- School of Law, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai, China
The shipping industry is featured by high carbon emissions. The 2023 IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships sets forth the global goals of shipping decarbonization. Shipping decarbonization involves complicated issues of economy, technology, policy and law etc., and implies the conflicts between economic interests and environmental interests, between individual interests and public interests, between individual States’ interests and international common interests and between current interests and long-term interests. This research suggests that balancing such conflicting interests need to follow the principle of prioritizing the international public environmental interests while taking into account the other interests because protection of environmental interests should be taken as the basic value orientation in shipping decarbonization governance and the principle of collaborating governmental intervention and market mechanisms by reference to the theory on the relationship between government and market in economics. Under the guidance of these principle, by reference to the equilibrium analysis method in economics and following the progressive decision theory in management, this research demonstrates that the main pathways in achieving such balance may include: making strategic plan and basic policy for reducing GHG emissions from ships by the government, implementing economic incentive policies such as tax incentives and fiscal subsidies, implementing ship energy efficiency measures, prudently implementing shipping carbon emissions trading mechanism, accelerating the establishment of alternative marine fuel supply chain, innovating alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology, and actively engaging in international cooperation.
1 Introduction
With the intensification of global climate change and the continuous increase of responsibility for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, reduction of GHG emissions from ships and ultimate net zero emissions are increasingly attracting attention from the international community (Shao and Wang, 2011). GHGs are gas components in the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect and CO2 is the most significant one. Usually, GHG emissions are summarized as CO2 emissions or carbon emissions for short, and the reduction of GHG emissions and ultimately net zero emissions are summarized as decarbonization. Shipping is a general term for maritime transport and inland navigation. The shipping industry is featured by high carbon emissions (Bullock et al., 2020). GHG emissions in shipping industry are mainly manifested as GHG emissions from ships, while other GHG emissions such as those originated from port facilities are rather few. The GHGs emitted from a ship while her main engine, auxiliary engine and boiler consume the conventional fossil fuel oils are composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur oxides (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOX), carbon monoxide (CO), unburned coals (HC), and particulate matters (PM2.5, PM10) all of which contribute to the climate change (Richter et al., 2004; Traut et al., 2018).
Shipping activities have the global nature and, as a result, the impact of GHG emissions from ships on climate change is not limited to the scope of individual counties. Therefore, their governance depends not only on the individual actions of the shipping countries, but more importantly on the joint efforts of the international community. The system of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) does not regulate the GHG emissions from ships and these emissions are governed by International Maritime Organization (IMO). For this purpose, IMO has made great efforts to support the UN Sustainable Development Goal 13, i.e. taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts, in line with the 2015 Paris Agreement to cut GHG emissions (IMO, 2024). Besides IMO, other governmental organizations, NGOs, EU as regional organization and national governments have taken or are taking efforts in this regard at various levels.
Shipping decarbonization is an irreversible global trend and is rife with challenges. It involves complex issues of economy, technology, policy and law etc., and implies the severe conflicts of various interests, especially the conflicts between economic interests and environmental interests. In essence, balancing the conflicting interests is balance between the responsibility for reducing carbon emissions and the rights to development and is an issue of carbon justice (Ying and Jun, 2024). Presumably, how to balance the conflicting interests plays an important role of theoretical guidance in the shipping decarbonization governance, because shipping decarbonization should be achieved on the basis of the balanced interests. However, balancing the conflicting interests involves many complicated factors and is by no means easy to be achieved. Therefore, it needs to analyze the manifestations and reasons of the conflicts of interests, the principles to be followed and the main pathways to be taken in shipping decarbonization governance from the perspective of balancing the conflicting interests.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
The materials contained in the literatures reviewed in this research focus on the following four aspects:
2.1.1 Examinations of the extent of GHG emissions from ships and their contributions to the climate change
GHG emissions from ships are recognized as main contributors to the global climate change. The Fourth IMO Greenhouse Gas Study 2020 estimated that the share of shipping emissions in global anthropogenic emissions increased to 2.89% in 2018 (IMO, 2020). The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCTAD) estimates in Review of Maritime Transport 2023 that international shipping is responsible for nearly 3% of all global GHG emissions and shipping GHG emissions increased by 20% in the past decade (UNCTAD, 2024). International Chamber of Shipping (ICS) estimated that shipping GHG emissions was about 3% in the global GHG emissions (ICS, 2022). Longspur Research estimated in its report Methanol and Shipping issued on 25 January 2022 that shipping represented 3-4% of global GHG emissions, roughly equivalent to Germany’s emissions (Longspur Research, 2022). A few academic literatures also estimated that currently shipping GHG emissions was about 3% in the global GHG emissions (Dong et al., 2022; Zheng and Wang, 2022). Presumably, this percentage has an increasing trend if no effective measures are to be taken to reduce the emissions.
2.1.2 Efforts made globally, regionally or nationally to reduce GHG emissions from ships
IMO has been actively engaged in a global approach to enhance ship’s energy efficiency and develop measures to reduce GHG emissions from ships (Longspur Research, 2022). The IMO’s efforts have mainly achieved the following results:
First, enactment of ship’s energy efficiency standards.
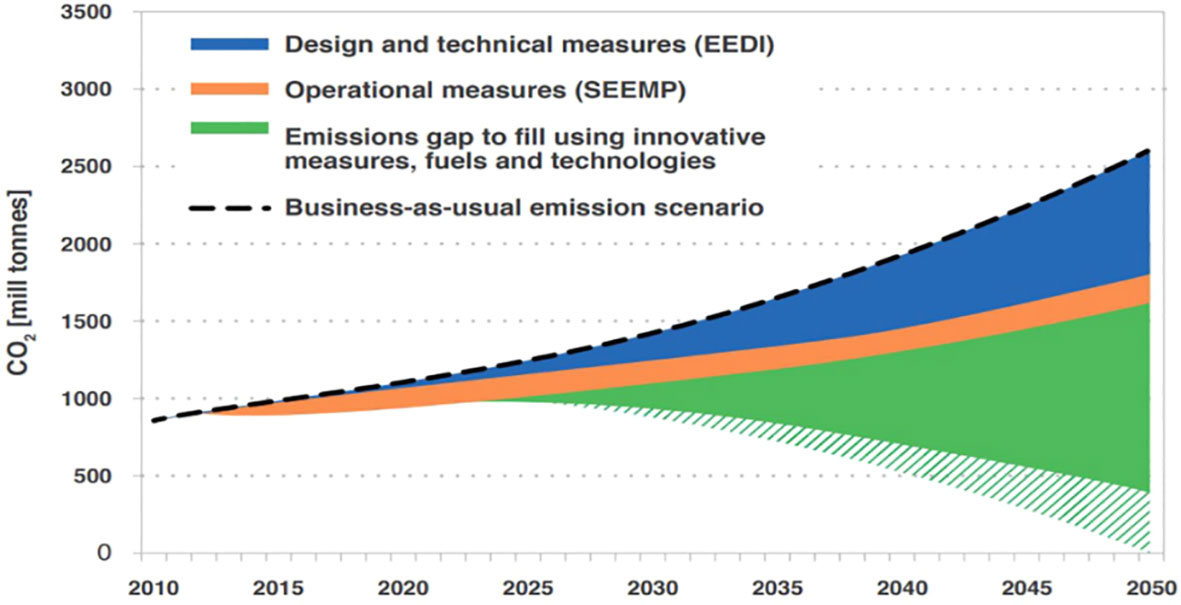
In 2011, IMO adopted Resolution MEPC.203(62) on amendments to Annex VI to MARPOL 73/78 to mandate technical and operational energy efficiency measures, i.e. the Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) and the Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) which entered into force on 1 January 2013 (IMO, 2011). Figure 1 shows the importance of EEDI and SEEMP in reducing GHG emissions from ships.
In 2021, IMO adopted Resolution MEPC.328(76) to enforce the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) and the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) which entered into force on 1 January 2023 (IMO, 2021).
EEDI and EEXI are technical measures incentivizing the use of energy-efficient technologies, and SEEMP and CII are operational measures optimizing the operational performance of a ship, both for the purpose of reducing the amount of CO2 emissions from international ships. In tandem with the alternative marine fuel switch, technology should be leveraged for greater energy efficiency gains (UNCTAD, 2024). China Classification Society (CCS) envisages that IMO will complete the evaluation of these short-term measures as required by Annex VI to MARPOL 73/78 (CCS, 2023).
Second, promulgation of strategies on reduction of GHG emissions from ships.
In April 2018, IMO adopted Resolution MEPC.304(72) on the Initial IMO Strategy on reduction of GHG emissions from ships (IMO, 2018). This Strategy envisaged to reduce CO2 emissions per transport work, as an average across international shipping, by at least 40% by 2030, pursuing efforts towards 70% by 2050, as compared to 2008, and the total annual GHG emissions from international shipping should be reduced by at least 50% by 2050 as compared to 2008.
In July 2023, IMO adopted Resolution MEPC.377(80) on 2023 IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships (IMO, 2023). This revised Strategy includes a commitment to ensure an uptake of alternative zero and near-zero GHG fuels by 2030, as well as indicative check-points for international shipping to reach net-zero GHG emissions for 2030 (by at least 20%, striving for 30%) and 2040 (by at least 70%, striving for 80%), and an enhanced ambition to reach net-zero GHG emissions from international shipping by or around 2050. IMO will amend the 2023 IMO Strategy in 2028 according to the situations (CCS, 2023).
