
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 10 March 2025
Sec. Marine Megafauna
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1529913
 Yufei Dai1,2,3†
Yufei Dai1,2,3† Fanyi Meng1,4†
Fanyi Meng1,4† Fuxing Wu1*
Fuxing Wu1* Xing Miao1
Xing Miao1 Denghui Yan5
Denghui Yan5 Mingding Zhong2
Mingding Zhong2 Shunan Cao2
Shunan Cao2 Yuli Wei4,6
Yuli Wei4,6 Longshan Lin1*
Longshan Lin1*The Southern Ocean, a critical marine region on Earth, is undergoing significant environmental changes due to global climate change, including reductions in sea ice extent, ocean acidification, and alterations in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC). The Cosmonaut Sea, notable for its dynamic sea ice and rich biological activity, remains one of the least explored regions in the Southern Ocean, with limited data on its marine mammal populations. This study conducted during the 38th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE) from January to March 2022, collected systematic data on marine mammal occurrences. Species distribution modeling (SDM) was used to assess the influence of environmental variables on the distribution of the most abundant marine mammal species observed in the Cosmonaut Sea, including humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae), crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophaga), and Antarctic minke whales (Balaenoptera bonaerensis). Our results indicated significant performance variations among the different algorithms, with ensemble model yielding more accurate predictions. Environmental variables such as water depth, sea surface height, and mixed layer thickness were identified as significant factors influencing habitat suitability for different species. Humpback whales were found to have the widest distribution range, followed by Antarctic minke whales and crabeater seals. Generally, the study provides the first comprehensive analysis of marine mammal distribution in the Cosmonaut Sea, highlighting the effectiveness of ensemble models in ecological predictions. The findings emphasize the importance of integrating high-resolution data and incorporating predator-prey interactions in future studies to improve our understanding and conservation of these complex ecosystems.
The Southern Ocean is one of the most critical regions on Earth, covering 10% of the global sea surface and interconnecting the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans (Cheung et al., 2013; Hunt et al., 2007). It establishes a relatively isolated and autonomous marine ecosystem through the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) (Hunt et al., 2007). However, under the influence of global climate change, the Southern Ocean is experiencing significant environmental transformations (Cheung et al., 2013), including the reduction of sea ice extent (De La Mare, 2009), ocean acidification (McNeil and Matear, 2008), marine heatwaves and alterations in the ACC’s dynamics (Sokolov and Rintoul, 2009). These environmental changes may lead to habitat modifications, biodiversity loss and decreased prey availability, ultimately disrupting the stability of the ecosystem (De La Mare, 2009; Lin et al., 2022; Ran et al., 2022; Sorte et al., 2010). For example, on the western Antarctic Peninsula, the 2020 marine heatwaves affected the ecosystem at all tropic levels, including coastal plankton metabolism and community fish structure (Latorre et al., 2023).
The Cosmonaut Sea, located in the western region of Enderby Land in East Antarctica (between 30-60°E longitude and 60-70°S latitude), spans an area exceeding 699,000 km², making it one of the least explored zones of the Southern Ocean (Hunt et al., 2007). The confluence of southward coastal currents and the eastward ACC results in dynamic sea ice conditions in the Cosmonaut Sea, fostering abundant biological activity akin to a sanctuary (Pakhomov, 1993). Previous studies have investigated the oceanographic (Cheung et al., 2013; Kuvaas et al., 2005) and climatic nuances (Geddes and Moore, 2007; Solli et al., 2008), the structure and distribution of benthic and planktonic organisms (Hunt et al., 2007; Van de Putte et al., 2010), as well as mid-trophic level fish (Mou et al., 2023; Van de Putte et al., 2010; Zhu et al., 2020). Despite these efforts, comprehensive ship-based oceanographic surveys of the Cosmonaut Sea are infrequent, leading to a limited understanding of local marine mammals.
Marine predator species of the Southern Ocean, such as crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophaga), weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddelli), humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) and Antarctic minke whales (Balaenoptera bonaerensis), serve as crucial indicators of climate change and pivotal ecosystem stewards of the ecosystem (Chevallay et al., 2024a; Meynecke et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022). For example, weddell seals exhibit heightened sensitivity to the concentration and spatial distribution of sea ice (Forcada et al., 2012), while humpback whales are predominantly found in regions characterized by upwelling and elevated chlorophyll-a concentrations (Meynecke et al., 2021). Moreover, in actively managed Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) waters, marine predators are used to identify changes in the marine environment, e.g. species identified under the CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Program (CEMP) including the crabeater seal. Therefore, to enhance conservation endeavors and elucidate the impact of climate change on the Cosmonaut Sea ecosystem, a deeper understanding of the geographic distribution of top predators and their response mechanisms to climatic circumstances is imperative.
The interaction between ocean currents and topography in the Cosmonaut Sea strongly influences the marine environment, particularly in the near shelf zone (Hunt et al., 2007). For instance, coastal currents intensify nearshore flow velocity in the Cosmonaut Sea, which is higher than that recorded in other sectors of Antarctica (Ackley et al., 2003a); The mixing zone between coastal currents and shelf waters creates a strong near shelf frontal zone, which markedly alters local physical marine environment, including temperature, salinity, flow velocity, and mixed layer thickness (Ackley et al., 2003a; Hunt et al., 2007). Furthermore, a distinctive feature of the Cosmonaut Sea is the recurrent formation of polynyas (Arbetter et al., 2004; Geddes and Moore, 2007). The frequent cycles of sea ice freezing and melting in these areas exert substantial effects on the chemical marine environment, impacting variables such as chlorophyll-a concentration, pH levels, and dissolved oxygen (Arbetter et al., 2004).
Species Distribution Modeling (SDM), also known as habitat modeling, is a robust tool used for forecasting the potential distribution of species (Cianfrani et al., 2018; Marcer et al., 2013). SDM utilizes a range of environmental factors to assess the likelihood of a given species’ presence through statistical and/or mechanistic approaches (Elith and Leathwick, 2009). This model is widely applied in evaluating species habitats, identifying regions of biodiversity significance, and managing endangered species (Sánchez-Mercado et al., 2010; Siniff et al., 2008). In recent years, SDM has seen increased use in predicting organismal responses to climate change (Vega et al., 2017), understanding the impacts of invasive species (Srivastava et al., 2019), and planning conservation efforts targeted at marine organisms (Nachtsheim et al., 2017), particularly in marine fish (Sánchez-Mercado et al., 2010). Various algorithms are introduced for SDM, including the maximum entropy model (Maxent), artificial neural networks (ANN), and generalized linear models (GLM). According to a review of SDM’s algorithms conducted by Robinson et al. (2017), ensemble model is the optimal approach. Ensemble model mitigates the limitations associated with specific models, enhancing accuracy and predictive capacity while addressing model-based uncertainties (Ran et al., 2022). For example, Salas et al. (2018) conducted a comparative analysis of a single-model algorithm and an ensemble modeling approach to simulate the habitat distribution of Marco Polo sheep (Ovis ammon polii) under climate change scenarios. The findings revealed that the ensemble model exhibited greater conservatism, characterized by reduced variability, and enhanced stability. Consequently, ensemble model is gaining increasing traction (Breiner et al., 2015; Hao et al., 2020; Kindt, 2018).
This paper aims to analyze the potential distribution of major marine mammals in the Cosmonaut Sea using ensemble model. Our objectives are (a) to estimate distribution of most abundant marine mammal species observed in the Cosmonaut Sea, (b) to identify pivotal environmental drivers influencing their distribution, and (c) to compare habitat disparities across the most abundant marine mammal species.
