
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 14 March 2025
Sec. Marine Pollution
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1487001
This article is part of the Research TopicThe Effects of Freshwater Runoffs on Marine PollutionView all articles
Coastal eutrophication has become a persistent environmental crisis around world driven by human activities and climate change. Nowadays, frequent and intense tropical typhoon disturbances has strongly affected the distribution and composition of nutrients in the land-ocean interface, resulting in the eutrophication risk in coastal water. However, the mechanistic links between tropical typhoon and land-based sources transport have not been well understood due to the complex processes. In this study, nutrient concentration, composition and flux of three estuaries and one sewage outlet in Zhanjiang Bay (ZJB) were analyzed. Before the typhoon, the average concentrations of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) and dissolved silicate (DSi) in the land-based source of ZJB were 61.77 ± 28.56 μmol/L, 6.79 ± 4.61 μmol/L, and 113.26 ± 64.52 μmol/L, respectively. The average concentration of DIN decreased by approximately 41.8%, the average concentration of DIP increased by approximately 46.2%, and the average concentration of DSi increased by approximately 1.7% after Typhoon Kompasu made landfall. At the same time, the DIN/DIP and DIN/DSi of the land-based sewage outlets and estuary of ZJB after typhoon landfall were much smaller than the Redfield ratio, indicating different degrees of nitrogen limitation. In addition, significant spatial and temporal variations in nutrients fluxes were observed in land-based sources before and after the typhoon. Before the typhoon, the total input fluxes of DIN, DIP, and DSi in the estuary and outfall of land-based sources in ZJB were 9.98 × 104 mol/h, 1.38 × 104 mol/h, and 9.78 × 104 mol/h, respectively. In contrast, after the typhoon, the total input fluxes of DIN increased by 3.21 × 103 mol/h, the total fluxes of DIP decreased by 3.01 × 103 mol/h, and the total fluxes of DSi increased by 5.20 × 104mol/h. After the typhoon, the concentration, composition and flux of nutrients entering the sea from land-based sources changed significantly compared with those before the typhoon. Moreover, the nutrients fluxes model of discharge were established, which can estimate the input fluxes of DIN, DIP and DSi based on field investigation. This study reveals the effects of tropical typhoon event on the nutrients fluxes from land-based sources into the semi-enclosed ZJB, which provides a scientific basis for further research on the impacts of typhoons on nutrients enrichment in coastal waters, as well as deepening the understanding eutrophication of coastal ecosystem under climate change.
Nutrients are the main chemical elements of nitrogen, phosphorus, silicon in coastal water, also known as the key biological source elements (Zhu et al., 2024; Wu A et al., 2021). It is an essential nutrient for the growth and reproduction of marine phytoplankton and the foundation of marine primary productivity and the food chain (Jani and Toor, 2018; Strokal et al., 2014; Tan et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022). Nitrogen in seawater can be classified into total dissolved nitrogen (TDN) and particulate nitrogen (PN) based on its form of existence. TDN comprises dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) (Sun et al., 2022). Upon entering the ocean, these various forms of nitrogen undergo transformations through intricate biogeochemical processes (Zhang et al., 2019). Phosphorus exists in a variety of forms in marine waters, organisms, sediments, and suspensions. Based on its forms and distribution, phosphorus can be primarily categorized into two major types: Total Dissolved Phosphorus (TDP) and Particulate Phosphorus (PP). Among them, Total Dissolved Phosphorus (TDP) includes Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus (DIP) and Dissolved Organic Phosphorus (DOP), while Particulate Phosphorus (PP) consists of Particulate Inorganic Phosphorus (PIP) and Particulate Organic Phosphorus (POP) (Björkman and Karl, 1994; Zee et al., 2007; Lin et al., 2012; Karl, 2014; Lin and Guo, 2016; Xu et al., 2021). Silicon is the second most prevalent element in the Earth’s crust and constitutes a significant proportion of seawater (Papush et al., 2009). The predominant form of silicon in seawater is that of soluble silicates, colloidal silica compounds, suspended silica, and silicon present in marine biological tissues. Among these, dissolved silicates and suspended silica are the most prevalent. Dissolved silicates (DSi) are a vital nutrient for the growth of diatoms in coastal waters (Cao et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020c). However, coastal eutrophication has become a persistent environmental crisis around world driven by human activities and climate change at present (Dai et al., 2023). The excessive loading of nutrients, which results in the eutrophication of water bodies, represents a significant global challenge to water quality. The consequences of poor water quality include the formation of harmful algal blooms, which have been linked to the destruction of water resources, a reduction in the value of water utilization, and an increase in the cost of water treatment (Wells et al., 2015; Watson et al., 2016; Mukundan et al., 2020; Li et al., 2014). Additionally, these blooms have been associated with the massive death of fish and aquatic animals, further contributing to the destruction of aquatic resources and the emergence of water quality pollution phenomena, such as “algal blooms” and “red tides” (Watson et al., 2016; Thompson et al., 2023). In addition, the serious consequence is the significant mortality of fish and other aquatic organisms, even increased risk of hypoxia and acidification in coastal water (Paerl et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2024; Yunev et al., 2007).
A typhoon is a type of tropical cyclone, a low-pressure vortex that occurs over tropical or subtropical oceans. As a result of global climate change, these storms are becoming increasingly destructive and intensifying (Chan et al., 2004; Nayak and Takemi, 2019; Thyng et al., 2020). Strong winds and rainfall caused by typhoons will change the direction and speed of water flow, which will affect the nutrient exchange flux in the water body, especially the transfer and distribution of nutrients from the land-based source to the coastal water. As indicated by Murray and Ebi (2012) and Robinson (2021), extreme weather event such as heavy precipitation are likely to become more frequent and intense. This will have an impact on the water quality of rivers and lakes (Thyng et al., 2020; Tilahun et al., 2024). For instance, intense precipitation can result in elevated levels of phosphorus from land-based sources, which may contribute to the exacerbation of future water quality issues (Motew et al., 2018). Typhoon event have the potential to impact the nutrient composition of coastal waters. For instance, the direct wet sedimentation driven by Typhoon Bilis is an important source of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in surface seawater in the western Taiwan Strait, where the N/P ratios were considerably higher than the Redfield ratios in the seawater (Du et al., 2008). Furthermore, typhoons elevate the probability of harmful algal blooms, which exert a dual impact on coastal fisheries and give rise to ecological issues such as ocean hypoxia and acidification (Paerl et al., 2020; Thompson et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). For example, previous study posited that typhoons may precipitate the formation of harmful algal blooms by introducing substantial quantities of freshwater and nutrients, thereby modifying phytoplankton communities in temperate and inner bays (Jiang et al., 2022; Han et al., 2023; Thompson et al., 2023).
Land-based sources inputs are the main sources of nutrients in seawater, and an increased flux of nutrients into coastal waters is identified as a principal factor contributing to the deterioration of water quality (Meng et al., 2015). The deterioration of water quality is mainly caused by the flow of rivers from coastal bay into coastal water (Zhang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2020b; Zhang H et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2024). These rivers carry with them a range of pollutants, including domestic sewage from residents of towns and villages along the river, wastewater from agricultural fields, and polluted wastewater discharged from agricultural activities along the bay. This increases the loading of nutrients from agricultural, urban, and industrial activities (Deegan et al., 2012; Wurtsbaugh et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2022). The health of coastal ecosystems is significantly impacted by the influx of water from a multitude of sources, including rivers, freshwater, saline groundwater, and wastewater from livestock, agricultural, and industrial facilities, both natural and anthropogenic (Oh et al., 2021). Therefore, the coastal ecosystem is inherently vulnerable to external forces, particularly those associated with climate change, human activities, and extreme weather event (e.g., tsunamis, storm surges) (Yu et al., 2024; Zhang P et al., 2022; Herbeck et al., 2011). Heavy precipitation from typhoons has been demonstrated to increase surface runoff or river flow, while simultaneously introducing considerable quantities of land-based nutrients from terrestrial sources (Chen and Li, 2002; Paerl et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2021). It has been demonstrated that the prevailing weather conditions, specifically wind and rainfall, exert a significant influence on the spatial distribution and fluxes of nutrients in aquatic ecosystems (Lisboa et al., 2020). Climate change is driving an ongoing increase in tropical cyclone activity (Feehan et al., 2024). It is anticipated that extreme weather event, such as typhoons and periods of heavy rainfall, will become more prevalent and exert a significant influence on the trophic structure of the coastal ecosystem (IPCC, 2019).
Zhanjiang Bay (ZJB) is situated on the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea (Lao et al., 2022). The bay is a typhoon-prone area in the South Sea of China (Lao et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020b). The bay’s connection to the South China Sea is facilitated by a narrow channel, which measures approximately 2 km in width at the bay's mouth (Wang P et al., 2022). Previous studies have shown that typhoon-induced ocean fronts, combined with adverse hydrodynamic conditions, limit the dispersal of land-based pollutants, leading to deterioration of water quality (Lao et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020c). Since the 1980s, the rapid socio-economic development of Zhanjiang has resulted in an expansion of the impacts of human activities, including pollutant discharges from land-based sources along the coast, marine aquaculture, and shipping in ports and harbors (Zhang et al., 2020b). A considerable volume of industrial and domestic wastewater is discharged into the bay via rivers, resulting in a notable deterioration of seawater quality and a heightened incidence of red tide disasters (Zhang P et al., 2022; Feehan et al., 2024). Although previous studies have shown that typhoons have a certain impact on nutrient dynamics in coastal waters, the mechanistic links between tropical typhoon and land-based sources transport have not been well understood due to the complex processes in land-ocean interface.
Thus, to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of typhoons on land-based nutrients source entering coastal water in ZJB, we concentrated our research on DIN, DIP, and DSi as the primary subjects of investigation. Four typical stations, including three estuaries, and one outfall, were selected as sampling sites for the purpose of exploring the nutrients from land-based sources inputs and comparing the changes in the concentration, composition, and flux of nutrients before and after the typhoon. This study reveals the impacts of tropical typhoon events on the nutrients fluxes from land-based sources into the semi-enclosed ZJB, which provides a scientific basis for further research on the impacts of typhoons on nutrients enrichment in coastal waters, as well as deepening the understanding eutrophication of coastal ecosystem under climate change.
ZJB is situated in the northeastern region of the Leizhou Peninsula, within the western portion of Guangdong province. It represents the most substantial harbor within the confines of Zhanjiang City. The bay is of a typical semi-enclosed variety, exhibiting a narrow outlet measuring only 1.9 km at its narrowest point. Its topography is characterized by a complex configuration. ZJB has an elongated shape, measuring 54 km in length and 24 km in width from north to south, with an area of 193 km2 (Zhang P et al., 2022). The area is endowed with a rich diversity of marine resources. Over the past three decades, human activities have resulted in significant disruption to the coastal ecosystem, particularly in areas of rapid urbanization and industrialization within ZJB. There are more than 10 small seasonal rivers and outfalls discharging into the bay with varying water and nutrient loads, encompassing rivers like the Suixi River, Nanliu River, and Lvtang River, along with several others (Jian et al., 2022). However, with the rapid economic development and population increase in Zhanjiang, a considerable number of these rivers have become conduits for industrial, agricultural, and domestic wastewater.
