
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Mar. Sci., 27 January 2025
Sec. Marine Biology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1488376
Parasites in mollusks are often neglected by humans, while some species were reported to be harmful to economic mollusks and caused production decrease. Metazoan parasites of mollusk studies from the China Seas started relatively later than other countries. To promote long-term studies on the distribution and diversity of metazoan parasites of mollusks from the China Seas, a comprehensive review has been carried out based on the available literature. The purpose of this study was to perform a critical review about the metazoan parasites associated with mollusks that are useful for the discovery of new metazoans. This publication summarizes information on metazoan parasites of Chinese mollusks from 1932 to 2024. The information is presented and contains 128 species of parasites, distributed among the higher taxa as follows: Turbellaria (2 species), Trematoda (34 species), Cestoda (1 species), Annelida (38 species), Arthropoda (48 species), Porifera (2 species), Cnidaria (1 species), and Mollusca (2 species). Many records of parasites not identified to the species level are also included. Collectively, this review provides a synopsis of the known metazoan parasites of mollusks from the China Seas, as well as presents the known relationship between metazoan parasites and the mollusks, which will broaden our knowledge on the metazoan parasites of mollusks. It is important as it highlights the lack of metazoan parasite studies done in the China Seas and the need for more parasite biodiversity work.
Mollusks [soft-bodied animals that have a hard shell (majority of the species)] have a tremendous role in the ecosystem and economy of various countries. Certain species of this group are edible and delicious and have a market value; therefore, they have attracted attention for cultivation. Members of this phylum inhabit the terrestrial world, fresh waters, and marine waters, with the highest number of species found in marine waters. Many species belonging to different classes of the phylum are edible, such as species of class Gastropoda (Haliotis corrugata, Turbo bruneus, and Rapana venosa), Bivalvia (Tegillarca granosa, Perna viridis, and Magallana gigas), and Cephalopoda (Amphioctopus fangsiao, Octopus minor, and Loligo vulgaris). It has been reported that 65 species of mollusks have been farmed globally until the year 2020 (Tacon, 2020). China has approximately 14,500 km of coastline and mollusks are being cultured all along the Chinese coast. It is one of the top mollusk exporter countries in the world. The increase in the number of cultured species also led to an increase in per-capita consumption.
Nevertheless, certain species of parasites are harmful to the breeding industry of mollusks around the world including China. The parasite is an important causative agent that can harm the industry and brings significant mass mortality. Parasitic infestation investigations are lacking especially from Chinese waters. Metazoan parasites of mollusks are members of the main phyla like Platyhelminthes, Annelida, and Arthropoda. Moreover, there have been few reports on Porifera, Cnidaria, Nemertea, Nematoda, and Mollusca (Russell, 1967; Rohde, 2005). To promote long-term studies on the distribution and diversity of metazoan parasites of mollusks from the China Seas, a comprehensive review has been carried out based on the available literature, which would be useful for understanding the present and forthcoming infestation and migration.
A scoping review was performed to characterize and summarize the available information on metazoan parasites of mollusk research from the China Seas. Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed databases were searched using combinations of the terms “metazoa*”, “parasit*”, “mollusk or mollusc”, “Platyhelminth*”, “Turbellaria*”, “Trematod*”, “Cestod*”, “Annelid*”, “Polychaet*”, “Arthropod*”, “copepod*”, “Malacostraca*”, “pea crab”, “Pinnotherid*”, “prawn”, “Palaemonoid*”, “Pontoniinae”, “sea spider”, “Pycnogonid*”, “sponge”, “Porifera”, “Cnidaria*”, “Nemertea*”, “Nematod*”, and “Mollusca*” plus the name of the China Seas. For each search result obtained, the abstract was reviewed to determine relevance. In addition to the databases, gray literature from university theses and the conference presentations were searched.
Platyhelminthes (Turbellaria, Trematoda, and Cestoda) (Figure 1A): Two species of turbellarians were recorded; Stylochus sp. was found inside oysters from Fujian in the East China Sea and Guangdong in the South China Sea. Stylochoplana maculata (Quatrefage, 1845) was inside bivalves from Hong Kong in the South China Sea (Figure 1D). There are 23 known species of trematodes in the East China Sea and the South China Sea, and a few undefined species existed in the China Seas. Additionally, the hosts including bivalves and gastropods (see Table 1; Figure 1D) and Tylocephalum sp. belonging to the order Lecanicephalidea parasitize oysters in Taiwan, the East China Sea (Sun and Chen, 2007) (Figure 1D).
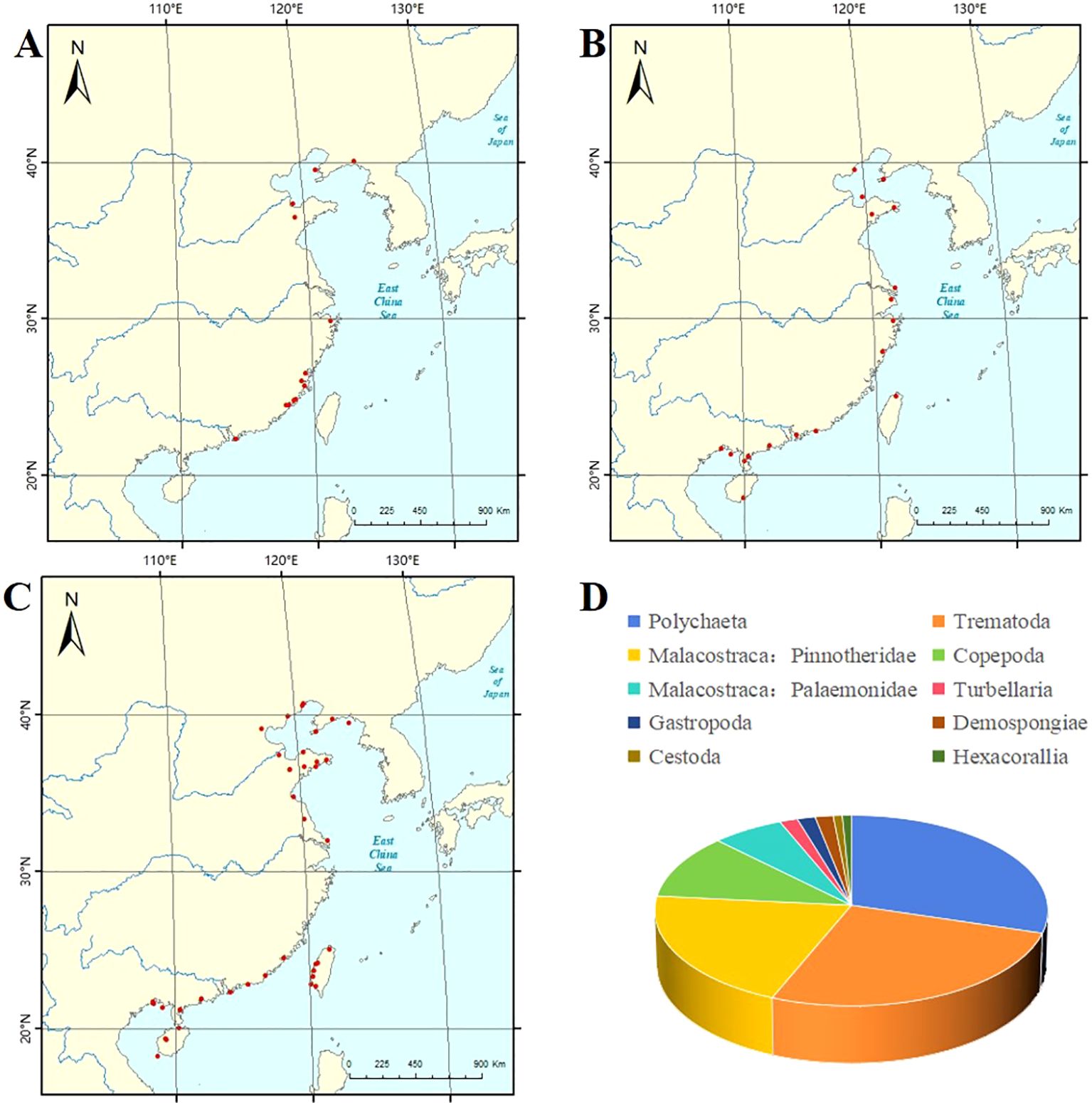
Figure 1. (A) The map showing the collection areas of platyhelminths parasitizing mollusks in the China Seas. (B) The map showing the collection areas of annelids parasitizing mollusks in the China Seas. (C) The map showing the collection areas of arthropods parasitizing mollusks in the China Seas. (D) Metazoan parasites associated with marine mollusks inhabiting the China Seas. (A–C) do not show the Peninsula, Islands, Bay, River, and Sea.
