- 1School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China
- 2College of Fisheries, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China
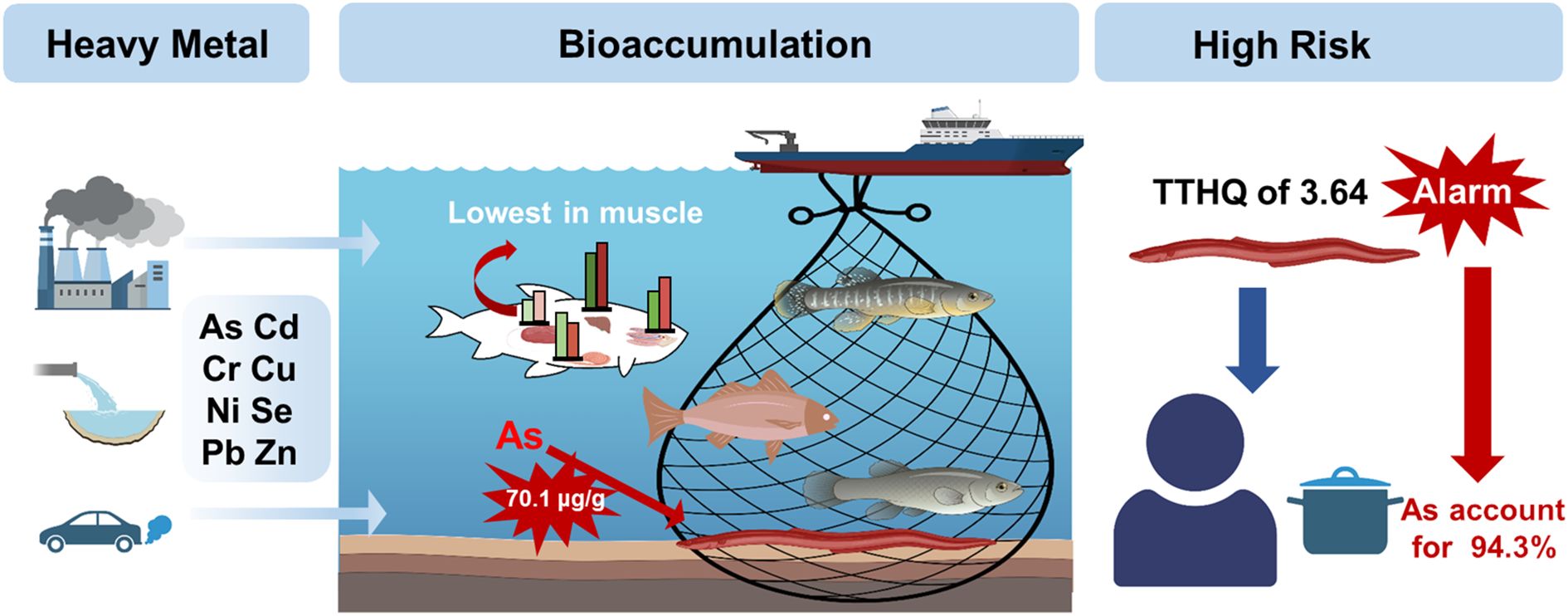
Heavy metal pollution presents a significant concern in marine ecosystems, posing a serious threat. Monitoring the levels of heavy metals in marine fish is crucial for safeguarding human health. This study specifically investigates the bioaccumulation of eight elements (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), selenium (Se), and zinc (Zn)) in marine fish in the Qiongzhou Strait in the South China Sea. Zn emerged as the predominant heavy metal, with an average concentration of 39.5 μg/g. Most marine fish showed a low risk of heavy metal intake, Pampus argenteus exhibited the lowest risk at 10–6. Moreover, caution is advised regarding the consumption of Uroconger lepturus due to its elevated risk of As bioaccumulation, with levels reaching 70.1 μg/g, contributing significantly to the total target hazard quotient at 94.3% (3.64). This study provides valuable recommendations for coastal environmental protection and the prevention of ecological incidents.
1 Introduction
Heavy metal pollution has become a significant environmental issue globally, particularly in marine ecosystems (Wang, 2012; Zhang et al., 2022). The excessive discharge resulting from anthropogenic activities has established heavy metals as the predominant pollutants in marine environments. Along coastal waters, substantial quantities of heavy metals exhibit properties such as bioaccumulation, biotransformation, and biomagnification within marine fish, thereby posing substantial threats to both local ecosystem and human health (Zhang et al., 2018), with particular concerns revolving around arsenic (As) (Zhang and Wang, 2012), mercury (Hg) (Wei et al., 2024), and copper (Cu) (Vignardi et al., 2023). Among these heavy metals, As is particularly alarming due to its widespread use and high toxicity to humans, potentially resulting in significant consequences regarding the impact of heavy metals.
Marine fish not only serve as a vital protein source for human consumption but also play a crucial role in monitoring heavy metal pollutants (Wang et al., 2014). The consumption of marine fish has become essential for human protein needs, encompassing raw fish consumption, fish processing, and fish trade. Roughly 1 billion individuals worldwide depend on the fishing trade and processing industry for their sustenance (Oosterveer, 2008). Fish protein is a nutritive infant food and is recommended for pregnant women to meet their protein and vitamin B12 requirements (Mamun et al., 2024). Global fish consumption has significantly increased from 23 kg/person to 42 kg/person in recent years (Desiere et al., 2018). Nevertheless, as the modern fish trade chain strengthens the connection between production and consumption, there is an urgent necessity to monitor the pollution of marine fish sources to mitigate potential risks associated with heavy metals.
The contamination of marine fish by heavy metals presents a persistent and significant challenge within various marine ecosystem issues, representing a long-standing global aquatic concern (Gui et al., 2017; Yan et al., 2022). Over the past 5 years, numerous incidents involving marine organisms in Asia, Europe, and America have triggered widespread alarm. For instance, in Jiaozhou Bay, marine fish, crustaceans, and mollusks have been discovered to be contaminated with several heavy metals, with fish showing chromium (Cr) concentrations reaching up to 0.35 mg/kg (Vignardi et al., 2023; Hou et al., 2024). Carcinogenic heavy metals such as As and lead (Pb) are also increasing prevalent in marine fish, with Pb concentrations in the muscle tissue of female and male Merluccius merluccius measuring 0.258 mg/kg and 0.315 mg/kg, respectively, in Oran Bay on the western Algerian Mediterranean coast (Djellouli et al., 2023). Given the discharge of heavy metals into coastal waters, rapidly developing coastal regions should prioritize addressing the issue of heavy metal contamination in marine fish. Monitoring heavy metal pollution in marine fish is crucial not only for the ecosystem but also for the well-being of local communities.
The Qiongzhou Strait and its adjacent areas, situated in the South China Sea, are subject to substantial human impact. Consequently, these waters have been selected as a typical marine ecosystem for assessing the levels of heavy metal pollutants in coastal fish populations. The South China Sea, renowned for its robust economic activities and maritime transportation, serves as a prominent tropical fishery region for seafood consumption. Responsible for the exchange of seawater between the northern South China Sea and the Beibu Gulf, the flow in the Qiongzhou Strait is robust and subject to seasonal variability, leading to a complex distribution of metal pollutants with fluctuations of up to threefold (Ouyang et al., 2024). Given the distinctive characteristics of the waters surrounding in Qiongzhou Strait (Chen et al., 2019), it is crucial to monitor the levels of heavy metal in marine fish and assess the potential health risk stemming from rapid economic development, agricultural practices, and transportation activities in these regions. Variations in pollutant levels were observed in marine fish within the South China Sea; for instance, the carcinogenic risk (CR) associated with Pb remained below the acceptable threshold (10-4) for residents (Gu et al., 2018), while As levels in most species exceeded the corresponding guidelines, warranting careful monitoring (Yang et al., 2021). Consequently, particular attention was given to the CRs linked to Pb and As pollution issues (Cooke et al., 2022), with additional consideration for cadmium (Cd) due to its carcinogenic properties and potential to induce chronic diseases (Pavlaki et al., 2016; Feng et al., 2022). To date, limited research has been conducted on heavy metal pollution in marine fish in the waters surrounding the Qiongzhou Strait.
Therefore, in order to evaluate the extent of heavy metal contamination in marine fish, a total of 20 sampling stations were established around the Qiongzhou Strait. At each station, a diverse range of fish samples were meticulously collected and pretreated, followed by the analysis of metal concentrations in these marine fish, with the data being documented in a database. Additionally, the target hazard quotient (THQ), the total target hazard quotient (TTHQ), and carcinogenic risk (CR) were utilized as reliable metric to assess the levels of heavy metals present in marine fish inhabiting the waters surrounding the Qiongzhou Strait. This study not only facilitated the monitoring of heavy metal concentrations in marine fish but also systematically assessed the risks associated with local fish consumption, consequently providing timely warnings regarding the risks of heavy metal exposure.
