- 1School of Economics, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China
- 2School of International Business, Dalian Minzu University, Dalian, China
Introduction: China’s marine cities have reached a critical juncture after 40 years of rapid development. In this new stage, where internal circulation is the main focus, there is a need to enhance the internal circulation capabilities of these cities and unleash their full economic potential. This paper aims to explore the positioning and improvement path of marine cities in China's internal circulation network, and fully unleash the development potential of marine cities.
Methods: Based on data from 284 prefecture-level cities in China, this paper constructs the social network of China's urban internal circulation with the help of the modified gravity model, and explores the conditional configuration of the improvement of the status of marine cities in internal circulation network by using the fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) method.
Results and discussion: (1) The development level of marine cities' internal circulation can be categorized into three tiers, led by Shanghai. The development gap between the 14 marine cities has gradually widened over recent years. (2) Chinese marine cities can be divided into three groups in the topological structure of China's urban internal circulation network: core, periphery, and edge, with Shanghai being the core "bridge" in the network. The traditional advantages of some northern economically strong cities in the construction of the internal circulation network have gradually been lost, and many marine cities have seen their leadership and control over the internal circulation network significantly weakened. (3) No single factor is a necessary condition for achieving a high-level status of marine cities in the internal circulation network. (4) The four conditional variables of demand side, supply side, industrial linkage and inter-regional integration have two sufficient condition configurations to enhance the status of marine cities in internal circulation network. Among them, the "industry-regional integration"-dominated configuration with the core of unblocking the bottlenecks of the internal circulation is the main path.
1 Introduction
Since the reform and opening up, especially after joining the WTO, China has actively participated in international trade, achieving rapid economic growth through external circulation. This process not only accelerated industrialization but also led to significant technological advancements and industrial upgrading. While promoting China to become the “world factory”, the international external circulation has also helped China accumulate a large amount of foreign exchange reserves, enhanced China’s international economic status and ability to reduce external risks. However, in recent years, both domestic and international environments have shifted dramatically. China’s traditional way of participating in the international circulation has also faced new challenges.
Internally, the role of export trade, one of the key drivers of China’s economic growth, has gradually weakened in importance. While the contribution of net exports to GDP peaked at around 5-10% in the early 21st century, by 2023, this figure had dropped to -11.4%. Meanwhile, consumption and investment now contribute 82.5% and 28.9%, respectively, indicating that strong domestic demand, driven by consumption and investment, has become the primary force driving China’s economic growth. Externally, factors such as the global financial crisis, sluggish recovery, and recession in certain countries have weakened external demand. Moreover, escalating trade tensions, particularly the US-China trade war, and geopolitical issues have further increased uncertainty in China’s external economic environment. In addition, efforts by Western countries to repatriate supply chains, along with export controls and technological blockades aimed at China, have created challenges, particularly in key areas of production. Against this backdrop, the development of internal circulation has emerged as a strategic choice for China to address both internal and external economic challenges and ensure long-term stable growth. This approach not only aligns with the need for economic restructuring domestically but also serves as an inevitable response to the changing external environment.
In May 1984, China announced the establishment of 14 marine cities, including Shanghai, Guangzhou, Wenzhou, Fuzhou, Qingdao, Yantai, Tianjin, Dalian, Qinhuangdao, Lianyungang, Nantong, Ningbo, Zhanjiang, and Beihai. Marine cities have achieved fruitful results in the early stage of reform and opening up, and they are the important basement of China’s early urban opening up. The function of the establishment of marine cities is not only to form a frontier position for China’s opening up, but also to give them a full play to the leading role of domestic economic development, and then become the central hub of the domestic and foreign affairs and an important node for internal and external circulation (Liu et al., 2022). After 40 years of development, these marine cities have concentrated a large number of high-end industries and innovation resources, and are an important source of power for China’s economic growth. In addition, the residents of marine cities have higher incomes and strong consumption capacity, which is an important force to promote domestic demand. More importantly, marine cities have developed ports and logistics systems, and have the technical infrastructure for the construction of an internal circulation network. In addition, marine cities are both core areas of domestic circulation and international circulation. They can continue to play a bridging role in international trade while promoting China’s internal economic circulation. Therefore, this paper takes marine cities as an example to examine the path to improve the level of internal circulation and the status of the internal circulation network, so as to expand technology and resources to inland areas from marine cities through internal circulation, and help to accelerate the circulation and the upgrading of China’s economy.
Furthermore, marine cities have concentrated a large number of high-end industries and innovative resources, which can have a strategic radiation on inland cities through internal circulation. First of all, marine cities rely on their superior transportation conditions, especially the high accessibility of ports, to maintain close connectivity with the global market. Under the internal circulation model, marine cities have become hubs for the transportation of resources and products to inland, significantly promoting the extension of the industrial chain and the construction of supporting systems in the surrounding inland cities. Secondly, the industrial cluster effect of marine cities provides the main driving force for economic development in inland cities. Through the “enclave economy” model, inland cities can take over some manufacturing links from marine areas and achieve effective flow and allocation of resources, thereby attracting foreign investment and increasing local employment and economic vitality. In addition, the pioneering development of marine cities in the fields of technological innovation and digital economy generates technological spillover effects through the internal circulation network, assisting the technological upgrading and industrial transformation of inland cities. Finally, marine cities are not only production centers, but also important supports for the domestic consuming market. Under the internal circulation model, expanding domestic demand is the core strategy to promote economic growth. The escalating consumer demand in marine cities has also promoted innovative adjustments on the supply side in inland cities to adapt to growing market demand and support overall economic development. In the future, with the further deepening of regional integration strategies, marine cities will continue to play a key role in the internal circulation, providing economic power and development paths for inland cities. Therefore, this paper examines the positioning and enhancement path of marine cities in China’s internal circulation network, using the development of marine cities as a starting point, and expanding technology and resources to inland cities through China’s internal circulation network to help the circulation and upgrading of China’s overall economy.
The internal circulation requires all regions to break down barriers and establish extensive and deep economic connections. Therefore, there are complex network characteristics in space and spatial flow is the underlying logic of the smooth internal circulation. The spatial circulation of economic activities shapes the integrated Chinese internal circulation network. Therefore, study the internal circulation from the perspective of social network is important. However, there are few literatures that explore the spatial correlation characteristics of the internal circulation from the perspective of social network. There is a lack of interpretation of the spatial network structure and the role of individual cities under internal circulation. This paper uses 284 prefecture-level cities data in China, constructs the Chinese internal circulation network based on the modified gravity model, and explores the spatial topological characteristics and the conditional configuration for improving network status of 14 marine cities in China’s internal circulation network. The marginal contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) Based on Marx’s social reproduction theory, we construct an internal circulation evaluation index system and uses Chinese prefecture-level data as samples, which helps to evaluate the internal circulation level’s status and changes. (2) Based on the modified gravity model, we construct the Chinese prefecture-level internal circulation network and study the internal circulation from spatial and social network dimensions. (3) Based on the configuration analysis of fuzzy qualitative-set comparative analysis (fsQCA), we demonstrate the factors that can affect marine cities’ internal circulation, which is helpful for marine cities to establish new development strategies under internal circulation.
2 Literature review
2.1 Definition and measurement of the internal circulation
The concept of economic “internal circulation” is widely agreed upon in current research, referring to economic activities and processes that occur within a country. Several scholars have defined it as the organic integration and seamless connection of production, distribution, circulation, and consumption (Liu, 2020). Others interpret internal circulation as an internal loop that emphasizes domestic markets, from supply to demand (Tang et al., 2020), asserting that it begins and ends with the fulfillment of domestic demand (Chen et al., 2022).
Under the context of the dual circulation strategy, many literatures have conducted discussions on the internal circulation. As the first country to propose a dual circulation strategy, China defines the dual circulation as a coordinated development system of internal and external circulation, and further verifies the core position of the internal circulation in the strategy through the Marxist input-output analysis model (Javed et al., 2023). Based on the assessment of the current rising uncertainty in the global economy, the literature points out that the development of the internal circulation is crucial to achieving sustainable growth of China’s economy, upgrading the industrial structure (Lin and Wang, 2021) and resisting external risks. In addition, the internal circulation is considered to be a key path to cope with the economic impact brought about by the trend of deglobalization, which once again emphasizes the necessity and urgency of promoting the development of the internal circulation economy (Shi et al., 2024).
Regarding the measurement of the internal circulation, current research mainly includes the following three aspects. From the perspective of qualitative analysis, some literature measures the level of internal circulation through different indicators based on the definition of internal circulation, and constructs an internal circulation evaluation index system for Chinese different provinces including consumption and production (Pan and Long, 2024; Dai and Hua, 2024). From the perspective of quantitative analysis, some literature measures the internal circulation level by decomposing GDP. Simple measurements such as using the proportion of domestic investment and consumption in gross domestic product (GDP) (Qian and Pei, 2022), or using input-output tables to further decompose GDP through the contribution rate of different behaviors (Xue and Lu, 2023), or decomposing GDP based on the global value chain by using domestic and foreign supply and demand data (Huang and Ni, 2021). Some other literatures take the factors of intermediate products into account, and measure the internal circulation level through the value-added decomposition method under the value chain analysis system. At the country level, the international input-output table is used to measure the proportion of internal circulation in different countries (Huang and Ni, 2021; Li, 2021), or based on the international input-output table, the degree of China’s internal circulation level is measured through domestic demand dependence (Chen et al., 2022); at the industry level, by decomposing the global value chain into forward links and backward links to measure different industry’s internal circulation level in China (Chen and Fu, 2022; He et al., 2022); at the regional level, based on the domestic input-output table, the internal circulation is divided into intra-provincial and inter-provincial circulation to measure the degree of circulation’s smoothness (Dai and Hua, 2024) and the mutual influence between different provinces (Jiang and Zhang, 2024).
2.2 Driving factors of the internal circulation
In other literature related to the internal circulation, most of the literature affirms the importance of China’s internal circulation to its economic development (Ni and Tian, 2023; Xue et al., 2024), and find that the degree of internal circulation in different regions and industries in China is different (Jiang and Zhang, 2024; Guang et al., 2023), and prove that the level of internal circulation in various provinces has increased through time (Fang et al., 2023). Regarding the impact of the internal circulation, studies believe that the smooth flow of internal circulation within and between provinces in China can promote the quality of exports (Dai and Hua, 2024), the length of NVC under the internal circulation will reduce the level of China’s economic fluctuations (Wen et al., 2024), and the internal circulation, especially the internal circulation of China, has become the driving force of global economic growth (Xue and Lu, 2023). Regarding the factors affecting the level of internal circulation, literature research believes that supply-side technological progress can promote internal circulation by optimizing the allocation of resources among industries (Jiang and Xu, 2024), the development of the digital economy (Zou et al., 2024) and the establishment of free trade pilot zones (Su et al., 2023) can also promote the circulation of the domestic economy.
Under the background of the dual circulation strategy, relevant literature points out that China’s internal circulation strategy may lead to a slowdown in domestic credit growth (Zhang et al., 2023), but have a positive impact on stock market performance (Shi et al., 2024). Further analysis shows that after the domestic value chain is subdivided into intra-provincial and inter-provincial value chains, the development of the intra-provincial value chain is conducive to promoting employment and labor productivity (Ou and He, 2023). At present, China’s economy is undergoing a transformation from external circulation to internal circulation. In this process, the domestic value chain continues to strengthen due to the continuous improvement of production efficiency and technological innovation, while the share of the global value chain shows a downward trend (Gao et al., 2024).
2.3 Research on the internal circulation of marine cities
Promoting internal circulation in marine cities is vital to the overall success of China’s economic restructuring. Research on marine cities, maritime industries, and marine economy highlights their positive impact on China’s economic growth. Marine cities, by leveraging industrial agglomeration, stimulate export growth and drive economic development through scale of economy (Zhang, 2012). Although there are disparities in the development of different marine cities (Liang et al., 2009), most of the research has focused on national policies and external factors such as open trade policies (Sun et al., 2024), industrial structures within the marine economy (Zhai, 2020), and regional differences in marine production inputs (Sun and Zhu, 2020).
Existing literature has conducted a comparative analysis of the internal and external circulation levels in China’s coastal areas, and believes that the internal circulation level in coastal areas is higher than the external circulation, and is driven by multiple factors such as technological innovation capabilities, per capita income levels, circulation system perfection, marketization process, digitalization level, and financial development level (Wang et al., 2023). However, there is currently a lack of research that systematically analyzes the current status and development trends of the internal circulation of China’s marine cities from a network perspective, and there is also a lack of comparative analysis of the differences in the internal circulation network at the city level. This paper constructs an internal circulation evaluation index system at the city level and deeply analyzes the heterogeneity of the internal circulation development of different marine cities in China and its influencing factors from the perspective of social networks to make up for the shortcomings of existing research.
3 Research design and data description
3.1 Research methods
3.1.1 Combinatorial weighting method
In view of the problems of strengthening the correlation of indicators and generating negative weights in the principal component analysis method (Hu, 2012), this paper adopts the combinatorial weighting method, which is the multiplication of information weight and independence weight, to evaluate the weight of sub-indicators of the internal circulation evaluation indicator system. This method has the excellent characteristics of both and can show the importance of indicators from different angles. At the same time, the comprehensive weight can effectively reduce the negative impact of indicator correlation while reflecting the amount of information and has a better evaluation effect. The information weight is constructed by the entropy weight method in this paper, that is, the information entropy of the indicator is used to weight the information. The basic idea of the independence weight is to normalize the correlation coefficient matrix of the sub-indicators, and then obtain the independence weight vector of the indicator.
