- 1Institute of Marine Sustainable Development, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian, China
- 2University Collaborative Innovation Center of Marine Economy High-Quality Development of Liaoning Province, Dalian, China
Using social network analysis, spatial econometric method and structural equation model, based on the patent citation data of China’s marine industry from 2008 to 2019, this paper analyzes the temporal-spatial characteristics and influencing factors of knowledge spillover network of marine Industry in China. The results show that: the knowledge spillover network with Qingdao, Beijing and Shanghai as the main distribution centers has expanded rapidly, and the network status of Zhoushan, Wuhan and other cities has improved significantly. The network space structure tends to be multi-core and complex, extending from coast to inland; There are significant differences in cyberspace. The central and western regions are low value areas, while the eastern region is the core area, and the core cities have built an “X” shaped spatial structure with Qingdao as the intersection; Knowledge proximity, social proximity, cognitive proximity and economic proximity are important factors that affect knowledge spillover networks. Geographic proximity has a reinforcing effect on knowledge proximity and economic proximity. This paper is beneficial in that it provides a reference and experience for the innovation of the marine industry and the high-quality development of the marine economy by effectively analyzing the spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of China’s marine knowledge diffusion network.
1 Introduction
Amidst the resource and environmental pressures stemming from the swift advancement of the social economy, the ocean, which constitutes approximately 71% of the Earth, represents a “blue ocean” abundant in resources and possessing extensive development potential. The financial sector’s growing interconnection with the marine economy (Song et al., 2020; Su et al., 2021) has emerged as a pivotal factor in propelling future human economic progress. As a prominent maritime nation, China’s marine economy has emerged as a new focal point for economic growth; however, the economic efficiency of marine science and technology innovation remains inadequate (Wu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020), and the disjointed development of the marine economic ecosystem (Peng et al., 2018) has hindered the advancement of the marine industry. Within the framework of the new development model, establishing a marine innovation system and expediting the transition between traditional and emerging driving factors has become crucial for advancing the marine economy. Knowledge, learning, and invention are fundamentally interconnected (Rao and Li, 2006). Knowledge accumulation underpins innovation activities, while knowledge spillover among enterprises, universities, and research institutions fosters the creation of new knowledge and serves as an internal mechanism for advancing regional innovation development (Liu and Ge, 2018). The widespread use of new technologies in the Internet economy facilitates cross-regional knowledge transfer and information interchange, rendering knowledge spillover beyond R&D investment a significant method of knowledge acquisition.
Knowledge spillover denotes the phenomenon wherein the knowledge generated by one economic organization is employed by another, often without enough pay or at a value lower than its worth (Jaffe, 1996). Explicit knowledge embedded in products and documents, along with implicit knowledge inherent in individuals, may unconsciously transfer to other industries or areas (Tijssen, 2001). Knowledge spillover, being an intangible phenomenon, poses challenges for quantification using conventional data and measuring techniques (Braunerhjelm and Svensson, 2024). Griliches first developed a knowledge production function and depicted knowledge spillover using a knowledge stock adjusted by a distance function, establishing the groundwork for the quantitative analysis of knowledge spillover (Griliches, 1979). Knowledge spillover in Western new economics predominantly illustrates a process of spatial interaction (Li et al., 2013). Rodriguez-Pose, Crescenzi and Qiu (Rodriguze-pose and Crescenzi, 2008; Qiu et al., 2020) employed spatial weight matrices to examine the geographical confines of regional knowledge spillovers in Europe and China, respectively. Alongside geographical distance and concealed obstacles, including social, cognitive, and institutional barriers (Abramo et al., 2020), the examination of information spillover effects through network linkages has deepened significantly. Many empirical research rely on knowledge input or output data. The cross-regional impacts of knowledge spillovers, facilitated by varying proximity or network links, were assessed (Sheng and Lesage, 2021; Cortinovis and Van Oort, 2019; Ma et al., 2018). Conversely, Choi established a global knowledge spillover network utilizing trade and FDI data to investigate the influence of network structure on country innovation performance (Choi and Zo, 2022). Zhang utilized patent data to develop a technology connectedness index and matrix, examining the technology spillover network characteristics of Chinese innovation firms (Zhang et al., 2022). Li and Wang examined the attributes and determinants of knowledge spillover networks in China’s biopharmaceutical and knowledge-intensive sectors, utilizing data from scientific paper writing and patent citations (Li et al., 2013; Wang and Gu, 2021). These scholars have examined the avenues of knowledge spillover from a network approach.
Patent data, as an accessible and timely source of technical information, encompasses geospatial and citation data that facilitate the examination of the temporal and spatial attributes of knowledge spillover, thereby reflecting its characteristics and possessing distinct advantages (Wang and Gu, 2021). When a creative entity applies for a patent, it will reference analogous patents to demonstrate its distinction from prior patents, so illustrating the advancement of the patent. Such citations are prevalent in patent applications (Steensma et al., 2015), signifying that knowledge transfer has occurred. Knowledge sources can be identified by analyzing citation data in patent literature (Hussler, 2004; Maurseth and Verspagen, 2002). Despite the presence of noisy information, patent data can nevertheless indicate knowledge connections or future knowledge flows (Li, 2017). Granovetter contended that the network model’s focus on strong ties restricted its relevance to small, defined groups, asserting that weak ties might enhance the diversity of knowledge or information obtained within the creation of loose networks (Granovetter, 1973). Wang discovered that the significance of weak links in semiconductor manufacturers’ knowledge spillover networks, as measured by patent citation data, had been underestimated in the acquisition of external knowledge (Wang et al., 2017). The citation of information data partially represents the innovation of the original knowledge, therefore enabling these data to characterize the Marine innovation network (Li et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021). In recent years, evolutionary economic geographers have examined the accumulation effect of innovation space through the lens of multidimensional proximity theory, addressing the effects of cognitive proximity, socio-cultural proximity, organizational proximity, and social institutional proximity (Rigby, 2015; Martinez et al., 2024). illustrates the spatio-temporal variability of the knowledge spillover network.
Current research seldom addresses the knowledge spillover within the marine industry, and there is insufficient discourse regarding the primary sources, directions, and intensities of marine knowledge spillover, along with the spatio-temporal variations of the knowledge spillover network. Consequently, utilizing the notion of weak ties and proximity, we aim to delineate the attributes of the knowledge spillover network in the developmental trajectory of the marine industry through patent data pertaining to the sector. This paper employs patent citation data from China’s marine industry spanning 2008 to 2019 to construct a knowledge spillover network at the prefecture level. It utilizes social network analysis and multidimensional proximity theory to thoroughly investigate the evolutionary characteristics and potential mechanisms of network state, external connections, and urban spatial distribution within the spatial knowledge spillover of the marine industry.
2 Data source and research methodology
2.1 Building a knowledge spillover network
The research concentrates on prefecture-level cities in mainland China, omitting Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan, and employs certain criteria and methodologies for data filtration (Figure 1): Initially, patent applicants must be Chinese citizens, and only the geographic location details of the primary applicant are preserved to guarantee data accessibility. Secondly, patents categorized as marine patents are those including “Marine” in the title or abstract inside the worldwide patent database (IncoPat) from 2008 to 2019. These patents encompass domains pertaining to marine resources, energy development, and the delivery of associated products and services. Moreover, the forward and backward citations of patent data elucidate knowledge spillover from the viewpoints of technological diffusion and spillover origins, respectively. Forward citations may signify the advancement, investigation, application, and dissemination of succeeding innovations derived from earlier information (Alcácer and Gittelman, 2006; Hall et al., 2001; Marco, 2007). We investigate the knowledge spillover effect by examining backward citations in patent literature and acquiring geographical location data via publication numbers and database links. The research categorizes the timeframe from 2008 to 2019 into three distinct phases: 2008-2011, 2012-2015, and 2016-2019, to analyze the configuration of the knowledge spillover network. Following screening and processing, these three eras encompass 887, 3044, and 5112 citation linkages, respectively, thereby establishing a patent citation network with prefecture-level cities as nodes. The research employs Ucinet 6.0 and ArcGIS 10.2 software for social network analysis (SNA) and geographical analysis.