During the 38th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE), visual surveys of marine mammals were conducted aboard the icebreaker XUE LONG 2. Data on marine mammal occurrences were systematically collected while traversing the Cosmonaut Sea from January 27th to March 10th, 2022 (Figure 1). The survey was conducted based on standard marine survey transects to ensure systematic and comprehensive data collection. The visual observation range was approximately 3 kilometers. The vessel maintained an average speed of approximately 10 knots during the survey. This speed was kept constant under normal observation conditions, with minor adjustments made occasionally due to weather or operational requirements. Marine mammals were observed at distances far from the vessel, and no significant behavioral changes were noted during the observation process. Observations were made during daylight hours from the bridge or its exterior wings by experienced observers (author Y.D. and X.M.), with additional sightings assisted by the pilots and other crew members onboard. Species identification was performed using reticule binoculars (7×50 magnification, STEINER) and EOS-1D X Mark II camera (with 100–400 mm L series lens, Cannon). Observations were halted when Beaufort’s sea state exceeded level 4. For each sighting, species, group size, GPS coordinates, time, and vessel speed were documented. Photographs were taken to assist in species identification when weather conditions allowed. Due to the difficulty in identifying species at sea from a distance, animals lacking distinguishing characteristics were classified as ‘unknown’.
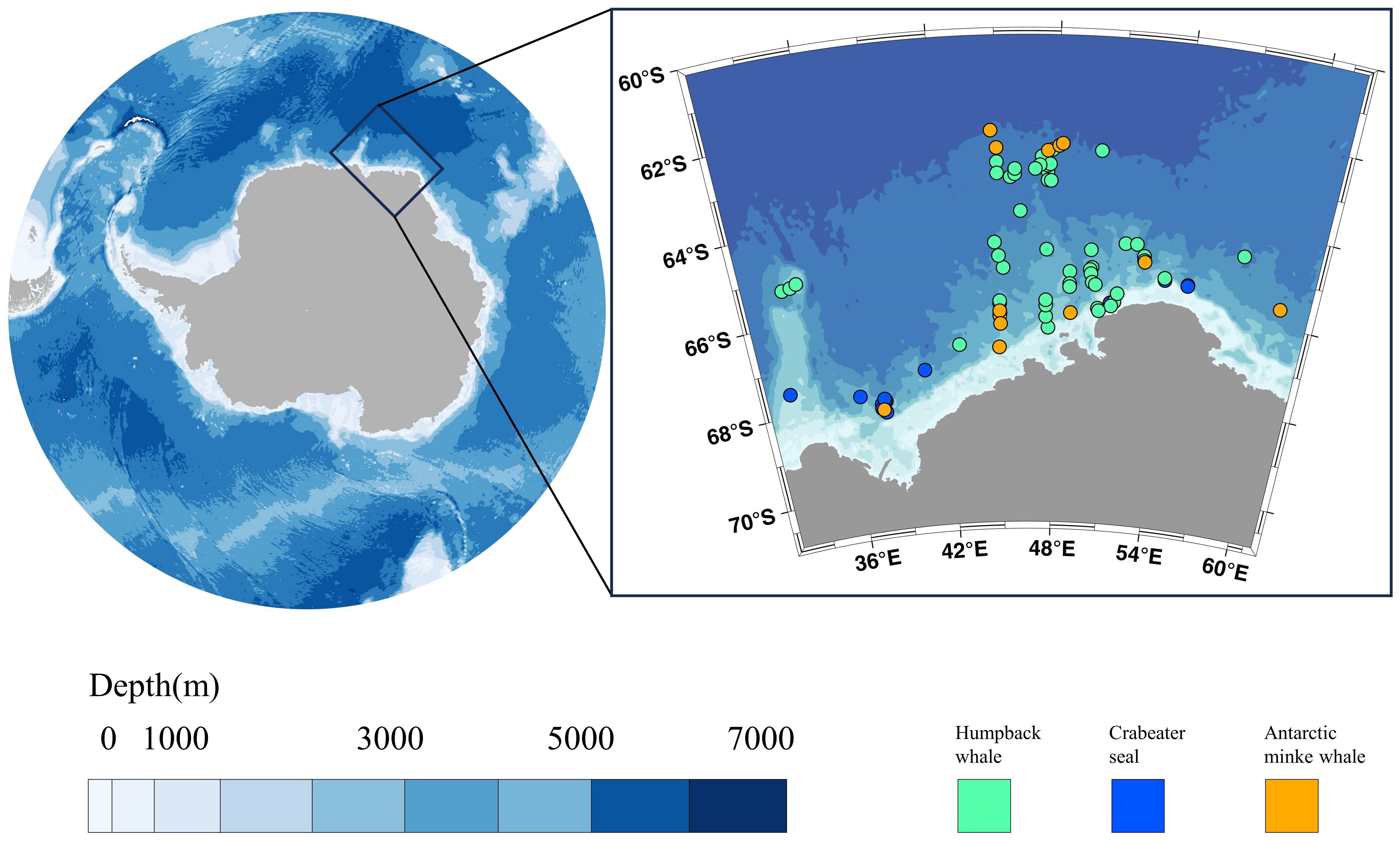
Figure 1. Location of the Cosmonaut Sea (left) and sighting locations, with humpback whales, crabeater seals, and Antarctic minke whales represented in green, blue, and orange, respectively.
To meet the sample size requirements of SDM (Lin et al., 2022; Ran et al., 2022), only data on major marine mammals (sightings >10) were used for further analysis. Additionally, points with a distance of <0.1° were randomly removed to match the spatial resolution of environmental variables and to prevent sampling bias. The available data reflect species presence information only, it’s difficult to obtain true absences for mobile species (Haughey et al., 2021; Peddemors, 1999). Previous studies have shown that incorporating absence data can significantly improve model performance, even if the absence data are pseudo-absences generated based on functions (Brotons et al., 2004; Srivastava et al., 2019). Following the methods described by Haughey et al. (2021) and Srivastava et al. (2019), pseudo-absence points were established by generating 100 points for each species. These points were randomly sampled from areas located more than 3 km away from presence points to minimize ecological niche overlap.
Environmental variables were obtained from the global ocean reanalysis dataset (GLORYS2V4) (https://www.mercator-ocean.fr). For each variable, the mean values from January to March 2022 were calculated to match the observation dates and standardized to a 0.1° × 0.1° resolution within the same coordinate system and range. Initially, 24 potential environmental variables were selected based on the distinctive physical and chemical oceanographic conditions shaped by the near shelf frontal zone and polynyas of the Cosmonaut Sea. This selection was further informed by previous studies on SDM for marine mammals (Haughey et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022) (Table 1). However, due to predictor collinearity and model over-parameterization, using a large number of environmental variables in the prediction model can significantly reduce predictive capability (Bosch et al., 2018). Multiple studies have shown that a small number of environmental variables can accurately predict species distribution (Tyberghein et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2019). Therefore, we preliminarily filtered the environmental factors using the following methods: (1) when the correlation coefficient between two variables exceeded 0.80, the variable with higher significance was retained; (2) pre-modeling was conducted using Generalized Linear Model, and environmental variables with contributions lower than 5% were excluded.
Twelve common models were pre-modeled as candidate models, specifically: Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Classification Tree Analysis (CTA), Flexible Discriminant Analysis (FDA), Generalized Additive Model (GAM), Generalized Boosting Model (GBM), Generalized Linear Model (GLM), Multiple Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS), Maximum Entropy (Maxent), Maxent over glmnet (MAXNET), Random Forest (RF), Surface Range Envelop (SRE), and eXtreme Gradient Boosting Training (XGBOOST).
