
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mater. , 15 May 2020
Sec. Smart Materials
Volume 7 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00093
This article is part of the Research Topic Smart Materials for Energy Conversion and Sensor Based Technologies View all 6 articles
 Nikesh Ingle1
Nikesh Ingle1 Savita Mane1
Savita Mane1 Pasha Sayyad1
Pasha Sayyad1 Gajanan Bodkhe1
Gajanan Bodkhe1 Theeazen AL-Gahouari1
Theeazen AL-Gahouari1 Manasi Mahadik1
Manasi Mahadik1 Sumedh Shirsat2
Sumedh Shirsat2 Mahendra D. Shirsat1*
Mahendra D. Shirsat1*In the present investigation, a composite of “nickel benzene carboxylic (Ni3BTC2)” and “OH-functionalized single walled carbon nanotubes (OH-SWNTs)” was synthesized using the solvothermal method. The synthesized Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs were drop casted on gold micro electrode tip on Si/SiO2 substrate. The synthesized composite materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) for structural analysis, electrical analysis using current-voltage (I/V) characteristics, Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) for surface morphology, Field effect transistor (FET) by using transfer and output characteristics, and spectroscopic analysis using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). This composite was used for the detection of SO2. The proper incorporated OH-SWNTs in Ni3BTC2 MOF exhibits increased conductivity and sensing performance (better response and recovery time and repeatability). This work reveals that the composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs can be used for reversible sensing of SO2 gas in ChemFET modality at room temperature.
During the last two decades, Metal-Organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted considerable attention among research communities due to their unique tunable physical and chemical properties which build on the selecting organic linker and central metal (Campbell et al., 2015; Avery et al., 2016; Bodkhe et al., 2019). MOFs have large surface areas with high porosity. MOFs have been used for various applications like gas adsorption, storage, separation, sensors, and catalysis (Koo et al., 2016; Ullman et al., 2016; Dmello et al., 2018; Li H. et al., 2018). MOFs are newly introduced materials in electronics and optoelectronic devices (Dolgopolova and Shustova, 2016; Campbell and Dincă, 2017; Stassen et al., 2017). Campbell and Dincă (2017) reported successful synthesis of Cu3(HITP)2 and Ni3(HITP)2 MOFs with high electrical conductivity and reported that it was able to be used for chemiresistive ammonia vapor sensing. The results obtained for Cu3(HITP)2 show a good response to ammonia, whereas Ni3(HITP)2 did not show any observable response to ammonia vapor under identical experimental conditions.
SWNTs are well known for their unique electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties (Patil et al., 2017; Deshmukh et al., 2018). These properties make them a unique material for sensing applications. Pristine CNTs are not very active in a chemical process. Therefore, activation/functionalization of CNTs need to be performed through various methods viz. wet chemical methods, photo-oxidation, and oxygen-plasma or gas phase treatment, which shows great chemical reactivity of carbon nanotubes (Patil et al., 2017; Gurova et al., 2019; Hoang et al., 2019). The CNTs are familiarized with a graphite surface which contains oxygen-containing groups, mainly carboxyl and hydroxyl (Zhang et al., 2003; Yook et al., 2010; Liang et al., 2016). This introduces the possibility of further modification which will affect the solubility and reactivity of OH-SWNTs.
There are many research groups focusing on SO2 gas sensor due to its toxicity (Farmanzadeh and Ardehjani, 2018; Li Q. et al., 2018; Nagarajan and Chandiramouli, 2018; Khan et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2019). The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) permissible exposure limit (PEL) for SO2 is 5 ppm. Advancement in civilization has had severe impacts on the environment. Researchers across the globe are taking crucial efforts to scale new materials for the detection hazardous gases. Some of them are using functionalized or composites of OH-SWNTs for SO2 detection (Li Q. et al., 2018; Nagarajan and Chandiramouli, 2018).
SWNTs have walls of graphene sheet which leads to π– π electron conjugation to interact with functional group. The functional groups on the SWNTs outer side and tips make them more active channels in a chemical reaction, which is why they have better sensitivity and repeatability. Importantly, Wen et al., 2015 reported that the SWNTs act as an excellent backbone and conductive surface with Ni-MOF. In the present investigation, the composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs was synthesized through a solvothermal method and it was used for the detection of Sulfur dioxide (SO2) in ChemFET modality. To the best of our knowledge, no one has yet reported reversible SO2 gas sensing on a Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite.
The gold micro electrodes on Si/SiO2 substrate were prepared as reported earlier (Shirsat et al., 2009). The gold microelectrodes had a 3 μm gap between the two electrode tips, which had a length of 200 μm, and these microelectrodes were deposited on Si (thickness 525 μm) /SiO2 (100 nm thickness) using a standard photolithography process. The gold (Au) had a thickness of 180 nm and the underneath layer of chromium (Cr) had a thickness of 20 nm, and these were deposited on Si/SiO2 substrate. Finally, the desired micro-pattern was developed using Lift-off technique.