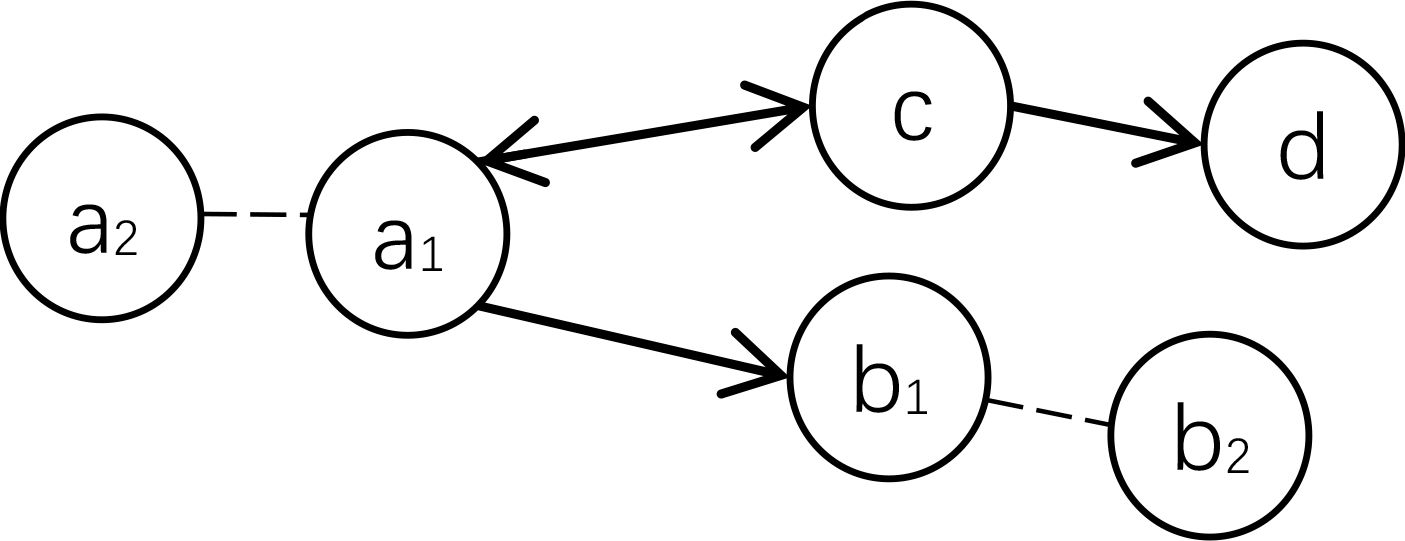
Figure 1. Data presentation Note: a1 and a2 are the geographic information of joint applications (so do b1 and b2), and c and d denote the geographic information of independent applicants.
2.2 Social network analysis
The SNA involves the following network structure indices:
(1) Network size: It denotes the total number (n) of nodes in a network.
(2) Network density: Network density reflects the degree of connection between network nodes. The higher the network density, the more significant the knowledge spillover between nodes, and the more convenient the knowledge flow:
where, m denotes the total number of actual relations in the entire network (it is n(n-1) in a directed network). The closer to 1 the D value, the closer the relations between network nodes.
(3) Node reciprocity: It denotes the proportion of two-way spillover relations in the entire network.
(4) Centrality: In this study, node centrality was measured in terms of degree centrality (CD(i)), betweenness centrality (CB(i)), and weighted centrality. Degree centrality reflects the ability of a node to connect with other nodes. The higher the degree centrality, the more nodes in the network that are directly connected to the node. In a directed network, degree centrality is the sum of in-degree and out-degree. Betweenness centrality reflects the degree of control of a node over network information. The higher the betweenness centrality, the more frequently a node is in the shortest path of other node pairs. In this study, the weighted in-degree and out-degree in a directed weighting network respectively reflected the intensity at which individuals cite patents and individuals’ patents are cited by others, and the sum of the two was weighted centrality. The first two centrality indicators are standardized to facilitate the comparison between networks of different sizes.
where, , respectively denote node out-degree and in-degree (the xij and values are 0 or 1).
where, denotes the probability that Node i is in the shortest path between Nodes k and j.
(5) Central potential: Degree central potential (CRD) reflects the overall concentration degree of a network, and star networks have the highest degree central potential. High betweenness central potential (CB) of a network implies a high degree of dependence on certain nodes in the process of knowledge transfer. Based on the degree centrality and betweenness centrality of nodes, the degree central potential and betweenness central potential of a network can be calculated as follows:
2.3 A structural equation model
2.3.1 Constructing a SEM
Using a measurement model and a structural model, structural equation modeling (SEM) is a technique for examining the connections between indicators and latent variables. Software like LISREL, AMOS, and SmartPLS are used to implement SEM, which offers more precise parameter estimations than typical linear regression. PLS-SEM is especially appropriate when the influence mechanism is still unclear and can manage individual variables (Hair et al., 2012). PLS-SEM is constructed in this work using SmartPLS 3.0 software, which analyzes 5,112 samples from 2016 to 2019. The model is validated using 5,000 bootstrap resamplings. Geographical, knowledge, social, economic, and cognitive proximity, as well as the interplay between knowledge, economic, and geographic proximity, are examples of exogenous latent variables in the PLS-SEM model, whereas the degree of knowledge spillover is an endogenous latent variable.
2.3.2 Multidimensional proximity variables
(1) Geographic proximity: It is measured in terms of nominal and spatial distance proximity. Nominal distance proximity is assigned a value according to the region in which a city is located (1 for the same provincial region; 0.5 for the same region (eastern, central, western and northeastern China specified in China’s 11th Five-Year Plan), and 0 for the whole country). Geographic distance is calculated based on a city’s latitude and longitude coordinates, and spatial distance proximity is calculated using the method specified by Wang (Wang, 2013):
where, dij denotes the geographic distance between cities i and j; max(dij) denotes the maximum geographic distance; Geoproij denotes the spatial distance proximity between cities i and j (value range: 0 to 1).
(2) Knowledge proximity and economic proximity: They reflect the differences in the number of invention patent applications and per-capita GDP between cities, and their ranges are standardized to facilitate their evaluation.
(3) Social proximity: The Jaccard index is used to measure the social proximity in a knowledge spillover network of the marine industry (Gui et al., 2018):
where, Iij denotes the edge weight from i to j; Ij denotes all input strengths of j; Oi denotes all output strengths of i (The value range of social proximity is 0 to 1).
(4) Cognitive proximity: Cognitive proximity is measured in terms of knowledge structure similarity (Knopro) and industrial structure similarity (Indpro):
According to the international patent classification standard, patents are classified into eight categories, and all industries are classified into primary, secondary, and tertiary industries; fin and fjn denote the number of all invention patent applications in the technological field n in Cities i and j; fik and fjk denote the proportion of Industry k in the industrial structure of Cities i and j, and the value range of knowledge structure similarity and industrial structure similarity is 0 to 1.
