Abstract
Introduction:
As Digital Industry 4.0 advances, shipping operators are progressively implementing digital technologies for maritime decarbonization efforts.
Methods:
This review employs a bibliometric methodology to thoroughly examine and analyze the application of digital technology in decarbonizing shipping from 2005 to 2024. Examining 201 publications from the SCI-EXPANDED and SSCI databases elucidates the present condition, challenges, and prospects of digital technology applications in this domain.
Results:
The review demonstrates the swift expansion of research on digital technologies for decarbonization within the shipping sector via an analysis of annual publication trends. Subsequent journal metrics and collaborative network analysis with VOSviewer identified particularly prolific journals, nations, institutions, and authors. Furthermore, this review delineates the field's principal research clusters and hotspots via keyword co-occurrence analysis, offering direction for future investigations. Ultimately, it examines research gaps in speed optimization, emission prediction, and autonomous ships by integrating keyword co-occurrence analysis with the content of recent publications, and then proposes prospective research options.
Discussions:
Future studies on ship speed optimization could benefit from adopting multi-objective optimization methods, combining more machine-learning techniques with the FCP model, etc. Concerning emission prediction, future research efforts could focus on integrating more diverse external data sources into emission prediction models, adopting emerging technology applications, such as ship-based carbon capture (SBCC), introducing blockchain into smart emission monitoring systems, etc. Future research regarding autonomous ships can further refine optimizing route planning and navigation safety, autonomous ship energy efficiency and emission control, maritime communications and navigation systems, ship electrification, and green design.
1 Introduction
The shipping industry is essential in the twenty-first-century global economy, underpinning international trade and acting as a crucial connection between various locations worldwide. Nonetheless, due to escalating worldwide apprehension around climate change, mitigating emissions from shipping has emerged as a critical issue (Xu et al., 2024a). Classification of shipping emissions is as follows (Serra and Fancello, 2020; Xu et al., 2024b):
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is the predominant Greenhouse Gas (GHG) in the vessels. GHG emissions are the primary contributor to global warming.
-
Sulfur Oxides (SOx) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) facilitate the development of acid rain, which is detrimental to human health.
-
Carbon Monoxide (CO), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC), and PM affect human health. The PM also includes Black Carbon (BC), which is not only particularly harmful to humans but is the second most important climate force after CO2.
This review primarily addresses GHG emissions, among other topics.
The international shipping industry is one of the largest GHG emitters in the global economy and is also expected to be one of the fastest-growing GHG emitters (Gibbs et al., 2014). The shipping sector contributes approximately 3% of total global GHG emissions, a figure that, while not substantial, warrants attention due to its long-term environmental ramifications (Lu et al., 2023). Consequently, decarbonizing the shipping industry is essential to address the global demand for emission reductions and secure the industry’s sustainable development. International organizations have introduced a series of clear milestones for emission reductions. According to the Fourth IMO GHG Study, the total GHG increased from 977 million tons to 1.076 million tons. In addition, the total GHG in the shipping industry increased by 10.1% (Fan et al., 2022). The IMO anticipated that by 2050, maritime transport would represent 15% of overall CO2 emissions, underscoring the necessity for emission reduction strategies in this sector (Dnv, 2019). Furthermore, the IMO is dedicated to attaining net zero emissions from maritime transportation by 2050 at the latest (IMO, 2020).
The ongoing innovation in digital technology, propelled by digital transformation and the swift advancement of the Internet, presents new potential for the maritime industry to achieve decarbonization. Before digital technologies, shipping decarbonization relied primarily on improving fuel efficiency, using alternative energy sources, optimizing routes, and technological transformation. However, these methods often rely on experience and static decisions and lack real-time data support to achieve optimal results. In contrast, through real-time monitoring and data analysis, digital technologies can accurately control energy consumption and emissions, optimize routes and predict ship failures in advance, significantly increasing the efficiency of decarbonization. Combining digitalization with traditional methods can improve operational efficiency while achieving more precise decarbonization targets, driving the shipping industry toward a greener and more sustainable direction. Digital technology encompasses a collection of technologies grounded in digitization, involving collecting, processing, transmitting, storing, and utilizing information via contemporary information technology platforms. Digital technologies include the following:
-
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT facilitates the interchange of information and communication between objects and individuals through the interconnection of sensors, devices, and networks (Al-Fuqaha et al., 2015).
-
Big data: Big data entails extracting essential insights from extensive volumes of intricate data (Manyika, 2011).
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI refers to technology that emulates human intelligence, allowing computer systems to execute activities, including learning, reasoning, and self-correction (McFarlane et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2024a).
-
Blockchain: Blockchain is a decentralized ledger system that securely, transparently, and immutably records transactions (Sidhu, 2017).
-
Digital Twin: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical entities that replicate their state and behavior (Grieves and Vickers, 2017).
Digital technologies are viable and sustainable solutions to significantly reduce GHG emissions associated with maritime transport in the short term. IoT enables real-time monitoring of ships’ energy use and emissions for enhanced energy management (Iris and Lam, 2019). Big data analytics enables maritime businesses to evaluate and forecast cargo flows, optimize routes, and minimize superfluous voyages, decreasing Fuel Consumption (FCP) and carbon emissions (Cariou et al., 2019). AI can facilitate the creation of intelligent vessels that autonomously modify speeds and courses to reduce energy consumption and emissions (Bouman et al., 2017). Furthermore, implementing blockchain in the shipping sector can enhance the transparency and efficiency of the supply chain while fostering the advancement of sustainable shipping practices (Horvath et al., 2018).
2 Literature review
Although technology holds significant relevance in the shipping sector, the existing literature on the subject is sparse and disjointed. This analysis delineates 15 literature surveys published from 2020 to 2023. The increasing focus on the environmental consequences of shipping is also seen in the literature of associated disciplines.
Specific assessments have concentrated on analyzing the implementation of particular digital technologies in the decarbonizing maritime sector, encompassing AI, AIS, machine learning, and blockchain, among others. Research on AI pertains to fuel optimization, predictive maintenance, route planning, autonomous shipping, and logistics management, studies on machine learning focus on ship design, ship emission forecasting, and hull shape enhancement. Investigations into digital twins are concerned with optimizing new energy ship power systems. The research on machine learning in the decarbonization of the shipping industry is the most comprehensive. Huang et al. (2022) provided a comprehensive analysis of the application of machine learning techniques to enhance ship sustainability in the domain of machine learning, addressing the fundamentals of machine learning and its applications in associated fields: ship design, operational performance, and trip planning. Tripathi and Vijayakumar (2024) investigated the enhancement of ship hulls in four domains: hull form, hull structure, hull cleaning, and hull lubrication, integrating uncertainty analysis, operations research, and machine learning with simulation models to create various software and methodologies to achieve optimal outcomes. Wang et al. (2022) examined the impact of neural networks, intelligent algorithms, and grey box models on forecasting energy emissions from vessels, probing theoretical analysis, AI-driven ship energy consumption model, and top-down and bottom-up ship emission forecast models. Durlik et al. (2024) examined the application of AI in fuel optimization, predictive maintenance, route planning, intelligent energy management, autonomous shipping, and logistics management through case studies of the Maersk Line and the Port of Rotterdam. Yin et al. (2023) demonstrated that three critical technologies are employed in new energy ship power systems: new energy spatiotemporal prediction technology, ship power scheduling technology, and digital twin.
These reviews examine the application, developmental trends, and challenges of particular digital technologies by analyzing their use in the decarbonizing shipping industry. Nonetheless, there exists a deficiency of research grounded in a holistic viewpoint in this domain. Only one evaluation offers a comprehensive overview of the application of digital technologies in decarbonizing the shipping industry. Xue and Lai (2024) introduced the idea of Digital Green Shipping Innovation (DGSI) and examined its application in research and practice, the antecedents and repercussions of DGSI application, along the problems and opportunities associated with it. The review is predicated on DGSI, and its formulation of green shipping encompasses not only decarbonization but also environmental preservation and the sustainability of shipping operations, among other factors. Thus, this review concentrates on shipping decarbonization and analyzes the implementation, challenges, and opportunities of digital technologies within this domain using a bibliometric methodology. The review initially presents the data collection and research methodology; evaluates annual publication trends and conducts a collaborative network analysis of interactions among countries, institutions, and authors; elucidates the use of digital technologies in shipping decarbonization via keyword co-occurrence analysis; and assesses the challenges and opportunities within the field. The subsequent sections of this review are structured as follows. Section 3 delineates the data collecting and research methods. Section 4 outlines the bibliometric analysis and its findings. Section 5 analyzes the research gaps and future research directions. Section 6 presents the conclusions.
3 Data and methodology
3.1 Data collection
This review examines publications on digital technology for the decarbonizing maritime sector. It picked the Web of Science (WoS) database for in-depth analysis to understand the newest academic advancements, which is essential for capturing worldwide scholarship (Li et al., 2018). This review’s dataset is sourced from the two primary indexes in WoS: the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) and the Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). It is confined to English-language literature, encompassing both journal articles and reviews, which cover the period from 2005 to 2024, as of November 12, 2024. English is the main language of international academic exchange, and the relevant literature is more representative. Considering the emergence of digital technologies, their application in the shipping industry, and the growing global focus on decarbonization, we set the starting point of our data as 2005. To ensure the publication search is both precise and exhaustive, thereby preventing the omission of critical information or the inclusion of irrelevant publications, we employed a strategy of selecting keywords that effectively articulate and explore the role of digital technologies in decarbonizing shipping. We examined research through four distinct processes, including a preliminary evaluation of keywords, broadening the spectrum of keywords, removing extraneous terms, iterative refinement of search terms, and removing predatory references. The publication search process is shown in Figure 1. The search criteria are shown in Table 1.
Figure 1

Publication search process.
Table 1
| Parameter | WoS |
|---|---|
| Database | SCI-EXPANDED and SSCI |
| Range | 2005-2024 |
| Date | November 12, 2024 |
| Document Type | Journal article or review article |
| Search field | Title, abstract, and keywords |
| Search formula | TS= (“maritime” OR “shipping” OR “ship”) AND TS= (“decarboniz*” OR “emission” OR “low carbon” OR “sustainab*”) AND TS= (“digitalization” OR “digital technology” OR “Artificial intelligence” OR “AI” OR “big data” OR “blockchain” OR “Internet of Things” OR “IoT” OR “machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR “digital twin”) |
| Results | 201 |
Search criteria.
3.2 Bibliometric method
Bibliometrics is a field that elucidates scientific trends and structures via the quantitative analysis of literary data. This entails employing mathematical and statistical techniques to examine data in publications, including authors, keywords, and citations, to elucidate the distribution of scientific knowledge, collaborative networks, research hotspots, and trends (Dalle Lucca Tosi and dos Reis, 2020). Moreover, the advantage of bibliometrics compared to other literature review methodologies is its capacity to yield more objective and dependable outcomes, hence furnishing scholars with comprehensive insights into the evolution of a discipline (Wallin, 2005). Investigations in this domain can assist researchers, policymakers, and academic institutions in comprehending the dynamics of disciplines, evaluating research impact, and directing future research trajectories. Bibliometrics possesses diverse applications, enabling the evaluation of research production and impact of a country or institution, and the identification of research frontiers and seminal literature within a specific domain (Ninkov et al., 2022). Moreover, citation analysis enables bibliometrics to elucidate knowledge flows and the distribution pathways of scholarly concepts (Markus, 2003). The advancement of big data is propelling the evolution of bibliometric research methods. Bibliometric analysis has been employed across various industry sectors to detect research trends, difficulties, and possibilities within a certain topic (Muhuri et al., 2019). This publication aims to identify the current focal points of digital technology in shipping decarbonization applications via bibliometric analysis. To explore the research hotspots in the relevant field, we employed VOSviewer, a complimentary Java-based software created by the Centre for Technology Research at Leiden University in the Netherlands, to visualize and analyze countries, authors, and institutions, culminating (Bui et al., 2020).