Concurrently, national and regional regulations are influencing the global process of reducing GHG emissions from ships.
Besides implementation of the mandatory provisions of Annex VI to MARPOL 73/78, national regulations and policies focus on the adoption of market-based mechanisms in some countries (Kirval and Çaliş̇kan, 2022), France, Japan, South Korea, Sweden and UK etc. are implementing carbon emission tax and/or trading scheme (Liao, 2022; Peng, 2020). Such mechanisms are designed to internalize the external costs of GHG emissions based on the polluter-pays principle (Wright, 2021) and provide economic incentives relating to GHG emissions reduction (HariLaos, 2012). Such market transaction policies are considered to enhance the economic and emission reduction potential more than the command control policy can (Wang et al., 2016).
Regional regulations are adopted at EU level and apply to ships calling at European ports. In July 2021, the European Commission released the package GHG reduction scheme called “Fit for 55” aiming at achieving the EU’s goal of reducing net carbon emissions by 55% by 2030 as compared to 1990 level and climate neutrality in 2050 (European Council, 2021; Hu et al., 2023). In July 2023, the FuelEU Maritime Initiative was adopted by the European Council (European Council, 2023; European Union, 2023). As a key part of the EU’s “Fit for 55” package, the main objectives of this initiative are to increase the demand for and consistent use of renewable and low-carbon fuels and to reduce GHG emissions from the shipping sector, while ensuring the smooth operation of maritime traffic and avoiding distortions in the internal market. In detail, it mandates that shipping reduce GHG intensity for energy used on board a ship by 2% from 2025, 6% from 2030, 14.5% from 2035, 31% from 2040, 62% from 2045 and 80% from 2050 (Tunagur, 2023). This initiative will apply to the CO2, CH4 and N2O emissions from all ships with gross tonnage of 5,000 tons or more calling at EU ports. Ships that comply with the regulations will be issued a FuelEU Document of Compliance, and ships without holding the document will face penalties in the form of fines, expulsion, prohibition and/or detention. An obvious feature of the initiative is putting maritime transport into the European Union Emissions Trading Scheme (EU ETS) from 1 January 2024 (Zheng and Wang, 2022). The years of 2024 and 2025 are the transitional period and shipping companies covered by EU ETS are required to pay their quotas of 40% and 70% respectively of the applicable CO2 emissions. 100% quota payment will be implemented from 1 January 2026. Currently, EU ETS covers CO2 emissions, but will also cover CH4 and N2O emissions from 1 January 2026. It currently applies to the cargo ships and passenger ships with gross tonnage of 5,000 tons or more, but will also cover offshore engineering ships with gross tonnage of 5,000 tons or more from 1 January 2027. Based on the estimated EU carbon emission quota price of 95 euros per ton, the quota cost per ton of fuel will presumably increase by approximately 300 euros (CCS, 2023). The impact of the Initiative on the shipping industry is expected to exceed that of EU ETS in both breadth and depth (CCS, 2023).
2.1.3 Examination of the current use of alternative marine fuels and its prospect
Shipping needs to replace the conventional fossil fuels with alternative marine fuels or renewable energy that emit fewer or no GHGs across their entire life cycle (well-to-wake) (UNCTAD, 2024). This has become a universal understanding. The introduction of alternative marine fuels and renewable energy is considered as an important strategy for shipping decarbonization (OECD, 2016; Chen et al., 2019). Alternative marine fuels and renewable energy may include liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, hydrogen, ammonia, liquefied biogas (LBG), ethanol, hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), fuel cells, nuclear power, wind power, solar power, and electricity (ITF, 2018; Wang and Wright, 2021; Santos et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). Within the scope of renewable energy, batteries are only suitable for short range (Wang et al., 2023), because as it stands today with the current battery technology, all electric vessels are primarily used for shorter distances in harbors and coastal shipping (Longspur Research, 2022); wind power can only assist propulsion, i.e. wind-assisted ship propulsion (WASP) (Longspur Research, 2022); nuclear power does not emit GHGs, but involves extremely high costs in construction and very high requirements of safety, operation and maintenance, resulting in its current application almost solely to big navy ships or submarines (Wang, 2020). Therefore, the introduction of alternative marine fuels is required to reduce the climate impact of shipping (Hansson et al., 2020). As a whole, many attentions have been paid to LNG, but more attentions are now paid to methanol, ammonia and hydrogen fuels (Ampah et al., 2021). Hydrogen, ammonia, methanol and biomethane are considered as the key contenders (Longspur Research, 2022). There is an increasing global demand for ammonia to be used as a versatile marine fuel (Cheliotis et al., 2021). One prediction is that ammonia will become one of the three most promising fuels in 2050 and its proportion in the marine fuels will increase from 7% in 2030 to 20% in 2050 (Sun, 2021). It is also predicted that a sustainable global energy future can be attained by utilizing hydrogen fuel in addition to other alternative fuels (Al-Enazi et al., 2021).
Life cycle (well-to-wake) emissions of alternative marine fuels from extraction and energy production to final use of the fuels in the ships is analyzed, covering well-to-tank emissions and tank-to-wake emissions (Figure 2) (Longspur Research, 2022). These emissions need be taken into account in evaluating particular alternative marine fuels.
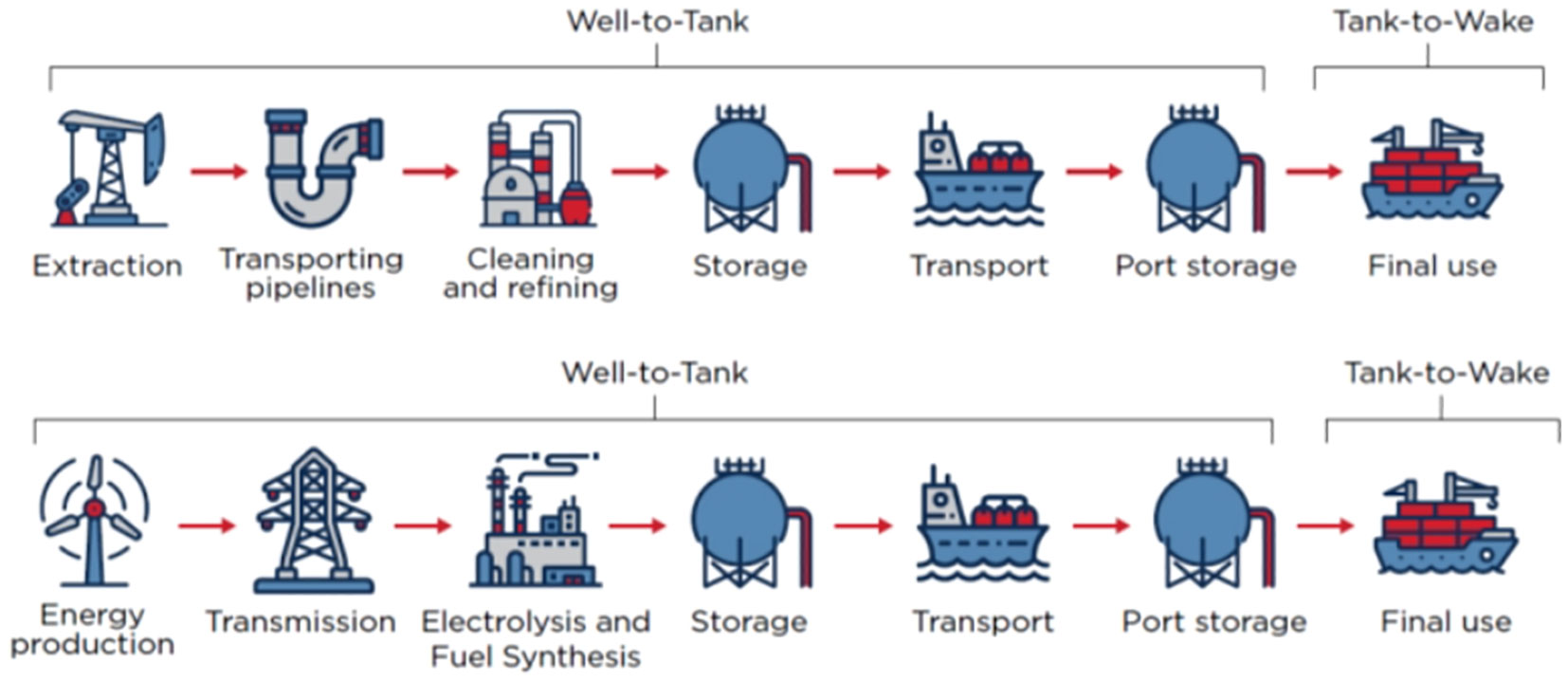
Figure 2. Shipping fuels and energy life circle (well to wake). Source: Longspur Research, 2022.
Noticeably, each alternative fuel has its advantages and disadvantages from perspectives of GHG reduction potential, density, cost, useability as shown in Table 1 and Longspur Research concludes that, taking all the above factors into account, methanol is the best solution available today (Longspur Research, 2022).
Table 1 above indicates that the conventional heavy fuel oil (HFO) has the lowest GHG reduction potential, although it has the advantage of density and cost and that hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, LNG and li-ion have the advantage of GHG reduction potential. However, the use of hydrogen, ammonia, LNG or li-ion currently involves high costs. In addition, the density of hydrogen and li-ion is low, which means their use may significantly reduce a ship’s cargo carrying capacity.