Each model was run twice using the bootstrapping method, with 80% of the occurrence data selected for training and the remaining 20% for testing. The relative importance of environmental variables was determined through correlation metrics. Subsequently, true skill statistic (TSS) and relative operating characteristic (ROC) were used as filters, retaining only candidate models with values above the thresholds (0.7 and 0.9, respectively) for ensemble model. Unless otherwise specified, TSS and ROC values were presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
The model predicts the habitat suitability index (HSI) for species based on environmental parameters, ranging from 0 to 1. An HSI greater than 0.7 is generally considered a highly suitable habitat (El-Gabbas et al., 2021; Meynecke et al., 2021; Nachtsheim et al., 2017). To mitigate potential biases due to unequal cell sizes, the results were projected onto the Cosmonaut Sea region using the Lambert method (Budic et al., 2016). All data processing and analysis in this study were conducted using MATLAB (https://www.mathworks.com/) and R (https://www.r-project.org/), with R’s “biomod2” package (Thuiller et al., 2024) playing a crucial role in constructing the ensemble models.
Visual surveys were conducted over 30 days between 27th January 2022 and 10th March 2022, totaling 256 hours. During these surveys, 103 marine mammal encounters were recorded by the observer and/or crew, encompassing at least 11 different species (Figure 2). Four sightings were classified as unknown, but they were definitively identified as cetaceans due to their large body size and the presence of blows in the water. Notably, 75.7% of these sightings were represented by three marine mammals: humpback whale, crabeater seal and Antarctic minke whale (Figure 2, Supplementary Table 1). Humpback whales were the most frequently observed, with 51 sightings. Crabeater seals and Antarctic minke whales were also observed more than 10 times, with 14 sightings and 13 sightings, respectively. These species were the most abundant marine mammal species observed in the Cosmonaut Sea, and their sighting data were subsequently subjected to SDM.
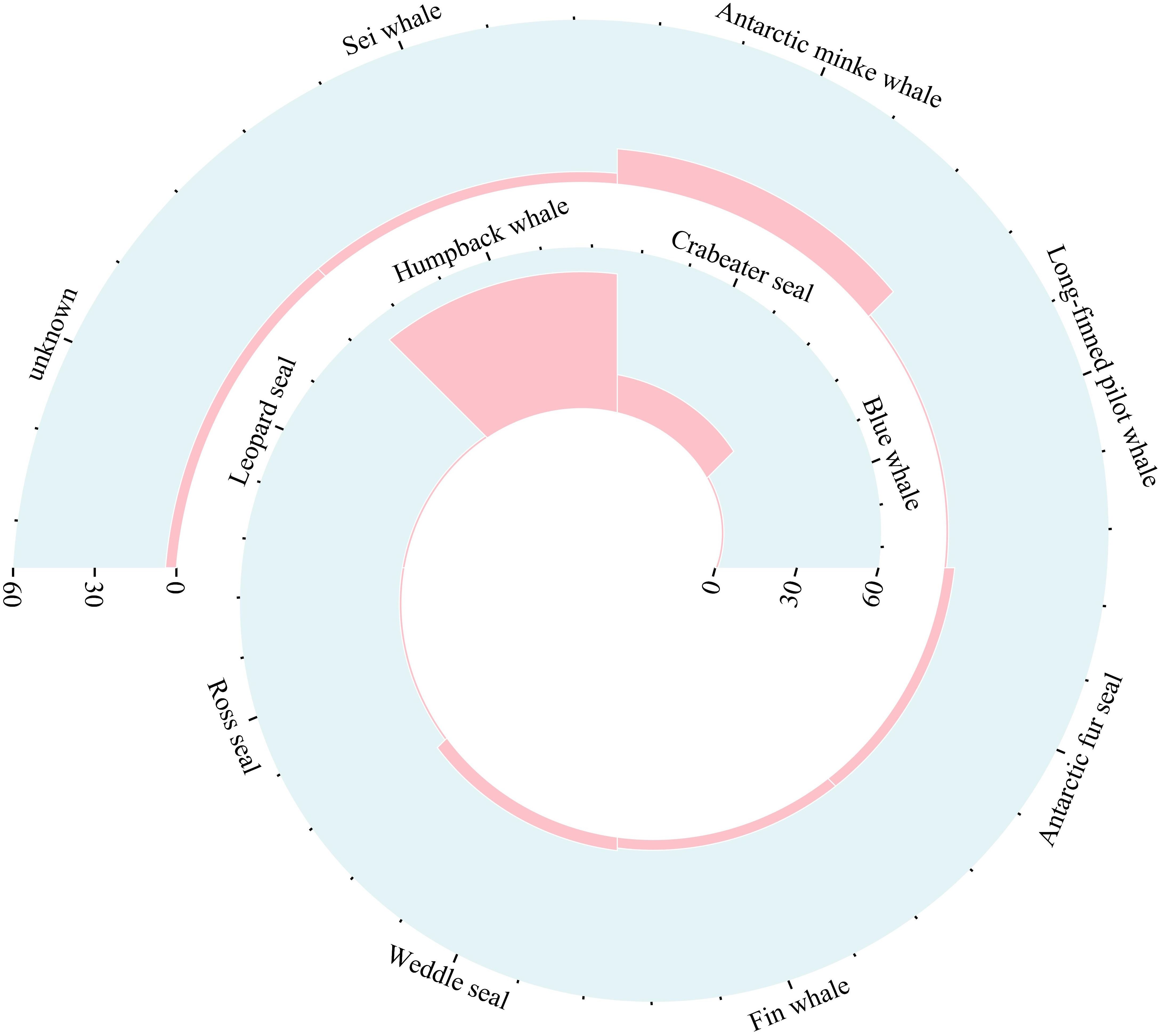
Figure 2. The number of sightings for each marine mammal species during the survey in the Cosmonaut Sea. Refer to Supplementary Table 1 for the detailed data.
Each marine mammal species was modeled using 12 different algorithms, all with identical parameters. The results revealed significant variations among the model performance (Figure 3). Algorithms such as CTA, GLM, and GAM generally performed well, whereas ANN and SRE showed poor performance. Additionally, the performance of individual model varied substantially across different species. For instance, Maxent demonstrated strong performance in the SDM of humpback whales (ROC: 0.96 ± 0.03; TSS: 0.92 ± 0.05) and crabeater seals (ROC: 0.90 ± 0.03; TSS: 0.81 ± 0.06), but underperformed for Antarctic minke whales (ROC: 0.80 ± 0.05; TSS: 0.60 ± 0.09). For the three species, appropriate candidate models were selected for ensemble model, resulting in relatively high overall model performance, which was suitable for assessing their potential habitats in the Cosmonaut Sea.