3.1.2 Spatial correlation analysis based on modified gravity model
At present, some scholars have used the gravity model to explore the spatial development correlation of economies (Tang et al., 2022; Lin et al., 2022). The gravity model can effectively convert the level of urban internal circulation development (attribute value) into the internal circulation development correlation (gravity value) between cities. Considering the economic distance of urban development, this paper uses the modified gravity model to measure the spatial correlation of China’s urban internal circulation development. The specific formula is:
In the formula, Fij is the internal circulation correlation strength between city i and city j, Mi and Mj are the internal circulation development score of city i and city j. Dij is the geographical distance between city i and city j, which is calculated according to the latitude and longitude information. and are the per capita GDP of city i zand city j from 2010 to 2022, respectively. Kij is the gravitational coefficient, the value of which is 1. According to formula 1, a 284 *284 national urban internal circulation spatial relationship matrix is obtained, and the mean value principle is adopted to binarize all lines of the matrix (Zhao et al., 2021). The matrix row mean value is taken as the threshold value. If F is greater than the row mean, and the value is 1, indicating that there is an internal circulation correlation between the two cities. If F is less than the row mean, and the value is 0, indicating that there is no correlation between the internal circulation development of the two cities.
3.1.3 Social network analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) can break through the analytical limitations of traditional “attribute value” data, conduct a systematic study of “relationship value” data (Márcia and Gama, 2012), and comprehensively describe the network characteristics and relative status of nodes in the integrated network (Serrano and Boguna, 2003). This method has been widely recognized and applied in the research on complex economic relations between regions in recent years. In this paper, social network analysis is used to construct the internal circulation network model of Chinese cities, and the internal circulation network characteristics of 14 marine cities are analyzed through relevant data. Based on the individual network characteristic dimension, the centrality analysis of marine cities is carried out. The centrality is used to represent the importance degree and spatial status of marine cities in China’s internal circulation network. The construction of the internal circulation network model and the analysis of related characteristics in this paper are realized with the help of Gephi and Ucinet 6 software.
3.1.4 Fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis
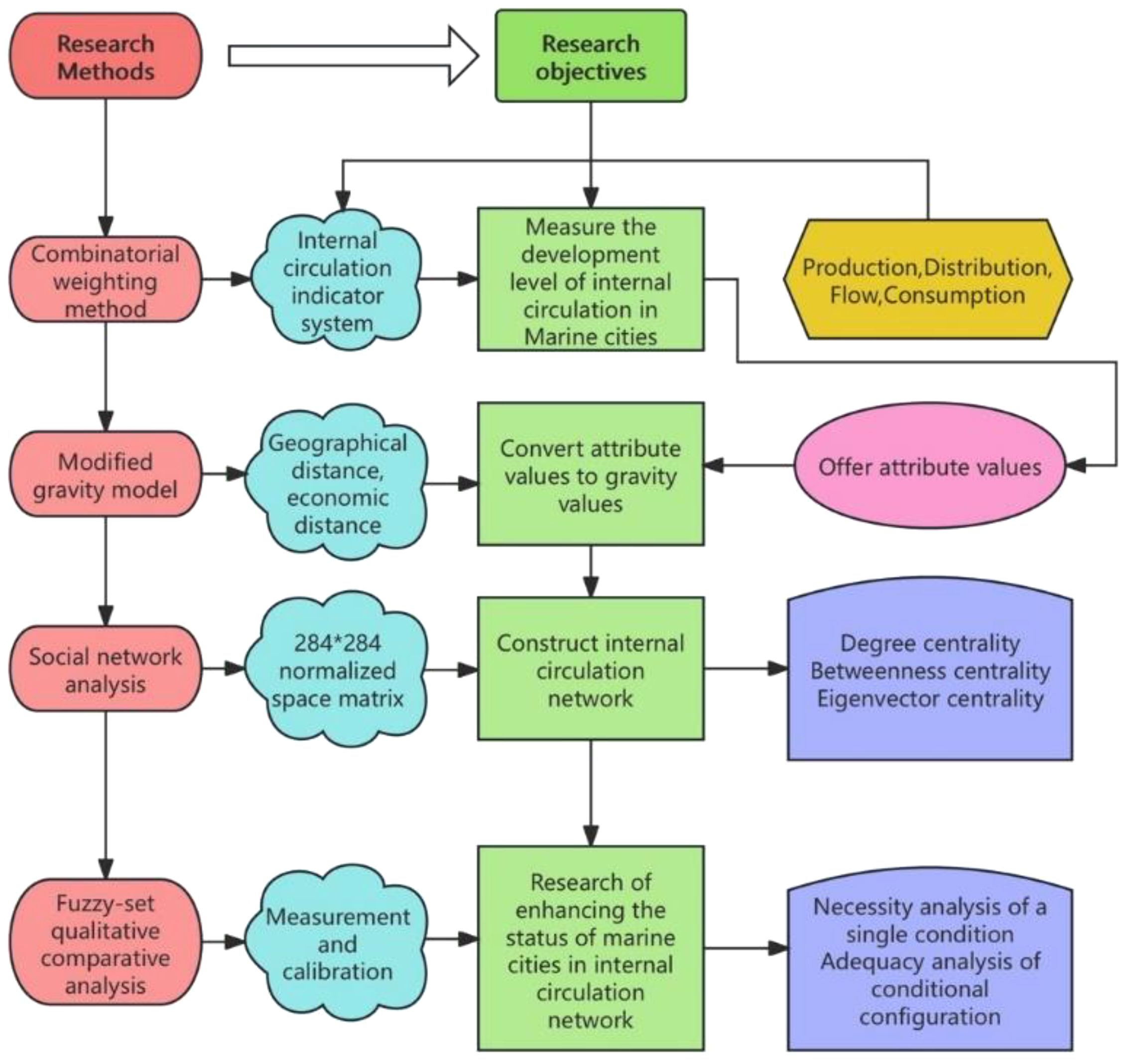
In this paper, we abandon the traditional binary relation statistical method and use the fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) based on the set theory to capture the conditional configuration that affects the circulation network structure of marine city, and then analyze the development mechanism of internal circulation network of marine cities. The main considerations are as follows: Firstly, unlike traditional statistical methods that can only reveal the independent influence of influencing factors or the interactive influence between them, fsQCA believes that there are concurrent multiple causal relationships between variables, which helps to deconstruct the differentiated driving mechanism of the development of the internal circulation network of marine cities. Secondly, although traditional statistical methods can analyze the influencing factors in a unified manner, they are limited to interpreting the degree of variation of the explained variables using the cumulative or substitution relationship of the explanatory variables (Wang et al., 2014). fsQCA can identify the equivalence of different antecedent condition configurations, effectively explore the sufficient and necessary conditions that lead to the results, explore the linkage effect of influencing factors and establish equivalent causal chains (Pappas and Woodside, 2021). Therefore, the fsQCA method is more suitable for exploring the improvement path of the development of the internal circulation network of marine cities. Figure 1 shows the research methods and specific analysis framework used in this paper.
3.2 Internal circulation indicator system
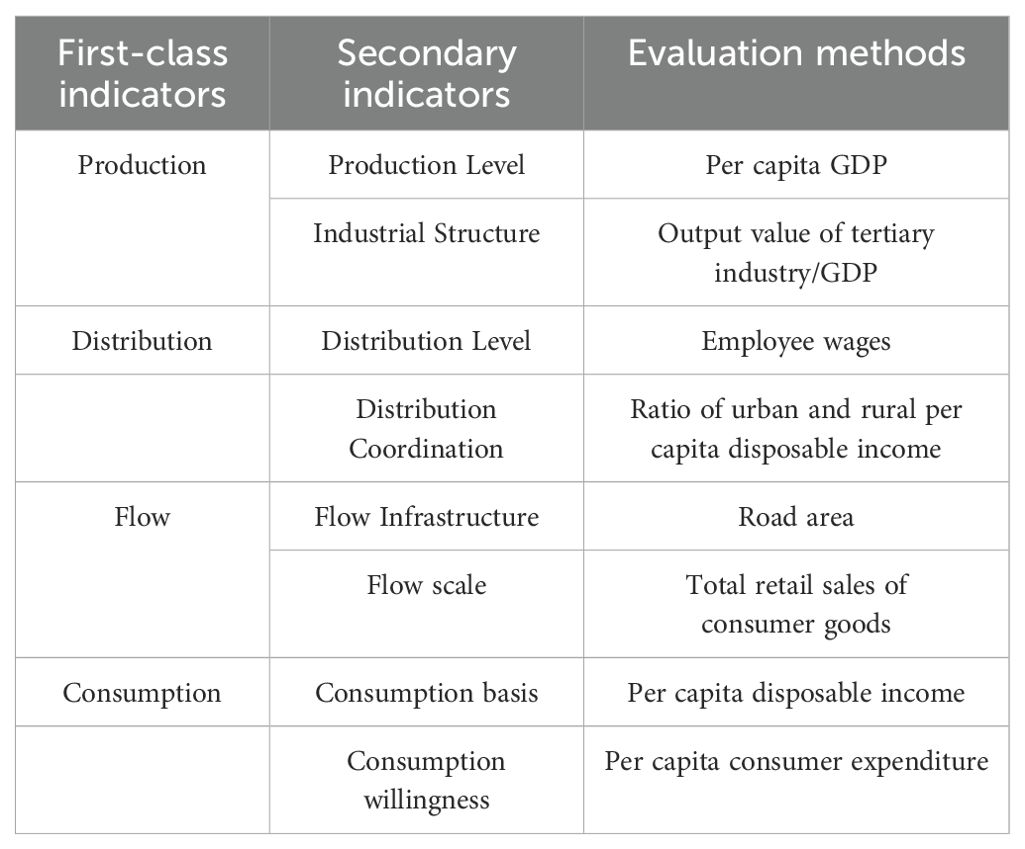
Quesnay, the founder of classical political economy, analyzed the reproduction and circulation of social products in the “Tableau Economique” and pioneered the idea of economic circulation. Later, in “Capital”, Marx interpreted the economic cycle from the perspective of capital circulation and proposed the theory of social reproduction, describing economic circulation activities as four links: production, distribution, flow and consumption. As a continuation of Marx’s theory of social reproduction, this paper measures the level of development of the internal circulation in the four links of production, distribution, flow and consumption, and constructs the evaluation indicator system of internal circulation (Table 1). Production is the origin of the internal circulation, distribution and flow are the bridges that connect the internal circulation, and consumption is the end of the internal circulation and the starting point of a new round of circulation. The internal circulation system is the coordinated planning and organic unity of the four links.
In the link of production, the production level is represented by per capita GDP (Zhao et al., 2014). At the same time, the upgrading of industrial structure can avoid the “path dependence” at the technology level and break through the shackles of development. It is the internal logic of building the internal circulation (Liu, 2020), which is specifically represented by the proportion of the tertiary industry. In the link of distribution, Keynes’s permanent income hypothesis, Friedman’s rational expectations theory and precautionary savings theory all point out that income distribution is the main factor affecting consumption. Therefore, a reasonable income distribution pattern is the core link to release the consumption potential of the domestic market and clear the bottlenecks of the internal circulation. Primary distribution is the basic content of income distribution, and employee wages are the decisive factor of primary distribution (Yi and Chen, 2022). Narrowing the income gap between urban and rural areas is the key to achieving distribution coordination. In the link of flow, high-level flow infrastructure and flow system are the basis for smooth internal circulation (Hao, 2020). This paper uses road area and total retail sales of consumer goods to represent the completeness of flow infrastructure and the efficiency of flow system. In the link of consumption, per capita disposable income determines the consumption basis. At the same time, a high level of consumption willingness can form effective consumption demand in the economic society (Long et al., 2021), and effective consumption demand is a necessary condition for smooth internal circulation (Zuo et al., 2022). The consumption willingness indicator is specifically represented by per capita consumption expenditure in this paper.
3.3 Data description
To construct a complete internal circulation network of China and accurately locate the internal circulation development capability of marine cities, 284 cities across China are selected as overall research samples. At the same time, 2010 and 2022 are used as measurement years to explore the evolutionary characteristics of the internal circulation development of marine cities. Per capita disposable income and per capita consumption expenditure are from the WIND and CEIC databases. The remaining sub-indicators are from the “China City Statistical Yearbook” and the “Statistical Bulletin of National Economic and Social Development” of various prefecture-level cities. Since the sub-indicators have different magnitudes and dimensions, the original data are standardized.
