
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci. , 28 October 2024
Sec. Marine Affairs and Policy
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1486230
This article is part of the Research Topic Advances in Marine Environmental Protection: Challenges, Solutions and Perspectives View all 41 articles
With the proliferation of human activities, a series of marine ecological and environmental problems have arisen. Judicial application is important to test legislative achievements, explore judicial difficulties, and examine the compliance with the law. There is no case law in China and the impact of judicial decisions on the protection of marine environment is therefore indirect. Judicial decisions can reflect the implementation of the Marine Environmental Protection Law and play a crucial role in improving the marine environmental protection. An analysis of 2,443 cases related to marine environmental protection heard by courts at all levels across China from 1 January 2019 to 31 December 2023 has been conducted. The findings indicate an overall downward trend in cases related to marine environmental protection, suggesting positive governance outcomes to some extent. However, certain problems remain in the judicial protection of marine environment. Therefore, legislative efficiency should be properly increased and an independent crime for marine environmental pollution should be introduced to further clarify the legal bases for marine environmental protection. The intelligent trial assistance technology should also be applied to shorten trial time, improve trial efficiency, and unify judicial rules. The People’s Courts should play an active role in the provision of evidence and specific evidentiary burden provisions for different types of marine environmental pollutions should be proposed. The data sharing channels between various systems should be facilitated and the functionality for case referral should be developed for the coordination of administrative enforcement and criminal justice within a unified administrative enforcement platform.
The ocean is an important component of the global life support system, affecting multiple aspects of global climate, biodiversity, and human society. At present, the marine economy has become one of the most dynamic and promising areas for economic growth in coastal countries and regions. In 2023, China’s marine economy continued to develop rapidly, with a gross marine product of 9909.7 billion yuan, an increase of 6.0% over the previous year, and a growth rate of 0.8% higher than the gross domestic product (GDP), which accounts for 7.9% of the GDP and increases 0.1% over the previous year (Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2024a). With the proliferation of human activities, the environmental pressure on the ocean is increasing and exceeds its own natural capacity for purification and recovery. This gives rise to a series of marine ecological and environmental problems, which can be categorized into two main types: first, there are issues of marine ecological destruction, such as the ecosystem disorder, a sharp decline in biodiversity, and the extinction of certain species; second, there are issues of marine environmental pollution, such as land-based pollutants entering the sea, the deposition of atmospheric pollutants and intensified eutrophication in coastal areas (Feng, 2023). The Chinese government attaches great importance to the protection of marine ecological environment, integrating it into the national ecological environment protection system. To strengthen the prevention and control of marine environmental pollution, significant progress has been made to prioritize the legislation on marine environmental protection (Zhu, 2016, p. 15). Simultaneously, active efforts have been made to carry out marine ecological protection and restoration. According to the Report on the State of the Ecology and Environment in China 2023 released by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the overall water quality in the maritime areas under China’s jurisdiction is stable and improving (Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2024b). However, there are still phenomena such as water quality degradation and excessive marine litter in some areas, and issues such as waste discharge and leakage, overfishing, and illegal mining cannot be ignored.
Judicial application is a key measure to test legislative achievements, explore judicial difficulties, and examine the current situation of compliance with the law (Nie and Zhang, 2022). In China, there is no case law and the impact of judicial decisions on the protection of marine environment is therefore indirect. However, judicial decisions can reflect the implementation of the Marine Environmental Protection Law (MEPL), for instance, whether there is an increase in the number of the cases related to marine environmental pollution, the main manifestations of marine environmental pollution, what difficulties exist in investigating marine environmental pollution, and whether the relevant legal regulations for marine environmental protection are effective. Marine environmental protection cases refer to cases that directly or indirectly cause legal disputes and resort to judicial procedures due to marine pollution and ecological destruction. Its scope is not limited to cases aiming at protecting the marine environment and redressing environmental public welfare, but also includes civil private interest disputes caused by marine environmental pollution or resource utilization, as well as administrative litigation cases brought against administrative actions taken by maritime administrative agencies concerning the development and utilization of the ocean, navigable waters, fisheries, environmental and ecological resource protection, and other activities (Mei and Yin, 2018). Cases involving marine environmental protection are characterized by professionalism, technicality and comprehensiveness. The study of cases involving marine environmental protection is conducive to discovering the problems existing in marine environmental governance, revealing the legal loopholes, management deficiencies and enforcement challenges within the governance framework, and then proposing corresponding improvement measures.
This paper conducts an analysis of 2,443 cases related to marine environmental protection, aiming at contributing to the formulation and implementation of relevant laws and policies for China’s marine environmental governance. Regarding the scope of the cases concerned, criminal cases related to marine environmental protection were analyzed to examine the manifestations of marine environmental pollution. Relevant administrative cases were also searched and selected, which can reflect the enforcement situation of administrative organs. Furthermore, marine environmental pollution may lead to civil disputes, such as aquaculture disputes caused by marine environmental pollution. It is found that due to the multi-source and spillover characteristics of marine ecological environment issues, there are problems such as unclear boundaries of administrative enforcement powers, unclear regulatory responsibilities, and even conflicts in marine environmental governance (Liang, 2024). There are also obstacles in marine environmental supervision, such as scattered enforcement forces and difficulties in obtaining evidence (Zeng et al., 2018). In the field of marine environmental protection, the crime of polluting the environment needs to be further activated (Hao, 2023). However, the Criminal Law in China does not specifically establish an independent crime for marine pollution, which makes it difficult to convict certain behavior that brought about significant damage to the marine ecological environment and should constitute a crime (Zhang, 2021). Marine environmental governance mainly relies on the leading role of the government and the involvement of other social forces such as enterprises, the public, and non-profit organizations is not very active. They may adversely influence the full play of governance effectiveness (Sun and Zhou, 2021). Therefore, improvements should be made to the legal rules related to marine environmental protection and the professional level of judicial protection should also be enhanced. In addition, it is essential to further strengthen the effective coordination between the judicial and administrative enforcement, reinforce the legal oversight, and jointly maintain the security of the marine ecological environment.
This paper will be divided into five sections. Following the introduction, the overview of the judicial protection of marine environment in China will be described on the basis of the analysis of 2,443 judicial cases. Then, the challenges in the judicial protection of marine environment in China will be examined. The fourth section will focus on how to improve the judicial protection of marine environment in China. Finally, a conclusion of this paper will be put forward.
The protection of the marine ecological environment plays a crucial role in safeguarding national ecological security and promoting the sustainable development of marine resources. To identify the challenges in marine ecological environment protection, promote efficient and rational exploitation of marine resources, and enhance China’s marine ecological environment governance, this paper analyzed 2,443 cases related to marine environmental protection heard by courts at all levels across China from 1 January 2019 to 31 December 2023. The analysis covers aspects such as case types, annual trends, regional distribution, distribution by trial levels, cause of action, criminal penalties, trial periods, and the rate of administrative agency defeats. The findings indicate an overall downward trend in cases related to marine environmental protection, suggesting positive governance outcomes to some extent. However, certain problems remain in the governance of marine environment, such as the limited application of criminal charges which are insufficient to cover all marine environmental damage behavior, light penalties with inadequate deterrence, prolonged trial periods, and the lack of professionalism of the administrative enforcement by administrative agencies.
All of the cases analyzed in this paper were sourced from the unified publication of first-instance, second-instance, and retrial judgments from courts at all levels on the “China Judgments Online” platform established by the Supreme People’s Court. By sorting out potential causes of action and keywords involved in the marine environmental protection, relevant cases were extracted. In this paper, criminal cases refer to the ones that involve crimes such as environmental pollution, smuggling of waste, illegal disposal of imported solid waste, unauthorized import of solid waste, illegal fishing of aquatic products, illegal hunting, illegal mining, destructive mining, illegal occupation of agricultural land, destruction of natural protected areas, endangering precious and endangered wildlife, and endangering key nationally protected plants, where one of the keywords “marine environment”, “marine ecology”, or “marine resources” is contained in the reasoning of the judgment. In this paper, civil cases refer to the ones that involve disputes related to water pollution liability, liability for ship pollution damage, public interest litigation, maritime and commercial disputes, environmental pollution liability, and ecological environment damage compensation disputes; as well as all disputes over marine and navigable water pollution damage and marine and navigable water aquaculture damage, where one of the keywords “marine environment”, “marine ecology”, or “marine resources” is contained in the reasoning of the judgment. In this paper, administrative cases are those where the court’s reasoning includes one of the keywords “marine environment”, “marine ecology”, or “marine resources”.
From 2019 to 2023, the courts in China concluded a total of 2,443 cases related to marine environmental protection disputes, with 196 criminal cases, 1,973 civil cases, and 274 administrative cases. From the perspective of the annual distribution, there were 1,020 cases in 2019; there were 526 cases in 2020, a year-on-year decrease of 48.43%; there were 303 cases in 2021, a year-on-year decrease of 42.40%; there were 282 cases in 2022, a year-on-year decrease of 6.93%; and there were 312 cases in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 10.64%. The overall trend of marine environment protection cases concluded by courts nationwide shows a decline, with an average annual decrease of 25.63%. The annual trend of national marine environmental protection cases from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the figure below (See Figure 1).
From the perspective of regional distribution nationwide, Fujian, Shandong, Tianjin, Liaoning, and Guangxi ranked among the top in the number of cases, accounting for 25.30%, 23.74%, 14.12%, 8.27%, and 7.74% respectively. The detailed distribution of the top 5 regions in terms of the number of marine environmental protection cases nationwide from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the table below. (See Table 1) Fujian had 618 cases, with aquaculture damage disputes accounting for 93.51% of civil cases and illegal mining at 95.24% in criminal cases. Shandong had 580 cases, with marine development disputes making up 43.58% and administrative compulsory enforcement cases accounting for 53.33%. Tianjin had 345 cases, with marine development disputes making up 47.48% and all administrative cases resulting in penalties. Liaoning had 202 cases, with administrative licensing at 92.78% and aquaculture damage at 54.95%. Guangxi had 189 cases, with pollution damage accounting for 79.78% and aquaculture damage accounting for 13.11% in civil cases.