Noticeably, hydrogen, ammonia and methanol are divided into gray, blue and green categories according to the energy used and process adopted. In simple terms, gray fuels are produced by using fossil energy such as coal or natural gas. Blue fuels are produced by using fossil energy, but the refining process uses the technology of carbon capture and storage (CCS) to reduce carbon emissions. Green fuels are produced by using renewable energy such as solar energy or wind power.
CCS estimates that in the life circle and as compared to HFO, green methanol can reduce 63%-99% of GHG emissions; grey hydrogen has higher GHG emissions than HFO, but green hydrogen can reduce 96% of GHG emissions; coal-to-ammonia has higher GHG emissions than HFO, and natural gas synthesis of ammonia can only reduce about 9% of GHG emissions, but green ammonia can reduce 93%-100% of GHG emissions. Therefore, using green methanol may achieve the medium and long-term emission reduction targets, and using green hydrogen and green ammonia may achieve the long-term emission reduction targets. Noticeably, grey fuels mean low costs, but have low GHG reduction potential or even cannot reduce any emission. To the contrary, green fuels mean much higher costs, but have much higher GHG reduction potential. To achieve zero GHG emissions in their life circle, grey alternative fuels need to be progressively transited to green ones.
In practice, LNG or methanol was chosen either as dual fuel or single fuel in most newbuilding of ships using alternative fuels in the past two years, and the percentage of using LNG or methanol in new shipbuilding seems roughly equal (CCS, 2023).
Worldwide use of alternative marine fuels has a long way to go. By the end of 2023, a mere 6% of the global fleet was equipped to operate alternative fuels and the nascent stage of the maritime decarbonization ecosystem means that alternative zero-carbon fuels are still in scare supply (OECD, 2023). Currently, rapid shipping energy transition and decarbonization depends on alternative fuel availability and costs, fuel technology maturation levels, technical feasibility, safety, bunkering infrastructure requirements and onboard storage, in addition to ship and engine design, and crew skills and capabilities (UNCTAD, 2024). So far as the availability of methanol is concerned, Zhongmin Zhonghang New Energy Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd. (ZMZH) estimated that nearly 65% was LNG-to-methanol, nearly 35% was coal-to-methanol, and bio-methanol was less than 1% in the world in 2023 (ZMZH, 2024). Bio-methanol has much higher GHG reduction potential than fossil methanol including LNG-to-methanol and coal-to-methanol, but the current availability of bio-methanol is far from satisfactory. Similar situation exists with respect to green hydrogen and green ammonia. Nevertheless, due to the progressive nature of introducing alternative marine fuels in the shipping industry, the share of conventional fuel oils in shipping energy will gradually decrease over a long period of time, but it is predicted that these oils will not be dramatically replaced (CCS, 2023).
2.1.4 The negative impacts of shipping decarbonization
Shipping decarbonization requires a transition in technology and operations, and an uptake of alternative low and zero GHG fuels. However, it entails increase in maritime logistics costs, because huge investments are required to generate the alternative marine fuels, to adjust ship designs, engines and operations, driving up costs for shipowners, industry and ultimately trade and the final consumers (UNCTAD, 2024). The most critical issues in the use of alternative marine fuels are envisaged to be: high costs (Prussi et al., 2021; Salmon and Bañares-Alcántara, 2021; Martin, 2021), GHG emissions (Pavlenko et al., 2020; Prussi et al., 2021; Jang et al., 2021), including emissions during manufacturing process, e.g., a large amount of GHG emissions is produced during the methanol manufacturing process (Martin, 2021), technical maturity (Valera-Medina et al., 2021; Van Hoecke et al., 2021), safety regulation (Deniz and Zincir, 2016), and expertise needed (Prussi et al., 2021), etc. In particular, green hydrogen and green ammonia have the potential of zero GHG emission, but involve the issues of operational safety and high prices (Hansson et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021b). However, with the continuous development of technologies in the production, transport and utilization of alternative marine fuels, the full life-cycle GHG emissions intensity of the fuels such as methanol and ammonia will gradually decrease in the future (CCS, 2023).
Besides, the cost of building ships using alternative marine fuels or dual fuels will also increase. For example, the cost of building a new LNG-powered ship is estimated at around 10%–20% higher than a conventional ship.
2.2 Methods
Shipping decarbonization entails the conflicts between various interests, especially between the economic interests of the shipping industry on one hand and the international environmental interests on the other. Achieving the shipping decarbonization goals involves complicated issues of economy, technology, policy and law, etc. This research aims at exploring and examining the main pathways relating to the governance in shipping decarbonization from perspective of balancing the conflicting interests. For this purpose, this research makes reference to: (a) the theory on the relationship between government and market in economics in addressing the principle of collaborating governmental intervention and market mechanisms in Section 3.2.2 and its application in Sections 3.3.2, 3.3.5 and 3.3.6, because shipping decarbonization needs the governmental intervention and the market mechanisms to play their respective roles; (b) the progressive decision theory in management in addressing the measure of formulating strategic plans and specific policies for shipping decarbonization by government in Section 3.3.1, because shipping decarbonization is a long process involving high costs and difficulties in technology innovation; (c) the equilibrium analysis method in economics in exploring the main pathway in shipping decarbonization in Section 3.3, because the measures should be taken on the basis of balance of the conflicting interests.
The basic analytical framework in this research is as follows: first, based upon the examinations of the available data sources used and other materials introduced in Section 2, critically examining the conflicting interests inherent in shipping decarbonization in Section 3.1; secondly, analyzing and putting forward the principles to be followed as guiding ideology in balancing the conflicting interests in Section 3.2; thirdly, on these bases and partly by reference to the empirical analysis of the situations in China, exploring the main pathways in the shipping decarbonization governance in Section 3.3.
3 Discussion
3.1 Manifestation and reasons of conflicts of interests in shipping decarbonization
Global climate change is an environmental crisis currently facing all the people in the world and entails the conflicts of interests around the environment. The new environmental perspective believes that the environmental benefits are no longer the currently existing benefits and human interests only, but involves conflicts between current interests and future interests, between national interests and international interests, and that the conflicts between economic interests and environmental interests are undoubtedly very prominent (Zhou, 2009). All these interests and their conflicts are reflected in the process of shipping decarbonization.
3.1.1 Conflict between economic interests and environmental interests
Environmental interests may be understood as the satisfaction of people’s material or spiritual needs by good natural environment. Presumably, people may strive to pursuing maximum economic profits from the natural world or develop the economy without duly considering the environmental costs, whereby transferring the environmental costs to society and others and causing external diseconomies and, as a result, the economic development sacrifices the environmental interests (Zhou, 2009).
It is well recognized that the GHGs into the atmosphere cause climate change resulting in various hazards including sea level rise, increase in water areas, disease and other harm to human health, mass extinction of living organisms, ecosystem destruction, storms, floods and drought, grain reduction and other economic losses. All these are reflections of harms to the environmental interests.
The ship’s GHGs into the atmosphere mainly come from the exhaust emissions caused by the use of conventional fuel oils by ship engines. These oils used in large ships are mainly diesel oil and HFO. Diesel oil includes marine gas oil (MGO) and marine diesel oil (MDO). The price of diesel oil is about twice that of HFO. Obviously, the use of HFO is to reduce fuel costs because fuel oils are the biggest cost of ship operation and conventional fuel oils account for approximately 30% -35% of the total operating costs of a ship. The level of harm to the climate caused by exhaust emissions from HFO is much greater than that of diesel oils.
The conflict between economic interests and environmental interests in the GHG emissions from ships is evident. On one hand, maritime transport has the feature of large capacity and low freights as compared to other modes of transport and is vital to the international trade. The use of HFO is a crucial factor of low freights. Over 80% of all cargo trade in the world flows through the high seas (UNCTAD, 2024). In China, nearly 95% of the goods in international trade were transported by sea in 2023 (MOT, 2024a). Therefore, it’s not an exaggeration to say that maritime transport ensures the development of international cargo trade and has brought enormous economic interests to the traders and shipowners, as well as the trading countries and the international community. On the other hand, however, GHG emissions from ships cause harm to the climate and thus the environmental interests. To decarbonize shipping, the fundamental solution lies in using alternative marine fuels or other energy sources to replace the conventional fossil fuels (Hansson et al., 2020). However, the use of alternative fuels currently and in the near future will significantly increase the shipbuilding costs and ship operating costs, resulting potentially significant increase of freights and consequently higher commodity prices, and may even involve the issues of operational safety. No doubt, this means a significant negative impact on the above economic interests generated by shipping.
3.1.2 Conflict between individual interests and public interests
Conflict between individual interests and public interests often occurs, because the individuals often pursue their economic interests in their production and business activities at the cost of damaging the environment. Consequently, the interests they pursue will bring harm to the public interests. So far as maritime transport is concerned, the individual shipping companies aim to reduce ship operating costs and improve economic efficiency by using low-cost HFO, but the GHG emissions cause harm to the climate, thereby damaging the public interest of the environment. To the contrary, using alternative marine fuels can reduce GHG emissions or achieve zero emission and thus benefit the public interest of the environment, but causes harm to the individual interests of shipping companies and cargo traders.
From perspective of a country, the conflict between individual interests and public interests can also be used to interpret the conflict between the interests of the shipping industry and the overall interests of the country. This is because using HFO serves the interests of the shipping industry, but GHG emissions from ships using HFO harms the overall environmental interests of the country.