2 Methods and materials
2.1 Data sampling
Illustrated in Figure 1, the sampling region is situated in the South China Sea, China. The study comprised 20 sites, with the Qiongzhou Strait acting as a natural boundary, assigning 10 sampling sites to both its eastern and western sectors. At each site, marine fish samples were gathered and promptly frozen at –20°C before being transported to the laboratory for subsequent processing. Our research entailed the sampling of 351 wild fish, representing a variety of 31 distinct species.
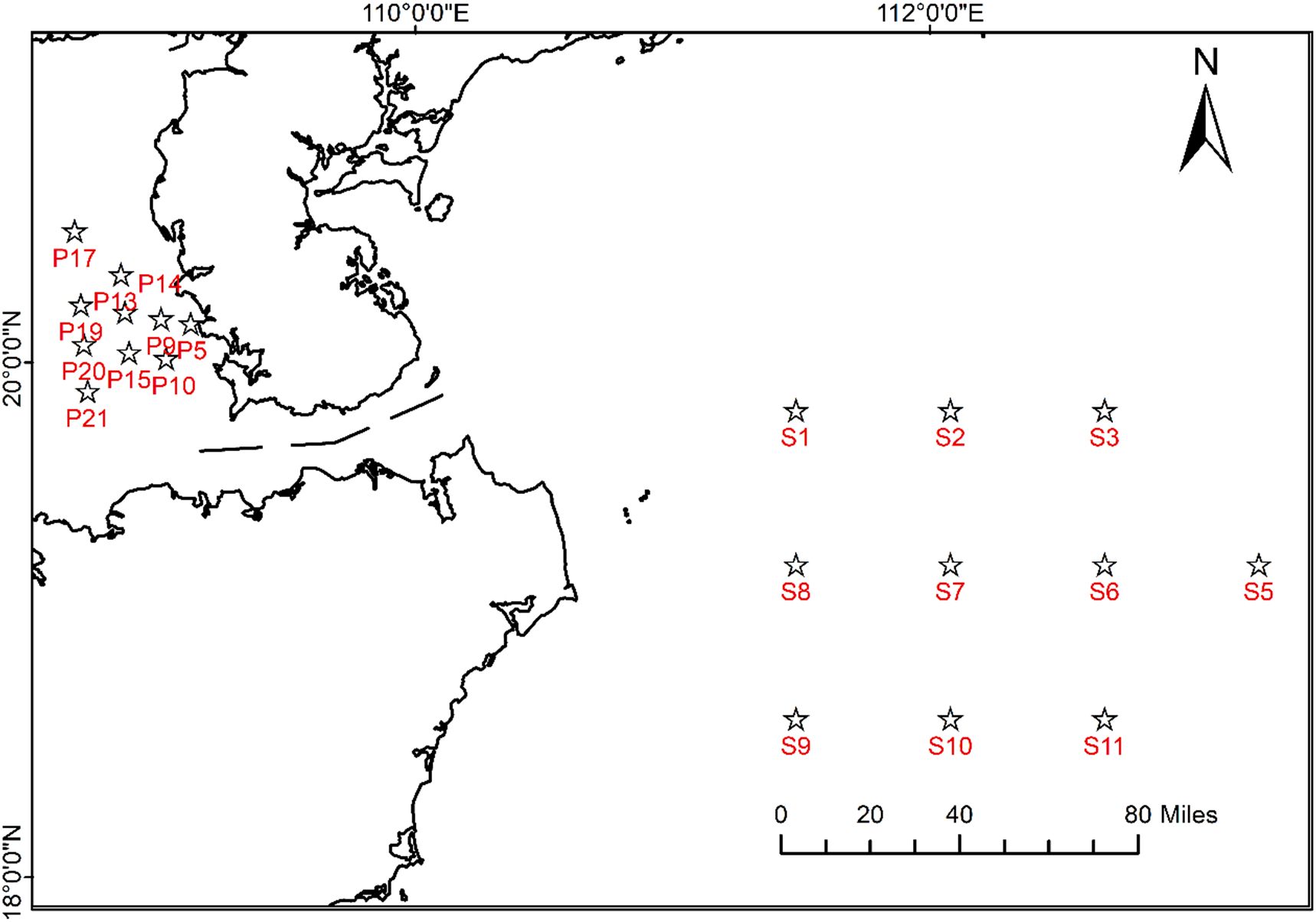
Figure 1. Field sampling sites surrounding Qiongzhou Strait in the South China Sea were designated on the figure with labels S and P. Here, S denoted locations in Wenchang waters, while P denoted locations in WuShi waters.
2.2 Sample pretreatment and metal analysis
Each frozen fish sample was dissected and subsequently freeze-dried at –80°C for 96 hours. The moderately dried muscle tissue was then transferred into a 15 mL tube (Corning, USA), with the addition of HNO3 (Fisher Scientific, Geel, Belgium) to each muscle sample. After digestion, the sample was diluted with ultrapure water to achieve the appropriate concentration for testing. Metal analysis was conducted using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS), NexION350X, PerkinElmer, USA. The certified reference material for mussels (GBW08571, China) was chosen as the standard material and analyzed every 20 samples to ensure the reliability of the testing method. The Ar flow rate was set at 0.8 L/min, with identified potential interferences being ArCl, Sm2+, Nd2+, and Eu2+. The detected concentration levels ranged from 0.4 to 50 μg/L to prevent any interference with the equipment. Specific internal standard metal elements were selected to ensure the accuracy of the testing process: 72Ge for As, Se, and Zn; 45Sc for Cr, Cu, and Ni; 115In for Cd; and 209Bi for Pb, and the rate of recovery was between 70–130%. Finally, the metal concentration in marine fish muscle was calculated and reported in μg/g dry weight. In further analysis, a wet/dry weight conversion factor of 4 was utilized in the risk assessment. The proportion of inorganic As to total As was estimated as 10%, as per the guidelines provided by the United States Food and Drug Administration in 1993, for the assessment of As’s carcinogenic risk (Zhang and Wang, 2012).
2.3 Heavy metals pollution index and health risk
In evaluating the potential risks associated with marine fish consumption, the metal pollution index (MPI), THQ, and total target hazard quotient (TTHQ) were chosen as non-CR indices for heavy metal pollution assessment. The MPI was chosen to characterize the specific levels of various metal pollutants (Hao et al., 2013). The formula was presented as following:
Where, the MPI is the pollution index of heavy metal, Ci is the concentration of heavy metal.
The estimated daily intake (EDI) was chosen to quantify the average metal intake. Both the THQ and TTHQ were utilized to assess non-cancer risks and total non-cancer risks, respectively (Iaquinta et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023). The formula was presented as following:
Where, Ci is the concentration of heavy metal; Cconsumption is the daily fish consumption in average, assuming that the daily fish consumption being 59.91 g (Biswas et al., 2023); Bw is the body weight of consumer (the average body weight of Chinese people is 61.2 kg) (Zhang et al., 2023). RfDi is the oral reference dose of heavy metal U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA, 2024), the Oral RfDi values are 0.005 mg/kg/day for As, 0.001 mg/kg/day for Cd, 0.003 mg/kg/day for Cr, 0.04 mg/kg/day for Cu, 0.02 mg/kg/day for Ni, 0.0035 mg/kg/day for Pb, 0.005 mg/kg/day for Se, and 0.25 mg/kg/day for Zn.
2.4 Carcinogenic risk
The CR was chosen to assess the potential risk of carcinogenic exposure when an individual is exposed to carcinogenic heavy metals over a lifetime (Liu et al., 2022). The formula was presented as following:
Where, Cancer Slope Factor (CSF) represents the carcinogenic slope factor for As, Cd, and Pb as provided by USEPA and Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA). Specifically, the CSF for inorganic As is determined to be 1.5, estimated from total As detailed in Section 2.2 on Sample Pretreatment and Metal Analysis, 0.38 for Cd, and 0.0085 for Pb, respectively; EDIi is the estimated intake of As, Cd and Pb mentioned before.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis and graphic presentation of data were conducted using R, which involved the utilization of packages such as xlsx, car, plyr, reshape2, and ggplot2. Specifically, Wilcoxon rank sum test was employed to analyze the variations in heavy metal concentrations among tissues and locations, as well as differences in THQ and CR values. The data were represented as mean ± standard error.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Concentration of heavy metals in marine fish tissues
Figure 2 illustrates the concentrations of heavy metals, such as As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Se, and Zn in various tissues (gill, intestine, liver, and muscle) of wild marine fish. The average concentrations of all detected heavy metal were notably higher in the gill, intestine, and liver compared to the muscle tissue. These results align with prior studies indicating a tendency for heavy metals to accumulate more prominently in organs like the gill and liver rather than in muscle tissue (Bilgin et al., 2023). The gill and intestine play crucial roles in pollutant influx for marine fish, with the gill serving as the primary site for ion and micro-molecule exchange with seawater, and the intestine responsible for food digestion and nutrient absorption. In Mugilogobius chulae, Cd absorption is primarily mediated through gill and intestine tissues, with gill absorption accounting for 77.2% to 89.4% of waterborne Cd absorption and intestinal absorption contributing to 81.3% to 98.7% of dietary Cd absorption, leading to Cd storage in the fish of 22.8% to 51.6% and 47.1% to 80.4%, respectively (Guo et al., 2019). In addition to Cd, the gill and intestine play crucial roles in the bioaccumulation and distribution of As and Zn in marine fish. These organs serve as key pathways through which marine fish efficiently acquire heavy metals from the marine environment and food chain, utilizing both waterborne and dietary routes (Zhang and Wang, 2006; Zhang et al., 2011). The liver is considered the primary organ for detoxification in marine fish. Metallothionein, a crucial macromolecule found in the liver, plays a key role in binding metals and mitigating the adverse effects of heavy metals (Magnuson and Sandheinrich, 2023; Paylar et al., 2023). The liver exhibited the highest accumulation of heavy metals, with concentrations of Cu and Zn significantly surpassing those found in muscle tissue. This phenomenon may function as a protective mechanism for the organism (Jayasinghe et al., 2024). Therefore, the muscle tissue consistently displayed markedly lower concentrations of heavy metals compared to gill, intestine, and liver tissues.
