
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 07 April 2025
Sec. Marine Pollution
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1569583
This article is part of the Research TopicStrategies for Remediating Marine and Coastal Pollution towards a Sustainable DevelopmentView all articles
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) has caused significant pollution in marine environments, with potential EPS-degrading bacteria identified on long-term floating EPS biofilms. However, studies on bacterial interactions and consortium reconstruction based on in-situ bacterial diversity remain limited. Marine EPS wastes of different sizes were collected from subtropical coast of Xiamen island, and subjected to bacterial diversity analyses. Co-occurrence network and bacterial characterization revealed that Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales play important roles in polystyrene (PS) degradation. Bacterial isolation characterization confirmed that Fulvimarina pelagi, Pseudosulfitobacter pseudonitzschiae, Devosia nitrariae, Cytobacillus kochii, and Cytobacillus oceanisediminis as novel PS-degraders. Based on their abundance in situ and PS degradation activity, a consortium was constructed, constituted of F. pelagi, P. halotolerans. and O. granulosus, showed a high degradation capability with PS weight loss by 18.9% in 45 days. These results contribute to marine plastic pollution remediation and resources recycling.
It is estimated that 4-23 million metric tonnes of plastic pollution per year enter the ocean as part of the Global Plastic Cycle (Borrelle et al., 2020). As reported, the density of plastics in the ocean is increasing, with microplastic pollution levels in seawater and sediment environments ranging from 0.001 to 140 particles/m3 and 0.2 to 8,266 particles/m3, respectively (Thushari and Senevirathna, 2020). Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic resin produced through the radical polymerization of styrene monomers with the form of general purpose polystyrene (GPPS), high impact polystyrene (HIPS), and EPS (Muthukumar et al, 2024). Its molecular formula, (C8H8)n, primarily consists of benzene rings, vinyl groups, and single bonds. Benzene rings constitute the repeating units of the polymer, connected by vinyl groups and single bonds (Salisu et al., 2022). An annual growth rate of 4% is expected between 2021 and 2026 (Muthukumar et al., 2024).
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a material known for its low cost, ease of processing, and high buoyancy, making it suitable for various applications such as shockproof packaging and fast-food containers (Matjašič et al., 2021). It is widely used as a buoy in marine aquaculture. However, its recycling rate is extremely low (Ali et al., 2021), and it acts as a potential carrier of biotic or abiotic pollutants. EPS is also prone to fragmentation due to physical, mechanical, and biological forces, resulting in significant marine debris that disperses globally through ocean currents (Chelomin et al., 2023).
So far, diverse marine bacteria residing on the surfaces of EPS or PS have been observed, but few have been isolated and confirmed in their role in the plastic biosphere. Bacteria from Flavobacteriaceae, Hyphomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Comamonadaceae, Alcanivoracaceae, Oceanospirillaceae, Vibrionaceae families, Pseudoalteromonas (Guezennec, 2002), Bacillus (Mohan et al., 2016), and Vibrio (Zanchetta et al., 2003) have been retrieved from PS surface in the North Sea, the Baltic Sea and other coastal waters. We found that marine bacteria of Sphingomonadaceae, Rhodanobacteraceae, Rhizobiaceae, Dermacoccaceae, Rhodocyclaceae, Hyphomicrobiaceae, and Methyloligellaceae constituted the major compositions of the PS-degradation consortium, derived from EPS samples from a subtropical mangrove area (Liu et al., 2023). In our latest report, bacteria of Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Halomonadaceae, Exiguobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae, and Pseudoalteromonadaceae were found predominant on EPS surface biofilms in the coast of Xiamen (Zhang et al., 2024). Recently, we also discovered that the main EPS-degrading bacteria in the gut of EPS-ingesting clamworms, which were mainly composed of Acinetobacter and Ruegeria (Zhao et al., 2024). These studies convey the high diversity of PS associated marine bacteria.
Although more and more bacteria that can degrade PS plastic have been isolated from both terrestrial and marine environments. Few show the degradation potential with untreated plastic weight loss over 8% (James-Pearson et al., 2023; Sanluis-Verdes et al., 2022). For an example, we found that marine bacteria of Novosphingobium, Gordonia, Stappia, Mesobacillus, Alcanivorax, Flexivirga, Cytobacillus, Thioclava, and Thalassospira showed PS degradation capability in a pure culture. Among them the key degrading bacteria of Gordonia showed relatively high weight losses of 4.69% to 7.73% for 30 days (Liu et al., 2023). Previously, PS-degrading bacteria Rhodococcus ruber showed 0.8% weight loss of PS films after eight weeks of incubation (Mor and Sivan, 2008), and strain Exiguobacterium sp. YT2 isolated from the gut of mealworms showed 7.4% weight loss of PS pieces (2500 mg/L) over a 60-day- incubation (Yang et al., 2015). The studies conducted thus far on plastic biodegradation have typically focused on individual isolates.
It is recognized that in natural environments, biofilms form on plastic surfaces and highlighting the role of the bacterial cooperation in biofilm in plastic biodegradation. However, the interactions and synergistic mechanisms of plastic degradation between different strains within the microbial consortium are not well understood. In the case of aromatic-aliphatic copolyester plastics, marine microbial consortia exhibit stronger degradation capabilities (Meyer-Cifuentes et al., 2020). And, microorganisms in the consortium could effectively cooperate through various enzymatic activities, metabolic processes, and other pathways, thereby increasing the rate of plastic degradation (Zhang et al., 2023). To date, there has been a paucity of efficient microbial consortia capable of degrading plastics. Furthermore, the degradation efficacy of engineered bacterial consortia remains suboptimal. The consortium composed of Rhodococcus sp., Shewanella sp., Pseudomonas sp. which used seawater containing PS as the sole carbon source, had the weight loss 2.3% after 6 months (Syranidou et al., 2017). Two consortia consisted of Bacillus flexus + Pseudomonas azotoformans and B. flexus + B. subtilis, respectively, with a weight loss of 1.95% and 1.45% after one year of culture (Aravinthan et al., 2016).
This study aims to optimize a marine PS-degrading microbial consortium. EPS wastes were sampled from the coast of Xiamen Island at the Jiulong River Estuary, followed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing to observe the bacterial abundance in environments samples and recombinant consortium. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Water Contact Angle (WCA), Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), were used for the evaluation of the PS-degrading ability of the constructed consortium and weight loss of each consortium was quantified. The results have expanded the PS-degrading bacterial diversity on marine EPS plastic and microplastics, and provided insight into the interactions of in biofilms on plastic surfaces, which leads to the construction of an efficient degrading consortium.
EPS wastes, seawater, and surface sandy sediments were collected from the coast of Xiamen Island, and macro-pieces of EPS with microplastic formations on the surface were specially selected (Figures 1a, b). The EPS samples were named LP (larger than 5 mm, Figures 1c, d), MP (smaller than 5 mm, collected from the surface of LP, Figure 1c), seawater (nearshore seawater), and sand (surface sediment). In the lab, to incubate PS-degrading bacteria, the LP and MP sample were respectively resuspended in 50 mL centrifuge tubes containing 40 mL liquid MMC medium (pH = 7.4, NaCl 20 g/L, NH4Cl 0.67 g/L, KCl 0.7 g/L, NaNO3 1.06 g/L, KH2PO4, 2.0 g/L, Na2HPO4·12H2O 7.65 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O 3.5 g/L in 1 L of deionized water), then samples were vortexed for 10 minutes using a Vortex Genie (Scientific Industries, Inc., USA). Subsequently, they were centrifuged at 7000 rpm and 4°C for 10 minutes using an Eppendorf centrifuge (Germany), and the supernatant was removed. The remaining was used for DNA extraction and isolation of the PS-degrading bacteria.
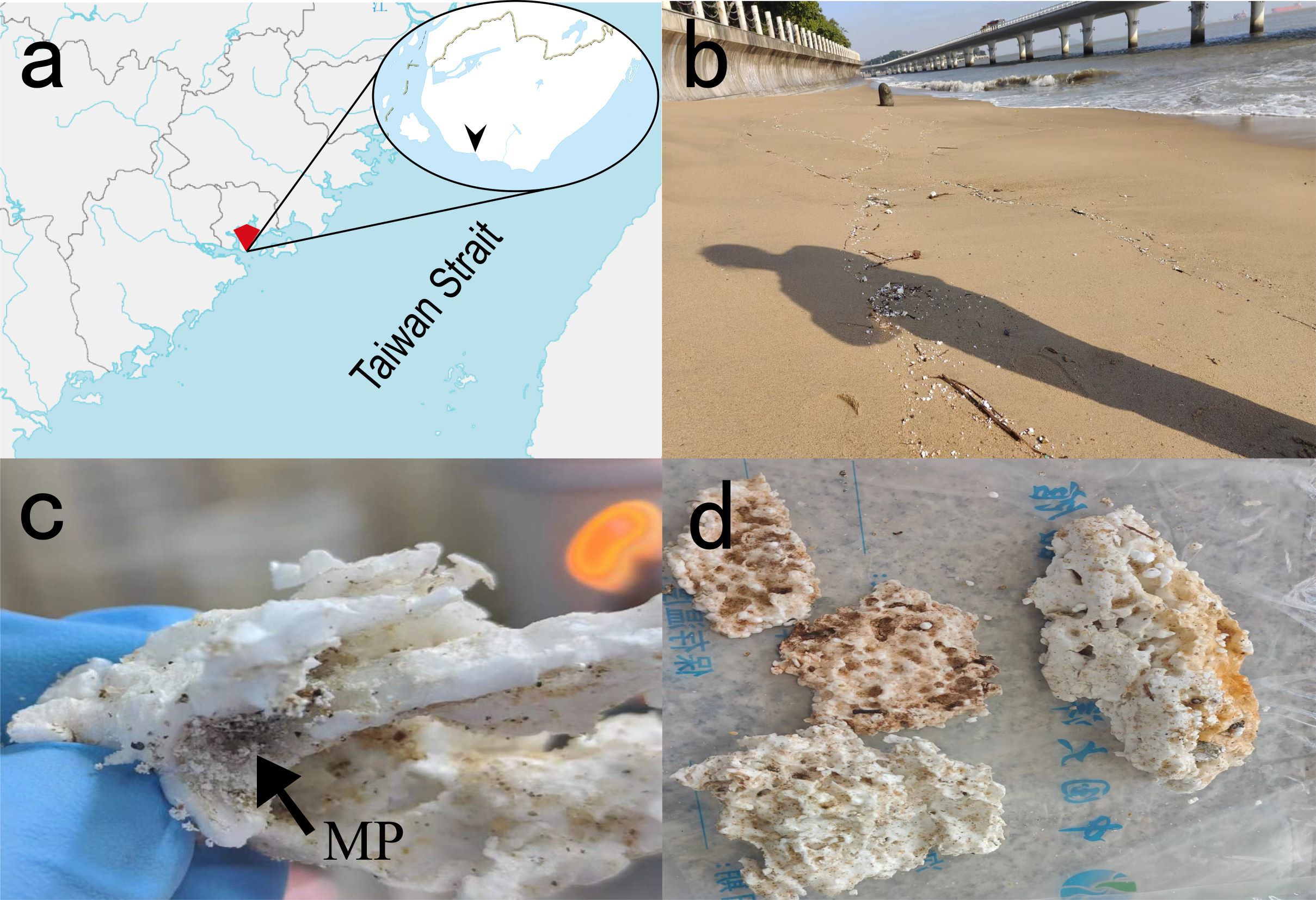
Figure 1. ESP debris in Bai-cheng beach of Xiamen Island and sampled items. (a), Map of sampling sites; (b), Xiamen Island coast; (c), MP, particles smaller than 5 mm indicated by arrows; (d), LP, plastics larger than 5 mm.
