- 1Faculty of Forestry and Environment, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Selangor, Seri Kembangan, Malaysia
- 2Faculty of Agriculture, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Selangor, Seri Kembangan, Malaysia
Introduction: Power plants discharge thermal and cold effluents that significantly alter marine environments, impacting various organisms, including benthic communities. While thermal discharge has received considerable research attention, the impacts of cold discharge remain underexplored. This systematic review synthesizes existing research on the effects of power plant discharges on marine benthic ecosystems.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted using Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science, following PRISMA guidelines, covering studies from 1974 to 2024. A total of 58 articles were included in this review. CiteSpace was used to visualize trends, and statistical analysis was conducted to assess relationships between environmental parameters and changes in benthic abundance.
Results: A significant negative correlation was observed between temperature differentials, ambient temperature, and benthic abundance. Thermal discharge generally led to reduced benthic diversity and abundance, with occasional increases under low ambient temperatures. Cold discharge effects remain less documented, with evidence primarily focused on phytoplankton and fish. Additionally, dissolved oxygen, pH, and bottom sediment composition were significantly altered by power plant discharge. Detection and mitigation measures are crucial to managing these impacts. Mitigation measures include distributed discharge for cold effluents, advanced heat recovery systems, and careful site selection to minimize impacts on sensitive ecosystems. Long-term management and adaptive strategies are essential to reduce adverse effects and maintain ecological balance.
Discussion: Thermal discharges adversely impact marine benthic organisms by decreasing biodiversity and changing community structure, largely due to elevated temperatures and reduced oxygen levels. Cold discharges present unique challenges that require further research to fully understand their ecological impacts. Mitigation measures, such as distributed discharge for cold effluents and advanced heat recovery systems for thermal discharges, are essential to minimize the environmental impact of power plant operations.
Highlights
● Research on cold discharge’s impact on benthos is notably deficient.
● Temperature difference is negatively correlated with changes in benthic abundance.
● The discharge alters the levels of dissolved oxygen, pH, and bottom material.
● Mitigation measures are available for both thermal and cold emissions’ impacts.
1 Introduction
Electricity is one of the driving forces of economic development in all nations. In 2021, the world’s total electrical energy generated was 617791617 TJ (IEA, 2024). The world’s existing electricity generation is mainly divided into six types of sources: fossil fuels (57.2%), nuclear (11.7%), hydroelectricity (13.5%), wind (10.8%), solar (3.1%), and other renewables (3.7%). The performance of thermoelectric power generation depends heavily on cooling systems, which are the most water-consuming component of the thermoelectric power generation process (Pan et al., 2018).
In a thermal power plant system, the cooling mechanism involves drawing water from nearby estuaries or oceans. Following heat exchange in the condenser, this water is discharged back into the corresponding aquatic ecosystem via an outflow channel, despite being at a higher temperature. In the case of the Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) power plant, cold water is utilized for condenser heat exchange before being released into the aquatic ecosystem via the discharge channel, typically at a temperature lower than that of the surrounding environment (Masutani and Takahashi, 2001). Those power plants required substantial water intake to facilitate the cooling process for the condensers. According to the current production process, directly cooled power plants are typically situated on open coastlines or estuaries and requires 35–50 m³/s of cooling water per 1000 MWe of power produced (Venugopalan et al., 2011; Wither et al., 2012), and a large amount of discharge leads to disturbances in the substrate (Deabes, 2020). The large volumes of water used for cooling and discharged by power plants can modify the physical and chemical properties of the surrounding environment, including the stratification and circulation of seawater, as well as the levels of salinity, dissolved oxygen, and pH (Muthukumar et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2021). Additionally, chlorine is commonly employed to mitigate biofouling within cooling ducts (Padhi et al., 2019; Taylor, 2006). However, the impact of elevated temperatures will be exacerbated by the concurrent discharge of biocides like chlorine (Chavan et al., 2017; Jenner et al., 1997). Marine organisms are highly sensitive to changes in temperature, dissolved oxygen, and salinity gradients (Mariu et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2023), and the thermal and cold discharge from power plants have significant impacts on their behavior and ecology.
The discharge of thermal and cold effluents carry significant implications for marine ecosystems, exerting considerable impacts on the growth and reproductive patterns of numerous species (Michie et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2017), as well as on the structure and composition of various communities, such as phytoplankton (Chuang et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2017), zooplankton (Jebakumar et al., 2018), fish (Teixeira et al., 2012), and benthic organisms (Bensoussan et al., 2010; Riera et al., 2011; Mazik et al., 2013; Bozorgchenani et al., 2018).
Benthos plays a crucial role as both consumers and decomposers in the food chain of aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, the study of benthic organisms is essential for understanding the structure and function of these ecosystems (Baldanzi et al., 2013; Nicastro and Bishop, 2013; Lamadrid-Rose and Boehlert, 1988). Benthic organisms inhabited the seabed or its immediate vicinity. Benthos can be classified into three categories according to their size: macrobenthos, meiobenthos, and microbenthos. Macrobenthos are primarily composed of Cnidaria, Polychaeta, Mollusca, Crustacea, and echinoderms, as well as other species such as sponges, bryozoans, sipunculans, spoonworms, worms, and benthic fishes (Li and Xu, 2021). Macrobenthos play a crucial role in the energy and material cycling within the benthic ecosystem, including nutrient cycling, decomposition, pollutant diffusion and burial, and secondary productivity (Ellingsen and Gray, 2002; Snelgrove, 1998). Meiobenthos is a diverse group of small benthic organisms that play a critical role in the structure and function of benthic ecosystems (Schratzberger and Ingels, 2018). They are typically between 42 and 500 μm in size and include over 20 categories of Metazoa and Protozoa, such as Nematodes, Cnidarians, Platyhelminthes, Nemerteans, Rotifers, Priapulids, Annelids (primarily Polychaetes), Arthropods (including Copepods, Halacaroids, Ostracods, etc.), and Mollusks (McIntyre, 1969; Urban-Malinga, 2014). Meiobenthos act as an intermediate link between microbenthos and macrobenthos and play an essential role in the marine benthic ecosystem. They are involved in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the diffusion and burial of pollutants (Schratzberger and Ingels, 2018). Moreover, they have a short life cycle, high fecundity, and are sensitive to environmental changes, making them valuable indicators of environmental pollution (Islam et al., 2024; Ridall and Ingels, 2021).
Various factors play pivotal roles in shaping the abundance, diversity, distribution, and functional attributes of aquatic organisms. These factors include but are not limited to water temperature, salinity levels, hydrodynamic dynamics, sedimentary processes, oxygen concentrations, sediment grain size, prevailing currents, and the availability of nutrients (Ingels et al., 2011; Zeppilli et al., 2013; Górska et al., 2014; Pusceddu et al., 2014). Benthos is a highly vulnerable group when it comes to the impact of thermal discharge, as their capacity to evade is limited. With many benthic species being either sessile or sedentary, some even have remained in the same spot throughout their entire lives (Zeppilli et al., 2015; Schratzberger et al., 2023). For this reason, benthos is regarded as an ideal group to monitor and determine the effects of various types of pollutants (Warwick and Clarke, 1993). Compared with cold discharge, research on the impact of power plants on benthic ecosystems predominantly focuses on thermal discharge. This phenomenon is acknowledged to pose a substantial threat to benthic organisms, resulting in habitat degradation and heightened mortality rates (Vaquer-Sunyer and Duarte, 2011). This thermal discharge is observed to hinder growth and development (Kim et al., 2017), as well as affect metabolic activity (Kim et al., 2017). Furthermore, there is substantial empirical evidence highlighting the detrimental effects of thermal discharge on benthic abundance, biodiversity, and community structure (Farshchi et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2023; West et al., 2021; Bozorgchenani et al., 2018). Conversely, exploring cold discharge effects on marine organisms remains relatively scant, with existing studies predominantly focusing on phytoplankton and fish (Myers et al., 1986; Billman et al., 2006; Golmen et al., 2005; Liu, 2018; Giraud et al., 2019). This phenomenon underscores the insufficient understanding of the effects of cold discharge on marine benthic communities.
In recent years, the impact of power plant discharge on Marine ecosystems, especially benthic organisms, has received increasing attention. This review uses sources such as Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science to develop a detailed database compiling existing literature on the effects of power plant discharge on benthic organisms. This review seeks to 1) employ CiteSpace software to analyze and visualize the literature, elucidating the spatial and temporal distribution of research in this area and identifying emerging hotspots of interest; 2) examine the effects of coastal power plant discharge on benthos community structure, with a particular focus on the relationship between temperature differentials and variations in benthic abundance; 3) assess how various environmental factors—including dissolved oxygen, pH, and bottom material—affect benthic organisms, emphasizing the complex interplay among these factors; 4) provide insights that can inform the formulation of environmental policies designed to mitigate the impacts of thermal and cold effluents on marine biodiversity, advocating for a holistic approach to address these challenges.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Data collection
The initial phase of this study involved the systematic identification of relevant scholarly literature through a comprehensive review of peer-reviewed scientific articles available on the Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science platforms spanning the period from 1974 to 2024 by adopting PRISMA methodology (Moher et al., 2015). The search fields encompassed titles, abstracts, and keywords, utilizing the following search criteria (Guimarães et al., 2023): (“sea*” OR “marine” OR “shore” OR “ocean*” OR “coastal zone” OR “coastline” OR “estuary”) AND (“thermal discharge” OR “thermal pollution” OR “thermal stress” OR “cold discharge” OR “cold shock” OR “cooling water” OR “warming” OR “temperature” OR “heat”) AND (“power plant*” OR “thermal plant*” OR “power station*” OR “Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion power station” OR “Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion power plant”) AND (“benthos” OR “benthic*” OR “invertebrate” OR “mussel” OR “mollusca” OR “crustacea” OR “polychaeta” OR “community” OR “biodiversity” OR “diversity”) NOT (“river*” OR “lake*”). Macrobenthic and microbenthic organisms are selected as biological indicators in this study due to their ease of observation, identification, and greater stability, which render them suitable for assessing environmental changes (Islam et al., 2024; Nayak et al., 2022). These organisms’ characteristics facilitate the monitoring of ecological shifts with precision.