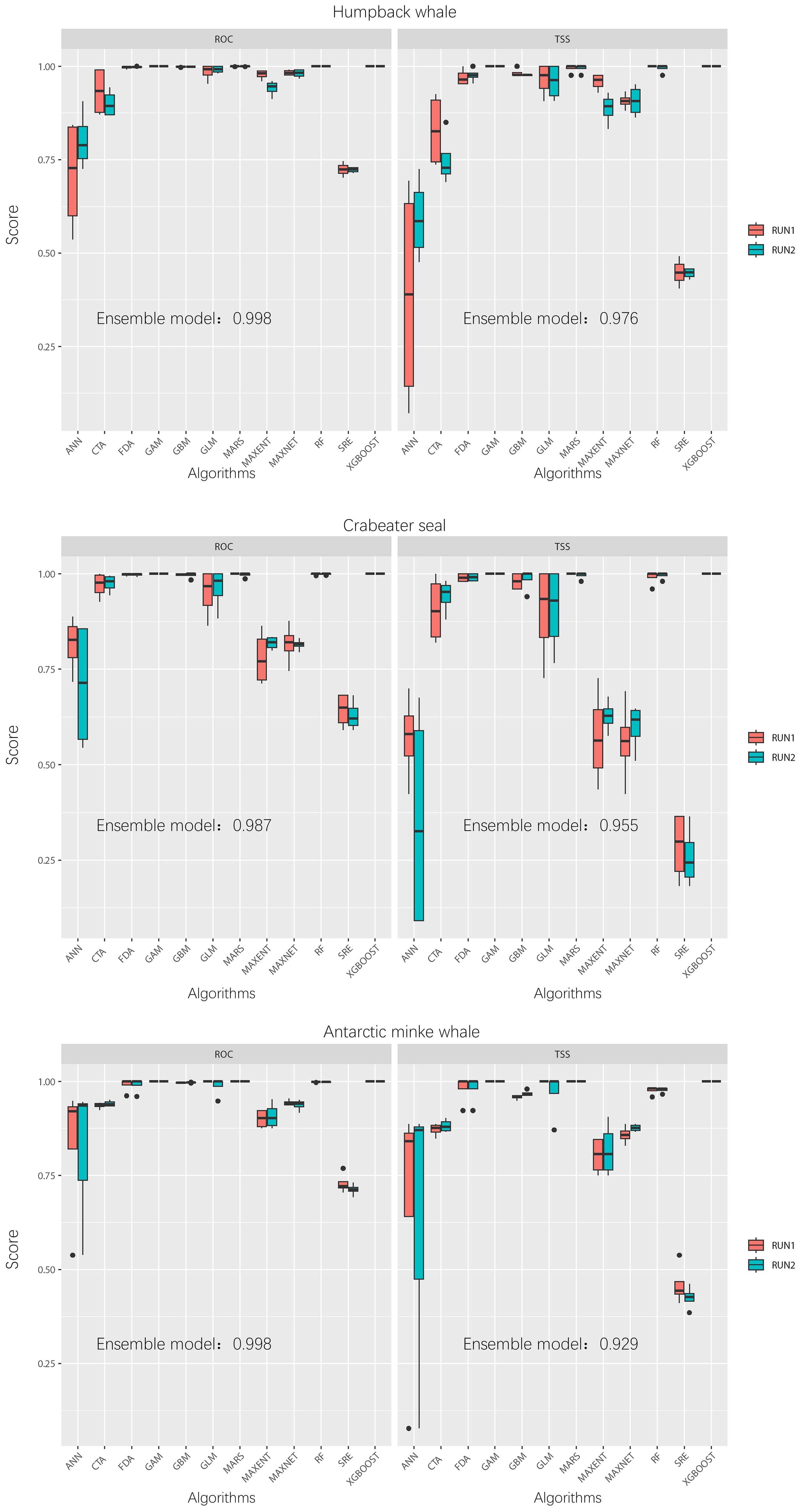
Figure 3. Boxplot of model performance. The left and right panels depict the evaluation metrics: relative operating characteristic (ROC) and true skill statistic (TSS), respectively.
Ten environmental variables (Table 1) were retained for SDM, with their importance and response curves varying by species (Figure 4). For humpback whales, the primary contributing variable was sea water pressure at sea floor (pbo) at 42.1%, followed by sea surface height above geoid (zos) at 25.3% and ocean mixed layer thickness defined by sigma theta (mlost) at 16.7%. The optimal habitat conditions for humpback whales occurred when pbo was less than 2000 dbar, zos was -1.7 m, and mlost was 60 m (Supplementary Table 2). For crabeater seals, age of sea ice (siage) contributed 27.2% and pbo contributed 21.0%, with favorable environmental conditions being pbo less than 3000 dbar and siage greater than 0.2 (Supplementary Table 3). For Antarctic minke whales, the primary influencing factors were mole concentration of dissolved molecular oxygen (o2) at 39.8% and pbo at 21.1%, with relatively suitable habitat conditions being o2 ranging from 350 to 380 mmol/m3 and pbo ranging from 0 to 1500 dbar (Supplementary Table 4).
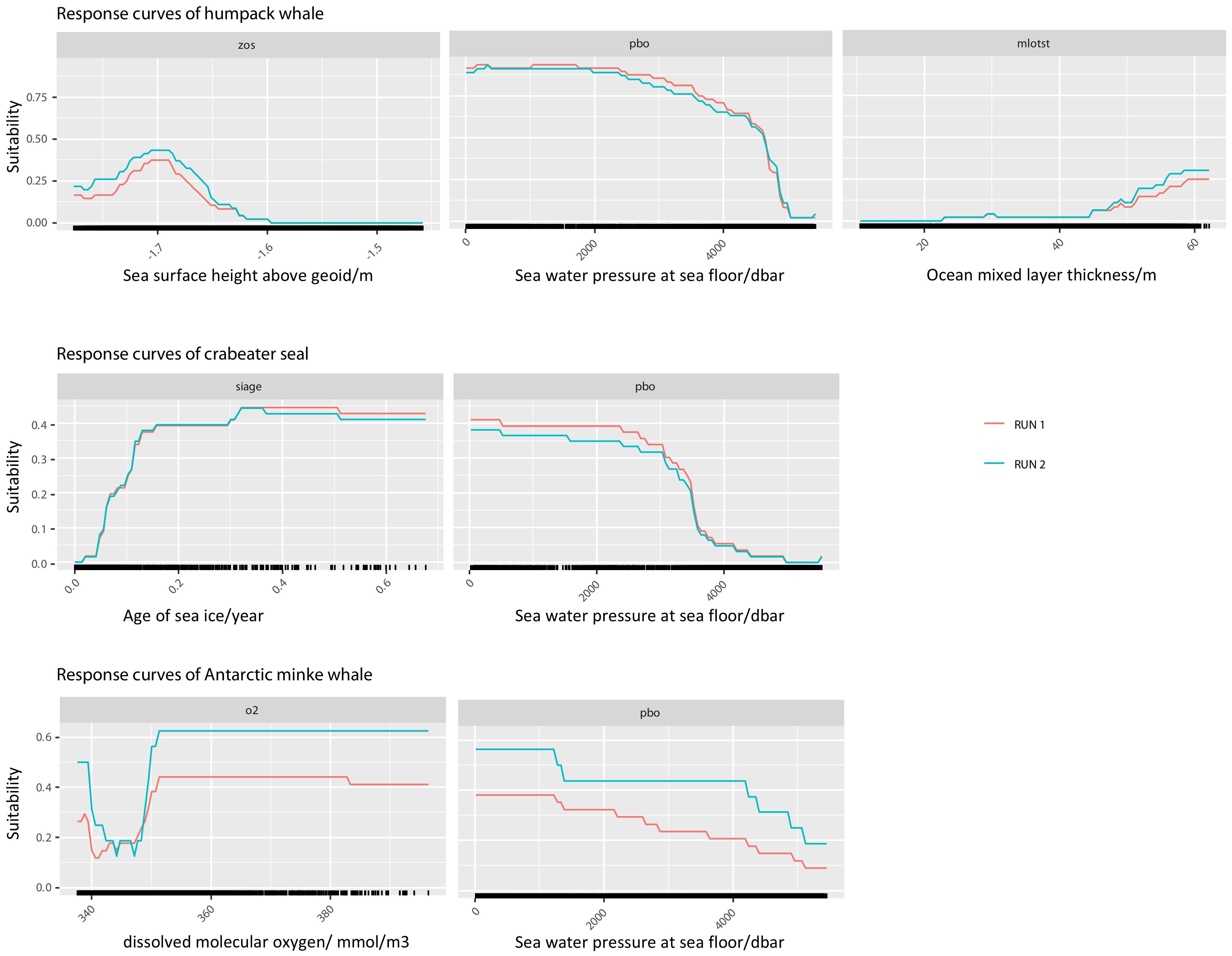
Figure 4. Response curves of high-contribution environmental factors for humpback whales, crabeater seals, and Antarctic minke whales in the ensemble model.