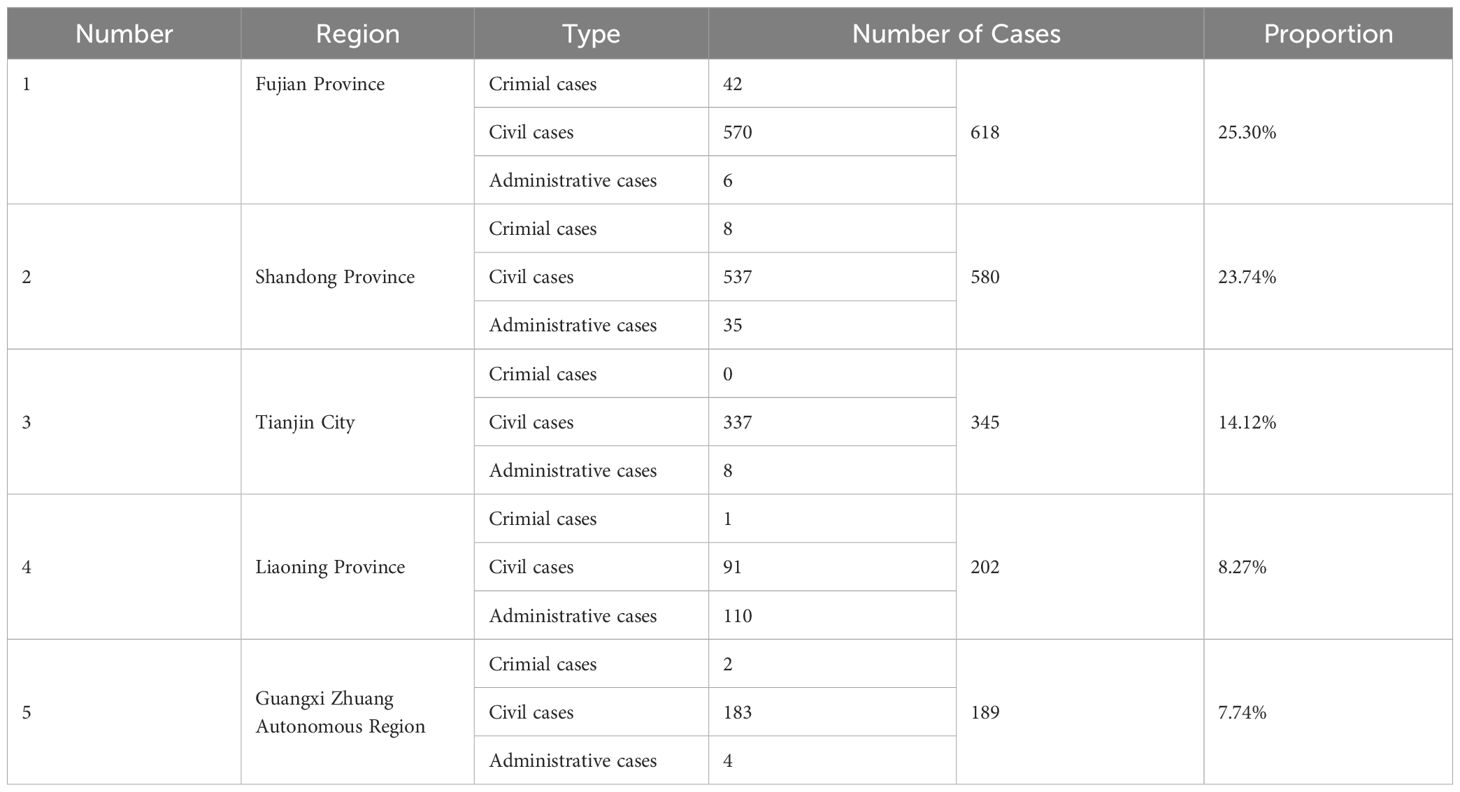
Table 1. Distribution of the Top 5 Regions in National Marine Environmental Protection Cases from 2019 to 2023.
From the perspective of trial level distribution, there were 2,002 first-instance cases, accounting for 81.95% of the total concluded cases; there were 435 second-instance cases, accounting for 17.81% of the total concluded cases; and there were 6 retrial cases, accounting for 0.25% of the total concluded cases. In 2019, there were 932 first-instance cases, 85 second-instance cases, and 3 retrial cases, respectively accounting for 91.37%, 8.33% and 0.29% of the total cases concluded that year. In 2020, there were 361 first-instance cases, 165 second-instance cases, and no retrial cases, respectively accounting for 68.63%, 31.37% and 0.00% of the total cases concluded that year. In 2021, there were 221 first-instance cases, 81 second-instance cases, and 1 retrial case, respectively accounting for 72.94%, 26.73% and 0.33% of the total cases concluded that year. In 2022, there were 227 first-instance cases, 53 second-instance cases, and 2 retrial cases, respectively accounting for 80.50%, 18.79% and 0.71% of the total cases concluded that year. In 2023, there were 261 first-instance cases, 51 second-instance cases, and 0 retrial cases, respectively accounting for 83.65%, 16.35% and 0.00% of the total cases concluded that year. The annual distribution of trial levels in national marine environmental protection cases from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the figure below (See Figure 2).
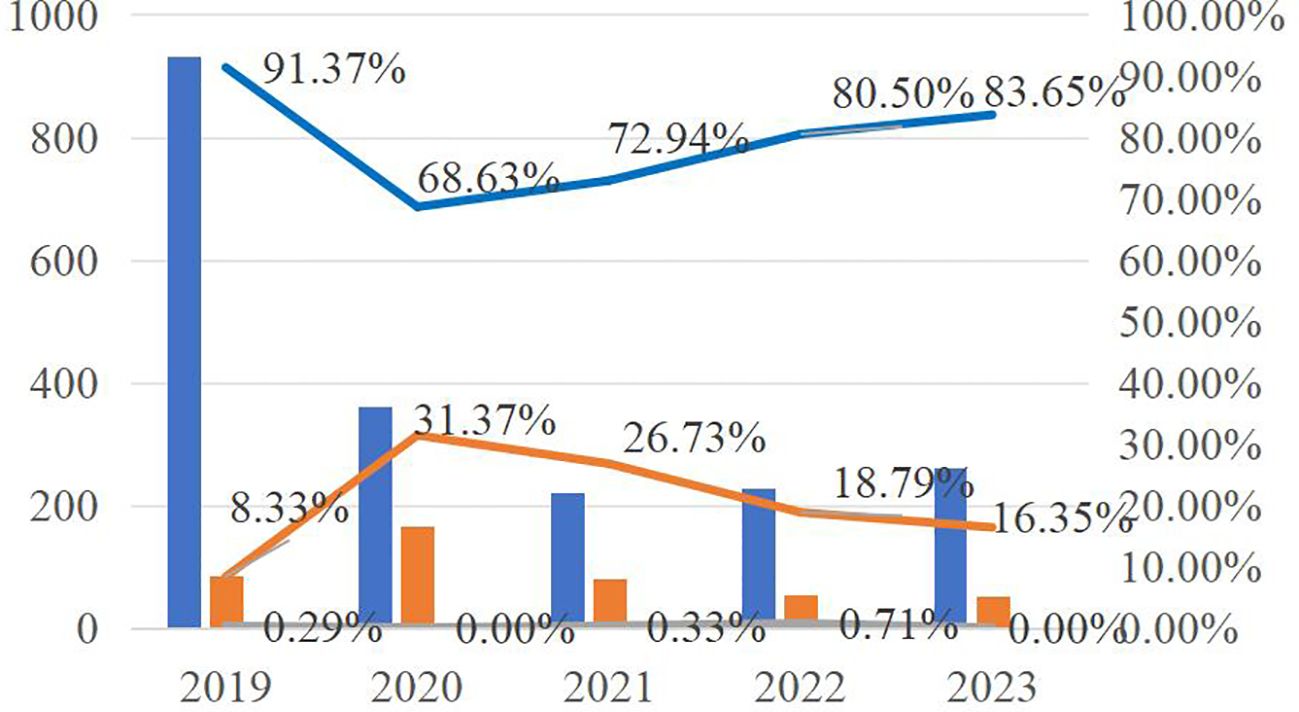
Figure 2. Annual Distribution of National Marine Environmental Protection Cases by Trial Level from 2019 to 2023.
From the annual trend of the main causes of action, in criminal cases, the crime of illegal fishing of aquatic products showed a downward trend, and the crime of illegal mining showed a downward trend after an increase. In civil cases, disputes over liability for aquaculture damage and disputes over liability for pollution damage in offshore and sea-connected waters showed a downward trend, while disputes over marine development and utilization presented an up-and-down trend. The disputes over salvage contracts showed an upward trend followed by a downward trend. In administrative cases, both administrative licensing and administrative punishment cases were on the decline. The annual trend of the main causes of marine environmental protection in China from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the table below (See Table 2).
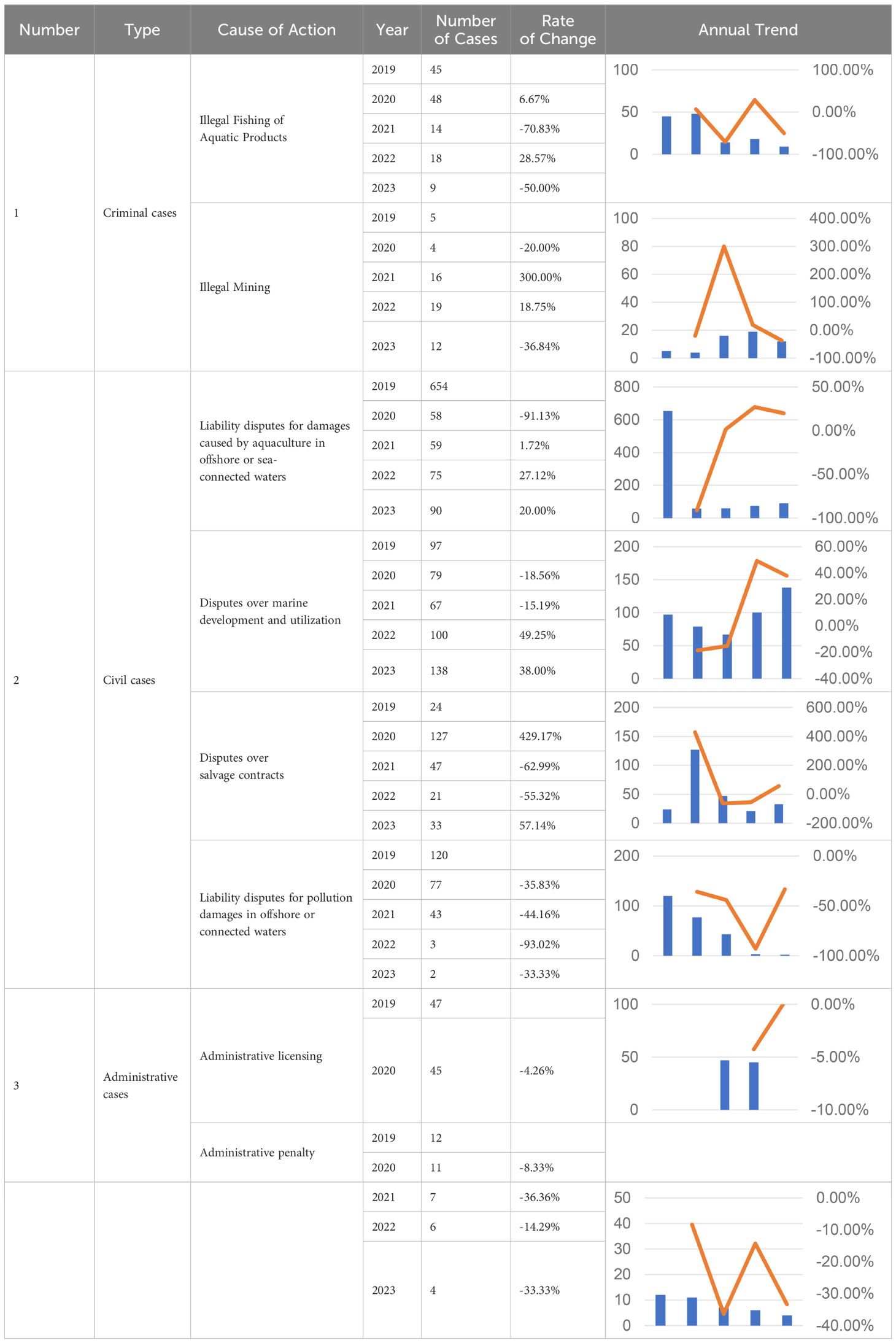
Table 2. Annual Trend of Main Causes of Action Related to Marine Environmental Protection in China from 2019 to 2023.