3.3 Analytic measures
The H-index, or Hirsch index, quantifies the academic effect of an individual scholar, researcher, or research organization. Introduced by American physicist Jorge Hirsch in 2005, the fundamental concept of the H-index posits that a scholar’s H-index corresponds to the number of instances in which at least h of their publications have been mentioned no fewer than h times, while citations for any additional publication do not surpass h (Hirsch, 2005). The H-index possesses multiple advantages: firstly, it amalgamates the number of publications and citations of researchers, thereby reflecting their academic impact; secondly, the H-index exhibits relative stability, remaining unaffected by atypically high citations of individual publications, rendering it a more objective metric for academic assessment; lastly, the H-index is straightforward to comprehend and compute, contributing to its widespread application in academic circles. This review uses the H-index to evaluate the research performance of institutions and nations.
4 Results
4.1 Scientometric analysis
Analyzing the fluctuations in publication volume within a specific domain can elucidate the evolving patterns and focal points of research in that area (Adnan et al., 2023; Shi et al., 2023). The annual number of publications from 2015 to 2024 is shown in Figure 2. This review examines the trend in publications on digital technology used for decarbonizing shipping during the past decade. The writing on this topic commenced in 2015, with a single publication, which may be attributed to the fact that in the early 21st century, there were fewer studies on digital technologies such as AI in shipping due to the slow development of technologies such as AI (Xiao and Xu, 2024; Xiao et al., 2024b). Conversely, the total number of annual publications in 2023 is 55, representing a 54-fold rise in the overall count. The period from 2015 to 2020 marks the beginning of a growing publication volume within the discipline, culminating in the release of 28 publications. This results from the groundbreaking research conducted by scholars in this domain, including Gkerekos et al. (2019), who investigated the efficacy of various multiple regression algorithms for predicting the Fuel Oil Consumption (FOC) of a vessel using diverse data sampling frequencies. From 2020 to 2023, the quantity of publications in this domain increased substantially, by almost threefold. Furthermore, 45 publications in this domain were published between January and November 12, 2024, indicating a foreseeable increase. This signifies that an increasing number of scholars have focused on studying the application of digital technology in decarbonizing shipping in recent years.
Figure 2
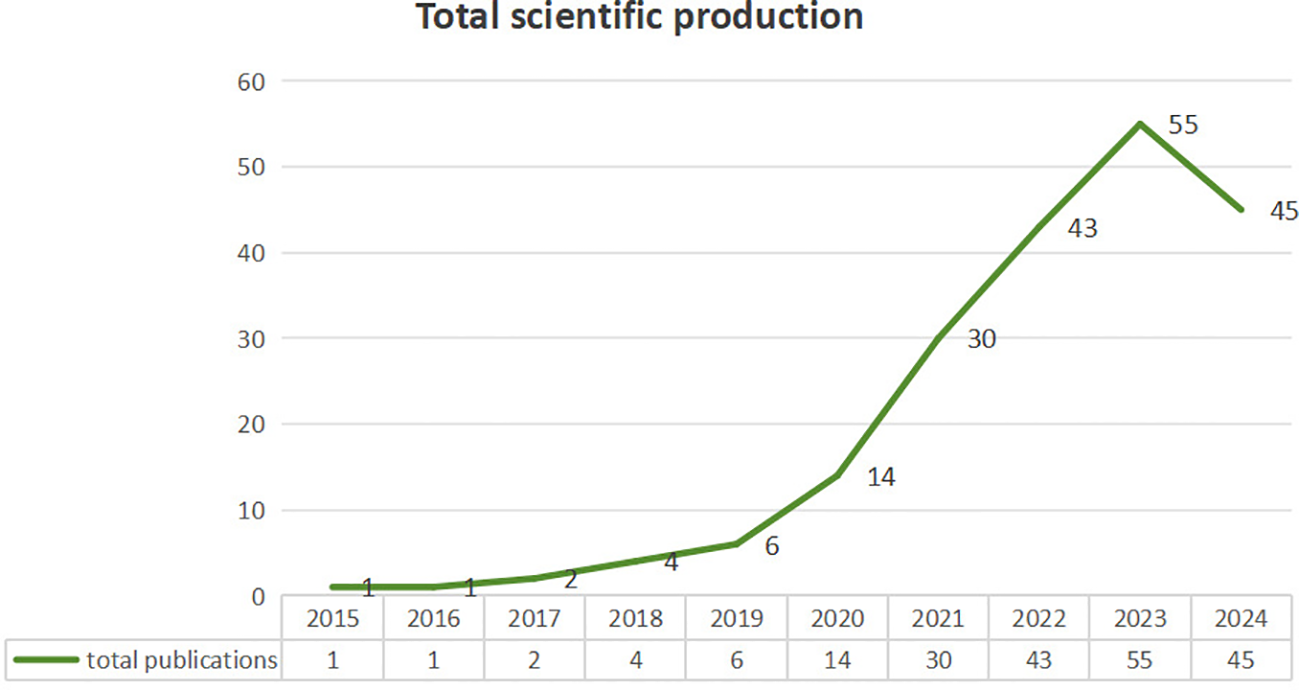
Annual number of publications and citations from 2015 to 2024. (The data were retrieved on November 12, 2024).
4.1.1 Journal analysis
This review comprises 201 publications published across 94 journals, with the ten most prolific journals detailed in Table 2, accounting for approximately 44.3% of the total publications. Among the examined fields, Sustainability is the journal with the most published publications, with 24 or 11.94% of the overall publications. Ocean Engineering published 21 publications, accounting for 10.45% of the total publications. This may suggest that they serve as a significant reference for scholars in this area. Moreover, Sustainability and Ocean Engineering are the most impactful journals for the H-index, each with an H-index of 8. In the most frequently cited paper in Sustainability, the authors present a methodology to enhance the AIS dataset by correcting and extending its features, focusing on using crbm to improve the prediction and clustering algorithms (Xiao et al., 2025). Nonetheless, the quantity of publications does not inherently correlate with the H-index; for instance, IEEE Access and Engineering Applications of AI published 4 and 3 publications, respectively, yet the latter possesses a higher H-index, suggesting that Engineering applications of Artificial Intelligence are more frequently cited within this domain.
Table 2
| Journal | Publications | Percentage (%) | H-index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | 24 | 11.94% | 8 |
| Ocean Engineering | 21 | 10.45% | 8 |
| Journal of Marine Science and Engineering | 13 | 6.47% | 6 |
| Energies | 6 | 2.99% | 4 |
| Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review | 6 | 2.99% | 4 |
| Ocean & Coastal Management | 5 | 2.49% | 4 |
| IEEE Access | 4 | 1.99% | 2 |
| Maritime Policy & Management | 4 | 1.99% | 2 |
| Applied Sciences-Basel | 3 | 1.49% | 2 |
| Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence | 3 | 1.49% | 3 |
Most productive journals.
4.1.2 Country analysis
Analyzing publishing data by country allows for assessing research contributions from each nation to the domain and collaboration among countries. From 2005 to 2024, 53 countries contributed to the SCI and SSCI databases. Table 3 enumerates the top ten countries based on publication volume, detailing the number of publications and their respective percentages, and the H-index of research from these nations, including China, the United Kingdom, the United States, Norway, Singapore, etc. The chart indicates that China leads in the number of publications within the domain, with 67 publications, followed by the UK with 15 and the US with 13. China has authored 33.33% of the total publications in this discipline, surpassing any other nation. In 2023, the most cited publication originated from China, presenting a machine learning approach utilizing AIS data, incorporating AADTW, SCAF, and an innovative route optimization algorithm for feature extraction and unsupervised route planning for Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS) (Li and Yang, 2023). It underscores China’s growing emphasis on augmenting innovation and competitiveness via technological progress and demonstrates China’s substantial contribution to the deployment of the domain, which may be attributed to three primary factors: First, governmental policy and fiscal assistance (Xiao and Cui, 2023). Second, the atmosphere for technical improvement and innovation. Third, industrial size and market demand. The table further illustrates the academic influence and quality of published publications by country through H-index, and SCI categorization of publications. China holds the top position in the H-index, boasting an H-index of 13 and 38 publications published in Q1 journals. The quantity of published publications is positively connected with the H-index (Hou and Wang, 2023).
Table 3
| Country | Publications | Percentage (%) | H-index | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 67 | 33.33% | 13 | 38 | 17 | 7 | 3 |
| England | 15 | 7.46% | 5 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| USA | 13 | 6.47% | 6 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Norway | 11 | 5.47% | 6 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Singapore | 11 | 5.47% | 6 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Spain | 11 | 5.47% | 6 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Croatia | 10 | 4.98% | 6 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 |
| Italy | 9 | 4.48% | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| South Korea | 9 | 4.48% | 4 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
| India | 8 | 3.98% | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
Most productive countries.
We employed VOSviewer to create a collaboration network of countries. Figure 3 illustrates the collaboration network of countries, predicated on a minimum of five publications per country, encompassing 18 items with a cumulative collaboration intensity of 108, organized into 9 clusters. In Figure 3, each item symbolizes a country, with its size reflecting the quantity of publications published in that nation. The connections among the items signify international collaboration, while the thickness of the links reflects the quantity of joint publications. The dimensions of the items indicate that China is the nation that has produced the most publications. Thirteen countries partnered with China, resulting in a total collaboration intensity of 24. Subsequently, the UK has 13 cooperating countries with a total collaboration intensity of 8, while Denmark has 11 participating countries with the same intensity of 8. Based on the chain’s thickness, China and the United States exhibit the most robust collaboration, with a collaboration intensity of 4. However, several countries including Greece, Spain, and Italy exhibit fewer publications and collaborative engagement with other nations. Additionally, several countries, such as South Korea and Scotland, appear to be isolated from the collaboration network.
Figure 3

Cooperation network of countries (From: VOSViewer).
The overall participation in the collaboration network is limited. While the countries involved have engaged in collaboration, the degree of cooperation remains minimal, with most countries exhibiting limited interactions with others. The reasons for this may be twofold: first, the disparate levels of technological advancement, and second, variations in policies and regulations. Proposed enhancement strategies may encompass, firstly, the creation of a global collaboration platform to facilitate information exchange, technology dissemination, and collaborative research among nations in the domain of shipping decarbonization. Secondly, international organizations and governments can unify maritime decarbonization policies and diminish barriers to collaboration through conversation and consultation. Thirdly, co-financing research initiatives through global collaborative projects and funding, as well as co-financing research and development on maritime decarbonization technology.
