- California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, Biological Sciences Department, San Luis Obispo, CA, United States
Coral reefs are experiencing more intense and frequent disturbances induced by climate change, such as cyclones and bleaching events. This necessitates a better understanding of the ongoing environmental conditions that stress these systems and the subsequent arc of longer-term reef responses to these stressful conditions. From March of 2014 to May of 2017, the Lizard Island reefs in the northern region of the Great Barrier Reef experienced four consecutive annual disturbances; Cyclone Ita in 2014, Cyclone Nathan in 2015, and two massive bleaching events in 2016 and 2017. Between the concentrated patches of physical damage from the cyclones and the uniform impact of the bleaching events, these reefs were devastated, with none of the eight study sites harboring more than 20% live coral cover by May of 2017. In November of 2023, after six years of relatively calmer conditions with no conspicuous region-wide, large-scale disturbances, I documented the extant coral community on eight previously-monitored reefs around Lizard Island. All reefs showed significant (p = 0.0054, F = 3.46, df = 47) improvement from their 2017 immediate post-disturbance degradation. Living coral at my study sites had recovered to between 18.4 ± 0.6 (mean ± 1 SE) to 59.9 ± 5.3% of the reef area per site by 2023, with many sites towards the higher end of that range. Recovery of coral extent appeared to follow a north-south trend in which more Trade Wind-sheltered northerly sites had generally greater recovery and higher live coral cover compared to more exposed southern sites, which experienced significantly less coral recovery. Fast-growing Acroporid corals drove the recovery of coral extent in these more northern sites. While family richness across all sites improved by 2023 (4.0 ± 0.1; grand mean ± 1 se), Lizard Island reefs have yet to reach their pre-disturbance diversity (4.8 ± 0.6 in 2014). Future annual surveys of the study sites as well as others surveyed in 2017 may better clarify the relationship between reef location and the rate of recovery of coral cover post-disturbance.
Introduction
Coral reefs globally are ecologically (Wilson et al., 2006), economically (Santavy et al., 2021), and culturally significant (Cinner et al., 2009) to developed and developing countries alike (Laurans et al., 2013). Extants reefs are subject to increasingly frequent and intense disturbances, including climate change-induced factors (Hughes et al., 2017). Major proximate threats to the world’s largest coral reef system–the Great Barrier Reef–include predation by Crown-of-Thorns starfish (Pratchett, 2010), unsustainable fishing practices (Santavy et al., 2021), disease outbreaks (Roff et al., 2011), and bleaching due to climate-induced high temperature stress (Hoegh-Guldberg, 1999). As these disturbances occur more often and with greater intensity, heterogenous coral recovery drives changes in reef composition (Madin et al., 2018). This often reduces the quality of immediate recovery and is correlated with negative long-term trends in biodiversity (Wakeford et al., 2008). Future bleaching events in coming decades will likely surpass the thermal tolerance of essential corals, impeding their continued growth, development, and ecological function (Hoegh-Guldberg, 1999). Given that reefs continue to face these intense conditions, it is critical to understand how reef assemblage will be impacted in the long term.
From 2014-2017, the northern Great Barrier Reef faced a harsh sequence of disturbances–Cyclone Ita in 2014, Cyclone Nathan in 2015, and two massive bleaching events in 2016 and 2017 (Wakeford et al., 2008). The physical damage caused by those cyclones coupled with the large-scale bleaching to devastate reefs around the island. Before these stressors, most Lizard Island reefs were coral-rich (typically >40% coral cover; Done et al., 2010; Johns et al., 2014), but by late 2017 many were close to 4% of live coral cover (Madin et al., 2018).These collective phase shifts away from more structurally secure, complex reefs have had dramatic impacts on fish abundance and species richness (Jones et al., 2004; Wilson et al., 2006). Since changes in composition of coral communities tend to be discrete following these episodic stressors, recovery can occur if a reef has sufficient time between perturbations (Gilmour et al., 2013). However, as the time between these events continues to decrease, phase-shifts become more common, rendering such reefs less able to effectively recover to a pre-disturbance condition (T. P. Hughes and Connell, 1999). The rising prevalence of phase-shifts, together with increasingly frequent disturbances, hinders and, in some cases, completely inhibits coral recruitment and community succession, leaving these potential habitats in a volatile state (Baird and Hughes, 2000).
There are extant examples of other reefs undergoing similar conditions. Following a high urchin mortality event in 1983, grazing was greatly reduced across Caribbean reefs where herbivorous fish populations were overfished, leading to the emergence of alternate stable states in which macroalgae made up the majority of cover in previously coral-dominated areas (Mumby et al., 2007). This weakened the resilience of these reefs against future disturbances that target corals more specifically. Between 1980 and 2001, 286 Caribbean reefs experienced ~17% coral cover reduction in years following hurricanes, with no evidence of recovery to a pre-storm condition for at least eight years post-disturbance (Gardner et al., 2005). This suggests that not only does reef condition decline with more frequent and damaging impacts, but that reef recovery is also being impaired. Caribbean reefs have continued to experience a decline in structural and biological complexity to this day, with Caribbean-wide homogenization of current structures and species (Alvarez-Filip et al., 2009). Similar trends of more homogenized, less healthy reefs have been documented across the same time scale in the Philippines (Licuanan et al., 2019), Indonesia (Wolfe et al., 2020), Papua New Guinea (Berzunza-Sanchez et al., 2013). Each of these reefs have also suffered from overexploitation of resources and poor management decisions, but the negative impacts of cyclones and bleaching cannot be mitigated at the source in the same way. This makes it imperative that we better understand how reefs cope with these large-scale disturbances.
In the immediate wake of these disturbances, researchers characterized the post-impact composition of 13 reef sites around the island in 2017. They found that coral cover across 10 of the 19 sites was below 4%, with only two sites having cover above 40%, the highest cover for most sites prior to the four years’ disturbances (Madin et al., 2018). Researchers predicted reef structure and complexity would begin to return. I sought to document any potential coral recovery six years after the 2017 surveys to determine if that recovery had begun on Lizard Island reefs. In the fall of 2023, I sought to test the hypothesis that coral cover and composition were unchanged from 2017.