3.1.3 Conflict between interests of individual countries and public interests of the international community
In front of the natural environment, countries around the world are a community with a shared future. All countries on earth can benefit together from the natural world, but also have to bear the natural catastrophic harms together (Xiang, 2003). From global perspective, where the policy and law of a country relax environment protection for the purpose of pursuing economic interests in a certain field, the economic activities in that country will not only have the effect of damaging the environment within its borders, but may also have cross-border negative environmental impacts, thereby causing harm to the public environmental interests of the international community.
Due to air circulation, the GHG emissions from ships into the atmosphere will not only damage the atmospheric environment of the country where the emissions are located, but will also damage that of the neighboring countries. The navigation range of international ships is not limited to the waters of the flag State. Therefore, where a ship is sailing in the waters of other countries or on the high seas, her emissions of GHG will damage the atmospheric environment of other countries or the international atmospheric environment, consequently damaging the international environmental interests. As a result, conflict between the economic interests of individual countries and the public environmental interests of the international community arises. Such conflict of interests well implies that reducing the negative impact of GHG emissions from ships in shipping decarbonization cannot be achieved through the efforts of several individual countries only, but should rely on the joint efforts of the international community.
3.1.4 Conflict between current interests and long-term interests
Such conflict is also called intergenerational conflict of interests (Hou and Nie, 2016), and is unique in the area of environmental protection. Presumably, damage to the environment by contemporary people may bring damage to the interests to the future generations because atmospheric self-purification is rather slow and the purifying effect of large-scale afforestation on the air is quite limited and as a result, recovery of the severely damaged environment often takes very long time and/or incurs huge costs. Therefore, if the contemporary people fail to pay sufficient attention to the environmental protection as driven by the current interests, the damaged environment will harm the environmental interests of the future generations and as a result, intergenerational conflict will arise.
For this reason, the atmospheric environment severely damaged by the emission of GHG into the atmosphere from ships and other sources of pollution may cause the conflict of intergenerational interests, i.e. conflict between the economic interest of the contemporary people and the environmental interests of the future generations.
3.2 Principles to be followed in balancing conflicting interests in shipping decarbonization governance
Balance of conflicting interests means the state of relatively peaceful coexistence within a certain pattern and system of interests (Feng, 2007). When conflict of interests cannot be resolved through spontaneous social adjustment, balancing interests through external means is needed to coordinate the conflicting factors, whereby maximizing the satisfaction of the interests and needs of all conflicting parties, and at the same time trying utmost to avoid wasting resources. Needless to say, the principles to be followed in balancing the conflicting interests in shipping decarbonization governance are crucial. This research suggests that the following two principles to be followed.
3.2.1 The principle of prioritizing international public environmental interests while taking into account the other interests
The rationale of this principle is mainly the basic value orientation in balancing the conflicting interests in shipping decarbonization. Theoretically, balancing the conflicting interests needs to be guided by specific basic values. In legal terms, the balance of interests serves as a standard of basic value judgment of law and plays a guiding role in the selection of interests in the process of social resource allocation (Luo, 2012). Shipping decarbonization is within the category of environmental protection, but involves many factors such as economy, technology, policy and law among which the economic and technological factors are the basis of formulating policy and law. Therefore, balancing the conflicting interests in shipping decarbonization should take the protection of public environmental interests as the basic value orientation and consequently adhere to prioritizing international public environmental interests.
International public environmental interests may be understood as the common interests of all or most members of the international community benefited from good natural environment. Such interests are environmental interests firstly, public interests secondly and international interests finally. As aforementioned, when conflict occurs between public interests and individual interests, decisions and actions should be guided by the priority of public interests. Where free competition causes damage to public interests, the government needs to use its public power to rectify in order to coordinate the development of public interests and individual rights (Yu, 2008). Due to the international nature of shipping and the air circulation, the GHG emissions from ships cause harm to the international public environmental interests. The goal of shipping decarbonization is to reduce GHG emissions from ships and ultimately achieve net zero emissions. Therefore, the protection of international public environmental interests should undoubtedly be the basic value orientation in shipping decarbonization. Consequently, such interests should be prioritized in balancing the various conflicting interests.
However, prioritizing the international public environmental interests cannot ignore other related interests. Instead, all the other related interests should also be taken into account. Theoretically, prioritizing public interests requires a moderate tilt in its protection by the individual States and their governments, but it is not a unilateral restriction or deprivation of rights and freedoms of individual persons. Instead, appropriate restrictions should be placed on public interests in order to achieve the optimal balance between natural resource allocation and utilization in social development. In other words, balancing the conflicting interests involved in shipping decarbonization is to achieve the goal that the protection of international public environmental interests is given priority, while the other related interests, especially the economic interests of maritime transport are taken into account. Otherwise, if no economic interests are pursued, environmental interests would be meaningless.
3.2.2 The principle of collaborating governmental intervention and market mechanisms
Noticeably, the IMO Policies and Practices Related to the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ships adopted in 2003 indicate that the international community should adopt market mechanisms to address carbon emissions from ships (IMO, 2003). This is because IMO envisaged that due to the continuous growth of global trade volume in the future, the increase in carbon emissions caused by the increase in the number of ships would offset the reduction in carbon emissions due to the improvement in ship energy efficiency and, therefore, international shipping carbon emissions could not be controlled solely through technological means. Market mechanisms are considered an essential means to address carbon emissions from ships, as they can control the total carbon emissions from shipping within a certain range, and have dynamic efficiency to stimulate the shipping industry to invest in energy efficiency technology research and development (Zheng and Wang, 2022).
However, shipping activities are market behaviors and the climate change caused by the GHG emissions from ships is the negative externality of these behaviors. The consequential inability to achieve optimal allocation of atmospheric environmental resources is in the nature of market failure in economics. Therefore, the governmental intervention is needed to rectify such market failure. The theory on the relationship between government and market in economics believes that market failure requires governmental regulation on market mechanisms to compensate for the market deficiencies. Obviously, solving the external negative effect of market behaviors on the damage to the environment cannot solely rely on market mechanisms. Instead, the government needs adopt appropriate economic, legal and administrative measures for macroeconomic regulation and control. At the same time, however, the important role of the market mechanisms cannot be ignored in environmental governance. Under the guidance and constraints of government macro-control measures, it is necessary to leverage market mechanisms to effectively mobilize the enthusiasm of enterprises and other individuals, encouraging them to allocate resources according to market demand, reducing damage to the environment through environmental technology innovation and other environmental protection measures.
The necessity of governmental intervention can be further demonstrated by the role of the driving mechanism of governmental policies for shipping decarbonization. There are three main driving mechanisms for shipping decarbonization, i.e. governmental policy and law, moral and social responsibility, and economic interests of shipping companies. The first and second driving mechanisms are proactive, and the third one is passive. Undoubtedly, shipping decarbonization will increase operating costs significantly to shipping companies and is thus not preferred by the vast majority of shipping companies. Some big shipping companies, e.g. the major international container lines have expressed to support shipping decarbonization mainly because of the constraints of EU ETS and other currently applicable or potential regulatory schemes including the 2023 IMO Strategy, although partly in consideration of moral and social responsibility and of the need for maintaining or promoting competitiveness in the market. Therefore, the driving force generated by the third mechanism is rather week, while that generated by the second mechanism is quite limited. Reducing GHG emissions from ships entails the industries and enterprises relating to the production and supply of alternative fuels and renewable energy, green technology innovation, equipment manufacturing, ship operation, financing, standard setting, and market transaction, etc., far exceeding the scope of traditional shipping supply chain (CCS, 2023). The industries and enterprises need to jointly promote the safe application of alternative fuels, renewable energy and green technology in the shipping industry, and build green and sustainable shipping development industry chain (CCS, 2023). In so doing, however, the industries and enterprises need the governmental guidance and support. As a result, shipping decarbonization shall mainly rely on the first mechanism and consequently needs necessary governmental intervention.
3.3 Specific pathways in shipping decarbonization governance
Following the above two principles and the equilibrium analysis method in economics, this research explores and suggests the following specific pathways in shipping decarbonization governance from perspective of balancing the conflicting interests.
3.3.1 Formulating strategic plans and specific policies for shipping decarbonization by government
Formulating strategic plans and specific policies is within the governmental functions and is important in shipping decarbonization. As aforementioned, shipping decarbonization will significantly increase the shipbuilding costs and ship operating costs, thereby causing harm to the interests of shipping and cargo trading companies, as well as the overall economic interests of shipping countries. In addition, shipping decarbonization requires the empowerment of alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology. However, the development and mature application of such new technology at reasonable costs requires a long process. In addition, shipping decarbonization closely relates to international public environmental interest. Therefore, shipping decarbonization will be inevitably a global and long-term goal and task and thus needs to be viewed from strategic perspective and thinking, requires effective collaboration between governments and industries. Primarily, the governments need to formulate targeted strategic plans and specific unified development policies. This kind of planning has a guiding role for shipping companies and other relevant stakeholders to take actions, and are the basis for the governments to formulate policies and for the legislative organs to formulate laws and regulations as well as for their implementation. Such planning and specific policies should adhere to the principle of prioritizing the protection of environmental public interests and taking other interests into account, and adopt a progressive path.