To evaluate the organisms impacted by thermal emissions, we encompassed all benthic organisms exhibiting alterations in biological and ecological indices (e.g., morphology, reproduction, diversity). Given the scarcity of research about the effects on benthic organisms caused by cold discharge, investigations into organisms affected by cold emissions were expanded to include phytoplankton and fish. Owing to the heterogeneity observed in the taxonomic classification systems utilized across diverse scholarly articles, ranging from species-level to genus-level classifications, the resultant data have been systematically organized and analyzed at the class level to facilitate coherent comparisons.
Factors documented in preliminary studies regarding the impact of thermal and cold emissions from power plants on local biodiversity were extracted and consolidated. The influencing factors of the main study were categorized into three groups: (1) solely temperature; (2) temperature and other factors; and (3) solely other factors, such as salinity, nutrients, chlorine, radioactivity, and so on. The systematic analysis was limited to effects falling within the first and second categories, as they explicitly delineated the impact of temperature variations on benthic organisms.
A total of 615 articles were identified, comprising 296 from the Web of Science, 254 from Scopus, and 65 from PubMed. Following the removal of duplicate studies, the remaining articles underwent screening based on title and abstract. Subsequently, the content of the articles underwent screening to exclusively include studies focusing on the impact of water temperature on benthic organisms. Finally, 58 articles were deemed suitable for inclusion in the systematic review, while 9 articles were included in the quantitative analysis (Figure 1). Readers are directed to consult the supplementary material, “List of Articles Included in the Systematic Review,” for specific documents referenced in this study. Forty-nine studies were excluded from the quantitative analysis due to the absence of data on benthic abundance or temperature.
2.2 Analysis methods
The effects of five factors on changes in benthic abundance between influence and reference sites were assessed. Two of these factors were intrinsic to the operation of the power plant under investigation, namely 1) generation capacity and 2) cooling water discharge. Additionally, 3) the distance (0–100 m) between the discharge point and sampling sites (the influence point), 4) ambient water temperature, and 5) the temperature difference between the influence point and the reference point were considered regulatory factors.
Changes in benthic abundance determined based on Equation 1:
Where Ai is the abundance of benthos at the influence site, and Ar is the abundance of benthos at the reference site.
If an impacted site was contrasted with multiple reference sites, the average temperature was computed by aggregating data from all reference sites. In cases where multiple study areas were delineated, the data closest to the outfall was prioritized. When textual information regarding temperature, standard deviation, and the sample size was absent but figures were available, data were extracted using the WebPlotDigitizer tool (https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer/).
The temporal evolution of scientific findings regarding the impacts of thermal and cold emissions from power stations on benthos over the past decade was analyzed using CiteSpace. Additionally, the categories with the highest number of publications on this topic were identified. After compiling the data for each power plant investigated in the preliminary study (Table 1), distribution plots were generated utilizing R 4.3.1 software (R Core Team, 2023). All statistical analyses were conducted in R 4.3.1 software.
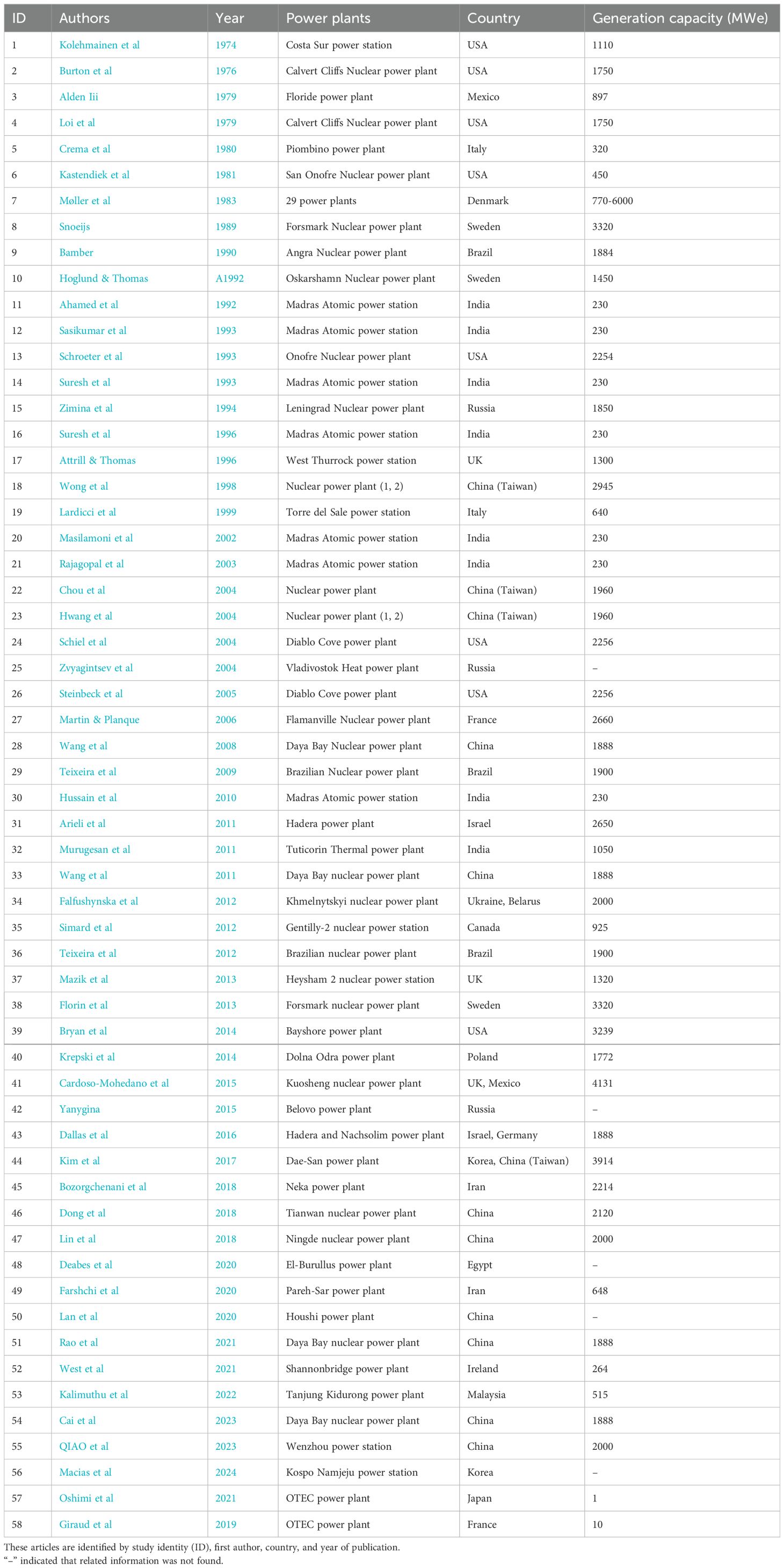
Table 1. Electrical generating capacity (MWe) of the power plants studied by the articles included in the systematic review.