The SWNTs oxidation process was carried out by using HNO3 oxidizing agent (Hu et al., 2003). The purified 0.1 g of SWNTs (Sigma Aldrich) was mixed with 20 ml of HNO3. Then the mixture was continuously stirred for 20 h. The prepared suspension releases bubbles which indicates oxygen formation. Then, resultant suspension was ultrasonicated for 60 min at medium power level (VWR 100C ultrasonic bath) followed by centrifugation (REMI R-24) at 12,000 rpm for 60 min. The decanted suspension was sucked using a syringe and used for further process.
0.1 mol of oxidized OH-SWNTs mixed with nickel (II) acetate tetrahydrate (molychem, 98%) and 3 mmol Trimesic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, 95%) mixed with 20 ml of N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) (Sigma-Aldrich, 99.8%) was continuously stirred for 30 min. at 1000 rpm. The solvothermal method was used for the synthesis of the desired material by using a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave, sealed, and placed in a furnace. The mixture was heated for 140°C for 24 h. After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled at room temperature. The resultant composite was filtered and washed with DMF. Remaining pure precipitate powder was dried at room temperature.
Finally, 0.1 mmol composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs was mixed with 10 ml DMF solvent and sonicated for 60 min. at medium power. A 0.2 μl drop from the resultant suspension was used to bridge a 3 μm gap between two gold microelectrodes on Si/SiO2 substrate, as shown in the schematic and optical image (Figure 1).
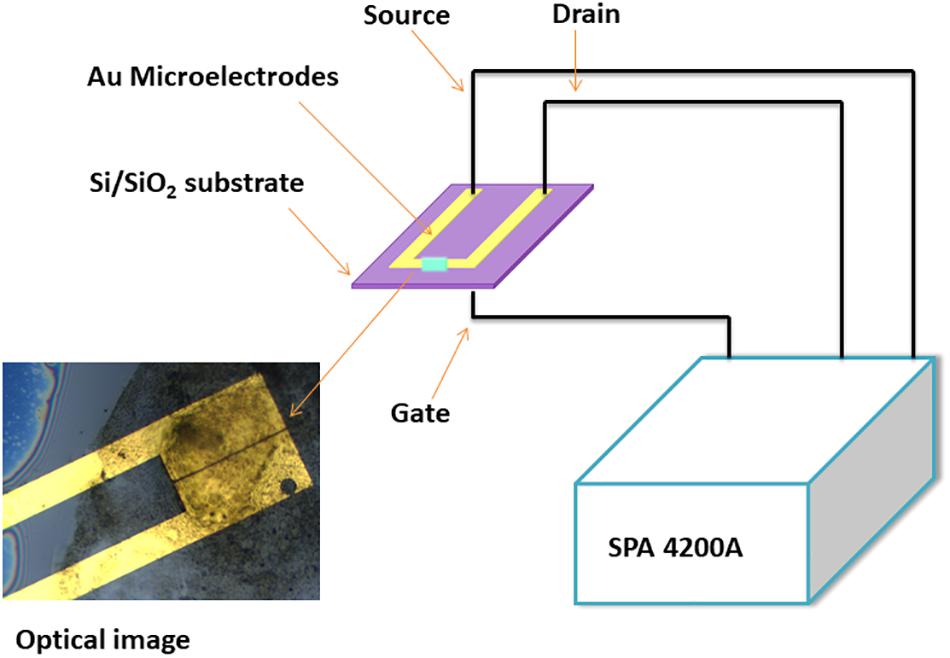
Figure 1. Schematic and optical image for a single microelectrode, drop casted with Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs material.
The X-ray diffraction patterns were measured using Bruker D8 Advanced system, with a potential difference of 40 kV and a current of 40 mA with source Cu Kαλ = 1.5406 Å radiation. The XRD patterns of pristine Ni3BTC2 and Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite were shown in Figure 2. The pristine Ni3BTC2 signature peaks (12.54°, 18.49°, 21.29°, and 25°) of the diffraction pattern are well matched with reported data (Jin et al., 2013; Figure 2a). The percentage of crystallinity for pristine Ni3BTC2 was 43.3%. The reduction in crystallinity was observed (27.1%) after incorporation of OH-SWNTs in Ni3BTC2, calculated by DIFFRAC.EVA software. The composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs diffraction pattern (Figure 2b) having the same 2θ° peaks position with a decrease in intensity compared with pristine Ni3BTC2 pattern confirms there was no change in the crystal structure of Ni3BTC2. The peak intensity decreased for Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs diffraction pattern, indicating incorporation of OH-SWNTs inside the Ni3BTC2 MOF. The XRD pattern of functionalized OH-SWNTs incorporated in Ni3BTC2 is shown in Figure 2b, whereas the extra peak at 2θo = 26o confirms the existence of OH-SWNTs (Figure 3b) which is attributed to the graphite structure (002) of OH-SWNTs (Xiao and Xu, 2012).
