
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci. , 27 November 2024
Sec. Marine Fisheries, Aquaculture and Living Resources
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1491129
The large yellow croaker, an endemic migratory species in China’s coastal waters, holds considerable economic importance. It is very necessary and significant to study the spatio-temporal evolution of large yellow croaker fishery based on environmental factors. In this paper, the HY-1C/D Coastal Zone Imager was applied to reveal distributional details of suspended sediment concentration and chlorophyll-a concentration in large yellow croaker fishery. Furthermore, combined with multi-source data, the characteristics of other environmental parameters such as temperature, salinity, current, wind and fronts were analyzed to reveal the changing of large yellow croaker fishery location. The results show that: (1) The environmental factors of large yellow croaker fishery exhibit pronounced spatial and temporal characteristics. Generally, the temperature (9-28°C), salinity (20-34 ‰) and other water environmental factors of the fishing ground are conducive to the survival and growth of large yellow croaker. The formation and change of fishery are closely related to environmental factors in the water. (2) The change of environmental factors in the water may induce the change of large yellow croaker fishery location. Winter sea surface temperature has significantly risen over the past two decades (2004-2023). With the sea surface temperature rising by approximately 2°C west of 125°E, the overwintering ground has expanded westward, increasing by nearly 29%. In addition, the scale and number of offshore windmills increased by 836% and 456% respectively over the decade (2013-2023). In 2023, offshore wind farms cover an area of 145.47 km2 and have 200 windmills. Wind turbine piles resembling artificial reefs. It can not only promote the waters vertical exchange to enhance the nutrients in upper waters but also provide a protective base for fish spawning. Thus, effectively attracting fish species. The construction of offshore wind farms has extended spawning ground north-westward to the mouth of the Yangtze River Estuary, expanding by nearly 21%. This study improved the cognition level of resources, habitat environment and change trend of large yellow croaker. It also provided technical support for the construction and protection of the large yellow croaker fishery.
Large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea), a migratory(1) fish endemic to China’s offshore waters, is one of the four traditional Chinese fishery products (Larimichthys crocea, Larimichthys polyactis, Trichiurus lepturus, and Sepiella maindroni), which has high economic value (Zhao, 1990). The large yellow croaker belongs to the Sciaenidae family of the Perciformes order. The large yellow croaker population was divided into three stocks based on body size measurements. The stock that is distributed offshore in the southern Yellow Sea and the northern East China Sea belongs to the Dai-Qu group. This includes the spawning grounds of Lvsi, Daiqu, Damu, and Maotou, as well as the reproductive stocks in the overwintering grounds of Jiangwai, Zhouwai, and Dasha fisheries. The other stocks are the Min-Yuedong and Naozhou groups (Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, 1987; Zheng et al., 2003; Xu and Chen, 2011). Among the three geographic populations, Dai-Qu large yellow croaker is a typical population with wide feeding habits, long life span, late sexual maturity and long growth cycle (Zhao, 1990).
In the early years, the production of large yellow croaker in the East China Sea area accounted for more than 98% of the national production of this species. Furthermore, the Dai-Qu large yellow croaker constituted a significant proportion (more than 80%) of the total production of large yellow croaker (Yu et al., 2022). However, due to heavy human fishing and over-exploitation, the large yellow croaker is listed as “critically endangered” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List in 2020 (Liu and Cheng, 2020). In recent years, national protection of marine fishery resources and environment has been strengthened. Measures, such as marine fish proliferation and release (Chen et al., 2023), and the construction of the marine ranching (Le et al., 2022) have been taken to increase large yellow croaker fishery resources. In addition, the development of nearshore human constructions also contributes to the change of fishery. Will the combination of human factors and natural factors change the area of large yellow croaker fishing ground? This is a question worth discussing. It is urgent to study the restoration and change of large yellow croaker fishery resources.
At present, research on large yellow croaker involves biological characteristics (Kong et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021), culture technology (Liu et al., 2005), migration routes (Xu and Chen, 2011; Xu et al., 2023), spatio-temporal distribution of resources (Yin et al., 2022), and production variations (Hu, 2006; Li et al., 2022). In addition, in the theory of “three fields and one channel” proposed by previous studies (Zhou and Lee, 2018), the research results on spawning grounds, feeding grounds, overwintering grounds and migration routes of large yellow croaker (Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, 1987) found that higher catches (Xu et al., 2023) were obtained outside these three areas. However, the details of environmental factors, such as small changes in sea temperature (Wang, 2021), evolution and changes affecting large yellow croaker fishery are still unknown.
In the 1960s, the United States successfully launched weather satellites and began to realise the application potential of satellite remote sensing in marine fisheries. From the 1970s to the 1990s, satellite remote sensing was applied to marine fisheries and developed rapidly (Santos, 2000), but it was limited to the retrieval of a single environmental factor, such as sea surface temperature (SST, °C) (Sund et al., 1981), chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a, μg/L) (Abbott and Chelton, 1991), sea surface height (SSH, m), etc. With the successful launch of accurate and reliable sensors such as Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner (OCTS), Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS), and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), marine fishery applications have developed from a single element to a stage of multiple analysis and comprehensive application (Fan, 2004). The research and application of satellite remote sensing on information-rich fishery service, fishery forecast (Chen et al., 2013) and fishery environment analysis (Druon, 2010; Kachelriess et al., 2014; Guan et al., 2017) are carried out. With the launch of higher resolution satellites (HaiYang-1C/D, Gao-Fen series, etc.), support is provided for the research of offshore fishery resources (Cai et al., 2020, 2022a).
In this paper, the characteristics and changes of environmental factors in the recent 20 years of large yellow croaker fishery were studied, and the regional change trend of large yellow croaker fishery was revealed. Combined with the characteristics of environmental factors in the fishery and the catch data of large yellow croaker, the specific changes of large yellow croaker overwintering ground were further revealed. At the same time, due to the influence of human factors, this paper also discussed the changes in nearshore spawning ground. This study has a certain reference significance for the development and evolution of large yellow croaker fishery.
For the yellow croaker fishery, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of water environmental factors near the Yangtze River Estuary (Sections 3.1 and 3.2). This analysis lays the foundation for the discussion of the formation of the yellow croaker fishery in Section 4.1. Furthermore, Section 3.3 analyzes the changes in natural and human factors affecting the fishery over the past two decades. Based on this, we reveal the factors influencing the variations in the yellow croaker fishery (Section 4.2). Finally, by integrating the distribution of large yellow croaker catch, we propose possible current locations of the large yellow croaker fishery near the Yangtze River Estuary in Section 4.3.
The large yellow croaker is mainly distributed in the offshore area (28°-35°N, 121°-126°E, Figure 1B) of the southern Yellow Sea and northern East China Sea (Figure 1A). The three fields of large yellow croaker (spawning, feeding, and overwintering grounds, Figure 1B) are an important part of the East China Sea’s fishery (Zhou and Lee, 2018). The unique geographic and aquatic environmental provide good conditions for the spawning, feeding, and overwintering of the large yellow croaker (Chen, 2006).
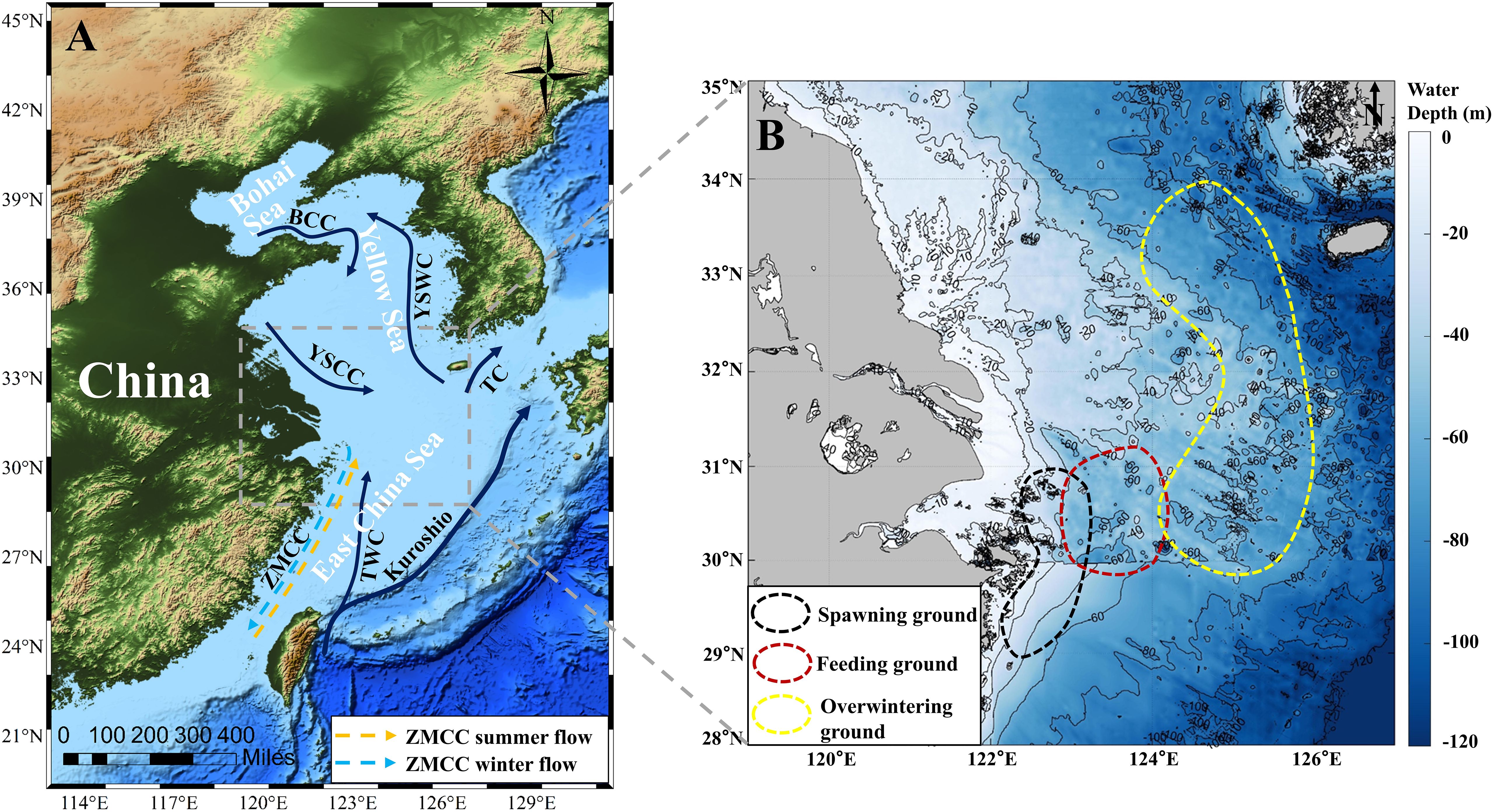
Figure 1. The study area. (A) Distribution of large yellow croaker on a topographic map. BCC, Bohai Coastal Current; YSWC, Yellow Sea Warm Current; YSCC, Yellow Sea Coastal Current; TC, Tsushima Current; ZMCC, Zhe-Min Coastal Current; TWC, Taiwan Warm Current; (B) Three fields of large yellow croaker in the last century (Xu and Chen, 2011; Zhou and Lee, 2018) includes spawning (black dotted line), feeding (red dotted line) and overwintering (yellow dotted line) grounds. The base map shows the water depth near the Yangtze Estuary.
This sea is bounded to the west by fresh water injections from the Yangtze, Qiantang, and Yong Rivers. To the east, it is affected by the passage of the Kuroshio warm current. To the north, it is influenced by the southward extension of the North Jiangsu coastal water and the Yellow Sea Cold-Water Mission. To the south, it is affected by the northward advance of the Taiwan warm current (Figure 1A). The coast is dotted with numerous islands that are abundant in nutrient salts (Chen, 2014), and the substrate is mainly mud and sand which are beneficial to the reproduction of bait organisms (Saito and Yang, 1995).
Satellite data from HY-1C/D, Landsat-8/9, SNPP and MODIS were used to retrieve typical environmental parameters. Specifically, the satellite image from HY-1C/D Coastal Zone Imager (CZI) and SNPP VIIRS were used to estimate the suspended sediment concentration (SSC, mg/L). HY-1C/D CZI and MODIS Aqua images were also utilized to derive the Chl-a map. In addition, SST was retrieved from Landsat-8/9 Operational Land Imager (OLI) and Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS). The long-term series changes of SSC, Chl-a and SST are obtained by MODIS Aqua calculation. The data details are listed in Table 1.