Total DNA was extracted strictly according to the instructions provided by the commercial environmental sample DNA extraction kit (QIAGEN, Germany). The purity and concentration of the extracted DNA were measured using NanoDrop2000 (Thermo, U.S.A) and stored at -80°C for high-throughput sequencing. The V3 - V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the universal bacterial primers 341F (5’- ATGCGTAGCCGACCTGAGA-3’) and 805R (5’-CGTCAGACTTTCGTCCATTGC-3’), and then sequencing was performed using the Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform (Illumina, U.S.A).
Purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar amounts and paired-end sequenced (2 ×300) on an Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA) according to the standard protocols by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Raw reads were deposited into the National Genomics Data Center database (Accession Number: CRA018003).
All 16S rRNA sequences were analyzed using QIIME v1.9.1 (Caporaso et al., 2010). Then, operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with a 97% similarity cut-off were clustered using UPARSE (version 7.1) (Edgar, 2013), and chimeric sequences were checked and removed using UCHIME (Edgar et al., 2011). The taxonomy of each OTU representative sequence was analyzed by the RDP Classifier (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the 16S rRNA database Silva (Release132: http://www.arb-silva.de) using a confidence threshold of 0.7.
We calculated all possible Spearman’s rank correlations between OTUs with more than fifty sequences (306 OTUs). This previous filtering step removed genus with relative abundance less than 0.005, reduced network complexity, facilitating the determination of the core community. We considered a valid co-occurrence event to be a robust correlation if Spearman’s correlation coefficient (ρ) was both >0.7 and statistically significant (P-value <0.05) (Lu et al., 2022). To describe the topology of the resulting network, a set of measures (average node connectivity, average path length, diameter, cumulative degree distribution, clustering coefficient, and modularity) was calculated. All statistical analyses were carried out in the R environment (http://www.r-project.org) using Hmisc (Wu et al., 2023) and igraph packages (Layeghifard et al., 2018). Networks were explored and visualized with the interactive platform Gephi v 0.10.1 (Bastian et al., 2009).
Microbial attachment and the subsequent formation of a stable biofilm on the surface of plastics are crucial initial steps in the degradation process, as the biofilm is known to enhance bacterial proliferation and biodegradation (Meera et al., 2022). In the temperature range of 25 ~ 30°C, the oxidation range of PS is more extensive (Matyakubov and Lee, 2024). Biofilms on the surface of LP and MP were examined using SEM (LEO-1530, Germany), and biofilms formed on PS films by the six constructed consortia after 45 days at 28 °C were also observed. PS films treated by the consortium were randomly collected and treated with 2% SDS for 4 h at 50 °C to remove extracellular secretions or biofilms from the PS film surface and observed by SEM (Kim et al., 2020).
To isolate pure culture strains from EPS plastic surfaces, the samples described in Part 2.1 were used for gradient dilution and cultivated on Marine Broth 2216 (BD Difco) and R2A medium (BD Difco) plates for 5-7 days. The individual colonies were selected and transferred to fresh media of the same type of plates for cultivation. This process was repeated until pure cultures were obtained. Next, single colonies were selected and subjected to PCR using the 27F (5′-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG-3′) and 1492R (5′-TAC GGC TAC CTT GTT ACG ACT T-3′) primers. The PCR products were purified and sequenced. Lastly, the amplified DNA sequences were aligned with organisms present in the EzbioCloud database (https://www.ezbiocloud.net/) and the GenBank database using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). Confirmed pure cultures were preserved in 25% glycerol and stored at -80°C. Additionally, these cultures were deposited in the Marine Culture Collection of China (MCCC).
The degradation ability of the obtained pure culture strains was verified with PS (Sigma, GF94795701, 150 mm × 150 mm × 0.19 mm) as the sole carbon source. Based on the biomass increase of the strains at 28°C and 150 rpm over a period of 10 days, bacteria exhibiting the ability to degrade PS were screened.
PS films (1.5 cm×1.5 cm) were weighed and immersed in 75% ethanol for 24 hours, then dried after the ethanol removed. Four bacterial strains, namely Paracoccus halotolerans, Fulvimarina pelagi, Pseudosulfitobacter pseudonitzschiae and Oceanicola granulosus, were inoculated into liquid culture media Marine Broth 2216 or R2A. Cell growth was determined by measuring the OD600 with a spectrophotometer. When the OD600 of each bacterial strain reached a value between 0.6 and 0.8 (indicating nearly equivalent bacterial numbers), equal volumes of each strain in different combinations of the consortium were combined in a 1:1 ratio. The mixture was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded, then cells were resuspended in MMC, and this process was repeated three times to thoroughly discard the original medium. Subsequently, inoculation was performed at a volume ratio of 2% into MMC medium containing PS films (4 pieces, 1.5 cm×1.5 cm). Three biological replicates were set up, and each replicate with a 2% inoculum was inoculated into 100 mL/250 mL MMC liquid medium. The cultures were incubated at 150 rpm and 28°C for 45 days. Finally, the surface biofilm was removed with 2% SDS for 4 h at 50°C (Kyaw et al, 2012), followed by washing with sterile water and drying. The weight of the films was measured, and the weight loss rate was calculated.
After microbial consortium growth using PS film as the sole carbon source, the characteristics of plastic surface may change, resulting in alterations in the hydrophobicity of the PS film (Zhang et al., 2022). Randomly selected PS films from each microbial consortium were subjected to contact angle measurements (OCA20, German Data Physics company). Briefly, 2 μL of pure water was deposited on the surface of PS film at 1 μL/s at room temperature. The contact angles formed by the left and right edges of the water droplet in contact with the PS film were measured as indicators of PS degradation. Measurements were taken at 4-5 points on the surface of each PS film (Jaleh et al., 2011).
PS films degraded by the different consortia were randomly selected for analysis after the biofilms on the PS surface were removed with 2% SDS and dried. The changes in the structure of the PS films due to the bacterial incubation were analyzed using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy, with a Thermo Scientific iS50 (Nicolet iS50, USA) infrared spectrometer with an integrated attenuated total reflection ATR attachment. Briefly, the measurement spectra range was from 4000-400 cm-1, and the data were treated using OMNIC software. Images were taken with a spectral resolution of 4 cm-1 over an average of 32 scans. The data were transformed using N-B strong apodization and Mertz phase correction according to a protocol for plastic identification. All the ATR-FTIR spectra measured were compared with the spectra in a commercial library (Cross Sections Wizard, Polymer Laminate Films).
Microbial cultivation with PS as a growth substrate was conducted at 28°C and 150 rpm. The flasks were shaken once a day during the incubation period to prevent bacterial attachment to the flask walls. On the 10th, 20th, and 35th days, three replicates were randomly sampled, followed by the remaining three replicates the on 45th day. Subsequently, all supernatants obtained from the centrifugation of the replicates were subjected to high-throughput sequencing to observe changes in species ratios.
Biofilm formation by microorganisms on the surface of plastics is a prerequisite for biodegradation (Bhagwat et al., 2021). Subsequently, plastics are degraded by internal and external enzymes secreted by these microorganisms (Sivan et al., 2006). The released monomers or mesostates serve as a carbon source that can be readily absorbed by microorganisms, leading to an increase in microbial biomass (Degli-Innocenti, 2014). SEM observations showed obvious biodegradation on the surfaces of macro- and microplastic debris, the latter rotten more severely (Figure 2). The irregular structure of the EPS and the obvious biofilm on the surface indicate that it was degraded in the marine environment, suggesting the presence of bacterial strains capable of degrading EPS on the surface.