In the current environment of the Cosmonaut Sea, humpback whales exhibited the broadest distribution range, covering an estimated 36.71% of the sea region (Figure 5). High suitable habitats (HSI > 0.7) were predominantly located south of 63°S. Crabeater seals had a distribution area covering 24.23%, with high suitable habitats distributed throughout the coastal zone, primarily south of 66°S. Antarctic minke whales had a distribution area covering 31.56%, with highly suitable habitats predominantly located east of 42°E, and their latitudinal distribution spanning the entire sea region.
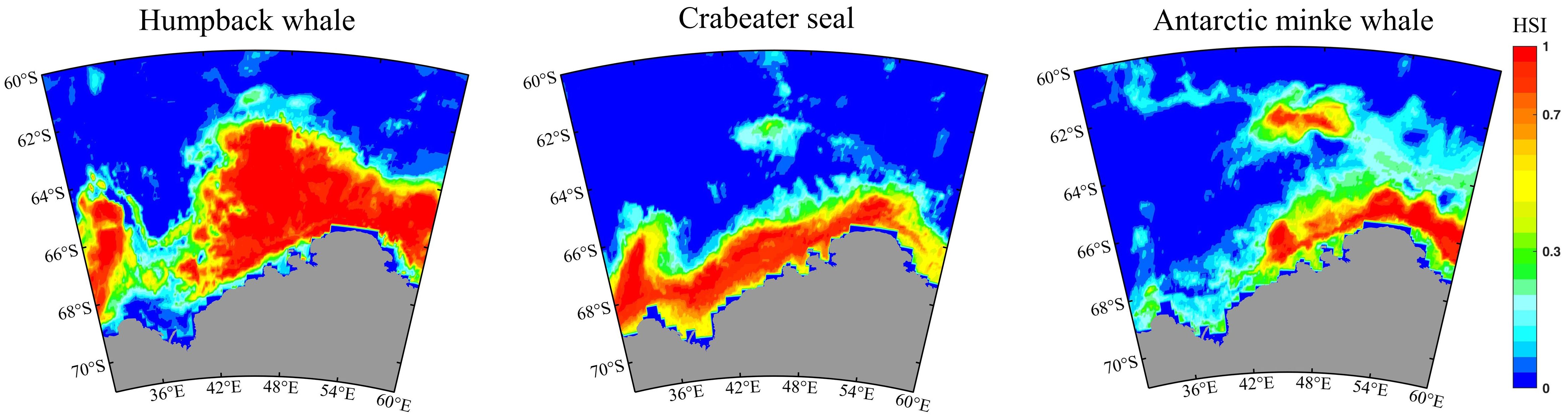
Figure 5. Potential suitable area for humpback whales, crabeater seals, and Antarctic minke whales in the Cosmonaut Sea. The habitat suitability index (HSI) for species is predicted by the ensemble model using key environmental variables.
Understanding the habitat distribution of marine mammals is essential for their study and conservation. SDM is a crucial tool for gaining insights into species distribution and informing biodiversity conservation and management (Robinson et al., 2017). To date, many studies on marine species distribution have relied on the Maxent model (Fourcade et al., 2014; Lin et al., 2022; Phillips et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2013). This model has been effective in predicting the potential habitat, but it has limitations and does not always yield optimal results (Phillips et al., 2006). In our study, the Maxent model’s performance in predicting the habitat of Antarctic minke whales was suboptimal.
In contrast, ensemble model provided more accurate and robust predictions in the SDM of the three marine mammals studied. Ensemble model combines predictions from multiple algorithms, avoiding the performance degradation caused by the limitations of any single algorithm and enhancing overall accuracy and robustness (Hao et al., 2020; Ran et al., 2022). This approach is supported by Mohammadi et al. (2019), who found that an ensemble model outperformed the Maxent algorithm in simulating the habitat distribution of two terrestrial animals, highlighting the value of a multi-algorithm approach.
There is a significant data gap in marine mammal surveys, particularly in logistically constrained polar regions (Hückstädt, 2018; Rotella, 2023). This study provided a comprehensive analysis of the distribution of the most abundant marine mammal species observed in the Cosmonaut Sea, including humpback whales, Antarctic minke whales, and crabeater seals. The findings may inform future conservation and management efforts for marine mammals in the Antarctic region. To our knowledge, this was the first exhaustive marine mammal survey conducted in the Cosmonaut Sea (Kaschner et al., 2012). Our survey documented at least 11 species of marine mammals, with species composition similar to other regions in the Southern Ocean (El-Gabbas et al., 2021; Rotella, 2023; Torterotot et al., 2022). Notably, humpback whales, Antarctic minke whales, and crabeater seals were the most abundant species observed.
Humpback whales are large, long-distance migratory baleen whales found in all oceans, migrating between high-latitude feeding grounds in summer and tropical and subtropical breeding grounds in winter (El-Gabbas et al., 2021; Meynecke et al., 2021). Antarctic minke whales are small baleen whales distributed in the Southern Hemisphere, known for their dark gray back and white belly (Risch et al., 2019; Risch et al., 2014). Crabeater seals are ice-dependent pinnipeds of the Southern Ocean, residing exclusively in the circum-Antarctic pack ice zone (Ackley et al., 2003a; Nachtsheim et al., 2017; Southwell, 2004). Despite significant differences in taxonomy, morphology, and lifestyle, these three species congregate in the Southern Ocean during the austral summer, primarily feeding on Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba).
In oceanography, Sea water pressure at sea floor (pbo) is an equivalent depth measure reflecting seafloor topography and offshore distance (Boyer et al., 2022; Chapman et al., 2020). It is a significant factor influencing the distribution of the three marine mammals. Humpback whales primarily inhabit open waters at depths of 2000-4000 decibar (dbar, a unit commonly used in oceanography, equivalent to meters), while the ice edge at 0-2000 dbar, provides crucial foraging grounds due to high Antarctic krill biomass. The mixed layer (mlotst) represents the upper ocean water volume where various physical properties are homogeneous (Sverdrup, 1953). Within the mixed layer, the relatively ample sunlight and abundant nutrients such as nitrates, phosphates, and other trace elements are conducive to photosynthesis and promote phytoplankton growth, providing primary productivity for the entire ocean (Ohlmann et al., 1996; Polovina et al., 1995; Vernet et al., 2008). Sea surface height is related to the hydrodynamics of the mid-upper water column, such as ocean currents, water masses, and tides (Hill et al., 2024; Kürzel et al., 2023; McMahon et al., 2023). These factors are important indicators of highly suitable habitats for top predators, especially in open waters (Chevallay et al., 2024b; Li et al., 2021; Libourel et al., 2023).