Materials and methods
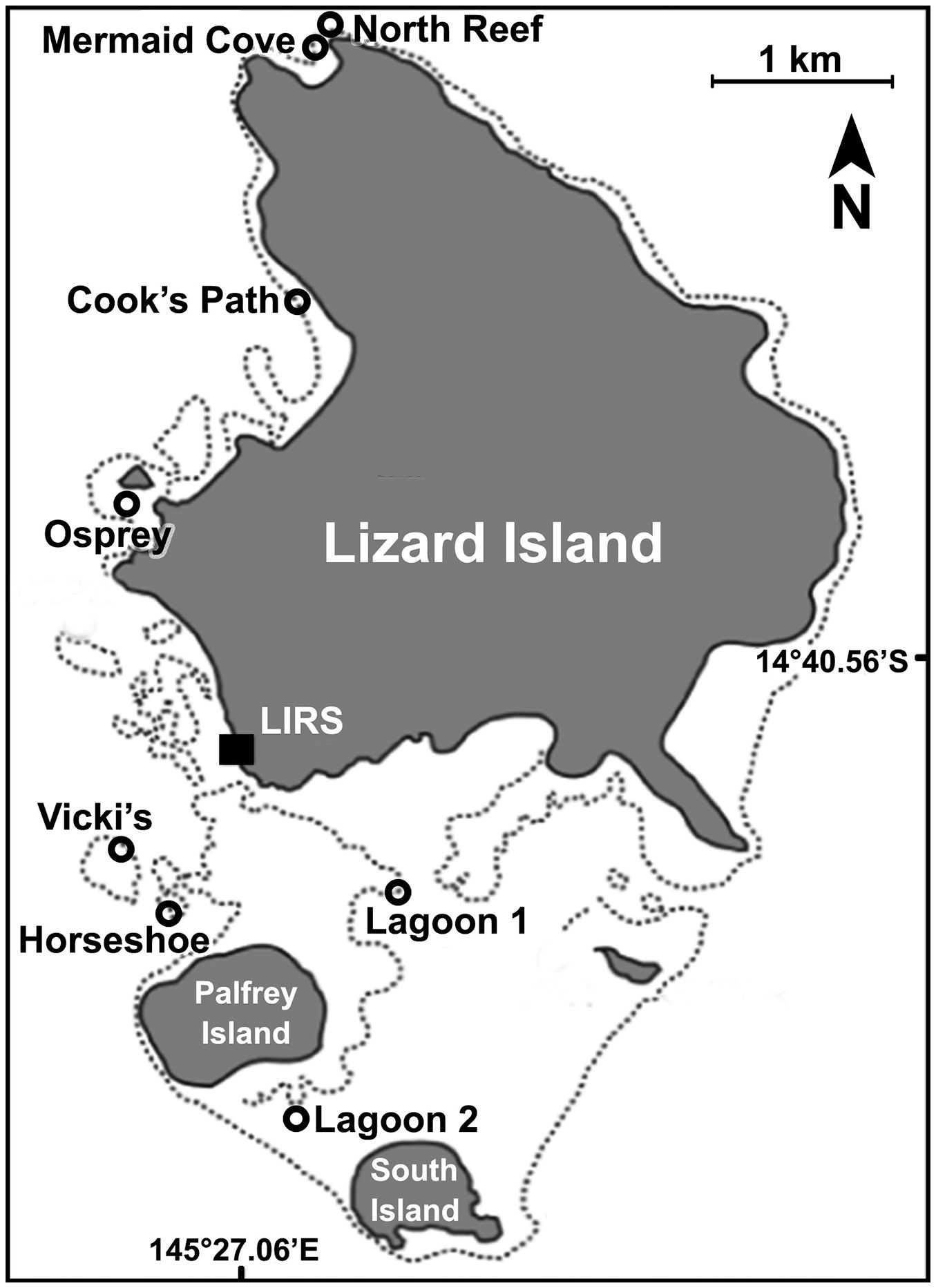
I explored coral reefs around the Lizard Island Research Station (14.6688° S, 145.4594° E), on the northern portion of Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. I sampled eight reef sites at Lizard Island from 23 October to 18 November,2023, using the same site name and locations as the previous study (Madin et al., 2018)–Cook’s Path (14.660557° S, 145.453396° E), Lagoon 1 (14.686888° S, 145.456658° E), Lagoon 2 (14.698240° S, 145.450682° E), Horseshoe (14.687851° S, 145.444216° E), Vicki’s (14.685130° S, 145.442876° E), Osprey (14.667579° S, 145.443119° E), Mermaid Cove (14.647248° S, 145.453939° E), and North Reef (14.645044° S, 145.453987° E). These sites are dispersed across the relatively protected side of Lizard Island, leeward of the prevailing Southeast Trade Winds (Figure 1). Risk management concerns (restrictions to remain in range of radio contact and avoid the rougher sea conditions of Lizard Island’s east side) prevented me from collecting data on the Northeast to Southeast of the island and as such I could only sample a subset of the representative sites across the island reefs.
At each site, six 10-meter line-intercept transects were randomly laid out over the reef face at one to two meters deep, with each transect no further than 10 meters apart from the last (Madin et al., 2018). The substrate type beneath the transect tape was recorded to the nearest milimeter, and hard corals were classified by family to determine the percent cover. The categories recorded at each site included soft coral, Acropora, Porites, Pocillopora, encrusting coralline algae, hard dead coral, rubble, sand, and algae. In data visualization, these types were put into the following groups: hard coral (Acropora, Porites, and Pocillopora), soft coral, algae, encrusting coralline algae, and abiotic substrate (hard dead substrate, rubble, and sand). Transect data were analyzed with JMP Pro (v 17). I compared the proportion of total live coral cover by reef, family proportion of total cover by year, grand means of coral cover proportion by year, and grand means of family richness by year using analysis of variance.
Results
In the wake of the 2014-2017 sequence of disturbances, total live coral cover declined dramatically from pre-disturbance conditions in 2014. Some reefs had single percent coverage of live coral by 2017. In the six years since, total live coral cover on all reefs increased dramatically, with six out of eight reefs harboring more live coral cover than in 2014. The remaining two sites (Lagoon 1 and Lagoon 2) show lower coral cover than pre-disturbance 2014 levels (Figure 2). Grand means of live coral cover across my eight sites went from 39.6% in 2014 to 12% in 2017 to 51% in 2023.
