- 1Fisheries College, Jimei University, Xiamen, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Mariculture Breeding, Fisheries College of Jimei University, Xiamen, China
- 3Fishery College, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China
- 4Zhejiang Province Key Lab of Mariculture and Enhancement, Zhejiang Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Zhoushan, China
Effectively assessing the basic genomic information of a species is fundamental for conducting molecular research and provides a foundation for constructing whole-genome maps. Hapalogenys analis is a temperate and tropical nearshore marine fish in China’s coastal waters, with significant economic value and high aquaculture potential. However, the genomic differences between male and female individuals of this species are not yet apparent. This study conducted whole-genome survey analyses on male and female H. analis to provide basic genomic information. According to K-mer analysis, the genome sizes of female and male fish were 436.24 Mb and 493.21 Mb. The heterozygosity rates were 0.58% for females and 0.23% for males. The proportion of repetitive sequences of female and male fish were 42.95% and 51.20%. The GC content of the genomes was 43.30% for female and 43.20% for male. The sizes of the assembled genomes were 589.18 Mb for female and 592.02 Mb for male, with N50 lengths of 3,135 bp and 3,041 bp, respectively. SSR screening results showed that 959,447 and 894,158 SSR sequences were detected in the genomes of female and male, respectively. The lengths of the assembled mitochondrial genome sequences were 19,755 bp for female and 19,754 bp for male, each containing 38 genes. Among these mitochondrial sequences, 13 protein-coding genes were identified, including 7 NADH dehydrogenase, 3 cytochrome c oxidase, 1 cytochrome b, and 2 ATP synthase genes. Both sequences contained 23 tRNA genes and 2 rRNA genes. This study provides a theoretical basis for constructing a high-quality whole genome of H. analis and valuable data for subsequent molecular breeding research.
1 Introduction
Hapalogenys analis Richardson (1844), belongs to the order Perciformes, the family Pomadasyidae, and the genus Hapalogenys. It is widely distributed in the coastal waters of China and is an economically important temperate and tropical nearshore marine fish (Zheng et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2023). This species prefers to inhabit rocky reef areas at a depth of 30-50 meters. It feeds on small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Its flesh is tender and flavorful, with high nutritional value, making it a species with great potential for aquaculture (Mohapatra et al., 2013). In recent years, due to the overexploitation of fishery resources and the intensification of environmental pollution, the wild populations of H. analis have sharply declined. Protecting and sustainably utilizing these resources have become urgent issues that must be addressed. The species’ euryhaline and cold-tolerant characteristics make it particularly suitable for artificial breeding and stock enhancement to restore resources. However, the genomic differences between male and female individuals of this species have not been systematically analyzed, severely hindering its artificial breeding development. Therefore, analyzing the genomic characteristics of male and female H. analis and gaining an in-depth understanding of their genetic structure and gender differences are crucial. This analysis can provide genomic resource data for molecular breeding efforts.
With the rapid development of molecular biology techniques, sequencing technologies have continuously advanced while costs have decreased. Whole-genome sequencing has become a standard method in biological research. Simplified genome sequencing based on second-generation sequencing technologies has been widely applied (Raffini et al., 2017). Genomic sequencing technology provides a powerful tool for uncovering the genetic background, sex differences, and adaptive evolution of species. Through genome survey sequencing, the genomic structure of a species can be analyzed, revealing functional genes and their regulatory mechanisms. This provides a crucial foundation for species conservation, breeding, and resource management (Goodwin et al., 2017). Research on genomic differences between male and female individuals is vital for understanding sex-related traits and reproductive mechanisms. The H. analis exhibits significant sexual dimorphism, with males and females showing notable differences in growth rate, body structure, and reproductive capacity. These sex differences are significant for biological research and provide new insights for aquaculture and management. However, there have been few reports on genomic research on H. analis. For example, Zheng et al. (2020) obtained the complete mitochondrial genome of this species using whole genome sequencing technology, and Sun et al. (2023) studied its population structure. This has somewhat deepened the understanding of the species at the genomic level.
Additionally, genome assembly based on next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology can significantly improve the integrity and continuity of the genome, facilitating more accurate analysis of genome structure and function (Miller et al., 2010). As an efficient molecular marker tool, the development and analysis of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers are widely used in genetic diversity assessment, population structure analysis, and breeding research (Vieira et al., 2016). Meanwhile, the annotation and analysis of mitochondrial genomes also play an essential role in understanding species’ evolutionary history, phylogeny, and population dynamics (Boore, 1999). In recent years, remarkable progress has been made in the genomic sequencing of male and female fish. Researchers have utilized high-throughput sequencing technology to perform genomic sequencing on various economically important fish species and have analyzed their sex-related genes, including Nothobranchius furzeri (Reichwald et al., 2015), Danio rerio (Wilson et al., 2014), Salmo salar L. (Timmerhaus et al., 2011) and Thunnus alalunga (Montes et al., 2012). These studies provide important genomic data and analytical tools for understanding gender differences and evolution in fish.
