- 1National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries (NIOF), Cairo, Egypt
- 2Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
- 3Department of Zoology, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
- 4Environmental and Life Sciences Programme, Faculty of Science, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei
- 5Department of Pharmacognosy, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 6Department of Aquaculture and Biotechnology, Faculty of Aquaculture and Marine Fisheries, Arish University, Arish, Egypt
Phytobiotics are promising diet alternatives, yet their effectiveness in high-risk aquaculture conditions remains underexplored. Therefore, a 90-day feeding trial was conducted based on dietary supplementation of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, with herbal extracts, namely, lemon balm [Melissa officinalis (MOE)], marjoram [Origanum majorana (OME)], and chamomile [Matricaria chamomilla (MCE)] with 0% water change. The treated groups were compared to groups untreated with herbs or control groups [positive control (PC; 0% water change) and negative control (NC; 20% water exchange per day]. Fish were cultured at stocking density (20 fish m-3: 1.8kg of biomass/m3). We conducted a physicochemical analysis of the water and the clinical responses, growth, and immune responses of the fish were evaluated. Furthermore, the herbal-supplemented fish were then challenged with a pathogenic Edwardseilla tarda strain and mortality was monitored. In the 1st and 2nd months, the water parameters were within the permissible limits. After that, a fatally low dissolved oxygen concentration and the highest levels of ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and pH were recorded during the 3rd month. Blood and immune assays were conducted in the treated groups and control groups. The herbal-treated groups appeared healthy, but during the 3rd month, lethargy and decreased appetite were evident. Generally, the herbal-treated fish showed improved growth performance parameters, survival rates, and resistance against pathogenic bacteria E. tarda, particularly in the OME and MOE-treated groups compared to the positive control group. Finally, phytobiotic supplements were shown to improve fish stress tolerance and immune activation for a certain period under stressful conditions or unchanged water, based on the stocking density, dosages of herbs used, and the extent of deterioration of the water quality.
Introduction
Recently, water scarcity, harsh climate, rapid population growth, and per capita consumption of animal protein have weighed on the modern aquaculture sector. The aquaculture sector is the largest contributor to the fish supply as production from sea-caught fisheries has almost stagnated in recent years (FAO, 2022; El-Sayed et al., 2022; Eyayu et al., 2024). However, the rapid evolution of intensification practices is exaggerating stressors on fish, increasing the risk of low water quality and disease outbreaks (Ndashe et al., 2023). Other challenges include wastewater-based agriculture, a major source of nitrogenous components, organic carbon, suspended matter, and phosphates, which pose a major threat to aquatic ecosystems (Kim et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023). These sources of pollution can lead to a rapid deterioration of water quality, which negatively affects fish health and the proliferation of pathogenic microbes; this can eventually lead to fish death and economic losses in farmed fish species (Mehrim and Refaey, 2023). Another important factor, fish stocking density, affects water quality as oxygen requirements vary with fish species, age, fish size, and water temperature (Dunham, 2023).
Faced with the water scarcity crisis, several alternative systems have been proposed including water exchange, biofilters for recirculating aquaculture systems, Biofloc technology, and aquaponics to maintain aquaculture water quality and quantity (Abdel-Aziz et al., 2024; Salin and Vinh, 2023). These aquaculture maintenance technologies have tended to provide sustainable models based on minimal and zero water use. However, some of these water-saving technologies can be laborious and expensive, incur high electricity generation costs, and introduce pathogens (Zimmermann et al., 2023). In addition, chemotherapeutic options have limitations such as negative effects caused by the excessive use of chemicals, disinfectants, and antimicrobials, which also pose risks to humans, the aquatic environment, and the development of microbial resistance (Bondad-Reantaso et al., 2023).
Nonetheless, these alternative technologies have shown differential efficacy responses in growth performance, immune response, and nutritional value. In Zero Exchange Biofloc (BFT) technology, adult Nile cichlids were stored in high densities and experienced poor growth performance, disturbances in clinical biochemistry, and a reduction in crude protein in their carcasses. Furthermore, high levels of settleable solids (74 ml L-1) and nitrate (1.09 g L-1) and degenerative effects on the gill structure of all stocking densities were found (Manduca et al., 2020).
Therefore, environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative approaches to aquaculture disease and ecosystem control have recently received attention (Hossein et al., 2023). For example, functional nutrition, optimized feeds, and feeding regimes help promote fish health and resistance to infection. Also, enhanced immunity is largely regulated by immune stimulants such as algae and plant extracts, probiotics, prebiotics, yeast extracts, and micro-ingredients such as minerals and vitamins (Sharawy et al., 2020; Van Doan et al., 2020). Phytobiotics or herbal extracts are promising alternatives because they minimize chemotherapeutic risks and help maintain ecosystem balance (Dien et al., 2023; Rabelo-Ruiz et al., 2023).
The effectiveness of phytobiotics is related to their bioactive metabolites, which may act as immunostimulants, improve digestive system functionality, increase feed conversion efficiency, improve growth performance, and increase antioxidant activities (Gabriel et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2015; Yilmaz, 2019; and Abdul Kari et al., 2022). In addition, phytobiotics are considered inexpensive alternative immunostimulants that are biofriendly and biodegradable (Hoseinifar et al., 2020; Zakaria et al., 2022). Among the vital dietary herbs, lemon balm, Melissa officinalis L., is a therapeutic herb and an aromatic perennial plant; it commonly grows in the Mediterranean region and Western Asia and is intensively cultivated in Europe. It is a good source of antioxidants, antimicrobials, and rosmarinic acid, all of which have beneficial effects on fish survival rates, growth performance, and immune response (Ghiulai et al., 2020; Bilen et al., 2020; Jafarpour and Fard, 2016). Also, Origanum majorana (marjoram) is a tender perennial undershrub, is naturalized in Mediterranean regions, and is particularly found in the temperate regions of the Himalayas. Its leaves are known to contain antioxidant and antimicrobial compounds and high concentrations of phenolic compounds that improve fish growth, nutrition, and economic efficiency (El-Dakar et al., 2004; El-Kholy, 2012; Roby et al., 2013). Currently, Matricaria chamomilla (chamomile) is widely distributed all around the world. M. chamomilla is an annual herb that grows on all soil types and is resistant to cold. It is native to southern and eastern Europe, and northern and western Asia. Its flower supplements have been found to improve non-specific immune responses and increase fish growth rates (Abdelhadi et al., 2010; Zaki et al., 2012).
Edwardsiellosis is a dangerous bacterial infection that infects various aquatic habitats and causes economic losses worldwide (Oh et al., 2020; Haenen et al., 2023). The Edwardsiella genus includes E. tarda, E. ictaluri, E. hoshinae, E. piscicida, and E. anguillarum (Shao et al., 2015). Outbreaks of Edwardsiellosis have been ecologically correlated with highly stressful conditions in poor water quality (Davies et al., 2018).
Although phytobiotics are a new frontier in aquaculture, there is a fundamental need to achieve a clear and direct dose-dependent stimulatory effect on fish growth, immune status, and physiology. Furthermore, there is limited knowledge on the effectiveness of herbal-based phytobiotics for maintaining fish health under stressors such as reduced and/or absent water exchange and intensive aquaculture conditions. Therefore, the efficacy of Matricaria chamomilla flower extract (MCE), Melissa officinalis leaf extract (MOE), and Origanum majorana leaf extract (OME) as feed additives in tilapia feeds was assessed in stressful conditions with unchanged water. We also measured immunological response, growth performance, and histological indications. Additionally, using the same severe culture conditions, an experimental study was conducted to determine the antibacterial efficacy of herbal feed additives against the pathogenic bacteria E. tarda.
Materials and methods
Study location
Both the nutritional experiment and the bacterial challenge experiment were conducted at the Aquatic Nutrition Laboratory of the Aquatic Wealth Research Station, NIOF, in Shakshouk, National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries NIOF, Fayoum Governorate (Coordinates: 29° 28′ 20″ N, 30° 36′ 51″ E). The laboratory is equipped with cement ponds of different sizes coated with epoxy.
Management of rearing unit and basic water quality tests
Management practices were monitored to ensure proper pond health including aeration and filtration. The filtered water was stored in two large 10 m3 ponds for dechlorination before being used for water exchange. During the study period, the water was left untouched and water samples were taken regularly to assess the water quality. The water quality parameters were regularly recorded. Water temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen (DO) were measured in situ. Total ammonia (TA), nitrite (NO2), and nitrate (NO3) were measured by chemical methods (APHA, 2012) using a spectrophotometer (LKB Bichrom UV visible spectrophotometer). Unionized ammonia was calculated by a correlation coefficient between temperature and pH (Emerson et al., 1975).
Preparation and phytochemical analysis of dietary herbal extracts
One kg of each freshly harvested herbal plant, i.e., lemon balm, marjoram, and chamomile (M. officinalis, O. majorana, and M. chamomilla flowers), was purchased from the National Agriculture Research Center NARC, Egypt. In order to obtain ethanolic (alcoholic) extracts, herbal parts were washed, dried by air circulation at 40°C for 3 days, and finally ground using an electric grinder into powder. Then, 200 g of the resultant powders of each plant were separately added to ethanol alcohol 70% (1:10 w/v) and blended. The mixtures were left at room temperature for 72 h and then mixed again using a magnetic stirrer (150 rpm for 24 hours) and filtered through Whatman papers No. 1 (42 μm pore size) twice. To create a concentrated powdered extract, the mixtures were distilled in a rotary evaporator to allow the alcohol to entirely evaporate. The extracts were eventually kept in sterile, dark glass containers at -20°C until usage (Van Hai, 2015; Mohammadi et al., 2020).
Determination of total phenolic compounds
The concentrations of total phenolics in all extracts were measured using a UV spectrophotometer (Jenway-6405-UV/VIS) based on a colorimetric oxidation/reduction reaction. The used oxidizing reagent was the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (AOAC, 2010). To 0.5 mL of diluted extract, 2.5 ml of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (diluted 10 times with distilled water) and 2 ml of Na2CO3 (75 g/1L) were added (Škerget et al., 2005). The sample was incubated for 5 min at 50°C and then cooled. For a control sample, 0.5 mL of distilled water was used. The absorbance was measured at 763 nm. Total phenolic contents were expressed as the gallic acid equivalent (GAE). The GAE was calculated based on the calibration curve using the following linear equation: y = 0.0187x + 0.0786, R² = 0.998, where y is the absorbance, x is the concentration (mg GAE g−1 extract), and R2 is the correlation coefficient.
Determination of total flavonoids
Total flavonoid contents were determined using the method of Ordonez et al. (2006) with some modifications. A 3 mL aliquot of a 10 g L−1 aluminum chloride (AlCl3) ethanolic solution was added to 0.5 mL of extract. After 1 hour of incubation in the dark, the absorbance at 420 nm was measured at room temperature. A yellow color indicated the presence of flavonoids. Extract samples were evaluated at a final concentration of 1 mg/ml. Total flavonoid contents were expressed as the quercetin equivalent (QE). The QE was calculated based on the calibration curve using the following equation: y = 0.0148x - 0.0118, R² = 0.9996, where x is the absorbance, y is the concentration (µg QE), and R2 is the correlation coefficient.
Experimental fish, rearing conditions, and dietary supplemention
A total of 300 healthy Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with an average initial weight of 55.89 ± 1.06 g was obtained from a commercial farm in Shakshouk, Fayoum Governorate. The fish stock appeared to be healthy with no history of infectious diseases or rearing problems. It was then quickly transported to the laboratory and adapted for 2 weeks before experimental implementation. After fitting, the fish were distributed evenly over five treatments in 15 concrete ponds. All ponds were equipped with good aeration at a density of 20 fish/pond or 1.8kg/m3 (N=60 fish/group; pond size= 1 m3). The 1st group, T1 (negative control, NC), was fed the basal diet with 20% daily water changes. The 2nd group, T2 (positive control, PC), was fed the basal diet of completely unaltered water with 0% water change. The 3rd, 4th, and 5th groups were herbal-treated groups, named T3, T4, and T5, and received the basal diet supplemented with a 16.2 g MOE kg-1 diet (Haselmeyer et al., 2018), a 10 g OME kg-1 diet, and a 10g MCE kg-1diet (Van Hai, 2015) with 0% water changes per day, respectively.
Following NRC (National Research Council) (2011) recommendations, the basal fish diet was prepared to meet the optimal nutritional needs of tilapia (30% crude protein). The ingredients were ground and then combined mechanically using water (300 ml of water per kg of mixture for both the control and experimental diets). The mixtures were then pelleted using a 3 mm meat grinder, dried in an oven at 30°C, and stored at 4°C (Table 1). All fish groups were fed 3% of their biomass, adjusted weekly according to their average body weights. Fish were fed twice daily at 9:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m. for six consecutive days per week for 90 days.