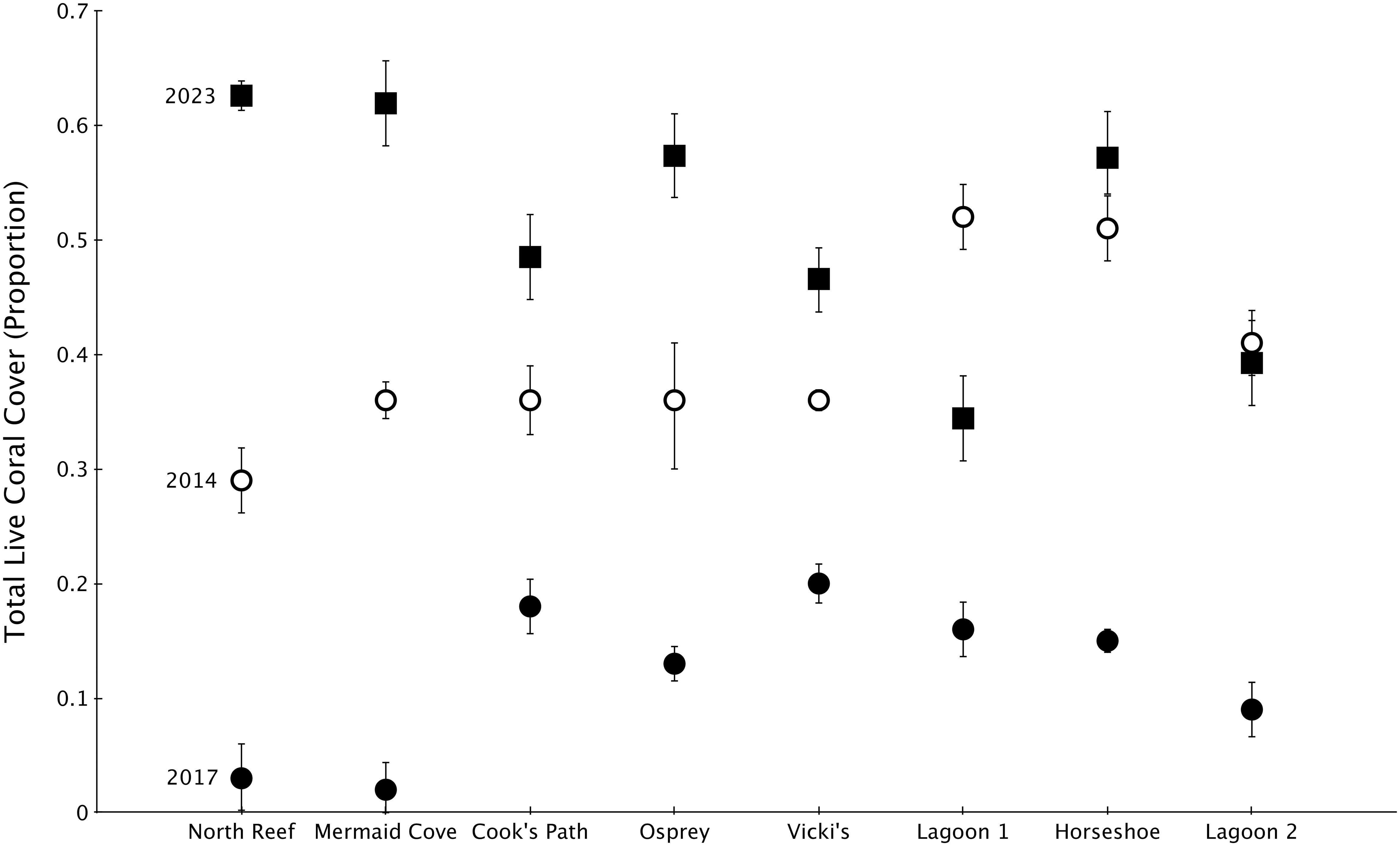
Figure 2. Proportion of total live coral cover ± 1 SE at my eight reef sites in 2014 (pre-disturbance), 2017 (post-disturbance), and 2023 (6 years post-disturbance). 2014 and 2017 data sourced from Madin et al., 2018. Reefs are ordered from northern-most on the left to southernmost on the right.
The proportion of soft coral and Acropora cover declined heavily, while the proportion of Pocillopora and Porites cover fluctuated more moderately (Figure 3). By 2023 (six years post-disturbance), all groups recovered by various margins, with the proportion of cover of all groups increasing–Acropora by 20.1% (p = 0.049, F = 2.03, df = 7), soft coral by 9.5% (p = 0.025, F = 1.97, df = 7), Pocillopora by 6.8% (p = 0.015, F = 2.49, df = 7), and Porites by 4.2% (p = 0.009, F = 1.42, df = 7). All groups except soft coral recovered to 2014 (pre-disturbance) proportion of cover (Tables 1–3).
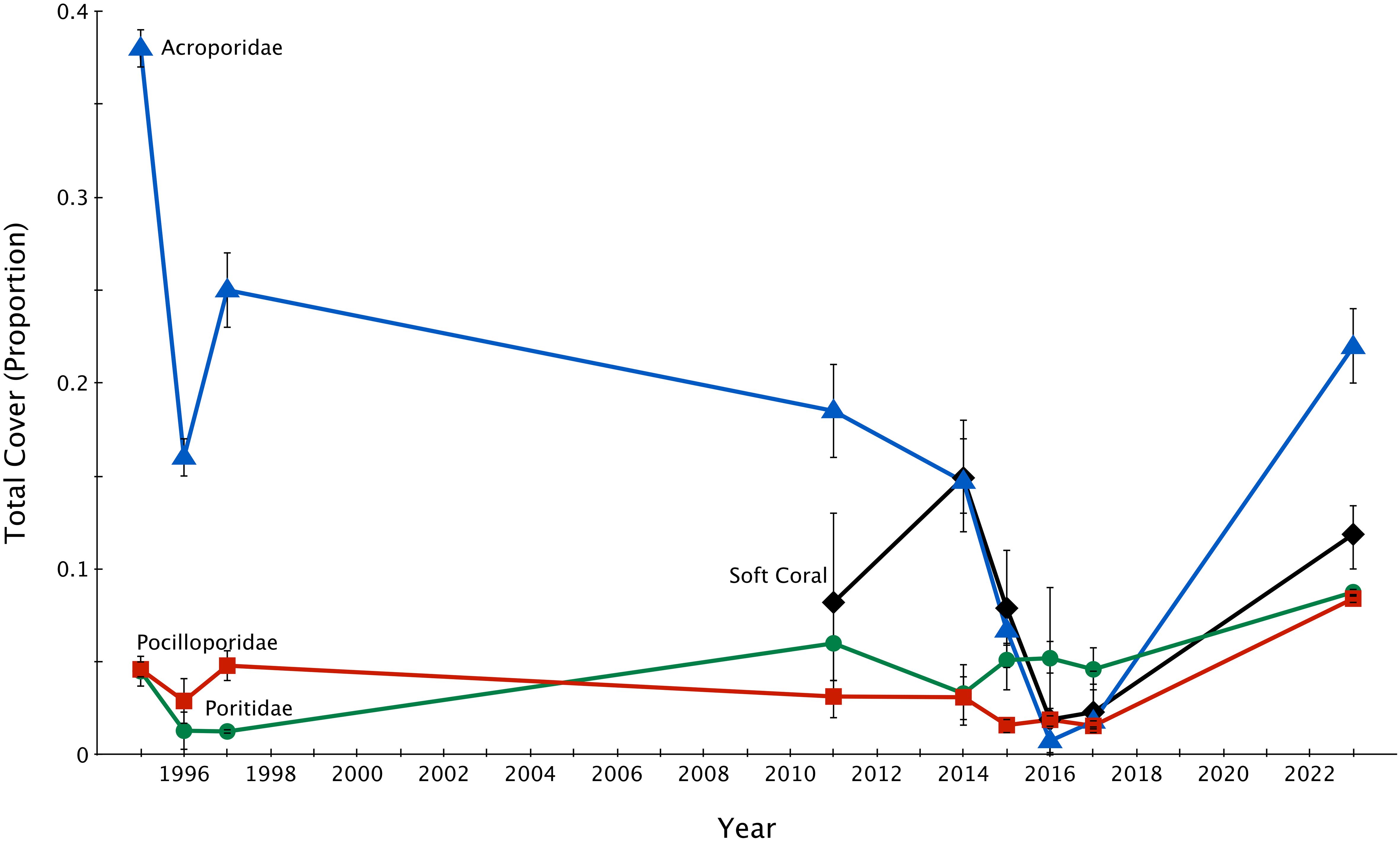
Figure 3. Proportion of soft coral and dominant hard coral families (Acroporidae, Poritidae, and Pocilloporidae) cover ± 1 SE across Lizard Island reefs from 1995-2023. 1995-2017 data sourced from Madin et al., 2018.
