Abstract
The Yangtze River Delta has experienced intricate sedimentary and environmental changes throughout the Holocene, driven by the interplay of fluvial and marine forcings. This study presents quartz optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) ages and luminescence sensitivity data from a Holocene sediment core MQ, analyzed across four grain-size fractions, ranging from silt to sand. The results reveal substantial variability in OSL ages and sensitivity among grain sizes, with the medium-grain (45–63 μm) fraction yielding the most consistent and reliable results. In contrast, finer and coarser grains tend to overestimate ages due to incomplete bleaching, with the accurate dating of coarser grains requiring more aliquots or single-grain measurements. The variability in luminescence sensitivity reflects changes in sediment provenance and depositional conditions between estuarine and deltaic environments. OSL ages indicate that the sedimentary evolution of the Yangtze River Delta progressed through distinct phases: rapid accumulation during the early Holocene (10–7 ka) driven by rising sea level and valley infilling; reduced sedimentation during the middle Holocene (7–3 ka) related to a dry climate in the catchment; and accelerated deposition in the late Holocene (3 ka–present) associated with enhanced fluvial input linked to intensified human activities. This study highlights the importance of selecting suitable appropriate grain sizes and carefully comparing different fractions in OSL analysis to reconstruct deltaic chronologies accurately. The finding that the medium-grain fraction yields more reliable OSL ages than finer and coarser fractions should be tested in similar settings elsewhere. The results provide valuable insights for future research on complex depositional environments and contribute to a better understanding of long-term environmental changes.
1 Introduction
As one of the most densely populated and economically dynamic regions in the world, the Yangtze River Delta faces growing ecological and socio-economic challenges driven by sea-level rise and increased human activity linked to global warming (Wang et al., 2018; Nian et al., 2022). Investigating the Holocene evolution of the delta and its governing mechanisms is critical to understanding global climate change and offers practical insights for developing sustainable strategies for coastal management (Stanley and Warne, 1994; Syvitski et al., 2009).
During the Last Glacial Maximum, sea level was ~130 m (Spratt and Lisiecki, 2016) lower than present, resulting in the formation of incised paleo-valleys across the Yangtze River Delta due to intense erosion (Li et al., 2000). As sea level gradually rose during the post-glacial period, the entrance of the Yangtze River estuary shifted inland, reaching as far as the Zhenjiang and Yangzhou regions around 8 ka ago (Yan and Xu, 1987; Song et al., 2013) (Figure 1). With the subsequent deceleration of sea-level rise and continuous sediment accumulation, sedimentation rates began to surpass sea-level rise, driving coastal progradation. The infilling of incised valleys resulted in the formation of Holocene deposits up to ~80 m thick (Delta Research Group, 1978; Wang et al., 1981; Li et al., 2000). These deposits provide a high-resolution archive essential for reconstructing paleoclimate variability and land-sea interactions over the Holocene.
Figure 1

Map showing the location of MQ core in the Yangtze River, along with referenced cores from this study, including JD01 (Li et al., 2009), TZ and NT (Nian et al., 2018a), HQ98 (Hori et al., 2001), HM (Nian et al., 2021), CM01, CM02 and HSD (Chen et al., 2021; Nian et al., 2022). The dashed line represents coastline shifts of the Yangtze River delta over the last 7 ka (Delta Research Group, 1978; Wang et al., 1981; Hori et al., 2001; Song et al., 2013).
Understanding sedimentary processes and establishing precise depositional chronologies are fundamental to reconstructing the environmental evolution of coastal and deltaic systems (Li and Wang, 1998). Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) dating has become a critical technique for reconstructing sedimentary histories (Aitken, 1998), particularly in areas where radiocarbon dating is hindered by the absence of organic material or by age inversions caused by complex sedimentary processes (Stanley and Chen, 2000; Marwick et al., 2015).
OSL dating measures the time since quartz or feldspar grains were last exposed to sunlight and covers a broad temporal range, from less than 100 years to several hundred thousand years (Aitken, 1998). As advancements in OSL technology continue, it has become a preferred tool for dating sediments in estuarine and deltaic environments (Jacobs, 2008; Lamothe, 2016; Nian and Zhang, 2018). However, the accuracy of OSL dating can be affected by partial bleaching, where sediment grains are insufficiently exposed to sunlight before burial, a challenge especially relevant to young Holocene sediments (Murray and Olley, 2002; Wallinga, 2002). To address these challenges, researchers increasingly use different grain size comparisons and integrate OSL with other independent dating methods. This approach has been successfully applied in complex deltaic systems such as the Mississippi (Shen and Mauz, 2012; Shen et al., 2015), Mekong (Sanderson et al., 2003; Yuji et al., 2020), and Yangtze River (Nian and Zhang, 2018; Nian et al., 2021, 2024; Gao et al., 2022), where sedimentary reworking often complicates age estimations.
The grain size composition of deltaic sediments varies significantly across temporal and spatial scales (Chen et al., 1988), which influences OSL ages due to differences in exposure history and transport pathways. Factors such as sediment provenance, transport mechanisms (e.g., suspended load vs. bedload), transport distance, and erosion or reworking processes play a role in resetting the OSL signal (Fuchs and Lang, 2009; Rhodes, 2011; Nian et al., 2021). Therefore, selecting the appropriate grain size for analysis is critical to obtaining accurate and reliable OSL ages.
In the Yangtze River Delta, the effectiveness of OSL dating is often constrained by the low luminescence sensitivity and poor luminescence efficiency of quartz minerals (Nian et al., 2018b, 2019), complicating age determination. To address these limitations, Wang et al. (2022) demonstrated the robustness of the standardised growth curve (SGC) approach, based on the single-aliquot regenerative (SAR) protocol, to enhance the efficiency of OSL dating in the region.
In this study, the least squares normalization of the SGC (LS-SGC) technique (Li et al., 2016; Fu et al., 2020) is applied to core MQ, situated at the southern margin of the Huangqiao sand body (Figure 1). This approach is employed to construct a Holocene chronological framework by analyzing four different quartz grain-size fractions: 4–11 μm, 45–63 μm, 63–90 μm, and 90–125 μm. We assess the consistency and discrepancies among age estimates for these different grain sizes and analyze the factors influencing these variations. Building on previous research and the luminescence sensitivity of quartz, this study aims to shed light on the Holocene formation processes and chronological evolution of river-mouth sand bar deposits within the Yangtze River Delta. This study not only provides new insights into the chronological development of the sand body and sedimentary processes but also contributes to a better understanding of the complex interactions between fluvial and marine forcings in the Yangtze River Delta. The methodology developed here can be transferred to deltaic systems with similarly complex sedimentary processes worldwide.
2 Study area and samples
The modern Yangtze River Delta has evolved since the last glacial maximum through the dynamic interaction of fluvial discharge, tidal forces, and changing sea level (Li and Wang, 1998). The sedimentary and geomorphic evolution of the Yangtze Delta can be categorized into six distinct stages throughout the Holocene (Delta Research Group, 1978): the Hongqiao Stage (6.0–5.5 ka, revised from 7.5–6.0 ka by Song et al., 2013), the Huangqiao Stage (6.5–4.0 ka), the Jinsha Stage (4.5–2.0 ka), the Haimen Stage (2.5–1.2 ka), the Chongming Stage (1.7–0.2 ka), and the Changxing Stage (0.7 ka to the present). These stages illustrate the framework that has shaped the evolution of the Yangtze River Delta (Wang et al., 1981; Li et al., 2000; Hori et al., 2001; Song et al., 2013) (Figure 1).
