
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Mar. Sci., 27 January 2025
Sec. Marine Biotechnology and Bioproducts
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1531239
Phaeodactylum tricornutum is considered a potential lipid production platform due to its high growth rates and elevated natural neutral lipid and polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) contents. Furthermore, microalgae are emerging as promising sources of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). In this study, phosphomolybdic acid (PMo12), as a photocatalyst, can enhance the synthesis of neutral lipids and PUFAs by influencing the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes and photosynthesis in P. tricornutum. We also observed the contents of EPA and PUFA in engineered microalgae nearly doubled compared to the wild type, while neutral lipid content showed a significant increase of 69.7% in engineered microalgae. Notably, the growth rate of engineered microalgae remained comparable to that of the wild type. This work presents an effective approach to enhance the production of microalgal bioproducts, suggesting that photocatalysts such as PMo12 could serve as viable alternatives to genetic engineering technology, facilitating the commercialization of microalgal biodiesel.
The need for secure, low-cost, and renewable energy sources has become increasingly urgent due to the depletion of fossil fuels and global geopolitical tensions (Lv et al., 2019). Biofuels have emerged as a critical renewable energy source, with each generation of biofuels building on the limitations of the previous one. First-generation biofuels rely on feedstocks like corn and soybeans, while second-generation biofuels utilize non-food sources such as switchgrass and food waste. The third and fourth generations have shifted to microalgae as a feedstock, with the latter focusing on genetically modified strains (Wang et al., 2024).
Microalgae are gaining attention for their rapid growth, high photosynthetic efficiency, minimal land use, and ability to produce a wide range of biofuel products (Maliha and Abu-Hijleh, 2022). Moreover, they offer significant environmental benefits, including a carbon sequestration capacity that is 10–50 times greater than that of terrestrial plants (Wei et al., 2020). High value-added bioproducts produced by microalgae can provide antioxidants, carotenoids, proteins, and essential vitamins, which are of great benefit to human health (Del Mondo et al., 2020; Singh et al., 2020). Additionally, microalgae have potential applications in vaccine development against various infectious diseases (Ramos-Vega et al., 2021). Historically, algae have been an essential nutrient-rich food source, often surpassing traditional crops in nutritional value. The expanding toolkit for improving algae varieties offers a viable solution to the global food shortage challenges of the twenty-first century (Torres-Tiji et al., 2020).
Microalgae research gained momentum with the US Department of Energy’s Aquatic Species Program, which screened over 3,000 microalgae species for biofuel potential between 1978 and 1996 (Sheehan et al., 1998). In recent years, species such as Chlorella vulgaris, Nannochloropsis oceanica, and Dunaliella salina have been identified as suitable candidates for biodiesel production (Fu et al., 2019; Gui et al., 2021). Additionally, various abiotic stresses, such as heat and light intensity, have been shown to stimulate the production of bioactive compounds in algae (Liu et al., 2020; Fu et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2021). Among these compounds, PUFAs like EPA and DHA have attracted attention due to their health benefits, including their role in mitigating neurological disorders, inflammatory diseases, and even certain cancers (Ghasemi Fard et al., 2018; Kapoor et al., 2021). As the demand for sustainable sources of PUFAs grows, marine microalgae are emerging as a viable alternative to overexploited deep-sea fish (Colombo et al., 2019; Kumari et al., 2023).
Research has demonstrated that optimizing environmental factors such as temperature, nutrients, and light can enhance lipid and PUFA production in microalgae. For example, the DHA content in Tisochrysis lutea increased significantly under low-temperature conditions, and similar results were observed for EPA in Nannochloropsis oculata (Gao et al., 2022; Sousa et al., 2022). However, these methods often reduce biomass production and are not practical for large-scale applications.
In the past decade, genetic engineering has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing lipid accumulation in microalgae, particularly in species with sequenced genomes (Bhattacharjya et al., 2021). Previous research has identified Δ4-FAD, Δ5-FAD, and GPAT as critical enzymes for DHA, EPA, and TAG synthesis in microalgae (Kumari et al., 2023). The overexpression of the native Δ5-FAD gene in P. tricornutum has been shown to increase EPA production by up to 58% (Peng et al., 2014). Genetic modifications, such as the deletion of specific genes or the overexpression of key enzymes, have led to significant increases in lipid and PUFA yields (Han et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Han et al., 2022). Advanced genome editing techniques like CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN have further refined these capabilities (Fayyaz et al., 2020). However, the outdoor cultivation of genetically modified microalgae remains limited due to high costs and environmental concerns (M. U et al., 2019). Thus, there is a pressing need for methods that could enhance lipid production without compromising growth or economic viability.