3 Spatiotemporal characteristics of China’s knowledge spillover network of the marine industry
3.1 The core positions of Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai are continuously strengthening, while cities like Zhoushan, Wuhan, and Guangzhou are developing rapidly
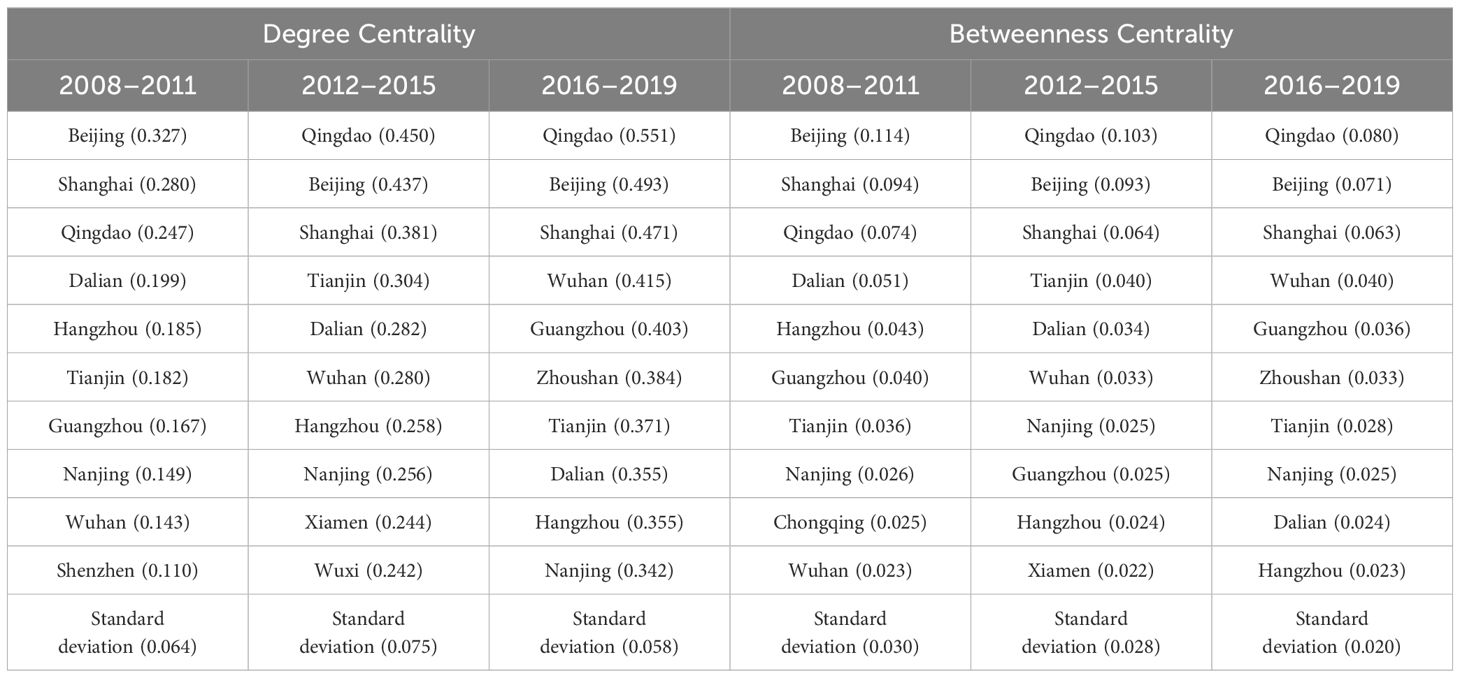
Table 1 presents the ten leading node cities ranked by centrality across three periods from 2008 to 2019, with Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai consistently occupying the top three positions, signifying their pivotal role in the marine sector knowledge spillover network. The ranks of sub-core cities, including Wuhan, Guangzhou, Zhoushan, Tianjin, Dalian, Hangzhou, and Nanjing, are both stable and subject to change. Between 2008 and 2011, Beijing’s dominance was most pronounced. Between 2012 and 2015, Qingdao’s centrality attained a value of 0.450, surpassing that of Beijing and Shanghai, while significantly trailing other cities. Between 2016 and 2019, the rankings of Zhoushan and Guangzhou improved markedly, the disparity among core cities diminished, and the overall centrality of the network increased to 44.54% (Table 2), signifying a shift towards a multicentric network model, with knowledge increasingly concentrated in a select number of core cities.
Between 2008 and 2019, Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai consistently occupied the top three positions in intermediary centrality. As centers of information dissemination, they have increased opportunity to obtain diverse knowledge, however their intermediate centrality experienced a modest decline. The intermediary centrality of sub-core cities like Wuhan, Guangzhou, and Zhoushan is increasing, narrowing the disparity among core cities, and the intermediary effect of cities is becoming more distributed. From 2016 to 2019, Qingdao’s central role as a hub continued to strengthen, despite a decline in intermediary centrality, which remained the highest. Zhoushan’s position increased from 14th to 6th (period 3), indicating its progressively significant role in the marine sector knowledge spillover network.
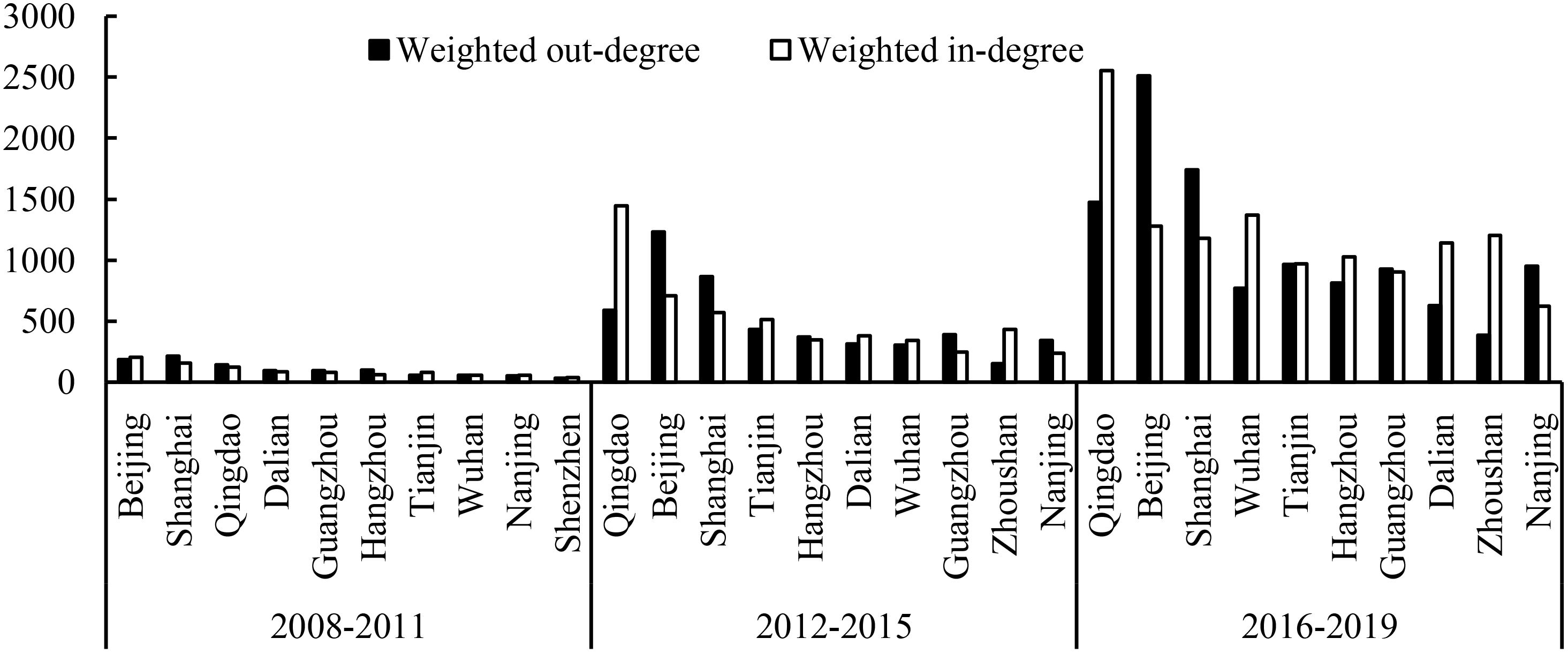
Figure 2 illustrates the top 10 cities ranked by weighted centrality across several periods, with findings mostly aligning with those in Table 1. Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai occupy the top three positions regarding weighted centrality, outgoing degree, and incoming degree, making them the most dynamic nodes in the knowledge spillover network. The weighted export degree of Beijing and Shanghai consistently surpasses the weighted import degree, and as the network’s radiation centers, their power and control are intensifying. Conversely, the weighted import degree of Qingdao consistently surpasses the weighted export degree, ranging from 142 to 2554, signifying the swift advancement of marine industry patents in Qingdao, which has now emerged as the preeminent hub in the network. In recent years, the weighted income of Wuhan, Zhoushan, and Dalian has markedly increased.