From 2019 to 2023, courts nationwide concluded a total of 196 marine environmental protection criminal cases. In terms of the annual distribution, there were 50 cases in 2019, 52 cases in 2020, which is an increase of 4.00% compared to the previous year; there were 35 cases in 2021, a year-on-year decrease of 32.69%; there were 37 cases in 2022, a year-on-year increase of 5.71%; and there were 22 cases in 2023, a year-on-year decrease of 40.54%. Overall, the number of criminal cases related to marine environmental protection nationwide shows a downward trend, with an average annual decrease of 18.56%. In terms of trial level distribution, there were 192 first-instance cases, accounting for 97.96% and 4 second-instance cases, accounting for 2.04%.
Among the marine environmental protection criminal cases concluded by courts nationwide from 2019 to 2023, in terms of the distribution of charges, there were 134 cases of illegal fishing of aquatic products, accounting for 68.37%; 56 cases of illegal mining were concluded, accounting for 28.57%; and there were also 6 cases of crimes of endangering precious and endangered wildlife, accounting for 3.06%. No cases of environmental pollution crimes or other charges were found. The distribution of charges in national marine environmental protection criminal cases from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the table below (See Table 3).
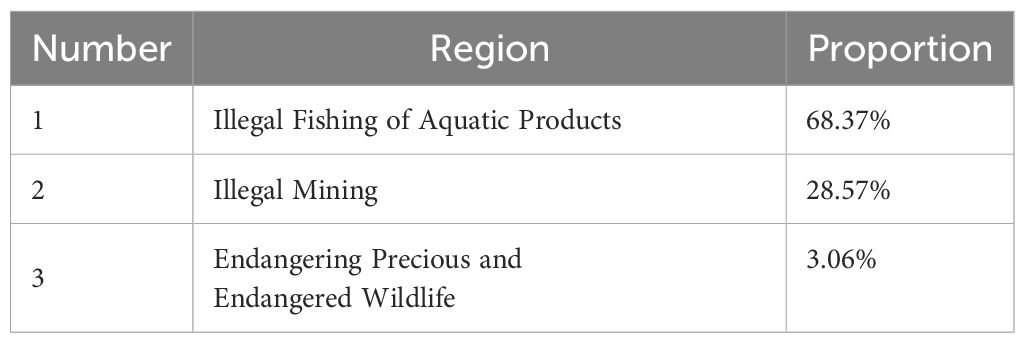
Table 3. Distribution of Charges in National Marine Environmental Protection Criminal Cases from 2019 to 2023.
In criminal cases concerning marine environmental protection, there are actions of severe destruction of the marine ecological environment, which do not fall within in the scope of illegal fishing of aquatic products, illegal mining, and endangering precious and endangered wildlife. However, no cases of environmental pollution crimes were found among the marine environmental protection criminal cases concluded by courts nationwide from 2019 to 2023, indicating that this charge needs to be activated. For example, in the civil public interest litigation case of the Haikou City People’s Procuratorate vs. Hainan Zhonghui Dredging Engineering Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Zhonghui Company), Chen Si, and Haikou Liuyuan Earthwork Engineering Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Liuyuan Company) regarding environmental pollution liability disputes, Liuyuan Company subcontracted part of the construction waste transportation work generated from its earthwork excavation project to Zhonghui Company. Zhonghui Company used ships to dump the construction waste into the sea. According to the appraisal and assessment opinion issued by the South China Institute of Environmental Sciences of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the construction waste dumped into the sea contained harmful and toxic substances such as cadmium, mercury, nickel, lead, arsenic, and copper. These substances entered the marine food chain, causing quantified ecological environmental damage amounting to 8.60064 million yuan.1
From 2019 to 2023, among the marine environmental protection criminal cases concluded by courts nationwide, 53.65% of the defendants were sentenced to imprisonment of one year or less; 35.19% were sentenced to imprisonment of more than one year (excluding one year) and up to three years (including three years); 7.73% were sentenced to imprisonment of more than three years (excluding three years) and up to five years (including five years); 1.72% were sentenced to imprisonment of more than five years (excluding five years) and up to seven years (including seven years); and 0.86% were sentenced to imprisonment of more than seven years (excluding seven years). In terms of fines, 28.57% of the defendants were fined 10,000 yuan or less; 33.71% were fined more than 10,000 yuan (excluding 10,000 yuan) and up to 50,000 yuan (including 50,000 yuan); 23.43% were fined more than 50,000 yuan (excluding 50,000 yuan) and up to 100,000 yuan (including 100,000 yuan); and 14.29% were fined more than 100,000 yuan (excluding 100,000 yuan) and up to 500,000 yuan (including 500,000 yuan). Compared with the high profits generated from illegal fishing of aquatic products, illegal mining, and hunting and trading of precious and endangered wildlife, the amounts of the fine for marine environmental protection crimes are relatively low.
From 2019 to 2023, in China, 59.50% of marine environmental protection criminal cases with specified time by prosecutors occurred at night or in the early morning. Defendants also used methods like tampering with ship identifiers to conceal crimes. In a criminal case, the defendant painted over the ship’s true identifier and disabled the Beidou and Automatic Identification System (AIS) to evade maritime enforcement.2
From 2019 to 2023, a total of 1,973 civil cases related to marine environmental protection were concluded by courts nationwide. With respect to the annual distribution, there were 901 cases in 2019, 358 cases in 2020 (a year-on-year decrease of 60.27%), 235 cases in 2021 (a year-on-year decrease of 34.36%), 212 cases in 2022 (a year-on-year decrease of 9.79%), and 267 cases in 2023 (a year-on-year increase of 25.94%). A downward trend has been shown on the civil cases related to marine environmental protection, with an average annual decrease of 26.22%. In terms of trial level distribution, there were 1,622 first-instance cases, accounting for 82.21%; there were 346 second-instance cases, accounting for 17.54%; and there were 5 retrial cases, accounting for 0.25%.
From 2019 to 2023, among the civil disputes related to marine environmental protection concluded by courts nationwide, the disputes over liability for damage caused by aquaculture in offshore and sea-connected waters were the most prevalent, accounting for 47.42%, significantly higher than the number of cases for other causes. This was followed by disputes over marine development and utilization, which accounted for 24.37%; and disputes over maritime salvage contracts accounts for 12.82%. The distribution of the causes of action for civil disputes related to marine environmental protection from 2019 to 2023 is shown in the table below. Challenges such as investigation, evidence collection and scarcity of plaintiffs were among the issues (See Table 4).
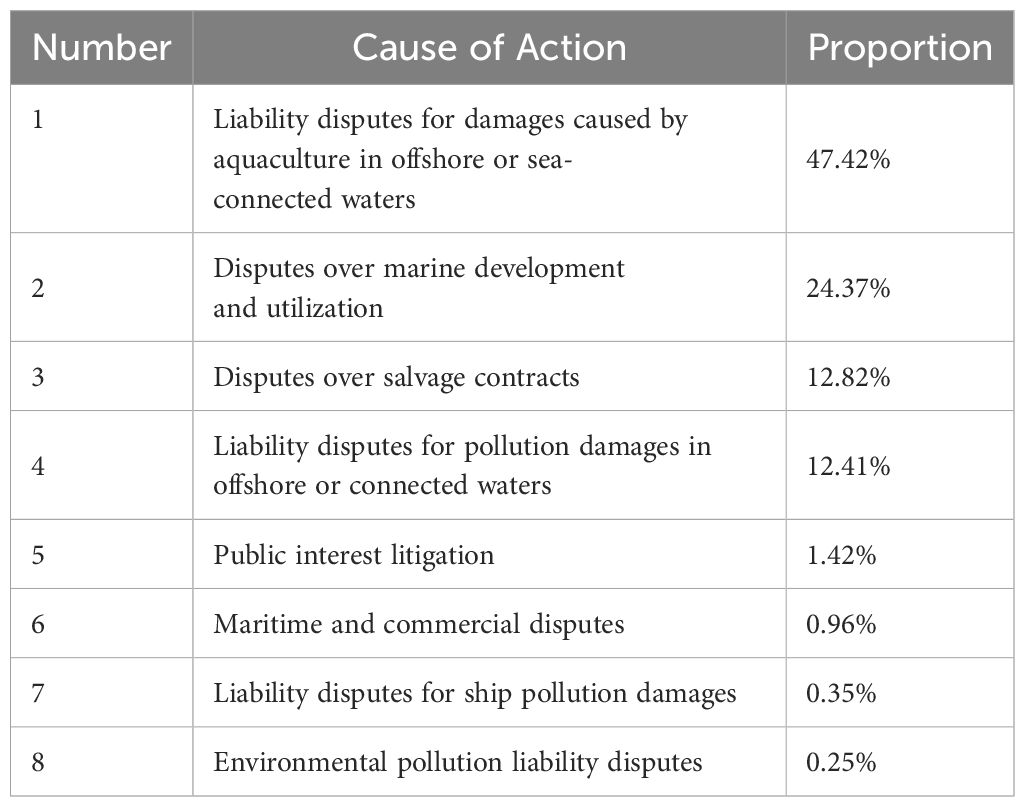
Table 4. Distribution of Causes of Action for Civil Disputes Related to Marine Environmental Protection from 2019 to 2023.