Noticeably, according to the progressive decision theory in management, any hasty approach will make it difficult to coordinate and balance the conflicting interests during any revolutionary transition like ultimately net zero GHG emissions from ships. In particular, while protecting the international public environment interests in shipping decarbonization, it is necessary to maintain the long-term survival and development interests of many medium-sized and small shipping enterprises. As aforementioned, progressive reduction of GHG emissions from ships and ultimately achieving net zero emissions is also the pathway adopted by IMO and EU. Furthermore, it is crucial that the governmental policies are systematic, objective, transparent and efficient and have continuity without radical and significant change thereof in order to ensure the market certainty, because the shipping companies and other related stakeholder need a steady policy environment which help them to predict the potential risks of costs, technology etc. and to avoid or minimize the risks in making big and long-term investments for the purpose of ship decarbonization.
Det Norske Veritas (DNV) indicates in Energy Transition Outlook China 2024 that in China, the central government formulates the policy direction and goals and has the authority to ensure their implementation (DNV, 2024a). In the context of China’s national situations, therefore, the role of governmental intervention in shipping decarbonization process is particularly evident and feasible. Till now, China has not developed specific strategy plan for shipping decarbonization yet. However, On 31 July 2024, the CPC Central Committee and the State Council jointly released the Opinions on Accelerating the Comprehensive Green Transformation of Economic and Social Development (CPC and State Council, 2024) which may be deemed as the current general policy of greenization in China. The Opinions emphasize the general requirements of collaboration, innovation and safety in green transformation. So far as shipping decarbonization is or may be concerned, the Opinions require promoting non-fossil energy to replace fossil energy safely, reliably and progressively, encouraging innovation, production and use marine fuels of zero-carbon emission, accelerating innovation of key technologies, establishing sound financial and tax policies and market mechanisms, promoting national carbon emission trading market and voluntary GHG emissions reduction trading market, formulating green development standard system, and strengthening international cooperation. In addition, several instruments have been individually or jointly released by the Ministry of Transport (MOT) and other ministerial department under the State Council which describe China’s general active attitude and directions or specifying the goals of development in shipping decarbonization. It can be envisaged that China will follow its pragmatic pace in shipping decarbonization (DNV, 2024a). At present, China needs to develop specific strategy plan for reducing GHG emissions from ships in response to the 2023 IMO Strategy and based on its own specific situations. As a whole, China is a shipping and trading power in the world. Besides China COSCO Shipping, China Merchants Energy Shipping and a few large shipping enterprises, however, China has many medium-sized and small shipping enterprises causing significant structural imbalance of the shipping industry. This situation necessitates the Chinese government to take positive and prudent attitude towards shipping decarbonization policy. Especially, adopting progressive measures in shipping decarbonization is of particular significance in China. However, when IMO’s mandatory standards of reducing GHG emissions from ships through amendment to Annex VI to MAROPOL 73/78 come into force, these standards are envisaged to be strictly implemented in China.
3.3.2 Implementing economic incentive measures
Theoretically, when individual interests are harmed due to the need for the protection of public interests, the government is required to provide compensation, whereby achieving a balance between the public interests and the individual interests (Fan, 2009). In shipping decarbonization, the economic incentives are necessitated by the significant increase in the construction and operating costs of ships and the need for ensuring the steady development of shipping industry.
Currently, two main technical measures have been taken to significantly reduce GHG emissions from ships by using alternative marine fuels, i.e. (a) dual fuel design for ships by which their engines can simultaneously use conventional fossil fuels and alternative fuels, mainly methanol and LNG, and (b) ship’s use of single alternative fuel. However, it is estimated that dual fuel design for a ship normally increases the construction cost by 10%-20%, and that currently the delivery prices of alternative fuels are about twice that of HFO and even higher. Figure 3 shows DNV’s estimation of increase of shipping costs of three main kinds of ships by using alternative marine fuels in short, medium and long term respectively.
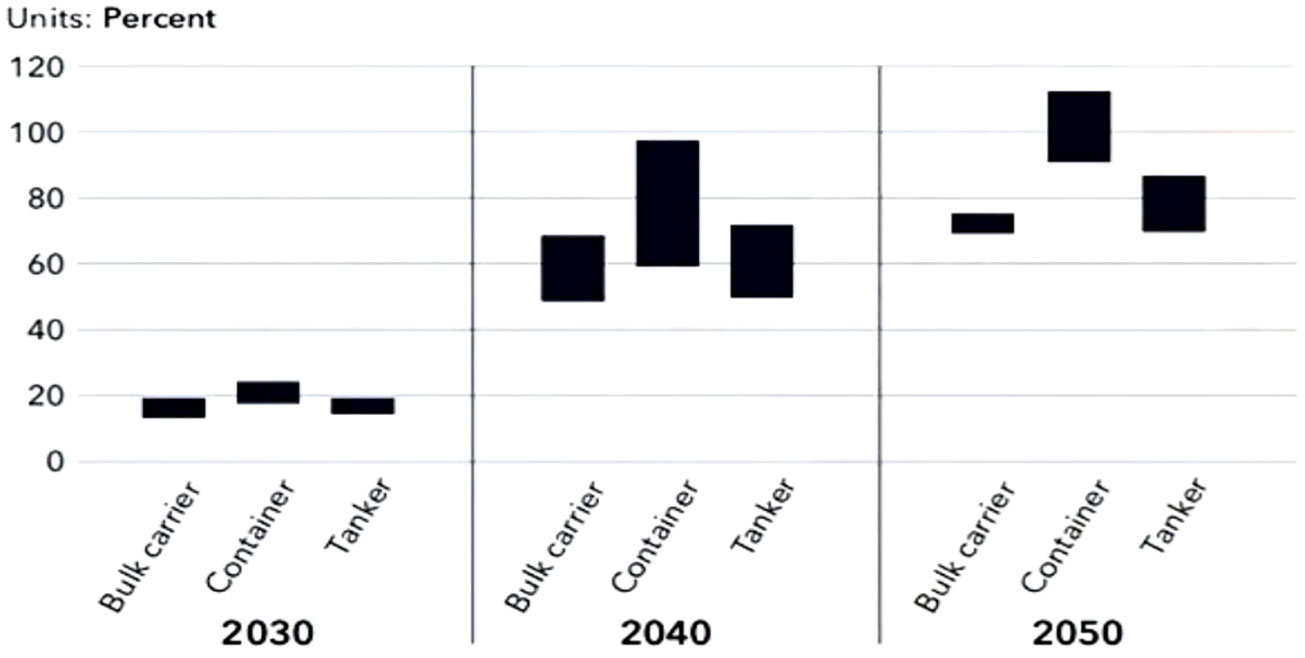
Figure 3. Range of increase in total costs per transport work (USD/DWT-nm for baulk and tank, USD/TEU-nm for containers) from decarbonization in 2030, 2040, and 2050, relative to a business-as-usual scenario. Source: DNV. 2024 edition of Maritime Forecast to 2050 (DNV, 2024b).
The significant increase of the construction and operating costs of ships in shipping decarbonization will bring two consequences. First, it will affect the enthusiasm and initiative of shipping companies to participate in shipping decarbonization transition. Secondly, the significant increase in operating costs of ships will be passed on to the cargo traders through the increase in freights and ultimately passed on to the commodity consumers (UNCTAD, 2024).
Presumably, rapidly and dramatically implementing high-intensity mechanism for reducing GHG emissions from ships may force many small and even medium-sized shipping companies to exit the market and consequently may even affect the international competitiveness of shipping industry and foreign trade in a shipping country like China. In order to avoid or minimize the damage to industry interests and even the overall economic interests of a shipping country, balancing the conflicts between the industry interests and national overall interests on one hand and the international public environmental interests on the other hand, it is necessary for the government to implement appropriate economic incentive measures in the form of tax incentives, financial subsidies, etc. in the initial stage of shipping decarbonization, ensuring the steady supply and reasonable pricing of alternative fuels for ships, and encouraging the innovation and application of new technologies regarding alternative fuel safety and ship propulsion. However, the economic incentives shall be provided by the governments on the condition of non-violation of the rules of anti-subsidies and other competition rules in anti-monopoly law. Inevitably. the economic incentives are subject to the government’s financial capability and consequently may become problems of the week countries. These countries shall do according to their respective capability and international assistance in called for.
Limited economic incentive measures have been implemented or are being implemented to support shipping decarbonization in China. For examples, Shanghai, Shenzhen and several other cities implement financial subsidies for ship projects using LNG instead of conventional fuel oils (Yang et al., 2023). The ships which save energy or use new energy may be exempted from tax on vessel by virtue of Article 4 of the Vehicle and Vessel Tax Law of 2011 as amended in 2019. On 2 August 2024, MOT and the National Development and Reform Commission under the State Council jointly released the Implementation Rules on Subsidies for Scrapping and Updating Old Operating Ships in Transportation (MOT, 2024b). By virtue of Article 7 of these Rules, the owners of a newly-built vessel engaged in transport in inland waters or coastal waters may apply for financial subsidy where the vessel’s main propulsion uses LNG, methanol, hydrogen, ammonia or battery, or uses dual fuels of LNG and fossil oil if the fossil oil substitution rate of more than 60% or dual fuels of methanol and fossil oil if the fossil oil substitution rate of more than 50%. However, currently the amounts of these economic incentives are rather limited and incentives are not applicable to ships engaged in international transport. Therefore, the economic incentive policies in China need be updated as time goes on.
3.3.3 Implementing energy efficiency measures for ships
The rationale of this pathway is that implementing the technical measures (EEDI and EEXI) and the operational measures (SEEMP and CII) currently meet the needs of progressive shipping decarbonization development. It is estimated that adopting corresponding GHG emissions control technologies and operational measures by international shipping industry may be able to reduce the existing GHG emissions from ships by 25%-50% (Nast, 2013). DNV estimates in the 2024 edition of Maritime Forecast to 2050 that implementing the technical and operational measures may reduce fuel consumptions by 4%-16% (DNV, 2024b).