In this study, samples were collected mainly at monitoring stations at river inlets and land source outlets discharging into ZJB. These four stations were selected as important land sources in ZJB (Figure 1). In order to ascertain the impact of the typhoon on alterations in the nutrient composition of the water column, four land-based sources were sampled prior to and following the typhoon to investigate these four land-based source input stations. These included one outfall (S1) for nearshore outflow and three estuaries (S2, S3, and S4) for discharge into the bay.S1 collected wastewater from Donghai Island, which is a center of aquaculture (Zhang et al., 2020b). S2 collected water samples from the Nanliu River, which is situated in close proximity to an industrial plants. S3 collected water samples from the Lvtang River, which is located at the discharge outlet of urban sewage. S4 collected water samples from the Suixi River, which drains a catchment area of 1,486 km2. The Suixi River transports significant agricultural runoff and serves as the largest freshwater contributor to Zhanjiang Bay in terms of flow volume. In addition, the flow at all four stations changed before and after the typhoon landfall.
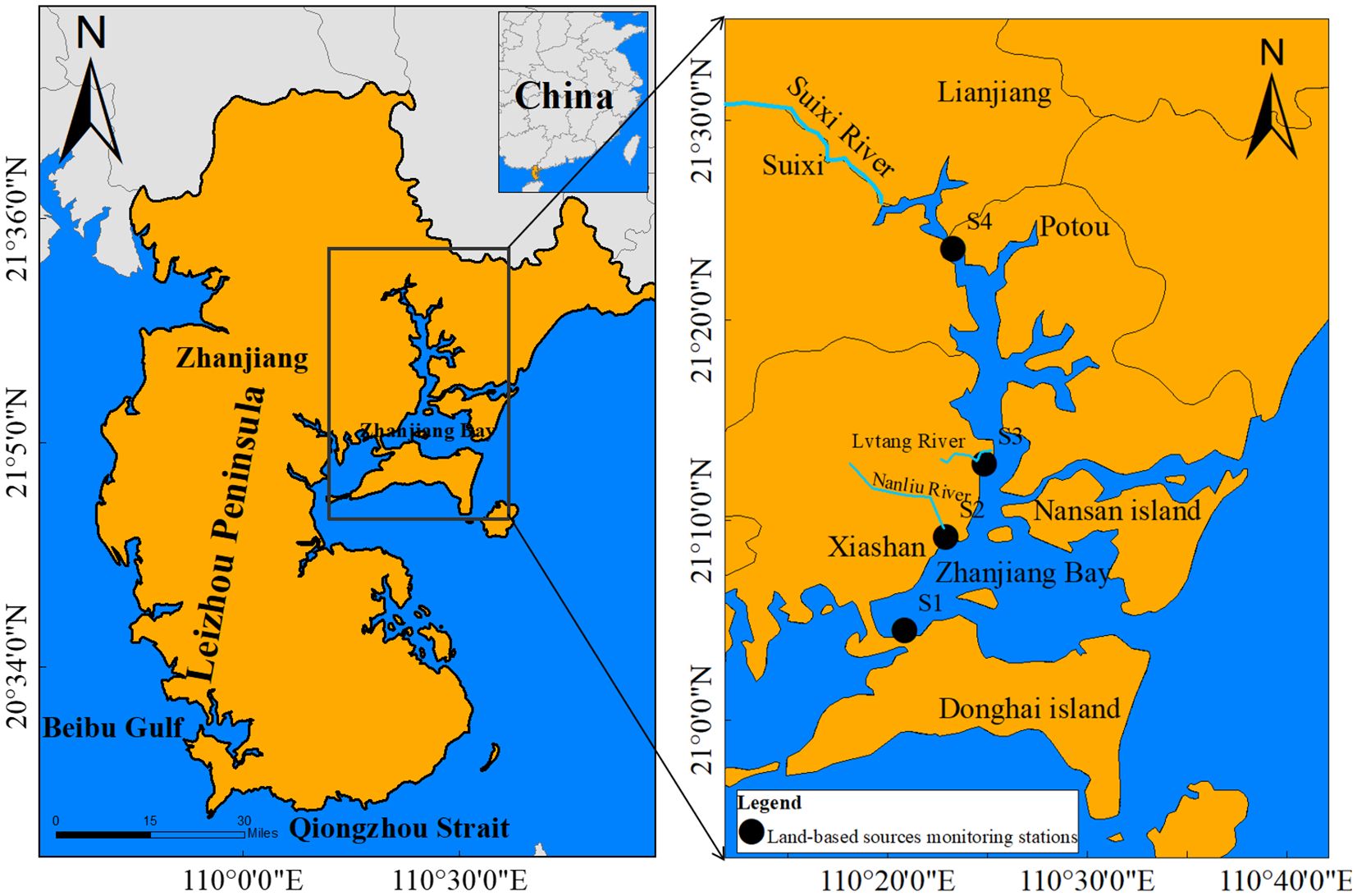
Figure 1. Geographic location and land-based sources monitoring stations in Zhanjiang Bay (Jian et al., 2022).
On the afternoon of October 8, 2021, a tropical depression situated to the east of the Philippines intensified into a tropical storm, designated Typhoon Kompasu, which became the 18th typhoon of 2021 (Wan et al., 2022; Wang S et al., 2022). The Central Meteorological Station (CMS) upgraded Typhoon Kompasu to a typhoon and reported that it made landfall off the coast of Qionghai City, Hainan Province, at approximately 15:40 on the same day. The CMS also determined that the typhoon was of significant strength. As reported by the People’s Government of Guangdong Province, the city of Zhanjiang was subjected to the influence of typhoon circulation and cold air from the night of October 13 to October 14, 2021. Meanwhile there was heavy rainfall continued (People’s Government of Guangdong Province, 2021). It has been reported that the typhoon has become the most intense typhoon to make landfall in Hainan since Super Typhoon Sharika in 2016. Strong winds, huge waves, and heavy rains associated with this typhoon caused severe damage to the coastal areas.
Water samples were collected from four land-based source stations in September and October 2021 (before and after the typhoon). All tools were sanitized with distilled water prior to the collection of samples. Water samples were collected using a High density polyethylene collector in order to obtain a volume of 5 L of surface water. The surface water was collected from the upper 50 centimeters of the water column as a surface water sample. Subsequently, the water samples were expeditiously conveyed back to the laboratory for analysis. The collection, preservation, and measurement methods of the river water and wastewater samples were conducted in strict accordance with the “Requirements for Technical Specifications for Surface Water and Wastewater Monitoring.” (HJ/T91-2002) (National Environmental Protection Agency, 2002). In accordance with the Specification for River Flow Tests (GB50179-93) (Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, 2005), a portable sampler was employed for the collection of water samples, while a rotor flow meter was utilized to monitor the river flow at each intake simultaneously. Upon arrival at the laboratory, the samples were immediately filtered using a glass fiber filter membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm. The extracted water samples were then packed into High density polyethylene bottles that had been cleaned with medical ultrapure water (resistivity = 18.25 MΩ•cm). Prior to chemical analysis, the water samples were frozen in a refrigerator (-20°C). In this study, DIN concentrations included those of NO3-N, NO2-N, and NH4-N (Grasshoff et al., 2009), the concentration of PO43- was considered as the concentration of DIP, and the concentration of SiO32- was considered as the concentration of DSi. Where NO2-N, NO3-N and NH4-N, DIP and DSi were determined by diazo-diazo, zinc-cadmium reduction, sodium hypobromite oxidation, phosphorus-molybdenum blue, and silico-molybdenum blue methods, respectively (Al-Mur, 2020). The aforementioned methods were employed in the treatment, after which the absorbance values of each indicator were determined using a Shimadzu UV2600i UV-visible photometer. The concentration values were subsequently calculated using a standard curve.
An important indicator regarding the analysis of nutrients is the flux of nutrients into coastal waters. The study of nutrient fluxes from coastal land sources has been the subject of considerable attention from the scientific community and those responsible for monitoring such processes. Given the significant impact that these fluxes have on water quality, it is of importance to determine the fluxes of nutrients from land-based sources in ZJB both before and after the typhoon, as will be done in this study (Bonometto et al., 2018). The fluxes of DIN, DIP, and DSi per unit time were calculated using the following equation:
Where: FR is the input flux of DIN, DIP and DSi from land-based sources into the estuary (mol/h); CR is the concentration of various forms of DIN, DIP and DSi in coastal water (μmol/L); QR is the runoff volume of the river intake and outfall (m3/s).
ArcGIS (10.2) was employed for the mapping of the aforementioned four land-based source input stations. The data pertinent to this study were analyzed using Microsoft Excel 2019, and Origin 2021 software was employed to map the composition of DIN, DIP, and DSi concentrations and fluxes into the sea. Furthermore, linear regression was employed to examine the correlation between the fluxes of diverse nutrient compositions and forms and the flow before and after the typhoon. A statistically significant difference between variables was indicated if the p-value was less than 0.05. In this study, mean values were expressed as arithmetic means ± standard deviations (means ± SD).
In this study, the collection, preservation, and determination of water samples were carried out in accordance with the specifications set forth in the Specification for Marine Surveys, Part 4: Survey of Seawater Chemical Elements (GB/T 12763.4-2007). The sampling and sample pretreatment procedures were conducted in strict adherence to the specified protocols and operational requirements. The experiment was conducted with the researchers attired in laboratory coats and nitrile gloves throughout. The requisite experimental reagents were prepared into solutions in accordance with the specified conditions, preserved under the specified conditions, and utilized within the specified period. The analytical determination and data processing were carried out in accordance with the requirements of the above national standards, and the detection limits were 0.10 μmol/L for SiO32-Si, 0.02 μmol/L for NO2-N and PO43-P, 0.03 μmol/L for NH4-N, and 0.05 μmol/L for NO3-N. The relative standard deviation (RSD) of the repeated measurements of the selected samples was<5%.
As illustrated in Table 1, the seawater flow at the estuary of the Nanliu River (S2) exhibited a declining trend in response to the typhoon event, whereas the flow at the remaining three stations demonstrated an increasing trend, particularly at the estuary of the Suixi River (S4). Following the typhoon, the surface water temperature of seawater at all stations was observed to be lower than that recorded prior to the typhoon. In contrast, the surface salinity of seawater at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) and the Suixi River estuary (S4) exhibited a notable decline following the typhoon, in comparison to the levels observed prior to the storm. In contrast, the surface salinity of seawater at the mouths of the Nanliu River estuary (S2) and the Lvtang River estuary (S3) demonstrated minor variation before and after the typhoon.