This study aims to conduct genome survey sequencing of male and female individuals of H. analis, perform genome assembly using NGS technology, conduct SSR analysis, and annotate the mitochondrial genome. Specific objectives include constructing genomic drafts of male and female H. analis individuals, analyzing genome size, GC content, repetitive sequences, and genome integrity, providing a preliminary description of the genomic characteristics of male and female individuals. This study will establish foundational data for research on the genomic characteristics, genetic resource development, and conservation management of H. analis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sample collection, DNA extraction and genome sequencing
The two H. analis samples (1 female and 1 male) used for genome survey sequencing were collected from the Zhoushan sea area in Zhejiang. Samples were cryopreserved and transported to the Marine Fishery Resource and Biodiversity Laboratory of Zhejiang Ocean University. Approximately 1 g of muscle tissue was extracted from each sample for DNA extraction.
The phenol/Chloroform extraction method was used to extract the DNA from muscle tissue (Sambrook et al., 1982). The extracted DNA concentration was assessed using NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc, USA) and verified through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. After ultrasonic fragmentation, libraries were constructed with insert fragment sizes of approximately 350 bp for sequencing (Supplementary Figure S1). All libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform according to the manufacturer′s protocol.
2.2 Data quality control and genome survey analysis
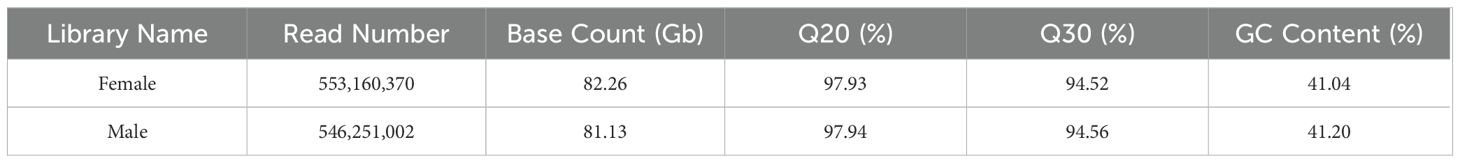
We utilized FASTP (V0.23.2) (Chen et al., 2018) with default parameters for raw data filtering and quality control, resulting in the acquisition of clean data. Following the step, high-quality data of 82.26 Gb for female and 81.13 Gb for male (averaging 139.6× and 137.0× coverage of the genome for female and male, respectively) were retained for further analysis. Metrics such as quality values Q20 and Q30, along with GC content, were calculated to assess sequencing quality. GCE (V1.0.0) (Liu et al., 2013) was used to estimate each sample’s genome characteristics, with a K-mer size of 17. The outcomes of the K-mer analysis were leveraged to estimate genome size, heterozygosity, and repeat ratio. The algorithm used for determining genome size is as follows: genome size = K-mer_num/peak_depth, where K-mer_num represents the total number of K-mers, and peak_depth is the expected value of the K-mer depth.
2.3 Genome assembly, evaluation and SSR identification
SOAPdenovo2 (Vr240) (Luo et al., 2012) was employed to assemble the clean reads into distinct contigs individually. The assembly genome sequences were evaluated by Quast (V5.0.2) (Gurevich et al., 2013). Simultaneously, the conserved gene sequences of each genome were identified. Potential microsatellite motifs were identified using the Perl script “misa.pl” from the MISA software (Beier et al., 2017). The minimum number of SSR repeats for dinucleotide, trinucleotide, tetranucleotide, pentanucleotide, and hexanucleotide microsatellite motifs with 6, 5, 5, 5, 5, respectively.
3 Results
3.1 Genomic survey sequencing of male and female H. analis
After quality control and filtering of raw data, sequencing data of 82.26 Gb and 81.13 Gb were obtained from the libraries of female and male H. analis, respectively. All samples’ Q20 and Q30 values were higher than 97.93% and 94.52%, respectively, indicating an exceptionally high overall sequencing quality (Table 1). Then, we used the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST), random 10,000 single-end reads from the libraries of male and female fish were compared with the Nucleotide Sequence Database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), revealing no significant exogenous contamination in the reads (Supplementary Tables S1, S2).
3.2 Genomic K-mer analysis
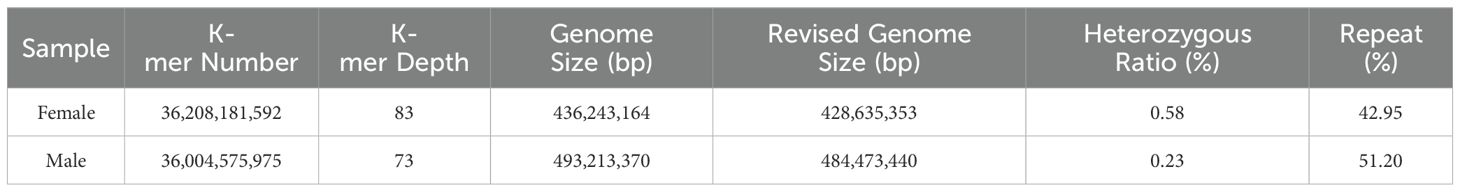
We conducted K-mer (K=17) analysis on the sequencing data to evaluate the genome size, heterozygosity, and proportion of repetitive sequences in different samples. The genome survey results showed a main peak for females at a depth of 50 (Figure 1A) and for males at 73 (Figure 1B). After excluding K-mers with abnormal depths, there were a total of 36,208,181,592 K-mers used to estimate the genome length of females, and a total of 36,004,575,975 K-mers used to estimate the genome length of males. All samples were diploid, with the genome size of female dotted gudgeon was 436.24 Mb, heterozygosity was 0.58%, and proportion of repetitive sequence was 42.95%. The genome survey results for male showed that after excluding K-mers with abnormal depths, the genome size of male dotted gudgeon was 493.21 Mb, heterozygosity was 0.23%, and proportion of repetitive sequence was 51.20% (Table 2). This implies significant diversity in adequate population size among these fish under natural conditions.
