
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 26 February 2025
Sec. Coastal Ocean Processes
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1491085
To address the issue of vegetation obstructing water bodies and resulting in missing information in vegetation sea areas, existing methods that focus on various types of shorelines often exhibit limited algorithm stability and accuracy. This study introduces a method, termed Shoreline_veget. The method comprises four modules: data preprocessing, point cloud boundary extraction and processing, elevation gradient function design, modified fused boundary point cloud, and tidal correction. This method can reduce the overall shoreline accuracy from 0.6658, 0.3854, and 0.4127 (as observed with three comparative methods) to 0.1531. Compared to the least accurate method, this method improved the overall shoreline accuracy by 0.5127 m. The result confirm that the proposed method offers superior stability, and this methodology provides new technology to measure, map, and manage shorelines, offers valuable insight for related research.
The majority of existing methods for extracting shorelines from airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) point clouds target all shoreline types without tailoring specific, robust extraction techniques to the unique characteristics of each shoreline category. Consequently, the accuracy of these methods is relatively low. In vegetation coastal areas, the boundary between water and land is often obscured by dense vegetation, complicating the task for various remote sensing techniques to accurately discern these features. The Shoreline_veget method, developed in this study, leverages point cloud intensity value and elevation gradient function to mitigate the interference caused by vegetation, thereby enhancing the accuracy of shoreline extraction.
Historically, shoreline extraction research has primarily utilized aerial or satellite imagery (Wei et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Zollini et al., 2023; Benhur et al., 2024; Colak, 2024; Pardo-Pascual et al., 2024). However, With the advancement of airborne LiDAR technology, it has emerged as a promising tool for shoreline measurement owing to its distinct advantages. Junbo Wang et al (Wang et al., 2023). and Andrzej Stateczny et al (Stateczny et al., 2023). provided a review of methods for extracting shorelines using airborne lidar technology. It has conducted a comprehensive analysis of the current methods for extracting shorelines using airborne LiDAR. Sheng Xu et al (Xu et al., 2019). proposed a new method for extracting shorelines from airborne point clouds. The method first removes water bodies based on flatness search, and then uses a minimum cost boundary model to obtain the boundary of land. Hongxing Liu et al (Liu et al., 2007). proposed a new method for extracting shorelines using airborne point clouds. Firstly, the point cloud is generated into a digital elevation model, which is segmented into binary images containing land and water bodies. Image processing algorithms and some mathematical morphological methods are used to process the binary images and then obtain shorelines. In Su Lee et al (Lee et al., 2011), research was conducted on the application of coastal lines extracted from airborne point clouds in cadastral surveying. They used contour lines and combined point clouds to generate digital elevation models to extract coastal lines. Abdullah Harun Incekara et al (Incekara et al., 2018). derived intensity images from airborne point clouds and used them as infrared bands for shoreline extraction. They applied Mean shift segmentation as smoothing on the intensity images, preserving details while removing noise. The method adopted by Hilary F. Stockdon et al (Stockdonf et al., 2002). can be referred to as the coastal profile method, which defines the position of the shoreline as at the shoreline reference plane. This method constructs a cross shore profile fitting function using laser elevation data around the shoreline reference plane. From the above literatures, it can be seen that researchers have processed airborne point clouds from different perspectives to extract shorelines. However, it can also be seen that these methods treat shorelines as a unified quantity.
Some scholars have also considered the type of shoreline and conducted research on its classification and extraction. Li W et al (Li et al., 2022a). proposed an optimal method for extracting shoreline at cliffs, while Hua Yang et al (Yang et al., 2024). studied shoreline extraction at low tide beaches, which is suitable for shoreline extraction at low tide beaches. Weihua Li et al (Li et al., 2022b). proposed a method for extracting shorelines from shallow waters and silty soils using airborne point clouds. This method combines the laser echo intensity values of points to initially separate sand, gravel, and water, and then processes the boundary point clouds to obtain shorelines. Some researchers do not directly start with shoreline extraction, but classify water bodies by processing airborne point clouds. Julien Smeeckaert et al (Smeeckaert et al., 2013). designed a specific definition based on laser point clouds and route information as the classifier input. With the help of a semi-automatic region growth strategy, SVM learning steps are performed in small but targeted areas to draw the water area range of coasts, rivers, etc. Shunshi Hu et al (Hu et al., 2020). conducted research on water extraction by combining tile threshold segmentation with active model contours. There are many research literatures on separating water bodies from land, which involves first obtaining the boundary between water bodies and land, and then obtaining the shoreline. B. Deronde et al (Deronde et al., 2008). studied the position of the shoreline using airborne LiDAR data and hyperspectral remote sensing, and estimated the sediment content within the shoreline range; Jaroslav Obu et al (Obu et al., 2017). measured the shoreline using airborne lidar elevation data and used this information to determine coastal erosion and other related factors; Some studies (Vaaja et al., 2013; Demir et al., 2019; Nassif et al., 2020; Spinosa et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2023) may not have high requirements for the accuracy of shoreline extraction, and only extract the shoreline superficially, and then use the shoreline information to study marine environment, marine protection, etc. Although these aspects are not high-precision extraction of shorelines, they are also implemented through airborne lidar technology, and these studies have a promoting effect on using airborne lidar to extract shorelines.
Shorelines are categorized into natural and artificial types, with natural shorelines further subdivided into bedrock, sandy, and silty types, and artificial shorelines into port, dock, construction, and aquaculture embankment types. The data distribution across different regions and shoreline types is complex and often contains unpredictable and irregular data points. When the data distribution does not align with the algorithm, the extraction fails. Currently, no unified algorithm exists that can adapt to various shoreline types with high accuracy. Therefore, this study conducted a detailed analysis of the distribution characteristics of airborne point clouds in the coastal zone of vegetation sea areas and proposed a method that accurately adapts to and extracts the shoreline of these areas. This method addresses the challenges of acquiring water and land information in vegetation marine areas. This method facilitates high-precision and efficient extraction of vegetation along marine shorelines, offering a solution to the challenges of measurement and accuracy in marine areas. It provides technical support for ocean mapping and shoreline surveying and serves as a reference and inspiration for related shoreline extraction research.
This article selects a vegetation sea area point cloud set in Longkou City, Shandong Province, China as the experimental data. The total airborne LiDAR point cloud data size is 913MB, with a total of 18338833 points, and the coordinates in the lower left corner are x=512449.1250, y=3370331.5000, z=217.6900, the coordinates in the upper right corner are x=523174.0312, y=3369392.0000, z=410.5400. The red box represents the sea area with abundant vegetation coverage, with a data size of 6.912MB and a total of 138288 points. The coordinates in the lower left corner are x=518663.219, y=3369729, z=382.92, the coordinates in the upper right corner are x=519114.343, y=3370653.5, z=58.68. Each point contains three-dimensional spatial coordinate information, color RGB value information, echo intensity value and echo frequency information. The sea area point clouds and vegetation sea area point clouds are shown in Figure 1.
The method comprises four modules: data preprocessing, point cloud boundary extraction and processing, elevation gradient function design, modified fused boundary point cloud, and tidal correction. (1) The boundary of the vegetation sea area, which is biased toward the water body, is extracted and the vegetation sea area point cloud is re-extracted. The re-extracted vegetation sea area point cloud is classified into vegetation and land point cloud. (2) The boundaries of vegetation and land point cloud are precisely extracted. Project the boundary of the vegetation point cloud onto the water surface and corrects the elevation of each boundary point, shifting it toward the land side by an average distance of the points. Subsequently, merge the vegetation boundary and the land boundary. (3) Considering the topographic and terrain characteristics of the vegetation sea area, an elevation gradient function is formulated. The attributes of each point are assigned based on the values derived from the elevation gradient function, and each point is corrected accordingly. (4) The tidal correction module initially performs the processed merged boundary point cloud completion. Subsequently, it transforms the merged boundary point cloud into a shoreline point cloud, utilizing several years of local tidal observation data and a shoreline tidal correction model. This process is illustrated in Figure 2.