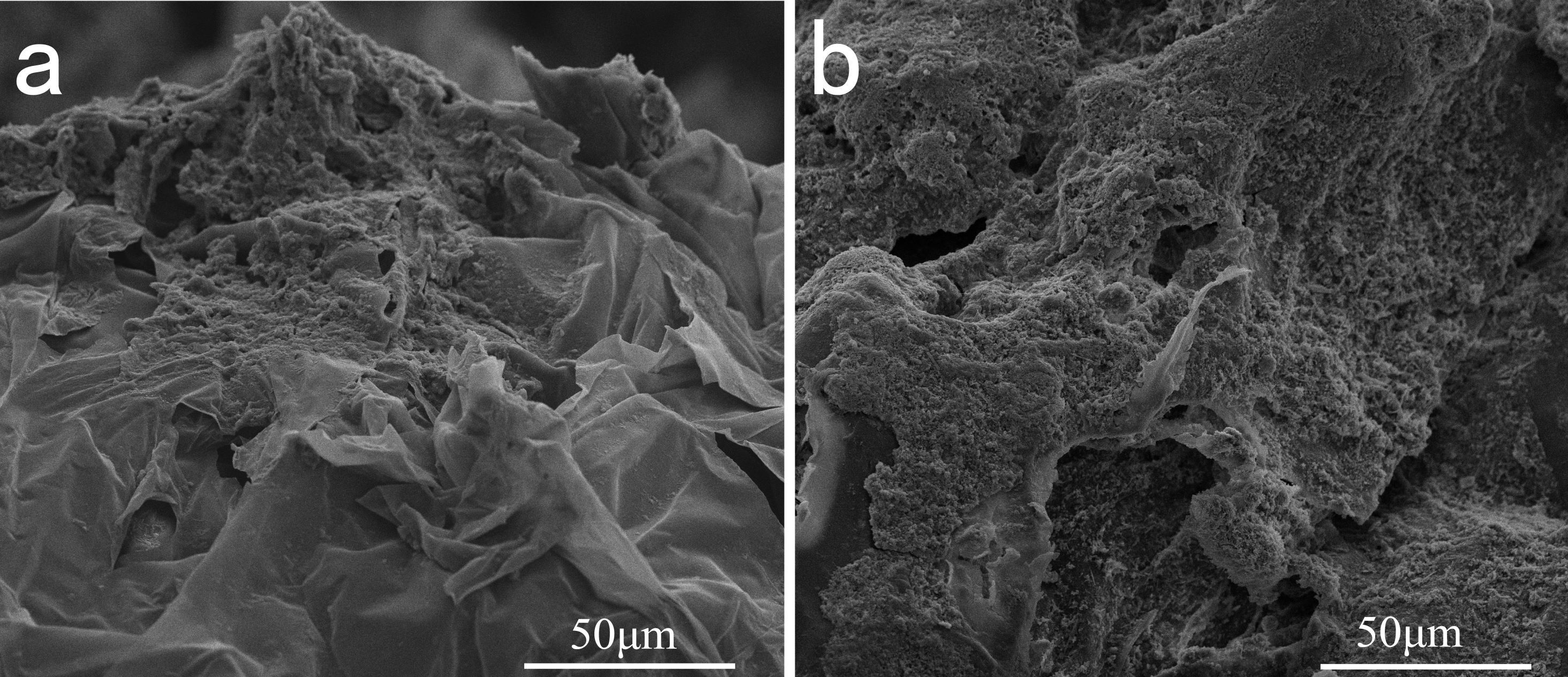

Figure 2. Surface micrographs of the in-situ EPSs observed using SEM. Samples were selected randomly from the collections, (a) surface of the LPs and (b) MPs, respectively.
To explore the diversity and composition of bacterial communities on the surfaces of EPS in coastal, we performed high-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing analysis on environmental samples, including nearshore seawater, surface sandy sediment, and various sizes of EPS debris collected from the coast of Xiamen Island. In total, we identified 30 phyla, 82 classes, 150 orders, 325 families, and 813 genera of bacteria. Figure 3a showed the relative abundance of taxa at the order level, the top 10 orders on in-situ macroplastics as Rhizobiales (18.58%), Pseudonocardiales (16.5%), Sphingomonadales (9.42%), Bacillales (8.33%), Rhodobacterales (7.15%), Rubrobacterales (4.91%), Rhodothermales (4%), Frankiales (3.88%), Thermomicrobiales (1.89%), and Sphingomonadales (1.7%). The top 10 orders in surface of in-situ microplastics were Rhizobiales (23.25%), Sphingomonadales (9.86%), Rhodothermales (7.97%), Rhodobacterales (5.61%), Frankiales (4.56%), Bacillales (4.12%), Propionibacteriales (3.81%), Microtrichales (3.4%), Rubrobacterales (3.12%), and Pseudonocardiales (2.34%). The relative abundance of Pseudonocardiales on in-situ microplastics significantly decreased compared to macroplastics, indicating variations in bacterial consortium composition across various plastic sizes.
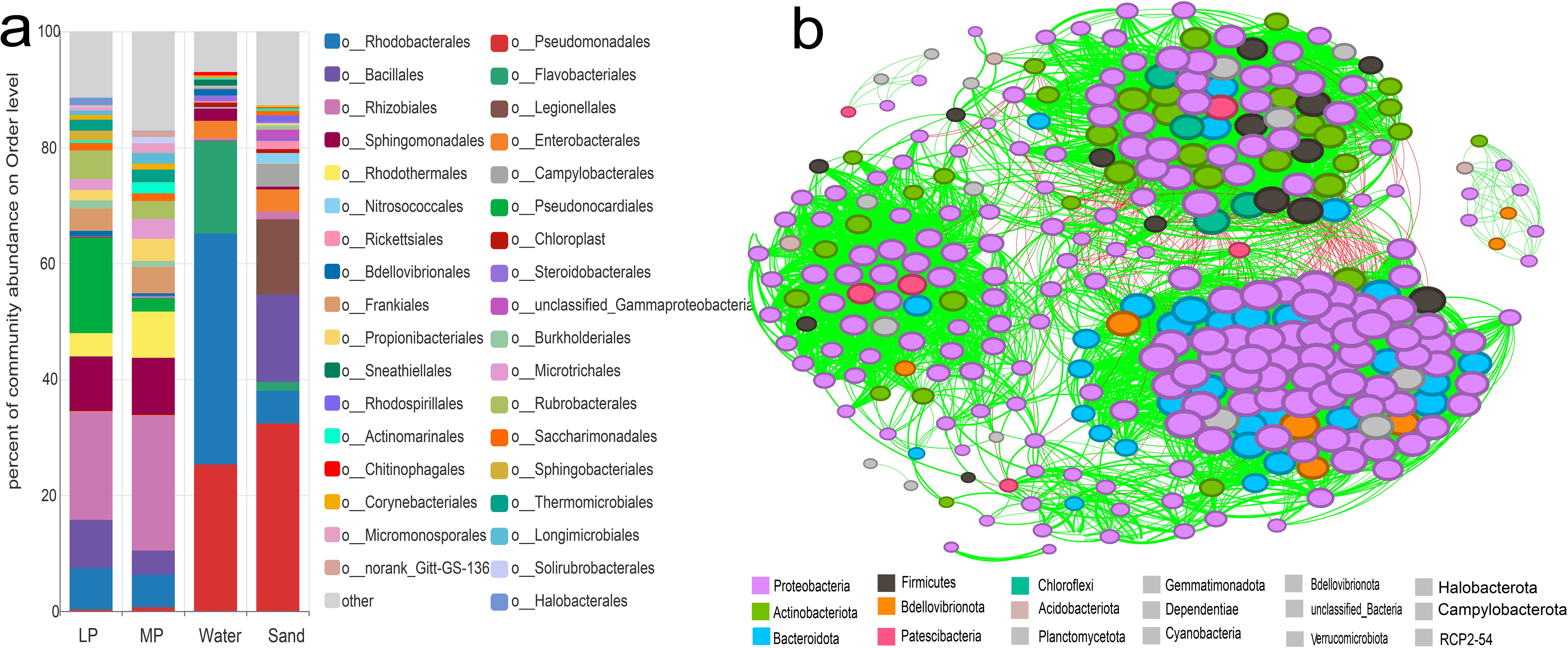
Figure 3. Relative abundance of the original bacterial consortia and the co-occurrence network analysis. (a), The original consortium diversity of the samples of LP, MP, seawater, and surface sand at the order level. (b), Network analysis of all the samples. The color of the nodes displays different dominant phyla. Red lines between nodes represent negative correlations, while green lines indicate positive correlations.
In-situ seawater samples exhibited a high diversity of bacterial communities dominated by Rhodobacterales (39.81%), Pseudomonadales (25.31%), Flavobacteriales (15.98%), Enterobacterales (3.04%), Sphingomonadales (2.1%), and Bdellovibrionales (1.08%). Bacterial communities in surface sandy sediments displayed distinct composition, the top 10 orders including Pseudomonadales (32.35%), Bacillales (15.09%), Legionellales (12.96%), Rhodobacterales (5.66%), Campylobacterales (3.97%), Enterobacterales (3.81%), Nitrosococcales (1.78%), unclassified_Gammaproteobacteria (1.6%), Rickettsiales (1.38%), and Rhizobiales (1.33%). Thus, the microbial diversity in nearshore seawater and sand surface differed significantly from that on EPS, indicating a substantial carrier-mediated selection of microorganisms in the environments. Rhizobiales, Pseudonocardiales, Sphingomonadales, Rhodobacterales, exhibit high relative abundance on both micro- and macro-EPS, making them the dominant component of biofilms. Previous studies have identified Rhizobiales, Rhodobacterales, Streptomycetales, and Cyanobacteria, playing a key role in plastic biofilms (Debroas et al., 2017). In the laboratory, mangrove sediments with and without polyethylene terephthalate (PET) particles showed differences in the abundance of Rhizobiales after two months (Jiménez et al., 2024a). Rhodobacteraceae also exhibited a high relative abundance in microplastic from Yellow Sea (Jiang et al., 2018) and in exposed microplastic from the Yellow Sea and South China Sea (Xu et al., 2019). Moreover, on the EPS biofilms investigated on Xiamen Island, the relative abundance of Rhodobacteraceae was 1.9%-18.81% in different seasons (Zhang et al., 2024). In this study, Rhizobiales represented the majority at bacterial order level in-situ on EPS microplastics, with relative abundance of 22.33%, followed by Rhodobacterales of 5.63%. It has also been found that Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales were major groups enriched by PE and PS in marine environment (Syranidou et al., 2019). Combined with the above research, we hypothesized that Rhizobiales and Rhodobacterales may play a key role in marine PS biodegradation.