4.1.3 Author analysis
The authors’ analysis was executed in two manners: the first emphasizes the most prolific contributors to digital technologies within the decarbonizing shipping through Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI), while the second delineates the collaboration links among authors via collaboration networks. Table 4 enumerates the ten most impactful authors in the domain. Li has five publications and is the most prolific author among these researchers. He is succeeded by Sun (4 publications) and Lam (4 publications). Li possesses an FWCI of 2.58, which indicates his citation impact exceeds the global average by 158 percent, representing the highest metrics among the top ten authors. The publications by leading authors primarily concentrate on optimizing ship speed, planning ship routes, predicting ship emissions, and enhancing FCP efficiency. Researchers mostly employ machine learning for ship speed optimization analysis (Li et al., 2022, 2024a). In ship route planning research, authors mostly employ digital twins (Vasilikis et al., 2023). In ship emission prediction research, researchers predominantly utilize Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), multi-task learning, Artificial Neural Network (ANN), AIS, machine learning, and blockchain (Cao et al., 2021; Pu and Lam, 2021; Kurchaba et al., 2022, 2023; Feng et al., 2024; Kurchaba et al., 2024). Researchers mostly employ machine learning to examine FCP optimization (Xie et al., 2023b).
Table 4
| Author | Publications | Percentage (%) | FWCI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xiaohe Li | 5 | 2.49% | 2.58 |
| Baozhi Sun | 4 | 1.99% | 0.56 |
| Jasmine siu lee Lam | 4 | 1.99% | 2.28 |
| Evangelos Boulougouris | 3 | 1.49% | 1.36 |
| Irmina Durlik | 3 | 1.49% | 1.88 |
| Qinyou Hu | 3 | 1.49% | 0.88 |
| Solomiia Kurchaba | 3 | 1.49% | 1.55 |
| Yong Li | 3 | 1.49% | 0.82 |
| Zhengjie Liu | 3 | 1.54% | 1.64 |
| Qiang Mei | 3 | 1.54% | 0.88 |
Most productive authors.
We used VOSviewer to create an author collaboration network to examine the partnerships among authors in the domain (Waltman et al., 2010). Figure 4 illustrates the collaboration network among authors, comprising 39 items and 5 clusters. Each item represents an author, with the size denoting the quantity of publications produced by that individual. The connections among the items signify the collaboration between authors, while the thickness presents the strength of their collaboration. The hue of the objects illustrates the outcomes of the clustering, with elements sharing the same color (i.e., authors), indicating affiliation to the same study team. For example, the research team of Li and Sun specializes in ship speed optimization and FCP prediction (Li et al., 2022; Xie et al., 2023b, 2023; Li et al., 2024a). Furthermore, the cluster distribution in Figure 4 reveals a higher frequency of connections within clusters, alongside some inter-cluster connections; however, there is insufficient contact among authors from disparate l. The potential reasons for this include, firstly, that research on the domain remains in its developmental phase, characterized by limited collaboration within research teams and insufficient exploration of inter-team cooperation. Secondly, there is a disparity in professional expertise, which may result in challenges to interdisciplinary communication. Thirdly, there may be inadequate avenues for collaboration among authors from diverse research fields due to geographic limitations, institutional restrictions, or insufficient conference engagement. To resolve the abovementioned issues, three strategies may be implemented: facilitate multidisciplinary seminars and workshops, create a collaborative research fund, and enhance the development of academic communication platforms.
Figure 4
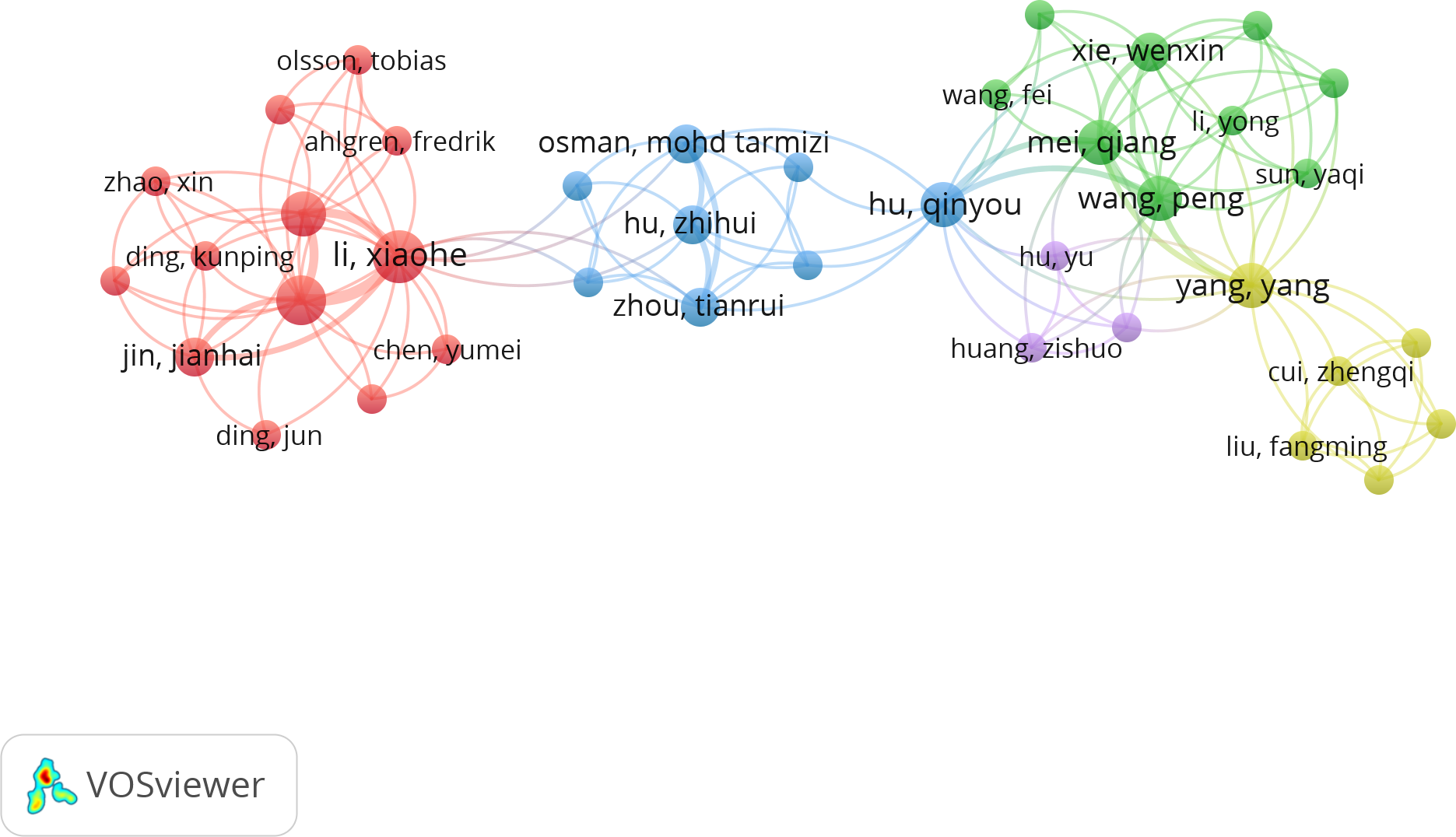
Cooperation network of authors (From: VOSViewer).
4.1.4 Institution analysis
The institution analysis is performed in two manners: the first identifies the most prolific institutions facilitating the domain, and the second delineates the collaborative relationships among institutions via collaboration networks. The 201 publications were published by 337 institutions. Table 5 enumerates the ten most productive institutes in research. Seven publications originate from China, while the remaining three are from the UK (University of Strathclyde), Singapore (Nanyang Technological University), and India (Indian Institute of Technology). Dalian Maritime University and Shanghai Maritime University were rated highest among these universities, with 11 publications and an H-index of 4, indicating they have significantly contributed to the advancement of the domain. Despite publishing only eight publications in this domain, Nanyang Technological University achieved the highest H-index, indicating the institution’s exemplary research quality in applying digital technology within the decarbonizing shipping.
Table 5
| Institution | Publications | Percentage (%) | H-index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dalian Maritime University | 11 | 5.47% | 4 |
| Shanghai Maritime University | 11 | 5.47% | 4 |
| Nanyang Technological University | 8 | 3.98% | 5 |
| Harbin Engineering University | 7 | 3.48% | 4 |
| Wuhan University of Technology | 7 | 3.48% | 4 |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | 6 | 2.99% | 2 |
| University of Strathclyde | 6 | 2.99% | 4 |
| Hong Kong Polytechnic University | 5 | 2.49% | 4 |
| Indian Institute of Technology | 5 | 2.49% | 1 |
| South China University of Technology | 5 | 2.49% | 2 |
Most productive institutions.
We used VOSviewer to create a collaboration network of institutions to examine their partnerships in the domain. Figure 5 illustrates the collaboration network of institutions, comprising 49 items and 7 clusters, with a minimum document threshold of 2 and a total connection strength of 268. In Figure 5, each item denotes an institution, and the size reflects the quantity of publications. The connections between items signify institutional collaboration, while the thickness of the links reflects the intensity of this collaboration. The size of publications indicates that Dalian Maritime University is the leading university in publication output, it also cooperated with ten universities, resulting in a total collaboration intensity of 10. Nonetheless, regarding link strength, Dalian Maritime University’s collaboration with all ten partner universities is relatively weak. This may be attributed to the geographical remoteness of Dalian Maritime University from other universities, hindering ongoing academic exchanges; conversely, Dalian Maritime University may choose to foster tighter collaboration within. The Chinese Academy of Sciences partnered with seven universities, achieving a total collaboration intensity of 13, the highest ranking. The Chinese Academy of Sciences engaged in a more profound collaboration with both Beijing University of Technology and Jimei University.