Annelida: Studies on the parasitic polychaetes of mollusks were recorded in the China Seas. More than 30 species of polychaetes belong to Polychaeta, and the hosts are marine bivalves and gastropods. There are 27 known species of polychaetes in the China Seas. A few undefined species are found in the Yellow Sea and the South China Sea (see Table 2; Figures 1B, D).
Arthropoda (Copepoda, Malacostraca, and Pycnogonida) (Figure 1C): Studies on the copepods of mollusks in the China Seas focus on cyclopoid copepods. There are 14 species of parasitic copepods from the China Seas and the hosts are bivalves and cephalopods (see Table 3; Figure 1D). There are 34 species of parasitic malacostracans from the China Seas, and the hosts are bivalves and gastropods (see Table 4; Figure 1D). Parasitic sea spiders of mollusks in the China Seas have not been recorded.
Porifera: Suberites carnosus (Johnston, 1842) (Suberitida: Suberitidae) was recorded at Xiagu Strait from Xiamen, the East China Sea attached to the outer shell of oysters. Another recorded species is Mycale phyllophila Hentschel, 1911, which was attached to the farmed oysters in the southern part of Hong Kong Island (Huang and Lin, 2012) (Figure 1D).
Cnidaria: In the China Seas, one species of parasitic cnidarian of mollusks has been recorded. Paraiptasia radiata (Stimpson, 1856) was found on Nassarius sp. at Wu Kai Sha, Hong Kong (Huang and Lin, 2012) (Figure 1D).
Nemertea: No records available.
Nematoda: No records available.
Mollusca: A kind of snail, Brachystomia omaensis (Nomura, 1938), which was semi-parasitic on Turbo sp. and abalone shells, was recorded in Beidaihe, Hebei, and Qingdao, Shandong, as well as in the East China Sea (Qi et al., 1989). In addition, Crepidula onyx Sowerby, 1824 was attached to the outer shell of Perna viridis (Linnaeus) from Hong Kong in the South China Sea (Huang and Lin, 2012) (Figure 1D).
Turbellaria is considered as an invalid class because it is a paraphyletic group. (i.e., having descendants, namely, the parasitic classes, which are not classified within it) (Ehlers, 1985). Several species of turbellarians have been reported to be associated with commercially important marine mollusks (Russell, 1967). Wu et al. (1997) reported that some species of suborders Acotylea (Rhabditophora: Polycladida) and Dalytyphloplanida (Rhabditophora: Rhabdocoela) are turbellarians that parasitize mollusks. Some species of Stylochus Ehrenberg, 1831 and Pseudostylochus Yeri and Kaburaki, 1918 (belonging to Acotylea) parasitize oysters and other invertebrates (Russell, 1967). Species of Graffilla Ihering, 1880 and Paravortex Wahl, 1906 (belonging to Dalytyphloplanida) were found in mollusks. Depending on species, they were located in the mantle and gills, in the stomach and digestive gland, or in the heart and the kidney (Rohde, 2005). In addition, turbellarians belonging to the order Fecampiida (belonging to Rhabditophora) were found in mollusks; Urastoma cyprinae (Graff, 1882) causes pathological reactions in the hosts, leading to disorganization of the gill filaments (Robledo et al., 1994) and Octopoxenus antarcticus Gordeev, Biserova, Zhukova and Ekimova, 2022 was found in the intestine and liver of the octopuses (Gordeev et al., 2022). The two species (Stylochus sp. and Stylochoplana maculata) of turbellarians discovered in our country belong to Acotylea from the East China Sea and the South China Sea, and their hosts are bivalves (Figure 1D). There should be more opportunities to discover parasitic turbellarians in other sea areas of our country.
Trematoda use mollusks as first and second intermediate hosts (Lauckner, 1983). There are two subclasses, the Aspidogastrea and Digenea, the species of which parasitize marine bivalves, gastropods, and cephalopods (Russell, 1967; Rohde, 2005; Magalhães, 2018; Hochberg, 1990; Paladini et al., 2017; Madsen and Stauffer, 2024). As an important intermediate host in the life cycle of trematodes, the problem of diseases caused by the parasitic trematode larvae in economic mollusks is becoming increasingly prominent. Many kinds of trematodes often infect the liver, heart, and gonads of mollusks, and destroy the tissues and organs and their functions, resulting in poor growth, low condition factor, and low nutritional value. They even damage the reproductive capacity of mollusks and lead to death in severe cases (Yang and Shi, 2000). In China, there are more than 30 species of trematodes recorded and they are all affiliated to Digenea (belonging to Rhabditophora); the hosts are marine bivalves and gastropods from the China Seas, mostly in the East China Sea and the South China Sea. Mollusks often appear as the first intermediate host and occasionally as the second intermediate host (see Table 1; Figure 1D). At present, it is statistically found that all the mollusks acting as the second intermediate hosts are bivalves. It remains to be further studied in the future whether it is a coincidence.