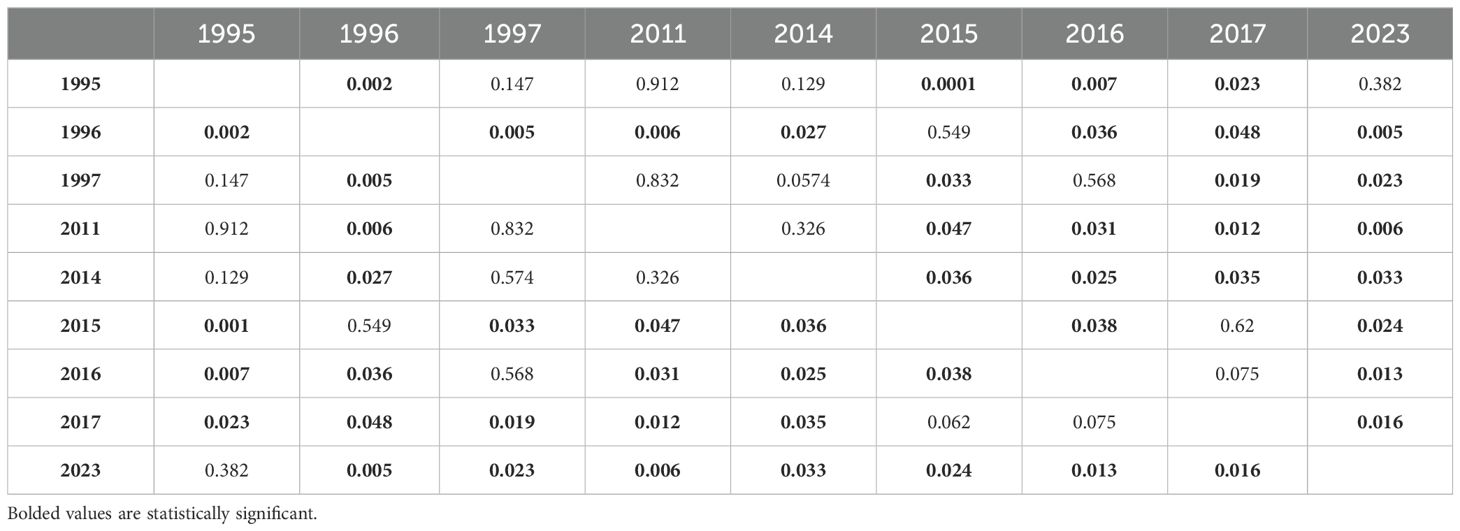
The grand mean of live coral cover significantly declined from 2014-2017 (mid-disturbance) but rose significantly higher by 2023 (six years post-disturbance) to rise above the pre-disturbance grand mean of live coral cover (Figure 4). The grand mean of family richness declined from 2014-2017 (mid-disturbance) and recovered significantly by 2023, but not to the 2011 or 2014 (immediate pre-disturbance) grand means of family richness (Figure 5). Family richness across all sites improved by 2023 (4.0 ± 0.11; grand mean ± 1 se); however, Lizard Island reefs have yet to reach their pre-disturbance family diversity (4.77 ± 0.58 in 2014).
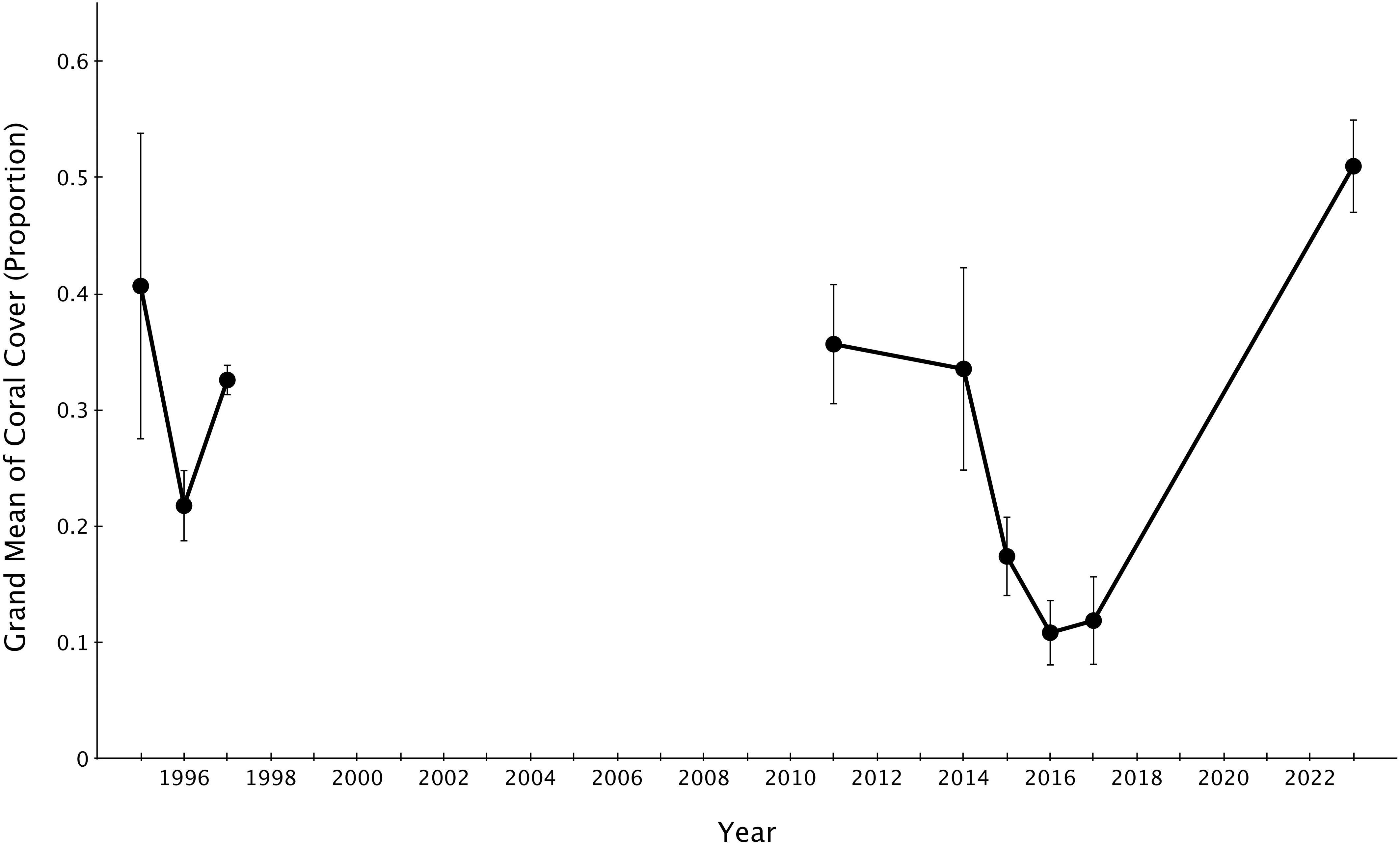
Figure 4. Grand means ± 1 SE of proportion of live coral cover across Lizard Island reefs from 1995-2023. 1995-2017 data sourced from Madin et al., 2018.
