- Environment and Resource Convergence Center, Advanced Institute of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Republic of Korea
Distribution patterns of benthic dinoflagellates that are widely observed in tropical and temperate waters and have toxic potential are changing in response to ocean climate change. Although there have been no outbreaks associated with the genus Coolia affecting humans, it is crucial to understand their changing distribution and clearly identify the species in the study area to prepare for potential toxic events. In this study, five strains of Coolia species were isolated from macroalgae samples collected from Jeju Island and the eastern coastal waters of Korea. Through morphological and molecular analysis of these isolates, one strain was identified as Coolia palmyrensis, marking the first report of this species in Korea, and four strains as C. malayensis. One of the C. malayensis strains was isolated in Pohang on the eastern coast of Korea, where it had not been previously reported. From 2021 to 2023, monitoring of Jeju Island using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay revealed that C. palmyrensis cells occurred mostly in autumn, with a maximum density of 242 cells g-1, and overwintering populations were observed in 2023. However, C. malayensis cells were not observed in this area. Additionally, C. malayensis was observed in Pohang and Ulsan, located further north than Jeju Island with maximum cell densities of 537 and 201 cells g-1, respectively. These data and our decade of monitoring experience confirmed the introduction and establishment of C. palmyrensis and habitat shift of C. malayensis in Korean coastal waters. This study provides advances for understanding of the relationships between climate-driven alterations and biogeographic distribution of these species.
1 Introduction
Dinoflagellates—unicellular microeukaryotes—are crucial to complex marine ecosystems worldwide (Gómez, 2012; De Vargas et al., 2015). Less than 10% of dinoflagellate species inhabit benthic environments, where their characteristics, including morphology and biodiversity, have been adapted for symbiotic relationships with substrates, such as macroalgae (Rhodes et al., 2000; Hoppenrath et al., 2014). Research on benthic microalgae has focused on their potential to produce toxic compounds, resulting in harmful algal blooms (HAB) that threaten human health and aquatic environments (Ballantine et al., 1988; Granéli et al., 2002; Penna et al., 2005; Riobó et al., 2006). Since the 1970s, numerous studies have reported on the toxigenicity of benthic dinoflagellates: the genus Gambierdiscus produces ciguatera toxins, maitotoxin, and gambierol, whereas Ostreopsis and Prorocentrum produce palytoxin and okadaic acid, respectively (Yasumoto et al., 1987; Ten-Hage et al., 2000a; Cagide et al., 2011; Yogi et al., 2011; Parsons et al., 2012; Hoppenrath et al., 2013; Boente-Juncal et al., 2019). Owing to their potential toxicity affecting marine organisms and humans, numerous studies have focused on the early detection of these species and understanding their ecological characteristics, including artificial substrates (Tester et al., 2022), metabarcoding approach (Smith et al., 2017), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays (Lee et al., 2021).
The benthic dinoflagellate genus Coolia co-occurs with other epiphytic genera, such as Ostreopsis species, and exhibits a cosmopolitan distribution spanning tropical and temperate regions (Leaw et al., 2016). To date, no HAB events or outbreaks associated with Coolia species affecting humans have been reported, despite the observation of toxic molecules, such as yessotoxin analogs, 44-methylgambierone (44-MG), anhydrogambierone, and gambierone, in certain strains of C. tropicalis and C. malayensis (Holmes et al., 1995; Wakeman et al., 2015; Tibiriçá et al., 2020; Murray et al., 2024). However, it is necessary to monitor Coolia species regarding their distributions, substrate preferences, and toxic production. Alterations in existing environmental conditions in response to ocean climate change may be associated with an increase in their toxic potential (Wells et al., 2020; Anderson et al., 2021).
Molecular techniques in taxonomy enable accurate species identification, aiding in elucidating the distribution and biodiversity of Coolia species, despite their morphological similarity. The genus Coolia comprises eight species: Coolia monotis (Faust, 1992), C. tropicalis (Faust, 1995), C. areolata (Ten-Hage et al., 2000b), C. canariensis (Fraga et al., 2008), C. malayensis (Leaw et al., 2010), C. santacroce, C. palmyrensis (Karafas et al., 2015), and C. guanchica (David et al., 2020). Before applying molecular data to confirm these taxa, morphologically similar species were occasionally misidentified because of their phenotypic plasticity and the presence of cryptic or pseudo-cryptic features within the species (Leaw et al., 2016). However, by combining morphological and molecular analyses, certain strains previously classified as C. monotis have now been reassigned to C. malayensis, C. santacroce, and C. palmyrensis (Karafas et al., 2015). Although there are no molecular data for C. areolata, its cells can be distinguished based on their morphological characteristics (Ten-Hage et al., 2000b). Recently, C. canariensis, which exhibits cryptic diversity, has been divided into four clades in phylogenetic relationships, known as the Coolia canariensis species complex. The geographic distribution of each phylogroup has been studied in distinct intraspecific taxa (Miralha et al., 2023).
Based on the literature that provides insights into both morphological and molecular data of isolated strains, C. malayensis is widely distributed in temperate and tropical regions. In contrast, C. santacroce, C. palmyrensis, C. tropicalis, and C. canariensis are observed in tropical waters of both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, though C. canariensis is primarily found in the subtropical Canary Islands (Leaw et al., 2016). However, the distribution patterns of benthic dinoflagellates, such as Ostreopsis, are changing in response to climate change (Wells et al., 2020; Verma et al., 2023). Similarly, Coolia species known to inhabit tropical waters have been observed in the South Atlantic and Pacific waters. For example, C. tropicalis and C. canariensis have been observed on Trindade Island, Brazil (Nascimento et al., 2019), C. tropicalis and C. palmyrensis on Heron Island, Australia (Larsson et al., 2019), and C. santacroce and C. palmyrensis on Bahia, the northeastern Brazilian coast (Tibiriçá et al., 2020). Additionally, C. monotis has been observed on Rhode Island, USA, northwestern Atlantic waters, and Nova Scotia, Canada, although this species has been traditionally recorded only in the Mediterranean Sea (Lewis et al., 2018). Since 2011, benthic dinoflagellates, including Coolia, have been reported in Korea and identified at the genus level based on morphological analysis without molecular support (Kim et al., 2011; Baek, 2012; Shah et al., 2013). Subsequently, two Coolia species (C. canariensis and C. malayensis) were observed in the waters of Jeju Island that were confirmed through their morphological and molecular data (Jeong et al., 2012). However, the occurrence and distribution patterns of C. palmyrensis, which has not been previously observed in Korean coastal waters, and C. malayensis remain unexplored in Korea.
In this study, we performed a comprehensive sampling of benthic dinoflagellates collected from macroalgae and isolated one strain of C. palmyrensis and four strains of C. malayensis from Jeju Island and the eastern coastal waters of Korea. These strains were examined using light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and molecular data derived from the D1-D3 regions of large subunit ribosomal DNA (LSU rDNA) and internal transcribed spacer (ITS rDNA) regions for taxonomical analysis. To better understand the geographic distribution patterns of Korean Coolia species, we monitored the occurrence of C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis in environmental samples collected from macroalgae on Jeju Island, Korea, from 2021 to 2023, using the species-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sampling, isolation, and establishment of strain
From 2021 to 2023, seasonal sampling was conducted 4 to 5 times per year at four locations on Jeju Island, Korea—Dodu (33°30'38.9"N 126°28'46.0"E), Seogwi (33°14'21.0"N 126°34'10.9"E), Seongsan (33°27'36.9"N 126°56'02.0"E), and Sinchang (33°20'57.7"N 126°10'45.7"E)—representing the north, south, east, and west of the island (Figure 1). The number of sampling events varied slightly due to weather conditions and the need for additional surveys during periods of heightened benthic dinoflagellate activity. Along the eastern coast of Korea, additional samples were collected sporadically from two sites, Pohang (36°08'32.0"N and 129°23'48.2"E) and Ulsan (35°36'46.2"N and 129°27'29.0"E), during June and August 2021, and June and October 2023. At each site, 2 to 4 macroalgal samples were collected, depending on the weather conditions at the time of sampling. Physical parameters, such as seawater temperature and salinity, were recorded at each sampling site using a YSI Professional Plus (Xylem, Inc., Rye Brook, USA).
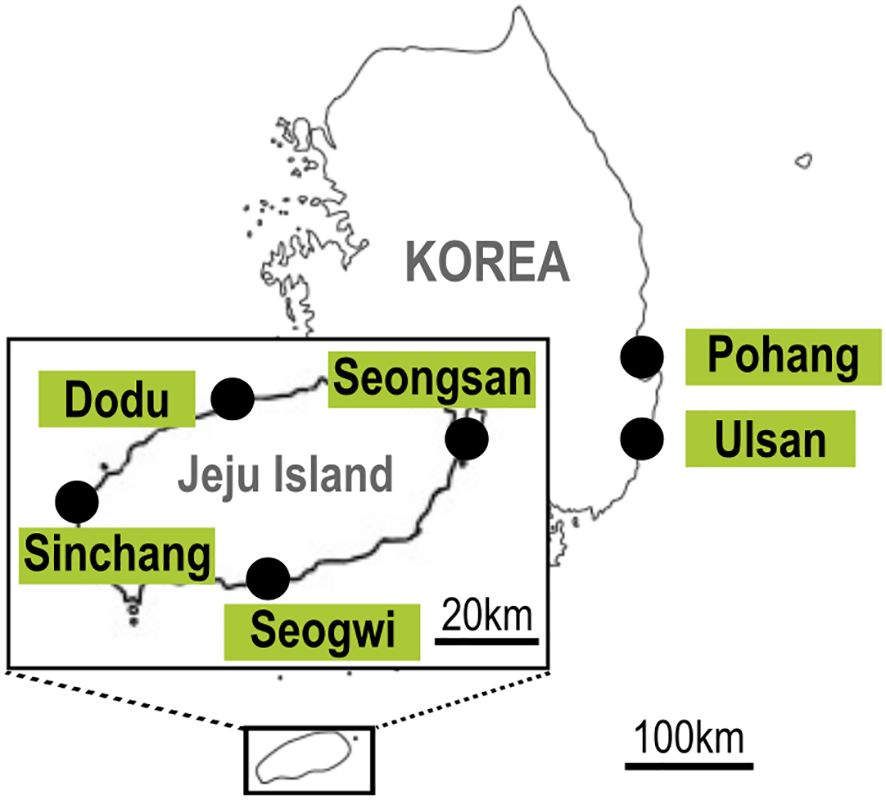
Figure 1. Location maps of sampling sites on Jeju Island covering the north, south, east, and west: Dodu, Seogwi, Seongsan, and Sinchang. Further sampling sites include Pohang and Ulsan in the eastern coastal waters of Korea.
In this study, various species of macroalgae were collected and analyzed, representing three major groups: red algae (including Corallina pilulifera, Grateloupia cornea), brown algae (including Marginisporum crassissimum, Sargassum fusiforme), and green algae (including Ulva australis, Ulva linza). At each site, macroalgal samples were collected through scuba diving using clean sealable plastic bags. Subsequently, they were transferred to polycarbonate (PC) bottles and gently shaken to detach benthic dinoflagellate cells from the substrates. The mixed seawater samples were filtered through glass microfiber filters with a 1.2 µm pore size (GF/C; Whatman® Inc., Maidstone, United Kingdom) to obtain environmental DNA (eDNA). All samples were frozen on dry ice, delivered to the laboratory, and stored at -80°C until DNA extraction. The final volumes of seawater collected for each macroalgal species in the plastic bag and the fresh weights of each macroalgal species were measured to quantify the cell concentrations using qPCR. For the isolation of microalgae strains, 300 mL of mixed seawater samples were collected and transported live to the laboratory.
To establish the clonal strains of Coolia, the live sample transported to the laboratory was placed in a six-well plate, and single-cell isolation was performed under a dissecting microscope (SZX10; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). After single-cell isolations with 5 washings were established, the cells were cultured at 21°C with continuous illumination of 65 μmol m−2 s−1 photon irradiance in autoclaved filtered seawater containing f4-si media (Guillard and Ryther, 1962). After sufficient growth, the dense cultures were transferred to 50, 250, and 500 mL PC bottles, established as monoclonal culture strains, and subcultured monthly. The C. palmyrensis strain was used for morphological and molecular identification, including phylogenetic relationships, while all four strains of C. malayensis were taxonomically identified for molecular phylogeny.
