
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 19 December 2024
Sec. Marine Biotechnology and Bioproducts
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1498223
 Qingyu Ren1†
Qingyu Ren1† Yu Sheng1,2†
Yu Sheng1,2† Ling Sun1†
Ling Sun1† Feijian Zheng3†
Feijian Zheng3† Chengwu Hu1
Chengwu Hu1 Jianqing Chen1
Jianqing Chen1 Zhengbing Lyu1
Zhengbing Lyu1 Chen Yuan4*
Chen Yuan4* Xiaofeng Jiang1,3,4*
Xiaofeng Jiang1,3,4*Introduction: B-cell lymphoma, a malignant proliferative disease originating from lymphoid tissue, poses a grave threat to human health. CD20 has emerged as a promising target for lymphoma treatment. However, due to the significant heterogeneity of B-cell lymphomas, conventional CD20 monoclonal antibodies show limited penetration, severely impeding the progress of B-cell lymphoma therapies.
Methods: In contrast, single-domain antibody molecules derived from cartilaginous fish have a molecular weight as small as 12 kDa, granting them robust penetration capabilities and making them the smallest known molecules of efficiently targeting specific antigens.
Results: As a result, these molecules hold tremendous potential as candidate drugs for lymphoma treatment. In this study, the whitespotted bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum) was immunized with recombinant human CD20 to generate specific single-domain antibodies (sdAbs) targeting CD20. By utilizing phage display technology, the variable new antigen receptors (VNARs) were successfully screened and identified, and play an important role in the inhibition of Raji lymphoblastoma.
Discussion: The sdAbs obtained through this research represent promising candidates for B-cell lymphoma treatment, displaying significant potential for clinical applications and offering a new direction for the development of targeted therapies against lymphoma.
B-cell lymphoma accounts for more than 80% of all lymphomas and can manifest in various locations within the human body (King and Myatt, 2014). Research has consistently demonstrated that over 95% of B-cell lymphomas exhibit abnormally high expression of CD20, characterized by a dense distribution on the cell surface (Pavlasova and Mraz, 2020). CD20, also known as B-lymphocyte surface antigen B1, is a non-glycosylated protein predominantly found on the surface of B‐lymphocytes. Its expression begins during early B-cell development and persists throughout the mature B-cell stage, but it diminishes after differentiation into plasma cells. Importantly, CD20 is not expressed in hematopoietic stem cells or other normal tissues (D’Amico et al., 2019; Engelhard, 2016). Comprising 297 amino acids, the molecular weight of the CD20 protein varies depending on the degree of phosphorylation, ranging from 33 to 37 kDa. It is a member of the MS4A (membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A) protein family (Tedder et al., 1989).
The primary role of CD20 lies in regulating B‐lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation. When antibodies bind to CD20, they generate signals that control cell growth and induce apoptosis in various cells, including tumor cells, thereby promoting tumor cell death. In its natural state, CD20 does not form heterooligomers (Zuccolo et al., 2013) but exists as homodimers and homotetramers on the cell surface, engaging in signal transduction alongside other cell surfaces and cytoplasmic proteins (Bubien, 1993; Polyak et al., 2008). Furthermore, CD20 exhibits minimal internalization upon antibody binding and remains largely associated with B cells without being shed from their surface (Cragg et al., 2005). Due to the absence of CD20 expression in hematopoietic stem cells, plasma cells, and certain immature B cells, even if anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies eliminate tumor cells and potentially B cells, the host immune function would be maintained as the number of B cells can be promptly replenished (Maloney et al., 1994). Consequently, CD20 represents an ideal target for antibodies and has been clinically validated as a treatment target for B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases (Marshall et al., 2017). However, the biological functions of CD20 in B cells and its physiological ligands remain unclear, warranting further research in this area (Pavlasova and Mraz, 2020).
The CD20 protein comprises four hydrophobic transmembrane domains and possesses an intracellular domain and two extracellular loops, large and small, with both the N- and C-termini located in the cytoplasm (Teeling et al., 2006; Anbouhi et al., 2012). The large extracellular loop, situated between the third and fourth transmembrane domains, serves as the target binding domain for the majority of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. One such specific monoclonal antibody, rituximab (RTX), binds to a site consisting of residues 163–187 on CD20 (Teeling et al., 2006; Deans et al., 2002). Within the large extracellular loop of CD20, a critical antigenic determinant cluster (170ANPS173) exists, where residues A170 and P172 play a crucial role in forming the antibody-binding epitope. These residues are essential for the interaction between CD20 and the antibodies.
Raji cells, a widely utilized leukemia cell line with high CD20 expression derived from patients diagnosed with Burkitt lymphoma, serve as a vital instrument for investigating leukemia and associated disorders. These cells are frequently utilized as a model to explore the biology of B lymphoma, gene expression, drug responsiveness, and the creation of innovative treatment approaches. Raji cells can sustain propagation in laboratory settings and display morphological features akin to lymphoblasts.
In 1995, Greenberg et al. (1995) discovered a novel immunoglobulin antigen receptor in the nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum) called “immunoglobulin new antigen receptor” (IgNAR), which bears structural similarities to camel heavy chain antibodies. Unlike conventional antibodies, IgNAR is devoid of light chains and is composed of five constant domains (C1–C5) and one variable domain (V region) in each chain (Zielonka et al., 2015). IgNAR binds antigens specifically through its single heavy‐chain variable region. Using molecular biology techniques, researchers successfully cloned and recombinantly expressed novel antibodies derived from IgNARs, namely variable new antigen receptors (VNARs), while retaining their antigen‐binding activity (Kovaleva et al., 2014). Among cartilaginous fish heavy chain antibodies, VNARs represent the smallest functional antigen‐binding fragments. Despite having a molecular weight of only 12 kDa, recombinant VNAR molecules exhibit stability and binding activity comparable to full‐length antibodies. As a result, VNARs currently stand as the smallest known molecules capable of effectively targeting specific antigens found in nature (Zielonka et al., 2015; De Silva et al., 2019). Unlike mammalian variable domains, VNAR domains possess just two complementarity‐determining regions, namely CDR1 and CDR3 (Zielonka et al., 2015). The diversity of VNARs primarily arises from CDR3, which is exceptionally long, structurally complex, and plays a pivotal role in antigen binding (Feige et al., 2014). VNARs exhibit excellent unique properties, including stable quality, low production cost, ease of preservation, and long half-life (Jiang et al., 2023). Thus, they are particularly suitable for clinical applications (Qin et al., 2023) such as immunoassays, molecular imaging (Traenkle and Rothbauer, 2017), diagnosis, and treatment of tumors. The previous study shows that single-domain antibodies (sdAbs) binding to internalizing receptors such as HER2 can enhance tumor retention of radioiodine (Feng et al., 2021). VNARs are currently being explored through modifications and adaptations, including combining with immunofluorescence, with a view to meeting the requirements of cancer-based imaging tools.
In the present study, the whitespotted bamboo shark was used as the experimental animal (Wei et al., 2021), and CD20 (NCBI Reference Sequence: NP_068769.2) was selected as the immunogen. Employing phage display technology, we conducted a screening to identify anti-CD20 VNAR single-domain antibodies. Subsequent investigations will focus on exploring the biological activities of these sdAbs, which demonstrate specific binding to CD20. Given their ability to selectively bind to CD20 and exert biological effects, these sdAbs hold promising clinical applications in lymphoma treatment, providing a novel direction for the development of targeted drugs against lymphoma.