HY-1C was launched on 7 September 2018 as China’s first Ocean color satellite. HY-1D was launched on June 11, 2020, and together with the HY-1C satellite, formed the Ocean Color Satellite Constellation. This enabled the grouping of morning and afternoon satellite observations into a network. It increased observation frequency and improved global coverage. The HY-1C/D satellite payload is equipped with the CZI, the resolution and width of which can better satisfy the environmental monitoring in coastal zones (Table 1). HY-1C/D CZI images of L1B and L2A for 2020-2023 used in this study are from the China Ocean Satellite Data Service (https://osdds.nsoas.org.cn/) (Liu et al., 2021, 2022, 2023).
The Landsat-8 satellite was successfully launched by NASA on February 11, 2013. Following Landsat-8, Landsat-9 was launched on September 27, 2021. Both carry two sensors (OLI and TIRS) and have 11 bands. The spatial resolution of bands 1-7 and 9-11 is 30 meters and that of panchromatic band 8 is 15 meters. Landsat-8/9 operates on a 16-day revisit cycle and covers the study area every 9 days (Table 1). Landsat-8/9 TIRS images of L1 for 2019.2022.2023 used in this study are from the United States Geological Survey (USGS, https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/) (Irons et al., 2012; Chu et al., 2013; Xu, 2015).
The SNPP satellite platform was launched on October 28, 2011, equipped with VIIRS sensors, which observe and collect global satellite observations that span the visible and infrared wavelengths across land, ocean, and atmosphere. In this study, the Level2 ocean color productions for 2022 and 2023, obtained from National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Coast Watch (https://coastwatch.noaa.gov/), were used to derive SSC maps.
The monthly mean Chl-a and long-term series changes of SSC, Chl-a and SST were obtained from MODIS Aqua Level-3 Mapped data (https://oceandata.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov). The spatial-temporal resolution of the monthly mean Chl-a data was 1 month and 4 km, and the others were 1 year and 4 km.
SST (°C), sea surface salinity (SSS, ‰), wind (m/s), and ocean current (m/s) data (Table 2) are the crucial parameters describing the hydrological environment and hydrodynamic conditions of the study area. The spatial-temporal distributions of these parameters were utilized to analyze the relationship between the large yellow croaker fishery and environmental factors. They were used to reveal the variation of large yellow croaker fishery.
The daily SST and temperature front data (spatial resolution: 0.05°) were obtained from Operational Sea Surface Temperature and Ice Analysis (OSTIA, https://datamarine.copernicus.eu/products). It is a fusion dataset of in situ data and satellite observations from infrared and microwave radiometers (Good et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2022a). The monthly SSS data (spatial resolution: 0.083°), a product of physical analysis and forecasting, was provided by Copernicus Marine Service (https://datamarine.copernicus.eu/products) (Cai et al., 2022a). The hourly wind data (spatial resolution: 0.25°), incorporating both u-component and v-component at 10 m, was obtained from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis v5 (ERA, https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu). This data is a reanalyzed product that merges model data with observations (Hersbach et al., 2020). This data is also used to analyze long-term series wind speed changes. Next, the monthly ocean current data employed in this study, with a spatial resolution of 0.083°, was obtained from the Copernicus Marine service (https://datamarine.copernicus.eu/products) (Lellouche et al., 2023).
Besides, long-term series of SSS and current data (spatial resolution: 0.083°) were obtained from Global Ocean Physics Reanalysis (https://datamarine.copernicus.eu/products). The earliest data is available from 1993.
Based on the fishing data (Table 3) of large yellow croaker from 2020-2023 in the East China Sea, the spatial and temporal distribution of fishery resources was analyzed.
All data processing includes preprocessing and parameter retrieval. The HY-1C/D CZI Remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) was obtained by atmospheric correction. Data preprocessing for Landsat-8/9 OLI/TIRS includes radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction. The SSC, Chl-a and SST were obtained by selecting the retrieve algorithm suitable for the study area.
The HY-1C/D CZI Rayleigh Corrected Reflectivity Product (L2A) was obtained by the National Center for Satellite Ocean Applications. Rrs can be accurately corrected for the atmosphere, including Rayleigh correction and aerosol scattering correction. The waters near Zhoushan Islands are turbidity water dominated by suspended matter. Rayleigh correction can eliminate most of the atmospheric influence, so we chose the image of dry weather, which can effectively reduce the influence of aerosols (Cai et al., 2022b). The aerosol correction of CZI is based on MODIS aerosol data and land mask retrieval using normalized differential moisture index (NDWI) (Chen et al., 2019). Finally, we apply an atmospheric correction algorithm to process HY-1C/D CZI data in muddy water to obtain Rrs (Tong et al., 2019).
Based on the previous HY-1C/D CZI SSC retrieval model (Equation 1) (Cai et al., 2020) specifically for Zhoushan offshore,
where and are the reflectance of red and near-infrared bands observed by CZI.
Additionally, a SSC retrieval algorithm (Zhang et al., 2010) as follows (Equation 2), specifically developed for the Yellow and East China Seas, was utilized for VIIRS images for deriving SSC maps,
where = 0.6311, = 22.2158, = − 0.5239.
According to previous studies, the retrieval model (Equations 3, 4) of Chl-a is constructed by combining the blue, green and red bands of HY-1C/D CZI, which is suitable for the Zhoushan coastal waters (Cai et al., 2022b),
where is Chl-a, and the unit is μg/L. , , and are the reflectance of blue, green, and red bands observed by CZI.
For Landsat data, firstly, radiometric calibration was performed on Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS data, and the original DN value was converted to the radiance value. Secondly, FLAASH was used for atmospheric correction of the image to eliminate the atmospheric influence (Cooley et al., 2002). Finally, the sea surface temperature was retrieved with an improved single-window algorithm as Equations 5–7) (Wang et al., 2015),
where is the Land Surface Temperature (LST) retrieved from Landsat 8 TIRS band 10 data, is the effective mean atmospheric temperature. is the brightness temperature of TIRS band 10 of Landsat 8. and are constants (Table 4). and are the internal parameters of the algorithm, where is the atmospheric transmittance of Landsat 8 TIRS band 10, and is the ground emissivity of the band.
The spawning, feeding and overwintering activities of large yellow croaker are closely associated with a range of marine environmental factors, including SSC, Chl-a and SST.
The monthly average distribution of SSC reveals that the most significant spatial characteristic is higher SSC near the coast and lower SSC offshore (Figure 2). There are notable seasonal variations in SSC, with generally higher levels observed during the winter and spring (Figures 2A–C, J–L) compared to summer and autumn (Figures 2A–C, J–L). Furthermore, the distribution of high suspended sediments in winter and spring is broader than in summer and autumn. Specifically, in autumn (Figure 2), suspended sediments begin to spread towards the sea surface (overwintering ground), with concentrations reaching as far as 126°E during winter (Figures 2J–L). In spring (Figure 2C), the area of high suspended sediments notably decreases, reaching its smallest range and concentration during summer (Figures 2D–F).
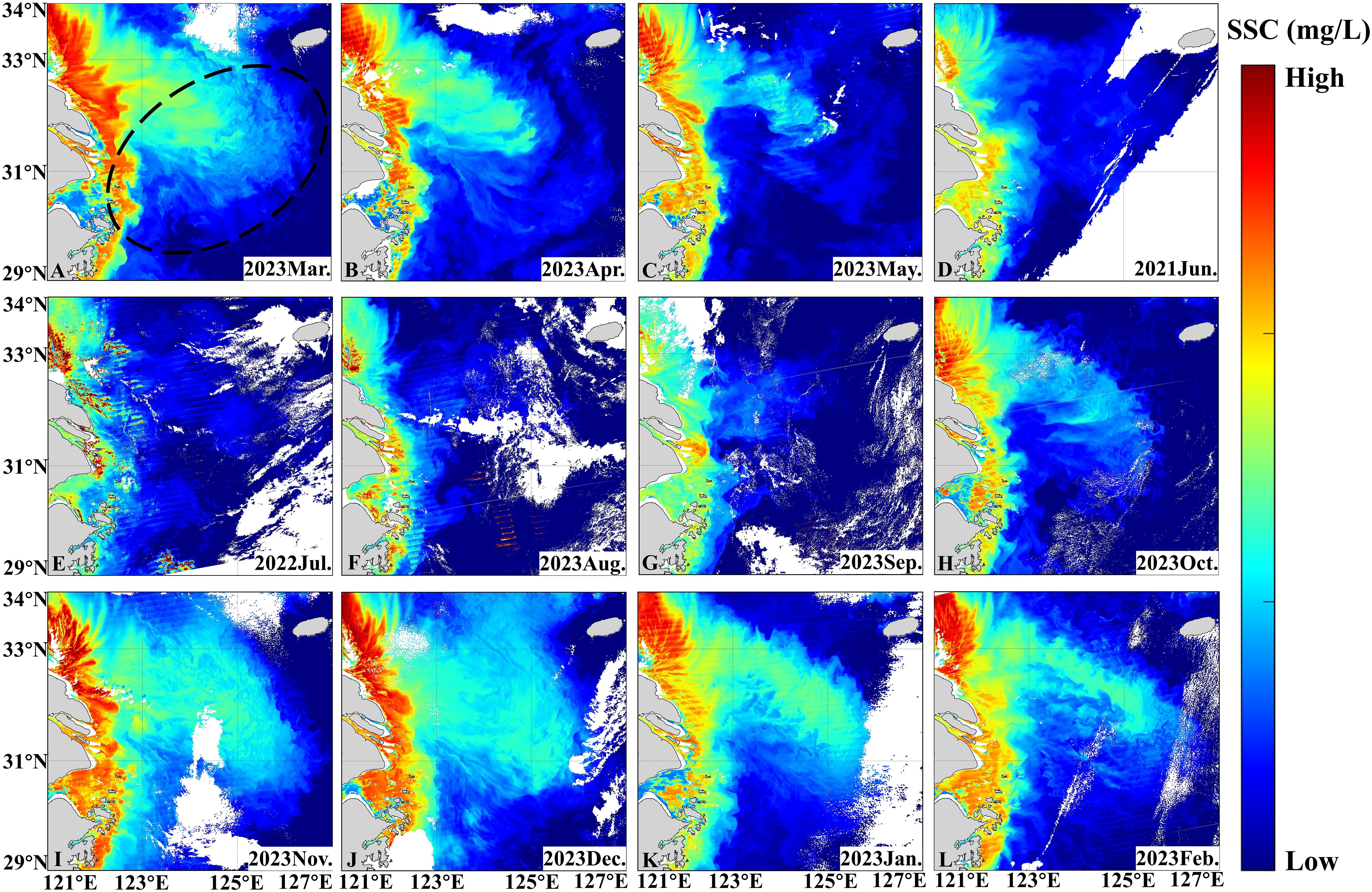
Figure 2. Distribution of monthly average SSC in spring (A–C), in summer (D–F), in autumn (G–I) and in winter (J–L) obtained from SNPP in 2022-2023. The location of the large yellow croaker fishery is indicated by a black dotted line.
The SSC of large yellow croaker fishery near the Yangtze River estuary is roughly in the range of 5-1500 mg/L (Figure 3). Specifically, SSC is higher in the western region (spawning and feeding grounds of large yellow croaker) compared to the eastern region. The high-value (500-1500 mg/L) areas are mainly located in the Yangtze River Estuary, Hangzhou Bay, and the Zhoushan Archipelago. In contrast, low SSC levels (5-600 mg/L) are found in the offshore areas east of the Zhoushan Archipelago (122.5°E), with SSC decreasing further into the open sea (below 200 mg/L, Figures 3A, D, E–L). Furthermore, SSC is higher in the sea area where the islands are dense, and decreases with increasing distance from the islands (Figures 3A, D, E–L). The interaction between ocean currents and islands generates distinct wake flows downstream of the islands, resulting in higher SSC levels downstream compared to those upstream (Figures 3A, D, G, I–L, pink rectangle).