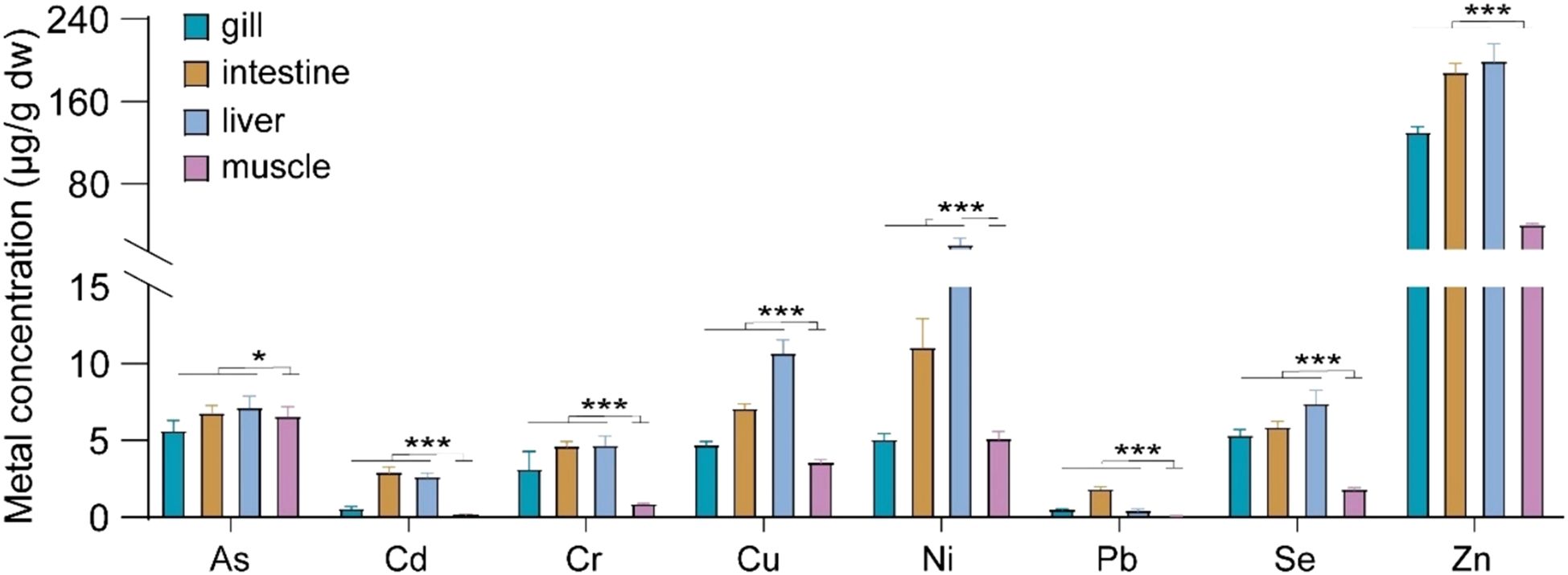
Figure 2. The variances in heavy metal concentrations in gill, intestine, liver, and muscle tissues of marine fish. *P ≤ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001.
Muscle tissue is commonly selected as an indicator of metal contamination levels in marine fish due to its role in metal distribution and storage. In our investigation, heavy metal concentrations in the muscle of marine fish were as follows: 6.56 ± 0.628 μg/g for As, 0.170 ± 0.0352 μg/g for Cd, 0.847 ± 0.0681 μg/g for Cr, 3.56 ± 0.222 μg/g for Cu, 5.08 ± 0.494 μg/g for Ni, 0.0700 ± 0.0170 μg/g for Pb, 1.78 ± 0.140 μg/g for Se, and 39.5 ± 1.71 μg/g for Zn (Table 1). The heavy metals were ranked by concentration in the following order: Zn > Ni > As > Cu > Se > Cr > Cd > Pb. Among these, Zn emerged as the predominant heavy metal in marine fish muscle, surpassing Pb by nearly 567-fold. Consistently, Zn concentrations in marine fish muscle were consistently the highest, reaching levels up to 103 times greater than those of Pb (Zhang and Wang, 2012), aligning with our research findings.
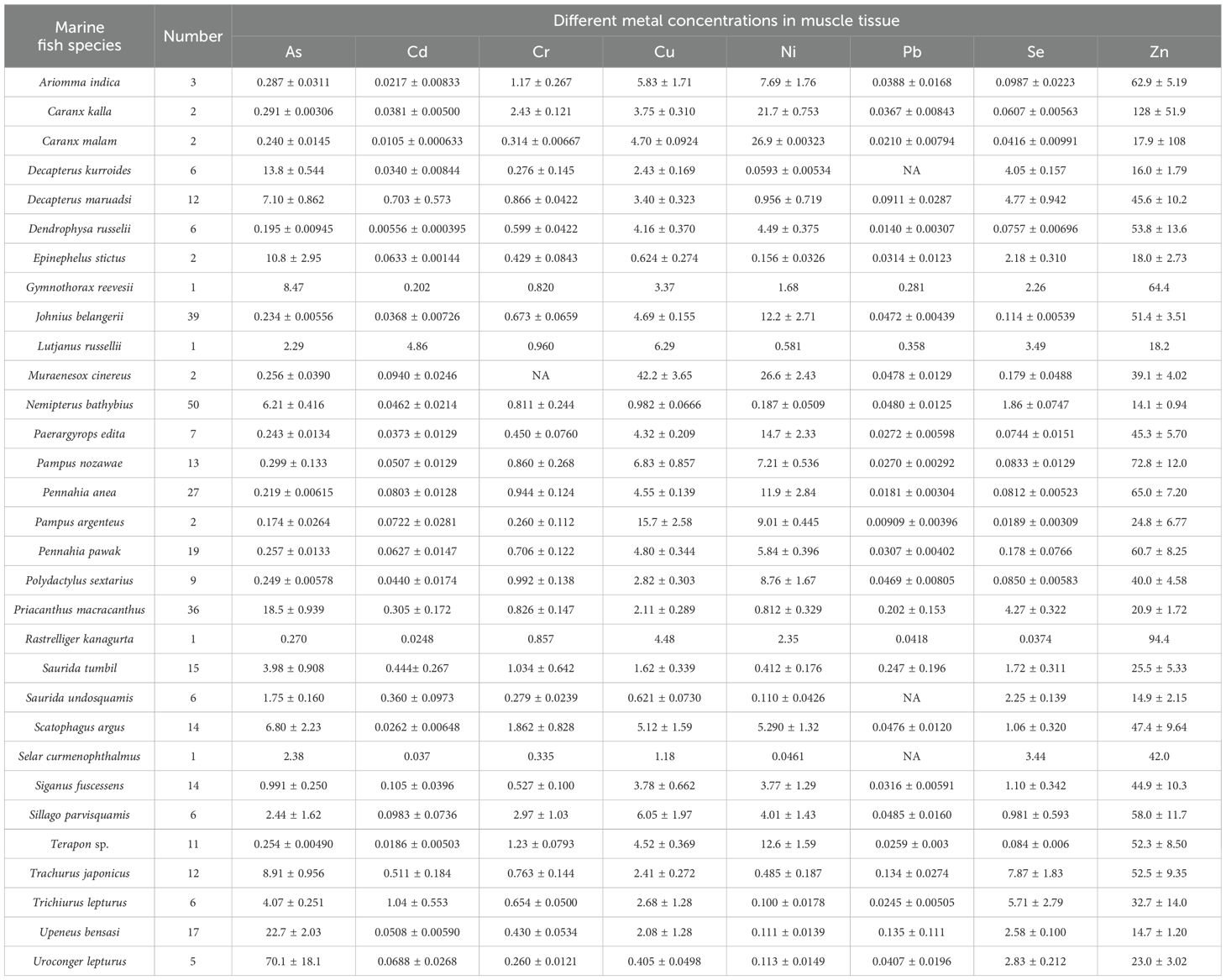
Table 1. The concentrations of heavy metals in muscle of different marine fish (mean ± standard error μg/g).
