fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 76, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.11.029Available at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:136673838.
Vanhatalo, A., Blackwell, J. R., L’Heureux, J. E., Williams, D. W., Smith, A., van der Giezen, M., et al. (2018). Nitrate-responsive oral microbiome modulates nitric oxide homeostasis and blood pressure in humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 124, 21–30. doi:10.1016/J.FREERADBIOMED.2018.05.078
Wang, X., Li, X., Yan, X., Tu, C., and Yu, Z. (2024). Environmental risks for application of iron and Steel slags in soils in China: a review. Pedosphere 31 (1), 28–42. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60058-3
Keywords: road base material, red mud, blast furnace slag, lime production waste, natural loam, road construction materials
Citation: Aibuldinov YK, Alzhanova GZ, Iskakova ZB, Abdiyussupov GG, Omirzak MT, Gazizova AD and Vafaeva KM (2025) Optimization of road-building materials from industrial waste (red mud, blast furnace slag, lime production waste, and natural loams). Front. Mater. 11:1400935. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1400935
Received: 14 March 2024; Accepted: 18 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Marc Marin, University of Rovira i Virgili, SpainReviewed by:
Mercedes Regadío, Autonomous University of Madrid, SpainJianzhong Lou, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Aibuldinov, Alzhanova, Iskakova, Abdiyussupov, Omirzak, Gazizova and Vafaeva. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yelaman Kanatovich Aibuldinov, ZWxhbWFuX0BtYWlsLnJ1; Galiya Zhanzakovna Alzhanova, Z2FsaXlhLmFsemhhbm92YUBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Khristina Maksudovna Vafaeva, dmFmYWV2YS5raG1AZ21haWwuY29t
 Yelaman Kanatovich Aibuldinov
Yelaman Kanatovich Aibuldinov Galiya Zhanzakovna Alzhanova2*
Galiya Zhanzakovna Alzhanova2* Aizhan Doldashevna Gazizova
Aizhan Doldashevna Gazizova Khristina Maksudovna Vafaeva
Khristina Maksudovna Vafaeva