This study focuses on core MQ, located in Maqiao Town, Jingjiang City, Jiangsu Province, at the southern edge of the Huangqiao sand body (32°2.0667’N, 120°12.88’E) (Figure 1). Core MQ extends to a depth of 73.3 m with a recovery rate of 93%. Based on lithological characteristics, grain-size distributions and stratigraphic correlation with neighboring cores (Cheng et al., 2021), four distinct sedimentary units are identified within the core (Figure 2). The lowest unit, Unit 1 (tidal river facies, 73.3–52.3 m), is composed primarily of yellow-brown sand with occasional gravel, sporadically containing shell fragments, marking the coarsest deposits within the core. Unit 2 (estuarine facies, 52.3–32 m) consists of gray-yellow to bluish-gray silty sand to sand, with a gradual increase in silt content and a corresponding decrease in sand content upward. Unit 3 (shallow marine facies, 32–24.9 m) contains predominantly dark-green to dark-gray clayey silt, featuring numerous nodules and occasional brown mottling. The uppermost unit, Unit 4 (deltaic facies, 24.9–0 m), is composed of interbedded brownish-gray clayey silt and sandy silt, with increasing clay and silt content toward the surface. To construct a robust chronological framework and explore the sedimentary evolution of the sand body, seven OSL samples were collected from various depths within core MQ (Figure 2).
Figure 2
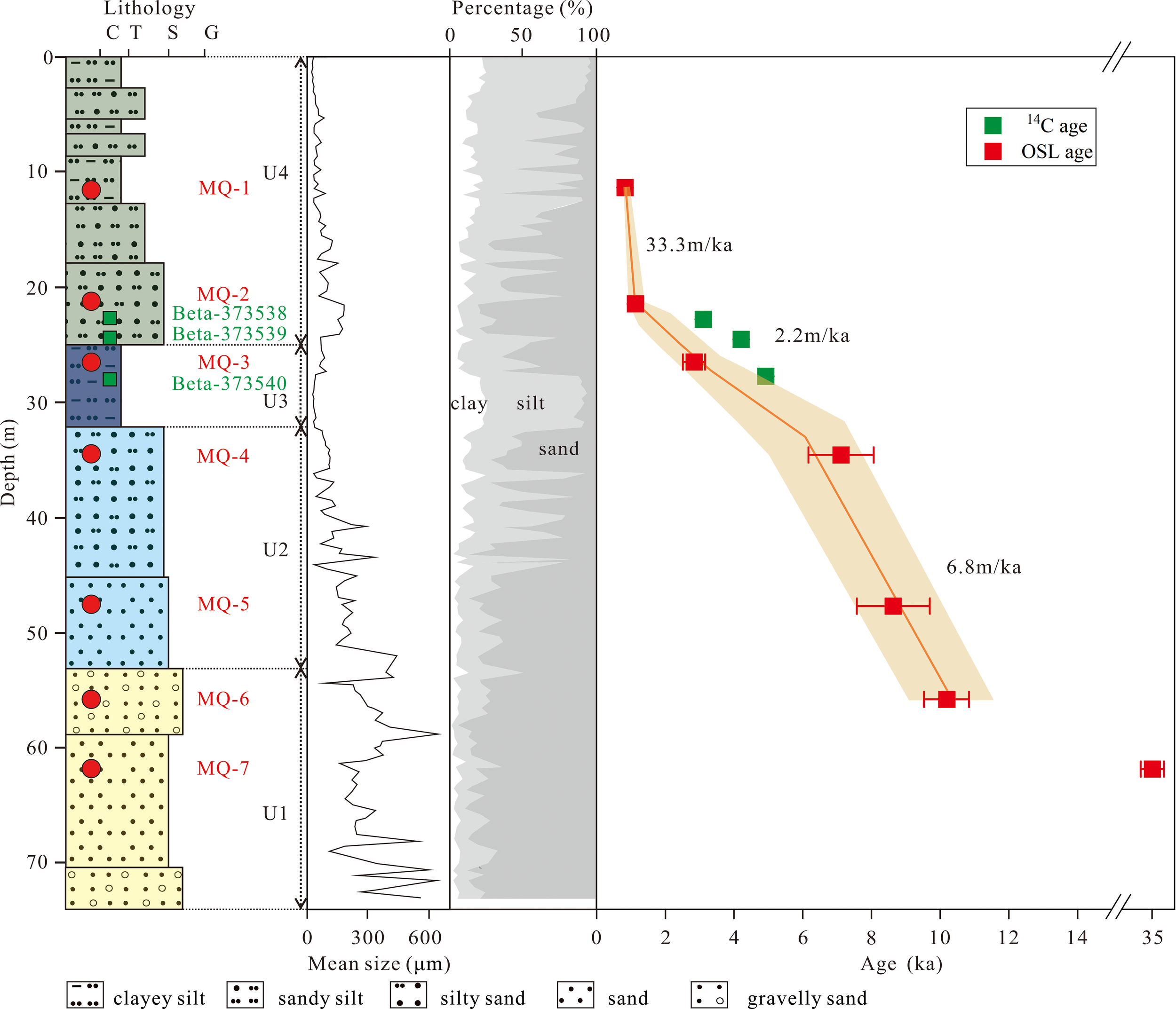
Lithological profile of core MQ, showing the positions of OSL samples (red dots) and 14C samples (green squares), along with mean grain size and grain-size composition throughout the core. The right panel shows the age-depth model for core MQ, based on the final OSL ages listed in Table 1. The “rbacon” model was used to generate the best-fit curve and its corresponding 95% confidence intervals.
3 Methods
3.1 Grain size analysis
Grain size data for the upper part (above 41 m) were sourced from Ji (2016), while data for the lower part were measured in this study. A total of 62 samples were measured at intervals of 25–60 cm. Grain size analysis was performed using a Coulter LS 13320 laser particle size analyzer, with a measurement range of 0.04–2000 μm. For each sample, 0.2 g of dry sediment was weighed and treated with 10% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to remove organic matter, followed by 10% dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to eliminate carbonates. The samples were then rinsed to a neutral pH, and 5% sodium hexametaphosphate ((NaPO3)6) was added as a dispersing agent. After 20 mins of ultrasonic treatment to ensure complete dispersion, the samples were analyzed.
3.2 Quartz OSL and luminescence measurements
OSL sample preparation and measurement were conducted under darkroom conditions. The unexposed inner part of each sample was used for quartz extraction, while the light-exposed portion was reserved for dose rate measurements. Standard pretreatment procedures were followed: 30% H2O2 was used to remove organic matter, and 10% HCl to eliminate carbonates, followed by rinsing with distilled water. Grain-size fractions of 4–11 μm (fine grain, FG) were separated using Stoke’s Law sedimentation in 0.01 M sodium oxalate solution, while the 45–63 μm (medium grain, MG), 63–90 μm (medium-coarse grain, MCG), and 90–125 μm (coarse grain, CG) fractions were obtained through wet sieving. Quartz grains were purified by etching the FG and MG fractions in 30% supersaturated fluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6) for 3–7 days, and the MCG and CG fractions were treated with 40% hydrofluoric acid (HF) for 40–60 mins. The coarser fractions (>45 μm) were mounted on stainless steel discs using silicon spray (2 mm small aliquots), while the FG fractions were dispersed in acetone and deposited onto aluminum discs. The purity of quartz separates was verified for each aliquot using the infrared depletion ratio (OSL-IR depletion) method (Duller, 2003).