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Temporal and spatial variations in the influence of coastal power plant cooling water on benthic organisms
Supplementary Figure S1 depicts the number of research articles and reviews concerning the impacts of thermal and cold effluents from coastal power plants on benthic biodiversity spanning from 1974 to 2024. Notably, there was a steady increase in the number of publications over ten years, with the most substantial surge observed between the periods 1995–2004 and 2005–2014, rising from 10 to 15 articles (Supplementary Figure S1). In terms of publication frequency by category, the highest proportion of articles was published in the category ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES (26.7%), followed by the categories MARINE & FRESHWATER BIOLOGY (16.1%) and ECOLOGY (10.7%) (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.1.1 Spatial variation of related studies
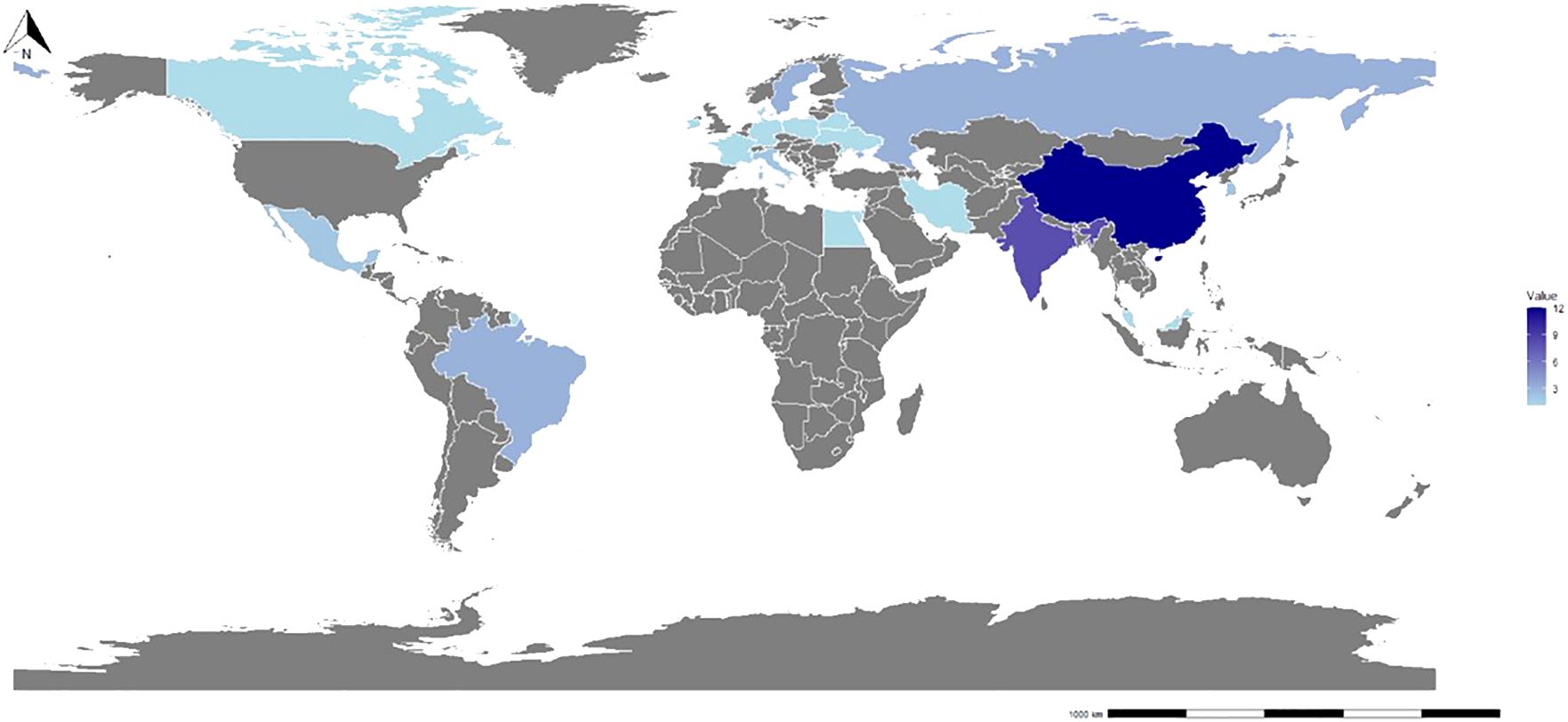
Figure 2 demonstrated a wide geographical representation in the study, with contributions from 22 countries and regions. Nevertheless, research on this topic exhibits uneven distribution worldwide. Among coastal regions, China, the USA, India, and Russia exhibited the highest number of publications in this review, accounting for 12, 8, 8, and 3 articles, respectively. These countries contributed approximately 52.5% of the total studies. The underlying reason for this phenomenon could be attributed to the dominant role of power generation in these countries on a global scale, thereby amplifying the environmental challenges associated with power plant emissions. According to data released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) as of 2024, these four countries were ranked 1, 2, 3, and 4 in terms of power generation (IEA, 2024). Among the countries examined, the United States stood out as the first to focus on the impact of thermal discharge from power plants on marine benthic organisms (Kolehmainen et al., 1974; Burton et al., 1976). In relative terms, China’s research in this field commenced more than two decades later. However, it is noteworthy that China has increasingly devoted attention to this research direction in recent years (Cai et al., 2023; Qiao et al., 2023). Concurrently, research in India predominantly concentrated on assessing the effects of the Madras Atomic Power Station on marine life, including benthic organisms (Murugesan et al., 2011).
This study identified a scarcity of research addressing the impact of power plant discharge on marine benthic organisms within tropical regions, with current literature primarily limited to India (8), Brazil (3), Mexico (2), and Malaysia (1). Interestingly, all 14 articles identified within these regions exclusively examined the effects of thermal discharge. Conversely, there were limited studies investigating the impacts of cold discharge from power plants on marine benthic organisms in tropical areas. Furthermore, on a global scale, only two studies were located concerning the effects of cold discharge from power plants on marine life, with a primary emphasis on fish populations (Oshimi et al., 2021) and phytoplankton dynamics (Giraud et al., 2019). This notable absence of research on the effects of cold discharge from power plants, particularly Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) plants, underscored a significant gap in understanding the potential ecological impacts within tropical marine ecosystems.
3.1.2 Temporal variation of relevant studies
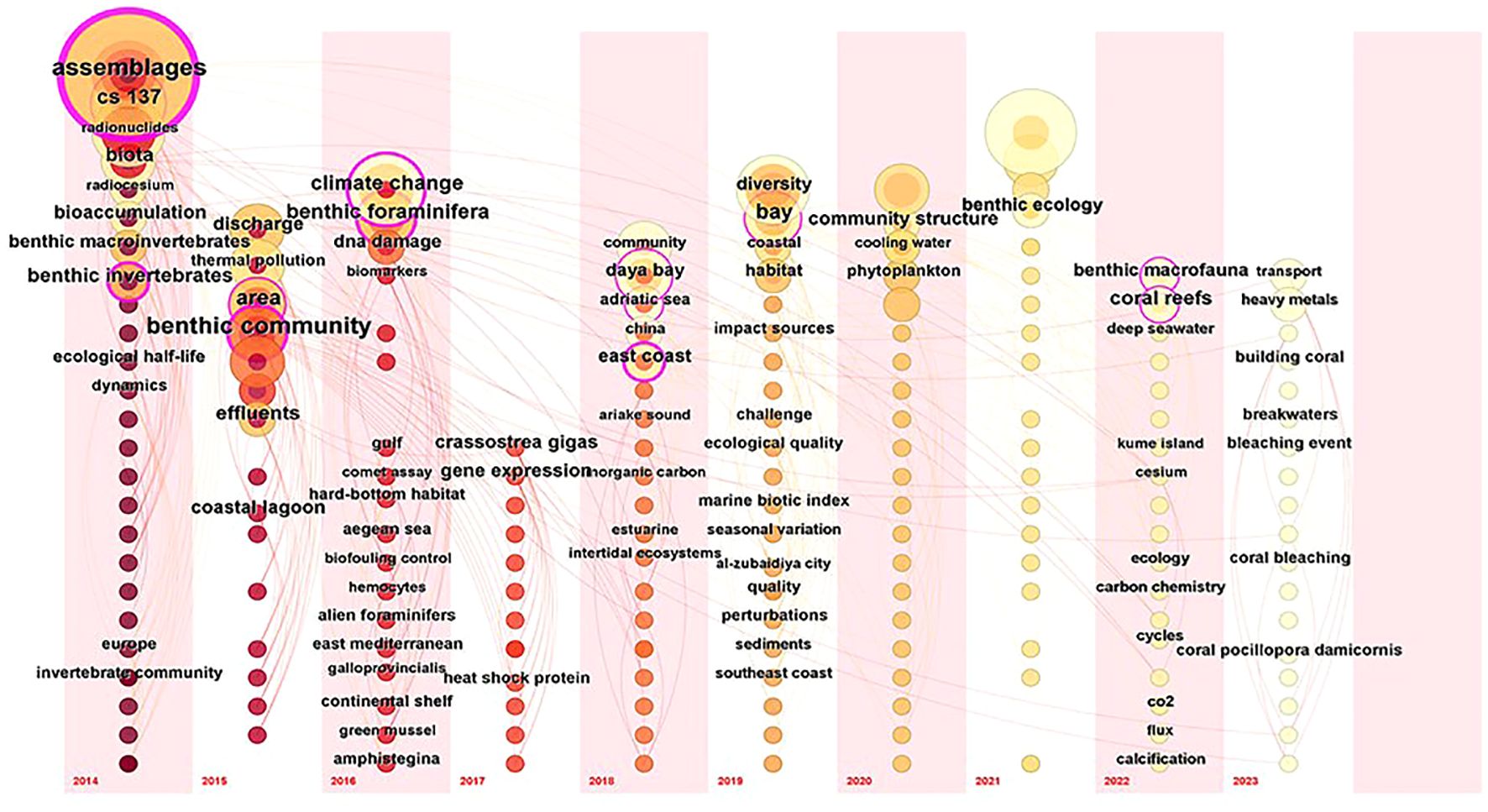
Figure 3 presented a time series keyword map delineating the study of power plant impacts on coastal benthic organisms spanning the years 2014 to 2023. This visualization encompassed 197 high-frequency words interconnected by 622 lines. The density of the network map is 0.0322, indicating that 3.22% of the potential relationships in the network have been realized. This result underscores the limited interaction among those keywords. Notably, the modularity degree Q attained a value of 0.8055, surpassing the threshold of 0.3, thereby indicating a reasonable level of structural organization within the dataset. Furthermore, the silhouette score, registering at 0.957, exceeded the threshold of 0.4, thereby supporting the credibility and coherence of Figure 3.
Figure 3 highlights high-frequency keywords (frequency > 7) over the past decade, with the size of each circle representing the co-occurrence frequency of the corresponding keyword. Notably, during this period, nine keywords — “assemblages”, “benthic community”, “benthic macrofauna”, “benthic foraminifera”, “benthic invertebrates”, “coral reefs”, “east coast”, “bay”, and “climate change”—were observed with high frequency. These keywords respectively highlight the most researched organism groups, biological indices, study sites, and environmental issues contributing to the increase in water temperatures.
The high frequency with which the term “assemblages”, “benthic community”, and “benthic invertebrates” appeared in the 2014 and 2015 keyword clouds indicates a substantial volume of research focused on the impact of power plant thermal emissions on the benthic community and assemblages of benthic invertebrates (Bryan et al., 2014; Cardoso-Mohedano et al., 2015).
The frequent use of the term “climate change” reflects its role in exacerbating the impact of thermal emissions from power plants on benthic organisms. This is due to the fact that the burning of fossil fuels in power plants is a significant contributor to climate change (Osman et al., 2023). Furthermore, climate change has accelerated ocean surface warming (Garcia-Soto et al., 2021; Oh et al., 2024; Dalpadado et al., 2024), thereby intensifying the effects of thermal emissions on benthic organisms (Farshchi et al., 2020; Wasti et al., 2022).