Figure 5
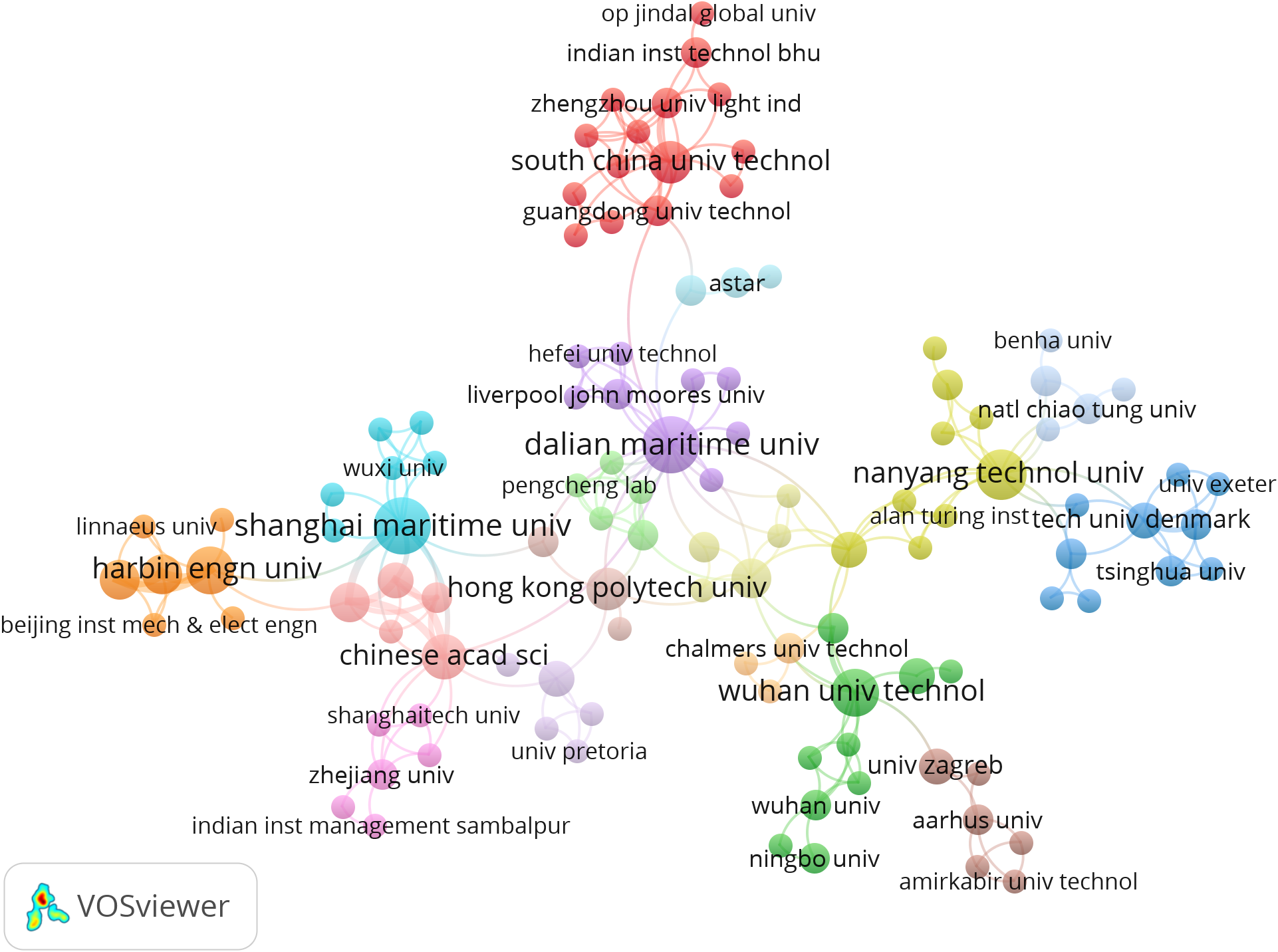
Cooperation network of institutions (From: VOSViewer).
4.2 Co-occurrence analysis
Co-occurrence analysis is a content analysis method that accurately represents the intensity of correlation between information items in textual data (Wang et al., 2012). The co-occurrence of literature terms is studied to assess the intensity of association among keywords and ascertain the composition, research focus, and future trends. We employed VOSviewer to create the keyword co-occurrence network, depicted in Figure 6. Keyword co-occurrence denotes the concurrent emergence of two keywords; each item signifies a keyword, with larger nodes indicating a higher frequency of keyword occurrence. The proximity between two elements (i.e., keywords) signifies the intensity of their relationship, with a reduced distance reflecting a more robust association. The color of the items signifies the clustering outcomes, with items sharing the same color denoting membership in the same cluster. This keyword co-occurrence network has five distinct clustering groups, as Figure 6 illustrates, which results in five distinct domains.
Figure 6
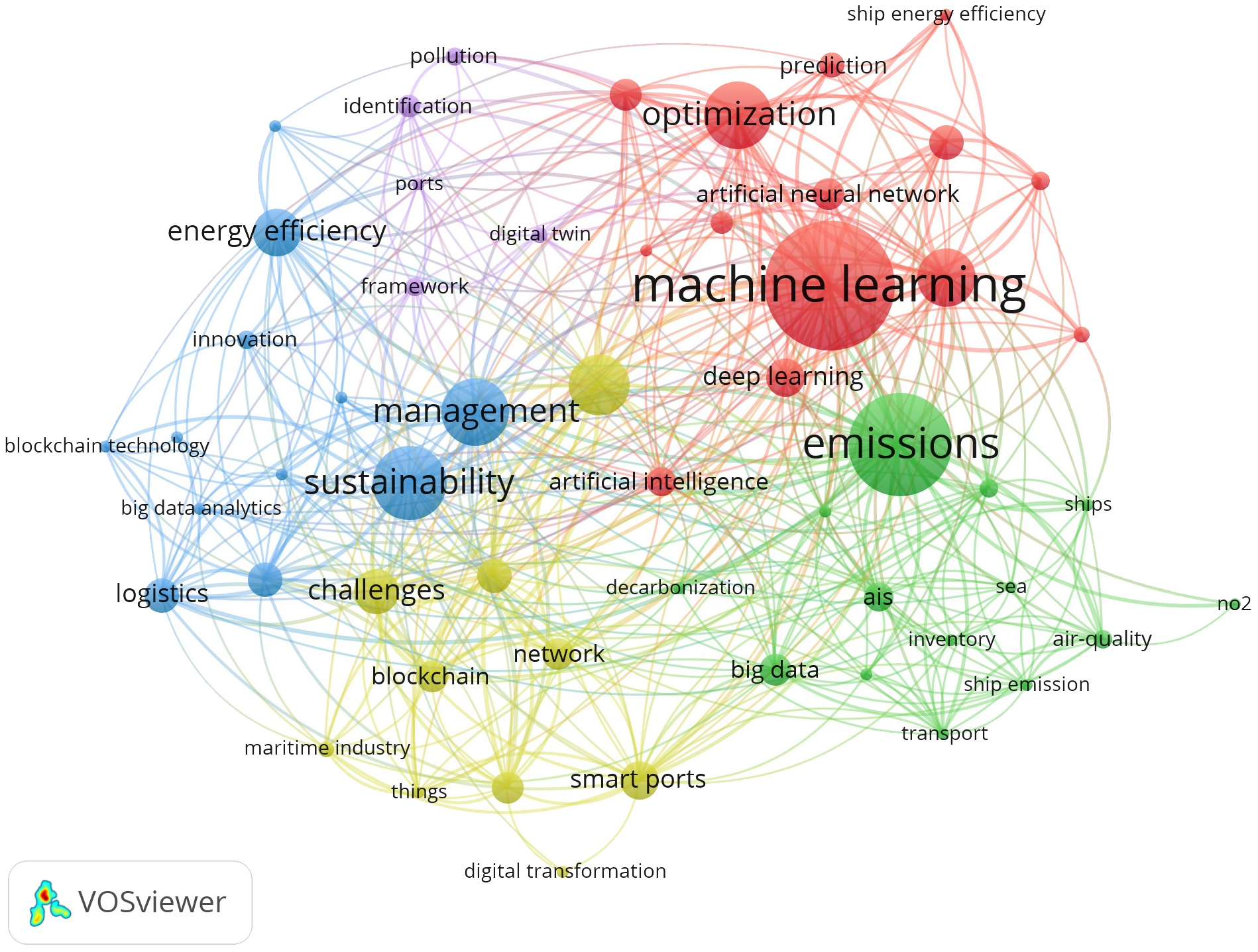
Keyword co-occurrence network (From: VOSViewer).
Figure 7A depicts the application of digital technology in optimization, and prediction, encompassing ship speed optimization, trim optimization, oil consumption forecasting, energy consumption forecasting, and hull design. Emissions from vessels in seaports are progressively eliciting concerns regarding environmental sustainability. Precise emission forecasts can facilitate the monitoring and resolution of this issue, hence enhancing the sustainability of maritime transportation (Liu et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024a). To attain optimal environmental sustainability, the selected energy technology on board must be integrated with the operational mode within specified limits, such as routes, operations, and speed (Elg et al., 2023). In this domain, machine algorithms have been utilized most frequently, with 40 instances, links to 40 keywords, and an overall cooperation intensity of 107, the highest among all keywords. Due to their significance, we enumerated the applications of machine learning and deep learning in Table 6. Simultaneously, machine learning, optimization, speed optimization, prediction, and oil consumption prediction have connection strengths of 8, 7, 4, and 7, respectively, making them the most interconnected keywords to these four terms.
Figure 7
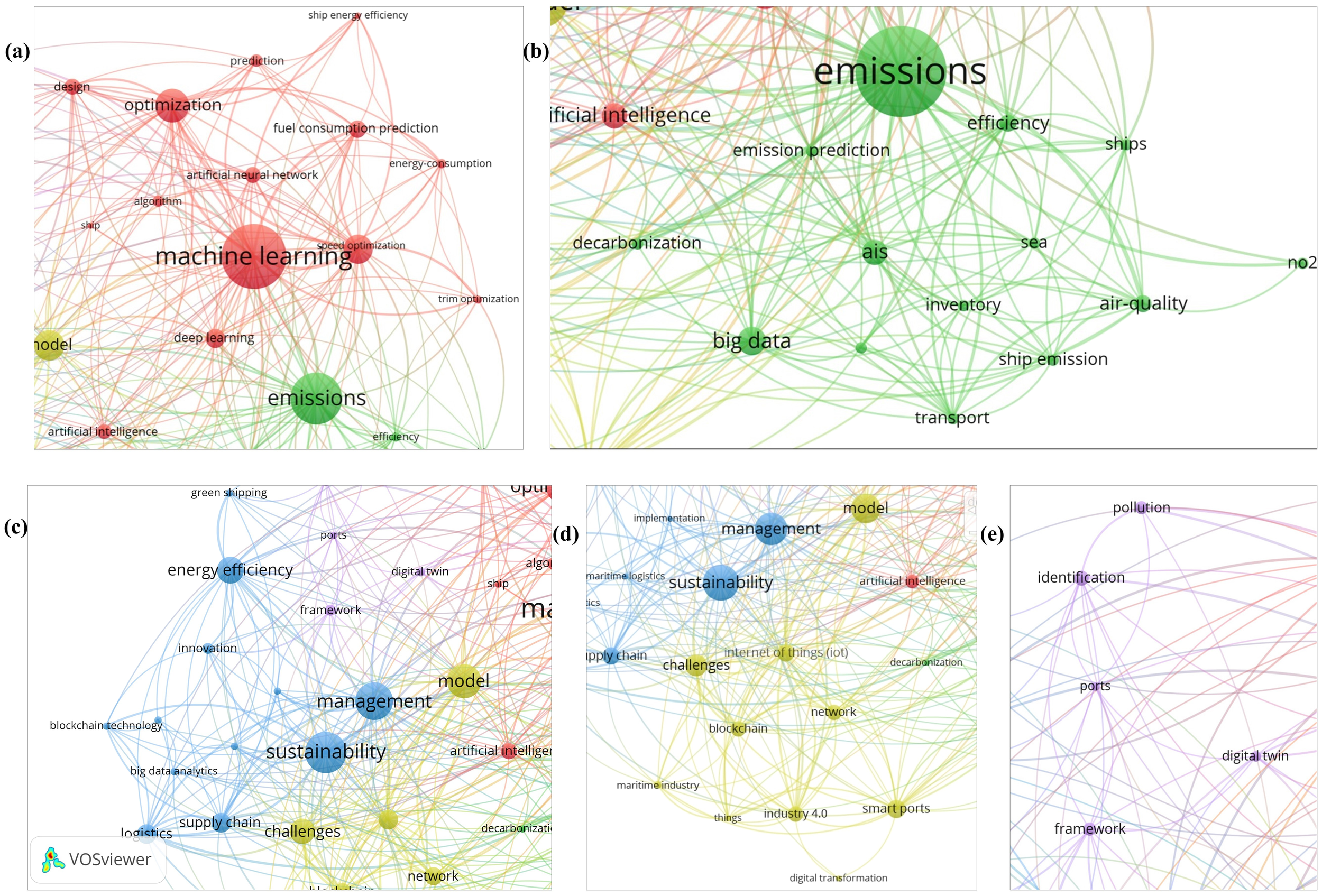
Clusters of keyword co-occurrence network. (A) represents the application of optimization and prediction. (B) represents the application of emission prediction. (C) represents the application of logistics management and supply chain management. (D) represents the application of ship FCP model. (E) represents other applications (From: VOSViewer).