3.2 The spillover of marine knowledge in cyberspace exhibits significant polarization effects and is evolving towards a multi-core complex model with three major distribution centers as the focal points
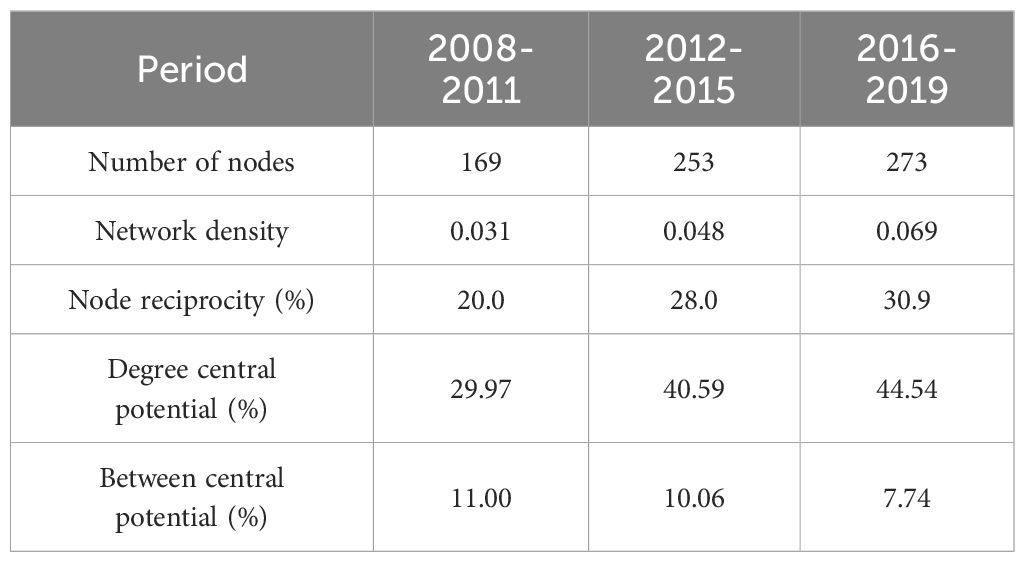
Table 2 illustrates the topological attributes of the knowledge spillover network within China’s marine sector from 2008 to 2019. The nodes in the knowledge spillover network rose from 169 to 273, while the network density grew from 0.031 to 0.069, signifying an intensification of network expansion and knowledge flow. In comparison to the degree center potential, the intermediary center potential was diminished and persisted in its decrease. As innovation capacity improves, the quantity of nodes directly associated with the core node rises, signifying an increase in network concentration. Nonetheless, the overall network density and node reciprocity are minimal, with reference linkages predominantly unidirectional and tenuous. Between 2016 and 2019, 3,094 city pairings produced 5,112 bilateral reference links, resulting in a network reciprocity of 30.9%. The natural fracture method in ArcGIS software categorizes the number of patent cross-citations in the Marine industry among cities into five tiers. Figure 3 illustrates the spatial distribution of the knowledge spillover network within China’s marine industry. The findings indicated that, in all three periods, the low-strength bond prevailed, with cities exhibiting bond strength below the average constituting 78.08%, 81.83%, and 82.81%, respectively. First-tier and second-tier cities serve as the primary overflow conduits, with side number proportions of 1.63%, 0.76%, and 0.97%, respectively, and total citation proportions of 17.52%, 18.88%, and 26.48%. The concentrated technology transfer indicates that the knowledge spillover network exhibits a notable spatial polarization effect.
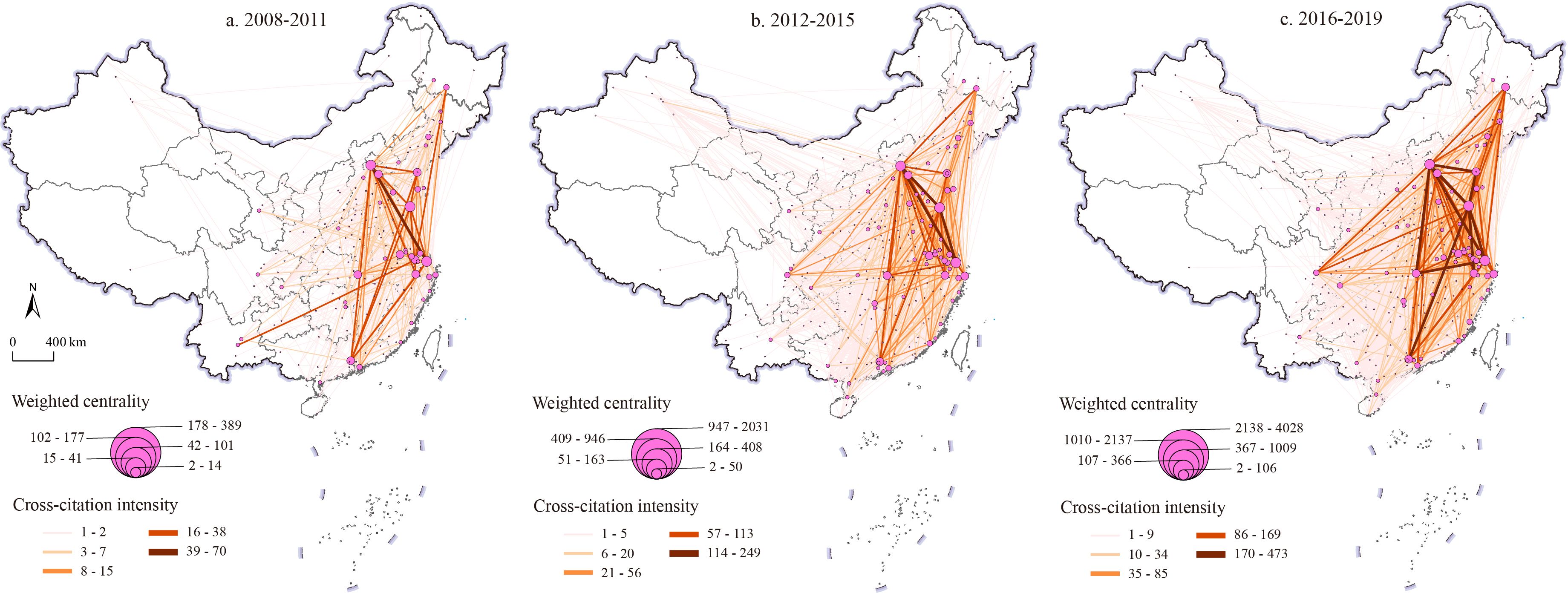
Figure 3. Spatial characteristics of China’s knowledge spillover network of the marine industry (A) 2008-2012; (B) 2012-2016; (C) 2016-2019.
Between 2008 and 2011, the mutual referrals between the Beijing and Shanghai regions were the highest, indicating a primary-level link. The citation count for other relational patents is below 40, with the majority utilized for long-distance applications across geographies. Between 2012 and 2015, the first-tier city network comprised Beijing - Qingdao, Shanghai - Qingdao, Beijing - Shanghai, and Beijing - Tianjin, during which the patent citations of Qingdao in Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Dalian, and Guangzhou experienced substantial growth; additionally, Wuhan and Zhoushan became part of the second-tier city network. Between 2016 and 2019, the triangular configuration of Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai was significantly reinforced, resulting in closer connections and a substantial expansion of the first-tier city network. The knowledge spillover strength from Shanghai and Qingdao to Zhoushan was notably augmented.
From 2008 to 2019, the intensity of knowledge spillover in China’s marine industry experienced significant growth. Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai have emerged as the three principal distribution centers, distinct from the “trapezoidal” core structure of “Beijing-Qingdao-Shanghai-Guangzhou” identified in Guo et al.’s study on the geographical characteristics of the marine scientific research network (Guo et al., 2021). The network has transitioned from a dual-core framework to a multi-core framework, and technology dissemination has progressed from coastal regions to interior areas. The significance of inland cities like Wuhan is growing daily, and the correlation between patent citations and regions, as well as short distances within the network of prominent cities, is intensifying.