4 Analysis of the internal circulation development level and network characteristics of marine cities
4.1 Internal circulation development level of marine cities
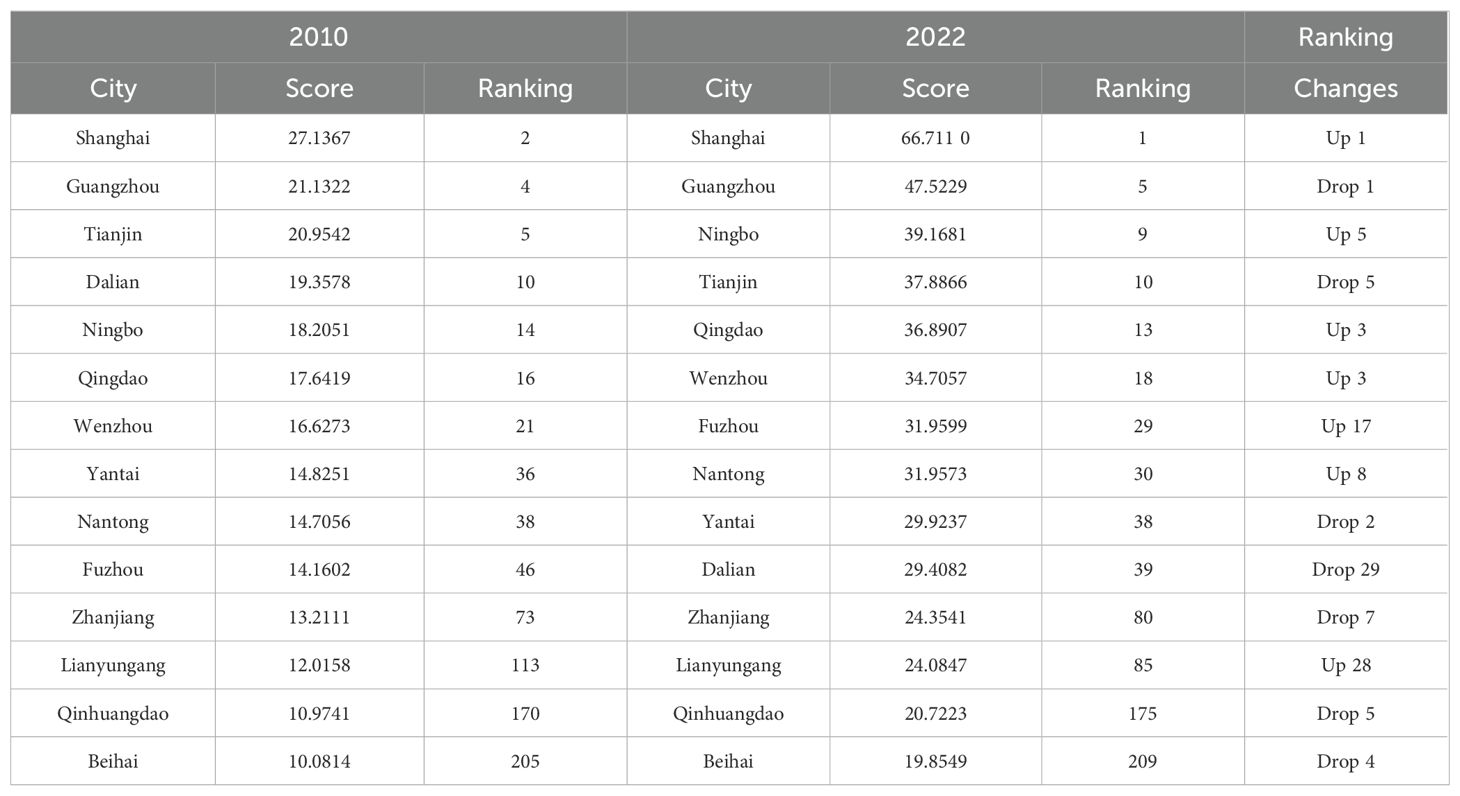
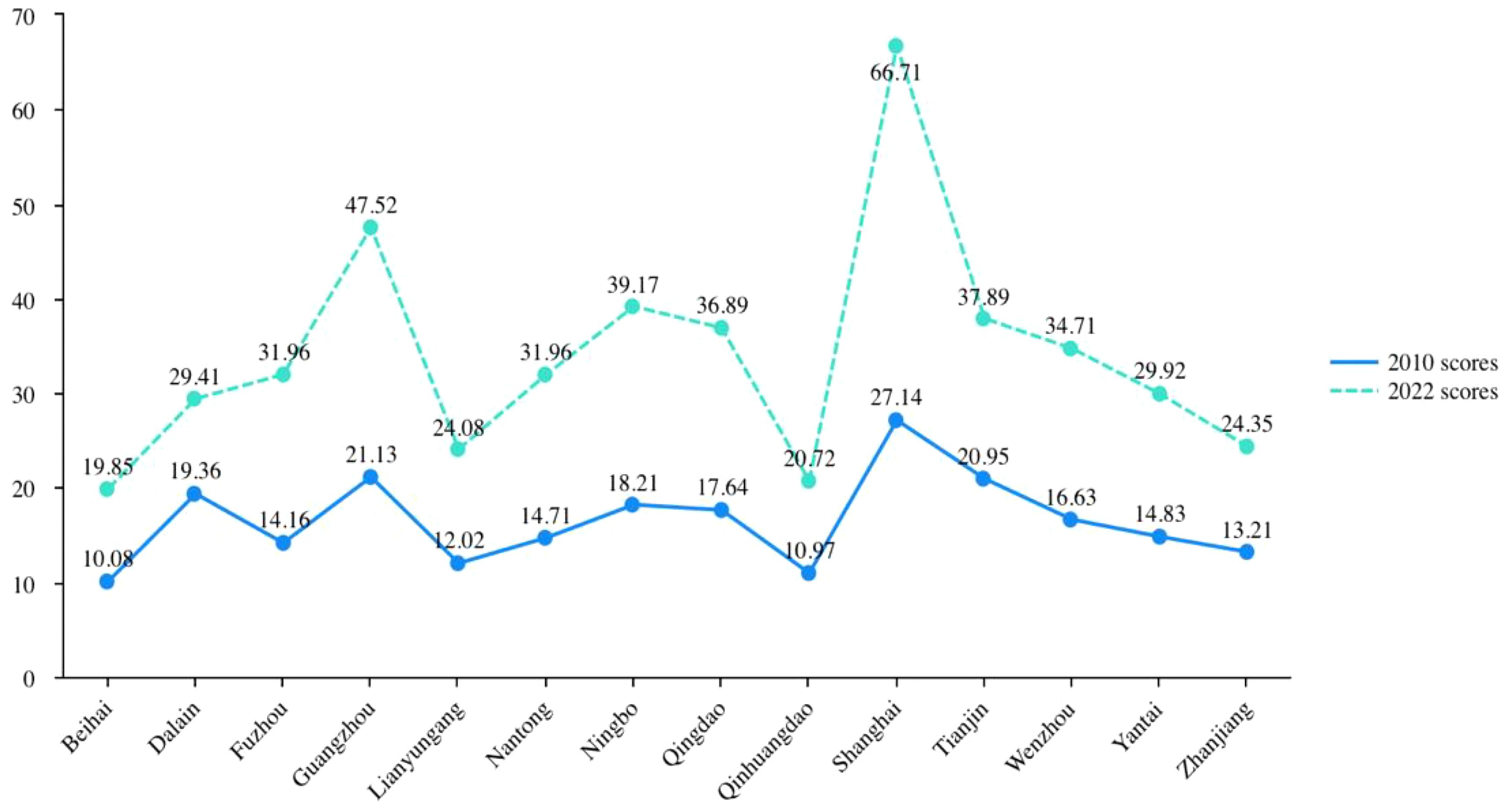
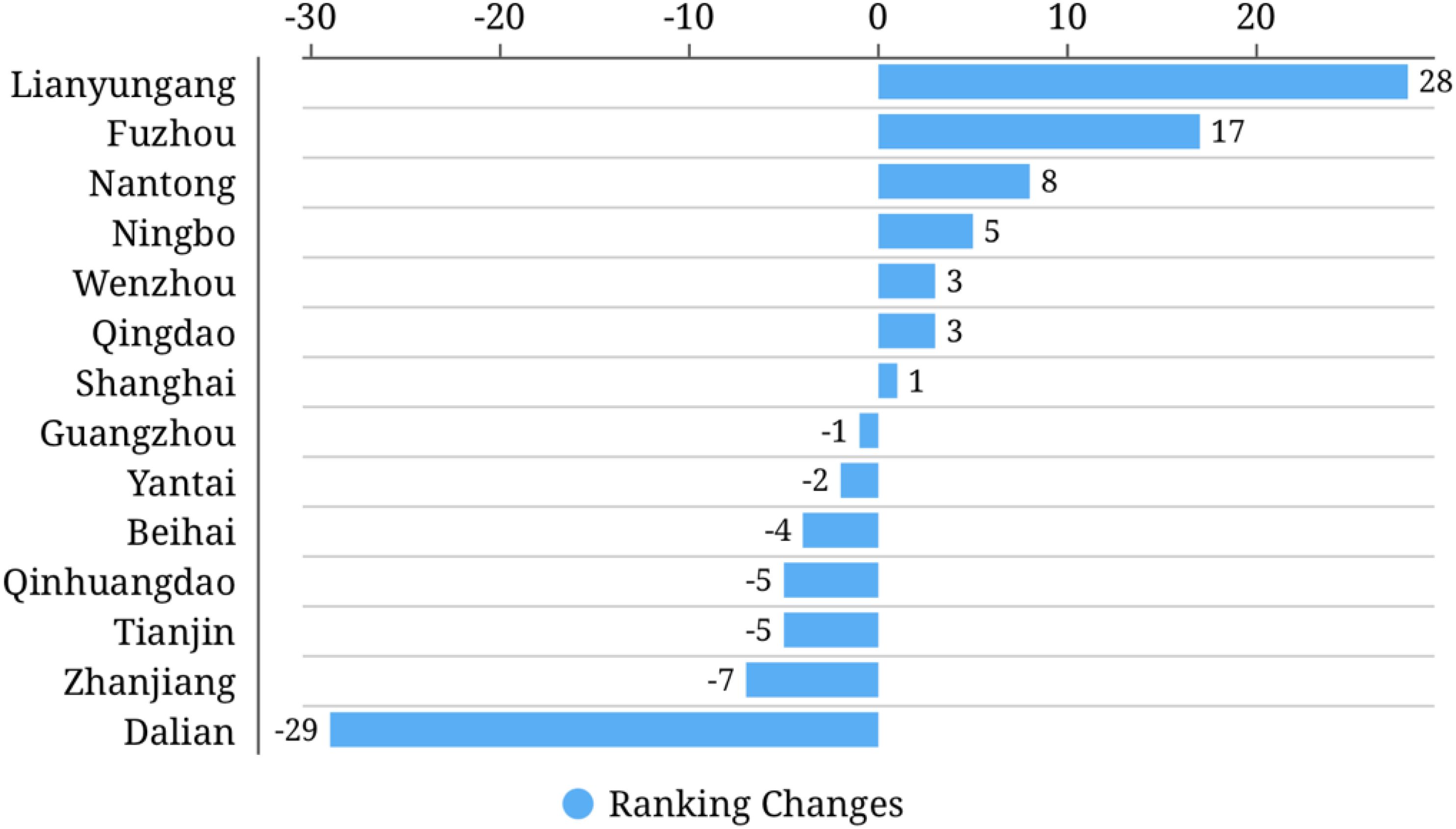
Through the above data standardization processing and indicator weighting ideas, the internal circulation development level of 284 cities across the country in 2010 and 2022 is measured, and finally the specific scores and national rankings of 14 marine cities are obtained (Table 2). Figures 1, 2 are the visible results of the internal circulation scores and the changes in national ranking of marine cities respectively.
Table 2 and Figure 2 show that the internal circulation development level of marine cities has spatial non-balanced characteristics. In 2022, the internal circulation development level of 14 marine cities can be divided into three echelons. The first echelon is Shanghai and Guangzhou, both of which are the “leaders” of the full internal circulation development. Among them, Shanghai leads the country with a high score of 66.7, fully demonstrating its leading position in the development of internal circulation. This is due to its strong economic strength, highly developed industrial system, international market, and superior geographical location, which give it strong support and leadership capabilities in various aspects such as production and consumption.
The second echelon is Ningbo, Tianjin and other traditional coastal economic development cities, which are located in the upper reaches of the national city rankings. Among them, the higher scores of Tianjin and Ningbo may benefit from the spatial spillover and radiation effects of the high-level internal circulation development of Beijing and Shanghai. Qingdao, Wenzhou, Fuzhou and others are all in a leading position in their provinces, which indirectly shows that marine cities have a certain leading role in the construction of the internal circulation development pattern. The third echelon is Zhanjiang, Qinhuangdao, Lianyungang and Beihai, which have relatively weak internal circulation development capabilities and may face problems such as a single industrial structure, insufficient economic development momentum, and limited market consumption capacity, placing them at a relative disadvantage in regional economic competition.
Figure 3 shows the changes in national ranking of marine cities. Compared with 2010, 7 out of 14 marine cities in 2022 have improved their national score ranking for internal circulation, reflecting that these cities have actively taken measures to promote the development of internal circulation in the past decade, and have achieved certain results in industrial upgrading, infrastructure construction, market cultivation, and other aspects. However, except for Lianyungang and Fuzhou, which have risen by 28 and 17 places, the improvement effect of the other 5 marine cities is not significant.