Table 6
| Application | Method Description | Application Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCP estimation | A data-driven machine learning model based on real-time monitoring of intergranular air temperature, Relative Humidity (RH), and CO2 concentration to predict soybean quality during bulk transport. | For predicting the FCP of a ship’s main engine. | Jaques et al. (2023) |
| A combination of Monte Carlo (MC) simulation methods and ANN was applied to develop a probabilistic model based on machine learning techniques. | Main diesel engine FCP prediction for bulk carriers from launch to current state. | Tran (2021) | |
| A machine learning-based classification model to identify operational phases by analyzing motion behavior-related and geospatial feature-related features in AIS data. | Used to improve the accuracy of emission estimates. | Duan et al. (2024) | |
| The algorithmic model based on ridge regression was developed through data fusion techniques, combining dynamic information of the ship and meteorological conditions. | For automatic estimation of carbon emissions and FCP of container ships under different weather conditions during the voyage. | Ren et al. (2022) | |
| An FCP model is proposed using machine learning algorithms, in particular, XGBoost regression models. | For predicting the FCP of Very Large Crude Carriers (VLCCs). | Papandreou and Ziakopoulos (2022) | |
| Developed a black-box model based on machine learning and a white-box model based on mathematical methods and also used Kwon’s formula as a data preprocessing cleaning method for the black-box model. | For predicting FCP rates of ships. | Xie et al. (2023b) | |
| A model for predicting FCP and carbon emissions using operational data from dual-fuel-propelled ships is presented. | For predicting FCP and carbon emissions. | Lee et al. (2024) | |
| Machine learning techniques, particularly back propagation neural networks (BPNN) and Gaussian process regression (GPR), predicted the FCP of ships under the influence of different marine environmental factors. | For predicting FCP in different marine environments. | Hu et al. (2019) | |
| A Near Real-Time (NRT) carbon accounting framework that combines key factors such as ship sailing characteristics, weather, and sea state, which utilizes machine learning models to enable carbon emissions tracking at 15-minute intervals. | For accurate carbon accounting. | Li et al. (2024b) | |
| Established a pilot-scale experimental platform for solvent-based SBCC and developed a carbon capture model based on it | For reducing GHG emissions in the marine transportation. | Wang et al. (2024) | |
| Air quality monitoring | A machine learning tool for predicting local pollutant concentrations. | For estimating the impact of port and cruise ship traffic on urban air quality. | Dai et al. (2023) |
| energy management | An Approximate Model Predictive Control (AMPC) based real-time energy management strategy for hybrid energy ships. | Real-time operation for energy management of hybrid energy vessels. | Gan et al. (2022) |
| Development of a mathematical relationship using simple linear regression, polynomial regression, K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) regression, and Gradient Booster (GBM) regression algorithms to estimate engine power based on the length (L), gross tonnage (GT), and age of the vessel. | Estimated main and auxiliary engine power for new vessels. | Okumus et al. (2021) | |
| An FCP prediction model using machine learning techniques such as Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest, Extra Tree, Gradient Boosting, Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), and CatBoost. | For reducing energy consumption. | Melo et al. (2024) | |
| Ship speed optimization | A comprehensive optimization methodology that takes into account speed, aspect, and speed-aspect adjustments for different loading conditions to achieve minimized FCP over the entire voyage. | For optimizing the ship’s courier and longitudinal inclination to reduce the ship’s FCP. | Xie et al. (2023a) |
| route planner | A machine learning approach to feature extraction and unsupervised route planning for MASS using AADTW, SCAF, and a new route optimization algorithm based on AIS data. | Optimal routes for simulating different types of vessels in complex traffic waters. | Li and Yang (2023) |
| ship emissions estimation | Four machine learning algorithms, lasso regression, support vector machine, extreme gradient enhancement, and ANN, were introduced to predict ship-related BC emissions. A prediction model was developed using datasets of similar ship engines under different steady-state conditions. | For predicting BC emissions from ships. | Sun et al. (2022) |
| Predicting GHG emissions from peanut supply chains, including those from maritime transportation, by applying Machine Learning-Based Predictive Modeling (MLPM) using FAOSTAT and EDGAR databases. Moreover, building smart contracts on Hyperledger Fabric to secure predictive analytics against fraud. | For predicting GHG emissions in the peanut supply chain. | El Hathat et al. (2024) | |
| A shipping emissions inventory model that incorporates machine learning tools. | For estimating gas emissions. | Fletcher et al. (2018) | |
| A model for estimating FCP and emissions of ships based on hydrodynamic modeling of ships and machine learning techniques using information from AIS, ship information databases, and met ocean data. | Estimating ship FCP at high computational speeds using machine learning techniques to assess new measures to reduce GHG emissions. | Guo et al. (2022) | |
| ship detection | Combining machine learning models and TROPOMI satellite data, an automated and scalable method was developed to select potentially non-compliant ships by predicting the amount of NO2 expected to be produced by a ship in a given atmospheric condition to determine the value of the ship’s inspection. | Automated and scalable options for potentially non-compliant ships. | Kurchaba et al. (2023) |
Application of machine learning relevant to decarbonizing shipping.
Figure 7B emphasizes the application of digital technology in maritime emissions, encompassing emission prediction, inventory management, and air quality assessment (He et al., 2022). Considering global warming, effectively measuring and reducing ship emissions has emerged as a significant problem for the transportation industry and society. In recent years, a significant advancement in emission accounting has arisen, specifically using big data, particularly data derived from AIS (Yin et al., 2021).
Figure 7C emphasizes the application of digital technologies in logistics and supply chain management, encompassing ship energy efficiency optimization and emission forecasting, using technologies such as blockchain, big data, and machine learning. Maritime supply chain management is critical to ensuring the smooth flow of global trade, reducing transport costs, and improving logistics efficiency (Xu et al., 2021, 2022). For instance, Perera, etc. introduced a Machine Intelligence (MI)-based data processing framework for ship performance and navigation data to formulate suitable navigation strategies (Perera and Mo, 2017).
Figure 7D emphasizes model development and optimization, centering on the ship FCP model, which incorporates digital technologies, including blockchain, IoT, machine learning, and AIS. The FCP in ships is crucial to decarbonization initiatives, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing GHG emissions from international shipping (Nguyen et al., 2023). Figure 7E illustrates additional applications of digital technology in carbon reduction within shipping, encompassing ship-port interfaces, identification systems, and route optimization.
A burst keyword is a phenomenon where a keyword exhibits a high frequency of occurrence within a designated timeframe. This information illustrates the history of research hotspots, indicates recent research trends, and aids in forecasting future research directions (Lyu et al., 2023). To better understand the evolution of research trajectories, the burst word analysis is presented in Table 7. The years during which the 12 burst words emerged are 2016–2024. The term “algorithm” emerged as a prominent buzzword from 2016 to 2018. Oil depletion, environmental change, condition monitoring, and blockchain have been extensively examined since 2020. Air quality, AIS, and autonomous ships emerged as prominent research topics in 2021–2022. Since 2022, ANN, speed optimization, and neural networks have emerged as prominent research focal points.
Table 7
| Keywords | Year | Strength | Begin | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | 2016 | 1.65 | 2016 | 2018 |
| Optimization | 2018 | 0.98 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Big data analytics | 2019 | 0.83 | 2019 | 2021 |
| FCP | 2020 | 2.37 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Climate Change | 2020 | 1.41 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Condition monitoring | 2020 | 0.95 | 2020 | 2022 |
| AIS | 2021 | 1.56 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Air quality | 2021 | 1.34 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Autonomous ship | 2021 | 0.78 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Neural network | 2022 | 1.57 | 2022 | 2024 |
| Speed optimization | 2018 | 1.19 | 2022 | 2024 |
| ANN | 2021 | 0.87 | 2022 | 2024 |
Top 12 keywords with the strongest citation bursts.
5 Analysis of research gaps and future research directions
The bibliometric analysis indicates that digital technology enhances the efficiency, intelligence, and sustainability of shipping decarbonization. While advancements in this domain have accelerated in recent years, several challenges remain to be resolved. This review delineates three research focal points in shipping decarbonization, derived from keyword co-occurrence, burst word analysis, and literature review: speed optimization, emission prediction, and autonomous ships. This section emphasizes three recent developments and examines their associated difficulties and opportunities.
5.1 Speed optimization
The relationship between FCP and speed is not linear. FCP is considered to be proportional to the third power of the ship’s speed, so a small decrease in speed implies a significant decrease in FCP (Alvarez et al., 2010; Fagerholt et al., 2010). Shipping companies have widely used digital technology for speed optimization. For example, global shipping company Maersk uses a speed optimization system based on big data and machine learning, which has helped Maersk reduce FCP by about 10-15% on several routes (Luo et al., 2024b). Several researchers have offered valuable insights and technical solutions through various methodologies and viewpoints in speed optimization, they have continued to refine their research from the perspective of using weather archive data and route segmentation methods and combining longitudinal inclination optimization. Kim and Lee (2018) centered on employing Dynamic Programming (DP) techniques to develop speed adjustment strategies for ships, targeting energy conservation and emission reduction by efficiently managing external factors. Their research integrated AIS data with marine environmental data through MapReduce to analyze and quantify speed variations caused by external factors. Previous literature has included theoretical FCP functions in speed optimization models; however, these functions are constrained by meteorological circumstances encountered during navigation. Lee et al. (2018) adopted an alternative strategy by creating a decision support system to enhance speed by integrating weather archive data and a Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) methodology. Li et al. (2022) utilized the route segmentation approach to develop a machine-learning model for predicting FCP and shaft speed. They introduced an iterative strategy for optimizing route segmentation, weather loading, and speed. (Xie et al., 2023a) integrated the FCP prediction model from the prior study. They introduced optimization techniques for speed, longitudinal gradient, and nodes across various wind and wave conditions in each segment.
Summary and prospects: Speed affects only a quarter of total supply chain costs, but it impacts half of delivery times and more than 70% of the carbon footprint. To reduce ship emissions, scholars have proposed rational control of ship speed, acceleration, engine speed, and torque (Fan et al., 2024). Future research directions of digital technology in speed optimization can focus on the in-depth exploration of multi-objective optimization methods, such as real-time balance between economic benefits and environmental impacts by introducing dynamic weight adjustment strategies (Li et al., 2024a). In addition, the FCP prediction model is optimized by combining more advanced machine learning techniques to improve prediction accuracy and adaptability. Intelligent algorithms are further developed to solve multivariate dynamic speed optimization problems in complex environments, such as integrating wind and wave conditions, shiploads, and route adjustments. At the same time, practitioners and people who develop digital technologies can promote deeper integration between digital technologies, such as synergizing machine learning with IoT, big data analytics, and real-time sensing technologies to enhance comprehensive optimization capabilities. Finally, global optimization methods based on big data and real-time information processing are explored to provide more efficient solutions for ship decarbonization.