The gene sequences of the CD20 between the third and fourth transmembrane regions from humans were retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) databases. The whole gene was synthesized and cloned into the pET-41b(+) vector, with the GST and His tags fused at the 5’ end (Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Corporation). The plasmids were transformed into E.coli BL21 (DE3) cells for protein expression and the single colonies that were regarded as correct were selected and cultured in LB media with 50 µg/mL Kan.
When OD600 reached 0.4–0.6, the culture underwent 1 mM IPTG induction and was cultivated for 4 hours for soluble protein production at 37 °C. Induced and naïve bacteria pellets were respectively spun down at 4,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, resuspended in 4ml PBS, and broken by ultrasound. Protein extracts were collected by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C. The CD20 protein extracts containing GST-tag were filtered using a 0.22 µm filter membrane and were purified by GST-tag Purification Resin (Beyotime). Endotoxins were removed from the purified protein using a high-capacity endotoxin removal spin column (Thermofisher), and following the endotoxin removal procedure, the EU concentration of the purified protein samples was diminished to less than 5 EU/mL. The dissolved protein was detected by Western blot and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
Healthy male bamboo sharks (Chiloscyllium plagiosum) with body lengths of 50-60 cm and body weights of approximately 600 g were purchased from the coastal area of Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province, China, kept in Zhejiang, and used as the experimental animals. The animals were given blood or immunized following a sufficient period of acclimatization (approximately 1 or 2 weeks) so that the sharks could determine the size of the tank and not hit the tank with their heads during swimming. During the immunization period of this study, the animals were reared in a laboratory marine fish culture system with a salinity of 1.018-1.025 and a temperature of 22-25°C and fed 2–3 shrimps per week regularly. The sharks were sedated with MS-222 prior to any procedure. As a result, the swimming speed of the shark gradually slowed and the gill movement gradually decreased, and when the shark was not able to turn over after turning it to be belly up, the shark was shown to be successfully anesthetized.
The bamboo sharks were immunized with hCD20 protein as an antigen at each injection time in the immunization program. ISA201 adjuvant (SEPPIC) was used as an immunopotentiator and prepared as an antigen emulsion. The sharks were immunized on a monthly basis for 6 months, and 100 μg of antigen was injected with ISA201 adjuvant in each immunization. Multiple injection spots were used to avoid tissue damage and infection. Negative whole blood was collected before the study and 1 month after all immunizations. Furthermore, 500 μL of blood was taken 2 weeks after each immunization and placed in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight. On the second day, the upper layer of serum was sucked out carefully, centrifuged at 1000 rpm and 4°C for 15 min, and stored in an empty EP tube before storage at -80 °C. After immunization, the shark was dissected and the spleen was removed and stored at -80 °C. All the sharks were maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions and used in accordance with the animal experimental guidelines set by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Protocol no. 202001066.
The changes in antibody levels in shark serum after immunization were detected using an ELISA. 96-well plates were coated with CD20 with respective concentrations of 2 µg/mL and incubated overnight at 4°C. After washing in 0.05% PBST and blocking by 1% BSA, serum, diluted to 1:100, 1:200, 1:400, and 1:800, was added to each immune tube and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. After washing three times, rabbit polyclonal antibody against VNAR prepared by our laboratory, diluted to 1:2000, was added to each immune tube and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Goat anti-rabbit lgG (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai) was then diluted to 1:5000 and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. After the final wash, the samples were further incubated in the dark with a freshly prepared TMB Single-Component Substrate solution (Solarbio, Beijing) for 15 min at 37°C to develop the signals. After the stop solution (2M H2SO4) was added, the plates were read at 450 nm on a plate reader.
Using the TRIzol method, total mRNA was extracted from the spleen after the bamboo sharks were immunized and the concentration was measured using optical density at 260 nm. The VNAR fragments were obtained after polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the cDNA using specific primers (Tables 1 and 2). The PCR products corresponding to VNAR genes were analyzed using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The PCR products were then digested with the SfiI restriction enzyme, and inserted into the phagemid p3RdV with T4 ligase. Using electroporation, recombinant plasmids were transformed into MC1061F’ cells and plated onto 2 × YT-Agar plates (1.6% tryptone, 1% yeast extract, 0.5% NaCl, 1.5% agar, 1% glucose) containing 15 µg/mL tetracycline and 100 µg/mL carbenicillin and cultured at 37°C overnight.
Three rounds of panning were performed. The 96-well plates coated with 5 mL of CD20 with respective concentrations of 5 µg/mL (round 1), 2 µg/mL (round 2), and 1 µg/mL (round 3) were incubated overnight at 4°C. After washing and blocking with 3% BSA (round 1), a 0.05g/mL casein-blocking solution (round 2), and a 2% no protein blocking solution (round 3), 100 µL of the amplified phage display library (2×1013 pfu/mL) was added to each well and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. In rounds 2 and 3, the amplified phage display library was added with one-third of the bound phages collected after the previous round of panning. The unbound phages were removed by washing six times with 0.1% PBST (round 1), 0.25% PBST (round 2), and 0.5% PBST (round 3). The number of washes was increased to eight times for subsequent rounds of panning. Phagemid particles were eluted, neutralized to pH=7, and reinfected with MC1061F’ cells. After 30 min of incubation on a shaker, the cells were plated onto 2 × YT plates containing 1% glucose, 15 µg/mL tetracycline, and 100 µg/mL carbenicillin and cultured at 37 °C overnight. The negative control was a non-related phage, and the positive control was an anti-CD20 antibody. The screening procedures were not repeated to prevent additional false positive signals.
CD20-specific VNARs were demonstrated and screened using a monoclonal ELISA and a phage ELISA. The antigen coating and blocking solutions are referred to in section 2.3. A total of 88 MC1061F’ clones were randomly selected, and the phage supernatants containing the VNAR fragments were obtained using the phage display technique. Thus, 100 µL phage supernatant was added to each plate and the binding ability was detected using an HRP-conjugated mouse anti-flag antibody. Meanwhile, the phage library and specific binding phage particles obtained by three rounds of panning with 4-fold gradient dilution were added to the phage ELISA plate, and the binding ability was detected by an HRP-conjugated mouse anti-M13 antibody.
The positive clones were identified using a monoclonal ELISA, and the bacterial solution was sent for sequencing. According to the sequencing results, CD20-specific VNAR sequences were screened out. A microplate reader AMP-100 was purchased from Hangzhou Allsheng Instruments Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). The read-out range was 0~4.000 Abs and linearity was [0.000~3.000 Abs] R²≥0.995.
According to the DNA sequencing results, CD20-specific VNAR sequences with His tags in the N-terminal and C-terminal were cloned into pET-28a (+) and were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells. The VNARs that could not be soluble expressed were also cloned into pET-41b(+) and transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells. Soluble VNARs containing His-tags were purified from the cell lysate by Ni-NTA resin, and soluble VNARs containing GST-tags were purified from the cell lysate by GST resin. The proteins produced and purified are shown in Table 1.
The VNAR was serially dilution from 3.5 µM to 0.01 fM in the ELISA coating buffer. CD20 was used as a specific binding molecule and for the antigen coating and blocking solution, please refer to section 2.3. Furthermore, 100 µL of commercial anti-CD20 antibody at 31.25 ng/ml was added to each plate, and binding ability was detected using an HRP-labeled Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) antibody diluted to 1:1000.