To effectively design and implement subsequent algorithms, it is necessary to eliminate many unrelated land point clouds. Based on the observed trends in the plane coordinates (x and y) of point clouds in vegetation sea areas, a method can be developed to extract rough boundary point clouds of these areas. Utilizing the rough boundary point clouds, combined with designated distance and elevation parameters, the required range of sea area point clouds can be regenerated. This method is elaborated in Ref (Li et al., 2022b). Regarding the naming conventions and definitions used for point cloud data: let P denote a set of point clouds, Ptext denotes a point cloud set named “text”, Ptext(i) represents the i-th point in this set, Ptext(i)_x, Ptext(i)_y, Ptext(i)_z,represents the x, y, z coordinates of this point, Ptext(i)_I denotes its laser echo intensity, and Ptext(i)_N indicates the number of laser echoes.
For classifying vegetation point clouds, it is sufficient to set the number of echoes to two or more. For land point clouds, the number of echoes should be set to one, and the echo intensity value should be slightly lower than the minimum echo intensity value among the main land features. According to the calibrated ground laser echo intensity statistics, the echo intensity values for sand, gravel, and soil range from 150–250, with values of 35.1 for rock and 73.1 for loess block. Therefore, the echo intensity threshold for distinguishing these features could be set slightly lower than that for rock. Assuming that the regenerated vegetation point cloud in Section 2.2 is denoted as Pcoastal, the classified vegetation and land point clouds are represented as Pveget and Pland, respectively, and the extraction formula is defined as Equation 1.
where i1 denotes the echo intensity threshold, which was set slightly below the echo intensity value for rock at 31. If the threshold difference was not significant, it did not impact the classification results of the land point cloud.
This method categorizes shoreline trends in the data uniformly. However, in large-scale sea-area data, shoreline trends may vary irregularly. To more accurately extract the shoreline in future studies, the point clouds should be segmented according to different shoreline trends. Typically, for a specific boundary point cloud, the process involves sorting the x-coordinates of each point in ascending order (when the shoreline is manually judged as east–west based on the x-coordinate; when judged as north–south, sorting is based on the y-coordinate) to establish a new index. Starting from the first point, the coordinate azimuths of the subsequent and preceding points are sequentially detected. The coordinate azimuth is defined as the angle rotated clockwise from the positive axis pointing to the North Pole to a straight line. When the coordinate azimuth of each point is “similar” to the previous one, “similar” here refers to the coordinate azimuth consistently falling within either Group A (45°–135° and 225°–315°) or Group B (0°–45°, 135°–225°, and 315°–360°). The points in Group A correspond to the east–west orientation of the water–land boundary line, while the points in Group B correspond to the north–south orientation, as illustrated in Figure 3. The orientation of the water–land boundary is influenced by the terrain at the interface between land and water bodies. In certain areas, the orientation may shift from east–west to north–south, or vice versa. The variations in the orientation over short distances (less than 50 m) can be disregarded, whereas changes over longer distances necessitate a reevaluation of the boundary’s direction. A threshold of 50 m has been established for this purpose. If the change exceeds this distance, the boundary line is segmented and a new direction is assigned. If the change is shorter than this threshold, the existing direction is maintained. This method allows for the delineation of either a single or multiple boundary point clouds with varying orientations, which are temporarily designated as Pveget_b.
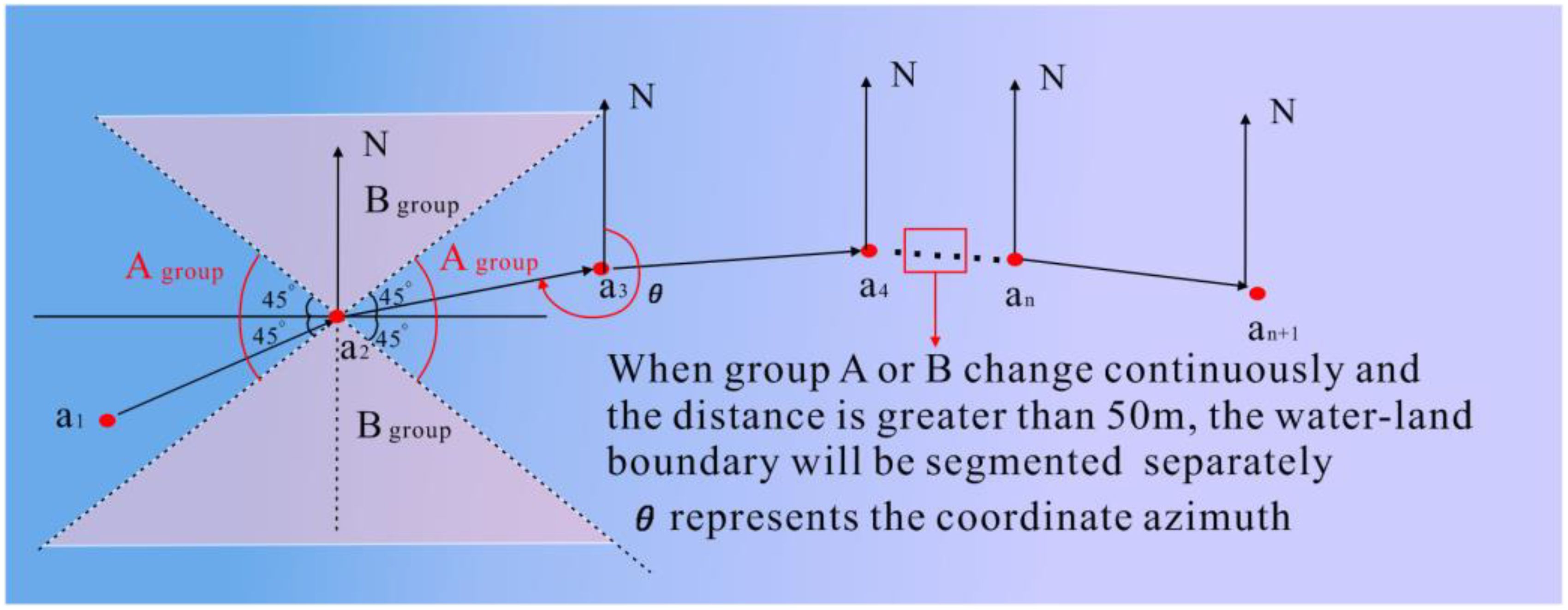
Figure 3. The calculation of boundary point cloud orientation and segmentation of boundary point cloud with different orientations.
The vegetation boundary point cloud Pveget_b complicates the determination of the water–land boundary beneath it, as the vegetation can obscure the water or ground, resulting in sparse or absent point clouds in these areas. To enhance the accuracy of identifying the water-land boundary beneath the vegetation, the vegetation boundary point cloud can be vertically projected onto the water surface. This projection involves maintaining the x- and y-coordinates of the boundary points while transforming the elevation z to approximate the water surface elevation below, according to a specific transformation relationship, as depicted in Figure 4.