Crabeater seals are typical pack-ice residents, with critical life history stages (resting, breeding, and nurturing) occurring on the ice, and they almost never utilize multi-year ice (Davis et al., 2008). Therefore, sea ice of a specific age (0.2-0.4) is more favorable. Our study also indicates that crabeater seals’ highly suitable habitats are located in the 0-3000 dbar region. They are rarely found in waters where pbo exceeds 4000 dbar, which is consistent with previous studies (Nachtsheim et al., 2017; Southwell et al., 2005; Wall et al., 2007).
Antarctic minke whales have evolved to exploit the ecological niches provided by pack-ice regions (Lee et al., 2017). These cetaceans are frequently observed in areas heavily covered by sea ice, associated with pancake ice and newly formed ice near the marginal ice zone (Ainley, 2010). They utilize leads within the ice for respiration and create breathing holes in newly formed ice (Ainley, 2010; El-Gabbas et al., 2021; Tynan, 1997). The strong affinity of Antarctic minke whales for sea ice habitats, typically within the 0-1500 dbar range, is hypothesized to serve as a protective mechanism against predation by killer whales (Orcinus orca) (Lin et al., 2023; Pitman and Ensor, 2003). Additionally, this preference may reduce competition for food resources with humpback whales, which predominantly inhabit open waters (Friedlaender et al., 2021). The distribution of Antarctic minke whales may also be influenced by biogeochemical factors such as oxygen concentration, although the specific mechanisms underlying this relationship remain unclear (Ainley, 2010; El-Gabbas et al., 2021).
We utilized ensemble modeling analysis to identify suitable habitats for major marine mammals in the Cosmonaut Sea and to ascertain the primary environmental factors influencing their distribution. The accuracy of species distribution models depends on the quality of the input data, including the distribution and density of species occurrence records, as well as the type and resolution of environmental parameters (Cianfrani et al., 2018; Marcer et al., 2013). Due to limited comprehensive data, we adopted a simplified hypothesis that may not fully capture the complex dynamics of the Cosmonaut Sea ecosystem. For instance, the absence of long-term, continuous, multi-route observational datasets, combined with concurrent krill distribution data, has hindered our ability to incorporate predator-prey interactions into the models. Additionally, our aim was to analyze the responses of marine mammals to environmental changes on a broad scale. However, given the high sensitivity of these animals to environmental fluctuations, the averaged large-scale environmental data may not accurately reflect the conditions experienced by the animals, potentially leading to misalignments between actual conditions and the environmental data used in the models (Elith and Leathwick, 2009; Sánchez-Mercado et al., 2010).
Looking forward, integrating higher-resolution satellite remote sensing data and in-situ environmental information gathered by biological tracking devices (e.g., animal-borne sensors) will enable more precise, small-scale assessments of habitat utilization (Forcada et al., 2012; Foster-Dyer et al., 2023; Gonçalves et al., 2020). Moreover, it is widely acknowledged that SDMs are prone to overfitting during the training and validation processes (Ploton et al., 2020). This overfitting can compromise the model’s ability to generalize predictions across different temporal and spatial scales, especially in scenarios involving habitat change projections (Bald et al., 2023; Ploton et al., 2020). Ensemble models face limitations in addressing this challenge due to the constraints posed by Tobler’s First Law of Geography (Tobler, 1970). This principle posits that environmental variables typically exhibit spatial autocorrelation, leading to data points that are not entirely independent. Consequently, models trained and validated on spatially correlated data often yield inflated performance outcomes and overly complex model structures (Kass et al., 2021; Valavi et al., 2019).
To mitigate these issues, Valavi et al. (2019) introduced the spatial blocking method as a viable strategy for reducing overfitting issues in modeling exercises. Implementing such techniques in marine mammal habitat assessments holds promise for enhancing the accuracy of predictive modeling outcomes.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because The data in this study are all obtained by observation from the ship.
YD: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Methodology. FM: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Methodology. FW: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Conceptualization, Supervision. XM: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SC: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LL: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by “Impact and Response of Antarctic Seas to Climate Change, IRASCC2020-2024-NO.01-02-02 & 02-02”.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1529913/full#supplementary-material
Ackley S., Bengtson J., Boveng P., Castellini M., Daly K. L., Jacobs S., et al. (2003a). A top–down, multidisciplinary study of the structure and function of the pack-ice ecosystem in the eastern Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Rec. 39, 219–230. doi: 10.1017/S0032247403003115
Ainley D. G. (2010). A history of the exploitation of the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Rec. 46, 233–243. doi: 10.1017/S003224740999009X
Arbetter T. E., Lynch A. H., Bailey D. A. (2004). Relationship between synoptic forcing and polynya formation in the Cosmonaut Sea: 1. Polynya climatology. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans 109. doi: 10.1029/2003JC001837
Bald L., Gottwald J., Zeuss D. (2023). spatialMaxent: Adapting species distribution modeling to spatial data. Ecol. Evol. 13, e10635. doi: 10.1002/ece3.10635
Bosch S., Tyberghein L., Deneudt K., Hernandez F., De Clerck O. (2018). In search of relevant predictors for marine species distribution modelling using the MarineSPEED benchmark dataset. Diversity Distributions 24, 144–157. doi: 10.1111/ddi.2018.24.issue-2
Boyer T., Zhang H.-M., O’Brien K., Reagan J., Diggs S., Freeman E., et al. (2022). Effects of the pandemic on observing the global ocean. Bull. Am. Meteorological Soc. 1. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-21-0210.1
Breiner F. T., Guisan A., Bergamini A., Nobis M. P. (2015). Overcoming limitations of modelling rare species by using ensembles of small models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 6, 1210–1218. doi: 10.1111/mee3.2015.6.issue-10
Brotons L., Thuiller W., Araújo M. B., Hirzel A. H. (2004). Presence-absence versus presence-only modelling methods for predicting bird habitat suitability. Ecography 27, 437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-7590.2004.03764.x
Budic L., Didenko G., Dormann C. F. (2016). Squares of different sizes: effect of geographical projection on model parameter estimates in species distribution modeling. Ecol. Evol. 6, 202–211. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2016.6.issue-1
Chapman C. C., Lea M.-A., Meyer A., Sallée J.-B., Hindell M. (2020). Defining Southern Ocean fronts and their influence on biological and physical processes in a changing climate. Nat. Clim. Change 10, 209–219. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0705-4
Cheung W. W., Watson R., Pauly D. (2013). Signature of ocean warming in global fisheries catch. Nature 497, 365–368. doi: 10.1038/nature12156
Chevallay M., Guinet C., Goulet-Tran D., Jeanniard du Dot T. (2024a). Sealing the deal – Antarctic fur seals’ active hunting tactics to capture small evasive prey revealed by miniature sonar tags. J. Exp. Biol. 227, jeb246937. doi: 10.1242/jeb.246937
Chevallay M., Jeanniard du Dot T., Goulet P., Fonvieille N., Craig C., Picard B., et al. (2024b). Spies of the deep: An animal-borne active sonar and bioluminescence tag to characterise mesopelagic prey size and behaviour in distinct oceanographic domains. Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanographic Res. Papers 203, 104214. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2023.104214
Cianfrani C., Broennimann O., Loy A., Guisan A. (2018). More than range exposure: Global otter vulnerability to climate change. Biol. Conserv. 221, 103–113. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.02.031