Polyoxometalates (POMs), particularly phosphomolybdic acid (PMo12), have emerged as promising photocatalysts due to their low cost, high efficiency, and recyclability (Ilbeygi and Jaafar, 2024). POMs are known for their redox properties and strong Brønsted/Lewis acidity, making them useful in various applications, including microbial fuel cells, rechargeable batteries, and the conversion of biomass into biofuels (Bijelic et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2020; Zhong et al., 2021). Notably, PMo12 has been shown to catalyze the conversion of CO2 into high-value fuels with low energy requirements (Yang et al., 2019), and it has also been used in the production of biodiesel from waste cooking oil (Helmi et al., 2022).
In this study, we explored the potential of PMo12 to enhance lipid and PUFA accumulation in P. tricornutum. By incorporating PMo12 into the growth medium, we aimed to identify a strategy that boosts lipid production without adversely affecting growth while remaining economically feasible. The results of this research could pave the way for microalgae to serve as an alternative source of deep-sea fish oil, with significant implications for industrial applications.
P. tricornutum Bohlin (CCMP2561) was prepared in this research. Microalga strain was purchased from the Freshwater Algae Culture Collection of the Institute of Hydrobiology, CAS, China (No. FACHB-863). Microalgae were cultured in f/2 si− medium, which contains Na2MoO4 · 2H2O and filtered using 0.22-μm filter membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). PMo12 (1 mol/L), which was purchased from TCI America, with purity of 99%, was added in the medium as a photocatalyst, and the culture was maintained at 21 ± 0.5°C under a light/dark cycle of 15 h and 9 h, respectively. The light intensity is 4,000 lx.
The growth of the algae was monitored daily for 10 consecutive days using a hemocytometer and microscope. The number of algal cells was counted under an inverted microscope with a blood cell counting plate at the same time each day during the growth cycle. The growth status of the algal cells was calculated using the formula: cell density = (total number of 80 small square cells/80) × 4 × 106 × dilution times, and the growth curve was generated.
The morphology of engineered microalgae cells was observed under laser scanning confocal microscope LSM 510 META (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). After culture to the plateau stage (7 days), 1 mL algal solution was taken into 1.5 mL EP tube, and 10 μL Nile red solution (0.1mg/mL, soluble in acetone) was added to the algal solution, then incubated for 30 min under 37℃ in the dark. The fluorescence detection was 488 nm for excitation and 505–550 nm for emission.
Nile red as a fluorescent marker has been widely used in the determination of neutral lipid content in cells. Consequently, Nile red was employed as a fluorescent probe to assess the neutral lipid content in P. tricornutum cells (Yang et al., 2013). Algal cells were initially collected using a refrigerated centrifuge, followed by treatment with 20% DMSO for 20 min at room temperature. A total of 30 μL of Nile red, dissolved in 0.1 mg/mL acetone, was added to a 3-mL aliquot of pretreated cell culture in triplicates. The mixture was inverted rapidly and shielded with tin foil for 20 min at room temperature. Subsequently, the P. tricornutum cell cultures were transferred to a 96-well plate for fluorescence intensity determination using a Hitachi F4600 microplate reader (Hitachi, Japan). Fluorescence intensity was measured at 580 nm under 530 nm light excitation, with the intensity of the unstained algal liquid at this wavelength subtracted from the readings. Concurrently, the density of algal cells was assessed using a hemocytometer and microscope, enabling the calculation of neutral lipid content per algal cell.
Fatty acid composition of microalgae was detected by the previous research (Yang et al., 2013). The fatty acid extraction steps are as follows: first, diatom cells were harvested by centrifugation at 3,000×g for 10 min at 4°C. Then, 5 mL KOH–CH3OH(2 mol/L) was added to the cell culture. After ultrasonic breaking in an ice bath, the cell culture was filled with nitrogen for 1 min. The crushed algal cell culture was shaken with a turbine shaker and then reacted in a water bath at 75°C for 10 min. The layering is left standing at room temperature, and the supernatant is transferred to a new centrifuge tube. The above steps were repeated twice, and all the supernatant was collected in a centrifuge tube. Then, 4 mL of n-hexane was added to the centrifuge tube, and the upper extract was transferred to a new centrifuge tube after standing for stratification. Total lipids of microalgae were detected by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry according to Yang et al. (GC-MS) (Finnigan TRACE DSQ; Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) at the Guangdong University of Technology. To calculate the content of EPA and DHA at dry cell weight (DCW), 150 μL of N-nonadecyl ester (1 mg/mL) was added as an internal standard to the samples for analysis of fatty acid composition by gas chromatography−mass spectrometry (GC−MS). The concentration of fatty acids (CFA, mg/g) was determined by comparing the peak area of fatty acid in the sample with the peak area of internal standard, according to the following equation: CFA = AS/AIS × CIS/WS, where A indicates the peak area; C is the concentration; W is the weight; IS is the internal standard; S is the sample (Abdulkadir and Tsuchiya, 2008).