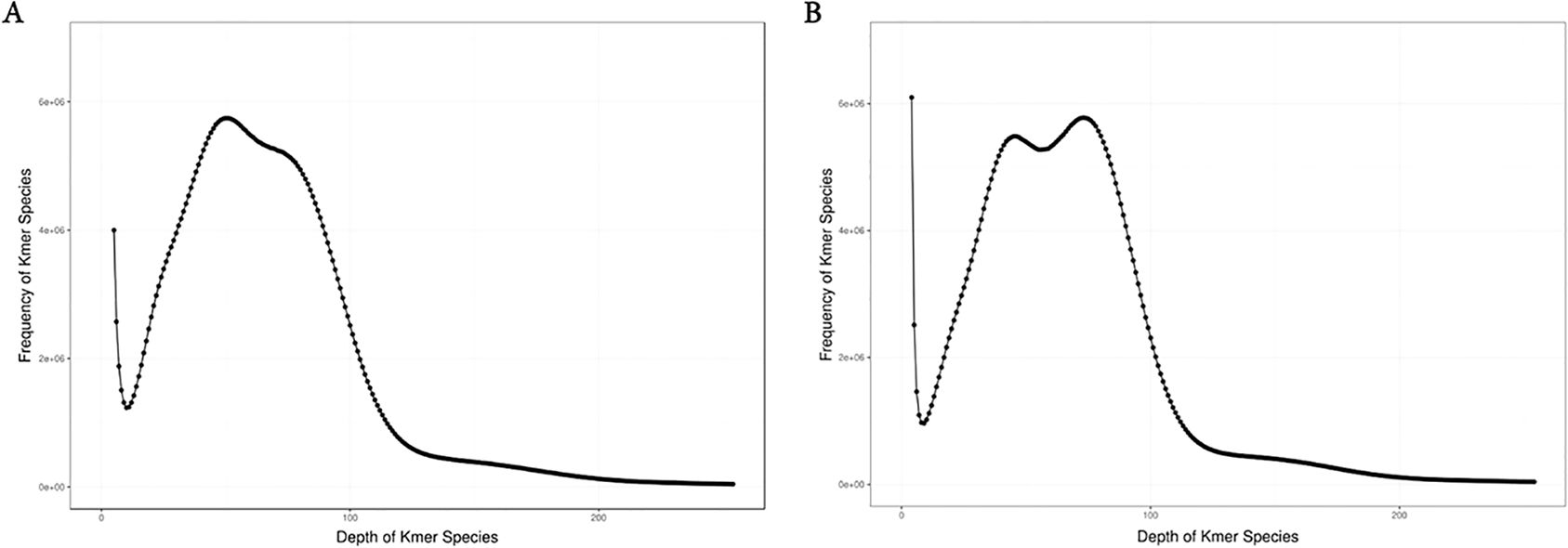
Figure 1. Distribution of K-mer (K=17) depth and frequency of female and male Hapalogenys analis: (A) Female Hapalogenys analis; (B) Male Hapalogenys analis.
3.3 Genomic assembly and estimation
We used SOAPdenovo2 software to perform de novo genome assembly on the NGS data of male and female H. analis. The total length of contigs for females was 589.18 Mb, with a contig N50 of 3,135 bp, a maximum sequence length of 49,858 bp, and a genome GC content of 43.30%. The total length of contigs for males was 592.02 Mb, with a contig N50 of 3,041 bp, a maximum sequence length of 56,240 bp, and a genome GC content of 43.20% (Table 3).
