- 1Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 2College of Marine Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
- 4Department of Biology, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong, China
- 5Hong Kong Branch of the Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China
- 6Research Centre for Marine Ecology and Environment, South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, Guangzhou, China
The coral reefs along Pakistan’s coastline are of ecological and economic significance. However, they are increasingly threatened by anthropogenic threats and climate change. These vulnerable ecosystems are declining due to various factors such as sedimentation, climate change, overfishing, destructive fishing practices, marine pollution, and tourism development. We found that 29%, 24%, 26%, 16% and 18% of the studies exceeding, marine pollution, overfishing/destructive fishing, coastal tourism, climate change and sedimentation, respectively; thus, indicating inadequate water quality status in part of Pakistan coastal water. These influences lead to several negative impacts, such as jeopardized coral health, decline in biodiversity, and the simplification of reef structures. In response to these threats, conservation efforts are imperative. This literature review provides an in-depth analysis of anthropogenic threats, climate change and the conservation of coral reefs in Pakistan. This review provides suggestions on how the country could better conserve its coral reef ecosystem. These include (1) initiatives such as establishing marine protected areas (MPAs), (2) encouraging sustainable fishing practices and reducing pollution, (3) developing the country as an ecotourism destination and implementing climate change adaptation measures, and (4) community engagement through awareness campaigns and fostering collaboration among, governmental organizations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and scientists. These comprehensive conservation policies address human-caused and other challenges, safeguarding their ecological, economic, and cultural relevance for future generations.
1 Introduction
Coral reefs epitomize one of the most aesthetically captivating, ancient, and complex ecosystems on earth (Majumdar et al., 2018; Oakley-Cogan et al., 2020; Oppermann, 2024). They support the highest marine biodiversity, although they cover only approximately 2284,300 km2, which accounts for merely 0.09% of the total surface area of the world’s oceans (Majumdar et al., 2018). Coral reefs provide a variety of ecological functions and services, and play a significant role in contributing billions of dollars per year through different activities such as coastal protection, tourism, food, and other goods (Sully et al., 2022). However, coral reefs are fragile ecosystems and most of them have faced serious threats in the decades (Burke et al., 2011; Bayraktarov et al., 2020; Smallhorn-West et al., 2020; Devlin, 2022). Recent statistics show that since the 1950s, the ability of coral reefs to provide ecosystem services has decreased by 50% (Eddy et al., 2021). Such a massive decline was caused by mounting environmental pressures from both global-scale effects and local-level impacts, which include elevated sea surface temperature (SST), sea level rise, and increased anthropogenic disruptions such as marine pollution, overfishing and destructive fishing, coastal tourism, and terrigenous sediments (Roberts, 1995; Mcclanahan, 2002; Brainard, 2008; Clark, 2009; Wenger et al., 2015). Assessing the conditions of coral reef ecology and conservation, as well as identifying threats, would provide significant support for the protection and management of these valuable marine resources.
In Pakistan, Ali et al. (2020) underscored a concerning trend of degradation in coral reefs over recent years. These reefs are mainly found along the 900 km long coastal area of Sindh and Balochistan, making it an important coastal belt, and fostering diverse ecosystems (Amjad and Rizvi, 1999; Iqbal et al., 2018). Coral reef communities are distributed at (a) Churna Island, near Karachi; (b) Mubarak Village; (c) Hawks Bay; (d) French Beach; (e) Sandspit; (f) Buleji; (g) Goth Abdul Rehman; (h) Ormara Rodrigues Shoals; (i) Astola Island; and (j) Jiwani (Ali et al., 2014) (Figure 1). The high biodiversity of coral reefs in Pakistan has been revealed by the gradual deepening of investigation and research in the last two decades. For example, Ali et al. (2020) discovered 50 live coral species in Pakistan’s coastal waters, among which Churna Island has the highest diversity. The abovementioned localities have a strong connection with human settlements, and these coral reefs are under significant harm due to human activities. Approximately 10% of Pakistan’s population lives in coastal areas, with 20% of these regions being somewhat developed, while about 40% of the industry is in these zones (Noor, 2023). Therefore major factors contributing to coral reef loss include the establishment of industrial areas, pollution, overfishing, the effects of tourism, increased sedimentation, and climate change (Saher et al., 2019; Ali et al., 2020, 2021; Noor et al., 2023). Several coral conservation and restoration initiatives are currently operating in Pakistan and are overseen by various organizations, regional communities, and local and national government bodies (e.g., the Marine Fisheries Department, National Institute of Oceanography (NIO), International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) (Ahmed Khan, 2011; Mohsin et al., 2017; Ullah et al., 2017). However, the evolving dynamics of coral reef assemblages, which are largely influenced by human threats, increased sedimentation rates, and climate change, pose significant questions for conservation scientists and natural resource managers. Given the multitude of impacts expected to affect coral reefs in Pakistan in the future, this review seeks to address the primary question ‘How have anthropogenic threats and climate change impacts, along with their interactions, affected coral reefs in Pakistan?’ Another question we interrogate is ‘What actions should be taken to protect coral reef resources in Pakistan”?
2 Materials and methods
The literature for this study was compiled primarily from online databases and search engines, including Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com/), Web of Science (https://www.webofknowledge.com/), PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and Science Direct (sciencedirect.com). Keywords such as “coral reefs,” “Pakistan,” “anthropogenic threats,” “climate change,” “ocean acidification,” “overfishing,” “coastal tourism,” eutrophication,” “marine pollution,” “coral bleaching,” “MPAs,” “restoration,” “conservation,” “estuaries,” and “coastal water ecosystem” were used for the search. Relevant journals in the fields of geology, marine geology, biology, marine biology, and environmental sciences were also consulted. Results from these libraries were imported to R (R Core Team, 2022) and subjected to analysis using the Bibliometrix package (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017). A total of 136 scientific articles published between 1997 and 2023 were collected for our analysis and discussion on the coral reef ecosystems in Pakistan. The trend depicted in (Figure 2A) indicates a consistent annual increase in the number of published articles every year. Based on specific anthropogenic threats we describe in this paper, most of the research focuses on marine pollution as their primary parameter to measure (29%), followed by overfishing (24%), coastal tourism (26%), sedimentation (18%), climate change (16%) and other related papers (23%) (Figure 2B). Additionally, we found that specific author keywords tended to occur more frequently during a certain period. Figure 2C shows the yearly occurrences of the main terms from 1997 to 2023, but some of them increased more dynamically compared than others. The terms with the greatest increase in use over time were ‘coral reefs’, ‘coral bleaching’, ‘marine pollution’, ‘MPAs’, ‘overfishing’, ‘coastal tourism’, ‘climate change’, ‘Pakistan’, ‘conservation’, and ‘restoration. Also, an extensive review of international, federal and provincial policy documents was carried out to identify those relevant to coral reef or coastal ecosystem conservation or restoration (see Table 1).
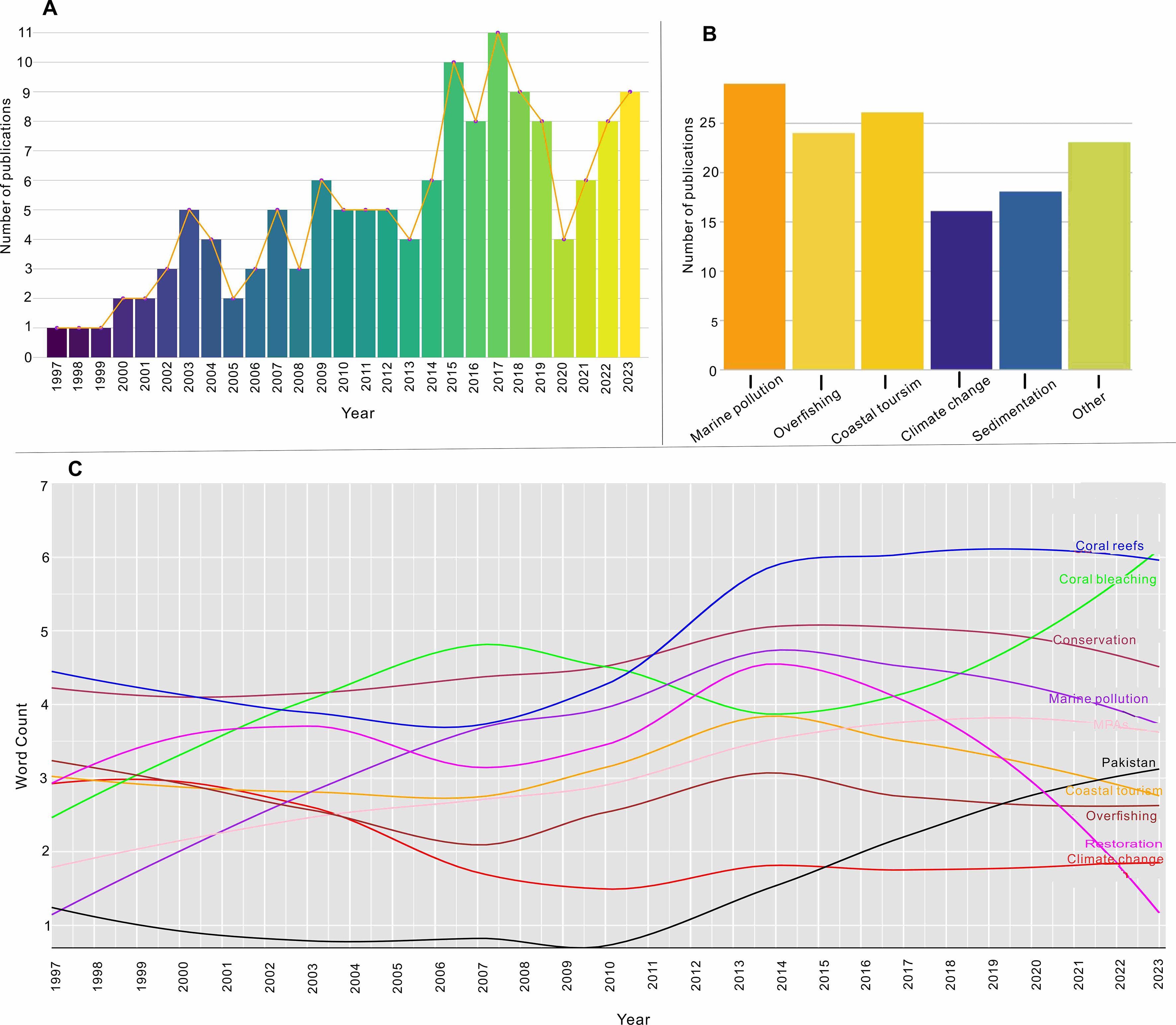
Figure 2. (A) Annual scientific production over the period from 1997 to 2023, (B) The number of articles published over time, (C) Analysis of the top 10 keywords from 1997 to 2023.
Finally, the collected literature was critically reviewed, during which significant information regarding the introduction, research status of coral reefs in Pakistan, anthropogenic threats, coral reef restoration, and conservation efforts was obtained, and the research gaps were carefully extracted and synthesized in the main sections of the review paper. The findings and insights in this review are based on the scientific knowledge available at the time of writing, and every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented.
3 Ecological status of coral reefs in Pakistan
Coral reefs in Pakistan are distributed in the southeastern part of the Arabian Sea (Wilson et al., 2002; Ali et al., 2014). However, the research on corals in Pakistan is still comparatively a more recent phenomenon. In 2006, a field visit conducted by the Pakistan Wetlands Programme (PWP), led by a coral expert from Millport University, UK, identified the first-ever coral reef habitat near Astola Island, Balochistan (Khan, 2011). Before this discovery, it was considered that corals do not exist within Pakistan’s jurisdiction of the Arabian Sea.