From 2019 to 2023, courts nationwide concluded 28 civil public interest litigation cases related to marine environmental protection. For example, in the civil public interest litigation case of the Haikou City People’s Procuratorate vs. Hainan Zhonghui Dredging Engineering Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Zhonghui Company), Chen Si, and Haikou Liuyuan Earthwork Engineering Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Liuyuan Company) regarding environmental pollution liability disputes, the clue of the case was sourced from public reports. During the investigation, drone footage was used and the maritime and fishery enforcement agencies collaborated with the procuratorate to jointly investigate and handle the case.3 In the civil public interest litigation case of the Second Branch of the Hainan Provincial People’s Procuratorate vs. Xing Zengren and Ningbo xiandeyi trading co., ltd, in response to the illegal sea sand mining activities of the defendants Xing Zengren and Ningbo xiandeyi trading co., ltd, the Second Branch of the Hainan Provincial People’s Procuratorate had issued an announcement and sent a letter to the Dongfang City Natural Resources and Planning Bureau, urging the eligible social organizations and entities to file a lawsuit, however, no eligible parties filed a lawsuit.4
In public interest litigation, the court requires the plaintiff to show evidence of the defendant’s polluting actions and their potential harm to the public. In a civil case about aquaculture damage, the plaintiff, who bore the burden of proof, failed to establish the specific location of the aquaculture and the damage caused by a towrope.5 Therefore, the plaintiff’s claim was not supported.
From 2019 to 2023, among the civil disputes related to marine environmental protection concluded by courts nationwide, in terms of case closure methods, 57.35% of the cases were closed by adjudication, 35.76% by judgment, and 6.89% by mediation. Among the cases closed by adjudication, 74.91% of the cases were withdrawn. Among cases concluded by judgment, 30.58% of first-instance civil disputes involving marine environmental protection had a trial period exceeding 200 days, with an average trial period of 206.20 days for all these first-instance cases. And the appeal revision rate was 5.08% due to incomplete facts, causality issues, wrong damage basis, and responsibility misallocation (See Table 5).
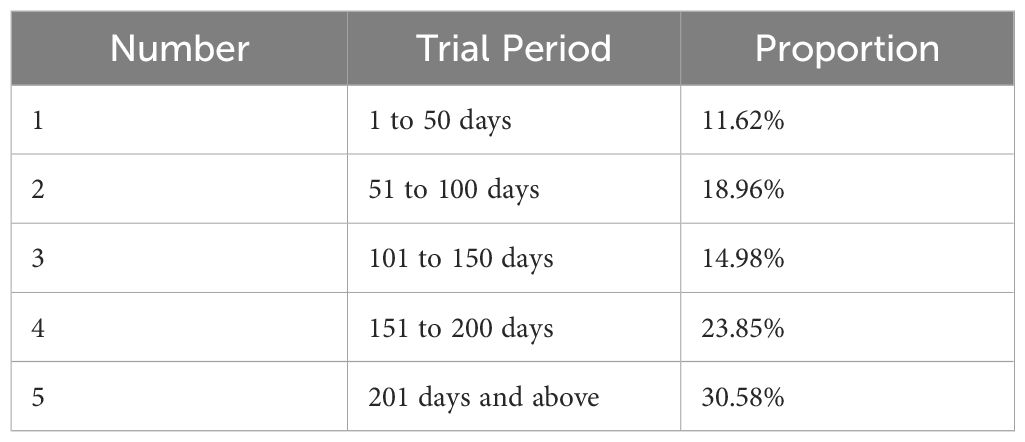
Table 5. Trial Periods for Nationwide First-Instance Civil Disputes Involving Marine Environmental Protection Concluded by Judgment from 2019 to 2023.
From 2019 to 2023, among the second-instance cases of civil disputes related to marine environmental protection concluded by courts nationwide, 295 cases were closed by judgment, of which 15 cases were retried. The main reasons for such retrials included omissions in the determination of damage facts, unreasonable allocation of responsibility, insufficient determination of causal relationships, errors in the determination of the basis for damage compensation, and errors in the determination of the subject qualification of public interest litigation. In the civil public interest litigation case of the Dongfang City Natural Resources and Planning Bureau vs. Mo Tuxiu, due to the high costs of on-site investigation and assessment, which exceeded the amount claimed in the damage compensation lawsuit, the Dongfang Natural Resources Bureau proposed using the compensation standard recognized by the court in another case as the basis for compensation in this case.6 The first-instance court did not support this claim, citing that China is not a case law country and that many specific factors that affect the quantification of compensation amounts, such as the time, place, method, and intensity of sand mining, influence the quantification of marine ecological environment damage. However, the second-instance court held that the sand mining behavior involved in the case was similar in location and method to those in another case, and the time periods were close, so it could be used as the basis for determining the compensation standard in this case.
From 2019 to 2023, the courts in China concluded a total of 274 administrative cases related to marine environmental protection. The annual distribution is as follows: 69 cases in 2019; 116 cases in 2020, an increase of 68.12% year-on-year; 33 cases in 2021, a year-on-year decrease of 71.55%; 33 cases in 2022, remaining the same as the previous year; and 23 cases in 2023, a decrease of 30.30% year-on-year. Overall, the number of administrative cases related to marine environmental protection handled by courts nationwide shows a declining trend, with a decrease of 24.02%. In terms of the level of trials, 188 cases were first-instance trials, accounting for 68.61%; 85 cases were second-instance trials, accounting for 31.02%; and 1 case was a retrial, accounting for 0.36%.
From 2019 to 2023, administrative disputes related to marine environmental protection concluded by courts across the country were predominantly administrative licensing cases, accounting for 50.83% of the total. The defendants in all these cases were the Zhuanghe Government, with plaintiffs alleging that the government delayed the processing of sea area usage rights certificates. This is followed by administrative penalties, making up 22.10%, primarily concerning the legality of administrative penalties imposed for illegal dumping, fishing, and aquaculture activities. Administrative enforcement cases accounted for 6.08%, with the main disputes concentrating on the legality of the seizure of vessels.
From 2019 to 2023, the first-instance defeat rate of administrative agencies in marine environmental protection administrative cases concluded by courts nationwide was 30.19%. In terms of judgment methods, they included ordering the defendant to perform their legal duties within a certain period (44.00%), revoking administrative actions (40.00%), and confirming the illegality of administrative actions (16.00%).
Regarding the reasons for the loss, the main causes included failure to perform administrative duties (33.33%), procedural violations (31.37%), unclear fact-finding and insufficient evidence (29.41%), and incorrect application of the law (5.89%).
The intensification of marine exploitation and utilization has led to a significant increase in the adverse effects of human activities on marine ecosystems (Chen et al., 2017). China is a major maritime power, with the ocean being a crucial resource and strategic domain for China’s sustainable economic and social development. Despite the rapid growth of the marine economy, the pressure on the marine ecological environment remains significant, with an increasing number of cases involving damage to natural resources and ecological environments (Sun, 2022). However, the judicial protection in the area of marine environment has faced great challenges which failed to effectively fulfill its intended role. The issues of judicial “absence” and “hesitation” are particularly pronounced (Yang, 2012). In this section, the challenges in the judicial protection of marine environment in China will be examined, such as the lack of clarified legal bases, the lack of professionalism, the difficulties in evidence provision and allocation of burden of proof and the lack of effective coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement.
With the development of marine environmental protection, China’s marine environmental protection has formed a legal system with the MEPL as the core, and the various laws on the protection of marine eco-environment, which has provided an effective guarantee for marine pollution prevention and ecological protection in China. However, compared with the inland environmental protection law, China’s research on marine environmental protection and marine ecology started relatively late. Considering the current status and needs of marine environmental protection in China, there are still deficiencies in the legal system, which may influence its implementation and the effectiveness of marine ecological environment protection (Miao and Liu, 2023). One of the most urgent issues that should be addressed is the lack of clarified legal bases.
First, the MEPL is the basic law for China’s marine ecological protection and the first important law in China’s environmental protection (Gao, 2024). Since its promulgation in 1982, it has undergone the first revision in 1999 and three amendments respectively in 2013, 2016 and 2017, and completed another revision in 2023 (MEPL2023) (Sun, 2023). The MEPL2023 focuses on the main contradictions, special problems and prominent characteristics of marine environmental protection, providing legal protection for the significantly changing marine environment in China (Mei, 2023; Liu, 2024). However, marine environmental pollution is characterized by strong persistence, wide diffusion, irreversibility, and difficulty in prevention and control (Quan, 2022). Objectively, marine environmental legislation should be forward-looking and moderately advanced, or at least respond in a timely manner to changes in marine environmental risks. While, the proposal or update of related regulations is relatively lagging (Gao, 2024). For example, according to Article 72(2) of the MEPL2023, “the list of wastes that can be dumped into the sea shall be made by the ecological and environmental department of the State Council.”7 However, after the Ministry of Ecology and Environment publicly solicited comments on the relevant regulations in January 2022, the regulations have not yet been officially released. In addition, as the demand for marine environmental protection rapidly evolves and the MEPL has been revised, legal documents such as the Regulation of the People’s Republic of China on the Control of Marine Waste Dumping are still lagging behind in terms of the pace of updating, even though revisions were made several years ago.
Second, many provisions of the MEPL2023 need to be implemented with the support of other laws, rules and regulations. For example, according to Articles 114(1) and 119 of the MEPL2023, marine environment can also be protected within the laws like the Civil Code and the Criminal Law.8 However, the imperfections of the relevant provisions pose obstacles to the judicial protection of the marine environment.
In aforementioned data analysis, no criminal cases related to marine environmental protection have been found concluded under the charge of “environmental pollution”. In fact, this issue has existed for a long time. The reasons can be attributed to the unscientific setting of the crime itself, the unreasonable establishment of the elements of the crime, and the irrational setting of statutory penalties (Tian, 2019). In addition, the protection of legal interests is not clearly defined, and there is a lack of functionality. As a result, issues such as the “pocketing” of regulatory scope, “abstracting” of interpretation standards, and “blurring” of criminal boundaries have emerged in judicial protection (Li and Yuan, 2021; Pan, 2022). Due to the absence of a specific independent crime for marine pollution in China’s Criminal Law, it is difficult to penalize certain behaviors that are sufficiently serious to constitute a crime and damage the marine ecological environment (Zhang, 2021). Moreover, international treaties cannot be directly applied as domestic law in China, which results in the reliance on civil compensation and administrative penalties to address some behaviors that pollute the marine environment (Zhao and Chen, 2019). In summary, it is still difficult to apply the provisions of the Criminal Law in China such as the crime of environmental pollution to acts that damage the marine ecological environment. This is also why this crime has not been activated in the field of marine environmental protection.