Davis C. S., Stirling I., Strobeck C., Coltman D. W. (2008). Population structure of ice-breeding seals. Mol. Ecol. 17, 3078–3094. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03819.x
De La Mare W. K. (2009). Changes in Antarctic sea-ice extent from direct historical observations and whaling records. Climatic Change 92, 461–493. doi: 10.1007/s10584-008-9473-2
El-Gabbas A., Van Opzeeland I., Burkhardt E., Boebel O. (2021). Dynamic species distribution models in the marine realm: predicting year-round habitat suitability of baleen whales in the southern ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.802276
Elith J., Leathwick J. R. (2009). Species distribution models: ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annu. Rev. ecology evolution systematics 40, 677–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.110308.120159
Forcada J., Trathan P. N., Boveng P. L., Boyd I. L., Burns J. M., Costa D. P., et al. (2012). Responses of Antarctic pack-ice seals to environmental change and increasing krill fishing. Biol. Conserv. 149, 40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2012.02.002
Foster-Dyer R. T. N., Goetz K. T., Pinkerton M. H., Iwata T., Holser R. R., Michael S. A., et al. (2023). First observations of Weddell seals foraging in sponges in Erebus Bay, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 46, 611–621. doi: 10.1007/s00300-023-03149-1
Fourcade Y., Engler J. O., Rödder D., Secondi J. (2014). Mapping species distributions with MAXENT using a geographically biased sample of presence data: a performance assessment of methods for correcting sampling bias. PloS One 9, e97122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097122
Friedlaender A. S., Joyce T., Johnston D. W., Read A. J., Nowacek D. P., Goldbogen J. A., et al. (2021). Sympatry and resource partitioning between the largest krill consumers around the Antarctic Peninsula. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 669, 1–16. doi: 10.3354/meps13771
Geddes J. A., Moore G. (2007). A climatology of sea ice embayments in the Cosmonaut Sea, Antarctica. Geophysical Res. Lett. 34. doi: 10.1029/2006GL027910
Gonçalves B. C., Spitzbart B., Lynch H. J. (2020). SealNet: A fully-automated pack-ice seal detection pipeline for sub-meter satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 239, 111617. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111617
Hao T., Elith J., Lahoz-Monfort J. J., Guillera-Arroita G. (2020). Testing whether ensemble modelling is advantageous for maximising predictive performance of species distribution models. Ecography 43, 549–558. doi: 10.1111/ecog.2020.v43.i4
Haughey R., Hunt T. N., Hanf D., Passadore C., Baring R., Parra G. J. (2021). Distribution and habitat preferences of indo-pacific bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) inhabiting coastal waters with mixed levels of protection. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.617518
Hill S. L., Atkinson A., Arata J. A., Belcher A., Nash S. B., Bernard K. S., et al. (2024). Observing change in pelagic animals as sampling methods shift: the case of Antarctic krill. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1307402
Hückstädt L. A. (2018). “Weddell Seal: Leptonychotes weddellii,” in Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 3rd ed. Eds. Würsig B., Thewissen J. G. M., Kovacs K. M. (Elsevier), 1048–1051. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-804327-1.00267-3
Hunt B., Pakhomov E., Trotsenko B. (2007). The macrozooplankton of the cosmonaut sea, east antarctica (30 e–60 e), 1987–1990. Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanographic Res. Papers 54, 1042–1069.
Kaschner K., Quick N. J., Jewell R., Williams R., Harris C. M. (2012). Global coverage of cetacean line-transect surveys: status quo, data gaps and future challenges. PloS One 7, e44075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044075
Kass J. M., Muscarella R., Galante P. J., Bohl C. L., Pinilla-Buitrago G. E., Boria R. A., et al. (2021). ENMeval 2.0: Redesigned for customizable and reproducible modeling of species’ niches and distributions. Methods Ecol. Evol. 12, 1602–1608. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13628
Kindt R. (2018). Ensemble species distribution modelling with transformed suitability values. Environ. Model. Software 100, 136–145. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.11.009
Kürzel K., Brix S., Brandt A., Brenke N., Enderlein P., Griffiths H. J., et al. (2023). Pan-atlantic comparison of deep-sea macro- and megabenthos. Diversity 15, 814. doi: 10.3390/d15070814
Kuvaas B., Kristoffersen Y., Guseva J., Leitchenkov G., Gandjukhin V., Løvås O., et al. (2005). Interplay of turbidite and contourite deposition along the cosmonaut Sea/Enderby land margin, east antarctica. Mar. Geology 217, 143–159.
Latorre M. P., Iachetti C. M., Schloss I. R., Antoni J., Malits A., de la Rosa F., et al. (2023). Summer heatwaves affect coastal Antarctic plankton metabolism and community structure. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 567, 151926. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2023.151926
Lee J. F., Friedlaender A. S., Oliver M. J., DeLiberty T. L. (2017). Behavior of satellite-tracked Antarctic minke whales (Balaenoptera bonaerensis) in relation to environmental factors around the western Antarctic Peninsula. Anim. Biotelemetry 5, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40317-017-0138-7
Li X., Sindihebura T. T., Zhou L., Duarte C. M., Costa D. P., Hindell M. A., et al. (2021). A prediction and imputation method for marine animal movement data. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 7, e656. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.656
Libourel P.-A., Lee W. Y., Achin I., Chung H., Kim J., Massot B., et al. (2023). Nesting chinstrap penguins accrue large quantities of sleep through seconds-long microsleeps. Science 382, 1026–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.adh0771
Lin S., Zhao L., Feng J. (2022). Predicted changes in the distribution of Antarctic krill in the Cosmonaut Sea under future climate change scenarios. Ecol. Indic. 142, 109234. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109234
Lin S.-Y., Zhao L., Liu L.-L., Feng J.-L. (2023). Habitat changes of antarctic minke whale (balaenoptera bonaerensis) in the cosmonaut sea under cmip6 climate change scenarios. Oceanologia Limnologia Sin. 54, 387–398.
Marcer A., Sáez L., Molowny-Horas R., Pons X., Pino J. (2013). Using species distribution modelling to disentangle realised versus potential distributions for rare species conservation. Biol. Conserv. 166, 221–230. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2013.07.001
McMahon C. R., Hindell M. A., Charrassin J. B., Coleman R., Guinet C., Harcourt R., et al. (2023). Southern Ocean pinnipeds provide bathymetric insights on the East Antarctic continental shelf. Commun. Earth Environ. 4, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s43247-023-00928-w
McNeil B. I., Matear R. J. (2008). Southern Ocean acidification: A tipping point at 450-ppm atmospheric CO2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 18860–18864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806318105
Meynecke J.-O., de Bie J., Barraqueta J.-L. M., Seyboth E., Dey S. P., Lee S. B., et al. (2021). The role of environmental drivers in humpback whale distribution, movement and behavior: A review. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.720774
Mohammadi S., Ebrahimi E., Moghadam M. S., Bosso L. (2019). Modelling current and future potential distributions of two desert jerboas under climate change in Iran. Ecol. Inf. 52, 7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2019.04.003
Mou J., Liu K., Huang Y., Lin J., He X., Zhang S., et al. (2023). Species diversity and community structure of macrobenthos in the cosmonaut sea, east antarctica. Diversity 15, 1197. doi: 10.3390/d15121197
Nachtsheim D. A., Jerosch K., Hagen W., Plötz J., Bornemann H. (2017). Habitat modelling of crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophaga) in the weddell sea using the multivariate approach maxent. Polar Biol. 40, 961–976. doi: 10.1007/s00300-016-2020-0
Ohlmann J. C., Siegel D. A., Gautier C. (1996). Ocean mixed layer radiant heating and solar penetration: A global analysis. J. Climate 9, 2265–2280. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2265:OMLRHA>2.0.CO;2
Pakhomov E. (1993). The faunistic complexes of macroplankton in the Cooperation Sea (Antarctica). Antarctica (32), 94–110.