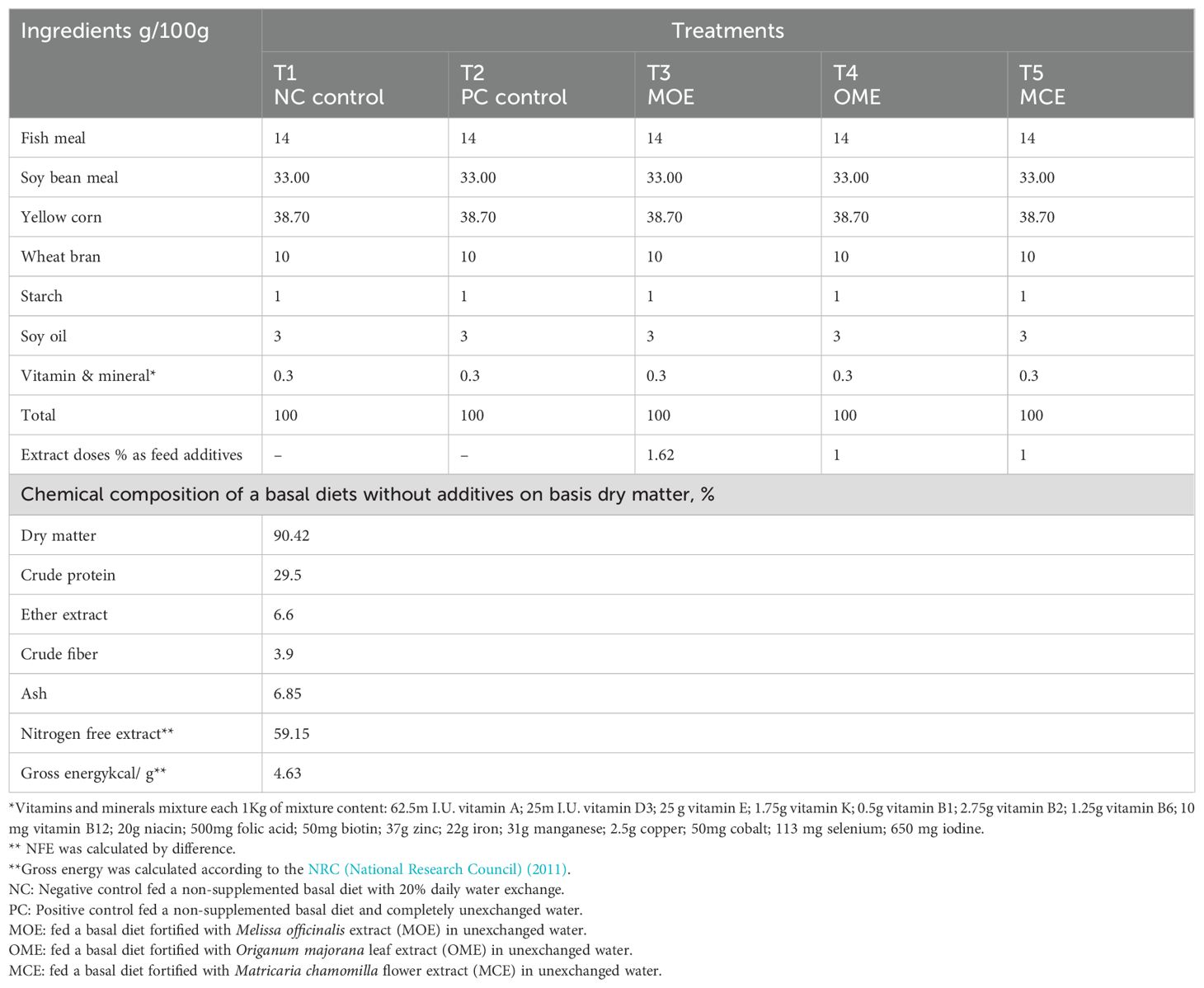
Table 1. Ingredients of the basal diet, plant extract feed additives, and a proximate chemical composition on a dry matter basis.
Fish behavior, clinical signs, and growth performance
A daily surveillance program was conducted during the trial period, which included behavioral and clinical signs, morbidity and mortality rates, and postmortem lesions (Noga, 2010). Growth performance was calculated based on the obtained feeding patterns in terms of fish number, weight, length, and food consumed throughout the experimental period according to prescribed equations (Yarmohammadi et al., 2012).
Measurements and calculations
where W1 is the initial weight, W2 is the final weight, g denotes grams, ln is the natural log, t is the time in days, and L2 is the final fish length in cm.
Chemical composition of fish carcass
Replicates of five fish selected at random from each group were removed, autoclaved, and homogenized to assume a slurry form, then dried in an oven and reground. The moisture, crude protein, crude lipid, and ash of the whole fish body were determined according to standard methods of the Analysis of Association of Official Analytical Chemists[AOAC (2010)]. The values were reported on a dry matter basis.
Hematological and immune assays
Three fish were randomly selected per replicate (nine fish per group) and anesthetized with MS-222 (0.1 g L-1 tricaine methanesulfonate; Sigma-Aldrich). A blood sample was taken from the caudal vessel for hematological examination. A portion of the sample was placed in a microtube containing EDTA potassium salt. The other part of the sample was placed in a tube without anticoagulant and then centrifuged at 3,000 g for 5 min; this served as a serum sample which was stored at 20°C for serum separation and then used in biochemical and immunological assays. Blood smear, erythrocyte, and total leukocyte counts were established for differential leukocyte counts using the method of Blaxhall and Daisley (1973). In addition, the hemoglobin concentration was measured using the cyanmethemoglobin method (Dorafshan et al., 2008). Total protein, albumin, glucose (RBs), creatinine, urea, uric acid, and transferase [aspartate aminotransferase (ALT) and alanine aminotransferase (AST)] activities in serum were analyzed photometrically using specific kits from Spectrum Diagnostics, Egyptian Company for Biotechnology, Egypt. Serum catalase (Chelikani et al., 2004), glutathione, immunoglobulin M, interleukin 10 (IL-10) (Li et al., 2012), interleukin 6 (IL-6) (Hirano, 1998), interleukin 1/interleukin 1F2 (IL-1/IL-1F2), superoxide dismutase, lysozyme/muramidase (Ellis, 1990), and malondialdehyde (MDA) (Farmer and Davoine, 2007) were measured using ELISA kits available from Biosource Inc. (San Diego, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. In addition, complement C3 was quantitatively determined using turbidimetry.
Histopathological evaluation
At the end of the experiment, 10 fish per group were randomly selected, and euthanized by decapitation, and representative tissue samples were collected from the gills, liver, and kidneys following standardized autopsy procedures. The collected samples were immediately fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution for 48 h, dehydrated in a series of graded ethyl alcohol (70%, 80%, 90%, and 100%, 1 hour each), clarified in two changes of xylene (1 hour each), impregnated and embedded in paraffin wax, microtomed in 5 m sections, stained with hematoxylin and eosin according to standard methods (Suvarna et al., 2018), examined microscopically, and any histological changes that occurred were recorded.
Multiparametric quantitative scoring for the recorded histopathological changes in the gill, liver, and kidney tissues was performed according to the protocol proposed by (Bernet et al., 1999). In summary, the recorded histopathological changes in the three organs were categorized into five reaction patterns depending on the type of change: regressive, progressive, circulatory, inflammatory, or neoplastic (each pattern has a set of associated changes).
Challenge test: assessment of the antibacterial activity of the herbal supplements against bacterial infection in unchanged water conditions
This experiment was complementary to the first experiment and was performed sequentially on the remaining fish within the same fish groups of the 1st experiment. It was the second experimental evaluator of the efficacy of herbal-treated fish to resist bacterial infection by inoculation of a pure culture of E. tarda isolated from O. niloticus. We obtained an E. tarda strain (sodB accession- ON186569) from the Department of Hydrobiology, Veterinary Research Institute, National Research Centre, 12622, Dokki, Cairo, Egypt. They isolated the pathogenic strain from a natural outbreak of infected Nile tilapia (O. niloticus). A pure culture of the obtained E. tarda isolated from O. nilotis was boosted by culturing on salmonella-shigella agar (SS agar) plates and incubated at 30°C for 24-48 h. To prepare the inoculum, three pure colonies were collected and inoculated into the broth at 30°C for 24-48 h, broth cultures of the bacteria were centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 30 min, after which the bacterial cells were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.9% NaCl and adjusted to a final concentration of 3 × 108 CFU (Amandi et al., 1982).
LD50 and pathogenicity test
A total of 270 O. niloticus fish (63 ± 4g) with no history of infectious diseases were obtained from a different source than the experimental fish (the farm of Aquatic Wealth Research Station, NIOF, in Shakshouk, National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries NIOF). They were then acclimated for 2 weeks in a fiberglassed pond (3000 L) which was filled with declorinated fresh water and connected to aeration and filtration systems. Post-acclimation, the fish were distributed equally into nine triplicated groups (groups 1-9, each with 30 fish). Prior to the injection, the fish were gently caught in the ponds and bathed in anesthetics (50 ppm clove oil) for 2–3 min. For the median lethal dose (LD50), the fish from eight groups were injected intraperitoneally (I/P) with 0.1 ml of the corresponding serial dilution (3x101-3x108 CFU/ml/fish). The control fish in group 9 were injected with 0.1 mL of sterile saline solution PBS. The LD50 assay at which 50% mortality occured was 3× 106CFU.
Based upon the LD50, the second experiment, a pathogenicity test, was conducted. The T2 (positive control) and herbal-treated groups, i.e., T3 (MOE), T4 (OME), and T5 (MCE), were injected I/P with 0.1 mL of a 3 × 106 CFU ml-1 E. tarda bacterial suspension. The T1 group (negative control) was injected with sterile TSB. The cumulative morbidities and mortalities of the fish were recorded 2 weeks post-challenge. In addition, dead fish were collected and examined to verify the cause of death. Mortalities were accounted for when isolating E. tarda in sterile broth to meet Koch’s postulates. The relative percentage survival (RPS) index is the survival rate of fish after vaccination when compared with control fish and is calculated according the following equation:
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) at a 95% confidence limit using SPSS (2007) software. Duncan’s multiple range test was used to compare means when the F values from the ANOVA were significant (P ≤ 0.05).
Results
Total flavonoids and phenolic compounds in the tested extracts
The phytochemical analysis of the extracted samples revealed significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) in the total flavonoids and phenolic compounds among them. The highest levels of total flavonoids and phenolic compounds were found in the marjoram leaf extract, followed by chamomile flowers and lemon balm leaves (Table 2).
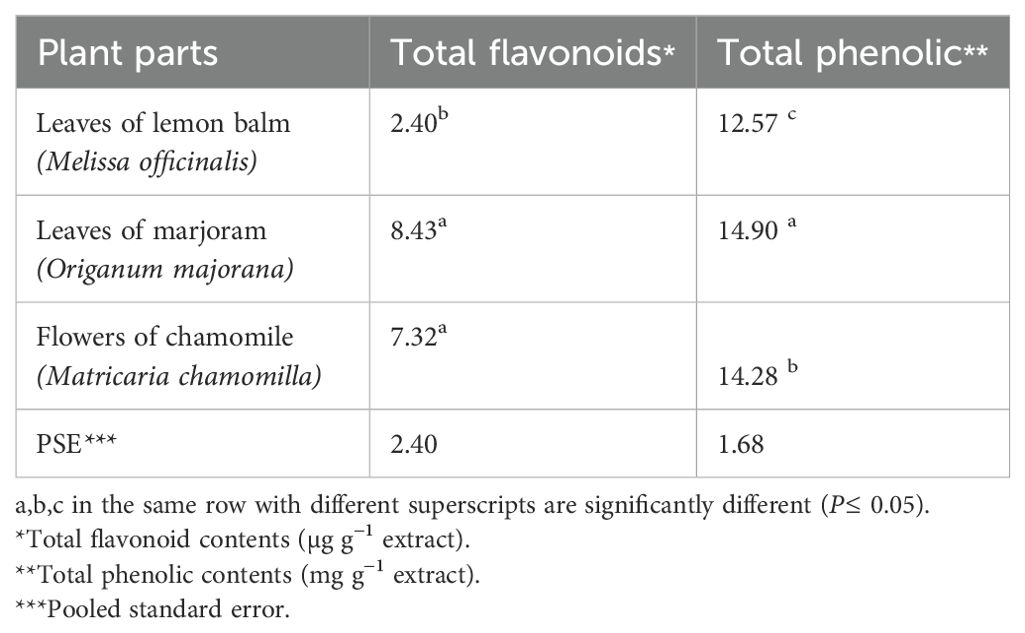
Table 2. Analysis of total flavonoids and total phenolic content of the experimental herbal extracts.
Basic water analysis
The water parameters of the NC group showed the most significant values (P≤ 0.05) compared to the PC group and the MOE-, OME-, and MCE-treated groups. The water parameters of the NC group remained within the safe ranges until the end of the trial. In contrast, the water parameters of the herbal-treated groups and the PC group cultured in unexchanged water conditions showed gradual deterioration but were within the allowable limits by the 2nd month. In the constant, unexchanged water conditions, the water parameters of the PC control and the herbal-treated group showed increasingly significant deterioration compared to the NC control. In the third month, the lowest oxygen levels and the highest levels of ammonia, non-ionized ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the PC control, MOE, OME, and MCE groups compared to NC group were recorded (Table 3).