To analyze relationships among bacterial communities, co-occurrence network analysis was conducted at the OTUs level across all samples. As shown in Figure 3b, the network analysis revealed 303 nodes, an average path length of 2.676, an average clustering coefficient of 0.566, an average modularity of 0.618, a diameter of 6, and 6,255 edges. Among them, 188 OTUs belonged to Proteobacteria, 37 for Actinobacteriota, and 31, 14, 7, for Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Bdellovibrionota, respectively. Especially, Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales belong to Proteobacteria, have been highlighted in multiple studies as key phyla involved in plastic biodegradation (Debroas et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2018; Vargas-Suárez et al., 2021). Rhizobiales has been designated as a biomarker for microplastic pollution (Rong et al., 2023). Biofilm on floating microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea were found dominated by the key bacterial groups in the biofilm of PS, PE, and PP, including Flavobacteriales and Rhodobacterales (Vaksmaa et al., 2021). Results in this study combined with the recent findings, propose that Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales may play a crucial role in plastic degradation.
To obtain the PS-degrading isolates from the EPS surface, we evaluated the ability of bacteria to degrade PS with PS as the sole carbon source. As shown in Table 1, a total of 51 strains belonging to 23 families were isolated from the EPS surface, which have been reported capable of degrading plastics and various organic compounds, some of which have been reported, such as Pseudoalteromonadaceae (Delacuvellerie et al., 2021), Pseudomonadaceae (Roberts et al., 2019), Rhodobacteraceae (Roager and Sonnenschein, 2019), and Sphingomonadaceae (He et al., 2022). Importantly, we identified 36 PS-degraded bacteria species, which not yet previously reported, including C. kochii, F. pelagi, P. pseudonitzschiae, D. nitrariae, C. oceanisediminis, N. rotundus, T. cyri, R. antarcticus, A. palladensis, L. soesokkakensis. They contribute to the diversity of new bacterial strains in the field of PS degradation.
Microbiome engineering can be defined as the modification or rearrangement of microbial communities to obtain desired functions, which include the selection, evolution and interaction of species (Jiménez et al., 2024b). Understanding the interactions of bacteria through various biochemical pathways is crucial for the discovery of key degrading bacteria, revealing the role of microbes in the process of plastic degradation. This study considered in-situ microbial diversity and degradation ability. Four isolates belonging to Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales, including P. halotolerans, F. pelagi, p. pseudonitzschiae, and O. granulosus, were chosen for the construction of the PS-degrading consortium. The selection was based on the overall diversity, in-situ abundance and co-occurrence, as well as individual capability to degrade PS films. A total of 15 microbial consortia were initially assembled using P. halotolerans, F. pelagi, P. pseudonitzschiae, and O. granulosus for preliminary screening. According to bacterial growth with PS, six consortia demonstrating significant growth increases were selected for further investigation, as presented in Table 2. Dynamic changes in their relative abundance of each strain in the course of 45 day-incubation among six consortia their roles in the biodegradation process were displayed by their increase in abundance in the consortium, as shown in Figure 4, as well as the PS degrading efficiency as showed next.
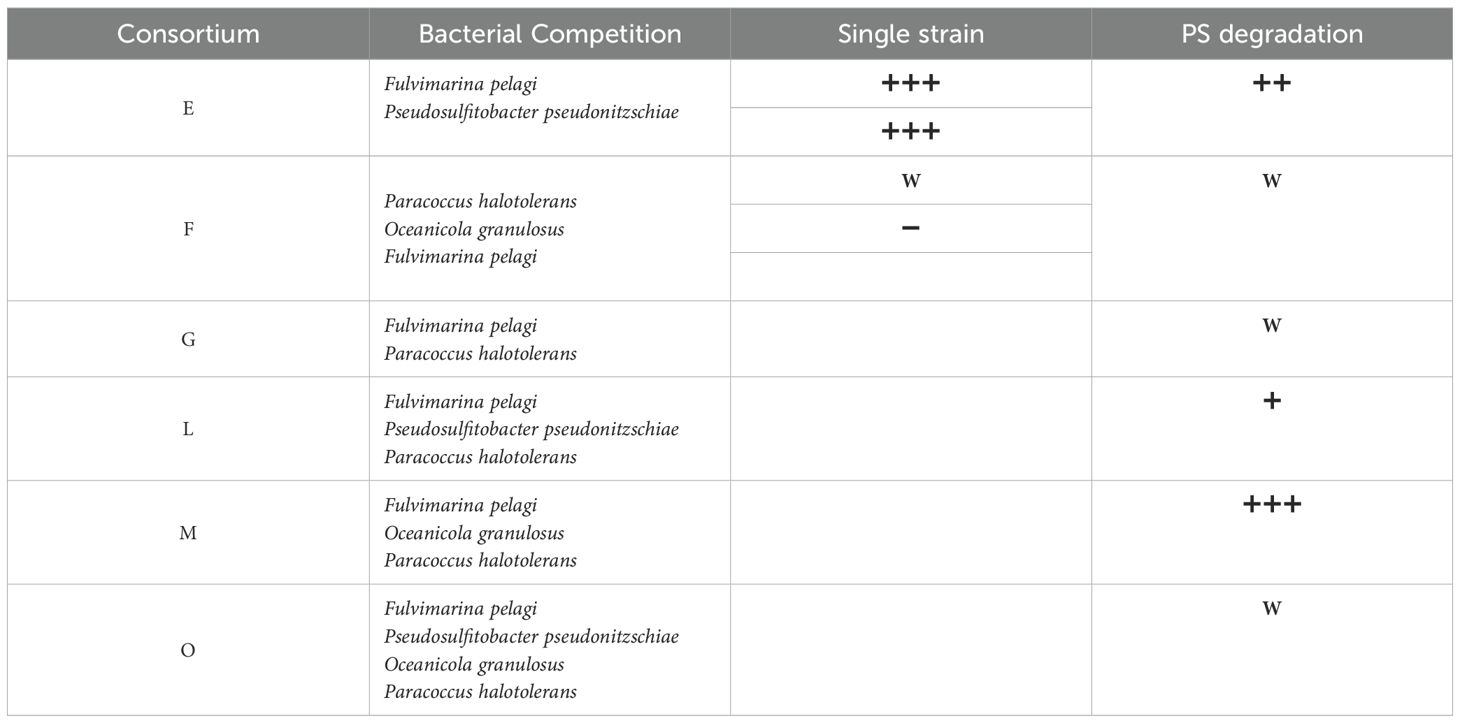
Table 2. Construction of artificial PS-degrading consortium based on diversity and PS degradation ability.
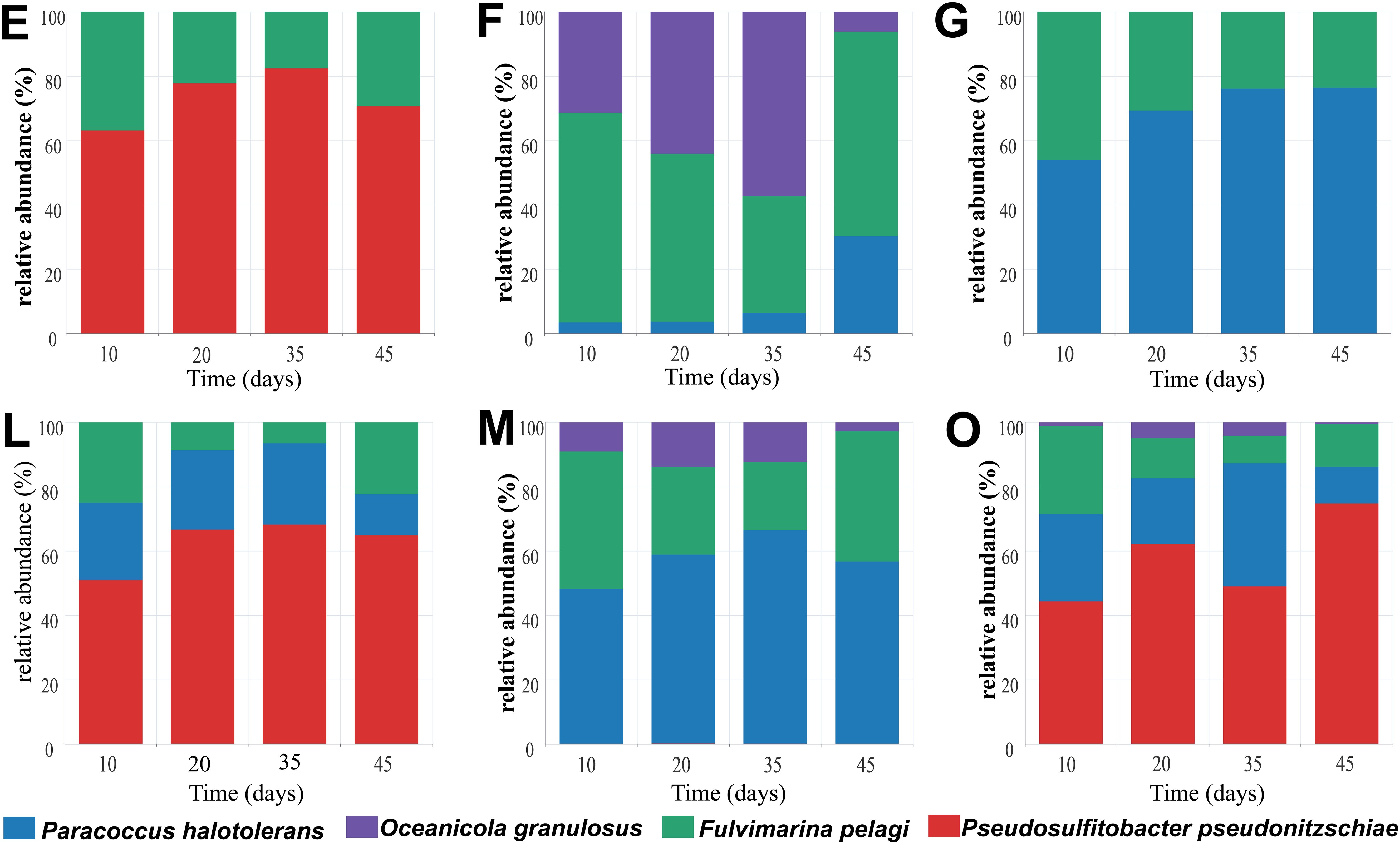
Figure 4. Dynamic change of bacterial consortium during PS degradation. After culturing F. pelagi, P. pseudonitzschiae, P. halotolerans, and O. granulosus, mixed them in a 1:1 ratio to construction combinations E, F, G, L, M and O containing 2 to 4 species, and observed the changes in relative abundance over 45 days.