The national ranking of internal circulation scores for the remaining 7 marine cities shows a downward trend, with Dalian experiencing the most severe decline, dropping 29th place. This indicates that it faces significant challenges in economic transformation, industrial restructuring, or market competition, and has failed to keep up with the pace of internal circulation development. Although the internal circulation scores of Qinhuangdao and Beihai have improved, their national rankings have further declined, ranking at the bottom of the 284 cities in the country. Moreover, the gap in internal circulation scores among marine cities has gradually widened, with the standard deviation rising from 4.65 in 2010 to 12.15 in 2022, exacerbating the imbalance. Except for Shanghai, the internal circulation capacity of other marine cities has not been empirically promoted, which may lead to further widening of regional economic development gaps, affecting the coordinated development of the overall economy, and highlighting the urgency of improving the level of internal circulation development in vulnerable cities.
4.2 Characteristics of internal circulation network of marine cities
4.2.1 Internal circulation network
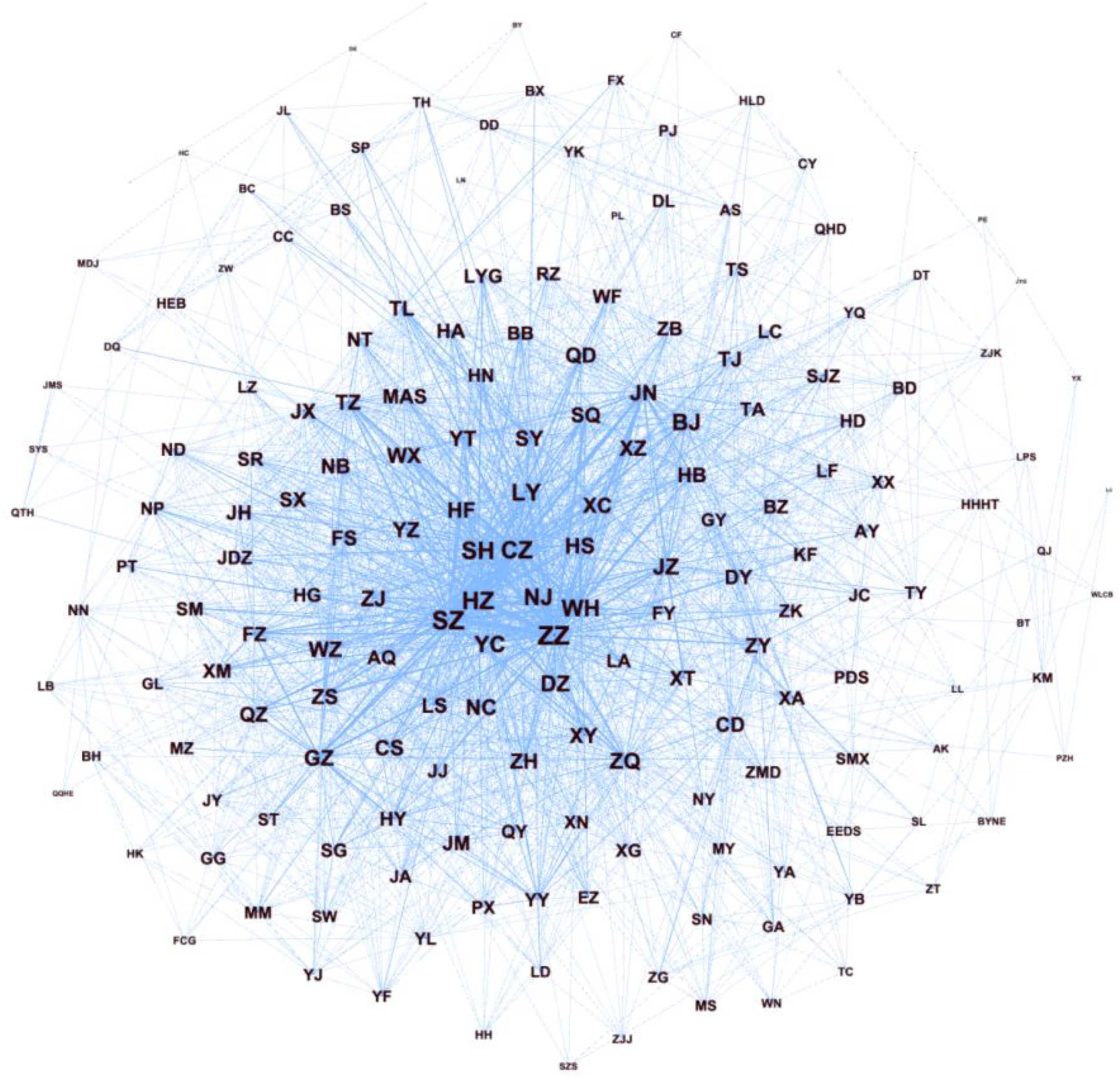
According to the social network theory, this paper takes 284 prefecture-level cities in China as network nodes and takes the spatial correlation coefficient matrix of the internal circulation development among prefecture-level cities obtained by the modified gravity model as the network connecting edge to form China’s internal circulation network. The overall density of the network is 0.086, indicating that the internal circulation between cities is relatively sparse, and the economic connections between cities need to be further strengthened. The average path length is 2.896 and the average clustering coefficient is 0.656, indicating that the network has certain small world characteristics, that is, there are relatively close connections between some cities, but there is still room for improvement in the overall connectivity and integration of the network. The network diameter is 11, indicating that the longest distance of cyclic connections between cities is relatively long, and there may be certain obstacles to information transmission and resource flow (Figure 4).
Based on the dimension of intercity interaction, the topological characteristics of the internal circulation network of 14 marine cities can be examined. It can be seen that Shanghai is located in the central position. As a national economic center and an international metropolis, it gathers abundant resources, funds, technology, and talents, becoming a key hub of the internal circulation network and having a strong radiating and driving effect on surrounding cities and the national economy. Nine cities, including Guangzhou and Qingdao, are located in peripheral areas, indicating that they play a relatively important role in the internal circulation, with close economic exchanges with the central city and other cities. However, their influence and control in the network are relatively weak compared to the central city. Qinhuangdao, Dalian and other four cities are located on the periphery, reflecting their low participation and connectivity in the internal circulation network. They may face problems such as geographical remoteness, unreasonable industrial structure, and lagging economic development, which have led to their insufficient role in the internal circulation and become weak links in the development of the internal circulation. The following paper will further explore the spatial structural characteristics of marine cities in the Chinese internal circulation network based on centrality indicators.
4.2.2 Centrality analysis
Based on the centrality of social network analysis, the spatial network correlation characteristics between regions are analyzed. “Centrality” describes what kind of power each region has in the social network, or what kind of central position it occupies, or how it is related to other regions. Therefore, this paper describes the importance of marine cities in the internal circulation spatial network from three dimensions: degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and eigenvector centrality.
4.2.2.1 Degree centrality
Degree centrality is the number of nodes connected to the target node (Kim and Hastak, 2018), which is specifically divided into in-degree and out-degree, reflecting the city’s inter-city connection ability and central position in the internal circulation network (Zhang et al., 2021). The specific calculation method is shown in formula 2:
Among them, is the sum of the in-degree of point a with other nodes, is the sum of the out-degree of the point a with other nodes.
4.2.2.2 Betweenness centrality
Betweenness centrality measures the role of “bridge” and “intermediary” in the internal circulation network of each region, which reflects the control degree, communication ability and hub role in the internal circulation network of a city (Freeman, 1977). The specific calculation method is shown in formulas 3, 4:
Among them, the number of shortcuts between region a and region x is , is the probability that the third region b is on the shortcut between region a and region x.
4.2.2.3 Eigenvector centrality
The importance of an individual in a network depends not only on its own network position characteristics, but also on the position characteristics of the other network individuals to which it is connected. The eigenvector centrality takes into account both the network structure type and the importance of network nodes (Bonacich, 2007), and describes the relative influence and connection quality of marine cities in the internal circulation network. The larger the value, the greater the influence of the member and the more important it is as a core participant in the interaction. The specific calculation method is shown in formula 5:
Among them, is the adjacency matrix of internal circulation network, when the node pair (a, b) is connected, is 1, otherwise it is 0. δ is the maximum eigenvalue of A and ea is the weight value of the node a.
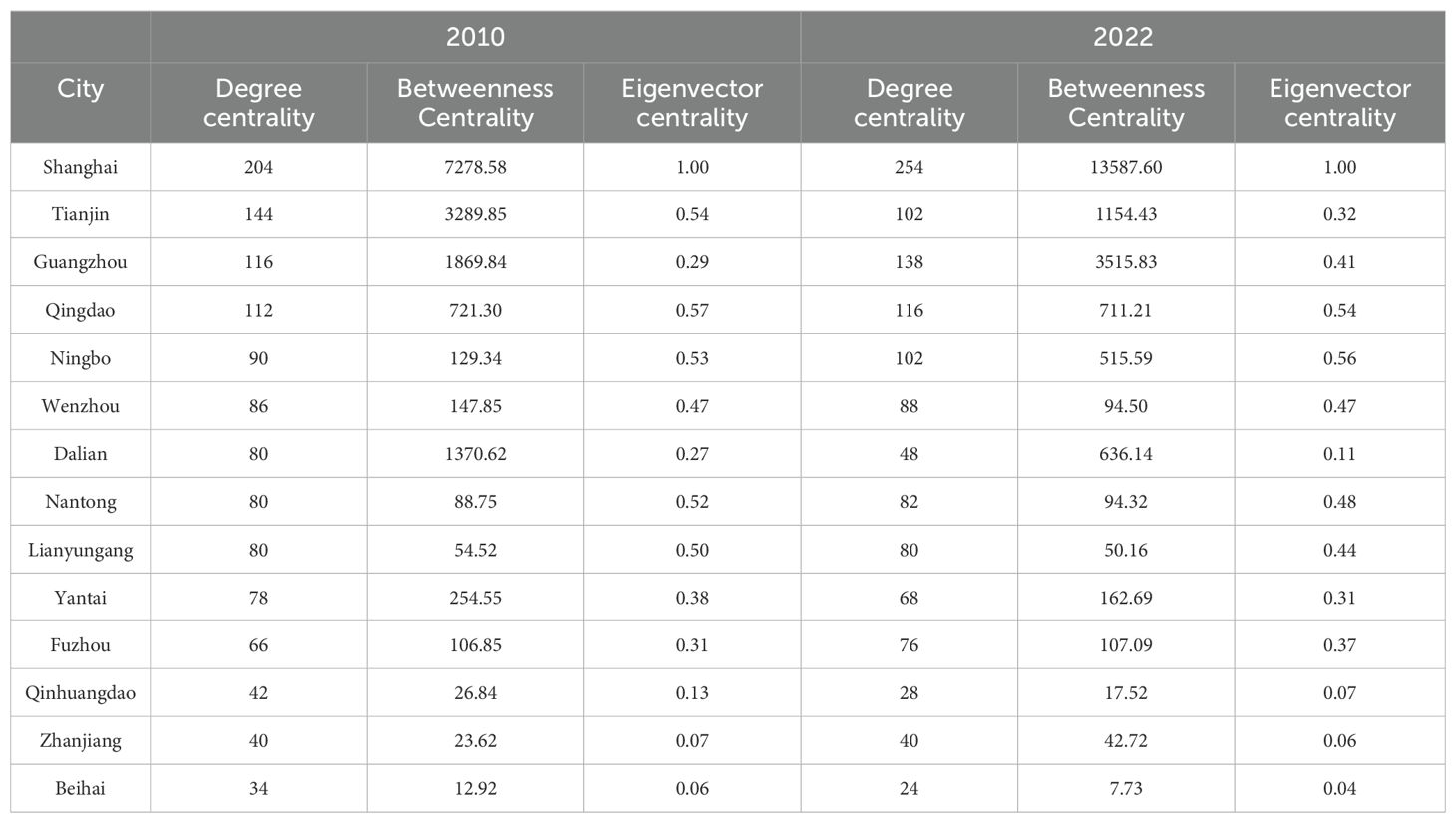
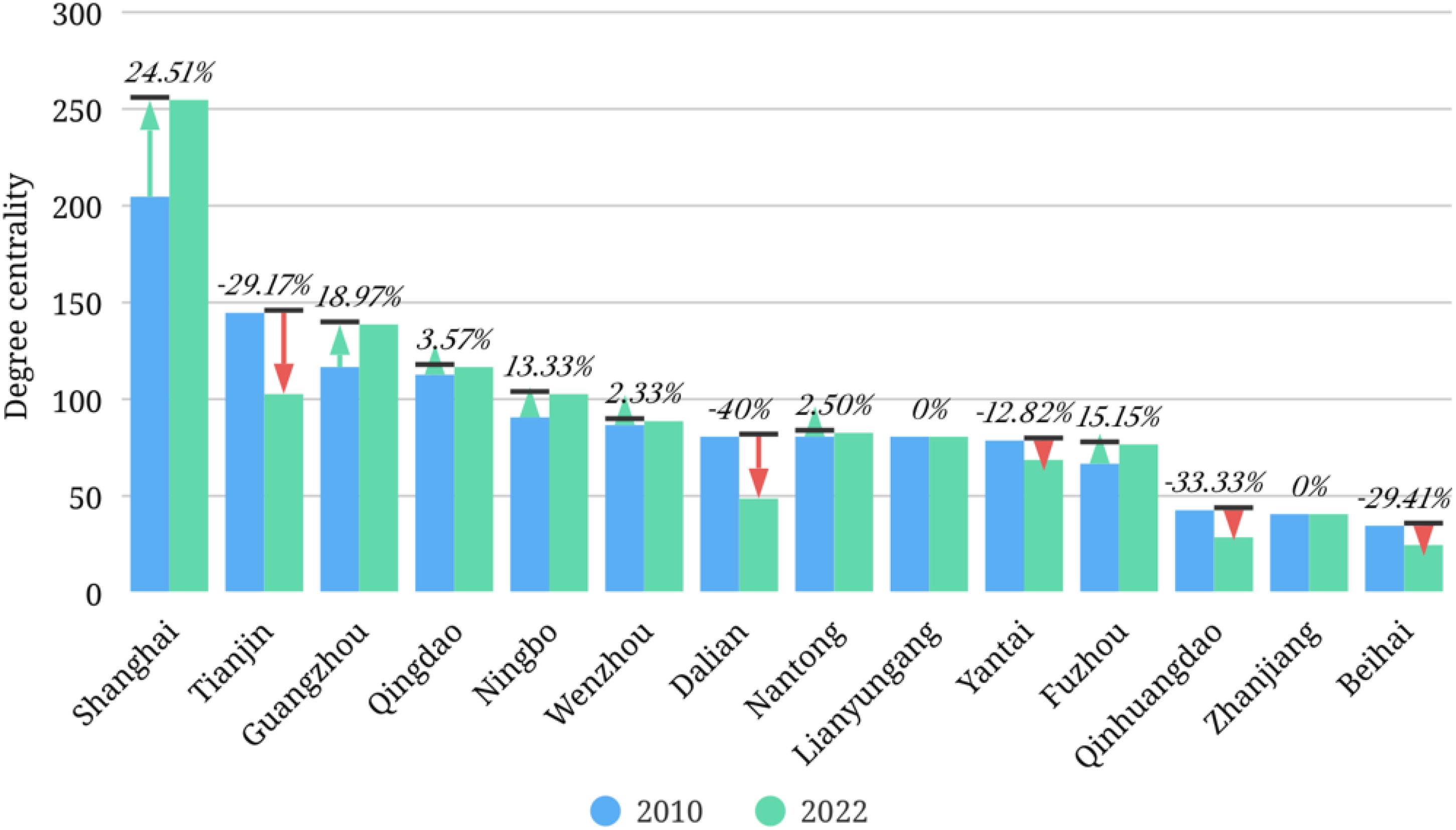
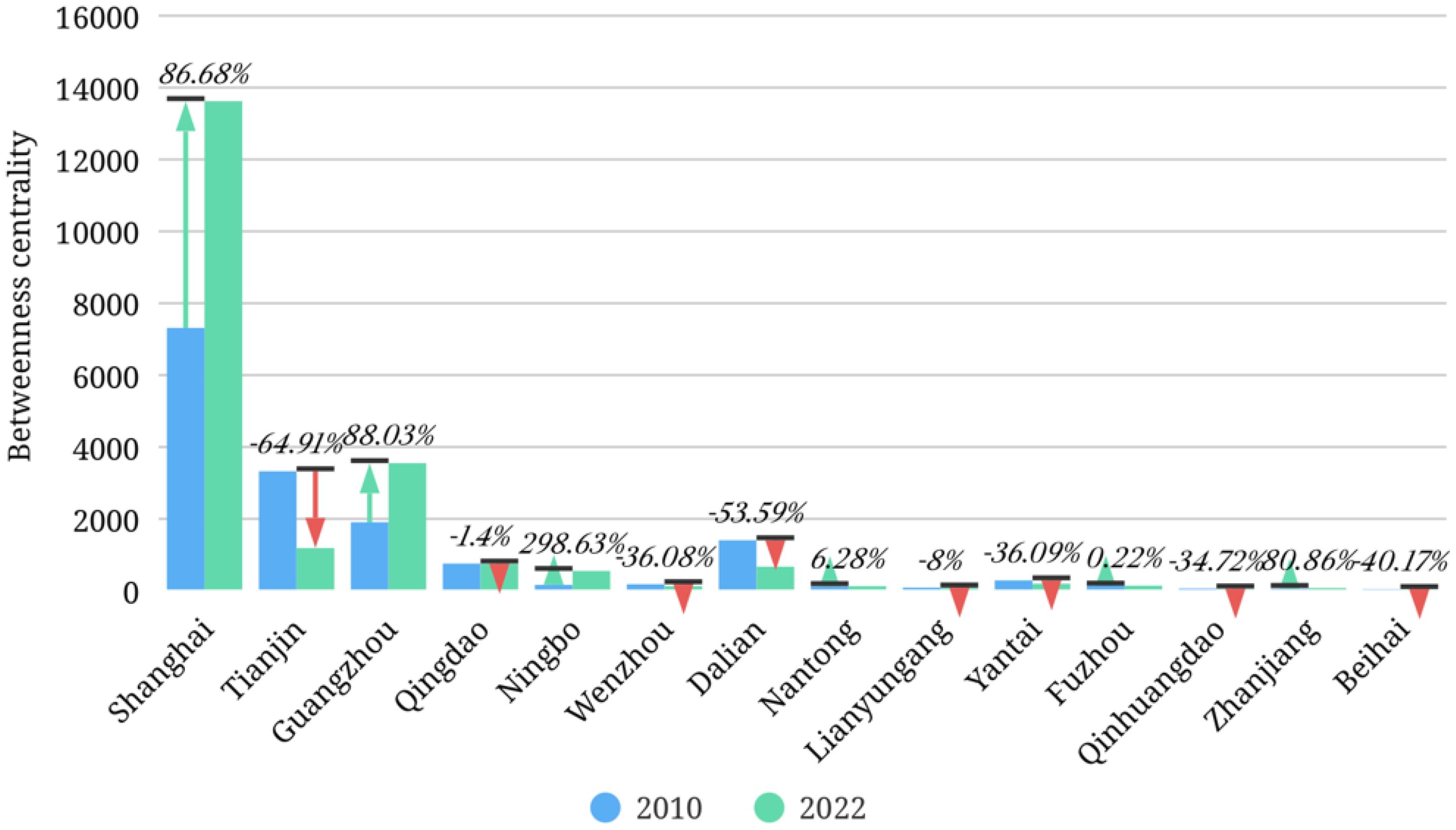
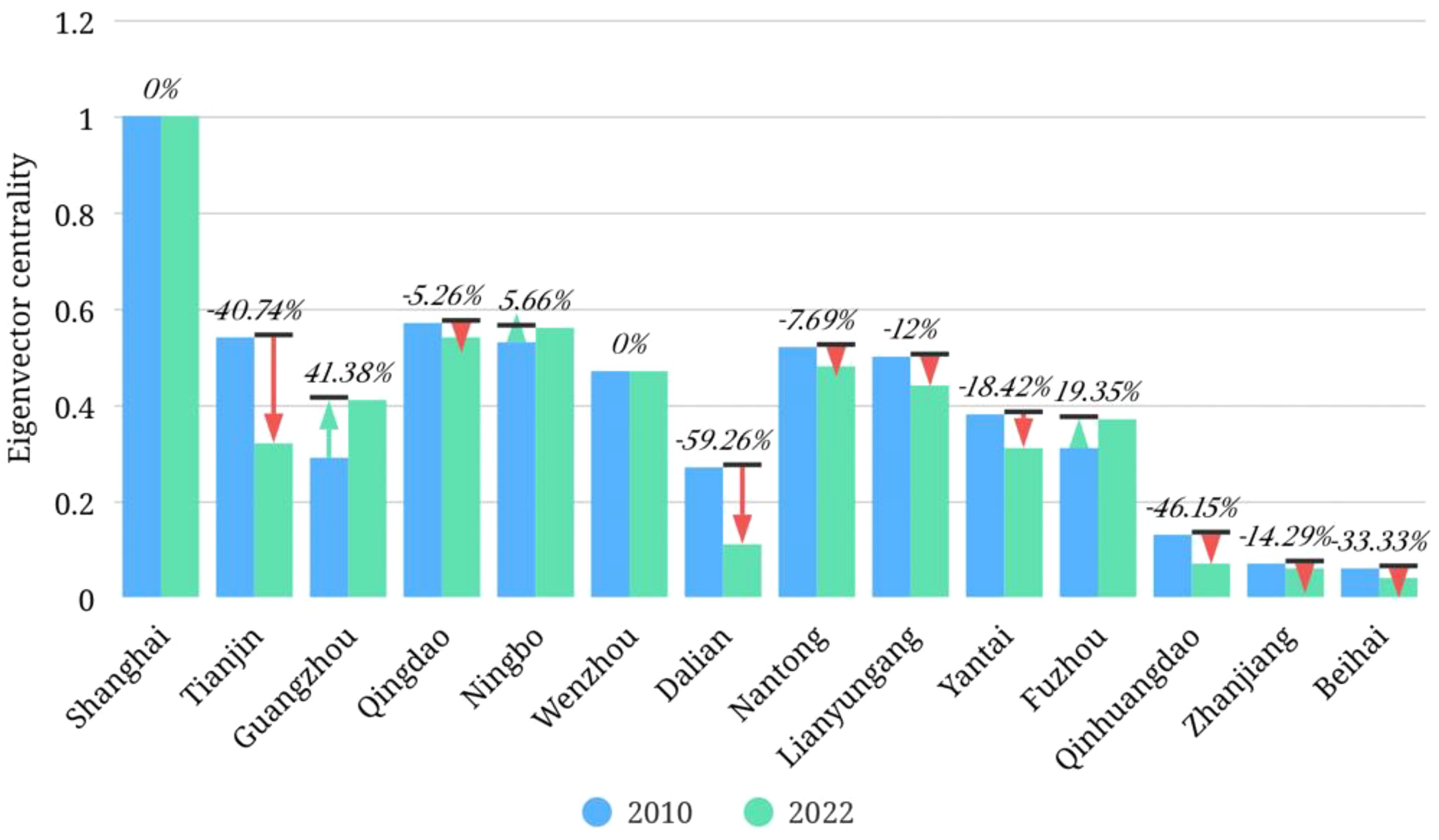
The results of degree centrality, betweenness centrality and eigenvector centrality of marine cities are shown in Table 3. Figures 5-7 are the corresponding visualized processing results, showing the changes in the data for 2010 and 2022.
In terms of centrality, with strong economic strength and excellent geographical location, Shanghai, located at the center of the network, achieved a centrality of 254 in 2022, far higher than the national average, indicating its close internal circulation relationship with many cities and absolute dominance in the internal circulation network. It can effectively integrate resources, promote factor flow and economic cooperation, and is the core engine of internal circulation development. Guangzhou leads the marine cities located in the peripheral areas of the network with a degree centrality of 138, while Ningbo and Tianjin have relatively consistent degree centralities. Among the four cities located in the edge of the network, Dalian has a relatively high degree centrality, while the degree centralities of the other three cities are in the range of 20-40, which is significantly different from other marine cities. Compared with 2010, the degree centrality of the five marine cities of Qingdao, Wenzhou, Nantong, Lianyungang and Zhanjiang has not changed significantly, while the degree centrality of the five marine cities of Tianjin, Dalian, Yantai, Qinhuangdao and Beihai has declined, among which Dalian and Tianjin have shown a significant decline, with the decline rates reaching 40% and 29% respectively. This may be related to factors such as the decline in urban industrial competitiveness, insufficient economic development momentum, and hindered regional cooperation, leading to a weakening of their intercity connectivity in the network. Among the marine cities with improved centrality, Shanghai’s development momentum is relatively rapid, with a 25% increase in intercity connectivity in 13 years, reflecting its continuous strengthening of advantages in regional cooperation and further consolidating its core position in the internal circulation network.
In terms of betweenness centrality, the differentiation characteristics of 14 marine cities are significant. In the sample of 2022, Shanghai is in the first echelon with an intermediary centrality of 13587. It plays a key role as an intermediary and bridge in China’s internal circulation network, with strong control over information transmission, resource allocation, and economic coordination. It can promote efficient interaction and cooperation between cities and facilitate the smooth operation of internal circulation. In recent years, Shanghai has actively developed emerging economic formats based on big data, cloud computing, the Internet of Things and other fields, providing strong element support for the dredging of the internal circulation. Wenzhou, Nantong, Lianyungang, Qinhuangdao, Zhanjiang, and Beihai have low betweenness centrality and a large gap with other marine cities, so they fail to effectively play the role of brokers in the internal circulation network. Compared to 2010, the intermediary centrality of marine cities has shown an overall downward trend, with the intermediary roles of Tianjin, Qingdao, Wenzhou, Dalian, Lianyungang, Yantai, Qinhuangdao, and Beihai gradually weakening. This may lead to hindered economic connections between cities and a decrease in internal circulation efficiency, with Tianjin and Dalian experiencing declines of up to 65% and 54%, respectively. As the central hub of China’s internal circulation network, Shanghai’s betweenness centrality has increased rapidly in recent years, with an increase of 87%. The accessibility and control of information have been further enhanced, playing a key supporting role in the construction and optimization of the national circulation network.