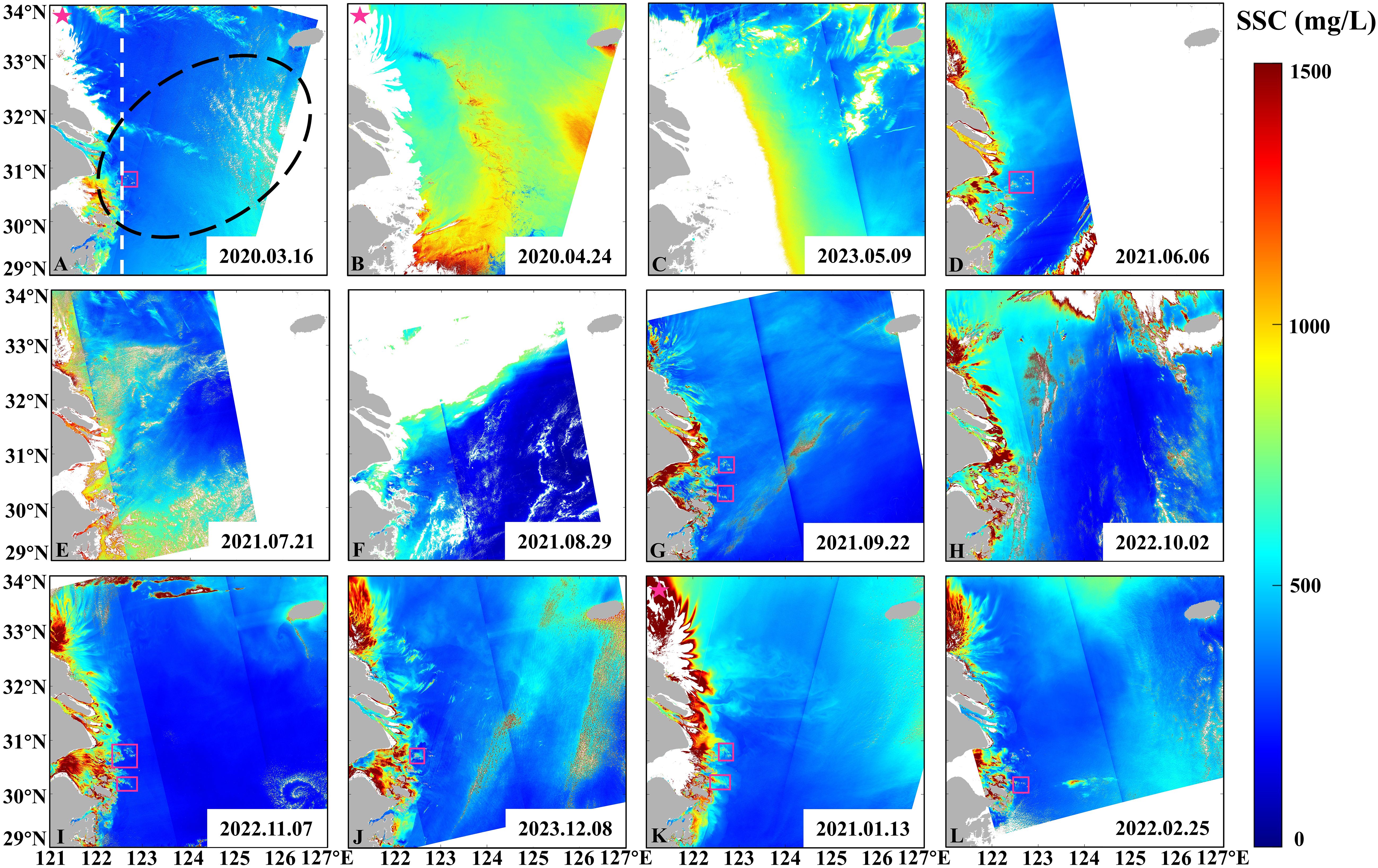
Figure 3. Distribution of SSC in spring (A–C), in summer (D–F), in autumn (G–I) and in winter (J–L) obtained from CZI of HY-1C (pink pentagram) and HY-1D (beyond pink pentagram) between 2020 and 2023, with the location of large yellow croaker fishery (black dotted line) marked. The wake and 122.5°E are marked by the pink rectangle and the white dotted line.
With regard to Chl-a, in general, the spatial distribution of Chl-a exhibited a “high-low-high” pattern (Figures 4A, B, D, F–J, L). The Chl-a value is about 0-3 μg/L (Figure 4). The value of Chl-a is higher in the western coastal islands (122° 20 ‘E, Figures 4A, B, D, H–L), with the value of Chl-a about 1.5-3 μg/L, primarily distributed in Zhoushan Islands. East of 122°20’E, the Chl-a value decreases. Moreover, the Chl-a varies with tidal currents. The interaction between the ocean and the islands creates unique wakes downstream of the islands, resulting in a higher Chl-a downstream of the island compared to upstream (pink rectangles in Figures 4B, D, I).
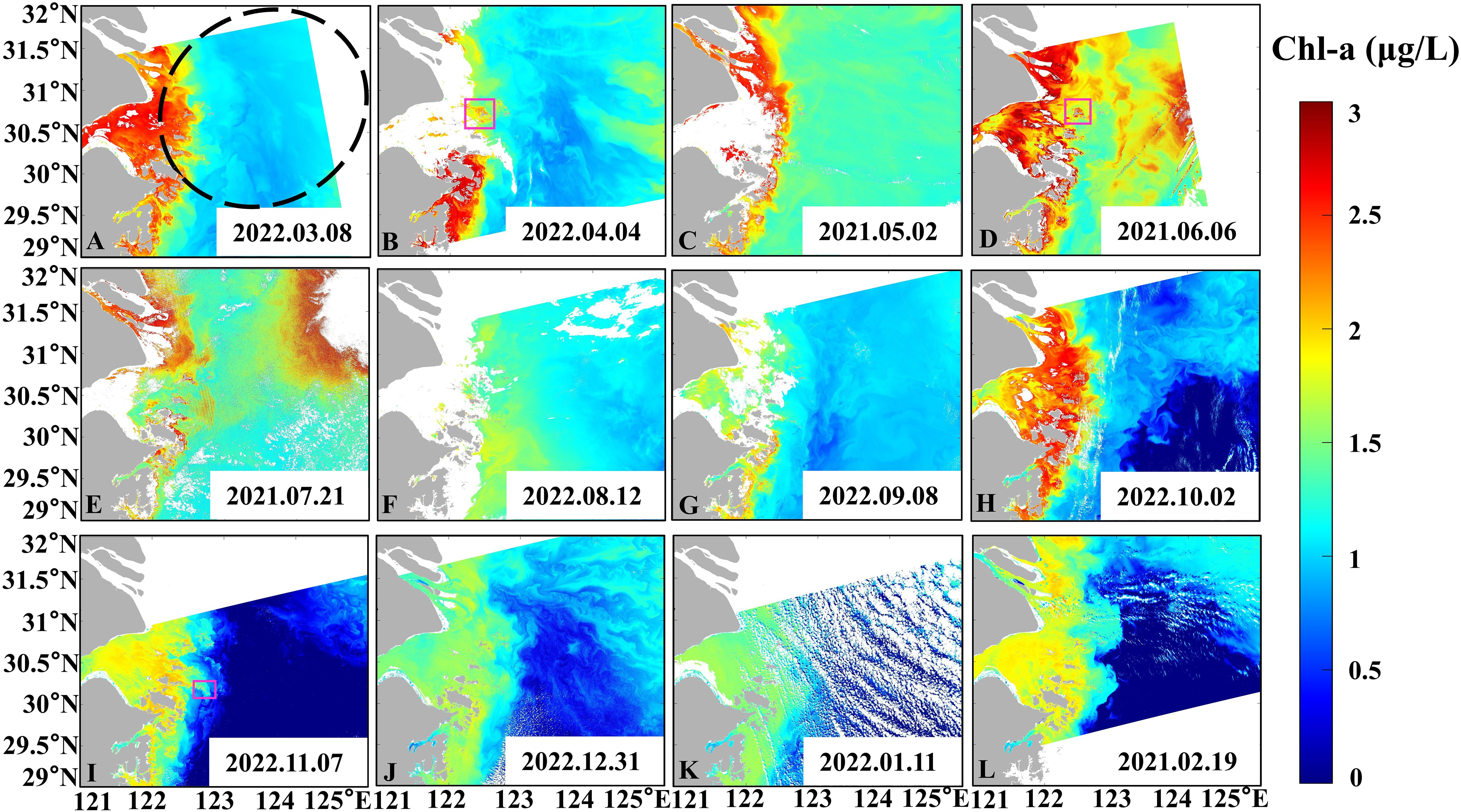
Figure 4. Distribution of Chl-α in spring (A–C), in summer (D–F), in autumn (G–I) and in winter (J–L) obtained from HY-1D in 2020, 2021, and 2022, with the location of large yellow croaker fishery (black dotted line) marked. The pink rectangle indicates the wake.
The seasonal variation characteristics of Chl-a are evident (Figure 5), with the highest values occurring in spring (April, spawning period), reaching an average of 1.47 μg/L. Subsequently, Chl-a levels rapidly decline, reaching its lowest value of the year in summer (June) at 1.11 μg/L. Chl-a levels slightly increase in July and August (feeding period), followed by a decrease in autumn (September). Chl-a levels continue to rise throughout autumn and winter, reaching their peak in spring.
In addition to SSC and Chl-a, SST was also analyzed in the study area. SST (5-30°C, Figure 6) in this region generally exhibits a pattern of higher temperatures in the southeast and lower temperatures in the northwest, with temperatures decreasing closer to the coast. Regarding seasonal variations, SST in this area during winter and spring (5-20°C) is significantly lower than in summer and autumn (16-30°C). Specifically, during spring (8-20°C, Figures 6A–C), SST gradually increases from northwest to southeast. Influenced by ocean currents, the isotherms exhibit a dense “W” shaped distribution, indicating significant temperature differences. In summer (20-30°C), the SST gradually rises, reaching its peak (26-30°C) in August (Figure 6F), accompanied by significant upwelling (Figures 6D–F, yellow square). The SST in the upwelling area is about 2°C lower than that in the surrounding sea (yellow rectangle in Figure 6F). The isotherms become less dense, and the temperature difference decreases, revealing a distribution trend of higher SST near the coast, lower around the islands, and higher in the open sea. By autumn (Figures 6G–I), SST gradually decreases (16-26°C), resulting in a “warm tongue” extending from southeast to northwest (Figures 6H, I). In winter (Figures 6J–L), SST reaches its lowest point (5-20°C) and gradually increases from northwest to southeast, with the isotherms distributed along the coastline.
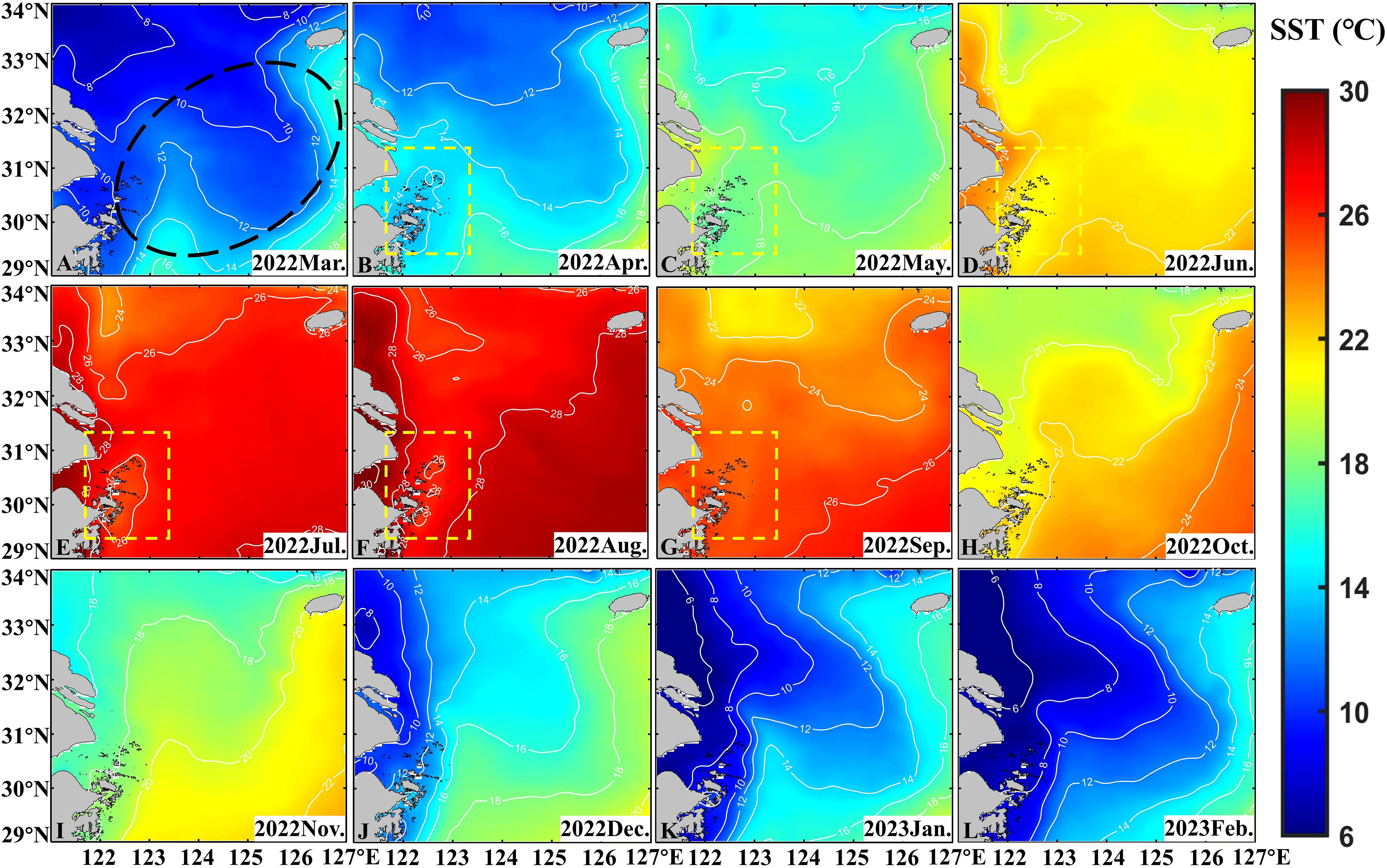
Figure 6. Distribution of monthly average SST in spring (A–C), in summer (D–F), in autumn (G–I) and in winter (J–L) obtained from OSTIA in 2022 and 2023, with the location of large yellow croaker fishery (black dotted line) marked. The yellow rectangle area indicates the upwelling area.