While affirming the role of implementing these technical and operational measures in reducing GHG emissions, we need to recognize their limitations, because these measures cannot contribute to achieving net zero GHG emissions from ships and therefore are considered as short-term measures. However, due to the current limitations of technology, availability and pricing of alternative marine fuels, these measures currently suit to reducing GHG emissions from ships and are in line with the balance of conflicts between current interests and long-term interests, and between individual economic interests and international public environmental interests. Therefore, efforts need to be continued to play this role in shipping decarbonization. DNV emphasizes in the 2024 edition of Maritime Forecast to 2050 that before carbon neutral fuels become a viable option, prioritizing the development and application of technologies to reduce energy consumption is crucial for shipping emissions reduction (DNV, 2024b).
In China, the Maritime Safety Administration (MSA) released the Administrative Measures for Ship Energy Consumption Data and Carbon Intensity on 22 November 2022 (MSA, 2022), in order to implement the requirements of Annex VI to MARPOL73/78. The provisions relating to carbon intensity are applicable to the ships with gross tonnage of 5,000 tons or more which fly Chinese flag and are engaged in international shipping, but currently not applicable to the Chinese ships engaged in coastal trade or inland navigation.
3.3.4 Prudently implementing of shipping carbon emissions trading mechanism
Appropriate implementation of shipping carbon emissions trading mechanism is helpful for reducing GHG emissions from ships, because this market mechanism may control the total quantity of CO2 emissions from ships by means of carbon emission quota trading under the regulations of the government. It seems this mechanism is widely regarded as a key for reducing carbon emissions from ships. It is even considered as an important direction for future emissions reduction in maritime industry (Peng, 2020; Liao, 2022).
While the role of this mechanism in reducing GHG emissions from ships should be acknowledged, however, its limitations are obvious. First, the establishment and operation of this mechanism involve complex factors with high implementation costs. Secondly, this mechanism can only help reduce GHG emissions from ships, but does not contribute to achieving net zero emissions. Thirdly, the allocation of carbon emission quotas involves the issues of fair value and conflicts of interests, because if the control on the total quantity carbon emissions is too strict and quota allocation is carried out through auction method, it is easy to lead to excessively high quota prices and even to market manipulation of pricing, as a result of which regardless of whether shipping companies purchase quotas at high prices or use low- or zero-carbon ship fuels at high prices, significant increase of the operating costs of shipping companies will result in higher freights, causing harm to the economic interests of the shipping and trading companies. Fourthly, this mechanism not only involves reduction of GHG emissions from ships, but may lie enormous economic benefits of a country behind it which may derogate from international public environmental interests. For these reasons, there have been critical comments from the academic circle in China regarding EU ETS. For examples, the EU’s move is suspected of violating the UNFCCC and its Kyoto Protocol of 1997 (Zhu, 2015); EU ETS pursues the discourse power of green shipping industry in the name of environmental protection, and by setting stricter green shipping standards, adopts the strategy of long-arm jurisdiction in the shipping industry and expands its export share in energy-saving and emission reduction technologies (Chen et al., 2016). Unilateral mechanism to reduce GHG emissions from ships may also possibly form green trade barriers. Presumably, all these mean that the functions of this mechanism cannot be exaggerated. In particular, its functions should be ensured to solely reduce GHG emissions from ships. Consequently, this mechanism needs to be implemented prudently in order to overcome its limitations to the utmost extent.
In China, carbon emission trading started in 2021. Currently it applies to power plants only, and there is no specific schedule to apply it to GHG emissions from ships. The only exception is that 31 shipping companies based in Shanghai have been incorporated into the local carbon emission trading market conducted by Shanghai Environment and Energy Exchange. The Global Green Shipping Development Report 2023 issued Shanghai International Shipping Institute (SISI) shows that in 2023, the trading volume of carbon emission allowances (CEA) with respect to shipping was 770,000 tons and the transition amount was CNY55 million (SISI, 2024). It can be envisaged that China will take a prudent attitude towards nationwide shipping carbon emission trading mechanism after considering the balance of multiple interests.
3.3.5 Accelerating the establishment of alternative marine fuels supply chain
Shipping decarbonization is mainly dependent upon deploying alternative marine fuels, especially green marine fuels and such deploying on a large scale needs the establishment of their supply chain. As a result of adaptability analysis of alternative marine fuels based upon comprehensive consideration of their availability, economic acceptability, technological maturity, environmental adaptability and regulatory completeness together the current situation of being attempted or in the research and development stage, low- or zero-carbon liquid fuels mainly include LNG, methanol, ammonia and hydrogen. However, the development of alternative marine fuels is mainly in the hands of out-of-sector stakeholders (fuel producers and suppliers, engine manufacturers, shipyards, etc.) and therefore collaboration across the wide-ranging stakeholders including shipping companies, port and terminal operators, manufacturers, cargo traders, investors, energy producers and distributors from inside and outside the shipping sector is crucial (UNCTAD, 2024). The establishment of the supply chain will become an important factor in measuring a country’s competitiveness in the international shipping market.
Noticeably, the establishment of such a supply chain has two features. One is that the establishment requires large investment (DNV, 2022; Krantz et al., 2020). The other is that, besides the research and application of new energy technologies and ship propulsion technologies, establishing such a supply chain requires collaboration among upstream and downstream stakeholders of production, transport, storage, refueling, etc. as well as shipping and shipbuilding companies. These two features imply that in the initial stage of establishing such a supply chain, the two principles put forward in Section 3.2 need to be guided. Especially, it needs the play of joint role of government intervention and market mechanisms, and progressive but rapid advancing. For this purpose, it is vital for the government to carry out comprehensive planning, provide necessary concessional loans, tax incentives, financial subsidies or other economic support to balance the conflicting interests concerned.
In China, some big projects for producing, transporting, storing or refueling alternative marine fuels are currently either in progress or already planned. The port of Shanghai as the busiest container terminal in the world became the first port in China and the third port in the world capable of ship-to-ship refueling bonded LNG and successfully refueled LNG of 260 million m3 in 2023 (DNV, 2024a). However, the currently available capacity of alternative marine fuel supply is still very limited in China as a whole as compared to the China’s position as the largest port State in the world. Therefore, it is an urgent need to establish alternative marine fuels supply chain in China which shall be planned, laid out and implemented as a national strategic goal, to ensure the availability, safety, certainty and reasonable pricing of alternative marine fuels.
3.3.6 Innovating the alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology
As aforementioned, the key to achieve reduction of GHG emissions from ships and ultimate net zero emissions is to use alternative marine fuels, especially green fuels. Such use requires the empowerment of new energy technologies and ship propulsion technologies to overcome the impact of shortcomings of each alternative fuel.
For examples of such shortcomings, the density of liquid methanol needs be increased to reduce its impact on the cargo carrying capacity of ships. LNG faces problems such as methane slip, ‘well-to-tank’ emissions and difficulty in storage at a temperature of minus 161.5°C. The production process of ammonia consumes a large amount of energy and grey ammonia generates a large amount of CO2 emissions. Ammonia poses a risk of explosion due to improper use, and has significant toxicity and its leakage may cause personal injury to crewmembers on board or other persons (Yadav and Jeong, 2022). Liquid hydrogen needs to be stored in an environment of minus 253 °C and is difficult to transport, causing a significant increase in the prices of refueling to ships. In addition, ammonia and hydrogen have the shortcoming of refueling prices much higher than the conventional HFO, causing significant increase of ship operating costs (Wang et al., 2021a; Hansson et al., 2020). Therefore, corresponding high-cost technical and operational measures are often required in the use of alternative fuels as a safety guarantee (Xing et al., 2021; Salmon and Bañares-Alcátara, 2021).
It is believable that the continuous development of technologies in alternative fuel production, transport, storage and utilization will gradually overcome the above shortcomings in the future, including decrease of the full life-cycle GHG emissions intensity of methanol and ammonia (CCS, 2023). Consequently, innovation and mature application of technology are essential to ensure the availability, safety of use and reasonableness of pricing of alternative fuels, so as to achieve the value orientation of protecting international public environmental interests and the balance of various conflicting interests involved. However, technical innovation has uncertainties and such uncertainties are an important concern of the shipping industry. Consequently, the governments should take such uncertainties into account in formulating shipping decarbonization strategies and policies in this regard.
In recent years, driven by the background of reducing GHG emissions from ships in the international shipping industry, China has introduced the policy of developing the innovation of alternative fuel technology and ship propulsion technology. Noticeably, such innovation is original and revolutionary, and guarantees the sustainable development of shipping and maritime trading industry. It can be envisaged that more and more efforts will be made in this regard in China.
3.3.7 Actively engaging in international cooperation
Global environmental issues have the feature of transcending ethnicity and ideology, and involving the current and long-term interests of all humanity. This commonality and interconnectedness require to overcome the biases of nations, ethnicities and groups beyond ideological differences, to strengthen cooperation and jointly promote the resolution of global environmental issues (Yang, 2007). As international environmental cooperation transcends national borders and regions, and involves cooperation on a global scale, multilateral mechanisms are crucial by taking the international public environment interests as the basic value orientation, and emphasizing equality and common interests among countries. Meanwhile, it is vital that international organizations play the role as bridges among different countries, and that inclusive and universal international rules are jointly established through consultations and dialogues and effectively implemented.