The projection of vegetation point cloud Pveget onto water surface can partially compensate for the point cloud gaps under the branches and leaves caused by vegetation occlusion. The projection principle is: first, set Pcoastal, which has deleted the point cloud Pveget, as Pcoastal_1, calculate the average elevation of Pcoastal_1, and attach this average elevation value to the z-coordinate of each point in the Pveget to obtain the point cloud set Pveget_1. After fusion of the point cloud set Pveget_1 and Pcoastal_1, the point cloud set Pcoastal_2 can be obtained. The average elevation of the points in the k-order neighborhood of each point in Pveget_1 are calculated, and this value to the z-coordinate of this point in Pveget_1 were assigned. Accordingly, each point in the vegetation point cloud set Pveget is projected onto land or water surface with a better elevation value, filling in the information gaps under the branches and leaves to a certain extent. For vegetation boundary point cloud set Pveget_b, the plane coordinates x and y are used as constraints to search for the k-order neighborhood of each vegetation boundary point, and the average elevation of points within the k-order neighborhood are regarded as the elevation of the vegetation boundary point. Assuming a point of the vegetation boundary point cloud is Pveget_b(i), and the point located in and belonging to the k-order neighborhood is , then the elevation of the vegetation boundary point Pveget_b(i) is converted according to Equation 2.
Where n is the total number of points in .
Given that the distance between points in airborne lidar data is relatively large, often several tens of centimeters, the offset value can be set to one time the average distance between points. According to Section 2.3 (1), the direction of the water–land boundary calculated in part (a) determines the offset direction. If the water–land boundary runs east–west, the offset is applied to the y-coordinate; if it runs north–south, the offset is applied to the x-coordinate. The corrected point cloud for the vegetation boundary is denoted as .
Therefore, using the precise boundary extraction method described in Section 2.3 (1) (a), the extracted boundary point cloud—biased toward the water body—includes both terrestrial point clouds near the water-land boundary and shallow water surface point clouds.
The boundary point cloud extracted from the land point cloud set is referred to as the corrected vegetation boundary point cloud , which is a part of the water–land boundary. Combined with the land boundary point cloud Pland_b, it more accurately represents the direction of the water–land boundary. Thus, it is necessary to fuse these two boundary point clouds, and the resulting fused boundary point cloud is designated as Pland_b.
The likelihood of the fused boundary point cloud being precisely located on the water-land boundary is minimal, with the majority of points situated on either side of the boundary. To enhance the alignment of the fused boundary point cloud with the water–land boundary, it is essential to ascertain the relative positions of each point in the fused boundary point cloud to the water–land boundary and make corrections to increase the accuracy of the fused boundary point cloud.
For the points in the fusion boundary point cloud set Pmerge, place the points in Pmerge back into the point cloud set , where the blank space under the branches and leaves has been filled, and the “surrounding points” correspond to each point in Pmerge. This “surrounding” is judged according to the following method: when the main body of the water–land boundary line is along the north-south direction, the “surrounding” of a certain point Pmerge(j) in Pmerge is represented as the angle of the shoreline direction (shoreline direction refers to the line connecting the starting and ending points of the water–land boundary line, the same below) and the line connecting the point in and the point Pmerge(j) is less than 30°, as depicted in Figure 5A. When the boundary line runs east–west, the “surrounding” is similarly defined by an angle less than 30°, as portrayed in Figure 5B. The 30° angle is an empirical value intended to ensure that the selected “surroundings” are close to the boundary point area without being excessively large. However, the subsequent step involves selecting the point nearest to the boundary point from the “surroundings” for evaluation, thus the size of the angle has minimal impact on the selection of the nearest point.
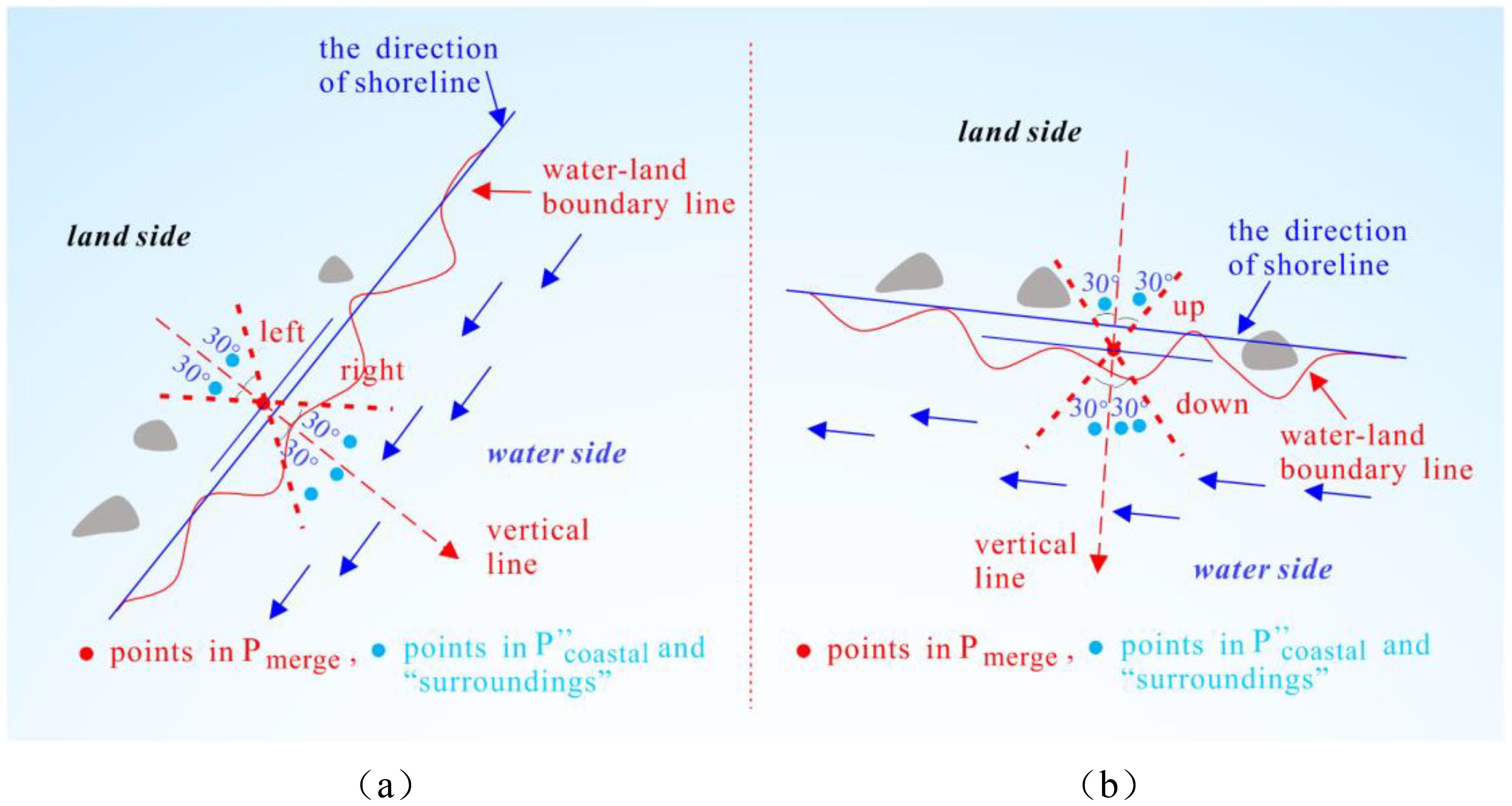
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the “surrounding” of each point in Pmerge: (A) when the shoreline direction is roughly north-south; (B) when the shoreline direction is roughly east-west.