2.2 Morphology
The morphology of living cells of C. palmyrensis or C. malayensis was observed using an inverted microscope (Olympus BX53) for drawing the cell shape and thecal plate pattern. The live cell dimensions were measured using a digital camera (Olympus DP73; Tokyo, Japan). For scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, Sigma 500/VP; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany), culture samples (20 mL) containing approximately 3,000 cells mL-1 of C. palmyrensis or C. malayensis were fixed in seawater with a final concentration of 2% (v/v) glutaraldehyde for 1 h. The fixed cells were collected on a PC membrane filter (pore size 5 µm) without additional pressure and rinsed thrice with distilled water to remove salts. Dehydration was performed using a graded ethanol series (10, 30, 50, 70, 90, and 100% ethanol, followed by two 100% ethanol steps), and the final drying was performed using a critical point dryer (EM CPD300; Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) (Kang et al., 2010). The anteroposterior (AP) length, dorsoventral (DV) length, and width of C. palmyrensis or C. malayensis cells were measured using SEM micrographs, selecting only those images demonstrating the complete shape and size of each plate (viewed from directly above).
2.3 DNA extraction, PCR, and sequencing
Each monoclonal culture (30 mL) of the five Coolia strains was centrifuged (3000 × g, 10 min), harvested as cell pellets, and frozen at -80°C until DNA extraction. The preserved cell pellets were homogenized using Bel-Art® Disposable Micro Pestles, and genomic DNA (gDNA) was extracted using a GeneAll® Exgene™ Plant SV mini kit (GeneAll Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Korea), following the manufacturer’s protocol.
For species identification based on ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequence analysis, the ITS region was amplified using the primer pairs ITSF2-LSUB and ITSF2-ITSR2 (Litaker et al., 2003) obtained from the extracted gDNA samples. Amplification of the D1-D3 region of LSU rDNA was performed using the primer pairs D1R-D3B (Nunn et al., 1996) and D2CF-1256R (Momigliano et al., 2013). The PCR mixture was 50 µL, containing 5 µL of 10× F-Star Taq Reaction Buffer, 38.75 µL of UltraPure™ DNAse/RNAse-Free Distilled Water (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), 1 µL of 10 mM deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTPs), 0.25 μL of 5 U μL−1 BioFACT™ F-Star Taq DNA Polymerase (BioFACT Co., Ltd., Daejeon, Korea), 0.02 μM of both forward and reverse primers, and 3 µL of template DNA. PCR was performed using the Eppendorf Master Cycler PCR machine (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) under the following thermocycling conditions for the primer pair ITSF2-LSUB: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 56°C for 30 s and 72°C for 1 min; with a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The thermocycling conditions for ITSF2-ITSR2, D1R-D3B, and D2CF-1256R were pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 50°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min, with a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. All PCR products were purified using an AccuPrep PCR Purification Kit (BIONEER) and sent to Bionics (Bionics Co., Ltd., Daejeon, Korea) for Sanger sequencing. The results were aligned using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
2.4 Phylogenetic analysis
The analyzed sequences of five isolates for each gene region were aligned using the ClustalW algorithm with other sequences of the Coolia relatives obtained from the public GenBank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). In the ITS region, 46 sequences were compared, including the five isolates from this study and four outgroups. For the D1-D3 region of LSU rDNA, 65 sequences were taxonomically analyzed, including one outgroup. After alignment, all data were manually trimmed, and misalignments were inspected using the SILVA alignment and software package ARB project 6.0.6 (Pruesse et al., 2012). A Maximum Likelihood (ML) analysis was performed using MEGA7, calculating the bootstrap values for both ITS and D1-D3 LSU regions with 1000 replicates based on the Jukes-Cantor model to assess statistical reliability (Kumar et al., 2016). Phylogenetic reconstruction for sequence alignment was inferred using Bayesian inference (BI) by estimating evolutionary distances using BEAST 1.10.4 (Drummond et al., 2012). Consensus trees were generated and visualized using the TreeAnnotator 1.10.4 (Rambaut and Drummond, 2013) and Figtree 1.4.5 (Rambaut, 2009), respectively. The BI tree displayed Bayesian posterior probability values, which indicated statistical reliability.
2.5 TaqMan-based qPCR assay
Based on the sequences acquired from the isolates C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis, the species-specific primer and Taqman probe sets were designed using Beacon Designer 8.21 and Primer3 (version 0.4.0) software (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3-0.4.0/), targeting the D1-D3 region of the LSU rDNA and ITS region, respectively (Table 1). It was confirmed that all the delta G values of self-dimers, hairpins, and cross-dimers were weaker (more positive) than -2.4 kcal mol-1 from the designed primer and probe sets. The specificity of the primer sequences was confirmed using BLAST at the NCBI. The qPCR assay for cross-reactivity testing with other dinoflagellate species was assessed using gDNA samples extracted from clonal cultures of C. palmyrensis JSGP strain, four isolates of C. malayensis, and other established laboratory species using the GeneAll® Exgene™ Plant SV mini kit as described above (Table 2). For qPCR assays, the presence of C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis was quantified in samples collected from macroalgae on Jeju Island from 2021 to 2023. To assess the distribution of the benthic dinoflagellate Coolia in the East Sea of Korea, we analyzed the occurrence of these two species using qPCR at Pohang and Ulsan in the eastern coastal waters of Korea during June and August 2021 and June and October 2023. The qPCR mixtures contained 10 µL of qPCRBIO Probe Mix no-ROX (2×) (PCR Biosystems, London, England), 1 µL of 10 µM primer pairs, 0.5 µL of 10 µM TaqMan probe, 4.5 µL of UltraPure™ DNAse/RNAse-Free Distilled Water (Invitrogen), and 3 µL of template DNA in a final volume of 20 µL. Thermal cycling of the qPCR assay was performed using a PCRmax Eco 48 Real-time PCR System (Staffordshire, UK) under the following conditions: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min; 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 s and extension at 57°C (C. palmyrensis) or 54.5°C (C. malayensis) for 30 s, in the presence of no template control. Each standard curve of C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis for the qPCR assay was determined using the extracted gDNA based on a specific number of cells (40000, 20000, 4000, 2000, 400, and 40). The coefficient of determination (R2) and amplification efficiency for each assay were calculated from the standard curve-derived linear regression curves. For the assay performed using 10-fold serially diluted DNA extracts from each species, the limit of detection for both C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis was below 0.4 cells per reaction.

Table 1. Sequences of primers and probes for the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay targeting Coolia palmyrensis and Coolia malayensis.
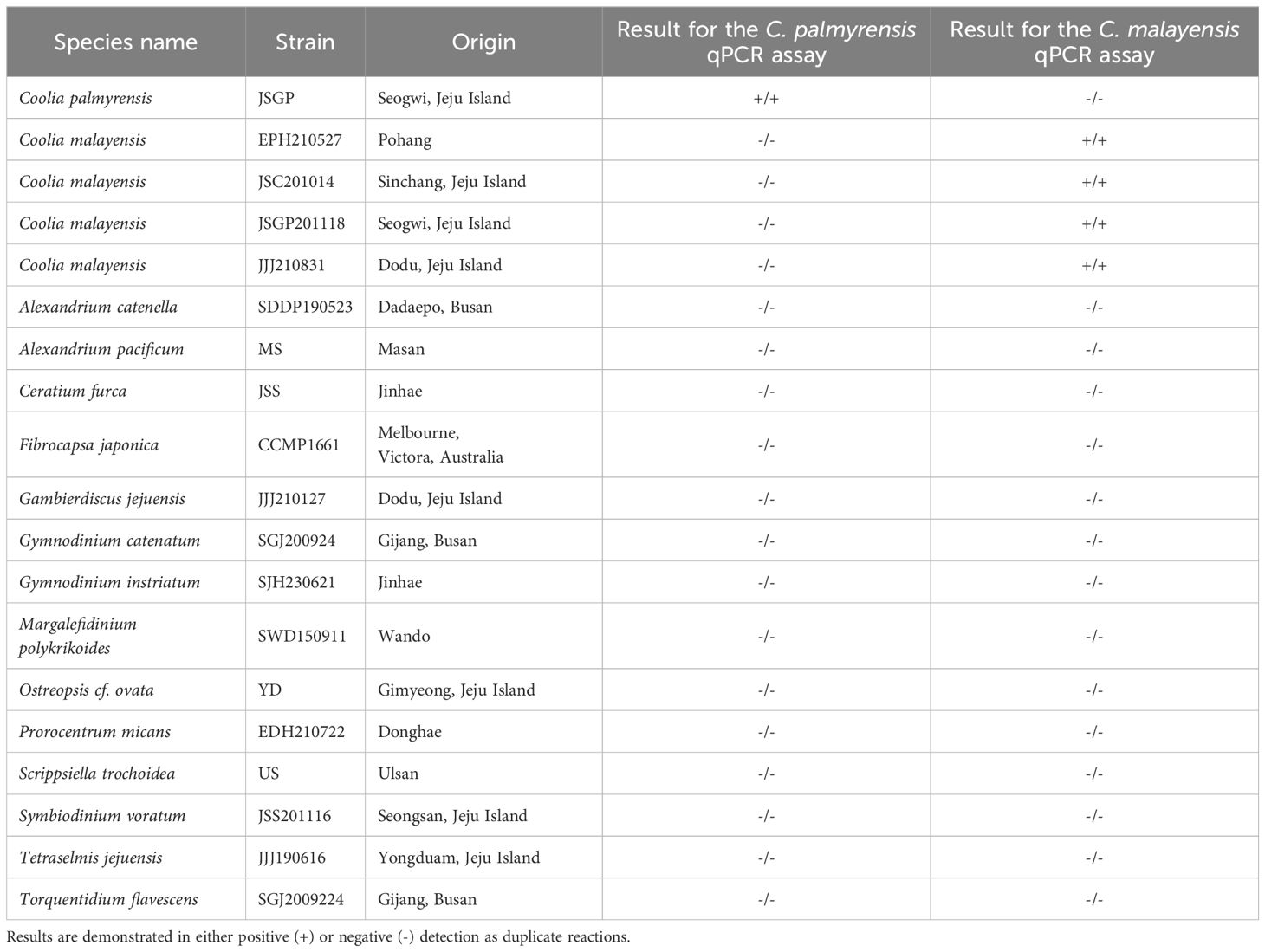
Table 2. Strains used for validating the specificity of Coolia palmyrensis and Coolia malayensis quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay.
3 Results
3.1 Environmental conditions of isolated strains
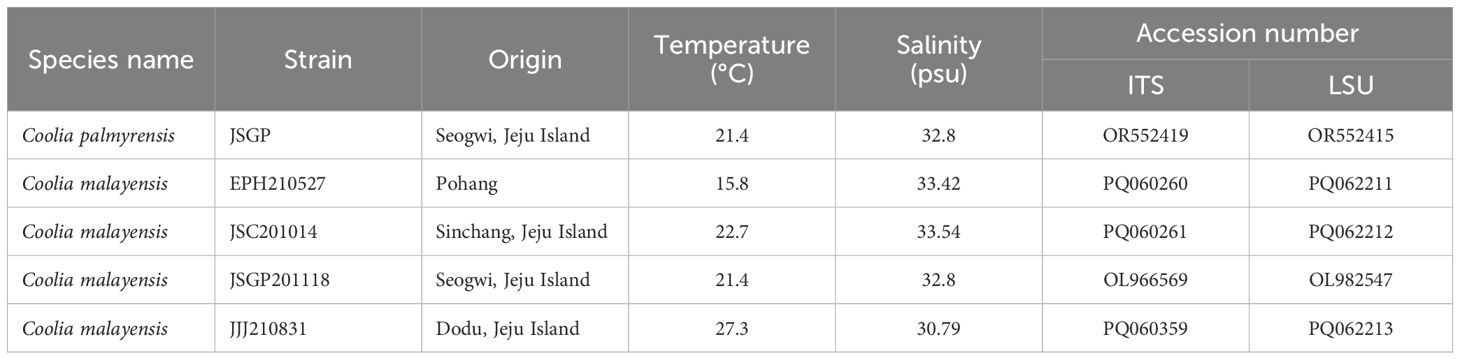
Five monoclonal culture strains of the Coolia species were established in the laboratory: one strain of Coolia palmyrensis (JSGP) and four strains of C. malayensis (EPH210527, JSC201014, JSGP201118, and JJJ210831). The JSGP strain of C. palmyrensis was isolated from Seogwi on Jeju Island, Korea, where the seawater temperature was 21.4°C and salinity was 32.80 psu (Table 3). Three strains of C. malayensis (JSGP201118, JJJ210831, and JSC201014) were isolated from Seogwi, Dodu, and Shinchang sites on Jeju Island, with water temperatures and salinities as follows: 21.4°C and 32.80 psu, 27.3°C and 30.79 psu, and 22.7°C and 33.54 psu, respectively. Another strain, EPH210527, was isolated from Pohang on the eastern coast of Korea, with a seawater temperature of 15.8°C and salinity of 33.42 psu. The surface seawater temperature and salinity data in Table 4 summarize the seasonal variations observed at Jeju Island from 2021 to 2023. For the stations in Pohang and Ulsan on the eastern coast of Korea, data were collected in June and August in 2021, and June and October in 2023 (Table 5).