Furthermore, research conducted by Ali et al. (2014) revealed that twenty-nine hard coral species (eight families and fourteen genera), one black coral species, and eight soft coral species (three families and seven genera) were identified across eighteen dive sites located in nine distinct places along the coastline of Pakistan (Figure 3). Subsequent studies by Ali et al. (2017) revealed the existence of 48 fossil coral species in the uplifted ancient coral reefs along the Balochistan coast. Additionally, a study by Ali et al. (2021) reported 58 species of fish species in the reef habitat along Churna Island. With the high biodiversity of coral communities, its ecological importance of the coral reef ecosystems has been received more and more attention (Amjad et al., 2020). However these coral reefs in Pakistan, particularly near Astola Island in Baluchistan and Churna Island in Sindh are under threats from anthropogenic threats and other natural changes (Aslam et al., 2020; Ali et al., 2021; Chanda, 2022). For example, according to Ali et al. (2020) if further shifts in community structure continue, it appears that only Porite species will survive in Pakistan’s coastal waters. Therefore, Churna Island has been recommended for designation as an MPA because of its ecological significance (Ali et al., 2021).
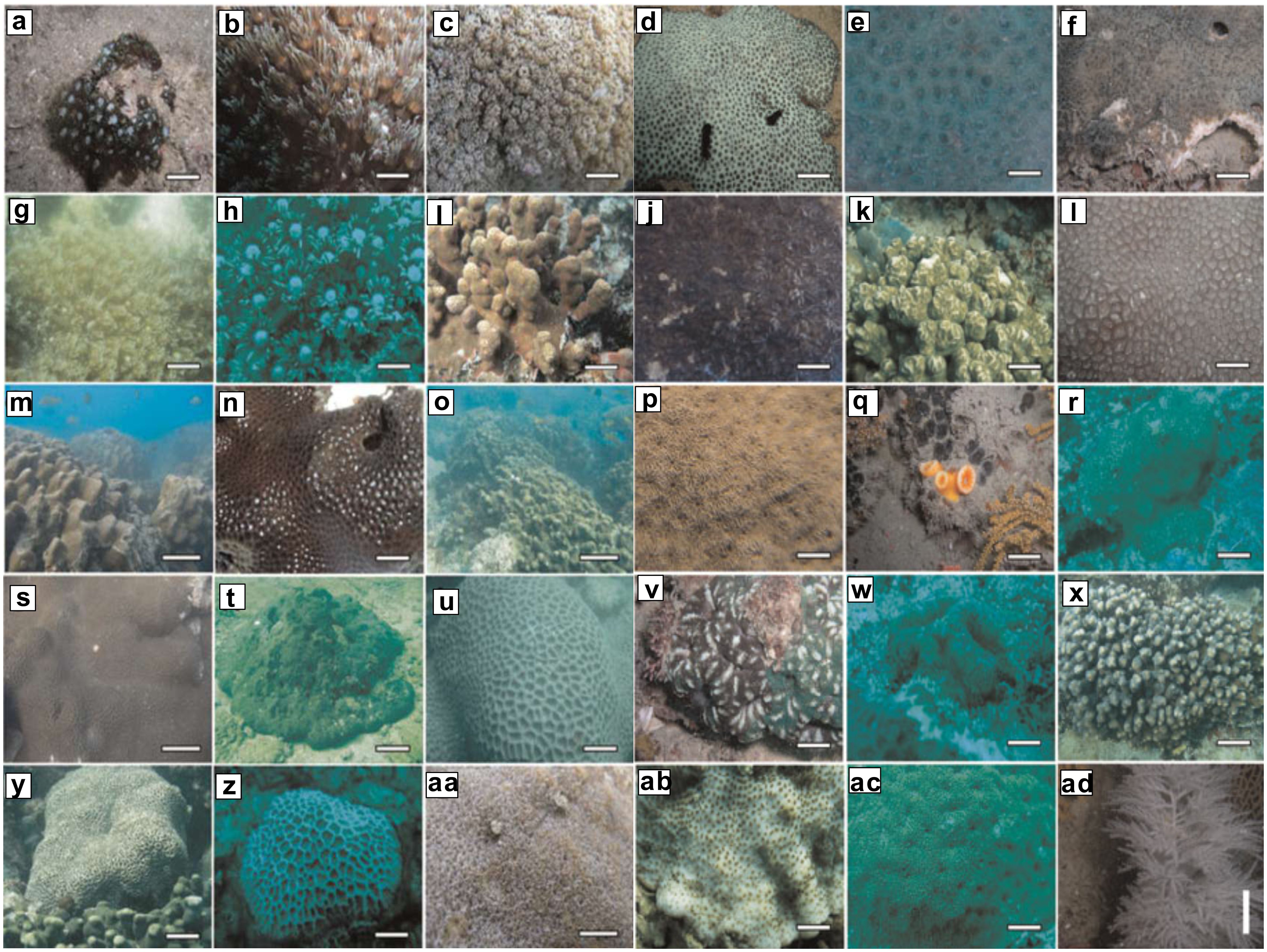
Figure 3. Hard coral species diversity in Pakistan coastal waters [modified after Ali et al. (2014)]: (A) Goniopora albiconus; (B) Goniopora columna; (C) Goniopora djiboutiensis; (D) Goniopora albiconus; (E) Goniopora columna; (F) Goniopora djiboutiensis; (G) Goniopora cf. savignyi; (H) Goniopora somaliensis; (I) Porites harrisoni; (J) Coscinaraea sp.; (K) Psammocora obtusangulata; (L) Psammocora superficialis; (M) Porites lobata/lutea; (N) Porites monticulosa; (O) Porites nodifera; (P) Porites solida; (Q) Psammocora sp.; (R) Dendrophyllia robusta; (S) Turbinaria sp.; (T) Acanthastrea hillae; (U) Alveopora sp.; (V) Favites complanata; (W) Favites pentagona; (X) Favites spinosa; (Y) Leptastrea bottae; (Z) Acanthastrea maxima; (AA) Pocillopora damicornis; (AB) Montipora mollis; (AC) Pavona explanulata; (AD) Antipathes sp. Reprinted in a modified form with permission from Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 94(1), 75-84. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315413001203. Copyright © 2013 Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.
4 Threats impacting coral reefs in Pakistan
In Pakistan, according to Ali et al. (2020) coral reefs have experienced the degradation in recent few years, as shown in (Figure 4), with extensive patches of bleaching in some areas in the northeastern region of Churna Island in October 2020 (Jamal, 2020). Therefore, anthropogenic threats and other challenges discussed below underscore the persistent difficulties confronting coral reefs in Pakistan to highlight the critical need for conservation and management efforts.
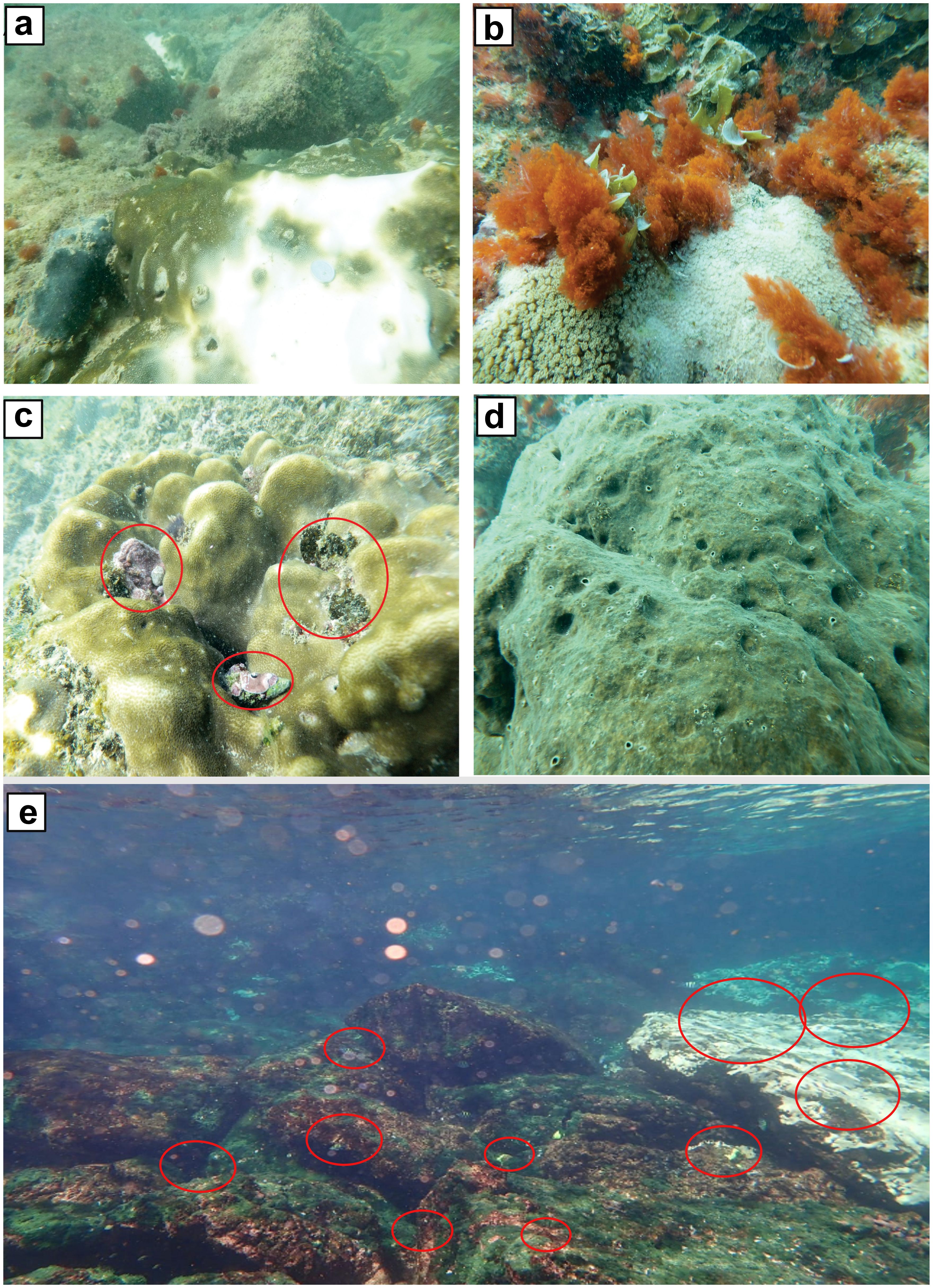
Figure 4. Coral reef degradation in Pakistan: (A, B, E) caused by thermal stress leading to coral bleaching, and (C, D) caused by bioerosion [modified after Ali et al. (2020); Jamal (2020)]. The red circles in the pictures clearly emphasize the areas where degradation is attributed to bioerosion.