Between 2022 and 2023, the most prevalent keywords are “ benthic macrofauna “ and “coral reefs”. This trend underscored the growing importance of studying the influence exerted by coastal power plant wastewater on the composition and dynamics of macrobenthic and coral reef communities in the specified region (West et al., 2021; Qiao et al., 2023).
3.2 Impact of water temperature changes on benthos
The literature reviewed in this study does not indicate any instances where thermal emissions from power plants have no impact on benthic communities and their abundance. Specifically, 62.5% of the studies reported that thermal emissions have detrimental effects on benthic organisms, leading to reduced biodiversity and abundance (Arieli et al., 2011; Hussain et al., 2010; Teixeira et al., 2009; West et al., 2021). Conversely, 25% of the studies noted an increase in benthic abundance attributed to thermal emissions, primarily due to low ambient temperatures (Farshchi et al., 2020; Simard et al., 2012) or minimal temperature differentials (Bozorgchenani et al., 2018; Bryan et al., 2014). Additionally, 12.5% of the studies indicated that the impact of thermal emissions on benthic organisms varied seasonally; specifically, during winter, lower ambient temperatures resulted in increased benthic abundance, while in other seasons, the effects were generally negative (Titelboim et al., 2016).
3.2.1 Benthic biodiversity parameters for population, community, and ecosystem
Of the 58 articles, 56 specifically highlighted temperature as a crucial factor in the observed alterations of ecological indicators among benthic organisms. These articles further conducted qualitative investigations into these phenomena. The most cited biodiversity parameters among those that suffered alterations were related to changes in the structure and composition of populations, communities, and ecosystems, namely: abundance (20.5%), community structure (13.94%), distribution (13.12%), species richness (9.84%), density (8.2%), and species evenness (6.56%), which together accounted for >70% of the total parameters affected (Figure 4).
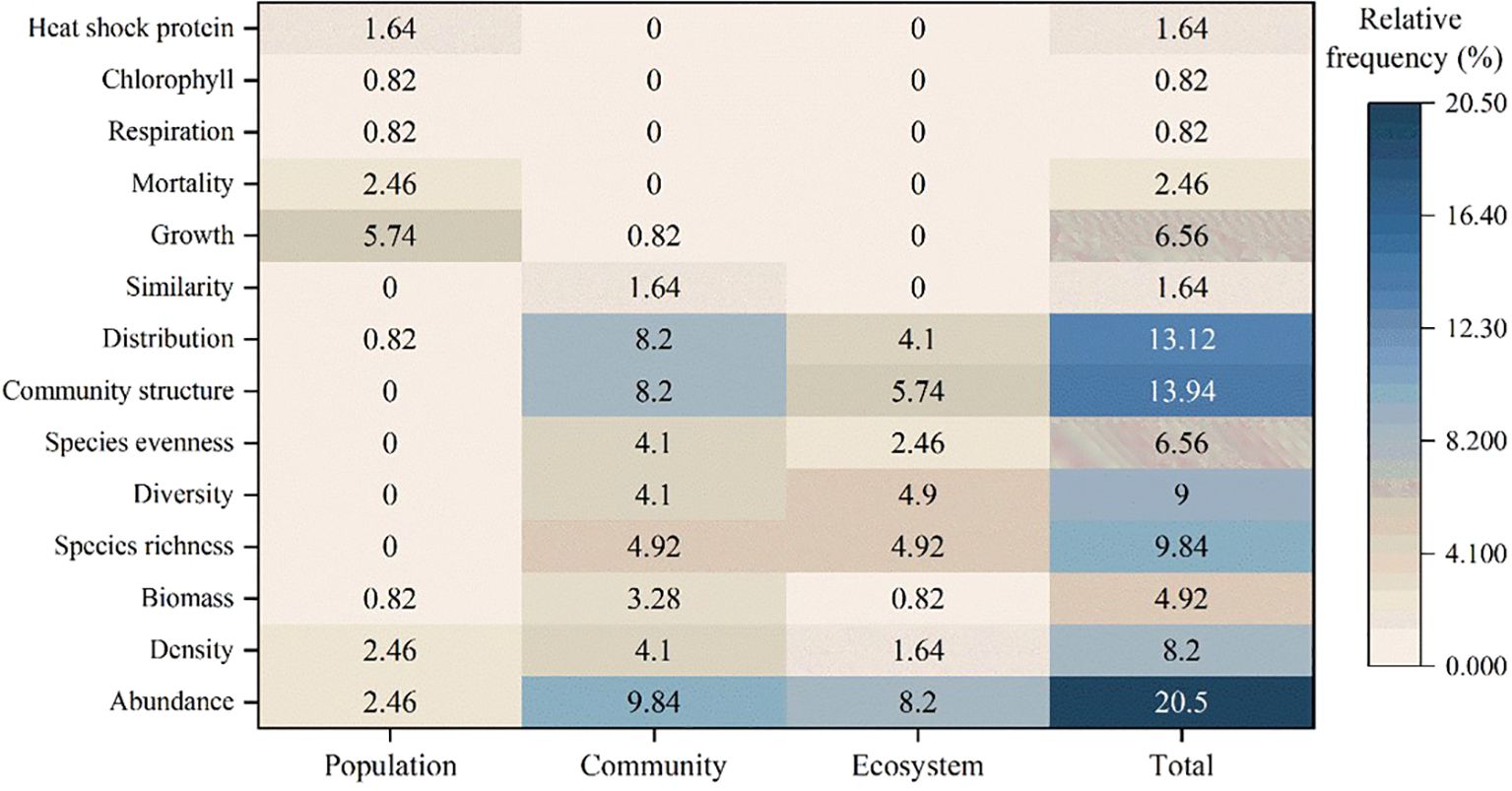
Figure 4. The relative citation frequency (%) of benthic biodiversity parameters affected by coastal power plant discharge is analyzed across population, community, and ecosystem levels.
There is clear evidence that the abundance, community structure, and distribution of benthic organisms are influenced by thermal discharges. A meta-analysis of 75 studies conducted by Guimarães et al. (2023) demonstrated a significant increase in water temperature near nuclear power plants due to thermal emissions compared to reference areas, with a mean increase of 4.38°C (95% CI = 3.72-5.03). This increase in temperature can harm benthic communities, potentially leading to habitat loss, decreased biodiversity indices, or even species extinction. These findings are consistent with those of Farshchi et al. (2020), who studied macrobenthos near the outlet of the Neka power plant in the southern Caspian Sea. Farshchi et al. (2020) determined that thermal emissions from the power plant significantly affected macroinvertebrate abundance, species richness, species composition, and assemblage structure when comparing impacted and control stations. Although there is limited research on the impact of cold emissions on benthic community structure, studies examining seasonal variations have shown that lower ambient temperatures can lead to significant shifts in community structure (Li et al., 2020) and diversity (Bacouillard et al., 2020), and a marked decrease in biomass (Ying et al., 2020).
Temperature affects not only the ecological indices of benthic communities but also significantly influences the physiological activities of individual organisms (Deldicq et al., 2021). Vaquer-Sunyer and Duarte (2011) demonstrated that higher temperatures reduce the mean survival time of marine benthic organisms by more than 50% under anoxic conditions. Similarly, Kim et al. (2017) reported that proximity to thermal wastewater outlets results in decreased abundance and smaller sizes of Crassostrea gigas, alongside significantly elevated levels of heat shock proteins hsp70 and hsp90 mRNA (Kim et al., 2017). Conversely, excessively low temperatures have been shown to hinder the growth and development of benthic invertebrates’ eggs and larvae (Zeng et al., 2020; Everall et al., 2015), and even cause high mortality rates of benthic invertebrates (Colella et al., 2012; Thieltges et al., 2004). Furthermore, the metamorphosis of marine benthos is temperature-dependent, with colder water significantly prolonging the time to metamorphosis (Gangur and Marshall, 2020; Gall et al., 2021).
3.2.2 Benthic assemblage structure and species composition
The effects of elevated temperatures linked to power plant discharge were frequently discerned through alterations in the composition of biological communities, facilitating the assessment and observation of ecological parameters about community composition and structure. These parameters included abundance, spatial distribution, dominance, density, and species richness (Farshchi et al., 2020).
Utilizing data extracted from 56 published articles investigating alterations in benthic organisms near power plant outfalls, it was noted that Mollusca garnered the highest citation frequency (35.71%), followed by Arthropoda (28.57%), and Annelida (20.24%). Collectively, these taxa accounted for over 84.52% of the total benthic community impacted by power plant effluents (Figure 5).
