- 1School of Civil Engineering, Sanjiang University, Nanjing, China
- 2Institute of Geotechnical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China
- 3China Nuclear Power Engineering co., Ltd., Beijing, China
- 4Jiangsu Engineering Research Center for Low Carbon Materials and Green Structures, Nanjing, China
Long-term cyclic loading can have a significant effect on the modulus of sand, and the influence on saturated coral sand has yet to be established. In this paper, the significant influence of non-plastic fines content (FC) and relative density (Dr) on dynamic elastic modulus (E) of saturated coral sand has been evaluated by a series of cyclic triaxial drainage tests. The results show that the dynamic elastic modulus increases rapidly at the beginning of loading; then the growth slows down and finally stabilizes. In general, the development of E is influenced collectively by FC, Dr and cyclic stress ratio (CSR). The initial dynamic elastic modulus Ed-1 and steady-state dynamic elastic modulus Ed-s increase with the increase of Dr, and decrease as FC increases. The linear fitting equations are given by introducing the equivalent skeleton void ratio esk*. Furthermore, the relative dynamic elastic modulus Er is defined as the ratio of Ed-N to Ed-s, and the prediction equation for Er was developed to provide a basis for the engineering mechanical parameters of coral sands under long-term loads.
1 Introduction
The carbonate sand formed by marine biological deposition, whose CaCO3 content is >90%, is referred to as coral sand. Coral sand is abundant in nature (e.g. in the Persian Gulf and the South China Sea) and is often used as the primary geotechnical material for constructing infrastructures such as coral islands and reefs or harbors (Ding et al., 2021). Coral islands and reefs or harbors are located in marine environments that are susceptible to dynamic loads from long-term waves, storm surges, tsunamis, and earthquakes. Differential subsidence or permanent deformation caused by these marine dynamic loads can have a remarkable impact on the foundations of coral sand (Wen et al., 2021). During analysis of soil dynamics problems, the dynamic elastic modulus of the soil is considered a key parameter for studying the soil’s ability to resist deformation (Seed and Idriss, 1970; Rollins et al., 1998, 2020; Chen et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2024a). This modulus effectively reveals the complex nonlinear relationship between dynamic stress and strain in soils, thereby providing an important theoretical basis for investigating the dynamic properties of soils. The dynamic elastic modulus of a sandy soil is an important parameter when describing its deformation features under dynamic loading. In the fields of earthquake, foundation, and geotechnical engineering, the dynamic elastic modulus is one of the key indicators for assessing the response of a sandy soil under seismic or other dynamic loads.
There are many researches on the dynamic deformation characteristics of soils in different regions, but most of the researches devoted to clay and granular soils (Iwasaki et al., 1978; Kallioglou et al., 2008; Vucetic and Mortezaie, 2015; Kantesaria and Sachan, 2021; Nong. and Park, 2021), studies on the dynamic elastic modulus of coral sand are rather limited. Long et al. (2022) investigated the impact of coral sand grain breakage on its dynamic properties. The result of resonant column tests indicated that the maximum dynamic shear modulus (Gmax) of the coral sand first increased and then decreased with the increase in the degree of coral sand grain breakage. Furthermore, Wu et al. (2022) conducted a series of resonant column tests on coral sand with different fines content (FC) and found that the shear modulus ratio G/Gmax - shear strain γ curves show FC-dependent development and are characterized by nonlinear enhancement with increasing FC. Catano and Pando (2012) investigated the CaboRojo coral sand and found the shear modulus G value of coral sand was smaller than that of quartz sand. Alternatively, Jafarian and Javdanian (2020) investigated the Bushehr coral sand using the resonant column technique and found that the relative density had a minor impact on the dynamic shear modulus ratio. While, the decay of G/Gmax gradually slows down as the effective confining pressure increases. Liang et al. (2023) studied the small-strain shear modulus G0 of coral sands from Nansha and Xisha Islands. A G0 prediction model for different types and gradations of sandy soils is proposed by introducing the concept of critical porosity ratio. Wichtmann et al. (2015) focused on the impacts of FC on Gmax of quartz sands. At the same porosity ratio e, when FC< 10%, Gmax decreases substantially with increasing FC; when FC = 10%–20%, Gmax increases with increasing FC; however, when FC is >20%, Gmax does not change significantly with FC. These findings provide an important basis for a deeper understanding of the impacts of FC on the mechanical properties of quartz sands.
Previous studies have investigated the development of G of sands within small strain conditions using resonant column tests. In this study, the drained cyclic triaxial tests have been conducted to study the influence of FC and relative density (Dr) on the initial dynamic elastic modulus (Ed-1) and steady-state dynamic elastic modulus (Ed-s). Based on the experimental results, a prediction equation for the relative elasticity modulus ratio (Er) is given, so as to provide a basis for the engineering mechanical parameters of coral sands with non-plastic fines under long-term loads.
