- 1School of Transport and Logistics, Guangzhou Railway Polytechnic, Guangzhou, China
- 2School of Transport and Communications, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai, China
The 21st-century Maritime Silk Road initiative by the Chinese government has garnered growing global attention. As pivotal facilitators of international trade, the maritime routes and ports along this route are attracting the interest of various stakeholders. There is a pressing need for extensive research to augment the existing theoretical frameworks. This paper introduces a Self-Organizing Map (SOM) neural network-based methodology for port function clustering, applied to 24 major ports spanning from the South China Sea to the ASEAN region in 2023. The clustering outcomes are cross-validated against port rankings derived from Principal Component Analysis. The study reveals several key insights: (1) Singapore Port, Hong Kong Port, Shenzhen Port, and Guangzhou Port emerge as the principal shipping hubs within the region; (2) The relationship between China and Singapore is identified as a linchpin for the sustainable development of the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road; (3) Guangdong Province is highlighted as a central economic and logistical node. Finally, the recommendations for the accelerated development of the Hainan Free Trade Port and Fujian Coastal Port is concluded.
1 Introduction
In 2013, the Chinese government introduced the strategic vision known as the “New Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road” (referred to as the Belt and Road Initiative, BRI) (Li et al., 2020). This initiative has attracted significant attention and garnered substantial support from the countries involved, regions concerned, and indeed, the global community at large. In March 2015, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Commerce of China jointly published the “Visions and Actions on Jointly Building Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road.” This document underscored the primary maritime route of the “21st-Century Maritime Silk Road” (21st-MSR), which extends from the South China Sea, through the Indian Ocean, and onward to Europe (Peng et al., 2024).
As international trade continues to surge, container liner services have emerged as the preferred mode for global cargo transportation, attributed to their substantial loading capacity and cost-effectiveness (Zhu et al., 2024). The enhancement of ports along the 21st-MSR has become a pivotal initiative in advancing the BRI. Increasingly, scholarly focus is being directed towards the study of ports along the 21st-MSR (Xu et al., 2024a). For instance, to elucidate the spatio-temporal evolution of the port system within this corridor, Zhang et al. (2023c) have employed the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index and the rank-size rule to scrutinize the spatio-temporal correlation characteristics of container ports spanning the period from 2000 to 2019. Furthermore, the studies have conducted in-depth analyses on the sustainability and operational facets of the ports along the 21st-MSR (Wang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024).
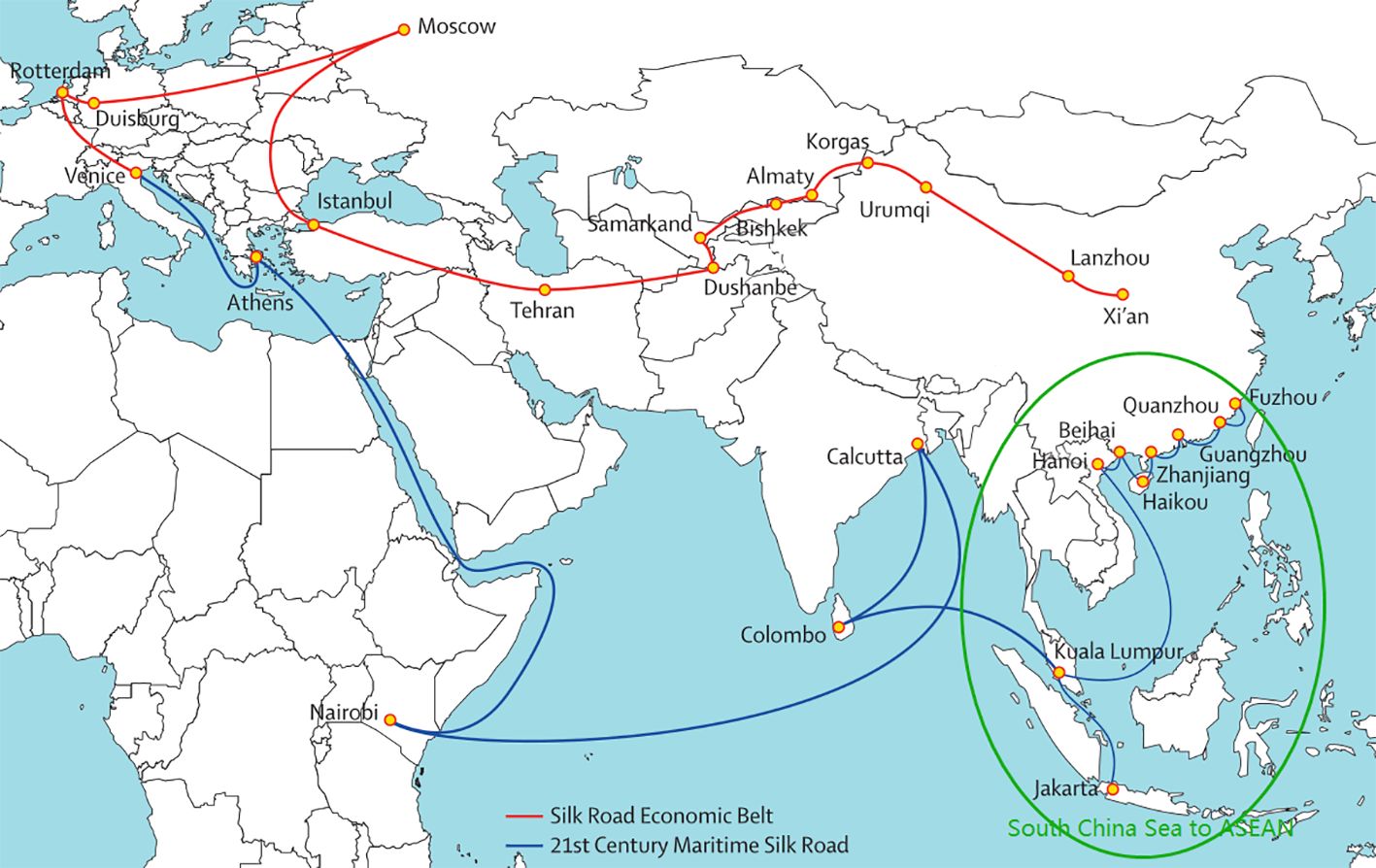
The 21st-MSR is a pivotal part of the BRI, serving as the southern corridor among the initiative’s five economic belts. The primary shipping routes of the 21st-MSR extend from Quanzhou through Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Haikou, Beihai, Hanoi, Kuala Lumpur, Jakarta, Colombo, Kolkata, Nairobi, Athens, and Venice, highlighting the integral role of ASEAN countries in connecting the South China Sea to Europe and the South Pacific (Lin and Liu, 2023). ASEAN region is not only a crucial component of the the 21st-MSR but also one of the most significant container markets in Asia. The emphasis on the joint development of smooth, safe, and efficient transport corridors with key ports as nodes is a strategic priority within the BRI (Nguyen et al., 2020). The studies on shipping logistics from the South China Sea to ASEAN are of great significance to the sustainable development of BRI (Song and Fabinyi, 2022; Chen et al., 2024; Ardine et al., 2023).
In the context of direct Origin-Destination flows between various ports, the transportation of goods necessitates a substantial fleet of vehicles, often leading to suboptimal full load rates (Kalahasthi et al., 2022). This approach can engender the return of empty vehicles, thereby incurring higher costs and contributing to the wastage of energy and resources. Conversely, when the Origin-Destination flow is predominantly channeled through specific hubs, the aggregation of goods for transportation can leverage economies of scale, which not only reduces costs but also mitigates environmental pollution (Xu et al., 2024b). Within the framework of a sustainable shipping network, it is imperative to categorize all ports based on their distinct capacities and functions (Notteboom and Haralambides, 2023).