5.2 Emission prediction
The shipping industry, a significant contributor to GHG and pollutant emissions, has garnered international attention about emission reduction due to the escalating global concern over climate change and environmental protection (Xiao et al., 2023; Luo et al., 2024a). In the area of emission prediction, researchers have used techniques such as machine learning and big data to improve their research in terms of optimization of prediction models, data sources, and expansion of prediction methods.
Initially, researchers created numerous machine learning models to enhance predictive accuracy regarding emission prediction. Ren et al. (2022) developed an algorithmic model based on ridge regression through data fusion techniques, combining dynamic information of the ship and meteorological conditions. Papandreou and Ziakopoulos (2022) developed an FCP model using machine learning algorithms, especially XGBoost. Some researchers also improved the study by combining machine learning, big data, and neural networks, in terms of optimizing the FCP prediction model, and data sources and extending the prediction methods. Hu et al. (2019) developed machine learning to predict the FCP of ships under the influence of different marine environmental factors, in particular Back Propagation Neural Networks (BPNN) and Gaussian Process Regression (GPR). Tran (2021) applied a combination of Monte Carlo (MC) simulation methods and ANN to develop a probabilistic model based on machine learning, for main diesel engine FCP prediction. Using meteorological data and machine learning, Jaques et al. (2023) developed a ridge regression-based algorithmic model to automate FCP estimation under different weather conditions through data fusion techniques, combining the ship’s dynamic information and meteorological conditions. Cao et al. (2021) suggested a methodology that integrates optical remote sensing with deep learning approaches to forecast pollutant concentrations and assess fuel sulfur content by analyzing ship exhaust plume images. He et al. (2022) devised a rapid approach utilizing data panning, which markedly enhances the computing efficiency of emission dispersion concentrations from many vessels over extended durations and distances while maintaining accuracy. Nonetheless, these publications have also uncovered several hurdles to emission reduction within the maritime sector. The initial issue is the quality and accessibility of data. Su et al. (2024) demonstrated that the CatBoost algorithm excelled in estimating the FCP of PCTC ships, although random forests or neural networks may be more appropriate in alternative investigations. The research conducted by Yuan et al. (2024) uncovered the unintended consequences of emission reduction strategies, including the IMO 2020 fuel sulfur regulation, which may exacerbate global warming even as air quality improves, indicating the necessity for a thorough evaluation of the long-term effects of such measures.
Summary and prospects:
-
Model improvement and data integration. Developers should integrate more diverse data sources into emission prediction models, such as fuel price fluctuations, port operating practices, and regulatory changes, among other external factors. For example, Duan et al. (2024) introduced a Random Forest-based approach to improve the accuracy of emission estimation by examining the AIS data of a ship to determine the ship’s operational phase. Meanwhile, the study is extended to more ports and ship types to address the limitations of current models in specific contexts.
-
Selection and optimization of intelligent algorithms. Practitioners should select appropriate machine learning algorithms based on specific application scenarios. For example, Su et al. (2024) mentioned that CatBoost performs well in certain prediction tasks, while random forests or neural networks may be more suitable for complex alternative surveys. Developers should continuously explore the performance advantages of different algorithms and optimize parameter settings to improve accuracy.
-
Emerging technology applications. Practitioners and developers can adopt various technological measures and business strategies, especially SBCC, which is considered a viable way to reduce emissions in the future. For example, Wang et al. (2024) Established a pilot-scale experimental platform for solvent-based SBCC and developed a carbon capture In addition, real-time carbon accounting technologies that integrate with digital technologies are also noteworthy, as Li et al. (2024b) developed an NRT carbon accounting framework that combines key factors such as ship sailing characteristics, weather, and sea state.
-
Blockchain technology is introduced into smart emission monitoring systems. Blockchain technology (e.g., Hyperledger Fabric) is used to achieve transparency and traceability of emission data and enhance data management efficiency. Practitioners can verify the authenticity of the predicted data through the blockchain platform, providing a reliable basis for regulation and decision-making. For example, Elsisi et al. (2024) proposed an IoT architecture that integrates deep learning and signal processing technologies to monitor ship emissions in real time while also resisting cyber-attacks.
5.3 Autonomous ship
Autonomous ships can significantly reduce shipping carbon emissions by optimizing operations to improve fuel efficiency while integrating alternative power systems such as methanol and electricity (Yan et al., 2024). These technologies have demonstrated clear environmental and economic advantages in short- and medium-haul routes. In light of the swift advancement of the global transportation sector and increasing apprehensions regarding climate change, the marine industry is diligently investigating alternative energy sources and using innovative technology to improve safety efficiency and facilitate decarbonizing shipping (Xiao et al., 2024a; Xiao and Xu, 2024). Autonomous ships and navigation facilitated by digital technology have emerged as a prominent research focus. In this area, the study advances from optimizing the establishment and optimization of alternative fuel and power systems, efficient communication systems, and precise navigation systems.
Jovanovic et al. (2022) studied the feasibility of unmanned ro-ro passenger ships in the Adriatic Sea region, analyzing the life cycle, environmental, and economic performance of three ships on short, medium, and long routes. They found that combining automation with alternative fuels can bring environmental and economic benefits in specific cases. Of these, methanol-powered and electric vessels perform best. In addition, the economic advantages of automated vessels are affected by the price volatility of fossils and alternative fuels, highlighting the environmental advantages and economic uncertainties in the development of autonomous vessels. The enhancement of marine communication systems has emerged as a critical concern concurrent with the advancement of autonomous ships, and it is this challenge that the research by Jurdana et al. (2021) offers a unique solution to. These systems help to optimize route and traffic management by supporting real-time navigation, monitoring, and operational control of autonomous vessels, thereby reducing FCP. Current maritime communication systems encounter limitations, including low data rates, high costs, and restricted capacity, particularly in the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) and AIS. Jurdana et al. proposed a variable record length data compression technique utilizing differential binary coding to mitigate this issue. This approach accomplished compression by transmitting solely the data items that have altered since the previous transmission, thus markedly diminishing the volume of data sent. A recent publication examines the enhancement of route planning and navigational safety for MASS in maritime environments. Li and Yang (2023) introduced a machine learning methodology leveraging AIS data, employing AADTW, SCAF, and a novel route optimization algorithm for MASS to facilitate feature extraction and unsupervised route planning. The strategy significantly enhanced route planning for real-time collision avoidance by emphasizing safety at critical hotspots at intersections of established routes through a temporal analysis approach.
Summary and prospects: These publications indicate several critical avenues for the advancement of autonomous ships:
-
Route planning and navigation safety optimization. Current research has applied AIS data and advanced machine learning techniques (e.g., AADTW and SCAF) to develop models for simulating optimal routes in complex waters. For example, the route optimization algorithm based on AIS data proposed by Li and Yang (2023) has been able to extract features and implement unsupervised route planning in real scenarios.
-
Autonomous ship energy efficiency and emission control. At this stage, there are already technology applications for energy efficiency optimization of autonomous ships. For example, (Su et al., 2024) showed that by combining the CatBoost algorithm and the FCP Prediction model, it is possible to optimize the speed and energy consumption of autonomous ships in real navigation. In addition, specific studies targeting alternative energy sources (e.g., electric boats and methanol fuels) have shown significant environmental and economic advantages in selected routes.
-
Maritime communications and navigation systems. Maritime communication and data compression technologies have specific improvement programs, such as the differential binary coding method proposed by Jurdana et al. (2021)has significantly reduced the amount of data transmission in AIS and GMDSS systems. This technique is currently being deployed in selected pilot projects to support the real-time communication and monitoring needs of autonomous ships.
-
Ship electrification and green design. Existing research on ship electrification and green design has achieved initial practice. Retrofitting of methanol-powered vessels has also demonstrated the practical feasibility of alternative energy technologies.
In addition, Given the increasing global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions, changes in relevant policies and regulations will play a substantial role in shaping the trajectory of decarbonization efforts within the shipping industry (Chen et al., 2023, 2024b). The IMO has implemented several regulations to reduce the carbon footprint of maritime transportation. Two important emission regulations are the EU Monitoring, Reporting and Verification (EU-MRV) and the IMO Data Collection System (IMO DCS), both of which are part of the Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) (Kanberoglu and Kökkülünk, 2021). To reduce CO2 emissions, the Chinese government has established a carbon trading mechanism that allocates free emission allowances to industrial companies, while companies exceeding the emission allowances are not allowed to use CO2 in their operations (Wang et al., 2023). Researchers should continually monitor and incorporate these evolving policies to ensure that their findings are both consistent with market demand and relevant to regulatory expectations.
6 Conclusions
This review offers a thorough assessment and analysis of digital technology applications in decarbonization within the shipping industry using a bibliometric methodology. Utilizing the SCI-EXPANDED and SSCI databases, 201 publications published between 2005 and 2024 were gathered through bibliometric methods to elucidate the prevailing challenges and opportunities in the domain, alongside the current status and trends regarding the application of digital technologies in decarbonizing shipping. The review commences with an exposition of the data collecting and research technique, followed by an examination of collaboration among countries, institutions, and authors through annual publication patterns and collaboration network analysis. The review revealed a substantial increase in research publications regarding the application of digital technologies in shipping during 2015, signifying heightened interest in this field. Journal studies indicate that publications like Sustainability, Ocean Engineering, and the Journal of Marine Science and Engineering have disseminated numerous works in this domain, potentially establishing a significant academic stance about the employment of digital technology in decarbonizing shipping. The survey identified China, the UK, and the US as the primary contributors to research in this domain, with China significantly ahead, indicating its prominence and impact in the research of decarbonization technology for shipping. Nonetheless, international collaboration in this domain has not attained the requisite intensity and requires enhancement and reinforcement in forthcoming research initiatives. Specific measures can be implemented to enhance international collaboration, including the creation of an international cooperation platform, the alignment of policies and regulations, and the joint funding of research initiatives. The authors’ analysis indicates that Li, Sun, and Lam possess the highest research outputs, concentrating on ship speed optimization, route planning, emission prediction, and FCP optimization. These publications demonstrate that machine learning and deep learning methodologies are crucial. Institution analysis indicates that Dalian Maritime University, Shanghai Maritime University, and Nanyang Technological University are leading research on shipping decarbonization. Examining the collaboration networks among these institutions indicates that while certain partnerships exist, the overall degree of collaboration is weak. Strategies to mitigate this phenomenon encompass promoting interdisciplinary seminars and workshops, creating collaborative research funds, and improving academic communication platforms.
Co-occurrence analysis of keywords elucidates the research focal points in shipping decarbonization, encompassing optimization, forecasting, design, emission prediction, logistics management, supply chain management, and ship FCP modeling. Machine learning and deep learning are the predominant digital technologies employed in shipping decarbonization. In addition, this publication examines the developmental trajectory of exploding words in pertinent domains by exploded word analysis and identifies that ANN, speed optimization and neural networks are current research focal points. This publication identifies three research hotspots in shipping decarbonization: speed optimization, emission prediction, and autonomous ships, based on keyword co-occurrence, exploded word analysis, and literature review. The discourse encompasses advancements, challenges, and opportunities in speed optimization, emission prediction, and autonomous ship, along with potential avenues for future research.