In terms of eigenvector centrality, 14 marine cities show a “spindle-shaped” development characteristic with Shanghai as the central pole and a decreasing gradient from north to south. Shanghai, located in the center of the network, ranked first in eigenvector centrality in both sample years, which is relatively consistent with the ranking of degree centrality, further confirming the absolute influence of Shanghai in the topological structure of the internal circulation network. The eigenvector centrality of nine cities, including Qingdao, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Nantong, Lianyungang, Yantai and Fuzhou, is at a mid-level in the internal circulation network, while the eigenvector centrality scores of the two northernmost cities, Dalian and Qinhuangdao, and the two southernmost cities, Beihai and Zhanjiang, are extremely low. Although they have development potential and latecomer advantages to a certain extent, they may still be “dead corner cities” with internal circulation development for a long time due to the influence of geographical location and administrative barriers. Remote geography may lead to inconvenient transportation and high logistics costs, limiting the flow of economic factors and industrial development. Administrative barriers may hinder cooperation and collaborative development between regions, making it difficult to integrate into a broader internal circulation network and facing the risk of lagging development. Compared with 2010, the eigenvector centrality of Tianjin and Dalian has obviously degraded. Combined with the analysis of the results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality above, it can be seen that Tianjin and Dalian, two traditional marine cities that have not effectively completed economic transformation, play the role of “gatekeepers” in China’s internal circulation network.
From the above analysis of the internal circulation development level and the internal circulation network model, it can be seen that the internal circulation development scores of some marine cities have dropped significantly in recent years, and their leadership, control and influence in the internal circulation network have declined apparently. After 40 years of development, the policy-driven effect of marine cities has gradually been lost, the relevant institutional dividends have gradually disappeared, and the overall development has shown a weak trend, which can no longer meet the new development requirements based on the internal circulation. Therefore, this article will further analyze the improvement path of the internal circulation development of marine cities, so as to strengthen the development leadership and release the vigorous vitality of marine cities.
5 Configuration research of enhancing the status of marine cities in internal circulation network
5.1 Measurement and calibration
In fsQCA, each independent set contains a conditional variable and an outcome variable, and the sample cases all have membership scores in the independent sets. Calibration is to give the case set membership scores, and then construct a fuzzy set of 0-1. The size of this value determines the membership of the variable. Referring to existing research, this paper adopts the direct calibration method to calibrate the data and convert the original data into fuzzy set membership scores (Tao et al., 2021). At the same time, variable calibration points are set up with the quartile method of 25%, 50% and 75% (Fiss, 2011). Quantile method can effectively avoid defects caused by subjective bias (Zhang et al., 2020). In order to maximize the integrity of the sample, the original data after calibration is corrected by 0.001.
5.1.1 Outcome variable
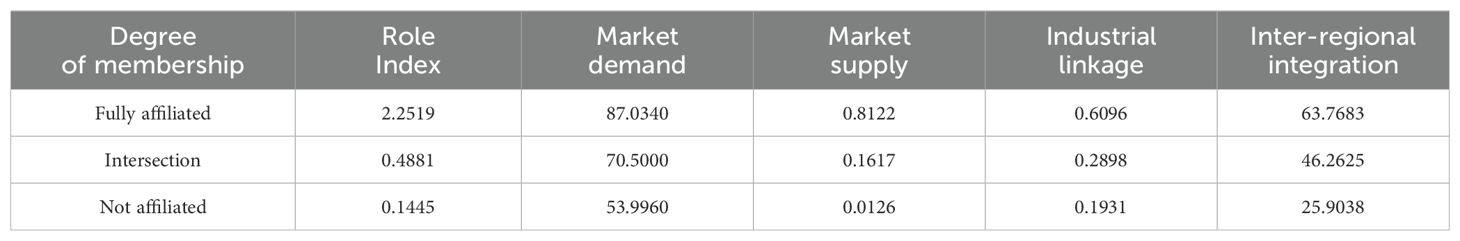
In order to accurately evaluate the internal circulation network status of marine cities, this paper standardizes the centrality data and adopts the urban right role evaluation method to obtain the internal circulation network role index of 14 marine cities by adding the degree centrality, betweenness centrality and eigenvector centrality with equal weights (Lin et al., 2022). This is used to characterize the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network and serve as the outcome variable of fsQCA.
5.1.2 Conditional variables
The demand side and the supply side are the logical starting point and endogenous driving force of the internal circulation (Qian and Pei, 2022). The lack of correlation between upstream and downstream industries and inter-regional barriers are the key obstacles to the internal circulation (Zheng et al., 2022). Marine cities need to build a path to enhance the leadership of the internal circulation based on the endogenous driving force and key obstacles of the internal circulation, and establish a new strategic positioning for the development of the internal circulation. On the demand side, the Chinese government’s 14th Five-Year Development Plan emphasizes that “expanding domestic demand is the strategic basis for building a new development pattern.” Expanding domestic demand is the main engine of the internal circulation, which can stimulate domestic consumption and investment potential, achieve dynamic equilibrium with supply, and thus promote the internal circulation of the economy. At the same time, increasing domestic final demand is the basic connotation of the internal circulation. The key to promoting the development of the internal circulation lies in fully releasing the potential of market demand (Geng and Liu, 2021). On the supply side, the 2020 meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee proposed “deepening supply-side reform and building a new development pattern of dual circulation.” China’s economy has entered a new normal. The mismatch and imbalance between market supply and demand are the main contradictions of the internal circulation. The smoothness of the internal circulation is mainly affected by the supply side (Tang et al., 2020). High-level supply capacity can penetrate the bottlenecks of the internal circulation and eliminate bottleneck constraints. At the same time, the supply side will also affect the efficiency and sustainability of the internal circulation. Therefore, the internal circulation needs to adjust the production and consumption structure with supply-side reform as the main line (Li, 2021). In terms of industrial linkages, the organic combination and nesting of multi-level industrial linkages between cities, regions and countries can maintain the effective operation of the internal circulation, and smooth industrial linkages can effectively promote the internal circulation (Guan, 2023). In terms of inter-regional barriers, there are currently problems such as local protectionism, market segmentation and local government competition caused by the tax-sharing system between regions in China (Qian et al., 2012). Breaking through regional boundaries, building a unified domestic market and realizing regional economic integration are the keys to smooth the internal circulation.
The internal circulation development of marine cities is affected by the demand side, supply side, industrial linkage and inter-regional integration. This paper uses the four as conditional variables of fsQCA to explore multiple paths and equivalent conditional configurations. On the demand side, promoting urbanization is an important measure to expand domestic demand (Jiang and Meng, 2021). Urbanization can release a large amount of market demand, such as housing, education, health and cultural needs (Zheng and Li, 2020). At the same time, urbanization can effectively increase investment demand and stimulate private investment (Sun and Zhou, 2024). Therefore, the urbanization rate can represent the market demand capacity, which is measured by the proportion of urban population in the permanent population of each city. On the supply side, the high-quality innovation capability of the supply system is the fundamental requirement for building a new development pattern. Technological innovation helps to deepen the supply-side structural reform, solve the “stuck neck” problem in the field of technology, effectively connect domestic demand with high-quality and personalized products, and promote the smooth circulation of the national economy with high-level industrial chains and innovation chains. Therefore, innovation capability can represent the market supply capacity and supply quality, and is measured by the number of patent authorizations and R&D expenditures of each city. In terms of industrial linkage, the digital economy can improve the degree of industrial linkage through digital industrialization and industrial digitization, thereby unblocking the “blocking points” of the internal circulation (Wang and Qi, 2023). At the same time, promoting digital industrialization and industrial digital transformation is an important development task mentioned in the “Government Work Report”. Using the digital economy to represent the modern industrial linkage capacity can provide a contemporary development idea for marine cities in the new development pattern stage. Specifically, the number of people employed in the information transmission computer service and software industry, the number of Internet broadband access users, the number of mobile phone users and the digital inclusive finance index from the Digital Finance Research Center of Peking University are used for measurement. In terms of inter-regional integration, information asymmetry is currently common among regions in China, and the degree of information transmission barriers is relatively large. At the same time, local markets and regulatory rules are not transparent. The above factors have led to problems such as local protectionism and market segmentation (Su and Shao, 2022), hindering the construction of a unified domestic market and the integration of inter-regional economic development. Therefore, the anti-corruption and information transparency index can characterize the inter-regional integration capacity, and is measured using the two primary indicators of government integrity and government transparency in the “China Government-Business Relations Index”. The calibration anchor points of each variable are shown in Table 4.
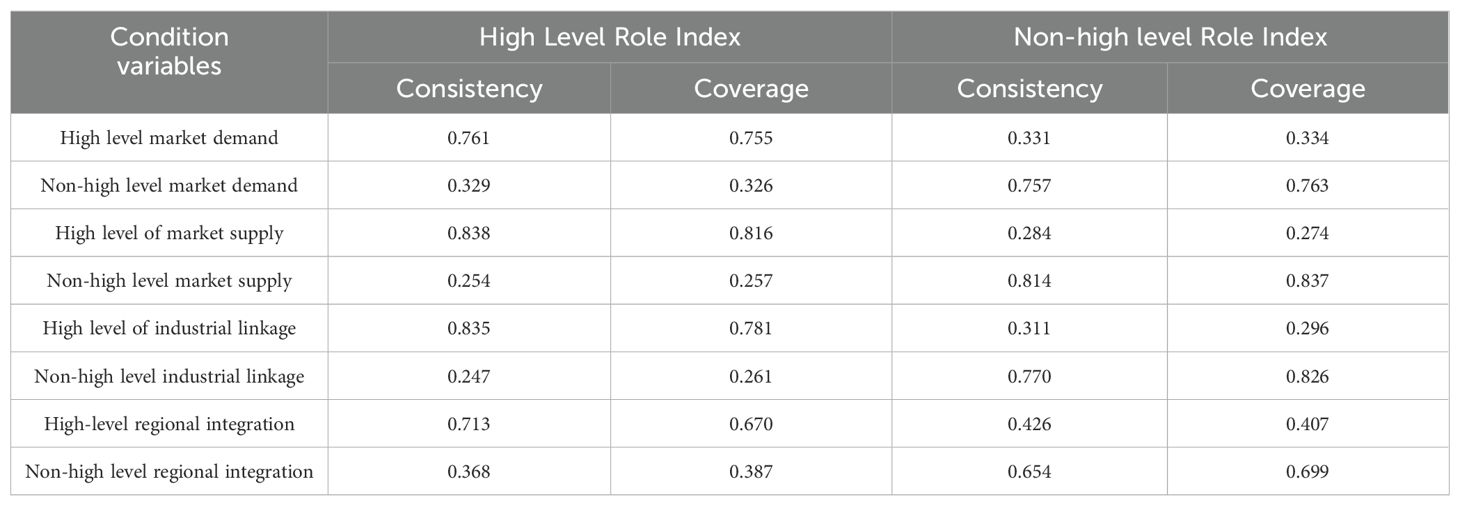
5.2 Necessity analysis of a single condition
fsQCA can clearly identify the sufficient and necessary conditions that lead to the results, among which the necessary conditions are the core conditions that always exist (Ragin and Fiss, 2008). Consistency is the core criterion for judging the necessity of a single condition. When the consistency of the conditional variable is greater than 0.9, it can be regarded as a necessary condition that affects the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network. Table 5 shows the necessary condition analysis results of the high-level role index and the non-high level role index calculated using the fsQCA software. The results of Table 5 show that none of the conditional variables meets the requirement of consistency greater than 0.9, that is, there is no necessary condition that affects the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network.