4.1 Overfishing and destructive fishing
The coastal communities of Pakistan, particularly along the 682 miles from Sir Creek in Sindh to Jiwani in Balochistan, have relied on fishing as their primary source of food and livelihood (Pakistan, 2016; Biagi and Starnini, 2020). The marine fishing industry in Pakistan provides direct livelihoods for 125,000 people and indirectly provides nearly one million people, including dependents (Khan and Khan, 2011). The fish populations in the two marine provinces vary due to the differences in their topography. The majority of the fishing community is located in Karachi, Sindh, the most populous industrial city with over 18 million residents (Jilani, 2018), and other concentrations are in Thatta, Sindh; Pasni, Gwadar, Balochistan (Abbas et al., 2013). This coastal stretch features four harbors and nine significant landing sites and jetties (for details, see Birwani et al. (1999). The fishing industry is supported by a fleet of more than 15,000 vessels of various sizes, including medium and small-sized boats, as well as large launches, and trawlers (Khan and Khan, 2011). The smaller boats, ranging from 18 to 25 feet are used for fishing in coastal waters (Siddiqui and Amir, 2010). Fishermen utilize hand-cast shrimp nets (known as thukri or phat) while medium-sized boats, ranging between 25 to 35 feet, use gill nets (locally known as “rach lara”, “lathay ka ban”) (Khan and Khan, 2011). Despite the extensive fishing activities, the fisheries sector plays a minimal contribution in Pakistan’s economy, contributing 0.32% to the national GDP and 1.4% to the agricultural GDP, whereas employment from fisheries is minimal, at only 0.01% (Wasim and Abbas, 2024). In 2022, fish production reached 800,000 metric tons, only 25% was exported, generating 496 million US dollars (Wasim and Abbas, 2024). In response, the fishing industry in Pakistan has grown quickly, resulting in overfishing and destructive fining in several coastal and offshore areas (Pakistan, 2016). It is worth noting, however, that many of the existing reports are from heavily fished areas, such as coastal areas of Sindh and Balochistan (Siddiqi, 1992; Ajazuddin and Moazzam, 2007; Siddiqui and Amir, 2010; Khan and Khan, 2011; Gore et al., 2012; Nawaz and Moazzam, 2014; Kidwai et al., 2019). Karachi Fish Harbour, the country’s primary landing area, is already overcrowded. Despite being equipped with essential facilities like a net-mending shed, chill room, and flake ice factory, the harbor faces significant challenges (Kidwai et al., 2019). The harbor’s turning basin is large, but the area is heavily polluted. Ironically, the seawater, despite its contamination, is still used to clean the harbor floor. The handling of decaying fish contributes to making Karachi Fish Harbour one of the dirtiest in Pakistan. Despite efforts to expand the harbor’s facilities, there is general concern that these changes will not improve the harbor’s functionality or address the existing unsanitary conditions (Nawaz and Moazzam, 2014). Compounding the issue, Local fishing boats avoid using the Korangi Fish Harbour, as it was designed for vessels with drafts exceeding five meters (Wasim and Abbas, 2024). Similarly, Gwadar Port has been deemed unsuitable for local fishing boats. The flood of 2022 devastated most of the floating jetties in Sindh province, leaving the region without adequate landing facilities (Wasim and Abbas, 2024). Additionally, no landing site in the country has a functioning cold chain maintenance system. The stagnant trend in fish production, particularly in Sindh, signals that fish stocks are being severely overfished (Ali et al., 2021). From 2009 to 2015, the Government of Pakistan’s Marine Fisheries Department, in collaboration with the FAO, conducted several fish stock assessment surveys (Jayabalan et al., 2021). The final report states that large fishing fleets and current practices are “fishing for catastrophe,” with important fish populations in Pakistani waters decreased by 60-90 percent (Wasim and Abbas, 2024). This drastic decline highlights significant ecological changes and a concerning reduction in marine species. Also, according to Ali et al. (2021) these coral-associated fish communities in Pakistan are facing a threatened environment and MPAs should be prioritized in conservation efforts can greatly improve environmental and ecosystem management, giving these fish communities a great chance of surviving and thriving.
4.2 Marine pollution/contamination
Pollution in coastal waters is receiving attention worldwide, whereas Pakistan’s coastal areas have been given limited attention, despite being significantly affected by anthropogenic threats and environmental challenges (Saher et al., 2019). In Pakistan, the pollution threat on the Balochistan coast is currently low because there are no major cities or large-scale projects along the coastline. Similarly, pollution levels in the delta are comparatively lower because there is no direct pollution in the area. However, the coast of Karachi is facing a significant threat from pollution generated by industry, municipal wastewater, the shipbreaking industry, and plastic waste (Ali et al., 2020; Mukheed and Alisha, 2020). Karachi, home to more than half of the country’s industrial units and 70% of the international trade being controlled by this city, experienced a dramatic increase of population from approximately 10,000 during the 1990s and has now gone beyond 30,000 (Rafique, 2018). Various studies have profiled Karachi’s coastal belt based on pollution levels (Majeed et al., 2021a, b; Neelam, 2021; Nergis et al., 2021). The accumulation of hospital waste, single-use plastics, industrial effluents and nuclear discards, contribute significantly to coastal pollution (Pakistan, 2016). Tanneries also release chemically rich effluents into coastal waters, with heavy metals from these sources concentrating in marine life and ultimately biomagnifying in humans, leading to toxicity (Iqbal and Heidegger, 2013; Karim, 2017). A study (Majeed et al., 2021b) assessed pollution levels at Karachi’s ports, revealing heavy metal contamination in coastal waters from port and harbor operations. Similarly, another study (Alamgir et al., 2019) found water samples from the Lyari River mouth, Fish Harbor, and KPT boat-building area to be highly contaminated with heavy metals. The major contributors to this pollution are eutrophication and plastic waste, wreaking havoc on the fragile ecosystems along the coast of Karachi and Gaddani (Zuo et al., 2023). Eutrophication causes a significant threat to coral reefs due to excess nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus in the marine environment (Bell, 1991; Dorgham, 2014; Naumann et al., 2015; Albright, 2018). Algal blooms that outcompete corals for space and light, eventually smothering the corals and depriving them of essential sunlight for photosynthesis (Mccook, 2001; Hernandez-Pacheco et al., 2010; Wenger et al., 2015; Devlin and Brodie, 2023). Excessive algal growth in coral reefs not only causes ecological issues but also exacerbates plastic waste pollution, since the algae trap and accumulate plastic trash, creating a complex mess that threatens the survival of these ecosystems (Gregory, 2009; Sweet, 2019). These nutrients come from different sources such as agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial processes (Ansari et al., 2011). In Pakistan, the rapidly growing population and increasing industry, along with weak regulatory measures, have led to uncontrolled waste and industrial discharge in coastal areas (Baqar et al., 2017). Industries, such as the Port Qasim, Korangi Power Plant, and Hub Power Plant (HUBCO) in Gaddani, often use seawater to cool heavy machinery and discharge warm salty water into adjacent coastal areas (Ullah et al., 2016). These discharges add a range of pollutants and excess nutrients to marine ecosystems, resulting in decreased water quality and increased turbidity, which has severe consequences for coral reefs, making it difficult for them to survive (Ahmad, 1997).
In addition to eutrophication, plastic pollution is a growing and concerning issue in the coastal areas of Pakistan and has a greater impact on the reefs and other marine ecosystems (Qaimkhani, 2018; Saher et al., 2019). Among South Asian countries, Pakistan has the highest percentage of mismanaged plastic (Ahmad et al., 2023). But there are limited studies regarding plastic pollution in coastal areas of Pakistan (Qari and Shaffat, 2015; Chaudhry, 2018; Neelam et al., 2018; Qaimkhani, 2018; Ahmad et al., 2023). However, a study conducted by (Qari and Shaffat, 2015) investigated the distribution and abundance of marine debris along the coast of Karachi and revealed that plastic is more dominant than other debris. In a recent study, Ahmad et al. (2023) asserted that microplastic pollution is emerging as a significant environmental concern in the coastal regions of Pakistan, exerting considerable impact on marine ecosystems.
4.3 Coastal tourism
Tourism in Pakistan’s coastal areas has increased in recent years, with a diverse range of tourism attractions for climatic conditions, high mountain ranges, immense deserts, vast delta plains, and an amazing coastline (Arshad et al., 2018; Shahzad, 2020; Ahmed et al., 2022). These coastal regions are reflected globally, as maritime tourism is of important economic importance for various countries (Diakomihalis, 2007; Karani and Failler, 2020; Martínez Vázquez et al., 2021). Ullah et al. (2010) highlighted that the tourism is currently playing a key role in strengthening Pakistan’s shrinking economy. According to Nigar (2018) in 2015, the travel and tourism sector directly contributed $328.3 million to Pakistan’s GDP, representing 2.8% of the total GDP. Realizing the importance of tourism in Pakistan’s coastal zone, the government upgraded it to the status of an industry in 1989, highlighting its importance in promoting it to grow but has never been taken seriously as part of the overall tourism planning and development process (Ullah et al., 2018). There are approximately 28 beaches along its coastline, with most of them located in Sindh (20 beaches) and the remaining (8 beaches) in Balochistan (Shahzad, 2020), where coral reefs are scattered around the nearby waters. However, unsustainable tourism activities in Pakistan, such as boat anchoring and visitor snorkeling, pose direct damage by breaking or stepping on corals as well as indirect hazards to the reef ecosystem due to water pollution from shipping oil and visitor sunscreen (Siddiqui et al., 2008; Pakistan, 2016). Additionally, pollution from tourist-related actions such as litter, sewage, and boat-related oil spills can contaminate coastal waters and negatively impact marine ecosystems (Qaimkhani, 2018; Faran and Ejaz, 2022). Uncontrolled recreational activities such as snorkeling, scuba diving, and water sports can also harm coastal ecosystems with tourists potentially causing unintentional harm to coral reefs and disrupting delicate habitats, resulting in coral bleaching and decreased fish populations, with long-term consequences for the region’s biodiversity (Sayied, 2007; Qaimkhani, 2018; Ali et al., 2021). According to Siriwong et al. (2018) tourism has had terrible impacts on the marine ecosystems and coral reefs that are valuable to the tourism industry, have suffered severe consequences because of misuse by human activities such as sedimentation, habitat loss, waste dumping, and decreased light, endangering their health and existence.
4.4 Climate change and other challenges
Over recent years, South Asia has faced several devastating events due to the rapid increase of climate change (Rajasuriya et al., 2002). These effects include an increase in extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and sea-level rise, all of which have had severe impacts on marine ecosystems in the region. In Pakistan, the situation is particularly alarming (Khan et al., 2016). The increasing sea temperatures and ocean acidification, along with changing ocean currents, are profoundly affecting marine life (Ali and Hussain, 2023). The increase in sea temperatures is leading to coral bleaching, which causing coral reefs to lose their vitality, disrupting the intricate symbiotic relationships they support and leading to the degradation of these vital ecosystems (Ali and Hussain, 2023). The rise in sea levels and alterations in ocean currents further complicate the issue, influencing marine species distribution and abundance and potentially causing significant ecological shifts (Mahmood and Hassan, 2022). The National Institute of Oceanography (NIO) in Karachi reports a sea-level rise of approximately 1.1 millimeters per year in Pakistan’s coastal region, which aligns with global trends and highlights the significant regional impacts of climate change observed over the past two decades (https://niopk.gov.pk/). For further studies related to climate change readers are directed to (Farooqi et al., 2005; Mustafa, 2011; Mahmood and Hassan, 2022; Ali and Hussain, 2023). Despite these pressing issues, climate change-related studies investigating these effects on Pakistan’s coastal water are still very limited (Qureshi, 2005). This gap in research is critical given that Pakistan is ranked fifth on the Global Climate Risk Index for vulnerability to climate change impacts (Salik et al., 2015).