When the shoreline is approximately oriented in a north–south direction, as depicted in Figure 5A, the angle α between the shoreline direction and the horizontal axis can be evaluated. Based on geometric relationships, the absolute value of the tangent of the angle between the line connecting the two points , Pmerge(j), and the horizontal axis can be calculated. The limiting condition of Figure 5A can be expressed as follows:
where θ denotes the angle between the line connecting two points , Pmerge(j), and the horizontal axis, α denotes the angle between the shoreline direction and the horizontal axis, Pmerge(j) is a certain boundary point in Pmerge, represents a certain point in . Similarly, when the shoreline is oriented broadly in the east–west, the constraint condition in Figure 5B is equivalent to that in Equation 3.
When the main body of the water-land boundary is north-south, as shown in Figure 5A, the points detected by the boundary points within the “surrounding” area can be divided into left and right parts. The points closest to the point Pmerge(j) in three-dimensional space can be found from the left and right parts, respectively, and set as point (1) and point (2). There are four types of elevation relationships between point (1), Pmerge (j) and point (2), as shown in Figure 6: (1)point (1)_z < Pmerge (j)_z and Pmerge (j)_z < point (2)_z; (2)point (1)_z < Pmerge (j)_z and Pmerge (j)_z >point (2)_z; (3)point (1)_z > Pmerge (j)_z and Pmerge (j)_z < point (2)_z; (4)point (1)_z > Pmerge (j)_z and Pmerge (j)_z > point (2)_z,.
When the elevation of three points satisfies conditions (1), (2), and (3), the point Pmerge(j) is classified as a boundary point on the land side. Conversely, if condition (4) is met, the point Pmerge(j) is classified as a boundary point of the water body. Terrain analysis suggests that when the elevation of three points meets the first three conditions, the point is likely on the land side. If it meets the fourth condition, the point Pmerge(j) typically exhibits the characteristic of decreasing elevation from land to water. There are exceptional cases under the fourth condition where all three points are on land, or point (1) and Pmerge(j) are on land. However, these cases are rare and are generally disregarded in this analysis.
When the primary orientation of the water-land boundary line is east-west, as depicted in Figure 5B, the detected boundary points within the “surrounding” area can be divided into upper and lower sections. From these sections, the points closest to the point Pmerge(j) in three-dimensional space, specifically point (1) and point (2), can be identified and categorized as mentioned above.
Assuming the elevation gradient function is defined as f(Pmerge(j), z), when the elevation of point Pmerge(j) within the “surrounding” area relative to the elevation satisfies conditions (1), (2), and (3), the gradient function value is assigned as 1. When condition (4) is satisfied, the gradient function value is assigned as 0. Therefore, the gradient function value at each boundary point can be used to determine whether it is on the land side or the water side. The relationship between the gradient function value and the point attribute is expressed as shown in Equation 4.
Boundary point cloud are generally located on both sides of the water-land boundary at a certain distance. The obtained boundary point cloud should be appropriately corrected based on the attribute of each boundary point. The boundary points on the land side should be offset toward the water body, and the boundary points on the water body side should be offset toward the land direction. Assuming the average distance between points in the point cloud set is σ, due to the displacement of the vegetation boundary point cloud set by once tine, here, set the offset distance to 0.5σ. Actually, setting it to 0.5σ is just to make the boundary points closer to the water-land boundary line and improve the overall accuracy of the water land boundary., it can also be set to other appropriate value (Generally the value is related to σ, but should be less than σ, so this article takes its median value). In the two different cases of Figures 5A, B, the offset method is also different. (1) When the boundary between water and land is roughly north-south: ① If the land is on the left side of the water-land boundary, the y-coordinate of the land side boundary points should increase by 0.5σ, and the y-coordinate of the water side boundary points should decrease by 0.5σ; ② If the land is located to the right of the water-land boundary, the y-coordinate of the land side boundary points should be reduced by 0.5σ, and the y-coordinate of the water side boundary points should be increased by 0.5σ; (2) When the water-land boundary line is in an east-west direction, referring to the situation in category (1), shift the x-coordinate by 0.5σ in the corresponding direction, and the point cloud Pmerge that is shifted according to the above method is called the pre-extracted shoreline point cloud, denoted as Pline.
The distance between adjacent points in the pre-extracted shoreline point cloud Pline is generally large. If a line is directly generated, the shoreline will appear undulating in many places. Therefore, the pre-extracted shoreline point cloud cannot accurately describe the direction of the shoreline, which will reduce the overall accuracy of the shoreline. Therefore, it is necessary to perform point interpolation and completion processing. The completion principle is to perform appropriate point interpolation according to the distance between adjacent two points, as detailed in reference (Li et al., 2022b).
As depicted in Figure 7, the traditional tidal correction model assumes that the coast has a constant slope. The horizontal distance difference between the water–land boundary lines at different times (C1 and C2) in the same area is calculated. Using current tidal data, the inclination angle of the coastal slope is determined. The current water–land boundary in this area is then calculated by combining tidal data with the coastal inclination, facilitating the determination of the corrected distance from the water-land boundary to the annual average high-tide line.
Vegetation in deep water areas that are seldom visited by humans presents challenges for conventional survey methods. To assess the accuracy of shoreline extraction by various remote sensing techniques, the average shoreline point cloud extracted by each method was initially computed. For shorelines oriented east–west, each is intersected by a vertical line with a small fixed increment, and the coordinates of the intersection points are calculated. Accordingly, the difference between the x-coordinates of each intersection point and the average x-coordinate of the shoreline intersection points is used to compute the standard deviation and variance of the x-coordinates for each shoreline. Similarly, for north–south oriented shorelines, a horizontal line with a small fixed increment intersects the shoreline, and the coordinates of these intersection points are determined. The deviation of the y-coordinate of each intersection point from the average y-coordinate of the shoreline intersection points is used to compute the standard deviation and variance of the y-coordinates for each shoreline. These statistical measures (standard deviation and variance of the x- or y-coordinates) serve as indicators of the overall accuracy of the shoreline extraction, as detailed in (Li et al., 2022b).
In order to verify the effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed method in extracting shoreline of vegetation coastal areas, the data in section 2.1 (1) was selected as the experimental object. Using C++language and point cloud library (PCL) to implement the algorithms in sections 2.2-2.5, the process of extracting vegetation sea shoreline using this method is explained as follows. In Figure 8, (a) shows the point cloud of the original vegetation sea area, with a data size of 6.912 MB and a total of 138288 points. (b) shows the rough boundary point cloud extracted by the boundary coarse extraction algorithm, with a size of 28 KB and a total of 958 points. (c) is based on the point cloud in (b), and points within a range of 50 meters from the point cloud in (a) are selected. The data size in (c) is 1345 KB, with a total of 26445 points. (d) is the front view of (c).