To evaluate geographical variations in pollutant levels within marine fish muscle, the average concentrations of heavy metals were compared between the eastern waters (Wenchang) and the western waters (Wushi), as depicted in Figure 3. The various heavy metal elements exhibited distinct contamination levels, leading to their classification into two groups based on the observed average concentration differences across the sampling sites. This categorization enables the provision of specific health risk recommendations for the populations residing in these areas. In this study, metals with significant carcinogenic potential, namely As, Cd and Pb, were categorized into group 2, which also encompassed Se due to its association with As. Group 1, composed of the heavy metals Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn, exhibited higher average levels in Wushi, whereas group 2, consisting of As, Cd, Pb, and Se, displayed elevated concentrations in Wenchang.
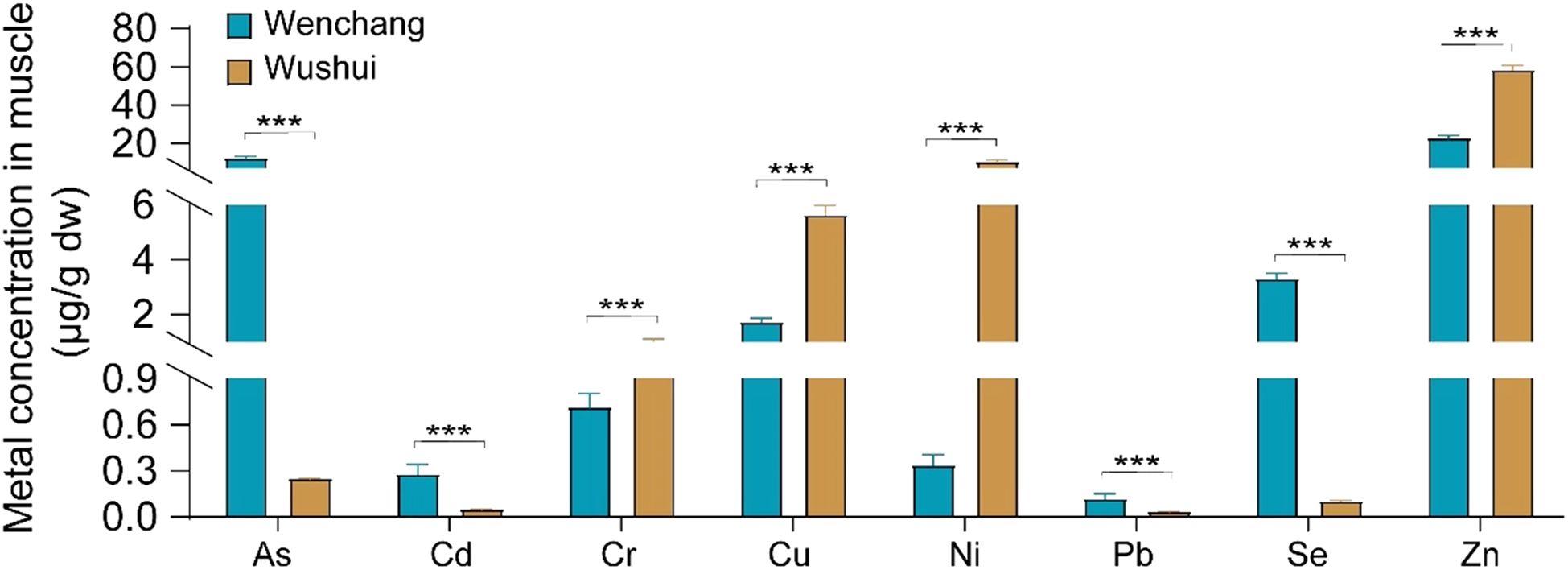
Figure 3. The variances in heavy metal concentrations in marine fish across different locations. ***P ≤ 0.001.
It is noteworthy that the heavy metals posing CR (As, Cd, and Pb) were significantly higher in the Wenchang region. The concentrations of metal elements in group 1 were as follows: 1.01 ± 0.101 μg/g in Wushi and 0.712 ± 0.0908 μg/g in Wenchang for Cr, 5.62 ± 0.377 μg/g in Wushi and 1.71 ± 0.154 μg/g in Wenchang for Cu, 10.4 ± 0.873 μg/g in Wushi and 0.333 ± 0.0717 μg/g in Wenchang for Ni, and 58.3 ± 2.55 μg/g in Wushi and 22.6 ± 1.44 μg/g in Wenchang for Zn (Figure 3). Residents in the vicinity of Wushi should exercise increased vigilance regarding these non-carcinogenic heavy metals. Conversely, the concentrations of metal elements in group 2 were 12.2 ± 1.02 μg/g in Wenchang and 0.248 ± 0.00361 μg/g in Wushi for As, 0.277 ± 0.0656 μg/g in Wenchang and 0.0497 ± 0.00504 μg/g in Wushi for Cd, 0.337 ± 0.00202 μg/g in Wenchang and 0.114 ± 0.0373 μg/g in Wushi for Pb, and 3.29 ± 0.211 μg/g in Wenchang and 0.0990 ± 0.00934 μg/g in Wushi for Se (Figure 3). The carcinogenic heavy metals As, Cd, and Pb exhibited similar geographical trends, with higher concentrations in the eastern waters. The As pollution level showed a significant disparity, with marine fish in Wenchang waters accumulating nearly 49 times more As than those in Wushi waters, underscoring the necessity for increased health risk awareness among Wenchang residents. The Pb pollution level also revealed a substantial difference, with the concentration in Wenchang at 0.337 μg/g compared to 0.114 μg/g in Wushi, nearly three times higher. While Cd and Pb displayed similar bioaccumulation patterns to As geographically, the health risks may not differ as significantly as with As. As is particularly concerning due to its potential to impair neuropsychological development and memory, along with its significant CR, particularly for skin and lung carcinoma. It is crucial for residents to refrain from consuming foods contaminated with As (Zhang and Wang, 2012; Zhang et al., 2016; Soler-Blasco et al., 2023; Hua et al., 2024). Therefore, individuals should prioritize monitoring of carcinogenic heavy metals such as As, Cd, and Pb in marine fish in Wenchang.
The variations in heavy metal bioaccumulation among different marine fish muscle are elaborated in Table 1. As stands out as a critical hazardous metal necessitating immediate and rigorous monitoring. As concentrations in fish muscle spanned from 0.174 to 70.1 μg/g across all species. The highest concentration was not found in the dominant fish species Nemipterus bathybius, Johnius belangerii, and Priacanthus macracanthus, with their respective As concentrations at 6.21 μg/g, 0.234 μg/g, and 18.5 μg/g. Pampus argenteus exhibited the lowest As accumulation, while the benthic fish Uroconger lepturus displayed an exceptionally high As accumulation, approximately 402 times greater, reaching 70.1 μg/g. Remarkably, benthic marine fish like U. lepturus inherently demonstrated a potential for higher As bioaccumulation, consistent with prior research findings. Benthic marine fish that feed on clams showed an increased rate of As biotransformation, likely attributed to the As content in their dietary supplementation (Zhang et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2017). It is crucial to acknowledge that the bioaccumulation and biomagnification of As have been demonstrated to transfer and accumulate within wild ecosystems through the food chain. This occurrence has been documented in field studies and trophic level analyses, showcasing As magnification in Daya Bay during winter. Benthic invertebrates, in particular, displayed notably elevated concentrations, contributing significantly to As accumulation (Du et al., 2021). The bioaccumulation of As was linked to dietary sources. Studies have shown that the dietary habits of fish notably influenced As bioaccumulation, with carnivorous fish accessing higher levels of As when their diet included more marine animals (Zhang and Wang, 2012; Zhang et al., 2022). In this study, the species with the highest accumulation of As, U. lepturus, is a nearshore benthic warm-water fish that feeds on small fish, shellfish, and other organisms in its natural habitat. The combination of its diet and the environmental conditions of residing in bottom sediments likely contributes to the remarkably elevated As concentration found in its muscle tissue. The benthic carnivorous fish Trypauchen vagina has the ability to accumulate 133.7 μg/g dw of As in its muscle tissue (Zhang and Wang, 2012). Therefore, the public must carefully monitor the issue of As contamination in marine benthic fish.