Obviously, the measures for reducing GHG emissions from ships taken by individual countries or regions can play a certain role. However, their effects have obvious limitations, because it is not difficult for shipping companies to evade them, and they may also make international governance fragmented and may even be driven by underlying economic interests of a country or region to form green trade barriers. From international perspective, promoting international cooperation should be regarded as an important means to respond to global climate change and to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and pragmatic cooperation among all parties under various international mechanisms should be promoted (Wang, 2023). The sharing of concepts, goals, information and technology, and the coordination of policies, laws, standards and management, etc. are the connotations of international cooperation in shipping decarbonization.
As a conclusion, the fundamental governance of shipping decarbonization requires unified actions from the international community and countries need to actively cooperate under the regulations and guidance of IMO.
In particular, it is vital to establish international standards and implementation methods for shipping decarbonization through the future revision of Annex VI of MARPOL 73/78 or formulation of other international instruments. Such standards and methods are international public policies in essence and their formulation need the joint participation and interest consultation of the international community to find out the balance point that maximizes the satisfaction of all parties and conflicting interests.
It is also vital to share resources including shipping decarbonization technology in the international community. The level of technological innovation and application is bound to experience an international imbalance and technical barriers may easily be formed for competitive considerations. Currently, this kind of technological developments are basically dominated by several EU members and a few other developed countries (Zheng et al., 2020). However, environmental interests have no borders and as a result, the technologies used to protect the environment should be taken as public goods without borders. Therefore, application of the alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology achieved in a country needs to be allowed in other countries under market mechanisms. Otherwise, the shipping industry of countries lacking such technology may drag the international shipping decarbonization back, making it difficult or even impossible to reduce GHG emissions and ultimately achieve net zero emission from ships. From perspective of balancing the interests of different individual countries and the protection of international public environmental interests, technical barriers should be eliminated and technology transfer at excessively high costs should be avoided.
A country like China needs to have an open and cooperative development concept, maximize the integration of domestic and foreign advantageous resources, and enhance alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology and their application rapidly.
4 Conclusions
Shipping decarbonization entails various conflicts of inherent interests. Balancing these conflicting interests should follow the principle of prioritizing the international public environmental interests while taking into account the other interests and the principle of collaborating governmental intervention and market mechanisms. On this premises, the government in shipping decarbonization governance has its primary function of making strategic planning and basic development policies and ensuring their implementation, and such planning and policies shall focus on the governmental domination-based pathways including adopting necessary and appropriate economic incentive measures, enforcing ship’s technical and operational energy efficiency measures, prudently implementing shipping carbon emissions trading mechanism, supporting the acceleration of establishing supply chain of alternative marine fuels, and encouraging the innovation of alternative marine fuel technology and ship propulsion technology. Meanwhile, the shipping and/or other related industry stakeholders need to focus on market-based pathways of ship’s technical and operational energy efficiency measures, shipping carbon emissions trading mechanism, supply chain of alternative marine fuels, innovation of the new technologies under the guidance of the governmental plans and policies. In addition, both the governments and industry stakeholders need to attach importance to the international cooperation, and the IMO’s continuous and unique role in this regard is essential in this regard.
Hopefully, the results of this research may be helpful for further study on shipping decarbonization governance, especially on formulating plans and policies of shipping decarbonization by individual States, and also on decarbonization governance in other fields due to the commonalities or similarities in decarbonization governance. However, this research has limitations due to the lack of sufficient empirical data resources of the application of alternative marine fuels and innovation of ship propulsion technology for utilizing such fuels as well as implementation of policies of individual States. Advisably, future study needs to pay attention to the potential development of IMO’s strategy on and specific standards of reduction of GHG emissions from ships, progress of application of alternative marine fuels and new ship propulsion technology as well as the policies of individual States and regions for improving the existing solutions or for finding out new solutions in shipping decarbonization governance from the perspective of balancing the conflicts of interests.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WL: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Enazi A., Okonkwo E. C., Bicer Y., Al-Ansari T. (2021). A review of cleaner alternative fuels for maritime transportation. Energy Rep. 7, 1962–1985. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.03.036
Ampah J. D., Yusuf A. A., Afrane S., Jin C., Liu H. (2021). Reviewing two decades of cleaner alternative marine fuels: Towards IMO’s decarbonization of the maritime transport sector. J. Cleaner Production 320, 128871. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128871
Bullock S., Mason J., Broderick J., Larking A. (2020). Shipping and the Paris climate agreement: A focus on committed emissions. BMC Energy 2, 5. doi: 10.1186/s42500-020-00015-2
CCS (2023). Outlook for low carbon development of shipping 2023. Available online at: https://www.ccs.org.cn/ccswz/articleDetail?id=202312081257422748&columnId=201900006000000014 (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Cheliotis M., Boulougouris E., Trivyza N. L., Theotokatos G., Livanos G., Mantalos G., et al. (2021). Review on the safe use of ammonia fuel cells in the maritime industry. Energies 14, 3023. doi: 10.3390/en14113023
Chen J., Zhang H., Luo P. (2016). EU carbon tax on maritime transport: Industrial impact and coping strategy. Taxation Economy 5, 94–100.
Chen J., Zheng T., Garg A., Xu L., Li S., Fei Y. (2019). Alternative maritime power application as a green port strategy: Barriers in China. J. Cleaner Production 213, 825–837. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.177
CPC and State Council (2024). Opinions on accelerating the comprehensive green transformation of economic and social development. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-02/22/content_5588304.htm (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Deniz C., Zincir B. (2016). Environmental and economical assessment of alternative marine fuels. J. Cleaner Production 113, 438–449. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.089
DNV (2022). Maritime Forecast to 2050. Available online at: https://www.dnv.com/publications/maritime-forecast-to-2050-2022-edition-235251/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
DNV (2024a). Energy transition outlook China 2024. Available online at: https://www.dnv.com/publications/China-energy-transition-outlook/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
DNV (2024b). Maritime forecast to 2050. Available online at: https://www.dnv.com/maritime/publications/maritime-forecast/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Dong J., Zeng J., Yang Y., Hua Wang H. (2022). A review of law and policy on decarbonization of shipping. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1076352
European Council (2021). Council of the European union, fit for 55. Available online at: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/search/?FormatFilters=PAGE&keyword=Council+of+the+European+Union%2C+Fit+for+55 (Accessed October 31, 2024).
European Council (2023). FuelEU maritime initiative: Council adopts new law to decarbonise the maritime sector. Available online at: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2023/07/25/fueleu-maritime-initiative-council-adopts-new-law-to-decarbonise-the-maritime-sector/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
European Union (2023). Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on the use of renewable and low-carbon fuels in maritime transport, and amending Directive 2009/16/EC. Available online at: https://data.consilium.europa.eu/doc/document/PE-26-2023-INIT/en/pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Fan X. (2009). On the balance between public interest and individual interest. Yunnan Soc. Sci. 6, 43–47.
Feng X. (2007). On the principle of balance of interests and its application in intellectual property law. Jianghai Acad. J. 1, 141–146.
Hansson J., Brynolf S., Fridell E., Lehtveer M. (2020). The potential role of ammonia as marine fuel - based on energy systems modeling and multi-criteria decision analysis. Sustainability 12, 3265. doi: 10.3390/su12083265
HariLaos N. (2012). Market-based measures for greenhouse gas emissions from ships: A review. WMU J. Maritime Affairs 11, 211–232. doi: 10.1007/s13437-012-0030-5
Hou Y., Nie B. (2016). Analysis of the issues of current ecological intergenerational justice in China. J. @ Soc. Sci. Harbin Normal Univ. 3, 32–34.
Hu Z., Huang. Y., Sun. L., Qi X., Pan X. (2023). Study on international carbon emission quota allocation of shipping industry-based on fairness and efficiency. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1269643
ICS (2022). Shipping, world trade and the reduction of CO2 emissions - United Nations framework convention on climate change (UNFCCC). Available online at: https://www.ics-shipping.org/publication/shipping-world-trade-andthe-reduction-of-co2-emissions-needs-compressing-no-clear-date/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2003). IMO policies and practices related to the reduction of greenhouse gas emission from ships. Available online at: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/AssemblyDocuments/A.963(23).pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2011). Amendments to the annex of the protocol of 1997 to amend the international convention for the prevention of pollution from ships 1973, as Modified by the Protocol of 1978 Relating thereto. Available online at: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.203(62).pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2018). Resolution of initial IMO strategy on reduction of GHG emissions from ships. Available online at: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.304(72).pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2020). Fourth IMO greenhouse gas study 2020. Available online at: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Fourth-IMO-Greenhouse-Gas-Study-2020.aspx (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2021). Resolution MEPC.328(76) Amendments to the Annex of the Protocol of 1997 to Amend the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships 1973, as Modified by the Protocol of 1978 Relating thereto 2021 Revised MARPOL Annex VI. Available online at: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.328(76).pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2023). Resolution MEPC.377(80) on 2023 IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG emissions from Ships. Available online at: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/MediaCentre/PressBriefings/Documents/Resolution%20MEPC.377(80).pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
IMO (2024). IMO’s work to cut GHG emissions from ships. Available online at: https://www.imo.org/en/MediaCentre/HotTopics/Pages/Cutting-GHG-emissions.aspx (Accessed October 31, 2024).