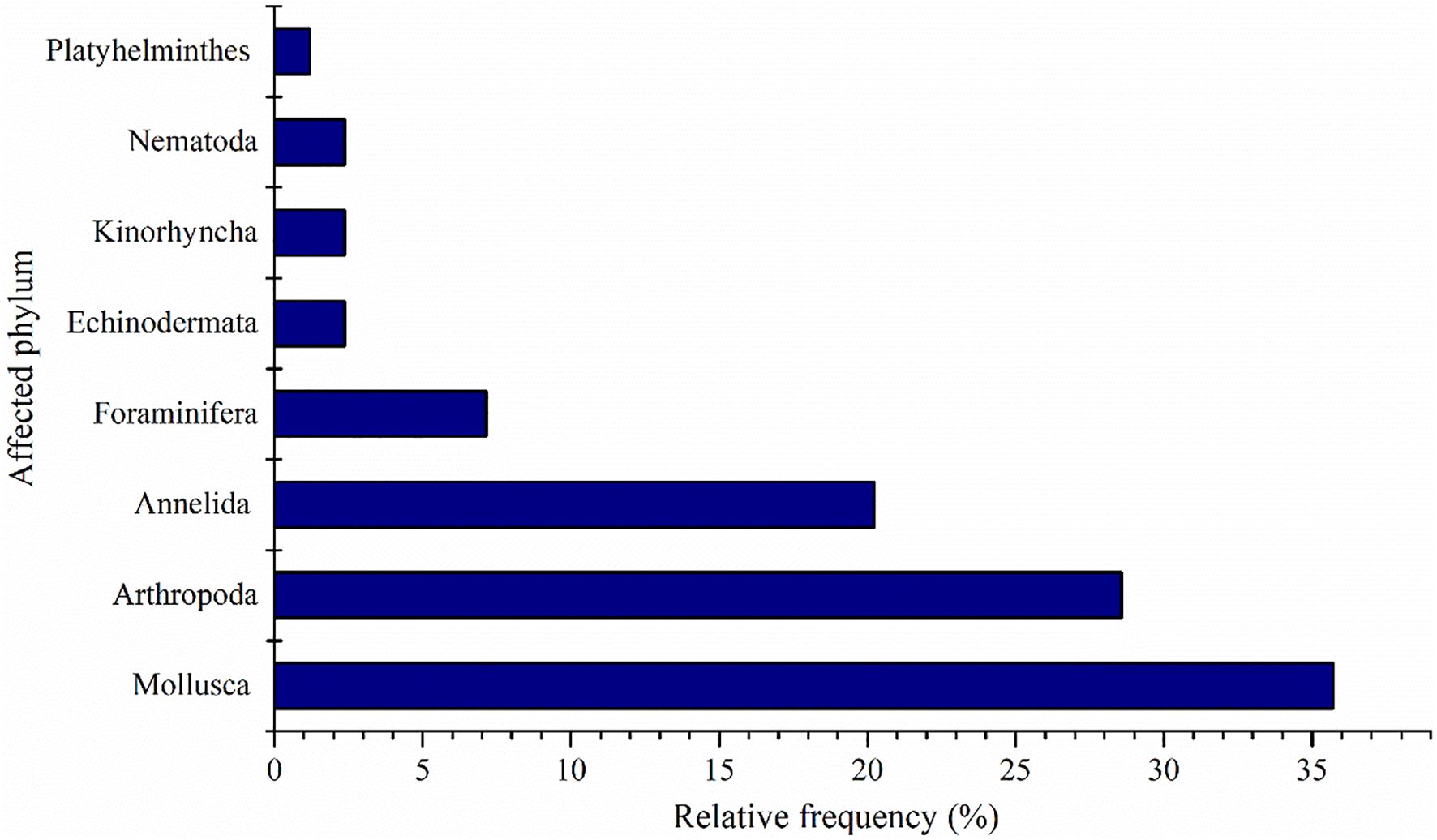
Figure 5. Relative frequency (%) of benthic classes impacted by temperature variations in the discharge area of power plants.
The significant alteration of benthic community structure by power plant discharge could be attributed to the limited ability of sessile and slow-moving benthic organisms to migrate to less stressful environments, rendering them particularly vulnerable to acute temperature stress (Smith et al., 2023). Elevated temperatures were associated with mass mortality events in Gastropoda and Foraminifera (Arieli et al., 2011; Schiel et al., 2004; Titelboim et al., 2016). Additionally, these temperature increases could result in reduced egg production in scallops and crabs, posing challenges to recovering losses incurred through fishing activities (Caputi et al., 2019). Nevertheless, thermal discharge could create a conducive environment for thermal-tolerant species of Mytilopsis leucophaeata (Florin et al., 2013), Periwinkles, and Cthamalid barnacles (Suresh et al., 1993). Conversely, lower water temperatures influence benthic community dynamics. Heip and Craeymeersch (1995) investigated benthic organisms in the same marine region and observed that macrofaunal body weight, density, and diversity increased linearly as water temperatures decreased. In contrast, the distribution patterns and trends within the meiofauna differed significantly, which had a notable impact on the overall structure of the benthic community.
3.2.3 Benthic abundance
Considerable evidence attests to the significant elevation of temperature within thermal discharge zones in contrast to reference regions (Farshchi et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2023; Bozorgchenani et al., 2018). Guimarães et al. (2023), through a meticulous meta-analysis, demonstrated a substantial increase of 4.38°C in water temperature adjacent to nuclear power plant outlet. Furthermore, their findings revealed a correlation between temperature fluctuations and the geographical latitude of power plant installations (Guimarães et al., 2023). Nevertheless, consensus remained elusive regarding the precise impact of variables such as temperature differentials, ambient environmental conditions, and the volume of power plant effluent on benthic organisms. Our research utilized the Spearman correlation coefficient to examine the impact of several variables, including generation capacity, cooling water discharge, distance between discharge points and sampling locations, ambient water temperature, and temperature differential between influence and reference points, on variations in benthic abundance. Findings indicated that plant age, temperature difference (P < 0.05) and ambient temperature (P < 0.01) exhibited statistically significant effects, displaying a negative correlation (Figure 6). Notably, the analysis revealed no statistically significant associations between changes in benthic abundance and factors such as generation capacity, cooling water discharge, or the distance between discharge points and sampling points.
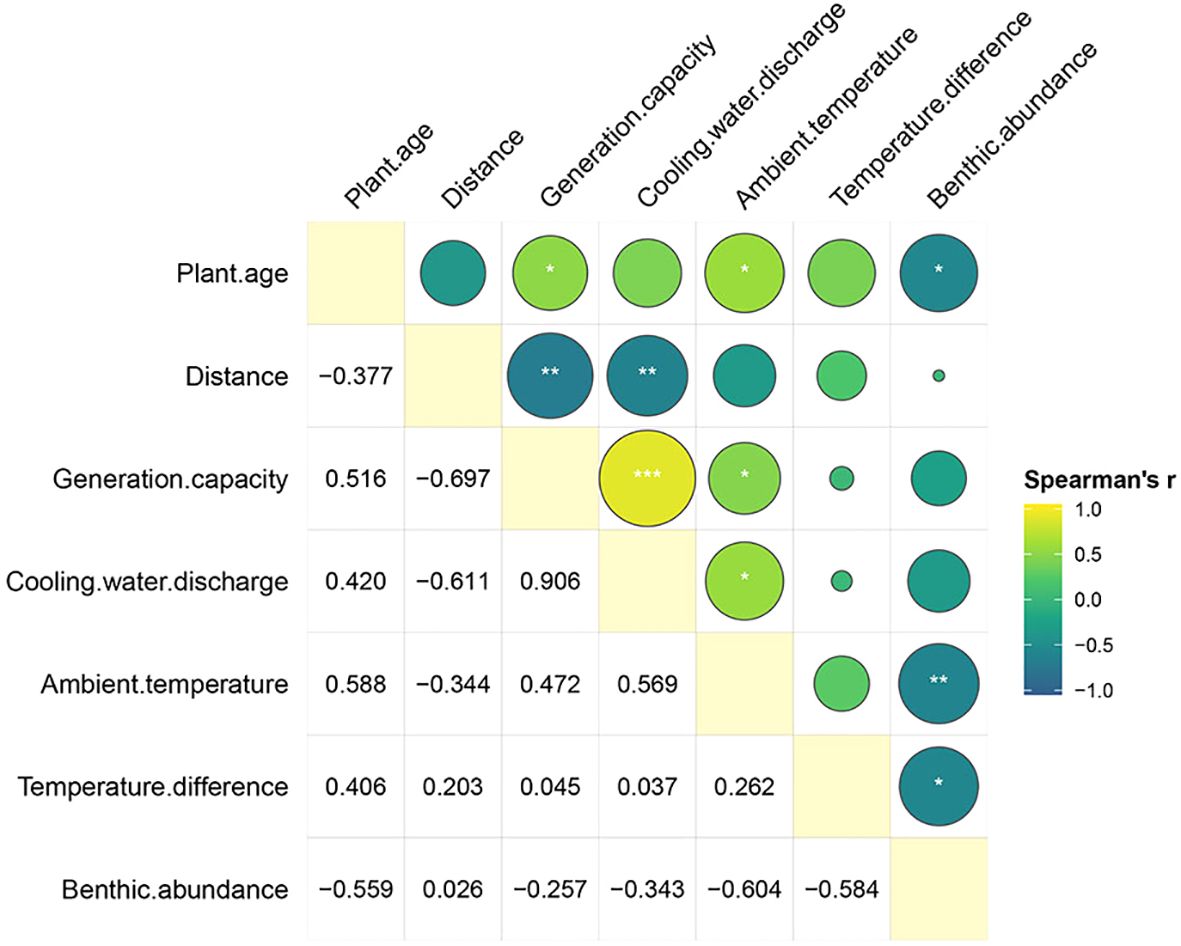
Figure 6. Spearman correlation coefficients (r) assessed relationships between 5 factors and benthic abundance changes. Significance levels were denoted by asterisks (***, **, and *) for p-values < 0.001, 0.01, and 0.05, respectively.
This study revealed a direct correlation between the magnitude of the temperature variance between the impacted and control sites and the extent of benthic abundance decline. Indeed, as far back as 1984, GESAMP emphasized that to uphold the ecological integrity of marine environments, temperature differentials near power plants should not have surpassed 7°C in subtropical waters and 5°C in tropical waters (GESAMP, 1984). Arai et al. (2015) demonstrated that the composition of benthic communities was substantially influenced by temperature disparities.