Large ports serve as the nucleus of the transportation network, designated as hub ports, while smaller and medium-sized ports feed into these hubs, known as feeder ports (Sugimura et al., 2023). Hub ports fulfill dual roles in transportation, that acts as centralized nodes for the aggregation and distribution of goods, akin to transit warehouses, logistics centers, and distribution centers within a logistics system (Nie et al., 2023). The interaction between hub ports and feeder ports at varying load levels establishes a radial, efficient shipping network that facilitates trade. To categorize ports effectively, researchers have proposed the use of cluster analysis. This method involves grouping objects or variables with similar characteristics, thereby facilitating a more systematic and organized approach to port classification (Guo et al., 2023). For example, Kaliszewski et al. (2020) adopt the cluster analysis to container ports into three distinct groups along three dimensions: number of containers handled, berth length, and number of berths. Ke and Wang (2017) combine cluster analysis, hierarchical analysis, and principal component analysis to classify the Chinese maritime centers of the main port cities, and rank the latter according to their soft and hard infrastructure. Souza et al. (2023b) improve a clustering method to analyze the competitiveness of Brazilian container port terminals. In their study, thirteen criteria are selected for the analysis taking into consideration both the previous literature and the characteristics of Brazilian ports. Saeed and Cullinane (2023) group China’s 155 maritime trading partners into distinct meaningful clusters by a hierarchical clustering technique. Mohd Rozar et al. (2023) use a hierarchical cluster analysis to categorize 18 Malaysian bulk terminals into two different classes and find that the Westport and Northport of Klang Port have the best performance of all.
Due to constraints in data collection, traditional clustering algorithms, such as hierarchical clustering and K-means clustering, primarily analyze sample eigenvalues based on a limited set of indicators selected by experts. This approach is employed with a small number of indicators and samples to prevent multicollinearity, which can arise from high-dimensional data (Schumacher et al., 2022). However, with the advent of the big data era, there is a growing need for novel intelligent algorithms capable of managing high-dimensional data and large sample sizes in order to effectively cluster ports (Bai et al., 2023). The traditional clustering algorithms are indeed limited when it comes to handling the vast amounts of data generated by large samples. These methods struggle with scalability and become computationally expensive or even infeasible as the dimensionality and volume of data increase. The need for new intelligent algorithms capable of managing high-dimensional samples for port clustering is evident.
One approach to address this challenge is through the development of advanced intelligent techniques that can handle large and complex datasets more efficiently. Neural networks are a classic class of intelligent algorithms extensively utilized in various domains, including image processing, text analysis, and data processing (Rahmani et al., 2023). These networks can be broadly categorized into two types: supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms. Unsupervised neural networks are capable of processing unstructured data and making decisions without external guidance, particularly in cluster analysis. A notable example of this type is the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) neural network (Zhang et al., 2023a).
The SOM neural network is a unsupervised algorithm that excels in handling nonlinear problems and complex datasets (Zhang et al., 2022). It is frequently utilized for pattern recognition and assessing relationships among variables. Unlike other unsupervised methods, SOM also has the capacity to manage large datasets and offers the added benefit of visually exploring the results (Licen et al., 2023). The core idea of SOM is to simulate the self-organization process of the human brain’s nervous system. Through training, it enables similar input data points to be mapped to adjacent neurons on a grid, thereby forming a topological structure on the map that reflects the relationships between the input data (Shahid, 2023). Due to these functionalities and advantages, numerous researchers are inclined to employ SOM neural networks for conducting cluster analysis. For example, Shahid (2023) conduct a comparison of SOM neural network and hierarchical clustering. It is presented that hierarchical clustering has the tendency to commit classification errors when empirical data departs from ideal conditions of compact isolated clusters. Rabelo et al. (2023) propose a SOM neural network to characterize the main agricultural land systems in western Mediterranean areas into five main clusters. In their study, the implemented clustering approach leads to the municipality aggregation into output units on the basis of proximity. de Souza et al. (2023a) introduce a non-supervised clustering analysis with SOM neural network as a strategy of decision-making to identify potential variables in routine blood tests. Based on the SOM features, it detects discrimination power around 83% to positive patients.
As previously discussed, the SOM neural network has been effectively applied to cluster analysis in various domains, including agriculture and logistics (Xu et al., 2024d). This technique also holds potential applications in port research. The SOM achieves clustering by projecting high-dimensional input data onto a low-dimensional space (typically two-dimensional) while preserving the topological relationships inherent in the input data (Wang et al., 2023). The map learns to categorize variables based on their groupings within the input space and undergoes training across variables that occupy competitive layers of neighboring neurons. The SOM is capable of learning both the distribution and topology of input variables, and it excels at managing high-dimensional indicators and large sample sizes, offering advantages over traditional clustering methods (Zhang et al., 2023b).
In this study, an unsupervised SOM neural network-based port clustering algorithm is introduced, which is applied to the shipping route from the South China Sea to the ASEAN region. Initially, the ports along the 21st-MSR and the relevant cluster indicators are analyzed. Subsequently, the SOM neural network-based port clustering algorithm is developed to categorize the selected ports along the 21st-MSR. To ascertain the efficacy of this approach, the clustering outcomes are juxtaposed with the port rankings derived from Principal Component Analysis (PCA). The key contributions of this paper are as follows:
1. Compared with the traditional clustering algorithms, the SOM serves as a non-linear dimension-reduction tool, effectively mapping high-dimensional data to lower dimensions, which is particularly beneficial in handling the complexity and volume of big data algorithm.
2. By incorporating trade indicators along the BRI, a cluster analysis of major ports from the South China Sea to the ASEAN region is conducted. The findings offer a valuable theoretical foundation for the sustainable development of the 21st-MSR.
3. The integration of the SOM neural network into port clustering research presents a novel domain for the application of this intelligent, thereby expanding the application domain of this intelligent algorithm.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 illustrates the preparation of the art. Section 3 describes the SOM neural network-based port clustering method. Section 4 presents the validity test and discussion. The conclusion and future works are given in Section 5.
2 Preparation
This section is organized into four subsections. The first subsection introduces the port nodes under study. The second subsection identifies the indicators used for clustering ports. The third subsection examines the methods capable of achieving the clustering objectives. The final subsection details the research data used in this study.
2.1 Node determination
ASEAN is one of China’s largest trading partners. Regardless of whether shipping routes extend to Europe or the South Pacific from the South China Sea, ASEAN’s port nodes are essential. To simplify calculations, this paper focuses on studying the main ports from the South China Sea to ASEAN regions.
The main cities along the South China Sea to ASEAN include Quanzhou, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Haikou, Beihai, Hanoi, Kuala Lumpur, and Jakarta (Tang et al., 2017), as shown in in Figure 1. Based on the characteristics of the BRI, previous literature suggests four distinct roles for shipping ports: international hub ports, regional hub ports, node ports, and regional ports (Wang et al., 2021).