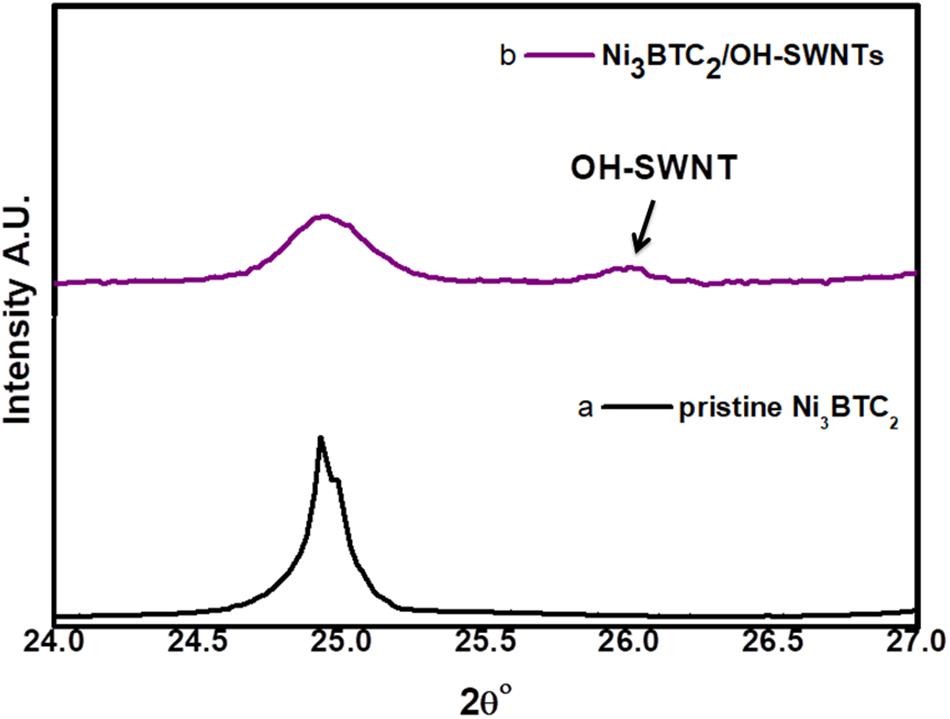
Figure 3. XRD patterns (2θ° range 24° to 27°), (a) pristine Ni3BTC2 and (b) composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs.
The crystallite size of pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs was calculated using the Debye–Scherrer’s formula in Equation (1).
where D is crystallite size, λ is the wavelength of x-ray source radiation, i.e., CuKα wavelength is 1.5406Å, β is full width at half maxima (FWHM) calculated from Gauss fitting, pristine Ni3BTC2 is 0.126, and composite Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs is 0.122. The θ° (12.44°) is the Braggs angle of diffraction. The calculated crystallite size for pristine Ni3BTC2 was 705.2 Å and for composite Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs was 730.1 Å.
The FTIR spectra was recorded using Bruker Alpha ATR with a ZnSe window in the range of 4000–500 cm–1. The recorded graph shows a transmittance spectra of pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs as shown in Figures 4a,b, respectively). The spectra of pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs samples have been confirmed by the asymmetric and symmetric stretching peaks of the –C = O group at 1620 and 1416 cm–1, respectively. The –C-OC stretching (etheric) group was found at 1080 cm–1 (Saber-Samandari and Gazi, 2013). The peaks at 1145 cm–1 were attributed to C-O group, whereas the C-C vibrations band presented at 1456 cm–1. The peak at 1632 cm–1 was attributed to C = O functional group. The aromatic C = C stretching vibration band corresponds with 1539–1658 cm–1. The intensity of mentioned peak decreases in composite Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs spectra (Figure 4b) as compared to pristine Ni3BTC2 is due to the interaction between carboxyl groups of Ni3BTC2 and amide groups of functionalized SWNTs (Karkeh-abadi et al., 2016). The stretching peak of O-H at 3024 cm–1 appeared in the composite material, which confirms the carboxylic group gained oxidation with HNO3. Defect formation in sp3 C-H stretching of the benzene ring in the OH-SWNTs is shown in Figure 4b.