To investigate the influence of PMo12 on regulatory genes associated with lipid metabolism in Phaeodactylum tricornutum, several molecular biological experiments were conducted. For the detection of mRNA expression levels in P. tricornutum, quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was performed. The target gene are Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene (PTD5b), Δ4 fatty acid desaturase gene (PTD4), and glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (PTGPAT). Primers used for qPCR were as follows: Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene PTD5b (forward primer, CATCACGGACCCAATCAATAC; reverse primer, CGACGGACAATCTGGAAGAC), PTD4 (forward primer, GCGAC GATTGGGCTTGACCT; reverse primer, TCCG TGGAT GATG CTTTGATTTCT), PTGPAT (forward primer, ACGATTCGGACGAAGATCAG; reverse primer, CCA TGCAACAATCGTAGTGG), and β-actin (forward primer, AGGCAAAGCGTGGTGTT CTTA; reverse primer, TCTGGGGAGCCTCAGTCAATA). In P. tricornutum genome, putative β-actin (ACT1, Phatrdraft_51157) was used as a housekeeping marker. The relative expression level of PTD5b, PTD4, and PTGPAT gene was calculated by normalization to β-actin expression.
Cultured solution of P. tricornutum after a culture cycle was dried at 95℃, then resolved in D2O for 31P NMR; the spectral data were collected on a Bruker Avance/DMX 400MHz NMR spectrometer with an 8-s pulse delay, and the internal standard is triphenyl phosphate (TPP).
SPSS software was used for statistical analysis. In the study, we used t-test to analyze whether there were significant differences between the experimental algae strains and wild strains. p<0.05 indicates a significant difference, p < 0.01 indicates an extremely significant difference.
As shown in the growth curves, the overexpression of Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene in P. tricornutum did not adversely affect the growth of the algae (Figure 1A). Moreover, the growth rate of the microalgae with PMo12 (1mol/L) added to the medium was slightly slower compared to both the wild-type and transgenic strains. Notably, during the late exponential growth phase, the algae with PMo12 supplementation exhibited a significantly lower growth rate than the wild type, and the inclusion of PMo12 caused P. tricornutum to enter the decline phase more rapidly. The slower growth rate observed in P. tricornutum supplemented with PMo12 may be attributed to the photocatalytic properties of PMo12. As a photocatalyst, PMo12 can oxidize and degrade photosynthetic products under light conditions. These products, including natural antioxidants, carotenoids, proteins, polysaccharides, PUFAs, triacylglycerols (TAGs), sterols, and vitamins, are crucial for the growth and survival of P. tricornutum. The degradation of these essential compounds likely contributes to the observed reduction in growth rate.

Figure 1. Growth and lipid analysis in diatom cells. (A) Growth curves of P. tricornutum. (B) Neutral lipid content of P. tricornutum. ** indicate extremely significant difference (p<0.01). (C) Fatty acid composition of P. tricornutum.