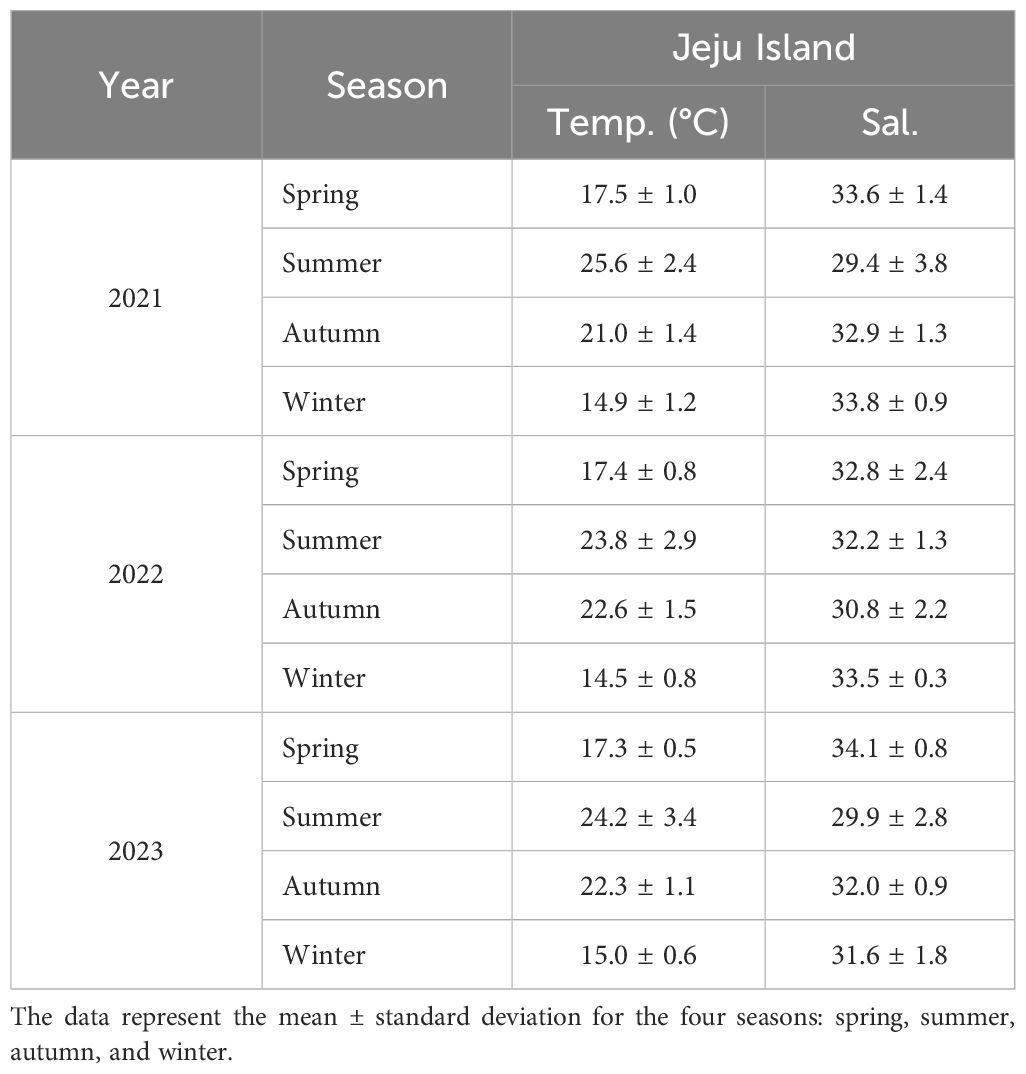
Table 4. Seasonal variations in surface seawater temperature (°C) and salinity at Jeju Island, Korea, from 2021 to 2023.
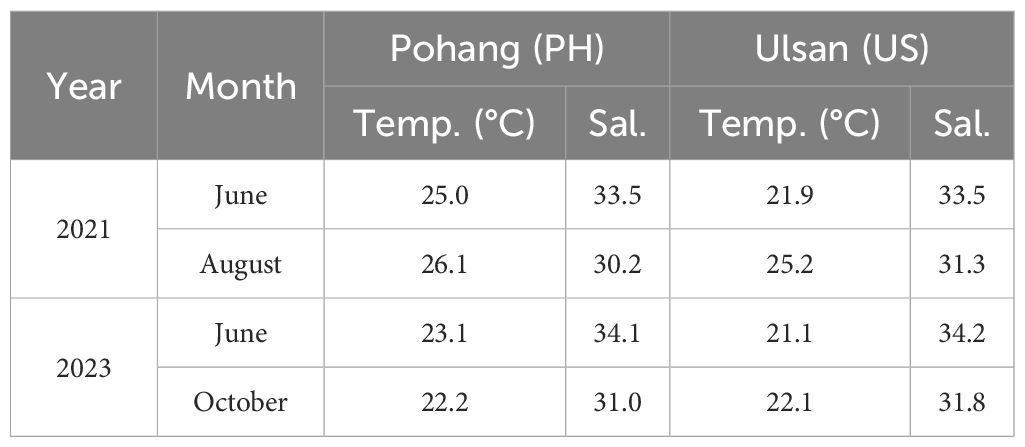
Table 5. Surface seawater temperature (°C) and salinity data collected from Pohang (PH) and Ulsan (US) on the eastern coast of Korea during June and August in 2021, and June and October in 2023.
3.2 Morphology of the Korean strain of Cooila palmyrensis
The cells were nearly spherical or ovoidal in both apical and antapical views and slightly compressed in the lateral view (Figures 2A–F). The hypotheca was slightly larger or similar in size to that of the epitheca. The AP length of the cells ranged from 17.4–30.1 μm, and the width ranged from 18.6–29.4 μm. The DV depth ranged from 19.5–26.0 μm. The thecal surface was generally smooth. The cingulum, which was indented in the equatorial region, encircled the transverse axis of the cell. The sulcus was deeply indented on the ventral side of the hypotheca, but did not extend to the bottom (Figure 2D).
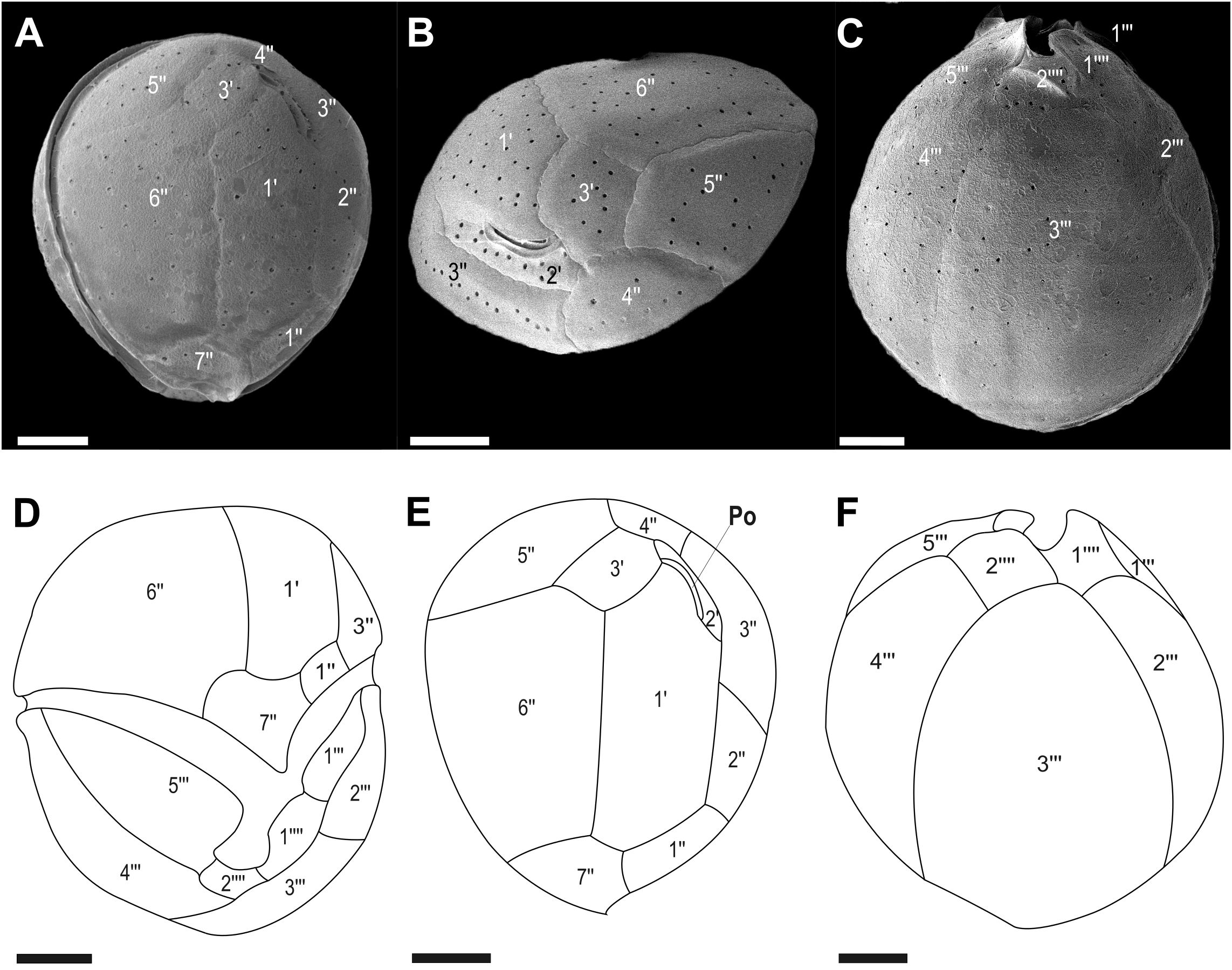
Figure 2. Micrographs of Coolia palmyrensis cells obtained using scanning electron microscopy (SEM): (A, B) apical views and (C) antapical view. Line drawings of (D) ventral view, (E) apical view, and (F) antapical view. Scale bar = 5 µm.
The thecal plate formula was apical pore complex (APC), 3', 7", 5''', and 2"". The epitheca consisted of three apical plates (1'–3'), APC, and seven pre-cingular plates (1"–7"). The pentagonal plate 6" was the largest in the epitheca, followed by the hexagonal plate 1'. The 3' plate was pentagonal (Figures 2A, B, E). The pentagonal plate 7" ranged from 3.8–9.1 μm in height and 5.5–8.3 μm in width, with a width-to-height ratio of 1.2 to 2.1. The hypotheca was composed of five post-cingular (1'"–5'") and two antapical (1""–2"") plates. Plates 3'" and 4'" occupied the majority of the hypotheca, with plate 3'" being the widest, often covering more than half of the hypotheca surface area. Plates 2'" and 5'" followed in size. Plate 2'" was adjacent to plates 1'", 3'", and 1"" (Figures 2C, F).
3.3 Morphology of the Korean strain of Cooila malayensis
In this study, the morphological characteristics of C. malayensis isolated in this study were identical to those reported for the first time in Korea (Jeong et al., 2012). The cell shape was nearly spherical, with a slight depression in the center when viewed ventrally. From the lateral view, it appeared slightly tilted and ovoid, resembling a pointed teardrop when viewed apically (Figures 3A–D). The hypotheca was similar in size or slightly larger than that of the epitheca. The AP cell length ranged from 20.8–27.0 μm, width ranged from 22.4–27.9 μm, and DV thickness ranged from 24.6–30.3 μm. Circular pores were randomly distributed across the thecal surface. The sulcus was deeply indented in the ventral hypotheca, but did not extend to the bottom.