As a group, mollusks are not common hosts for cestode parasites but have been reported to serve as intermediate hosts for cestodes in exceptional cases (Russell, 1967). A few species of cestodes have been reported from marine mollusks. Six orders of cestodes (Tetraphyllidea, Trypanorhyncha, Lecanicephalidea, Cyclophyllidea, Diphyllidea, and Tetrabothriidea), belonging to the subclass Eucestoda of the subphylum Rhabditophora, have been found in mollusks including cephalopods, pelecypods, and gastropods (Rohde, 2005). The life cycle of tetraphyllidean cestodes involves the mollusk as their hosts (Cake, 1978). Heavy infections of trypanorhynch larvae in the guts of pelecypod mollusks prevent the passage of food (Rohde, 2005). Heavy infections of larval lecanicephalideans may result in physiological stress and affect the growth and reproduction of pelecypod mollusks (Cake, 1978). Rohde (2005) recorded several marine animals serving as intermediate hosts for marine cestodes. As we can see from Figure 3.22 of that article, it clearly shows that cephalopods, pelecypods, and gastropods serve as intermediate hosts of cyclophyllideans, lecanicephalideans, tetraphyllideans, diphyllideans, trypanorhynchans, and tetrabothriideans (Rohde, 2005). Only one species (Tylocephalum sp.) parasitize oysters in Taiwan, the East China Sea (Figure 1D). There is an urgent need to discover more species.
Several species of polychaetous annelids are known to live in association with marine mollusks. Polychaeta, a class of Annelida, parasitizes mollusks (Russell, 1967). Polychaetes exhibit great biodiversity in marine ecosystems, and many of them are involved in symbiotic relations (Martin and Britayev, 1998; Rouse and Pleijel, 2001). The molluscan hosts include bivalves, gastropods, limpets, chitons, squids, and octopuses (Jimi et al., 2019). Polychaetes parasitic on cultured shellfish such as pearls, oysters, scallops, and abalones affect the survival rate, yield, and quality of mollusks (Martin and Britayev, 1998; Nel et al., 1996; Caceres-Martinez et al., 1998; Fitzhugh and Rouse, 1999). Lankester (1868) has suggested that the polychaete can secrete a strong acid, which accounts for the tunnels that they burrow in the shell. In addition, the parasitic marine leech Pontobdella moorei Oka, 1910 along the northwest Mexican Pacific coast was described, and this ectoparasite was collected from the skin of the Octopus bimaculatus (Verrill) (López-Peraza et al., 2017). The annelids discovered in China all belong to the polychaetes. They are found in the China Seas; however, most of them are located in the South China Sea and the hosts are mainly bivalves, along with a small number of gastropods (see Table 2; Figures 1B, D).
Among copepod crustaceans, numerous species have been reported as “parasites” or as “commensals” of mollusks including several from commercially important marine species (Russell, 1967). Copepods are typically small and inconspicuous aquatic crustaceans but they are extremely abundant. Two orders (Cyclopoida and Monstrilloida) of Copepoda were reported in mollusks (Rohde, 2005; Gejima et al., 1999; Suárez-Morales et al., 2010). Copepods parasitize most mollusk groups, ranging from aplacophorans and polyplacophorans to the cephalopods. Knowledge about the effects of copepod parasites on mollusks is still limited. Some species are reported to be harmful to economic mollusks. For example, the red copepod Mytilicola intestinalis Steuer, 1902 may be the cause of heavy mortalities for the mussel Mytilus edulis Linnaeus in Europe (Blateau et al., 1992); the scallop copepod Pectenophilus ornatus Nagasawa, Bresciani and Lutzen, 1988 can attain a prevalence of 100% and cause significant loss of condition in the Japanese scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis (Jay) (Nagasawa and Nagata, 1992; Suzuki and Matsutani, 2009); Mytilicola orientalis Mori, 1935 and Ostrincola koe Tanaka, 1961 have been reported to harm mollusks (Ho and Zheng, 1994; Streftaris and Zenetos, 2006). The potential impact of the other copepod parasites on mollusks remains to be studied. Our findings in the China Seas all belong to Cyclopoida. Among them, in the East China Sea and the South China Sea, unknown species are urgently in need of discovery. Octopicola huanghaiensis Du, Dong and Sun, 2018 was found from cephalopods, and the remaining species were part of bivalves (see Table 3; Figure 1D).
Castro (2015) stated that parasitic crabs including two families, namely, Aphanodactylidae and Pinnotheridae, have 322 species in 57 genera. All known members of the Aphanodactylidae for which hosts have been recorded are associated with tube building polychaete worms (belonging to Terebellidae) (Ahyong and Ng, 2009). Species of Pinnotheridae are associated with various invertebrates including mollusks (Dai et al., 1980). Among the malacostracans, a number of decapods are known to live symbiotically with commercially important marine mollusks at least during one phase of their life cycles (Russell, 1967). Specifically, certain species of crabs of Pinnotheridae are known to live within the mantle cavities of oysters and other pelecypods (Russell, 1967). Pea crabs have been shown to cause damage to the gills of their bivalve hosts. Infected mussels have been shown to have lower tissue weights and slightly greater shell weights than equivalent uninfected mussels (Seed, 1969). They retard the growth of some commercial mollusks and cause millions of dollars in losses in aquaculture (Trottier and Jeffs, 2015). All the pea crabs found in China so far belong to Pinnotheridae. They were found in the China Seas. Most of their hosts are bivalves, and only an extremely small number are gastropods (see Table 4; Figure 1D).
The crabs belong to the family Pinnotheridae, especially the genus Pinnotheres. Meanwhile, the prawns are members of the family Palaemonidae. Most species of the family are commensal and are mainly associated with coelenterates, sponges, bivalve mollusks, echinoderms, and tunicates, and several species are cleaners of fishes (Li, 2004). The association between bivalves and pinnotherid crabs is relatively well known and has often been studied but little attention has been paid to the palaemonid commensals (Johnson and Liang, 1966). In terms of both the number of host species and the number of shrimp associates, the most important group of host organisms seems to be Scleractinia (Grave, 1999). Nevertheless, bivalve mollusks are also important as hosts for shrimps. Commensalism with bivalve mollusks is not restricted to palaemonid shrimps, but also occurs in Alpheidae (Grave, 1999). We have not been able to show any damage to host tissues caused by prawns. The amount of food consumed by prawns is minimal. Thus, even in cases of multiple infections, it is likely to be insignificant compared to the total food supply available to bivalves. Therefore, prawns seem to be harmless commensals (Johnson and Liang, 1966). Eight species of palaemonid prawns have been reported in China. They are distributed in the East China Sea and the South China Sea and all their hosts are bivalves (see Table 4; Figure 1D). The parasitic prawns still need further investigation and research.