Observations from confocal laser scanning microscopy indicated that the morphology and size of the engineered microalgae cells were comparable to those of the wild type. However, the volume of organelles (oil bodies) storing triacylglycerol (TAG) in the engineered microalgae strains was significantly larger, and their number was also slightly increased (Figure 2). Furthermore, when compared to transgenic algae, the volume and number of organelles (oil bodies) storing TAG in engineered algae strains treated with PMo12 (1 mol/L) showed a slight increase. The neutral lipid content in microalgae supplemented with PMo12 (1mol/L) demonstrated a notable increase of 69.7% and 25.7% compared to the wild-type and transgenic microalgae, respectively (Figure 1B). These findings suggest that PMo12 more effectively promotes neutral lipid accumulation in P. tricornutum than the overexpression of the PtD5b gene. Monoacylglycerols (MAGLs), diacylglycerols (DAGs), and triacylglycerols (TAGs) are the most abundant neutral lipids found in the microalgae (Muñoz et al., 2021). A substantial accumulation of TAG has been observed in the microalgae Nannochloropsis gaditana under nitrogen starvation conditions (Janssen et al., 2018). The first step of TAG synthesis is catalyzed by glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT), which is considered a key regulator in this process (Yu et al., 2018). The overexpression of endogenous GPAT in the P. tricornutum resulted in a significant increase in neutral lipid accumulation compared to the wild type, without any growth inhibition (Niu et al., 2016; Balamurugan et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). The subsequent enzyme in TAG synthesis, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAT), has also been overexpressed in C. reinhardtii, leading to an increase in lipid content (Yamaoka et al., 2016). Diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) is the final enzyme involved in triacylglycerol (TAG) synthesis, and the overexpression of genes encoding DGAT has emerged as a promising strategy for enhancing TAG content in microalgae, including C. reinhardtii, Nannochloropsis, and Phaeodactylum (La Russa et al., 2012; Ahmad et al., 2014; Zienkiewicz et al., 2017). In this context, PMo12 may be considered a putative positive regulator of genes related to GPAT or DGAT.

Figure 2. The confocal observation of Nile red-stained P. tricornutum cells. Part (A) indicates wild-type cells, part (B) indicates transgenic microalgae, part (C) indicates PMo12 (1 mol/L) added in the medium of microalgae. Left, red fluorescence of oil bodies; middle, differential interference contrast (DIC); right, overlay image. Bars = 5 μm.
The results indicate that the contents of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), and saturated fatty acid (SFA) in P. tricornutum have significantly increased due to PMo12 (Figure 1C). Specifically, the contents of EPA and overall PUFA nearly doubled in P. tricornutum with PMo12 treatment, while both MUFA and SFA also exhibited significant increases compared to the wild type. Similar results were observed in transgenic microalgae. However, it is noteworthy that the content of DHA in P. tricornutum decreased by 27.2% with PMo12 compared to the transgenic microalgae. The fatty acid desaturases (FADs) and elongases (ELOs) are critical enzymes in PUFA synthesis, and regulating the expression of these genes through genetic engineering is a common approach to enhance PUFA accumulation in P. tricornutum. The results suggest that PMo12 may stimulate the expression of genes related to fatty acid desaturases and elongases, thereby promoting PUFA and EPA synthesis in P. tricornutum. In contrast, the key enzymes involved in DHA synthesis in P. tricornutum exhibited lower activity than the overexpression of PtD5b. Previous research has identified Δ4-FAD as a critical enzyme for DHA synthesis in microalgae. For instance, overexpression of Δ4-FAD in C. reinhardtii resulted in a 66.7% increase in total monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) content (Zäuner et al., 2012). Future studies should focus on the key enzymes involved in DHA synthesis in microalgae to further understand and optimize DHA production.
The transcript abundance of PTD5b in P. tricornutum was quantified using qPCR (Figure 3A), revealing a similar increase of 3.1-fold in both transgenic and PMo12 compared to the wild type. Δ5-FAD is the key enzyme responsible for EPA synthesis in P. tricornutum. The results indicate that PMo12 exhibits effects comparable to those of genes associated with the overexpression of Δ5 fatty acid desaturase in P. tricornutum, leading to a greater accumulation of EPA relative to the wild type. In contrast, Δ4 fatty acid desaturase (Δ4-FAD) serves as the key regulator of DHA synthesis in microalgae. The mRNA expression of the PTD4 gene was assessed through qPCR (Figure 3B), showing a relative expression level that increased by 2.3-fold in transgenic microalgae compared to the wild type. However, the mRNA expression of the PTD4 gene in PMo12 was similar to that of the wild type, suggesting that PMo12 negatively affects the expression of Δ4 fatty acid desaturase-related genes in P. tricornutum. Additionally, the transcript abundance of PTGPAT was also measured using qPCR (Figure 3C), revealing significant increases of 3.1- and 4.3-fold in transgenic microalgae and PMo12, respectively, compared to the wild type. Thus, PMo12 promotes the expression of the GPAT gene in P. tricornutum more effectively than in transgenic algae. Overall, these results demonstrate that PMo12 enhances the accumulation of neutral lipids in P. tricornutum more effectively than genetic engineering approaches involving transgenic microalgae.