The distribution details of SST (Figure 7), indicate that SST varies with the changes in ocean current. As a result, higher SST is observed downstream of the island compared to upstream, forming a distinct wake in the downstream area (pink rectangle in Figures 7D, I). Specifically, the SST in the northern part of the island is higher than that in the southern part due to the influence of south-to-north currents in summer (pink rectangle in Figure 7D). In winter, the SST in the southern part of the island is higher than that in the northern part due to the influence of north-to-south currents (Figure 7I, pink rectangle).
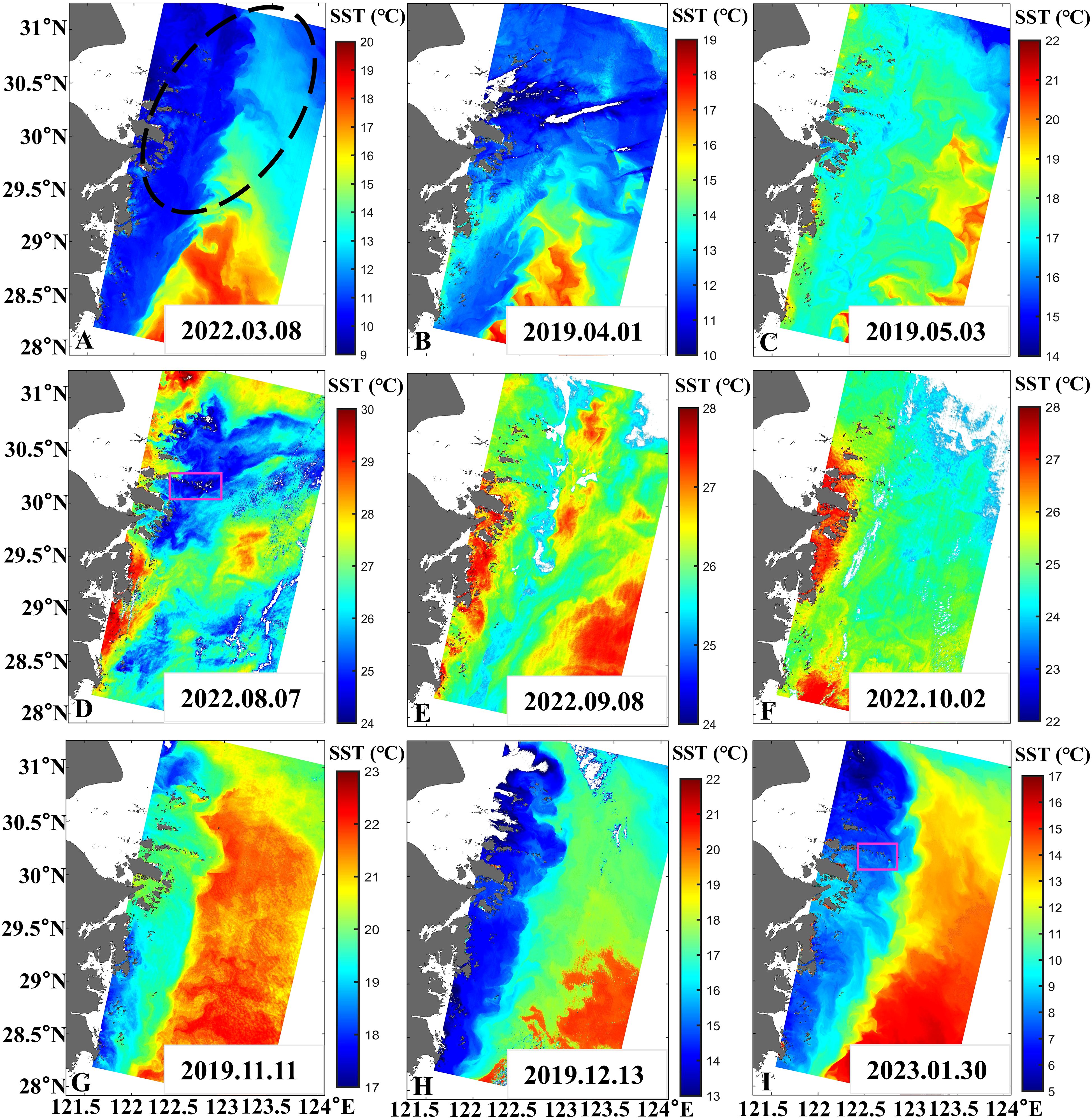
Figure 7. Distribution of SST in spring (A–C), in summer (D), in autumn (E–G) and in winter (H, I) obtained from Landsat-8/9 TIRS in 2019, 2022, and 2023, with the location of large yellow croaker fishery (black dotted line) marked. The pink rectangle indicates the wake.
Other environmental factors in the large yellow croaker fishery including salinity, salinity front, temperature front, wind, and ocean current were also analyzed.
The spatial distribution of SSS exhibited a gradual increase from nearshore to the open sea (Figures 8A–D), with a range of 0 to 35 ‰. The variation range was larger near the shore (Figures 8E–H, 0-20 ‰) compared to the smaller variation range (20-35 ‰) in the open sea area east of Zhoushan Islands (122°E). SSS was lower in summer (Figure 8B) and higher in winter (Figure 8D). The temperature front near the shore (Figures 8I–L) exhibits greater intensity, with stronger fronts observed in both summer (Figure 8J, 0.1-0.2 °C/km) and winter (Figure 8L, 0.15-0.3 °C/km).
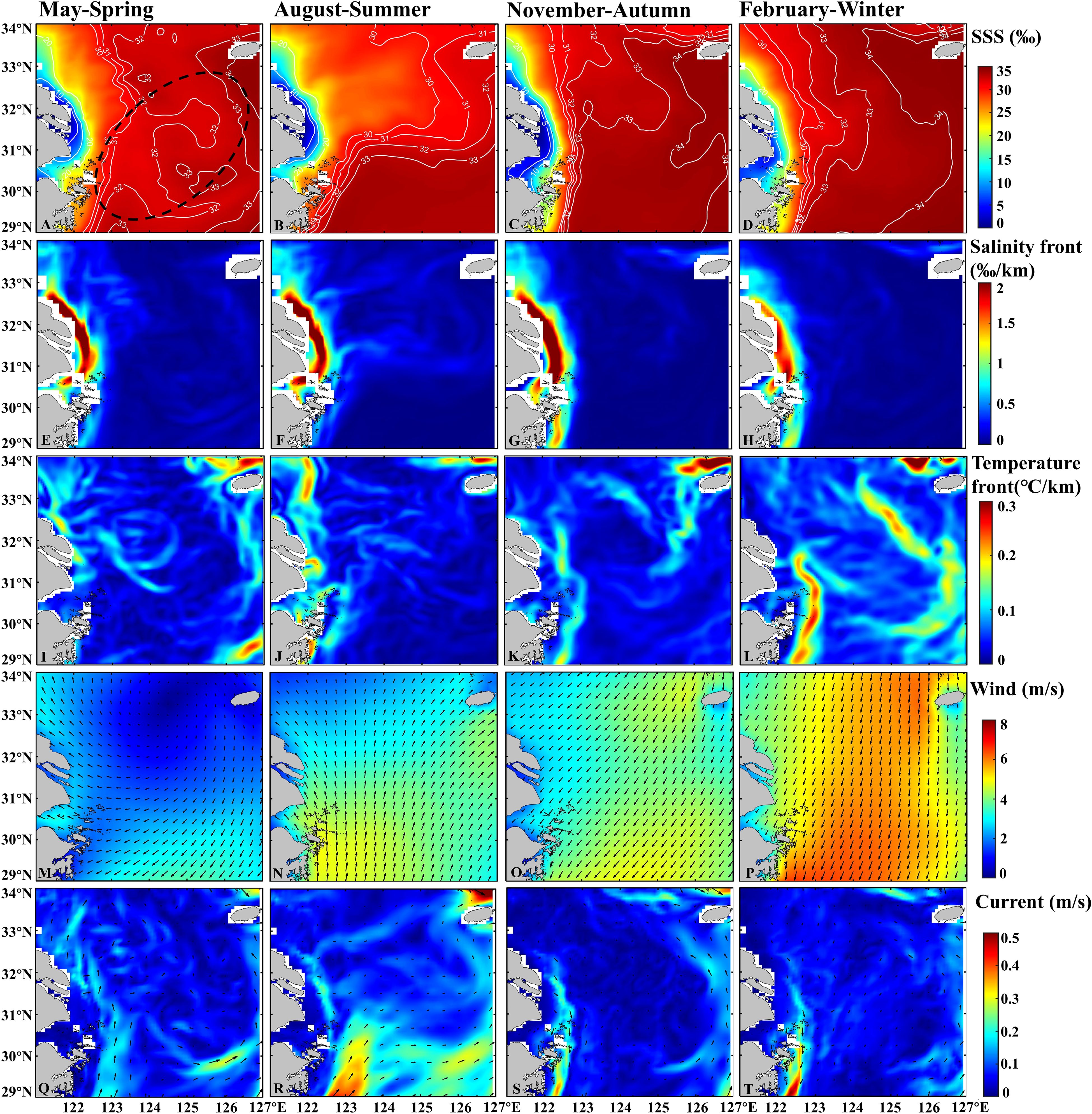
Figure 8. The seasonal variations of SSS (A–D), salinity front (E–H), temperature front (I–L), wind (M–P) and current (Q–T) in 2022 and 2023, with the location of large yellow croaker fishery (black dotted line) marked.
The wind and current exhibit clear seasonal variation. Easterly wind speeds (0-3 m/s) in spring (Figure 8M), southerly winds in summer (Figure 8N) which induce upwelling, northeasterly winds in autumn (Figure 8O), and higher wind speeds (4-6 m/s) in winter (Figure 8P). Ocean currents also show distinct seasonal characteristics. From spring (Figure 8Q) to summer (Figure 8R), the Zhejiang-Fujian Coastal Current flow from south to north, with gradually increasing velocities (0.2-0.4 m/s) and wider influence ranges. Flow velocities decrease in autumn (Figure 8S), and gradually increase (0.1-0.5 m/s) in winter (Figure 8T), with the flow direction shifting from north to south. The intensity of the Kuroshio gradually increases from spring to summer, with velocities ranging from 0.2 to 0.4 m/s.
In summary, the environmental factors characteristics of large yellow croaker fishery are shown in the following table (Table 5).