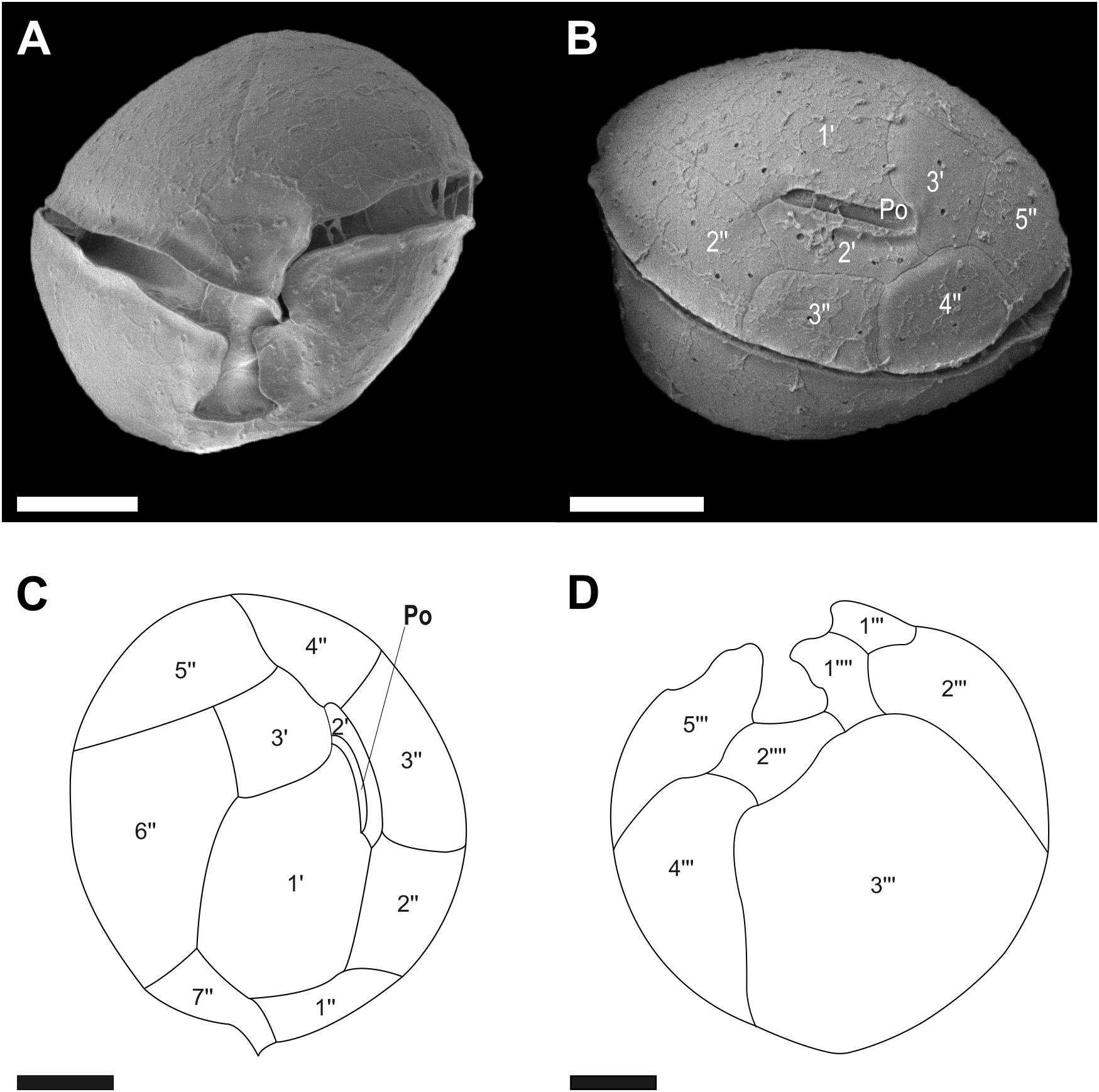
Figure 3. Micrographs of Coolia malayensis cells obtained using scanning electron microscopy (SEM): (A) ventral view and (B) dorsal view. Line drawings of (C) apical view and (D) antapical view. Scale bar = 5 μm.
The thecal plate formula comprised APC, 3', 7", 5'", and 2"". The epitheca consisted of three apical plates (1'–3'), APC, and seven pre-singular plates (1"–7") (Figure 3C). In the side view, it appeared as a straight slit, slightly covered by plates 1', 2', and 3', with an APC length of 4.6–5.7 μm (Figure 3B). Plates 1" to 7" were arranged counterclockwise around the sulcal axis. The hypotheca consisted of five post-cingular plates (1'"–5'") and two antapical (1""–2"") plates. Plates 3'" and 4'" occupied the majority of the hypotheca. Plate 1"" was on the right side and plate 2"" on the posterior part of the sulcus. The thecal surface contained numerous pores (Figure 3D).
3.4 Phylogeny of Coolia species
The molecular taxonomy of Coolia strains isolated from Jeju Island and the East Sea of Korea was analyzed using Bayesian phylogenies of ITS regions and D1-D3 LSU rDNA sequences. This included the strains from this study and additional reference sequences from GenBank. In the ITS trees, four strains—JSGP201118, JJJ210831, and JSC201014, isolated from Jeju Island, and EPH210527 from Pohang in the East Sea—were placed within the phyletic clade of C. malayensis, with highly supported statistical values of ML and posterior probabilities of BI at node (93/1.00) (Figure 4). The strain EPH210527 diverged from the other three statins within C. malayensis, with ML and BI values of 78 and 1.00, respectively, at node. However, the strain JSGP isolated in this study was clustered with the C. palmyrensis and supported by ML and BI values of 99 and 1.00, respectively. In the LSU trees, the four strains of Coolia were grouped into the phyletic clade of C. malayensis with high ML and BI values of 99 and 1.00, respectively (Figure 5), whereas JSGP was clustered with the C. palmyrensis, supported by ML and BI values of 94 and 1.00, respectively.
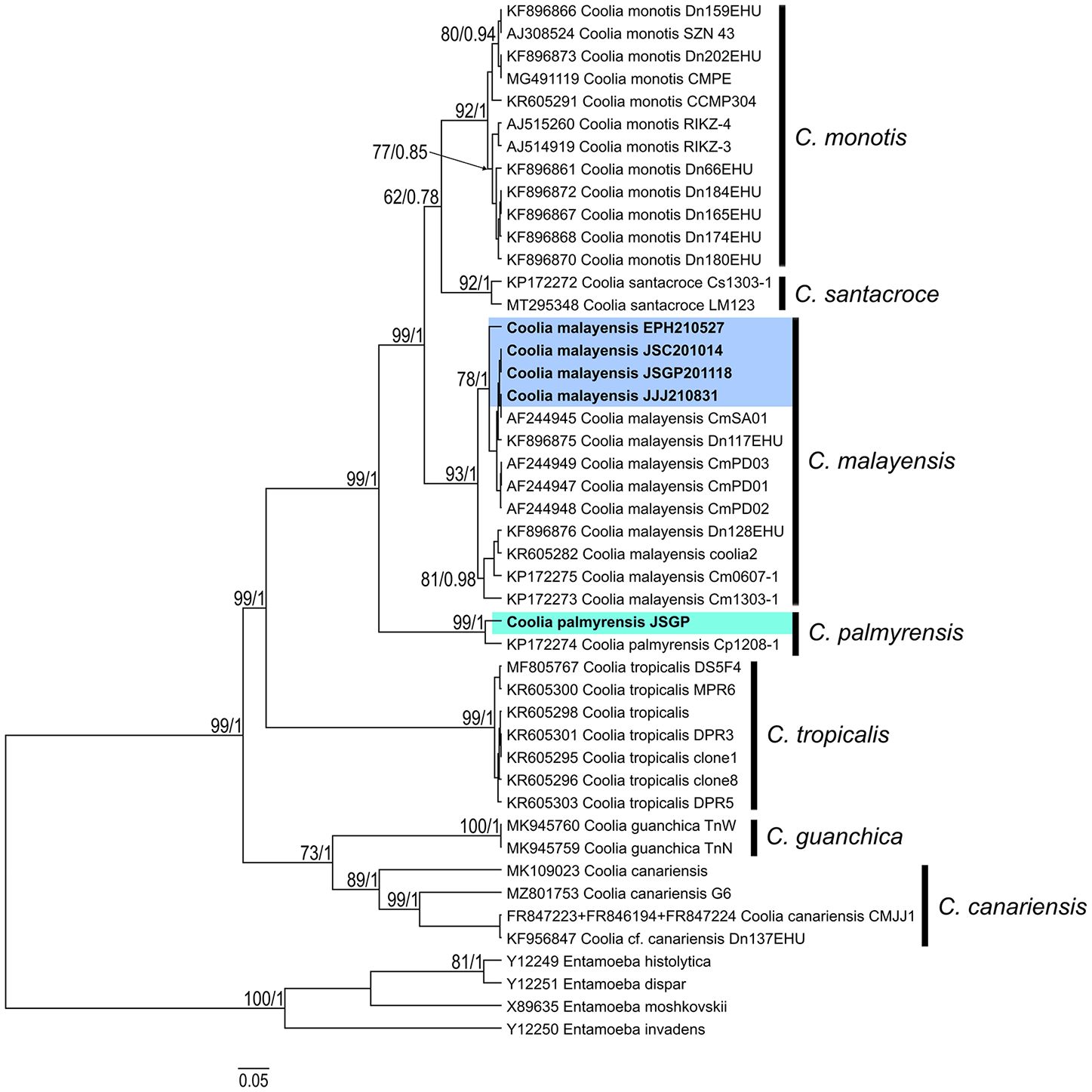
Figure 4. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of Coolia palmyrensis and Coolia malayensis isolates from Jeju Island and the East Sea of Korea based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions of ribosomal DNA (rDNA). Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap support values from Maximum Likelihood (ML) on 1000 replicates and posterior probabilities from Bayesian Inferences (BI). The scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
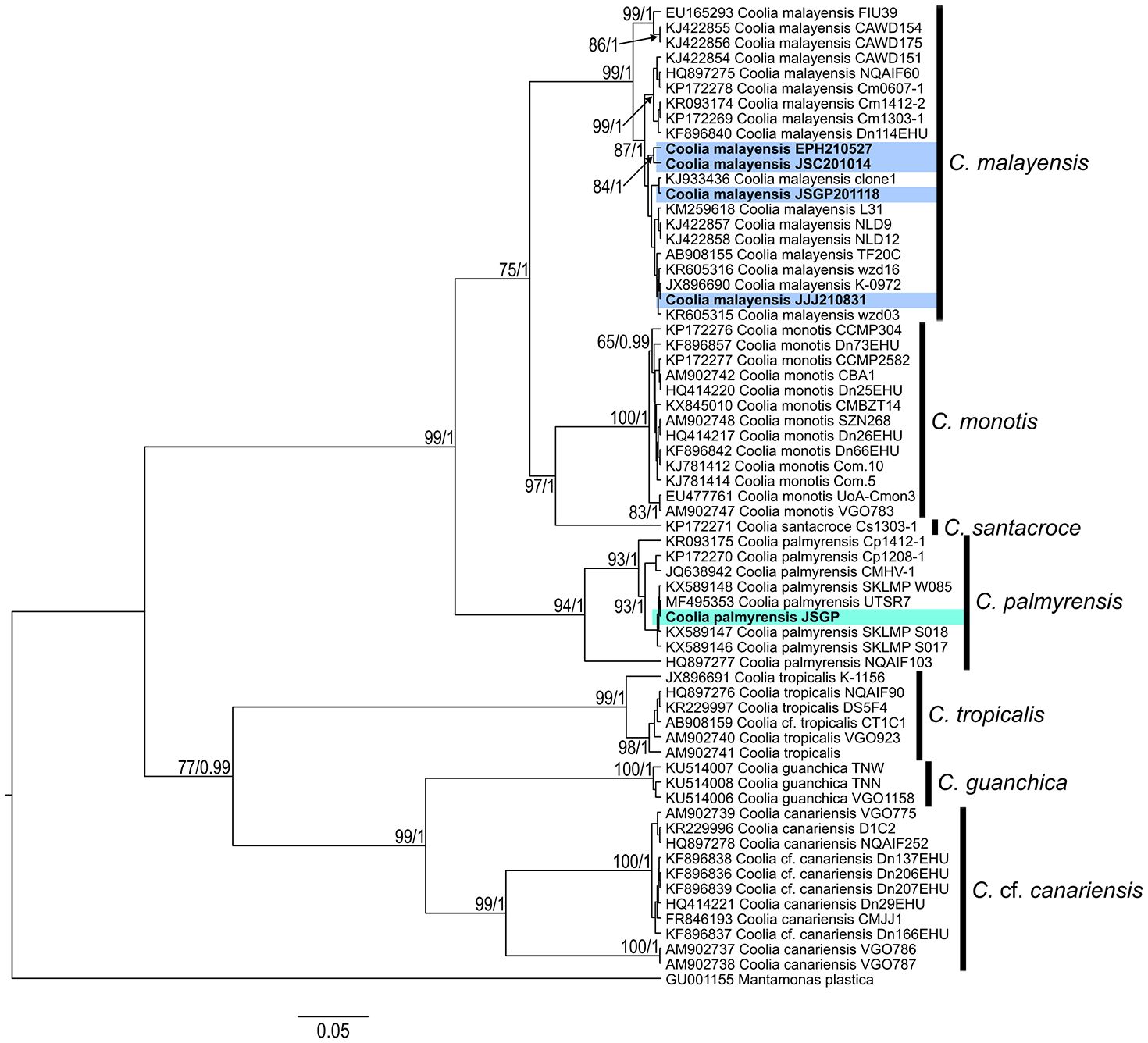
Figure 5. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of Coolia palmyrensis and Coolia malayensis isolates from Jeju Island and the East Sea of Korea based on the D1-D3 large subunit ribosomal DNA (LSU rDNA) sequences. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap support values from Maximum Likelihood (ML) on 1000 replicates and posterior probabilities from Bayesian Inferences (BI). The scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
3.5 Distributions of Coolia species
For the qPCR assay, a cell-based standard curve was established based on a linear slope between the log cell numbers of C. palmyrensis and cycle threshold (Ct) values, with R2 and amplification efficiency of 0.94 and 85%, respectively (Figure 6A). Additionally, the qPCR assays using primers targeting the ITS region of the rDNA of Coolia malayensis amplified the target species, with no detection of other Coolia species and dinoflagellates. The cell-based standard curve, plotted using a log-linear portion, exhibited good R2 and amplification efficiency of 0.98 and 108%, respectively (Figure 6B).