Raji cells were centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 3 min to collect cells. Then, 1 mL RPMI-1640 was added to the sediment and resuspended for adequate dissolution, and cell counts were performed. Subsequently, 96-well plates were coated with 5×103 Raji cells/well and cultured overnight in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C. The purified VNARs were added to the 96-well plate so that the final concentrations were 5 μM, 500 nM, and 50 nM, 100 μL/well. The negative control was a non-correlated VNAR with a final concentration of 5 μM, and 1×PBS was added to the blank control. Ten μLCCK-8 were added to each plate after 48 h of culturing in the cell incubator. After that, the 96-well plates were cultured in the cell incubator for 3 h, and the plates were read at 450 nm on a plate reader.
Raji cells were centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min to collect cells. After washing two times with PBS, 500 μL PBS was added to the sediment and resuspended for adequate dissolution. Then, 50 μL cell drops were taken and added to adhesive slides and settled for 2 h. After the liquid on the slides was discarded, 50 μL 4% paraformaldehyde fixing solution was added and incubated at room temperature for 20 min. The adhesive slides were washed four times with PBS for 5 min each time. After blocking with 5% BSA for 1 h and washing with PBS four times, 50 μL of 50 μg/mL VNAR was added and incubated at 4°C overnight. Furthermore, 50 μL His-tag mouse monoclonal antibody diluted to 1:200 was added and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. After washing with PBS, 50 μL Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) diluted to 1:500 was added and incubated for 1 h at room temperature away from light. After washing with PBS and ddH2O, DiL dye with a working concentration of 5 μM was added and dyed at 37°C for 20 min. After washing with PBS, the samples were placed under an inverted fluorescent microscope to view the results. A TE2000-U inverted microscope was purchased from the Nikon Corporation Healthcare Business Unit (Shanghai, China). The filter magnification is 100× and the wavelength is 488 nm.
For all the results, data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 8 and the one-way ANOVA statistical method.
To obtain anti-CD20 VNAR single-domain antibodies, we used the purified extracellular truncated peptide of CD20, encompassing the domain positioned between the third and fourth transmembrane regions, as the antigen, expressed via the E. coli expression system (Figure 1A). The purification and identity of the CD20 protein derived from the bamboo shark were further confirmed through Western blot analysis (Figure 1B). Subsequently, the antibody titers in the serum of bamboo sharks immunized with recombinant CD20 were assayed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Figure 1C). The results indicated a gradual increase in serum antibody levels with an escalating number of immunizations, yielding a robust immune response. Additionally, glutathione S-transferase (GST) and histidine (His) tags were incorporated into the recombinant antigen to enhance its immunogenicity and protein expression, while ensuring no interference with the protein’s functional activity (Figure 1D).
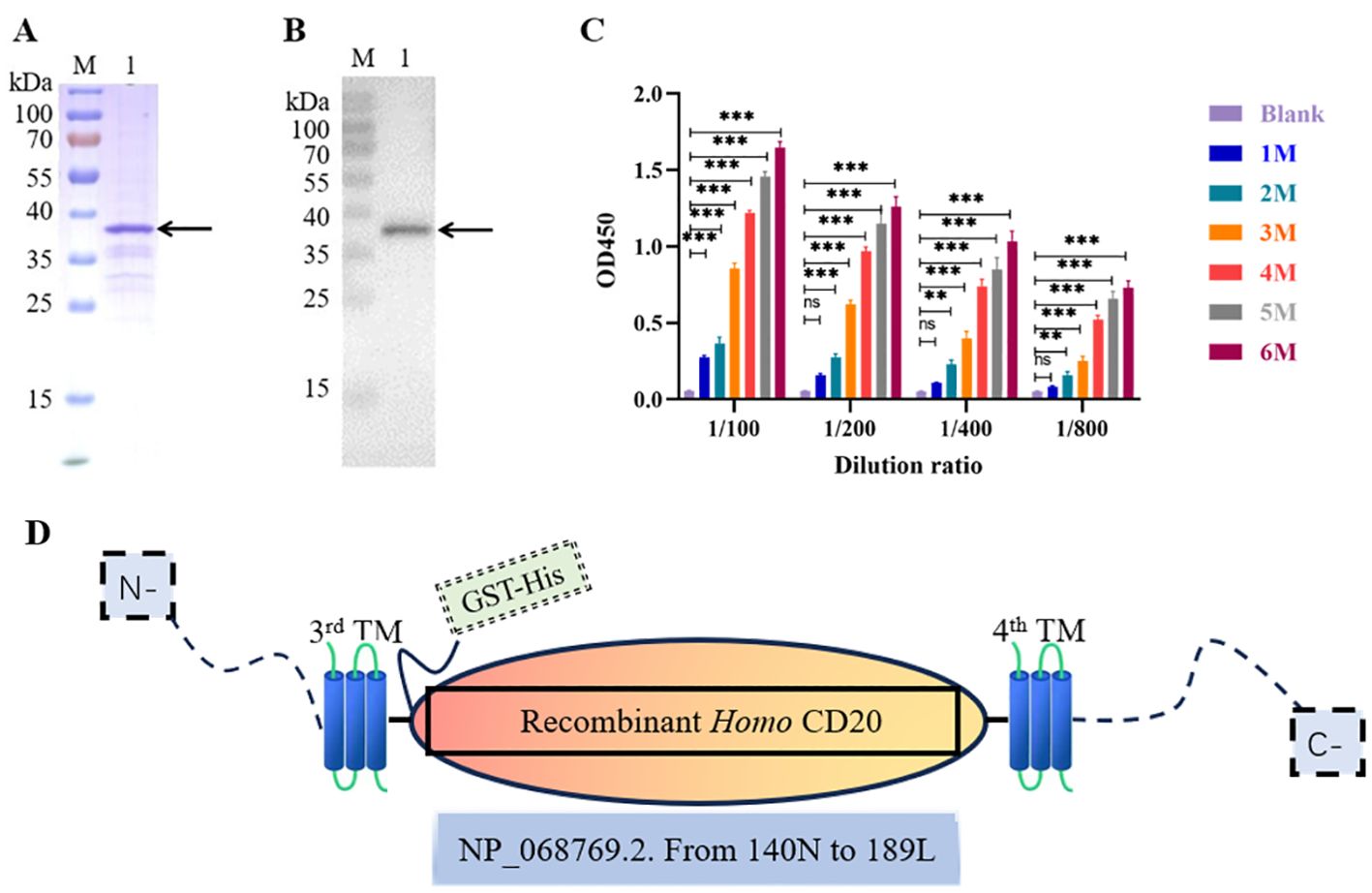
Figure 1. Preparation of the CD20 antigen and evaluation of the immunization effect of bamboo shark. (A) Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis of CD20 purification using GST-tag Purification Resin. (B) The identification of purified CD20 protein from the bamboo shark was validated by Western blot. (C) ELISA was used to detect the changes in antibody levels in the shark serum after different immunization times. (D) The schematic depiction illustrates the closed region of hCD20 (NP_068769.2). Specifically, the antigen fragment was cloned, encompassing amino acid residues ranging from the 140N to the 189L positions, utilizing a GST-His tag for facilitated purification and detection. This cloned fragment was subsequently expressed in E. coli via the pET-41b(+) vector. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
Total RNA was extracted from the spleen after immunization of the bamboo shark with the CD20 protein. The VNAR encoding gene fragments were then amplified by nested PCR with approximately 500-600 bp fragments (Round1) and 200-400 bp fragments (Round2) purified with gel extraction, which were then inserted into p3RdV vectors and electroporated into MC1061F’ cells. After obtaining the anti-CD20 VNAR phage-displayed library, the library capacity and the insert ratio were then determined. The correct insert ratio was approximately 100% through the colony PCR assay, and the library capacity reached approximately 2.7 × 109 colony-forming units (CFU). Three rounds of panning were performed and CD20-specific VNARs were demonstrated and screened by a phage ELISA (Figure 2A) and a monoclonal ELISA (Figure 2B). The results of the phage ELISA showed that the phages that could bind CD20 were gradually enriched through three rounds of panning. At the same time, combined with the color rendering of the negative sieve plate, the results of the monoclonal ELISA showed that the number of positive clones gradually increased with the increase in panning times, and the number of positive clones in the third round of panning was much more than that in the first and second rounds, further proving that the specific sequences were gradually enriched with the three rounds of panning. Overall, these results indicated that a CD20-specific, phage-displayed VNAR library was successfully established. The positive clones were sequenced, and the five VNAR sequences with the most frequent occurrences were selected for subsequent experiments; the results are shown in Figure 2C.