This review’s findings offer significant insights for researchers in shipping decarbonization and indicate directions for further research. However, this publication has limitations, as it exclusively focused on SCI-EXPANDED and SSCI inside the WoS database for literature collection, potentially constraining the range and diversity of the scholarly publications acquired. As digital technology progresses and applications broaden, future research is expected to investigate a more extensive array of keywords and search methodologies to capture the research dynamics and trends within the discipline.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
GX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52472323, and Beijing Natural Science Foundation, grant number 9244032.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions that greatly improved this work. We also express our gratitude to the editors for their professional guidance throughout the review process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Adnan A. R. Widowati R. Nuryakin (2023). Evolution and trends in Indonesian green marketing research: A systematic review, (2018-2023). J. Green Econ Low-Carbon Dev.2, 162–174. doi: 10.56578/jgelcd020305
2
Al-Fuqaha A. Guizani M. Mohammadi M. Aledhari M. Ayyash M. (2015). Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv Tutor.17, 2347–2376. doi: 10.1109/comst.2015.2444095
3
Alvarez J. F. Longva T. Engebrethsen E. S. (2010). A methodology to assess vessel berthing and speed optimization policies. Marit Econ Logist.12, 327–346. doi: 10.1057/mel.2010.11
4
Bouman E. A. Lindstad E. Rialland A. I. Strømman A. H. (2017). State-of-the-art technologies, measures, and potential for reducing GHG emissions from shipping – A review. Transp Res. D Transp Environ.52, 408–421. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.03.022
5
Bui T. D. Ali M. H. Tsai F. M. Iranmanesh M. Tseng M. L. Lim M. K. (2020). Challenges and trends in sustainable corporate finance: A bibliometric systematic review. J. Risk Financ Manage.13, 27. doi: 10.3390/jrfm13110264
6
Cao K. Zhang Z. D. Li Y. Xie M. Zheng W. B. (2021). Surveillance of ship emissions and fuel sulfur content based on imaging detection and multi-task deep learning. Environ. pollut.288, 117698. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117698
7
Cariou P. Parola F. Notteboom T. (2019). Towards low carbon global supply chains: A multi-trade analysis of CO2 emission reductions in container shipping. Int. J. Prod Econ.208, 17–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.11.016
8
Chen X. Q. Chen W. P. Wu B. Wu H. F. Xian J. F. (2024b). Ship visual trajectory exploitation via an ensemble instance segmentation framework. Ocean Eng.313, 119368. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119368
9
Chen X. Q. Ma D. F. Liu R. W. (2024a). Application of artificial intelligence in maritime transportation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.12, 439. doi: 10.3390/jmse12030439
10
Chen X. Q. Zheng J. B. Li C. F. Wu B. Wu H. F. Montewka J. (2023). Maritime traffic situation awareness analysis via high-fidelity ship imaging trajectory. Multimed Tools Appl.83, 48907–48923. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-17456-6
11
Dai T. J. Dai Q. L. Ding J. Liu B. S. Bi X. H. Wu J. H. et al . (2023). Measuring the emission changes and meteorological dependence of source-specific BC aerosol using factor analysis coupled with machine learning. J. Geophys Res-atmos.128, e2023JD038696. doi: 10.1029/2023jd038696
12
Dalle Lucca Tosi M. dos Reis J. C. (2020). Understanding the evolution of a scientific field by clustering and visualizing knowledge graphs. J. Inform Sci.48, 71–89. doi: 10.1177/0165551520937915
13
Dnv G. L. (2019). “Maritime forecast to 2050, energy transition outlook 2019,” in DNV GL, Høvik, Norway, 2019 edition, vol. 2019. (Dnv GL, Germany).
14
Duan K. Q. Li Q. B. Liu S. H. Liu Y. X. Wang S. Li S. et al . (2024). AIS-based operational phase identification using progressive ablation feature selection with machine learning for improving ship emission estimates. J. Air Waste Manag Assoc.74, 100–115. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2023.2274348
15
Durlik I. Miller T. Kostecka E. Lobodzinska A. Kostecki T. (2024). Harnessing AI for sustainable shipping and green ports: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Sci-Basel.14, 5994. doi: 10.3390/app14145994
16
Elg M. Korvola T. Molchanov B. Tran L. Lappalainen J. (2023). Improving ship sustainability by re-using engineering simulators in multi-objective optimization. Int. J. Marit Eng.164, 327–342. doi: 10.5750/ijme.v164iA3.1164
17
El Hathat Z. Venkatesh V. G. Sreedharan V. R. Zouadi T. Manimuthu A. Shi Y. Y. et al . (2024). Leveraging greenhouse gas emissions traceability in the groundnut supply chain: Blockchain-enabled off-chain machine learning as a driver of sustainability. Inf Syst. Front.26, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s10796-024-10514-w
18
Elsisi M. Yu J. T. Lai C. C. Su C. L. (2024). A drone-assisted deep learning based IoT system for monitoring ship emissions in ports considering adversarial attacks. IEEE Trans. Instrumentation Measurement.73, 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3374306
19
Fagerholt K. Laporte G. Norstad I. (2010). Reducing fuel emissions by optimizing speed on shipping routes. J. Oper Res. Soc61, 523–529. doi: 10.1057/jors.2009.77
20
Fan A. L. Xiong Y. Q. Yan J. H. Yang L. Shu Y. Q. Chen J. H. (2024). Microscopic characteristics and influencing factors of ship emissions based on onboard measurements. Transp Res. D Transp Environ.133, 24. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2024.104300
21
Fan A. L. Yang J. Yang L. Wu D. Vladimir N. (2022). A review of ship fuel consumption models. Ocean Eng.264, 17. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112405
22
Feng Y. W. Wang X. J. Luan J. L. Wang H. Li H. J. Li H. H. et al . (2024). A novel method for ship carbon emissions prediction under the influence of emergency events. Transp. Res. Pt. C-Emerg. Technol.165, 104749. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2024.104749
23
Fletcher T. Garaniya V. Chai S. Abbassi R. Yu H. Van T. C. et al . (2018). An application of machine learning to shipping emission inventory. Int. J. Marit Eng.160, A381–A395. doi: 10.3940/rina.ijme.2018.a4.500
24
Gan M. Hou H. Wu X. X. Liu B. Yang Y. W. Xie C. J. (2022). Machine learning algorithm selection for real-time energy management of hybrid energy ship. Energy Rep.8, 1096–1102. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.200
25
Gibbs D. Rigot-Muller P. Mangan J. Lalwani C. (2014). The role of sea ports in end-to-end maritime transport chain emissions. Energy Policy.64, 337–348. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2013.09.024
26
Gkerekos C. Lazakis I. Theotokatos G. (2019). Machine learning models for predicting ship main engine fuel oil consumption: A comparative study. Ocean Eng.188, 106282. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106282
27
Grieves M. Vickers J. (2017). “Digital twin: Mitigating unpredictable, undesirable emergent behavior in complex systems,” in Transdisciplinary perspectives on complex systems: New findings and approaches (Berlin: Springer International Publishing), 85–113.
28
Guo B. J. Liang Q. Tvete H. A. Brinks H. Vanem E. (2022). Combined machine learning and physics-based models for estimating fuel consumption of cargo ships. Ocean Eng.255, 111435. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111435
29
He S. L. Wu X. H. Wang J. Guo J. (2022). A ship emission diffusion model based on translation calculation and its application on Huangpu River in Shanghai. Comput. Ind. Eng.172, 108569. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2022.108569
30
Hirsch J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. P Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.102, 16569–16572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507655102
31
Horvath S. Fasihi M. Breyer C. (2018). Techno-economic analysis of a decarbonized shipping sector: Technology suggestions for a fleet in 2030 and 2040. Energy Convers Manage.164, 230–241. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2018.02.098
32
Hou Y. L. Wang Q. W. (2023). Big data and artificial intelligence application in energy field: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.30, 13960–13973. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1470330/v1
33
Hu Z. H. Jing Y. X. Hu Q. Y. Sen S. Zhou T. R. Osman M. T. (2019). Prediction of fuel consumption for enroute ship based on machine learning. IEEE Access.7, 119497–119505. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2933630
34
Huang L. F. Pena B. Liu Y. C. Anderlini E. (2022). Machine learning in sustainable ship design and operation: A review. Ocean Eng.266, 112907. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112907
35
International Maritime Organization London, UK (2020). Guidance for the commissioning testing of ballast water management systems Vol. 2020 (London, UK: International Maritime Organization).
36
Iris Ç. Lam J. S. L. (2019). A review of energy efficiency in ports: Operational strategies, technologies and energy management systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev.112, 170–182. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.04.069
37
Jaques L. B. A. Coradi P. C. Lutz E. Teodoro P. E. Jaeger D. V. Teixeira A. L. (2023). Nondestructive technology for real-time monitoring and prediction of soybean quality using machine learning for a bulk transport simulation. IEEE Sens J.23, 3028–3040. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3226168
38
Jovanovic I. Vladimir N. Percic M. Korican M. (2022). The feasibility of autonomous low-emission ro-ro passenger shipping in the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Eng.247, 110712. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110712
39
Jurdana I. Lopac N. Wakabayashi N. Liu H. Z. (2021). Shipboard data compression method for sustainable real-time maritime communication in remote voyage monitoring of autonomous ships. Sustainability13, 8264. doi: 10.3390/su13158264
40
Kanberoglu B. Kökkülünk G. (2021). Assessment of CO2 emissions for a bulk carrier fleet. J. Clean Prod.283, 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124590
41
Kim K. I. Lee K. M. (2018). Dynamic programming-based vessel speed adjustment for energy saving and emission reduction. Energies11, 1273. doi: 10.3390/en11051273
42
Kurchaba S. Sokolovsky A. van Vliet J. Verbeek F. J. Veenman C. J. (2024). Sensitivity analysis for the detection of NO2 plumes from seagoing ships using TROPOMI data. Remote Sens Environ.304, 114041. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114041
43
Kurchaba S. van Vliet J. Verbeek F. J. Meulman J. J. Veenman C. J. (2022). Supervised segmentation of NO2 plumes from individual ships using TROPOMI satellite data. Remote Sens.14, 5809. doi: 10.3390/rs14225809
44
Kurchaba S. van Vliet J. Verbeek F. J. Veenman C. J. (2023). Anomalous NO2 emitting ship detection with TROPOMI satellite data and machine learning. Remote Sens Environ.297, 113761. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2023.113761
45
Lee H. B. Aydin N. Choi Y. Lekhavat S. Irani Z. (2018). A decision support system for vessel speed decision in maritime logistics using weather archive big data. Comput. Oper.98, 330–342. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2017.06.005
46
Lee J. Eom J. Park J. Jo J. Kim S. (2024). The development of a machine learning-based carbon emission prediction method for a multi-fuel-propelled smart ship by using onboard measurement data. Sustainability16, 2381. doi: 10.3390/su16062381
47
Li X. H. Ding K. P. Xie X. W. Yao Y. Zhao X. Jin J. H. et al . (2024a). Bi-objective ship speed optimization based on machine learning method and discrete optimization idea. Appl. Ocean Res.148, 104012. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2024.104012
48
Li Z. J. Fei J. G. Du Y. Q. Ong K. L. Arisian S. (2024b). A near real-time carbon accounting framework for the decarbonization of maritime transport. Transp Res. E Logist Transp Rev.191, 28. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2024.103724
49
Li L. B. Lu W. Y. Niu J. W. Liu J. P. Liu D. X. (2018). AIS data-based decision model for navigation risk in sea areas. J. Navig.71, 664–678. doi: 10.1017/s0373463317000807
50
Li X. H. Sun B. Z. Jin J. H. Ding J. (2022). Speed optimization of container ship considering route segmentation and weather data loading: turning point-time segmentation method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 1835. doi: 10.3390/jmse10121835
51
Li H. H. Yang Z. L. (2023). Incorporation of AIS data-based machine learning into unsupervised route planning for maritime autonomous surface ships. Transp Res. E Logist Transp Rev.176, 103071. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2023.103171
52
Liu Z. F. Feng J. Uden L. (2023). Technology opportunity analysis using hierarchical semantic networks and dual link prediction. Technovation128, 17. doi: 10.1016/j.technovation.2023.102872
53
Lu B. Ming X. Lu H. M. Chen D. Y. Duan H. B. (2023). Challenges of decarbonizing global maritime container shipping toward net-zero emissions. NPJ Ocean Sustain.2, 11. doi: 10.1038/s44183-023-00018-6
54
Luo X. Yan R. Xu L. Wang S. A. (2024a). Accuracy and applicability of ship's fuel consumption prediction models: A comprehensive comparative analysis. Energy.310 (25), 133187. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.133187
55
Luo X. Yan R. Wang S. A. (2024b). Ship sailing speed optimization considering dynamic meteorological conditions. Transp Res Pt C-Emerg Technol.167 (10), 104827. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2024.104827
56
Lyu J. Y. Zhou F. L. He Y. D. (2023). Digital technique-enabled container logistics supply chain sustainability achievement. Sustainability15, 16014. doi: 10.3390/su152216014
57
Manyika J. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity (Washington, U. S. A.: Analytics. McKinsey Global Institute).