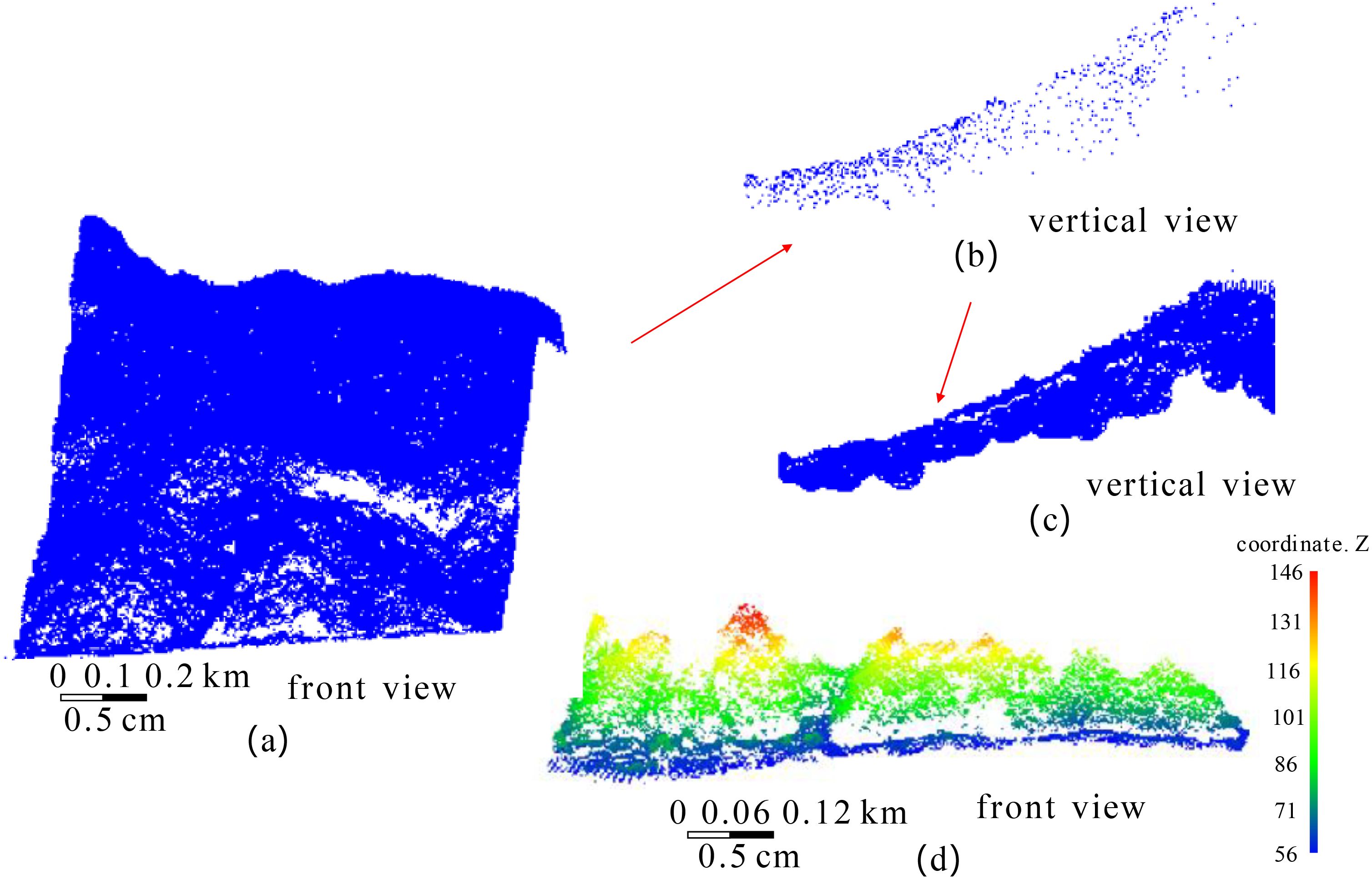
Figure 8. The regeneration of vegetation sea area point clouds. (a) the original vegetation sea area, (b) the rough boundary point cloud, (c) the re-constructed sea area point cloud, (d) is the front view of (c).
To classify the regenerated point cloud of the vegetation sea area, the method outlined in Section 2.2 (2) is applied to separate the vegetation and land point cloud sets. Figure 9A displays the regenerated vegetation sea area point cloud, corresponding to the point cloud in Figure 8C. Figure 9B illustrates the classified vegetation point cloud set, Figure 9C depicts the land point cloud set, and Figure 9D displays the superimposed vegetation and land point clouds.

Figure 9. The classification of point cloud in vegetation sea areas. (a) the regenerated vegetation sea area point cloud, (b) the vegetation point cloud set, (c) the land point cloud set, (d) the overlay image of vegetation and land point cloud set.
Using precise boundary extraction algorithms, we extracted the precise boundaries of vegetation and land point cloud sets Pveget_b and Pland_b, which are biased toward the direction of water body, as depicted in Figure 10A. The vegetation boundary point cloud is processed using the method described in Section 2.3 (1), projected onto the water surface, and offset by the average distance of to derive the point cloud set . The overlay display of Pveget_b and Pland_b is illustrated in Figure 10B.
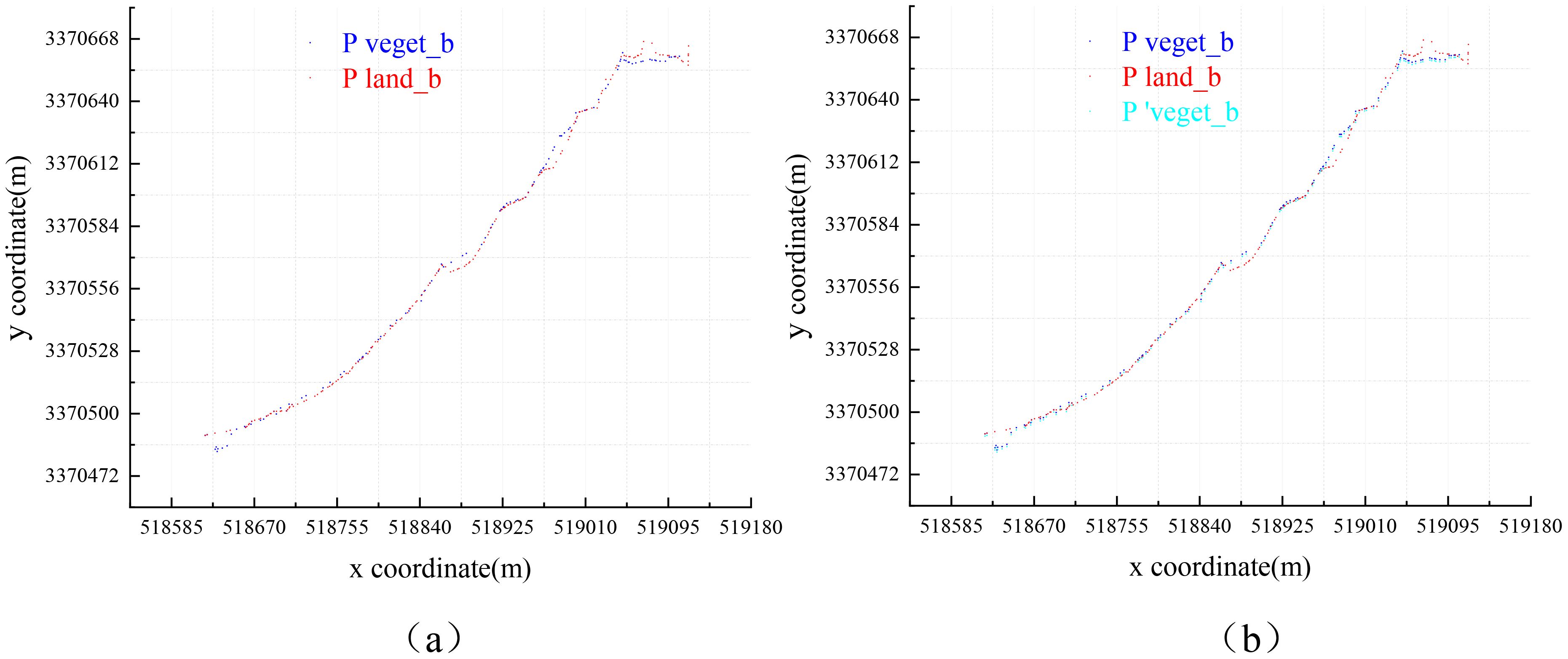
Figure 10. Overlay display of boundary point cloud: (A) overlay display of Pveget_b and Pland_b; (B) overlay display of , Pveget_b and Pland_b.