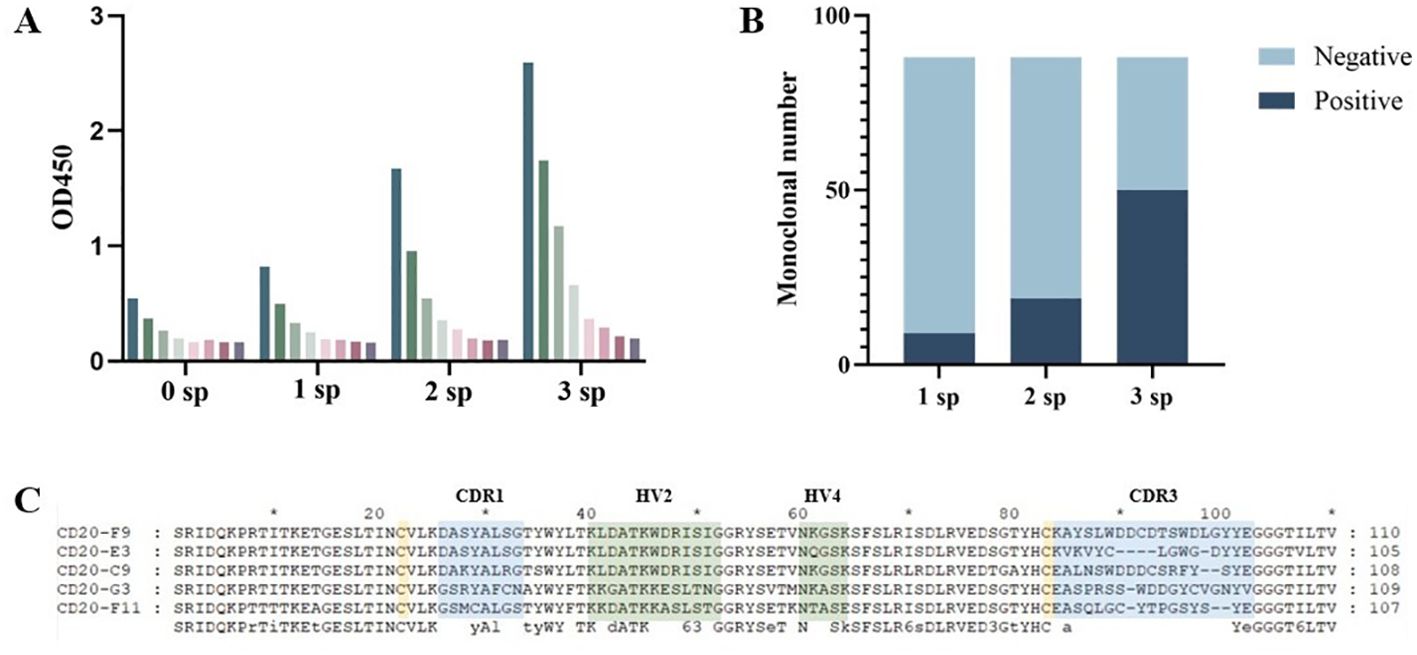
Figure 2. Anti-CD20 VNARs were selected by phage display panning. (A) The enrichment between specific VNARs and CD20 was detected by phage ELISA in three rounds of panning. (B) Independent clones (randomly picked from 1sp, 2sp, 3sp) were tested for their ability to bind to CD20 by ELISA. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of anti-CD20 VNARs. CDR denotes a complementarity-determining region; HV denotes a hypervariable region.
The molecular docking ability with CD20 of the five candidate VNARs was simulated using ZDOCK (Figure 3). The results showed that the CDR3 region of the five candidate VNAR sequences could bind to dimerized CD20, and the binding site was located in the large extracellular ring region of CD20.
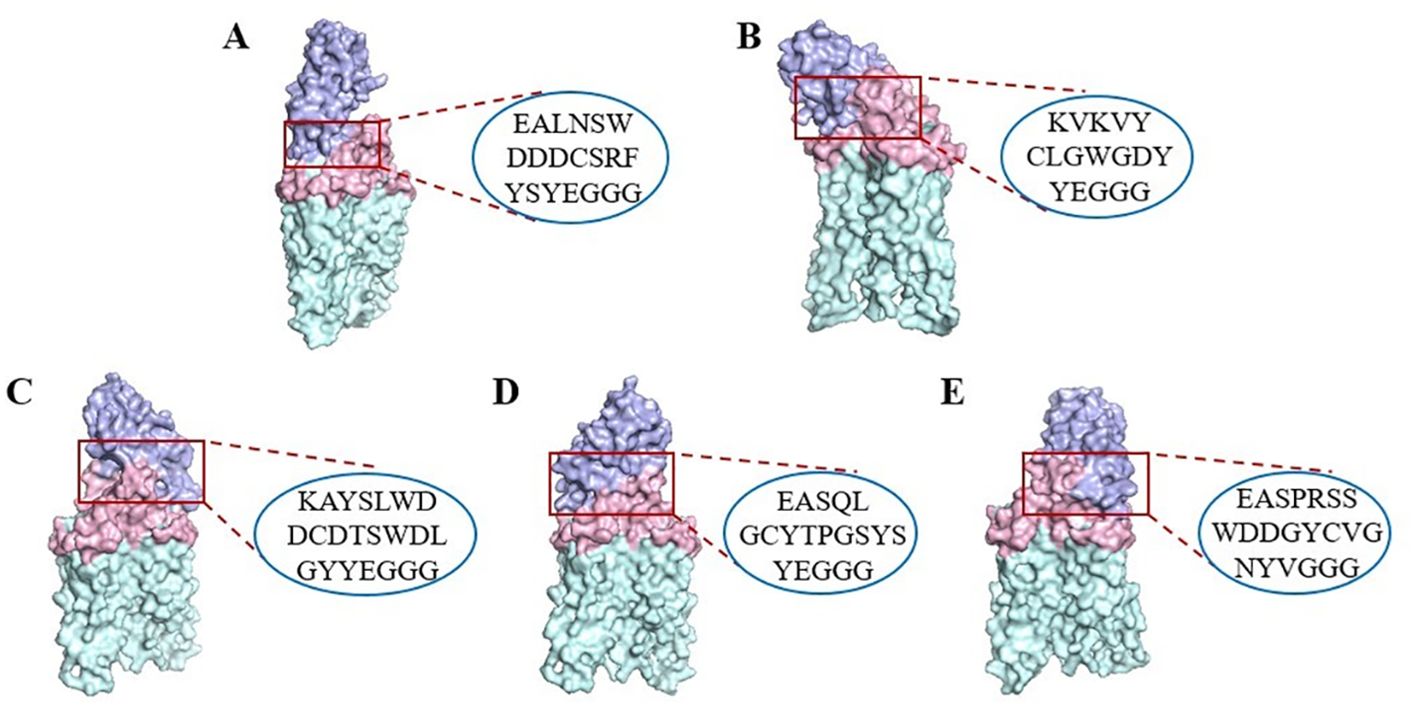
Figure 3. Surface representation of the five VNARs and CD20 (PDB ID: 6VJA) on CD20. (A) CD20-C9 (purple) and CD20 extracellular macrocyclic regions (pink) on the dimeric CD20 (green). (B) CD20-E3 (purple). (C) CD20-F9 (purple). (D) CD20-F11 (purple). (E) CD20-G3 (purple). The CDR3 region sequence in the VNARs is indicated by a red box.