2 Test materials and methods
2.1 Test materials
The coral sand from a reef in the Nansha Islands was used for testing, which is a unique marine soil formed from the remains of marine organisms through physical, chemical, and biological processes. The coral sand grains are mainly composed of aragonite, high-magnesium calcite, and 90% CaCO3. It is a calcareous sand with a specific gravity of 2.84. Coral sands are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical waters, and extensively found across China’s Nansha Islands, serving as the primary geotechnical media with yellowish–white grains in the Nansha Islands area. The coral sand used in this study was found in the complex marine environment of the Nansha Islands, which results in several distinctive properties of coral sand grains: they are angular, prone to cementation and breakage, and have rough surfaces and internal pores (Karatza et al., 2017; Deng and Haigh, 2022).
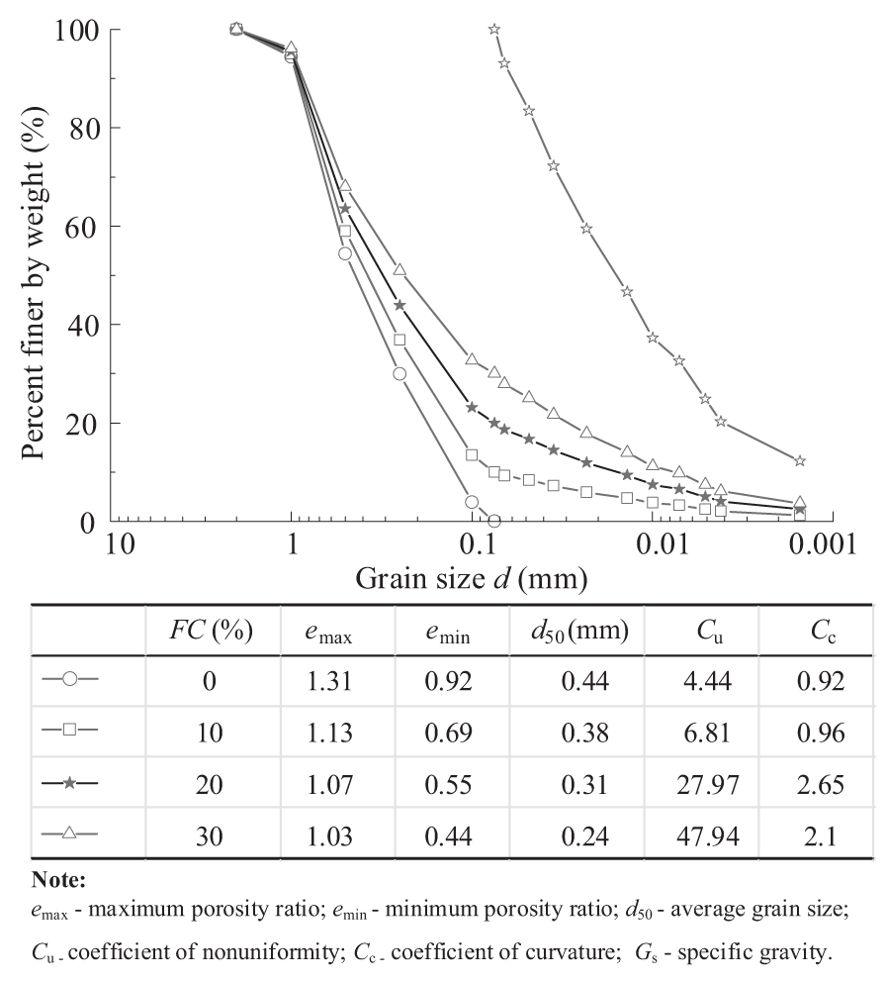
The coral sand was first dried in a constant temperature oven at 103°C. Then, to separate the fine grains of the coral sand from the sand grains, the coral sand was sifted using a standard sieve with a mesh size of 0.075 mm. This process allowed the separation of two types of coral sand grains based on the 0.075-mm threshold (Zhao et al., 2022). Coral sand grains<0.075 mm were considered as fine grains, while those above this size were considered sand grains. Fine particles have no discernible liquid or plastic limit and are classified as non-plastic particles (ASTM International, 2000). Fine and sand grains of different masses were uniformly mixed to obtain coral sands with different FC. The gradation curves of pure sand, pure fine, and coral sand grains with different FCs are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 lists the basic physical indicators of the coral sand. The maximum and minimum porosity ratios were measured according to ASTM specifications. To avoid changes in grain size distribution due to breakage during measurement, the minimum porosity ratio was measured using the vibration metho (ASTM D4253, 2016a; and ASTM D4254, 2016b).
2.2 Test apparatus and sample preparation
A GDS cyclic triaxial apparatus was used for performing stress-controlled drainage cyclic loading tests. This apparatus applies a maximum axial stress of ±5 kN with an accuracy of up to 0.001 kN. The confining pressure chamber can withstand a maximum pressure of 2 MPa. The axial displacement range is 100 mm with a displacement accuracy of 0.07% F.S (full scale). To ensure the uniformity of coral sand with fine grains, samples were prepared using the dry sampling method with a diameter of D = 50 mm and a height of H = 100 mm. According to gradations shown in Figure 1, the sand required for each specimen was weighed and evenly divided into five layers for filling into film-bearing cylinders. During the filling process, the layer height was strictly controlled, and the surface of each layer was brushed to ensure uniformity. Upon completion of sample preparation, CO2 was introduced to displace air, followed by presaturation using air-free water. Then, the samples were saturated using the graded back pressure saturation method. When the measured pore pressure coefficient B was ≥0.97, the samples were considered fully saturated. After saturation, an initial effective confining pressure σm’ = 100 kPa was uniformly applied for consolidation.