In addition, the sedimentation or siltation of sand and silt along Pakistan’s coast, primarily caused by the Indus River’s drainage system, has a significant impact on the marine ecosystems (Beg, 1995; Khan et al., 2021). Apart from free-living species, once-settled corals are sessile organisms (Chadwick, 1988; Chadwick-Furman and Loya, 1992; Pedersen et al., 2019), rely on their development form and physiological adaptations to regulate their interactions with the environment because they can’t move away from unfavorable conditions (Muller-Parker et al., 2015). Reef-building corals rely on symbiotic, unicellular algae known as zooxanthellae, which live as symbiotic inside the coral tissue, primarily in the gastrodermis, and through photosynthesis produce most of the coral’s energy requirements, because of this symbiotic interaction, most corals rely on light for survival (Harrison and Booth, 2007; Muller-Parker et al., 2015; El-Naggar, 2020). Turbidity and sedimentation caused by coastal building and dredging are the major causes of diminished light penetration and sediment deposition on the coral’s surface, making it difficult for the coral’s symbiotic zooxanthellae to capture enough light for photosynthesis. They also complicate the coral’s feeding when it is buried in sediment, as well as dealing with suspended sediments, particularly fine-grained, imposes additional energy costs on the coral due to the need for mucus production, sediment clearance, and impaired feeding, all of which harm zooxanthellae (Erftemeijer et al., 2012). Turbidity decreases ambient photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), which reduces zooxanthellae productivity and can lead to starvation. Sediment settling on coral tissue produces additional shadowing and smothering, contributing to a further decline in zooxanthellae photosynthetic activity and even coral bleaching (Borell and Bischof, 2008; Freitas et al., 2019).
5 Conservation status and management recommendations
Pakistan is a federal state with three tiers of government-local, provincial, and central. They are working by established laws and regulations but the federal government taking the responsibility for the overall strategy (Ullah et al., 2022). In this context various government departments, community-based initiatives, and NGOs in Pakistan collaborate directly with coastal communities to protect coastal habitats (Table 1). These attempts usually entail joint efforts with government departments, research institutions, and organizations with these three tiers of government to achieve their goals of conserving coastal ecosystems. There is potential legislation to protect marine life (Biodiversity Action Plan 1997, Pakistan Environmental Protection Act 1995, Environmental Protection Ordinance 1983, and the Wildlife Protection Ordinance 1972) (Rajasuriya et al., 2002). Despite this, clear policies for managing coastal and marine resources have not yet been fully covered, and the existing policies, laws, and legislation in the country remain confusing and complex (Ullah et al., 2017). These factors have led to uncertainty among organizations about involving coastal communities in the planning and development process. The current laws and regulations governing coastal and marine areas in Pakistan lack an integrated management framework and only provide guidelines for environmentally friendly economic activities. However, the present situation of coral reefs and other ecosystems shows that the conservation of coral reefs requires a paradigm shift in planning and policy frameworks, management practices, research with tangible outcomes, the active involvement and coordination of stakeholders, capacity building, and a strong commitment from all relevant government bodies (Figure 5).
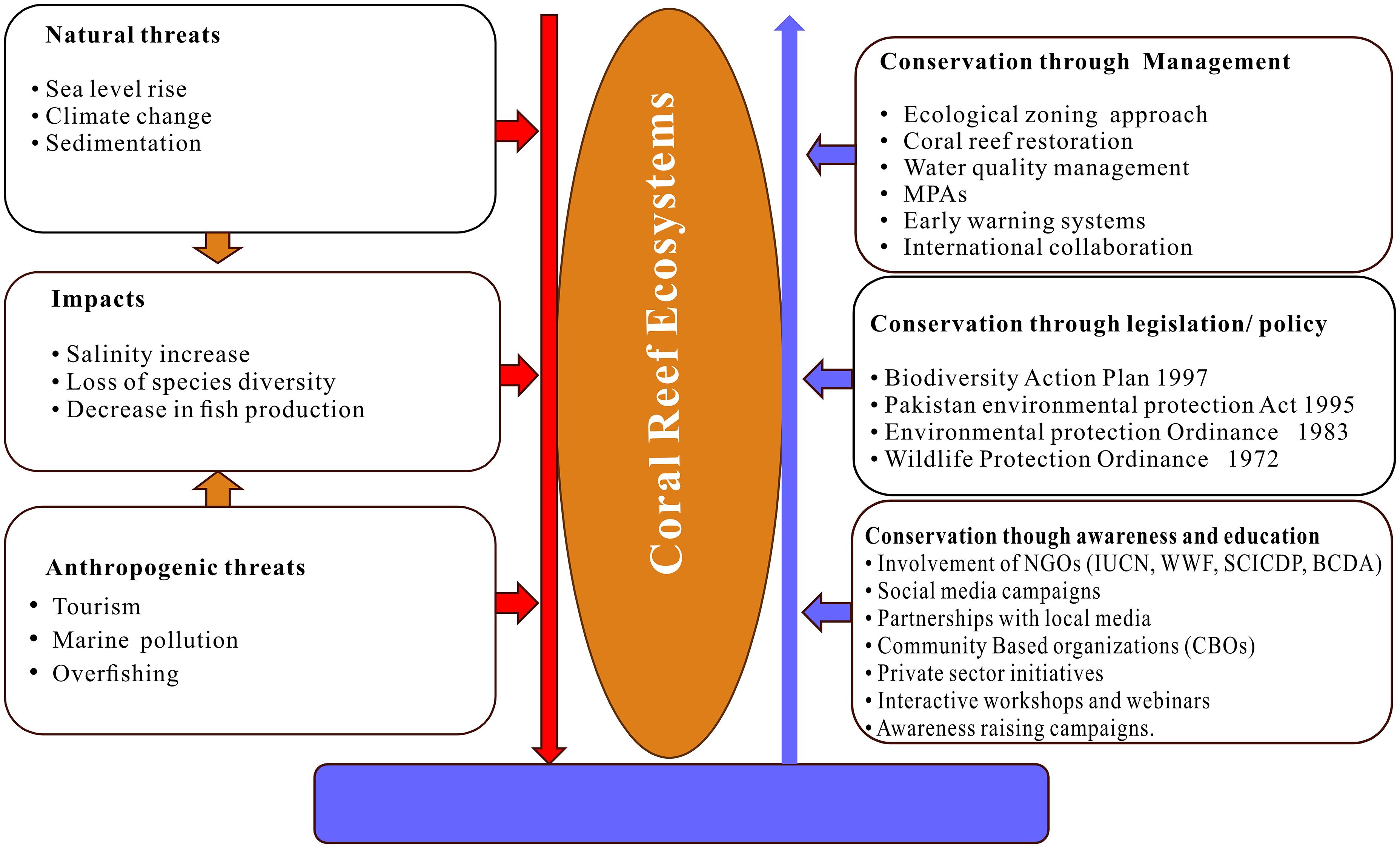
Figure 5. Comparison of coral reef conservation policies and practices in Pakistan with natural and anthropogenic threats.
5.1 Strengthen legislation and enforcement
Pakistan has implemented conservation policies and enacted laws, strategies, and policies for the conservation of coral reefs and other marine ecosystems. However, there is still a need for substantial efforts in this direction. The Karachi harbor area is a stark example of one of the most polluted areas for oil along the coast of Pakistan (Siddique et al., 2009). The harbor covers approximately 25 square kilometers, receives approximately 50 billion cubic meters of seawater per tidal cycle, and is visited by 3,000 to 4,000 ships annually (Sayied, 2007). During regular operations, ships discharge bilge water, oily ballast water, and cargo tank washings, with large amounts of pollution stemming from oily spills from both oil tankers and general cargo vessels (Sayied, 2007; Siddiqui and Amir, 2010). Although laws and regulations designed to control pollution are present, they are rarely enforced or implemented (Sayied, 2007). As highlighted by Mumtaz et al. (2023) poor governance has led to the degradation of marine ecosystems in coastal areas of Pakistan. Poor governance refers to the system and processes by which several actors (e.g., government, nongovernmental organizations, and the private sector) share authority and make decisions. This encompasses formal laws and regulations as well as more dispersed components such as media, trade, religion, and public opinion (Mumtaz et al., 2023). The absence of specific maritime laws addressing governance in Pakistan complicates the implementation of coastal and marine planning (Ullah et al., 2021). Despite existing laws, no legislation comprehensively covers the issues of the country’s coastal areas (Ullah et al., 2021). To enhance Pakistan’s coastal and marine conservation efforts, the country must adopt and adhere to effective guidelines, laws, and policy frameworks similar to those implemented by China. China’s governance model, which emphasizes rule by law, has fostered new initiatives and innovations in the sustainable development of coastal and marine resources (Chen and Pearson, 2015). Several laws and regulations have been enacted to oversee administrative jurisdiction rights pertaining to coastal and marine areas. The two most significant pieces of legislation, the Marine Environment Protection Law 1999 and the LAUSA 2001 have been enacted to regulate the marine environment and to utilize marine resources rationally and sustainably (Keyuan, 2001; Ullah et al., 2017). These two laws are considered as important and supportive legislation for China’s marine functional zoning (MFZ), covering all areas of environmental conservation and sustainable use of coastal and marine natural resources (Ullah et al., 2017). The effective enforcement of these two laws has bolstered and enhanced China’s sea use authorization system, marine environment protection measures, marine functional zoning framework, and marine legal infrastructure (Li, 2006; Cao and Wong, 2007; Lu et al., 2015). The implementation of laws within the MFZ schemes delineates the administrative responsibilities of the authorities engaged in managing coastal and marine zones. For Pakistan to achieve similar success, it must create specific policy frameworks/laws at various administrative levels and national, provincial, district, and tehsil levels. These frameworks require well-developed development strategies, good governance, improved stakeholder coordination, and continuous restoration and rehabilitation initiatives (Ali et al., 2021). Poor governance, inadequate planning, implementation of development plans, and a lack of coordination among stakeholders within the current framework may result in irreversible loss and degradation of coral reefs and other ecosystems in Pakistan (Ali et al., 2021).
Moreover, effective coral reef conservation laws require adequate financial resources to support these invaluable marine ecosystems (Dixit et al., 2010; Ali and Hussain, 2023). An effective approach to raising funds involves imposing an environmental surcharge on commercial entities, shipbreaking operations, cargo vessels, ferry services, industrial units, hotels, and others that utilize coral reef areas for their operations or contribute to marine pollution (Byrnes and Dunn, 2020). Therefore, the government should provide incentives and tax breaks to industries that adopt pollution prevention measures. Funding should be allocated for safeguarding and protecting critical habitats and providing training and capacity building for the staff engaged in the conservation and management of coral reefs. The country lacks a regulatory framework that would support an integrated management strategy to properly manage coastal and marine resources (Ullah et al., 2021). In Pakistan, however, plans and policies are developed at the national level and implemented by lower-level governments (Pakistan, 2014). These plans also fulfil sector-specific objectives and emphasize resource marketization and privatization, resulting in a prevalent paradigm of resource empowerment or ocean governance (Pakistan, 2014). Therefore, Pakistan should meet the needs of marine environment conservation and resource usage. Implementing such a legal framework is not only critical to the sustainable management of marine biodiversity, but also contributes to ensuring that conservation efforts are holistic, consistent, and strong in the long term. Pakistan may adopt global best practices to emulate a functional conservation framework, especially from countries with successful records in marine conservation. For example, Australia’s Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (GBRMPA) suggested a plan for managing large-scale marine parks through legally defined governance approaches, stakeholder engagement, and adaptive management processes (Evans et al., 2014; Stephenson et al., 2023). Similar strategies, when implemented, could act as a roadmap to enable Pakistan to develop robust marine protected areas. Pakistan can enhance its conservation practices, protect its valuable coral reefs, and ensure the sustainable utilization of marine resources for generations by understanding global lessons and localizing strategies. Adopting this integrated approach is necessary not only to address prevailing issues but also to develop resilience against other potential threats to the ecosystem. Figure 6 visually supports this discussion by illustrating the consequences of inadequate conservation laws and governance on reef systems. Showing the hierarchy of causes, global practices, proposed solutions, and implementation strategies. The arrows indicate the flow of influence and interactions between these elements, while the colors differentiate the categories for clarity.