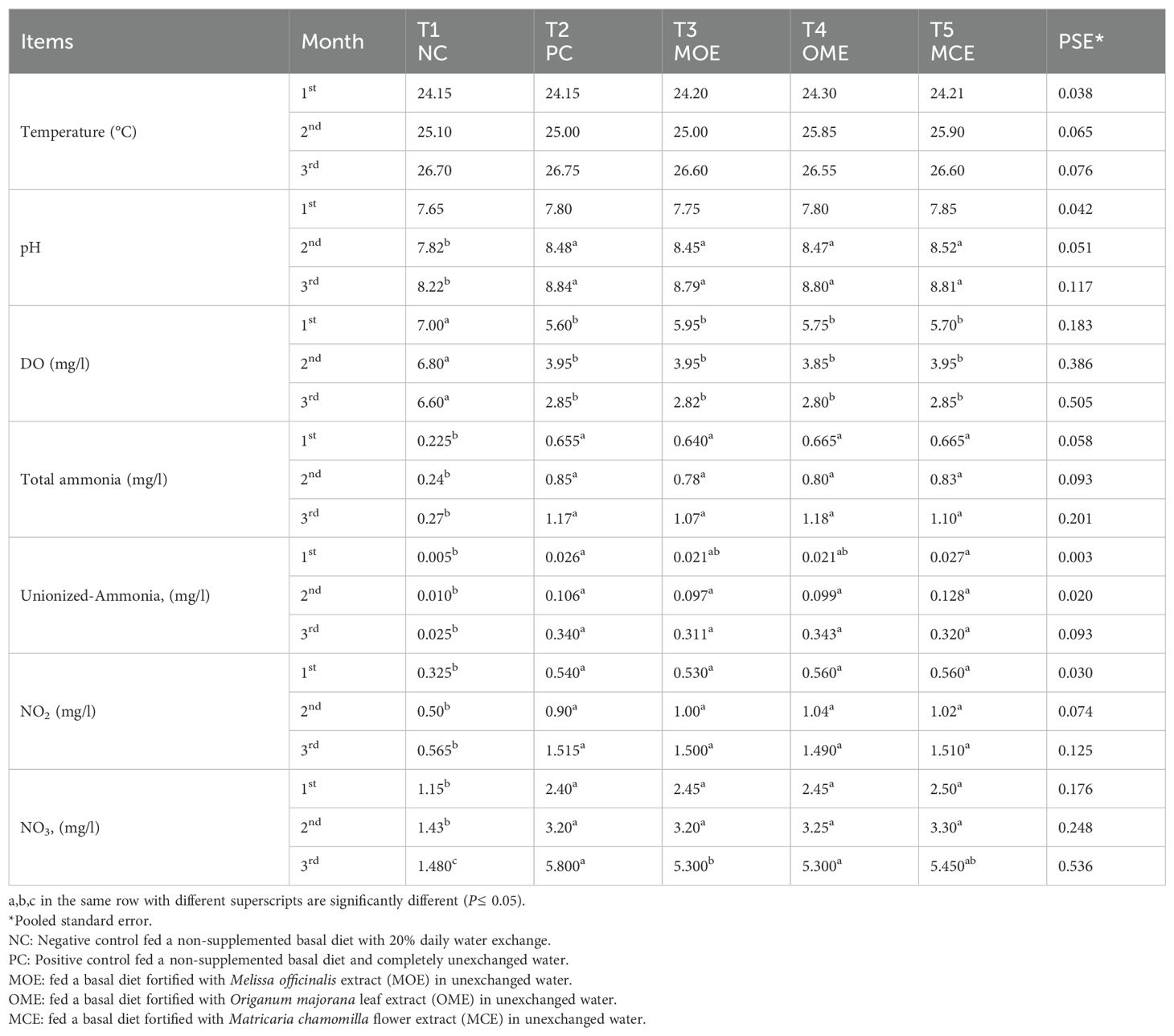
Table 3. Water parameter means of herbal-treated Nile tilapia in unexchanged water during the first, second, and third months.
Clinical signs and survival rate
The NC group appeared healthy by the end of the experiment, with a good appetite and without any behavioral or clinical symptoms. For the other groups of fish that were cultured in unexchanged water conditions, the OME- and MCE-treated groups and the PC control demonstrated good behaviors and clinical condition up to month 2. However, by month 3, the fish in both the herbal treatment groups and the PC group had darker skin, lethargy, and decreased appetite. Later, the recorded survival rates were 100% in the NC group, 47% in the PC group, 100% in the MOE group, 100% in the OME group, and 57% in the MCE-treated group.
Growth performance indexes
After 90 days of supplementation, the herbal-treated MOE, OME, and MCE groups achieved an overall significant (P ≤ 0.05) improvement in growth parameters compared to the PC group. The best weight gain (WG) values were recorded in the OME-treated group compared to the MOE- and MCE-treated groups. However, the NC group had a significantly higher WG than the herbal-treated groups (Table 4). Figures 1–3 show that specific growth rate (SGR), average daily gain (ADG), and feed conversion ratio (FCR) showed no significant variation between the NC group and the herbal-treated groups after 30 days. After 45 days, the herbal-treated OME group did not significantly differ from the NC group in SGR, ADG, and FCR, and these groups were followed by the herbal-treated MOE and MCE groups, respectively. The PC group had the worst of all growth indicators during the experimental stages. In addition, condition factor (CF), hepatosomatic index (his), and viscerosomatic (VSI) were reported in the herbal-treated groups, particularly in the OME-treated group after 90 days (Table 4).
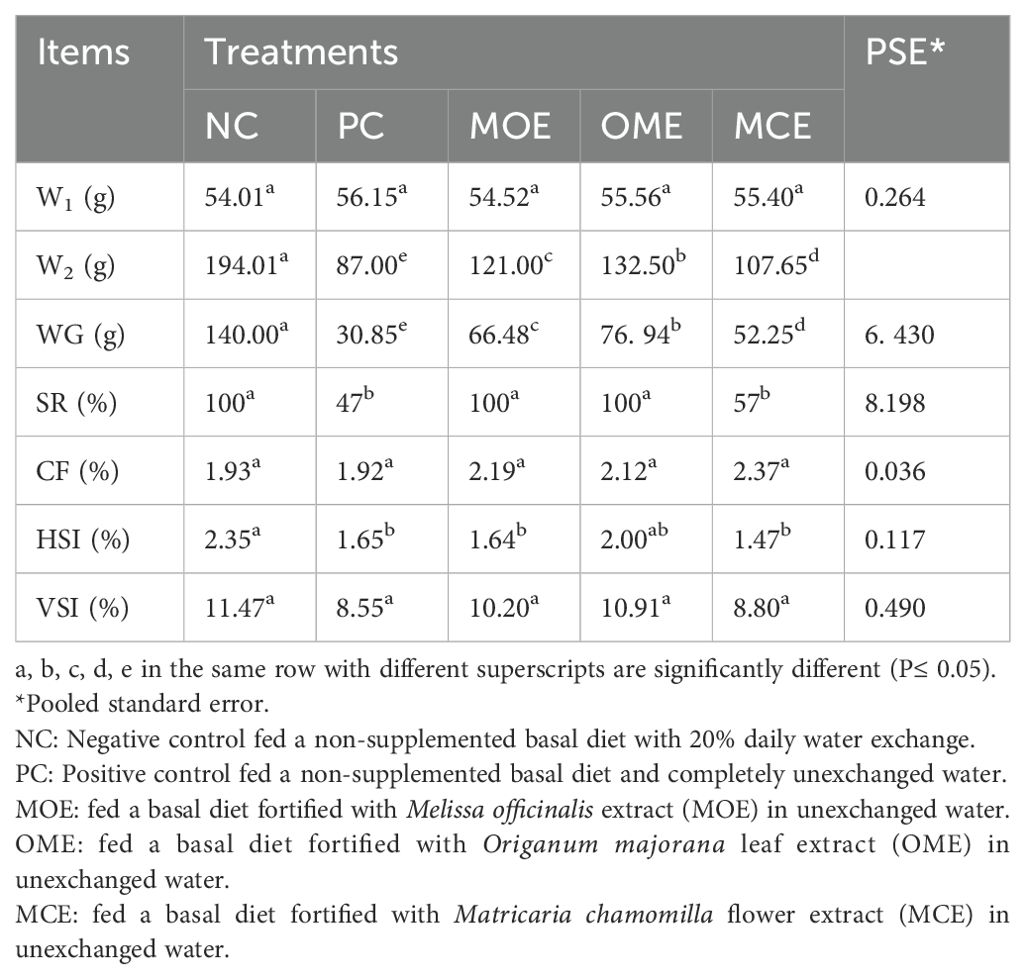
Table 4. Growth performance indexes after 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water.
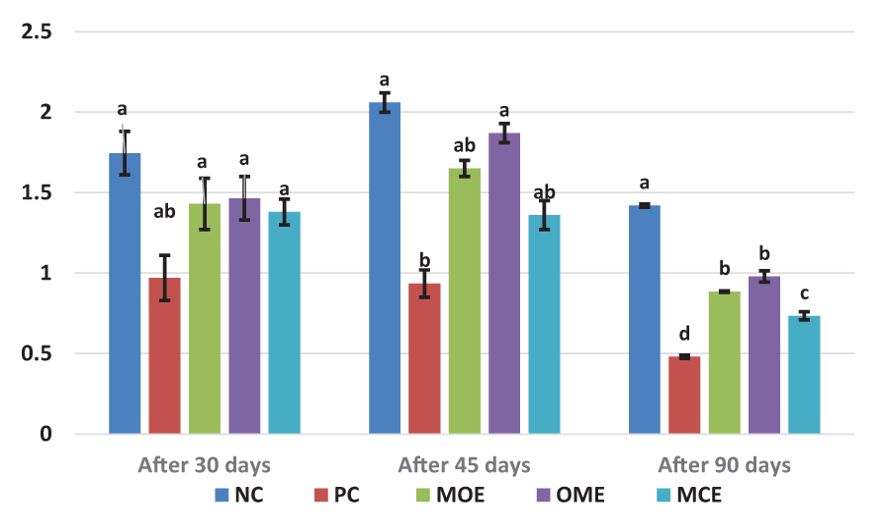
Figure 1. Specific growth rate (SGR, %/day) after 30, 45, and 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water. Specific growth rate SGR (%) = [(ln final body weight-ln initial body weight)/day] × 100. a, b, c, d in the same culomn color with different superscripts are significantly different (P≤0.05).
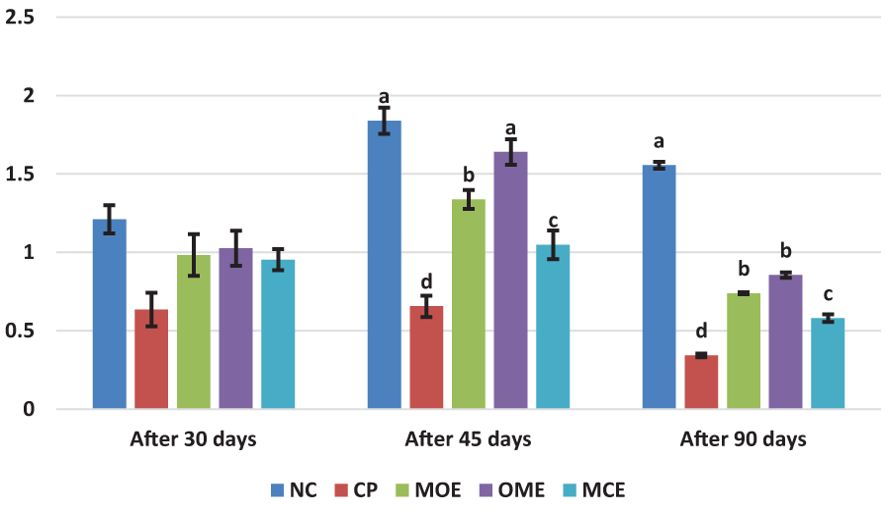
Figure 2. Average daily gain (ADG, g) after 30, 45, and 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water. Average Daily Gain ADG (g/day) = average weight gain (g)/experimental period (day). a, b, c, d in the same culomn color with different superscripts are significantly different (P≤0.05).
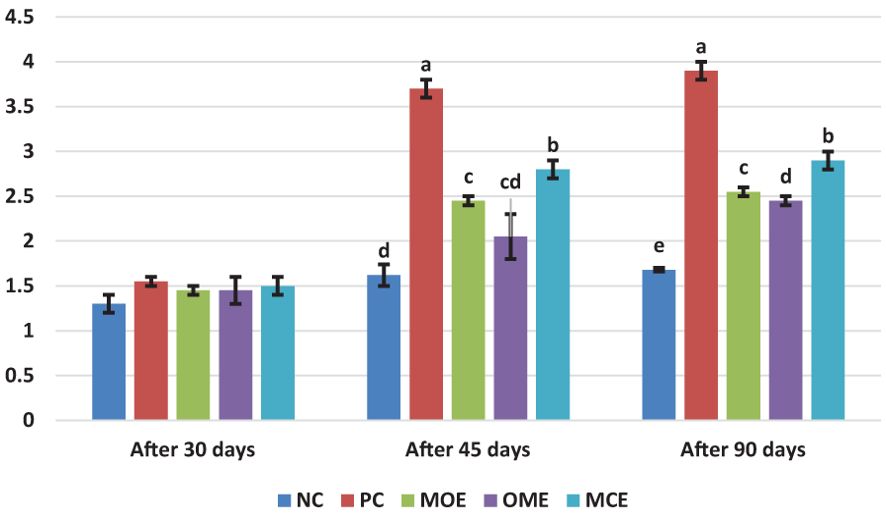
Figure 3. Feed conversion ratio (FCR) after, 30 45, and 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water. Feed Conversation ratio FCR = Feed intake (g)/Weight gain (g). a, b, c, d in the same culomn color with different superscripts are significantly different (P≤0.05).