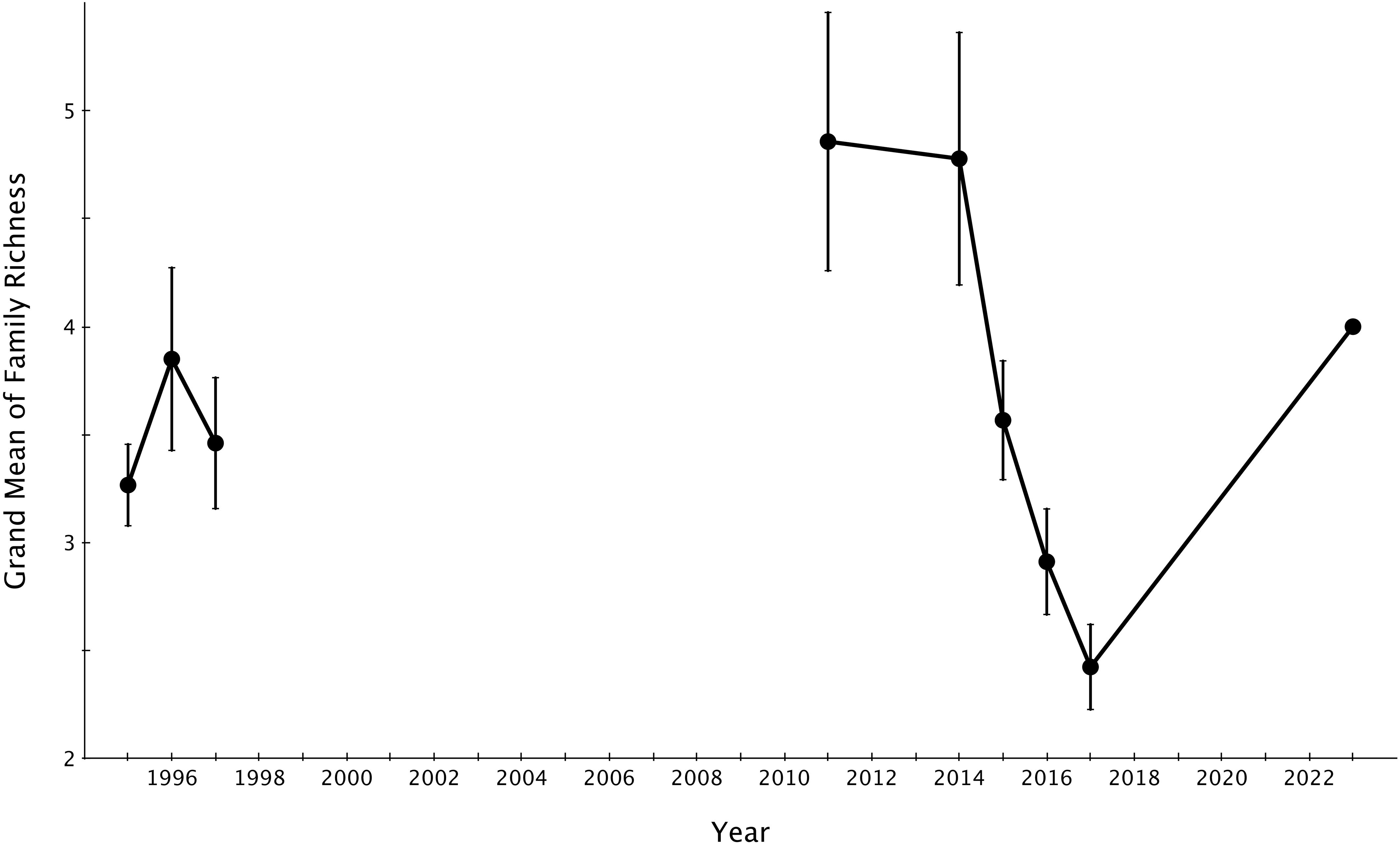
Figure 5. Grand means ± 1 SE of family richness across Lizard Island reefs from 1995-2023. 1995-2017 data sourced from Madin et al., 2018.
Discussion
Limitations: A coral-centric assessment
My study focused on the change of aggregate living coral cover at Lizard Island, and as such it speaks to the dynamics of the foundational ecosystem engineers of coral reef systems. That said, it is important to note that while these 2023 data characterize current reef conditions, I did not sample fish, other invertebrates, or other ecosystem dimensions. My insights about overall reef condition are driven by aggregate coral cover.