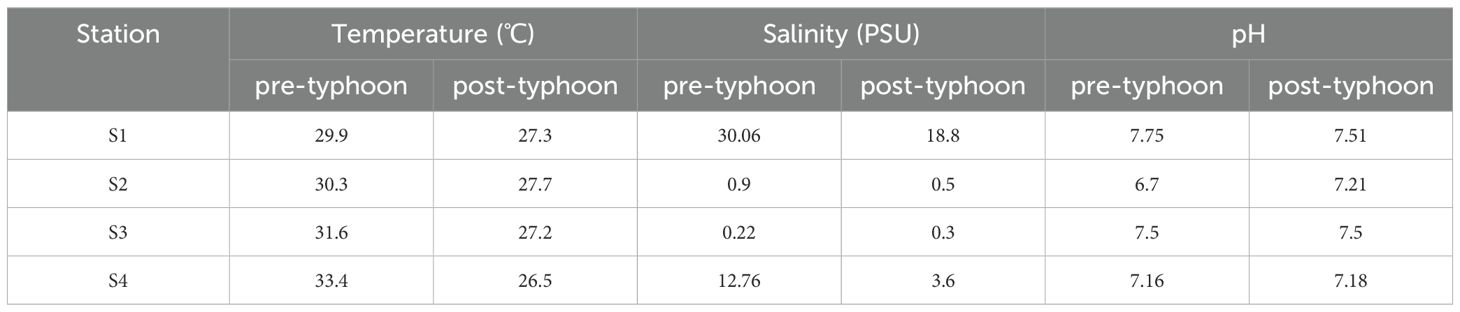
Table 1. Presents the physical and chemical parameters of each station in ZJB before and after the typhoon.
In the aftermath of the typhoon, the surface temperature of the seawater underwent a decline of 2.6°C to 6.9°C in comparison to the preceding conditions. The cooling of surface water as a consequence of Typhoon Kompasu can be attributed to a multitude of factors, including the mixing of seawater by the typhoon, upwelling, and the input of rainfall (Subrahmanyam, 2015). Moreover, the surface salinity of seawater in S1 and S4 following the typhoon was markedly diminished in comparison to the levels observed prior to the typhoon. The subsequent rainfall event resulted in the influx of freshwater into the ocean, thereby reducing the average salinity (Li et al., 2007; Wang, 2016). The volume of water flowing from the Nanliu River estuary (S2) into the sea was greater prior to the typhoon than it was subsequent to the typhoon. This is primarily attributable to the fact that there were a greater number of sluices situated upstream of the Nanliu River, which were utilized for the purpose of regulating the flow of water. Additionally, a greater number of sluices were closed in order to facilitate the implementation of flood control measures prior to the typhoon (Jian et al., 2022). Furthermore, the flow at the estuary of the Lvtang River (S3) into the sea exhibited a consistently lower position both before and after the typhoon. Therefore, the flow of surface seawater in S2 and S3 did not undergo a notable alteration as a consequence of the typhoon. Consequently, the salinity and pH fluctuations of S2 and S3 were not significantly influenced by the typhoon.
Following the typhoon event, the spatial distribution of DIN, DIP, and DSi from land sources entering the sea in ZJB is likely to undergo certain modifications. Figure 2 illustrates the alterations in the concentrations of land-source DIN, DIP, and DSi in ZJB in response to the typhoon event.
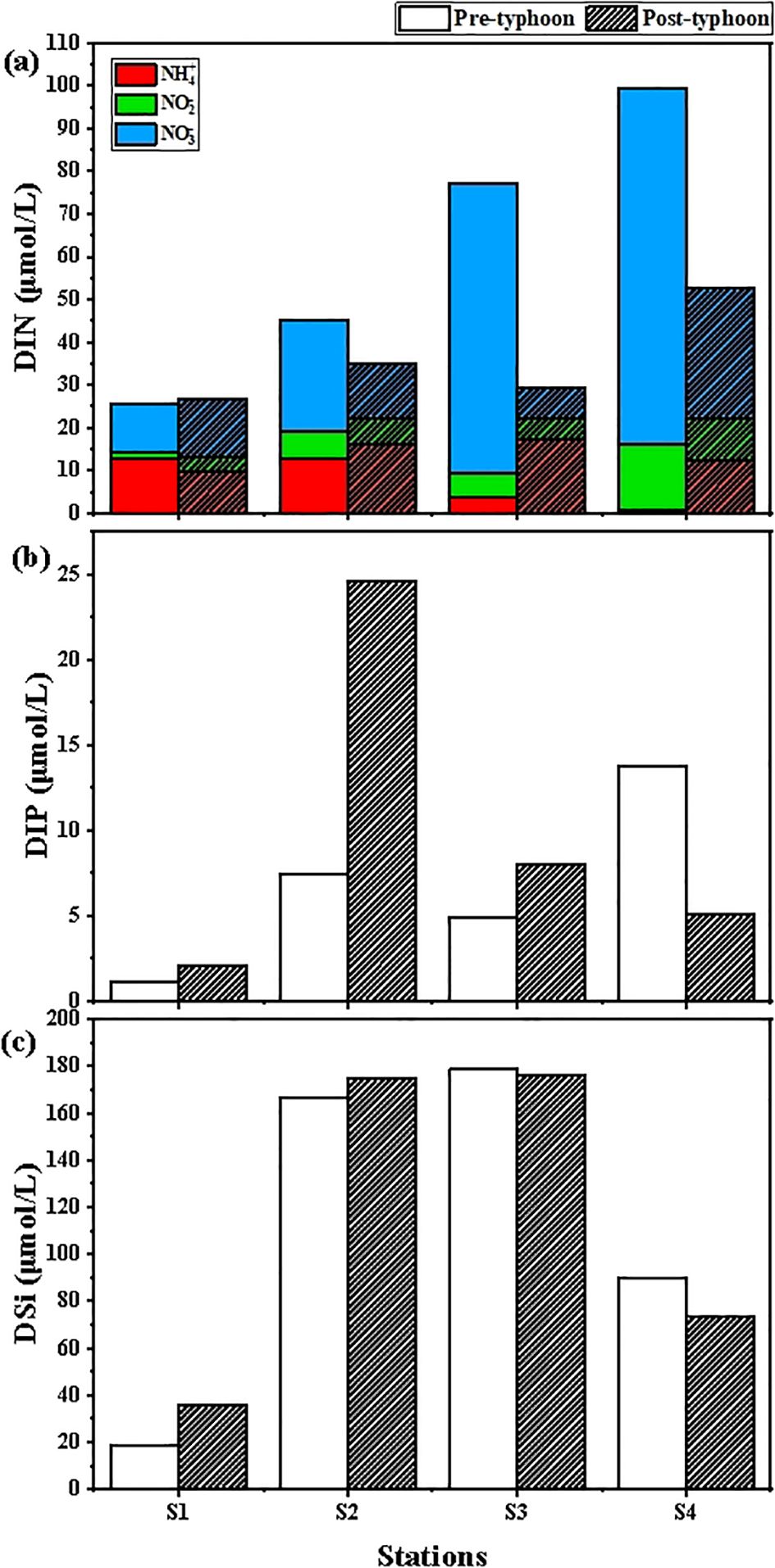
Figure 2. DIN (a), DIP (b), and DSi (c) concentration variations of land-based sources affected by typhoon event in ZJB.
As illustrated in Figure 2A, the results of the survey indicate that DIN was predominantly present in the form of NO3-N, NO2-N, and NH4-N in all water samples collected from the four stations. Its distribution exhibited a discernible spatial and temporal pattern. The mean concentration of DIN in land-based sources was 61.77 ± 28.56 μmol/L prior to the typhoon, and 35.96 ± 10.05 μmol/L subsequent to the typhoon. Compared with before typhoon, DIN concentration decreased significantly by 25.81μmol/L after typhoon. Before typhoon, DIN concentration was the highest at 99.47μmol/L in the estuary of Suixi River into the sea (S4), among which NO3-N concentration was the highest at 83.33μmol/L, and NH4-N concentration was the lowest at 0.76μmol/L. The lowest DIN concentration was observed at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1), at 25.37 μmol/L, while the highest NH4-N concentration was recorded at the same site, at 12.80 μmol/L. In contrast, the lowest NO2-N concentration was observed at this same site, at 1.34 μmol/L. After the typhoon event, the DIN concentration at the Suixi River outfall (S4) was still the highest at 52.58 μmol/L, with NO3-N accounting for the largest proportion of 30.37 μmol/L and NO2-N accounting for the smallest proportion of 9.79 μmol/L. The DIN concentration in Donghaidao aquaculture outlet (S1) was still the lowest, 26.76μmol/L. Among them, NO3-N occupies the largest proportion of 13.74μmol/L and NO2-N occupies the smallest proportion of 3.32μmol/L. The station with the largest difference in DIN concentration before and after the typhoon was the Lvtang River inlet (S3). After the typhoon, the DIN concentrations in the rivers entering the sea decreased significantly, except for the DIN concentration at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1), which remained relatively stable.
As can be seen from the survey results (Figure 2B), the distribution of DIP had significant temporal variations. The average concentration of DIP from land-based sources was 6.79 ± 4.61 μmol/L before the typhoon, and 9.93 ± 8.70 μmol/L after the typhoon. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the post-typhoon period showed an increase of 3.14 μmol/L. Before the typhoon, the DIP concentration in Suixi River estuary (S4) was the highest at 13.75μmol/L, while the DIP concentration in Donghai Island Aquaculture outlet (S1) was the lowest at 1.11μmol/L. After the typhoon landfall, the highest DIP concentration was found at the estuary of Nanliu River (S2) with 24.55 μmol/L, and the lowest DIP concentration was found at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) with 2.05 μmol/L. After the typhoon, the maximum DIP concentration appeared in the estuary of Nanliu River into the sea (S2), and the difference of DIP concentration before and after the typhoon was the largest in S2. After the typhoon, the DIP concentration of Suixi River into the sea estuary (S4) decreased significantly, and the DIP concentration of the other three stations increased.
In addition, the distribution of DSi did not change significantly in time (Figure 2C). The average DSi concentration in land-based sources was 113.26 ± 64.52 μmol/L before the typhoon and 115.20 ± 61.91 μmol/L after the typhoon. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the DSi concentration in the post-typhoon period was elevated by 1.94 μmol/L, but not significantly. Before the typhoon, the highest DSi concentration was found in the estuary of Lvtang River (S3), 178.62 μmol/L, and the lowest DSi concentration was found in the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1), 18.38 μmol/L. After the typhoon, the highest DSi concentration was still found in the estuary of Lvtang River (S3), 176.41 μmol/L, and the lowest DSi concentration was still found in the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1), 35.78 μmol/L. The largest difference in DSi concentration between before and after the typhoon was found in S1; after the typhoon, the DSi concentrations in the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) and the Nanliu River estuary (S2) increased slightly, and those in the Lvtang River estuary (S3) and the Suixi River estuary (S4) decreased slightly; the change in the concentration in S3 was not significant.