The I/V studies were carried out using a semiconductor parameter analyzer (SPA, Keithley 4200A) at room temperature. West bond wire bounder 7476D was used to have electrical contact from gold microelectrodes to PCB for further measurements. Experimental measurements were carried out at a constant voltage range from −1 V to 1 V. Resistance of pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs was determined by using an inverse slope of I–V curve. Both curves of pristine and composite materials were passed through origin and show an ohmic nature of materials (Figure 5). The pristine material resistance was 8.85 MΩ and after incorporation of OH-SWNTs resistance decreased substantially to 25.5 KΩ. It was clearly observed that functionalized OH-SWNTs actively help in the enhancement of conduction. The micro network of OH-SWNTs into Ni3BTC2 has created a channel connectivity. Moreover, free electron mobility was increased due to the incorporation of OH-SWNTs into pristine Ni3BTC2 material. This new network has provided a conductive pathway that can charge transport though the micro network of SWNTs into Ni3BTC2 (Choi et al., 2012; Eletskii et al., 2015).
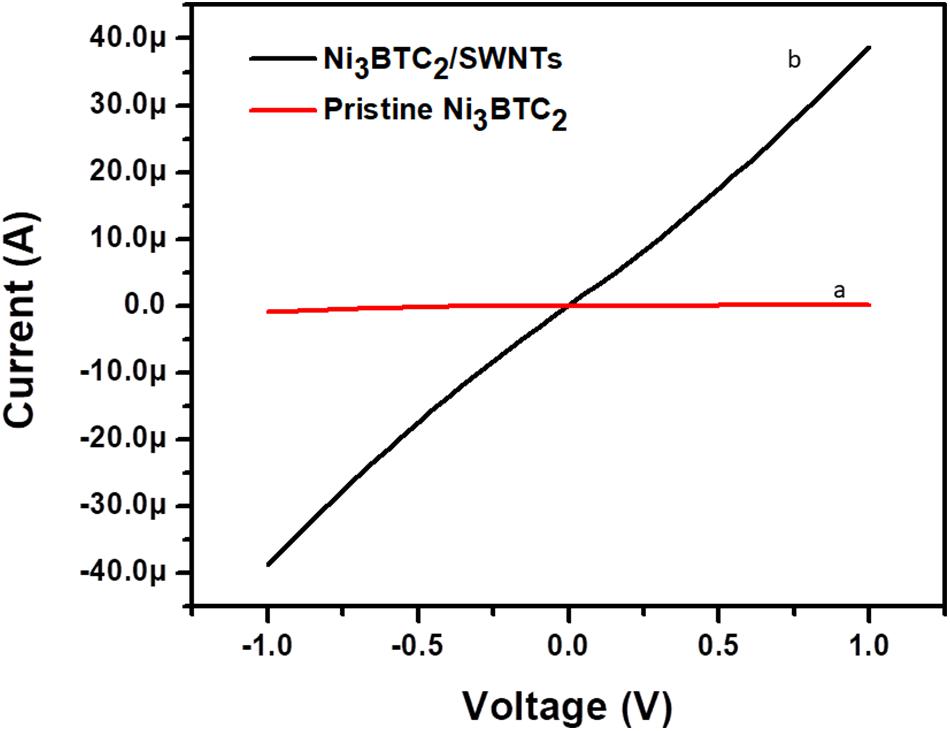
Figure 5. Electrical (I-V) characteristics of (a) pristine Ni3BTC2 and (b) composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs.
The morphology of pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite of Ni3BTC2/SWNTs was studied using a Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) (using Hitachi High-Tech, S-4800) (Figure 6). Figure 6a reveals the microstructure of pristine Ni3BTC2 in which the OH-SWNTs were apparently encapsulated, forming a micro-network structure which is visible in Figure 6b.
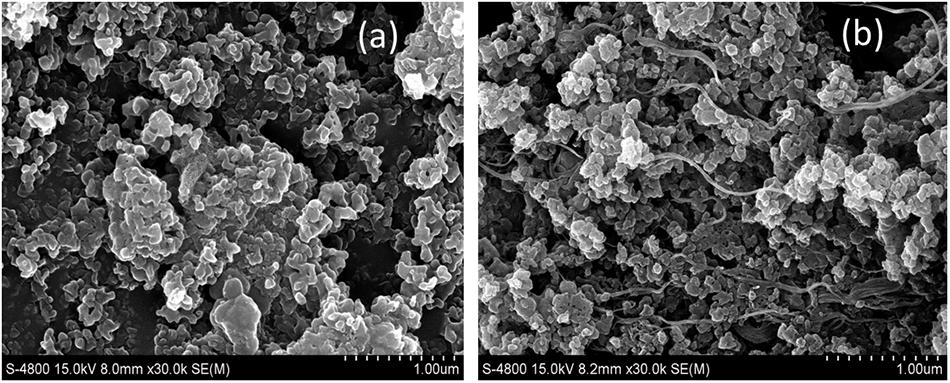
Figure 6. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images of (a) pristine Ni3BTC2 and (b) composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs.