Judicial protection of marine environment is a comprehensive institutional framework designed to protect and rehabilitate the marine environment through the application of legal mechanisms. It involves a multifaceted approach that includes legislation, law enforcement, and the judiciary. Judicial protection encompasses the essential function of transforming abstract legal principles into concrete operational guidelines (Su, 2000, p. 4). It enables the transition of legal statutes from static provisions to dynamic norms that guide and regulate the conduct of various entities in a structured and orderly manner (Chen, 2017). By converting legal doctrines into enforceable standards, judicial protection facilitates the consistent and effective implementation of the law, thereby fostering a legal environment that is both predictable and equitable for all stakeholders. Serving as the ultimate bulwark in the protection of marine environmental and the defense of the nation’s maritime ecological rights and interests, the judicial protection of marine environment plays a critical role in preventing and reducing marine environmental pollution, preserving marine ecological balance, and promoting the sustainable use of marine resources. The efficacy of judicial protection is underpinned by two fundamental pillars, namely judicial efficiency and judicial fairness. To realize these two objectives, it requires a large number of highly qualified staff with a strong legal background and necessary knowledge in environmental science, as well as the utilization of intelligent technologies. However, in the cases concerning the marine environmental protection, the lack of professionalism problem has become a contentious issue.
In terms of judicial efficiency, the paramount value lies in the efficiency of time (Yao, 2006), which refers to the ability of the legal system to process cases in a timely and cost-effective manner. However, as analyzed above, the average trial period for first-instance civil disputes concerning the marine environmental protection exceeds 200 days and in fact nearly 31% of the cases took more than 200 days to be settled down. It is stated that the trial period for marine environmental protection cases significantly exceeds that of general maritime disputes (Song, 2021). Another empirical study also found that the average trial period for disputes concerning the protection of marine environment was much longer than that for other civil, criminal, and administrative disputes (Research Team of Shanghai High People’s Court, 2022). From the above statistics on the judicial protection of marine environment, it can be seen that there is a notable gap of 441 cases between the total number of 2,443 cases and the total number of civil cases of the first instance, 2,002. This, to some extent, indicates that a considerable number of parties concerned did not agree with the corresponding judgment results, leading the cases to the second trial or retrial procedures, which accounts for 18.05% of the total sample cases. According to the main data of judicial trial work from January to September 2023 released by China’s Supreme People’s Court, the acceptance rate for civil and commercial first-instance cases is 89.22%, with an increase of 0.43% year-on-year (The Supreme People’s Court, 2023). Nevertheless, the acceptance rate for marine environmental protection cases, at 81.95%, exhibits a discernible disparity. This disparity is a significant contributing factor to the long and extended trial periods for such cases. Judicial efficiency is of great importance to maintain the public trust and to mitigate the burden on the parties involved. Consequently, the lengthy trial period and the relatively low acceptance of the judgements may also be an indicator for the professionalism to be improved.
In terms of judicial fairness, it emphasizes the impartiality and equity of the legal process. Judicial efficiency is the basic component of justice, but judicial justice is the fundamental source of justice. On the premise of achieving judicial fairness, it is necessary to continuously enhance judicial efficiency in order to ultimately realize the value pursuit and objectives of judicial protection (Zhou et al., 2019). Judicial fairness demands that all parties receive equal treatment under the law, without bias or favoritism, and that decisions are made based solely on the merits of the case and the applicable legal standards. However, the benchmarks for the judicial protection of the marine ecological environment are not fully unified and there is an inconsistency in the judicial rules, which poses challenges to the professionalism of judicial marine environmental protection. When courts deal with cases related to the marine ecological environment, they are often required to exercise their discretion to issues where the law is either silent or unclear. Notwithstanding, such discretion is not always appropriately and consistently applied and need further enhancement. For instance, it is shown in the aforementioned statistics that the appellate court has modified the initial judgments in 5.08% of the cases upon second-instance review as a result of the lapses in the recognition of damage facts, inadequate assessment of causal relationships, misjudgments in the criteria for damage compensation, and the unjustifiable distribution of liabilities. Furthermore, according to the Notice on the Establishment of Maritime Courts, maritime courts are positioned at the intermediate level within the judicial hierarchy, appeals from which should be handled by the high people’s courts located at the same region. As a consequence, marine environmental cases are initially under the jurisdiction of specialized courts, while the appellate process is conducted by general high courts. Such a dichotomy may undermine the pursuit of specialized judicial proceedings and the realization of a cohesive judicial protection for marine environmental cases. In addition, cases of marine environmental protection are entangled with intricate marine environmental science, necessitating a substantial reliance on specialized technical knowledge for monitoring and assessing the ecology. Environmental litigation is generally multifaceted, especially marine environmental disputes, frequently encompassing a complex interplay of environmental civil, administrative, and criminal legal relationships, in which the judgment of a case of a certain nature at times needs to be based on the determination of related cases of another nature (Yang, 2016). When it comes to the administrative cases, the situation seems to be more serious. Given the intricacies of environmental cases, the utilization of specialized knowledge in the examination of environmental administrative actions may prompt judges to exercise a prudent approach that defers to administrative decisions. This could result in insufficient substantive review, thereby affecting the quality of the judicial determination (The Supreme People’s Court, 2022). Therefore, inconsistencies in the judicial criteria for safeguarding marine environment pose a significant threat to the professionalism of the judicial protection and may impair the integrity of justice.
It can be seen from the data analysis above that in the past five years, some civil cases involving marine environmental protection in China have faced difficulties such as challenging investigations and evidence collection. In fact, whether in civil or criminal cases, clues in marine ecological environmental pollution cases are usually difficult to be discovered. To some extent, this leads to problems such as difficulties in obtaining evidence in judicial proceedings (Liu et al., 2023). The main reason is the unique circumstances surrounding the destruction of the marine ecological environment, which complicates the process of providing evidence.
One aspect that must be taken into account is that marine pollution often occurs in areas far from the inland, across different geographical boundaries, and the causes are complicated. Compared with the pollution of terrestrial rivers, more resources are needed to discover the clues of marine pollution. However, in the less developed coastal areas, due to the limitations in human resources, materials and financial resources, it is difficult for administrative agencies and judicial organs to organize special forces for long-term and large-scale investigations, which also pose great challenges to discover clues (Zhan and Xu, 2020). Given the vastness of the ocean, some marine ecological environment cases have transnational characteristics, such as involving certain sensitive sea areas or multinational enterprises (Chen and Bai, 2018), which increases the difficulties in obtaining and fixing evidence (Research Team of Shanghai High People’s Court, 2022). As mentioned in the case analysis in section 2.2.4 of this paper, in marine environmental protection cases, the timing of criminal acts and the hidden methods of crime make it difficult to detect the criminal behavior, increasing the difficulty of discovering clues related to polluting the marine environment.
Another aspect that should also be considered is that the harm or damages brought about by marine environmental pollution is relatively concealed. This may make it not only difficult to discover clues but also increases the difficulty of investigation and evidence collection. Taking oil pollution damage as an example, it is one of the main forms of marine ecological environment destruction and the consequences of such damage are quite serious. However, oil pollution damage has the characteristics of potential existence, continuous presence and slow emergence. Typically, after a certain period, the damage only gradually appears due to the combined effects and accumulation of various factors. Therefore, it is challenging to prove the causal relationship between the occurrence of damage and the manifestation of its consequences. Additionally, due to the strong fluidity of marine environment, some evidence of water pollution disappears or becomes concealed. Aquatic products as evidence are not easy to be preserved for a long time, which also brings great difficulties to the collection and fixing of relevant evidence (Wang and Du, 2017). In addition to the inherent characteristics of marine environmental cases, the lack of relevant specialized knowledge of marine environmental protection on the part of the investigators and the lack of necessary and appropriate facilities for evidence collection, may lead to the permanent loss of evidence. In the public interest litigation, the difficulty of investigation and evidence collection is particularly evident. Plaintiffs in such cases cannot legally use force like the police to gather evidence and violators may refuse to cooperate, making it impossible for the plaintiffs to obtain the necessary evidence. The method to collect evidence confirms such difficulty. It is found in a public interest case that the drone was used to capture the photos and videos, which were crucial evidence.9
The difficulty in collecting, fixing and identifying evidence in cases involving marine environment also influences the burden of proof of the relevant parties. For example, in the criminal cases, the Criminal Procedure Law of China articulates, if the People’s Procuratorate finds that the evidence is insufficient and does not meet the conditions for prosecution, a decision not to prosecute shall be made for cases that have undergone two supplementary investigations. If the difficulty in evidence collection results in the difficulty in evidence providing and there is a consequence of insufficient evidence, it may impede to the People’s Procuratorate from providing evidence, thereby hindering the investigation of criminal acts (Tang, 2021).
What is more, the allocation of burden of proof in marine environmental civil cases is another challenge that must be considered. China’s marine environmental public interest litigation has made remarkable achievements in protecting marine natural resources, protecting the marine ecosystem, as well as preventing marine pollution and ecological destruction (Yang, 2023). At present, although there are relevant judicial provisions for public interest litigation cases concerning marine natural and ecological environment (Zhai, 2024), relevant provisions on the burden of proof for marine environmental civil public interest litigation have not been issued yet. Therefore, the Civil Code, the Civil Procedure Law of China and the relevant rules of environmental civil public interest litigation will be applied in such cases. In civil litigation, there are both general rules of proof and special rules for reversed burden of proof, which needs to be further clarified by legislation (Wang, 2019). According to the judicial interpretations issued by the Supreme People’s Court, the rule of reversed the burden of proof in private interest litigation is applicable to civil environmental public interest litigation cases.10 Compared with general environmental public interest litigation, marine environmental public interest litigation has the characteristics of concealment, indirectness, complexity and extensiveness (Li et al., 2015). There are still some problems to be resolved, though the rule of reversed burden of proof can alleviate the burden of proof of the plaintiff and to some extent satisfy the high evidentiary capacity requirements brought by the strong professionalism of marine environmental public interest litigation (Song, 2021). For example, some culturists lacked legal awareness and failed to keep receipts when purchasing aquaculture species seedlings and feeding materials, which led to a lack of clear evidence when filing claims for damages. This is actually a relatively common situation in cases involving marine environmental protection.11 Besides, in China, cases of natural resource damage have been considered as ordinary torts and are not subject to the rule of reversed burden of proof rule. However, judicial interpretations have regarded damage compensation disputes over marine natural resources and the ecological environment as a special form of environmental civil public interest litigation and allowed the application of the reversed burden of proof rule, which seems to be inappropriate. In addition, the defendants in the marine environmental public interest litigation are often enterprises or units with strong economic power and professional knowledge, which may have easier access to the key evidence such as pollution data and technical information. However, it should not be assumed that all defendants have better evidence to assess the extent and impact of the pollution. It is also difficult for defendants to prove that there is no causal relationship between their conduct and the consequence of the harm, which could put them at a disadvantage in litigation. Therefore, there is still a lack of specific and clear provisions regarding the allocation of the burden of proof in China’s marine environmental public interest litigation.