North-south trends
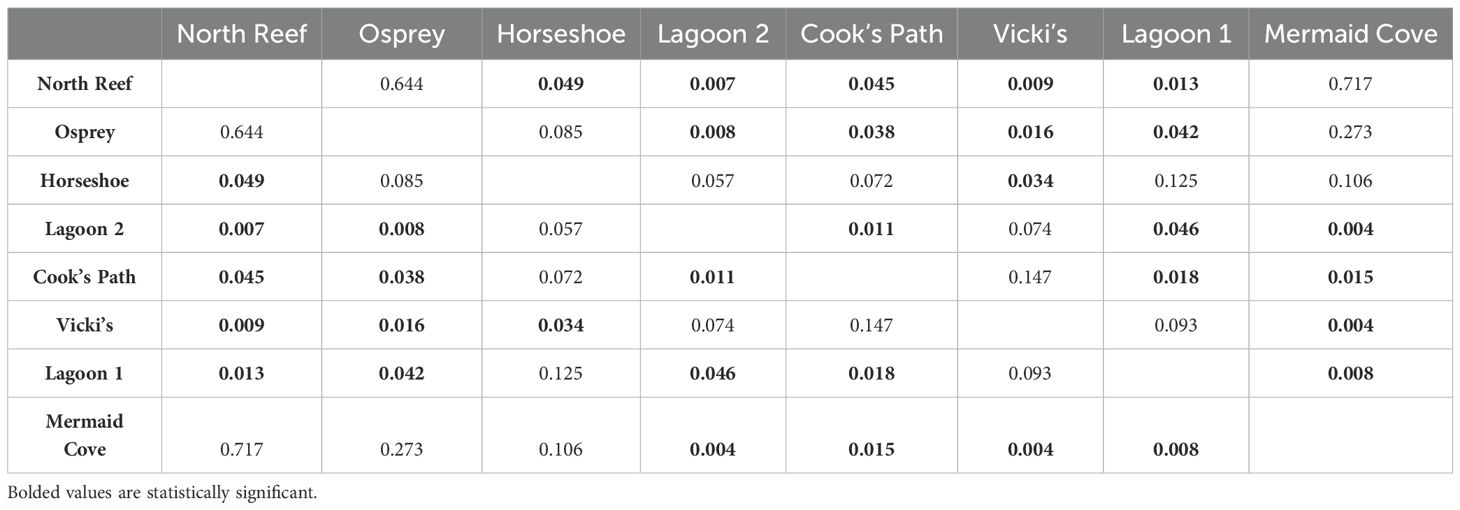
Higher coral recovery occurred in the more northerly reefs sites. This apparent north-south latitudinal gradient of recovery may in part be driven by the various wind and wave conditions across the island. The prevailing Southeast Trade Winds put the southeast-facing portion of Lizard Island under the most constant physical stress. While this study was unable to include previously-surveyed sites on the east side of the Island due to logistical constraints, the physical protection via South Island, Palfrey Island, and the exterior rim of the lagoon provide relatively calmer conditions for marine growth. The difference in wave action and nutrient availability between each site, influenced by physical barriers, also plays a role in which marine growth is best-adapted to each site. Wave action on a better-protected reef is relatively gentle and ideal for less rigid/robust life forms to settle and grow. Partially protected reefs with moderate wave action have more potential to be damaged but also are afforded a suite of potential benefits. First, there can be better circulation of sediment in the water column (Hench et al., 2008), which allows for more sunlight availability. Second, such sites allow sub-optimal conditions for potential hard coral competitors (i.e. macroalgae, soft corals) and provide hard corals a greater chance of successfully recruiting and establishing upon that reef. The most protected reef sites experience less water column circulation and more nutrient buildup, favoring competitors of hard corals better adapted to rapid growth who often quickly block otherwise accessible sunlight incident on the reef surface (D’Angelo and Wiedenmann, 2014). This is pivotal in creating a phase shift away from a primarily coral-based substrate and greatly obstructs further coral growth.
It seems that these gross differences in oceanographic conditions (moderate vs strong protections) may be encouraging potential phase shifts of these reefs. Sites with stronger protection, particularly lagoon sites, see lower rates of coral recovery (Baird and Hughes, 2000). Lagoon 1 and Lagoon 2 were in some of the calmest wave conditions I observed across Lizard Island in 2023. These quiescent sites appear to afford more ideal conditions for macroalgae to outcompete hard corals for space and ultimately for light once their thalli grow tall enough to overstory surrounding reef surfaces, reducing incident sunlight in their shadows. Vicki’s and Horseshoe, despite being protected by Palfrey Island, are still on the edge of the shallow reef habitat, and as such experience much more wave action. Osprey and Cook’s Path face similar conditions. Mermaid Cove and North Reef sit on the northern tip of Lizard Island where they receive a heavy amount of wave action and, despite being very protected from the southeast by the main body of the island, had the lowest percent cover of macroalgae and soft corals. In short, the degree of gross oceanographic protection seems to explain why Mermaid Cove and North Reef were the most recovered, and Lagoon 1 and Lagoon 2 the least-recovered, and the trend in the intermediary sites.
Coral composition
Equally noteworthy is that the bulk of the hard coral cover recorded was of the family Acroporidae. Acroporids are cosmopolitan reef-building corals, often the most common stony coral group across the expanse of Indo-Pacific reefs (Baird and Hughes, 2000). Past surveys (from 1995–2017) found the genus Acropora remained the most abundant taxon from 1995 through to 2014, then declined by 95% from 2014 to 2017, being one of the least abundant taxa post-disturbance (Madin et al., 2018). The two most well-recovered sites, Mermaid Cove and North Reef, had Acropora consisting of 80% of the hard corals identified. For reasons to be determined, Acropora seems to be on track to again become the most abundant hard coral taxon at Lizard Island, as it was in the 1995–2014 pre-disturbance area. The less recovered reefs, however, did not experience the same dominance of Acropora species. Instead, Porites was most dominant at Lagoon 2 and Pocillopora was most dominant at Lagoon 1 in 2023.
Acroporids tend to be a dominant family on shallow reefs due to their fast growth rate and structural advantage that allows them to outcompete understory growth (Baird and Hughes, 2000). However, the overabundance of Acropora on a reef can also have potentially harmful impacts on the resilience of that reef going forward. Acropora are highly susceptible to bleaching events (Marshall and Baird, 2000). Past bleaching events of 1998 and 2002 did not diminish the intensity of bleaching events in 2016 (Hughes et al., 2017), and those bleaching events saw a huge die-off of tabular and staghorn corals (Hughes et al., 2018), some of which belong to the Acropora family. Acroporids have also been documented to be among the preferred prey of Crown-of-Thorns starfish at Lizard Island (Pratchett, 2010). In a more general sense, less diverse reefs can suffer greatly from disease outbreaks–in the case of Acropora, Acroporid White Syndrome (Roff et al., 2011) could culminate in massive disturbance events due to the prevalence of Acropora at these recovering sites.
Reef resilience
With coral reefs declining globally (Wilson et al., 2006), many extant reef-dwelling species are at risk of becoming endangered or locally or regionally extinct (Sherman et al., 2023; Coker et al., 2009). With climate change bringing more frequent and intense disturbance events (Jentsch and Beierkuhnlein, 2008), communities of reef-dwelling species are likely to continue declining without updating current management decisions (van Woesik et al., 2022). Ideal management decisions should focus on an “ecosystem-based approach” (Harvey et al., 2018) that takes a more holistic perspective of all aspects of coral reef communities.
Species diversity has been found to be 5.7x more essential to maximizing biomass compared to other ecological and environmental influences (Lefcheck et al., 2021). This suggests coral reefs require a variety of reef-building corals for continued recovery of habitat health and biological diversity. In terms of coral cover, even the most well-recovered reefs on Lizard Island need to contain a relatively more diverse range of reef-building corals to support the benthic and mid-water species that not only rely on available coral reef habitat but could beneficially augment their recovery (Schneider et al., 2011; Harvey et al., 2018).
As coral reef habitats continue to degrade in the long term, many species that rely on such habitats are likely to suffer heavy population decline (Coker et al., 2009). Limited habitat complexity–combined with smaller, less reproductively-successful adult populations of reef-dwelling species–also inhibits recruitment to other reef habitats, which reduces adult replenishment and hinders reef habitat recovery overall (Roth et al., 2018). Recent research has found that among dominant reef-building corals, Acropora recovery and growth is heavily influenced by larval connectivity (Gouezo et al., 2019). Future studies at my Lizard Island sites could provide a more in-depth understanding of how significant a role larval connectivity plays in overall reef recovery.