3.3 Significant spatial variation in the knowledge spillover network, and X-shaped core area in eastern China with Qingdao as the intersection
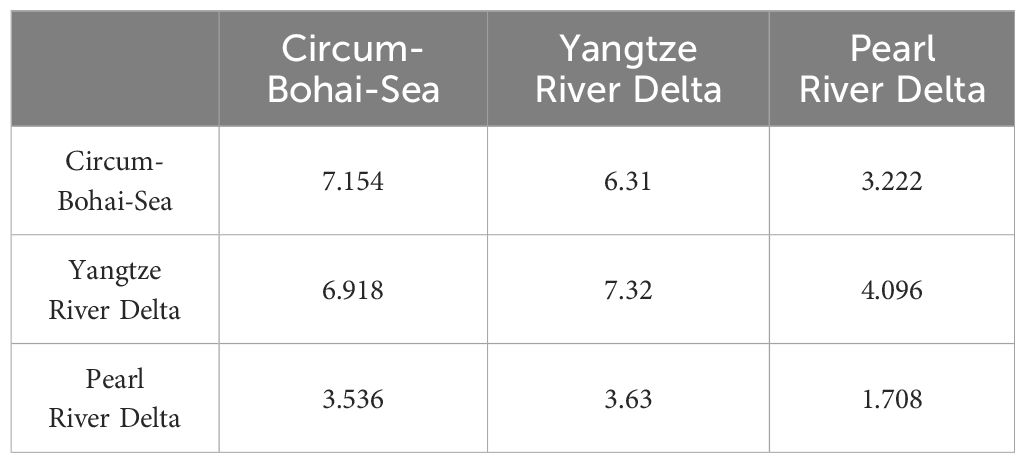
The ArcGIS kernel density analysis tool was utilized to create a distribution map of the knowledge spillover network in China’s marine industry (Figure 4), based on inter-city patent citation intensity. The findings indicate that: i) notable disparities exist within the spatial knowledge spillover network of China’s marine industry; ii) with the exception of Wuhan, the nuclear density in the central and western regions is predominantly low; iii) the eastern core area exhibits an X-shaped spatial configuration with Qingdao as the nexus, linking Beijing, Tianjin, Zhenjiang, Wuxi, Suzhou, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Zhoushan, Dalian, Yantai, Nanjing, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. The transfer of knowledge from the northeast to the southwest is somewhat feeble. The inner and inter-connections between the Bohai Sea Rim and Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations are notably strong. The analytical conclusion aligns closely with Ma et al.’s nuclear density examination of the spatial distribution evolution of urban innovation output (Ma et al., 2018), demonstrating that marine industrial innovation exhibits analogous spatial differentiation to urban innovation output in cities. Table 3 juxtaposes the information spillover network density throughout the Bohai Rim, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta regions. A density matrix is built based on the patent citation relationships within the marine industry. The row field denotes the overflow ground, the column field signifies the receiving ground density matrix, and the diagonal line illustrates the internal network density of the corresponding city clusters. The findings indicate that the density of the national directed weighted network is 0.306, whereas the regional network densities for the circum-Bohai Sea, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta are 7.154, 7.320, and 1.708, respectively, signifying the concentration of the knowledge spillover network. The internal network density of the Bohai Rim city cluster and the Yangtze River Delta city cluster significantly exceeds that of the entire nation, with network densities from the Bohai Rim to the Yangtze River Delta and from the Yangtze River Delta to the Bohai Rim city cluster measuring 6.310 and 6.918, respectively, indicating frequent knowledge exchange between the two regions. Conversely, the local network density of the Pearl River Delta city cluster, centered on Guangzhou, is comparatively low, yet the external network intensity with the Yangtze River Delta and the Bohai Sea rim surpasses that of the Pearl River Delta.
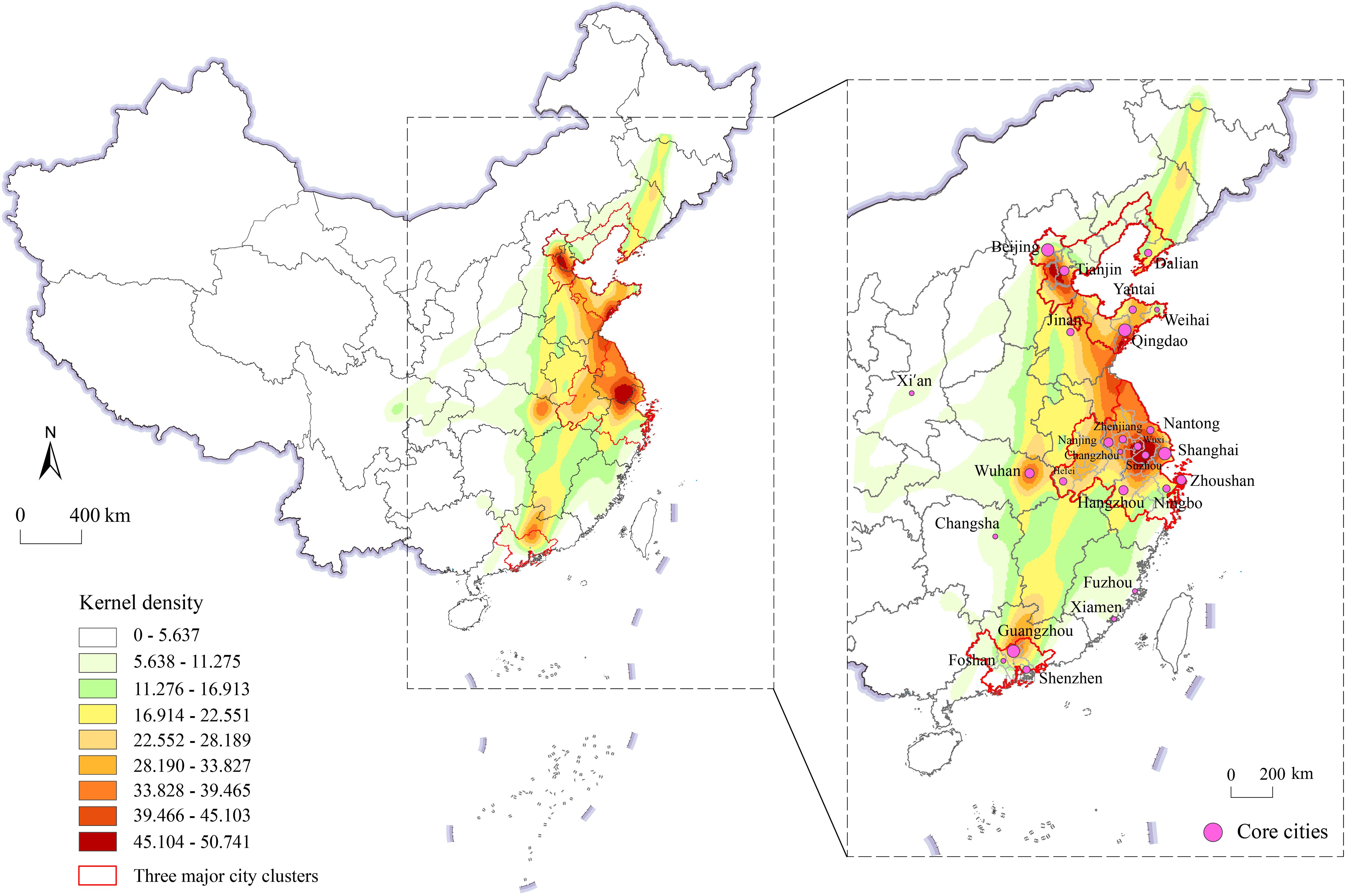
Figure 4. Kernel density of China’s knowledge spillover network of the marine industry from 2016 to 2019.