Hematological and immune assays
The herbal-treated groups showed significant (P ≤ 0.05) activity in the blood hematological, biochemical, and immunological assays compared to the untreated controls. Significantly (P ≤ 0.05) higher levels of white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), and hemoglobin (HGB) concentrations were achieved, particularly in the OME and MOE-treated groups. Conversely, lower hemocrit test (HCT), mean corpuscular Volume (MVC), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) levels were observed in the herbal-treated groups (Table 5). Serum biochemical indices recorded significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) between the herbal-treated and control groups. The herbal-treated groups had significantly (P ≤ 0.05) lower levels of creatinine, urea, ALT, and AST, and higher levels of albumin and total protein compared to the PC group (Table 5). In addition, the herbal-treated groups showed obvious activity in the immunoassays. In particular, the group treated with MOE had the highest nitric oxide, glutathione, lysozyme, catalase, superoxide dismutase, and IL-10 activity. Also, higher levels of immunoglobulin M, complement C, malondialdehyde, IL-1, and IL-6 were recorded in the OME- and MCE-treated groups compared to the PC group (Table 6).
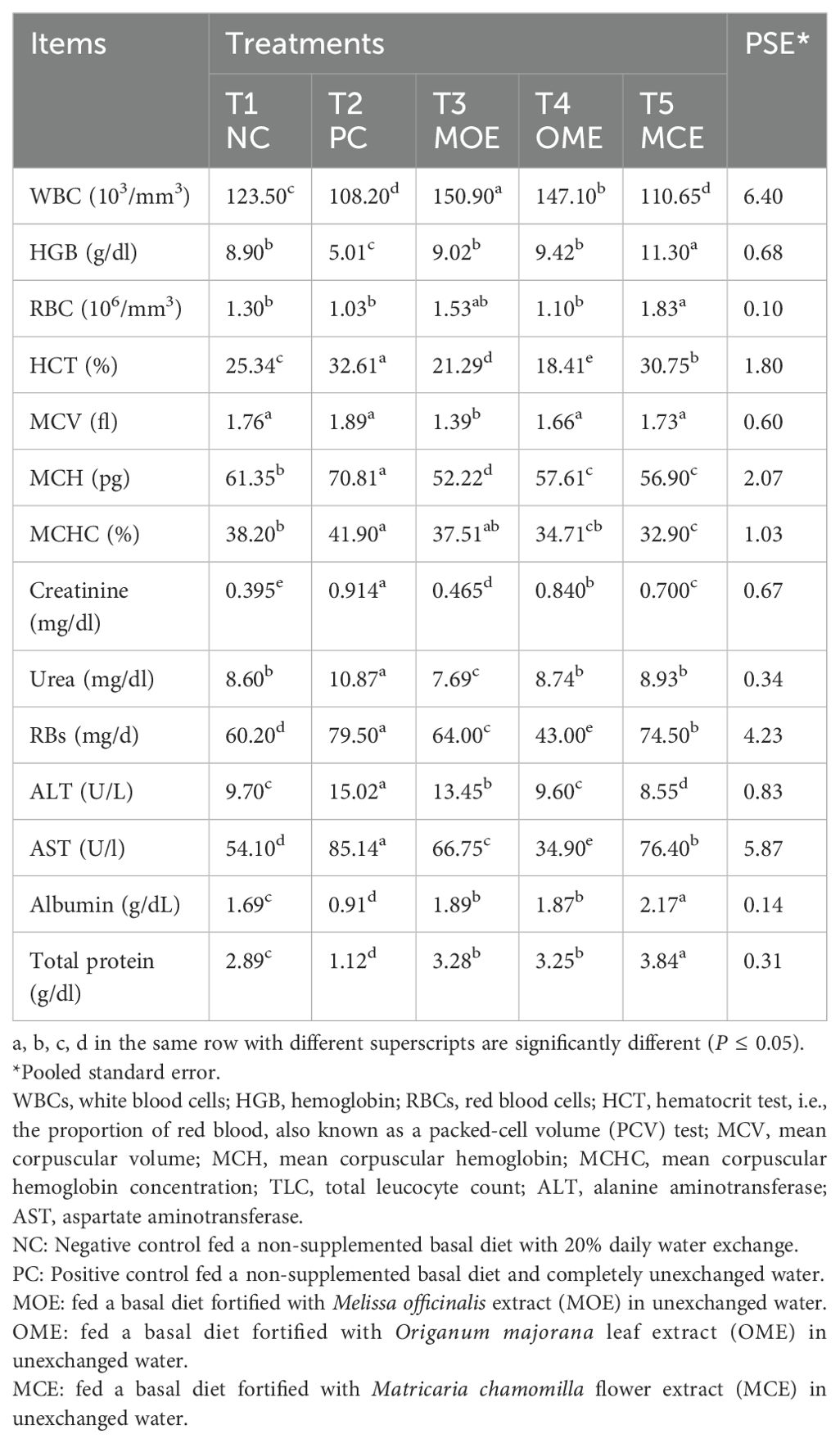
Table 5. Hematological parameters and serum biochemical assays after 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water.
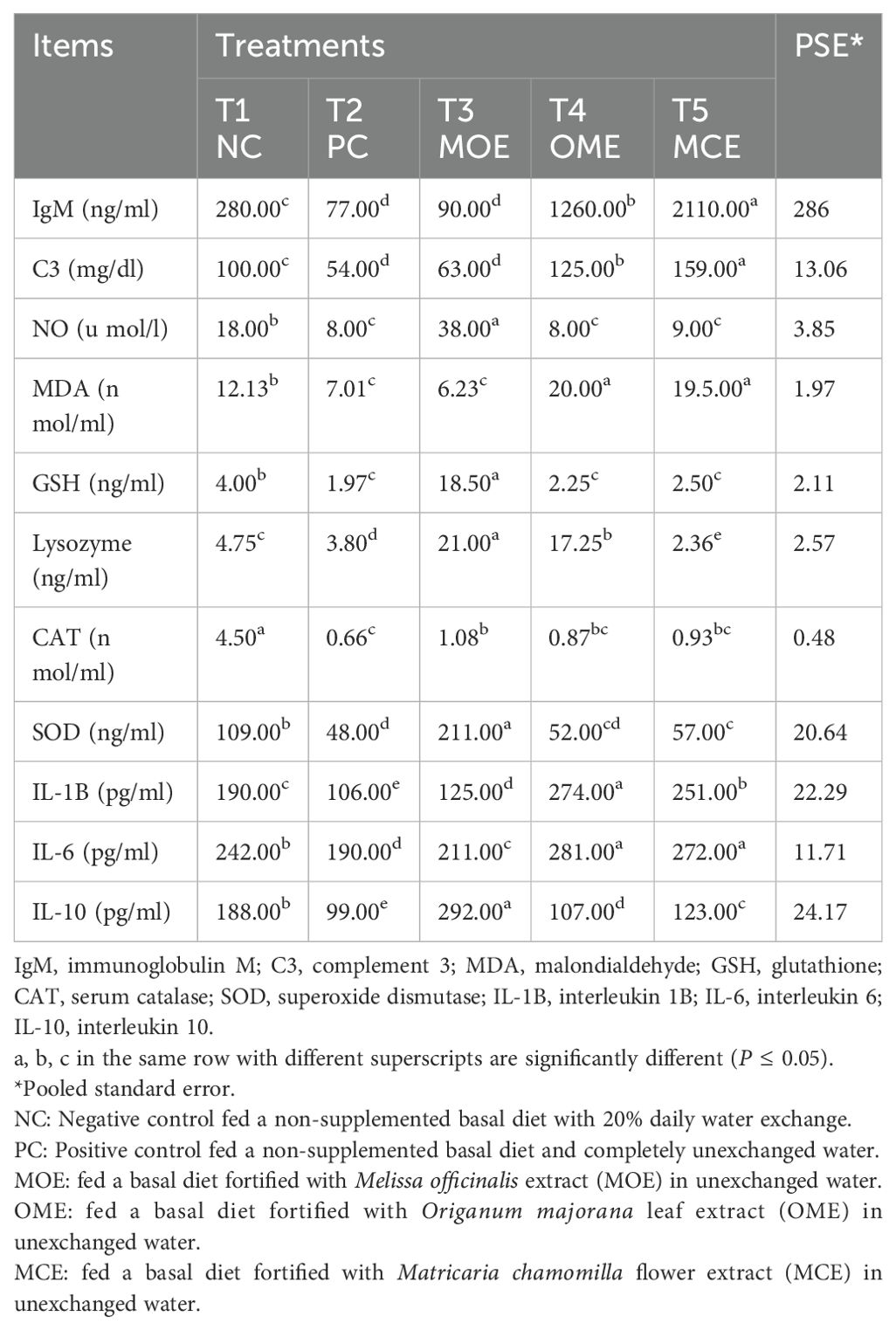
Table 6. Immunological assays after 90 days of herbal supplements in Nile tilapia cultured in unexchanged water.
Chemical analysis of fish carcass
The immediate chemical analysis of fish carcasses in the MOE-, OME-, and MCE-treated groups showed significantly (P ≤ 0.05) lower dry matter, fat, and ash content than that of the untreated control groups. Meanwhile, higher levels of crude protein were obtained in the herbal-treated groups compared to the non-treated control groups (Table 7).
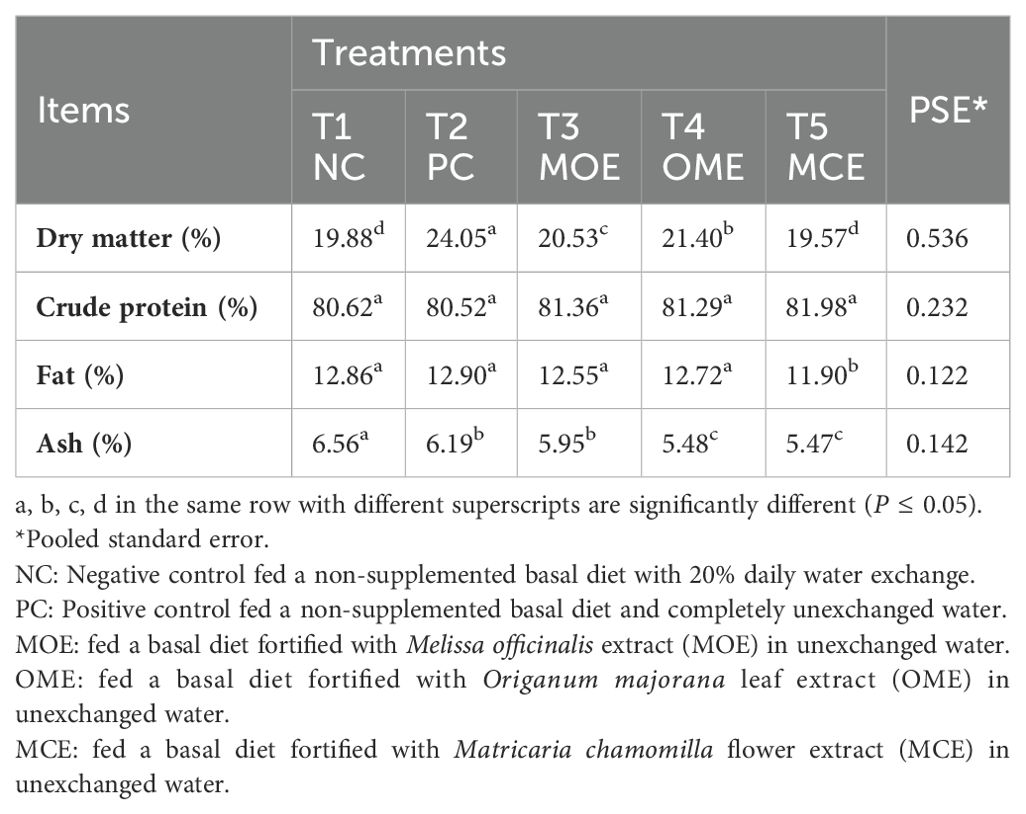
Table 7. Chemical composition of Nile tilapia fish carcasses on a dry matter basis after 90 days of herbal supplements and being cultured in unexchanged water.
Histopathological features
Gills
The gills of the NC control fish appeared bright red and shiny with no gross lesions (Figure 4A).The effect of non-exchanged water stress conditions was evident on the gill histology of the PC control, showing a variety of regressive, progressive, inflammatory, and circulatory changes as in Figures 4B, C. Concomitant supplementation with herbal extracts failed to maintain normal gill histology in all groups, but average recovery effects were observed in OME-treated fish, followed by mild recovery effects in MOE-treated fish, followed by weak beneficial effects in MCE-treated fish (Figures 4D-I).