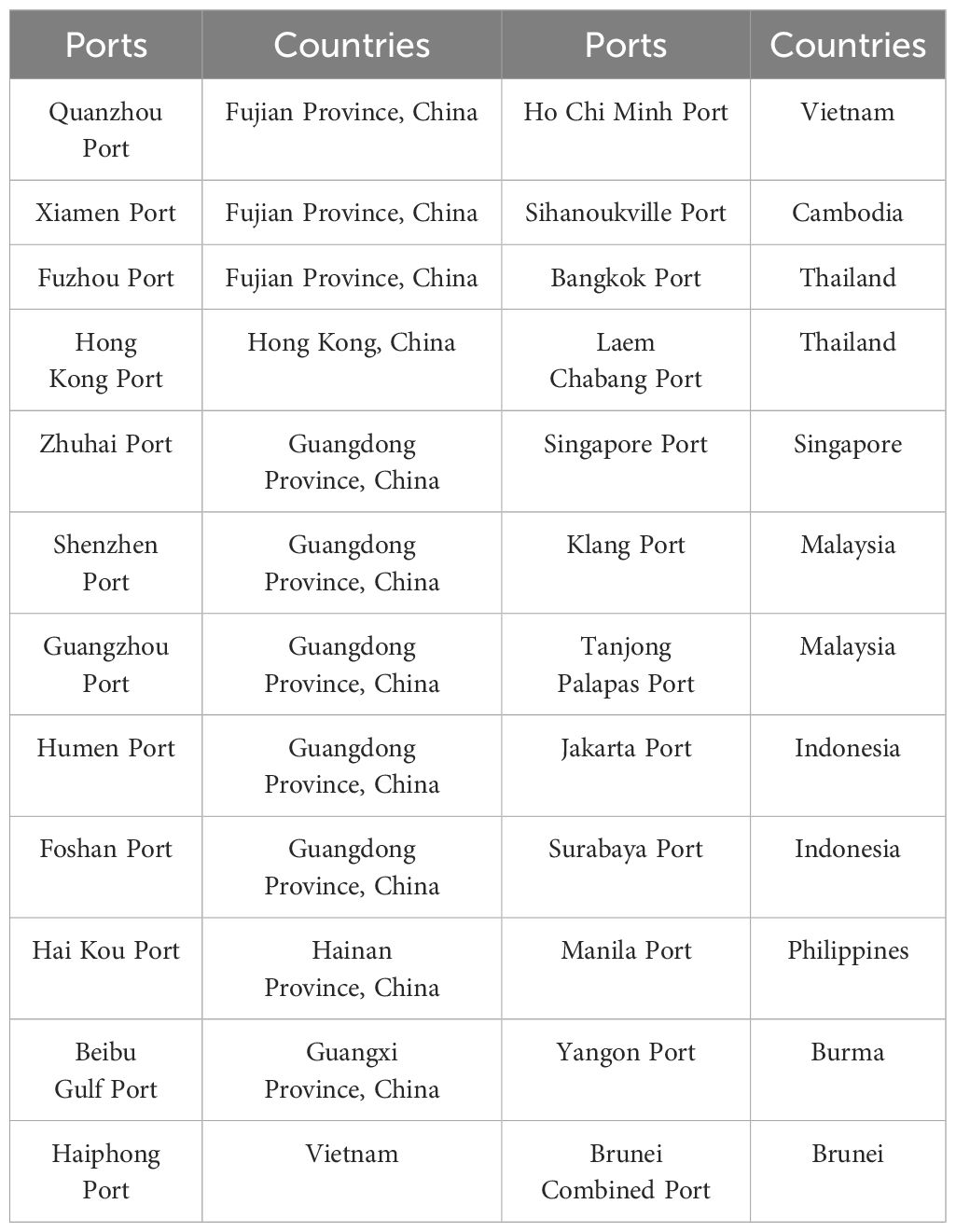
For the port selection along the aforementioned route, we have chosen the top 100 ports from Fujian, Hong Kong, Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, and ASEAN countries, as ranked by the 2023 Global Container Port Throughput published by the China Port Association. For countries not listed among the top 100, we have selected the largest seaport as an alternative (with the exception of Laos, which is landlocked). In total, 24 ports have been selected for the shipping route from the South China Sea to ASEAN. The geographic information of these ports, which serve as trade nodes, is presented in Table 1.
As shown in Table 1, there are 11 ports in China and 13 in ASEAN countries. Guangdong Province in China, which is the country’s largest by GDP, has the highest number of ports with five. Three ports are selected in China’s Fujian Province: Quanzhou Port, Xiamen Port, and Fuzhou Port, which is the starting point of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (21st-MSR). The smallest port is Brunei Combined Port, yet it is the largest port in Brunei.
2.2 Indicator selection
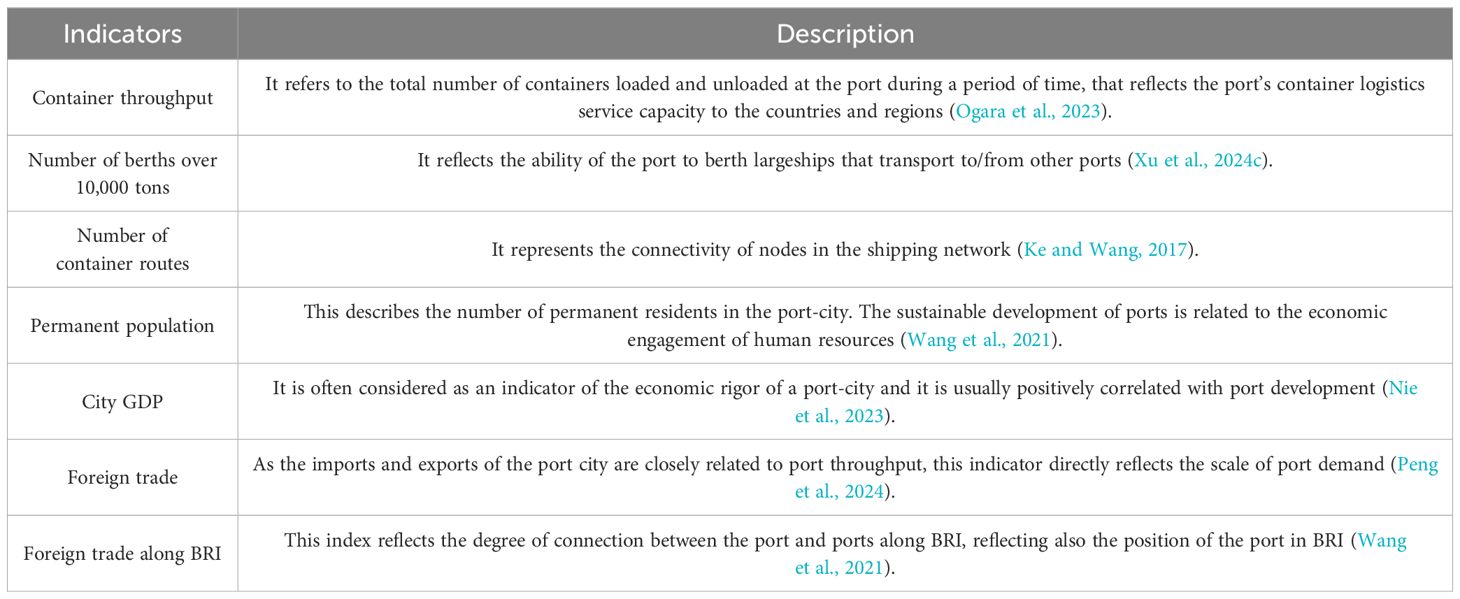
The indicators of the samples serve as the inputs for all clustering algorithms, with their values directly influencing the clustering outcomes. Wang et al. (2021) encapsulate the port development indicators within four dimensions: operational capacity, economic conditions, environmental factors, and human intellect and technology. Ke and Wang (2017) select the container cargo throughput, port city GDP, total foreign trade volume, and other indicators to study the competitiveness of major ports in China. Ogara et al. (2023) identify existing themes on port city and marine ecosystem sustainability indicator frameworks. Xu et al. (2024c) elaborate on the crucial support functions that port infrastructure provides for the development of shipping trade and the establishment of connecting routes.