In consortium E, P. pseudonitzschiae showed an increase in relative abundance to 82% during a 35-day cultivation, decreasing to 70% on 45th day. F. pelagi exhibited an increase from 17% to 30% in relative abundance from day 35 to 45. Consortium F initially included F. pelagi and O. granulosus, but P. halotolerans contamination occurred during the experiment. In consortium F, O. granulosus decreased to 6% over time, while P. halotolerans increased to 30%. F. pelagi initially decreased to 36% by day 35 due to the growth of O. granulosus, but rose to 64% by day 45. In consortium G, the relative abundance of P. halotolerans increased to 76%, while F. pelagi decreased to 24%. In consortium L, relative abundance of P. pseudonitzschiae was increasing, with a decrease in P. halotolerans, and F. pelagi decreased at the early stage and then increased. In consortium M, during a 45-day culturation, O. granulosus decreased to 3% with P. halotolerans increased to 57%, and F. pelagi was at the same level as in consortium L at 22%. In consortium O, relative abundance of O. granulosus decreased to 0.54% as in consortium M, in contrast, P. pseudonitzschiae increased to 75%, consistent with the performance in consortium E and L, additionally, P. halotolerans decreased to 11% after 45 days of cultivation, while F. pelagi decreased to 13%. In consortium E, the relative abundance of P. pseudonitzschiae significantly increased from the beginning of cultivation to the 35th day, indicating its potential dominance in the early stages of PS degradation. However, its abundance decreased at 45th day, possibly influenced by metabolic metabolites, whereas F. pelagi increased in relative abundance, suggesting a sustained degrading effect. P. pseudonitzschiae exhibits remarkable motility (Bartling et al., 2018), and may rapidly attach to plastic surfaces to form biofilms in in-situ. Additionally, F. pelagi showed increased biomass after 10 days of cultivation, but its proportion decreased when it was co-cultured with P. halotolerans. Given the low weight loss rate of 0.43% in consortium G, P. halotolerans might adversely affect F. pelagi. The consortium F and M showed that P. halotolerans also overcome O. granulosus by a high abundance.
F. pelagi and P. pseudonitzschiae showed significant biomass growth in the initial test of single bacterial degradation ability. Combined with the relative abundance of consortium, it can be considered that F. pelagi and P. pseudonitzschiae as key degraders within bacterial consortium.
With PS as the sole carbon source, different consortia were cultured in liquid MMC medium for 45 days, and SEM observation was performed to assess the biofilm formation and changes on the PS surface. The results showed that all the PS-degrading consortium could form dense biofilms on the PS surface, tightly attached to the PS surface after 45 days of incubation (Figure 5a). After removing the surface biofilm with 2% SDS, significant changes and obvious eroded pits were observed on the PS surface (Figure 5b). SEM observations confirmed the ability of different consortium to degrade PS plastic. Additionally, the hydrophobicity of the PS surface treated by bacterial consortium is decreased. To determine the change in hydrophobicity of PS plastic, the water contact angle was used to analyze the changes in the surface hydrophobicity “after PS degradation by the bacterial consortium for 45 days. After removing the biofilm on the PS surface using 2% SDS and drying overnight at 45°C, the contact angles were measured. As shown in Figure 6, the angles of consortium E, F, G, L, M, and O, were 70.99°, 72.02°, 71.30°, 79.38°, 80.12°, and 84.39°, respectively, which were much lower than the contact angle of the non-incubated control (93.26°). The results indicated that the hydrophobicity of the PS films was decreased due to the bacterial consortium. These results indicate that bacteria degrade PS plastic through extracellular oxidation, consistent with previous studies, wherein PS surfaces treated by consortium showed hydrophobicity decrease and hydrophilicity increase (Yang et al., 2014). In addition, this reduction in hydrophobicity makes it easier for bacteria to attach to the plastic surface and enhance the degradation ability of plastic (Yang et al., 2015).
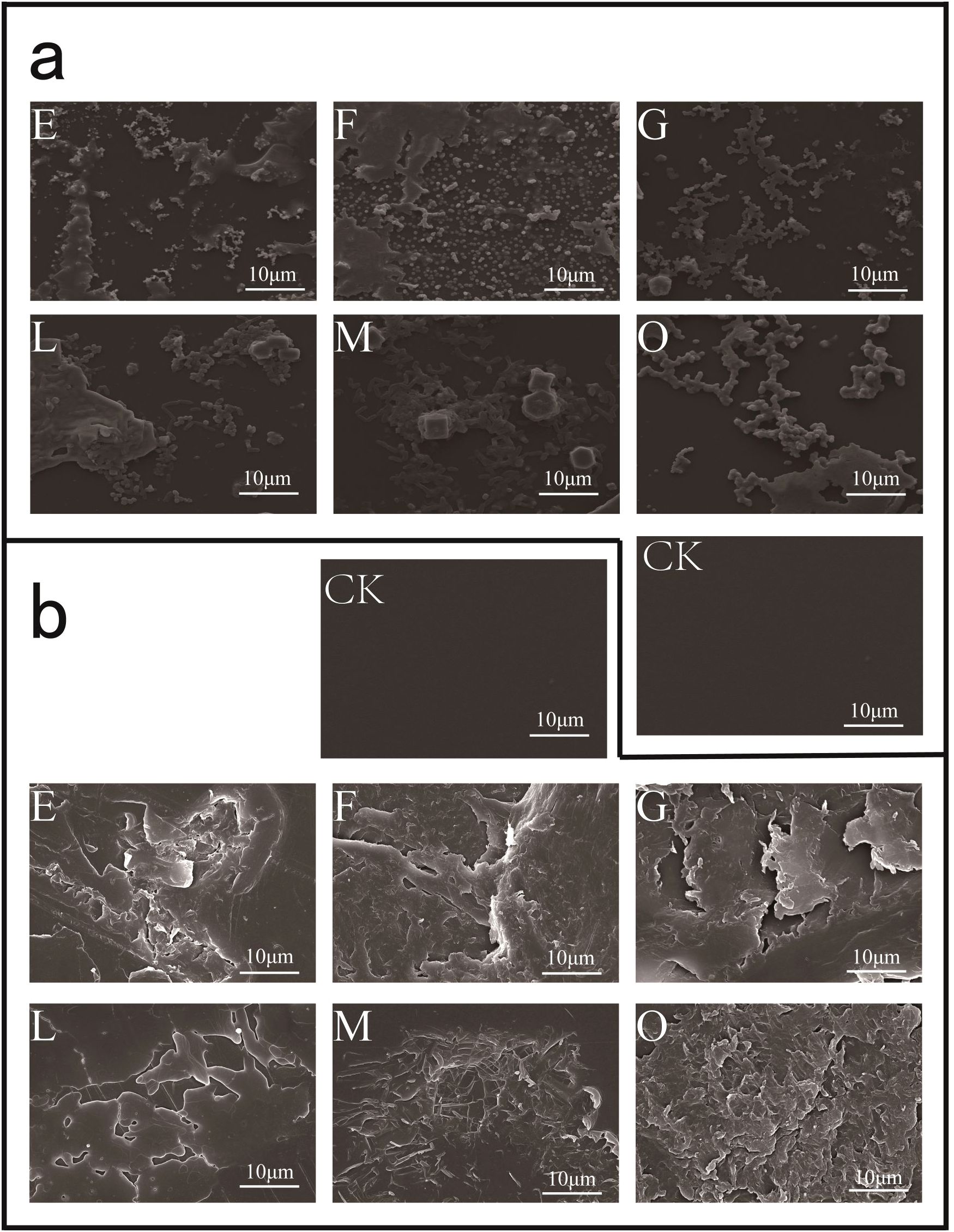
Figure 5. Observation of PS degradation by the six consortia for 45 days using SEM. (a), Observation PS film surface treated by consortia E, F, G, L, M, and O compared with the non-inoculated PS (CK); (b), treated by consortia E, F, G, L, M, and O were removed the biofilm with 2% SDS buffer, and evident etch pits were found on the PS surface.