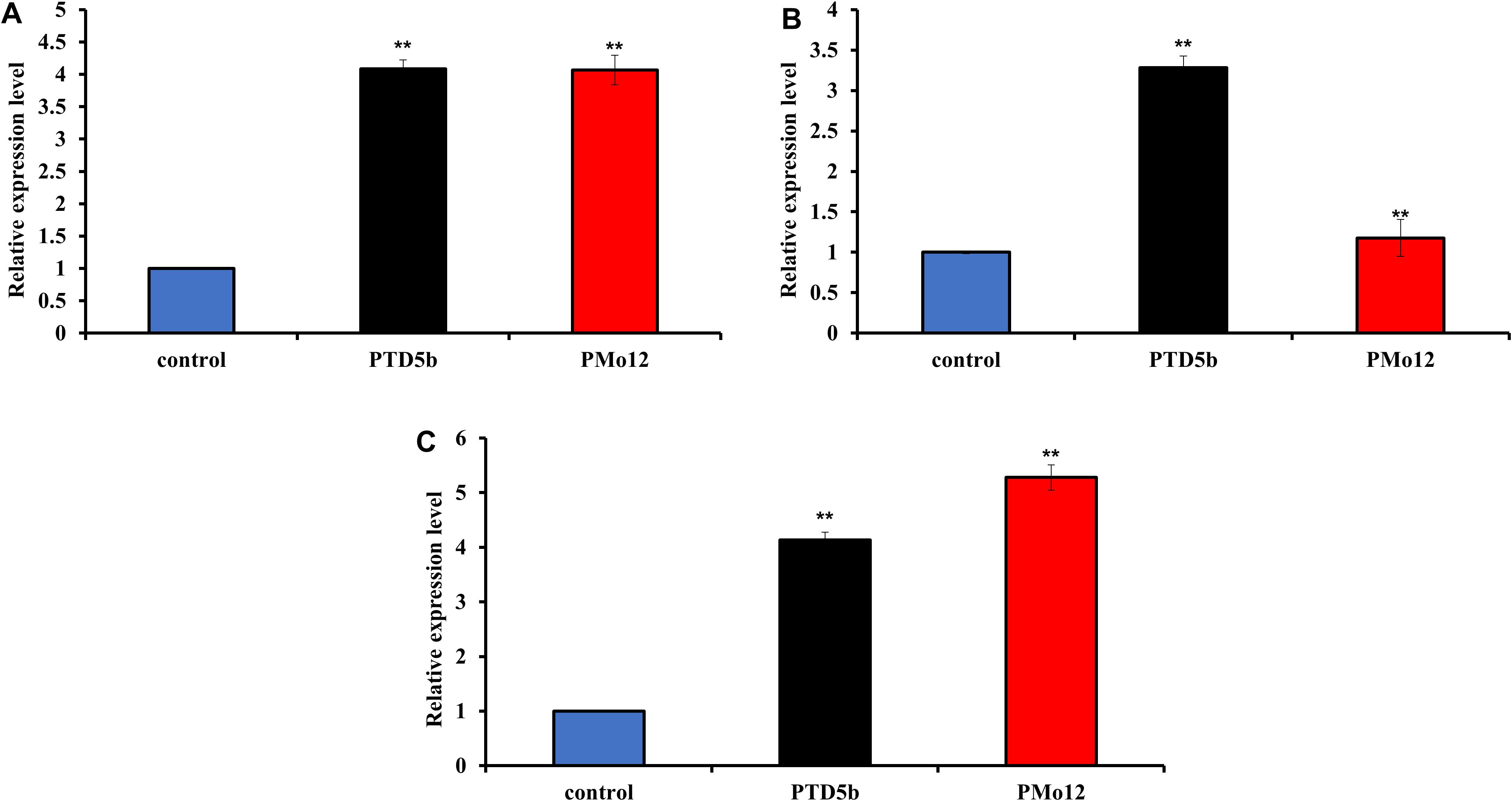
Figure 3. Analysis of lipid synthesis-related gene expression in diatom cells. (A) Relative mRNA level of PTD5b in P. tricornutum. (B) Relative mRNA level of PTD4 in P. tricornutum. (C) Relative mRNA level of PTGPAT in P. tricornutum. ** indicate extremely significant difference (p<0.01).