Phytoplankton in the ocean take up nutrients from seawater in a constant ratio, which is known as the Redfield ratio. The ratio is typically 16:16:1 for N:Si:P (Wang et al., 2006; Gui et al., 2006). If the molar ratio between N, P and Si in seawater deviates too high or too low from the Redfield ratio, the element content will be relatively low, which will restrict the growth of phytoplankton. Such elements that restrict the growth of phytoplankton are called nutrient limiting factors (Turner et al., 2003). Nutrient limitation is subject to variation as a consequence of the differing biogeochemical characteristics inherent to different ecosystems, as well as across seasonal cycles (Sun et al., 2022; Boesch et al., 2001). Following the occurrence of a typhoon event, the trophic structure of a water body is subject to alteration, which may result in changes to the trophic limiting factors of that water body. Figure 3 illustrates the alterations in DIN/DIP, DIN/DSi, and DSi/DIP in land-sourced seawater in ZJB as a consequence of the typhoon’s impact.
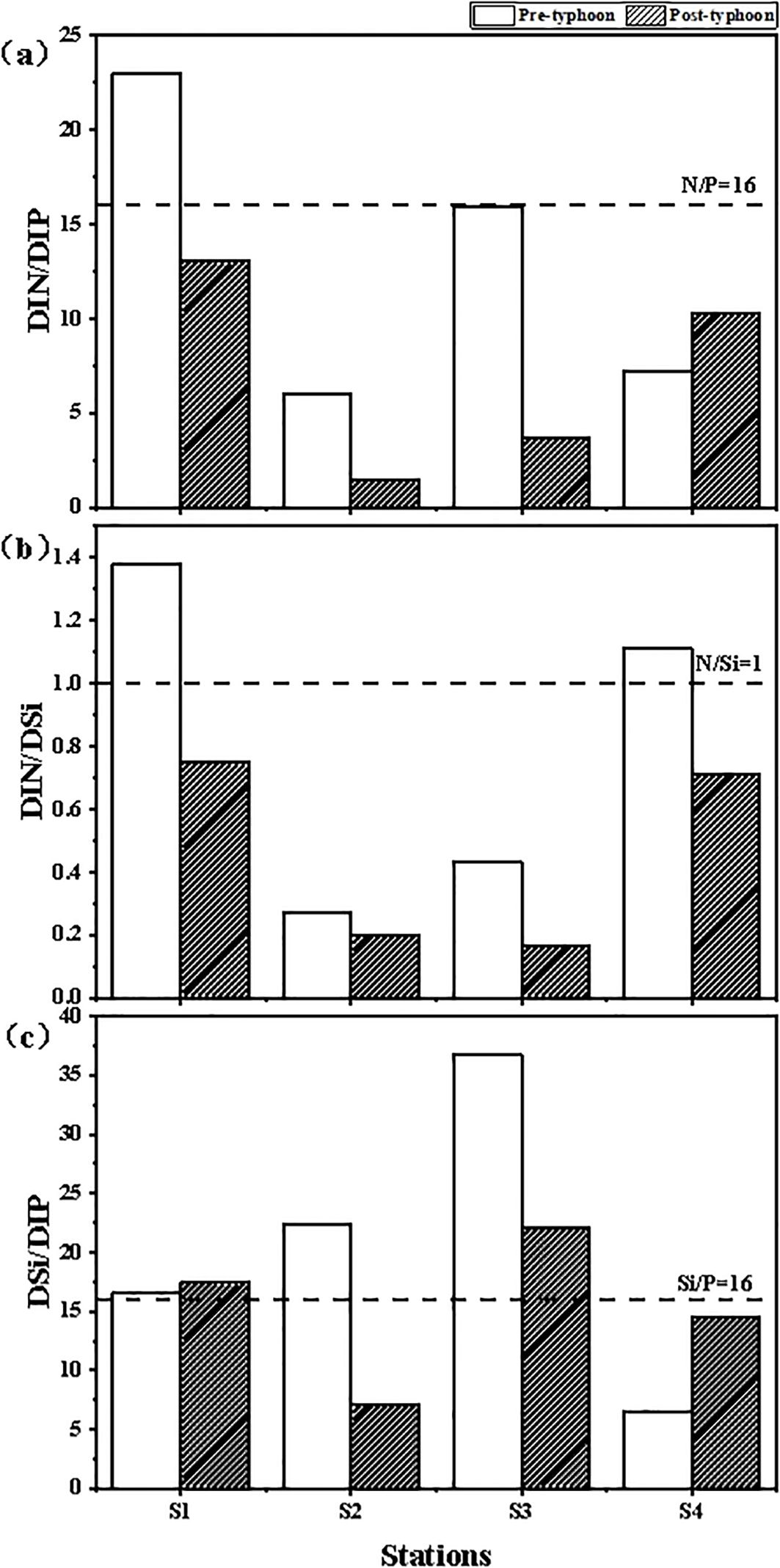
Figure 3. DIN/DIP (a), DIN/DSi (b), and DSi/DIP (c) variation of land-based sources affected by typhoon event in ZJB.
As can be seen from the survey results (Figure 3A), the average DIN/DIP of land-based sources in ZJB was 13.03 ± 6.87 before the typhoon, and 7.12 ± 4.73 after the typhoon. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the average DIN/DIP of the post-typhoon period was significantly lower. The highest DIN/DIP before the typhoon was 22.94 at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1), and the lowest was 6.04 at the Nanliu River outfall (S2). In general, the DIN/DIP at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) was greater than 16, which showed phosphorus limitation, and the other outfalls were basically lower than the Redfield ratio, which showed nitrogen limitation. The highest DIN/DIP after the typhoon was still the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) at 13.05, and the lowest was still the Nanliu River estuary (S2) at 1.43. After the typhoon, the DIN/DIP values of the investigated outfalls and inlet estuaries were all less than 16, and in general showed nitrogen-limiting characteristics. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the DIN/DIP was significantly lower at the three stations after the typhoon, except at the Suixi River estuary (S4), where the DIN/DIP was slightly higher.
From the survey results (Figure 3B), the average DIN/DSi of land-based sources in ZJB was 0.80 ± 0.46 before the typhoon, and 0.46 ± 0.27 after the typhoon; after the typhoon, the average DIN/DSi decreased compared with that before the typhoon. Before the typhoon, the highest DIN/DSi was 1.38 at the Donghai Island aquaculture outfall (S1), and the lowest was 0.27 at the Nanliu River estuary (S2).The DIN/DSi at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) and the Suixi River estuary (S4) were greater than 1, which showed silica limitation; and the DIN/DSi at the Nanliu River estuary (S2) and the Lvtang River estuary (S3) were less than 1, which showed nitrogen limitation. After the typhoon, the highest DIN/DSi was 0.75 at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) and the lowest was 0.17 at the Lvtang River estuary (S3). After the typhoon, DIN/DSi was less than 1 at all four sites, showing an overall nitrogen limitation. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, DIN/DSi decreased at all sites after the typhoon.
As can be seen from the survey results (Figure 3C), before the typhoon, the average DSi/DIP of the land source in ZJB was 20.56 ± 10.94. After the typhoon, the average DSi/DIP was 15.26 ± 5.41. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the average DSi/DIP of the post-typhoon period was slightly decreased, and the ratios of the two after experiencing the typhoon changed to different degrees. Before the typhoon, the DSi/DIP at the estuary of the Lvtang River into the sea (S3) was the highest at 36.79, which was much higher than 16, showing phosphorus limitation characteristics. The estuary of the Suixi River(S4) into the sea had the lowest DSi/DIP of 6.52, which was much lower than 16 and exhibited silica limitation. The DSi/DIP of the remaining three stations were all greater than 16 except for S4, which was less than 16. After the typhoon, the DSi/DIP of the estuary of the Lvtang River(S3) was the highest at 22.02, and that of the estuary of the Nanliu River (S2) was the lowest at 7.12. The DSi/DIP of the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) and the estuary of the Lvtang River (S3) were greater than 16, which showed phosphorus limitation; The DSi/DIP of Nanliu River estuary (S2) and Suixi River estuary (S4) were less than 16, showing silicon limitation.
Figure 4 shows the changes in DIN, DIP, and DSi inlet fluxes before and after the typhoon. The results from the four monitoring stations show the changes in nutrient fluxes before and after the typhoon (Figure 4A). The influx of nutrients into the marine environment was quantitatively assessed both prior to and following the typhoon event, using the calculation formula provided in Section 2.3. The total DIN flux into ZJB at the four monitoring stations was 9.98 × 104 mol/h before the typhoon and 1.03 × 105 mol/h after the typhoon. Compared with the pre-typhoon, the total DIN flux increased by 3.21 × 103 mol/h after the typhoon. The percentage of DIN flux into the sea in the Suixi River inlet stream (S4) was the highest before and after the typhoon, which was 9.61 × 104 mol/h (96.4%) and 9.90 × 104 mol/h (96.2%). In contrast, before and after the typhoon, the lowest DIN fluxes were observed in the Lvtang River inlet stream (S3), which were 266.76 mol/h (0.3%) and 127.31 mol/h (0.1%), respectively.