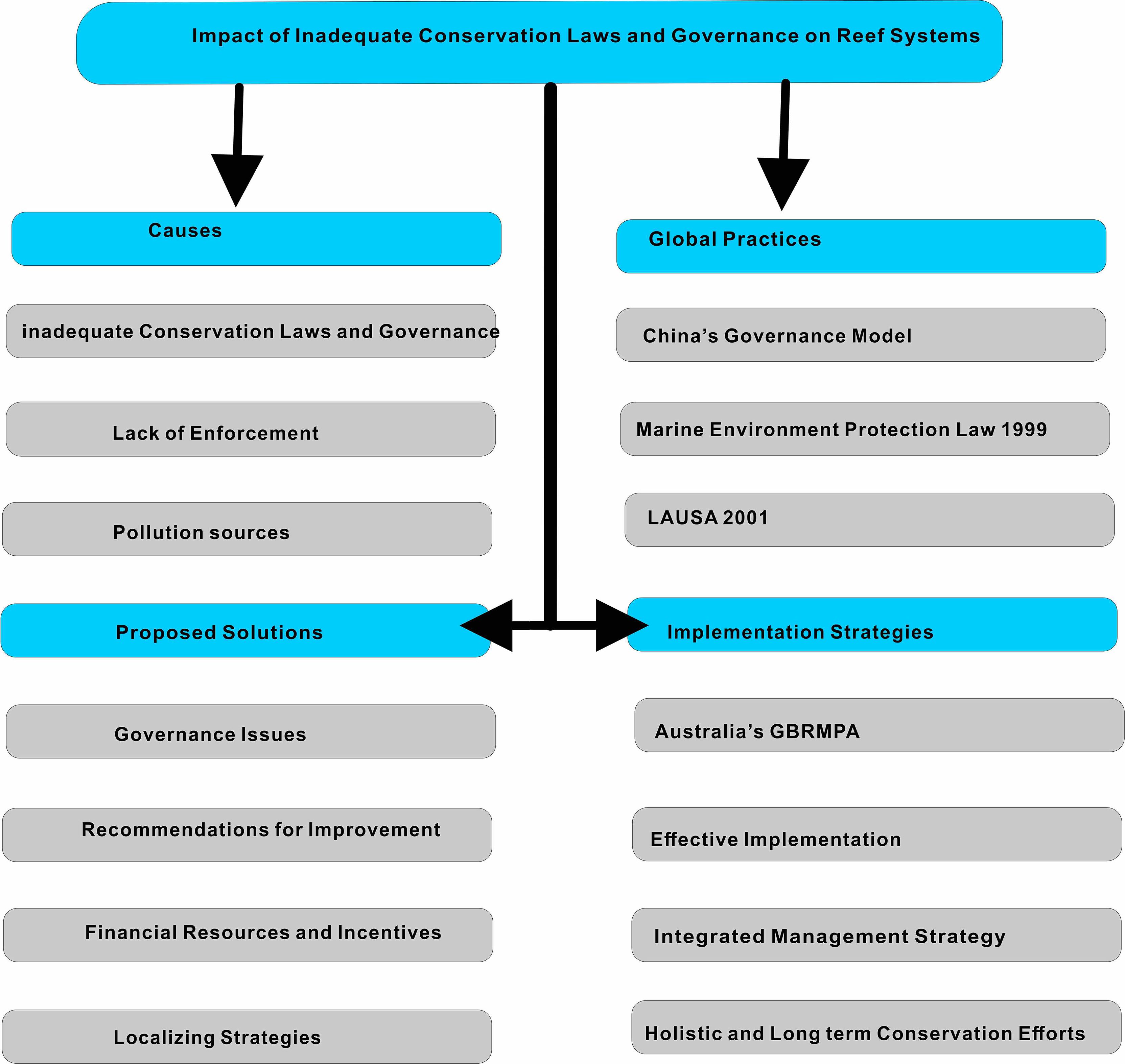
Figure 6. Framework for restoring coral reefs: A guide to coral reef restoration (The referenced literature and Table 1 were used to create this figure).
5.2 Enhance protection awareness
Insufficient awareness of ecological and environmental issues globally contributes to the degradation of coastal ecosystems (Kautsky et al., 2000; Garcia and De Leiva Moreno, 2003; Bayraktarov et al., 2016). The deterioration of marine ecosystems worldwide requires urgent global management strategies to safeguard their resilience (Mccook et al., 2009).
The coastal wetlands of Pakistan include a wide range of ecosystems such as coral reefs, mangroves, estuaries, and beaches (Chaudhry, 2010). Despite the ecological and economic importance of marine biodiversity protection, awareness in Pakistan remains critically inadequate due to weak protection awareness (Ullah et al., 2017). However, in Pakistan limited legislative improvements, rapid economic growth, and urbanization continue to overwhelm regulatory institutions, hampered by a lack of public awareness or concern regarding environmental degradation (Sardar, 2012; Mustafa et al., 2013). As a result, one of the serious threats to the coral reef ecosystem in Pakistan is a lack of awareness and understanding among the general population (Rajasuriya et al., 2002; Ali and Hussain, 2023). People who live near these areas are unaware of the importance of coral reefs in supporting coastal ecosystems (Chaudhry, 2010). Consequently, there is limited public support for conservation efforts (Ullah et al., 2016). The large commercial tours contribute to environmental litter, with items such as food and plastic being thrown into the water (Ullah et al., 2016). large resources allocated to monitoring coral reefs often render these ecosystems vulnerable to illegal activities like destructive fishing practices, overfishing, and coral mining, particularly along the Karachi coast where an increasing number of unauthorized fishing villages further exacerbate the situation (Qureshi, 2011; Mehak et al., 2023). This discussion emphasizes the need for the conservation of several species and habitats. However, between 2013 and 2016, there was a ban on fishing in the area from May to August, which was initially imposed by the Karachi Fisheries Harbor Authority to protect the population during the breeding season. However, the ban proved ineffective due to weak awareness among local communities and little logistical control over the area (Moazzam and Osmany, 2021; Osmany and Moazzam, 2022). This issue requires delicate handling, necessitating the exploration of alternative employment opportunities or income sources for residents. This can be achieved through the development of small-scale cottage industries or facilitating access to financing from banks for small businesses. Implementing a blanket ban may not always be feasible, especially in areas heavily dependent on fisheries. Central to this strategy will be the empowerment of communities whose lives are inextricably linked to the resources in question. Aguero and Costello (1986) observe that problems related to fisheries are rarely resolved by focusing solely on fishery management proposes. Ostrom (1990) has demonstrated that the conservation of natural resources is facilitated when local communities actively participate in the process. Additionally, Bromley (1992) argues that cooperation among people in conserving an open-access resource (OAR) is facilitated when they possess the capability to devise, oversee, and enforce regulations governing the utilization and allocation of natural resources by members.
To address these threats and enhance the protection and awareness of coral reefs in Pakistan’s coastal zone, a few sites are recommended for the designation of MPAs. The most important site may be Astola Island. However, Pakistan has designated Astola Island as an MPA (Siddiqui et al., 2008). Additionally, the IUCN has recommended Churna Island as one of the areas that should receive this protection (Hoon et al., 1997; Qaimkhani, 2018). While there might be some challenges for fishermen because of imposing protected areas. However, there might be some challenges for fishermen because of the need to establish protected areas. However, there are several advantages to the establishment of MPAs at various levels, such as marine ecosystem conservation, contributions to sustainable tourism, genetic diversity maintenance, potential enhancement of ecosystem-based fisheries management (especially in coastal areas crucial for breeding and spawning of economically valuable species), and preservation of prime locations for recreational activities such as SCUBA diving. Designating the MPA status would impose restrictions within a specified radius of the island, providing a safe breeding habitat for fish. Commercial activities should also be limited to reduce pollution and damage. Officially designating protected status could also raise public awareness of the island’s importance for biodiversity, making it more challenging for companies to disregard necessary protection. Additionally, various natural and anthropogenic pressures on Pakistan’s coral reefs can be reduced to the greatest extent possible by diverse management practices, development projects, legislative regulations, awareness-raising initiatives, and community and NGO involvement. Furthermore, strict environmental regulation enforcement is essential to counteract illegal activities that destroy coral reefs. Concerned departments should conduct comprehensive investigations of all coastal areas and collect data to determine the sites with the most potential for coral species rehabilitation, particularly for the restoration of extinct species. They should engage the assistance of local governments, local communities, volunteers, NGOs, religious leaders, elders, and the media to ensure that each sector of society contributes to the success of rehabilitation efforts and the efficient management and conservation of coral reefs.
5.3 Provide scientific support
In recent years, various countries have made significant progress globally in enhancing their scientific knowledge of coastal ecosystems. Consequently, the conservation of coastal ecosystems in Pakistan needs strong scientific support (Siddiqui et al., 2008; Ullah et al., 2017). In Pakistan, the continuous decline of the coral reef ecosystem further highlights the need for comprehensive scientific investigations (Ali et al., 2021; Ali and Hussain, 2023). Research on coral reefs has acquired critical significance globally due to their high biodiversity and aesthetic beauty (Brodie and Waterhouse, 2012; Muruganandam et al., 2023). However, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive scientific analysis of the threats confronting coral reefs in Pakistan. Assessing the extent of these unraveling and threats to their interconnections enables researchers to address the most pressing issues. For example, Ali et al. (2014) highlight the impacts of overfishing, destructive fishing practices, and pollution in the country’s coral reefs. Recommended management in response to these threats includes completing baseline assessments and coral reef research, establishing MPAs, and developing management initiatives and laws. Ali et al. (2017) investigated the factors influencing coral growth, focusing on the challenges posed by sedimentation and rising sea temperatures. The authors suggested the implementation of laws to manage coastal development and water quality. Iqbal et al. (2018) studied is about the coral reef responses to climate change. Their recommended proposed management approach involves remote sensing to monitor the impacts of climate change on the coral reef ecosystems. Ali et al. (2020) investigated the biodiversity reduction and faunal turnover in coral reefs. Their study suggested identifying and mitigating specific coral reef stresses. In addition, Ali et al. (2021) focused on unsustainable tourism practices and inadequate community involvement and awareness. Their study suggested reef restoration efforts and conservation initiatives.