In the modern national governance system, the administration and the judiciary are two vital branches, each bearing different responsibilities and missions, and jointly safeguarding the stability of the country and social justice. The administration branch serves as the representative of national interests, while the judiciary acts as the protector of the rights of the people (Mi and Zhu, 1997). The judiciary can not only provide a supplement to administrative enforcement but also supervise the exercise of administrative power, complementing each other effectively to enhance the governance capacity for the marine ecological environment (Mei, 2020). As a result, the effective coordination and collaboration between judiciary and administrative enforcement plays a key role in the marine environmental protection. However, it is stated that judicial collaboration is still confined to the scope of point-to-point or case-to-case interactions between specific judicial authorities and administrative agencies (Qin, 2021). In light of the increasing severity and complexity of current maritime issues, the effective integration and collaboration between the judiciary and administrative enforcement need to be further strengthened.
In particular, as stipulated in the Notice of the Ministry of Environmental Protection, the Ministry of Public Security and the Supreme People’s Procuratorate on Issuing the Measures for Coordination Work between Administrative Law Enforcement and Criminal Justice in Environmental Protection, and the Notice on Issuing the Provisions of the Supreme People’s Procuratorate on Promoting the Coordination between Administrative Law Enforcement and Criminal Justice, when administrative enforcement agencies are investigating marine environmental violations, they shall refer the case to the public security organ, if, based on the evidence collected and the facts of the case ascertained, there is a reasonable suspicion of a crime, and it is necessary for the public security organ to take measures to further obtain evidence to judge whether it meets the thresholds for filing and prosecuting criminal cases. Once receiving a case of suspected crime referred by an administrative enforcement agency, the public security organ shall examine it in accordance with the law. When the People’s Procuratorate is performing its legal duties, it should pay attention to check whether there are cases of suspected crimes that administrative enforcement agencies should refer to the public security organs for filing and investigation but have not done. It should be noted that, in most marine environmental violations, the Coast Guard Agency plays the role of the Public Security. However, neither at the national level nor at the local level do the relevant legal regulations explicitly define the timing and manner at which the procuratorate should involve in the coordination of administrative enforcement with criminal justice. In addition, administrative enforcement agencies, coast guard agencies, procuratorates and other departments all established their own information systems but the data sharing among them is still relatively limited. Business flow and data flow between administrative enforcement agencies have not yet been able to interact with or be compatible with the information system of coast guard agencies, procuratorates and courts, and the functions of the relevant system do not work well. This may to some extent results in the phenomenon of “information silos”. In practice, the case files and structured data records related to administrative penalties on marine environmental violations are in a “discrete state”, scattered across various departments or agencies with marine environmental supervision or management power. This makes them difficult to share (Sun and Kong, 2021). Cases related to marine environmental protection can be attributed into many different categories and the legal rules applied are from various sources, which gives rise to difficulties to automatically identify and find case clues. Plus, there is a lack of uniformity in the criteria to apply substantive law and procedural matters require further refinement, which hinders the efficiency of case referral across different departments. There may also be prominent issues such as the failure of administrative enforcement agencies for marine environmental protection to refer the cases that should be referred to the coast guard agencies for further investigation and prosecuting pursuant to relevant legal rules, or substituting administrative penalties for criminal punishment (Liu, 2012).
Given the complexities and diversity of the administrative enforcement agencies for marine environmental protection, the situation of coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement seems to be more serious. On 17 March 2018, the 13th National People’s Congress adopted the Institutional Reform Plan of the State Council (The Chinese Government, 2018). One important part of this Institutional Reform Plan is that the State Oceanic Administration is no longer in existence. To further enhance the governance of marine ecological environment and promote the sustainable development of economy and society in China, the Ministry of Natural Resources was established and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment was restructured. The responsibilities of the former State Oceanic Administration were integrated into the aforementioned two major departments, making their roles and responsibilities more clearly defined (Zhang and Chang, 2022). Moreover, the MEPL was revised again in 2023, which further clarifies and strengthen the distinct responsibilities of relevant departments at national and local levels (Liu, 2024). However, there are over a dozen departments or agencies involved in marine environment protection at the central level, including the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources, Ministry of Transport, Ministry of Water Resources, the Coast Guard Agency etc. and many branches of these departments at local level. Although there is a relatively clear boundary among their respective responsibilities, given the complexity and difficulty of marine environmental protection cases, this inevitably leads to overlapping powers and gives rise to frictions. There is a possibility that the overlapping jurisdiction may lead to institution rivalry over important and influential cases and to non-action over trivial cases. These frictions may also result in the ineffectiveness and inefficiency of the administrative enforcement and, simultaneously, cause confusion and uncertainties to the parties under investigation. Among the judicial administrative cases in the sample, a very important focus of dispute is whether the administrative enforcement agencies have the specific responsibilities. For example, in a first-instance administrative trial, the plaintiff challenged the defendant, the Qionghai Enforcement Bureau, on whether it possesses the authority to issue the Administrative Penalty Decision No. 002.12 In another second-instance administrative trial, one of the central issues in dispute is whether the appellee, the Maritime Police Qidong Station, has the jurisdiction to investigate the matters pertaining to the sea area in question.13 As a consequence, the overlapping and unclear responsibilities among so many administrative enforcement agencies for marine environmental protection may aggravate the difficulty of coordinating judiciary and administrative enforcement.
The oceans are a treasure trove of resources and a strategic space for future development, and marine ecological protection is a systematic project (The Chinese Government, 2024). Marine environmental protection requires the construction of the rule of law for marine, and the improvement of laws and regulations for the protection of the marine ecological environment. Stringent legal systems should be used to consolidate the foundation of marine ecological protection, in order to achieve important goals such as building a strong maritime nation (Gao and Liu, 2024).
On the one hand, the legislative efficiency should be enhanced and the introduction and updating of the complementary provisions to the MEPL2023 should be accelerated. First, marine environmental pollution and ecological damage are irreversible. To effectively improve marine environmental law enforcement and judiciary, relevant departments should expedite the revision of a series of supporting regulations and standards related to the MEPL2023. Provisions that are not in line with the current status of marine environmental protection and current management requirements should also be improved. Second, for regulations that are still in the draft stage for soliciting public opinions, they should be reviewed and formally promulgated as soon as possible to ensure that the entire chain of marine environmental protection can proceed in accordance with the law (Zhang et al., 2024). Third, the judicial system of marine environmental protection is marked by the complexity and variability of environmental situations, the diverse and peculiar nature of environmental violations, and the ever-increasing public demands for environmental quality. It is necessary to establish a dynamic mechanism for the continuous improvement of complementary legal rules to the MEPL2023, and evaluate relevant documents regularly. Based on this, these legal documents can be kept continuously adapted to the latest needs of marine environmental protection and possess clear operability (Cao, 2016). Fourth, the marine environment has a broad impact and involves many stakeholders. In the process of formulating and updating the aforementioned supporting regulations, it is important to further strengthen the cooperation among various departments, take into full account all aspects of marine environmental protection and ensure the scientific and comprehensive nature of the regulations.
On the other hand, other marine related laws and regulations such as the criminal legal system should be improved. For example, in response to the dilemma mentioned earlier that the “crime of environmental pollution” has not yet been activated, there is opposition to the establishment of a specific crime for marine pollution based on considerations of legislative costs. It is proposed that the relationship between this crime and others should be clarified from the perspective of interpretative theory (The Chinese Government, 2024). However, the existing theories do not agree with the interpretative theory, with more emphasis on advocating for the establishment of a separate crime. As far as judicial practice is concerned, its primary task is to interpret and apply the law (Che, 2023). Even with the relevant judicial interpretations, it is difficult in judicial practice to find an effective breakthrough within the legal provisions of environmental pollution crimes. On this basis, it is suggested that a separate crime be established for behaviors that pollute the marine environment. This would resolve the problem of criminal behavior being left unchecked due to the lack of specific criminal charges and can provide strong judicial protection for the conservation of the marine ecological environment.
As the foundational values in judicial practice, fairness and efficiency have always been of paramount significance. To ensure the efficacy of judicial protection of marine environment, judicial efficiency and judicial fairness should be promoted, which requires a high level of professionalism. One of the effective ways to improve the professionalism of judicial protection will be the application of the intelligent trial assistance technology to shorten trial time, improve trial efficiency, and unify judicial rules.
In 1970, a pivotal publication in the field of law and technology was unveiled by American academics Buchanan and Headrick, “Some Speculation about Artificial Intelligence and Legal Reasoning (Buchanan and Headrick, 1970)” This work served as the progenitor of a new era, heralding a profound inquiry into the synergies between artificial intelligence and the intricate processes of legal reasoning. In China, the wide application of artificial intelligent technologies in court trials has made China’s judicial system stand out in the world (Xinhua, 2023). The establishment and refinement of “intelligent courts” in China perfectly reflect the technological approaches to realizing the values of intelligent justice (Liu, 2019). As a cutting-edge analytical instrument in the realm of judicial trial, intelligent justice stands as a formidable aid in the trial. It embodies a series of advanced functionalities designed to augment the efficiency and efficacy of legal proceedings. In the field of judicial protection of marine environment protection, Chinese maritime courts play a crucial role. Modern technological means can be used by maritime courts to improve the informatization level of maritime trials, enhancing trial efficiency and quality. By building information technology infrastructure, the transparency and efficiency of trial work can also be improved and the specialization can be reinforced. The construction of intelligent maritime courts in China has yielded certain accomplishments. For example, the Shanghai Maritime Court, as the “Practice Base for the Construction of An Intelligent Maritime Court (Shanghai) under the Supreme People’s Court”, released “the Maritime Chain Full-Factor Intelligent Analysis System” in 2023, which integrated maritime judicial and shipping big data analysis for the first time in China, providing new technical means for finding out the facts of a case (Shanghai Maritime Court, 2023). However, the application of intelligent trial assistance technology in the judicial protection of the marine environment is still in its nascent stage and confronts a myriad of challenges, such as the inadequate practical application and issues related to the seamless integration of systems (Liu, 2022). In particular, existing intelligent support tools and technologies cannot adapt to the complexities and unique demands of marine environmental protection cases during the intelligent trial process, such as clarification of liabilities, ascertainment of evidence, evaluation of damages, and the presumption of causal relationships. Therefore, it is imperative to conduct more profound and extensive research into the development of intelligent trial assistance technologies tailored for cases involving marine environmental protection.
To develop and apply intelligent trial assistance technologies for cases pertaining to marine environmental protection, legal benchmarks and logical frameworks for intelligent trial in this domain should be constructed, as well as a knowledge base and knowledge system for such cases. At the same time, it is necessary to integrate advanced technological approaches, including deep learning, natural language processing, and rule-based inference, to digitally model evidence criteria in the case database and build a model for evaluating the credibility of case evidence. The automated generation and verification of document frameworks and content should also be carried out. The theoretical research on the reasoning of intelligent justice is the core to realize the auxiliary function of artificial intelligence in judicial practice. Throughout this endeavor, the research on intelligent trial assistance technology for marine environmental protection cases should focus on addressing the challenges of intelligent verification and assistance in trials involving similar facts, identical legal elements, or legal rules and judicial interpretations. The application of advanced information technologies, such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, should be maximized, adhering to the guiding principles in the knowledge system of the marine environmental protection cases. This adherence is vital for the exploration and creation of an intelligent trial assistance system that integrates a suite of intelligent methods comprising knowledge extraction, semantic analysis, inferential rules, and risk identification, specifically tailored for the marine environmental protection disputes.