Figure 6. Changes in the contact angle between water droplets and the PS surface. On the PS surfaces treated by the consortium E, F, G, L, M, and O, respectively; the contact angle formed between water droplets and PS surface was reduced compared to the control.
To further elucidate surface changes on PS after consortium treatment, characterization analysis was performed using ATR-FTIR. As shown in Figure 7, new functional groups appeared on the PS after treatment by the bacterial consortium. A new C-O group was detected at 1028 cm-1, and a carbonyl group (C=O) was observed at 1601 cm-1. These findings indicate that bacterial degradation of PS involves extracellular oxidation, consistent with previous studies on PS biodegradation (Arunrattiyakorn et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2021; Xing et al., 2021). In addition, it was observed that in the infrared spectrum (2800-3100 cm-1), the CH vibration intensity was higher than that of the control. The appearance of new oxygen-containing functional groups on the plastic surface provides evidence that PS film degradation primarily occurs through oxidation processes (Dey et al., 2024).
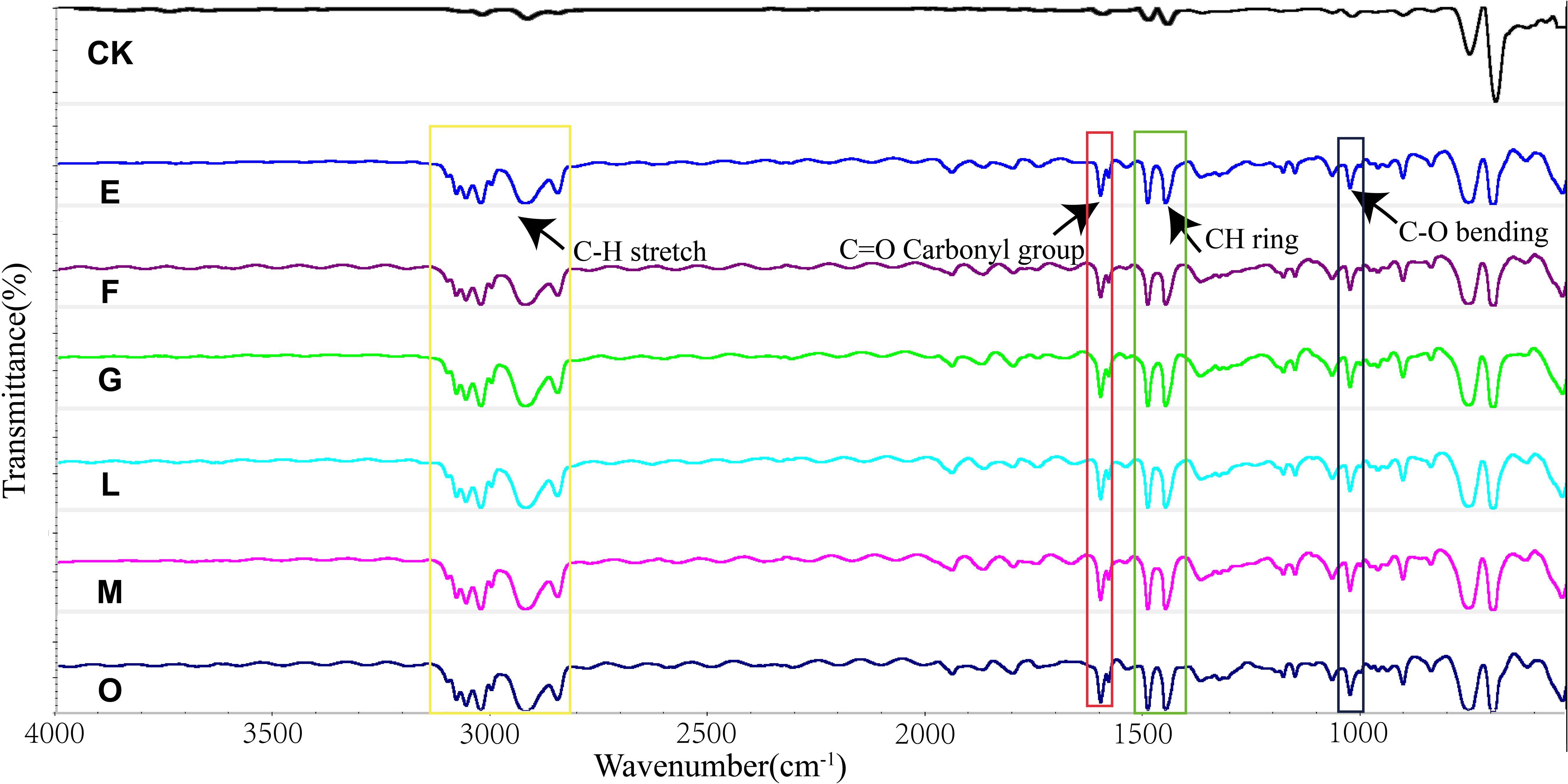
Figure 7. Characterization of biodegradation and oxidation of PS polymers by the six consortia using ATR-FTIR. Detection of C-O at 1028 cm-1, C=O carbonyl group at 1601 cm-1, and C-H vibrations at 2800-3100 cm-1 higher than CK for the consortium E, F, G, L, M, and O.
To evaluate PS biodegradability of the consortium, the weight loss of PS film was measured after 45 days’ cultivation with PS as the sole carbon and energy source in MMC medium. An independent-sample t-test was performed to assess the statistical significance of weight loss rate of PS (n = 3), evaluating biodegradation efficiency. The results showed that weight loss was statistically significant (P < 0.05) in all consortia. As depicted in Figure 8, consortium E exhibited a weight loss rate of 12.14%, however, P. halotolerans was added to consortium L, the weight loss rate decreased to 9.18%. The weight loss rate of consortium F was 3.91%, while consortium M was 18.9%, which was the same composition but in different proportions with consortium F. Furthermore, consortium G and O displayed extremely low weight loss rates, 0.43% and 1.57%, respectively.
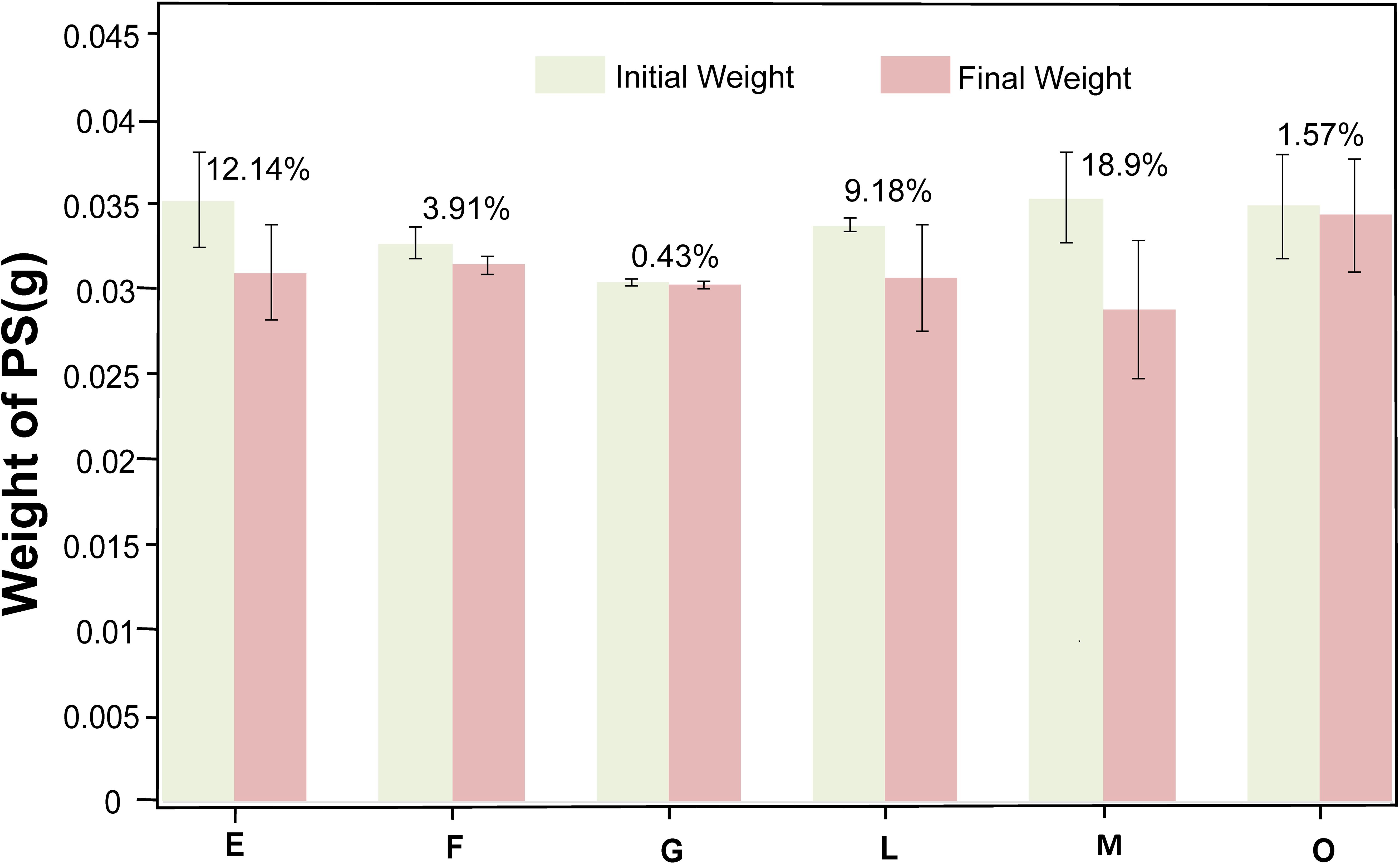
Figure 8. Weight loss of the PS film after being cultured for 45 days in consortia E, F, G, L, M, and O. After culturing the PS membrane as the sole carbon and energy source for 45 days, the biofilm was removed, and the weight loss of PS degraded by consortia E (12.14%), F (3.91%), G (0.43%), L (9.18%), M (18.9%), and O (1.57%) was measured, with three replicates per consortia.