Peddemors V. M. (1999). Delphinids of southern Africa: A review of their distribution, status and life history. J. Cetacean Res. Manage. 1, 157–165. doi: 10.47536/jcrm.v1i2.463
Phillips S. J., Anderson R. P., Schapire R. E. (2006). Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 190, 231–259.
Pitman R., Ensor P. (2003). Three forms of killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Antarctica. J. Cetacean Res. Manage 5.
Ploton P., Mortier F., Réjou-Méchain M., Barbier N., Picard N., Rossi V., et al. (2020). Spatial validation reveals poor predictive performance of large-scale ecological mapping models. Nat. Commun. 11, 4540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18321-y
Polovina J. J., Mitchum G. T., Evans G. T. (1995). Decadal and basin-scale variation in mixed layer depth and the impact on biological production in the central and north pacifi-88. Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanographic Res. Papers 42, 1701–1716. doi: 10.1016/0967-0637(95)00075-H
Ran Q., Duan M., Wang P., Ye Z., Mou J., Wang X., et al. (2022). Predicting the current habitat suitability and future habitat changes of Antarctic jonasfish. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanography 199, 105077. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2022.105077
Risch D., Gales N. J., Gedamke J., Kindermann L., Nowacek D. P., Read A. J., et al. (2014). Mysterious bio-duck sound attributed to the antarctic minke whale (Balaenoptera bonaerensis). Biol. Lett. 10, 20140175.
Risch D., Norris T., Curnock M., Friedlaender A. (2019). Common and antarctic minke whales: Conservation status and future research directions. Front. Mar. Sci. 6, 247.
Robinson N. M., Nelson W. A., Costello M. J., Sutherland J. E., Lundquist C. J. (2017). A systematic review of marine-based species distribution models (SDMs) with recommendations for best practice. Front. Mar. Sci. 4, 421. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00421
Rotella J. J. (2023). Patterns, sources, and consequences of variation in age-specific vital rates: Insights from a long-term study of Weddell seals. J. Anim. Ecol. 92, 552–567. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13870
Salas E. A. L., Valdez R., Michel S., Boykin K. G. (2018). Habitat assessment of Marco Polo sheep (Ovis ammon polii) in Eastern Tajikistan: Modeling the effects of climate change. Ecol. Evol. 8, 5124–5138. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4103
Sánchez-Mercado A., Ferrer-Paris J., Franklin J. (2010). Mapping species distributions: spatial inference and prediction. Oryx 44, 615.
Siniff D. B., Garrott R. A., Rotella J. J., Fraser W. R., Ainley D. G. (2008). Opinion: Projecting the effects of environmental change on Antarctic seals. Antarctic Sci. 20, 425–435. doi: 10.1017/S0954102008001351
Sokolov S., Rintoul S. R. (2009). Circumpolar structure and distribution of the antarctic circumpolar current fronts: 1. mean circumpolar paths. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans 114.
Solli K., Kuvaas B., Kristoffersen Y., Leitchenkov G., Guseva J., Gandjukhin V. (2008). The cosmonaut sea wedge. Mar. Geophysical Res. 29, 51–69. doi: 10.1007/s11001-008-9045-x
Sorte C. J., Williams S. L., Carlton J. T. (2010). Marine range shifts and species introductions: comparative spread rates and community impacts. Global Ecol. Biogeography 19, 303–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-8238.2009.00519.x
Southwell C. (2004). Satellite-linked dive recorders provide insights into the reproductive strategies of crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophagus). J. Zoology 264, 399–402. doi: 10.1017/S0952836904005928
Southwell C., Kerry K., Ensor P. (2005). Predicting the distribution of crabeater seals Lobodon carcinophaga off east Antarctica during the breeding season. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 299, 297–309.
Srivastava V., Lafond V., Griess V. C. (2019). Species distribution models (SDM): applications, benefits and challenges in invasive species management. CABI Rev. 2019, 1–13. doi: 10.1079/PAVSNNR201914020
Sverdrup H. U. (1953). On conditions for the vernal blooming of phytoplankton. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 18, 287–295. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/18.3.287
Thuiller W., Lafourcade B., Engler R., Araújo M. B. (2009). BIOMOD – a platform for ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Ecography 32, 369–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0587.2008.05742.x
Tobler W. R. (1970). A computer movie simulating urban growth in the detroit region. Economic Geogr.
Torterotot M., Béesau J., Perrier de la Bathie C., Samaran F. (2022). Assessing marine mammal diversity in remote Indian Ocean regions, using an acoustic glider. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanography 206, 105204. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2022.105204
Tyberghein L., Verbruggen H., Pauly K., Troupin C., Mineur F., De Clerck O. (2012). Bio-ORACLE: a global environmental dataset for marine species distribution modelling. Global Ecol. Biogeography 21, 272–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-8238.2011.00656.x
Tynan C. T. (1997). Cetacean distributions and oceanographic features near the kerguelen plateau. Geophysical Res. Lett. 24, 2793–2796.
Valavi R., Elith J., Lahoz-Monfort J. J., Guillera-Arroita G. (2019). blockCV: An r package for generating spatially or environmentally separated folds for k-fold cross-validation of species distribution models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 10, 225–232. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13107
Van de Putte A. P., Jackson G. D., Pakhomov E., Flores H., Volckaert F. A. (2010). Distribution of squid and fish in the pelagic zone of the cosmonaut sea and prydz bay region during the BROKE-west campaign. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanography 57, 956–967.
Vega G. C., Pertierra L. R., Olalla-Tárraga M.Á. (2017). MERRAclim, a high-resolution global dataset of remotely sensed bioclimatic variables for ecological modelling. Sci. Data 4, 170078. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017.78
Vernet M., Martinson D., Iannuzzi R., Stammerjohn S., Kozlowski W., Sines K., et al. (2008). Primary production within the sea-ice zone west of the antarctic peninsula: I–sea ice, summer mixed layer, and irradiance. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanography Palmer Antarctica Long Term Ecol. Res. 55, 2068–2085. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.021
Wall S. M., Bradshaw C. J., Southwell C. J., Gales N. J., Hindell M. A. (2007). Crabeater seal diving behaviour in eastern Antarctica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 337, 265–277. doi: 10.3354/meps337265
Yang X.-Q., Kushwaha S., Saran S., Xu J., Roy P. (2013). Maxent modeling for predicting the potential distribution of medicinal plant, justicia adhatoda l. @ in lesser himalayan foothills. Ecol. Eng. 51, 83–87.
Zhang Z., Xu S., Capinha C., Weterings R., Gao T. (2019). Using species distribution model to predict the impact of climate change on the potential distribution of Japanese whiting Sillago japonica. Ecol. Indic. 104, 333–340. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.05.023
Keywords: marine mammal distributions, species distribution modeling, ecological predictions, environmental variables, Southern Ocean
Citation: Dai Y, Meng F, Wu F, Miao X, Yan D, Zhong M, Cao S, Wei Y and Lin L (2025) Predicting the potential distribution of major marine mammals in the Cosmonaut Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1529913. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1529913
Received: 18 November 2024; Accepted: 20 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Xuelei Zhang, Ministry of Natural Resources, ChinaReviewed by:
Andrea Walters, University of Tasmania, AustraliaCopyright © 2025 Dai, Meng, Wu, Miao, Yan, Zhong, Cao, Wei and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fuxing Wu, d3VmdXhpbmdAdGlvLm9yZy5jbg==; Longshan Lin, bGlubG9uZ3NoYW5AdGlvLm9yZy5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.