The Cd concentrations in the muscle tissue of various marine fish species ranged from 0.00556 to 4.86 μg/g (Table 1). Among the key fish species, N. bathybius, J. belangerii, and P. macracanthus exhibited Cd concentrations of 0.0462 μg/g, 0.0368 μg/g, and 0.305 μg/g, respectively. Lutjanus russellii displayed the highest Cd accumulation, while Dendrophysa russelii exhibited the lowest, with a difference of approximately 7 times. The diverse habitats of marine fish play a significant role in their uptake of heavy metals (Guo et al., 2018). Cd has been demonstrated to be absorbed through waterborne sources, diet, and sediment in marine fish. The feeding strategies employed significantly influence the bioaccumulation of Cd (Guo et al., 2015; Guo et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2018). Caution should be exercised in consuming L. russellii to minimize exposure to Cd.
Pb concentrations in fish muscle varied from 0.00909 to 0.358 μg/g across all species (Table 1). In the largest fish group, N. bathybius, J. belangerii, and P. macracanthus, Pb concentrations measured 0.0480 μg/g, 0.0472 μg/g, and 0.201 μg/g, respectively. The highest and lowest Pb concentrations were found in L. russellii and Plectorhinchus argenteus, respectively, exhibiting a 39-fold difference. Human activities, particularly the use of leaded gasoline, influenced the Pb concentration in the marine environment (Nriagu, 2023). It was noted that the Pb concentration in Setipinna tenuifilis in Liaodong Bay, China, could reach up to 0.76 μg/g, whereas the Pb concentration observed in this study was slightly lower (Gao et al., 2021). The discrepancies observed can be attributed to various factors, including geographical variations, specific environmental conditions, and differences in the species under study.
Zn concentrations in fish muscle exhibited significant variability across all species, ranging from 14.1 to 128 μg/g (Table 1). In the predominant fish species group comprising N. bathybius, J. belangerii, and P. macracanthus, Zn concentrations were recorded at 14.1 μg/g, 51.4 μg/g, and 20.9 μg/g, respectively (Table 1). The highest and lowest Zn concentrations were found in Caranx kalla and N. bathybius, respectively, representing a 7-fold difference. Zn pollution in wild marine organisms was most severe in Laizhou Bay, China, with subsequent rankings of Cu, As, Cd, Cr, Ni, and Pb, suggesting that Zn may have a higher tendency for accumulation (Liu et al., 2015). The levels of Zn concentrations in the South China Sea area also warrant significant concern.
Various fish species exhibited differing levels of heavy metal contamination. In addition to marine species, attention should be directed towards species with substantial populations. Among all the species examined, N. bathybius had the largest population, followed by J. belangerii and P. macracanthus, indicating that N. bathybius and J. belangerii were the predominant catches in this study. Notably, the most abundant species, N. bathybius, J. belangerii, and P. macracanthus, did not show significantly high levels of heavy metal bioaccumulation in their muscle tissues, implying that commonly caught species may have lower contamination levels and be safer for consumption. Intriguingly, species with the highest metal accumulation, such as L. russellii for Cd and Pb, U. lepturus for As, and C. kalla for Zn, displayed a similar trend among carnivorous fish. This aligns with previous research indicating the bioaccumulation of heavy metals along the food chain (Lee et al., 2016; Wang and Wang, 2019; Xia et al., 2019). Carnivorous fish, typically consuming diets rich in crustaceans, fish, and zooplankton, are predisposed to accumulating pollutants. For instance, U. lepturus, a predator, tends to favor a diet that enhances trophic richness in marine ecosystems, potentially elucidating its elevated accumulation of specific heavy metals (Chaudhuri et al., 2014). Within this study area, species with substantial populations exhibited lower pollution levels, whereas benthic and carnivorous species showed higher contaminant concentrations.
3.2 Heavy metals pollution risk
The 31 fish species displayed varying MPI values, a metric used to compare heavy metal accumulation across different fish species. L. russellii exhibited the highest MPI at 111, followed by Gymnothorax reevesii and Trachurus japonicus with MPIs of 40.6 and 28.2, respectively. These elevated MPI values indicate potential contamination in these species, suggesting a heightened risk of contamination for L. russellii, G. reevesii, and T. japonicus. Apart from these species with exceptionally high MPIs, most species had MPIs below 1. The MPI serves as a direct indicator of heavy metal presence in marine fish, with prior research indicating that demersal fish tend to have higher MPIs than pelagic and mesopelagic fish, and omnivorous fish exhibit higher MPIs compared to carnivorous and herbivorous species (Liu et al., 2022). In this study, the highest MPI was recorded in L. russellii, a species that exhibits characteristics of both a demersal and carnivorous fish.
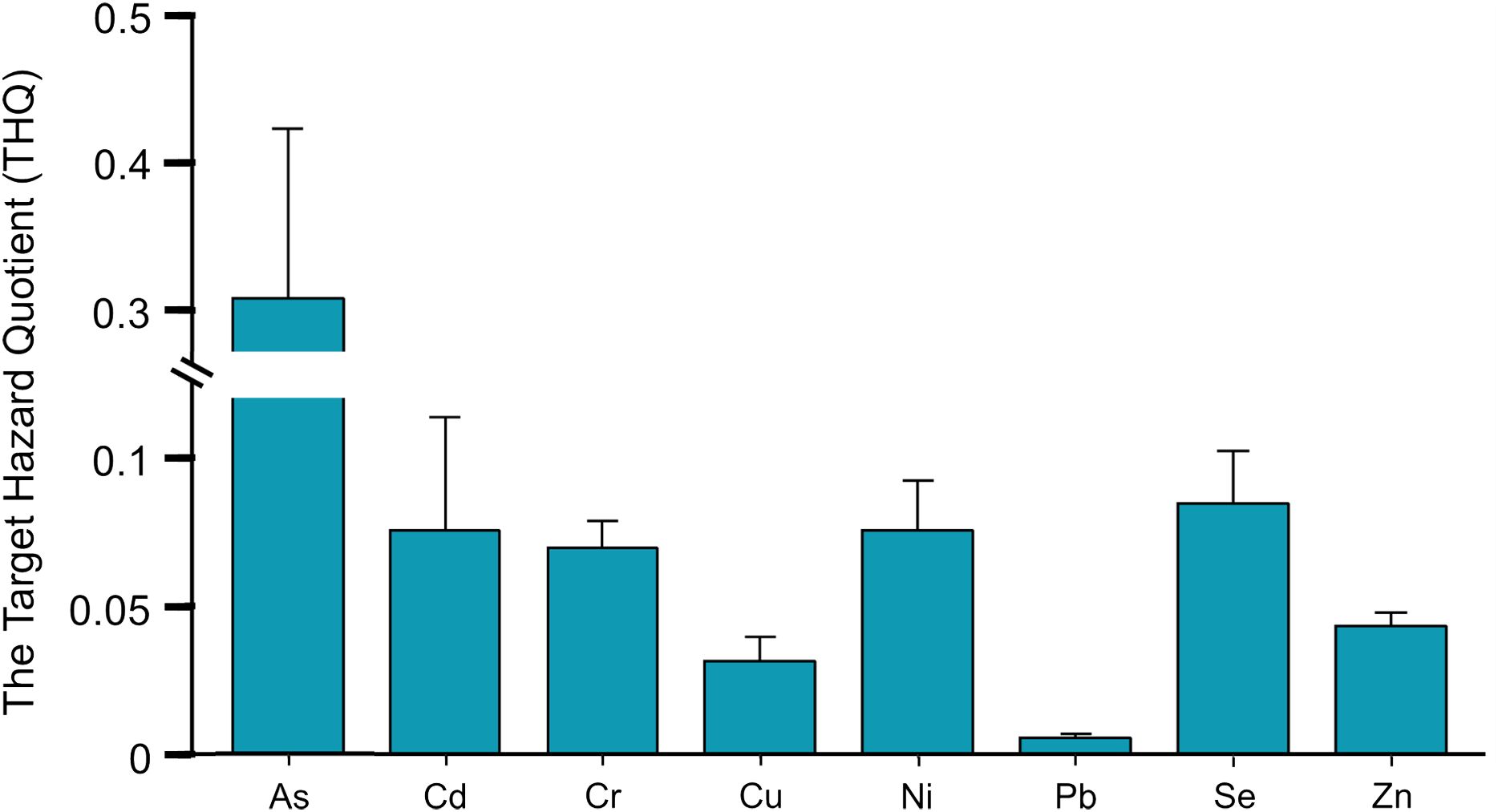
Figure 4 illustrates the non-CR associated with various heavy metals. Typically, if the THQ is less than 1, there is a low risk of dietary exposure to specific metals; however, if the THQ exceeds 1, there is a high risk of exposure. The average THQ values for metals ranked as follows: THQAs > THQSe > THQCd > THQNi > THQCr > THQZn > THQCu > THQPb. Notably, the average THQ for As was notably high at 0.308, indicating a significant non-CR associated with this metal. Specifically, U. lepturus exhibited an exceptionally high THQAs of 3.43 (Figure 5), indicating a significant bioaccumulation of As as mentioned earlier. The average THQ values for other metals were below 0.1, suggesting a lower non-CR compared to As. While previous studies have shown minimal health risks associated with the consumption of marine fish species and deemed them generally safe (Zhang and Wang, 2012; Zhang et al., 2016). Therefore, the significant health risk associated with U. lepturus warrants attention.