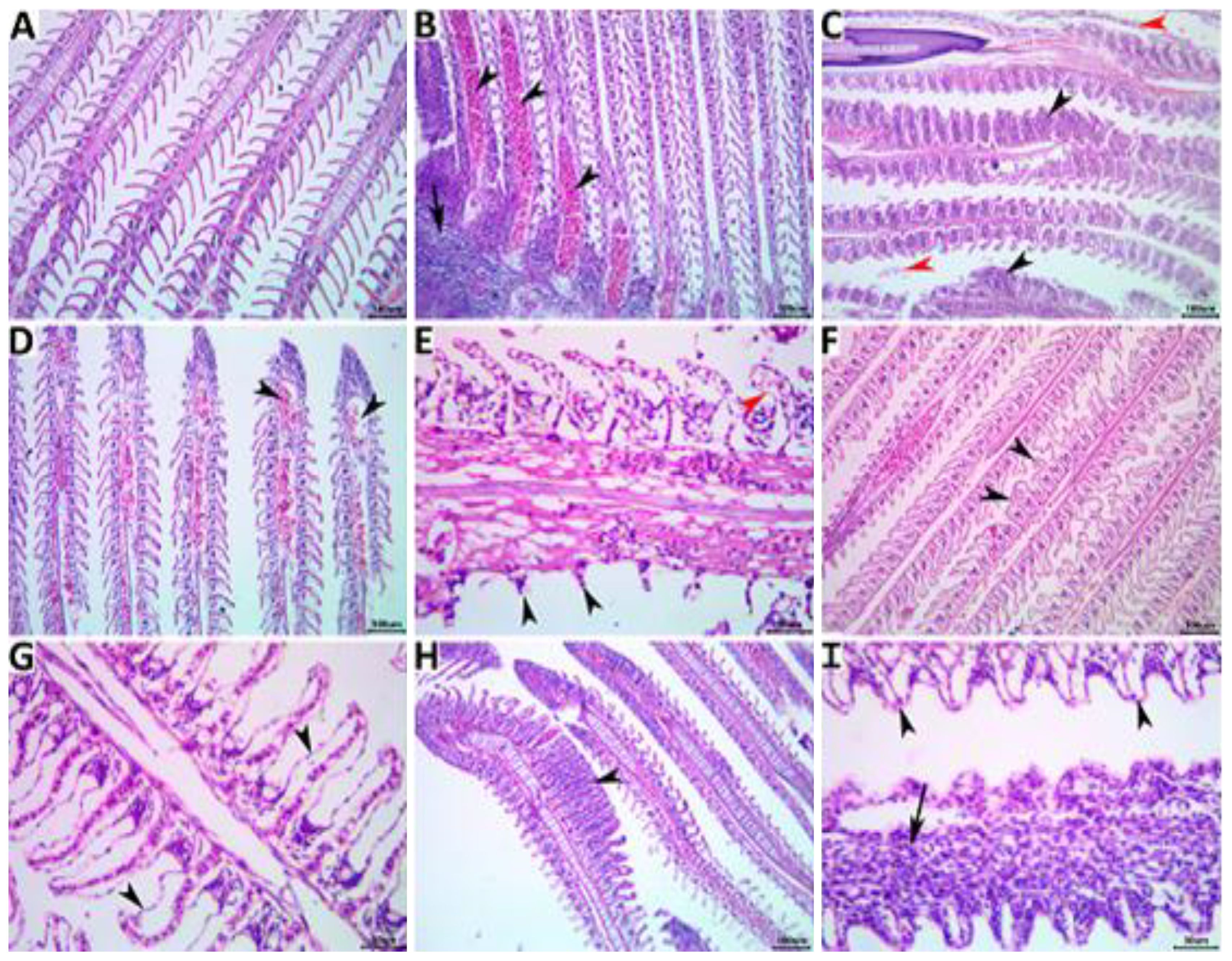
Figure 4. Representative photomicrograph of H&E-stained branchial tissue sections showing a normal histological picture in a fish from the NC group control (A). A PC fish showing notable congestions (arrowheads), inflammatory mononuclear cell infiltrate (arrow) (B), hyperplastic respiratory epithelium with the fusion of the secondary lamellae (black arrowheads), and desquamated lamellar epithelium (red arrowheads) (C). An MOE-treated fish showing aneurysm (arrowheads) (D), necrosis and sloughing of the secondary lamellae (black arrowheads), and epithelial lifting (red arrowhead) (E). An OME-treated fish showing disorganized secondary lamellae (arrowheads) (F) and epithelial lifting (arrowheads) (G). An MCE-treated fish showing focal hyperplasia of the respiratory epithelium with lamellar fusion (arrowhead) (H), and epithelial lifting (arrowheads), and mononuclear cell infiltrations of the primary lamella (arrow) (I).
Kidneys
The kidneys of the fish in the NC group showed normal histological structures (Figure 5A), while those of the PC group showed notable nephropathic regressive, progressive, inflammatory, and circulatory changes affecting the glomeruli, tubules, and interstitial tissue, as shown in Figures 5B, C. The ameliorating effects of concomitant herbal supplementation were significant with dietary OME (Figures 5D, E) and on average with both MOE (Figures 5F, G) and MCE (Figures 5H, I).
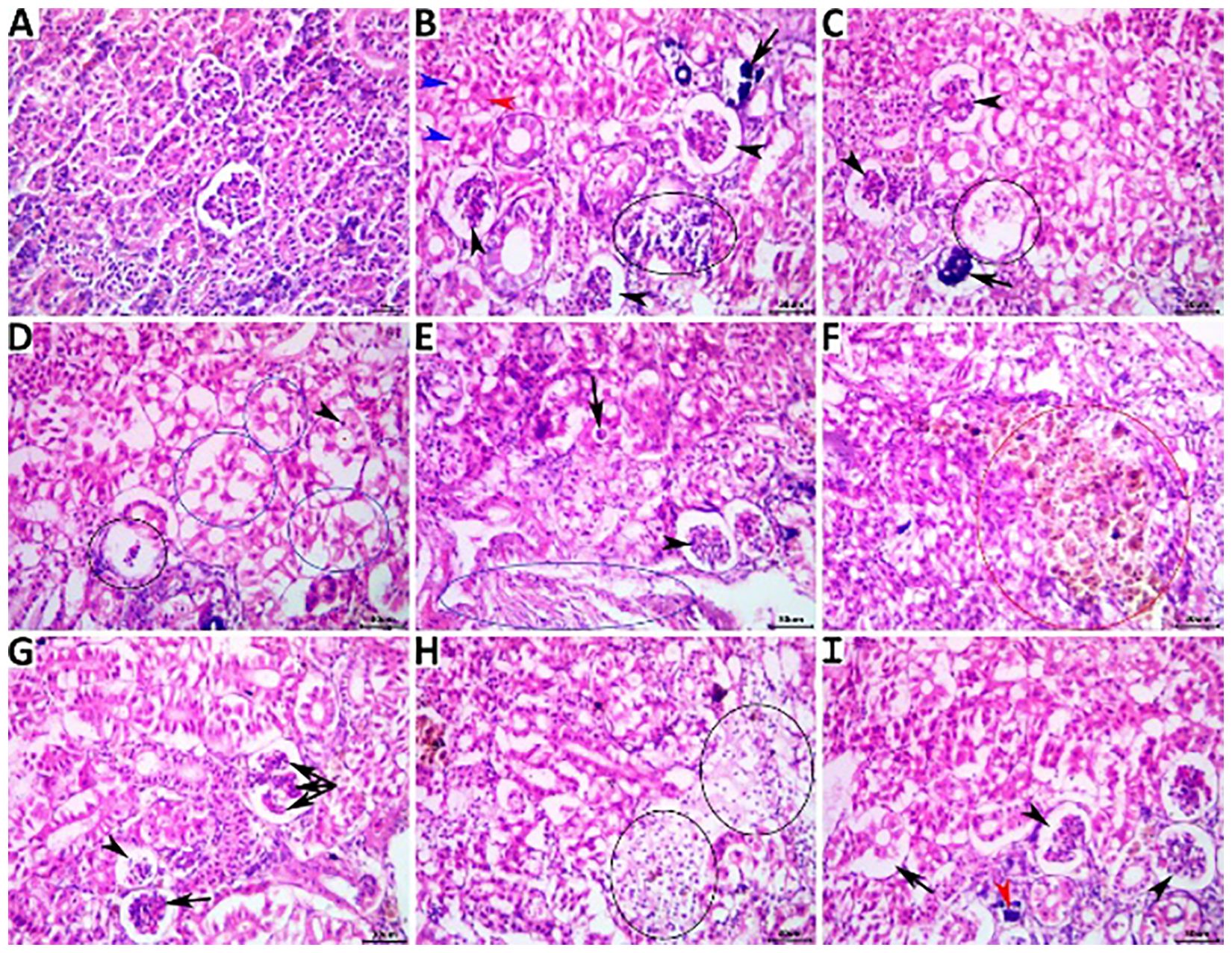
Figure 5. Representative photomicrograph of H&E-stained renal tissue sections showing a normal histological picture in a fish from the NC group (A). A PC fish showing collapsed glomeruli (black arrowheads), tubular vacuolation (blue arrowheads), single-cell necrosis (black arrowhead), tubular necrosis (arrow) (B), collapsed glomeruli (arrowheads), necrotic glomerulus (ellipse), and calcified glomerulus (arrow) (C). An MOE-treated fish showing necrotic glomerulus (black ellipse), pyknotic (arrowhead) vacuolated, and necrotic tubules (blue ellipses), (D), collapsed glomerulus (arrowhead), tubular cast (arrow), and interstitial fibroblastic proliferation (blue ellipse) (E). An OME-treated fish showing hyperplastic melanomacrophage aggregate (red ellipse) (F), atrophied glomerulus (arrowhead), collapsed glomerulus (arrow), and accentuated glomerular lobulation (Triple-head arrow) (G). An MCE-treated fish showing focal interstitial edema infiltrated with numerous erythrocytes (ellipses) (H), collapsed glomeruli (arrowheads), tubular vacuolation (black arrow), and minute calcification (red arrowhead) (I).
Liver
The livers of the fish in the NC group showed normal histological features in their hepatopancreases, as shown in Figure 6A. The sections of liver tissue from the fish in the PC group showed a wide spectrum of histological changes, as shown in Figures 6B, C. Concomitant herbal extracts demonstrated differential restorative effects on liver histology, with notable, moderate, and minor reductions in the severity and frequency of non-exchanged water stress-associated lesions in the fish treated with OME (Figures 6D, E), MOE (Figures 6F, G), and MCE (Figures 6H, I).
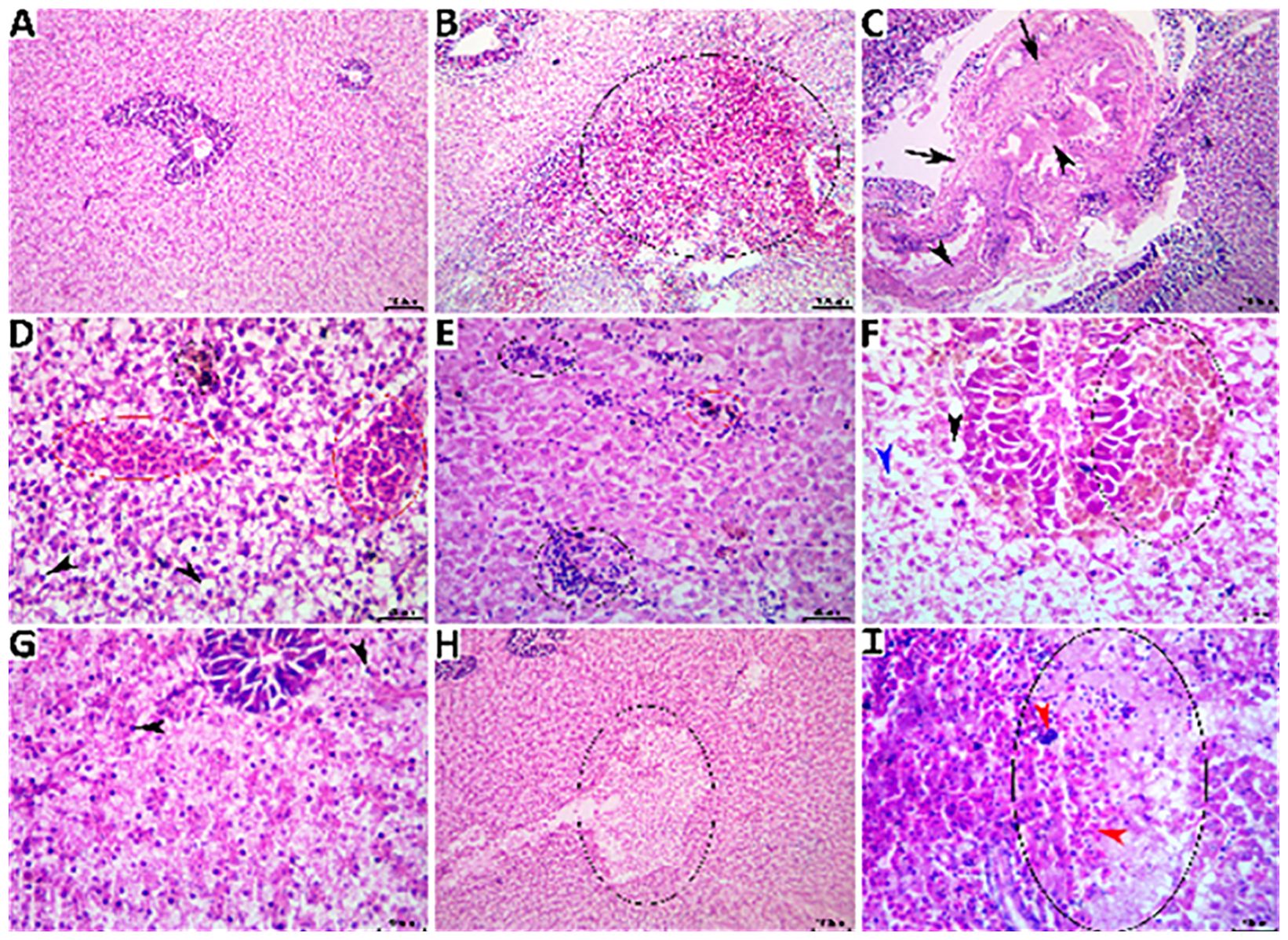
Figure 6. Representative photomicrograph of H&E-stained hepatic tissue sections showing a normal histological picture in a fish from the NC group (A). A PC fish showing notable hemorrhage (black ellipse0 (B), portal fibrous tissue proliferation (black arrows) and cholestasis (black arrowheads) (C). An MOE-treated fish showing vascular congestion (red ellipses), melanomacrophage aggregate (black ellipse), and numerous vacuolated hepatocytes (black arrowheads) (D), multifocal mononuclear inflammatory cell aggregations (black ellipses) and melanomacrophage aggregate (red ellipse) (E). An OME-treated fish showing hyperplastic melanomacrophage aggregates (black ellipse), vacuolated hepatocyte (black arrowhead), single-cell necrosis (blue arrowhead) (F), and almost normal hepatic tissue except for few pyknotic hepatocytes (black arrowheads) (G). An MCE-treated fish showing vacuolation focus (black ellipse) (H) and a necrotic area (black ellipse) infiltrated with mononuclear cells (blue arrowhead) and extravasated erythrocytes (red arrowheads) (I).