5.3 Adequacy analysis of conditional configuration
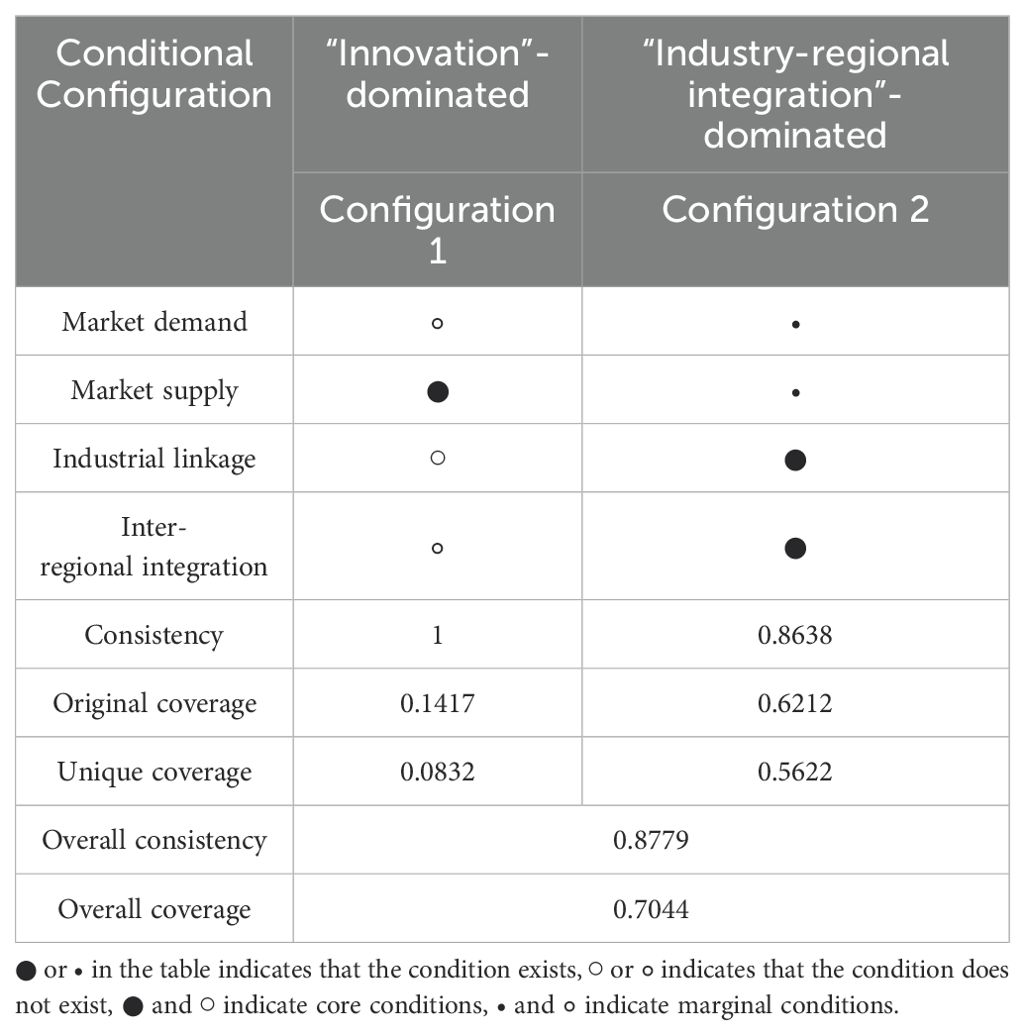
The fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis method based on set theory can clarify whether the result set contains the configuration set composed of conditional variables, that is, the sufficiency of the results caused by different conditional variable combinations can be tested in the configuration analysis stage. Based on the specific distribution of cases in the truth table, this paper follows the research method of Pappas and Woodside (2021) and uses the PRI consistency threshold of 0.7 as the judgment standard. Based on the characteristics of the sample size in this paper, the frequency threshold is set to 1. Table 6 shows the configuration analysis results of the four conditional variables on the improvement of the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network.
Table 6 shows that there are two sufficient condition configurations to enhance the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network, and the consistency of the single configuration and the overall configuration are higher than the minimum standard of 0.75, of which the consistency of the overall configuration is 0.8779 and the coverage is 0.7044. In configuration 1, the supply side based on innovation plays a core role, reflecting the specific path of enhancing the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network dominated by innovation capabilities. When a high level of innovation capability exists, the absence of other conditional variables will not hinder the improvement of the status of marine cities in China’s internal circulation network. The deepening of supply-side structural reforms caused by innovation capabilities can independently constitute a conditional configuration that affects the status of the internal circulation network of marine cities. Therefore, this configuration is named “innovation” -dominated, which means that innovation can improve production efficiency, optimize product structure, enhance industrial competitiveness through technological innovation, attract more economic resources and factors to gather, enhance the economic connections between cities and other cities, and even if there are certain deficiencies in other conditional variables such as demand side, industrial correlation, and regional integration, it can still have a positive impact on the improvement of the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network.
The consistency of configuration 1 is 1, the original coverage is 0.1417, and the unique coverage is 0.0832, that is, this path can explain 14.17% of the sample cases, and 8.32% of the sample cases can only be explained by this path. This indicates that this path has certain particularities and limitations in improving the status of marine cities in internal circulation network, and may only be applicable to a few cities with strong innovation capabilities and certain shortcomings in other aspects, or play an important role in specific development stages.
In configuration 2, industrial linkage and inter-regional integration play the core roles, while market demand and market supply play the auxiliary roles, reflecting the specific path of improving the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network by unblocking the development bottlenecks of the internal circulation network. Therefore, this configuration is named as the “industry-regional integration” -dominated. This means that by strengthening the upstream and downstream connections of industries, promoting the development of the digital economy to enhance industrial interconnectivity, breaking down regional barriers, promoting information flow and market integration, and taking expanding domestic demand and optimizing supply as the driving force, the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network can be effectively improved. This configuration emphasizes the collaborative cooperation of multiple factors, forming an organic whole that promotes each other and jointly drives the development of the internal circulation network.
The consistency of configuration 2 is 0.8638, the original coverage is 0.6212, and the unique coverage is 0.5622, that is, this path can explain 62.11% of the sample cases, and 56.22% of the sample cases can only be explained by this path, including marine cities such as Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Qingdao. These cities not only have the high level of urbanization and innovation capabilities, but also have modern digital industries, complete government information disclosure systems, and efficient political and business information sharing platforms, Therefore, they have the ability to build connections for internal circulation network with other cities. Compared with the lower coverage of configuration 1, it can be seen that configuration 2 is a key and normalized path to promote the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network. The “industry-regional integration” -dominated configuration means that marine cities need to follow the improvement path with unblocking circulation bottlenecks as the practical basis and expanding domestic demand and optimizing domestic supply as the endogenous driving force, thereby leading and promoting the establishment and deepening of the internal circulation network, accelerating the construction of a new development pattern with internal circulation as the main body, and assisting and achieving high-quality socio-economic development.
6 Conclusion and policy implication
6.1 Conclusion
This paper takes 284 cities in China as research samples and constructs a China’s internal circulation network based on a modified gravity model. Using centrality data, we explore the roles and positioning of 14 marine cities in internal circulation network. fsQCA method is used to conduct conditional configuration analysis on the role index of the internal circulation network of 14 marine cities, explore the improvement path of marine cities in internal circulation network. The key elements and complex interactive nature that affect the development of internal circulation in marine cities are revealed, injecting new development ideas and establishing new strategic positioning for marine cities in the new development pattern stage where internal circulation is the main body of development.
The key findings are as follows: (1) There is a marked spatial imbalance in the development of internal circulation across marine cities, which can be divided into three tiers. The gap between these cities has widened over the past 13 years. Shanghai, the leader in internal circulation development, has seen substantial progress. (2) In China’s internal circulation network, Shanghai is located in the central location. Cities like Guangzhou, Qingdao, Ningbo, and Tianjin are located on the network’s periphery, while cities such as Qinhuangdao, Dalian, Zhanjiang, and Beihai occupy the network’s edges. (3) In terms of degree centrality, Shanghai holds a dominant position in China’s internal circulation network, having increased its degree centrality by 25% over the past decade. Conversely, the overall centrality of other marine cities has declined. In terms of betweenness centrality, 14 marine cities have significant polarization characteristics. Shanghai plays a key role as an “intermediary” and “bridge” in China’s internal circulation network, while Wenzhou, Nantong, Lianyungang, Qinhuangdao, Zhanjiang and Beihai fail to effectively play the role of broker. In terms of eigenvector centrality, marine cities show a “spindle-shaped” development characteristic with a gradient decreasing from the central pole of Shanghai to the north and south. The two northernmost cities, Dalian and Qinhuangdao, and the two southernmost cities, Beihai and Zhanjiang, are “dead corner cities” in China’s internal circulation network. (4) Tianjin and Dalian, two traditional marine cities that have not effectively completed economic transformation, play the role of “gatekeepers” in China’s internal circulation network. (5) No single condition is necessary to determine a city’s internal circulation network status, highlighting the importance of multiple factors working in tandem. Improving the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network is the synergistic effect of multiple factors. In the “innovation” -dominated model, innovation capability plays a core role, reflecting the specific path of using scientific and technological innovation to enhance the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network. In the “industry-regional integration”-dominated model, industrial linkage and inter-regional integration play the core roles, while market demand and market supply play the auxiliary roles, reflecting the specific path of improving the status of marine cities in the internal circulation network by unblocking the development bottlenecks of the network.
6.2 Policy implication
6.2.1 Policy implication for “innovation” -dominated path
Firstly, we need to strengthen investment and policy support for innovation. The government should increase financial investment and set up a special innovation fund to focus on supporting scientific and technological innovation projects in marine cities, especially in strategic emerging industries such as advanced marine equipment manufacturing, marine new energy, and marine biomedicine. Promote supply-side structural reform, with innovation driven high-quality supply leading and creating new demand, thereby enhancing the position of marine cities in the internal circulation network. Improve innovation incentive policies, establish a sound intellectual property protection system, strengthen the protection of innovative achievements, and motivate enterprises and researchers to actively innovate. At the same time, it is necessary to formulate policies for rewarding innovative talents and create a highland for innovative talents, so as to attract domestic and foreign innovative talents to flow into marine cities and provide intellectual support for innovation driven development.
Secondly, cultivate innovative entities and innovation ecosystems. Support the construction of enterprise innovation capabilities, encourage enterprises in marine cities to increase investment in technological innovation, and establish enterprise technology research and development centers. Enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises, improve product quality and added value through innovation, meet the diversified needs of the domestic market, and thereby strengthen the market adaptability and development vitality of enterprises in the internal circulation. Build an innovative ecosystem, strengthen the construction of innovation carriers such as marine science and technology industrial parks and incubators, and provide a good platform and environment for innovation and entrepreneurship. Promote the aggregation and flow of innovative elements within the park, forming a development pattern of innovation resource sharing and collaborative innovation.
Thirdly, strengthen the transformation and application promotion of innovative achievements. To establish a service platform for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements, the government should integrate resources from all parties, establish a specialized platform for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements, and provide one-stop services for the evaluation, trading, and transformation of marine scientific and technological innovation achievements. Accelerate the process of innovative achievements from the laboratory to the market, and enhance the actual contribution of innovative achievements to the circular development of marine cities. At the same time, it is necessary to promote the application of innovative achievements in traditional industries and guide traditional industries in marine cities to actively apply new technologies, processes, and models for transformation and upgrading. Promote the intelligent and green development of traditional industries, achieve coordinated development between traditional and emerging industries, and expand the industrial space of internal circulation.
6.2.2 Policy implication for “industry-regional integration” -dominated path
Firstly, promote industrial synergy and integrated development. Optimize industrial layout and division of labor cooperation, formulate regional industrial coordinated development plans based on the resource endowment, industrial foundation, and development positioning of marine cities, clarify the division of labor and cooperation relationships among cities in the marine industry chain, form an industrial pattern of complementary advantages and coordinated development, improve the overall production efficiency and competitiveness of the marine industry, promote the play of industrial linkage effects, and enhance the stability and synergy of the internal circulation industry network. At the same time, it is necessary to promote the integrated development of industries, encourage the deep integration of the marine industry with other related industries, and cultivate new economic growth points. By integrating industries, expanding the development space of industries, enriching the internal circulation of industrial formats, and meeting the diverse needs of consumers.
Secondly, strengthen regional integration construction and cooperation. Promote infrastructure integration and increase overall planning and construction efforts for transportation, energy, communication and other infrastructure between marine cities. Accelerate the construction of comprehensive transportation systems such as coastal highways, railways, ports, etc., so as to improve the efficiency of transportation within the region. Promote the construction of information and communication infrastructure, enhance the level of regional informatization, reduce transaction and circulation costs between regions, promote the free flow of factors within the region, and provide solid hardware support for the development of internal circulation. Deepen the reform of regional market integration, break down administrative barriers and market segmentation between regions, and establish a unified, open, competitive and orderly regional market. Strengthen inter regional market supervision cooperation, unify market access standards and regulatory rules, eliminate local protectionism, and promote the free flow of goods and factors within the region. At the same time, it is necessary to promote the equalization of public services between regions, strengthen cooperation and sharing in education, healthcare, social security and other fields, improve the overall development level and attractiveness of the region, and thus enhance the radiation and driving ability of marine cities in the internal circulation network.
7 Research prospect
7.1 Research on the expansion of circulation network structure
Introduce diverse data to expand research perspectives and explore the implementation of multidimensional network structure analysis. Future research should integrate data from multiple fields such as economy, society, and ecology to construct a comprehensive network analysis model. In addition to economic data, further incorporate ecological environment and social population data to explore the interrelationships between economy, society, and ecology in the internal circulation network. Through multidimensional analysis, seek network optimization strategies to achieve a balance and coordinated development of economic, social, and ecological benefits.
7.2 Refinement and expansion of circulation network in marine and inland city
At the micro level, study the internal circulation relationship between enterprises in marine cities and inland cities. Build a supply relationship network between enterprises, analyze the cooperative relationship between marine enterprises and inland enterprises in terms of raw material supply, component matching, product sales, etc. Through the interaction between enterprises, reveal the impact of collaborative models and micro decisions on the internal circulation network.
At the micro level, focus on the connection between marine industry clusters and inland industry clusters, and build an internal circulation network between industry clusters. At the same time, considering the connections between functional zones within the city, studying the collaborative development model of functional zones in terms of industrial positioning, resource allocation, policy support, and how the interaction between functional zones promotes the optimization of urban circulation.