The transfer and output characteristics of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs were studied to understand the FET behavior using SPA-4200A (Figure 7). In this case, composite material Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs shows p-channel behavior. For FET measurement, OH-SWNTs conducting nature has effectively contributed in composite material. In output characteristics Vds measurements were carried out between −0.5 to 0.5 V by varying Vgs −1 to −3 V with step 1V. Negative back gated voltage has created a repulsive force between the oxide layer (free charge carrier) and the silicon substrates. It has affected the depletion region populated by positive charges, which is attracted toward electrons and results in a decrease in the depletion barrier. This confirms the presence of holes as a majority charge carrier in channel. This in turn confirms the p-type behavior of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite. Transfer characteristic was recorded at Vds −0.1 to −0.4V with step 0.1 V by changing Vgs −20 to 20 V. This confirms the switching behavior of the device with threshold voltage (VTH) 1.5 V at −0.1V Vds.
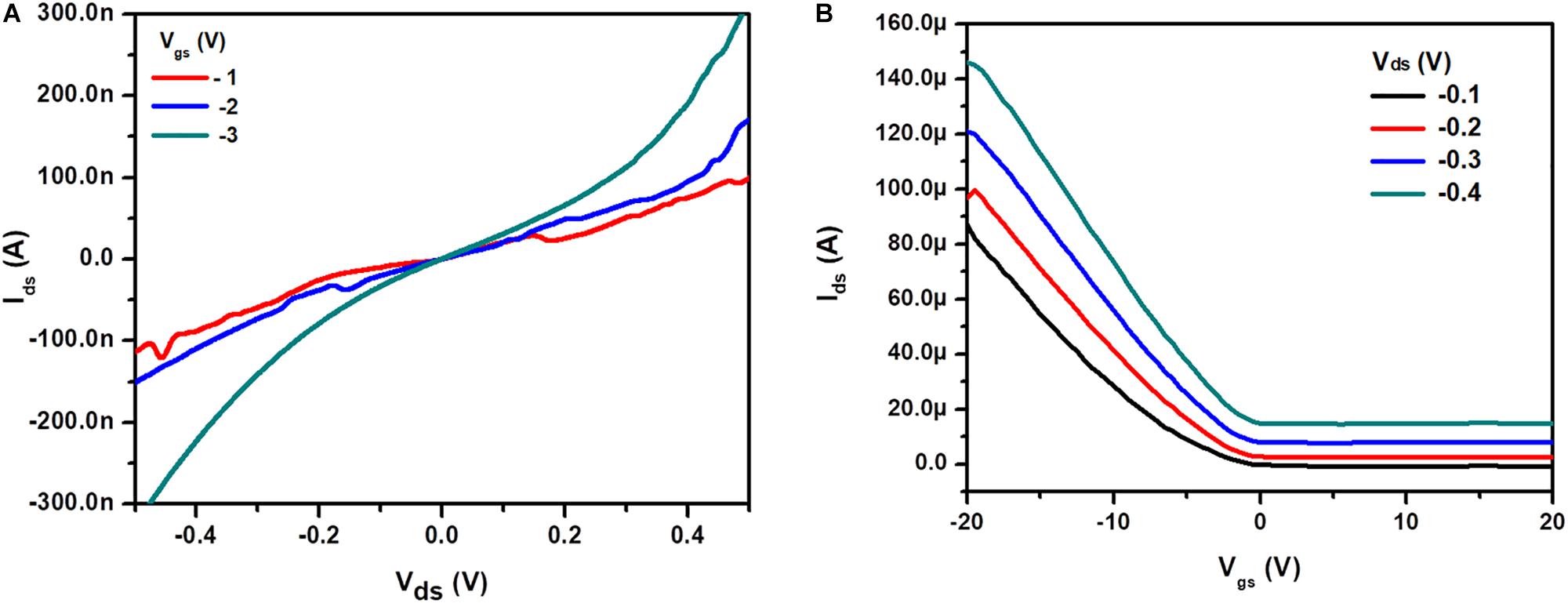
Figure 7. FET measurements of Ni3BTC2 /OH-SWNTs composite material (A) Output and (B) Transfer characteristics.
The charge carrier mobility was calculated by using Equation (2),
The was calculated from linear fit slope from transfer characteristics at Vds −0.1, where t was thickness of composite material Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs deposited on gold microelectrodes ∼50 μm and Cox is capacitance per unit area of 100nm SiO2 layer calculated by Equation (3)
where, ε0 is the permittivity of free space constant, i.e., 8.85 × 10–12 C2/Nm2 and t0 is the thickness of SiO2 layer, i.e., 100 nm. The charge carrier mobility of ∼2.18 × 10–6 cm2 V–1 s–1 was calculated from Equation (2) at Vds −0.1 V.