All pycnogonids parasitic on mollusks belong to the order Pantopoda, and the hosts are gastropods and bivalves (Arnaud and Bamber, 1988). Pycnogonids are most often found attached to the foot and mantle of the host by means of their chelifores, with their proboscides piercing and destroying the host tissue (Benson and Chivers, 1960). Juvenile ammotheid pycnogonid species of the genus Nymphonella Ohshima, 1927 have been reported to be living parasitically in several species of infaunal and epifaunal bivalve mollusks in Japanese waters. The young and adults of Achelia chelata (Hilton, 1939) were also found infesting the mussel Mytilus californianus Conrad, partly destroying the tissue (Benson and Chivers, 1960). Opisthobranchs are a diverse group of mollusks that include the bubble shells, the sea hares, and the nudibranchs, all of which have a documented parasitic association with pycnogonids. Young stages of Ammothea Leach, 1814 were recorded as ectoparasites on the nudibranch Armina variolosa (Bergh) (Ohshima, 1933). At present, there is no record of sea spiders in the China Seas and they are waiting to be discovered in the future.
Porifera parasitic in mollusks belong to the class Demospongiae (Rohde, 2005; Huang and Lin, 2012). The parasitic sponges have been responsible for extensive damage to commercial shellfish and other molluscan hosts (Lauckner, 1983; Rosique et al., 1996). The most visibly destructive cases of bioeroding sponge infections can be observed in edible oyster cultures infected with Pione vastifica (Hancock, 1849). Reported infection rates can reach up to 50% in some commercial oysters such as Saccostrea glomerata (Gould) (Wesche et al., 1997). The common practice of translocating young oyster spat between commercial oyster beds has led to nearly cosmopolitan distributions for some species (e.g., P. vastifica) (Rohde, 2005). Parasitic sponges are a major pest of commercial molluscan fisheries (Rohde, 2005). Two species of parasitic sponges (Suberites carnosus and Mycale phyllophila) are discovered from the East China Sea and the South China Sea (Figure 1D). The Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea have no records of parasitic sponges and there are more species waiting to be discovered.
Cnidarians parasitic in mollusks are generally found in the class Hydrozoa (Rohde, 2005). Cnidarians living on gastropod shells containing living mollusks or hermit crabs are either simple epibionts or even mutualists. Polyps of three hydrozoan species, Kinetocodium danae Kramp, 1921, Perigonella sulfurea (Chun, 1889), and Pandea conica (Quoy and Gaimard, 1827), live on the shells of pteropods and feed on their epithelium and on their embryos (i.e., they are real parasites). Polyps of five hydrozoan species live in the mantle cavity of bivalve mollusks, attached to the tissues of the mantle cavity by stolonal sucker-like structures or by hydrorhizae penetrating into the host tissues. They utilize food collected by the ciliary movements of the bivalve gills and the labial palps, but their exact parasitic relationships are not known. Some have been observed feeding on the larvae of other parasites of their hosts. The species include Eugymnanthea inquilina Palombi, 1936, Eugymnanthea japonica (Yamada, 1950), Eutima commensalis Santhakumari, 1970, Eutima ostrearum (Mattox and Crowell, 1951), and Eutima sapinhoa Narchi and Hebling, 1975 (Rohde, 2005). Additionally, Paraiptasia radiata (belonging to Hexacorallia) was found on the outer shell of the Perna virdis in the South China Sea, and more species need to be found in the China Seas (Huang and Lin, 2012) (Figure 1D).
The parasitic nemerteans of mollusks are relatively few. The species of two orders Monostilifera and Heteronemertea have been recorded to date (Rohde, 2005). The Malacobdellidae belonging to Monostilifera contains a single genus, Malacobdella Blainville, 1872, with six valid species (Gibson, 1995; Ivanov et al., 2002). They predominantly inhabit the mantle cavity of bivalves of the subclass Heterodonta, Protobranchia, and Pteriomorphia (Rohde, 2005). Tetrastemma fozensis Gibson and Junoy, 1991 (Monostilifera: Tetrastemmatidae) lives in the mantle cavity of the bivalve Scrobicularia plana (da Costa) (Gibson, 1995). There is no reliable evidence to indicate that Malacobdella spp. (Monostilifera: Malacobedellidae) are in any way injurious to their hosts (Russell, 1967). In addition, Uchidana parasita Iwata, 1967 (Heteronemertea: Valenciniidae) was collected from the cavity and the gap between the mantle and shell of the bivalve Mactra chinensis Philippi in Japan (Iwata, 1967). Currently, there is no documentation of nemerteans in the China Seas and they remain to be discovered in the future.
The species of the nematodes belong to the order Rhabditida (Russell, 1967). Only a few species of nematodes have been reported from commercially important marine mollusks, although they have been recorded in some unimportant marine mollusks either as larvae or as adults (Russell, 1967). Sulcascaris sulcata (Rudolphi, 1819), an anisakine parasite of marine turtles, however, has a relatively simple life cycle with marine bivalves (such as scallops and oysters) serving as intermediate hosts (Lauckner, 1983). The presence of S. sulcata at the larval stage in edible scallops has significant implications for the depreciation of the product and also has consequences for health and hygiene requirements in accordance with legislation (Marcer et al., 2020). Millemann (1951) described the larva of the species Echinocephalus pseudouncinatus Millemann, 1951, encysted in the foot of the pink abalones, Haliotis corrugata Wood (Millemann, 1951). Nemerteans have not been recorded in the China Seas and they are yet to be found.
Several species of mollusks belonging to the family Pyramidellidae have been reported as parasites of commercially important marine mollusks (Russell, 1967). All pyramidellids are ectoparasites as they are generally attached on the exterior, near the edges of the valves of pelecypods, and insert their long proboscis into the hosts’ soft tissues to feed on blood or tissue fluids (Russell, 1967). As foraging animals, pyramidellids are constantly moving between the host and the habitat substrate rather than parasitizing the host for life (Robertson and Mau-Lastovicka, 1979). Odostomia Fleming, 1813 have been reported as a pest of oysters and mussels (Cole and Hancock, 1955). Additionally, species of the mollusks from the family Modiolidae and Calyptraeidae are also reported as epibionts of the mollusk hosts. For example, Leiosolenus patagonicus (d’Orbigny, 1846) and Crepidula sp. are parasites of Aulacomya atra (Molina) and Ostrea puelchana (d’Orbigny) from Argentina (Cremonte et al., 2005). Moreover, bivalves of the family Mytilidae, such as internal bioeroders, boring bivalves Lithophaga spp. are parasites of mollusks (Cortés and Jiménez, 2003). The abalone piddock clam, Penitella conradi Valenciennes, 1846, and mussels of Lithophaga spp. bore into substrates including the shells of live abalone (Moore, 2023). In China, two species (Brachystomia omaensis and Crepidula onyx) of parasitic mollusks have been discovered from the China Seas and the hosts are all gastropods (Figure 1D). Research on parasitic mollusks of the mollusk hosts needs to be further carried out.