To determine the VNAR single-domain antibody binding and blocking activity, the five candidate anti-CD20 VNARs, F9, G3, C9, E3, and F11, were produced in an E. coli BL21(DE3) strain. Ni-NTA resin was used to purify the F9 and G3 VNAR proteins from the E. coli supernatants (Figure 4A). GST-tag purification resin was used to purify the C9, E3, and F11 VNAR proteins which were fused and expressed with a 26 kDa GST-tag (Figure 4B). SDS-PAGE analysis showed good quality with more than 90% purity after purification.
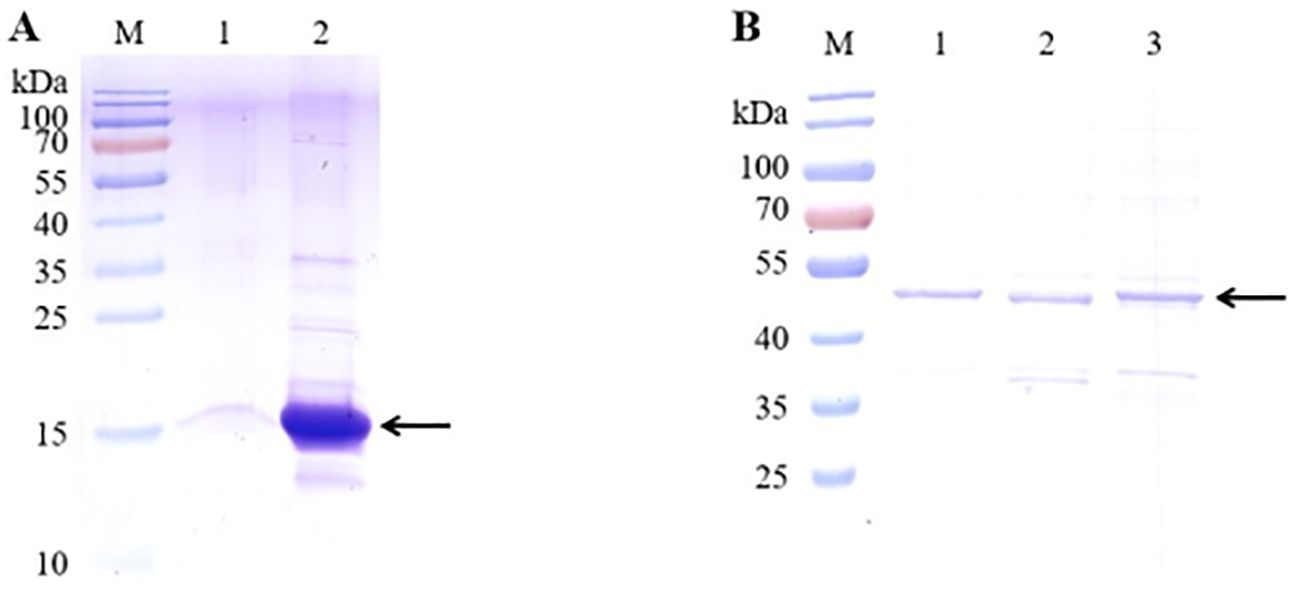
Figure 4. SDS-PAGE analysis of the five candidate VNARs’ purity using GST-tag Purification Resin. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of two candidate VNARs’ purity using Ni-NTA resin. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of three candidate VNARs’ purity using GST-tag Purification Resin. (The target VNARs were fused and expressed with a 26 kDa GST-tag).
To measure the affinity of the screened VNARs with CD20, a double antibody sandwich ELISA experiment was performed. The experimental results showed a good concentration gradient-dependent effect as the readings were 2.1 times higher than negative (Figure 5A, Supplementary Figure S2). The five VNARs and CD20 had good binding activity in vitro, among which F9 had the best binding activity. A non-related VNAR was used as the control group in the ELISA. The EC50 of the screened VNARs was calculated using the curve fitting method (Figure 5B).
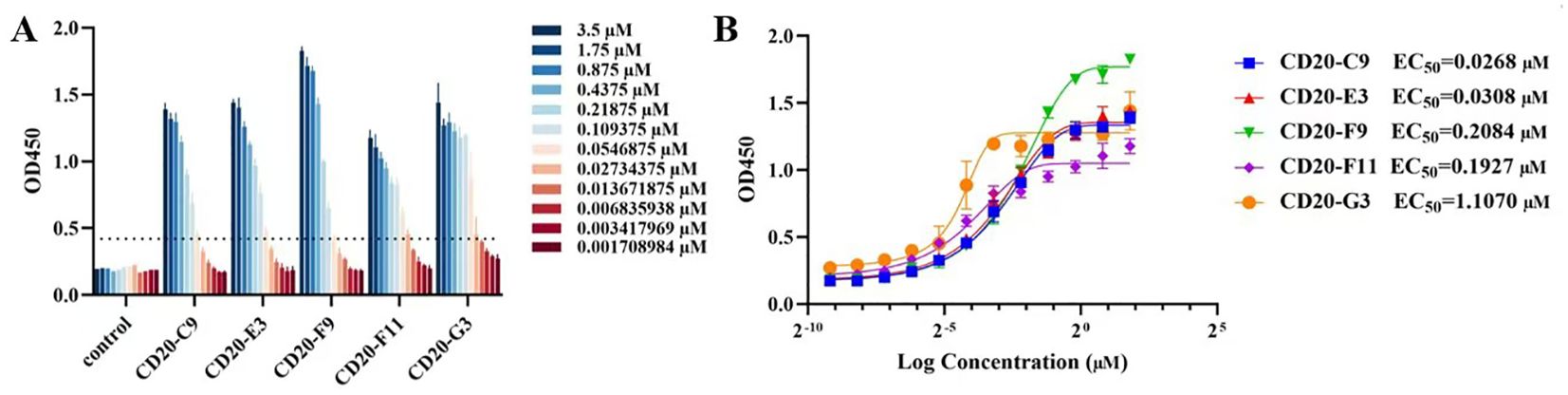
Figure 5. The affinity between VNARs and CD20 was detected using a double-antibody sandwich ELISA. (A) In vitro binding affinities of recombinant anti-CD20 VNARs at various concentration gradients to CD20. (B) The EC50 of each screened VNAR.
In order to detect the anti-Raji lymphocyte activity of the VNARs, the survival rate of Raji cells with different concentrations of the recombinant VNARs was measured using the CCK-8 method (Figure 6). As shown in Figure 6, F9, F11, and G3 all showed great inhibition and an obvious concentration gradient effect. However, C9 and E3 were similar to the non-correlated VNAR, and the inhibition effect was not strong. F9, F11 and G3 were selected for subsequent experiments.