3.4 Identification and statistics of SSR molecular markers
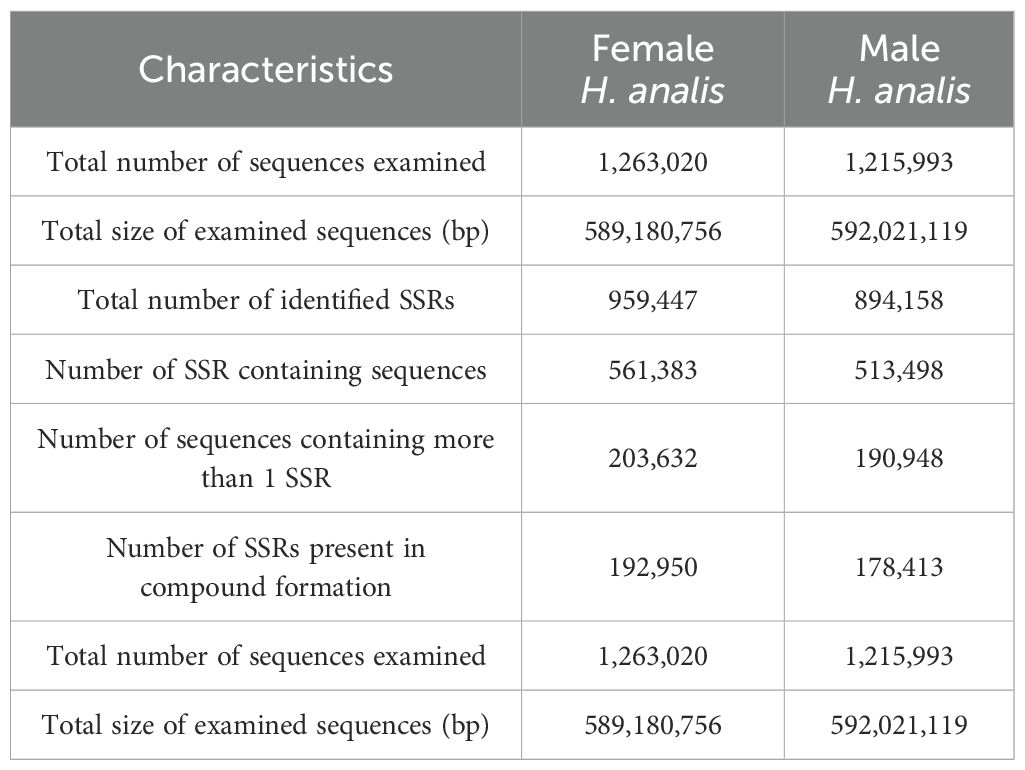
Utilizing the assembled genome, we used the MISA software (Beier et al., 2017) to predict simple sequence repeats (SSRs). The predicted SSR counts for male and female H. analis were very close, with 959,447 and 894,158 SSRs, respectively (Table 4); the SSR distribution density showed extreme similarity between sexes, with 1628.44 Mb SSRs for females genome sequence, while for males it was 1510.35 Mb SSRs. In the SSR sequences of female fish, dinucleotide repeats were the most abundant (55.56%), followed by mononucleotide repeats (11.30%) (excluding complex repeat types, Figure 2A). In the SSR sequences of male fish, dinucleotide repeats were the most abundant (54.94%), followed by mononucleotide repeats (12.14%) (excluding complex repeat types, Figure 2B).
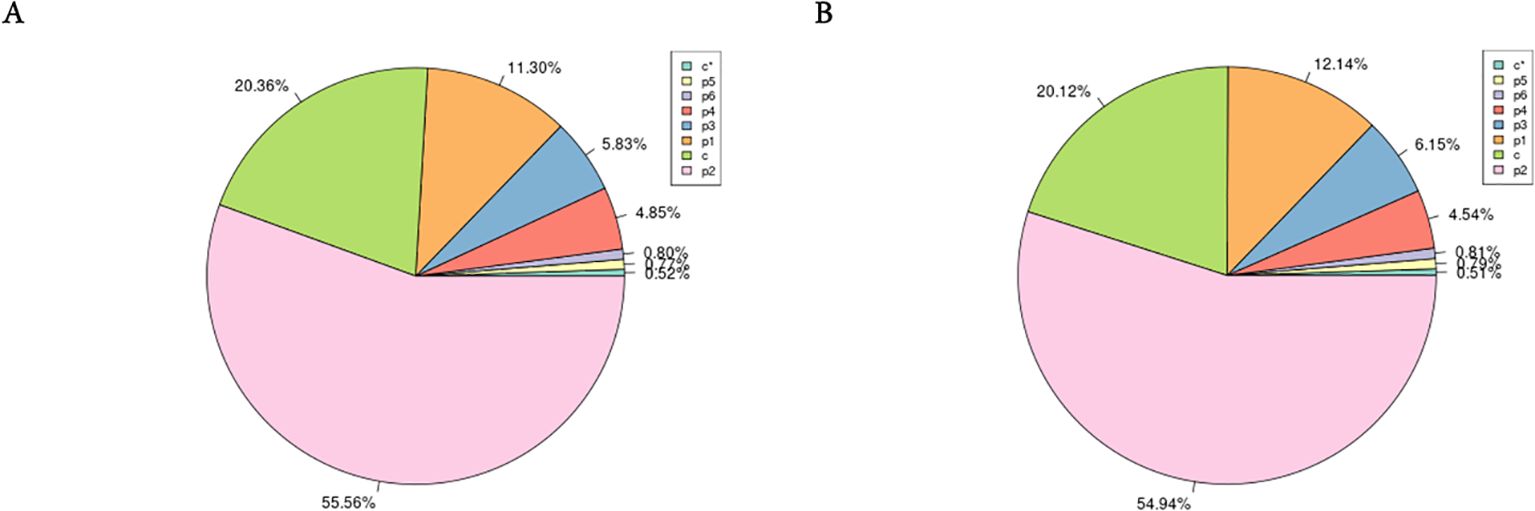
Figure 2. The frequency of simple sequence repeat (SSR) types in the female and male Hapalogenys analis genome survey. (A) Female Hapalogenys analis; (B) Male Hapalogenys analis. Note: P1 to P6 are SSRs with repeat unit lengths ranging from 1 to 6; c and c* are complex repeat types formed by mixing SSRs from P1 to P6.