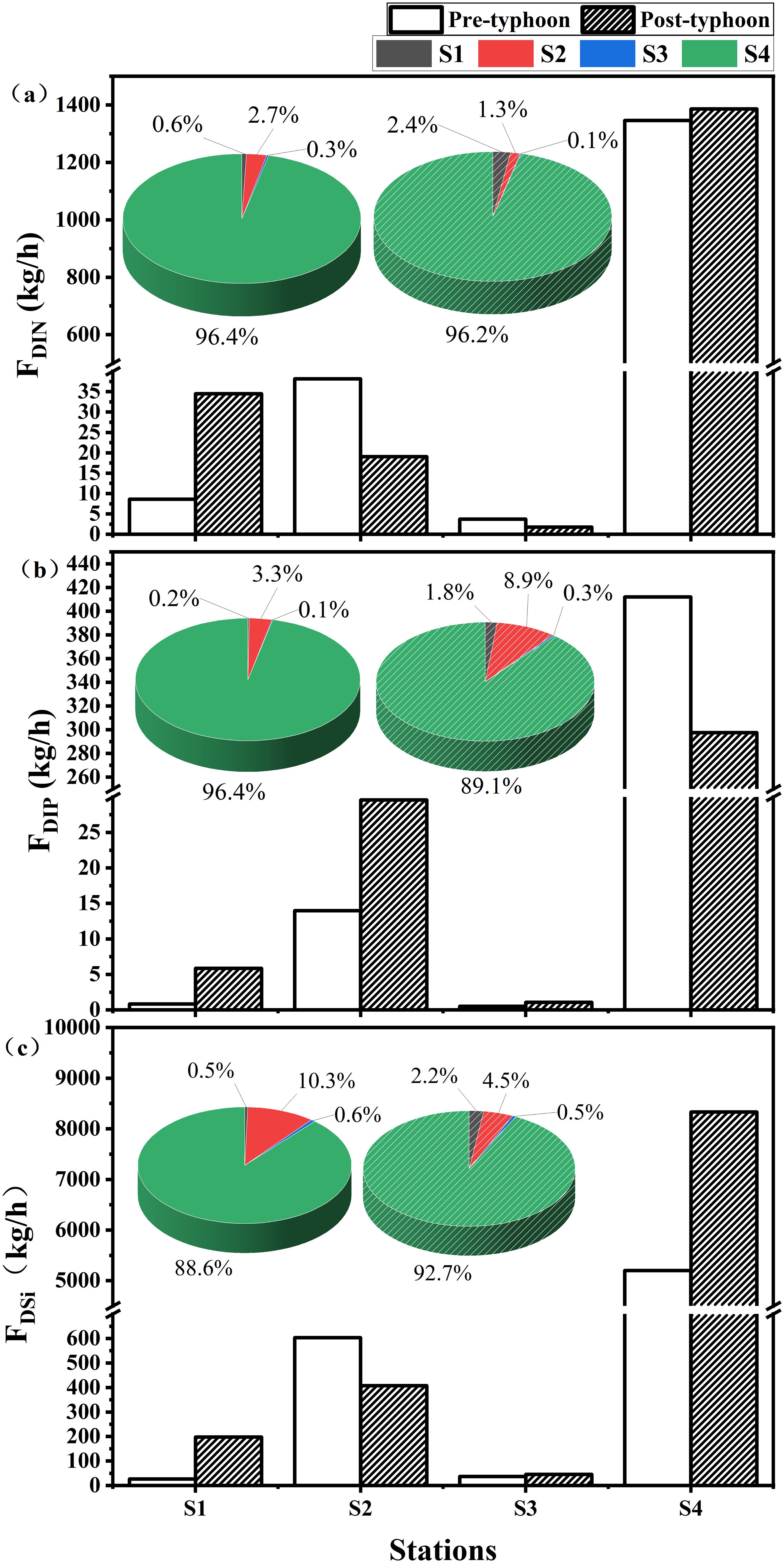
Figure 4. DIN (a), DIP (b), and DSi (c) fluxes of land-based sources affected by typhoon event in ZJB.
The results showed that the total DIP flux into ZJB at the four monitoring stations was 1.38 × 104 mol/h before the typhoon and 1.08 × 104 mol/h after the typhoon (Figure 4B). Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the total DIP flux after the typhoon was reduced by 3.01 × 103 mol/h. The percentage of the DIP flux into the sea-entering stream of the Suixi River (S4) was the highest before and after the typhoon, which was 1.33 × 104 mol/h (96.4%) and 9.60 × 103 mol/h (89.1%). Before and after the typhoon, the lowest DIP fluxes were observed in the estuary of the Lvtang River into the sea (S3), with 16.78 mol/h (0.1%) and 34.61 mol/h (0.3%), respectively.
The survey results (Figure 4C) showed that the total DSi flux into ZJB at the four stations was 9.78 × 104 mol/h before the typhoon and 1.50 × 104 mol/h after the typhoon. Compared with the pre-typhoon period, the total DSi flux after the typhoon increased by 5.20 × 104 mol/h. Before and after the typhoon, the Suixi River inlet stream (S4) had the highest percentage of DSi fluxes of 8.67 × 104 mol/h (88.6%) and 1.39 × 105 mol/h (92.7%). The lowest values of DSi flux did not occur at the same station. The lowest value of DSi flux before the typhoon appeared at the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet (S1) with 446.72 mol/h (0.6%), and the lowest value of DSi flux after the typhoon appeared at the estuary of the Lvtang River(S3) into the sea with 762.11 mol/h (0.5%).
To further elucidate the concentration levels of nutrients entering the sea from land-based sources in ZJB, we compared nutrient concentrations in rivers in China and around the world (Table 2) with the concentrations of nutrients (DIN, DIP, DSi) entering the sea from land-based sources in ZJB. The DIN concentrations observed in the pre-typhoon period were higher than those previously reported for a number of other locations, including Tapong Bay, Daya Bay, Jiaozhou Bay, Bohai Bay, Sishili Bay, Maowei Sea, and Laizhou Bay (Hung et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2006; Han et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the DIN concentrations in the typhoon were less than those observed in the Bay of Bengal and the Yellow River (Das et al., 2017; Wu N et al., 2021). As a consequence of the typhoon, there was a marked increase in nutrient inputs from land-based sources in ZJB. This resulted in a rapid rise in nutrient concentrations in the outfalls and estuaries, which in turn prompted phytoplankton growth. This was achieved by the absorption of significant quantities of nutrients in the water column (mainly DIN). Alternatively, in water bodies where anoxia occurred, denitrifying bacteria were able to convert NO3-N to N2. This resulted in a reduction in DIN concentration in the post-typhoon period compared to the pre-typhoon period. However, the DIN concentration subsequent to the typhoon remained elevated in comparison to that observed in Tapong Bay, Daya Bay, Bohai Bay, Sishili Bay, and Laizhou Bay (Hung et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2022). The results demonstrate that the DIN concentration in ZJB, both prior to and following the typhoon, is predominantly within the high to medium range. It is evident that the DIN concentration in ZJB is elevated in comparison to other regions. The DIP concentrations prior to the typhoon were observed to be higher than those recorded in the following locations: Tapong Bay, Daya Bay, Jiaozhou Bay, Bohai Bay, Sishili Bay, Yellow River, and Maowei Sea (Hung et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2006; Han et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2022; Wu N et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021). However, prior to the typhoon, the DIP concentration was observed to be lower than that recorded in the Bay of Bengal (Das et al., 2017). The effects of the typhoon, including increased river runoff and substance concentrations, resulted in higher DIP concentrations after the typhoon than before. However, the post-typhoon DIP concentrations were found to be generally consistent with the pre-typhoon DIP results when compared to other regions. The findings revealed that the DIP concentration in land-based sources within ZJB was observed to be higher than that in global rivers prior to the occurrence of the typhoon. Furthermore, the DIP concentration was found to be elevated following the typhoon. The pre-typhoon DSi concentrations were found to be higher than those observed in a number of other locations, including Tapong Bay, Daya Bay, Bohai Bay, Sishili Bay, Yellow River, Maowei Sea, and Laizhou Bay (Hung et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2022; Wu N et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022). Prior to the typhoon, DSi concentrations were observed to be lower than those recorded in the Bay of Bengal (Das et al., 2017). As a consequence of the typhoon, the DSi concentration exhibited a slight increase following the typhoon, although it remained elevated relative to that observed in Tapong Bay, Daya Bay, Bohai Bay, Sishili Bay, Yellow River, Maowei Sea, and Laizhou Bay (Hung et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2022; Wu N et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022). The findings indicated that the concentration levels of DSi in ZJB were at elevated levels both prior to and following the typhoon. In general, the nutrient concentration levels in Zhanjiang land-based sources before and after the typhoon were found to be relatively elevated in comparison to global rivers. This is primarily attributable to the impact of the reclamation project on ZJB, a semi-enclosed coastline that exhibits diminished hydrodynamic exchange conditions, particularly in the northeastern region of the bay.
The influx of precipitation, wind speed, and river flow resulting from typhoons has been observed to alter the nutrients concentrations in the nearshore seawater of ZJB. S1 represents the sewage outlet of aquaculture in Tiaobu Village, Donghai Island. The expansion of aquaculture operations will bring huge risks to estuarine and coastal ecosystems, such as the accumulation of active nitrogen leading to eutrophication, and the discharge of aquaculture pollutants will pollute water bodies (Chen et al., 2011; Lin and Lin, 2022; Luo et al., 2018). Following the typhoon, there was a notable increase in the concentrations of DIN, DIP, and DSi in comparison to the concentrations observed prior to the typhoon. The influx of surface material into the estuary offshore, caused by the heavy rainfall brought by the typhoon, results in an increase in the nutrient concentration in the upper layer of the water body in the region following the typhoon (Zhang et al., 2007; Hui et al., 2009). S2 represents the estuary of the Nanliu River in Xiashan. Following the typhoon, there was a slight increase in the concentrations of DIP and DSi compared to the concentrations observed prior to the typhoon. This increase can be attributed primarily to the effects of the typhoon. The Nanliu River is situated in close proximity to the fertilizer production plant, which has historically discharged a considerable volume of industrial wastewater into the coastal waters. This has resulted in significant eutrophication and the development of hypoxic conditions in the water body (Zhang P. et al., 2022). S3 is situated in proximity to the Lvtang River, in close proximity to an urban residential area. The discharge of untreated urban domestic wastewater has resulted in significant pollution of the Lvtang River (Chen et al., 2021). The changes in nutrients in the river before and after the typhoon were comparable to those observed at S2.S4 is representative of the Suixi River, which has a high flow rate. The adjacent areas of Suixi River are predominantly utilized for agricultural purposes, and the use of fertilizer increased the nutrients in the river both before and after the typhoon (Zhang et al., 2024). DIN, DIP, and DSi concentrations in S4 decreased after the typhoon compared to those before the typhoon because the rainfall brought by the typhoon diluted the coastal surface water and nutrients (Li et al., 2007; Wang, 2016), which led to a decrease in nutrient concentration and a relative decrease in salinity from 12.76 PSU to 3.6 PSU. It is worth noting that (a) (b) of Figure 3 shows that sewage outfalls and sea inlet estuaries have different degrees of nitrogen limitation after typhoon landfall. Meanwhile, except for the Donghai Island aquaculture outfall (S1), the DIN concentrations in the other three inlet estuaries (S2, S3, and S4) decreased significantly compared to the pre-typhoon period, with an increase in the concentration of NH4-N and a decrease in the concentration of NO3-N. This suggests that in anoxic environments, DIN in the water column is reduced due to denitrifying bacteria in the marine surface water that can convert NO3-N to N2 or reduce nitrate isomerization to ammonium (Zhang et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2023).In the past few decades, the increase in domestic sewage, industrial wastewater and agricultural fertilizers has led to the strengthening of nitrogen fixation, which has led to a dramatic increase in active nitrogen in estuarine and coastal ecosystems around the world, resulting in a series of serious ecological and environmental problems such as eutrophication, hypoxic expansion and harmful algal blooms (Huang et al., 2021; Cai et al., 2011; Deegan et al., 2012).