Collectively, Figure 1 indicates that arthropods, annelids, and platyhelminths take up a relatively large proportion. The largest phylum is Arthropoda, while other phyla have a relatively small proportion. This review provides a synopsis of the known metazoan parasites of mollusks from the China Seas and presents the known relationship between metazoan parasites and mollusks, which will broaden our knowledge on the metazoan parasites of mollusks. Compared with other countries, scientific research on the metazoan parasites of mollusks from the China Seas is relatively scarce. Higher species diversity may be uncovered if other mollusks are examined intensively in the future. The knowledge about the effects of metazoan parasites on mollusks is still limited. Most species are reported to be more or less harmful to economic mollusks, with the exception of prawns and nemerteans. The potential impact of other metazoan parasites on mollusks still needs to be studied. For instance, anisakine parasites that pose a threat to human health should be given more attention. It should be emphasized that the biology of zoosymbionts of marine mollusks, regardless of their economic or medical importance, has a great deal to contribute to our understanding of the nature of symbiotic relationships and deserves increased attention (Russell, 1967).
XD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HJ: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Writing – original draft. ZX: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision. XT: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XF: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MC: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project for Talented Scholars of Hebei Agricultural University (No. YJ2020020); the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of the Ocean College, Hebei Agricultural University (No. 2021KY15); the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2022106002); and the Science and Technology Program of Shijiazhuang (241460085A).
Thanks are expressed for the researchers who obtained and published the data adopted in this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahyong S. T., Ng P. K. L. (2009). Aphanodactylidae, a new family of thoracotreme crabs (Crustacea: Brachyura) symbiotic with polychaete worms. Zootaxa 2289, 33–47. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.191334
Arnaud F., Bamber R. N. (1988). The biology of pycnogonida. Adv. Mar. Biol. 24, 1–96. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2881(08)60073-5
Benson P. H. C., Chivers D. D. (1960). A pycnogonid infestation of Mytilus californicus. Veliger 3, 16–19.
Blateau D., Le Coguic Y., Mialhe E., Grizel H. (1992). Mussel (Mytilus edulis) treatment against the red copepod Mytilicola intestinalis. Aquaculture 107, 165–169. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(92)90062-P
Bruce A. J. (1979). Records of some pontoniine shrimps from the South China Sea. Cahiers l’Indo Pacifique 1, 215–248.
Caceres-Martinez J., De Oca P. M. M., Vasquez-Yeomans R. (1998). Polydora sp. infestation and health of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas cultured in Baja California, NW Mexico. J. Shellfish Res. 17, 259–264.
Cake E. W. (1978). Larval cestode parasites of edible mollusks of the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Gulf. Caribb. Res. 6, 1–8. doi: 10.18785/grr.0601.01
Cao H. (1989). Life cycle of Proctoeces orientalis sp. nov. in marine bivalves. Acta Zool. Sin. 35, 58–65. doi: CNKI:SUN:BEAR.0.1989-01-010a
Cao H. (1990). Infection of marine bivalves by Proctoeces orientalis in Fujian coast. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait. 9, 381–386.
Castro P. (2015). “Treatise on zoology-anatomy, taxonomy, biology,” in The Crustacea. Eds. Castro P., Davie P. J. F., Guinot D., Schram F. R., von Vaupel Klein C. (Brill, Leiden), 543–581.
Chen M. (1994). The parasitized location of larval Cercaria elegans Tang 1992 in Ruditapes philippinarum and its histochemistry. Acta Zool. Sin. 40, 377–383.
Chen Y. R. (2008). Taxonomic and phylogenetic studies on the Pinnotherid crabs (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) of Taiwan. (Thesis). (China: National Taiwan Ocean University).
Cole H. A., Hancock D. A. (1955). Odostomia as a pest of oysters and mussels. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK. 34, 25–31. doi: 10.1017/S0025315400008584
Cortés J., Jiménez C. (2003). “Corals and coral reefs of the Pacific of Costa Rica: history, research and status,” in Latin American Coral Reefs. Ed. Cortés J. (Elsevier Science B. V., Amsterdam), 361–385.
Cremonte F., Figueras A., Burreson E. M. (2005). A histopathological survey of some commercially exploited bivalve molluscs in northern Patagonia, Argentina. Aquaculture 249, 23–33. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.01.024
Cui X. L. (1995). Occurrence and prevention of black shell disease in scallop culture. Hebei Fish. (2), 16. doi: CNKI:SUN:HBYU.0.1995-02-008
Dai A. Y., Feng Z. Q., Song Y. Z., Chen G. X. (1980). New species and new records of family Pinnotheridae from Hainan island. Acta Zootax. Sin. 5, 129–143.
Dai A. Y., Yang S. L., Song Y. Z., Chen G. X. (1986). Crabs of China Sea (Beijing: China Ocean press).
Du X., Dong C., Sun S. C. (2018). Octopicola huanghaiensis n. sp. (Copepoda: Cyclopoida: Octopicolidae), a new parasitic copepod of the octopuses Amphioctopus fangsiao (d’Orbigny) and Octopus minor (Sasaki) (Octopoda: Octopodidae) in the Yellow Sea. Syst. Parasitol. 95, 905–912. doi: 10.1007/s11230-018-9819-8
Du X., Sun S. C. (2022). Studies on cyclopoid copepods parasitic in bivalvian mollusks from the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea. Period. Ocean Univ. China. 52, 42–55. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20190174
Du X., Xu X. N., Chen Z., Zhang Z. Q., Liu Z. T., Chang M. S. (2024). Molecular identification of parasitic copepods using cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 from Chinese marine waters. Pakistan J. Zool., 1–7. doi: 10.17582/journal.pjz/20230906072422
Fitzhugh K., Rouse G. W. (1999). A remarkable new genus and species of fan worm (Polychaeta: Sabellidae: Sabellinae) associated with marine gastropods. Invertebr. Biol. 118, 357–390. doi: 10.2307/3227007
Gao Y. (2011). Study on the biological characters and the parasitic behavior of Polydora. (Thesis). Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
Gejima K., Ohtsuka S., Konishi K., Nagasawa K. (1999). “Research on parasitic organisms of mollusks I. The parasitic situation of Pinnotheres sinensis and monstrilloid copepods occurring in bivalves,” in The 37th Meeting of the Carcinological Society of Japan (Toba, Japan), 48.