3.5 Assembly and annotation of mitochondrial DNA genome
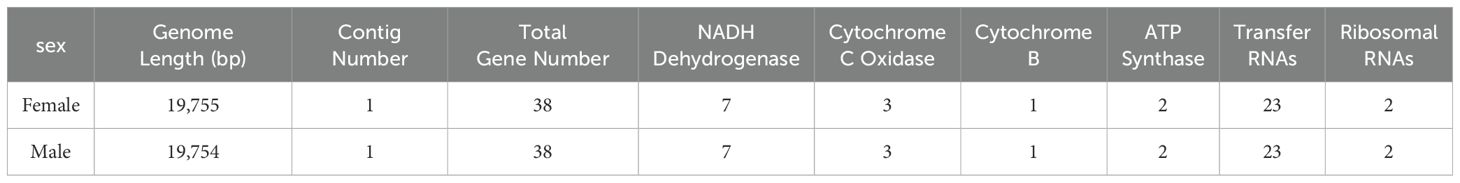
We used mitoz software (Meng et al., 2019) for the assembly and annotation of mitochondrial sequences. The assembled mitochondrial genome sequences of male and female H. analis were 19,755 and 19,754 bp in length, respectively. The mitochondrial genome contains 38 genes for each sex. Meanwhile, in these mitochondrial sequences, we identified 13 protein-coding genes comprising 7 NADH dehydrogenases, 3 cytochrome c oxidases, 1 cytochrome b, and 2 ATP synthases. The number of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes were consistent in number in both sequences, with both sexes having 23 tRNA genes and 2 rRNA genes (Table 5). The results of mitochondrial annotation circularization are shown in Figure 3.
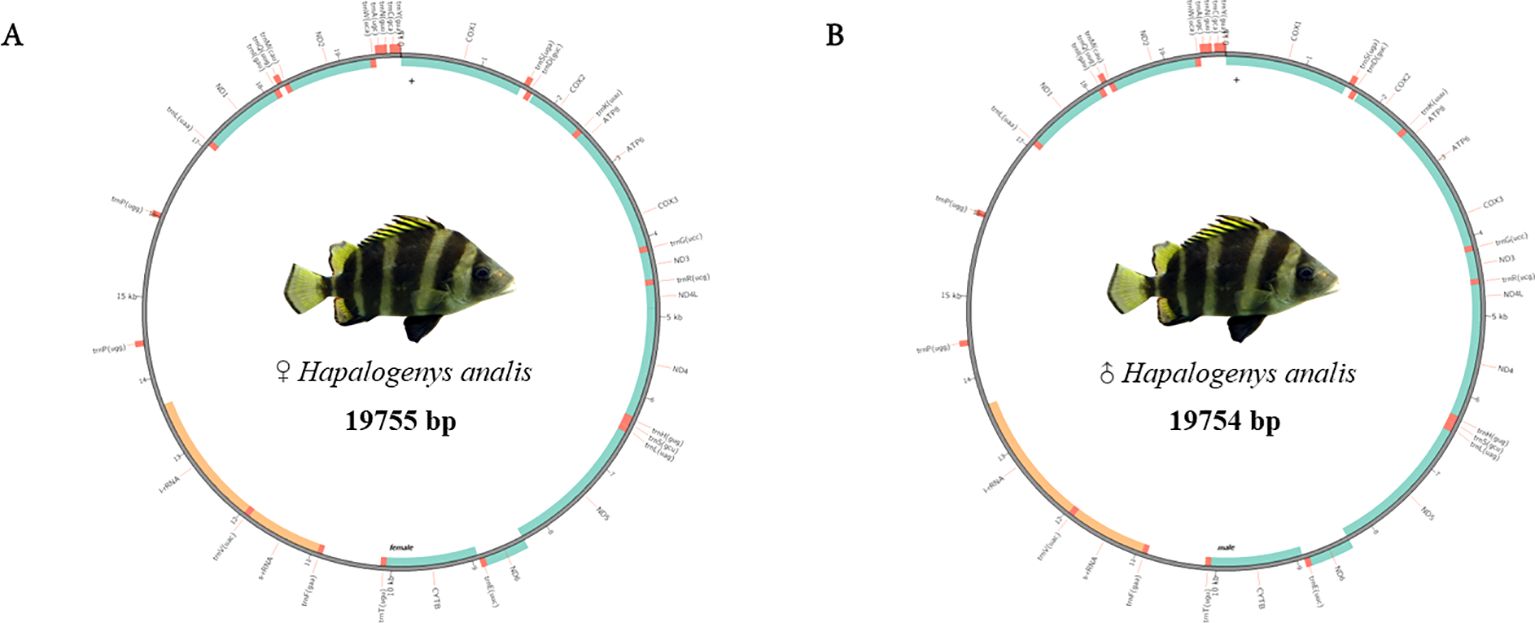
Figure 3. The mitochondrial annotation circular map of female and male Hapalogenys analis. (A) Female Hapalogenys analis; (B) Male Hapalogenys analis.