By analyzing the interannual variation trends of six key marine environmental factors from 2004 to 2023, this study aims to explore the changes in the fishery environment. The results (Figure 9G) indicate a significant (P< 0.05) increase in winter (December, January, February) SST in the past 20 years, with a slope of 0.04218 and an R² value of 0.20967. The trends for other environmental factors are not statistically significant. The SST in other months (Figure 9F) and SSC (Figure 9A) show slight upward trends; Chl-a (Figure 9B), SSS (Figure 9C), and wind (Figure 9D) exhibit slight downward trends; while current (Figure 9E) remains relatively stable.
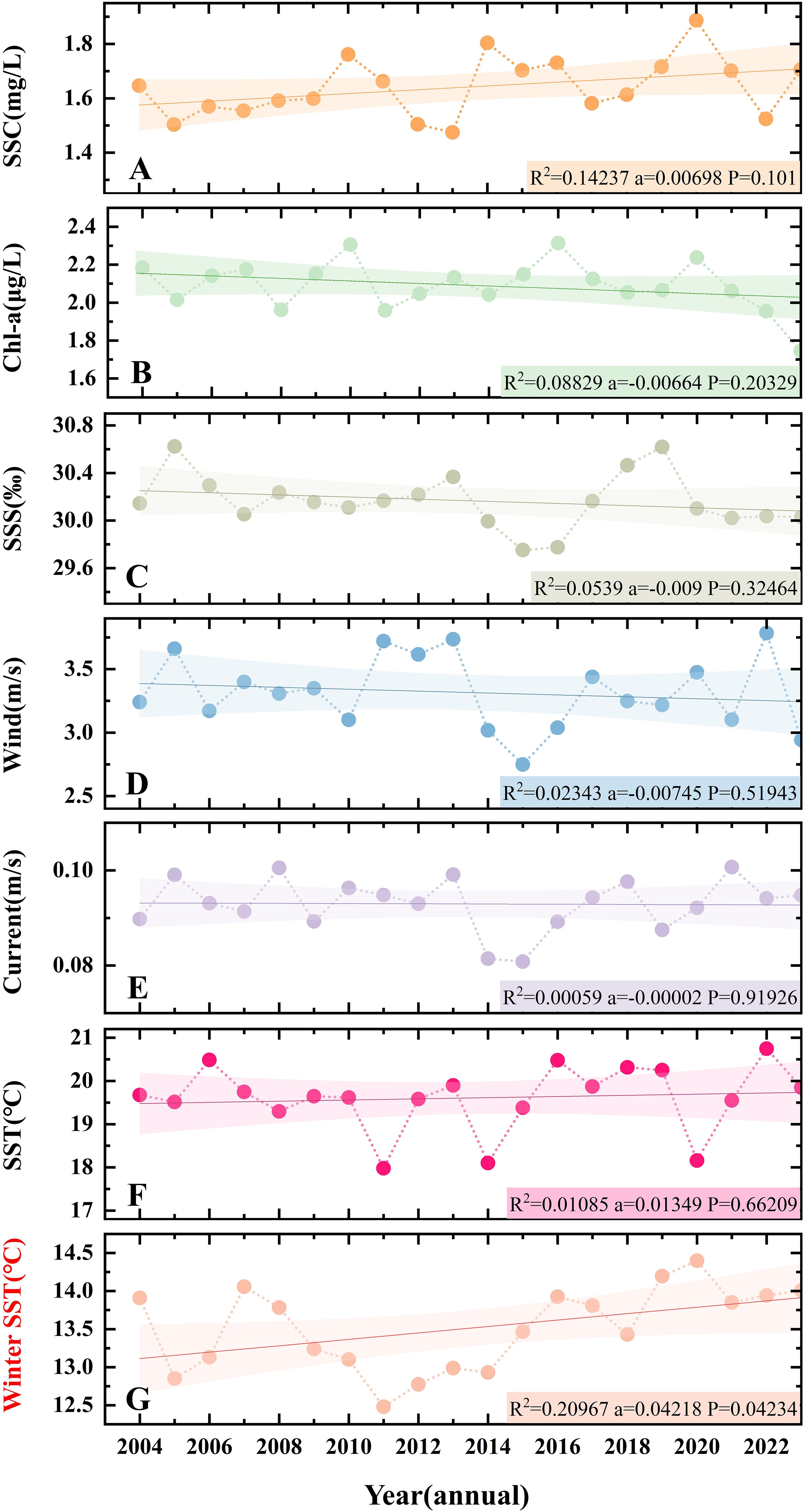
Figure 9. Long-term series (2004-2023, 20 years) of six environmental factors, such as (A) SSC, (B) Chl-a, (C) SSS, (D) Wind, (E) Current and (F, G) SST near the Yangtze River Estuary (29-34°N, 121-127°E).
In addition, human factors such as offshore engineering have developed rapidly in the past few years. The scale and number of offshore wind farms near the Yangtze River Estuary increased significantly from 2008 to 2023 (Figure 10). Specifically, construction of China’s first offshore wind farm (Shanghai Donghai Bridge Offshore Wind Farm) began in 2008 (Figure 10B, about 0.03 km2), with only one windmill. In 2013 (Figure 10C, about 15.54 km2), the first phase (34 windmills) of the East side of the Donghai Bridge was completed, and the second phase (2 windmills) of the west side is under construction (Chang and Jeng, 2014). In 2023 (Figure 10D, about 145.47 km2), the Fengxian (32 windmills), Donghai Bridge (62 windmills), Zhongguanghe Shengsi (45 windmills), Shanghai Lingang (55 windmills) and under construction (6 windmills) offshore wind farms were built (Zhang and Wang, 2022). Furthermore, windmills expanded into Hangzhou Bay and the Yangtze River Estuary, in addition to both sides of the East China Sea Bridge (Figure 10D).
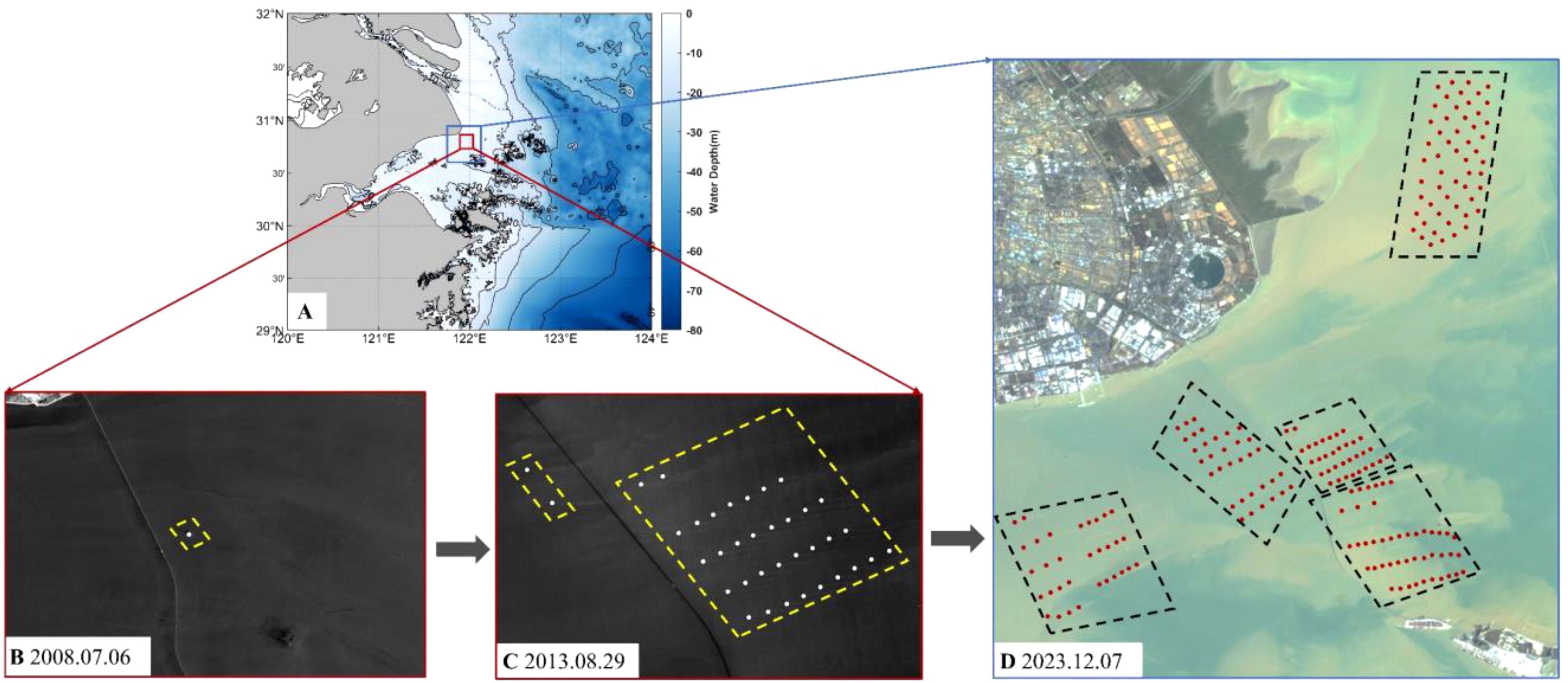
Figure 10. The changes in offshore wind farms near the Yangtze River Estuary. (A) Location of offshore wind farms (The red and blue boxes represent the positions of the B, C and D images). (B) Near-infrared image from Landsat7 ETM+ taken on July 6, 2008. (C) Near-infrared image from GF-1 WFV taken on August 29, 2013. (D) RGB composite image from HY-1C CZI taken on December 7, 2023. The yellow dotted line and black dotted line show the locations of offshore wind farms. The white dots and red dots represent windmills.
The size and the total number of windmills in the offshore near the Yangtze River Estuary (Figure 10A) increased by 836% and 456% over a decade, rising from 36 in 2013 to 200 in 2023, the offshore wind farm covers an area of about 145.47 km2.
Seasonal factors (SST, Chl-a, SSC, wind, current, etc.) along with other factors (topography, water depth, substrate) contribute to the formation of large yellow croaker fishery (overwintering ground, spawning ground, feeding ground). In general, from April to June, large yellow croaker spawn in the vicinity of the islands in the nearshore areas (Zhou and Lee, 2018). Then, from August to October, they migrate from the spawning ground to the feeding ground in all directions. Finally, from December to February, they move to the open sea for overwintering. Understanding the formation of the three fields can enhance our knowledge of large yellow croaker habits and offer valuable insights for the management and conservation of fishery resources.
The overwintering ground of the large yellow croaker is primarily located in the mid-sea areas of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea far away from the coast. The formation of the overwintering ground is primarily influenced by sea temperature. During the period between December and February, there is a decline in offshore sea temperatures. As a warm-water species (Xu and Chen, 2011), large yellow croaker migrates to the open sea in winter during winter in search of a suitable habitat (Figures 6J–L, 9-15°C). The vertical distribution of isotherms facilitates the descent of the large yellow croaker to depths of 50-80 meters for overwintering. This thermal stratification provides a stable and favorable environment for the species during the winter months. Additionally, during winter, the concentration of nutrient-rich suspended sediments in the open sea is relatively high, providing ample sustenance for plankton. This causes plankton to congregate in the waters near the temperature front (Figure 8L), thereby ensuring an adequate food supply for large yellow croaker (White et al., 2019). Specifically, the formation of these conditions can be attributed to two key factors: runoff transport and the re-suspension of particulate matter. On the one hand, the weakening of the Taiwan Warm Current in winter (Figures 8S, T) and the strengthening of the north wind (Figures 8O, P, 5-7 m/s) cause the diluted water of the Yangtze River to carry suspended substances into the sea (Liu, 2015). On the other hand, due to the weakening of runoff, tidal and wave effects are enhanced, promoting the re-suspension of sediment (Wang and Jiang, 2008; Zhu et al., 2020), which results in increased SSC (Figures 2J–L).
Besides, the distribution of the large yellow croaker’s spawning and feeding grounds are closely interrelated. The reasons for their formation are similar to some extent. They are primarily influenced by geographical features and other environmental conditions.
During the spawning season (April-June), large yellow croaker migrate to the waters near the dense reefs of the Zhoushan Islands. Specifically, the sea area exhibits dense isobath lines, predominantly parallel to the coastline and islands, with shallow water depths (Figure 1B, -10~-20 m), creating a conducive environment for fish spawning (Chang et al., 2012). The sediment environment can offer a suitable adhesion surface and conducive developmental conditions for the eggs of large yellow croaker, with its rough surface minimizing the risk of egg displacement and predation by other marine organisms (Holt, 1984; Hixon and Menge, 1991). The reef area serves as a gathering ground for numerous juvenile and adult fish of various migratory species, facilitating their feeding and providing refuge from predators (Amado-Filho and Pereira-Filho, 2012; Wang, 2016; Shen, 2023).