By examining the components of the BRI and reviewing the existing port literature, this paper introduces the most frequently occurring indicators, as presented in Table 2. All selected indicators are positively correlated with the evaluation outcomes. Notably, the last indicator, ‘Foreign trade along the BRI’ incorporates distinctive characteristics of the BRI that have not been widely considered in other port-related studies.
2.3 Data collection
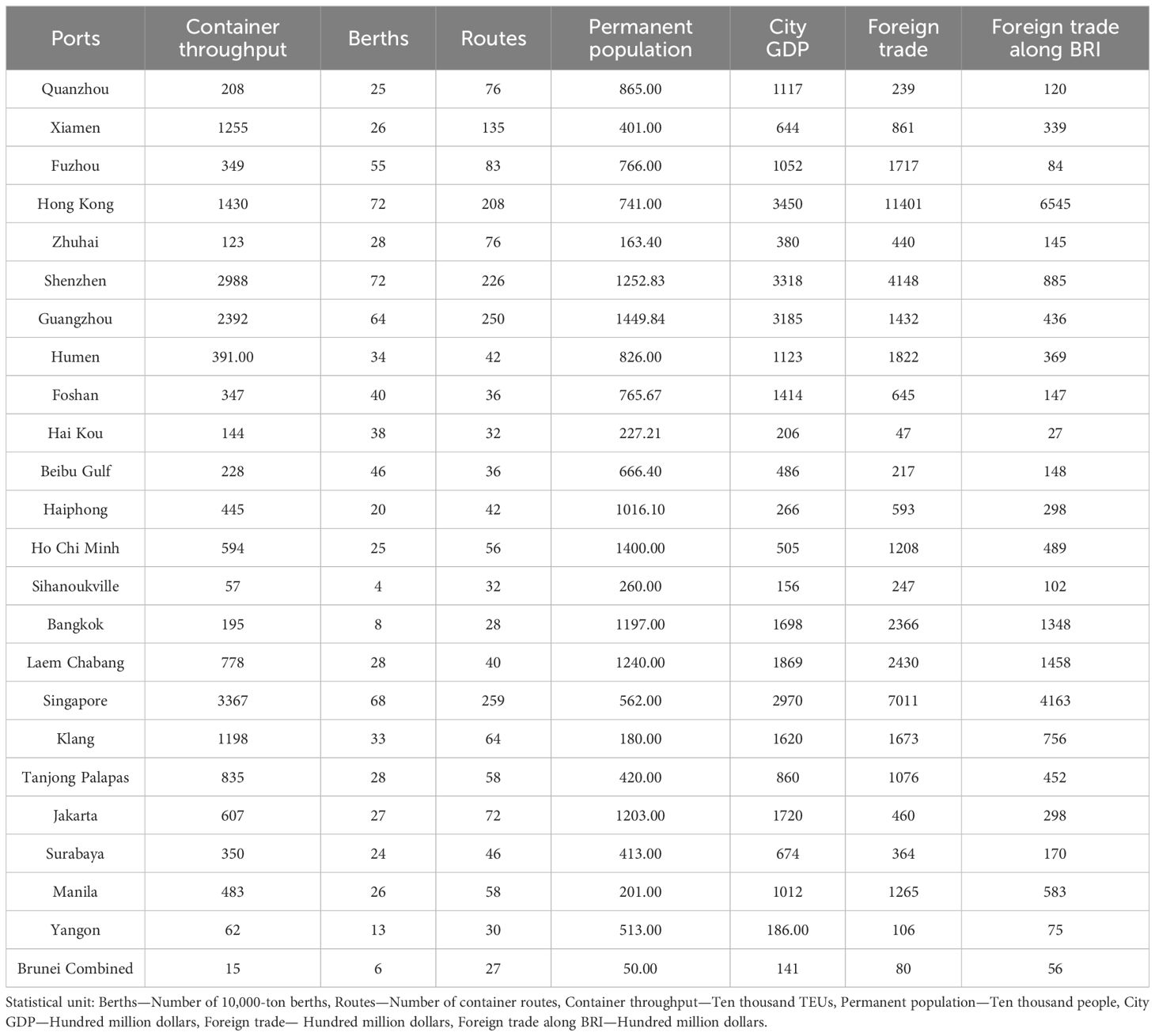
The evolution of shipping node structures is a gradual process. Taking into account the anomalous shipping data resulting from the Chinese government’s lockdown measures during the COVID-19 pandemic, we have collected port data 2023, the first year after the pandemic’s onset, to perform cluster analysis on ports along the South China Sea to ASEAN route. The key indicators’ data are presented in Table 3.
In Table 3, all port statistics are of a uniform caliber, ensuring consistency in data quality. The primary sources of this data include the ‘China Statistical Yearbook’, ‘China Statistical Yearbook of Relevant Provinces and Cities’, ‘China Yearbook of Cities’, and the ‘Statistical Bulletin of National Economy and Social Development of Relevant Cities of China’. Data for all economic indicators are rounded.
3 SOM neural network-based port clustering
3.1 Algorithm description
The SOM neural network is composed of input and hidden layers. Within the hidden layer, each node corresponds to a class that is to be formed during the aggregation process. The nodes in the input layer are fully connected to those in the competition layer, collectively constituting a nonlinear learning system.
The relationships among the input neurons are trained based on the original samples and are represented through weight coefficients. Compared to traditional clustering methods, this nonlinear learning system is well-suited to handle large datasets, making it a potent tool for the era of big data. The architectural layout of the SOM is depicted in Figure 2.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the training process of the SOM neural network employs a ‘competitive learning’ paradigm. For each input sample, the hidden layer is scanned to identify the node with the closest match, known as the winning neuron. The weight vector of the winning neuron is then updated using stochastic gradient descent or similar optimization techniques. Neurons surrounding the winning neuron also adjust their parameters in proportion to their topological distance from the winner. This means that not only are the weights and thresholds of the winning neuron modified, but also those of the neighboring neurons, providing a dynamic adjustment across the network. This training methodology significantly enhances the SOM’s generalization capabilities, allowing it to effectively capture the underlying structure of the data.
3.2 Model construction and calculation
In this section, the indicator data of major ports from China’s southern coast to ASEAN (shown in Table 3) are applied to the SOM neural network-based port clustering model. The method and calculation process are as follows:
3.2.1 Step 1: standardisation of data
In this stage, we standardize the values of the indicators to make them comparable across the 24 seaports. Let be the port, be the indicator, be the original data of indicator for port , be the normalised value of indicator for port . There is
where and denote the mean and standard deviation of indicator j for all ports, respectively. (Note: The subscript symbols i and j are only used in the data standardization. If the same symbols appear below, the corresponding meanings will be explained separately.)
3.2.2 Step 2: initialize parameters and set output neurons
In this study, we utilize the default initial values provided by the SOM neural network library functions in MATLAB 2016a for our network’s parameters. Each node’s parameters are initialized randomly.
The number of output neurons in our SOM corresponds to the number of cluster categories. Wang et al. (2021) propose four distinct roles for shipping ports: international hub ports, regional hub ports, node ports, and regional ports. Following the classification conventions outlined in the relevant literature, the 24 selected ports in this paper are categorized into these four groups. Consequently, the SOM neural network is configured with four output neurons during the training process to reflect these port categories.