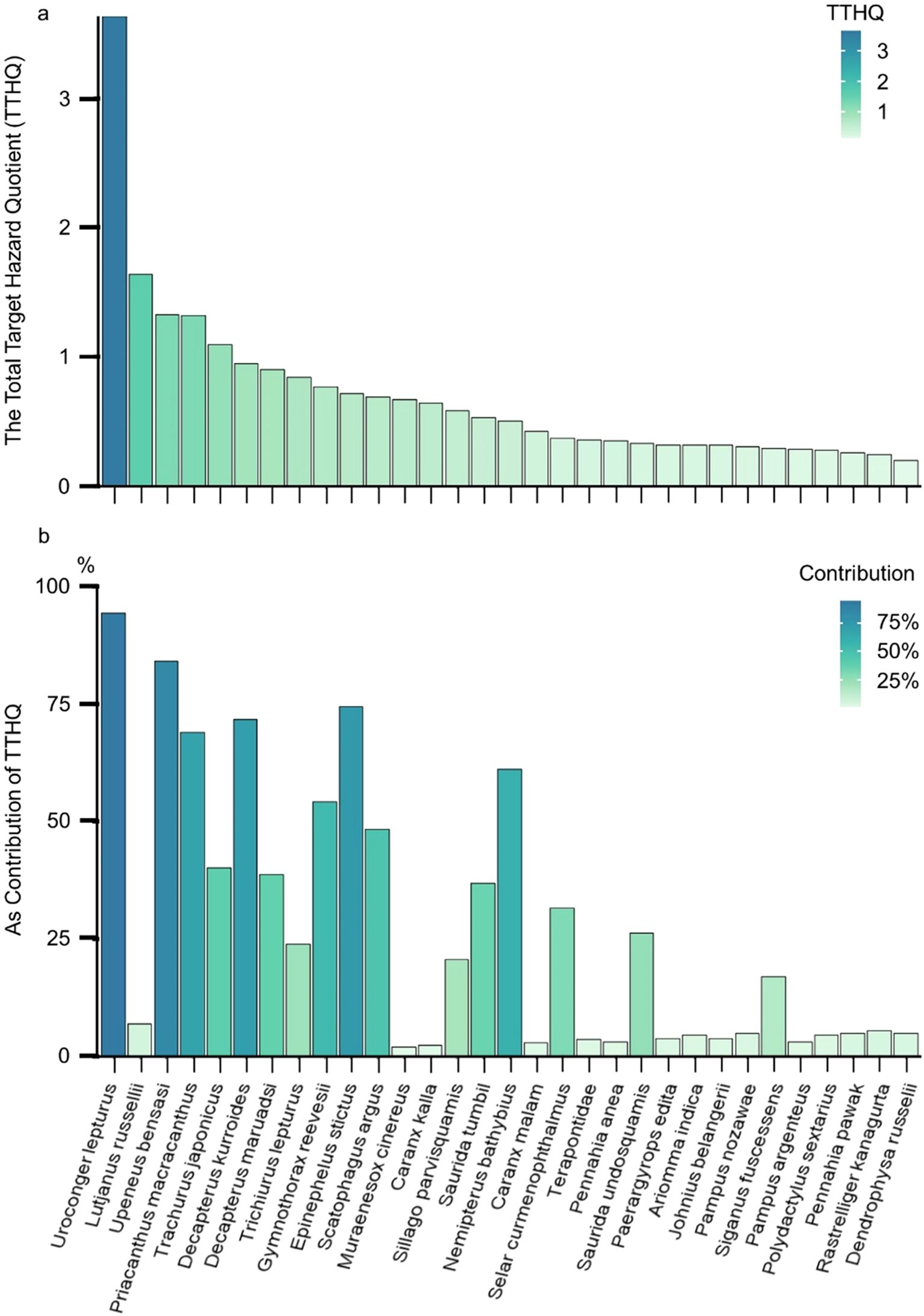
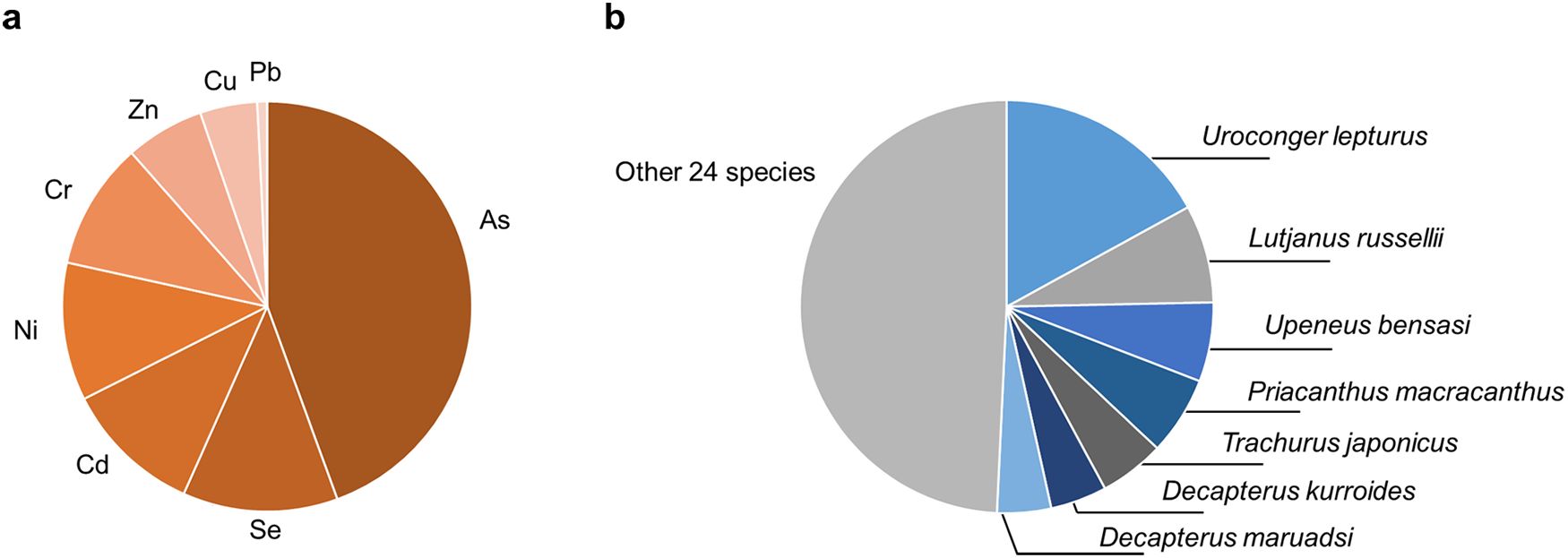
Figure 5. The contribution of TTHA by different metal and marine fish species. (a) The TTHQ of different fish, (b) The contribution of As in TTHQ of different fish.
Figure 5 presents the TTHQ for each species. U. lepturus exhibited the highest TTHQ value of 3.64, with the THQ of As accounting for 94.3% of this elevated TTHQ. Conversely, D. russelii, Rastrelliger kanagurta, and Pennahia pawak exhibited the lowest TTHQ values, measuring 0.196, 0.242, and 0.257, respectively. It is recommended that local consumers prioritize D. russelii, P. argenteus, and R. kanagurta for their daily fish protein intake because of their lower TTHQ values. Figure 6 illustrates the varying contributions of TTHQ by different heavy metals and fish species. As accounted for 44.4% of the TTHQ, while the contributions of other metals were all below 13%. This observation highlights As as the primary potential health risk in Qiongzhou Strait. In the TTHQ calculation, U. lepturus, L. russellii, and Upeneus bensasi accounted for 17.0%, 7.67%, and 6.20% of the total, respectively. Overall, the consumption of fish presents a limited non-carcinogenic health threat to local residents. However, consumers should be cautious in avoiding As pollutants and fish species with elevated TTHQ values mentioned like U. lepturus and U. bensasi.
3.3 Carcinogenic risk
Considering the carcinogenic properties of heavy metals such as As, Cd, and Pb, the potential CR associated with fish consumption emerges as a paramount concern in this context. As depicted in Figure 7, the CR for Pb, as indicated by CRPb values ranging from 1.89 × 10–8 to 7.44 × 10–7, suggests a relatively low risk associated with the consumption of marine fish. Most CRCd values fell between 10–6 and 10–4, except for one outlier at 4.52 × 10–4. However, CRAs values ranged from 6.40 × 10–6 to 2.57×10–3, emphasizing the need for consumers to be cautious in selecting marine fish species with lower risk profiles. The average CR values were ranked as CRAs > CRCd > CRPb, highlighting the significantly higher CR of As compared to Cd and Pb. Traditionally, a CR below 10–6 is considered safe, while a CR between 10–4 and 10–6 is deemed acceptable with limited damage; anything above 10–3 is considered unacceptable (Aendo et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2022). In this study, the CRPb was the lowest, indicating safety, while the CRCd suggested limited damage from Cd. However, the high CRAs values, especially exemplified by U. lepturus with a CRAs of 2.57×10–3 due to its elevated As contamination, underscore the need for caution when consuming certain fish species. Local residents should avoid consuming U. lepturus and consider P. argenteus as a seafood source due to its lowest CRAs and CRPb values among all marine species.