2.3 Test scheme
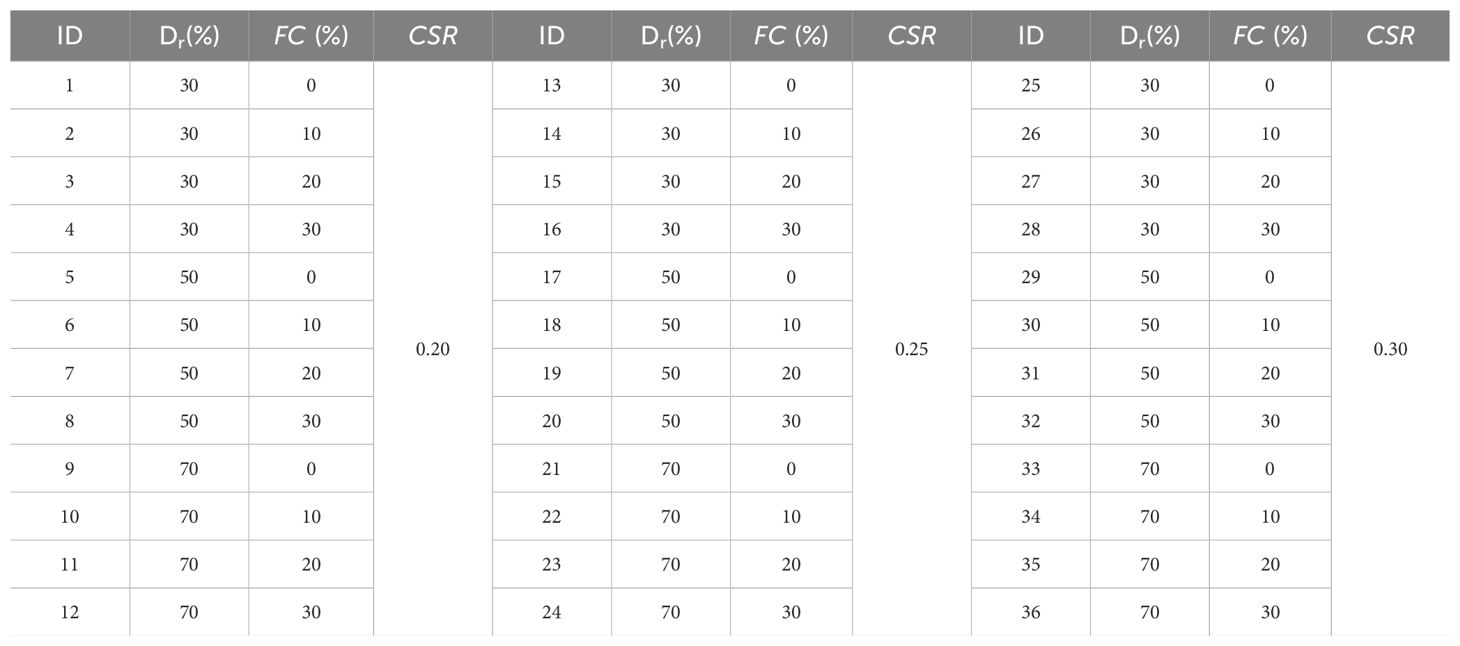
To investigate the development patterns of volumetric strain of coral sands with different Dr, FC, and cyclic stress ratio (CSR) values under cyclic drainage loading conditions, coral sands with FC = 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30% were used to prepare samples with Dr = 30%, 50%, and 70%, respectively, followed by uniform consolidation at σ’m = 100 kPa. After consolidation, drainage cyclic loading tests with CSR = 0.20, 0.25, and 0.30, were conducted. The detailed test scheme is shown in Table 1, with CSR:
where σd is the cyclic deviatoric stress. The test was performed using sine waves with a loading frequency of 0.1 Hz.
3 Test results and analysis
There is relatively limited documentation on how to use a dynamic triaxial apparatus to test the coral sand from the South China Sea under drainage cyclic loading conditions to obtain its dynamic elastic modulus. Hence, the analysis of the dynamic modulus of the soil is crucial, which is defined as:
where, σd and ϵd are axial dynamic stress and strain, respectively.
Under cyclic loading, the contact force between saturated coral sand grains gradually increases with increasing soil density, thereby increasing the dynamic elastic modulus Ed. When the dynamic elastic modulus stabilizes, the contact force between grains remains the same and Ed reaches a steady state. The average dynamic elastic modulus of saturated coral sand at the N-th cycle id denoted as Ed-N. Figure 2 illustrates the calculation of Ed-N using Equation 2b.