ITF (2018). Decarbonising maritime transport: Pathways to zero-carbon shipping by 2035. International transport forum policy papers (Paris: OECD Publishing). doi: 10.1787/b1a7632c-en
Jang H., Jeong B., Zhou P., Ha S., Nam D. (2021). Demystifying the lifecycle environmental benefits and harms of LNG as marine fuel. Appl. Energy 292, 116869. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116869
Kirval L., Çaliş̇kan U. Y. (2022). Influence of the European union (EU) on international maritime organization (IMO) about the market-based measures on emissions. Int. J. Environ. Geoinformatics 9, 146–153. doi: 10.30897/ijegeo.1047467
Krantz R., Søgaard K., Smith T. (2020). The scale of investment needed to decarbonize international shipping. Available online at: https://www.globalmaritimeforum.org/content/2020/01/Getting-toZero-Coalition_Insight-brief_Scale-of-investment.pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Liao B. (2022). Research on the path to carbon neutrality of China’s shipping industry under the double carbon target. Pacific J. 12, 89–100.
Longspur Research (2022). Methanol and shipping. Available online at: https://www.methanol.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Methanol-and-Shipping-Longspur-Research-25-Jan-2022.pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Luo F. (2012). On the interest relationship between trademark owners and trademark value creators. Intellectual Property 10, 65–69.
Martin A. (2021). A step forward for green methanol and its potential to deliver deep GHG reductions in maritime shipping. Available online at: https://theicct.org/a-step-forward-for-green-methanol-and-its-potential-to-deliver-deep-ghg-reductions-in-maritime-shipping%E2%80%AF/ (Accessed October 31, 2024).
MOT (2024a). Announcement of China maritime day 2024. Available online at: https://www.miit.gov.cn/jgsj/zbes/gzdt/art/2024/art_da0df71fbf9a461594464cf02f98a51c.html (Accessed October 31, 2024).
MOT (2024b). Implementation rules on subsidies for scrapping and updating old operating ships in transportation. Available online at: https://xxgk.mot.gov.cn/jigou/zhghs/202408/t20240802_4145816.html (Accessed October 31, 2024).
MSA (2022). Administrative measures for ship energy consumption data and carbon intensity. Available online at: https://www.msa.gov.cn/html/xxgk/tzgg/wgfw/20221124/E40C898D-11DD-41E4-8D97-62C28D65B.html (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Nast T. (2013). The response of the international shipping industry to global climate change. J. Maritime Law Commerce 1, 29–45.
OECD (2023). Charting a course to net aero: The crucial role of shipbuilding in greening the maritime sector. Available online at: https://www.oecd.org/en/blogs/2023/12/charting-a-course-to-net-zero-the-crucial-role-of-shipbuilding-in-greening-the-maritime-sector.html (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Pavlenko N., Comer B., Zhou Y., Clark N., Rutherford D. (2020). The climate implications of using LNG as a marine fuel. Available online at: https://www.stand.earth/sites/stand/files/20200128-ICCT-StandEarth-Climate-Implications-LNG-As-Marine-Fuel.pdf (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Peng X. (2020). Comparison of carbon emission trading mechanisms among multiple countries under the background of reducing greenhouse gas emissions in maritime transportation and China’s countermeasures. World Shipping 5, 1–5.
Prussi M., Scarlat N., Acciaro M., Kosmas V. (2021). Potential and limiting factors in the use of alternative fuels in the European maritime sector. J. Cleaner Production 291, 125849. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125849
Richter A., Eyring V., Burrows J. P., Bovensmann H., Lauer A., Sierk B., et al. (2004). Satellite measurements of NO2 from international shipping emissions. Geophysical Res. Lett. 31, L23110. doi: 10.1029/2004GL020822
Salmon N., Bañares-Alcántara R. (2021). Green ammonia as a spatial energy vector: A review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 5, 2814–2839. doi: 10.1039/D1SE00345C
Santos V. A., Silva P. P., Serrano L. M. V. (2022). The maritime sector and its problematic decarbonization: A systematic review of the contribution of alternative fuels. Energies 15, 3571. doi: 10.3390/en15103571
Shao Y., Wang H. (2011). New issues of climate change: Legal regulation on GHG emissions from ships. Environ. Economy 3, 61–62.
SISI (2024). Global green shipping development report. Available online at: http://www.sisi-smu.org/2024/0527/c8957a234886/page.htm (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Sun D. (2021). Can ammonia become the fuel of the future? Ship Economy Trade? Ship Economy Trade 9, 6–11.
Traut M., Larkin A., Anderson K., McGlade C., Sharmina M., Smith T. (2018). CO2 abatement goals for international shipping. Climate Policy. 18, 1066–1075. doi: 10.1080/14693062.2018.1461059
Tunagur E. (2023). FuelEU Maritime explained: What the new EU rules mean for shipping. Lloyd s List 7, 1–2.
UNCTAD (2024). Review of maritime transport 2023. Available online at: https://www.unctad.org/publication/review-maritime-transport-2023 (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Valera-Medina A., Amer-Hatem F., Azad A. K., Dedoussi I. C., Joannon M., Fernandes R. X., et al. (2021). Review on ammonia as a potential fuel: From synthesis to economics. Energy Fuels 35, 6964–7029. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c03685
Van Hoecke L., Laffineur L., Campe R., Perreault P., Verbruggen S. W., Lenaerts S. (2021). Challenges in the use of hydrogen for maritime applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 815–843. doi: 10.1039/D0EE01545H
Wang H. (2020). Analysis of the current status of ship fuel and future trends in clean fuel development. Technol. Innovation Appl. 30, 10–12.
Wang S. (2023). Significance and practical path of strengthening international cooperation on blue carbon. Contemp. World 11, 62–65.
Wang Y., Wright L. A. (2021). A comparative review of alternative fuels for the maritime sector: Economic, technology, and policy challenges for clean energy implementation. World 2, 456–481. doi: 10.3390/world2040029
Wang K., Xian Y., Zhang J., Li Y., Che L. (2016). Potential carbon emission abatement cost recovery from carbon emission trading in China. J. Model. Manage. 11, 842–854. doi: 10.1108/jm2-03-2016-0027
Wang Q., Zhang H., Huang J., Zhang P. (2023). The use of alternative fuels for maritime decarbonization: Special marine environmental risks and solutions from an international law perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1082453
Wang S., Zhen L., Psaraftis H. N., Yan R. (2021a). Implications of the EU’s inclusion of maritime transport in the emissions trading system for shipping companies. Engineering 7, 554–557. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.01.007
Wang Y., Zhou X., Liu L. (2021b). Theoretical investigation of the combustion performance of ammonia/hydrogen mixtures on a marine diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46, 14805–14812. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.01.233
Wright L. (2021). A comparative review of alternative fuels for the maritime sector: Economic, technology, and policy challenges for clean energy implementation. World. 2, 456–481. doi: 10.3390/world2040029
Xiang Y. (2003). Ethical analysis of conflicts in international environmental interests. Morality Civilization 2, 64–66.
Xing H., Stuart C., Spence S., Chen H. (2021). Alternative fuel options for low carbon maritime transportation: Pathways to 2050. J. Cleaner Production 297, 126651. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126651
Yadav A., Jeong B. (2022). Safety evaluation of using ammonia as marine fuel by analysing gas dispersion in a ship engine room using CFD. J. Int. Maritime Saf. Environ. Affairs Shipping 6, 99–116. doi: 10.1080/25725084.2022.2083295
Yang Q. (2007). Global environmental problem and international environmental cooperation. New Thinking 5, 66–76.
Yang W., Chen X., Liu Y. (2023). Review and reflections of legislation and policies on shipping decarbonization under China’s “dual carbon” target. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1131552
Ying T., Jun P. (2024). Promoting the achievement of carbon neutrality targets: systematic review of research dimensions and measure methods on carbon equity in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 9912–9924. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c09782
Yu S. (2008). On the conflict and coordination between public interest and individual rights. Tsinghua Law Rev. 2, 142–149.
Zheng J., Liu C., Lin Z. (2020). Low-carbon development of green ships and related strategies. Strategic Study CAE 6, 94–101. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2020.06.012
Zheng S., Wang H. (2022). On the international trading mechanism of carbon emission from shipping in the context of Shipping greenization. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Humanities Soc. Sci. Ed.) 5, 1–6.
Zhou C. (2009). On the balance of interest conflicts in environmental law. Yunnan Soc. Sci. 3, 105–108.
Zhu Z. (2015). Legitimacy of maritime shipping emission reduction policy of EU. Navigation China 4, 102–105.
ZMZH (2024). How will green methanol as carbon reduction tool shape the Future of energy? Available online at: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?:biz=Mzk0NTMyNzE4Ng==&mid=2247521537&idx (Accessed October 31, 2024).
Keywords: shipping decarbonization, conflict of interests, alternative marine fuel, economic incentive, carbon emission trading mechanism, supply chain, technology innovation
Citation: Li W and Hu Z (2024) Pathways in the governance of shipping decarbonization from perspective of balancing the conflicting interests. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1479528. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1479528
Received: 12 August 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 12 November 2024.
Edited by:
Yen-Chiang Chang, Dalian Maritime University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiuwen Wang, East China University of Political Science and Law, ChinaMehran Idris Khan, University of International Business and Economics, China
Copyright © 2024 Li and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhengliang Hu, emxodUBzaG10dS5lZHUuY24=
 Wenwen Li
Wenwen Li Zhengliang Hu
Zhengliang Hu