After merging and Pland_b, the attributes of each point in Pmerge will be determined using the method described in Section 2.4 (1). This involves classifying each point as either a land-side boundary point or a water-side boundary point. The results are depicted in Figure 11A. Subsequently, each point is corrected according to its classification as belonging to either land or water boundary points. This correction completes the point cloud, and with tidal adjustment, enables the determination of the shoreline direction, as illustrated in Figure 11B.
We attempted to overlay the shoreline generated from the shoreline point cloud onto the original vegetation sea area point cloud for visualization purposes. Through programming, we developed an algorithm that connects points in three-dimensional space into a line and overlays this line onto the point cloud set for display, as portrayed in Figure 12.
The boxes 1 and 2 in Figure 12 are magnified and displayed in Figure 13.
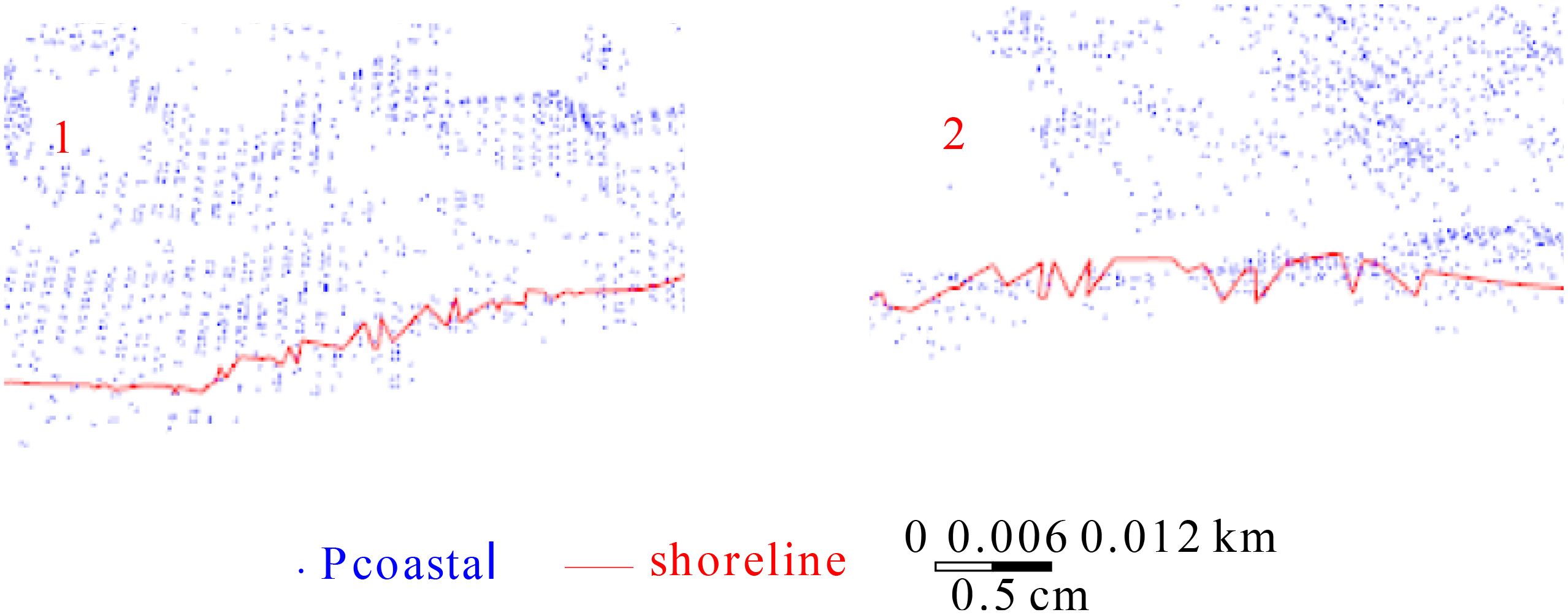
Figure 13. Enlarged display of boxes 1 and 2 in Figure 12.
Figures 12, 13 demonstrate that the method proposed in this paper effectively extracts the shoreline of vegetation sea areas. The extracted shoreline is generally smooth and complete, lacking scattered fractures or significant local fluctuations. The shoreline and terrain are largely similar. Overall, the proposed method effectively extracts the shoreline of vegetation sea areas.
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method for extracting shorelines from vegetation coastal areas, we compared it with the methods referenced in (Li et al., 2022a) and (Li et al., 2022b), which are known for their superior performance, as well as with conventional, reliable artificial image vectorization method. The shoreline obtained by image vectorization provides a rough description of the shoreline, and the timing of image acquisition may not coincide with that of the airborne LiDAR data collection. Consequently, the true values of the instantaneous water–land boundary obtained using these methods may differ. However, the shoreline directions calculated by the image vectorization method and other methods based on the water–land boundary should be broadly consistent to comparatively evaluate the accuracy of the shoreline extracted by other methods. According to measurement error theory, if the shoreline calculated using a certain algorithm is incorrect, it cannot be compared with other observed values. The measurement accuracy can only be compared when the observed values are correct. The shoreline direction obtained using the image vectorization method serves to determine whether the shorelines extracted by our method, and those in references (Li et al., 2022a) and (Li et al., 2022b), are accurate. A visual comparison of the images revealed that the shoreline directions obtained by the four methods were generally consistent and suitable for comparison. The shoreline point clouds calculated by these four methods were overlaid and displayed in a coordinate grid, as displayed in Figure 14, where red represents the shoreline extracted by our method, cyan represents the shoreline obtained by the method in Ref (Li et al., 2022a)., green represents the shoreline extracted by the method in Ref (Li et al., 2022b), and pink represents the shoreline obtained by the image vectorization method.
Figure 14 illustrates that the shoreline delineated by our method (red) and the image vectorization method (pink) share a similar overall shape, despite some discrepancies in the spatial positioning of specific points. Both methods exhibit similar directional trends. In contrast, the method described in Ref (Li et al., 2022a) (cyan) exhibits considerable deviation from the image vectorization method, with noticeable discontinuities and fluctuations, especially in areas such as the two horizontal lines and other obscured regions. The method from Ref (Li et al., 2022b) (green) also displayed differences, specifically in areas where the pink shoreline is more prevalent, exhibiting significant jitter at local points. Its resemblance to the image vectorization method is not as pronounced as that of our method. In the elliptical region, the cyan shoreline notably diverges from the pink shoreline, whereas the red shoreline aligns more closely with the pink, thereby capturing the finer details through smaller undulations. Furthermore, we attempted to superimpose the shoreline generated by four methods with the original vegetation sea area point cloud, as displayed in Figure 15.
Boxes 1 and 2 in Figure 15 are enlarged and displayed in Figure 16.