4 Analysis of influencing factors
4.1 Test of the measurement model
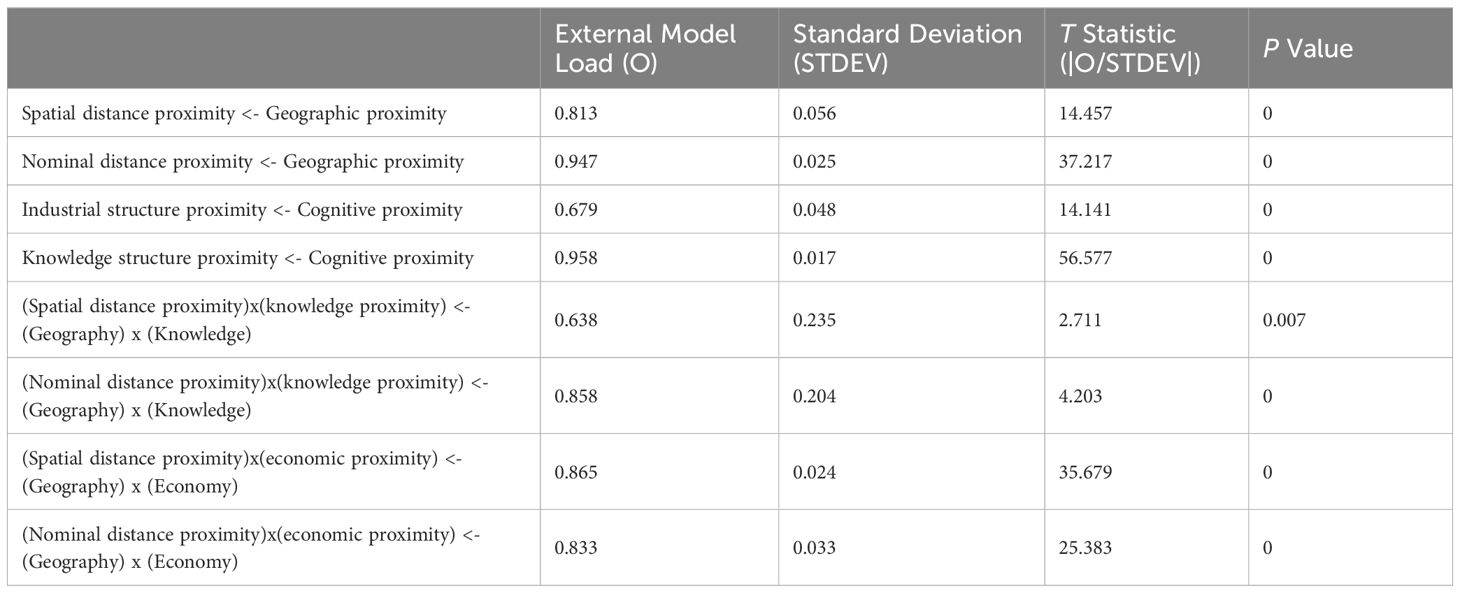
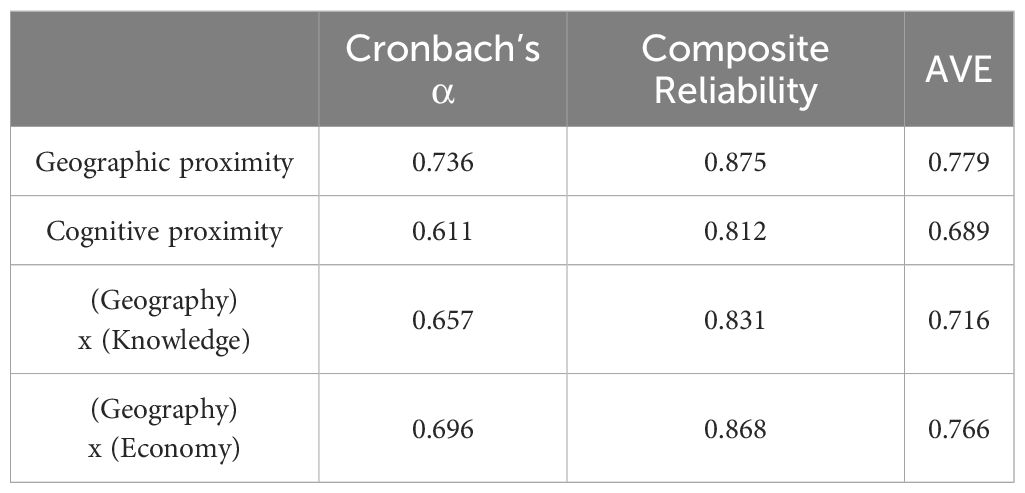
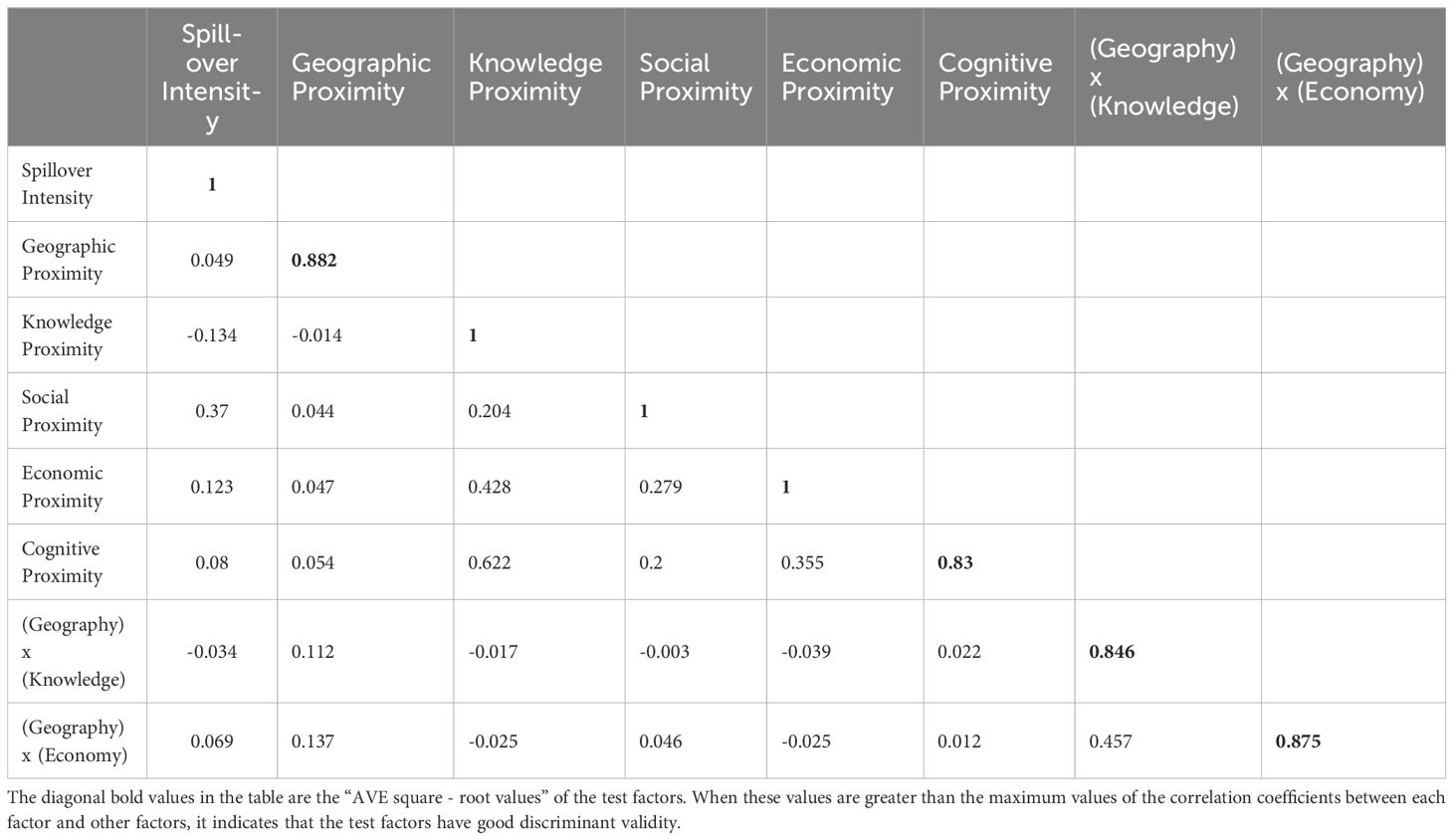
The measurement model involves a reliability and validity test. The reliability test involves the load coefficients, Cronbach’s α, and composite reliability of the measurement model. Table 4 lists the Bootstrap test results of the load coefficient of the measurement model. Specifically, the load coefficients of (Spatial distance proximity)x(knowledge proximity) <- (Geography) x (Knowledge) and Industrial structure proximity <- Cognitive proximity are slightly lower than 0.7 (0.638 and 0.679 respectively); all other latent variables are greater than 0.7, and all indicators are significant at the 0.01 level. As described in Table 5, Cronbach’s α of geographic proximity is 0.736, and Cronbach’s α of other variables are within an acceptable range of 0.6 to 0.7 and the composite reliability of all variables is greater than 0.8. Therefore, the measurement model is of high reliability. The validity test involves convergent validity and discriminant validity. The average variance extracted (AVE) of all reflective latent variables is greater than 0.5 (Table 5), indicating that the measurement model passes the convergent validity test. The root value of AVE (diagonal value) of each latent variable in Table 6 is greater than the Pearson correlation coefficients between it and other latent variables, and the load coefficient of each indicator in the measurement model is greater than its cross-load coefficients (load coefficients of the indicator relative to other latent variables), indicating that the measurement model passes the discriminant validity test.