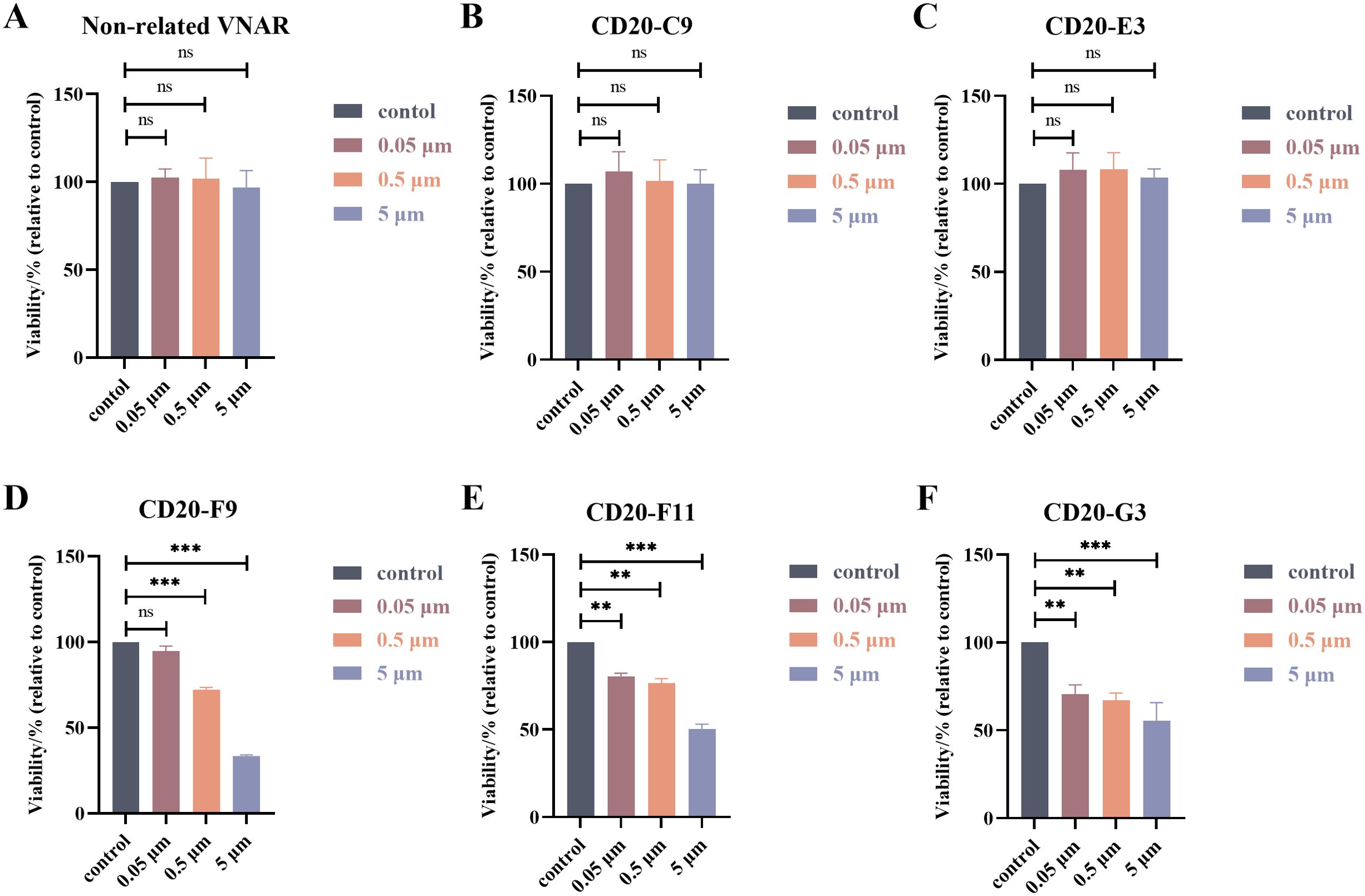
Figure 6. Results of the cytotoxicity assays. (A–F) Survival of Raji lymphoma cells treated with different concentrations of the recombinant VNARs. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
The ability of the VNARs to bind to Raji cells with high CD20 expression was demonstrated using a cellular immunofluorescence assay (Figure 7). The cell membranes were stained with Dil dye and gave off red fluorescence. Purified VNAR-Alexa Fluor 488 combined with Raji cells produced green fluorescence. The experimental results show that all three VNARs could recognize and bind to CD20 on the surface of the cell membrane.
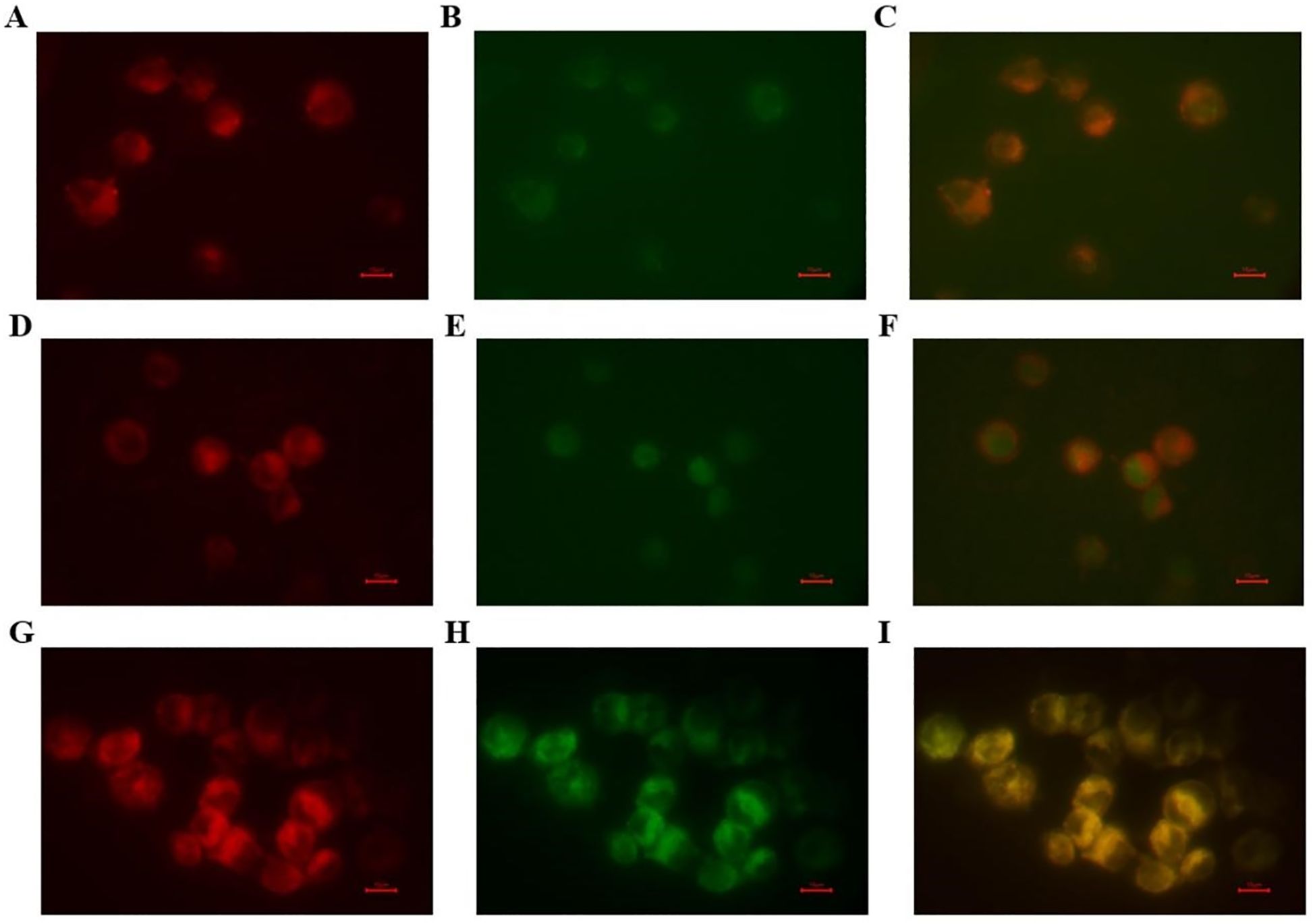
Figure 7. The targeted binding activities of the screened VNARs. The targeted binding activities of the screened VNARs were detected by cellular immunofluorescence. (A–C) The binding analysis of purified CD20-F9-Alexa Fluor 488 to Raji cells. (D–F) The binding analysis of purified CD20-F11-Alexa Fluor 488 to Raji cells. (G–I) The binding analysis of purified CD20-G3-Alexa Fluor 488 to Raji cells. The membranes were red when DiL stained and purified VNAR-Alexa Fluor 488 was green when bound to Raji cells.