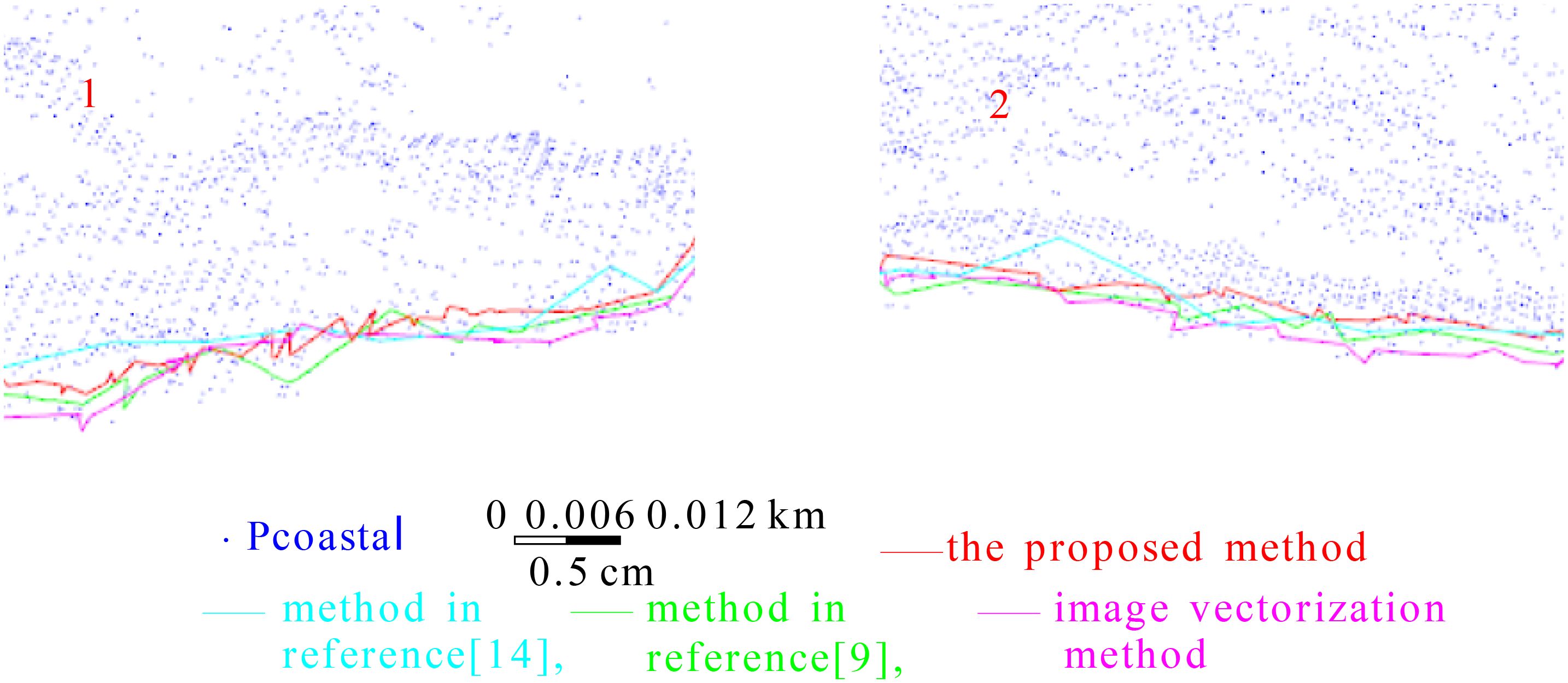
Figure 16. Enlarged display of boxes 1 and 2 in Figure 15.
Figures 15, 16 further demonstrate that the cyan shoreline generated by the method in Ref (Li et al., 2022a) is more pronounced and elevated compared to the other three shoreline types. These figures also reveal substantial local fluctuations in the cyan shoreline, whereas the red shoreline (our method) generally maintains a closer proximity and greater similarity to the pink shoreline (image vectorization method). The enlarged sections in Figure 16 illustrate that the cyan shoreline exhibits more pronounced shaking and larger jumps. In contrast, the red and pink shorelines display a higher spatial similarity, despite some differences. The cyan shoreline is characterized by longer straight segments across various areas, lacking the curved and undulating segments required to accurately represent the local shoreline details.
The orientation of the shoreline is discernible from the coordinate grid, although assessing accuracy for each individual point is challenging. The accuracies of shorelines generated by four different methods were evaluated using the procedure described in Section 2.5, with statistical results presented in Table 1. The y-coordinate error at each shoreline point was calculated to represent the main direction of the shoreline. Thereafter, the points were categorized into error intervals based on their y-coordinate errors, and the number of points within each interval was tallied. According to Table 1, intervals with larger y-coordinate errors contain fewer points when using our method, while intervals with smaller errors contain more points. Conversely, the methods cited in Refs (Li et al., 2022a; Li et al., 2022b), and the image vectorization method exhibit a higher count of points in intervals with larger errors and fewer points in intervals with smaller errors. This pattern suggests significant positional discrepancies between the shorelines calculated by these three methods and the average shoreline derived from all four methods, indicating superior extraction performance of our method compared to those in Refs (Li et al., 2022a) and (Li et al., 2022b).
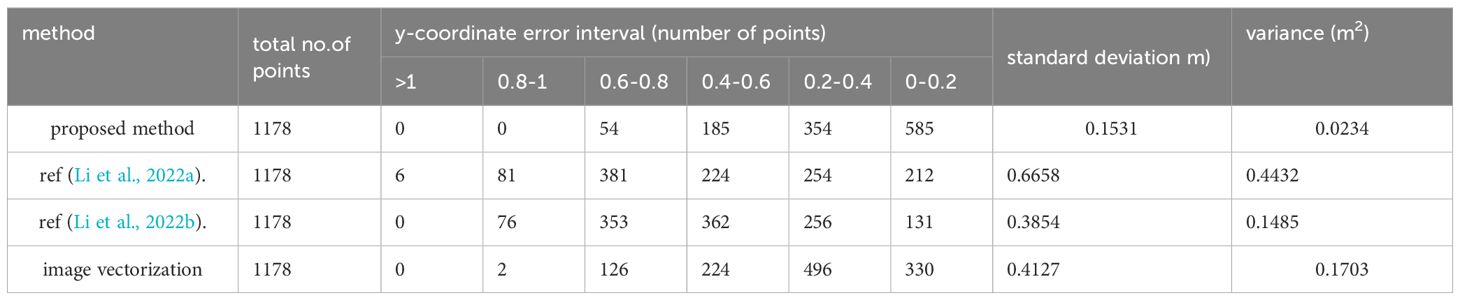
Table 1. Statistics of y-coordinate error values of shoreline obtained by four methods (for data one).
Furthermore, the standard deviation and variance of the y-coordinate errors across all points were calculated based on individual point errors. The standard deviation for our method is reported as 0.1531, compared to 0.6658 for the method in Ref (Li et al., 2022a), 0.3854 for the method in Ref (Li et al., 2022b), and 0.4127 for the image vectorization method. This demonstrates a reduction in the standard deviation of the overall shoreline by 0.5127 m compared to the value in Ref (Li et al., 2022a). Therefore, the proposed method achieved an improvement of 0.5127 m in the overall accuracy of the shoreline. Additionally, the proposed method exhibits the smallest variance, further indicating its superior performance relative to the other three methods.
For all types of coasts, some contain vegetation while others do not, and shorelines with vegetation can be extracted using the method described in this article. For the remaining shorelines without vegetation, the vegetation point set in this method can be set to empty. Therefore, the general framework for extracting coastlines based on airborne point clouds is shown in Figure 17.