Challenge test: assessment of the antibacterial activity of herbal supplements against bacterial infection under unexchanged water conditions
Neither mortality nor morbidity was recorded in the saline-injected control group whereas the E. tarda-infected control group had a mortality of 80%. Conversely, for the herbal-challenged groups, the MOE-, OME-, and CME-treated groups showed lower cumulative mortality rates of 23.3%, 20%, and 43.3%, respectively, under no water exchange conditions, compared to the control, as shown in Figure 7. Furthermore, the RPS was 100%, 0%, 75.87%, 70%, and 45.87% for the NC, PC, MOE, OME, and CME groups, respectively.
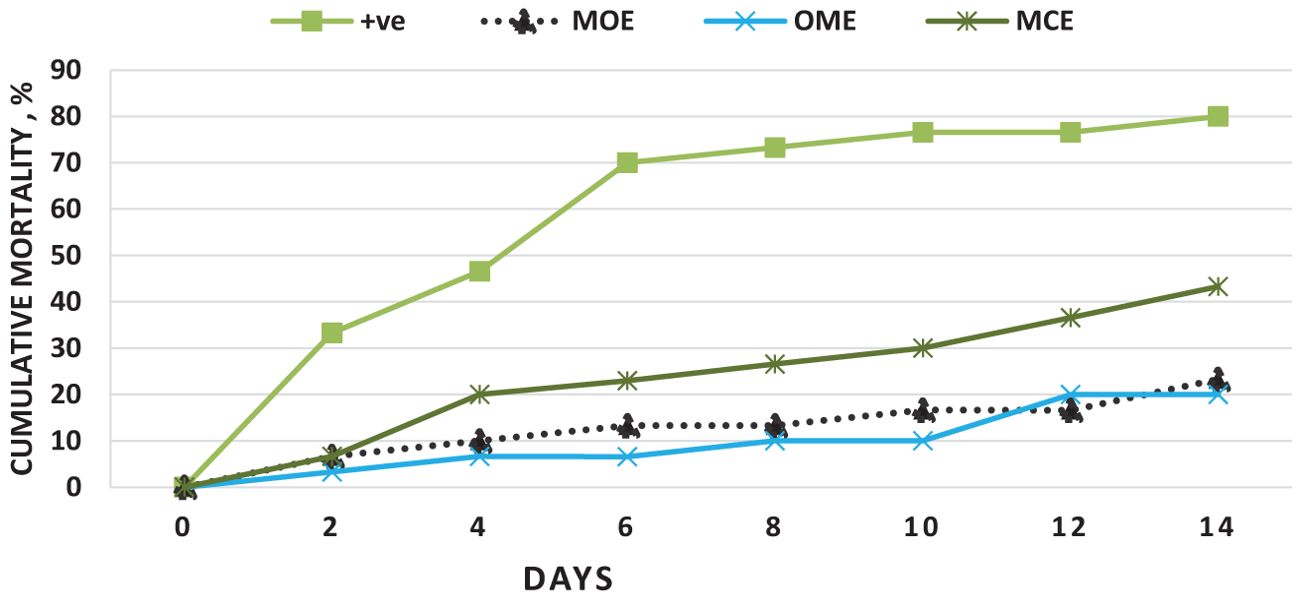
Figure 7. Cumulative mortality over 14 days after challenging O. niloticus with E. tarda in the herbal-treated and the postive control groups.
Discussion
Stimulating a non-specific immune system is a wise choice to enhance immunity and the growth performance of cultivated species. Therefore, ongoing research is consistently dependent on novel beneficial immunomodulating functional ingredients such as probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and herbal-based phytobiotics (Vallejos-Vidal et al., 2016). The use of phytobiotics or herbal extracts to increase growth and health status is becoming a major focus in fish nutrition (Venkatramalingam et al., 2007). Herbal phytobiotics have been reported to favor various activities such as anti-pathogenic properties, immune stimulation, anti-stress, growth promotion, and appetite stimulation. The herbal extracts have active ingredients such as flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenoids, tannins, saponins, phenols, steroids, or essential oils and also reduce treatment costs (Citarasu, 2010). However, little is yet known about the tolerability and immunomodulatory and antibacterial potential of herbal-based phytobiotic supplementation, particularly under stressors of long periods of unexchanged water and high stocking densities.
O. niloticus’s tolerance to the unreplaced water conditions was assessed over the course of a 90-day feeding study using growth rates, survival rates, immunological response, and water quality measures. The water parameters of the OME- and CME-treated groups and for the PC control and MOE-treated group differed from the NC group in progressively significant ways.
Temperature is a vital abiotic factor affecting the metabolism of obligate poikilothermic organisms and there is an optimal range for growth and/or other physiological functions. Furthermore, it has a significant impact on oxygen solubility (Noga, 2010). Our results showed that temperature during the three months of the study was within the acceptable range for tilapia growth (Azaza et al., 2008; Ngugi et al., 2007).
There was a gradual increase in average pH of 7.7, 8.55, and 8.81 at months 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Fish species differ in their optimum pH requirements. A pH range of 6.5 - 9.0 is generally recommended for freshwater fish (Swingle, 1969). This range is generally considered satisfactory for salmonids and channel catfish, and most other edible freshwater fish. However, the optimal pH ranges of freshwater fish have also been shown to be 7.5-8.5 (Boyd, 1998).
Oxygen is a vital indicator of water quality and is a critical factor in achieving fish’s full potential for growth and activity, as well as their overall well-being through behavioral and/or metabolic adaptations (Zhang et al., 2009; Noga, 2010). During the first month of this experiment, the average DO (5.75 mg L-1) was within the acceptable range and the optimal range for tilapia growth. Then, during the 2nd and 3rd months, it began to gradually decrease to 3.39 mg L-1 and 2.83 mg L-1, respectively. Below this level, decreased feed intake reduced growth performance, decreased immune response, and increased fish mortality (Riche and Garling, 2003). Although certain fish species are better adapted to coping with hypoxic encounters, this long-term suboptimal dissolved oxygen level in the culture system could lead to chronic environmental hypoxia, causing immunosuppression, predispose fish to opportunistic infections, and kill fish (Taylor et al., 2010; Obirikorang et al., 2020). In addition, long-term exposure of the fish to constant, unexchanged water conditions could result in lethal nitrogen enrichment and the dangerous occurrence of lethal hypoxia, ammonia, and nitrate toxicity.
Ammonia is the end product of protein breakdown and the main component of nitrogenous excretions (Salin and Williot, 1991). Ammonia arises from feed waste, uneaten and rotting feed, and dead fish. As shown by USEPA Environmental Protection Agency (1989) the optimal ranges of ionized NH4 and non-ionized NH3 required for fish production were 0.261.8 mg/l and <0.020 mg/l. It was observed that there was a gradual increase in total ammonia levels (0.65 mg/l, 0.82 mg/l, and 1.13 mg/l) during the study months, Therefore, our approach model mainly depends on unexchanged water conditions; there was undoubtedly a high probability of ammonia toxicity (Salin and Williot, 1991). Ammonia toxicity is affected by the aeration system, pH, temperature, algal population, and bacteria consuming ammonia (Boyd, 1998). The constant aeration systems usually mitigate ammonia toxicity, prevent environmental hypoxia, and allow for higher fish densities (Noga, 2010). The exact mechanism of ammonia poisoning in fish is unknown, but high levels of aqueous ammonia increase ammonia levels in blood and tissues, causing increased blood pH, disorders of osmoregulation, increased tissue oxygen consumption, and decreased blood oxygen transport (Schwedler et al., 1985). Chronic ammonia poisoning slows the growth and lowers disease resistance (Walters and Plumb, 1980).
Likewise, a gradual increase in nitrite NO2 (1.504, 0.547, and 0.99 mg/l) and nitrate NO3 (2.45, 3.23, and 5.46 mg mg/l) during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd months was recorded. These nitrogen levels were above the standard allowable limits: NO2< 0.5 mg/l and NO3< 3 mg/l (Swann, 1993). Thus, in month 3, we recorded the lowest oxygen levels and the highest concentrations of ammonia, unionized ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the PC, MOE, OME, and MCE groups compared to the NC group.
However, despite the constantly exceeded water parameter limits in the unexchanged water conditions, we did not observe the usual clinical toxicities of ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite. Surprisingly, the lowest mortality rates and dark skin, lethargy, and decreased appetite were reported in the MOE-treated group and the OME-treated groups, particularly in the third month. Therefore, we found that herbal dietary supplements have the potential to provide diverse mechanisms and diverse activities that enable fish to withstand constant exposure to high risks from harsh environments and management factors throughout the study period. These crops contain bioactive phytochemicals such as alkaloids, phenols, steroids, tannins, saponins, terpenoids, glycosides, and flavonoids (Galina et al., 2009; Mendam et al., 2015). Phytochemicals have been reported to stimulate appetite and promote growth performance, and have immunostimulant, antibacterial, antiviral, and antiparasitic effects in aquaculture (Gupta et al., 2021). Furthermore, it has been shown that herbal supplements have the ability to positively control the production of favorable gut microflora or microbial populations, which can enhance nutritional efficiency, improve digestion, and ultimately lower the amount of waste in the water (Noga, 2010).
Despite the lethal water parameter ranges, especially during the third month of the experiment, relative improvements were achieved in most growth parameters and there were higher survival rates in the herbal-treated groups compared to the PC group. Through periodic monitoring of growth rates, it was noted that the effect of herbal extracts as growth stimulants was clear until the middle of the second month of the experiment (45 days from starting the trial), that is, when water quality standards were within the optimal limits, as shown in Figures 1–3.
Compared to the positive control, the herbal-treated MOE, OME, and CME groups achieved an overall significant improvement in growth parameters. In particular, the group treated with OME achieved the best weight gain values and improved SGR, FCE, CF, HSI, and VSI percentages. Zhang et al. (2020) reported that dietary marjoram extracts improved gut morphology and increased the activity of digestive enzymes, which in turn promoted growth in fish. Nile tilapia fed diets containing 0.5% and 1.0% dried marjoram leaves had higher WG and FCE than the untreated controls (Khalafalla, 2009). Marjoram leaf meal as a feed supplement at 150 and 300 mg/kg improved the SGR of Nile tilapia when reared under optimal water quality conditions (El-Kholy, 2012). In another study, trout fed a M. officinalis-supplemented diet showed a significant increase in intestinal activity of amylase, lipase, and pepsin (Bilen et al., 2020). These beneficial effects of herbal extracts have been widely attributed to stimulating appetite and improving digestive performance (Chakraborty and Hancz, 2011). Herbal supplements can activate enzymatic digestive secretions and favorably stimulate eubiotic microflora (Wenk, 2003). In addition, herbal extracts have been shown to increase nutrient digestibility and bioavailability, which can ultimately increase feed conversion and cause higher protein synthesis and growth in fish (Nya and Austin, 2009). In contrast, the fish treated with CME were found to have lower growth performance and survival rates. Similar results were found in Nile tilapia supplemented with 1% chamomile flower meal which showed no significant differences in SGR compared to those fed a diet containing 1% dried marjoram leaves under optimal conditions (Khalafalla, 2009). Furthermore, red tilapia hybrids fed diets containing 2% and 4% chamomile flower powder had reduced WG compared to controls (Nordin et al., 2017). This nutritional efficiency can be attributed to herb type, dose, concentration, and the immune response to the herbal extract (Gabor et al., 2010). However, growth rates are impacted by the ongoing degradation of the water quality and the lengthening of the stress period that fish are subjected to. As a result, herbal extracts no longer function as growth stimulants; instead, they function as antioxidants and immune stimulants. Based on our findings, growth rates were significantly impacted in the second and third months. However, the survival rate was unaffected.
Therefore, the attainment of better growth performance in the herbal-treated groups, despite increasing ecological risk during the experimental period, is a true reflection of the strong immunological responses caused by the herbal supplements. Notably, the herbal-treated groups showed significant activity in the blood hematological, biochemical, and immunoassay tests compared to the untreated controls. Higher WBC, RBC, and HGB concentrations were achieved, especially in the OME- and MOE-treated groups. Furthermore, lower levels of creatinine, urea, ALT, and AST, and higher levels of albumin and total protein were found. In addition, the herbal-treated groups showed obvious activity of nitric oxide, glutathione, lysozyme, catalase, superoxide dismutase, and IL-10. Futhermore, higher levels of immunoglobulin M and G, complement C, malondialdehyde, IL-1, and IL-6 were recorded in the OME- and MCE-treated groups. Herbal supplementation has been found to enhance numerous immune-stimulating mechanisms in various fish species (Abd El-Naby et al., 2023). Herbal supplements have therapeutic immunostimulatory potential which is attributed to their active phytochemical compounds such as alkaloids, phenols, steroids, tannins, saponins, terpenoids, glycosides, and flavonoids (Galina et al., 2009). These bioactive phytochemicals act as antibiotics, antioxidants, antibacterial compounds, and antistress agents (Wenk, 2003; Harikrishnan et al., 2011; El Basuini et al., 2022). In addition, these phytochemical compounds enhance the activity of phagocytes and increase their bactericidal activity, stimulate natural killer cells, supplement activity, and proliferate lymphocyte, lysozyme, and antibody responses of fish (Abdel-Tawwab et al., 2023; Abdel-Aziz et al., 2023). In addition, herbal supplements contain active ingredients that counteract the negative effects of naturally occurring anti-nutritional factors such as gossypol, tannins, saponins, lectins, and phytic acid, thereby increasing feed efficiency (Alagawany et al., 2020).