CD20 has emerged as an ideal target for B-cell lymphoma therapy, attracting significant attention due to its clinical significance as a validated target for B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The large extracellular loop, positioned between the third and fourth transmembrane domains, is the binding domain for numerous anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, including RTX and ocrelizumab (Klein et al., 2021). However, the full-length recombinant CD20 protein often tends to misfold and aggregate when expressed in bacterial or cellular hosts (Anbouhi et al., 2012). To address this challenge and ensure correct secondary conformation, the recombinant expression of the CD20 large extracellular loop is frequently employed as the antigen. Nonetheless, due to its small size (only 5.5 kDa), the clonal sequences between the third and fourth transmembrane regions of hCD20 necessitate fusion with a protein (commonly using fusion partner proteins) to enhance its antigenicity (Figure 1D). In this study, the pET-41b(+) vector with a GST fusion tag was used due to advantages such as facilitating simple purification, not interfering with protein activity, and promoting soluble protein expression (Frangioni and Neel, 1993). The expression of CD20 (NP_068769.2) with the GST fusion tag yielded proper expression levels in the supernatant. Importantly, the antigen expressed and purified in the supernatant retained the original antigenic epitopes, enabling the generation of antibodies that specifically bind to these epitopes following immunization.
Prior studies have demonstrated that attaining the desired immune response in Chiloscyllium plagiosum may take approximately 4–6 months (Kovaleva et al., 2014). Building on preliminary findings from our laboratory, we observed that the optimal immune effects could be achieved after 4 months of immunization, involving a total of four immunizations with a 1-month interval between each immunization. The experimental results from this study were in line with previous findings, indicating a significant increase in the titer of IgNAR in the serum after the third and fourth immunizations, with the immune process concluding after the sixth immunization. As a result, the specific shark anti-serum with high IgNAR abundance was successfully obtained.
The variable regions of sdAbs are highly soluble, stable, and devoid of glycosylation and complex modifications, which facilitates their easy cloning and expression in prokaryotic expression systems (Muyldermans, 2013). Prokaryotic expression allows for the efficient and cost-effective production of sdAbs in large quantities, with a straightforward process that enables the rapid generation of specific single-domain antibodies. The antigen-binding affinity tests of the recombinant VNARs revealed a clear concentration gradient effect, and all five VNARs exhibited robust in vitro binding activity to CD20. Anti-CD20 VNAR specificity was highly active and only exhibited a specific affinity for cells expressing CD20 (Supplementary Figure S1). Even when diluted to 0.05 µM, the VNARs still maintained their binding activity. Further, cell experiments demonstrated that among these VNARs, only CD20-F9, CD20-F11, and CD20-G3 exhibited significant inhibitory effects on Raji lymphoma cells, and subsequent immunofluorescence experiments confirmed the specific binding of these three VNARs to the CD20 protein on the surface of Raji lymphoma cells. By comparing our results with those of existing studies (Lara et al., 2022), we found that two VNARs, CD20-F11 and CD20-G3, selected in our study could significantly inhibit Raji cells at a concentration as low as 0.05 µM (750 ng/mL), which is nearly 7 times lower than the lowest inhibitory concentration of various isotypes of rituximab for Raji cells. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of the CD20-specific VNARs was independent of complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby potentially broadening the therapeutic application spectrum of such agents in targeting CD20-positive cellular entities. These compelling results indicated that the screening in this study identified three VNARs, namely CD20-F9, CD20-F11, and CD20-G3, as possessing anti-human CD20 activity, and their mechanisms of action hold promise as directions for further investigation. CD20 is a promising therapeutic target for B-lymphoblastoma, exhibiting remarkable clinical efficacy. However, several limitations still need to be addressed. Notably, drug resistance poses a significant challenge, as some patients may develop resistance to anti-CD20 antibodies, leading to decreased treatment efficacy or recurrence of the disease. Moreover, there is a scarcity of therapeutic options for CD20-negative tumors, along with potential adverse effects, limitations associated with high-dose chemotherapy, and constraints due to antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC). It is imperative to continue monitoring the possible limitations and side effects of CD20-targeted therapies in practical applications and to pursue the development of novel therapeutic approaches and medications actively.
At present, VNAR technology exhibits a diverse array of applications across various fields. Shark-derived VNARs are emerging as a promising and non-toxic alternative to ochratoxin A, as evidenced by recent research conducted by Xie et al. (2024). Jiao et al. (2024) further demonstrated the substantial potential of VNARs in detecting tropomyosin in food samples through the application of lateral flow immunochromatographic assays. In the context of disease treatment, sensitive detection of cancer biomarkers plays a pivotal role in facilitating timely diagnosis and effective treatment interventions. By constructing phage libraries of VNAR anti-fetal protein and identifying VNAR with high detection accuracy, (Wang et al., 2024) have validated the robust immunodiagnostic potential of VNAR. Additionally, Liu et al. have shown that VNAR could serve as a valuable candidate for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infections.
As of now, research on VNAR-based drugs remains in the preclinical stage. However, considering their unique physiological and biochemical properties, the development of VNAR drugs for targeted therapy holds tremendous potential and serves as a crucial research focus in B-cell lymphoma treatment. The insights and experimental groundwork provided by this study lay the foundation for subsequent clinical research and the potential application of single-domain antibodies in the treatment of clinical anti-lymphoma.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
This study has been approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Zhejiang Sci-Tech University. Protocol no. 202001066.
QR: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – original draft. LS: Software, Writing – original draft. FZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JC: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. CY: Resources, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Zhejiang Provincial Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project, China, grant number: LGF18H090012, LTGY24H100001.