Gibson R. (1995). Nemertean genera and species of the world: an annotated checklist of original names and description citations, synonyms, current taxonomic status, habitats and recorded zoogeographic distribution. J. Nat. Hist. 29, 271–561. doi: 10.1080/00222939500770161
Gordeev I., Biserova N., Zhukova K., Ekimova I. (2022). The first report of a parasitic ‘turbellarian’ from a cephalopod mollusc, with description of Octopoxenus antarcticus gen. nov., sp. nov. (Platyhelminthes: Fecampiida: Notenteridae). J. Helminthol. 96, e73. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X22000657
Grave S. D. (1999). Pontoniinae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidea) associated with bivalve molluscs from Hansa Bay, Papua New Guinea. Biologie 69, 125–141.
Ho J. S., Liu W. C., Lin C. L. (2012). New record of Ostrincola koe Tanaka 1961 (Copepoda: Poecilostomatoida: Myicolidae) from hard clam (Meretrix lusoria) of Taiwan, with key to species of genus Ostrincola Wilson 1944. J. Fish. Soc Taiwan. 39, 137–148. doi: 10.29822/JFST.201209.0001
Ho J. S., Zheng G. X. (1994). Ostrincola koe (Copepoda, Myicolidae) and mass mortality of cultured hard clam (Meretrix meretrix) in China. Hydrobiologia 284, 169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00006888
Hochberg F. G. (1990). “Diseases of Mollusca: Cephalopoda (Diseases caused by protistans and metazoans),” in Diseases of Marine Animals. Ed. Kinne O. (Biologische Anstalt Helgoland, Hamburg), 47–202.
Huang S. Z. (2005). The research for classification of crab megalopae along the coast of Xiangshan Bay in Hsinchu-using cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) as an auxiliary identification tool. (Thesis). National Hsinchu University of Education, China.
Huang Z. G., Lin M. (2012). The Living Species and Their Illustrations in China’s Seas (Beijing: Ocean press).
Humes A. G., Boxshall G. A. (1988). Poecilostome copepods associated with bivalve molluscs and a brachiopod at Hong Kong. J. Nat. Hist. 22, 537–544. doi: 10.1080/00222938800770361
Humes A. G., Lee S. Y. (1985). The poecilostome copepod Anthessius mytilicolus Reddiah 1966, associated with the mussel Perna viridis (L.) at Hong Kong. Asian Mar. Biol. 2, 85–92.
Ivanov V. A., Bigatti G., Penchaszadeh P. E., Norenburg J. L. (2002). Malacobdella arrokeana (Nemertea: Bdellonemertea), a new species of nemertean from the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean entocommensal in Panopea abbreviata (Bivalvia, Heterodonta, Hiatellidae) in Argentina. P. Bio. Soc Wash. 115, 359–367.
Iwata F. (1967). Uchidana parasita nov. gen. et nov. sp., a new parasitic nemertean from Japan with peculiar morphological characters. Zool. Anz. 178, 122–136.
Jiang W. (2006). Taxonomic study of Pinnotheridae (Crustacea: Decapoda) of the China seas. (Thesis). Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
Jiang W., Liu R. Y. (2011). New species and new records of pinnotherid crabs (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) from the Yellow Sea. Zool. Anz. 250, 488–496. doi: 10.1016/j.jcz.2011.05.001
Jimi N., Moritaki T., Kajihara H. (2019). Polychaete meets octopus: symbiotic relationship between Spathochaeta octopodis gen. et sp. nov. (Annelida: Chrysopetalidae) and Octopus sp. (Mollusca: Octopodidae). Syst. Biodivers. 0, 1–6. doi: 10.1080/14772000.2018.1520753
Johnson D. S., Liang M. (1966). On the biology of the Watchman prawn, Anchistus custos (Crustacea; Decapoda; Palaemonidae), an Indo-West Pacific commensal of the bivalve Pinna. J. Zool. Lond. 150, 433–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1966.tb03017.x
Kuo A. L., Lin F. J., Hsu J. T., Chan Y. S., Ueng Y. T. (2018). The population structure and parasitic relationships of oyster (Crassostrea angulata), Arcotheres sinensis (Pinnotheridae), and Rhopalione sinensis (Bopyridae) at the oyster reefs of western Taiwan. Crustaceana 91, 1433–1451. doi: 10.1163/15685403-00003842
Lankester E. R. (1868). On lithodomous annelids. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1, 233–238. doi: 10.1080/00222936808695684
Lauckner G. (1983). “Diseases of Mollusca: Bivalvia,” in Diseases of Marine Animals. Ed. Kinne O. (Biologische Anstalt Helgoland, Hamburg), 477–970.
Li X. Z. (1997). Report on Gnathophyllidae and Pontoniinae (Decapoda, Palaemonoidea) shrimps from the Xisha Islands and adjacent waters, South China Sea. Stud. Mar. Sin. (38), 223–251.
Li X. Z. (2004). The Pontoniine shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidae) from Anambas and Natuna Islands, Indonesia, collected by Anambas Expedition 2002. Raffles. B. Zool. 11, 67–72.
Li X. Z., Liu R. Y. (2002). Report on Pontoniine shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda) collected by joint Chinese-German marine biology expeditions to Hainan Island, South China Sea I. Anchistus, conchodytes, coralliocaris. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 20, 371–377. doi: 10.1007/BF02847929
Liang F. L., Liu Y., Deng C. M., Mao Y. (2007). Survey on polychaete verminosis in farmed pearl oyster (Pteria penguin) in Liusha Bay, Leizhou, Guangdong. Mar. Fish. Res. 28, 84–89.
Lin C. L., Ho J. S. (1999). Poecilostomatoid copepods parasitic in bivalve mollusks of Taiwan. Publ. Seto. Mar. Biol. Lab. 38, 201–218. doi: 10.5134/176288
Liu H. L. (2003). Morphological observation on development stages of Polydora ciliata. J. Zhanjiang Ocean Univ. 23, 8–11.
Liu S. F. (1993). Studies on the Epizootics of Prosorhynchus facilis in the sea shore of Xiamen, China. J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 32, 377–381. doi: 10.1007/BF02677083
Liu S. F. (1994). On the life cycle of Prosorhynchuns facilis Eckmann 1932. Acta Zool. Sin. 40, 231–240. doi: CNKI:SUN:BEAR.0.1994-03-002
López-Peraza D. J., Hernández-Rodríguez M., Barón-Sevilla B., Bückle-Ramírez L. F., Grano-Maldonado M. I. (2017). First record of Stibarobdella moorei (Annelida, Hirudinea, Piscicolidae) a marine leech parasitizing (Mollusca: Octopodidae) from the Mexican Pacific coast. Helminthologia 54, 322–329. doi: 10.1515/helm-2017-0044
Lv D. W., Chu J. W., Wang S. G., Zhang X. L., Wang D. F., Wang X. M. (2004). The observation of histopathology of the Meretix meretrix Linnaeus parasitized by the larva of Bucephalidae. Mar. Fish. Res. 25, 47–52. doi: CNKI:SUN:JOKE.0.2003-11-024
Lv D. W., Zhang X. L., Lin J. B., Wang D. F., Yu C. H. (2003). Studies on the tissue variation caused by the larva of Bucephalidae of Meretrix Meretrix and its control. Shandong Fish. 20, 32–33.