Simultaneously, the waters adjacent to the islands and reefs offer ample food resources and protective cover. In the interaction with ocean currents, upwelling occurs on the oncoming surface of the reef, while eddy currents occur on the backflow surface (Wolanski and Hamner, 1988). Upwelling (Figures 6B–D, black dashed line box) facilitates the vertical exchange of water masses, promoting continuous upward transport of nutrients from the bottom (near the bottom) to the sea surface, accelerating nutrient circulation. Eddy currents transport deep nutrients vertically into the euphotic layer. Nutrient transport stimulates plankton growth, enhances Chl-a levels (Figures 4B–D), and attracts large yellow croaker to congregate there (Simon, 1989; Howe, 2003; Everett et al., 2014; White et al., 2019). Juvenile fish primarily feed on copepods, amphipods, and krill, while adult fish mainly prey on small fish and crustaceans (Zhou and Lee, 2018). The mutual promotion between Chl-a and plankton subsequently provides abundant food resources for juvenile fish.
Additionally, influenced by the strengthening of the Taiwan Warm Current, the coastal water temperature increased (Figures 6B–D, 15-22°C), creating conditions suitable for the development of large yellow croaker eggs (Lin et al., 1991) and promoting the growth of plankton. A low-salinity environment is conducive to the hatching of fertilized eggs of large yellow croaker (Li et al., 2012). Optimal hatching rates for fertilized eggs are observed at salinity levels of 21-33 ‰ (Ye, 2013; Wang, 2021). The increase in flow velocity (Figures 8Q, R, 0.2-0.4 m/s) accelerates the development of gonads and promotes sperm excretion (Wang, 2021).
During the feeding period (August to October), the combined influence of bait and other factors leads to the formation of large yellow croaker feeding ground. After large yellow croaker spawns, a large amount of bait is consumed in spawning grounds (Figure 5, lowest Chl-a), prompting large yellow croaker to disperse outward with the current (Figure 8R, Eastward) in search of more bait (Ciannelli et al., 2015). The summer Yangtze River runoff brings abundant nutrients (Xu et al., 2020), and under conditions of sufficient light (Oliver et al., 2010), plankton proliferates, resulting in increased Chl-a levels. South winds (Figure 8N) further support the formation and enhancement of upwelling. Upwelling transports nutrient-rich seawater from the mid-lower layers to the euphotic layer, providing ample nutrients and favorable growth conditions for plankton, thereby attracting numerous fish for feeding and reproduction (Oliveira et al., 2009).
The analysis of the dominant factors influencing the formation of large yellow croaker fishery shows that, in the past 20 years, various environmental factors have changed (Ji et al., 2018). The most significant change is observed in the winter SST (Figure 9), while changes in other factors are less pronounced. Additionally, it is noteworthy that over the past decade (2013-2023), the number and scale of offshore wind farms have increased significantly. Therefore, we focus on discussing the impact of winter SST and offshore wind farms on the changes in the large yellow croaker fishery.
The warming of China’s seas, particularly evident in the East China Sea, is influenced by global climate warming (Belkin, 2009). There was an obvious warming trend in both winter and summer in the northern part of the East China Sea during 1976-1996 (Tang et al., 2009). The East China Sea SST showed a slight upward trend during 2003-2016, and continued to rise during 2011-2016 (Ji et al., 2018). The growth and reproduction of fish occur within certain temperature ranges (Sunday and Dulvy, 2011). When the environmental temperature exceeds the preferred range of species, they respond by altering their distribution similarly to seasonal migrations (Piccolo, 2012; Girkar et al., 2017; Liang et al., 2018). The winter SST increased significantly during 2004-2023 (Figure 9), with a minimum of 12.48°C (2011) and a maximum of 14.40°C (2020). Since 2011, there has been a fluctuating upward trend. Therefore, the mean SST for winter 2011 and 2020 are compared (Figures 11A, B). The difference between the two was calculated (Figure 11C), and the overall SST was increased (1.92°C). Among them, the rise of SST west of 125°E is higher (>2°C) than that east. The increase of SST in the west of 125°E indicates an expansion of suitable area for large yellow croaker overwintering.
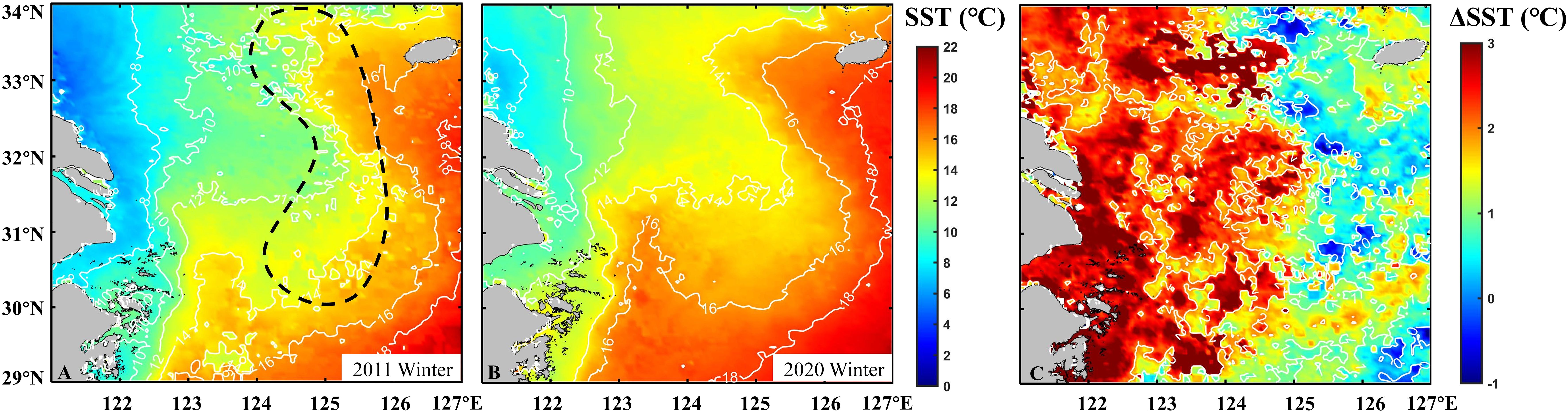
Figure 11. (A, B) Distribution of average winter SST obtained from MODIS Aqua in 2011 and 2020 winter. (C) The value of winter SST change (ΔSST) in 2020 relative to 2011. The overwintering location of the large yellow croaker fishery is indicated by a black dotted line.
In addition, the rapid development of offshore wind farms has also changed the water environment. The flat and sedimentary terrain in engineering waters provides good habitat and spawning grounds for benthic organisms (Bergström et al., 2014; Fang, 2015; Song et al., 2017). The monopiles with rock protection can attract fish, indicating that offshore wind turbines function as artificial reefs, potentially creating new suitable habitats for certain species (Thatcher et al., 2023; Werner et al., 2024). During fisheries resource surveys from November 2013 to August 2015, after the construction of wind farms, yellow croaker juveniles began appearing in the Dai-Quyang area (Jiang, 2023). The SSC and Chl-a near wind turbine arrays are higher than in surrounding waters, with downstream values higher than upstream in offshore wind farm areas (Cai et al., 2023), attracting yellow croaker downstream and transforming the area into a spawning ground for large yellow croaker (Coates et al., 2014; Pollock et al., 2021). Rapid development of offshore wind farms in China (Zhang and Wang, 2022; Wang et al., 2024). This expands the suitable environment for spawning and habitat of large yellow croakers. As the range of spawning ground is enlarged, the range of feeding ground for the large yellow croaker scattered outward is enlarged.
Based on the aforementioned study, we have observed that over the past 20 years, in the study area the winter SST has increased and numerous offshore wind farms have been constructed, leading to significant changes in the marine environment. Consequently, we guess that the current fishery of the large yellow croaker has shifted. Specifically, the overwintering ground have expanded overall, and the spawning ground have extended towards the Yangtze River Estuary.
The historical location of the three fields of large yellow croaker (Figure 12A) is documented in detail in the relevant literature (Xu and Chen, 2011; Zhou and Lee, 2018). The spawning ground is primarily located in Daiquyang and Damuyang (Figure 12A, pink dotted line, 29°N-31°N, 122°E-123.5°E). The feeding ground is situated outside the spawning ground (Figure 12A, red dotted line, 30°N-31°N, 122.5°E-124.5°E). The overwintering ground is mainly distributed in the sea from the Yangtze River Estuary to the sea off the Zhoushan Islands (Figure 12A yellow dotted line, 30°N-32°N, 124°E-126°E) and in the Dasha and Shawai overwintering ground (Figure 12A, yellow dotted line, 32°N-34°N, 123.5°E-125.5°E).
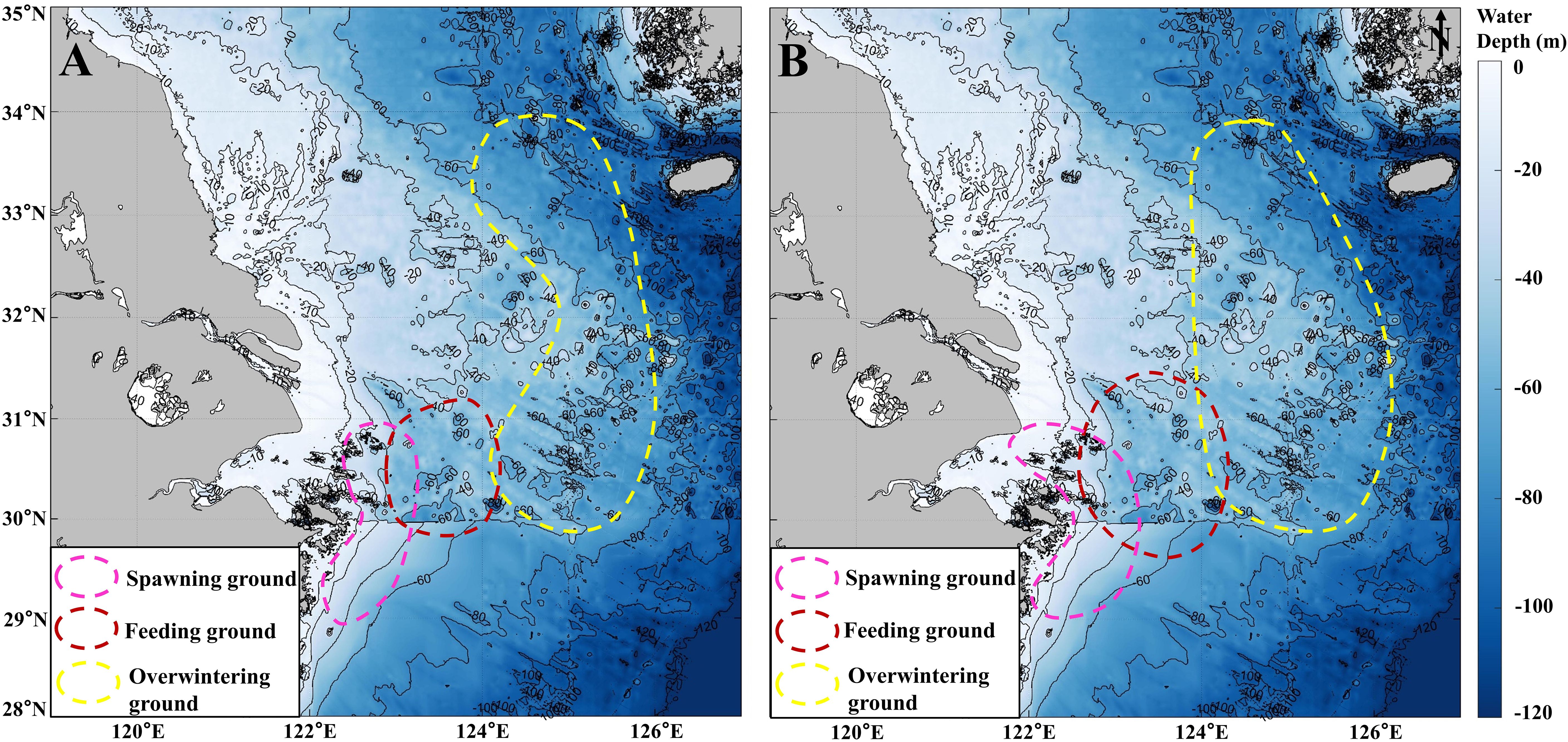
Figure 12. Location distribution of large yellow croaker fishery, includes spawning (pink dotted line), feeding (red dotted line) and overwintering (yellow dotted line) grounds. (A) Three fields of large yellow croaker in the last century (Zhou and Lee, 2018). (B) Currently (2020-2023) possible location of large yellow croaker fishery. The base map shows the water depth near the Yangtze Estuary.