4 Discussion
This study utilized NGS technology to conduct a genome survey analysis of H. analis, obtaining data on genome size, heterozygosity, proportion of repetitive sequences, GC content, and mitochondrial genome assembly and annotation for both male and female. The study comprehensively understood the genomic differences between male and female H. analis through comparative analysis. There have been few reports on genomic studies of the genus Hapalogenys. For instance, Liang et al. (2012) and Zheng et al. (2020) conducted genomic sequencing analyses at the chromosomal level for H. nigripinnis and H. analis, respectively. Additionally, Zhang et al. (2024) explored the genetic evolution mechanisms of H. analis using double-digest restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (dd-RAD). Therefore, the present study is significant for the whole-genome assembly and analysis and the development of genetic breeding technologies for H. analis. Based on the K-mer analysis results, the genome sizes of female and male fish were 436.24 Mb and 493.21 Mb. Some polyploid fishes have undergone genome doubling or polyploid events, resulting in larger genomes and enhanced adaptability to their environments, such as Cyprinus carpio, its genome size was about 1.7 Gb (Xu et al., 2014). Researchers also have performed whole genome sequencing and comparative analyses of three species in the cyprinid genus Sinocyclocheilus, a cavefish model, the assembled genome sizes of S. grahami, S. rhinoce-rous, and S. anshuie-nsis were 1.75 Gb, 1.73 Gb, and 1.68 Gb, respectively (Yang et al., 2016). However, most reported fish genome sizes are less than 1.0 Gb. For instance, a species of the family Haemulidae, Haemulon aurolineatum, has been recorded that its assembled genome size was 954.6 Mb (Pedraza et al., 2024). Meanwhile, the genome sizes of Cynoglossus semilaevis (Chen et al., 2014) and Larimichthys crocea (Wu et al., 2014) were reported as 520.0 Mb and 728.0 Mb, respectively. All samples in this study aligned with this pattern. Meanwhile, the heterozygosity rates were 0.58% for females and 0.23% for males, the proportion of repetitive sequences of female and male fish were 42.95% and 51.20%. The higher heterozygosity in female fish genomes highlights the complex evolutionary mechanisms influenced by reproductive strategies, environmental adaptability, and selective pressures. In some fish species, the mechanisms of sex determination may affect genomic heterozygosity. For example, in species with temperature-dependent sex determination, females might need to exhibit greater adaptability to environmental changes, resulting in increased genomic heterozygosity (Wang, 2005). Additionally, females always experience stronger selective pressures, particularly regarding mate choice and competition within populations, which may further enhance the diversity of their genomes (Mousseau and Roff, 1987). This finding deepens our understanding of H. analis genomic evolution and provides a crucial theoretical foundation for future research in this area. GC content is a crucial sequencing metric that significantly impacts genome randomness (Xu et al., 2014). Another species of genus Hapalogenys, H. nigripinnis was reported that its GC content was about 43.84%, similar with our results (Ji et al., 2020). The GC content in male and female H. analis was 43.20% and 43.30%, respectively, indicating a moderate level within the normal range (Zhou et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2020). Overall, considering the genome size, heterozygosity, repetitive sequence proportion, and GC content, the genome of H. analis is relatively simple, making it suitable for comprehensive whole-genome sequencing studies.
A large body of research shows that SSR are widely distributed in eukaryotic genomes and can exhibit polymorphism at both individual and population levels (Li et al., 2002; Ellegren, 2004; Gadgil et al., 2017). Short nucleotide repeat sequences are more abundant in most genomes than long ones. In this study, as the number of nucleotide repeat sequences increased, the quantity of all SSR sequences rapidly decreased. Among them, dinucleotide repeat sequences were the most abundant (female 719,060, male 662,242), while hexanucleotide repeat sequences were the least abundant (female 8,106, male 7,776). We speculate that this phenomenon may be related to the specific structure and function of the genome. Dinucleotide repeat sequences (such as AT/TA, AG/CT) are generally more common, possibly because they occur relatively easily in the genome and may not significantly affect gene function, thus they are more abundant in quantity (Neff and Gross, 2001). In contrast, hexanucleotide repeat sequences (such as ATAGAT, AGATCT) may be less abundant due to their longer length, making them more prone to mutations or selectively reduced in the genome. Specific reasons may also involve genome structural stability, mismatch repair mechanisms during replication, and the role of natural selection. Genetic diversity and adaptability among different fish populations may also influence the abundance and distribution of different nucleotide repeat sequences. Overall, male and female H. analis genomes show high similarity in SSR types and quantities.