Where σd,max and σd,min are the maximum and minimum cyclic deviatoric stresses at the Nth cycle, and ϵd,1 and ϵd,2 are the axial strains corresponding to σd,max and σd,min, respectively. Figure 3 shows the curve of dynamic elastic modulus of the saturated coral sand Ed-N versus N. As shown in this figure, Ed-N accumulates continuously with increasing N. It increases rapidly at the beginning of loading; then, its growth rate slows down until it stabilizes.During loading, the dynamic elastic modulus of the saturated coral sand increases with the increase in the relative density Dr; the growth rate of Ed-N decreases with increasing Dr and increases with increasing FC and CSR.
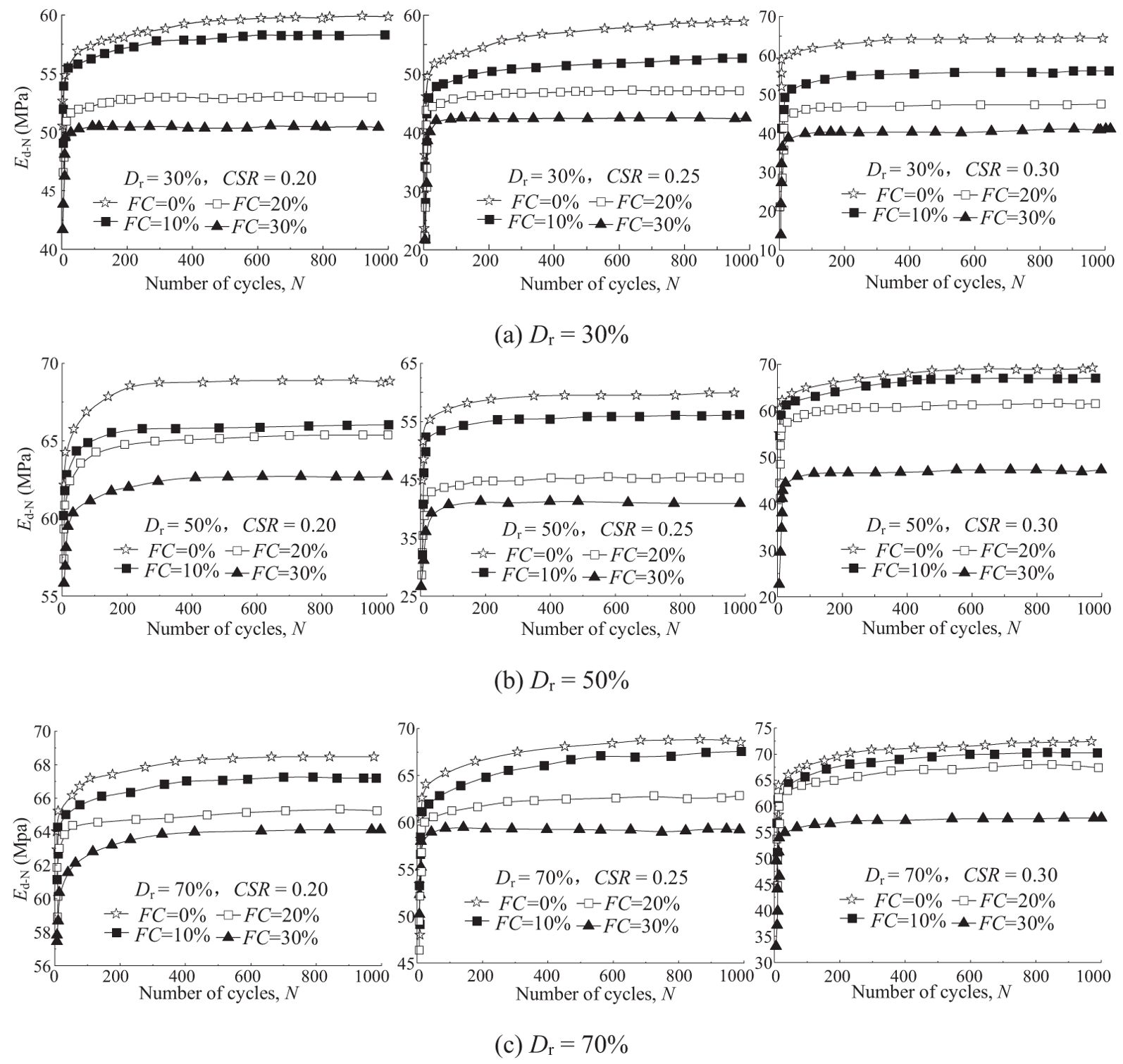
Figure 3. Development of dynamic elastic modulus Ed-N of saturated coral sand with N. (A) Dr = 30%, (B) Dr = 50%, (C) Dr = 70%.
3.1 Analysis of the initial dynamic elastic modulus
In this study, the dynamic elastic modulus Ed-1 at the first cycle N = 1 is defined as the initial dynamic elastic modulus. Figure 4 shows the relationship curve between the initial dynamic elastic modulus Ed-1 and FC. With FC ranging from 0 to 30%, the initial dynamic elastic modulus decreases with increasing FC and CSR and increases with increasing Dr. Thus, the magnitude of the initial dynamic elastic modulus is affected by FC, Dr, and CSR. This is because for Dr, the number of sand grains that make up the soil skeleton decreases gradually with the increase of FC and some of them are replaced by fine grains, thus decreasing the stiffness of the sample in the initial state and Ed-1. With the increase of Dr, the degree of compaction of the sample increases and the contact between grains is closer, thus increasing the stiffness of the sample and Ed-1. The above analysis indicates that the impacts of the composition of grains on Ed-1 cannot be reasonably characterized by FC or Dr alone. Thevanayagam (2000) proposed the equivalent skeleton void ratio esk* considering influence of fines on the contact of sand particles and the interparticle contact force chain. The formula is as follows:
where e is void ratio, b is the proportion of fines involved in the force chain between soil particles on the premise that FC is smaller than the threshold fines content FCth (FCth = 30% for the coral sand in this study). The parameter b is calculated using the semi-empirical formula proposed by Rahman et al. (2008) and Mohammadi and Qadimi (2015), and its validity has been verified by Chen et al. (2020).