Changes in the environment (rising SST, rapid development of offshore wind farms) have led to changes in the large yellow croaker fishery. At the same time, following the severe decline in large yellow croaker resources, the country implemented a series of protection policies, and there are now indications of resource recovery (Ding and He, 2010, 2011; Yu et al., 2022). Therefore, the current potential distribution range of three fields (Figure 12B) is larger than the traditional distribution range (Figure 12A). Specifically, the spawning ground extends northwestward to the vicinity of the Yangtze River Estuary, expanding by nearly 21% (Figure 12B, pink dotted line, 29°N-31°N, 121.5°E-123.5°E, April to June). The feeding ground has expanded both northward and southward (Figure 12B, red dotted line, 29.5°N -31.5°N, 122.5°E-124.5°E, August to October). Additionally, the overwintering ground extends west, expanding by nearly 29% (Figure 12B, yellow dotted line, 30°N-34°N, 124°E-126.5°E, December to February of the next year).
Furthermore, the large yellow croaker catch data from 2020-2023 (Figure 13) show that, the catches of large yellow croaker were mainly concentrated between 29°N and 34°N, 122°E and 126.5°E. Fishing data east of 124°E (Figure 13, red dotted box), which is consistent with the possible location of large yellow croaker overwintering ground (Figure 12B, yellow dotted line).
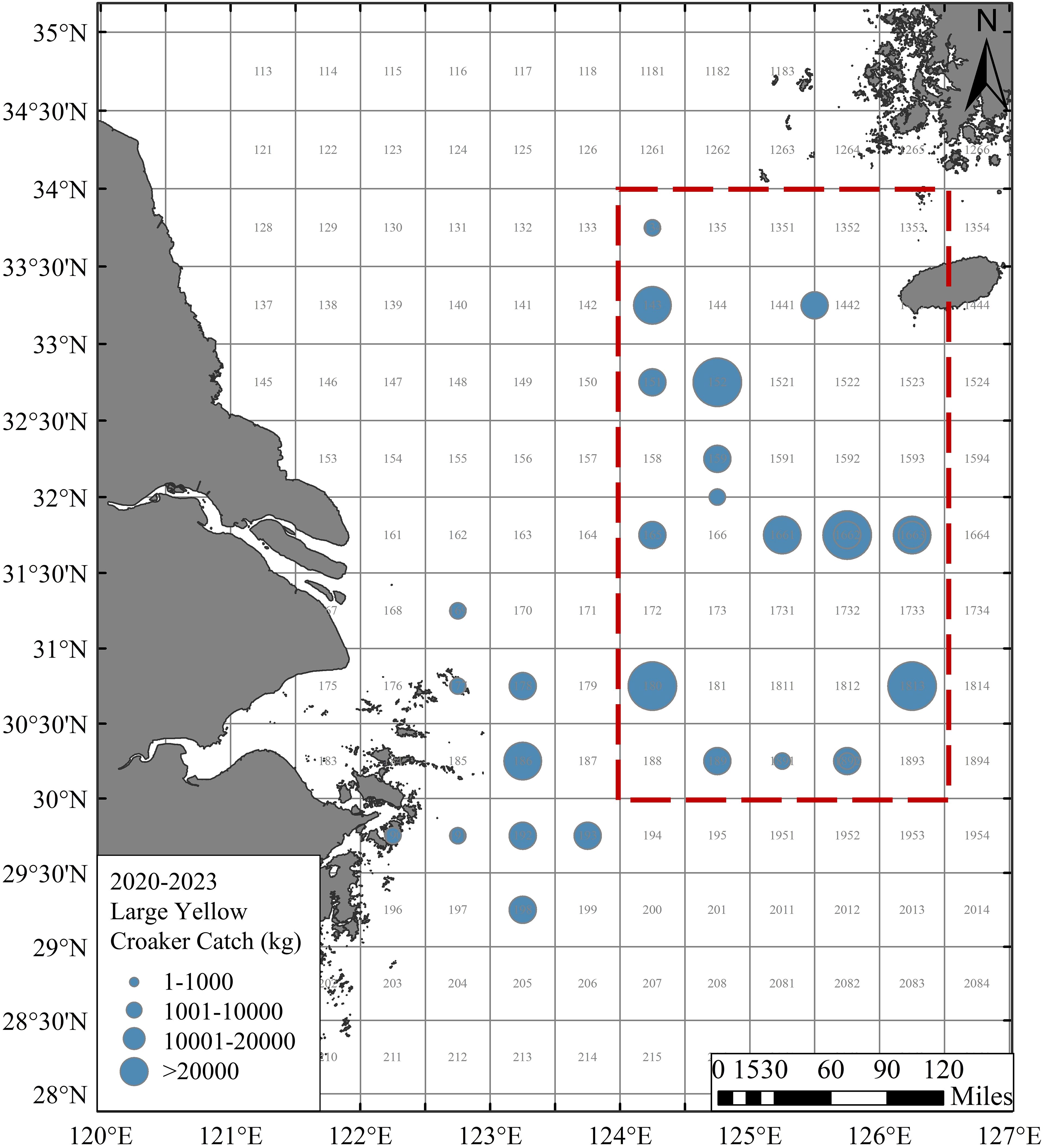
Figure 13. Recent (2020-2023) large yellow croaker catch. The red dotted box indicates the overwintering ground. Fishing zone number (numbers on the base map).
In this study, HY-1C/D CZI data was applied to reveal the details of SSC and Chl-a in large yellow croaker fishery, and the application potential of HY-1C/D fishery was explored. Combining with other multi-source data, the characteristics of other environmental factors (temperature, salinity, current, wind and front, etc.) in the large yellow croaker fishery were analyzed. The temperature (9-28°C), salinity (20-34 ‰) and other water environmental factors of the fishing ground are suitable for the survival and growth of large yellow croaker. The formation and change of fishery are closely related to environmental factors in the water. Based on the analysis above, the change of large yellow croaker fishery was revealed.
The change of environmental factors in the water may induce the change of large yellow croaker fishery. This study found a significant increase in winter SST over the last two decades (2004-2023). The temperature suitable area of large yellow croaker expands, which makes the overwintering ground expanded to the west, expanding by nearly 29%. Additionally, the expansion of offshore wind farms near the Yangtze River Estuary has surged, with their size and number increasing by 836% and 456% in the decade from 2013 to 2023. Wind turbine piles resembling artificial reefs. It can not only promote the waters vertical exchange to enhance the nutrients in upper waters but also provide a protective base for fish spawning. Thus, effectively attracting fish species. The spawning ground has extended northwest to the mouth of the Yangtze River, expanding by nearly 21%.
This study improved the cognition level of resources, habitat environment and change trend of large yellow croaker. It also provided technical support for the construction and protection of the large yellow croaker fishery.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
LC: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. JL: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XY: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RT: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD2401905); the Science Foundation of Donghai Laboratory (Grant No. DH-2022KF01010); the Basic Public Welfare Research Program of Zhejiang Province (LGF21D010004); the Science and Technology Plan of Dongtou District (N2022K04); the Research on group ideological and political subject teaching model of ocean remote sensing (132).
The authors would like to thank the NSOAS for providing the data free of charge. The authors thank the National Satellite Ocean Application Center, China, and the Sophisticated Ocean Front and Fisheries Investigation (SOPHI) for the data support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbott M. R., Chelton D. B. (1991). Advances in passive remote sensing of the ocean. Rev. Geophysics 29, 571–589. doi: 10.1002/rog.1991.29.s2.571
Amado-Filho G. M., Pereira-Filho G. H. (2012). Rhodolith beds in Brazil: a new potential habitat for marine bioprospection. Rev. Bras. Farmacognosia 22, 782–788. doi: 10.1590/S0102-695X2012005000066
Belkin I. M. (2009). Rapid warming of large marine ecosystems. Prog. Oceanography 81, 207–213. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2009.04.011
Bergström L., Kautsky L., Malm T., Rosenberg R., Wahlberg M., Åstrand Capetillo N., et al. (2014). Effects of offshore wind farms on marine wildlife—a generalized impact assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 34012. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/9/3/034012
Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries (1987). Survey and zoning of fishery resources in the East China Sea (Shanghai: East China Normal University Press).
Cai L., Hu Q., Qiu Z., Yin J., Zhang Y., Zhang X. (2023). Study on the impact of offshore wind farms on surrounding water environment in the yangtze estuary based on remote sensing. Remote Sens. 15, 5347. doi: 10.3390/rs15225347
Cai L., Tang R., Yan X., Zhou Y., Jiang J., Yu M. (2022a). The spatial-temporal consistency of chlorophyll-a and fishery resources in the water of the Zhoushan archipelago revealed by high resolution remote sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1022375
Cai L., Yu M., Yan X., Zhou Y., Chen S. (2022b). HY-1C/D reveals the chlorophyll-a concentration distribution details in the intensive islands’ Waters and its consistency with the distribution of fish spawning ground. Remote Sens. 14, 4270. doi: 10.3390/rs14174270
Cai L., Zhou M., Liu J., Tang D., Zuo J. (2020). HY-1C observations of the impacts of islands on suspended sediment distribution in zhoushan coastal waters, China. Remote Sens. 12, 1766. doi: 10.3390/rs12111766
Chang K.-T., Jeng D.-S. (2014). Numerical study for wave-induced seabed response around offshore wind turbine foundation in Donghai offshore wind farm, Shanghai, China. Ocean Eng. 85, 32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.04.020
Chang N.-N., Shiao J.-C., Gong G.-C. (2012). Diversity of demersal fish in the East China Sea: Implication of eutrophication and fishery. Continental Shelf Res. 47, 42–54. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.06.011
Chen X. (2006). Sustainable utilization assessment of marine fisheries resources (Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University).
Chen X., Gao F., Guan W., Lei L., Wang J. (2013). Review of fishery forecasting technology and its models. J. Fisheries China. 37, 1270–1280. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38313
Chen X., Xu K., Li P., Wang H., Zhou Y., Wang M. (2023). Analysis of the status of marine fish proliferation and release in zhejiang offshore. Ocean Dev. Management. 40, 128–135. doi: 10.20016/j.cnki.hykfygl.20231017.003
Chen X.-Y., Zhang J., Tong C., Liu R.-J., Mu B., Ding J. (2019). Retrieval algorithm of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid waters from satellite HY-1C coastal zone imager data. J. Coast. Res. 90, 146. doi: 10.2112/SI90-018.1
Chu Q., Zhang H., Wu Y., Feng Z., Chen B. (2013). Application research of landsat-8. Remote Sens. Information. 28, 110–114.
Ciannelli L., Bailey K., Olsen E. M. (2015). Evolutionary and ecological constraints of fish spawning habitats. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 72, 285–296. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsu145
Coates D. A., Deschutter Y., Vincx M., Vanaverbeke J. (2014). Enrichment and shifts in macrobenthic assemblages in an offshore wind farm area in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 95, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.12.008
Cooley T., Anderson G. P., Felde G. W., Hoke M. L., Ratkowski A. J., Chetwynd J. H., et al. (2002). “FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation,” in IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (Toronto), vol. 3, 1414–1418. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1026134
Ding A., He Y. (2010). Experiment on breeding of large yellow croaker of Daiqu nationality in Zhoushan. China Fisheries., 67–68.
Ding A., He Y. (2011). Test on release and proliferation of Pseudosciaena crocea in Daiquyang sea area. South China Fisheries Science. 7, 73–77.
Druon J.-N. (2010). Habitat mapping of the Atlantic bluefin tuna derived from satellite data: Its potential as a tool for the sustainable management of pelagic fisheries. Mar. Policy 34, 293–297. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2009.07.005
Everett J. D., Baird M. E., Roughan M., Suthers I. M., Doblin M. A. (2014). Relative impact of seasonal and oceanographic drivers on surface chlorophyll a along a Western Boundary Current. Prog. Oceanography 120, 340–351. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.10.016
Fan W. (2004). A study on application of satellite remote sensing in marine fishing-ground analysis and fishing condition forecasting – A case of Ommastrephes bartrami fisheries in Northwest Pacific Ocean (Shanghai: East China Normal University).