Zheng et al. (2020) obtained the complete mitochondrial genome of H. analis, excluding the control region, using whole-genome sequencing technology. This study identified 2 additional tRNA genes in both male and female in the newly assembled sequences. The evolution of fish in various ecological environments may induce changes in the number of tRNA genes, allowing them to adapt to specific physiological needs and metabolic processes. For instance, certain fish may need higher translation efficiency in their environments, driving the expansion of tRNA genes (Fiteha and Magdy, 2022). Additionally, gene duplication or loss can also contribute to variations in gene numbers. These phenomena may stem from genomic instability or selective pressures associated with adaptation (Santos and Del-Bem, 2022). Furthermore, mitochondrial annotation further refined the functional gene and provided insights into the genomic structure of this species. These findings establish a molecular research foundation for the evolution, breeding, and taxonomy studies of H. analis and related species.
5 Conclusion
In summary, we conducted a genome survey analysis of H. analis, obtaining data on genome size, heterozygosity, proportion of repetitive sequences, GC content, and mitochondrial genome assembly and annotation for both male and female. These results are conducive to subsequent high-quality genome assembly, providing necessary genomic resources for H. analis research.
Data availability statement
The raw sequence data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (Chen et al., 2021) of the National Genomics Data Center (CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners, 2023), China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA: CRA020131) that are publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Care and Use Ethics policies of Zhejiang Ocean University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
KL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-QQ: Writing – review & editing. H-LS: Writing – review & editing. H-LP: Writing – review & editing. T-XG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD2401903), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LTGN24C190010).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the reviewers for their insightful comments to improve the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1492138/full#supplementary-material
References
Beier S., Thiel T., Münch T., Scholz U., Mascher M. (2017). MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 33, 2583–2585. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198
Boore J. L. (1999). Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 1767–1780. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.8.1767
Chen T., Chen X., Zhang S., Zhu J., Tang B., Wang A., et al. (2021). The genome sequence archive family: toward explosive data growth and diverse data types. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 19, 578–583. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.08.001
Chen B., Sun Z., Lou F., Gao T.-X., Song N. (2020). Genomic characteristics and profile of microsatellite primers for Acanthogobius ommaturus by genome survey sequencing. Bioscience Rep. 40, BSR20201295. doi: 10.1042/bsr20201295
Chen S., Zhang G., Shao C., Huang Q., Liu G., Zhang P., et al. (2014). Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nat. Genet. 46, 253–260. doi: 10.1038/ng.2890
Chen S., Zhou Y., Chen Y., Gu J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners (2023). Database resources of the national genomics data center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D18–D28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1073
Ellegren H. (2004). Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 435–445. doi: 10.1038/nrg1348
Fiteha Y. G., Magdy M. (2022). The evolutionary dynamics of the mitochondrial tRNA in the cichlid fish family. Biology 11, 1522. doi: 10.3390/biology11101522
Gadgil R., Barthelemy J., Lewis T., Leffak M. (2017). Replication stalling and DNA microsatellite instability. Biophys. Chem. 225, 38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2016.11.007
Goodwin K. D., Thompson L. R., Duarte B., Kahlke T., Thompson A. R., Marques J. C., et al. (2017). DNA sequencing as a tool to monitor marine ecological status. Front. Mar. Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00107
Gurevich A., Saveliev V., Vyahhi N., Tesler G. (2013). QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29, 1072–1075. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Ji S. C., Kim J. H., Jung M. H., Kim J. H., Kim H. W., Kim M. S., et al. (2020). The complete mitochondrial genome analysis and phylogenetic position of the short barbeled grunter Hapalogenys nigripinnis (Lobotiformes: Hapalogenyidae) from Jeju Island, Korea. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 5, 3706–3707. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1831982
Li Y. C., Korol A. B., Fahima T., Beiles A., Nevo E. (2002). Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol. Ecol. 11, 2453–2465. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2002.01643.x
Liang R., Zheng W., Zou Q., Zeng Y., Zhu S., Zou J. (2012). The complete mitochondrial genome of black grunt Hapalogenys nigripinnis. Mitochondrial DNA 23, 444–446. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2012.710221
Liu B. H., Shi Y. J., Yuan J. Y., Hu X. S., Zhang H., Li N., et al. (2013). Estimation of genomic characteristics by analyzing k-mer frequency in de novo genome projects. arXiv. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1308.2012
Luo R., Liu B., Xie Y., Li Z., Huang W., Yuan J., et al. (2012). SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 1, 2047–2217X-2041-2018. doi: 10.1186/2047-217x-1-18
Meng G., Li Y., Yang C., Liu S. (2019). MitoZ: a toolkit for animal mitochondrial genome assembly, annotation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, e63–e63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz173
Miller J. R., Koren S., Sutton G. (2010). Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data. Genomics 95, 315–327. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.001
Mohapatra A., Ray D., Kumar V. (2013). A new fish species of the genus Hapalogenys (Perciformes: Hapalogenyidae) from the Bay of Bengal, India. Zootaxa 3718, 367–377. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3718.4.6
Montes I., Iriondo M., Manzano C., Arrizabalaga H., Jiménez E., Pardo M.Á., et al. (2012). Worldwide genetic structure of albacore Thunnus alalunga revealed by microsatellite DNA markers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 471, 183–191. doi: 10.3354/meps09991
Mousseau T. A., Roff D. A. (1987). Natural selection and the heritability of fitness components. Heredity 59, 181–197. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1987.113
Neff B. D., Gross M. R. (2001). Microsatellite evolution in vertebrates: inference from AC dinucleotide repeats. Evolution 55, 1717–1733. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00822.x
Pedraza M. C., Pirro S., Betancur R. (2024). NCBI Genbank. Available online at: https://api.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/v2/genome/accession/GCA_038406115.1/download?include_annotation_type=GENOME_FASTA&include_annotation_type=GENOME_GFF&include_annotation_type=RNA_FASTA&include_annotation_type=CDS_FASTA&include_annotation_type=PROT_FASTA&include_annotation_type=SEQUENCE_REPORT&hydrated=FULLY_HYDRATED.