Climate-exacerbated disturbances
Disturbance events are growing in frequency and intensity across many of the world’s ecosystems (Buma and Schultz, 2020; Iwasaki and Noda, 2018). A better understanding of the impact of such disturbances on various ecosystems not only enhances understanding of the particular system in question, but also contributes to understanding larger global-scale trends and multi-factor processes (Gough et al., 2024). For example, climate-exacerbated disturbances have altered fire return rates in temperate forests (Dale et al., 2001), frequency of drought in tropical rainforests (Tao et al., 2022), rate of sea level rise in mangrove forests (Carugati et al., 2018), and apparent phase shifts in kelp forests (Smith et al., 2016).
Coral reefs are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth (Moberg and Folke, 1999), and their decline is likely to have direct and indirect effects on species diversity, standing biomass, and an array of ecosystem services globally relied on by coastal communities (Hoegh-Guldberg, 1999). There is particular concern around decreased biodiversity driving reduced ecosystem productivity (Rogers et al., 2018) as well as ecosystem resistance to future disturbances (Shin et al., 2022). As coral reefs and other essential ecosystems continue to experience the pressures of climate change, it is crucial that we continue to monitor these changes, especially in the case of disturbances. Changing climate conditions, in combination with other anthropogenic disturbances, are gradually changing the assemblage of coral reefs and their inhabitants (Vanwonterghem and Webster, 2020). While some species or groups are more resistant under such new conditions, others struggle to recover at the same rate (Miller et al., 2011). The impacts of such changes will remain uncertain without further monitoring of coral reefs or other productive systems, as described above, to provide more clarity on these community-wide shifts and how they may change conservation or management strategies in the future.
Conclusion
Acropora dominance relative to total live coral cover may turn out to be a useful metric for forecasting future near-term condition of impacted reefs on Lizard Island. To the extent reef managers can influence reef communities, they should consider emphasizing efforts which promote restoration or recruitment of Acroporids. Recovering these key reef builders seems necessary to recover historic conditions as fast as possible. Before the four-year period of consecutive disturbance events, most Lizard Island reefs were relatively live-coral rich, typically with >40% coral cover (Done et al., 2010; Johns et al., 2014), but by late 2017 many were close to 4% (Madin et al., 2018). Between the intense patches of physical damage from the cyclones and the more uniform impact of the bleaching events, these reefs were devastated, with none of the eight study sites reaching more than 20% total coral cover (Madin et al., 2018). After six years of relatively calmer conditions with fewer conspicuous disturbances, living coral cover at the study sites improved by various margins between 18.4 ± 0.6 to 59.9 ± 5.3%, with many sites on the higher end of that spectrum. Aggregate coral cover across reefs at Lizard Island has recovered since the wake of disturbances ending in 2017, with their rate of recovery closely related to the physical environment they inhabit. More regular (annual or biennial) monitoring of each of these sites could also better inform scientific understanding of the long-term recovery of Lizard Island reefs in the face of continual disturbances at the hands of cyclones, bleaching, Crown-of-Thorns Starfish, and other environmental pressures.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
GA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to Lizard Island Research Station staff for providing facilities and transportation integral to data collection for this project. In addition, thank you to Dr. Joshua S. Madin for providing essential coral cover data from 1995-2017 at Lizard Island. My undergraduate research was generously supported by a Frost Scholarship via the William & Linda Frost Fund in the Bailey College of Science and Mathematics at California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alvarez-Filip L., Dulvy N. K., Gill J. A., Côté I. M., Watkinson A. R. (2009). Flattening of Caribbean coral reefs: region-wide declines in architectural complexity. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 276(1669), 3019–3025. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.0339
Baird A. H., Hughes T. P. (2000). Competitive dominance by tabular corals: an experimental analysis of recruitment and survival of understorey assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 251, 117–132. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00209-4
Berzunza-Sanchez M. M., del Carmen Gomez Cabrera M., Pandolfi J. M. (2013). Historical patterns of resource exploitation and the status of Papua New Guinea coral reefs1. Pacific Sci. 67, 425–405. doi: 10.2984/67.3.9
Buma B., Schultz C. (2020). Disturbances as opportunities: learning from disturbance-response parallels in social and ecological systems to better adapt to climate change. J. Appl. Ecol. 57, 1113–1235. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.13606
Carugati L., Gatto B., Rastelli E., Lo Martire M., Coral C., Greco S., et al. (2018). Impact of mangrove forests degradation on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Rep. 8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31683-0
Cinner J. E., McClanahan T. R., Daw T. M., Graham N. A.J., Maina J., Wilson S. K., et al. (2009). Linking social and ecological systems to sustain coral reef fisheries. Curr. Biol. 19, 206–125. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.11.055
Coker D. J., Pratchett M. S., Munday P. L. (2009). Coral bleaching and habitat degradation increase susceptibility to predation for coral-dwelling fishes. Behav. Ecol. 20, 1204–1105. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arp113
D’Angelo C., Wiedenmann J. (2014). Impacts of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: new perspectives and implications for coastal management and reef survival. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustainability 7, 82–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.11.029
Dale V. H., Joyce L. A., McNulty S., Neilson R. P., Ayres M. P., Flannigan M. D., et al. (2001). Climate change and forest disturbances: climate change can affect forests by altering the frequency, intensity, duration, and timing of fire, drought, introduced species, insect and pathogen outbreaks, hurricanes, windstorms, ice storms, or landslides. BioScience 51, 723–734. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0723:CCAFD]2.0.CO;2
Done T. J., DeVantier L. M., Turak E., Fisk D. A., Wakeford M., van Woesik R. (2010). Coral growth on three reefs: development of recovery benchmarks using a space for time approach. Coral Reefs 29, 815–833. doi: 10.1007/s00338-010-0637-y
Gardner T. A., Côté I. M., Gill J. A., Grant A., Watkinson A. R. (2005). Hurricanes and Caribbean coral reefs: impacts, recovery patterns, and role in long-term decline. Ecology 86, 174–845. doi: 10.1890/04-0141
Gilmour J. P., Smith L. D., Heyward A. J., Baird A. H., Pratchett M. S. (2013). Recovery of an isolated coral reef system following severe disturbance. Sci. (New York N.Y.) 340(6128), 69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.1232310
Gouezo M., Golbuu Y., Fabricius K., Olsudong D., Mereb G., Nestor V., et al. (2019). Drivers of recovery and reassembly of coral reef communities. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 286(1897), 20182908. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.2908
Gough C. M., Buma B., Jentsch A., Mathes K. C., Fahey R. T. (2024). Disturbance theory for ecosystem ecologists: A primer. Ecol. Evol. 14. doi: 10.1002/ece3.11403
Harvey B. J., Nash K. L., Blanchard J. L., Edwards D. P. (2018). Ecosystem-based management of coral reefs under climate change. Ecol. Evol. 8, 6354–6685. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4146