Fang N. (2015). Environmental impact of Donghai Bridge offshore wind farm on the marine sediments. J. Qingdao Technological University. 36, 79–82.
Girkar M. M., Ghatge S. S., Kunjir S. N., Tandale A. T., Bopanna B. (2017). Impacts of climate change on marine fisheries sector. Asian J. Environ. Sci. 12, 129–134. doi: 10.15740/HAS/AJES/12.2/129-134
Good S., Fiedler E., Mao C., Martin M. J., Maycock A., Reid R., et al. (2020). The current configuration of the OSTIA system for operational production of foundation sea surface temperature and ice concentration analyses. Remote Sens. 12, 720. doi: 10.3390/rs12040720
Guan W., Gao F., Chen X. (2017). Review of the applications of satellite remote sensing in the exploitation, management and protection of marine fisheries resources. J. Shanghai Ocean University. 26, 440–449. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20160701826
Hersbach H., Bell B., Berrisford P., Hirahara S., Horányi A., Muñoz-Sabater J., et al. (2020). The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorological Soc. 146, 1999–2049. doi: 10.1002/qj.3803
Hixon M. A., Menge B. A. (1991). Species diversity: Prey refuges modify the interactive effects of predation and competition. Theor. Population Biol. 39, 178–200. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(91)90035-E
Holt R. D. (1984). Spatial heterogeneity, indirect interactions, and the coexistence of prey species. Am. Nat. 124, 377–406. doi: 10.2307/2461465
Howe J. C. (2003). Artificial reef evaluation with application to natural marine habitats. Fisheries Res. 63, 297–298. doi: 10.1016/S0165-7836(03)00126-7
Hu Y. (2006). The historical and present status of large yellow croaker germplasm in east sea. J. Shaoxing University. 26, 49–53.
Irons J. R., Dwyer J. L., Barsi J. A. (2012). The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 122, 11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.026
Ji C., Zhang Y., Cheng Q., Tsou J., Jiang T., Liang X. S. (2018). Evaluating the impact of sea surface temperature (SST) on spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentration in the East China Sea. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 68, 252–261. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2018.01.020
Jiang J. (2023). Research on the Influence of East Sea Bridge and Windmill Array in Hangzhou Bay on coastal water environment based on satellite remote sensing technology (Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University). doi: 10.27747/d.cnki.gzjhy.2022.000161
Kachelriess D., Wegmann M., Gollock M., Pettorelli N. (2014). The application of remote sensing for marine protected area management. Ecol. Indic. 36, 169–177. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.003
Kong S., Zhou Z., Zhou T., Zhao J., Chen L., Lin H., et al. (2020). Genome-wide association study of body shape-related traits in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Mar. Biotechnol. 22, 631–643. doi: 10.1007/s10126-020-09983-2
Le X., Tang Y., Wang Z. (2022). Reason analysis and resource protection suggestions on the frequent catch of wild large yellow croaker in Zhejiang Province sea area. Chin. Fisheries Economics. 40, 53–60.
Lellouche J.-M., Le Galloudec O., Regnier C. (2023). Global production centre GLO_ANALYSISFORECAST_PHY_001_024. (Europe: CMEMS).
Li L., Yan X., Wang J., Xu Y., Zhou Y., Qian W., et al. (2022). Long-term change of yield and stock assessment of larimichthys crocea and trichiurus iepturus in zhejiang coastal waters based on historical data. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Natural Science). 41, 63–69.
Li B., Zhong Y. B., Lv W. Q. (2012). Salinity tolerance of Pseudosciaena crocea during early development. J. Shanghai Ocean University. 21, 204–211.
Liang C., Xian W., Pauly D. (2018). Impacts of ocean warming on China’s fisheries catches: an application of “Mean temperature of the catch” Concept. Front. Mar. Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00026
Lin D., Zhang J., Zheng Z., Weng Z., Su Y. (1991). Studies on the artificial propagation of the large yellow croake, pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson). J. Fujian Normal Univ. (nature science)., 71–79.
Liu X. (2015). Seasonal variation research of suspended sediments in the east China sea based on remote sensing (Qingdao: Ocean University of China).
Liu M., Cheng (2020).Larimichthys crocea. In: The IUCN red list of threatened species. Available online at: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.20201.RLTS.T49182559A49239394.en (Accessed November 28, 2023).
Liu B., Dong W., Wang Y., Zhu S., Wu W. (2005). Identification of germ plasm in pseudosciaena crocea TAI-CHU race by AFLP. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica. 29, 413–416. doi: 10.3724/issn1000-3207-2005-4-413-k
Liu J., Jiang X., Wang L., Ye X., Ding J., Zeng T., et al. (2021). Network observation and application of Haiyang-1 C and D satellites. Satellite Application., 19–26.
Liu J., Ye X., Lan Y. (2022). Remote sensing big data from Chinese ocean satellites and its application service. Big Data Res. 8, 75–88. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2022016
Liu J., Ye X., Song Q., Ding J., Zou B. (2023). Products of HY-1C/D ocean color satellites and thier typical applications. Natl. Remote Sens. Bulletin. 27, 1–13. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20235002
Oliveira P. B., Nolasco R., Dubert J., Moita T., Peliz Á. (2009). Surface temperature, chlorophyll and advection patterns during a summer upwelling event off central Portugal. Continental Shelf Res. 29, 759–774. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2008.08.004
Oliver R. L., Mitrovic S. M., Rees C. (2010). Influence of salinity on light conditions and phytoplankton growth in a turbid river. River Res. Apps 26, 894–903. doi: 10.1002/rra.1309
Piccolo J. (2012). Gasping fish and panting squids: oxygen, temperature and the growth of water-breathing animals. Fish Fisheries 13, 359–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2979.2012.00461.x
Pollock C. J., Lane J. V., Buckingham L., Garthe S., Jeavons R., Furness R. W., et al. (2021). Risks to different populations and age classes of gannets from impacts of offshore wind farms in the southern North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 171, 105457. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105457
Saito Y., Yang Z. (1995). Historical change of the Huanghe (Yellow River) and its impact on the sediment budget of the East China Sea. (Yokohama: M & J International), 7–12.
Santos A. M. P. (2000). Fisheries oceanography using satellite and airborne remote sensing methods: a review. Fisheries Res. 49, 1–20. doi: 10.1016/S0165-7836(00)00201-0
Shen H. (2023). Biological characteristics and spatial patterns of typical sciaenidae fishes in rocky island waters (Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University). doi: 10.27314/d.cnki.gsscu.2021.000537
Simon N. S. (1989). Nitrogen cycling between sediment and the shallow-water column in the transition zone of the Potomac River and Estuary. II. The role of wind-driven resuspension and adsorbed ammonium. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 28, 531–547. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(89)90028-0
Song C., Hou J., Zhao F., Zhang T., Wang S., Zhuang P. (2017). Macrobenthos community structure and its relationship with environment factors in the offshore wind farm of the East China Sea Bridge in spring and autumn. Mar. Fisheries. 39, 21–29. doi: 10.13233/j.cnki.mar.fish.2017.01.003
Sund P. N., Blackburn M., Williams F., Susanto R., Gordon A. L. (1981). Tunas and their environment in the Pacific Ocean: A review A review, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 443-512, 1981.
Sunday J. M., Dulvy B. N. K. (2011). Global analysis of thermal tolerance and latitude in ectotherms. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 278, 1823–1830. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2010.1295
Tang X., Wang F., Chen Y., Li M. (2009). Warming trend in northern East China Sea in recent four decades. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 27, 185–191. doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-9238-4
Thatcher H., Stamp T., Wilcockson D., Moore P. (2023). Residency and habitat use of European lobster (Homarus gammarus) within an offshore wind farm. J. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 80, 1410–1421. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsad067
Tong C., Mu B., Liu R.-J., Ding J., Zhang M.-W., Xiao Y.-F., et al. (2019). Atmospheric correction algorithm for HY-1C CZI over turbid waters. J. Coast. Res. 90, 156. doi: 10.2112/SI90-019.1
Wang Z. (2016). Fish community patterns in meta-habitat: A case study from Ma’an Archipelago (Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University).
Wang Y. (2021). Resource status and variation in critical habitat suitability of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea (Xiamen: Xiamen University). doi: 10.27424/d.cnki.gxmdu.2021.003179
Wang W., Jiang W. (2008). Study on the seasonal variation of the suspended sediment distribution and transportation in the East China Seas based on SeaWiFS data. J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 385–392. doi: 10.1007/s11802-008-0385-6
Wang F., Qin Z., Song C., Tu L., Karnieli A., Zhao S. (2015). An improved mono-window algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval from landsat 8 thermal infrared sensor data. Remote Sens. 7, 4268–4289. doi: 10.3390/rs70404268
Wang K., Xiao W., He T., Zhang M. (2024). Remote sensing unveils the explosive growth of global offshore wind turbines. Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev. 191, 114186. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.114186
Werner K. M., Haslob H., Reichel A. F., Gimpel A., Stelzenmüller V. (2024). Offshore wind farm foundations as artificial reefs: The devil is in the detail. Fisheries Res. 272, 106937. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2024.106937
White J. W., Carr M. H., Caselle J. E., Washburn L., Woodson C. B., Palumbi S. R., et al. (2019). Connectivity, dispersal, and recruitment connecting benthic communities and the coastal ocean. Oceanography 32, 50–59. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2019.310
Wolanski E., Hamner W. M. (1988). Topographically controlled fronts in the ocean and their biological influence. Science New Ser. 241, 177–181. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4862.177
Xu H. (2015). Retrieval of the reflectance and land surface temperature of the newly-launched Landsat 8 satellite. Chin. J. Geophysics. 58, 741–747. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150304
Xu Z., Chen J. (2011). Analysis of migratory route of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. J. Fisheries China. 35, 429–437. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231
Xu Y., Tang X., Yan X., Song W., Zhou Y., Zhang H., et al. (2023). Speculation of migration routes of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea based on otolith microchemistry. Haiyang Xuebao. 45, 1–13. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2023126
Xu L., Yang D., Greenwood J., Feng X., Gao G., Qi J., et al. (2020). Riverine and oceanic nutrients govern different algal bloom domain near the changjiang estuary in summer. JGR Biogeosciences 125, e2020JG005727. doi: 10.1029/2020JG005727
Ye J. (2013). Resource and biological characteristics of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in Guanjing (Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University).
Yin R., Zhou Y., Liang J., Jiang R., Xu K., Li Z., et al. (2022). Relationship between spatial and temporal distribution of larimichthys crocea and environmental factors in marine pasture of zhongjieshan islands. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Natural Science). 41, 483–489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2022.06.002
Yu C., Yan X., Jiang Q., Zang Y. (2022). Cause analysis of resources change and reconstruction strategy of Larimichthys crocea Daiqu group in the East China Sea. J. Fisheries China. 46, 616–625. doi: 10.11964/jfc.20211013126
Zhang M., Tang J., Dong Q., Song Q., Ding J. (2010). Retrieval of total suspended matter concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 114, 392–403. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.09.016
Zhang J., Wang H. (2022). Development of offshore wind power and foundation technology for offshore wind turbines in China. Ocean Eng. 266, 113256. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113256
Zhao C. (1990). China’s marine fishery resources (Hangzhou: Zhejiang science and technology publishing house).
Zhao J., Bai H., Ke Q., Li B., Zhou Z., Wang H., et al. (2021). Genomic selection for parasitic ciliate Cryptocaryon irritans resistance in large yellow croaker. Aquaculture 531, 735786. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735786
Zheng Y., Chen X., Cheng J., Wang Y., Shen X., Chen W., et al. (2003). Biological resources and environment of the continental shelf of the East China Sea (Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers).
Zhou Y., Lee S. (2018). Atlas of the main economic types of the East China Sea and the three fields and one passage and the protected area (Beijing: China Ocean Press).
Keywords: large yellow croaker, fishery, HY-1 C/D, Yangtze estuary, environmental factors
Citation: Cai L, Li J, Yan X, Tang R and Zhang X (2024) The change of environmental factors in the water near the Yangtze Estuary may induce the change of large yellow croaker fishery location there. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1491129. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1491129
Received: 04 September 2024; Accepted: 05 November 2024;
Published: 27 November 2024.
Edited by:
Guanqiong Ye, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Liang Guo, Hunan Normal University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Cai, Li, Yan, Tang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojun Yan, eWFueGpAempvdS5lZHUuY24=; Lina Cai, Y2xub3duQHpqb3UuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.