3.2.3 Step 3: set discriminant function
In training, it is necessary to find the most suitable node (winning neuron) for each input sample by discriminant function. The common discriminant functions include the Euclidean distance method, absolute value error, and so on. This section adopts the most classical Euclidean distance method as the discriminant function (also known as the loss function). The specific expression is shown in Equation 2:
In Equation 2, i and j represent the neuron of the input and competition layers, respectively. The symbol denotes the standardized value of each input sample. The number of input neurons is n (n = 7 in this paper).
3.2.4 Step 4: weight update of near nodes
Once the winning neuron I(x) has been found, the weights of other nodes need to be updated. Let Sij represent the distance between nodes i and j. The weight update rule of near nodes is shown in Equation 3:
From Equation 3, we can find that the updated degree varies according to the distance between adjacent nodes.
3.2.5 Step 5: parameter convergence
In training the SOM neural network, the criterion for successful training is determined by the achievement of a convergence state in the node parameters through successive iterative processes. To optimize parameter convergence, several advanced feedback adjustment algorithms are commonly employed. These include methods such as error backpropagation, gradient descent, and quasi-Newton methods, among others.
In existing feedback tuning algorithms, the gradient descent method has a small amount of computation and fast convergence speed. In this section, the gradient descent method is adopted to update parameters:
Gradient descent is a classical algorithm. The convergence proof of this function is not repeated due to layout limitations. For the calculation of the ports in this paper, MATLAB2016a is used. Its iterative result is shown in Figure 3A.
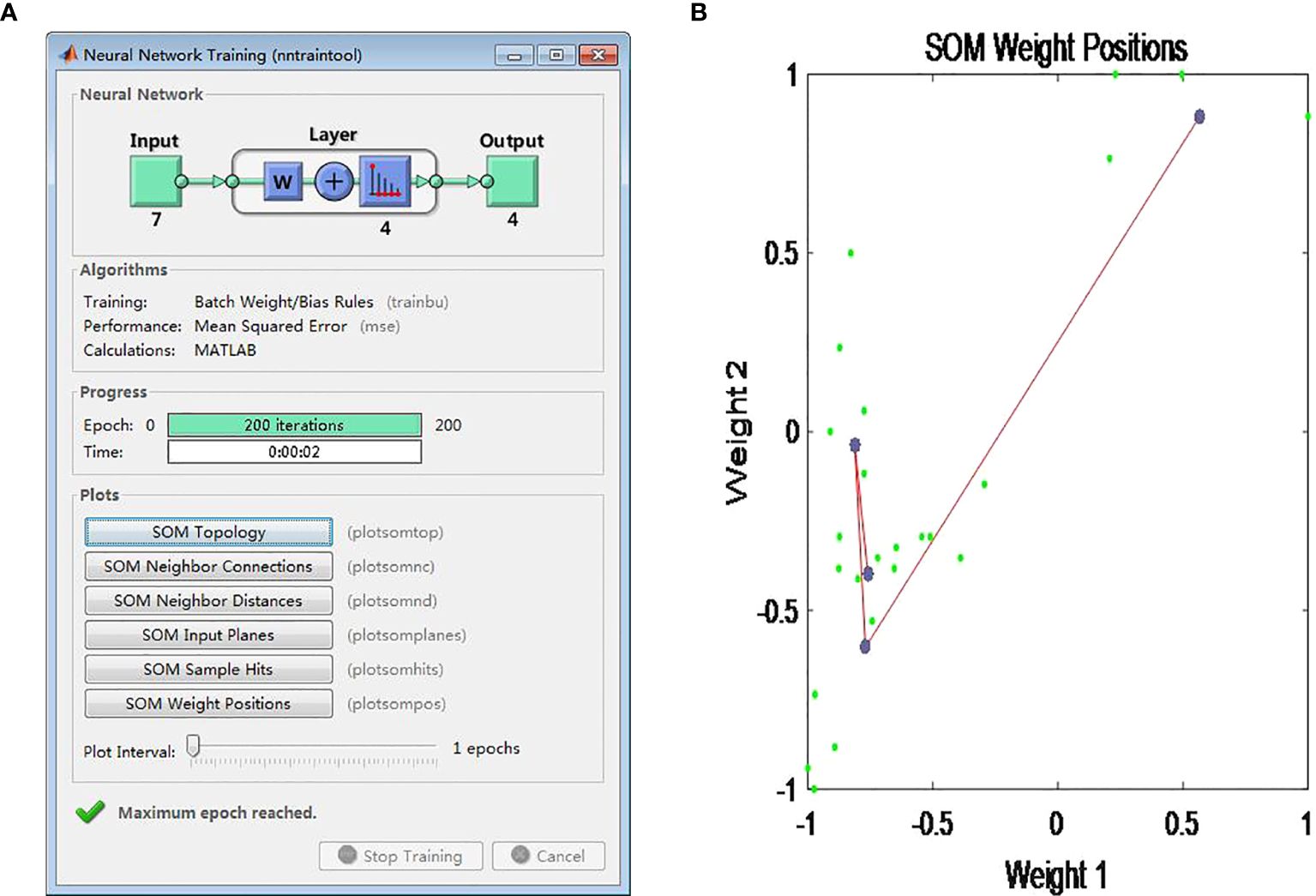
Figure 3. Training result of the SOM neural network. (A) Matlab iteration. (B) Cluster center points.
As shown in Figure 3A, the number of input layers is 7. The quantity of competition and output layers is 4. The iteration time is 200. The calculation time is 2 seconds.
3.2.6 Step 6: port clustering
Based on the convergent parameters trained by the SOM model, the distribution of clustering center location is shown in Figure 3B.
As depicted in Figure 3B, the 24 ports are grouped into 4 distinct categories, with each category containing 4, 4, 6, and 10 ports, respectively. The considerable distance between the centers of each category indicates the significance of the clustering results, suggesting that the ports within each group are relatively homogeneous while being distinct from ports in other groups.
To determine the grade levels within each category, this section proceeds to calculate the characteristic values for each cluster. The clusters are then ranked based on these values, which provide a quantitative measure of the prominence or significance of each category. The average characteristic values for the ports, along with their corresponding cluster assignments, are presented in Table 4.
As presented in Table 4, the first-tier ports comprise Hong Kong Port, Shenzhen Port, Guangzhou Port, and Singapore Port. These ports exhibit an average characteristic value of 0.738, which is significantly higher than the average values of the other groups. The second-tier ports include Ho Chi Minh Port, Bangkok Port, Laem Chabang Port, and Jakarta Port, with an average characteristic value of 0.5533.
As shown in Table 4, the third-tier ports include Quanzhou Port, Fuzhou Port, Humen Port, Foshan Port, Beibu Gulf Port, and Haiphong Port. These ports have an average characteristic value of 0.4107, which, while slightly lower than that of the second-tier ports, indicates a moderate standing within the clustering hierarchy. The fourth-tier, comprising Xiamen Port, Zhuhai Port, Haikou Port, Sihanoukville Port, Port Klang, Tanjong Palas Port, Surabaya Port, Manitra Port, Yangon Port, Brunei Port, and others, exhibits an average characteristic value of -0.4835. This negative value, resulting from the de-dimensionality processing of the original data, is considerably lower than the averages of the higher-tier groups, placing these ports at the lower end of the clustering hierarchy.
4 Validity test and discussion
4.1 Validity test by PCA
To validate the model developed in this paper, the results from Section 3 are compared with those obtained using established methods within this section. Traditional port evaluation models primarily consist of the Analytic Hierarchy Process and Principal Component Analysis (PCA), among others. This section employs PCA, a widely utilized method in evaluative studies, to assess the port ranking outcomes derived from the SOM neural network.