Therefore, the equivalent skeleton void ratio esk* is used to characterize Ed−1. It can be found that Ed−1 decreases with the increase of esk*, indicating a clear relationship between Ed-1 and esk*; esk* is an appropriate physical indicator for characterizing Ed−1. As shown in Figure 5, a clear linear relationship between the CSR-corrected initial dynamic elastic modulus and equivalent porosity ratio of the skeleton is established:
3.2 Analysis of the steady-state dynamic elastic modulus
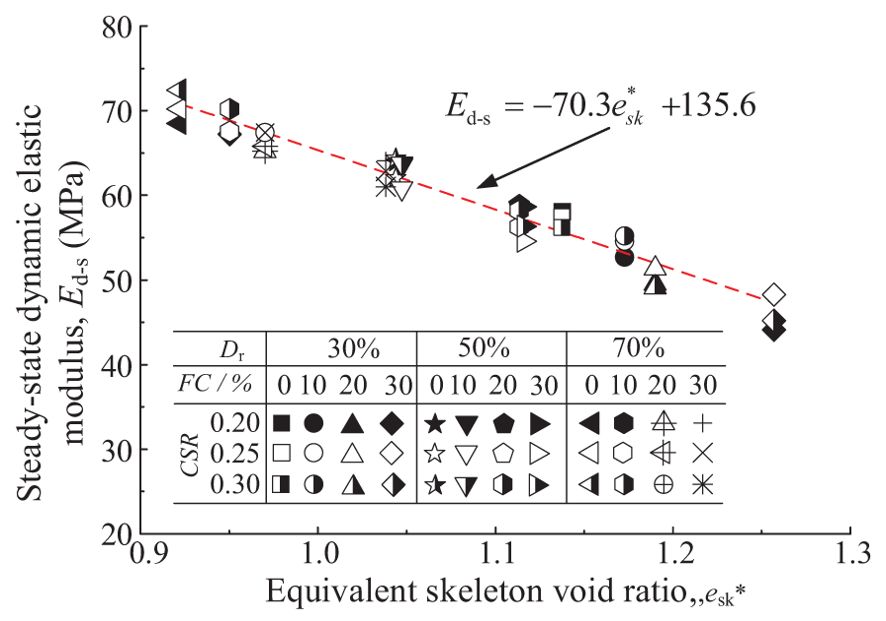
When the volumetric strain (Δϵv) development plateaus during drained cyclic loading (Δϵv/ΔN< 0.01), the specimen is considered to have reached steady state. The Ed−N in this state is defined as the steady-state dynamic elastic modulus Ed-s. The variation in the steady-state dynamic elastic modulus Ed-s is affected by Dr and FC, as shown in Figure 6. According to the experimental results, Ed-s decreases with increasing Dr, and increases linearly with decreasing FC. In addition, the experimental results show that Ed-s increases slightly with increasing CSR. This is consistent with the finding of Ma et al. (2024b) that elastic modulus increases slightly with increasing strain rate.
When Ed-N reaches Ed-s at a given Dr, it indicates that the sample has reached the maximum degree of compaction under the applied stress. When FC< FCth, fine grains fill in between the coarse particle skeleton or wrapped around the surface of the coarse sand, and their lubricating effect reduces the stiffness of the soil. This observation is consistent with the findings Huang et al. (2023) obtained using the three-dimensional discrete element method. The greater the FC, the more the fine grains in the soil skeleton, thus remarkably reducing the stiffness. An increase in the initial Dr would increase the degree of compaction of the consolidated sample, which strengthens the contact interaction between soil grains and manifests itself as an increase in the dynamic elastic modulus.
The equivalent skeleton void ratio esk* is introduced to characterize the combined impact Dr and FC. As shown in Figure 7, a clear linear correlation exists between Dr and FC, which allows us to conclude that
3.3 Prediction modeling for the relative dynamic elastic modulus
The ratio of Ed-N to Ed-s is defined as the relative dynamic elastic modulus Er (Equation 6). Er represents the stability development of the coral sand under cyclic drainage loading and is of guidance for the foundation design under long-term loading.
Figure 8 shows the development curve of the relative dynamic elastic modulus Er with the number of cycles N. It can be seen that the degrees of discreteness of Er–N curves at different FCs and the same Dr are extremely small, indicating that FC has almost no impact on the development of Er with N.Er eliminates the impact of various FC, and during cyclic loading, Er develops with N in the form of an approximate inverse tangent function.