4.2 Test of the structure model
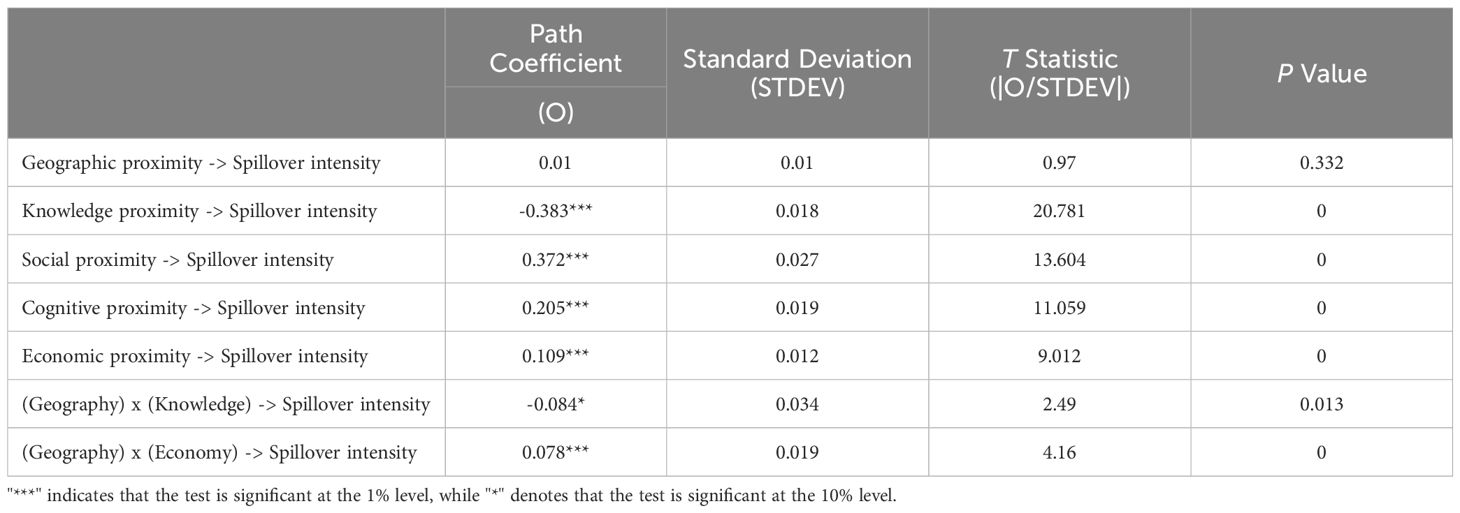
The test of the structure model mainly involves the significance of the path coefficients (measured by t-value) and the explanatory power of the structure model (measured by R2). The explanatory power of the model (R2) is equal to the product of the correlation coefficients and path coefficients between latent variables and different explanatory latent variables; R2 reflects the extent to which an explanatory latent variable explains a latent variable, or the fit effect of the structure model. The adjusted R2 of the structure model is 0.226 (greater than the minimum standard of 0.019), indicating that the explanatory power of several latent variables in the structure model is acceptable.
Table 7 lists the Bootstrap test results of the path coefficients of the structure model. Evidently, the effect of geographic proximity is not significant, the effect of knowledge proximity is significantly negative at the 1% level, and the effect of social, cognitive, and economic proximity is significantly positive at the 1% level. Followed by social proximity, knowledge proximity has the largest path coefficient, and the path coefficients of economic proximity and cognitive proximity are smaller than those of knowledge and social proximity to some extent. The interaction term between geographic and knowledge proximity is significantly negative at the 10% level, and the interaction term between geographic and economic proximity is significantly positive at the 1% level. Evidently, geographic proximity produces a positive moderating effect; specifically, it can strengthen the similarity of economic strength between regions, as well as the effect of knowledge stock gap on the intensity of knowledge spillover.
5 Conclusions and policy implications
Through a thorough examination of the patent citation data pertaining to China’s marine industry from 2008 to 2019, we develop an extensive knowledge spillover network. This network elucidates the patterns and attributes of knowledge dissemination within the Marine industry, while also offering recommendations to augment Marine innovation capacity and foster the high-quality advancement of the Marine economy. It aims to establish an analytical framework for the Marine economy in China and globally, viewed through the lens of knowledge spillover, and serves as a reference for enhancing regional Marine innovation capacity and stimulating the growth trajectory of the Marine economy.
Initially, Qingdao, Beijing, and Shanghai have consistently occupied the central role in the information spillover network, succeeded by Zhoushan, Wuhan, and Guangzhou. This indicates that they are pivotal in knowledge innovation and dissemination within the Marine business, aligning with the findings of Li. in their research on cooperative innovation networks in the Marine sector (Li et al., 2021). Over time, the dimensions and density of the network surrounding the three distribution hubs have progressively expanded, mirroring the more frequent and intense exchange of knowledge within the Marine industry. The transition of network topology from dual-core to multi-core illustrates the complex and varied nature of information spillover within the marine industry. Since 2016, the X-shaped spatial configuration in East China, centered around Qingdao, underscores its activity and impact on knowledge spillover.
The information spillover network exhibits a propensity to extend inland. Inland cities like Beijing, Wuhan, and Nanjing have emerged as primary support points of the X-type core area, serving as significant nodes for knowledge innovation in the marine sector. The growing prevalence of technology-intensive sectors, such as the contemporary marine service and advanced marine manufacturing industries, indicates that marine technological innovation is increasingly reliant on terrestrial knowledge, highlighting a pronounced terrestrial trend within the marine industry. Cities with favorable locational attributes will serve as more significant nodes in marine information dissemination. Nanjing, despite being an interior city, possesses abundant marine research resources, including multiple ocean-related universities and institutes, as well as significant geographical advantages, such as access to sea and inland river transit.
Thirdly, the empirical study of PLS-SEM elucidates the determinants driving knowledge spillover. The adverse impact of knowledge proximity suggests that a bigger disparity in knowledge potential increases the likelihood of information spillover, highlighting the significance of diverse knowledge in the innovation process. The beneficial impact of social proximity on knowledge spillover suggests that strong social connections and high familiarity among cities can significantly diminish barriers in information transfer mechanisms, hence facilitating the dissemination and exchange of knowledge. Cities with analogous knowledge and industrial frameworks incur reduced costs in the assimilation and implementation of new knowledge, hence enhancing the knowledge spillover within the Marine industry. 4) While geographical proximity does not significantly affect knowledge spillover, it moderates the impact of knowledge proximity and economic proximity on knowledge spillover, indicating the necessity of a comprehensive evaluation of the interplay among various factors in the context of knowledge spillover.
In light of the aforementioned research, we propose the subsequent policy recommendations:
Initially, the facilitation of information sharing across emergent nodes should be encouraged via various channels and innovation agents. Zhoushan can utilize university resources to proactively pursue marine patent applications and citations. To bolster regional independent innovation capacity, it is essential to promote the profound integration of universities, research institutes, and enterprises, facilitating knowledge diffusion, transformation, and renewal through various spillover mechanisms. Consequently, it is imperative to enhance the methods and avenues for knowledge acquisition and to facilitate the interaction and syn.
6 Restrictions and upcoming studies
This study offers a comprehensive analysis of the structural attributes and spatio-temporal evolution of China’s marine industry knowledge spillover network, serving as a significant reference for advancing policy interventions aimed at fostering innovative development in the marine sector. Given the expanding influence of the Marine industry on the global economy, our results and recommendations will hold substantial theoretical and practical importance in advancing the high-quality growth of the Marine economy. Nonetheless, the knowledge spillover network derived from patent citation data inadequately represents the efficacy of knowledge spillovers occurring through alternative channels (such as direct interpersonal interactions) in the advancement of Marine industry inventions, and it fails to account for the evolution of knowledge spillovers in the Marine industry across diverse data sources. Future research will thoroughly examine various relational data and investigate the analytical impact of alternative methodologies on the knowledge spillover effect, thereby elucidating the role of cities within the marine sector knowledge spillover network.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.incopat.com/.