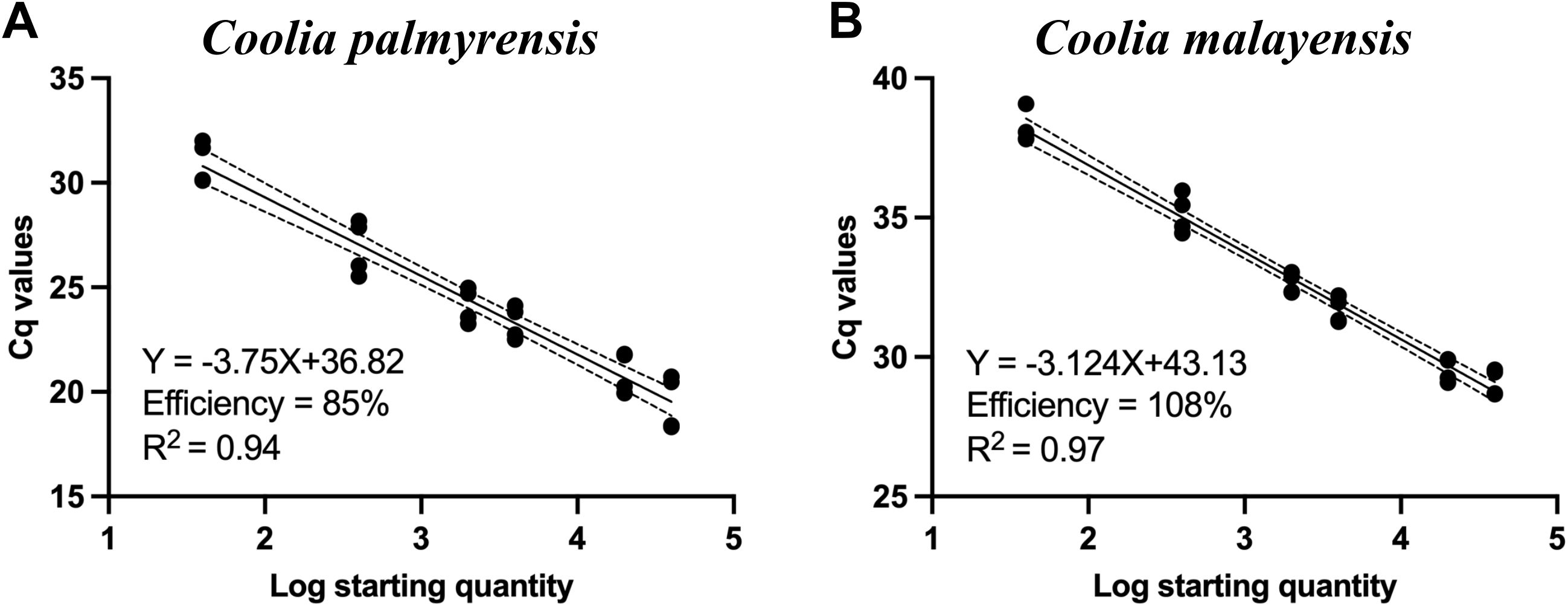
Figure 6. Standard curves of (A) Coolia palmyrensis and (B) Coolia malayensis for the species-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays with a specific number of cells of genomic DNA (gDNA) extracts from each established clonal culture.
We analyzed 154 samples collected across four locations (north, south, east, and west) on Jeju Island for the presence of C. palmyrensis using qPCR between 2021 and 2023. In 2021, positive detections were observed on diverse macroalgal species between the summer and autumn. During summer, low cell concentrations (2 cells g-1 fresh weight (FW) macroalgae) were detected only in the north, whereas in autumn, the cells were distributed throughout the region in all four directions (Figure 7A). The maximum abundances were 11 and 9 cells g-1 FW macroalgae in the north and south, respectively. However, significantly higher concentrations were recorded in the west and east, with 107 and 242 cells g-1 FW macroalgae, respectively. In 2022, the cells were detected in the north during spring at a density of 68 cells g-1 FW macroalgae, and in both the north and south during autumn at concentrations < 10 cells g-1 FW macroalgae. From spring to autumn of 2023, the cells were positively identified in the northern (Dodu) and eastern (Seongsan) regions. Concentrations were < 10 cells g-1 FW macroalgae at all points except in the north during summer, when the maximum cell density was 12 cells g-1 FW macroalgae. The cells survived during winter in the south (Seogwi) of Jeju Island at a density of 28 cells g-1 FW macroalgae on the macroalga Plocamium uncinatum. In contrast, C. malayensis was not detected in any of the samples collected from Jeju Island during the study period (Figure 7B).
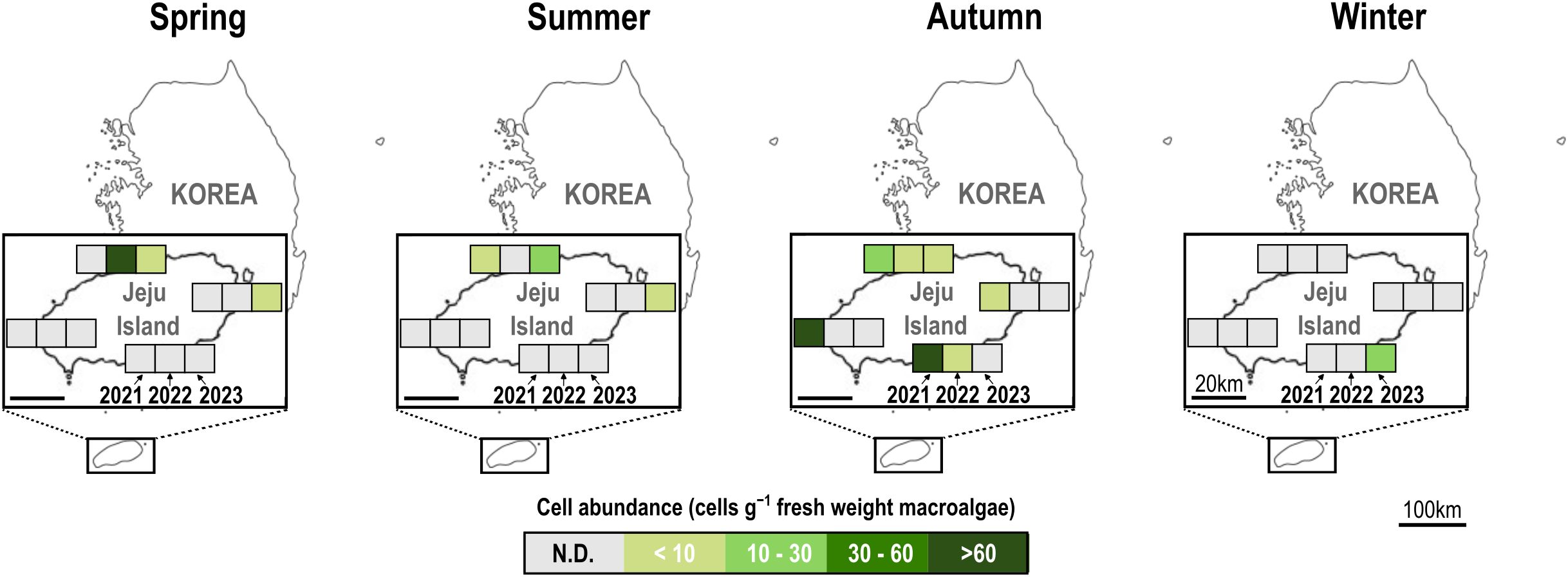
Figure 7. Seasonal cell abundance of Coolia palmyrensis in macroalgal samples collected from Jeju Island from 2021 to 2023, determined using a species-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay. Samples were collected from four locations on Jeju Island: Dodu (north), Seogwi (south), Seongsan (east), and Sinchang (west). Each square represents the abundance of C. palmyrensis cells (cells g-1 fresh weight macroalgae) in the respective location and season. The intensity of the color corresponds to the cell density, with darker shades indicating higher cell concentrations. N.D., not detected.
In June, cell densities on four macroalgal species (Ulva linza, Sargassum coreanum, Sargassum miyabei, and Ulva australis) collected in Pohang were 48, 312, 38, and 537 cells g-1 FW macroalgae, respectively (Figure 8, June #1–#4). In Ulsan, the cell density of the macroalgae Callophyllis adnata was 201 cells g-1 FW macroalgae, whereas no cells were identified in August. Coolia palmyrensis was detected with a maximum abundance of 13 cells g-1 FW macroalgae on the macroalgae Gracilariales in Pohang, and 8 cells g-1 FW macroalgae on the macroalgae Corallina pilulifera in Ulsan in August, with no cells detected in June. In 2023, C. palmyrensis cells were at a density of 1 cell g-1 FW macroalgae on Sargassum macroalgae in Pohang in June, whereas C. malayensis cells were at a density of 11 cells g-1 FW on Plocamium uncinatum in similar locations and months.