The 31P NMR results indicate peak species at −3.75 ppm and −5.36 ppm (Figure 4). According to the NMR spectrum, PMo12 and its reduced form are present independently in the microalgal culture medium after one culture cycle (Ishikawa and Yamase, 2000). Previous studies have shown that PMo12 acts as an oxidizing agent capable of catalyzing biomass degradation and functioning as an electron donor. The redox reaction cannot occur at room temperature, and PMo12 is only effective when exposed to light or elevated temperatures. In this study, carbohydrates produced through algal photosynthesis, such as starch, are degraded by PMo12 under illuminated conditions, leading to the generation of CO2. Subsequently, the reduced form of phosphomolybdate is reoxidized to its original state by oxygen produced during photosynthesis. This principle can be illustrated by the following reactions (Liu et al., 2016):
Consequently, PMo12 has been demonstrated to enhance the accumulation of neutral lipids and PUFAs in P. tricornutum by modulating the algal photosynthetic processes.
In conclusion, the application of PMo12 as a photocatalyst in P. tricornutum has proven to be a highly effective strategy for enhancing lipid and polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) production without compromising the growth of the microalgae. The significant increase in EPA, PUFA, and neutral lipid contents observed in the engineered strains underscores the potential of PMo12 to modulate lipid metabolism and photosynthesis-related pathways. This study not only highlights the capability of photocatalysts like PMo12 to improve the yields of valuable microalgal bioproducts but also suggests a promising alternative to traditional genetic engineering approaches. By providing a non-genetically modified route to enhance lipid production, this method could facilitate the commercial viability of microalgal biodiesel, thereby contributing to the development of sustainable and renewable energy sources. In future studies, we will explore whether PMo12 provides nutrients for the growth of P. tricornutum and considers whether PMo12 interfere with Moco synthesis in microalgae.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
KP: Formal analysis, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BX: Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. GC: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22278086).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdulkadir S., Tsuchiya M. (2008). One-step method for quantitative and qualitative analysis of fatty acids in marine animal samples. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 354, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2007.08.024
Ahmad I., Sharma A. K., Daniell H., Kumar S. (2014). Altered lipid composition and enhanced lipid production in green microalga by introduction of brassica diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2. Plant Biotechnol. J. 13, 540–550. doi: 10.1111/pbi.2015.13.issue-4
Balamurugan S., Wang X., Wang H.-L., An C.-J., Li H., Li D.-W., et al. (2017). Occurrence of plastidial triacylglycerol synthesis and the potential regulatory role of AGPAT in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Biotechnol. Biofuels 10, 97. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0786-0
Bhattacharjya R., Tiwari A., Marella T. K., Bansal H., Srivastava S. (2021). New paradigm in diatom omics and genetic manipulation. Bioresource Technol. 325, 124708. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124708
Bijelic A., Aureliano M., Rompel A. (2018). Polyoxometalates as potential next-generation metallodrugs in the combat against cancer. Angewandte Chemie Int. Edition 58, 2980–2999. doi: 10.1002/anie.201803868
Colombo S. M., Rodgers T. F. M., Diamond M. L., Bazinet R. P., Arts M. T. (2019). Projected declines in global DHA availability for human consumption as a result of global warming. Ambio 49, 865–880. doi: 10.1007/s13280-019-01234-6
Del Mondo A., Smerilli A., Sané E., Sansone C., Brunet C. (2020). Challenging microalgal vitamins for human health. Microbial Cell Factories 19, 201. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01459-1
Fayyaz M., Chew K. W., Show P. L., Ling T. C., Ng I. S., Chang J.-S. (2020). Genetic engineering of microalgae for enhanced biorefinery capabilities. Biotechnol. Adv. 43, 107554. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107554
Fu L., Li Q., Chen C., Zhang Y., Liu Y., Xu L., et al. (2021). Benzoic and salicylic acid are the signaling molecules of Chlorella cells for improving cell growth. Chemosphere 265, 129084. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129084
Fu W., Nelson D. R., Mystikou A., Daakour S., Salehi-Ashtiani K. (2019). Advances in microalgal research and engineering development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 59, 157–164. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2019.05.013
Gao F., Cabanelas I. T. D., Wijffels R. H., Barbosa M. J. (2022). Fucoxanthin and docosahexaenoic acid production by cold-adapted Tisochrysis lutea. New Biotechnol. 66, 16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2021.08.005
Ghasemi Fard S., Wang F., Sinclair A. J., Elliott G., Turchini G. M. (2018). How does high DHA fish oil affect health? A systematic review of evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59, 1684–1727. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1425978
Gui J., Chen S., Luo G., Wu Z., Fan Y., Yao L., et al. (2021). Nutrient deficiency and an algicidal bacterium improved the lipid profiles of a novel promising oleaginous dinoflagellate, prorocentrum donghaiense, for biodiesel production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 87, e01159-21. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01159-21