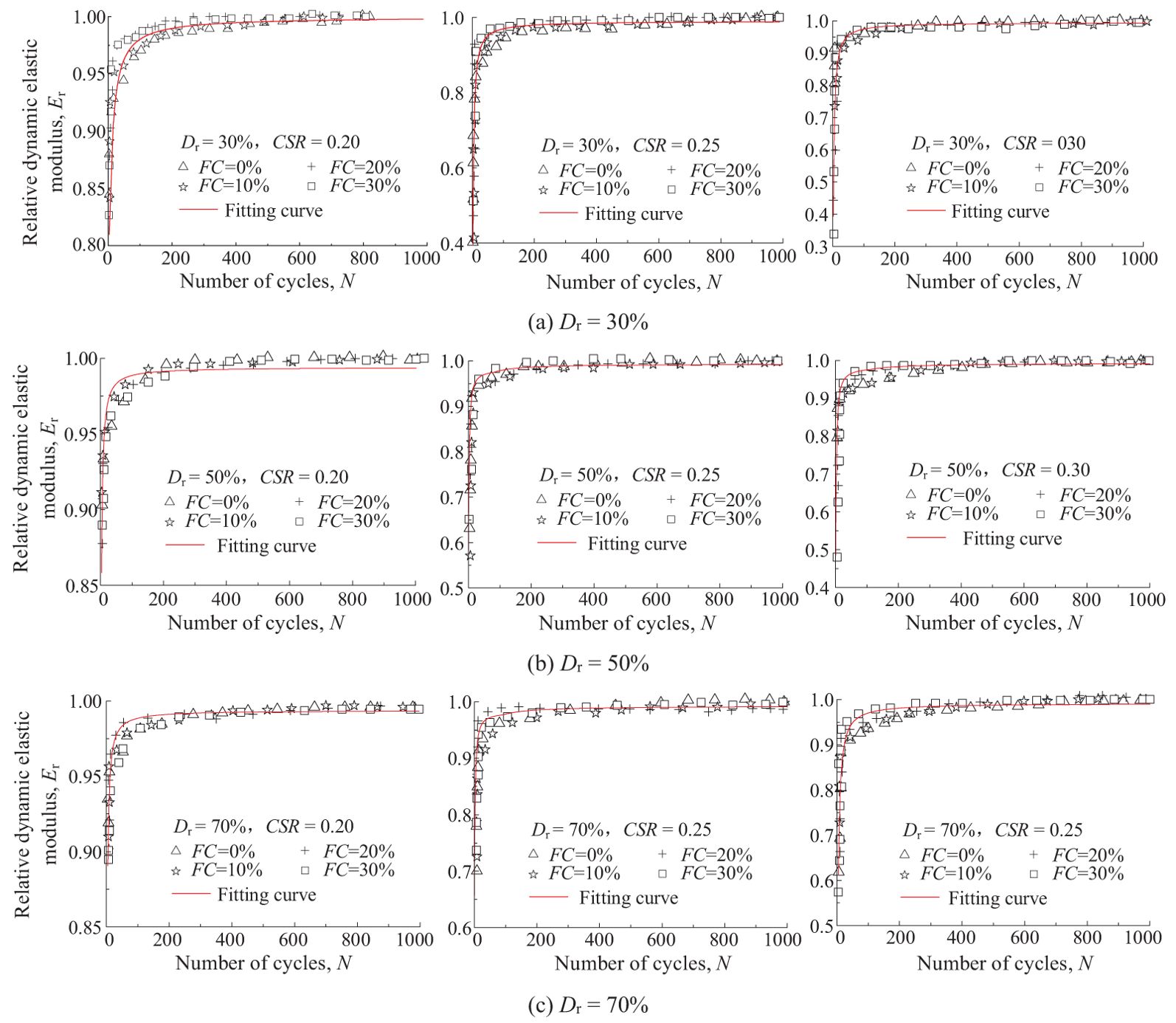
Figure 8. Relationships between the relative dynamic elastic modulus E r and N. (A) Dr = 30%, (B) Dr = 50%, (C) Dr = 70%.