The OSL measurements were conducted using a Risø TL/OSL-DA20 reader, and De values were determined through the LS-SGC procedure. Preheat and cut-heat temperatures were set at 200°C for 10 s and 160°C for 0 s, respectively, with OSL signals measured at 125°C for 40 s. The early-background subtraction method was applied by integrating the initial 0.4 s of OSL signals, with the subsequent 1 s average subtracted (Ballarini et al., 2007; Cunningham and Wallinga, 2010). Further procedural details, along with the parameters of the Risø reader, are provided in Wang et al. (2022).
In this study, aliquots were considered invalid if they met any of the following criteria: (1) an IR depletion ratio outside the range of 0.9–1.1, (2) a natural test dose signal less than three times the background, or (3) a maximum test dose error exceeding 20%. Aliquots passing these initial quality controls were then subjected to further screening, selecting those with De values within three standard deviations of the mean (Chamberlain et al., 2018). The final De values of the samples were derived from the aliquots that successfully passed the screening processes outlined above.
Neutron activation analysis (NAA) was used to determine the concentrations of U, Th, and K. Environmental dose rates for different grain-size fractions were calculated following the method outlined in Nian et al. (2021), with results presented in Supplementary Table S1. A water content of 30% with an uncertainty of ± 10% was applied for core MQ, based on average values from 112 OSL samples across 15 Holocene cores in the Yangtze River Delta (Supplementary Table S2).
The De values and OSL ages for the coarser fractions (>45 μm) of the OSL samples were calculated using both the central age model (CAM) and the minimum age model (MAM) (Galbraith et al., 1999). For the FG fractions, CAM was employed due to the averaging effect of fine grains. Based on previous OSL studies in the region, a well-bleached quartz sample typically exhibits an overdispersion (OD) of 10% (Nian et al., 2018b), so a sigma-b value of 10% was applied for MAM calculations in this study. Age model selection for coarser quartz fractions (CAM or MAM) followed the statistical procedure outlined by (Arnold et al., 2007). If OSL ages from different grain-size fractions were consistent, the weighted mean of these ages was used as the final age. The OSL dating results for core MQ are listed in Table 1.
Table 1
| Sample No. | Depth (m) | Grain size (μm) | a No. of aliquots | OD (%) | CAM De (Gy) | CAM age (ka) | MAM De (Gy) | MAM age (ka) | b Final age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQ-1 | 11. 24 | 4–11 | 12 | 0 | 2.79 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.06 | — | — | 0.83 ± 0.04 |
| 45–63 | 32 | 10 ± 2 | 2.72 ± 0.06 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | 2.72 ± 0.12 | 0.85 ± 0.07 | |||
| MQ-2 | 21. 24 | 4–11 | 12 | 8 ± 2 | 6.34 ± 0.17 | 2.62 ± 0.20 | — | — | 1.13 ± 0.09 |
| 45–63 | 34 | 21 ± 3 | 3.07 ± 0.12 | 1.37 ± 0.11 | 2.44 ± 0.17 | 1.09 ± 0.10 | |||
| 63–90 | 44 | 30 ± 4 | 3.72 ± 0.18 | 1.75 ± 0.15 | 3.22 ± 0.11 | 1.52 ± 0.12 | |||
| 90–125 | 41 | 41 ± 5 | 4.21 ± 0.28 | 2.00 ± 0.19 | 2.58 ± 0.31 | 1.23 ± 0.17 | |||
| MQ-3 | 26. 24 | 4–11 | 12 | 8 ± 2 | 10.67 ± 0.30 | 4.61 ± 0.36 | — | — | 2.84 ± 0.32 |
| 45–63 | 34 | 12 ± 2 | 6.32 ± 0.15 | 3.01 ± 0.21 | 6.32 ± 0.13 | 3.01 ± 0.21 | |||
| 63–90 | 34 | 16 ± 3 | 7.18 ± 0.23 | 3.65 ± 0.27 | 6.92 ± 0.44 | 3.52 ± 0.32 | |||
| 90–125 | 40 | 26 ± 4 | 6.69 ± 0.30 | 3.43 ± 0.27 | 4.96 ± 0.41 | 2.55 ± 0.27 | |||
| MQ-4 | 34. 23 | 45–63 | 32 | 61 ± 8 | 47.59 ± 5.22 | 22.43 ± 2.89 | 16.54 ± 1.67 | 7.79 ± 0.95 | 7.12 ± 0.95 |
| 63–90 | 30 | 59 ± 8 | 52.70 ± 5.82 | 26.32 ± 3.41 | 12.92 ± 1.69 | 6.45 ± 0.95 | |||
| 90–125 | 18 | 36 ± 7 | 88.19 ± 7.84 | 44.45 ± 4.96 | 56.57 ± 6.18 | 28.51 ± 3.66 | |||
| MQ-5 | 47. 24 | 4–11 | 13 | 16 ± 4 | 128.06 ± 6.11 | 53.29 ± 4.64 | — | — | 8.64 ± 1.06 |
| 45–63 | 31 | 56 ± 7 | 48.05 ± 4.93 | 21.82 ± 2.68 | 19.02 ± 1.96 | 8.64 ± 1.06 | |||
| 63–90 | 37 | 47 ± 6 | 65.94 ± 5.27 | 31.75 ± 3.33 | 27.41 ± 2.79 | 13.20 ± 1.61 | |||
| 90–125 | 49 | 40 ± 5 | 80.46 ± 4.87 | 39.10 ± 3.56 | 41.37 ± 3.36 | 20.10 ± 2.13 | |||
| MQ-6 | 55. 24 | 45–63 | 38 | 47 ± 6 | 56.52 ± 4.43 | 23.28 ± 2.40 | 23.92 ± 2.26 | 9.85 ± 1.14 | 10.19 ± 0.66 |
| 63–90 | 30 | 41 ± 6 | 84.63 ± 6.59 | 37.28 ± 3.83 | 42.89 ± 4.51 | 18.89 ± 2.36 | |||
| 90–125 | 40 | 56 ± 7 | 70.93 ± 6.50 | 31.54 ± 3.58 | 24.35 ± 3.14 | 10.83 ± 1.57 | |||
| MQ-7 | 61. 24 | 90–125 | 37 | 32 ± 4 | 101.39 ± 5.64 | 55.26 ± 4.93 | 64.52 ± 5.45 | 35.16 ± 3.85 | 35.16 ± 3.85 |
Summary of OSL dating data for quartz samples from core MQ.
The black bold values indicate the adopted data or final age.
The De values used in this study were obtained via the LS-SGC procedure and are cited from Wang et al. (2022).
The final ages are calculated as the weighted mean of the adopted ages from different grain-size fractions or, in cases where only one fraction was considered reliable, the age of that single fraction.
The protocol for OSL sensitivity measurements of single grains is outlined in Supplementary Table S3. For these measurements, quartz grains from the MG and MCG fractions were distributed on single-grain discs with 100 μm holes, while grains from the CG fraction were placed on single-grain discs with 150 μm holes.