The sensing study was carried out by using an indigenously developed dynamic gas sensing system. The Vgs (-3 V) and Vds (-0.4 V) was kept constant. Data collection was done by Keithley SPA-4200A source measuring unit at room temperature. The gas measuring device (Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs) was kept in an ∼8 cm3 seal packed chamber. Inserting gas concentration was balanced by using a mass flow controller (Alicat) flow rate 200 SCCM. A tedlar bag was used for accumulating different concentrations of SO2 gas. Dry air was used to inhabit initial conditions, i.e., for baseline and balancing gas concentrations to avoid any impact from humidity. Once the initial condition was achieved, the sensor was exposed to gas analytes with various concentrations ranging from 4 to 20 ppm at a constant value of Vgs (-3 V) and Vds (-0.4 V). The sensor device having composite material Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs shows excellence response and recovery for various (higher to lower) concentrations of SO2 (Figure 8). The response time of 4.59 s. with a recovery time of 11.04 s. was recorded at 15 ppm of SO2 concentration (Figure 9). The calibration plot is shown in Figure 10. It shows a little more deviation at higher concentrations as compared to lower concentrations.
The FET study confirms p-type Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite material with holes as a majority carrier. When electron acceptor (SO2) gas analytes (Yao et al., 2011) come in contact with p-type material, it causes a transfer of electrons from the composite material, as shown in Equation (4), and generates a number of vacancies (holes). It was responsible for decreasing the resistance of the material while interacting with SO2 gas analytes.
The sensitivity of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite sensor was investigated by exposing 5 ppm concentration of various gas analytes like NO2, CH4, CO, and C2H2, as shown in Figure 11. Using the same experimental conditions, SO2 gas showed a much higher sensitivity when compared with other tested gas analytes. These indicate that Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite sensor was highly sensitive toward SO2 gas. The low response for CH4, CO, and C2H2 was attributed to the nucleophilic nature of these gases (Zhang et al., 2017).
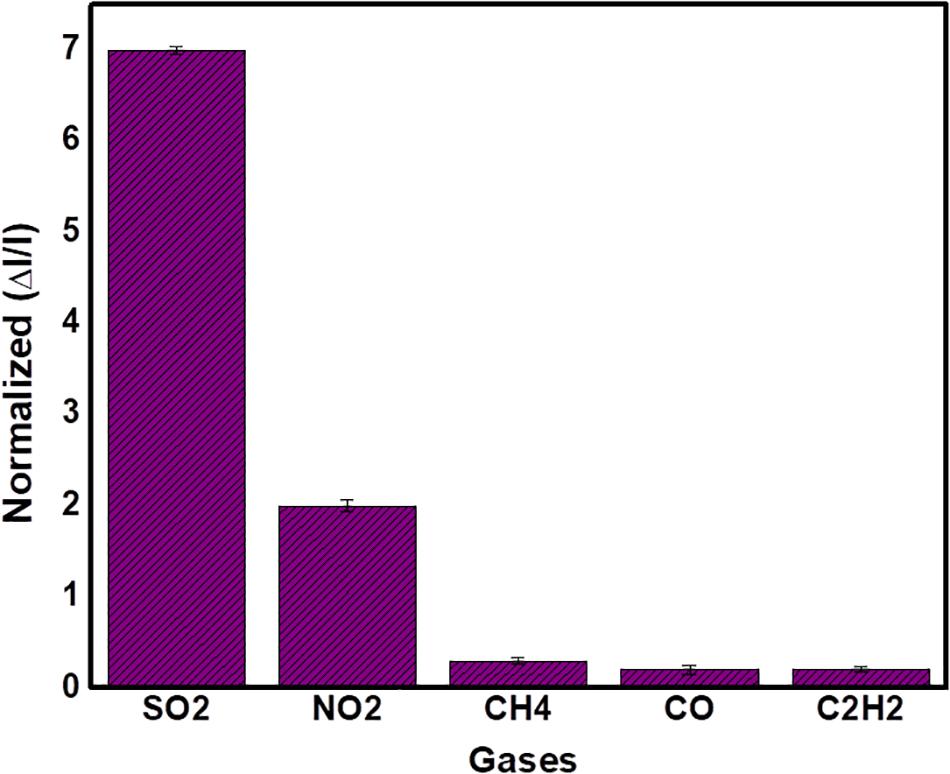
Figure 11. Selectivity of the Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite sensor toward 5 ppm of various gas analytes.
Pristine Ni3BTC2 and composite of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs were successfully synthesized using the solvothermal method. The electrical, structural, surface morphological, and spectroscopic characterization confirms the successful incorporation of OH-SWNTs in Ni3BTC2 MOF. The FET measurement confirms p-type behavior of Ni3BTC2/OH-SWNTs composite material. The ChemFET sensing at constant value of Vgs (-3 V) and Vds (−0.4 V) shows an excellent response. The incorporated OH-SWNTs in Ni3BTC2 MOF enhances the sensing properties of the composite material. The lower detection limit of 4ppm with a response time of 5 s. and recovery time of 10 s. was observed. The sensor shows excellent repeatability.
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/supplementary material.