Han X., Liu Y., Chen Z., Glass J. B. (2022). Zinc finger protein lipR represses docosahexaenoic acid and lipid biosynthesis in schizochytrium sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 88, e02063-21. doi: 10.1128/aem.02063-21
Han X., Zhao Z., Wen Y., Chen Z. (2020). Enhancement of docosahexaenoic acid production by overexpression of ATP-citrate lyase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase in Schizochytrium sp. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13, 131. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01767-z
Helmi M., Tahvildari K., Hemmati A., Azar P. A., Safekordi A. (2022). Converting waste cooking oil into biodiesel using phosphomolybdic acid/clinoptilolite as an innovative green catalyst via electrolysis procedure; optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Fuel Process. Technol. 225, 107062–107075. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.107062
Huang B., Yang D.-H., Han B.-H. (2020). Application of polyoxometalate derivatives in rechargeable batteries. J. Materials Chem. A 8, 4593–4628. doi: 10.1039/C9TA12679A
Huang L.-B., Peng L.-N., Yan X.-H. (2021). Multi-omics responses of red algae Pyropia haitanensis to intertidal desiccation during low tides. Algal Res. 58, 102376. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2021.102376
Ilbeygi H., Jaafar J. (2024). Recent progress on functionalized nanoporous heteropoly acids: from synthesis to applications. Chem. Rec. 24, e202400043. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202400043
Ishikawa E., Yamase T. (2000). Photoreduction processes of. ALPHA.-dodecamolybdophosphate in aqueous solutions: electrical conductivity, 31P NMR, and crystallographic studies. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan 73, 641–649. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.73.641
Janssen J. H., Driessen J. L. S. P., Lamers P. P., Wijffels R. H., Barbosa M. J. (2018). Effect of initial biomass-specific photon supply rate on fatty acid accumulation in nitrogen depleted Nannochloropsis gaditana under simulated outdoor light conditions. Algal Res. 35, 595–601. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2018.10.002
Kapoor B., Kapoor D., Gautam S., Singh R., Bhardwaj S. (2021). Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): uses and potential health benefits. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 10, 232–242. doi: 10.1007/s13668-021-00363-3
Kumari A., Pabbi S., Tyagi A. (2023). Recent advances in enhancing the production of long chain omega-3 fatty acids in microalgae. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 26, 1-19. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2226720
La Russa M., Bogen C., Uhmeyer A., Doebbe A., Filippone E., Kruse O., et al. (2012). Functional analysis of three type-2 DGAT homologue genes for triacylglycerol production in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Biotechnol. 162, 13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.04.006
Liu L., Lin L., Ma Z., Wang G., Wu M. (2020). iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis ofSargassum fusiformein response to high temperature stress. Aquaculture Res. 52, 185–195. doi: 10.1111/are.14880
Liu W., Cui Y., Du X., Zhang Z., Chao Z., Deng Y. (2016). High efficiency hydrogen evolution from native biomass electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 467–472. doi: 10.1039/C5EE03019F
Lv Z., Chu A. M. Y., Mcaleer M., Wong W.-K. (2019). Modelling economic growth, carbon emissions, and fossil fuel consumption in China: cointegration and multivariate causality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16, 4176. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214176
Maliha A., Abu-Hijleh B. (2022). A review on the current status and post-pandemic prospects of third-generation biofuels. Energy Syst. 14, 1185–1216. doi: 10.1007/s12667-022-00514-7
M. U N., Mehar J. G., Mudliar S. N., Shekh A. Y. (2019). Recent advances in microalgal bioactives for food, feed, and healthcare products: commercial potential, market space, and sustainability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 18, 1882–1897. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12500
Muñoz C. F., Südfeld C., Naduthodi M. I. S., Weusthuis R. A., Barbosa M. J., Wijffels R. H., et al. (2021). Genetic engineering of microalgae for enhanced lipid production. Biotechnol. Adv. 52, 107836. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107836
Niu Y.-F., Wang X., Hu D.-X., Balamurugan S., Li D.-W., Yang W.-D., et al. (2016). Molecular characterization of a glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase reveals key features essential for triacylglycerol production in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9, 60. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0478-1
Peng K.-T., Zheng C.-N., Xue J., Chen X.-Y., Yang W.-D., Liu J.-S., et al. (2014). Delta 5 fatty acid desaturase upregulates the synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the marine diatom phaeodactylum tricornutum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 8773–8776. doi: 10.1021/jf5031086
Ramos-Vega A., Angulo C., Bañuelos-Hernández B., Monreal-Escalante E. (2021). Microalgae-made vaccines against infectious diseases. Algal Res. 58, 102408. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2021.102408
Sheehan J., Dunahay T., Benemann J., Roessler P. (1998). A look back at the US Department of Energy’s aquatic species program: biodiesel from algae. National Renewable Energy Laboratory 328, 1–294.