PCA is a quantitative method that differs from the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Its primary process involves converting multiple indicators into a few comprehensive indicators, known as principal components, using the concept of dimensionality reduction. These principal components can reflect most of the information of the original variables. PCA is particularly useful for reducing the complexity of datasets while retaining the majority of the variability present in the data.
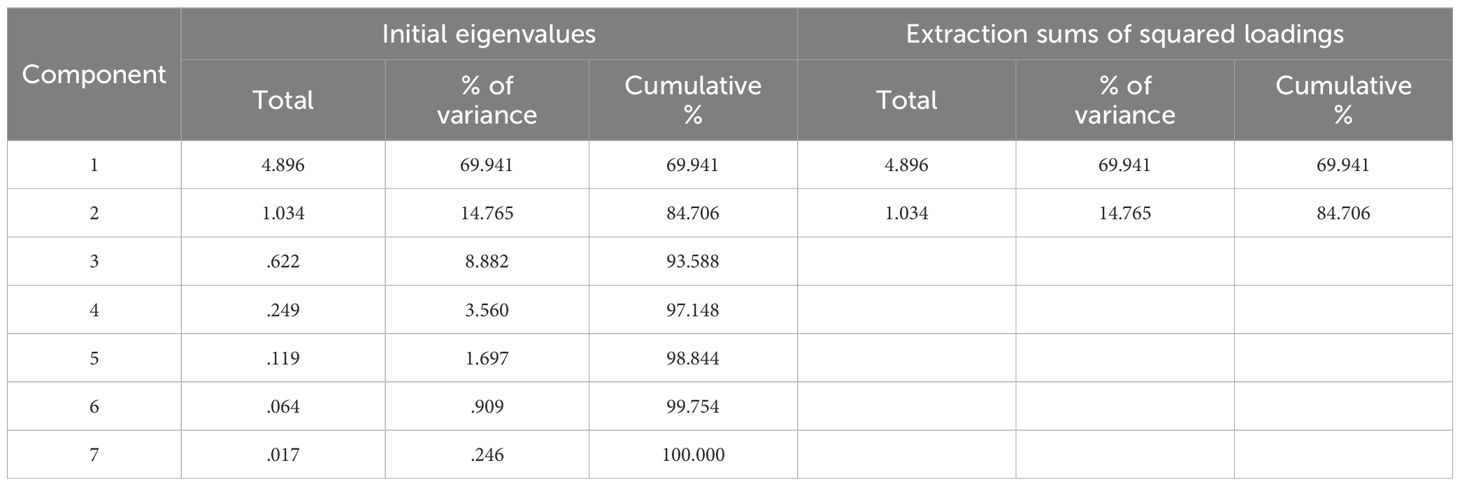
In this section, PCA serves as a comparative method for the SOM neural network model that has been constructed. Due to its universal application, a detailed description of PCA calculations is not repeated here. Instead, SPSS software is utilized to conduct PCA on 7 indicators of 24 ports along the 21st-MSR. Principal components with eigenvalues greater than 1.00 are selected, which is a common criterion for retaining components that explain a significant amount of variance in the data. The analysis results are shown in Table 5.
As depicted in Table 5, the original seven-dimensional data have been reduced to a two-dimensional representation. The cumulative contribution rate of the components, which have eigenvalues greater than 1.00, accounts for 84.7% of the variance, effectively mitigating the impact of multicollinearity among the total time-sharing variables for each port, as calculated in subsequent analyses. Table 6 presents the two-dimensional principal components along with the corresponding port scores post-dimensionality reduction.
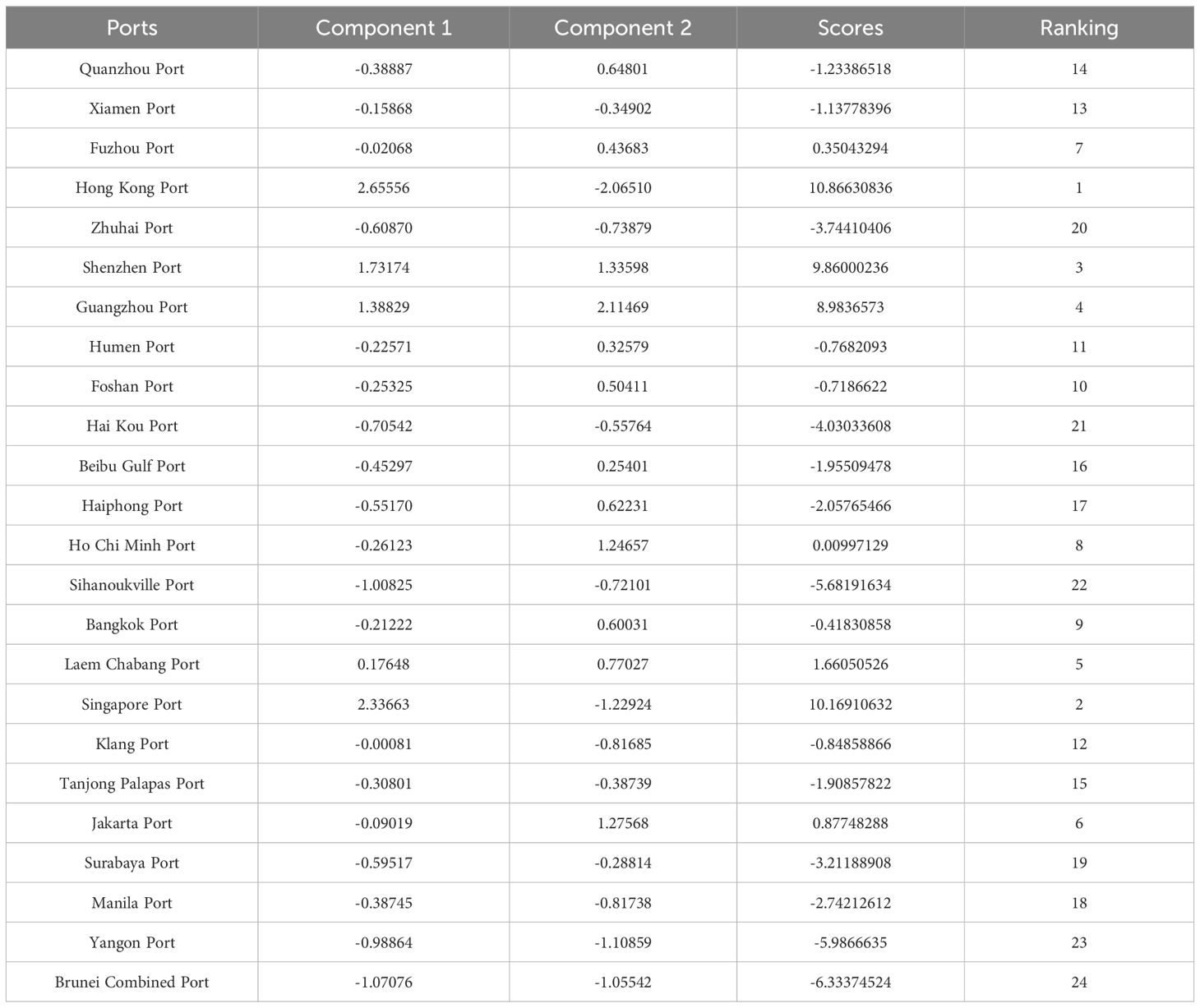
The PCA is conducted to evaluate the major ports spanning from the southern coastal regions of China to the ASEAN countries. As illustrated in Table 6, Hong Kong Port secured the highest ranking with a score of 10.86. Singapore Port closely followed in the second position with a score of 10.16. Shenzhen Port and Guangzhou Port were ranked third and fourth, respectively, with scores of 9.86 and 8.98. Notably, the top four ports identified by the PCA analysis correspond with the first-tier ports that were determined through the training of the SOM neural network, as detailed in Section 3.