NI, SM, and PS contributed to experimental work. NI contributed to formal analysis, GB contributed to XRD and FTIR analysis, and TA-G, MM, and SS contributed to FET analysis and gas sensing. NI contributed to the investigation and writing of the original draft. MS contributed to conceptualization, writing the review, editing, and supervision.
We extend their sincere thanks to Inter University Accelerator Center (IUAC), New Delhi, India (UFR nos. 62320 and 62321), UGC-DAE CSR (RRCAT), Indore (Project No. CSR-IC BL66/CRS- 183/2016-17/847), DST-SERB, New Delhi (Project No. EEQ/2017/000645), Rashtria Uchachatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA), Government of Maharashtra, UGC-SAP Programme (F.530/16/DRS-I/2016 (SAP-II) Dt.16-04-2016) and DST-FIST (Project No. SR/FST/PSI-210/2016(C) dtd. 16/12/2016) for providing financial support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Avery, A. D., Zhou, B. H., Lee, J., Lee, E.-S., Miller, E. M., Ihly, R., et al. (2016). Tailored semiconducting carbon nanotube networks with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Nat. Energy 1:16033.
Bodkhe, G. A., Deshmukh, M. A., Patil, H. K., Shirsat, S. M., Srihari, V., Pandey, K. K., et al. (2019). Field effect transistor based on proton conductive metal organic framework (CuBTC). J. Phys. D 52:335105. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab1987
Campbell, M., and Dincă, M. (2017). Metal-organic frameworks as active materials in electronic sensor devices. Sensors 17:1108. doi: 10.3390/s17051108
Campbell, M. G., Sheberla, D., Liu, S. F., Swager, T. M., and Dincã, M. (2015). Cu3 (hexaiminotriphenylene) 2: an electrically conductive 2D metal-organic framework for chemiresistive sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 4349–4352. doi: 10.1002/anie.201411854
Choi, H. H., Lee, J., Dong, K.-Y., Ju, B.-K., and Lee, W. (2012). Gas sensing performance of composite materials using conducting polymer/single-walled carbon nanotubes. Macromol. Res. 20, 143–146. doi: 10.1007/s13233-012-0030-5
Deshmukh, M. A., Patil, H. K., Bodkhe, G. A., Yasuzawa, M., Koinkar, P., Ramanaviciene, A., et al. (2018). EDTA-modified PANI/SWNTs nanocomposite for differential pulse voltammetry based determination of Cu (II) ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 260, 331–338. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.160
Dmello, M. E., Sundaram, N. G., and Kalidindi, S. B. (2018). Assembly of ZIF−67 metal-organic framework over tin oxide nanoparticles for synergistic chemiresistive CO2 gas sensing. Chem. A Eur. J. 24, 9220–9223. doi: 10.1002/chem.201800847
Dolgopolova, E. A., and Shustova, N. B. (2016). Metal-organic framework photophysics: optoelectronic devices, photoswitches, sensors, and photocatalysts. MRSBulletin 41, 890–896. doi: 10.1557/mrs.2016.246
Eletskii, A. V., Knizhnik, A. A., Potapkin, B. V., and Kenny, J. M. (2015). Electrical characteristics of carbon nanotube-doped composites. Phys. Uspekhi 58, 209–251. doi: 10.3367/ufne.0185.201503a.0225
Farmanzadeh, D., and Ardehjani, N. A. (2018). Adsorption of O3, SO2 and NO2 molecules on the surface of pure and Fe-doped silicon carbide nanosheets: a computational study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 462, 685–692. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.150
Gurova, O. A., Arhipov, V. E., Koroteev, V. O., Guselnikova, T. Y., Asanov, I. P., Sedelnikova, O. V., et al. (2019). Purification of single−walled carbon nanotubes using acid treatment and magnetic separation. Physi. Stat. Solidi 256:1800742. doi: 10.1002/pssb.201800742
Hoang, N. D., Van Cat, V., Nam, M. H., Phan, V. N., Le, A. T., and Van Quy, N. (2019). Enhanced SO2 sensing characteristics of multi-wall carbon nanotubes based mass-type sensor using two-step purification process. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 295, 696–702. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2019.06.046
Hu, H., Zhao, B., Itkis, M. E., and Haddon, R. C. (2003). Nitric acid purification of single-walled carbon nanotubes. I. Phys. Chem. B 107, 13838–13842. doi: 10.1021/jp035719i
Jin, L.-N., Liu, Q., and Sun, W.-Y. (2013). Room temperature solution-phase synthesis of flower-like nanostructures of [Ni3 (BTC) 2⋅12H2O] and their conversion to porous NiO. Chin. Chem. Lett. 24, 663–667. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2013.05.001
Karkeh-abadi, F., Saber-Samandari, S., and Saber-Samandari, S. (2016). The impact of functionalized CNT in the network of sodium alginate-based nanocomposite beads on the removal of Co(II) ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 312, 224–233. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.074
Khan, M. A. H., Rao, M. V., and Li, Q. (2019). Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for detecting toxic gases: NO2, SO2 and H2S. Sensors 19:905. doi: 10.3390/s19040905