Overall, P. pseudonitzschiae exhibited high relative abundance in all consortia, indicating its importance in the PS-degradation. In contrast, O. granulosus could not degrade PS, and in consortium F, a high initial proportion of O. granulosus correlated with poor degradation effects, but its sharp decrease over time suggests degradation occurred between days 35 and 45. Conversely, the consortium M showed an increased weight loss rate to 18.9% with the relative abundance of O. granulosus decreasing from 9% to 3% during a 45-day cultivation.
The notable efficiency of consortium comprising F. pelagi, O. granulosus, and P. halotolerans, may be attributed to impressive denitrification capabilities of the genus Paracoccus (Li et al., 2023),which has been reported as a typical S-oxidizing bacterium (Zhao et al., 2017). Studies indicate that endogenous microorganisms mainly including Rhizobiales significantly contribute to nitrogen cycling in coral reefs, particularly in coral skeletons (Moynihan et al., 2022). In plants, Rhizobium belonging to Rhizobiales forms symbiotic relationships with leguminous plants, which are crucial for nitrogen fixation processes (Lemos et al., 2021). The SoxB gene is detected in all investigated phototrophic and chemotrophic species (Meyer et al., 2007), primarily sourced from Alphaproteobacteria with Rhizobiales as the dominant group (Santana et al., 2021). Bacteria rich in sulfur-oxidizing genes encode and highly express genes for sulfur metabolism, carbon fixation, and nitrogen fixation (NifHDK) in a variety of conditions, demonstrating the connection between sulfur oxidation and nitrogen cycle mechanisms (Rolando et al., 2024). Oceanicola could produce poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), converting poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) into a more available internal carbon source, PHB, thereby enhancing denitrification activity (Ruan et al., 2016). Hence, the higher weight loss rate observed in consortium M might be attributed to the mutual promotion between sulfur-oxidation and denitrification.
P. pseudonitzschiae exhibited a high relative abundance across all reconstructed consortia, underscoring its significant role in PS degradation. However, P. pseudonitzschiae was excluded from the most efficient consortium, may be attributed to the production of certain metabolic byproducts by this bacterium, which inhibit the growth and degradation capabilities of other strains, a phenomenon frequently observed in microbial communities (Contreras-Salgado et al., 2024). Additionally, P. pseudonitzschiae possesses strong motility and biofilm formation capabilities, enabling it to rapidly attach to plastic surfaces and form biofilms in the early stages (Fei et al., 2020). This early attachment allows it to occupy advantageous positions, thereby inhibiting the attachment and growth of other strains. Results indicate that efficient degradation consortium is not merely a mixture of efficient PS degradation strains; non-degradation strains also play a crucial role within the consortium.
This study extended the bacterial diversity associated with EPS plastic wastes in the subtropical estuary coast of Xiamen Island, and obtained an engineered bacterial consortium constituted of F. pelagi, P. halotolerans. and O. granulosus showing a high weight loss by 18.9% in 45 days. The microorganisms enriched on EPS debris were exhibited differences from those in seawater and sandy sediments, and varied between microplastics and macroplastics. Co-occurrence network and bacterial characterization revealed that Rhodobacterales and Rhizobiales play important roles in PS degradation. The results expanded the diversity of PS-degrading bacteria, identifying several newly recognized bacterial taxa as PS degraders for the first time. Moreover, the non-degrading bacteria of Oceanicola also contribute to PS degradation, imply their role and interactions with PS-degraders in biofilms on plastic debris during plastic fragmentation and further breakdown in environments. The construction of a highly efficient consortium revokes further investigations in artificial consortia for plastic pollution remediation and recycling.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.cncb.ac.cn/search/specific?dbId=bioproject&q=cra018003, CRA018003.
JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZB: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42030412, 92251302 and 91851203 to ZS) and the China Ocean Mineral Resources Research and Development Association (COMRA) (No. DY135-B-01 to ZS).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ali S. S., Elsamahy T., Koutra E., Kornaros M., El-Sheekh M., Abdelkarim E. A., et al. (2021). Degradation of conventional plastic wastes in the environment: A review on current status of knowledge and future perspectives of disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 771, 144719. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144719
Aravinthan A., Arkatkar A., Juwarkar A. A., Doble M. (2016). Synergistic growth of Bacillus and Pseudomonas and its degradation potential on pretreated polypropylene. Preparative Biochem. Biotechnol. 46, 109–115. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2014.985836
Arunrattiyakorn P., Ponprateep S., Kaennonsang N., Charapok Y., Punphuet Y., Krajangsang S., et al. (2022). Biodegradation of polystyrene by three bacterial strains isolated from the gut of Superworms (Zophobas atratus larvae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 132, 2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/jam.15474
Bartling P., Vollmers J., Petersen J. (2018). The first world swimming championships of roseobacters—Phylogenomic insights into an exceptional motility phenotype. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 41, 544–554. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.08.012
Bastian M., Heymann S., Jacomy M. (2009). Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 3, 361–362. doi: 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937
Bhagwat G., O'Connor W., Grainge I., Palanisami T. (2021). Understanding the fundamental basis for biofilm formation on plastic surfaces: role of conditioning films. Front. Microbiol. 12, 687118. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.687118
Borrelle S. B., Ringma J., Law K. L., Monnahan C. C., Lebreton L., McGivern A., et al. (2020). Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science 369, 1515–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.aba3656
Caporaso J. G., Kuczynski J., Stombaugh J., Bittinger K., Bushman F. D., Costello E. K., et al. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chelomin V. P., Dovzhenko N. V., Slobodskova V. V., Mazur A. A., Kukla S. P., Zhukovskaya A. F. (2023). Expanded polystyrene-debris-induced genotoxic effect in littoral organisms. Toxics 11 (9), 781. doi: 10.3390/toxics11090781
Contreras-Salgado E. A., Sánchez-Morán A. G., Rodríguez-Preciado S. Y., Sifuentes-Franco S., Rodríguez-Rodríguez R., Macías-Barragán J., et al. (2024). Multifaceted applications of synthetic microbial communities: advances in biomedicine, bioremediation, and industry. : Microbiol. Res. 15, 1709–1727. doi: 10.3390/microbiolres15030113
Debroas D., Mone A., Ter Halle A. (2017). Plastics in the North Atlantic garbage patch: A boat-microbe for hitchhikers and plastic degraders. Sci. Total Environ. 599-600, 1222–1232. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.059
Degli-Innocenti F. (2014). Biodegradation of plastics and ecotoxicity testing: when should it be done. Front. Microbiol. 5, 475. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00475
Delacuvellerie A., Benali S., Cyriaque V., Moins S., Raquez J.-M., Gobert S., et al. (2021). Microbial biofilm composition and polymer degradation of compostabl e and non-compostabl e plastics immersed in the marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 419, 126526. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126526
Dey S., Veerendra G. T. N., Babu P. S. S. A., Manoj A. V. P., Nagarjuna K. (2024). Degradation of plastics waste and its effects on biological ecosystems: A scientific analysis and comprehensive review. Biomed. Materials Devices 2, 70–112. doi: 10.1007/s44174-023-00085-w
Edgar R. C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604
Edgar R. C., Haas B. J., Clemente J. C., Quince C., Knight R. (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 27, 2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Fei C., Ochsenkühn M. A., Shibl A. A., Isaac A., Wang C., Amin S. A. (2020). Quorum sensing regulates ‘swim-or-stick’ lifestyle in the phycosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 22, 4761–4778. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15228
Guezennec J. (2002). Deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A new source of innovative bacterial exopolysaccharides of biotechnological interest? J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 204–208. doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000298
He Y., Wei G., Tang B., Salam M., Shen A., Wei Y., et al. (2022). Microplastics benefit bacteria colonization and induce microcystin degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 431, 128524. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128524
Jaleh B., Madad M. S., Tabrizi M. F., Habibi S., Golbedaghi R., Keymanesh M. R. (2011). UV-degradation effect on optical and surface properties of polystyrene-TiO2 nanocomposite film. J. Iran. Chem. Soc 8, S161–S168. doi: 10.1007/BF03254293
James-Pearson L. F., Dudley K. J., Te'o V. S. J., Patel B. K. C. (2023). A hot topic: thermophilic plastic biodegradation. Trends Biotechnol. 41, 1117–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.03.016
Jiang P., Zhao S., Zhu L., Li D. (2018). Microplastic-associated bacterial assemblages in the intertidal zone of the Yangtze Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 624, 48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.105
Jiménez D. J., Chaparro D., Sierra F., Custer G. F., Feuerriegel G., Chuvochina M., et al. (2024a). Engineering the mangrove soil microbiome for selection of polyethylene terephthalate-transforming bacterial consortia. Trends Biotechnol. 43 (1), 162–183. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.08.013
Jiménez D. J., Sanchez A., Dini-Andreote F. (2024b). Engineering microbiomes to transform plastics. Trends Biotechnol. 42, 265–268. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.09.011
Kim H. R., Lee H. M., Yu H. C., Jeon E., Lee S., Li J., et al. (2020). Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Pseudomonas sp. Isolated from the Gut of Superworms (Larvae of Zophobas atratus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 6987–6996. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01495
Kim H.-W., Jo J.H., Kim Y.-B., Le T.-K., Cho C.-W., Yun C.-H., et al. (2021). Biodegradation of polystyrene by bacteria from the soil in common environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 416, 126239. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126239
Kyaw B. M., Champakalakshmi R., Sakharkar M. K., Lim C. S., Sakharkar K. R. (2012). Biodegradation of low density polythene (LDPE) by pseudomonas species. Indian J. Microbiol. 52 (3), 411–419. doi: 10.1007/s12088-012-0250-6
Layeghifard M., Hwang D. M., Guttman D. S.. (2018). “Constructing and analyzing microbiome networks in R,” in Microbiome analysis: methods and protocols. Eds. Beiko R. G., Hsiao W., Parkinson J. (Springer New York, New York, NY), 243–266.