As evidenced in Paragraph 3.4, prior to and following the typhoon, the highest DIN, DIP, and DSi fluxes were observed in the Suixi River estuary, while the lowest DIN and DIP fluxes were documented in the estuary of the Lvtang River. Moreover, a notable observation is that the minimum DSi flux values before and after the typhoon did not occur at the same station. Specifically, the minimum DSi flux before the typhoon was observed at S1, whereas the lowest DSi flux after the typhoon was recorded at S3.
As evidenced by the flux equations presented in paragraph 2.3, the flux of nutrients into coastal waters is not solely contingent upon the composition and concentration of pollutants at the study site. Rather, it is also influenced by the flow of coastal waters. Discharge is one of the key factors influencing material flux. The fluxes in marine waters are primarily influenced by the width of the channel, the depth of the channel, and the velocity of the flow at the study site. The linear regression relationship between the substance flux and the flow rate of the water body is illustrated in Figure 5. The linear regression relationships are distinct due to the varying concentrations of DIN, DIP, and DSi in seawater. The linear regression equations of DIN flux versus flow before and after the typhoon were Y = 1927.5 + 219.4X (n = 8, R2 = 0.864, p< 0.001); the linear regression equations of DIP flux versus flow before and after the typhoon were Y = 570.0 + 23.4X (n = 8, R2 = 0.675, p< 0.05). The linear regression equation of DSi flux versus flow before and after the typhoon was Y=1798.5 + 273.1X (n=8, R2 = 0.986,p<0.001). Furthermore, the geographic factors determined by the shape of the river have an impact on the river flow, which may result in the accumulation of nutrients in seawater.
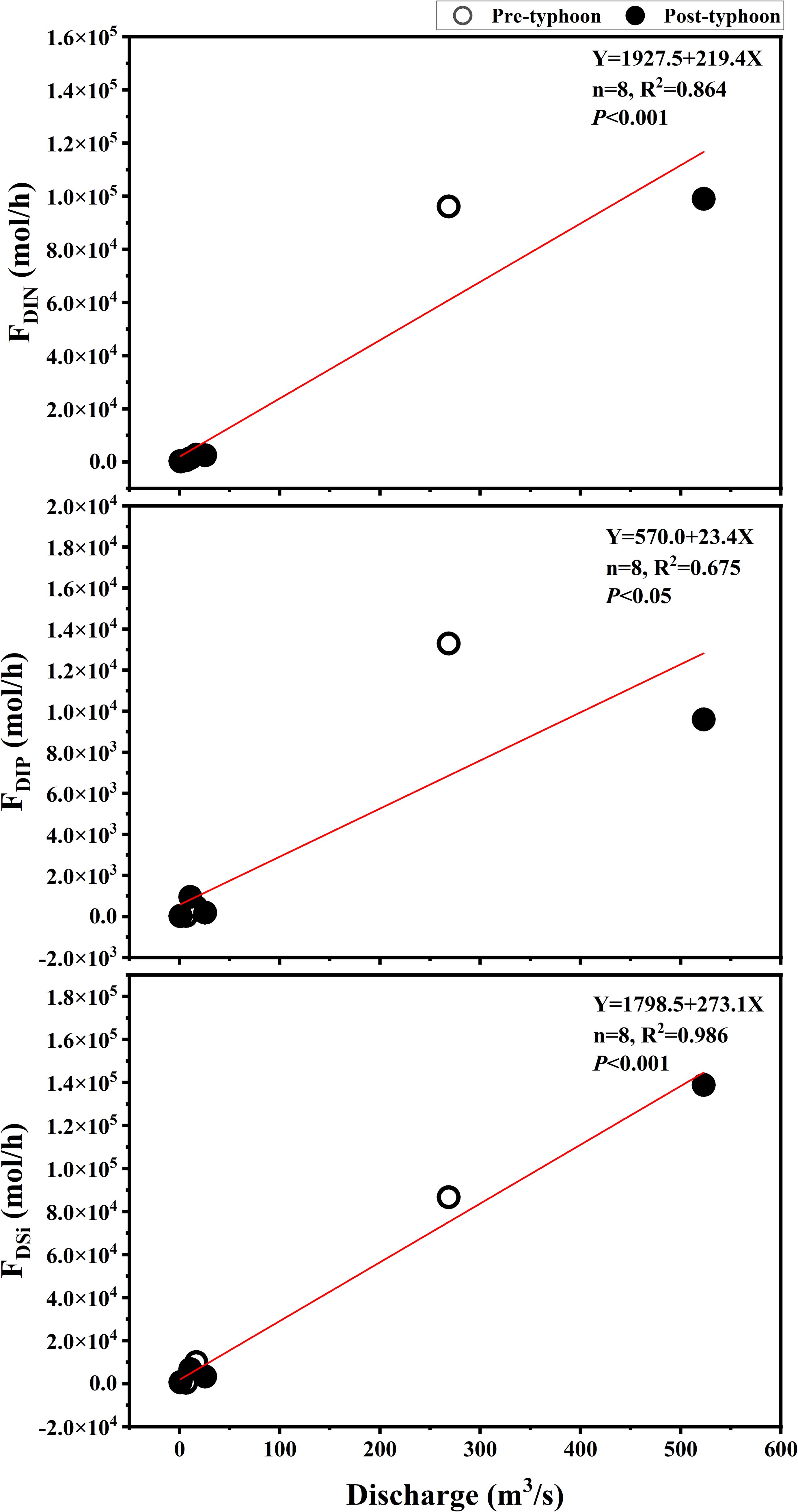
Figure 5. Relationship between nutrient fluxes from land-based sources and water flow discharge in ZJB before and after typhoons.
As illustrated in the figure, the post-typhoon flow rate out of the Donghai Island aquaculture sewage outlet(S1) exhibited an increase compared to the pre-typhoon period. This phenomenon can be attributed to the combined influence of typhoon wind speed and topographic factors. The primary source of pollution on Donghai Island is the discharge of aquaculture wastewater. Following the typhoon, an increase in flow was observed, accompanied by an increase in the concentration of pollutants (Chen et al., 2011). In contrast, the flow of the Nanliu River exhibited a decrease following the typhoon. This was primarily attributable to the substantial number of gates situated upstream of the Nanliu River (Jian et al., 2022), which were employed to regulate the river water flow. These gates were closed for the purpose of flood control in response to the typhoon, which resulted in a slight reduction in the flow at the mouth of the Nanliu River into the sea (S2) subsequent to the typhoon (Jian et al., 2022). While most of the Nanliu River is adjacent to industrial sites, its pollution source is mainly industrial discharge water, which is mainly manifested in the increase of DIP flux. Before and after the typhoon, the flow of the Lvtang River was smaller than that of the other stations due to the minimum width of the channel and the minimum depth of the Lvtang River. The Lvtang River traverses Xiashan District and Jingkai District, functioning as the primary drainage river within the urban core of Zhanjiang. The predominant source of pollution in the river is urban sewage, with inadequate sewage discharge, leading to a relatively low nutrient input flux (Zhang et al., 2020c). The Suixi River has the greatest width and the highest flux. The flow of this river increases dramatically under the influence of typhoons. The Suixi River basin is dominated by agricultural land, and the use of chemical fertilizers aggravates DIN pollution (Zhang et al., 2020b).
The rapid socio-economic development and sharp population growth that have occurred in recent decades have led to accelerated industrialization and urbanization (Du et al., 2019). This has resulted in an increased pursuit of material culture by humans, with a concomitant increase in the scope of their activities. This has led to a gradual increase in the discharge of nutrients from external inputs into water bodies (Chen and Chen, 2002; Yu et al., 2024). The findings of this study indicate that land-based sources of pollutants are not exclusive to areas inhabited by humans, but are also present in industrial, agricultural, and aquaculture zones (Huang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2008; Qi et al., 2019; Wen et al., 2024). At the same time, there has been an increase in inputs from land-based sources due to typhoons driven by climate change, which have the potential to affect coastal water quality and thus trigger algal bloom outbreaks. In the water bodies of ZJB, the implementation of water quality monitoring and algal bloom control measures is imperative for maintaining the integrity of the water ecosystem. First, a real-time water quality monitoring system needs to be established. Especially before and after typhoons, monitor the nutrient levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water body to detect changes in water quality and identify the risk of algal bloom occurrence in a timely manner. In addition, multidimensional observation and model synergy techniques can be applied to provide technical support for real-time monitoring, including ground-based navigation observation, online continuous high-frequency observation and numerical simulation techniques. Secondly, to control exogenous pollution, especially industrial and agricultural surface pollution, and to reduce the input of nitrogen and phosphorus are the fundamental measures to prevent and control algal bloom (Zhou et al., 2020). Furthermore, it is essential to consider both nutrient concentration and river flow when developing strategies to mitigate the eutrophication process (Wang et al., 2024). In this study, a model was constructed to simulate the discharge and DIN, DIP, and DSi fluxes. The model is capable of estimating the DIN, DIP, and DSi input fluxes into the estuary based on the land-based source discharge, and monitoring the DIN, DIP, and DSi fluxes in ZJB, thereby facilitating the implementation of more effective mitigation measures. Nevertheless, the existing input of pollutants from land-based sources has already resulted in a certain degree of nutrient loading to coastal estuaries. It is therefore imperative that the government implement more robust controls across the river-estuary-sea continuum that are closely connected, as well as the management of land-based sources discharges into the sea (Ke et al., 2022). In the long-term, integrated land-sea management of coastal water quality should be introduced as a means of effectively controlling river and coastal water quality and coastal algal bloom outbreaks in the future challenges of climate change and human activities (Gao et al., 2022).
In this paper, we analyzed the changes in nutrient concentrations, compositions and fluxes of nutrients at four stations in the land source of ZJB before and after the typhoon (September and October 2021) to reveal the effects of the tropical typhoon event on nutrient fluxes of nutrients into the sea from the land source of ZJB in the semi-enclosed ZJB, and the following conclusions were drawn. Compared to before the typhoon, the total DIN input flux increased by 3.21 × 103 mol/h, the total DIP input flux decreased by 3.01 × 103 mol/h, and the total DSi input flux increased by 5.20 × 104 mol/h after the typhoon. There were significant spatial and temporal variations in nutrient (DIN, DIP, DSi) concentrations, compositions, and fluxes into the sea from land-source estuaries and outfalls in ZJB before and after the typhoon. Meanwhile, the nitrogen limit in the estuary of ZJB after the typhoon is more serious than before the typhoon, and the DIN/DIP and DIN/DSi are both smaller than the Redfield ratio. In addition, ZJB was considered to have higher concentration levels of nutrients through a comprehensive comparison with other large domestic and international water bodies. This study provides valuable information for understanding the eutrophication of coastal waters caused by global climate change and human activities. Overall, these results revealed impacts of tropical typhoon events on the nutrient fluxes from land-based sources into the semi-enclosed ZJB before and after the typhoon, and provide important data for understanding the ecological effects under extreme weather event driven by climate change.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
JZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FX: Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2023A1515012769); Guangxi Key Research and Development Program (GuiKeAB22035065); Research and Development Projects in Key Areas of Guangdong Province (2020B1111020004); Research on the standards for total nitrogen and total phosphorus in the estuaries and bays of Guangdong Province and evaluation of their applicability (GDEEMC-2024-39); Guangdong Ocean University Fund Project (R18021).