This study introduces a method for extracting shorelines from vegetation areas, termed Shoreline_veget, which leverages laser point cloud echo intensity values and an elevation gradient function. Shoreline_veget addresses the challenges of extraction failures and inaccuracies due to vegetation occlusion and information gaps. Experimental validation on sea area point clouds demonstrates that this method outperforms existing techniques in Refs (Li et al., 2022a). and (Li et al., 2022b) in terms of extraction performance, stability, and accuracy. The analysis and experiments conducted in this study lead to several conclusions and future directions:
1. The elevation correction method described herein represents an advanced computational approach that performs reasonable calculations based on the available point cloud data. Therefore, the deviations from actual elevations are minimal and do not significantly impact subsequent analyses.
2. The elevation gradient function used to determine the attributes of each point in the fusion point-cloud set generally yields accurate results, despite a small number of points being inaccurately judged. The correction of point attributes produced a significant improvement in the overall positional accuracy of the shoreline.
3. If vegetation points are concentrated in an empty space, they can be interpreted as shallow shoals, muddy shorelines, low-precision bedrock shorelines or other shoreline types. For high-precision shoreline extraction, it is advisable to optimize the method based on the specific characteristics of this sea area.
4. The classification of vegetation and land point sets using laser echo intensity values allows for more precise calibration of the laser echo intensities associated with various land features, particularly prominent coastal elements such as sand, rocks, soil, silt, and water bodies. Additionally, calibrating echo intensity values according to changes in water depth enhances the utility of point clouds for shoreline extraction. Additionally, if the airborne lidar point cloud fuses multi-source remote sensing data such as aerial and space imagery, insar, etc., it will be able to improve the efficiency and accuracy of shoreline extraction, which is also the future research direction in this field.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
WL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. LL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TL: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This article has been supported by the funds of National Natural Science Foundation of China (42207208), the Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (GJJ2201631, GJJ201010), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jinggangshan University (JZ2002).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Benhur J., Vendhan M., Kumar P., Janagiraman R. (2024). Coastal resilience and shoreline dynamics: assessing the impact of a hybrid beach restoration strategy in Puducherry, India. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1426627
Colak A. T. I. (2024). Geospatial analysis of shoreline changes in the Oman coastal region (2000-2022) using GIS and remote sensing techniques.Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1305283
Demir N., Bayram B., Şeker D. Z., Oy S., İnce A., Bozkurt S. (2019). Advanced lake shoreline extraction approach by integration of SAR image and LIDAR data. Mar. Geodesy 42, 166–185. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2019.1581861
Deronde B., Houthuys R., Henriet J. P., Lancker Van V. (2008). Monitoring of the sediment dynamics along a sandy shoreline by means of airborne hyperspectral remote sensing and LIDAR: a case study in Belgium. Earth Surface Processes Landforms: J. Br. Geomorphological Res. Group 33, 280–294. doi: 10.1002/esp.1545
Hu S., Qin J., Ren J., Zhao H., Ren J., Hong H. (2020). Automatic extraction of water inundation areas using Sentinel-1 data for large plain areas. Remote Sens. 12, 243. doi: 10.3390/rs12020243
Incekara A. H., Seker D. Z., Bayram B. (2018). Qualifying the LIDAR-derived intensity image as an infrared band in NDWI-based shoreline extraction. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 11, 5053–5062. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
Lee I. S., Park H. J., Lee J. O., Kim Y. S. (2011). Delineating the natural features of a cadastral shoreline in South Korea using airborne laser scanning. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 4, 905–910. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
Li W., Liu H., Qin C. (2022a). A method for optimal estimation of shoreline in cliff zones based on point cloud segmentation and centroid calculation. Appl. Sci. 12, 10810. doi: 10.3390/app122110810
Li W., Liu H., Qin C. (2022b). A method for the extraction of shorelines from airborne lidar data in muddy areas and areas with shoals. Remote Sens. Lett. 13, 480–491. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2022.2042616
Liu H., Sherman D., Gu S. (2007). Automated extraction of shorelines from airborne light detection and ranging data and accuracy assessment based on Monte Carlo simulation. J. Coast. Res. 23, 1359–1369. doi: 10.2112/05-0580.1
Nassif F. B., Pimenta F. M., D'Aquino C. A., Assireu A. T., Garbossa L. H. P., Passos J. C., et al. (2020). Coastal wind measurements and power assessment using a LIDAR on a pier. Rev. Bras. Meteorologia 35, 255–268. doi: 10.1590/0102-7786351007
Obu J., Lantuit H., Grosse G., Günther F., Sachs T., Helm V., et al. (2017). Coastal erosion and mass wasting along the Canadian Beaufort Sea based on annual airborne LiDAR elevation data. Geomorphology 293, 331–346. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.02.014
Pardo-Pascual J. E., Almonacid-Caballer J., Cabezas-Rabadán C., Castelle B., Del Río L., Montes J., et al. (2024). Assessment of satellite-derived shorelines automatically extracted from Sentinel-2 imagery using SAET. Coast. Eng. 188, 104426. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2023.104426
Smeeckaert J., Mallet C., David N., Chehata N., Ferraz A. (2013). Large-scale classification of water areas using airborne topographic lidar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 138, 134–148. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.07.004
Spinosa A., Ziemba A., Saponieri A., Damiani L., El Serafy G. (2021). Remote sensing-based automatic detection of shoreline position: A case study in apulia region. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 575. doi: 10.3390/jmse9060575
Stateczny A., Halicki A., Specht M., Specht C., Lewicka O. (2023). Review of shoreline extraction methods from aerial laser scanning. Sensors 23, 5331. doi: 10.3390/s23115331
Stockdonf H. F., Sallenger A.H. Jr, List J. H., Hohnan R. A. (2002). Estimation of shoreline position and change using airborne topographic lidar data. J. Coast. Res. 18 (3), 502–513.
Vaaja M., Kukko A., Kaartinen H., Kurkela M., Kasvi E., Flener C., et al. (2013). Data processing and quality evaluation of a boat-based mobile laser scanning system. Sensors 13, 12497–12515. doi: 10.3390/s130912497
Wang H., Xu D., Zhang D., Pu Y., Luan Z. (2022). Shoreline dynamics of Chongming Island and driving factor analysis based on landsat images. Remote Sens. 14, 3305. doi: 10.3390/rs14143305
Wang J., Wang L., Feng S., Peng B., Huang L., Fatholahi S. N., et al. (2023). An overview of shoreline mapping by using airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 15, 253. doi: 10.3390/rs15010253
Wei X., Zheng W., Xi C., Shang S. (2021). Shoreline extraction in SAR image based on advanced geometric active contour model. Remote Sens. 13, 642. doi: 10.3390/rs13040642
Xu S., Ye N., Xu S. (2019). A new method for shoreline extraction from airborne LiDAR point clouds. Remote Sens. Lett. 10, 496–505. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2019.1569277
Yang H., Chen M., Xi X., Wang Y. (2024). A novel approach for instantaneous waterline extraction for tidal flats. Remote Sens. 16, 413. doi: 10.3390/rs16020413
Zhao J., Song F., Gong G., Wang S. (2023). Improved UNet-based shoreline detection method in real time for unmanned surface vehicle. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11, 1049. doi: 10.3390/jmse11051049
Keywords: airborne LiDAR, vegetation sea area, shoreline extraction, elevation gradient function, tidal correction
Citation: Li W, Liu L, Zhu W, Li J and Liu T (2025) Shoreline_veget— a new shoreline extraction method for vegetation seas, with high robustness, accuracy and scalability. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1491085. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1491085
Received: 04 September 2024; Accepted: 30 January 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Giandomenico Foti, Mediterranea University of Reggio Calabria, ItalyReviewed by:
Armin Moghimi, Leibniz University Hannover, GermanyCopyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Zhu, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weihua Li, bGl3ZWlodWFAamdzdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.