4 Results
4.1 OSL ages
To verify the suitability of measurement conditions for determining the De values of quartz samples, a dose recovery experiment (Murray and Wintle, 2003) was performed on the 45–63 μm quartz fraction of sample MQ-5. The aliquots were bleached twice using blue LEDs for 100 s at room temperature, with an interval of at least 10,000 s between exposures. A known laboratory dose of 45.5 Gy was then administered, and De values were measured using the SAR protocol. The dose recovery ratio (recovered dose/given dose) was 1.03 ± 0.03 based on 19 aliquots, and the recycling ratios fell within the acceptable range of 0.9–1.1, with a recuperation rate below 2%. Typical OSL decay and growth curves for the sample are shown in Supplementary Figure S1, where the OSL signals are dominated by the fast component, which is consistent with previous studies in the region. These results confirm that the experimental conditions used in this study were suitable for determining the De of quartz samples from core MQ. A summary of the OSL dating results for the seven quartz samples is provided in Table 1, while Figure 3 illustrates the age distributions of different grain-size fractions across various depths.
Figure 3

(A) Age distributions for different grain-size fractions across depths in samples MQ-1 to MQ-7. (B) A magnified view of samples MQ-1 to MQ-3 from (A), providing a clearer visualization of the age distributions. Each density curve represents the age distribution for a specific grain-size fraction. Solid squares and circles indicate the CAM and MAM values, respectively. Different colors represent the results for each grain-size fraction.
Four of the seven samples were measured using the FG fractions. Except for sample MQ-1, the OD values of samples MQ-2, MQ-3, and MQ-5 were relatively high, ranging from 8 ± 2% to 16 ± 4% (Table 1). Given the expected averaging effect of fine grains, their OD values should be negligible, but the observed high values suggest partial bleaching and low luminescence efficiency of quartz in these samples. The OSL ages derived from these fine-grain fractions consistently exceeded the CAM or MAM ages obtained from coarser fractions within the same samples, suggesting that the fine-grain ages are likely overestimated and unreliable. In the subsequent age comparisons, we exclude the fine-grain OSL ages from consideration, except for MQ-1.
For the other three coarser fractions, the CAM and MAM ages of the MG fractions of sample MQ-1 and the MG and CG fractions of sample MQ-3 were consistent within error. In contrast, for the other samples, CAM ages exceeded MAM ages by factors ranging from 1.13 to 4.09, indicating partial bleaching in most samples. The De distributions for the four grain-size fractions of sample MQ-5 are shown as Abanico plots in Supplementary Figure S2.
4.2 Luminescence sensitivity of single-grain quartz
The OSL sensitivity of different grain-size fractions is presented in Figure 4, where approximately 1,500 single quartz grains per fraction per sample were analyzed after removing feldspar-contaminated grains. Sensitivity values range from 0 to 290 counts/Gy for a given dose of 20 Gy, with over 90% of quartz grains exhibiting sensitivities below 0.5 counts/Gy. Most grains show low luminescence sensitivity, with only a small fraction significantly contributing to the total signal, in line with previous findings.
Figure 4
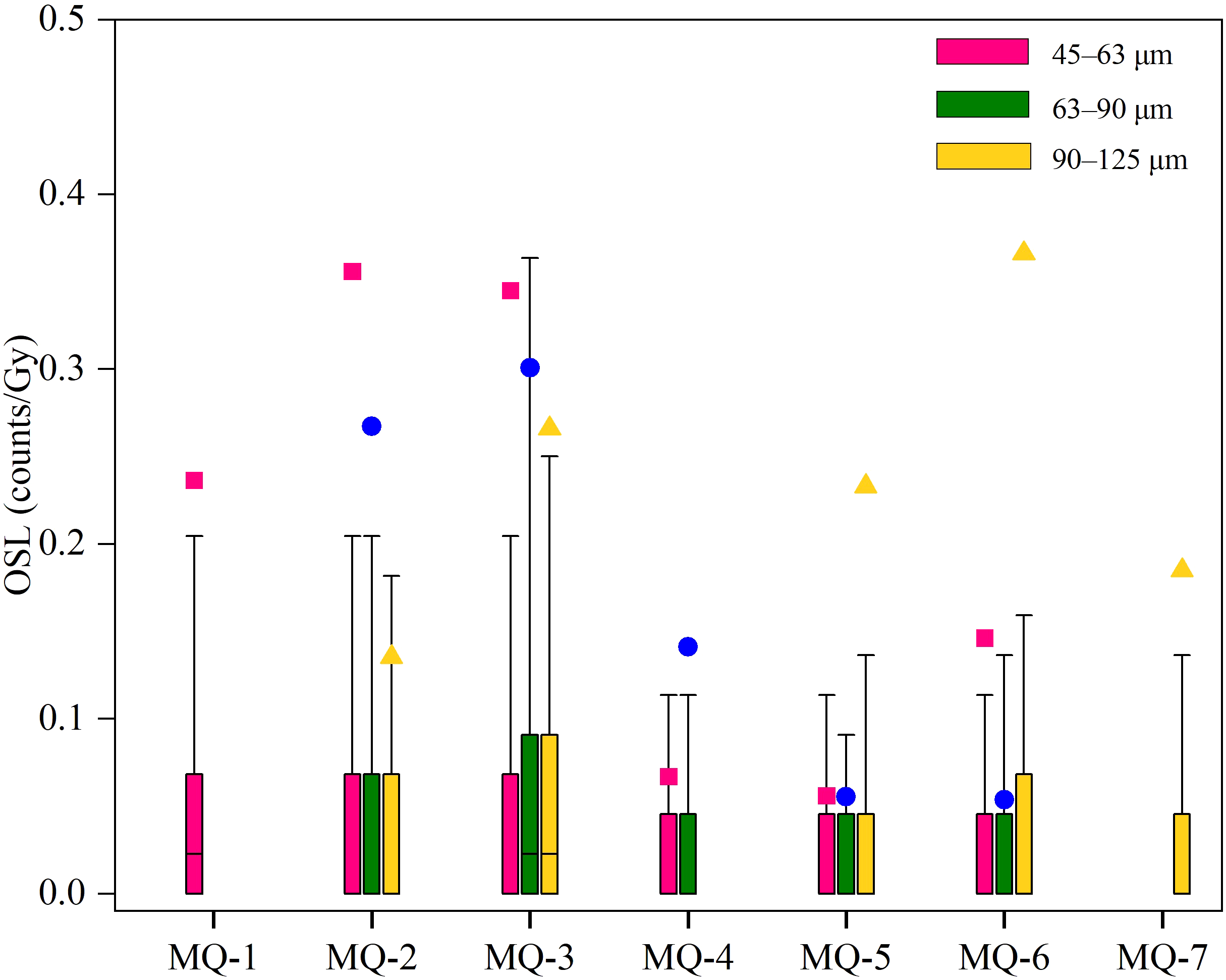
Box and whisker plots of the single-grain quartz OSL intensities for different grain-size fractions of seven samples (MQ-1 to MQ-7). The boxes represent the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentiles), while the whiskers extend to the 10th and 90th percentiles. Mean values for the MG (45–63 μm), MCG (63–90 μm) and CG (90–125 μm) fractions are indicated by solid squares, circles and triangles, respectively.