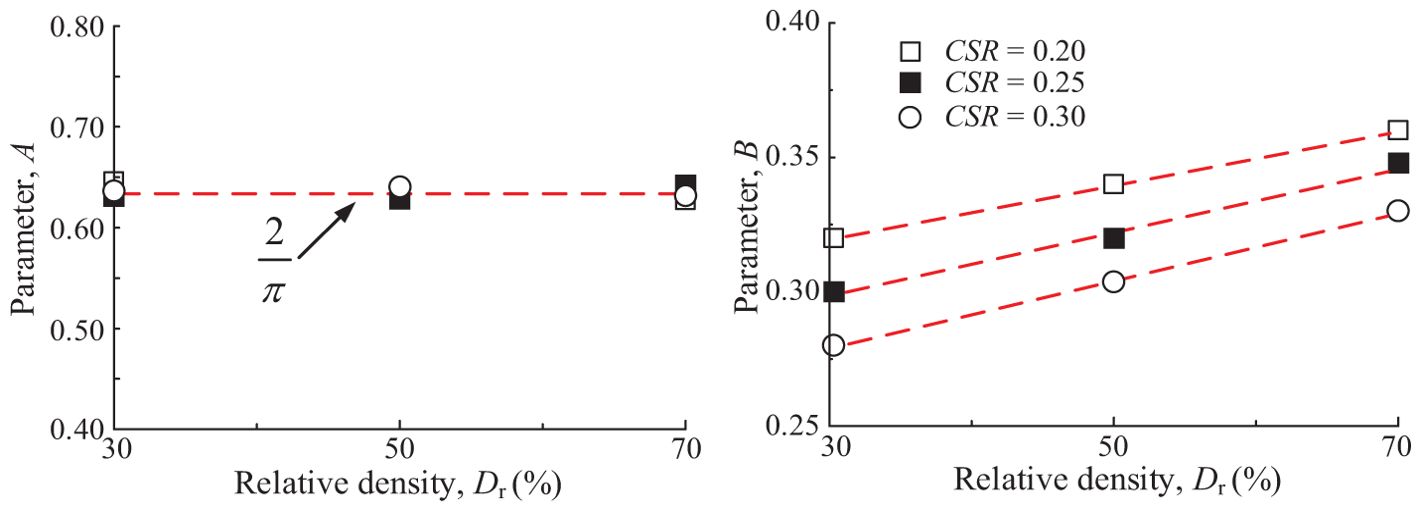
Equation 7 was used to analyze the development of Er, namely, parameters A and B. A mathematical analysis indicated that parameter A is related to the final value of the relative dynamic elastic modulus Er, while parameter B is a variable related to the growth rate of Er. According to the A–B relationship shown in Figure 9, parameter A is related to the soil, and remains constant at 0.63 for the saturated coral sand used in this study, unaffected by FC, CSR, or Dr. The growth rate of the Er is affected by the combined impact of FC, CSR, and Dr. When the impact of FC is eliminated, changes in Dr will substantially affect the fitting parameter B. The value of B shows a linear increase with increasing Dr. This is because an increase in the Dr would increase the degree of compaction of the loaded sample, which strengthens the contact interaction between soil grains and manifests itself as an increase in the dynamic elastic modulus.
Parameter B is corrected by CSR, and in this study, the density correction parameter DrCSR is used in place of the relative density Dr. As shown in Figure 10, there is a clear linear relationship between the two.
Thus, a prediction model for the dynamic elastic modulus of saturated coral sands can be developed as follows:
4 Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the impacts of Dr, FC, and CSR on the dynamic elastic modulus Ed-N of saturated coral sands with non-plastic fines and its development patterns, and drew the following conclusions:
(1) Ed-N of saturated coral sands keeps accumulating with increasing N during cyclic loading, and it increases with increasing Dr and decreases with increasing FC during the loading process.
(2) The initial dynamic elastic modulus Ed-1 is affected by FC, Dr, and CSR. Alternatively, the steady-state dynamic elastic modulus Ed-s is affected by the combined impact of FC and Dr and to a lesser extent by the CSR. Linear relationships between Ed-1 and esk* and Ed-s and esk* for FC< FCth were established respectively by introducing the equivalent skeleton void ratio esk*.
(3) The relative dynamic elastic modulus Er is defined as the ratio of Ed-N to Ed-s. Er is not affected by the FC, but increases with increasing N. A prediction model for Er in the form of an inverse tangent function was developed, and its fitting parameters A and B were analyzed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RZ: Writing – original draft. ZH: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. QL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. QY: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. QW: Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant no 52378346.
Conflict of interest
Author HZ was employed by China Nuclear Power Engineering co.,Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
ASTM International (2000). D2487-00. Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System) (West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International).
ASTM International (2016a). D4253-16. Standard test methods for maximum index density and unit weight of soils using a vibratory table (West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International).
ASTM International (2016b). D4254-16. Standard test methods for minimum index density and unit weight of soils and calculation of relative density (West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International).