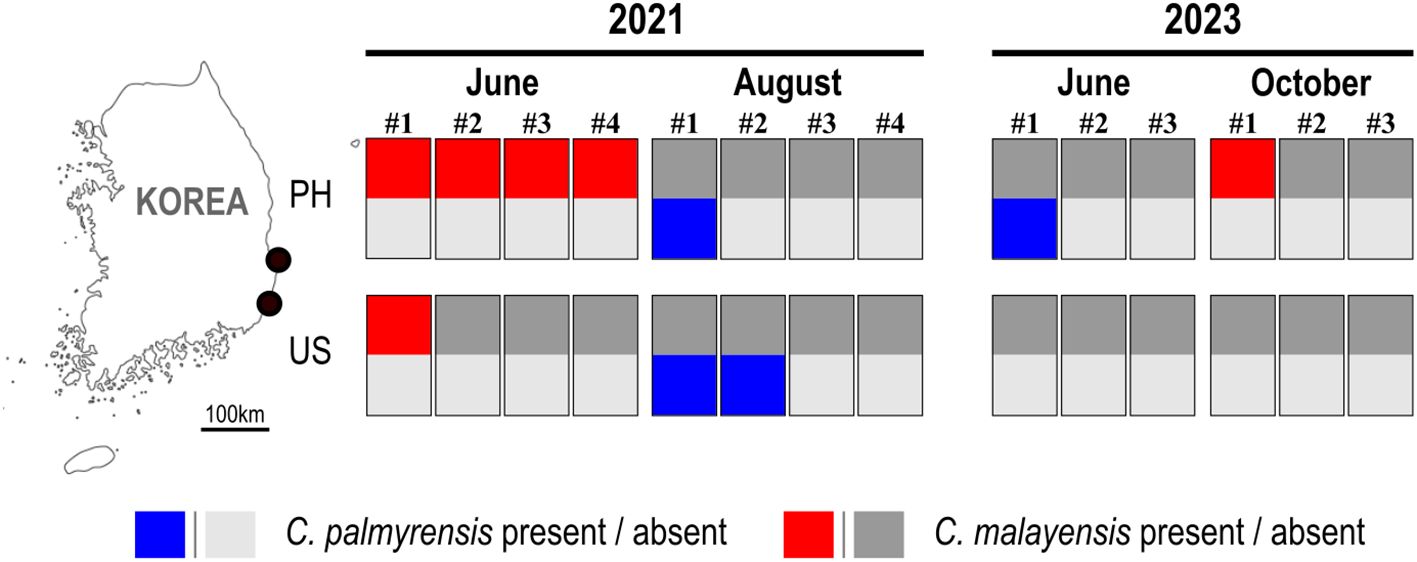
Figure 8. Map of the sampling sites in Pohang (PH) and Ulsan (US) showing the occurrence of the benthic dinoflagellates Coolia palmyrensis and Coolia malayensis in June and August 2021, and June and October 2023. Each numbered label represents individual macroalgal samples collected during that time period. Rectangular boxes correspond to qPCR assay results for these samples: the upper half of each box indicates the presence (red) or absence (gray) of C. malayensis, and the lower half indicates the presence (blue) or absence (gray) of C. palmyrensis. Light and bold grey colors are used to differentiate the absence of C. palmyrensis (light grey) and C. malayensis (bold grey).
4 Discussion
Species within the genus Coolia are predominantly found in tropical and temperate marine regions. To date, eight species have been reported: C. areolata, C. canariensis, C. guanchica, C. malayensis, C. monotis, C. palmyrensis, C. santacroce, and C. tropicalis (David et al., 2020; Faust, 1995; Fraga et al., 2008; Karafas et al., 2015; Leaw et al., 2010; Meunier, 1919; Ten-Hage et al., 2000b). C. palmyrensis was initially reported by Karafas et al. (2015) from Palmyra Atoll in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, near the equator. The plate formula of C. palmyrensis isolated from Jeju, Korea, was identical to that of the original report of this species. However, in this study, the 3' plate was pentagonal, whereas Karafas et al. (2015) described it as either pentagonal or hexagonal. In contrast, the 3' plate of C. malayensis was quadrangular and did not contact the 5" plate in its original description (Leaw et al., 2016), which differentiates it from C. palmyrensis, whose 3' plate is pentagonal and contacts the 5" plate. However, subsequent studies on other C. malayensis populations have demonstrated that the 3' plate can also be pentagonal and contact the 5" plate, similar to C. palmyrensis, indicating variability in the 3' plate shape within C. malayensis populations (Jeong et al., 2012; de Queiroz Mendes et al., 2019). Because C. areolata, C. canariensis, C. malayensis, C. monotis, and C. palmyrensis exhibit similar morphological characteristics, such as cell shape, cell size, and plate arrangement, distinguishing among these species is crucial to identify the potential causative species.
Following taxonomic revisions of the epiphyte dinoflagellates (Coolia) based on the cross-verification of morphological and molecular data, it was considered that the identification results of the species lacking reliable molecular data required further confirmation to prevent confusion in understanding their distribution (Leaw et al., 2016). In this study, both ITS regions and D1-D3 LSU rDNA sequences from C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis isolates in Korea demonstrated a well-resolved phylogeny with strongly supported statistical values for ML and BI (Figures 4, 5). These phylogenetic trees revealed similar branching patterns and phyletic clades in Coolia, which is consistent with previous studies (Jeong et al., 2012; Mohammad-Noor et al., 2013; Karafas et al., 2015; Wakeman et al., 2015; Larsson et al., 2019).
In 2016, Leaw et al. highlighted that identification based on both morphological differences and molecular lineages should be used to establish a more accurate classification of the benthic dinoflagellate taxonomy and the biogeography of Coolia species. The species C. palmyrensis was observed in various tropical regions: the Great Barrier Reef in Australia in the Southwestern Pacific (Momigliano et al., 2013) and Palmyra Atoll in the Pacific and the Dominican Republic in the Atlantic Ocean (Karafas et al., 2015), indicating that this species is likely restricted to tropical regions within the 30° north and south latitudinal range. Additionally, subsequent studies have confirmed its presence in tropical waters: Long Ke in the eastern waters of Hong Kong at 22° latitude (Leung et al., 2017); Heron Island Lagoon in Australia at 23° latitude (Larsson et al., 2019); Abrolhos Archipelago (Bahia) and Pernambuco in Brazil at 13 and 8° latitude, respectively (Tibiriçá et al., 2020); Pago Bay in Guam (Phua et al., 2021); and Isla San José in the southwest Gulf of California (Morquecho et al., 2022) (Figure 9). These identifications were confirmed based on both morphological and molecular data. In this study, we observed C. palmyrensis on Jeju Island, Korea, and identified its morphological and molecular lineages after establishing a clonal culture. This is the first report of C. palmyrensis in Korea, with confirmed overwintering populations in 2023. Overwintering cells of the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata were detected at an average density of 139 cells g-1 around Jeju Island, Korea (Park et al., 2020). These observations indicate that these species have adapted to the local environmental conditions in Korea. This adaptation highlights the resilience of these microorganisms and their potential implications in regional ecosystem dynamics. Consequently, C. palmyrensis may have integrated into the established benthic phytoplankton communities on Jeju Island. The isolation site in Seogwi is located at 33° latitude in temperate waters.
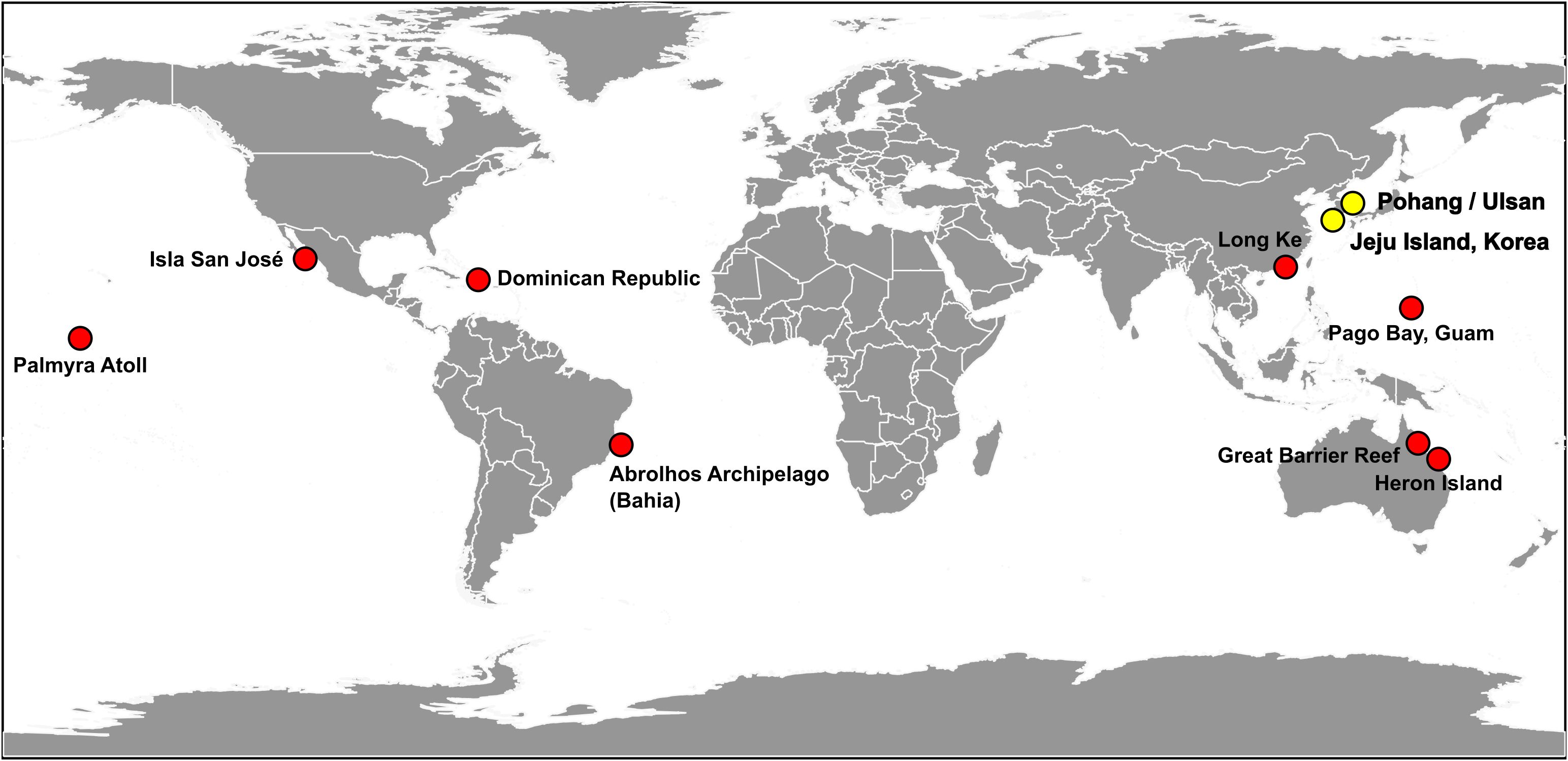
Figure 9. Global distribution of Coolia palmyrensis. The locations, where each strain has been isolated and identified through a combination of morphological and molecular assessment, are represented with circles. Red circles represent data reported from previous literatures, whereas yellow circles indicate data obtained from this study.
Because of global warming and rise in seawater temperature, the benthic dinoflagellates are expanding their biogeographic distribution to temperate waters (Wells et al., 2020). For example, Gambierdiscus species produce biotoxins that cause ciguatera fish poisoning (CFP), and were traditionally distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical waters. Recently, these species have been observed in the temperate regions of the Pacific Ocean (Litaker et al., 2010). The species G. toxicus was observed on macroalgae with a maximum cell density of 4.7 cells g-1 in the brown algae in Ago Bay, Japan, at 34° latitude (Ishikawa and Kurashima, 2010). Similarly, the occurrence of C. palmyrensis in the Seogwi area may be a result of habitat expansion of tropical benthic dinoflagellates driven by climate change, facilitating their survival within the thermal tolerance of each species. Our study further supports this hypothesis by revealing a steady rise in seawater temperature along both the eastern coast and Jeju Island in Korea from 2015 to 2021 (Figure 10). During this period, seawater temperatures on the eastern coast of Korea increased by approximately 3.0°C, while in Jeju Island, the increase was around 2.2°C. This consistent warming trend is likely contributing to the northward expansion of tropical benthic dinoflagellates, including C. palmyrensis, into temperate regions such as Jeju Island. Warmer temperatures may enhance the survival and reproduction rates of C. palmyrensis, allowing it to establish and maintain overwintering populations even in non-tropical waters. Therefore, the habitat expansion of C. palmyrensis in Korea appears closely linked to these changing thermal conditions, highlighting the ecological impacts of global warming on marine ecosystems. To fully understand the introduction and establishment of C. palmyrensis in Korea, further studies are needed to examine the relationship between seawater temperature alterations and their geographic distributions, along with other environmental factors such as the influence of the Tsushima Current and changes in macroalgal species composition. Long-term monitoring considering those factors will be essential to clarify the mechanisms driving the geographic expansion of benthic dinoflagellates in Korean waters.