The data reveals distinct variations between samples. MQ-1, MQ-2, and MQ-3 (0.8–3 ka) display higher overall OSL intensities compared to MQ-4 through MQ-7 (7–10 ka and 35 ka), which exhibit lower and more uniform intensities across all grain-size fractions. The variation within grain-size fractions is most pronounced in MQ-3, where the spread of sensitivities is much broader than those in other samples. The period from 0.8–3 ka corresponds to a phase of marine regression, during which rivers played a dominant role in transporting sediment to the sea. In contrast, the period from 7–10 ka aligns with a phase of marine transgression, characterized by landward sediment transport. These patterns highlight a shift in sediment provenance associated with direction of sediment transport.
5 Discussion
5.1 A comparison of quartz OSL ages obtained from difference grain-size fractions
The ages of the FG and MG fractions in sample MQ-1 align closely. In samples MQ-2, MQ-3, and MQ-6, the adopted OSL ages of the MG and CG fractions agree with each other, while the MCG fractions show higher ages by 0.2–9 ka. In sample MQ-4, the adopted MG and MCG fractions produce similar ages within error, whereas the CG fraction is considerably older, at 28.5 ± 3.7 ka—approximately 20 ka older than the other fractions, representing an overestimation of nearly four times. This discrepancy, combined with the lower OD value for the CG fractions, likely stems from a small number of aliquots (n=18), making it difficult to effectively select fully bleached grains, leading to an overestimated age. For sample MQ-5, the adopted OSL age of the MG fractions is 8.6 ± 1.1 ka, while the MAM ages for the MCG and CG fractions are 13.2 ± 1.6 ka and 20.1 ± 2.1 ka (Table 1), respectively—both higher than the MG quartz age. Notably, the OD values for the coarser fractions are lower than those for the medium-grained quartz. The fine grains in this sample display the highest OD value among all the samples (~16%), indicating significant partial bleaching. In sample MQ-7, the MAM age for the CG fraction is 35.2 ± 3.9 ka.
The findings indicate that grain-size fractions significantly influence the reliability of OSL age estimates. While the MG fractions generally provide reliable ages, the FG, MCG and CG fractions tend to yield older ages, likely due to partial bleaching. This trend highlights the importance of cautious interpretation, especially when high OD values or a limited number of aliquots are present. Increasing the number of aliquots could reduce uncertainties related to incomplete bleaching and obtain more accurate MAM ages. Meanwhile, the underestimation of MG quartz ages were observed in the tidal sand bodies of the coastal zone in northern Jiangsu Province, China (Nian et al., 2022, 2024). This underestimation may be attributed to the lateral infiltration of grains into the sand body, influenced by the dynamic channel-ridge system on the continental shelf. Such dynamic process likely complicates the bleaching history of the grains, resulting in inaccurate age estimates. In light of these challenges, performing different grain-size analyses is essential for detecting and mitigating the effects of partial bleaching and understanding the impact of complex environmental dynamics, particularly in coastal and shelf environments where sediment transport processes are highly variable.
The final age of each sample was determined using the weighted average of the adopted ages from various grain-size fractions, or, when only a single grain-size fraction was available or considered reliable, its age was adopted directly (Table 1). The resulting ages for the seven samples, from the shallowest to the deepest, are 0.83 ± 0.04 ka, 1.13 ± 0.09 ka, 2.84 ± 0.32 ka, 7.12 ± 0.95 ka, 8.64 ± 1.06 ka, 10.19 ± 0.66 ka and 35.16 ± 3.85 ka.
5.2 Comparison of AMS 14C and OSL ages
AMS ¹4C dating was conducted by Ji (2016) on three shell samples from core MQ. In this study, we recalibrated these ages using Calib 8.2 (Stuiver et al., 2021) and the Marine20 calibration curve (Heaton et al., 2020). A regional marine radiocarbon reservoir effect (ΔR) of zero was assumed (Hori and Saito, 2017). To ensure consistency with the OSL ages, the AMS ¹4C ages were converted to ka relative to AD 2013 (Table 2).
Table 2
| Lab no. | Depth (m) | δ13C (‰) | Conventional age (a BP) | Calibrated age (a BP, 2σ) |
ka (relative to AD 2013) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-373538 | 22.57 | -9.7 | 3370 ± 30 | 2877–3212 | 3.11 ± 0.17 |
| Beta-373539 | 24.3 | -10.1 | 4230 ± 30 | 3960–4326 | 4.21 ± 0.18 |
| Beta-373540 | 27.47 | -9.6 | 4790 ± 30 | 4688–5037 | 4.93 ± 0.18 |
Radiocarbon dating results for shell samples of core MQ (Ji, 2016).
The recalibrated shell ages at depths of 22.57 m and 24.3 m are ~3.11 ka and ~4.21 ka, respectively. These ages are older than the OSL ages of the overlying sample MQ-2 at 21.24 m and the underlying sample MQ-3 at 26.24 m. This discrepancy may result from reworking, leading to an overestimation of the ¹4C ages. In contrast, the shell age at 27.47 m is ~4.93 ka, which falls between the OSL ages of the overlying MQ-3 and the underlying MQ-4. This alignment with the rbacon age-depth model suggests that this ¹4C age is reliable. The reliability of ¹4C ages appears to be highly influenced by the depositional environment of the sediments. For instance, consistent overestimation of ¹4C ages has been observed in cores YZ07, TZ, SD and HM (Gao et al., 2017; Nian et al., 2018a, b, 2021), while cores NT (Nian et al., 2018a) show good agreement between ¹4C and OSL ages.
5.3 OSL ages overestimation of different grain-size fractions
A 9.7 mm aliquot contains about one million FG grains, meaning the resulting data represent the average signal from all these grains. When partial bleaching occurs, accurately determining the depositional age becomes challenging, as identifying fully bleached grains within such a large population is nearly impossible. This challenge is particularly evident in samples MQ-2, MQ-3, and MQ-5, which exhibit a high degree of dispersion in their ages. The high OD values and significant partial bleaching observed in the 4–11 μm quartz fractions have also been reported in core HM from the Yangtze River Delta. This may be attributed to factors such as rapid sedimentation, high water turbidity, transport distances, and sediment reworking, all of which can influence the bleaching history of the grains during deposition.
The 2-mm small aliquot contains 892 MG, 444 MCG, and 225 CG grains, respectively (Burow, 2020). Previous study has shown that, a very small percentage (< 0.8%) of quartz grains meet the criteria for De determination in this region (Nian et al., 2018b). With this acceptance rate, fewer than 7, 4, and 2 grains from MG, MCG, and CG, respectively, are suitable for calculating De values. Therefore, using small aliquots could theoretically yield accurate age estimates, especially for coarser grains like MCG and CG, which usually have fewer “valid” grains. However, our results deviate from this expectation: MG provides more reliable age estimates, whereas MCG and CG tend to significantly overestimate ages, particularly in the case of MCG. This indicates that MG quartz is better bleached than MCG and CG quartz, consistent with observations from cores SD (Nian et al., 2018b) and HM (Nian et al., 2021).