Catano J., Pando M. A. (2012). “Static and dynamic properties of a calcareous sand from Southwest Puerto Rico,” in GeoFlorida 2010: Advances in Analysis, Orlando, USA: Modeling & Design. 842–851. doi: 10.1061/41095(365)8
Chen G. X., Liang K., Zhao K., Yang J. (2024). Shear modulus and damping ratio of saturated coral sand under generalised cyclic loadings. Géotechnique 74, 116–133. doi: 10.1680/jgeot.21.00181
Chen G. X., Wu Q., Zhao K., Shen Z. F., Yang J. (2020). A binary packing material-based procedure for evaluating soil liquefaction triggering during earthquakes. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 146, 04020040. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002263
Deng C. H., Haigh S. K. (2022). Sand deformation mechanisms mobilised with active retaining wall movement. Géotechnique 72, 260–273. doi: 10.1680/jgeot.20.P.041
Ding Z., He S. H., Sun Y. F., Xia T. D., Zhang Q. F. (2021). Comparative study on cyclic behavior of marine calcareous sand and terrigenous siliceous sand for transportation infrastructure applications. Constr. Build Mater. 283, 122740. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122740
Huang C. X., Xu S. K., Shen Z. F., Zhang L., Wang L., Liu C. (2023). Effects of non-plastic fines on liquefaction properties of saturated silt using discrete element modeling. Eng. Geo. 317, 107091. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107091
Iwasaki T., Tatsuoka F., Takagi Y. (1978). Shear moduli of sands under cyclic torsional shear loading. Soils Found. 18, 39–56. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.18.39
Jafarian Y., Javdanian H. (2020). Dynamic properties of calcareous sand from the Persian Gulf in comparison with siliceous sands database. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 18, 245–249. doi: 10.1007/s40999-019-00402-9
Kallioglou P., Tika Th., Pitilakis K. (2008). Shear modulus and damping ratio of cohesive soils. J. Earthq Eng. 12, No. doi: 10.1080/13632460801888525//
Kantesaria N., Sachan A. (2021). Cyclic degradation and pore-water pressure response of high-plasticity compacted clay. J. Geotech Geoenviron. Eng. 147, 04021113. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002630
Karatza Z., Andò E., Papanicolopulos S.-A., Ooi J. Y., Viggiani G. (2017). Evolution of deformation and breakage in sand studied using X-ray tomography. Géotechnique 68, 107–117. doi: 10.1680/jgeot.16.P.208
Liang K., Chen G. X., Du X. L., Xu C. S., Yang J. (2023). A unified formula for small-strain shear modulus of sandy soils based on extreme void ratios. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 149, 04022127. doi: 10.1061/JGGEFK.GTENG-10913
Long H., Zhuang K., Deng B., Jiao J. L., Zuo J. J., You E. L. (2022). Dynamic characteristics of coral sand in the condition of particle breakage. Geofluids 2022, 5304179. doi: 10.1155/2022/5304179
Ma L. J., Deng J. J., Wang M. Y., Wang J. P., Fang B., Wu J. W. (2024b). Effect of diagenetic variation on the static and dynamic mechanical behavior of coral reef limestone. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 34, 893–908. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2024.07.004
Ma L. J., Ke L. W., Chen T., Wu J. N., Song Y. J., Xu X. Y. (2024a). Dynamic mechanical behaviors of coral sand under drop weight impact. Acta Geotech. 19, 699–716. doi: 10.1007/s11440-023-01911-7
Mohammadi A., Qadimi A. (2015). A simple critical state approach to predicting the cyclic and monotonic response of sands with different fines contents using the equivalent intergranular void ratio. Acta Geotech. 10, 587–606. doi: 10.1007/s11440-014-0318-z
Nong. Z. Z., Park S. S. (2021). Effect of loading frequency on volumetric strain accumulation and stiffness improvement in sand under drained cyclic direct simple shear tests. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engng. 147, 04021159. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002706
Rahman M. M., Lo S. R., Gnanendran C. T. (2008). On equivalent granular void ratio and steady state behaviour of loose sand with fines. Can. Geotech. J. 45, 1439–1455. doi: 10.1139/T08-064
Rollins K. M., Evans M. D., Diehl N. B., Daily W. D. III (1998). Shear modulus and damping relationships for gravels. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 124, 396–405. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:5(396
Rollins K. M., Singh M., Roy J. (2020). Simplified equations for shear-modulus degradation and damping of gravels. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 146, 04020076. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002300
Seed H. B., Idriss I. M. (1970). Soil moduli and damping factors for dynamic response analyses, Report EERC 70-10 (Berkeley, CA, USA: University of California).
Thevanayagam S. (2000). “Liquefaction potential and undrained fragility of silty sands,” in Proceedings of the 12th World Conference Earthquake Engineering CD-ROM (New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering, Wellington, New Zealand).
Vucetic M., Mortezaie A. (2015). Cyclic secant shear modulus versus pore water pressure in sands at small cyclic strains. Soil Dynam. Earthq. Eng. 70, 60–72. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.12.001
Wen B., Yuan N. Z., Kong L. W., Chen W. (2021). Application practice and settlement estimation of composite ground for high-rise building on coral sand site of hydraulic fill. China Civil Eng. J. 54, 85–93. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.12.006
Wichtmann T., Navarrete Hernández M. A., Triantafyllidis T. (2015). On the influence of a non-cohesive fines content on small strain stiffness, modulus degradation and damping of quartz sand. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 69, 103–114. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.10.017
Wu Q., Liu Q. F., Zhuang H. Y., Xu C. S., Chen G. X. (2022). Experimental investigation of dynamic shear modulus of saturated marine coral sand. Ocean Eng. 264, 112412. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112412
Keywords: saturated coral sand, dynamic elastic modulus, relative density, equivalent skeleton void ratio, cyclic triaxial drainage test
Citation: Zhou R, Huo Z, Liu Q, Yu Q and Wu Q (2024) Development patterns of the dynamic elastic modulus of saturated coral sand under different drainage conditions. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1474889. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1474889
Received: 05 August 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 25 October 2024.
Edited by:
Xianwei Zhang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Wei Duan, Southeast University, ChinaLei Zhang, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Huo, Liu, Yu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qifei Liu, TGl1cWlmZWk5NTczQDE2My5jb20=
 Ruirong Zhou1,2
Ruirong Zhou1,2 Qifei Liu
Qifei Liu Qi Wu
Qi Wu