Benthos had a limited tolerance for high temperatures, with a maximum water temperature range of approximately 35-45.8°C (Saraswat et al., 2011; Hamilton and Gosselin, 2020). Different species had different temperature preferences and tolerances, and changes in water temperature affected their growth, reproduction, and survival (Jones et al., 2010; Cardoso-Mohedano et al., 2015). In tropical regions where surface sea temperatures frequently exceed 30°C, even a temperature increase of less than 5°C also adversely affect certain organisms, pushing them beyond their thermal tolerance limits (Kimmerer and Weaver, 2013; Farshchi et al., 2020). Yang et al. (2020) investigated the effects of various environmental factors on benthic organisms and found that temperature variation is the most critical factor influencing changes in benthic abundance and tolerance characteristics. Specifically, benthic abundance was lower in summer compared to spring, when decreased temperatures led to an increase in abundance.
From Figure 6, there is a significant negative correlation between benthic abundance and power plant operational time (P < 0.05). This indicates that as the operational time of the power plants increases, benthic abundance decreases. In the initial years of operation, thermal discharges from power plants can significantly alter the community structure and abundance of benthic organisms; however, these changes typically stabilize over time. The Daya Bay Nuclear Power Station has been operational since 1994, and Wang et al. (2008) conducted an extensive assessment of ecological indicators in Daya Bay over a 22-year period (1982-2004). Their findings revealed a marked decline in both the average biomass and species richness of benthic animals near the nuclear power plant, with biomass decreasing from 317.9 g/m² in 1991 to 45.24 g/m² in 2004, and species richness declining from 250 species in 1991 to 177 species in 2004. However, field investigations conducted in 2021 and 2023 indicated that thermal discharges from the power plant had minimal impact on larger benthic organisms in the surrounding marine environment (Rao et al., 2021; Cai et al., 2023). This phenomenon may be attributed to the substantial influence of domestic and industrial sewage discharge, as well as mariculture activities, on the ecological integrity of Daya Bay, alongside the gradual stabilization of community structure and abundance trends over time. Consequently, no significant differences were observed in the composition and functional diversity of the macrobenthic community between the thermal discharge area and the control area (Rao et al., 2021).
Similarly, the Madras Atomic Power Station, which began full operations in 1984, has been the subject of seven studies examining the effects of thermal emissions on benthic communities from 1992 to 2010. Research conducted in 1992 and 1993 documented a 25% reduction in species richness at the outlet, with significant seasonal variations. During this period, ambient temperatures ranged from 37.0 to 37.6°C, resulting in near-total mortality of macrobenthos, with the exceptions of periwinkles and Chthamalid barnacles (Ahamed et al., 1992; Sasikumar et al., 1993; Suresh et al., 1993). Subsequently, the community structure evolved steadily, leading to a focus on the thermal tolerance and physiological characteristics of individual species. From 1996 to 2003, studies primarily investigated the thermal tolerance and physiological responses of copepods (Suresh et al., 1996), bivalves (Masilamoni et al., 2002), and oysters (Rajagopal et al., 2003) in proximity to the emission outlet. Additionally, Hussain et al. (2010) reported that the population of Donax cuneatus was notably rare within 100 meters of the mixing zone, while the control group exhibited a density of 64.0 ± 3.6 to 88.3 ± 9.6 ind/m².
3.3 Effects of power plant discharge on changes in other environmental parameters
As depicted in Table 2, thermal emissions from power plants generally coincided with a decline in dissolved oxygen, pH, chlorophyll-a, and phaeopigment levels in the vicinity of the discharge outlet, with the exception being during periods of exceptionally low ambient water temperature. Concurrently, there was an observable increase in conductivity, clay, and organic content near the outfall under these circumstances. Conversely, cold emissions from power plants exhibited an elevation in nitrate, silicic acid, phosphate, chlorophyll-a, and phaeopigment concentrations. Notably, fluctuations in other environmental factors, such as salinity, are comparatively restrained.
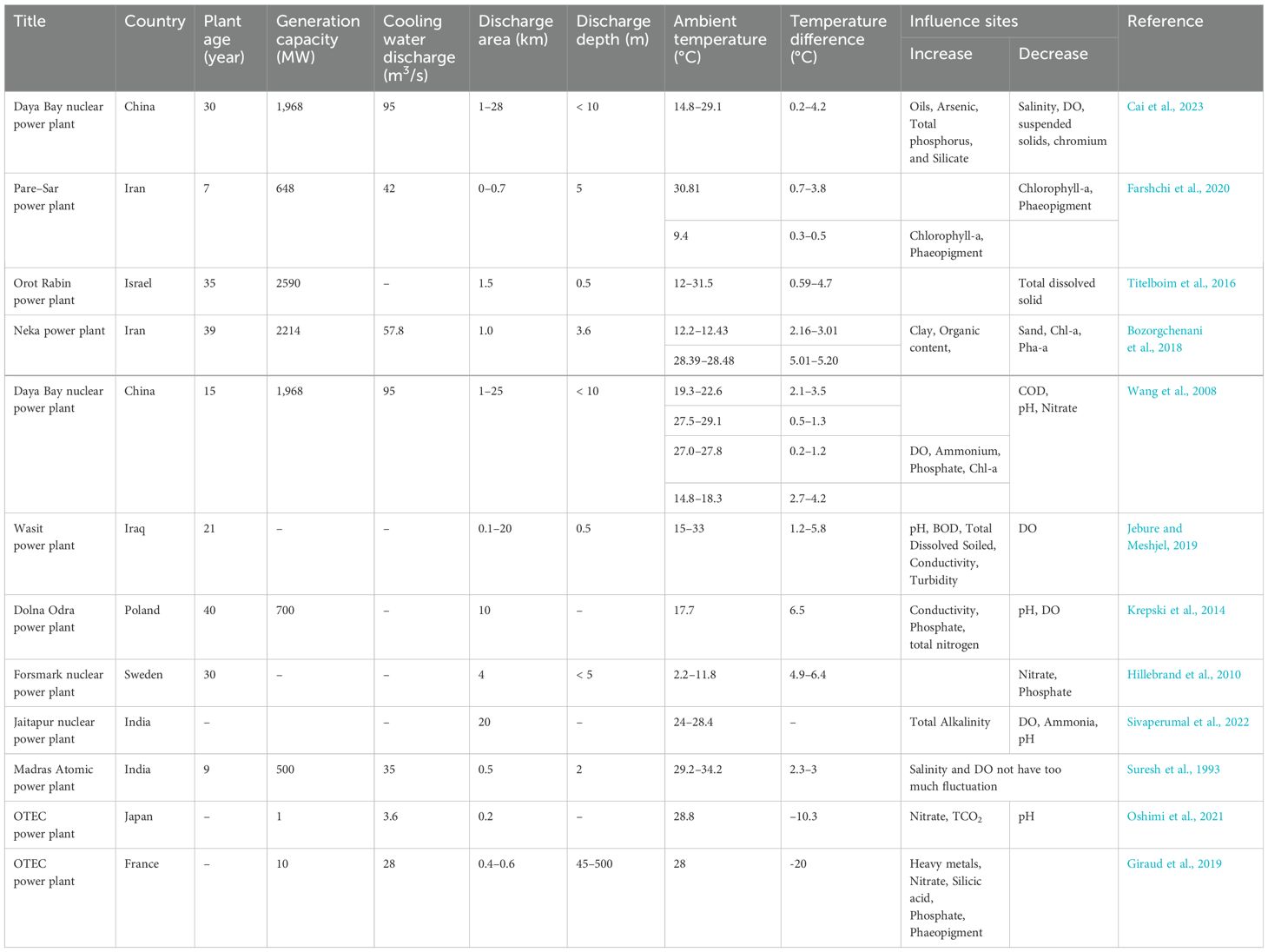
Table 2. List of various coastal environmental factors affected by cooling water discharge from power plants.
3.3.1 Dissolved oxygen
In the realm of Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC), where the process involved the uptake of deep, nutrient-rich seawater, a pertinent phenomenon emerges wherein the disparity in density between the discharged plume and its ambient surroundings triggered a tendency for the plume to either ascend or descend to an equilibrium depth. This intricate interplay gave rise to an artificially induced zone enriched with nutrients, as observed in the study by Comfort and Vega (2011). When this plume equilibrium occurs within the zone of light penetration, there is the potential to stimulate phytoplankton and algal blooms (Giraud et al., 2019).
Simultaneously, the discharge of thermal effluent from power plants introduced a marked temperature elevation in proximity to the outfall. This not only reduces water viscosity and increases water vapor pressure, directly influencing the dissolved oxygen-carrying capacity of seawater, as suggested by Ali et al. (2020), but also indirectly influenced the dissolved oxygen levels by affecting microbial activity due to the temperature elevation. Breitburg et al. (2018) observed that rising oceanic temperature, coupled with heightened nutrient discharge into coastal waters, synergistically accelerated microbial respiration-driven oxygen consumption. This process reduced oxygen solubility in water, and prolonged the replenishment duration of atmospheric oxygen to the aquatic environment.
Nevertheless, oxygen was vital for benthic organisms to conduct metabolic processes and sustain their physiological functions. Persistent exposure to environments with low dissolved oxygen content posed significant constraints on the life activities and behaviors of benthic organisms (Chan et al., 2008). Many benthic species could not thrive in oxygen-depleted waters, and those that managed to survive have experienced diminished growth rates, reproductive failures, and heightened vulnerability to diseases (Hyvärinen et al., 2022; Briggs et al., 2021). Furthermore, the decline in species diversity resulting from diminishing oxygen levels could have triggered cascading impacts on marine ecosystems, leading to the loss of food sources and disruptions in nutrient cycling (Sun et al., 2022). Singh et al. (2021) documented a positive correlation between the diversity index of Hanzawaia concentrica, Globocassidulina subglobosa, and Cancris sagra and dissolved oxygen levels in aquatic environments, underscoring the crucial role of dissolved oxygen in sustaining the survival and diversity of benthic communities (Singh et al., 2021).