The grain-size composition of modern Yangtze River sediments reveals that suspended sediments are dominated by silt and clay with minimal sand, while sediments on the river bed contain predominantly sand with lower silt content (Wang et al., 1997). Therefore, silt grains (MG), which are mainly transported in suspension, are generally more exposed to sunlight compared to sand grains that are predominantly carried as bedload. Consequently, silt is more likely to be thoroughly bleached, whereas sand grains are more susceptible to partial bleaching. Notably, when the OSL ages of sand grains are overestimated (even for MAM age), the corresponding FG ages also show overestimation, with high OD values. This may be attributed to high sediment concentrations in these environments, which can limit light penetration to coarse grains on the river bed. As a result, partial bleaching is a significant challenge for sand grains. To mitigate this, small-aliquot or single-grain OSL techniques can be applied to isolate well-bleached grains. However, finer sand fractions, such as MCG, may require a larger number of aliquots to ensure accurate results.
5.4 Sedimentary environment changes during the Holocene
The quartz luminescence sensitivity of sample MQ-7 (35 ka) and samples MQ-6 to MQ-4 (10–7 ka), derived from tidal river and estuary facies formed in the transgression stage, remained consistently low, except for the CG grains in MQ-6. This may suggest stable sediment sources with minimal variability in supply or transport processes during this period. In contrast, the samples MQ-3 to MQ-1 (3–0.8 ka), representing delta facies during regression stage, exhibited a marked increase in luminescence sensitivity, accompanied by considerable variability across depths. This shift can indicate changes in sediment provenance. The Yangtze River delta is a typical fluvial-tidal delta, with bi-directional sediment transport (Dalrymple and Choi, 2007). During the transgression stage, rising sea level favors flooding dominance and more proportions of sediments transported from the marine side. In contrast, during the regression stage with small sea-level fluctuations, fluvial discharge is dominant and sediment from the catchment has a higher proportion over the marine source.
An age-depth model, constructed using the final OSL ages from six upper Holocene samples, spans the core interval from 55 m to 11 m depth (Figure 2). This model reveals three distinct phases of sedimentation rates: an initial moderate rate of 7.0 m/ka from 10.2 to 7.1 ka, a subsequent reduced rate of 2.2 m/ka from 7.1 to 1.1 ka, and a sharp increase to 36 m/ka between 1.1 and 0.8 ka. After 0.8 ka, the coring site of MQ becomes aerial and receives no further deposition due to the continuing eastward shift of coastline.
The cores from river-mouth sand bars across the Yangtze River Delta from west to east (Figure 5) also reveal a three-phase pattern in sedimentation rates during the Holocene, following a fast-slow-fast trend. In the early Holocene (~10–7 ka), rapid sedimentation occurs as rising sea levels create accommodation space, promoting the infilling of incised valleys. After 8 ka, when maximum marine transgression occurs, delta begins to develop in the study area, and the coastline progradates eastward. During the mid-Holocene (~7–3 ka), sedimentation slowed as the rate of sea-level rise decreased, with drier climatic conditions in the catchment (Zhu et al., 2017) likely reducing soil erosion and limiting fluvial sediment delivery. In the late Holocene (~3 ka to present), sedimentation rates increased again, driven by possibly enhanced fluvial input due to intensified human activities (Wang et al., 2018). This three-stage pattern reflects the dynamic interplay between sea-level changes, sediment supply, and accommodation space, shaping the delta’s evolution from transgression in the early Holocene to later progradation during the mid-late Holocene.
Figure 5
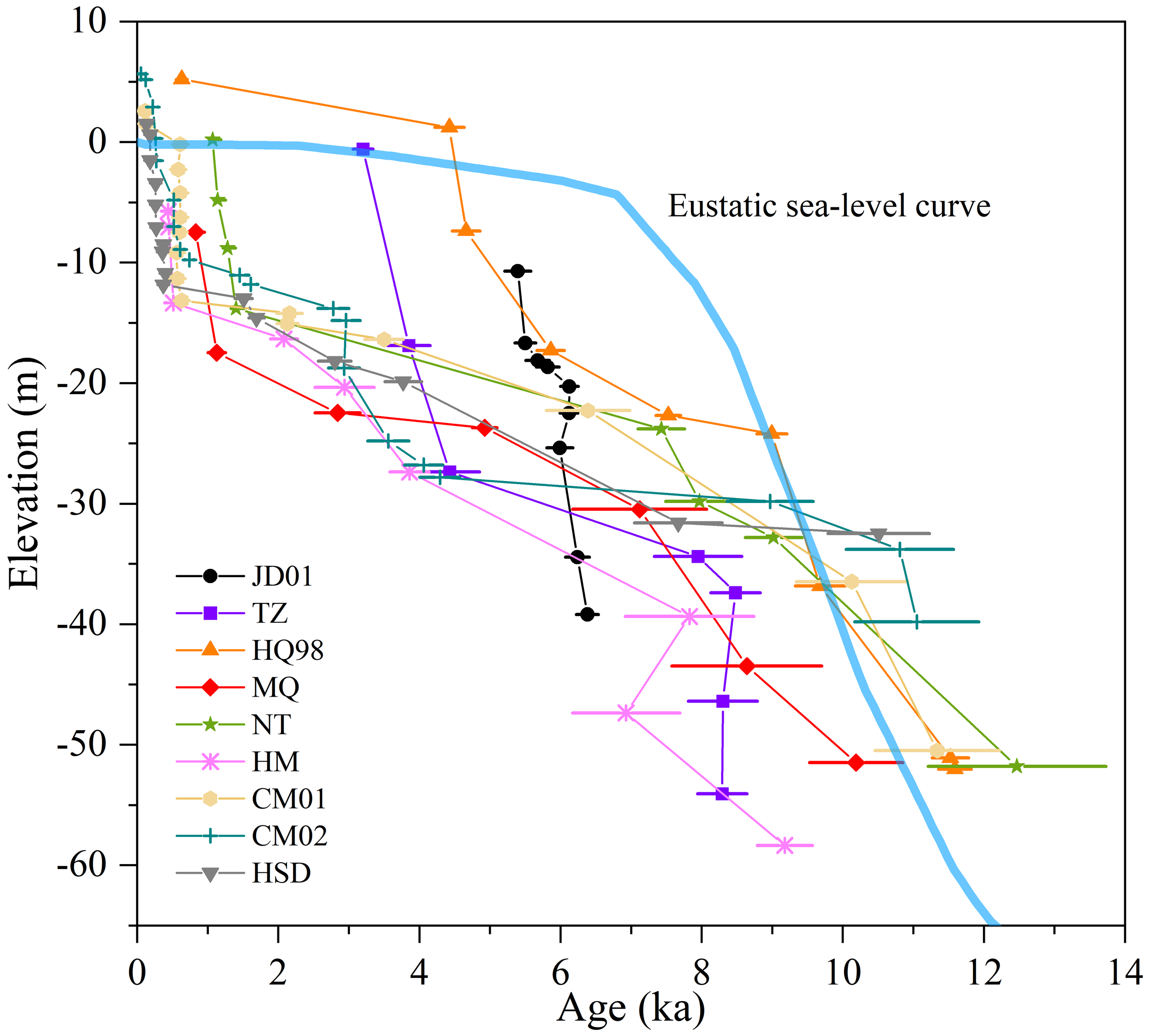
Age-elevation relationships of sedimentary cores from west to east across the Yangtze River Delta and eustatic sea-level curve (Lambeck et al., 2014). The locations of the cores are indicated in Figure 1. The OSL and AMS 14C ages are detailed in Supplementary Tables S4 and S5, respectively.