Hench J. L., Leichter J. J., Monismith S. G. (2008). Episodic circulation and exchange in a wave-driven coral reef and lagoon system. Limnology Oceanography 53, 2681–2694. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.6.2681
Hoegh-Guldberg O. (1999). Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world’s coral reefs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 50, 839–866. doi: 10.1071/mf99078
Hughes T. P., Anderson K. D., Connolly S. R., Heron S. F., Kerry J. T., Lough J. M., et al. (2018). Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the anthropocene. Science 359, 80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.aan8048
Hughes T. P., Connell J. H. (1999). Multiple stressors on coral reefs: A long -term perspective. Limnology Oceanography 44, 932–940. doi: 10.4319/lo.1999.44.3_part_2.0932
Hughes T. P., Kerry J. T., Álvarez-Noriega M., Álvarez-Romero J. G., Anderson K. D., Baird A. H., et al. (2017). Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 543, 373–377. doi: 10.1038/nature21707
Iwasaki A., Noda T. (2018). A framework for quantifying the relationship between intensity and severity of impact of disturbance across types of events and species. Sci. Rep. 8, 7955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19048-5
Jentsch A., Beierkuhnlein C. (2008). Research frontiers in climate change: effects of extreme meteorological events on ecosystems. Comptes Rendus Geoscience Ecosystèmes événements climatiques extrêmes 340, 621–628. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2008.07.002
Johns K., Osborne K., Logan M. (2014). Contrasting rates of coral recovery and reassembly in coral communities on the great barrier reef. Coral Reefs 33. doi: 10.1007/s00338-014-1148-z
Jones G. P., McCormick M. I., Srinivasan M., Eagle J. V. (2004). Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 101, 8251–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401277101
Laurans Y., Pascal N., Binet T., Brander L., Clua E., David G., et al. (2013). Economic valuation of ecosystem services from coral reefs in the South Pacific: taking stock of recent experience. J. Environ. Manage. 116, 135–144. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.11.031
Lefcheck J. S., Edgar G. J., Stuart-Smith R. D., Bates A. E., Waldock C., Brandl S. J., et al. (2021). Species richness and identity both determine the biomass of global reef fish communities. Nat. Commun. 12, 6875. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27212-9
Licuanan W. Y., Robles R., Reyes M. (2019). Status and recent trends in coral reefs of the Philippines. Mar. pollut. Bull. 142, 544–550. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.013
Madin J. S., Baird A. H., Bridge T. C.L., Connolly S. R., Zawada K. J.A., Dornelas M. (2018). Cumulative effects of cyclones and bleaching on coral cover and species richness at Lizard Island. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 604, 263–268. doi: 10.3354/meps12735
Marshall P. A., Baird A. H. (2000). Bleaching of corals on the Great Barrier reef: differential susceptibilities among taxa. Coral Reefs 19, 155–163. doi: 10.1007/s003380000086
Miller A. D., Roxburgh S. H., Shea K. (2011). How frequency and intensity shape diversity–disturbance relationships. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 5643–5485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018594108
Moberg F., Folke C. (1999). Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Economics 29, 215–335. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00009-9
Mumby P. J., Hastings A., Edwards H. J. (2007). Thresholds and the resilience of Caribbean coral reefs. Nature 450(7166), 98–101. doi: 10.1038/nature06252
Pratchett M. S. (2010). Changes in Coral Assemblages during an Outbreak of Acanthaster Planci at Lizard Island, Northern Great Barrier Reef, (1995–1999). Coral Reefs 29, 717–725. doi: 10.1007/s00338-010-0602-9
Roff G., Kvennefors E.C. E., Fine M., Ortiz J., Davy J. E., Hoegh-Guldberg O. (2011). The ecology of ‘Acroporid white syndrome’, a coral disease from the southern great barrier reef. PLoS One 6, e268295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026829
Rogers A., Blanchard J. L., Mumby P. J. (2018). Fisheries productivity under progressive coral reef degradation. J. Appl. Ecol. 55, 1041–1495. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.13051
Roth F., Saalmann F., Thomson T., Coker D. J., Villalobos R., Jones B. H., et al. (2018). Coral reef degradation affects the potential for reef recovery after disturbance. Mar. Environ. Res. 142, 48–58. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.09.022
Santavy D. L., Horstmann C. L., Sharpe L. M., Yee S. H., Ringold P. (2021). What is it about coral reefs? Translation of ecosystem goods and services relevant to people and their well-being. Ecosphere (Washington D.C) 12, 1–275. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.3639
Schneider K., Silverman J., Woolsey E., Eriksson H., Byrne M., Caldeira K. Potential influence of sea cucumbers on coral reef CaCO3 budget: A case study at one tree reef (Accessed September 3, 2024).
Sherman C.S., Simpfendorfer C. A., Pacoureau N., Matsushiba J. H., Yan H. F., Walls R. H.L., et al. (2023). Half a century of rising extinction risk of coral reef sharks and rays. Nat. Commun. 14, 15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35091-x
Shin Y.-J., Midgley G. F., Archer E. R.M., Arneth A., Barnes D. K.A., Chan L., et al. (2022). Actions to halt biodiversity loss generally benefit the climate. Global Change Biol. 28, 2846–2874. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16109
Smith J. G., Malone D., Carr M. H. (2016). Consequences of kelp forest ecosystem shifts and predictors of persistence through multiple stressors. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 291, 20232749. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.2749
Tao S., Chave Jérôme, Frison P.-L., Le Toan T., Ciais P., Fang J., et al. (2022). Increasing and widespread vulnerability of intact tropical rainforests to repeated droughts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 119, e2116626119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116626119
van Woesik R., Shlesinger T., Grottoli AndréaG., Toonen R. J., Vega Thurber R., Warner M. E., et al. (2022). Coral-bleaching responses to climate change across biological scales. Global Change Biol. 28, 4229–4250. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16192
Vanwonterghem I., Webster N. S. (2020). Coral reef microorganisms in a changing climate. iScience 23, 1009725. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100972
Wakeford M., Done T. J., Johnson C. R. (2008). Decadal trends in a coral community and evidence of changed disturbance regime. Coral Reefs 27, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s00338-007-0284-0
Wilson S. K., Graham N. a. J., Pratchett M. S., Jones G. P., Polunin N. V.C. (2006). Multiple disturbances and the global degradation of coral reefs: are reef fishes at risk or resilient? Global Change Biol. 12, 2220–2345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01252.x
Keywords: disturbance ecology, biodiversity loss, coral recovery, habitat resilience, coral bleaching
Citation: Anderson GD (2025) Recovery of coral cover at Lizard island Australia 6 years post-disturbance. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1509455. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1509455
Received: 11 October 2024; Accepted: 24 December 2024;
Published: 21 January 2025.
Edited by:
Charles Alan Jacoby, University of South Florida St. Petersburg, United StatesReviewed by:
Ernesto F. Weil, University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez, Puerto RicoSanqiang Gong, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Anderson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gabriel Dax Anderson, Z2FicmllbGRheDM4QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Gabriel Dax Anderson
Gabriel Dax Anderson