Intelligent trial assistance technologies should be based on sufficient data to guarantee the fairness of the judicial results through scientific algorithms. In the context of artificial intelligence, the realization of uniform judgments for analogous cases is fundamentally predicated on the selective aggregation and integration of data from prior judgments, followed by preprocessing, statistical analysis, and further in-depth mining of the data. The essence of this approach is to refer to precedent cases to guide and constrain subsequent judicial actions, thereby ensuring the legal certainty and consistency even when there is not a perfect alignment between the facts and legal norms. Since 1984, a total of more than 5,000 civil disputes over marine environment have been settled. Since 2015, the maritime courts have concluded more than 1,000 administrative litigation cases concerning the marine environment, exploring and exercising jurisdiction over criminal cases involving pollution of the marine environment, illegal sand mining at sea, and illegal harvesting of precious and endangered aquatic wildlife (The Chinese Government, 2024). These precedents provide valuable experience and robust data foundation that can guide future endeavors to leverage artificial intelligence technology for the judicial protection of the marine environment. The insights obtained from the precedents will be instrumental in enhancing the efficacy of the intelligent trail assistance technologies, ensuring that they are aligned with the complex realities of environmental litigation and the specific needs of marine protection efforts.
The application of the intelligent trial assistance technology for marine environmental protection cases based on artificial intelligence can facilitate retrieving analogous cases, effectively mitigate unreasonable differences in judicial trial standards of different judicial hierarchy and different geographical jurisdictions, and reasonably constrain discretionary power. Therefore, the professionalism of the judicial protection of marine environment can be considerably improved and the efficacy of judicial protection can also be realized. While, it should be noted that the role of the artificial intelligence technologies is only an assistant to facilitate the judicial trials and it should the human judges that make the final decisions.
The reasonable allocation of the burden of proof and the provision of evidence are keys to judicial adjudication.
First, given the challenges encountered in the discovery and collection of evidence in marine environmental protection cases, Article 14 of the Interpretations of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues concerning the Application of Law in the Conduct of Environmental Civil Public Interest Litigations stipulates that the People’s Court shall investigate and collect the evidence required for the trial of environmental civil public interest litigation cases, if necessary. Therefore, for the public interest litigation with the fundamental purpose of safeguarding social public interests, the facts involved in the litigation are those that may harm the social public interests. The People’s Court should take the initiative to investigate and collect such evidence, which may to some extent address the difficulties faced by other parties in investigating and collecting evidence in marine environmental protection cases. That is to say, when necessary, the People’s Courts should not simply delegate the task of evidence collection and investigation to the parties involved, while it is obliged to actively ascertain the facts of cases involving public interest. However, it should be noted that although the defendants in such cases are usually large enterprises such as shipping companies that cause marine environmental pollution, it should not be assumed that a party has strong evidentiary capabilities in cases where the parties involved are diverse. The court should aim to uphold the public interest as the ultimate goal, make objective judgments on the evidence provided, and achieve the determination of facts.
In order to facilitate the collection of evidence, technical means can be used, such as drones. When collecting evidence with drones, compliance with relevant legal provisions is necessary. However, the regulations on evidence collection by drones still need to be improved. Article 59 of the Interim Regulation on the Administration of the Flight of Unmanned Aircraft stipulates that the relevant departments of the State Council shall separately formulate measures for the administration of airworthiness, registration, operators, and other matters concerning the unmanned aircraft of the police, customs, and emergency management departments. While, no such provisions have been found. In terms of application, the drones should only be used for investigation when other investigation means are relatively exhausted and the objectives are still not achieved or effective evidence cannot be obtained. Simultaneously, the appropriateness of drone investigations should be ensured. The information collected by these devices should be limited solely to content related to law enforcement. Strict procedures and supervision should be provided regarding the storage and browsing rights of videos taken by drones. For example, the captured videos should not be leaked, and only professional enforcers should have access to them. Therefore, relevant laws and regulations should explicitly state that the abuses of the information collected by drones or the improper use for illegal purposes should be severely punished. In addition, a sound complaint and supervision mechanism should be established to enable the public to have convenient and effective channels for appeal when they find privacy infringements.
Second, it is recommended to initiate and improve the social supervision mechanism for marine environmental protection. Through this mechanism, the public can be mobilized to actively discover marine pollutions, which can not only broaden the ways to obtain case clues but also deepen the exploration of case clues (Zhan and Xu, 2020). At the same time, public participation is an important driving force in promoting the implementation of laws in China. Within this mechanism, the public cannot only directly participate in the process of pollution protection of the marine environment but also more clearly understand the status and the degree of the marine environment pollution. This further enhances the awareness of marine environmental protection, making them strong defenders and supervisors of the marine environment (Li, 2019).
Third, while the application of the reversed burden of proof rule in environmental public interest tort litigation does not absolutely increase responsibilities of the defendant to provide evidence, it is a process in which both the plaintiff and the defendant continuously present and refute evidence (Zhang, 2024). The allocation of burden of proof in existing cases related to marine environmental protection remains to be solved. Hainan Province has issued the Hainan High People’s Court on the Trial of Marine Ecological Environment and Natural Resources Dispute Judgment Guidelines (For Trial Implementation) and Typical Cases. It is pointed out that in marine environmental resources tort cases, the collection, extraction, and fixing of evidence are relatively difficult, and the recognition of facts is challenging. Where the plaintiff and the public interest litigant provide preliminary evidence to prove that the actor has committed an environmental tort and caused damage, the actor shall bear the burden of proof for the circumstances under which the law stipulates that the actor is not responsible or is mitigated in responsibility, and where there is no causal relationship between the act and the damage. This provision is a specific reflection of the of the reversal of the burden of proof in marine environmental protection cases and provides guidance for clarifying the allocation of the burden of proof. On this basis, the relevant legal provisions should be further clarified, especially taking into full consideration the needs of marine environmental protection and the characteristics of marine environmental public interest litigation. In addition, the principles and specific rules for the allocation of the burden of proof should be detailed, and specific interpretations on the burden of proof can be provided for different types of marine environmental pollutions.
To improve the coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement in the field of marine environmental protection, effective communication and contact, between judiciary, procuratorates, coast guard agencies and administrative enforcement agencies for marine environment protection, should be actively promoted (Quan and Sheng, 2020). The essence of the coordination between administrative enforcement and criminal justice lies in the following: when the administrative agencies, in the course of investigating illegal activities, identify the amounts, circumstances, or consequences that potentially indicate a criminal offense, they are mandated by law to refer the case to the public security agencies. This will initiate the criminal justice process, which is then carried forward through the “public security organs-people’s procuratorate-people’s court” sequence, ensuring that potential criminal acts are properly addressed within the judicial system. On this basis, one of the most effective approaches to improve the coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement is to make full use of modern information technologies to establish seamless data sharing channels among different departments, which should be accompanied by efforts to advance the development and utilization of data, as well as the research and development of intelligent system functionalities.
To address the current issue of limited interoperability and compatibility among cross-departmental information systems, it is essential to further facilitate data sharing channels between various systems. For instance, the functionality for case referral should be developed for the coordination of administrative enforcement and criminal justice within a unified administrative enforcement platform, which can be regarded as a strategic step. This would empower multiple departments, such as administrative enforcement agencies, coast guard agencies, and procuratorates by providing them with a centralized platform for case sharing. First and foremost, it is essential to prioritize and address the issues of low efficiency in offline circulation of case materials, the lack of clarity in the case referral process, and the prolonged delays in responses from relevant authorities. By ensuring that the entire process of case referral is documented and traceable, the efficiency with which various departments handle the referral of criminal cases between administrative and judicial proceedings can be enhanced. Second, in terms of data exploitation and application, the provincial integrated administrative enforcement platform, beyond merely collecting and storing data on administrative enforcement cases, should advance the development of intelligent case management capabilities, such as statistical analysis, trend identification, and predictive alert systems. These tools would enable administrative enforcement agencies to more effectively utilize accumulated case data, discern patterns, detect issues, and preemptively signal potential risks. As a result, the accuracy and efficiency of decision-making by administrative enforcement agencies in dealing with cases can be increased, thereby elevating the collective efficacy of administrative enforcement and the collaborative capacity. Third, the supervision platform for the coordination of administrative enforcement and criminal justice requires the support of intelligent scrutiny and alert mechanisms. These measures can to a great extent facilitate procuratorates to find clues of problematic cases more quickly and intervene at the right time.
Additionally, the improvement of coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement should be based on strengthening the legal oversight. It is of great importance to optimize the use of the complementary advantages and resources sharing between administrative enforcement and criminal justice and to integrate the enforcement resources. At the same time, it is suggested that the power of oversight of procuratorates should be extended from the judicial phase to each stage of the lifecycle of administrative enforcement cases. This extension is crucial for forming a more effective joint effort to combat issues such as the failure of administrative enforcement agencies for marine environmental protection to refer the cases that should be referred to the coast guard agencies for further investigation and prosecuting pursuant to relevant legal rules, or substituting administrative penalties for criminal punishment. For cases referred by administrative enforcement agencies to coast guard agencies for filing and investigation, procuratorates can also promptly oversee the coast guard agencies to see whether the case is filed or has been delayed, which can improve the convenience and effectiveness of the legal oversight.
In this way, the efficiency of the case referral process can be considerably increased, leading to faster and more effective processing of cases with criminal elements across various departments.
The ocean holds significant importance for the survival and development of human society. Though the governance of marine environment in China has made some achievements, as the proliferation of human activities and the rapid population growth near the coastal area in China, the marine environment is still under great press. Serving as the ultimate bulwark in the protection of marine environmental and the defense of the nation’s maritime ecological rights and interests, the judicial protection of marine environment plays a critical role. From the analysis of 2,443 cases related to marine environmental protection, it can be seen that the judicial protection of marine environment has faced great challenges which may impose adverse effects on the efficacy. These challenges include the lack of clarified legal bases to prevent the marine environmental pollution, the lack of professionalism to realize the judicial efficiency and judicial fairness to protect the marine environment, the difficulties to provide evidence and to allocate the burden of proof, and the lack of effective coordination between judiciary and administrative enforcement. Therefore, it is submitted in this paper that the legislative efficiency should be properly increased and an independent crime for marine environmental pollution should be introduced. In addition, it is imperative to conduct more profound and extensive research into the development of intelligent trial assistance technologies tailored for cases involving marine environmental protection. When necessary, the People’s Courts are obligated to actively ascertain the facts of cases that involve the public interest. It is also recommended to initiate and improve the social supervision mechanism for marine environmental protection, and to set out specific evidentiary burden provisions for different types of marine environmental pollutions. Finally, modern information technologies should be made full use to facilitate the data sharing channels between various systems of different administrative enforcement agencies for marine environment protection. The functionality for case referral should be developed for the coordination of administrative enforcement and criminal justice within a unified administrative enforcement platform. It is hoped that the proposals made in this paper can to some extent facilitate the judicial protection of the marine environment in China.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SL: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. YW: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Buchanan B. G., Headrick T. E. (1970). Some speculation about artificial intelligence and legal reasoning. Stan. L. Rev. 23, 1. doi: 10.2307/1227753
Cao H. (2016). On the straits and reflection of administrative enforcement in environmental protection. Acad. Explor. 11, 76–80.