6 Conclusion
This study presents quartz OSL ages and luminescence sensitivity results from Holocene sediment core MQ in the Yangtze River Delta, using different grain-size fractions (4–11 μm, 45–63 μm, 63–90 μm, and 90–125 μm). The results reveal significant variability in OSL ages and sensitivity across grain sizes. The medium grain (45–63 μm) fraction provides the most consistent and reliable OSL ages, while finer and coarser grains tend to overestimate ages due to incomplete bleaching. Accurate dating of coarser grains with more severe bleaching issues requires a larger number of aliquots or single-grain measurements. The observation that the medium-grain fraction produces more reliable OSL ages compared to finer and coarser fractions warrants validation in other comparable settings.
The variability in luminescence sensitivity reflects changes in sediment provenance and depositional environments associated with transgression-regression cycle. The sedimentary evolution of the Yangtze River Delta follows three stages pattern. The early Holocene (10–7 ka) is marked by rapid sediment accumulation driven by rising sea levels. In the middle Holocene (7–3 ka), sedimentation rates decrease reflecting a dry climate in the catchment. During the late Holocene (3 ka–present), sedimentation accelerates again driven by possible intensified human activities.
This study emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate grain sizes and comparing different grain-size fractions for OSL analysis to accurately reconstruct deltaic chronologies. The findings provide practical guidance for future research on complex depositional environments and contribute to a better understanding of environmental changes in delta regions.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
XW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XN: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FQ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42171009 and 41771009) for this research.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Professors Manoj Kumar Jaiswal and Xiao Fu for their constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1512462/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Aitken M. J. (1998). An introduction to optical dating (New York: Oxford University Press).
2
Arnold L. J. Bailey R. M. Tucker G. E. (2007). Statistical treatment of fluvial dose distributions from southern Colorado arroyo deposits. Quat. Geochronol.2, 162–167. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.003
3
Ballarini M. Wallinga J. Wintle A. G. Bos A. J. J. (2007). A modified SAR protocol for optical dating of individual grains from young quartz samples. Radiat. Meas.42, 360–369. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.12.016
4
Burow C. (2020). “calc_AliquotSize(): Estimate the amount of grains on an aliquot. Function version 0.31, 2020,” in Luminescence: Comprehensive Luminescence Dating Data Analysis. R package version 0.9.7. Eds. KreutzerS.BurowC.DietzeM.FuchsM. C.SchmidtC.FischerM.FriedrichJ.. Available at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Luminescence (accessed October, 2024).
5
Chamberlain E. L. Törnqvist T. E. Shen Z. Mauz B. Wallinga J. (2018). Anatomy of Mississippi Delta growth and its implications for coastal restoration. Sci. Adv.4, eaar4740. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar4740
6
Chen J. Shen H. Yun C. (1988). Processes of Dynamics and Geomorphology of the Yangtze Estuary (Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers) (In Chinese).
7
Chen Y. Zhang W. Nian X. Sun Q. Ge C. Hutchinson S. M. et al . (2021). Greigite as an indicator for salinity and sedimentation rate change: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth.126, e2020JB021085. doi: 10.1029/2020JB021085
8
Cheng Y. Zou X. Li X. Zhao Z. Zhang X. Guo G. et al . (2021). Sedimentary characteristics and evolution process of the Huangqiao sand body in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci.254, 107330. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2021.107330
9
Cunningham A. C. Wallinga J. (2010). Selection of integration time intervals for quartz OSL decay curves. Quat. Geochronol.5, 657–666. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.08.004
10
Dalrymple R. W. Choi K. (2007). Morphologic and facies trends through the fluvial–marine transition in tide-dominated depositional systems: A schematic framework for environmental and sequence-stratigraphic interpretation. Earth Sci. Rev.81, 135–174. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.10.002
11
Delta Research Group, Department of Marine Geology, Tongji University (1978). Holocene formation and development of the Yangtze Delta. Chin. Sci. Bull.35, 310–313 (In Chinese).
12
Duller G. A. T. (2003). Distinguishing quartz and feldspar in single grain luminescence measurements. Radiat. Meas.37, 161–165. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(02)00170-1
13
Fu X. Li B. Jacobs Z. Jankowski N. R. Cohen T. J. Roberts R. G. (2020). Establishing standardised growth curves (SGCs) for OSL signals from individual grains of quartz: A continental-scale case study. Quat. Geochronol.60, 101107. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2020.101107
14
Fuchs M. Lang A. (2009). Luminescence dating of hillslope deposits-A review. Geomorphology109, 17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.08.025
15
Galbraith R. F. Roberts R. G. Laslett G. M. Yoshida H. Olley J. M. (1999). Optical dating of single and multiple grains of quartz from Jinmium rock shelter, northern Australia: Part I, experimental design and statistical models*. Archaeometry41, 339–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4754.1999.tb00987.x
16
Gao L. Long H. Hou Y. Feng Y. (2022). Chronology constraints on the complex sedimentary stratigraphy of the paleo-Yangtze incised valley in China. Quat. Sci. Rev.287, 107573. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107573
17
Gao L. Long H. Shen J. Yu G. Liao M. Yin Y. (2017). Optical dating of Holocene tidal deposits from the southwestern coast of the South Yellow Sea using different grain-size quartz fractions. J. Asian Earth Sci.135, 155–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.036
18
Heaton T. J. Köhler P. Butzin M. Bard E. Reimer R. W. Austin W. E. N. et al . (2020). Marine20-The marine radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55,000 cal BP). Radiocarbon62, 779–820. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2020.68
19
Hori K. Saito Y. (2017). Differences in radiocarbon ages among molluscan shells, plant materials, and total organic carbon: An example from the paleo-Changjiang incised-valley fill, China. Quat. Int.455, 45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.07.037
20
Hori K. Saito Y. Zhao Q. Cheng X. Wang P. Sato Y. et al . (2001). Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during the last transgression. Mar. Geol.177, 331–351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00165-7
21
Jacobs Z. (2008). Luminescence chronologies for coastal and marine sediments. Boreas37, 508–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2008.00054.x
22
Ji R. (2016). Magnetic properties of Holocene sediments in core MQ from the Yangzte river delta and its implications for sedimentary environment reconstruction (Jianghua: Zhejiang normal university) (In Chinese with English abstract).
23
Lambeck K. Rouby H. Purcell A. Sun Y. Sambridge M. (2014). Sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.111, 15296–15303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411762111
24
Lamothe M. (2016). Luminescence dating of interglacial coastal depositional systems: Recent developments and future avenues of research. Quat. Sci. Rev.146, 1–27. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.005
25
Li C. Chen Q. Zhang J. Yang S. Fan D. (2000). Stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental changes in the Yangtze Delta during the Late Quaternary. J. Asian Earth Sci.18, 453–469. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00078-4
26
Li B. Jacobs Z. Roberts R. G. (2016). Investigation of the applicability of standardised growth curves for OSL dating of quartz from Haua Fteah cave, Libya. Quat. Geochronol.35, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2016.05.001
27
Li Z. Song B. Saito Y. Li J. Li Z. Lu A. (2009). “Sedimentary facies and geochemical characteristics of Jiangdou core JD01 from the upper delta plain of Changjiang (Yangtze) delta,” in Amorosi A. Proceedings of the 27th IAS Meeting of Sedimentologists (Medimond, Bologna, Italy), 55–65.