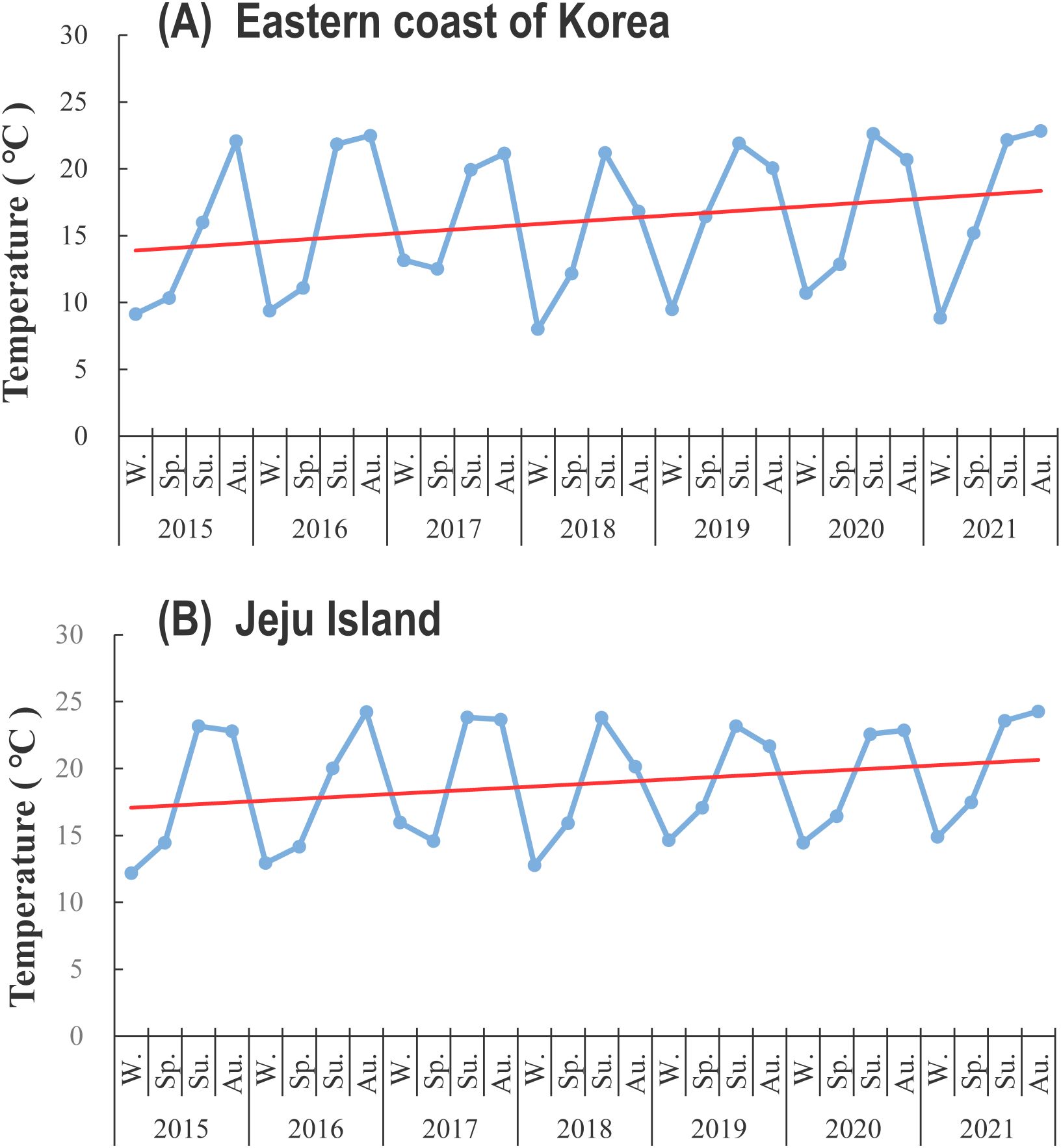
Figure 10. Temporal changes in seawater temperature (°C) from 2015 to 2021 at (A) the eastern coast of Korea and (B) Jeju Island. The blue line represents seasonal temperature variations, and the red line indicates the linear trend of temperature increase over time. The data suggest a total increase in seawater temperature of 3.0°C on the eastern coast and 2.2°C on Jeju Island over the 7-year period. W., Sp., Su., and Au. indicate winter, spring, summer, and autumn, respective.
The presence of epiphytic dinoflagellates in Korean waters was first reported in autumn 2009, with Coolia spp. reaching a maximum abundance of 710 cells g-1 on macroalgae, which was determined through light microscopy using a Sedgwick-Rafter counting chamber (Kim et al., 2011). In 2012, Korean strains of C. canariensis and C. malayensis were observed off Jeju Island at 33° latitude, and their identification was confirmed through morphological and molecular analyses (Jeong et al., 2012). However, there has been no further research on the distribution and occurrence of these species in the coastal waters of Jeju Island, or even in Korea.
In this study, although C. malayensis cells were not detected in macroalgal samples from Jeju Island using the species-specific quantitative PCR assay during the study period, we were able to isolate and establish a clonal culture of the species from the same macroalgal samples. This suggests that the cell abundance may have been below the detection limit of the qPCR assay, yet sufficient for successful isolation and culturing. Numerous researchers have been interested in understanding the alterations in biogeographic distributions of benthic dinoflagellates in response to ocean climate change (Hallegraeff, 1993, 2010; Aligizaki, 2009; Wells et al., 2020). For example, the species Ceratium hexacanthum (currently regarded as Tripos hexacanthus) has expanded its geographic range from the south of the British Isles to the North Sea of Scotland (Hays et al., 2005). The widespread distribution of the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis from tropical waters to higher latitudes is attributed to its ability to thrive at increased temperatures, driven by global warming (Shears and Ross, 2009; Accoroni et al., 2024). We identified C. malayensis in macroalgal samples from the coastal waters of Pohang and Ulsan in the East Sea of Korea, although the observations were sporadic. These two sites were located further north of Jeju Island at 36 and 35° latitude, respectively. Similarly, Coolia was detected in Pohang in 2012, with a maximum cell density of 3 cells g-1 using fluorescence microscopy, and this observation was confirmed even in Yangyang, which is further north of Pohang (Baek, 2012). Because benthic dinoflagellates on Jeju Island have migrated from tropical waters to the temperate regions of Korean coastal waters through the Tsushima Current (Lim et al., 2021), the northeastward migration of Coolia cells along the Korean Peninsula may be facilitated by the current and its branches, potentially in response to oceanic climate changes. In August 2023, C. malayensis cells were observed in plankton net samples collected from Yangyang at a high density of 5367 cells L-1, which was analyzed using qPCR (unpublished data). Additionally, the cells were identified at a similar site in October 2023 at a density of 3 cells g-1 in the macroalgae Amphiroa beauvoisii. Moreover, at the same time, Coolia palmyrensis occurred in Sokcho, which is located further north of Yangyang, at a cell density of 5 cells g-1. The distribution of C. malayensis from Jeju Island, where the cells were previously reported by Jeong et al. (2012), to the eastern coastal waters of Korea may be associated with environmental changes driven by climate-related changes. However, the intermittent monitoring results of the two Coolia species do not offer conclusive insights. Further studies based on long-term monitoring and measurements of environmental changes, such as the composition of macroalgae in habitats and increasing temperature, are required to clarify the reasons for the changing distributions and understand the migration patterns of Coolia species towards the north in Korea.
5 Conclusion
Among the five isolates of Coolia species, one was Coolia palmyrensis and the other four were Coolia malayensis, based on morphological and phylogenetic analyses. This study represents the first report of C. palmyrensis in Korea, with qPCR assay monitoring revealing an established population on Jeju Island, specifically during autumn, and overwintering populations in 2023. However, C. malayensis, previously observed only on Jeju Island, was not observed at the same sites during the study period. Considering the potential for climate change to shift coastal habitats of benthic organisms, the assessment was expanded to Pohang and Ulsan in the eastern coastal waters of Korea, located further north than Jeju Island. At these sites, a considerable number of C. malayensis cells were observed at Pohang sites, alongside the presence of C. palmyrensis, as determined through qPCR. Although these observations were sporadic, this study enhances our understanding of the migration patterns of benthic dinoflagellates. Further assessments are required to understand the relationships between the changing distribution of Coolia species and other environmental factors in response to climate change.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author. The genetic data produced for this study have been deposited in Genbank, with the accession numbers indicated in Table 3.
Author contributions
J-HH: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation. SM: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. HL: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Formal analysis. JP: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by National Research Foundation (NRF) grants (NRF-2022M3I6A1086447, NRF-2021R1A2C1005943) to JP funded by the Korean government (MSIT).
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Hae Jin Jeong at Seoul National University for providing the information on the species-specific primer for detecting C. malayensis. We also thank Dr. Nan Seon Kang at National Marine Biodiversity Institute of Korea for providing technical support with the Scanning Electron Microscopy. Additionally, we thank Eun Joo Kim, member of our research laboratory, for her support in field work and technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
LAMP, loop-mediated isothermal amplification; APC, apical pore complex.
References
Accoroni S., Neri F., Ubaldi M., Romagnoli T., Totti C. (2024). Trend of Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyceae) along the Conero Riviera (northern Adriatic Sea) over two decades. Phycologia 63, 261–270. doi: 10.1080/00318884.2024.2318819
Aligizaki K. (2009). “Spread of potentially toxic benthic dinoflagellates in the Mediterranean Sea: a response to climate change?” in Phytoplankton Response to Mediterranean Environmental Change, ed. Workshop C. (Tunisia: CIESM), 57–61.
Anderson D. M., Fensin E., Gobler C. J., Hoeglund A. E., Hubbard K. A., Kulis D. M., et al. (2021). Marine harmful algal blooms (HABs) in the United States: History, current status and future trends. Harmful Algae 102, 101975. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.101975
Baek S. H. (2012). First report for appearance and distribution patterns of the epiphytic dinoflagellates in the Korean peninsula. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 30, 355–361. doi: 10.11626/kjeb.2012.30.4.355
Ballantine D. L., Tosteson T. R., Bardales A. T. (1988). Population dynamics and toxicity of natural populations of benthic dinoflagellates in southwestern Puerto Rico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 119, 201–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(88)90193-1
Boente-Juncal A., Álvarez M., Antelo Á., Rodríguez I., Calabro K., Vale C., et al. (2019). Structure elucidation and biological evaluation of maitotoxin-3, a homologue of gambierone, from Gambierdiscus Belizeanus. Toxins 11, 79. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020079
Cagide E., Louzao M., Espiña B., Ares I., Vieytes M., Sasaki M., et al. (2011). Comparative cytotoxicity of gambierol versus other marine neurotoxins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 24, 835–842. doi: 10.1021/tx200038j
David H., Laza-Martínez A., Rodríguez F., Fraga S., Orive E. (2020). Coolia guanchica sp. nov.(Dinophyceae) a new epibenthic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Eur. J. phycol. 55, 76–88. doi: 10.1080/09670262.2019.1651400
de Queiroz Mendes M. C., de Castro Nunes J. M., Fraga S., Rodríguez F., Franco J. M., Riobó P., et al. (2019). Morphology, molecular phylogeny and toxinology of Coolia and Prorocentrum strains isolated from the tropical South Western Atlantic Ocean. Botanica Marina 62, 125–140. doi: 10.1515/bot-2018-0053
De Vargas C., Audic S., Henry N., Decelle J., Mahé F., Logares R., et al. (2015). Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit ocean. Science 348, 1261605.
Drummond A. J., Suchard M. A., Xie D., Rambaut A. (2012). Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 29, 1969–1973. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss075
Faust M. (1992). Observations of the morphology and sexual reproduction of Coolia monotis (Dinophyceae). J. phycol. 28, 94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1992.00094.x
Faust M. A. (1995). Observation of sand-dwelling toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from widely differing sites, including two new species. J. phycol. 31, 996–1003. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1995.00996.x
Fraga S., Penna A., Bianconi I., Paz B., Zapata M. (2008). Coolia canariensis sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new nontoxic epiphytic benthic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands 1. J. phycol. 44, 1060–1070. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2008.00555.x
Gómez F. (2012). A quantitative review of the lifestyle, habitat and trophic diversity of dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata, Alveolata). Systematics Biodiversity 10, 267–275. doi: 10.1080/14772000.2012.721021
Granéli E., Ferreira C., Yasumoto T., Rodrigues E., Neves M. (2002). Sea urchins poisoning by the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata on the Brazilian coast, Book of Abstracts of Xth International Conference on Harmful Algae. St. Petersburg Florida p, 113.
Guillard R. R. L., Ryther J. H. (1962). Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239. doi: 10.1139/m62-02
Hallegraeff G. M. (1993). A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32, 79–99. doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-32-2-79.1
Hallegraeff G. M. (2010). Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: a formidable predictive challenge 1. J. phycol. 46, 220–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00815.x
Hays G. C., Richardson A. J., Robinson C. (2005). Climate change and marine plankton. Trends Ecol. Evol. 20, 337–344. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2005.03.004
Holmes M. J., Lewis R. J., Jones A., Hoy A. W. W. (1995). Cooliatoxin, the first toxin from Coolia monotis (Dinophyceae). Natural toxins 3, 355–362. doi: 10.1002/nt.2620030506
Hoppenrath M., Chomérat N., Horiguchi T., Schweikert M., Nagahama Y., Murray S. (2013). Taxonomy and phylogeny of the benthic Prorocentrum species (Dinophyceae)—A proposal and review. Harmful algae 27, 1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2013.03.006
Hoppenrath M., Murray S. A., Chomérat N., Horiguchi T. (eds.) (2014). Marine Benthic Dinoflagellates - Unveiling Their Worldwide Biodiversity, Vol. 54. (Kleine Senckenberg-Reihe), 276.