The authors are grateful for the reviewers’ careful review and valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Al-Mur B. A. (2020). Assessing nutrient salts and trace metals distributions in the coastal water of Jeddah, Red Sea. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 27, 3087–3098. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.07.012
Björkman K., Karl D. M. (1994). Bioavailability of inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds to natural assemblages of microorganisms in Hawaiian coastal waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 111, 265–273. doi: 10.3354/meps111265
Boesch D., Burreson E., Dennison W., Houde E., Kemp M., Kennedy V., et al. (2001). Factors in the decline of coastal ecosystems. Science 293, 1589–1591. doi: 10.1126/science.293.5535.1589c
Bonometto A., Feola A., Rampazzo F., Gion C., Berto D., Ponis E., et al. (2018). Factors controlling sediment and nutrient fluxes in a small microtidal salt marsh within the Venice Lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 650, 1832–1845. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.142
Cai W. J., Hu X., Huang W. J., Murrell M. C., Lehrter J. C., Lohrenz S. E., et al. (2011). Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication. Nat. Geosci. 4, 766–770. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1297
Cao Z., Wang D., Zhang Z., Zhou K., Dai M. (2020). Seasonal dynamics and export of biogenic silica in the upper water column of a large marginal sea, the northern South China Sea. Prog. In Oceanography 188, 102421. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102421
Chan J. C., Liu K., Ching S. E., Lai E. S. (2004). Asymmetric distribution of convection associated with tropical cyclones making landfall along the South China coast. Monthly Weather Rev. 132, 2410–2420. doi: 10.1007/s00703-006-0244-1
Chen J.-y., Chen S.-l. (2002). Estuarine and coastal challenges in China. Chin. J. Oceanology&Limnology 20, 174–181. doi: 10.1007/BF02849656
Chen J. L., Chen J. Y., Wu Z. Y., Li L. F. (2021). Water quality analysis of Lvtang River and riverine ecological protection. Resource Conserv. Environ. Prot. 000, 12–14. doi: 10.16317/j.cnki.12-1377/x.2021.11.004
Chen R., Chen W. Z., Yao Y. Z., Liang G. L., Zhen L. P. (2011). Water quality analysis of haliotis diversicolor supertexta breeding ponds at Donghai island in Zhanjiang. Fishery Modernization 38 (5), 22–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9580.2011.05.005
Chen C. H., Li Q. X. (2002). Discussion on typhoon occurred in the Haikou Bay and influencing mechanism on the sea water quality. Oceanographic J. 24, 59–65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2002.02.007
Dai M., Zhao Y., Chai F., Chen M., Chen N., Chen Y., et al. (2023). Persistent eutrophication and hypoxia in the coastal ocean. Cambridge Prisms: Coast. Futures 1, e19.
Das S., Giri S., Das I., Chanda A., Ghosh A., Mukhopadhyay A., et al. (2017). Nutrient dynamics of northern Bay of Bengal (nBoB)—Emphasizing the role of tides. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 10, 116–134. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2017.01.006
Deegan A. ,. L., Johnson D. S., Scott R. S., Peterson B. J. (2012). Coastal eutrophication as a driver of salt marsh loss. Nature 490, 388–392. doi: 10.1038/nature11533
Du J., Chen L., Zhang Y., Lin Q., Yang X., Sun X., et al. (2008). Acid deposition characteristics of rainwater and inputs of inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus into the sea waters near Xiamen area during typhoon Bilis. Taiwan Strait 27, 339–346.
Du J., Fu Q., Fang S., Wu J., He P., Quan Z. (2019). Effects of rapid urbanization on vegetation cover in the metropolises of China over the last four decades. Ecol. Indic. 107, 105458.105451–105458.105411. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105458
Feehan C. J., Filbee-Dexter K., Thomsen M. S., Wernberg T., Miles T. (2024). Ecosystem damage by increasing tropical cyclones. Commun. Earth Environ. 5, 674. doi: 10.1038/s43247-024-01853-2
Gao J., An T., Shen J., Zhang K., Yin Y., Zhao R., et al. (2022). Development of a land-sea coordination degree index for coastal regions of China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 230, 230. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106370
GB/T 12763.4-2007. Specification for marine surveys, Part 4: Survey of chemical elements of seawater.
Grasshoff K., Kremling K., Ehrhardt M. (2009). Methods of seawater analysis Vol. 108 (John Wiley & Sons).
Gui D. X., Yuan Y. S., Jun G. Z. (2006). Analysis of nutrient structure and assessment of nutritive status in the Aoshan bay, Qingdao. J. Zhanjiang Ocean Univ. (natural sciences) 26, 22–26. doi: CNKI:SUN:SHDX.0.2006-01-004
Han H., Xiao R., Gao G., Yin B., Liang S., Lv X. (2023). Influence of a heavy rainfall event on nutrients and phytoplankton dynamics in a well-mixed semi-enclosed bay. J. Hydrology 617, 128932. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128932
Herbeck L. S., Unger D., Krumme U., Liu S. M., Jennerjahn T. C. (2011). Typhoon-induced precipitation impact on nutrient and suspended matter dynamics of a tropical estuary affected by human activities in Hainan, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 93, 375–388. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.05.004
Huang H., Dan S. F., Yang B., Ning Z., Liang S., Kang Z., et al. (2023). Spatiotemporal distributions of poorly-bound heavy metals in surface sediments of a typical subtropical eutrophic estuary and adjacent bay. Mar. Environ. Res. 189, 106076. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106076
Huang S., Sherman A., Chen C., Jaffé P. R. (2021). Tropical cyclone effects on water and sediment chemistry and the microbial community in estuarine ecosystems. Environ. pollut. 286, 117228. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117228
Hui Z., Tang D., Wang D. (2009). Phytoplankton blooms near the Pearl River Estuary induced by Typhoon Nuri. J. Geophysical Res. 114 (C12), C12027:1–C12027:9. doi: 10.1029/2009jc005384
Hung J. J., Hung C. S., Su H. M. (2008). Biogeochemical responses to the removal of maricultural structures from an eutrophic lagoon (Tapong Bay) in Taiwan. Mar. Environ. Res. 65, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2007.07.003
IPCC (2019).IPCC special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate. In: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Geneva, Switzerland: IPCC). Available online at: https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/chapter-6/ (Accessed 28 March 2022).
Jani J., Toor G. S. (2018). Composition, sources, and bioavailability of nitrogen in a longitudinal gradient from freshwater to estuarine waters. Water Res. 137, 344–354. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.042
Jian Q., Wang S., Zhang P., Zhang J., Zhao L., Liu D. (2022). Microplastic variations in land-based sources of coastal water affected by tropical typhoon events in zhanjiang bay, China. Water 14, 1455. doi: 10.3390/w14091455
Jiang T., Wu G., Niu P., Cui Z., Bian X., Xie Y., et al. (2022). Short-term changes in algal blooms and phytoplankton community after the passage of Super Typhoon Lekima in a temperate and inner sea (Bohai Sea) in China. Ecotoxicology Environ. Saf. 232, 113223. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113223
Karl D. M. (2014). Microbially mediated transformations of phosphorus in the sea: new views of an old cycle. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 6, 279–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010213-135046
Ke S., Zhang P., Ou S., Zhang J., Chen J., Zhang J. (2022). Spatiotemporal nutrient patterns, composition, and implications for eutrophication mitigation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 266, 107749. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2022.107749
Lao Q., Lu X., Chen F., Chen C., Jin G., Zhu Q. (2023). A comparative study on source of water masses and nutrient supply in Zhanjiang Bay during the normal summer, rainstorm, and typhoon periods: Insights from dual water isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 903, 166853. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166853
Lao Q., Wu J., Chen F., Zhou X., Li Z., Chen C., et al. (2022). Increasing intrusion of high salinity water alters the mariculture activities in Zhanjiang Bay during the past two decades identified by dual water isotopes. J. Environ. Manage. 320, 115815. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115815
Li H. M., Tang H. J., Shi X. Y., Zhang C. S., Wang X. L. (2014). Increased nutrient loads from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River have led to increased harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 39, 92–101. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2014.07.002
Li M., Zhong L., Boicourt W. C., Zhang S., Zhang D. L. (2007). Hurricane-induced destratification and restratification in a partially-mixed estuary. J. Mar. Res. 65, 169–192. doi: 10.1357/002224007780882550
Lin P., Chen M., Guo L. (2012). Speciation and transformation of phosphorus and its mixing behavior in the Bay of St. Louis estuary in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta 87, 283–298. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.040
Lin P., Guo L. (2016). Dynamic changes in the abundance and chemical speciation of dissolved and particulate phosphorus across the river-lake interface in southwest Lake Michigan. Limnology Oceanography 61, 771–789. doi: 10.1002/lno.10254
Lin G., Lin X. (2022). Bait input altered microbial community structure and increased greenhouse gases production in coastal wetland sediment. Water Res. 218, 11850. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118520
Lisboa M. S., Schneider R. L., Sullivan P. J., Walter M. T. (2020). Drought and post-drought rain effect on stream phosphorus and other nutrient losses in the northeastern usa. J. Hydrology: Regional Stud. 28, 100672. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrh.2020.100672
Liu X., Lei F., Dai S. (2022). Analysis of nutrients and water quality in Lianzhou bay of guangxi in autumn of 2021. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 38, 288–294. doi: 10.13657/j.cnki.gxkxyxb.20220804.001
Liu X., Liu D., Wang Y., Shi Y., Wang Y., Sun X. (2019). Temporal and spatial variations and impact factors of nutrients in Bohai Bay, China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 140, 549–562. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.02.011
Luo Z., Hu S., Chen D. (2018). The trends of aquacultural nitrogen budget and its environmental implications in China. Sci. Rep. 8, 10877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29214-y
Meng J., Yu Z., Yao Q., Bianchi T. S., Paytan A., Zhao B., et al. (2015). Distribution, mixing behavior, and transformation of dissolved inorganic phosphorus and suspended particulate phosphorus along a salinity gradient in the Changjiang Estuary. Mar. Chem. 168, 124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.09.016
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (2005). Code for Liquid Flow Measurement in Open Channels: GB50179-93; China Environmental Science (Beijing, China: Press).