28
Li C. Wang P. (1998). Late Quaternary Stratigraphy of the Yangtze Delta (Beijing: Science Press) (In Chinese).
29
Marwick T. R. Tamooh F. Teodoru C. R. Borges A. V. Darchambeau F. Bouillon S. (2015). The age of river-transported carbon: A global perspective. Global Biogeochem. Cy.29, 122–137. doi: 10.1002/2014GB004911
30
Murray A. S. Olley J. M. (2002). Precision and accuracy in the optically stimulated luminescence dating of sedimentary quartz: a status review. Geochronometria21, 1–16.
31
Murray A. S. Wintle A. G. (2003). The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: potential for improvements in reliability. Radiat. Meas.37, 377–381. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00053-2
32
Nian X. M. Zhang W. G. (2018). Application of optically stimulated luminescence dating to Late Quaternary coastal deposits in China. Quaternary. Sci.38, 573–586 (In Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.03.03
33
Nian X. Zhang W. Liu R. Qiu F. Seppä H. (2024). Underestimated single-aliquot quartz OSL ages of Late-Pleistocene sediments due to the dominance of medium component. Quat. Sci. Rev.332, 108656. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2024.108656
34
Nian X. Zhang W. Qiu F. Qin J. Wang Z. Sun Q. et al . (2019). Luminescence characteristics of quartz from Holocene delta deposits of the Yangtze River and their provenance implications. Quat. Geochronol.49, 131–137. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.04.010
35
Nian X. Zhang W. Wang X. Hutchinson S. M. Zhao X. Liu K.-b. (2022). Multi-centennial variability of yangtze delta growth over the last 2000 years: interplay of climate and people. Earth’s. Future10, e2021EF002461. doi: 10.1029/2021EF002461
36
Nian X. Zhang W. Wang Z. Sun Q. Chen Z. (2021). Inter-comparison of optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) ages between different fractions of Holocene deposits from the Yangtze delta and its environmental implications. Mar. Geol.432, 106401. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106401
37
Nian X. Zhang W. Wang Z. Sun Q. Chen J. Chen Z. (2018a). Optical dating of Holocene sediments from the Yangtze River (Changjiang) Delta, China. Quat. Int.467, 251–263. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.01.011
38
Nian X. Zhang W. Wang Z. Sun Q. Chen J. Chen Z. et al . (2018b). The chronology of a sediment core from incised valley of the Yangtze River delta: Comparative OSL and AMS 14C dating. Mar. Geol.395, 320–330. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.11.008
39
Rhodes E. J. (2011). Optically stimulated luminescence dating of sediments over the past 200,000 years. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci.39, 461–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040610-133425
40
Sanderson D. C. W. Bishop P. Stark M. T. Spencer J. Q. (2003). Luminescence dating of anthropogenically reset canal sediments from Angkor Borei, Mekong Delta, Cambodia. Quat. Sci. Rev.22, 1111–1121. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00055-6
41
Shen Z. Mauz B. (2012). Optical dating of young deltaic deposits on a decadal time scale. Quat. Geochronol.10, 110–116. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.01.014
42
Shen Z. Törnqvist T. E. Mauz B. Chamberlain E. L. Nijhuis A. G. Sandoval L. (2015). Episodic overbank deposition as a dominant mechanism of floodplain and delta-plain aggradation. Geology43, 875–878. doi: 10.1130/g36847.1
43
Song B. Li Z. Saito Y. Okuno J. Lu A. Hua D. et al . (2013). Initiation of the Changjiang (Yangtze) delta and its response to the mid-Holocene sea level change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl.388, 81–97. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.07.026
44
Spratt R. M. Lisiecki L. E. (2016). A Late Pleistocene sea level stack. Clim. Past.12, 1079–1092. doi: 10.5194/cp-12-1079-2016
45
Stanley D. J. Chen Z. (2000). Radiocarbon Dates in China’s Holocene Yangtze Delta: Record of sediment storage and reworking, not timing of deposition. J. Coast. Res.16, 1126–1132.
46
Stanley D. J. Warne A. G. (1994). Worldwide initiation of Holocene marine deltas by deceleration of sea-level rise. Science265, 228–231. doi: 10.1126/science.265.5169.228
47
Stuiver M. Reimer P. J. Reimer R. W. (2021). CALIB 8.2 [WWW program]. Available online at: http://calib.org (accessed October, 2024).
48
Syvitski J. P. M. Kettner A. J. Overeem I. Hutton E. W. H. Hannon M. T. Brakenridge G. R. et al . (2009). Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nat. Geosci.2, 681–686. doi: 10.1038/ngeo629
49
Wallinga J. (2002). Optically stimulated luminescence dating of fluvial deposits: a review. Boreas31, 303–322. doi: 10.1080/030094802320942536
50
Wang L. C. Chen X. L. Chu T. Q. (1997). A contrast analysis on the loads character of the Changjiang River and the Yellow River. Geogr. Res.16, 71–79.
51
Wang J. T. Guo X. M. Xu S. Y. Li P. Li C. X. (1981). Evolution of the holocene changjiang delta. Acta Geol. Sin.55, 67–81 (In Chinese with English abstract).
52
Wang X. Qiu F. Nian X. Liu R. Zhang W. (2022). Testing the applicability of standardised growth curves (SGCs) for OSL signals of quartz grains from the Yangtze Delta, China. Quat. Geochronol.72, 101348. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2022.101348
53
Wang Z. Saito Y. Zhan Q. Nian X. Pan D. Wang L. et al . (2018). Three-dimensional evolution of the Yangtze River mouth, China during the Holocene: impacts of sea level, climate and human activity. Earth Sci. Rev.185, 938–955. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.08.012
54
Yan Q. S. Xu S. Y. (1987). Recent Yangtze Delta Deposit (Shanghai: East China Normal University Press) (In Chinese).
55
Yuji I. Toru T. Daniel S. C. Bunnarin B. (2020). Applicability of OSL dating to fine-grained fluvial deposits in the Mekong River floodplain, Cambodia. Geochronometria. 48, 351–363. doi: 10.2478/geochr-2020-0006
56
Zhu Z. Feinberg J. Xie S. Bourne M. Huang C. Hu C. et al . (2017). Holocene ENSO-related cyclic storms recorded by magnetic minerals in speleothems of central China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 852–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610930114
Summary
Keywords
optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating, Yangtze River Delta, different grain-size fractions, partial bleaching, Holocene evolution
Citation
Wang X, Nian X, Zhang W and Qiu F (2024) Cross-checking OSL ages from different grain sizes to improve chronological reliability in deltaic environments: an example from the Yangtze River Delta. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1512462. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1512462
Received
16 October 2024
Accepted
03 December 2024
Published
16 December 2024
Volume
11 - 2024
Edited by
Juan Jose Munoz-Perez, University of Cádiz, Spain
Reviewed by
Manoj Kumar Jaiswal, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Kolkata, India
Xiao Fu, Zhejiang University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Wang, Nian, Zhang and Qiu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaomei Nian, xmnian@sklec.ecnu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.