These studies significantly contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the challenges confronting coral reefs and encourage conservation strategies. The scientific research, monitoring actions, and engagement community have emerged as a consistent thread, reflecting a concerted effort to increase the resilience and long-term survival of coral reefs. For example, China, a country with an extensive coastline (South China Sea), faces similar challenges regarding the conservation of its coastal environment (Huang et al., 2016). The South China Sea, located in the central Indo-Pacific region, is a large semi enclosed marine environment that supports diverse coral reef ecosystems (Morton and Blackmore, 2001). In the South China Sea, scientific research strongly supports the conservation of coral reefs, underlying their critical role in sustaining marine biodiversity, fisheries, and other ecosystem services. Various studies have highlighted the ecological importance and long-term conservation of this fragile ecosystem to overcome the impacts of climate change, overfishing, pollution, and other threats (Chou et al., 2009; Arai, 2015; Huang et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2016; Asner et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2019). Similarly, scientific research should be considered in Pakistan to enhance the effective conservation of coral reefs, following the example set by China. To overcome the challenges confronting these ecosystems, collaboration among managers and experts from various fields, such as marine geology, marine biology, oceanography, ecology, and local knowledge, is needed. Scientific efforts should be made to understand the distinctive dynamics of coral reefs in coastal areas of Pakistan. By collaborating with managers and experts from different backgrounds, Pakistan can gain a holistic perspective on the threats affecting its coral reef ecosystem.
Furthermore, collaborative research involving local researchers such as (Ali et al., 2014) and foreign researchers is needed to collect accurate and current data on coral distribution, variety, abundance, and threats in the coastal area of Pakistan.
6 Conclusion
The threats and conservation efforts to coral reefs in Pakistan have been thoroughly examined in this review. Coral reefs are an important coastal resource in Pakistan, contributing significantly to the country’s rapid social and economic growth. However, these fragile ecosystems have been disturbed by a variety of human activities with high frequency and intensity. The main anthropogenic threats to a country’s coral ecosystems are overfishing, pollution, and tourism. The effective protection and management of coral reef ecosystems are emergent for both local and central governments. The difficulties lie in the lack of protection awareness, targeted law, and adequate scientific basis. The promotion of national awareness of environmental protection is necessary and critical for reducing destructive activities and increasing conservation activities. Various targeted and effective protection measures could be implemented according to environmental policy and regulations; for example, the discharge of untreated sewage and destructive fishing are forbidden. In addition, rich and accurate information on coral reef ecosystems could provide a solid scientific foundation for the rapid understanding and management of coral reefs. To effectively address the conservation challenges affecting the country’s coral reefs, government support, researchers, and academia are needed. Furthermore, it is urgent to establish MPAs along Pakistan’s coastline to protect these ecosystems from further degradation.
Author contributions
IA: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Software. PG: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. M-XZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Investigation, Funding acquisition. YZ: Writing – review & editing, Software. X-YZ: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. S-QZ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. J-WQ: Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. QS: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. H-QY: Writing – review & editing, Validation. S-CT: Writing – review & editing, Project administration. L-JX: Writing – review & editing, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3100600), National Natural Science Foundation of China project (Grant Nos. 41876132,41806139 and 42376165), Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (Grant No. ZDYF2022SHFZ072), and the Open Research Fund Program of Guangxi Key Lab of Mangrove Conservation and Utilization (Grant No. GKLMC-201904).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbas G., Khan M. W., Ahmed M. (2013). Coastal and Marine Fisheries Management in. Coastal and Marine Fisheries Management in SAARC Countries, Vol. 245. Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Aguero M., Costello G. (1986). “Constraints to the development of effective fisheries management in the LDCs: implications for training and research,” in Groupe d’etude des Resources Maritime, Proceedings of the International Conference on Fisheries.
Ahmad M. (1997). “Natural and human threats to biodiversity in the marine ecosystem of coastal Pakistan,” in Coastal zone management imperative for maritime developing nations (Netherlands: Springer).
Ahmad M. (2015). Pakistan’s Maritime Department: A promising future for the country (Pakistan: Scientia. Biology).
Ahmad I., Aslam S., Hussain U. (2023). Assessment of plastic pollution in coastal areas of Karachi: Case study of West Warf, Kemari Jetty, and Manora. Mar. pollut. Bull. 195, 115501. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115501
Ahmed M., Ahmed S., Abbas R. (2022). Tourism in Pakistan, challenges and opportunities. J. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2, 130–137. doi: 10.54183/jssr.v2i3.102
Ajazuddin S., Moazzam M. (2007). Species composition in the intertidal fishing operations during s. w. monsoon along Balochistan coast. Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol., 101–106.
Alamgir A., Fatima N., Khan M. A., Rehman M., Shaukat S. S. (2019). A preliminary pollution appraisal of western backwater at Karachi Coastal area. Appl. Water Sci. 9, 1–6. doi: 10.1007/s13201-019-1049-y
Albright R. (2018). “Ocean acidification and coral bleaching,” in Coral Bleaching: Patterns, Processes, Causes and Consequences, 295–323. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-75393-5_12
Ali S. H., Hussain Z. (2023). Impact of climate change on south asia: shifting marine ecosystems in Pakistan. Pakistan Horizon. 76, 65–83.
Ali A., Ormond R., Leujak W., Siddiqui P. J. A. (2014). Distribution, diversity and abundance of coral communities in the coastal waters of Pakistan. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United. Kingdom. 94, 784. doi: 10.1017/s0025315413001203
Ali A., Siddiqui P. J. A., Bromfield K., Khan A. A., Iqbal P. (2017). Quaternary fossil coral communities in uplifted strata along the Balochistan coast of Pakistan: understanding modern coral decline in the Arabian Sea. Arabian. J. Geosci. 10, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s12517-017-3306-4
Ali A., Siddiqui P. J. A., Rasheed M., Ahmad N., Shafique S., Khokhar F. N. (2020). Status of corals along the Sindh coast of Pakistan: Prevailing environmental conditions, their impacts on community structure and conservation approaches. Regional. Stud. Mar. Sci. 39, 101391. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101391
Ali A., Siddiqui P. J. A., Shafique S., Burhan Z.-U.-N., Ahmad N., Masroor R. (2021). Ecology of fish communities in coral habitats along the coast of Pakistan: potential threats and conservation strategies. Pakistan J. Zool. 53, 1341–1351. doi: 10.17582/journal.pjz/20180602100601
Amjad S., Khan N., Ishaq S. (2020). Coral community: preliminary biodiversity survey of churna island, northern arabian sea. Mehran. Univ. Res. J. Of Eng. Technol. 39, 390–397. doi: 10.22581/muet1982.2002.15
Amjad S., Rizvi M. S. N. (1999). Pakistan’s national programme of action under the global programme of action for the protection of the marine environment from land based activities (karachi, Pakistan: Ministry of Environment & Local Government and Rural Development, Government of Pakistan & National Institute of Oceanography).
Ansari A. A., Gill S. S., Khan F. A. (2011). “Eutrophication: threat to aquatic ecosystems,” in Eutrophication: causes, consequences and control. Dordrecht, Heidelberg, London, 143–170. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-9625-8_7
Arai T. (2015). Diversity and conservation of coral reef fishes in the Malaysian South China Sea. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fisheries. 25, 85–101. doi: 10.1007/s11160-014-9371-9
Aria M., Cuccurullo C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. informetrics. 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Arshad M. I., Iqbal M. A., Shahbaz M. (2018). Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia. Pac. J. Tourism. Res. 23, 121–132. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2017.1410192
Aslam S., Chan M. W. H., Siddiqui G., Boczkaj G., Kazmi S. J. H., Kazmi M. R. (2020). A comprehensive assessment of environmental pollution by means of heavy metal analysis for oysters’ reefs at Hab River Delta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Mar. pollut. Bull. 153, 110970. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.110970
Asner G. P., Martin R. E., Mascaro J. (2017). Coral reef atoll assessment in the South China Sea using Planet Dove satellites. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 3, 57–65. doi: 10.1002/rse2.42
Baqar M., Arslan M., Sadef Y., Mahmood A., Qadir A., Ahmad S. R. (2017). Persistent organic pollutants in Pakistan: Potential threat to ecological integrities in terms of genotoxicity and oxidative stress. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment.: Int. J. 23, 1249–1271. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2017.1292843
Bayraktarov E., Banaszak A. T., Montoya Maya P., Kleypas J., Arias-González J. E., Blanco M., et al. (2020). Coral reef restoration efforts in Latin American countries and territories. PloS One 15, e0228477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228477
Bayraktarov E., Saunders M. I., Abdullah S., Mills M., Beher J., Possingham H. P., et al. (2016). The cost and feasibility of marine coastal restoration. Ecol. Appl. 26, 1055–1074. doi: 10.1890/15-1077
Beg M. A. A. (1995). Ecological imbalances in the coastal areas of Pakistan and Karachi Harbour. Pakistan J. Mar. Sci.
Bell P. R. (1991). Status of eutrophication in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Mar. pollut. Bull. 23, 89–93. doi: 10.1016/0025-326x(91)90655-c
Biagi P., Starnini E. (2020). Prehistoric fishing along the coasts of the Arabian Sea: a short overview from Oman, Balochistan and Sindh (Pakistan). Summertown Pavilion, Middle Way, Oxord OX2 7LG: Archaeopress Publishing Ltd, 18–24. doi: 10.2307/j.ctv10crdr5.7
Birwani Z., Ercelawn A., Shah M. (1999). Sustainable and just livelihoods for coastal fisherfolk: securing rights in environmental law and policy (Karachi: Pakistan Institute of Labor Education and Research).
Borell E. M., Bischof K. (2008). Feeding sustains photosynthetic quantum yield of a scleractinian coral during thermal stress. Oecologia 157, 593–601. doi: 10.1007/s00442-008-1102-2
Brainard R. (2008). Coral reef ecosystem monitoring report for American Samoa 2002-2006 (US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration).
Brodie J., Waterhouse J. (2012). A critical review of environmental management of the ‘not so Great’Barrier Reef. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 104, 1–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.03.012
Bromley D. W. (1992). “The commons, property, and common-property regimes,” in Making the commons work. Bloomington, Indiana, 3–16. doi: 10.1007/bf00324686
Burke L., Reytar K., Spalding M., Perry A. (2011). Reefs at risk revisited: technical notes on modeling threats to the world’s coral reefs (Washington, DC: World Resources Institute). doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-2639-2_274
Byrnes T. A., Dunn R. J. (2020). Boating-and shipping-related environmental impacts and example management measures: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 8, 908. doi: 10.3390/jmse8110908
Cao W., Wong M. H. (2007). Current status of coastal zone issues and management in China: a review. Environ. Int. 33, 985–992. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.04.009
Chadwick N. E. (1988). Competition and locomotion in a free-living fungiid coral. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 123, 189–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(88)90041-X
Chadwick-Furman N., Loya Y. (1992). Migration, habitat use, and competition among mobile corals (Scleractinia: Fungiidae) in the Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 114, 617–623. doi: 10.1007/bf00357258
Chanda A. (2022). “An overview of the Indian ocean coral ecosystems,” in Blue Carbon Dynamics of the Indian Ocean: The Present State of the Art. Switzerland: Springer Nature, Switzerland, 203–225. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-96558-7_7
Chaudhry A. A. (2010). “Wetlands in Pakistan: What is happening to them,” in World Environment Day. Pakistan, vol. 5.
Chaudhry A. A. (2018). Plastic pollution: Impacts on biodiversity (Punjab, Pakistan: On Behalf of Pakistan Engineering Congress; Pakistan Engineering Congress), 73.
Chen S.-N., Pearson S. (2015). Managing China’s coastal environment: using a legal and regulatory perspective. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 6, 225. doi: 10.7763/ijesd.2015.v6.595
Chou L. M., Yeemin T., Yaman A. R. B. G., Vo S. T., Alino P. (2009). Coral reef restoration in the South China Sea. Galaxea. J. Coral. Reef. Stud. 11, 67–74. doi: 10.3755/galaxea.11.67
Devlin M. J. (2022). Coral reefs: The good and not so good news with future bright and dark spots for coral reefs through climate change. Global Change Biol. 28, 4506. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16271
Devlin M., Brodie J. (2023). “Nutrients and Eutrophication,” in Marine Pollution–Monitoring, Management and Mitigation (Springer).