Author YS was employed by the company Zhejiang Shengyu Medical Technology Co., Ltd. Authors FZ and XJ were employed by the company Jiangsu Baiying Biotech Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1498223/full#supplementary-material
Anbouhi M. H., Abolhassani M., Bouzari S., Khanahmad H., Aghasadeghi M. R., Madadkar-Sobhani A., et al. (2012). Immunological evaluation of predicted linear B-cell epitopes of human CD20 antigen. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 59, 186–192. doi: 10.1002/bab.v59.3
Bubien J. K. (1993). Transfection of the CD20 cell surface molecule into ectopic cell types generates a Ca2+ conductance found constitutively in B lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 121, 1121–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.1121
Cragg M. S., Walshe C. A., Ivanov A. O., Glennie M. J. (2005). The biology of CD20 and its potential as a target for mAb therapy. Curr. Dir. In Autoimmun. 8, 140–174. doi: 10.1159/000082102
D’Amico E., Zanghì A., Gastaldi M., Patti F., Zappia M., Franciotta D. (2019). Placing CD20-targeted B cell depletion in multiple sclerosis therapeutic scenario: Present and future perspectives. Autoimmun. Rev. 18, 665–672. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.05.003
Deans J. P., Li H., Polyak M. J. (2002). CD20-mediated apoptosis: signalling through lipid rafts. Immunology 107, 176–182. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01495.x
De Silva D. P. N., Tan E., Mizuno N., Hosoya S., Reza M. S., Watabe S., et al. (2019). Transcriptomic analysis of immunoglobulin novel antigen receptor (IgNAR) heavy chain constant domains of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 84, 370–376. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.004
Engelhard M. (2016). Anti-CD20 antibody treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Clin. Immunol. (Orlando Fla.) 172, 101–104. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.08.011
Feige M. J., Gräwert M. A., Marcinowski M., Hennig J., Behnke J., Ausländer D., et al. (2014). The structural analysis of shark IgNAR antibodies reveals evolutionary principles of immunoglobulins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 111, 8155–8160.
Feng Y., Zhou Z., McDougald D., Meshaw R. L., Vaidyanathan G., Zalutsky M. R. (2021). Site-specific radioiodination of an anti-HER2 single domain antibody fragment with a residualizing prosthetic agent. Nucl. Med. Biol. 92, 171–183.
Frangioni J. V., Neel B. G. (1993). Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione S-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Analytical Biochem. 210, 179–187. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1170
Greenberg A. S., Avila D., Hughes M., Hughes A., Mckinney E. C., Flajnik M. F. (1995). A new antigen receptor gene family that undergoes rearrangement and extensive somatic diversification in sharks. Nature 374, 168–173. doi: 10.1038/374168a0
Jiang X., Sun L., Hu C., Zheng F., Lyu Z., Shao J. (2023). Shark IgNAR: The next broad spplication antibody in clinical diagnoses and tumor therapies? Mar. Drugs. 21 (9), 496–514.
Jiao S., Xie X., He Z., Sun Z., Wang Z., Zhang S., et al. (2024). Lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for competitive detection of crustacean allergen tropomyosin using phage-displayed shark single-domain antibody. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 1811–1821. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07569
King H., Myatt R. (2014). An overview of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancer Nurs. Pract. 13, 31–38. doi: 10.7748/cnp2014.02.13.1.31.e1042
Klein C., Jamois C., Nielsen T. (2021). Anti-CD20 treatment for B-cell Malignancies: current status and future directions. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 21, 161–181. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1822318
Kovaleva M., Ferguson L., Steven J., Porter A., Barelle C. (2014). Shark variable new antigen receptor biologics - a novel technology platform for therapeutic drug development. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 14, 1527–1539. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.937701
Lara S., Heilig J., Virtanen A., Kleinau S. (2022). Exploring complement-dependent cytotoxicity by rituximab isotypes in 2D and 3D-cultured B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 22, 678–688. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09772-1
Maloney D. G., Liles T. M., Czerwinski D. K., Waldichuk C., Rosenberg J., Grillo-Lopez A., et al. (1994). Phase I clinical trial using escalating single-dose infusion of chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8) in patients with recurrent B-cell lymphoma. Blood 84, 2457–2466. doi: 10.1182/blood.V84.8.2457.2457
Marshall M. J. E., Stopforth R. J., Cragg M. S. (2017). Therapeutic antibodies: what have we learnt from targeting CD20 and where are we going? Front. Immunol. 8, 22. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01245
Muyldermans S. (2013). “Nanobodies: natural single-domain antibodies,” in Annual Review of Biochemistry, vol. 82 . Ed. Kornberg R. D. (Annual Reviews, Palo Alto).
Pavlasova G., Mraz M. (2020). The regulation and function of CD20: an “enigma” of B-cell biology and targeted therapy. Haematologica 105, 1494–1506. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.243543
Polyak M. J., Li H., Shariat N., Deans J. P. (2008). CD20 homo-oligomers physically associate with the B cell antigen receptor. Dissociation upon receptor engagement and recruitment of phosphoproteins and calmodulin-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 18545–18552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800784200
Qin L., Ren Q., Lu C., Zhu T., Lu Y., Chen S., et al. (2023). Screening and anti-glioma activity of Chiloscyllium plagiosum anti-human IL-13Rα2 single-domain antibody. Immunol. 170 (1), 105–119.
Tedder T. F., Klejman G., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. (1989). Structure of the gene encoding the human B lymphocyte differentiation antigen CD20 (B1). J. Immunol. 142, 2560–2568. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.142.7.2560
Teeling J. L., Mackus W. J. M., Wiegman L. J. J. M., Van Den Brakel J. H. N., Beers S. A., French R. R., et al. (2006). The biological activity of human CD20 monoclonal antibodies is linked to unique epitopes on CD20. J. Immunol. (Baltimore Md.: 1950) 177, 362–371. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.1.362
Traenkle B., Rothbauer U. (2017). Under the Microscope: single-domain antibodies for live-cell imaging and super-resolution microscopy. Front. Immunol. 8, 1030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01030
Wang Z., Xie X., He Z., Sun Z., Zhang Y., Mao F., et al. (2024). Development of shark single domain antibodies specific for human α-fetoprotein and the multimerization strategy in serum detection. Anal. Chem. 96, 4242–4250. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05675
Wei L. K., Wang M. N., Xiang H. T., Jiang Y., Gong J. H., Su D., et al. (2021). Bamboo shark as a small animal model for single domain antibody production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 16. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.792111
Xie X., He Z., Sun Z., Zhang S., Cao H., Hammock B. D., et al. (2024). Shark anti-idiotypic variable new antigen receptor specific for an alpaca nanobody: Exploration of a nontoxic substitute to ochratoxin A in immunoassay. J. Hazard Mater. 477, 135264. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.135264
Zielonka S., Empting M., Grzeschik J., Konning D., Barelle C. J., Kolmar H. (2015). Structural insights and biomedical potential of IgNAR scaffolds from sharks. Mabs 7, 15–25. doi: 10.4161/19420862.2015.989032
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma, CD20, Chiloscyllium plagiosum, vNAR, phage display
Citation: Ren Q, Sheng Y, Sun L, Zheng F, Hu C, Chen J, Lyu Z, Yuan C and Jiang X (2024) The screening and anti-Raji lymphoma effect of Chiloscyllium plagiosum anti-CD20 VNARs. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1498223. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1498223
Received: 19 September 2024; Accepted: 28 November 2024;
Published: 19 December 2024.
Edited by:
Saravana Periaswamy Sivagnanam, Munster Technological University, IrelandReviewed by:
Abhishek Asthana, Cleveland Clinic, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Ren, Sheng, Sun, Zheng, Hu, Chen, Lyu, Yuan and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaofeng Jiang, eGZqaWFuZ0B6c3R1LmVkdS5jbg==; Chen Yuan, MTI0MzY2MDM2M0BxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.