Lemos L. N., de Carvalho F. M., Gerber A., Guimarães A. P. C., Jonck C. R., Ciapina L. P., et al. (2021). Genome-centric metagenomics reveals insights into the evolution and metabolism of a new free-living group in Rhizobiales. BMC Microbiol. 21, 294. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02354-4
Li L., Xiong S., Wang Q., Xue C., Xiao P., Qian G. (2023). Enhancement strategies of aerobic denitrification for efficient nitrogen removal from low carbon-to-nitrogen ratio shale oil wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 387, 129663. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129663
Liu R., Zhao S., Zhang B., Li G., Fu X., Yan P., et al. (2023). Biodegradation of polystyrene (PS) by marine bacteria in mangrove ecosystem. J. Hazard. Mater. 442, 130056. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130056
Lu M., Wang X., Li H., Jiao J.J., Luo X., Luo M., et al. (2022). Microbial community assembly and co-occurrence relationship in sediments of the river-dominated estuary and the adjacent shelf in the wet season. Environ. pollut. 308, 119572. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119572
Matjašič T., Simčič T., Medvešček N., Bajt O., Dreo T., Mori N. (2021). Critical evaluation of biodegradation studies on synthetic plastics through a systematic literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 752, 141959. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141959
Matyakubov B., Lee T.-J. (2024). Optimizing polystyrene degradation, microbial community and metabolite analysis of intestinal flora of yellow mealworms, Tenebrio molitor. Bioresource Technol. 403, 130895. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2024.130895
Meera S. P., Bhattacharyya M., Nizam A., Kumar A. (2022). A review on microplastic pollution in the mangrove wetlands and microbial strategies for its remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 29, 4865–4879. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17451-0
Meyer B., Imhoff J. F., Kuever J. (2007). Molecular analysis of the distribution and phylogeny of the soxB gene among sulfur-oxidizing bacteria - evolution of the Sox sulfur oxidation enzyme system. Environ. Microbiol. 9, 2957–2977. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01407.x
Meyer-Cifuentes I. E., Werner J., Jehmlich N., Will S., Neumann-Schaal M., Öztürk B. J. N. C. (2020). Synergistic biodegradation of aromatic-aliphatic copolyester plastic by a marine microbial consortium. Nat. Commun. 11.5790 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19583-2
Mohan A. J., Sekhar V. C., Bhaskar T., Nampoothiri K. M. (2016). Microbial assisted High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) degradation. Bioresource Technol. 213, 204–207. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.021
Mor R., Sivan A. (2008). Biofilm formation and partial biodegradation of polystyrene by the actinomycete Rhodococcus ruber: biodegradation of polystyrene. Biodegradation 19, 851–858. doi: 10.1007/s10532-008-9188-0
Moynihan M. A., Goodkin N. F., Morgan K. M., Kho P. Y. Y., Lopes dos Santos A., Lauro F. M., et al. (2022). Coral-associated nitrogen fixation rates and diazotrophic diversity on a nutrient-replete equatorial reef. ISME J. 16, 233–246. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01054-1
Muthukumar J., Kandukuri V. A., Chidambaram R. (2024). A critical review on various treatment, conversion, and disposal approaches of commonly used polystyrene. Polymer Bull. 81 (4), 2819–2845. doi: 10.1007/s00289-023-04851-0
Roager L., Sonnenschein E. C. (2019). Bacterial candidates for colonization and degradation of marine plastic debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 11636–11643. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b02212
Roberts C., Edwards S., Vague M., León-Zayas R., Scheffer H., Chan G., et al. (2020). Environmental consortium containing Pseudomonas and Bacillus species synergistically degrades polyethylene terephthalate plastic. mSphere 5 (6), 01151–20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.01151-20
Rolando J. L., Kolton M., Song T., Liu Y., Pinamang P., Conrad R., et al. (2024). Sulfur oxidation and reduction are coupled to nitrogen fixation in the roots of the salt marsh foundation plant Spartina alterniflora. Nat. Commun. 153607. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47646-1
Rong L., Wang Y., Meidl P., Wang L., Sun H. (2023). Microplastics affect soybean rhizosphere microbial composition and function during vegetative and reproductive stages. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 252, 114577. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114577
Ruan Y.-J., Deng Y.-L., Guo X.-S., Timmons M.B., Lu H.-F., Han Z.-Y., et al. (2016). Simultaneous ammonia and nitrate removal in an airlift reactor using poly(butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 216, 1004–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.056
Salisu A., Maigari Y. S. (2022). “Polystyrene and its recycling: a review,” in Proceedings of Materials Science and Technology Society of Nigeria (MSN). 195–203.
Sanluis-Verdes A., Colomer-Vidal P., Rodriguez-Ventura F., Bello-Villarino M., Spinola-Amilibia M., Ruiz-Lopez E., et al. (2022). Wax worm saliva and the enzymes therein are the key to polyethylene degradation by Galleria mellonella. Nat. Commun. 13.5568 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33127-w
Santana M. M., Dias T., Gonzalez J. M., Cruz C. (2021). Transformation of organic and inorganic sulfur– adding perspectives to new players in soil and rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 160, 108306. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108306
Sivan A., Szanto M., Pavlov V.. (2006). Biofilm development of the polyethylene-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus ruber. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 72, 346–352. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0259-4
Syranidou E., Karkanorachaki K., Amorotti F., Franchini M., Repouskou E., Kaliva M., et al. (2017). Biodegradation of weathered polystyrene films in seawater microcosms. Sci. Rep. 7, 17991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18366-y
Syranidou E., Karkanorachaki K., Amorotti F., Avgeropoulos A., Kolvenbach B., Zhou N.-Y., et al. (2019). Biodegradation of mixture of plastic films by tailored marine consortia. J. Hazard. Mater. 375, 33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.078
Thushari G. G. N., Senevirathna J. D. M. (2020). Plastic pollution in the marine environment. Heliyon 6, e04709. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04709
Vaksmaa A., Knittel K., Abdala Asbun A., Goudriaan M., Ellrott A., Witte H. J., et al. (2021). Microbial communities on plastic polymers in the mediterranean sea. Front. Microbiol. 12, 673553. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.673553
Vargas-Suárez M., Savín-Gámez A., Domínguez-Malfavón L., Sánchez-Reyes A., Quirasco-Baruch M., Loza-Tavera H., et al. (2021). Exploring the polyurethanolytic activity and microbial composition of landfill microbial communities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105, 7969–7980. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11571-w
Wu J., Zhu Z., Waniek J. J., Niu M., Wang Y., Zhang Z., et al. (2023). The biogeography and co-occurrence network patterns of bacteria and microeukaryotes in the estuarine and coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 184, 105873. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.105873
Xing R. Z., Zhao Z. Q., Zhao W. Q., Chen Z., Chen J. F., Zhou S. G. (2021). Biodegradation of polystyrene by geobacillus stearothermophilus. Huan Jing Ke Xue 42, 3056–3062. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202009298
Xu X., Wang S., Gao F., Li J., Zheng L., Sun C., et al. (2019). Marine microplastic-associated bacterial community succession in response to geography, exposure time, and plastic type in China’s coastal seawaters. Mar. pollut. Bull. 145, 278–286. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.05.036
Yang J., Yang Y., Wu W.-M., Zhao J., Jiang L. (2014). Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 13776–13784. doi: 10.1021/es504038a
Yang Y., Yang J., Wu W. M., Zhao J., Song Y., Gao L., et al. (2015). Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: part 2. Role of gut microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 12087–12093. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02663
Zanchetta P., Lagarde N., Guezennec J. (2003). A new bone-healing material: A hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif. Tissue Int. 72, 74–79. doi: 10.1007/s00223-001-2091-x
Zhang Y., Pedersen J. N., Eser B. E., Guo Z. (2022). Biodegradation of polyethylene and polystyrene: From microbial deterioration to enzyme discovery. Biotechnol. Adv. 60, 107991. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107991
Zhang C., Mu Y., Li T., Jin F. J., Jin C. Z., Oh H. M., et al. (2023). Assembly strategies for polyethylene-degrading microbial consortia based on the combination of omics tools and the “Plastisphere. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1181967. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1181967
Zhang B., Liu R., Xu H., Zhao S., Wang J., Shao Z. (2024). Bacterial diversity in the biofilms on mariculture polystyrene foam at Xiamen’s coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 11, 1409399. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1409399
Zhao C., Gupta V. V. S. R., Degryse F., McLaughlin M. J. (2017). Abundance and diversity of sulphur-oxidising bacteria and their role in oxidising elemental sulphur in cropping soils. Biol. Fertility Soils 53, 159–169. doi: 10.1007/s00374-016-1162-0
Keywords: expanded polystyrene (EPS), biodegradation, consortium, marine bacteria, construction
Citation: Wang J, Liu R, Zhao S, Zhang B and Shao Z (2025) Construction of an efficient polystyrene-degrading microbial consortium based on degrading and non-degrading bacteria predominant in biofilms of marine plastic debris. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1569583. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1569583
Received: 01 February 2025; Accepted: 19 March 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited by:
Marius Nils Müller, Federal University of Pernambuco, BrazilReviewed by:
Youssef Lahbib, Tunis University, TunisiaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Liu, Zhao, Zhang and Shao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zongze Shao, c2hhb3p6QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.