Koo, W.-T., Choi, S.-J., Kim, S.-J., Jang, J.-S., Tuller, H. L., and Kim, I.-D. (2016). Heterogeneous sensitization of metal-organic framework driven metal@ metal oxide complex catalysts on an oxide nanofiber scaffold toward superior gas sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13431–13437. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b09167
Li, H., Wang, K., Sun, Y., Lollar, C. T., Li, J., and Zhou, H.-C. (2018). Recent advances in gas storage and separation using metal-organic frameworks. Materialstoday 21, 108–121. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.07.006
Li, Q., Wu, J., Huang, L., Gao, J., Zhou, H., Shi, Y., et al. (2018). Sulfur dioxide gas-sensitive materials based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 12115–12124. doi: 10.1039/c8ta02036a
Liang, S., Li, G., and Tian, R. (2016). Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 3513–3524. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9671-z
Nagarajan, V., and Chandiramouli, R. (2018). A novel approach for detection of NO2 and SO2 gas molecules using graphane nanosheet and nanotubes-A density functional application. Diam. Relat. Mater. 85, 53–62. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2018.03.028
Patil, H. K., Deshmukh, M. A., Gaikwad, S. D., Bodkhe, G. A., Asokan, K., Yasuzawa, M., et al. (2017). Influence of oxygen ions irradiation on polyaniline/single walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite. RPC 130, 47–51. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.07.030
Saber-Samandari, S., and Gazi, M. (2013). Removal of mercury (II) from aqueous solution using chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide semi-IPN hydrogels. Separ. Sci. Technol. 48, 1382–1390. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2012.729121
Shirsat, M. D., Bangar, M. A., Deshusses, M. A., Myung, N. V., and Mulchandani, A. (2009). Polyaniline nanowires-gold nanoparticles hybrid network based chemiresistive hydrogen sulfide sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94:083502. doi: 10.1063/1.3070237
Stassen, I., Burtch, N., Talin, A., Falcaro, P., Allendorf, M., and Ameloot, R. (2017). An updated roadmap for the integration of metal-organic frameworks with electronic devices and chemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 3185–3241. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00122c
Ullman, A. M., Brown, J. W., Foster, M. E., Léonard, F., Leong, K., Stavila, V., et al. (2016). Transforming MOFs for energy applications using the guest@MOF concept. Inorg. Chem. 55, 7233–7249. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b00909
Wen, P., Gong, P., Sun, J., Wang, J., and Yang, S. (2015). Design and synthesis of Ni-MOF/CNT compositesand rGO/carbon nitride composites for anasymmetric supercapacitor with high energy andpower density. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 13874–13883.
Xiao, F., and Xu, Y. (2012). Electrochemical co-deposition and characterization of MnO2/SWNT composite for supercapacitor application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1913–1920. doi: 10.1007/s10854-012-1034-9
Yao, F., Duong, D. L., Lim, S. C., Yang, S. B., Hwang, H. R., Yu, W. J., et al. (2011). Humidity-assisted selective reactivity between NO2and SO2gas on carbonnanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 21:4502. doi: 10.1039/c0jm03227a
Yook, J. Y., Jun, J., and Kwak, S. (2010). Amino functionalization of carbon nanotube surfaces with NH3 plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 6941–6944. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.04.075
Zhang, D., Liu, J., Jiang, C., Li, P., and Sun, Y. (2017). High-performance sulfur dioxide sensing properties of layer-by-layer self-assembled titania-modified graphene hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 245, 560–567. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.200
Zhang, J., Zou, H., Qing, Q., Yang, Y., Li, Q., Liu, Z., et al. (2003). Effect of chemical oxidation on the structure of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 3712–3718.
Keywords: metal-organic framework, single walled carbon nanotube, chemiresistive sensor, SO2 gas sensing, reproducibility
Citation: Ingle N, Mane S, Sayyad P, Bodkhe G, AL-Gahouari T, Mahadik M, Shirsat S and Shirsat MD (2020) Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Detection Using Composite of Nickel Benzene Carboxylic (Ni3BTC2) and OH-Functionalized Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes (OH-SWNTs). Front. Mater. 7:93. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2020.00093
Received: 09 December 2019; Accepted: 26 March 2020;
Published: 15 May 2020.
Edited by:
Jaehwan Kim, Inha University, South KoreaCopyright © 2020 Ingle, Mane, Sayyad, Bodkhe, AL-Gahouari, Mahadik, Shirsat and Shirsat. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mahendra D. Shirsat, bWRzaGlyc2F0LnBoeUBiYW11LmFjLmlu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.