For the second-tier ports, namely Laem Chabang Port, Jakarta Port, Bangkok Port, and Ho Chi Minh Port as listed in Table 4, their PCA rankings are 5th, 6th, 9th, and 8th, respectively. Upon comparing the PCA results with those of the SOM neural network, a high degree of correlation is observed between the distribution of the ports across the four groups as identified by the SOM neural network and their PCA rankings. This concordance validates the robustness and reliability of the clustering results yielded by the SOM neural network method.
4.2 Conclusion
The previous content introduces a SOM neural network-based port function clustering. Through MATLAB training and calculation, 24 major ports from the South China Sea to ASEAN are successfully categorized into 4 clusters. The clustering results are cross-validated with port rankings obtained through PCA method. Based on the SOM neural network and PCA performed in this study, three noteworthy outcomes have emerged:
1. Guangdong Province in China serves as a core logistics node within the 21st-MSR. The clustering analysis conducted using the SOM neural network indicates that Singapore Port, Hong Kong Port, Shenzhen Port, and Guangzhou Port are categorized as first-tier ports along the South China Sea to ASEAN route. Among these, Shenzhen Port and Guangzhou Port, located in Guangdong Province, stand out as the largest container ports in southern China. Guangdong Province’s GDP reached 13.57 trillion yuan in 2023, a figure that exceeds the GDP of some developed countries, including Australia and the Netherlands. Among other ports in Guangdong Province, Humen Port has established an extensive network of international container liner routes, connecting to major ports across 30 countries and regions worldwide. These strategic developments have significantly bolstered Guangdong’s connectivity with nations along the BRI.
2. China’s extensive transportation infrastructure plays a pivotal role in the development of the 21st-MSR. In the context of port clustering, the vast majority—three quarters—of first-tier ports are located in China, including Hong Kong Port, Guangzhou Port, and Shenzhen Port. Each of these ports is projected to handle over 20 million TEUs of container traffic in 2023. In the second and third tiers of ports, Chinese ports make up half of the total, including Quanzhou Port, Fuzhou Port, Humen Port, and Foshan Port. In port rankings, three out of the top four ports with the highest scores are also Chinese, offering an efficient logistics channel that serves the Chinese government’s strategic interests within the 21st-MSR.
3. China-Singapore cooperation is of paramount importance to the sustainable development of the BRI. Both Singapore and Hong Kong ports are strategically positioned as maritime hubs along the 21st-MSR. These ports have long been at the forefront of Asia’s maritime industry, leading in areas such as shipping trade, shipping insurance, and shipping finance. Singapore is strategically located at the heart of Southeast Asia, guarding the vital maritime passage connecting the Pacific and Indian Oceans—the Strait of Malacca. This strategic position makes Singapore one of the world’s busiest maritime transportation hubs and attracts a multitude of shipping companies to establish their presence there. Singapore and China exhibit strong industrial complementarity. Singapore excels in finance, technology, and services, while China boasts strengths in manufacturing and infrastructure. Through the 21st-MSR, both countries aim to enhance industrial collaboration, leverage their respective strengths, and jointly foster regional economic growth.
5 Policy implications and future works
5.1 Policy implications
Given the pivotal role of ports along the 21st-MSR in the sustainable development of the BRI, this study introduces a port clustering approach that utilizes a SOM neural network. This method was applied to train a dataset of 24 major ports spanning from the South China Sea to ASEAN countries. The resulting clusters were then validated against port rankings obtained through Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Drawing from these comprehensive analyses, the paper presents three substantive recommendations:
1. Promoting the construction of ports in Fujian Province is essential. As the inception point of the 21st-MSR, Fujian Province plays a vital role in the sustainable development of the BRI. However, the findings of this study indicate a significant disparity between Fujian Province’s current status and its optimal positioning within the BRI. The ports of Quanzhou, Xiamen, and Fuzhou all fall within the lower-middle range in terms of clustering and ranking scores. Moreover, when considering shipping potential, the aggregate GDP of the cities of Xiamen, Fuzhou, and Quanzhou is surpassed by that of Guangzhou alone.
2. The acceleration of the Hainan Free Trade Port’s construction is of strategic importance. Positioned at the crossroads of Asia and the Pacific Ocean, and midway between Japan and Singapore, Hainan Island serves as a maritime nexus connecting the Pacific and Indian Oceans. With a coastline stretching 1944.35 kilometers, Hainan Island possesses distinct advantages along the trade route corridor between China and ASEAN. However, despite its strategic location, Hainan Island’s container throughput reached only 1.445 million TEU in 2023, placing it in the fourth tier of port clustering.
3. Improving the shipping structure of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area is crucial. As one of China’s most open and economically dynamic regions, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area occupies a significant strategic position within the BRI. Notably, Hong Kong Port, Shenzhen Port, and Guangzhou Port are classified as first-level ports in this region, while other ports are ranked as third or fourth-level. The lack of second-level ports indicates a generational gap. The uneven development of ports in this region has substantially impeded the progress of the 21st-MSR.
5.2 Future work
Compared to traditional clustering methodologies, the SOM neural network-based port clustering approach demonstrates potential for managing large datasets in the forthcoming era of big data, attributed to its non-linear learning system. Nonetheless, there are limitations that require further investigation. For instance, to validate the new method against classical approaches, this study employs traditional indicators and datasets. The efficacy of the SOM neural network in clustering large samples merits deeper exploration.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
FX: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LZ: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AX: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LX: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by Talent Introduction Scientific Research Startup Project of Guangzhou Railway Polytechnic GTXYR2309, and in part by the Tertiary Education Scientific research project of Guangzhou Municipal Education Bureau 2024312460.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ardine V., Revindo M. D., Rezki J. F., Dewi C. E. (2023). The impact of logistic performance on intra-asean trade. Jurnal Ekonomi Studi Pembangunan 24, 32–53. doi: 10.18196/jesp.v24i1.16546
Bai X., Ma Z., Hou Y., Li Y., Yang D. (2023). A data-driven iterative multi-attribute clustering algorithm and its application in port congestion estimation. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transportation Syst. 24, 12026–12037. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3286477
Chen F., Cui Z., Wu J., Jiang Y., Cai F. (2024). Protection pattern and driving mechanism of typical marine ecosystems: a case study of China-asean countries. Front. Mar. Sci. 11, 1378188. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1378188
de Souza A. A., de Almeida D. C., Barcelos T. S., Bortoletto R. C., Munoz R., Waldman H., et al. (2023a). Simple hemogram to support the decision-making of covid-19 diagnosis using clusters analysis with self-organizing maps neural network. Soft Computing 27, 3295–3306. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-05810-5
Guo D., Gao D., Chen Z., Li Y., Zhao X., Song W., et al. (2023). Classification of inbound and outbound ships using convolutional neural networks. Front. Mar. Sci. 10, 1151817. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1151817
Kalahasthi L., Holguín-Veras J., Yushimito W. F. (2022). A freight origin-destination synthesis model with mode choice. Transportation Res. Part E: Logistics Transportation Rev. 157, 102595. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2021.102595