Madsen H., Stauffer J. R. (2024). Aquaculture of animal species: their eukaryotic parasites and the control of parasitic infections. Biology 13, 1–20. doi: 10.3390/biology13010041
Magalhães L. V. D. S. (2018). Inventory, dynamics and impact of the trematodes parasites in bivalves with high economic importance. (Thesis). Universidade de Aveiro, Portugal.
Marcer F., Tosi F., Franzo G., Verti A., Ravagan S., Santoro M., et al. (2020). Updates on ecology and life cycle of Sulcascaris sulcata (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in Mediterranean grounds: molecular identification of larvae infecting edible scallops. Front. Vet. Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00064
Martin D., Britayev T. A. (1998). Symbiotic polychaetes: Review of known species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 36, 217–340. doi: 10.1007/s002489900063
Meng X. Y., Tan Y., Yang W. W., Rbbani G., Yan X. W., Fang L., et al. (2019). Gonad status and gene expression of the manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum infected by a digenetic trematode. J. Shellfish Res. 38, 1–8. doi: 10.2983/035.038.0207
Millemann R. E. (1951). Echinocephalus pseudouncinatus n. sp., a nematode parasite of the abalone. J. Parasitol. 37, 435–439. doi: 10.2307/3273250
Moore J. D. (2023). “Disease and potential disease agents in wild and cultured abalone,” in Abalone: Biology, Ecology, Aquaculture and Fisheries. Eds. Cook P. A., Shumway S. E. (Academic Press, United States), 189–250.
Nagasawa K., Nagata M. (1992). Effects of Pectenophilus ornatus (Copepoda) on the biomass of cultured Japanese scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. J. Parasitol. 78, 552–554. doi: 10.2307/3283669
Nel R., Coetzee P. S., Van Niekerk G. (1996). The evaluation of two treatments to reduce mud worm (Polydora hoplura Claparède) infestation in commercially reared oysters (Crassostrea gigas Thunberg). Aquaculture 141, 31–39. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(95)01212-5
Paladini G., Longshaw M., Gustinelli A., Shinn A. P. (2017). “Parasitic diseases in aquaculture: their biology, diagnosis and control,” in Diagnosis and Control of Diseases of Fish and Shellfish. Eds. Austin B., Newaj-Fyzul A. (John Wiley & Sons Ltd, USA), 37–107.
Qi Z. Y., Ma X. T., Wang Z. R., Lin G. Y., Xu F. S., Dong Z. Z., et al. (1989). Molluscks from the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea (Beijing: Agriculture Press).
Radashevsky V. I., Hsieh H. L. (2000). Polydora (Polychaeta: Spionidae) species from Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 39, 203–217. doi: 10.2108/zsj.15.689
Ren S. L., Song W. B. (2002). Histopathology of bucephalidae larvae-caused disease in Meretrix meretrix. J. Fish. China. 26, 459–464. doi: 10.1360/biodiv.050121
Ren S. L., Yang X. C., Song W. B. (2005). A treamatode larva parasitized in cultured marine bivalve, Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus and its histopathology. Period. Ocean Univ. China. 35, 387–391.
Robertson R., Mau-Lastovicka T. (1979). The ectoparasitism of Boonea and Fargoa (Gastropoda: Pyramidellidae). Biol. Bull. 157, 320–333. doi: 10.2307/1541058
Robledo J. A. F., Caceres-Martinez J., Sluys R., Figueras A. (1994). The parasitic turbellarian Urastoma cyprinae (Platyhelminthes: Urastomidae) from blue mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in Spain: occurrence and pathology. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 18, 203–210. doi: 10.3354/dao018203
Rosique M. J., Cano J., Rocamora J. (1996). Influence of the sponge Cliothosa hancocki on the European flat oyster bed (Ostrea edulis) in the Mar Menor (Murcia, SE Spain). Oebalia 22, 99–111.
Sato-Okoshi W., Okoshi K., Abe H., Li J. Y. (2013). Polydorid species (Polychaeta, Spionidae) associated with commercially important mollusk shells from eastern China. Aquaculture, 406–407, 153–159. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.05.017
Seed R. (1969). The incidence of the pea crab, Pinnotheres pisum in the two types of Mytilus (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from Padstow, south-west England. J. Zool. 158, 413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1969.tb02158.x
Shen Y. L., Yu Y. S. (1994). Preliminary report on Bacciger sp. of Meretrix Meretrix in Jiangsu. Stud. Fish. Dis. 16, 17.
Shi L. (2000). Studies on pathogenology and histopathology of disease in Sinonovacula constricta caused by metacercariae of Monorchis xiamenensis. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait. 19, 60–65.
Shi L., Wang J. (2001). Biochemical and immunological characterization of excretory-secretory products of Vesicocoelium solenophagum and plasma proteins of its bivalve host, Sinonovacula constricta. J. Helminthol. 75, 279–284. doi: 10.1079/JOH200044
Shi Y. H., Wang A. M., Wu X. (2004). Survey on polychaete infestation of farmed pearl oyster, Pinctada martensii in China. Mar. Sci. 28, 13–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2004.07.004
Shin J. W., Wen C. M., Kou G. H., Chen S. N. (1996). Cercaria meretrix n. sp., from the hard clam Meretrix meretrix. Zool. Stud. 35, 68–70.
Soong K. (1997). Some life history observation on the pea crab, Pinnotheres tsingtaoensis, symbiotic with the bivalve mollusk, Sanguinolaria acuta. Crustaceana 70, 855–866. doi: 10.1163/156854097X00474
Streftaris N., Zenetos A. (2006). Alien marine species in the Mediterranean - the 100 ‘worst invasives’ and their impact. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 7, 87–118. doi: 10.12681/mms.180
Suárez-Morales E., Scardua M. P., Da Silva P. M. (2010). Occurrence and histopathological effects of Monstrilla sp. (Copepoda: Monstrilloida) and other parasites in the brown mussel Perna perna from Brazil. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 90, 953–958. doi: 10.1017/S0025315409991391
Sun W. M., Sun S. C., Wang Y. Q., Yang B. W., Song W. B. (2006). The prevalence of the pea crab, Pinnotheres sinensis, and its impact on the condition of the cultured mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, in Jiaonan waters (Shandong Province, China). Aquaculture 253, 57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.07.037
Suzuki H., Matsutani T. (2009). Infection of the parasitic copepod, Pectenophilus ornatus on juvenile Japanese scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis. Aquac. Sci. 57, 513–514. doi: 10.11233/aquaculturesci.57.513
Tacon A. G. J. (2020). Trends in global aquaculture and aquafeed production: 2000-2017. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 28, 43–56. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2019.1649634
Tang B. (2015). Taxonomic and histologic studies of polydora complex in the coastal area of China. (Thesis). Shanghai Ocean University, China.