3.3.2 pH levels
According to Henry’s law, the solubility of gases in water decreases as temperature rises, so higher temperatures reduce the solubility of carbon dioxide. In regions with warm ambient water, thermal discharge from power plants can increase pH levels (Jebure and Meshjel, 2019). However, in other areas, thermal discharge may lower seawater pH (Table 2). The impact of power plant discharges on water bodies is influenced by both the discharge volume and the temperature difference from ambient water. Larger discharge volumes and higher temperature differences can significantly elevate local water temperatures, affecting wider areas of the water body (Raptis et al., 2016; Issakhov and Zhandaulet, 2021). In semi-enclosed bodies, like estuaries and bays with limited water exchange, thermal discharges can impact the entire system, as poor circulation exacerbates temperature retention and affects local ecosystems more extensively (Raptis et al., 2016). Similarly, cold discharges with large volumes and high temperature differences have greater effects, determining the extent of cooling and the area impacted (Issakhov and Zhandaulet, 2021).
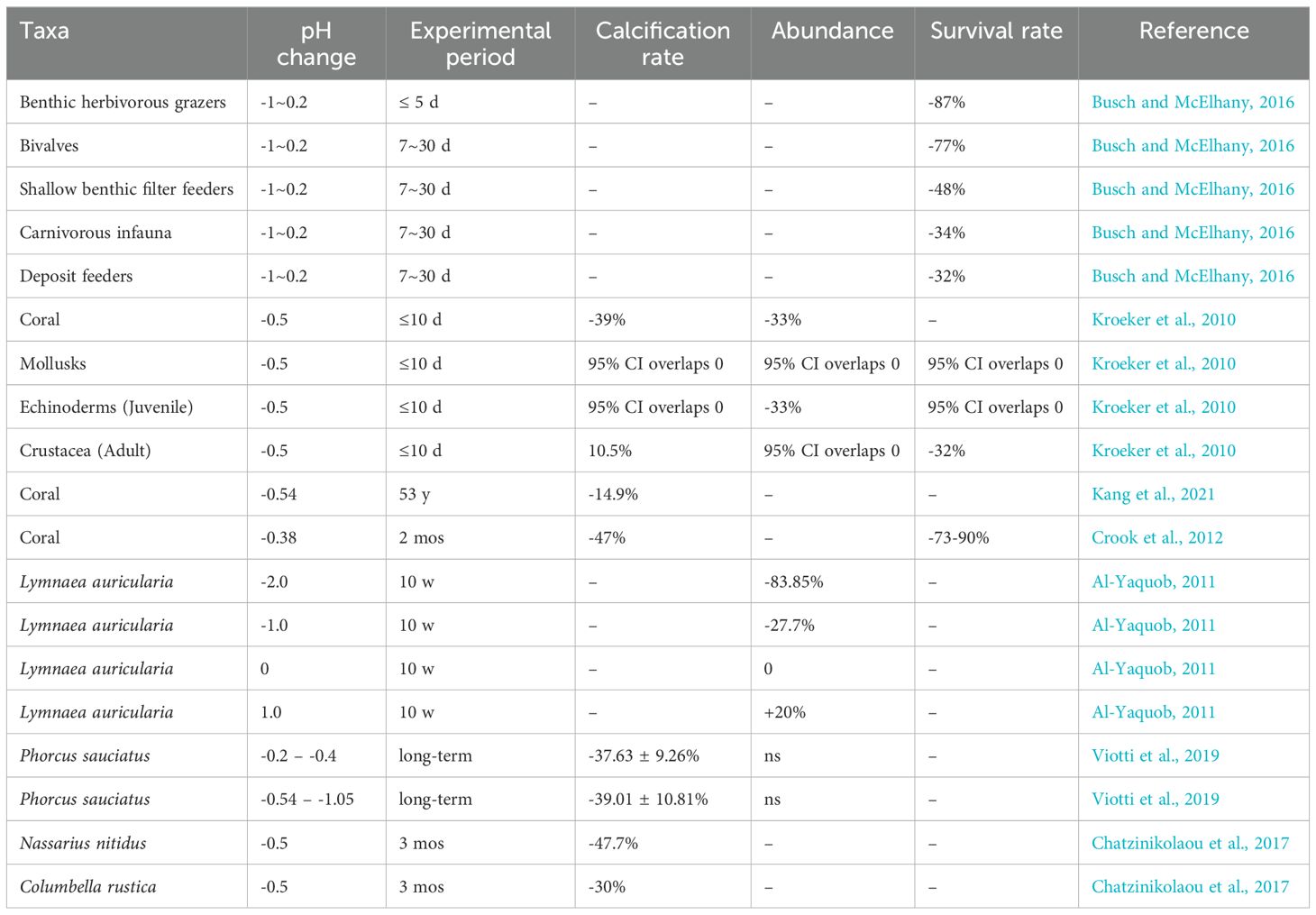
Changes in pH can alter the chemical properties of the water and directly affect the physiology, behavior, and distribution of marine organisms (Table 3). Kroeker et al. (2013) comprehensively analyzed the results of 228 studies examining the biological effects of ocean acidification. Their results suggest that acidification leads to decreased survival, calcification, growth, reproduction and development in a wide range of marine organisms, as well as significant character-mediated variation between taxa and enhanced sensitivity to early life history stages. In addition, their results indicate that mollusks are significantly sensitive to acidification, especially during the larval stage, and that vulnerability to acidification increases with simultaneous exposure of multiple organisms to elevated sea temperature.
pH levels can impact the availability of dissolved minerals and nutrients that are essential for the growth and reproduction of benthic organisms. Additionally, high or low pH levels can directly affect the acidity or alkalinity of the water, which can be harmful to benthic organisms if it exceeds their tolerance range (Fabricius et al., 2014).
The pH tolerance range of benthic organisms has been extensively studied, with research defining specific thresholds that delineate conditions for optimal health and survival across various taxa (Feugere et al., 2021; Dong et al., 2020). Benthic macroinvertebrates, particularly sensitive to pH fluctuations, generally experience adverse effects when pH levels fall below 5 or exceed 9 (Yuan, 2004). The pH of a fluid is positively correlated with the concentration of carbonate, bicarbonate, and other related salts in the aquatic environment. Calcifying invertebrates, such as corals, gastropods, and bivalves, rely on calcium carbonate for structural formation. Ocean acidification, by reducing the availability of carbonate ions necessary for calcification, weakens these structures, often increasing mortality rates (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2017; Beesley et al., 2008; Vargas et al., 2015). When the pH value of seawater decreases below 7, it can have severe impacts on marine organisms such as shrimp, snails, and bivalves with calcium carbonate shells, which experience difficulties in surviving. Additionally, if the pH value drops below 6.5, the benthic population will degrade, and their reproductive capacity will be significantly reduced (Busch and McElhany, 2016). Dong et al. (2020) investigated the growth, development, and community structure changes of various types of foraminifera (hyaline, porcelaneous, and agglutinated) in different pH environments. The study revealed that the species richness and individual growth of hyaline and porcelaneous foraminifera were positively correlated with pH, while the agglutinated foraminifera exhibited a negative correlation (Dong et al., 2020).
In a key experimental study, Kroeker et al. (2011) specifically investigated pH tolerance among invertebrates, conducting a controlled trial on Castello Aragonese d’Ischia, a small island, in May and September. By releasing carbon dioxide at a depth of 0.5–3 meters around the site, the researchers adjusted pH levels and assessed species abundances near the vents, sampling over 15,000 individuals across 82 taxonomic families. This study quantified suitable pH ranges for different invertebrate taxa, finding that a pH of 8.1 ± 0.1 was optimal for 4% of gastropods, 22% of decapods, 10% of amphipods, 29% of tanaids, 38% of isopods, 47% of polychaetes, and 75% of sipunculids. For 26% of gastropods, 30% of bivalves, 39% of decapods, 7% of amphipods, and 38% of isopods, a broader pH range of 7.8 ± 0.3 to 8.1 ± 0.1 was suitable, while amphipods, 29% of tanaids, 13% of isopods, and 7% of polychaetes tolerated a range of 6.6 ± 0.5 to 8.1 ± 0.1.
From the above, the impact of pH on the benthic community is contingent upon several factors, including the extent of pH fluctuations, the type of pre-existing benthic community, and the ecological backdrop of the ecosystem.
3.3.3 Bottom material
The process of piping large quantities of cooling water from power plants into the ocean contributes to the transport of coastal sediment (Venugopalan et al., 2011; Wither et al., 2012). Bozorgchenani et al. (2018) conducted a parallel investigation, which revealed a prevailing dominance of clay and silt in the sediment composition at both discharge outlets of power plants. This observation was derived from year-round monitoring of sediment particle sizes. In contrast, the control group exhibited a prevailing dominance of sand. Furthermore, Bozorgchenani et al. (2018) noted a marked elevation in the total organic matter (TOM) content at the discharge point in comparison to the control point. In tandem, studies have substantiated that the elevated temperatures at the thermal discharge points played a pivotal role in fostering an increase in organic matter content. Interestingly, in certain regions, there was a notable increase in organic matter content during summer compared to winter. This phenomenon is attributed to the augmented primary production resulting from higher temperatures (Cheng et al., 2004; Sarkar et al., 2005). The impact of power plant discharge extended significantly to sediment composition.