Kaliszewski A., Kozłowski A., Dabrowski J., Klimek H. (2020). Key factors of container port competitiveness: A global shipping lines perspective. Mar. Policy 117, 103896. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.103896
Ke R., Wang C. (2017). Comparative analysis of the shipping center competitiveness of major port cities in China. Transportation J. 56, 35–53. doi: 10.5325/transportationj.56.1.0035
Li K. X., Lin K.-C., Jin M., Yuen K. F., Yang Z., Xiao Y. (2020). Impact of the belt and road initiative on commercial maritime power. Transportation Res. Part A: Policy Pract. 135, 160–167. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2020.02.023
Licen S., Astel A., Tsakovski S. (2023). Self-organizing map algorithm for assessing spatial and temporal patterns of pollutants in environmental compartments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 878, 163084. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163084
Lin W., Liu W. (2023). Resilience evaluation of ports along the maritime silk road from the perspective of investment and construction. J. Advanced Transportation 2023, 8818667. doi: 10.1155/2023/8818667
Liu J., Guangsheng W., Xuejun F., Tong Y., Zhiyi L. (2024). Study on cascading failure vulnerability of the 21st-century maritime silk road container shipping network. J. Transport Geogr. 117, 103891. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2024.103891
Mohd Rozar N., Sidik M. H., Razik M. A., Ahmad Kamaruddin S., Rozar M. K. A. M., Usman I., et al. (2023). A hierarchical cluster analysis of port performance in Malaysia. Maritime Business Rev. 8, 194–208. doi: 10.1108/MABR-07-2020-0040
Nguyen P. N., Woo S.-H., Beresford A., Pettit S. (2020). Competition, market concentration, and relative efficiency of major container ports in Southeast Asia. J. Transport Geogr. 83, 102653. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2020.102653
Nie A., Wan Z., Shi Z., Wang Z. (2023). Cost-benefit analysis of ballast water treatment for three major port clusters in China: evaluation of different scenario strategies. Front. Mar. Sci. 10, 1174550. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1174550
Notteboom T., Haralambides H. (2023). Seaports as green hydrogen hubs: advances, opportunities and challenges in Europe. Maritime Economics Logistics 25, 1–27. doi: 10.1057/s41278-023-00253-1
Ogara D. A., Morishita J., Davies P. J., Mbui M., Gamoyo M., Njoroge N., et al. (2023). An indicator-based approach to assess sustainability of port-cities and marine management in the global south. Front. Mar. Sci. 10, 1052128. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1052128
Peng Y., Du D., Zhang X., Wang X. (2024). Potential effects of polar silk road on the global foreland evolution of China’s coastal container ports. Front. Mar. Sci. 11, 1436552. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1436552
Rabelo M. C., Tonini M., Silvestri N. (2023). Dynamics of agricultural land systems in western mediterranean areas: a clustering approach based on the self-organizing map. Ital. J. Agron. 18, 2199. doi: 10.4081/ija.2023.2199
Rahmani S., Baghbani A., Bouguila N., Patterson Z. (2023). Graph neural networks for intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transportation Syst. 24, 8846–8885. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3257759
Saeed N., Cullinane K. (2023). Identifying the characteristics of China’s maritime trading partners on the basis of bilateral shipping connectivity: A cluster analysis. Maritime Policy Manage. 50, 42–57. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2021.1954256
Schumacher M., Huvenne V. A., Devey C. W., Arbizu P. M., Biastoch A., Meinecke S. (2022). The atlantic ocean landscape: A basin-wide cluster analysis of the atlantic near seafloor environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 9, 936095. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.936095
Shahid N. (2023). Comparison of hierarchical clustering and neural network clustering: an analysis on precision dominance. Sci. Rep. 13, 5661. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32790-3
Song A. Y., Fabinyi M. (2022). China’s 21st century maritime silk road: Challenges and opportunities to coastal livelihoods in asean countries. Mar. Policy 136, 104923. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104923
Souza F., Yang D., Moreira A., Barreto L., Pitombo C. (2023b). Assessment of container terminals competitiveness in the Brazilian market: a cluster analysis. Maritime Policy Manage. 50, 1147–1165. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2022.2093417
Sugimura Y., Akakura Y., Yotsushima T., Kawasaki T. (2023). Evaluation of Japanese port policies through network analysis. Transport Policy 135, 59–70. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2023.03.011
Tang K., Li Z., Li W., Chen L. (2017). China’s silk road and global health. Lancet 390, 2595–2601. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32898-2
Wang C., Haralambides H., Zhang L. (2021). Sustainable port development: The role of Chinese seaports in the 21st century maritime silk road. Int. J. Shipping Transport Logistics 13, 205–232. doi: 10.1504/IJSTL.2021.112924
Wang L., Yan Z., Yan H., Liu J., Liu J., Wang Y. (2023). “Load aggregation method for electric vehicle based on som neural network clustering,” in 2023 IEEE/IAS Industrial and Commercial Power System Asia (I&CPS Asia) (Chongqing, China: IEEE), 908–912. doi: 10.1109/ICPSAsia58343.2023.10294770
Xu L., Huang J., Chen J. (2023). How does the initiative of 21st century maritime silk road incentive logistics development in China’s coastal region? Ocean Coast. Manage. 239, 106606. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2023.106606
Xu L., Shen C., Chen J. (2024a). The impact of the maritime silk road initiative on the carbon intensity of the participating countries. Marit. Econ. Logist. 26, 1–19. doi: 10.1057/s41278-024-00295-z
Xu L., Shen C., Chen J., Pan X., Xiao G. (2024b). Efficiency evaluation and improvement pathway of sulfur-oxide emissions in European ports based on context-dependent sbm-dea model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 208, 117002. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117002
Xu L., Wu J., Zhao Q., Chen J., Liu J., Gao F., et al. (2024c). Spatial-temporal characteristics of port infrastructures on sulfur-oxide concentrations of coastal port in China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 258, 107399. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2024.107399
Xu W., Zhang L., Wang H. (2024d). Machine learning–based feature prediction of convergence zones in ocean front environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 11, 1337234. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1337234
Zhang H., Jiang B., Cheng C., Huang B., Zhang H., Chen R., et al. (2023a). A self-rectifying synaptic memristor array with ultrahigh weight potentiation linearity for a self-organizing-map neural network. Nano Lett. 23, 3107–3115. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c03624
Zhang L., Khalgui M., Li Z., Zhang Y. (2022). Fairness concern-based coordinated vehicle route guidance using an asymmetrical congestion game. IET Intelligent Transport Syst. 16, 1236–1248. doi: 10.1049/itr2.12205
Zhang L., Khalgui M., Li Z., Zheng S., Zhang Y. (2023b). A unified model for the fairness mechanism-based coordinated vehicle route guidance. IET Intelligent Transport Syst. 17, 2369–2380. doi: 10.1049/itr2.v17.12
Zhang X., Lu J., Peng Y. (2023c). Spatio-temporal evolution of the container port system along the 21st-century maritime silk road. Maritime Policy Manage. 50, 668–691. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2021.2017038
Keywords: 21st-century Maritime Silk Road, SOM neural network, port function analysis, principal component analysis, South China Sea to the ASEAN
Citation: Xie F, Zhang L, Zheng S, Xu A, Li Z, Dai J and Xu L (2025) SOM neural network-based port function analysis: a case study in 21st-century Maritime Silk Road. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1522071. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1522071
Received: 03 November 2024; Accepted: 19 December 2024;
Published: 15 January 2025.
Edited by:
Tsz Leung Yip, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Yusheng Zhou, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaLiangshi Zhao, Liaoning Normal University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Zhang, Zheng, Xu, Li, Dai and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Le Zhang, bGUuemhhbmcuY2hpbmVzZUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Fahao Xie1†
Fahao Xie1† Le Zhang
Le Zhang Lang Xu
Lang Xu