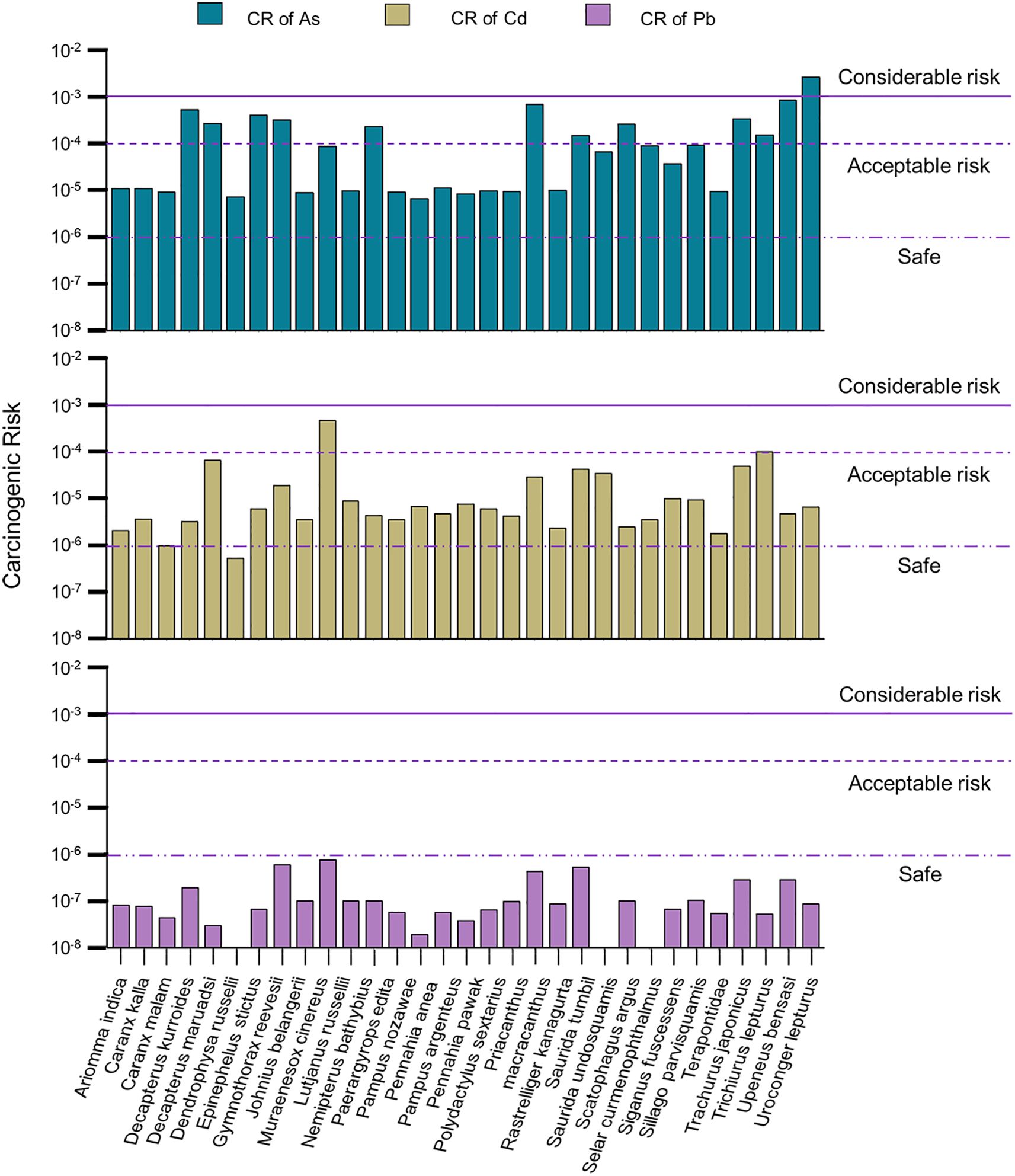
Figure 7. The carcinogenic risk posed by As, Cd and Pb in various marine fish species. The data below the violet long dashed line represents the estimated consumption levels. The data between the violet long dashed line and the short-dashed line signifies acceptable risk thresholds. Values exceeding the violet line indicates significantly unacceptable risk levels.
4 Conclusion
This study assessed the concentrations of heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Se, and Zn) in various marine fish species and evaluated the associated health risks. The results highlight a pressing concern regarding fish consumption, particularly crucial for the well-being of local communities. As emerged as the primary risk factor among the heavy metals, necessitating close monitoring of its emissions and bioaccumulation pathways. Of significant worry is the consumption of marine fish protein by coastal residents, with U. lepturus showing a notably high As bioaccumulation level of 70.1 μg/g. Heavy metals are typically transferred within marine organisms, predominantly accumulating in marine fish through the food web. Human health is also influenced by purchasing habits, and residents should exercise caution when consuming local marine fish. U. lepturus, in particular, poses significant carcinogenic and non-CR to general consumers, underscoring the crucial need for As monitoring. The bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine fish warrants increased attention in littoral environments. The ecological risk data on heavy metals will serve as a valuable database for further investigations. It is advisable to establish a regular monitoring program, and the health risks identified should alert the public to potential hazards.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Guangzhou University Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
PZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZY: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported National key research and development program of China (2024YFD2401803), by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42307361, 42477280), by the Outstanding Youth Project of Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2022B1515020030).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aendo P., Thongyuan S., Songserm T., Tulayakul P. (2019). Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in duck eggs and meat as a warning scenario in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 689, 215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.414
Bilgin M., Uluturhan E., Darilmaz E., Katalay S. (2023). Combined evaluation of multi-biomarkers and metal bioaccumulations in two different fish species (Sparus aurata and Chelon labrosus) from Izmir Bay, Turkiye (Aegean Sea): Spatial, temporal and tissue-specific approaches. Mar. pollut. Bull. 197, 115709. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115709
Biswas A., Kanon K. F., Rahman M. A., Alam M. S., Ghosh S., Farid M. A. (2023). Assessment of human health hazard associated with heavy metal accumulation in popular freshwater, coastal and marine fishes from south-west region, Bangladesh. Heliyon 9, e20514. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20514
Chaudhuri A., Mukherjee S., Homechaudhuri S. (2014). Food partitioning among carnivores within feeding guild structure of fishes inhabiting a mudflat ecosystem of Indian Sundarbans. Aquat. Ecol. 48, 35–51. doi: 10.1007/s10452-013-9464-x
Chen B., Xu Z. X., Ya H. Z., Chen X. Y., Xu M. B. (2019). Impact of the water input from the eastern Qiongzhou Strait to the Beibu Gulf on Guangxi coastal circulation. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 38, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1472-2
Cooke C. A., Curtis J. H., Kenney W. F., Drevnick P., Siegel P. E. (2022). Caribbean lead and mercury pollution archived in a crater lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 1736–1742. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c06791
Desiere S., Hung Y., Verbeke W., D’Haese M. (2018). Assessing current and future meat and fish consumption in sub-sahara Africa: Learnings from FAO food balance sheets and LSMS household survey data. Glob. Food Secur-agr. 16, 116–126. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2017.12.004
Djellouli F., Kaddour A., Belhoucine F., Alioua A. (2023). Heavy metals concentrations in hake (Linnaeus, 1758) from the bay of Oran (Mediterranean Sea): Potential human health risk estimation. Acta Adriat. 64, 125–134. doi: 10.32582/aa.64.2.4
Du S., Zhou Y., Zhang L. (2021). The potential of arsenic biomagnification in marine ecosystems: A systematic investigation in Daya Bay in China. Sci. Total Environ. 773, 145068. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145068
Feng S., Deng S., Tang Y., Liu Y., Yang Y., Xu S., et al. (2022). Microcystin-LR combined with cadmium exposures and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A case-control study in central China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 15818–15827. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c02287
Gao Y., Wang R., Li Y., Ding X., Jiang Y., Feng J., et al. (2021). Trophic transfer of heavy metals in the marine food web based on tissue residuals. Sci. Total Environ. 772, 145064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145064
Gu Y. G., Ning J. J., Ke C. L., Huang H. H. (2018). Bioaccessibility and human health implications of heavy metals in different trophic level marine organisms: A case study of the South China Sea. Ecotox Environ. Safe. 163, 551–557. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.114
Gui D., Yu R. Q., Karczmarski L., Ding Y., Zhang H., Sun Y., et al. (2017). Spatiotemporal trends of heavy metals in Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) from the western Pearl River estuary, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 1848–1858. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b05566
Guo Z., Gao N., Wu Y., Zhang L. (2017). The simultaneous uptake of dietary and waterborne Cd in gastrointestinal tracts of marine yellowstripe goby Mugilogobius chulae. Environ. pollut. 223, 31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.007
Guo Z., Ni Z., Ye H., Xiao J., Chen L., Green I., et al. (2019). Simultaneous uptake of Cd from sediment, water and diet in a demersal marine goby Mugilogobius chulae. J. Hazard Mater 364, 143–150. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.045
Guo Z., Ye H., Xiao J., Hogstrand C., Zhang L. (2018). Biokinetic modeling of Cd bioaccumulation from water, diet and sediment in a marine benthic goby: A triple stable isotope tracing technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 8429–8437. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b00027
Guo Z., Zhang W., Zhou Y., Gao N., Zhang L. (2015). Feeding ratio and frequency affects cadmium bioaccumulation in black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Aquacult. Env. Interac. 7, 135–145. doi: 10.3354/aei00140
Hao Y., Chen L., Zhang X., Zhang D., Zhang X., Yu Y., et al. (2013). Trace elements in fish from Taihu Lake, China: Levels, associated risks, and trophic transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 90, 89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.12.012
Hou W., Wang Q., Xiang Z., Jia N., Hu J., Wu Z., et al. (2024). Comprehensive assessment of occurrence, temporal-spatial variations, and ecological risks of heavy metals in Jiaozhou Bay, China: A comprehensive study. Mar. pollut. Bull. 198, 115883. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115883
Hua W., Han X., Li F., Lu L., Sun Y., Hassanian-Moghaddam H., et al. (2024). Transgenerational effects of arsenic exposure on learning and memory in rats: Crosstalk between arsenic methylation, hippocampal metabolism, and histone modifications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 6475–6486. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c07989
Iaquinta F., Pistón M., MaChado I. (2021). In vitro bioaccessibility of Cu and Zn in cooked beef cuts. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 150, 112027. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112027