Raffini F., Fruciano C., Franchini P., Meyer A. (2017). Towards understanding the genetic basis of mouth asymmetry in the scale-eating cichlid Perissodus microlepis. Mol. Ecol. 26, 77–91. doi: 10.1111/mec.13699
Reichwald K., Petzold A., Koch P., Downie B. R., Hartmann N., Pietsch S., et al. (2015). Insights into sex chromosome evolution and aging from the genome of a short-lived fish. Cell 163, 1527–1538. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.071
Richardson J. (1844). The zoology of the voyage of HMS sulphur: under the command of captain sir edward belcher during the years 1836-42 (Vol. 1). Smith, Elder and Company.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F., Maniatis T. (1982). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (New York NY, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press).
Santos F. B., Del-Bem L. E. (2022). The evolution of tRNA copy number and repertoire in cellular life. Genes 14, 27. doi: 10.3390/genes14010027
Sun C.-H., Lao Y.-L., Huang J.-L., Huang X.-Y., Zhang Q. (2023). Genetic structure and phylogeography of the endemic species broadbanded velvetchin Hapalogenys analis in the Northwest Pacific. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 62, 102956. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2023.102956
Timmerhaus G., Krasnov A., Nilsen P., Alarcon M., Afanasyev S., Rode M., et al. (2011). Transcriptome profiling of immune responses to cardiomyopathy syndrome (CMS) in Atlantic salmon. BMC Genomics 12, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-459
Vieira M. L. C., Santini L., Diniz A. L., Munhoz C. D. F. (2016). Microsatellite markers: what they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 39, 312–328. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-gmb-2016-0027
Wang J. (2005). Estimation of effective population sizes from data on genetic markers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B Biol. Sci. 360, 1395–1409. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1682
Wilson C. A., High S. K., Mccluskey B. M., Amores A., Yan Y.-L., Titus T. A., et al. (2014). Wild sex in zebrafish: loss of the natural sex determinant in domesticated strains. Genetics 198, 1291–1308. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.169284
Wu C., Zhang D., Kan M., Lv Z., Zhu A., Su Y., et al. (2014). The draft genome of the large yellow croaker reveals well-developed innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 5, 5227. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6227
Xu P., Zhang X., Wang X., Li J., Liu G., Kuang Y., et al. (2014). Genome sequence and genetic diversity of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Nat. Genet. 46, 1212–1219. doi: 10.1038/ng.3098
Yang J., Chen X., Bai J., Fang D., Qiu Y., Jiang W., et al. (2016). The Sinocyclocheilus cavefish genome provides insights into cave adaptation. BMC Biol. 14, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0223-4
Zhang Q., Sun C.-H., Huang J.-L., Lao Y.-L., Chang X.-Y., Cao J.-N. (2024). Genetic diversity of Hapalogenys analis in the northwest Pacific assessed using dd-RAD sequencing. Front. Ecol. Evol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2024.1345739
Zheng Y., Feng L., Liu H., Song R., Xu S., Shi H., et al. (2020). The complete mitochondrial genome of Hapalogenys analis (Perciformes, Haemulidea) except for control region, obtained by whole genome sequencing. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 5, 2807–2808. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1788463
Keywords: Hapalogenys analis, genome survey, genomic characteristics, genome assembly, genomic comparison
Citation: Liu K, Qu Y-Q, Shi H-L, Ping H-L and Gao T-X (2024) The genome survey of male and female Hapalogenys analis. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1492138. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1492138
Received: 06 September 2024; Accepted: 12 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Yu Zhang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kai Liu, Hangzhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaKhaled Mohammed Geba, Menoufia University, Egypt
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Qu, Shi, Ping and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tian-Xiang Gao, Z2FvdGlhbnhpYW5nMDYxMUAxNjMuY29t
 Kai Liu
Kai Liu Yin-Quan Qu
Yin-Quan Qu Hui-Lai Shi4
Hui-Lai Shi4 Tian-Xiang Gao
Tian-Xiang Gao