Consequently, the herbal-supplemented fish produced high-quality carcasses compared to the unsupplemented groups. Immediate chemical analysis of fish carcasses in the MOE-, OME-, and MCE-treated groups showed significantly (P ≤ 0.05) lower dry matter, fat, and ash and higher levels of crude protein compared to the untreated control groups. This was consistent with the results of Shalaby et al. (2021) who found a significant decrease in fish body dry matter content and an increase in ash content at high TA concentrations. In contrast, El-Kholy (2012) and Alsaiad and AL-Zayat (2019) found an increase in total body DM content and a decrease in ash content in tilapia given varying amounts of powdered marjoram and ginger extract. Other studies found no significant impact of herbal supplementation on fish body composition (El-Dakar et al., 2004; Khalafalla, 2009).
A pathogencity test was considered another evaluator of the antibacterial properties of herbal supplements despite the accumulated deadly water stressors. When challenged with E. tarda, the herbal-treated groups showed significantly lower cumulative mortality rates compared to the non-treated challanged group. Similarly, higher RPS values were recorded for the herbal-treated groups compared to positive control group. Furthermore, Baba et al. (2016) reported herbal additives have been shown to stimulate immune responses, defense mechanisms, and resistance to pathogenic bacteria in various species of fish. For example, the incorporation of Citrus limon lemon peel at 0.50%, 0.75%, and 1.00% into the diet of O. mossambicus for 2 months improved the activities of respiratory bursts, lysozymes, myeloperoxidase, total protein, and resistance to E. tarda. Following the same trend, Asian sea bass Lates calcarifer fed Citrus depressa lemon leaves for 56 days showed enhanced respiratory blast, phagocytosis, lysozyme activity, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila (Shiu et al., 2016). Improvement in both the immunity and growth performance of O. niloticus as well as bactericidal effects against A. hydrophila were observed after 3 months of feeding with Camellia sinensis and green tea leaves (Abdel-Tawwab et al., 2010). Therefore, the role of herbal supplementation in relieving stress has been illustrated. These anti-stress effects were elicited in the supplemented diets with phytobiotics alone or in combination with antioxidant micronutrients, synbiotics, and probiotics (Gupta et al., 2021).
Conclusion
After culturing O. niloticus with different water quality and stocking density risk variables, it can be inferred that herbal dietary supplements have immunostimulatory, growth-promoting, and antipathogenic properties. The supplements increased the capacity of O. niloticus to tolerate well-exceeded deteriorated water limits that cause clinical toxicities of ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite. In addition, the herbal supplements yielded improvements in growth performance, feed conversion rate, and antibacterial effectiveness compared to the positive control group. Despite the benefits of the dietary herbal extracts, prolonged stress caused a significant decrease in growth rate and mortality rates. The current study confirmed the possibility of rearing fish without changing the water for 30 days using the tested doses of dietary supplementation with all the herbal extracts and for 45 days using the tested dose of leaf marjoram extract.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
This study was conducted with the strict recommendations and approval of The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee for Zagazig University, Egypt (ZU-IACUC) with approval number: ZU-IACUC/2/F/58/2023. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AF: Resources, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation. MM: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Resources, Methodology, Investigation. HH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AA: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration. TA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MA: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MA-A: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Software, Resources, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Researchers Supporting Project for funding this work through the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R728), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia and Universiti Brunei Darussalam under the Faculty/Institute/Centre Research Grant: - (No.UBD/RSCH/1.4/FICBF(b)/2022/051,UBD/RSCH/1.4/FICBF(b)/2023/057,UBD/RSCH/1.4/FICBF(b)/2023/060).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge all members and staff of the Aquatic Wealth Research Station, NIOF in Fayoum, Egypt for their help and support in completing this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The handling editor MB declared a past co-authorship with the author MA-A.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Aziz M. F., El Basuini M. F., Sadek M. F., Elokaby M. A., El-Dakar A. Y., Metwally M. M., et al. (2024). Unchanged water stress induces growth retardation, histopathological alterations, and antioxidant-immune disruptions in Oreochromis niloticus: the promising role of dietary organic acids. Aquacult Int. 32, 6031–6052. doi: 10.1007/s10499-024-01454-y
Abdel-Aziz M. F., El Basuini M. F., Teiba I. I., Metwally M. M., El-Dakar A. Y., Helal A. M., et al. (2023). Growth performance, feed utilization, hematological parameters, and histological features of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed diets with supplementary herbal extracts under prolonged water exchange. Ann. Anim. Sci. 23, 1147–1157. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2023-0017
Abdelhadi Y. M., Saleh O., Sakr S. F. (2010). Study on effect of wormseed plants and chamomile on growth parameters and immune response of African catfish. J. Fisheries Int. 5, 1–7. doi: 10.3923/jfish.2010.1.7
Abd El-Naby A. S., El Asely A. M., Hussein M. N., Fawzy R. M., Abdel-Tawwab M. (2023). Stimulatory effects of dietary chia (Salvia hispanica) seeds on performance, antioxidant-immune indices, histopathological architecture, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 563, 738889. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738889
Abdel-Tawwab M., Ahmad M. H., Seden M. E., Sakr S. F. (2010). Use of green tea, Camellia sinensis L., in practical diet for growth and protection of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. J. World Aquaculture Soc. 41, 203–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-7345.2010.00360
Abdel-Tawwab M., Selema T. A. A., Abotaleb M. M., Khalil R. H., Sabry N. M., Soliman A. M., et al. (2023). EffEcts of a commErcial fEEd additivE (sanacorE® Gm) on immunE-antioxidant profilE and rEsistancE of GilthEad sEabrEam (SparuS aurata) aGainst Vibrio alginolyticuS infEction. Ann. Anim. Sci. 23, 185–193. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2022-0053
Abdul Kari Z., Wee W., Mohamad Sukri S. A., Che Harun H., Hanif Reduan M. F., Irwan Khoo M., et al. (2022). Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: A mini-review. Front. Vet. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1023784
Alagawany M., Farag M. R., Salah A. S., Mahmoud M. A. (2020). The role of oregano herb and its derivatives as immunomodulators in fish. Rev. Aquaculture 12, 2481–2492. doi: 10.1111/raq.12453
Alsaiad S., AL-Zayat A. (2019). Utilization of ginger extract in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets. Egyptian J. Aquat. Biol. Fisheries 23, 23–37. doi: 10.21608/ejabf.2019.61969
Amandi A., Hiu S. F., Rohovec J. S. (1982). Isolation and characterization of Edwardsiella tarda from fall Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. J. 43, 1380–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1380-1384.1982
AOAC (2010). Official Methods of Analysis of Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 18th Edition. (Washington, DC).
APHA (2012). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water. 22nd Edition, Rice E. W., Baird R. B., Eaton A. D., Clesceri L. S. (Washington, DC: American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF)).
Azaza M. S., Dhraïef M. N., Kraïem M. M. (2008). Effects of water temperature on growth and sex ratio of juvenileNile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) reared in geothermal waters in southern Tunisia. J. ThermBiol. 33, 98–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2007.05.007
Baba E., Acar Ü., Öntaş C., Kesbiç O. S., Yılmaz S. (2016). Evaluation of Citrus limon peels essential oil on growth performance, immune response of Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus challenged with Edwardsiella tarda. Aquaculture 465, 13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.08.023
Bernet D., Schmidt H., Meier W., Burkhardt-Holm P., Wahli T. (1999). Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J. Fish Dis. 22, 25–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.1999.00134.x
Bilen S., Altief T. A. S., Özdemir K. Y., Salem M. O. A., Terzi E., Güney K. (2020). Effect of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) extract on growth performance, digestive and antioxidant enzyme activities, and immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 46, 471–481. doi: 10.1007/s10695-019-00737-z
Blaxhall P. C., Daisley K. W. (1973). Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. J. fish Biol. 5, 771–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1973.tb04510.x
Bondad-Reantaso M. G., MacKinnon B., Karunasagar I., Fridman S., Alday-Sanz V., Brun E., et al. (2023). Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquaculture. 15, 1421-1451. doi: 10.1111/raq.12786
Boyd C. E. (1998). Water quality management for pond fish culture: research and development. Int. Center Aquaculture Aquat. Environments 43, 1–37. Available at: http://soiltesting.tamu.edu/publications/AU43.pdf.
Chakraborty S. B., Hancz C. (2011). Application of phytochemicals as immunostimulant, antipathogenic and antistress agents in finfish culture. Rev. Aquaculture 3, 103–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-5131.2011.01048.x
Chelikani P., Fita I., Loewen P. C. (2004). Diversity of structures and properties among catalases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 61, pp.192208. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3206-5
Citarasu T. (2010). Herbal biomedicines: a new opportunity for aquaculture industry. Aquaculture Int. 18, 403–414. doi: 10.1007/s10499-009-9253-7
Davies M. Y., Xavier de Oliveira M. G., Paulo Vieira Cunha M., Soares Franco L., Pulecio Santos S. L., Zanolli Moreno L., et al. (2018). Edwardsiella tarda outbreak affecting fishes and aquatic birds in Brazil. Veterinary Q. 38, 99–105. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2018.1540070
Dien L. T., Ngo T. P. H., Nguyen T. V., Kayansamruaj P., Salin K. R., Mohan C. V., et al. (2023). Non-antibiotic approaches to combat motile Aeromonas infections in aquaculture: Current state of knowledge and future perspectives. Rev. Aquaculture. 1-31. doi: 10.1111/raq.12721
Dorafshan S., Kalbassi M. R., Pourkazemi M., Mojazi-Amiri B., Soltan-Karimi S. (2008). Effects of triploidy on the Caspian salmon (Salmo trutta, caspius) hematology. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 34, 195–200. doi: 10.1007/s10695-007-9176-z
El Basuini M. F., Teiba I. I., Shahin S. A., Mourad M. M., Zaki M. A., Labib E. M., et al. (2022). Dietary Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia) enhanced the growth performance, antioxidative capacity, immune response and ameliorated stress-related markers induced by hypoxia stress in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish shellfish Immunol. 120, 337–344. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.12.002
El-Dakar A. Y., Hassanein G. D. I., Gad S. S., Sakr S. E. (2004). Use of medical and aromatic plants in fish diets: 1- Effect of dried marjoram leaves on performance of hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis nilticus x Oreochromis auraus, fingerlings. J. Egypt. Acad. Soc Environ. Dev. B (Aquaculture). 5, 67–83.
El-Kholy K. F. (2012). Effect of marjoram (Marjorana hortensis) or sage (Salvia officinalis) additives on growth performance and feed utilization of tilapia hybrid (Oreochromis niloticus× Oreochromis aureus) monosex fingerlings. J. Anim. Poultry Production 3, 115–126. doi: 10.21608/JAPPMU.2012.82781
Ellis A. E. (1990). Lysozyme Assays. In: Stolen J. S., Fletcher T. C., Anderson D. P., Roberson B. S., Van Muiswinkel W. B. Eds., Techniques in Fish Immunology Fair Haven, SOS Publications, Fair Haven, 1, 101–103.
El-Sayed A. F. M., Nasr-Allah A. M., Dickson M., Gilmour C. (2022). Analysis of aquafeed sector competitiveness in Egypt. Aquaculture 547, 737486. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737486
Emerson K., Russo R. C., Lund R. E., Thurston R. V. (1975). Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. J. Fisheries Board Canada 32, 2379–2383. doi: 10.1139/f75-274
Eyayu A., Getahun A., Keyombe J. L. (2024). A review of the production status, constraints, and opportunities in East African freshwater capture and culture fisheries. Aquacult Int. 32, 929–930. doi: 10.1007/s10499-023-01178-5
FAO (2022). The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2020: Sustainability in action. Roma, Italia: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Farmer E. E., Davoine C. (2007). Reactive electrophile species. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10, 380–386. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.019
Gabor E. F., Şara A., Barbu A. (2010). The effects of some phytoadditives on growth, health and meat quality on different species of fish. Sci. Papers Anim. Sci. Biotechnologies 43, 61–65.