Tang C. T. (1989). A survey of larval trematodes from marine and fresh water molluscs of Hong Kong. Acta Zool. Sin. 35, 196–204.
Tang C. T. (1990a). “Philophthalmid larval trematodes from Hong Kong and the coast of South China,” in Proceedings of the Second International Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China. Ed. Tang C. T. (Hong Kong Univeristy Press, Hong Kong), 213–232.
Tang C. T. (1990b). “Further studies on some cercariae of molluscs collected from the shores of Hong Kong,” in Proceedings of the Second International Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China. Ed. Tang C. T. (Hong Kong Univeristy Press, Hong Kong), 233–257.
Tang C. T. (1992). “Some larval trematodes from marine bivalves of Hong Kong and freshwater bivalves of coastal China,” in Proceedings of the Fourth International Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China. Ed. Tang C. T. (Hong Kong Univeristy Press, Hong Kong), 17–28.
Tang C. T. (1995). Spatial variation in larval trematode infections of populations of Nodilittorina Trochoides and Nodilittorina Radiata (Gastropoda: Littorinidae) from Hong Kong. Asian Mar. Bio. (12), 18–26.
Tang C. T., Hsu C. T., Huang M. C., Lu S. L. (1975). Studies on the parasitic disease of Chinese razor clam (Sinonovacula contricta Lamarck) in the northern estuary of Chiulung River, Fukien. J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 14, 161–177.
Tang C. T., Xu Z. Z. (1979). The ‘black root’ disease of the razor clam in estuary of Jiulong River, Fujian. Acta Zool. Sin. 25, 336–346.
Trottier O., Jeffs A. G. (2015). Mate locating and access behaviour of the parasitic pea crab, Nepinnotheres novaezelandiae, an important parasite of the mussel Perna canaliculus. Parasite 22, 1–10. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2015013
Wang A. M., Shi Y. H., Wu X. (2004). The comparison among effects of four treatments to reduce polychaete infestation in pearl oyster, Pinctada martensii. Mar. Fish. Res. 25, 41–46.
Wang C. H., Xu P. F., Lang S. (1983). In vitro cultivation of metacercaria found on gills of Chinese razor clam and its identification. Acta Zool. Sin. 29, 55–58.
Wang M. F., Liu Y., Yang T., Yu X. Y. (2006). A preliminary study on the main fouling organisms in Pteria penguin. J. Zhanjiang Ocean Univ. 26, 88–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2006.04.019
Wang Y., Sun S. C., Song W. B. (2002). Investigations on the prevalence and adverse effects of the pea crab, Pinnotheres sinensis, on the mussel, Mytilus edulis, in Qingdao area. J. Ocean Univ. Qingdao. 32, 720–726.
Wesche S. J., Adlard R. D., Hooper J. N. A. (1997). The first incidence of clionid sponges (Porifera) from the Sydney rock oyster Saccostrea commercialis (Iredale and Roughley 1933). Aquaculture 157, 173–180. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00139-7
Wu X. Z., Pan J. P., Jiang J. B. (1997). Advances in studies on marine molluscan diseases III. Pestology and neoplasia of marine molluscs. Mar. Sci. Bull. 16, 82–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02951625
Yang H. Y., Wu K. C., Li Y. N., Wang J. Y., Chen M. Q., Jiang J. Z., et al. (2012). Epidemiology of polychaete in the Pinctada fucata in Hainan Xincun port. Guangdong Agr. Sci. 39, 170–173. doi: 10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z
Yang Y. C., Li F. X. (1997). The reproduction and growth of Pinnotheres pholadis living in the mantle cavity of Hiatula acuta. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 19, 89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02951625
Yang Y. C., Li F. X., Cai L. Z. (1998). Propagation and growth of Pinnotheres pholadis living in mantle cavity of Hiatula acuta. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 17, 233–241.
Yang Y. R., Shi L. (2000). “Studies on the larval stage of trematodes and its damage of the marine economic mollusks,” in The 6th symposium of young parasitologists, Zoological Society of China (Hebei, China), 21–22.
Ye L. T., Tang B., Wu K. C., Su Y. L., Wang R. X., Yu Z. N., et al. (2015). Mudworm Polydora lingshuiensis sp. n is a new species that inhabits both shell burrows and mudtubes. Zootaxa 3986, 88–100. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3986.1.4
Zhan W. B., Meng Q. X., Yu K. K., Zhao Y. G. (1993). Primary investigation and studies on the parasitic desease of Solen gouldi and Mactera veneriforemis. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. (4), 81–85.
Zhang C. L., Zou Y. M., Zhang Z. H., Liu Q., Ding Z. F., Chen J. Q. (2019). “A preliminary study on the effect of Pinnotheres sinensis on the growth of Crassostrea gigas,” in The symposium of Genetics Society of Jiangsu (Jiangsu, China), 108.
Zhang T., Lei Y. L., Gao Y., Sun R. P., Xue D. N., Sun Y. (2007). “A preliminary study on the biodiversity of commensal fouling organisms and the development of the larva of polychaeta of Patinopecten yessoensis,” in The 8th Congress and 13th symposium of the Zoological Society and the Shellfish Society of the Marine Limnology Society of China (Shandong, China), 88.
Zhou J., Ji W. W., Li X. Z. (2010). Records of Polydora complex spionids (Polychaeta: Spionidae) from China’s coastal waters, with emphasis on parasitic species and the description of a new species. Mar. Fish. 32, 1–15.
Zhu C. J., Cui X. L., Chen G. Z., Yao Z. G. (1980). Experimental report on killing Arcotheres sinensis with lamp. Hebei Fish. 6, 33–37.
Keywords: metazoan parasites, mollusks, distribution, diversity, the China Seas
Citation: Du X, Sun J, Ju H, Xu Z, Tang X, Fang X and Chang MS (2025) Metazoan parasites associated with marine mollusks inhabiting the China Seas: a review. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1488376. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1488376
Received: 03 September 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yunyan Deng, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Florencia Cremopnte, National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), ArgentinaCopyright © 2025 Du, Sun, Ju, Xu, Tang, Fang and Chang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huidong Ju, anVodWlkb25nNjE1QDE2My5jb20=; Muhammad Saleem Chang, c2FsZWVtLmNoYW5nQHVzaW5kaC5lZHUucGs=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.