Ishikawa A., Kurashima A. (2010). Occurrence of the toxic benthic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus in Ago Bay, central part of Japan. Bull. Japanese Soc. Fisheries Oceanogr. (Japan) 74, 13–19.
Jeong H. J., Yih W., Kang N. S., Lee S. Y., Yoon E. Y., Yoo Y. D., et al. (2012). First report of the epiphytic benthic dinoflagellates Coolia canariensis and Coolia malayensis in the waters off Jeju Island, Korea: morphology and rDNA sequences. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 59, 114–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00610.x
Kang N. S., Jeong H. J., Moestrup Ø., Shin W., Nam S. W., Park J. Y., et al. (2010). Description of a new planktonic mixotrophic dinoflagellate Paragymnodinium shiwhaense n. gen., n. sp. from the coastal waters off western Korea: morphology, pigments, and ribosomal DNA gene sequence. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 57, 121–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2009.00462.x
Karafas S., York R., Tomas C. (2015). Morphological and genetic analysis of the Coolia monotis species complex with the introduction of two new species, Coolia santacroce sp. nov. and Coolia palmyrensis sp. nov.(Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 46, 18–33. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2015.05.002
Kim H. S., Yih W., Kim J. H., Myung G., Jeong H. J. (2011). Abundance of epiphytic dinoflagellates from coastal waters off Jeju Island, Korea during autumn 2009. Ocean Sci. J. 46, 205–209. doi: 10.1007/s12601-011-0016-9
Kumar S., Stecher G., Tamura K. (2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
Larsson M. E., Smith K. F., Doblin M. A. (2019). First description of the environmental niche of the epibenthic dinoflagellate species Coolia palmyrensis, C. malayensis, and C. tropicalis (Dinophyceae) from Eastern Australia. J. phycol. 55, 565–577. doi: 10.1111/jpy.12833
Leaw C. P., Lim P. T., Cheng K. W., Ng B. K., Usup G. (2010). Morphology and molecular characterization of a new species of thecate benthic dinoflagellate, Coolia malayensis sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) 1. J. phycol. 46, 162–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00778.x
Leaw C. P., Tan T. H., Lim H. C., Teng S. T., Yong H. L., Smith K. F., et al. (2016). New scenario for speciation in the benthic dinoflagellate genus Coolia (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 55, 137–149. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.02.010
Lee E. S., Hwang J., Hyung J., Park J. (2021). Detection of the benthic dinoflagellates, Ostreopsis cf. ovata and Amphidinium massartii (Dinophyceae), using Loop-mediated Isotermal amplication. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 885. doi: 10.3390/jmse9080885
Leung P. T., Yan M., Yiu S. K., Lam V. T., Ip J. C., Au M. W., et al. (2017). Molecular phylogeny and toxicity of harmful benthic dinoflagellates Coolia (Ostreopsidaceae, Dinophyceae) in a sub-tropical marine ecosystem: the first record from Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 124, 878–889. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.017
Lewis N. I., Wolny J. L., Achenbach J. C., Ellis L., Pitula J. S., Rafuse C., et al. (2018). Identification, growth and toxicity assessment of Coolia meunier (Dinophyceae) from Nova Scotia, Canada. Harmful Algae 75, 45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2018.04.001
Lim A. S., Jeong H. J., Lim A. S., Jeong H. J. (2021). Benthic dinoflagellates in Korean waters. Algae 36, 91–109. doi: 10.4490/algae.2021.36.5.31
Litaker R. W., Vandersea M. W., Faust M. A., Kibler S. R., Nau A. W., Holland W. C., et al. (2010). Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 56, 711–730. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.05.017
Litaker R. W., Vandersea M. W., Kibler S. R., Reece K. S., Stokes N. A., Steidinger K. A., et al. (2003). Identification of Pfiesteria piscicida (Dinophyceae) and Pfiesteria-like organisms using internal transcribed spacer-specific PCR assays. J. Phycol. 39, 754–761. doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.02112.x
Meunier A. (1919). “Microplancton de la Mer Flamande. III. Les Peridiniales,” in Mèm. Mus. R. Hist. Nat. Belg. Brux, ed. Hayez M. (Bruxelles: Hayez), 1–116.
Miralha A., Nascimento S. M., Neves R. A. (2023). Coolia Species (Dinophyceae) from the Tropical South Atlantic Region: Evidence of Harmfulness of Coolia cf. canariensis Phylogroup II. Phycology 3, 242–254. doi: 10.3390/phycology3020015
Mohammad-Noor N., Moestrup Ø., Lundholm N., Fraga S., Adam A., Holmes M. J., et al. (2013). Autecology and phylogeny of Coolia tropicalis and Coolia malayensis (Dinophyceae), with emphasis on taxonomy of C. tropicalis based on light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and LSU r DNA. J. Phycol. 49, 536–545. doi: 10.1111/jpy.12062
Momigliano P., Sparrow L., Blair D., Heimann K. (2013). The diversity of Coolia spp. (Dinophyceae Ostreopsidaceae) in the central Great Barrier Reef region. PloS One 8, e79278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079278
Morquecho L., Gárate-Lizárraga I., Gu H., Morquecho L., Gárate-Lizárraga I., Gu H. (2022). Morphological and molecular characterization of the genus Coolia (Dinophyceae) from Bahía de la Paz, southwest Gulf of California. Algae 37, 185–204. doi: 10.4490/algae.2022.37.9.2
Murray J. S., Passfield E. M., Rhodes L. L., Puddick J., Finch S. C., Smith K. F., et al. (2024). Targeted metabolite fingerprints of thirteen gambierdiscus, five coolia and two fukuyoa species. Mar. Drugs 22, 119. doi: 10.3390/md22030119
Nascimento S. M., da Silva R. A., Oliveira F., Fraga S., Salgueiro F. (2019). Morphology and molecular phylogeny of Coolia tropicalis, Coolia malayensis and a new lineage of the Coolia canariensis species complex (Dinophyceae) isolated from Brazil. Eur. J. phycol. 54, 484–496. doi: 10.1080/09670262.2019.1599449
Nunn G., Theisen B., Christensen B., Arctander P. (1996). Simplicity-correlated size growth of the nuclear 28S ribosomal RNA D3 expansion segment in the crustacean order Isopoda. J. Mol. Evol. 42, 211–223. doi: 10.1007/bf02198847
Park J., Hwang J., Hyung J.-H., Yoon E. Y. (2020). Temporal and spatial distribution of the toxic epiphytic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the coastal waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Sustainability 12, 5864. doi: 10.3390/su12145864
Parsons M. L., Aligizaki K., Bottein M.-Y. D., Fraga S., Morton S. L., Penna A., et al. (2012). Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis: Reassessment of the state of knowledge of their taxonomy, geography, ecophysiology, and toxicology. Harmful algae 14, 107–129. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.017
Penna A., Vila M., Fraga S., Giacobbe M. G., Andreoni F., Riobó P., et al. (2005). Characterization of Ostreopsis and Coolia (Dinophyceae) isolates in the western Mediterranean Sea based on morphology, toxicity and internal transcribed spacer 5.8 S rDNA sequences 1. J. phycol. 41, 212–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.04011.x
Phua Y. H., Roy M. C., Lemer S., Husnik F., Wakeman K. C. (2021). Diversity and toxicity of Pacific strains of the benthic dinoflagellate Coolia (Dinophyceae), with a look at the Coolia canariensis species complex. Harmful Algae 109, 102120. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102120
Pruesse E., Peplies J., Glöckner F. O. (2012). SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28, 1823–1829. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252
Rambaut A. (2009). FigTree. Tree figure drawing tool. Available online at: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (Accessed February 11, 2008).
Rambaut A., Drummond A. (2013). TreeAnnotator v1. 7.0. 2013. Available online at: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk (Accessed January 20, 2014).
Rhodes L., Adamson J., Suzuki T., Briggs L., Garthwaite I. (2000). Toxic marine epiphytic dinoflagellates, Ostreopsis siamensis and Coolia monotis (Dinophyceae), in New Zealand. New Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 34, 371–383. doi: 10.1080/00288330.2000.9516939
Riobó P., Paz B., Franco J. M. (2006). Analysis of palytoxin-like in Ostreopsis cultures by liquid chromatography with precolumn derivatization and fluorescence detection. Analytica chimica Acta 566, 217–223. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2006.03.013
Shah M. M. R., An S.-J., Lee J.-B. (2013). Presence of benthic dinoflagellates around coastal waters of Jeju Island including newly recorded species. J. Ecol. Environ. 36, 347–370. doi: 10.5141/ecoenv.2013.347
Shears N. T., Ross P. M. (2009). Blooms of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Ostreopsis; an increasing and ecologically important phenomenon on temperate reefs in New Zealand and worldwide. Harmful algae 8, 916–925. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2009.05.003
Smith K. F., Kohli G. S., Murray S. A., Rhodes L. L. (2017). Assessment of the metabarcoding approach for community analysis of benthic-epiphytic dinoflagellates using mock communities. New Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 51, 555–576. doi: 10.1080/00288330.2017.1298632
Ten-Hage L.c., Delaunay N., Pichon V., Couté A., Puiseux-Dao S., Turquet J. (2000a). Okadaic acid production from the marine benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum arenarium Faust (Dinophyceae) isolated from Europa Island coral reef ecosystem (SW Indian Ocean). Toxicon 38, 1043–1054. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(99)00216-0
Ten-Hage L., Turquet J., Quod J., Couté A. (2000b). Coolia areolata sp. nov.(Dinophyceae), a new sand-dwelling dinoflagellate from the southwestern Indian Ocean. Phycologia 39, 377–383. doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-39-5-377.1
Tester P. A., Litaker R. W., Soler-Onís E., Fernández-Zabala J., Berdalet E. (2022). Using artificial substrates to quantify Gambierdiscus and other toxic benthic dinoflagellates for monitoring purposes. Harmful Algae 120, 102351. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2022.102351
Tibiriçá C., Sibat M., Fernandes L. F., Bilien G., Chomérat N., Hess P., et al. (2020). Diversity and toxicity of the genus coolia meunier in Brazil, and detection of 44-methyl gambierone in coolia tropicalis. Toxins 12, 327. doi: 10.3390/toxins12050327
Verma A., Hoppenrath M., Smith K., Murray J., Harwood D., Hosking J., et al. (2023). Ostreopsis Schmidt and Coolia Meunier (Dinophyceae, Gonyaulacales) from Cook Islands and Niue (South Pacific Ocean), including description of Ostreopsis tairoto sp. nov. Sci. Rep. 13, 3110. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29969-z
Wakeman K. C., Yamaguchi A., Roy M. C., Jenke-Kodama H. (2015). Morphology, phylogeny and novel chemical compounds from Coolia malayensis (Dinophyceae) from Okinawa, Japan. Harmful Algae 44, 8–19. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2015.02.009
Wells M. L., Karlson B., Wulff A., Kudela R., Trick C., Asnaghi V., et al. (2020). Future HAB science: Directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful algae 91, 101632. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.101632
Yasumoto T., Seino N., Murakami Y., Murata M. (1987). Toxins produced by benthic dinoflagellates. Biol. Bull. 172, 128–131. doi: 10.2307/1541612
Keywords: benthic dinoflagellate, Coolia palmyrensis, Coolia malayensis, geographic distributions, ocean climate change
Citation: Hyung J-H, Moon SJ, Lee H and Park J (2024) First report of Coolia palmyrensis in Korea: seasonal and spatial distribution of C. palmyrensis and C. malayensis in Korean coastal waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1469015. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1469015
Received: 23 July 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Christine Johanna Band-Schmidt, Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas (IPN), MexicoReviewed by:
Olga Carnicer, Polytechnic University of Cartagena, SpainMargarita Fernández Tejedor, Institute of Agrifood Research and Technology (IRTA), Spain
Copyright © 2024 Hyung, Moon, Lee and Park. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jaeyeon Park, YmFkYTBAc251LmFjLmty
 Jun-Ho Hyung
Jun-Ho Hyung Jaeyeon Park
Jaeyeon Park