Gabriel N. N., Qiang J., He J., Ma X. Y., Kpundeh M. D., Xu P. (2015). Dietary Aloe vera supplementation on growth performance, some haemato-biochemical parameters and disease resistance against Streptococcus iniae in tilapia (GIFT). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 44, 504–514. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.03.002
Galina J., Yin G., Ardo L., Jeney Z. (2009). The use of immunostimulating herbs in fish. An overview of research. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 35, pp.669–pp.676. doi: 10.1007/s10695-009-9304-z
Ghiulai R., Avram S., Stoian D., Pavel I. Z., Coricovac D., Oprean C., et al. (2020). Lemon balm extracts prevent breast cancer progression in vitro and in ovo on chorioallantoic membrane assay. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020 (1), 6489159. doi: 10.1155/2020/6489159
Gupta A., Gupta S. K., Priyam M., Siddik M. A., Kumar N., Mishra P. K., et al. (2021). Immunomodulation by dietary supplements: A preventive health strategy for sustainable aquaculture of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Rev. Aquaculture 13, 2364–2394. doi: 10.1111/raq.12581
Haenen O. L., Dong H. T., Hoai T. D., Crumlish M., Karunasagar I., Barkham T., et al. (2023). Bacterial diseases of tilapia, their zoonotic potential and risk of antimicrobial resistance. Rev. Aquaculture 15, 154–185. doi: 10.1111/raq.v15.S1
Harikrishnan R., Kim M. C., Kim J. S., Balasundaram C., Heo M. S. (2011). Protective effect of herbal and probiotics enriched diet on haematological and immunity status of Oplegnathus fasciatus against Edwardsiella tarda. Fish shellfish Immunol. 30, 886–893. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2011.01.013
Haselmeyer A., Nowotny N., Heistinger H., Kolodziejek J., Homola J., Nöbauer K., et al. (2018). Melissa officinalis L. extract and its main phenolic compound rosmarinic acid as phytoprophylactic feed additives against koi herpesvirus infection in a pilot study. Wien Tierärztl Mschr 105, 175 183.
Hirano T. (1998). Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int. Rev. Immunol. 16, 249–284. doi: 10.3109/08830189809042997
Hoseinifar S. H., Sun Y. Z., Zhou Z., Van Doan H., Davies S. J., Harikrishnan R. (2020). Boosting immune function and disease bio-control through environment-friendly and sustainable approaches in finfish aquaculture: herbal therapy scenarios. Rev. Fisheries Sci. Aquaculture 28, 303–321. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2020.1731420
Hossein M., Asha R., Bakari R., Islam N. F., Jiang G., Sarma H. (2023). Exploring eco-friendly approaches for mitigating pharmaceutical and personal care products in aquatic ecosystems: A sustainability assessment. Chemosphere, 137715. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137715
Jafarpour M., Fard A. N. (2016). The effects of aqueous extract of Melissa officinalis on some blood parameters and liver of Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture Aquarium Conserv. Legislation 9, 748–758.
Khalafalla M. (2009). Utilization of some medical plants as feed additives for Nile tilapia, oreochromis niloticus, feeds. Mediterr. Aquaculture J. 2, 9–18. doi: 10.21608/MAJ.2009.2665
Kim J., Kang S., Kim H. S., Kim S., Lee S. S. (2020). Pilot plant study on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in marine wastewater by marine sediment with sequencing batch reactor. PloS One 15, e0233042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233042
Li H., Cui Z., Cui H., Bai Y., Yin Z., Qu K. (2023). Hazardous substances and their removal in recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Aquaculture, 739399. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739399
Li X., Mai J., Virtue A., Yin Y., Gong R., Sha X., et al. (2012). IL-35 is a novel responsive anti-inflammatory cytokine—a new system of categorizing anti-inflammatory cytokines. PloS One 7, e33628.
Manduca L. G., da Silva M. A., de Alvarenga E. R., de Oliveira Alves G. F., de Araújo Fernandes A. F., Assumpcao A. F., et al. (2020). Effects of a zero exchange biofloc system on the growth performance and health of Nile tilapia at different stocking densities. Aquaculture 521, 735064. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735064
Mehrim A. I., Refaey M. M. (2023). An overview of the implication of climate change on fish farming in Egypt. Sustainability 15, 1679. doi: 10.3390/su15021679
Mendam K., Kavitha B., Naik S. J. K. (2015). Natural sources used for treatment and prevention of filariasis. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. (WJPPS) 4, 1621–1628.
Mohammadi G., Rafiee G., Abdelrahman H. A. (2020). Effects of dietary Lactobacillus plantarum (KC426951) in biofloc and stagnant-renewal culture systems on growth performance, mucosal parameters, and serum innate responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 46, 1167–1181. doi: 10.1007/s10695-020-00777-w
Ndashe K., Hang’ombe B. M., Changula K., Yabe J., Samutela M. T., Songe M. M., et al. (2023). An assessment of the risk factors associated with disease outbreaks across tilapia farms in central and Southern Zambia. Fishes 8, 49. doi: 10.3390/fishes8010049
Ngugi C. C., Bowman J. R., Omolo B. O. (2007). A New Guide to Fish Farming In Kenya (USA: USAID), pp 34–pp 48. doi: 10.10.11.5/handle/123/481
Nordin S. F., Nordin M. L., Osman A. Y., Hamdan R. H., Shaari R., Arshad M. M. (2017). The effect of matricaria chamomilla L on the growth performance of red hybrid tilapia. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 10, 1905–1915. doi: 10.13005/bpj/1310
NRC (National Research Council) (2011). Nutrient Requirements of fish and shrimp (Washington, D. C., USA: National Academy Press).
Nya E. J., Austin B. (2009). Use of garlic, Allium sativum, to control Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. fish Dis. 32, 963–970. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01100.x
Obirikorang K. A., Acheampong J. N., Duodu C. P., Skov P. V. (2020). Growth, metabolism and respiration in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to chronic or periodic hypoxia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 248, 110768. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110768
Oh W. T., Jun J. W., Kim H. J., Giri S. S., Yun S., Kim S. G., et al. (2020). Characterization and pathological analysis of a virulent Edwardsiella Anguillarum strain isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Korea. Front. veterinary Sci. 7, 14. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00014
Ordonez A. A. L., Gomez J. D., Vattuone M. A. (2006). Antioxidant activities of Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz extracts. Food Chem. 97, 452–458. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.024
Rabelo-Ruiz M., Peralta-Sánchez J. M., Martín-Platero A. M., Ruiz A. J., Agraso M. D. M., Bermúdez L., et al. (2023). Allium-derived compound propyl propane thiosulfonate (PTSO) reduces vibrio populations and increases body weight of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Antibiotics 12, 134. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010134
Riche M., Garling D. (2003). Feeding Tilapia in Intensive Recirculating Systems (North Central Regional Aquaculture Center), p.114. Available at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/ncrac_factsheets/6. Fact sheet series.
Roby M. H. H., Sarhan M. A., Selim K. A. H., Khalel K. I. (2013). Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oil and extracts of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare L.) and chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.). Ind. Crops products 44, 437–445. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.10.012
Salin K. R., Vinh N. T. (2023). “Biofloc technology in aquaculture,” in Frontiers in Aquaculture Biotechnology (Academic Press), 69–88.
Salin D., Williot P. (1991). “Acute toxicity of ammonia to Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri),” in Acipenser. Ed. Williot P. (Cemagref Publ), 153–167.
Schwedler T. E., Tucker C. S., Beleau M. H. (1985). “Noninfectious diseases,” in Channel Catfish Culture. Ed. Tucker C. S. (Elsevier, New York), 497–541.
Shalaby A., Khames M., Fathy A., Gharieb A., Abdel-Hamid E. (2021). The impact of zeolite on ammonia toxicity, growth performance and physiological status of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromius niloticus). Egyptian J. Aquat. Biol. Fisheries 25, 643–663. doi: 10.21608/EJABF.2021.148524
Shao S., Lai Q., Liu Q., Wu H., Xiao J., Shao Z., et al. (2015). Phylogenomics characterization of a highly virulent Edwardsiella strain ET080813T encoding two distinct T3SS and three T6SS gene clusters: propose a novel species as Edwardsiella Anguillarum sp. nov. Systematic Appl. Microbiol. 38, 36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2014.10.008
Sharawy Z. Z., Ashour M., Abbas E., Ashry O., Helal M., Nazmi H., et al. (2020). Effects of dietary marine microalgae, Tetraselmis suecica, on production, gene expression, protein markers and bacterial count of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture Res. 51, 2216–2228. doi: 10.1111/are.14566
Shiu Y. L., Lin H. L., Chi C. C., Yeh S. P., Liu C. H. (2016). Effects of hirami lemon, Citrus depressa Hayata, leaf meal in diets on the immune response and disease resistance of juvenile barramundi, Lates calcarifer (bloch), against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish shellfish Immunol. 55, 332–338. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.06.001
Škerget M., Kotnik P., Hadolin M., Hraš A. R., Simonič M., Knez Ž. (2005). Phenols, proanthocyanidins, flavones and flavonols in some plant materials and their antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 89, 191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.02.025
SPSS (2007). Statistical Package for Social Science (for windows) (Chicago, USA: SPSS Inc.). Release 16 Copyright ©.
Suvarna K. S., Layton C., Bancroft J. D. (2018). Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. eighth edition (Elsevier Health Sciences). E-Book.
Swann L. (1993). Water quality water sources used in aquaculture (West Lafayette, Ind: Illinois- Indiana Sea Grant Program. Purdue University). Available at: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US9735387. Water quality fact sheet as486. Aquaculture Extension.
Swingle H. S. (1969). Methods of analysis for waters, organic matter, and pond bottom soils used in fisheries research. Auburn, Alabama, U.S.A.: Auburn University, 119 pp.
Taylor E. W., Leite C. A. C., McKenzie D. J., Wang T. (2010). Autonomic control of cardiorespiratory interactions in fish, amphibians and reptiles. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 43, 600–610. doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2010007500044
USEPA Environmental Protection Agency (1989). Ambient water quality criteria for ammonia (saltwater) (Springfield, VA: National Technical Information Service).
Vallejos-Vidal E., Reyes-Lopez F., Teles M., MacKenzie S. (2016). The response of fish to immunostimulant diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 56, 34–69. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.06.028
Van Doan H., Hoseinifar S. H., Ringø E., Ángeles Esteban M., Dadar M., Dawood M. A., et al. (2020). Host-associated probiotics: a key factor in sustainable aquaculture. Rev. fisheries Sci. aquaculture 28, 16–42. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2019.1643288
Van Hai N. (2015). The use of medicinal plants as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 446, 88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.03.014
Venkatramalingam K., Christopher J. G., Citarasu T. (2007). Zingiber officinalis an herbal appetizer in the tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fabricius) larviculture. Aquaculture Nutr. 13, 439–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00495.x
Walters G. R., Plumb J. A. (1980). Environmental stress and bacterial infection in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus Rafinesque. J. Fish Biol. 17, 177–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1980.tb02751.x
Wenk C. (2003). Herbs and botanicals as feed additives in monogastric animals. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 16, 282–289. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2003.282
Yang X., Guo J. L., Ye J. Y., Zhang Y. X., Wang W. (2015). The effects of Ficus carica polysaccharide on immune response and expression of some immune-related genes in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish shellfish Immunol. 42, 132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.037
Yarmohammadi M., Shabani A., Pourkazemi M., Soltanloo H., Imanpour M. (2012). Effect of starvation and refeedingon growth performance and content of plasma lipids, glucose and insulin in cultured juvenile Persiansturgeon (Acipenser persicus Borodin 1897). J. App Ichthyol 28, 692–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2012.01969.x
Yilmaz S. (2019). Effects of dietary blackberry syrup supplement on growth performance, antioxidant, and immunological responses, and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus to Plesiomonas shigelloides. Fish shellfish Immunol. 84, 1125–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.012
Zakaria M. K., Kari Z. A., Van Doan H., Kabir M. A., Che Harun H., Mohamad Sukri S. A., et al. (2022). Fermented soybean meal (FSBM) in african catfish (Clarias gariepinus) diets: effects on growth performance, fish gut microbiota analysis, blood haematology, and liver morphology. Life 12, 1851. doi: 10.3390/life12111851
Zaki M. A., Labib E. M., Nour A. M., Tonsy H. D., Mahmoud S. H. (2012). Effect some medicinal plants diets on mono sex Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), growth performance, feed utilization and physiological parameters. APCBEE Proc. 4, 220–227. doi: 10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.11.037
Zhang H., Ludsin S. A., Mason D. M., Adamack A. T., Brandt S. B., Zhang X., et al. (2009). Hypoxia-driven changes in the behavior and spatial distribution of pelagic fish and mesozooplankton in the northern Gulf of Mexico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 381, S80–S91. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2009.07.014
Zhang R., Wang X. W., Liu L. L., Cao Y. C., Zhu H. (2020). Dietary oregano essential oil improved the immune response, activity of digestive enzymes, and intestinal microbiota of the koi carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 518, 734781. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734781
Zimmermann S., Kiessling A., Zhang J. (2023). The future of intensive tilapia production and the circular bioeconomy without effluents: Biofloc technology, recirculation aquaculture systems, bio-RAS, partitioned aquaculture systems and integrated multitrophic aquaculture. Rev. Aquaculture 15, 22–31. doi: 10.1111/raq.v15.S1
Keywords: Oreochromis niloticus, Melissa officinalis, Origanum majorana, Matricaria chamomilla, unchanged water
Citation: Fadel A, Metwally MMM, Hassan HU, Abdelmageed AA, Arai T, Ahmed MZ and Abdel-Aziz MFA (2024) Growth, immunomodulatory, histopathological, and antibacterial effects of phytobiotic-incorporated diets on Oreochromis niloticus in unchanged water. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1473053. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1473053
Received: 30 July 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 12 November 2024.
Edited by:
Mohammed Fouad El Basuini, Tanta University, EgyptCopyright © 2024 Fadel, Metwally, Hassan, Abdelmageed, Arai, Ahmed and Abdel-Aziz. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Amr Fadel, ZmFkZWxfYXF1YUB5YWhvby5jb20=; Mohamed F. A. Abdel-Aziz, bV9mYXRoeTg3ODlAeWFob28uY29t
 Amr Fadel1*
Amr Fadel1* Mohamed F. A. Abdel-Aziz
Mohamed F. A. Abdel-Aziz