Jayasinghe J., Tharanga E. M. T., Sirisena D., Jeyakanesh J. T., Wan Q., Lee J. (2024). A metallothionein from disk abalone (Haliotis discus discus): Insights into its functional roles in immune response, metal tolerance, and oxidative stress. Fish Shellf. Immunol. 150, 109645. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109645
Lee C. S., Lutcavage M. E., Chandler E., Madigan D. J., Cerrato R. M., Fisher N. S. (2016). Declining mercury concentrations in bluefin tuna reflect reduced emissions to the North Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 12825–12830. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b04328
Liu X. B., Lin C., Wu Y. Y., Huang H. N., Zhu L. T., Jiang R., et al. (2022). Dataset-based assessment of heavy metal contamination in freshwater fishes and their health risks. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. Int. 29, 49985–49997. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19427-0
Liu J. L., Xu X. R., Ding Z. H., Peng J. X., Jin M. H., Wang Y. S., et al. (2015). Heavy metals in wild marine fish from South China Sea: Levels, tissue- and species-specific accumulation and potential risk to humans. Ecotoxicology 24, 1583–1592. doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1451-7
Magnuson J. T., Sandheinrich M. B. (2023). Relation among mercury, selenium, and biomarkers of oxidative stress in Northern Pike (Esox lucius). Toxics 11, 244. doi: 10.3390/toxics11030244
Mamun A. A., Rifat M. A., Wahab M. A., Rahman M. A., Nahiduzzaman M., Thilsted S. H., et al. (2024). Nutrient composition of dried marine small fish in Bangladesh and their potential to address hidden hunger. J. Food Compos. Anal. 131, 106241. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2024.106241
Nriagu J. (2023). Sixty years since the report of global lead pollution. Nature 619, 704–706. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-02196-2
Oosterveer P. (2008). Governing global fish provisioning: Ownership and management of marine resources. Ocean Coast. Manage. 51, 797–805. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2008.08.002
Ouyang X., Wang Z., Liu X. (2024). Distribution patterns, risk assessment and potential sources of heavy metals in sediment in the Qiongzhou Strait, China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 203, 116481. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116481
Pavlaki M. D., Araujo M. J., Cardoso D. N., Silva A. R. R., Cruz A., Mendo S., et al. (2016). Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of cadmium in different marine trophic levels. Environ. pollut. 215, 203–212. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.010
Paylar B., Bezabhe Y. H., Mangu J. C. K., Thamke V., Igwaran A., Modig C., et al. (2023). Assessing organism differences in mixed metal sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 905, 167340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167340
Soler-Blasco R., Llop S., Riutort-Mayol G., Lozano M., Vallejo-Ortega J., Murcia M., et al. (2023). Genetic susceptibility to neurotoxicity related to prenatal inorganic arsenic exposure in young spanish children. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 15366–15378. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c03336
Vignardi C. P., Adeleye A. S., Kayal M., Oranu E., Miller R. J., Keller A. A., et al. (2023). Aging of copper nanoparticles in the marine environment regulates toxicity for a coastal phytoplankton species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 6989–6998. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00334
Wang W. X. (2012). Dietary toxicity of metals in aquatic animals: Recent studies and perspectives. Chin. Sci. Bull. 58, 203–213. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5413-7
Wang W. X., Pan K., Tan Q., Guo L., Simpson S. L. (2014). Estuarine pollution of metals in China: Science and mitigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 9975–9976. doi: 10.1021/es503549b
Wang X., Wang W. X. (2019). The three ‘B’ of fish mercury in China: Bioaccumulation, biodynamics and biotransformation. Environ. pollut. 250, 216–232. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.034
Wei H., Xie D., Wang D. Z., Wang M. (2024). A meta-analysis reveals global change stressors potentially aggravate mercury toxicity in marine biota. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 219–230. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c07294
Xia W., Chen L., Deng X., Liang G., Giesy J. P., Rao Q., et al. (2019). Spatial and interspecies differences in concentrations of eight trace elements in wild freshwater fishes at different trophic levels from middle and eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 672, 883–892. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.134
Yan X., An J., Yin Y., Gao C., Wang B., Wei S. (2022). Heavy metals uptake and translocation of typical wetland plants and their ecological effects on the coastal soil of a contaminated bay in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 803, 149871. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149871
Yang C., Zhang Z., Liu Y., Shan B., Yu W., Li H., et al. (2021). Heavy metal pollution and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in marine organisms from the Northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. pollut. Bull. 166, 112230. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112230
Zhang W., Guo Z., Song D., Du S., Zhang L. (2018). Arsenic speciation in wild marine organisms and a health risk assessment in a subtropical bay of China. Sci. Total Environ. 626, 621–629. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.108
Zhang W., Huang L., Wang W. X. (2011). Arsenic bioaccumulation in a marine juvenile fish Terapon jarbua. Aquat. Toxicol. 105, 582–588. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.08.009
Zhang C., Miao X., Du S., Zhang T., Chen L., Liu Y., et al. (2023). Effects of culinary procedures on concentrations and bioaccessibility of Cu, Zn, and As in different food ingredients. Foods 12, 1653. doi: 10.3390/foods12081653
Zhang W., Miao A. J., Wang N. X., Li C., Sha J., Jia J., et al. (2022). Arsenic bioaccumulation and biotransformation in aquatic organisms. Environ. Int. 163, 107221. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107221
Zhang L., Wang W. X. (2006). Alteration of dissolved cadmium and zinc uptake kinetics by metal pre-exposure in the black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegeli). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25, 1312–1321. doi: 10.1897/05-262r.1
Zhang W., Wang W. X. (2012). Large-scale spatial and interspecies differences in trace elements and stable isotopes in marine wild fish from Chinese waters. J. Hazard Mater. 215-216, 65–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.032
Zhang W., Wang W. X., Zhang L. (2013). Arsenic speciation and spatial and interspecies differences of metal concentrations in mollusks and crustaceans from a South China estuary. Ecotoxicology 22, 671–682. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1059-8
Zhang W., Wang W. X., Zhang L. (2016). Comparison of bioavailability and biotransformation of inorganic and organic arsenic to two marine fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 2413–2423. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b06307
Keywords: heavy metal, marine fish, health risk, Qiongzhou strait, South China Sea
Citation: Zhang P, Ye Z, Huang L, Wang X and Zhang W (2025) Heavy metal alarm of marine fish consumption surrounding Qiongzhou Strait, the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1557963. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1557963
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 17 March 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited by:
Jia Li, Yibin University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chen-Feng You, National Cheng Kung University, TaiwanSatyanarayan Bramha, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Ye, Huang, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Zhang, emhfd2VpQGd6aHUuZWR1LmNu; Xuefeng Wang, eHVlZmVuZzE5OTlAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Peng Zhang1
Peng Zhang1 Xuefeng Wang
Xuefeng Wang Wei Zhang
Wei Zhang