Author contributions
KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TX: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. QD: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JT: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study is funded by Liaoning Social Science Planning Fund Project of China (L22AJY008).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Editors and the reviewers for the useful and constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abramo G., D’angelo C. A., Costa F. D. (2020). Knowledge spillovers: Does the geographic proximity effect decay over time? A discipline-level analysis, accounting for cognitive proximity, with and without self-citations. J. Informetrics 14, 101072. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2020.101072
Alcácer J., Gittelman M. (2006). Patent citations as a meas-ure of knowledge flows: The influenceofexaminer cita-tions. Rev. Economics Stat 88, 774–779. doi: 10.1162/rest.88.4.774
Braunerhjelm P., Svensson R. (2024). Inventions, commercialization strategies, and knowledge spillovers in SMEs. Small Business Economics 63, 275–297. doi: 10.1007/s11187-023-00812-z
Choi H., Zo H. (2022). Network closure versus structural hole: the role of knowledge spillover networks in national innovation performance. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage. 69, 1011–1021. doi: 10.1109/tem.2020.2972347
Cortinovis N., Van Oort F. (2019). Between spilling over and boiling down: network-mediated spillovers, local knowledge base and productivity in European regions. J. Economic Geogr. 19, 1233–1260. doi: 10.1093/jeg/lby058
Granovetter M. S. (1973). The strength of weak ties. Am. J. sociology 78, 1360–1380. doi: 10.1086/225469
Griliches Z. (1979). Issues in assessing the contribution of research and development to productivity growth. Bell J. Economics 10, 92–116. doi: 10.2307/3003321
Gui Q. C., Liu C. L., Du D. B. (2018). International knowledge flows and the role of proximity. Growth Change 49, 532–547. doi: 10.1111/grow.12245
Guo J. K., Ding Y. D., Qin Y. F. (2021). Spatial Linkages in China’s Marine research cooperation Network. J. Trop. Geogr. 41, 584–595. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003342
Hair J. F., Sarstent M., Ringle C. M., Mean J. A. (2012). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Marketing Sci. 40, 414–433. doi: 10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hall B., Jaffe A., Trajtenberg M. (2001). The NBER patent cita-tion data file: Lessons, insights and methodological tools. NBER WP No. 8498. Available online at: https://www.nber.org/papers/w8498 (Accessed June 20, 2024).
Hussler C. (2004). Culture and knowledge spillovers in Europe: New perspectives for innovation and convergence policies? Economics Innovation New Technol. 13, 523–541. doi: 10.1080/1043859042000234302
Jaffe A. B. (1996). Economic analysis of research spillovers implications for the advanced technology program. US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Li X. C. (2017). Do patent citations indicate knowledge linkage? The evidence from text similarities between patents and their citations. J. Informetrics 11, 63–79. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2016.04.018
Li Y., Ma S., Fu N. ,. N., Yi K., Peng F. (2021). Characteristics and proximity of Marine industry cooperation innovation network in China’s coastal areas. Economic Geogr. 41, 129–138. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2021.02.014
Li D. D., Wang T., Zhou H. (2013). Structural characteristics of knowledge spillover networks basedon different spatial and temporal scales. Scientia Geographica Sin. 33, 1180–1187. doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2013.10.004
Liu X. L., Ge S. (2018). Exploring the internal mechanism of innovation-driven economic growth in China in the past 20 years: From the perspective of the New Schumpeterian Growth Theory. Sci. Sci. Manage. Sci. Technol. 39, 3–18.
Ma J., Deng H. B., Zhang H. (2018). Spatial pattern of urban innovation output in China from theperspective of spatial knowledge spillover. Economic Geogr. 38, 96–104. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2018.09.011
Marco A. (2007). The dynamics of patent citations. EconomicsLetters 94, 290–296. doi: 10.1016/j.econlet.2006.08.014
Martinez M. G., Zouaghi F., García M. S. (2024). Geographical and cognitive proximity effects on innovation performance: Which types of proximity for which types of innovation? Eur. Manage. Rev. doi: 10.1111/emre.12641
Maurseth P. B., Verspagen B. (2002). Knowledge spillovers in Europe: A patent citations analysis. Scandinavian J. Economics 104, 531–545. doi: 10.1111/1467-9442.00300
Peng F., Sun C. Z., Liu T. B., Li Y., Hu W. (2018). The spatial and temporal evolution of vulnerability and coordination of Marine eco-economic system in China’s coastal areas. Economic Geogr. 38, 165–174. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2018.03.021
Qiu J. W., Liu W. J., Ning N. (2020). Evolution of regional innovation with spatial knowledge spillovers: convergence or divergence? Networks Spatial Economics 20, 179–208. doi: 10.1007/s11067-019-09477-2
Rao Y. D., Li F. G. (2006). Geographical Proximity and Innovation: Regional knowledge flow and collective learning Perspective. China Sci. Technol. Forum, 20–24.
Rigby D. L. (2015). Technological relatedness and knowledge space: entry and exit of US cities fromPatent classes. Regional Stud. 49, 1922–1937. doi: 10.1080/00343404.2013.854878
Rodriguze-pose A., Crescenzi R. (2008). Research and development, spillovers, innovation systems, and the genesis of regional growth in Europe. Regional Stud. 42, 51–67. doi: 10.1080/00343400701654186
Sheng Y. X., Lesage J. (2021). A spatial regression methodology for exploring the role of regional connectivity in knowledge production: Evidence from Chinese regions. Papers Regional Sci. 100, 847–874. doi: 10.1111/pirs.12601
Song Y., Chen Bo., Tao R., Su C. W., Muhammad U. (2020). Too little, just right or too much? Assessing how people evaluate their conscientiousness levels. Per-sonality Individ. Dif. 197, 101324. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2022.111789
Steensma H. K., Chari M., Heidl R. (2015). The quest for expansive intellectual property rights and the failure to disclose known relevant prior art. Strategic Manage. J. 36, 1186–1204. doi: 10.1002/smj.2279
Su C. W., Song Y., Umar M. (2021). Financial aspects of marine economic growth: From the perspective of coastal provinces and regions in China*. Ocean Coast. Manage. 204, 105550. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105550
Tijssen R. J. W. (2001). Global and domestic utilization of industrial relevant science: patent citation analysis of science-technology interactions and knowledge flows. Res. Policy 30, 35–54. doi: 10.1016/s0048-7333(99)00080-3
Wang B. B. (2013). Structural evolution of knowledge networks from the perspective of multidimensionalproximity. [master's thesis]. [Nanjing (Jiangsu)]: Nanjing Normal University
Wang T. F., Gu R. X. (2021). Characteristics and Influencing factors of regional Knowledge spillover networks in China: An empirical study on knowledge-intensive Industries. Soft Sci. 35, 94–99. doi: 10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2021.08.14
Wang X. C., Han Z. L., Peng F., Cai X. Z. (2020). Evolution of development pattern and classification of Marine science and technology innovation efficiency in China. Sci. Geogr. 40, 890–899. doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.06.004
Wang C. C., Sung H. Y., Chen D. Z., Huang M. H. (2017). Strong ties and weak ties of the knowledge spillover network in the semiconductor industry. Technological Forecasting Soc. Change 118, 114–127. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2017.02.011
Wu F., Gao Q., Liu T. (2019). Efficiency measurement of Marine science and technology innovation on Marine economic growth. Stat Decision 35, 119–122. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.23.026
Keywords: knowledge spillover network, marine industry, spatiotemporal characteristics, influencing factors, social network analysis, structural equation model
Citation: Liu K, Zhang Y, Peng F, Xie T, Du Q and Tan J-y (2025) Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of China’s knowledge spillover network of the marine industry. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1509523. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1509523
Received: 11 October 2024; Accepted: 12 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Kevin Li, University of Windsor, CanadaReviewed by:
Yu Song, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaWang Shufang, Tianjin Normal University, China
Yi Li, Hohai University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhang, Peng, Xie, Du and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Liu, ZGFsaWFubGl1a2FpQGxubnUuZWR1LmNu
 Kai Liu
Kai Liu Yi Zhang1
Yi Zhang1 Fei Peng
Fei Peng Tong Xie
Tong Xie