58
Markus G. (2003). Co-citation analysis and the search for invisible colleges: A methodological evaluation. Scientometrics57, 27–57. doi: 10.1023/A:1023619503005
59
McFarlane D. Sarma S. Chirn J. L. Wong C. Y. Ashton K. (2003). Auto ID systems and intelligent manufacturing control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.16, 365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0952-1976(03)00077-0
60
Melo R. F. Figueiredo N. M. D. Tobias M. S. G. Afonso P. (2024). A machine learning predictive model for ship fuel consumption. Appl. Sci-Basel.14, 23. doi: 10.3390/app14177534
61
Muhuri P. K. Shukla A. K. Abraham A. (2019). Industry 4.0: A bibliometric analysis and detailed overview. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.78, 218–235. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2018.11.007
62
Nguyen S. Fu X. J. Ogawa D. Zheng Q. (2023). An application-oriented testing regime and multi-ship predictive modeling for vessel fuel consumption prediction. Transp Res. E Logist Transp Rev.177, 103261. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2023.103261
63
Ninkov A. Frank J. R. Maggio L. A. (2022). Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect. Med. Educ.11, 173–176. doi: 10.1007/s40037-021-00695-4
64
Okumus F. Ekmekçioglu A. Kara S. S. (2021). Modelling ships main and auxiliary engine powers with regression-based machine learning algorithms. Pol. Marit Res.28, 83–96. doi: 10.2478/pomr-2021-0008
65
Papandreou C. Ziakopoulos A. (2022). Predicting VLCC fuel consumption with machine learning using operationally available sensor data. Ocean Eng.243, 110321. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110321
66
Perera L. P. Mo B. (2017). Machine intelligence based data handling framework for ship energy efficiency. IEEE Trans. Veh Technol.66, 8659–8666. doi: 10.1109/tvt.2017.2701501
67
Pu S. Y. Lam J. S. L. (2021). Greenhouse gas impact of digitalizing shipping documents: Blockchain vs. centralized systems. Transp Res. D Transp Environ.97, 102942. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2021.102942
68
Ren F. Y. Wang S. H. Liu Y. Z. Han Y. (2022). Container ship carbon and fuel estimation in voyages utilizing meteorological data with data fusion and machine learning techniques. Math. Probl. Eng.2022(1), 4773395. doi: 10.1155/2022/4773395
69
Serra P. Fancello G. (2020). Towards the IMO’s GHG Goals: A critical overview of the perspectives and challenges of the main options for decarbonizing international shipping. Sustainability12, 32. doi: 10.3390/su12083220
70
Shi J. M. Liu X. T. Feng Z. X. (2023). Age-friendly cities and communities and cognitive health among Chinese older adults: Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Studies. Cities132, 104072. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2022.104072
71
Sidhu J. (2017). “Syscoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system with blockchain-based services for E-business,” in 26th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN)) (New York, U. S. A: IEEE). 1–6.
72
Su M. Lee H. J. Wang X. Bae S. H. (2024). Fuel consumption cost prediction model for ro-ro carriers: A machine learning-based application. Marit Policy Manage.51, 1–21. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2024.2303120
73
Sun Y. Lü L. Cai Y. K. Lee P. (2022). Prediction of black carbon in marine engines and correlation analysis of model characteristics based on multiple machine learning algorithms. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.29, 78509–78525. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20496-4
74
Tran T. A. (2021). Comparative analysis on the fuel consumption prediction model for bulk carriers from ship launching to current states based on sea trial data and machine learning technique. J. Ocean Eng. Sci.6, 317–339. doi: 10.1016/j.joes.2021.02.005
75
Tripathi S. Vijayakumar R. (2024). Review of hydrodynamics, design and optimisation of stern flap on high-speed displacement ships. Ships Offshore Struc.19, 1–16. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2024.2355411
76
Vasilikis N. Geertsma R. Coraddu A. (2023). A digital twin approach for maritime carbon intensity evaluation accounting for operational and environmental uncertainty. Ocean Eng.288, 115927. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115927
77
Wallin J. A. (2005). Bibliometric methods: Pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol.97, 261–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_139.x
78
Waltman L. van Eck N. J. Noyons E. C. M. (2010). A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J. Informetr.4, 629–635. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2010.07.002
79
Wang H. Q. Yan R. Wang S. A. Zhen L. (2023). Innovative approaches to addressing the tradeoff between interpretability and accuracy in ship fuel consumption prediction. Transp Res Pt C-Emerg Technol.157 (12), 104361. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2023.104361
80
Wang Z. Y. Li G. Li C. Y. Li A. (2012). Research on the semantic-based co-word analysis. Scientometrics90, 855–875. doi: 10.1007/s11192-011-0563-y
81
Wang Z. H. Lu M. J. Dong S. J. Tang M. Yan X. P. Li K. et al . (2024). Study of ship-based carbon capture optimization considering multiple evaluation factors and main engine loads. J. Clean Prod.478, 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143996
82
Wang K. Wang J. H. Huang L. Z. Yuan Y. P. Wu G. T. Xing H. et al . (2022). A comprehensive review on the prediction of ship energy consumption and pollution gas emissions. Ocean Eng.266, 112826. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112826
83
Xiao G. N. Cui W. Y. (2023). Evolutionary game between government and shipping enterprises based on shipping cycle and carbon quota. Front. Mar. Sci.10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1132174
84
Xiao G. N. Wang T. Luo Y. H. Yang D. Q. (2023). Analysis of port pollutant emission characteristics in United States based on multiscale geographically weighted regression. Front. Mar. Sci.10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1131948
85
Xiao G. N. Wang Y. Q. Wu R. J. Li J. P. Cai Z. Y. (2024a). Sustainable maritime transport: A review of intelligent shipping technology and green port construction applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.12, 1728. doi: 10.3390/jmse12101728
86
Xiao G. N. Xu L. (2024). Challenges and opportunities of maritime transport in the post-epidemic era. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.12, 1685. doi: 10.3390/jmse12091685
87
Xiao G. N. Yang D. Q. Xu L. Li J. P. Jiang Z. R. (2024b). The application of artificial intelligence technology in shipping: A bibliometric review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.12, 21. doi: 10.3390/jmse12040624
88
Xiao G. N. Tong H. L. Shu Y. Q. Ni A. N. (2025). Spatial-temporal load prediction of electric bus charging station based on S2TAT. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst.164 (2), 110446. doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2024.110446
89
Xie X. W. Sun B. Z. Li X. H. Olsson T. Maleki N. Ahlgren F. (2023b). Fuel consumption prediction models based on machine learning and mathematical methods. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.11, 738. doi: 10.3390/jmse11040738
90
Xie X. W. Sun B. Z. Li X. H. Zhao Y. H. Chen Y. M. (2023a). Joint optimization of ship speed and trim based on machine learning method under consideration of load. Ocean Eng.287, 115917. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115917
91
Xu L. Shen C. X. Chen J. H. (2024b). The impact of the Maritime Silk Road Initiative on the carbon intensity of the participating countries. Marit Econ Logist.26, 1–19. doi: 10.1057/s41278-024-00295-z
92
Xu L. Shen C. X. Chen J. H. Pan X. Y. Xiao G. N. (2024a). Efficiency evaluation and improvement pathway of sulfur-oxide emissions in European ports based on Context-dependent SBM-DEA model. Mar. pollut. Bull.208, 8. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117002
93
Xu L. Shi J. Chen J. H. (2021). Platform encroachment with price matching: Introducing a self-constructing online platform into the sea-cargo market. Comput. Ind. Eng.156, 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107266
94
Xu L. Zou Z. Y. Zhou S. R. (2022). The influence of COVID-19 epidemic on BDI volatility: An evidence from GARCH-MIDAS model. Ocean Coast. Manage.229, 10. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106330
95
Xue Y. M. Lai K. H. (2024). Digital green shipping innovation: Conception, adoption, and challenges. J. Glob Inform Manage.32, 1–28. doi: 10.4018/jgim.349929
96
Yan R. Yang D. Wang T. Y. Wang S. A. (2024). Improving ship energy efficiency: Models, methods, and applications. Appl. Energy.368 (16), 123132. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123132
97
Yin Y. W. Lam J. S. L. Tran N. K. (2021). Emission accounting of shipping activities in the era of big data. Int. J. Ship Trans. Log.13, 156–184. doi: 10.1504/ijstl.2021.112922
98
Yin H. Lan H. Hong Y. Y. Wang Z. W. Cheng P. Li D. et al . (2023). A comprehensive review of shipboard power systems with new energy sources. Energies16, 2307. doi: 10.3390/en16052307
99
Yuan T. L. Song H. Oreopoulos L. Wood R. Bian H. S. Breen K. et al . (2024). Abrupt reduction in shipping emission as an inadvertent geoengineering termination shock produces substantial radiative warming. Commun. Earth Environ.5, 281. doi: 10.1038/s43247-024-01442-3
Summary
Keywords
digital technology, shipping, decarbonization, application, bibliometric analysis
Citation
Xiao G, Pan L and Lai F (2025) Application, opportunities, and challenges of digital technologies in the decarbonizing shipping industry: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1523267. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1523267
Received
05 November 2024
Accepted
14 January 2025
Published
31 January 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Xu Xin, Tongji University, China
Reviewed by
Juan Moreno-Gutiérrez, University of Cádiz, Spain
Yusheng Zhou, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Ran Yan, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
Octavian Postolache, O. Postolache, University Institute of Lisbon (ISCTE), Portugal
Qi Xu, Guilin University o Electronic Technology, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Xiao, Pan and Lai.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guangnian Xiao, gnxiao@shmtu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.