Motew M., Booth E. G., Carpenter S. R., Chen X., Kucharik C. (2018). The synergistic effect of manure supply and extreme precipitation on surface water quality. Environ. Res. Lett. 13, 079601. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaade6
Mukundan R., Hoang L., Gelda R. K., Yeo M.-H., Owens E. M. (2020). Climate change impact on nutrient loading in a water supply watershed. J. Hydrology 586, 124868. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124868
National Environmental Protection Agency (2002). Technical Specifications Requirements for Monitoring of Surface Water and Waste Water: HJ/T 91—2002 (Beijing, China: China Environmental Science Press).
Nayak S., Takemi T. (2019). Dynamical downscaling of typhoon lionrock, (2016) for assessing the resulting hazards under global warming. J. Meteorological Soc. Japan 97, 69–88. doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2019-003
Oh Y. H., Kim Y., Park S. R., Lee T., Son Y. B., Park S.-E., et al. (2021). Spatiotemporal change in coastal waters caused by land-based fish farm wastewater-borne nutrients: Results from Jeju Island, Korea. Mar. pollut. Bull. 170, 112632. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112632
Paerl H. W., Hall N. S., Hounshell A. G., Rossignol K. L., Barnard M. A., Luettich R. A. Jr., et al. (2020). Recent increases of rainfall and flooding from tropical cyclones (TCs) in North Carolina (USA): implications for organic matter and nutrient cycling in coastal watersheds. Biogeochemistry 150, 197–216. doi: 10.1007/s10533-021-00770-2
Papush L., Danielsson A., Rahm L. (2009). Dissolved silica budget for the Baltic Sea. J. Sea Res. 62, 31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2009.03.001
People’s Government of Guangdong Province (2021). Available online at: http://www.gd.gov.cn/ (Accessed 8 February 2022).
Qi Z., Shi R., Yu Z., Han T., Li C., Xu S., et al. (2019). Nutrient release from fish cage aquaculture and mitigation strategies in Daya Bay, southern China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 146, 399–407. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.079
Strokal M., Yang H., Zhang Y., Kroeze C., Li L., Luan S., et al. (2014). Increasing eutrophication in the coastal seas of China from 1970 to 2050. Mar. pollut. Bull. 85, 123–140. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.011
Subrahmanyam M. ,. V. (2015). Impact of typhoon on the north-west Pacific sea surface temperature: a case study of Typhoon Kaemi, (2006). Natural Hazards 78, 569–582. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-1733-7
Sun X., Dong Z., Zhang W., Sun X., Hou C., Liu Y., et al. (2022). Seasonal and spatial variations in nutrients under the influence of natural and anthropogenic factors in coastal waters of the northern Yellow Sea, China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 175, 113171. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113171
Tan H. J., Cai R. S., Du J. G., Hu W. J. (2022). Climate change and marine ecosystems: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Trans. Atmos Sci. 45, 489–501. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.dqkxxb.20220411001
Thompson P. A., Paerl H. W., Campbell L., Yin K., McDonald K. S. (2023). Tropical cyclones: what are their impacts on phytoplankton ecology? J. Plankton Res. 45, 180–204. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbac062
Thyng K. M., Hetland R. D., Socolofsky S. A., Fernando N., Turner E. L., Schoenbaechler C. (2020). Hurricane harvey caused unprecedented freshwater inflow to galveston bay. Estuaries Coasts 43, 1836–1852. doi: 10.1007/s12237-020-00800-6
Tilahun A. B., Dürr H. H., Schweden K., Flrke M. (2024). Perspectives on total phosphorus response in rivers: Examining the influence of rainfall extremes and post-dry rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 940, 173677. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173677
Turner R. E., Rabalais N. N., Justic’ D., Dortch Q. (2003). Future aquatic nutrient limitations. Mar. pollut. Bull. 46, 1032–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00049-3
Wan J. W., Li Q. S., Han X. L., Xu K. (2022). Investigation of structural responses and dynamic characteristics of a supertall building during Typhoon Kompasu. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodynamics 230, 105209. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2022.105209
Wang T. (2016). Effects of typhoon on the material transport and water environment in the estuaries and adjacent sea of eastern China. East China Normal University. Doctoral dissertation.
Wang P., Lao Q., Wu j., Huang C., Lu X., Zhu Q., et al. (2022). Distribution characteristics and influence factors of COD in Zhanjiang Bay. China. J. Guangxi Sci. 29, 498–510. doi: 10.13656/j.cnki.gxkx.20220616.001
Wang Y. S., Lou Z. P., Sun C. C., Sun S. (2008). Ecological environment changes in daya bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar. pollut. Bull. 56, 1871–1879. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.07.017
Wang Z., Qi Y., Chen J., Xu N., Yang Y. (2006). Phytoplankton abundance, community structure and nutrients in cultural areas of Daya Bay, South China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 62, 85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.04.008
Wang L., Shao H., Guo Y., Bi H., Lei X., Dai S., et al. (2024). Ecological restoration for eutrophication mitigation in urban interconnected water bodies: Evaluation, variability and strategy. J. Environ. Manage. 365, 121475. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121475
Wang G. Y., Wang G. Y., Zhao J., Lin X. (2023). Dynamics of benthic nitrate reduction pathways and associated microbial communities responding to the development of seasonal deoxygenation in a coastal mariculture zone. Environ. Sci. And Technol. 57, 15014–15025. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c03994
Wang S., Yang K., Shi Y., Yang F. (2022). Observations of anomalous over-the-horizon propagation in the evaporation duct induced by Typhoon Kompasu, (202118). IEEE Antennas Wireless Propagation Lett. 21, 963–967. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3153389
Watson S. B., Miller C., Boyer G. L., Carmichael W., Charlton M. N., Depew D. C., et al. (2016). The re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Harmful algal blooms and hypoxia. Harmful Algae 56, 44–66. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.04.010
Wells M. L., Trainer V. L., Smayda T. J., Karlson B. S. O., Trick C. G., Kudela R. M. (2015). Harmful algal blooms and climate change: Learning from the past and present to forecast the future. Harmful Algae 49, 68–93. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2015.07.009
Wen S., Liu X., Chen S., Song L., Wang T., Chen Y., et al. (2024). Hazard zoning of harmful algal bloom disasters in Zhejiang coastal waters using GIS: 1933-2021. J. Mar. Environ. Eng. 11, 115–128. doi: 10.32908/JMEE.v11.2024040101
Wu N., Liu S. M., Zhang G. L., Zhang H. M. (2021). Anthropogenic impacts on nutrient variability in the lower Yellow River. Sci. total Environ. 755, 142488. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142488
Wu A., Zhong Z., Yu S., Sui X., Yao X., Zou L., et al. (2021). The current status and 20 years of evolution of nutrient structure in the Yellow River estuary. Prog. Fishery Sci. 45, 01–13. doi: 10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.2023103100
Wurtsbaugh W. A., Paerl H. W., Dodds W. K. (2019). Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wiley Interdiscip. Reviews: Water 6, e1373. doi: 10.1002/wat2.1373
Xu C., Dan S. F., Yang B., Lu D., Ning Z. (2021). Biogeochemistry of dissolved and particulate phosphorus speciation in the Maowei Sea, northern Beibu Gulf. J. Hydrology 593, 125822. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125822
Yu X., Liu J., Chen X., Yu H., Du J. (2024). Fresh and saline groundwater nutrient inputs and their impacts on the nutrient budgets in a human-effected bay. Mar. pollut. Bull. 199, 116026. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116026
Yunev O. A., Carstensen J., Moncheva S., Khaliulin A., Rtebjerg G., Nixon S. (2007). Nutrient and phytoplankton trends on the western Black Sea shelf in response to cultural eutrophication and climate changes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 74, 63–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2007.03.030
Zee C. V. D., Roevros N., Chou L. (2007). Phosphorus speciation, transformation and retention in the Scheldt estuary (Belgium/the Netherlands) from the freshwater tidal limits to the North Sea. Mar. Chem. 106, 76–91. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2007.01.003
Zhang P., Chen Y., Peng C., Dai P., Zhang J. (2020a). Spatiotemporal variation, composition of DIN and its contribution to eutrophication in coastal waters adjacent to Hainan Island, China. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 37, 101332. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101332
Zhang Z., Fukushima T., Onda Y., Gomi T., Fukuyama T., Sidle R., et al. (2007). Nutrient runoff from forested watersheds in central Japan during typhoon storms: implications for understanding runoff mechanisms during storm events. Hydrological Processes: Int. J. 21, 1167–1178. doi: 10.1002/hyp.6677
Zhang P., Liang-Ru W., Lai J. Y., Dai P. D., Zhang J. B. (2019). Concentration, composition and fluxes of land-based nitrogen and phosphorus source pollutants input into zhanjiang bay in summer. J. Guangdong Ocean University. 39, 63–72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2019.04.000
Zhang P., Long H., Li Z., Chen R., Peng D., Zhang J. (2024). Effects of typhoon events on coastal hydrology, nutrients, and algal bloom dynamics: Insights from continuous observation and machine learning in semi-enclosed Zhanjiang Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 924, 171676. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171676
Zhang P., Peng C., Zhang J., Zhang J., Chen J., Zhao H. (2022). Long-term harmful algal blooms and nutrients patterns affected by climate change and anthropogenic pressures in the zhanjiang bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.849819
Zhang P., Peng C. H., Zhang J. B., Zou Z. B., Shi Y. Z., Zhao L. R., et al. (2020b). Spatiotemporal urea distribution, sources, and indication of DON bioavailability in zhanjiang bay, China. Water 12, 633. doi: 10.3390/w12030633
Zhang H. X., Shen Y. M., Zhao A. D., Tang J. (2022). Numerical modelling of storm surge, nutrient pollution and saltwater intrusion in a large estuary with typhoon effects. Environ. Model. Software 155, 105449. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2022.105449
Zhang P., Xu J. L., Zhang J. B., Li J. X., Luo X. Q. (2020c). Spatiotemporal dissolved silicate variation, sources, and behavior in the eutrophic zhanjiang bay, China. Water 12, 3586. doi: 10.3390/w12123586
Zhou Q., Wang S., Liu J., Hu X., Liu Y., He Y., et al. (2022). Geological evolution of offshore pollution and its long-term potential impacts on marine ecosystems. Geological Frontiers: English Edition 13, 14. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101427
Zhou Y., Wang L., Zhou Y., Mao X. Z. (2020). Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 705, 135760.135761–135760.135711. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135760
Keywords: nutrients, typhoon, land-based sources, flux, coastal water
Citation: Zhang J, He Y, Zhang P and Xv F (2025) Effects of tropical typhoon event on land-based nutrients sources fluxes in the semi-enclosed eutrophic Zhanjiang Bay coastal water, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1487001. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1487001
Received: 27 August 2024; Accepted: 20 February 2025;
Published: 14 March 2025.
Edited by:
Vishnu Vardhan Kanuri, Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE), IndiaReviewed by:
Satyanarayan Bramha, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), IndiaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, He, Zhang and Xv. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peng Zhang, emhhbmdwZW5nQGdkb3UuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.