Diakomihalis M. N. (2007). Greek maritime tourism: evolution, structures and prospects. Res. Transport. Econ. 21, 419–455. doi: 10.1016/s0739-8859(07)21013-3
Dixit A. M., Kumar L., Kumar P., Pathak K. (2010). “Valuing the services of coral reef systems for sustainable coastal management,” in Valuation of Regulating Services of Ecosystems: Methodology and Applications. London, Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780203847602
Dorgham M. M. (2014). “Effects of eutrophication,” in Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control: Volume 2 Dordrecht Heidelberg London New York: Springer, 29–44. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7814-6_3
Eddy T. D., Lam V. W., Reygondeau G., Cisneros-Montemayor A. M., Greer K., Palomares M. L. D., et al. (2021). Global decline in capacity of coral reefs to provide ecosystem services. One Earth 4, 1278–1285. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2021.08.016
El-Naggar H. A. (2020). “Human impacts on coral reef ecosystem,” in Natural resources management and biological sciences (IntechOpen).
Erftemeijer P. L., Riegl B., Hoeksema B. W., Todd P. A. (2012). Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: a review. Mar. pollut. Bull. 64, 1737–1765. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.05.008
Evans L. S., Ban N. C., Schoon M., Nenadovic M. (2014). Keeping the ‘Great’in the Great Barrier Reef: large-scale governance of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Int. J. Commons. 8, 396–427. doi: 10.18352/bmgn-lchr.405
Faran F., Ejaz K. (2022). Blue economy of maritime nations in south asia: challenges and prospects. Lahore, Pakistan: South Asian Studies, vol. 37.
Farooqi A. B., Khan A. H., Mir H. (2005). Climate change perspective in Pakistan. Pakistan J. Meteorol. 2.
Freitas L. M., Oliveira M. D. D. M., Leão Z. M., Kikuchi R. K. P. (2019). Effects of turbidity and depth on the bioconstruction of the Abrolhos reefs. Coral. Reefs. 38, 241–253. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01770-3
Garcia S. M., De Leiva Moreno I. (2003). “Global overview of marine fisheries,” in Responsible fisheries in the marine ecosystem. United kingdom: CABI Publishing, vol. 10.
Gore M., Kiani M., Ahmad E., Hussain B., Ormond R., Siddiqui J., et al. (2012). Occurrence of whales and dolphins in Pakistan with reference to fishers’ knowledge and impacts. J. Cetacean. Res. Manage. 12, 235–247. doi: 10.47536/jcrm.v12i2.581
Gregory M. R. (2009). Environmental implications of plastic debris in marine settings—entanglement, ingestion, smothering, hangers-on, hitch-hiking and alien invasions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B.: Biol. Sci. 364, 2013–2025. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0265
Harrison P. L., Booth D. J. (2007). Coral reefs: naturally dynamic and increasingly disturbed ecosystems. Mar. Ecol., 316–377.
Hernandez-Pacheco R. H.-D., Sabat E. A., Alberto M. (2010). “DECADAL-SCALE DEMOGRAPHICS OF MASSIVE BLEACHING AND MORTALITY IN THE MAJOR CARIBBEAN REEF-BUILDING STAR CORAL, MONTASTRAEA ANNULARIS,” in Puerto Rico Coral Reef Long-Term Ecological Monitoring Program: CCRI-Phase III and Phase IV, (2008-2010) Final Report. Mayaguez, PR: Caribbean Coral Reef Institute, University of Puerto Rico, 82. doi: 10.1890/es10-00065.1
Hoon V., Chong K.-C., Roy R., Bierhuizen B., Rubens J., Kanvinde H. (1997). Regional Workshop on the Conservation and Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs. Manila, Pilippines: Interantional Marinelife Alliance.
Huang D., Hoeksema B. W., Affendi Y. A., Ang P. O., Chen C. A., Huang H., et al. (2016). Conservation of reef corals in the South China Sea based on species and evolutionary diversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 25, 331–344. doi: 10.1007/s10531-016-1052-7
Iqbal K. M. J., Heidegger P. (2013). “Pakistan ship-breaking outlook,” in Sustainable development Policy Institute, and NGO Ship-Breaking Platform(Brussels, Belgium).
Iqbal A., Qazi W. A., Shahzad N., Nazeer M. (2018). “Identification and mapping of coral reefs using Landsat 8 OLI in Astola Island, Pakistan coastal ocean,” in 14th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET). (Islamabad, Pakistan: IEEE), 1–6.
Jamal S. (2020). Coral bleaching reported for first time in Pakistan: WWF- Pakistan appeeals to government to declare churna Island as a Marine Protected Area, Gulf News 1 Decmber. Available at: https://gulfnews.com/environment/coral-bleaching-reported-for-first-time-in-pakistan-wwf-pakistan-appeals-to-government-to-declare-churna-island-as-a-marine-protected-area-1.75631275.
Jamali H. A. (2009). Investment in the ‘Blue Economy’of Balochistan: Potential, Prospects, and Policy Options for Improvement in the Light of Global Best Practices. Pakistan: Journal of National School of Public Policy (NSPP) Vol. 15, 1.
Jayabalan N., Al-Marzouqi A., Zaki S., Al-Kharusi L. (2021). “Strategies for monitoring and management of marine fisheries resources of the sultanate of Oman,” in The arabian Seas: Biodiversity, Environmental Challenges and Conservation Measures. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzealand AG, 859–881. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51506-5_37
Jilani S. (2018). Present pollution profile of Karachi coastal waters. J. Coast. Conserv. 22, 325–332. doi: 10.1007/s11852-017-0581-x
Karani P., Failler P. (2020). Comparative coastal and marine tourism, climate change, and the blue economy in African Large Marine Ecosystems. Environ. Dev. 36, 100572. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2020.100572
Karim M. S. (2017). Shipbreaking in developing countries: a requiem for environmental justice from the perspective of Bangladesh (Routledge).
Kautsky N., Rönnbäck P., Tedengren M., Troell M. (2000). Ecosystem perspectives on management of disease in shrimp pond farming. Aquaculture 191, 145–161. doi: 10.1016/s0044-8486(00)00424-5
Keyuan Z. (2001). Historic rights in international law and in China’s practice. London, United kingdom: Ocean Development & International Law. vol. 32, 149–168. doi: 10.1080/00908320151100280
Khan N. (2011). Marine resources in Pakistan: A tentative inventory. Pakistan Business. Rev., 834–843.
Khan U., Janjuhah H. T., Kontakiotis G., Rehman A., Zarkogiannis S. D. (2021). Natural processes and anthropogenic activity in the Indus river sedimentary environment in Pakistan: A critical review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 1109. doi: 10.3390/jmse9101109
Khan S. R., Khan S. R. (2011). Fishery degradation in Pakistan: a poverty–environment nexus? Can. J. Dev. Studies/Revue. Can. d’études. du. développement. 32, 32–47. doi: 10.1080/02255189.2011.576140
Khan A., Muhmmad T., Rahim A. (2011). Coral reefs in Gwadar bay. In: Discovery of Corel Reefs in Gwader. The ministry of environments Pakistan welands program, Pakistan.
Khan M. A., Khan J. A., Ali Z., Ahmad I., Ahmad M. N. (2016). The challenge of climate change and policy response in Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 75, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5127-7
Kidwai S., Ahmed W., Tabrez S. M., Zhang J., Giosan L., Clift P., et al. (2019). “The Indus delta—Catchment, river, coast, and people,” in Coasts and Estuaries (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier).
Li H. (2006). The impacts and implications of the legal framework for sea use planning and management in China. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 49, 717–726.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2006.06.015. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2006.06.015
Lu W.-H., Liu J., Xiang X.-Q., Song W.-L., Mcilgorm A. (2015). A comparison of marine spatial planning approaches in China: Marine functional zoning and the marine ecological red line. Mar. Policy 62, 94–101. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2015.09.004
Mahmood S., Hassan Q. (2022). Climate change: its impacts on Pakistan. Int. Res. J. Soc. Sci. Humanities. 1, 20–32.
Majeed R., Fatima S. U., Khan M. A., Khan M. A., Shaukat S. S. (2021b). Spatio-temporal analysis of pollutants in Karachi coastal water. EQA-International. J. Environ. Qual. 42, 6–21.
Majeed R., Fatima S., Khan M. A., Khan M. A., Urooj S. (2021a). A QUANTITATIVE APPRAISAL OF SEDIMENT CONTAMINATION AT KARACHI COAST, PAKISTAN.
Majumdar S. D., Hazra S., Giri S., Chanda A., Gupta K., Mukhopadhyay A., et al. (2018). Threats to coral reef diversity of Andaman Islands, India: A review. Regional. Stud. Mar. Sci. 24, 237–250. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2018.08.011
Martínez Vázquez R. M., Milán García J., De Pablo Valenciano J. (2021). Analysis and trends of global research on nautical, maritime and marine tourism. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 93. doi: 10.3390/jmse9010093
Mcclanahan T. R. (2002). The near future of coral reefs. Environ. Conserv. 29, 460–483. doi: 10.1017/s0376892902000334
Mccook L. (2001). Competition between corals and algal turfs along a gradient of terrestrial influence in the nearshore central Great Barrier Reef. Coral. Reefs. 19, 419–425. doi: 10.1007/s003380000119
Mccook L., Almany G., Berumen M. L., Day J., Green A., Jones G., et al. (2009). Management under uncertainty: guide-lines for incorporating connectivity into the protection of coral reefs. Coral. Reefs. 28, 353–366. doi: 10.1007/s00338-008-0463-7
Mehak A., Mu Y., Mohsin M., Zhang X.-C. (2023). MCDM-based ranking and prioritization of fisheries’ Risks: A case study of sindh, Pakistan. Sustainability 15, 8519. doi: 10.3390/su15118519
Memon S. H. (2012). “An overview of mangrove restoration efforts in Pakistan,” in Sharing lessons on mangrove restoration, vol. 51.
Moazzam M., Osmany H. B. (2021). Species composition, commercial landings, distribution and conservation of fishes belonging to order Myliobatiformes from Pakistan. Karachi. Univ. J. Sci. 49, 01–26.
Mohsin M., Mu Y., Memon A. M., Kalhoro M. T., Shah S. B. H. (2017). Fishery stock assessment of Kiddi shrimp (Parapenaeopsis stylifera) in the Northern Arabian Sea Coast of Pakistan by using surplus production models. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 35, 936–946. doi: 10.1007/s00343-017-6096-3
Morton B., Blackmore G. (2001). South China sea. Mar. pollut. Bull. 42, 1236–1263. doi: 10.1016/s0025-326x(01)00240-5
Mukheed M., Alisha K. (2020). Plastic pollution in Pakistan: Environmental and health Implications. J. pollut. Effects. Contr. 4, 251–258.
Mukhtar I., Hannan A. (2012). Constrains on mangrove forests and conservation projects in Pakistan. J. Coast. Conserv. 16, 51–62. doi: 10.1007/s11852-011-0168-x
Muller-Parker G., D’elia C. F., Cook C. B. (2015). “Interactions between corals and their symbiotic algae,” in Coral reefs in the Anthropocene, 99–116. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7249-5_5
Mumtaz S., Ali S. H., Rashid M. T. (2023). Global warming and marine life in Pakistan: A looming crisis. Cent. Eur. Manage. J. 31, 402–411.