Singh S. K., Kaur R., Bansal A., Kapur S., Sundaram S. (2020). Biotechnological exploitation of cyanobacteria and microalgae for bioactive compounds. Biotechnol. Production Bioactive Compounds 11, 221–259. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64323-0.00008-4
Sousa S., Freitas A. C., Gomes A. M., Carvalho A. P. (2022). Modulated stress to balance Nannochloropsis oculata growth and eicosapentaenoic acid production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 106, 4017–4027. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11968-1
Torres-Tiji Y., Fields F. J., Mayfield S. P. (2020). Microalgae as a future food source. Biotechnol. Adv. 41, 107536. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107536
Wang M., Ye X., Bi H., Shen Z. (2024). Microalgae biofuels: illuminating the path to a sustainable future amidst challenges and opportunities. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioproducts 17, 10. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02461-0
Wang X., Liu S.-F., Li R.-Y., Yang W.-D., Liu J.-S., Lin C. S. K., et al. (2020). TAG pathway engineering via GPAT2 concurrently potentiates abiotic stress tolerance and oleaginicity in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13, 160. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01799-5
Wang Z., Wang S., Feng Y., Wan W., Zhang H., Bai X., et al. (2021). Obtaining high-purity docosahexaenoic acid oil in thraustochytrid aurantiochytrium through a combined metabolic engineering strategy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 10215–10222. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03781
Wei L., You W., Gong Y., El Hajjami M., Liang W., Xu J., et al. (2020). Transcriptomic and proteomic choreography in response to light quality variation reveals key adaption mechanisms in marine Nannochloropsis oceanica. Sci. Total Environ. 720, 137667. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137667
Yamaoka Y., Achard D., Jang S., Legéret B., Kamisuki S., Ko D., et al. (2016). Identification of a Chlamydomonas plastidial 2-lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase and its use to engineer microalgae with increased oil content. Plant Biotechnol. J. 14, 2158–2167. doi: 10.1111/pbi.2016.14.issue-11
Yang L., Liu W., Zhang Z., Du X., Dong L., Deng Y. (2019). Low energy electro-reduction of carbon dioxide coupling with anodic glycerol oxidation catalyzed by chemical regenerative phosphomolybdic acids. J. Power Sources 420, 99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.02.087
Yang Z.-K., Niu Y.-F., Ma Y.-H., Xue J., Zhang M.-H., Yang W.-D., et al. (2013). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of neutral lipid accumulation in diatom following nitrogen deprivation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6, 67. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-67
Yu J., Loh K., Song Z.-Y., Yang H.-Q., Zhang Y., Lin S. (2018). Update on glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases: the roles in the development of insulin resistance. Nutr. Diabetes 8, 34. doi: 10.1038/s41387-018-0045-x
Zäuner S., Jochum W., Bigorowski T., Benning C. (2012). A Cytochrome b5-Containing Plastid-Located Fatty Acid Desaturase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eukaryotic Cell 11, 856–863. doi: 10.1128/ec.00079-12
Zhong J., Pérez-Ramírez J., Yan N. (2021). Biomass valorisation over polyoxometalate-based catalysts. Green Chem. 23, 18–36. doi: 10.1039/D0GC03190A
Keywords: phosphomolybdic acid, microalgae, lipid, polyunsaturated fatty acid, EPA, DHA
Citation: Peng K-T, Xiong B-H, Cheng G, Zhong Y-H and Yu L (2025) Phosphomolybdic acid boosts polyunsaturated fatty acid and neutral lipid production in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1531239. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1531239
Received: 20 November 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
Puja Kumari, Scottish Association For Marine Science, United KingdomReviewed by:
Angel Llamas, University of Cordoba, SpainCopyright © 2025 Peng, Xiong, Cheng, Zhong and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Yu, Z3ljaEBnZHV0LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.