Che H. (2023). Disputes over the order of legislation and interpretation: Taking the crime of buying abducted women as an example. Mod. Law Sci. 45, 2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2397.2023.02.13
Chen H. Z., Bai J. H. (2018). The dilemma of determining the qualified plaintiff in the marine environmental civil litigation for public interests under the new situation and its solution. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Edi.) 2, 162–169.
Chen S., Pearson S., Wang X. H., Ma Y. (2017). Public participation in coastal development applications: A comparison between Australia and China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 136, 19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2016.11.016
Chen W. (2017). The Chinese experience of judicial system reform. Chin. J. Law. 39, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6676.2017.21.036
Feng S. (2023). Marine ecological environment governance from the perspective of international law: Model transformation and China’s contributions. Jinan J. (Philos. Soc Sci.). 45, 12.
Gao H. (2024). A review of the revision, improvement and application perspective of the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Marine Environment. Asia-Pacific Secur. Marit. Aff. 3, 73–90.
Gao Z. G., Liu Z. H. (2024). Extraterritorial application of China’s Marine Environmental Protection Laws: International practices, major issues, and feasible suggestions. Chin. J. Marit. Law. 35, 2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7659.2024.02.004
Hao Y. (2023). The doctrinal unfoldment of marine pollution wrongdoing: On the activation of environmental pollution crime. Ocean Dev. Manage. 40, 12.
Li L. F. (2019). Forty years of rule of law in China’s marine environment: Development history, practical dilemmas and legal improvements. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Humanities Soc Sci. Edi.) 36, 3.
Li Y. S., Yuan H. X. (2021). Judicial dilemmas and solutions of the “crime of environmental pollution”: Centering on the dual legal interests of ecology and humanity. Hubei Soc Sci. 1, 141–151.
Li C., Zhao Y. H., Sun P. Y. (2015). Study on the judicial authentication of marine environmental pollution damage and its evidentiary effect. Mar. Environ. Sci. 34, 1.
Liang H. (2024). Administrative public interest litigation of marine ecology and environment: System generation and practical review. Seeking Truth. 51, 1.
Liu F. (2012). Several problems in the convergence of administrative law enforcement and criminal justice. J. Natl. Prosecutors Coll. 20, 1.
Liu Y. (2019). Theoretical basis and practical development of the modernization of trial system and trial ability in the era of big data. J. Anhui Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Edi.). 43, 3.
Liu Y. (2022). Practical application and prospects of AI technology in the construction of smart court. J. Comp. Law. 1, 1–11.
Liu R. (2024). Revision of China’s Marine Environmental Protection Law: History, background and improvement. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1409772
Liu Z. Y., Guo S. H., Bai S. W. (2023). Strengthening judicial protection of marine ecological environment (Procuratorate Daily). Available online at: https://newspaper.jcrb.com/2023/20230305/20230305_007/news-zgjcb-10150-20230305-m-007-300.pdf (Accessed August 24, 2024).
Mei H. (2020). The judicial protection subject of marine environment and its linkage mechanism. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Humanities Sci.). 37, 1.
Mei H. (2023). The new revision of Marine Environmental Protection Law: Uphold fundamental principles and break new ground. Environ. Prot. 51, 21.
Mei H., Yin Y. (2018). The status quo and strategies of trying marine-related environmental cases: A study based on the analysis of 418 cases in the past 18 years. J. Poyang Lake. 1, 90–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6848.2018.01.009
Miao Z., Liu H. (2023). Review of the newly revised Marine Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China. Ocean Dev. Manage. 40, 12.
Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2024a). In 2023, the gross marine product will increase by 6.0%, and the quantity and quality of China’s marine economy will increase simultaneously. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202403/content_6940912.htm (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2024b). Report on the state of the ecology and environment in China 2023. Available online at: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/jagb/202405/P020240522601361012621.pdf (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Nie L., Zhang Z. (2022). Empirical analysis of judicial application of Marine Environmental Protection Law. J. Hebei Univ. Environ. Eng. 32, 6. doi: 10.13358/j.issn.2096-9309.2022.0620.01
Pan J. (2022). Rethinking on the legal interests of the “crime of environmental pollution. Soc Sci. Xinjiang 5, 103–110.
Qin T. (2021). Transformation and reconstruction of judicial protection for river basins’ environment. Oriental Law. 2, 158–167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1466.2021.02.012
Quan Y. (2022). Judicial coordination and relief of cross-regional marine environmental governance. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Soc Sci. 42, 4.
Quan Y., Sheng H. J. (2020). Construction of marine ecology and environment legal system from the perspective of Maritime Community with Shared Future. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 45, 2.
Research Team of Shanghai High People’s Court (2022). An empirical study on judicial protection of marine ecological environment (I). Mar. Law Policy 1, 18–41.
Shanghai Maritime Court (2023). Intelligent shipping, empowered by technology. The full-factor intelligent analysis system for the shipping chain of the Shanghai Maritime Court is officially launched. Available online at: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_21608206 (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Song W. (2021). Study on the legal issues of judicial protection of marine environment in Bohai Sea-Taking Bohai Sea pollution cases from 2011 to 2019 as the analysis object. Tianjin Legal Sci. 37, 1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-828X.2021.01.008
Su L. (2000). Sending the Law to Countryside (Beijing: China University of Political Science and Law Press).
Sun H. (2022). Strengthening judicial protection of the Marine environment to serve the building of a maritime power (People’s Court Daily). Available online at: http://society.people.com.cn/n1/2022/0512/c1008-32419914.html (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Sun Y. H. (2023). Interpretation on the major changes and contents of the revised Marine Environmental Protection Law of 2023. Environ. Prot. 51, 21.
Sun N., Kong F. (2021). Research on the early warning mechanism of marine environmental pollution incidents in China. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 30, 6. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20190602699
Sun J., Zhou L. (2021). China’s marine environmental governance in the new normal context. J. Ocean Univ. China (Soc. Sci.). 1, 32–39.
Tang H. B. (2021). Research on legal issues of Marine ecological environment protection. China Trial. 17, 92–95.
The Chinese Government (2018). The institutional reform plan of the state council. Available online at: http://www.gov.cn/guowuyuan/2018-03/17/content_5275116.htm (Accessed August 23, 2024).
The Chinese Government (2024). Marine eco-environmental protection in China. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202407/content_6962503.htm (Accessed August 23, 2024).
The Supreme People’s Court (2022). Report on the development of environmental judiciary in China. Available online at: https://www.court.gov.cn/zixun/xiangqing/361301.html (Accessed August 23, 2024).
The Supreme People’s Court (2023). The Supreme People’s Court announced the main data of judicial trial work from January to September 2023. Available online at: https://www.court.gov.cn/zixun/xiangqing/415692.html (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Tian G. B. (2019). Review of legislation on “crime of environmental pollution” in China. Law Rev. 37, 1.
Wang X. W. (2019). Rethinking and reconstruction on the allocation of burden of proof in environmental civil public interest litigation in China. Law Rev. 37, 2.
Wang Y. F., Du Y. X. (2017). On the issues of evidence in environmental criminal litigation in China. Available online at: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BY3nmPlJ4O51rvj0aTluYA (Accessed August 24, 2024).
Xinhua (2023). “Intelligent courts” highlight of Chinese judiciary: SPC. Available online at: https://www.Chinadaily.com.cn/a/202303/07/WS6406f118a31057c47ebb2d7d.html (Accessed August 23, 2024).
Yang J. (2012). After the stage fright of “rule of law” – taking the breakthrough of the predicament of environmental governance as the analysis object. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Soc. Sci. Edi.). 12, 60.
Yang C. (2016). Two magic weapons of environmental justice: Specialization of environmental justice and the right of environmental resources. J. CUPL. 1, 81–96.
Yang L. (2023). China’s marine environmental public interest litigation: current situation, challenges, and improvement approach-analysis based on 339 cases. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1302190
Yao L. (2006). Judicial efficiency: Theoretical analysis and system construction. Stud. Law Business 3, 94–101.
Zeng R., Xu Y., Yang Y., Wang X., Qu Y. (2018). Current situation and countermeasures of the utilization of marine dumping area in China. Ocean Dev. Manage. 35, 1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.01.007
Zhai T. (2024). An empirical study of marine environmental civil public-interest litigation in China: Based on 216 cases from 2015 through 2022. Ocean Coast. Manage. 253, 107164. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2024.107164
Zhan Y. J., Xu Z. R. (2020). Guard the ocean blue with public interest litigation. Outlook Weekly 39, 48–49.
Zhang L. (2021). Judicial construction and legislative improvement of the trial of maritime criminal cases by maritime courts–taking marine environmental crime as the break point. Chin. J. Marit. Law 32, 2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7659.2021.02.007
Zhang R. (2024). Burden of proof and allocation rules in environmental public interest tort litigation. J. South-Central Minzu Univ. (Humanities Soc Sci.). 44, 3.
Zhang K., Chang Y. C. (2022). Daily penalty system under revision of the Marine Environment Protection Law in China: Review and prospect. Sustainability 14, 22. doi: 10.3390/su142214994
Zhang H., Hu Z., Shi R., Li Y. (2024). Research on marine dumping management from the perspective of the newly revised Marine Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China. Environ. Prot. 52, 59–62.
Zhao W., Chen Y. (2019). Difficult position of criminal accusation of oil spilling in the ocean and its way out. People’s Procuratorial Semimonthly 11, 37–40.
Zhou Z., Xia X., Ran R. (2019). Judicial protection, legal service and technology innovation. Sci. Res. Manage. 40, 2.
Keywords: judicial protection, marine environmental protection, marine environment, burden of proof, intelligent trial assistance technology, administrative enforcement
Citation: Liu X, Liu S and Wang Y (2024) The improvement of judicial protection of marine environment in China: based on the analysis of 2,443 judicial cases. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1486230. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1486230
Received: 25 August 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Yen-Chiang Chang, Dalian Maritime University, ChinaReviewed by:
M. Jahanzeb Butt, Shandong University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Liu, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuting Wang, d2FuZ3l1dGluZ0BjdXBsLmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.