At the macro level, further refine the collaborative network between the regions where marine cities and inland cities are located. In addition to the overall connection between coastal and inland areas, research on the internal circulation network relationships across watersheds and economic zones. Analyze the collaborative mechanisms and network structure characteristics between regions in resource sharing, ecological environment protection, industrial transfer and undertaking, and explore how to promote balanced development and overall efficiency improvement of circulation networks nationwide through regional cooperation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JS: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XG: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. XZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. GD: Formal analysis, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Social Science Planning Research Project of Liaoning Province: Research on the Mechanism and Pathways of Digital-Green Integration to Promote the Construction of Modern Industrial System in Ethnic Areas of Liaoning Province. (L24CJY005).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bonacich P. (2007). Some unique properties of eigenvector centrality. Soc. Networks 29, 555–564. doi: 10.1016/j.socnet.2007.04.002
Chen P., Fu Y. H. (2022). Measurement and application of domestic economic cycle from the perspective of global value chain. Stat. Res. 39, 19–31. doi: 10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2022.11.002
Chen Q. R., Xu J., Xia Y. (2022). The measurement method of domestic and international double cycle and the analysis of the evolution trend of China’s double cycle pattern. Chin. Manage. Sci. 30, 12–19. doi: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2020.2045
Fang X. P., He T. T., Liu K., Jin Y. D. (2023). Study on measurement and spatiotemporal characteristics of provincial economic cycle level. Stat Decision. 39, 87–92. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2023.14.016
Fiss P. C. (2011). Building better causal theories:A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organization research. Academy of management journal. Acad. Manage. J. 54, 393–420. doi: 10.5465/amj.2011.60263120
Freeman L. C. (1977). A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 40, 35–41. doi: 10.2307/3033543
Gao C. C., Chang S. Q., Wang Y. S. (2024). From global to national: the role of urban agglomerations in China’s new development paradigm. PloS One 19, e0305594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305594
Geng X., Liu J. Z. (2021). The internal logic and implementation strategy of demand-side reform to drive internal circulation. J. Commercial. Econ. 8, 189–192.
Guan G. J. (2023). Research on the industrial correlation of China’s economic internal circulation: based on the data of the fourth period of input-output table. Stat Decision. 8, 86–90. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2023.08.015
Guang F. T., Lu X. D., Deng Y. T. (2023). Spatial difference and dynamic evolution of domestic economic circulation level. Stat Decision. 39, 102–107. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2023.12.018
Hao Y. Z. (2020). Reviews on coordinately promoting the development of modern logistics system under the new development pattern of dual circulation. China Business and Market. 34, 3–17. doi: 10.14089/j.cnki.cn11-3664/f.2020.11.001
He Z. Y., Gao C. Y., Li J. Z. (2022). China’s internal circulation potential, short board and welfare—Based on the reservation price and supply-Demand matching perspectives. China Ind. Econ. 06, 24–41. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2022.06.018
Hu Y. H. (2012). Understanding and discussion of some problems in statistical synthesis evaluation. Stat. Res. 29, 26–30. doi: 10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2012.01.005
Huang Q. H., Ni H. F. (2021). Measurement of domestic and international double cycle of China’s economy: the essential characteristics of the new development pattern. J. Manage. World 37, 40–58. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0182
Javed S. A., Bo Y., Tao L., Dong W. (2023). The “Dual circulation” Development model of China: background and insights. Rajagiri. Manage. J. 17, 2–20. doi: 10.1108/RAMJ-03-2021-0016
Jiang J., Zhang Z. J. (2024). The internal circulation of the chinese economy: evidence from the evolution of input-output in multiple regions. Ind. Economy. Rev. 15, 92–110. doi: 10.14007/j.cnki.cjpl.2024.02.006
Jiang X. G., Xu W. W. (2024). On the theoretical logic and implementation path of domestic economic circulation. J. Hefei. Univ. 41, 31–36.
Jiang X. J., Meng L. J. (2021). Mainly inner circulation, outer circulation empowerment and higher level double circulation: International experience and chinese practice. J. Manage. World 37, 1–19. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0001
Kim J., Hastak M. (2018). Social network analysis: characteristics of online social networks after a disaster. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 38, 86–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2017.08.003
Li F. (2021). Internal and International double cycle: Theoretical framework and Chinese practice. Financial. Res. 04, 4–18. doi: 10.16538/j.cnki.jfe.20210113.202
Liang X. H., Wu X. Q., Liu Y. H. (2009). The economic gap between China’s coastal open cities Trends and internal composition of the study. Stat Decision. 05, 115–117.
Lin Z. H., Chen Y., Liu X. F., Ma Y. F. (2022). Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of cooperation network of China’s inbound tourism cities. Acta Geographica. Sin. 77, 2034–2049. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202208013
Lin J. Y., Wang X. (2021). Dual circulation: A new structural economicsView of development. J. Chin. Economy. Business. Stud. 20, 303–322. doi: 10.1080/14765284.2021.1929793
Liu Z. B. (2020). Seeking the new logic of reshaping chinese economic cycle in domestic and foreign markets. Explor. Free Views. 7, 42–49.
Liu C. J., Chen Y. T., Chen Q. J., Zhou J. P., Wang J. D. (2022). Evolution characteristics and driving mechanism of China’s dual circulation co-ordinated development. Economy. Geogr. 42, 1–8. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2022.11.001
Long S. B., Zhang M. X., Tian H. (2021). Research on the mechanism of “Double upgrade” of industries and consumption to smooth economic double cycles. Reform 02, 90–105.
Márcia O., Gama J. (2012). An overview of social network analysis. Wiley. Interdiplinary. Rev. Data Min. Knowledge. Discovery 2, 99–115. doi: 10.1002/widm.1048
Ni H. F., Tian Y. (2023). The dynamic changes of China’s economic double cycle and international comparison—A new framework of global value chain decomposition with factor ownership. China Economy. Q. 23, 1668–1685. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2023.05.02
Ou J. J., He L. Y. (2023). Opportunity or challenge? Carbon emissions reduction under new development pattern of dual circulation. Sustainability 15, 1757. doi: 10.3390/su15031757
Pan Y. R., Long L. M. (2024). The integration of traditional and new infrastructure enables the coordinated development of dual circulation: measurement and mechanism. Reform 07, 95–110.
Pappas I. O., Woodside A. G. (2021). Fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA): Guidelines for research practice in Information Systems and marketing. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 58, 102310. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102310
Qian X. F., Huang J. L., Huang Y. H. (2012). Is the local government taxing agglomeration rents? An empirical study based on the micro data of enterprises in prefecture-level cities in China. J. Manage. World 2, 19–29 + 187. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2012.02.003
Qian X. F., Pei T. (2022). From supply to demand: the new shift in trade theory research. J. World Econ. 45, 3–29. doi: 10.19985/j.cnki.cassjwe.2022.08.004
Ragin C. C., Fiss P. C. (2008). Net effects analysis versus configurational analysis: An empirical demonstration. Redesigning. Soc. Inquiry:Fuzzy. Sets. Beyond. 240, 190–212.
Serrano M. A., Boguna M. (2003). Topology of the world trade web. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlin. Soft. Matter. Phys. 68, 634–646. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.68.015101
Shi Y., Hong X., Wang L. (2024). Exploring the impact of China’s internal circulation strategy on its stock market under deglobalization. Asian Economy. Papers. 23, 87–113. doi: 10.1162/asep_a_00880
Su Z. D., Gong S., Cao J. X. (2023). Spatial network structure of China’s domestic circulation and its cause identification—Also on the important role of pilot free trade zones as a power source to smooth the domestic circulation network. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 42, 142–152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-910X.2023.11.013
Su J., Shao Y. J. (2022). A unified domestic market: definition, current status and policy suggestions. J. Xinjiang. Normal. Univ. 43, 98–109. doi: 10.14100/j.cnki.65-1039/g4.20220601.001
Sun C. Z., Miao H. J., Yang Y. D. (2024). Sources of differences in China’s regional marine economy based on theory of unequal opportunities. Economy. Geogr. 44, 1–12. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2024.06.001
Sun J. W., Zhou X. L. (2024). Transformation of kinetic energy and strategic focus of high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin and the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Sci. 46, 435–449.
Sun C. Z., Zhu Y. L. (2020). Discussion on the spatial disequilibrium pattern and causes of regional marine innovation in China based on dagum gini coefficient. Economy. Geogr. 40, 103–113. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2020.01.012
Tang D. W., Liu X. L., Ni H. F., Yang Y. W., Huang Q. H., Zhang X. J. (2020). The changing global economic landscape and China’s potential growth rate and high-quality development in the post-epidemic era. Economy. Res. J. 55, 4–23.
Tang A. D., Lu Y., Du Q. Y. (2022). The spillover effect of China’s foreign exchange reserve: analysis based on the gravity model. J. Financial. Res. 4, 1–19.
Tao K. T., Zhang S. D., Zhao Y. H. (2021). What does determine performance of government public health governance? A study on co-movement effect based on QCA. J. Manage. World 37, 128–138 + 156. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0069
Wang F. B., Jiang H., Wang C. (2014). The evolution of the control frameworkChina’s central SOEs: is it strategy determined, institution driven, or dependence on the path?—An attempt of a quality comparative analysis. J. Manage. World 12, 92–114 + 187-188. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2014.12.009
Wang J., Liu S., Zhao Y. (2023). Spatial–temporal evolution and driving factors of economic dual circulation coordinated development in China’s coastal provinces. Sustainability 15, 11009. doi: 10.3390/su151411009
Wang D. Y., Qi Y. (2023). Research on the spatial action mechanism of digital economy enabling dual-cycle development–based on the perspective of digital industrialization and industrial digitization. Foreign. Economy. Manage. 45, 3–21. doi: 10.16538/j.cnki.fem.20221122.401
Wen W., Liu L., Zhan M. H. (2024). National value chain length under internal circulation and economic volatility. J. Nanjing. Univ. Finance. Econ. 03, 1–11.
Xue C., Lu J. Y. (2023). Evolution of international circulation, expansion of domestic circulation and global economic growth. Rev. Econ. Manage. 39, 148–160. doi: 10.13962/j.cnki.37-1486/f.2023.06.012
Xue C., Lu J. Y., Zhang P. (2024). Production network structure and China’s economic growth. China Economy. Stud. 02, 151–165. doi: 10.19365/j.issn1000-4181.2024.02.11
Yi D. H., Chen X. (2022). Wage formation mechanism in China: concept definition, current situation analysis and future prospects. Jiangxi. Soc. Sci. 42, 31–41 + 206 + 2.
Zhai S. (2020). Spatio-temporal differences of the contributions of marine industrial structure changes to marine economic growth. J. Coast. Res. 103, 1–5. doi: 10.2112/SI103-001.1
Zhang C. (2012). Low-cost, export, spatial agglomeration and urban growth. China Economy. Stud. 2, 33–43. doi: 10.19365/j.issn1000-4181.2012.02.004
Zhang M., Lan H. L., Chen W. H., Zeng P. (2020). Research on the antecedent configuration and performance of strategic change. J. Manage. World 9, 168–186. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2020.0145
Zhang F., Ning Y., Lou X. (2021). The evolutionary mechanism of China’s urban network from 1997 to 2015: an analysis of air passenger flows. Cities 109, 103005. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2020.103005
Zhang L., Yang D., Guo Y. (2023). Dual circulation development model and credit growth. Finance. Res. Lett. 55, 103873. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2023.103873
Zhao L., Fang C., Ding Y. (2014). The comparison of intercountry economic development inequality and polarization in zhejiang province. Economy. Geogr. 34, 36–43. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2014.07.036
Zhao L., Gao X. T., Liu Y. X., Han Z. L. (2021). Evolution characteristics of spatial correlation network of inclusive green efficiency in China. Economy. Geogr. 41, 69–78 + 90. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2021.09.008
Zheng D. K., Li L. (2020). Urbanization, population density and household consumption rate. J. Capital. Univ. Econ. Business. 2, 13–24. doi: 10.13504/j.cnki.issn1008-2700.2020.02.002
Zheng X. X., Liu Q., Zhao Z. X. (2022). Mutual Promotion of Dual Circulation of Domestic and Foreign Markets under the Influence of Industrial Linkage and Inter-provincial Boundary: An Empirical Study based on Simultaneous Equations Model. J. Manage. World 38, 56–70 + 145 + 71-80. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2022.0166
Zou X., Lyu J. Y., Yang X. (2024). Intercity digital information flow and economic internal circulation power. J. Hohai. Univ. 26, 118–131. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1671-4970.2024.01.011
Keywords: marine cities, internal circulation network, social network analysis, fsQCA, conditional configuration
Citation: Sun J, Gao X, Zhang X and Dai G (2024) Research on the positioning and enhancement path of marine cities in China’s internal circulation network. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1506903. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1506903
Received: 06 October 2024; Accepted: 14 November 2024;
Published: 04 December 2024.
Edited by:
Song Ding, Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics, ChinaReviewed by:
Yang Benshuo, Qingdao University, ChinaGuangxue Wan, Shandong University, Weihai, China
Zhu Yixue, Yancheng Teachers University, China
Copyright © 2024 Sun, Gao, Zhang and Dai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinyue Gao, Z2FveGlueXVlQG91Yy5lZHUuY24=
 Junkai Sun
Junkai Sun Xinyue Gao
Xinyue Gao Xindan Zhang
Xindan Zhang Guilin Dai1
Guilin Dai1