Muruganandam M., Rajamanickam S., Sivarethinamohan S., Reddy M. K., Velusamy P., Gomathi R., et al. (2023). Impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on aquatic ecosystem–A review. Environ. Res., 117233. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117233
Mustafa Z. (2011). “Climate change and its impact with special focus in Pakistan,” in Pakistan Engineering Congress, Symposium, Lahore. 290.
Mustafa D., Akhter M., Nasrallah N. (2013). Understanding Pakistan’s water-security nexus (Washington, DC: United States Institute of Peace).
Naumann M. S., Bednarz V. N., Ferse S. C., Niggl W., Wild C. (2015). Monitoring of coastal coral reefs near Dahab (Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea) indicates local eutrophication as potential cause for change in benthic communities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 187, 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4257-9
Nawaz R., Moazzam M. (2014). “An assessment of cetacean mortality in the tuna fisheries of Pakistan,” in Final Report Australian Marine Mammal Centre Grants Program (Pakistan: WWF-Pakistan), 89p.
Neelam A. (2021). Quality characterization and assessment of coastal water of karachi, Pakistan. doi: 10.31031/eaes.2022.09.000725
Neelam A., Salih Hussain F., Alamgir A., Kanwal S. (2018). Quantification and Composition of Solid waste abundance on the beaches of Karachi, Pakistan. Curr. World Environ. 13. doi: 10.12944/cwe.13.2.08
Nergis Y., Butt J. A., Sharif M. (2021). Assessment of marine coastal water pollution from Karachi Harbour Pakistan. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 12, 27–31. doi: 10.46660/ijeeg.vol12.iss2.2021.583
Nigar N. (2018). Ecotourism for sustainable development in Gilgit-Baltistan. Strategic. Stud. 38, 72–85. doi: 10.53532/ss.038.03.00145
Noor R., Pande C. B., Zahra S. M., Maqsood A., Baig A., Misaal M. A., et al. (2023). “Review of various impacts of climate change in south asia region, specifically Pakistan,” in Climate Change Impacts on Natural Resources, Ecosystems and Agricultural Systems (Cham, Switzerland: Springer).
Oakley-Cogan A., Tebbett S. B., Bellwood D. R. (2020). Habitat zonation on coral reefs: Structural complexity, nutritional resources and herbivorous fish distributions. PloS One 15, e0233498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233498
Oppermann S. (2024). Reading Storied corals with the scientific poetics of water. Configurations 32, 281–303. doi: 10.1353/con.2024.a932026
Osmany H. B., Moazzam M. (2022). Species composition, commercial landings, distribution and some aspects of biology of shark (Class Pisces) of Pakistan: Large demersal sharks. Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 19, 89–111.
Ostrom E. (1990). Governing the commons: The evolution of institutions for collective action (Cambrige, UK: Cambridge university press).
Pakistan M. (2014). Pakistan national strategy and action plan (Islamabad, Pakistan: MFF Pakistan and Climate Change Division, Government of Pakistan).
Pakistan M. (2016). A handbook on Pakistan’s coastal and marine resources (Pakistan: MFF Pakistan, Pakistan, Daccan printers (Pvt) Ltd).
Pedersen N. E., Edwards C. B., Eynaud Y., Gleason A. C., Smith J. E., Sandin S. A. (2019). The influence of habitat and adults on the spatial distribution of juvenile corals. Ecography 42, 1703–1713. doi: 10.1111/ecog.04520
Qaimkhani A. M. (2018). The marine Litter Action Plan-Status Report (Pakistan) Vol. 36 (Islamabad, Pakistan: Government of Pakistan).
Qari R., Shaffat M. (2015). Distribution and abundance of marine debris along the coast of Karachi (Arabian Sea), Pakistan. Pakistan J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. B. Biol. Sci. 58, 98–103. doi: 10.52763/pjsir.biol.sci.58.2.2015.98.103
Qureshi A. S. (2005). Climate change and water resources management in Pakistan. Climate Change Water Resour. South Asia., 197–230. doi: 10.1201/9780203020777.ch8
Rafique M. (2018). A review on the status, ecological importance, vulnerabilities, and conservation strategies for the Mangrove ecosystems of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 50, 1645–1659.
Rajasuriya A., Zahir H., Muley E., Subramanian B., Venkataraman K., Wafar M., et al. (2002). “Status of coral reefs in South Asia: Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Sri Lanka,” in Proceedings of the Ninth International Coral Reef Symposium, Bali, 23-27 October 2000. 841–845.
R Core Team (2022). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Available at: https://www.R-project.org/.
Roberts C. M. (1995). Effects of fishing on the ecosystem structure of coral reefs. Conserv. Biol. 9, 988–995. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.9051332.x-i1
Saher N. U., Siddiqui A. S., Kanwal N., Narejo A. H., Gul A., Gondal M. A., et al. (2019). An overview of pollution dynamics along the Pakistan coast with special reference of nutrient pollution. Sarjah, United Arab Emirates: Bentham Science Publishers, 136–172. doi: 10.2174/9789811412691119010012
Salik K. M., Jahangir S., Ul Hasson S. (2015). Climate change vulnerability and adaptation options for the coastal communities of Pakistan. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 112, 61–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2015.05.006
Sardar S. (2012). Looming urban sprawl and its implications: an overview of South Asian urbanization. Regional. Stud. 33, 1–21.
Sayied N. (2007). Environmental issues in coastal waters-Pakistan as a case study. Malmo, Sweden: World maritime University.
Shahzad S. M. (2020). De-constructing the problematic maritime tourism in Pakistan: opportunities and challenges. Int. J. @ Multidiscip. Curr. Res. 8, 378–387. doi: 10.53963/pjmr.2022.003.4
Siddiqi A. H. (1992). Fishery resources and development policy in Pakistan. GeoJournal 26, 395–411. doi: 10.1007/bf02629820
Siddique A., Mumtaz M., Zaigham N. A., Mallick K. A., Saied S., Zahir E., et al. (2009). Heavy metal toxicity levels in the coastal sediments of the Arabian Sea along the urban Karachi (Pakistan) region. Mar. pollut. Bull. 58, 1406–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.06.010
Siddiqui P. J., Amir S. A. (2010). Baseline survey of Fish Diversity at Astola Island, Balochistan (Karachi: Center of Excellence in Marine Biology University of Karachi).
Siddiqui P. J., Farooq S., Shafique S., Farooqi Z. (2008). Conservation and management of biodiversity in Pakistan through the establishment of marine protected areas. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 51, 377–382. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2008.01.006
Siriwong S., True J. D., Piromvarakorn S. (2018). Number of tourists has less impact on coral reef health than the presence of tourism infrastructure. Songklanakarin. J. Sci. Technol. 40.
Smallhorn-West P., Gordon S., Stone K., Ceccarelli D., Malimali S. A., Halafihi T. I., et al. (2020). Biophysical and anthropogenic influences on the status of Tonga’s coral reefs and reef fish fishery. PloS One 15, e0241146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241146
Stephenson R. L., Hobday A. J., Butler I., Cannard T., Cowlishaw M., Cresswell I., et al. (2023). Integrating management of marine activities in Australia. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 234, 106465. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106465
Sully S., Hodgson G., Van Woesik R. (2022). Present and future bright and dark spots for coral reefs through climate change. Global Change Biol. 28, 4509–4522. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16083
Sweet M. (2019). Plastics and shallow water coral reefs: synthesis of the science for policy-makers.
Tambunan B. P. (2004). Pakistan: Sindh Coastal and Inland Community Development Project. Philippines: Asian Development Bank (ADB).
Ullah Z., Johnson D., Micallef A., Williams A. T. (2010). Coastal scenic assessment: unlocking the potential for coastal tourism in rural Pakistan via Mediterranean developed techniques. J. Coast. Conserv. 14, 285–293. doi: 10.1007/s11852-009-0078-3
Ullah Z., Khan J., Haq Z. U. (2018). Coastal tourism & CPEC: opportunities and challenges in Pakistan. J. Political. Stud. 25, 261–272.
Ullah Z., Pg W. W., Xiaoru X. (2016). Coastal zone issues and counter measures through an integrated approach for Pakistan. Lasbela, U . j . Sci., Pakistan.
Ullah Z., Wu W., Guo P., Yu J. (2017). A study on the development of marine functional zoning in China and its guiding principles for Pakistan. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 144, 40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2017.04.017
Ullah Z., Wu W., Wang X. H., Pavase T. R., Shah S. B. H., Pervez R. (2021). Implementation of a marine spatial planning approach in Pakistan: An analysis of the benefits of an integrated approach to coastal and marine management. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 205, 105545. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105545
Ullah Z., Wu W., Wang X. H., Pervez R., Ahmed A., Baloch A. (2022). Improving coastal and marine resources management through a co-management approach: a case study of Pakistan. Environ. Res. Commun. 4, 025003. doi: 10.1088/2515-7620/ac5088
Wasim M. W. K., Abbas G. (2024). Review on fisheries resources and the effect of marine pollution in coastal waters of Pakistan. J. Zool. Syst. 2, 23–43. doi: 10.56946/jzs.v2i1.312
Wenger A. S., Fabricius K. E., Jones G. P., Je B. (2015). 15 Effects of sedimentation, eutrophication, and chemical pollution on coral reef fishes. Ecol. Fishes. Coral. Reefs. 145. doi: 10.1017/cbo9781316105412.017
Wilson S., Fatemi S. M. R., Shokri M. R., Claereboudt M. (2002). Status of coral reefs of the Persian/Arabian Gulf and Arabian Sea region. Status Coral. Reefs. World 2002, 53–62.
Zhao M., Yu K., Shi Q., Yang H., Riegl B., Zhang Q., et al. (2016). The coral communities of Yongle atoll: status, threats and conservation significance for coral reefs in South China Sea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 67, 1888–1896. doi: 10.1071/mf15110
Zhao M., Zhang H., Zhong Y., Jiang D., Liu G., Yan H., et al. (2019). The status of coral reefs and its importance for coastal protection: a case study of Northeastern Hainan Island, South China Sea. Sustainability 11, 4354. doi: 10.3390/su11164354
Keywords: marine protected areas (MPAs), coral reef restoration, ecosystem, marine pollution, overfishing, sedimentation
Citation: Ahmad I, Guo P, Zhao MX, Zhong Y, Zheng XY, Zhang SQ, Qiu J-W, Shi Q, Yan HQ, Tao SC, and Xu LJ (2024) Coral reefs of Pakistan: a comprehensive review of anthropogenic threats, climate change, and conservation status. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1466834. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1466834
Received: 18 July 2024; Accepted: 04 September 2024;
Published: 30 September 2024.
Edited by:
Robert Mortimer, York St. John University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Fabio Favoretto, University of California, San Diego, United StatesAbhra Chanda, Jadavpur University, India
Copyright © 2024 Ahmad, Guo, Zhao, Zhong, Zheng, Zhang, Qiu, Shi, Yan, Tao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mei-Xia Zhao, emhhb21laXhAc2NzaW8uYWMuY24=
†These authors share first authorship
 Ishfaq Ahmad
Ishfaq Ahmad Pu Guo1†
Pu Guo1† Mei-Xia Zhao
Mei-Xia Zhao Jian-Wen Qiu
Jian-Wen Qiu Qi Shi
Qi Shi Hong-Qiang Yan
Hong-Qiang Yan