3.4 Mitigation measures
To effectively address hazards to marine ecology, various management strategies have been employed. These include marine spatial planning (Ehler, 2008), adaptive management (Williams, 2011), and risk retirement, which involves reducing or eliminating potential environmental risks associated with marine activities to safeguard marine ecosystems (Copping et al., 2020). These strategies encompass a range of actions, including siting, permitting, monitoring, and, when necessary, mitigating potential risks (O’Hagan, 2020; Jansujwicz and Johnson, 2015). When selecting mitigation measures, priority was given to the location of outfalls and the placement of energy equipment to minimize environmental impact while ensuring safety for shipping and fishing activities. Mitigation measures aimed at preventing and controlling the adverse effects of power plant effluent on marine benthos are detailed in Table 4.

Table 4. List of mitigation measures to prevent hazards to marine benthos from power plant discharge.
Cold discharge from Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems can significantly impact the marine ecological environment. Distributed discharge serves as an effective mitigation strategy for managing cold discharge water. By dispersing cold, nutrient-rich deep seawater over a broader area, this approach minimizes localized environmental impacts, such as excessive fertilization of surface waters, which can lead to harmful algal blooms (Giraud et al., 2019). Research suggests that strategically placing discharge outlets at optimal depths—generally below the mixed layer—enhances nutrient dilution and reduces potential ecological effects (Viviani et al., 2011; Comfort and Vega, 2011). For example, positioning discharge outlets where light penetration is limited, ideally at depths of 90 meters or below, can further mitigate risks to phytoplankton communities (Jia et al., 2012).
In contrast, the discharge of high-temperature water can pose additional risks to marine ecosystems. To mitigate these impacts, strategies such as thermal plume modeling and controlled mixing with ambient seawater can be employed. The discharge temperature should be carefully monitored to ensure it remains within acceptable limits to prevent thermal shock to marine life (Liu et al., 2023). Additionally, using cooling towers or heat exchangers can help reduce the temperature of the discharged water before it enters the marine environment (Kumar and Sharma, 2020). However, these technologies often result in increased initial and operating costs, which should be considered in the overall assessment of their effectiveness and feasibility (Ayoub et al., 2018; Castro et al., 2000).
Pre-experimental assessments could be conducted on-site to evaluate potential impacts on the marine ecological environment. For instance, Giraud et al. (2019) investigated the potential impacts of discharging cold, nutrient-rich deep seawater on the phytoplankton community residing in warm, oligotrophic surface waters. This study, conducted before the installation of the pilot plant, determined the optimal outlet depth to minimize adverse effects. Cold emissions from OTEC power plants are designed to prevent excessive fertilization of surface seawater; thus, it is crucial that the plume settlement area is situated below the mixed layer. It is recommended that the discharge pipe be positioned in conditions where only 1% of light penetrates. Based on data from the ALOHA station and model predictions, the optimal depth for the discharge pipe is at or below 90 meters (Viviani et al., 2011). This recommendation considers that certain phytoplankton can still absorb nutrients from the descending plume at higher levels within the water column. Conservative estimates for emission depths suggest that discharges should occur at 120 meters or below (Comfort and Vega, 2011).
Jia et al. (2012) found that cold discharge results in the formation of a layer characterized by nearly uniform temperature, salinity, and density at depths ranging from 150 to 200 meters. As the plume approaches this homogeneous layer, its downward momentum allows it to penetrate the layer and migrate into deeper, denser regions. Additionally, tidal currents can create short-circuiting effects on the water intake. Consequently, it is recommended that the discharge outlet be positioned above this uniform layer to optimize environmental outcomes (Jia et al., 2012).
Martínez et al. (2021) underscored the importance of long-term management and monitoring of environmental conditions, including physicochemical parameters and marine biological attributes, as essential complements to mitigation measures during and post-installation of energy devices. However, it was noted that very few project sites possess long-term datasets persistently monitored for marine environmental conditions, encompassing physicochemical parameters and marine biological attributes such as abundance, distribution, and behavior across various temporal scales (daily, seasonal, annual, or multi-annual) and spatial scales (local, regional) (Kolar et al., 2013; Williamson et al., 2017; O’Carroll et al., 2017). Such comprehensive data was imperative for understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic components and their feedback into energy devices (McClure et al., 2010).
Of particular concern is the absence of environmental standards for the impact of deep-sea water discharge, emphasizing the critical need for implementing rigorous monitoring measures for marine biocommunities, biogeochemical parameter distribution, and water column stratification during and after the ongoing operation of Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems.
3.5 Framework for managing thermal discharge
Regarding the regulatory context, it is important to highlight that there is currently no universally established environmental standard defining the threshold level of temperature change resulting from Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) deep seawater discharge. This gap in regulation is concerning, as the absence of a consensus can lead to varied practices that may undermine marine ecosystems globally. Existing studies primarily reference the 3°C temperature difference limit at the edge of the initial mixing dilution zone, as recommended by the International Finance Corporation (2007), which underscores the necessity for careful monitoring to prevent adverse ecological impacts. However, this recommendation may not sufficiently capture the complexities of thermal discharges, particularly in diverse marine environments.
In addition to this, various national regulations concerning thermal emissions from power plants typically focus on the quality of effluents, encompassing critical parameters such as temperature, dissolved oxygen, and pH levels. For instance, Egypt’s environmental law stipulates that the maximum absolute water temperature due to effluent discharge should not exceed 35°C, while also mandating that the temperature outside the mixing zone must not exceed 5°C above the ambient water temperature (Egypt Government, 2009). Such regulatory measures reflect an awareness of the need to protect marine biodiversity and ecosystem functionality.
Furthermore, the Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection (GESAMP) has consistently emphasized the importance of maintaining ecological integrity in marine environments. They recommend that temperature differentials near power plants should not exceed 7°C in subtropical waters and 5°C in tropical waters (GESAMP, 1984). These guidelines are critical in safeguarding sensitive marine organisms that are particularly vulnerable to temperature fluctuations, as extensive research has demonstrated that even minor deviations from natural temperature ranges can lead to significant disruptions in marine ecosystems (Jawad, 2021; Przeslawski et al., 2008).
Moreover, the inconsistency in regulations across different countries raises concerns regarding the potential for cumulative impacts of thermal discharges, as emphasized by several studies which call for a more unified approach to managing thermal pollution (Issakhov and Zhandaulet, 2021; Baram, 1972). This lack of harmonization not only complicates enforcement efforts but also hampers global initiatives aimed at preserving marine biodiversity in the face of climate change and other anthropogenic pressures.
Thus, local regulations governing the construction and operation of marine outfalls, discharge locations, and effluent quality limitations (including temperature and chemical substances) are essential for managing the environmental impact of these discharges. However, tracking the diverse environmental laws applicable to each power plant across different countries and regions can be challenging. Therefore, this paper focuses on analyzing changes in water and sediment quality indicators and their effects on benthic organisms following discharge from power plants.
4 Conclusion
In this study, a comprehensive database about the effects of power plant discharge on benthic organisms is curated through the screening of literature sourced from Scopus, PubMed, and the Web of Science. CiteSpace software is employed to analyze and visualize the selected literature, thereby elucidating the spatial and temporal distribution of research on this topic and identifying research hotspots across different periods. Emerging areas of interest encompassed issues such as the impact of coastal power plant discharge on macrobenthos and coral community structure.
The study confirms a significant negative correlation between the temperature differential at the influence site and the control site, as well as ambient temperature, and variations in benthic abundance. Furthermore, apart from temperature fluctuations, other environmental factors, including dissolved oxygen, pH, chlorophyll-a, phaeopigment, conductivity, clay, and organic content exhibit varying degrees of alteration. It is noteworthy that the interplay among these factors appears to be more influential than the impact of any single factor alone. Changes in benthic organisms have the potential to induce alterations in the dynamics of coastal marine ecosystems. These findings underscore the importance of considering relevant information in environmental policy formulation aimed at mitigating the potential impacts of thermal and cold effluents on marine biodiversity.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KR: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NZ: Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MH: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to express their gratitude to Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) for supporting this project through the Science Start Scholarship (GP-IPS/2023/9768600). We also extend our thanks to the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), and the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MoHE) for their contributions through the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) Program. This initiative, titled “Development of Advanced Hybrid Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) Technology for a Low Carbon Society and Sustainable Energy System: First Experimental OTEC Plant of Malaysia,” has been instrumental in our research.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their appreciation to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions aimed at enhancing the quality of the manuscript. The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Authors used ChatGPT 4.0 to improve the language.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1465289/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahamed M. S., Durairaj G., Suresh K., Nair K. V. K. (1992). Effect of power plant heated effluent on distribution of sedentary fauna and flora. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 21, 188–191.
Alden Iii R. W. (1979). Effects of a thermal discharge on the mortality of copepods in a subtropical estuary. Environ. pollut. (1970) 20 (1), 3–19. doi: 10.1016/0013-9327(79)90049-1
Ali M. F., Salman A. H., Guda M. A., Abojassim A. A., Almayabi B. (2020). The hydroclimatic effects of the thermal pollution on surface waters in Iraq and its biological effects. Prensa Med. Argent 106, 189–196. doi: 10.47275/0032-745X-189
Al-Yaquob A. J. (2011). Effect of salinity and pH on hatchability and survival of the snails Lymnaea auricularia. Marsh Bull. 6, 62–72.
Arai R., Nukazawa K., Kazama S., Takemon Y. (2015). Variation in benthic invertebrate abundance along thermal gradients within headwater streams of a temperate basin in Japan. Hydrobiologia 762, 55–63. doi: 10.1007/s10750-015-2336-8
Arieli R. N., Almogi-Labin A., Abramovich S., Herut B. (2011). The effect of thermal pollution on benthic foraminiferal assemblages in the Mediterranean shoreface adjacent to Hadera power plant (Israel). Mar. pollut. Bull. 62, 1002–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.036
Attrill M. J., Thomas R. M. (1996). Long-term distribution patterns of mobile estuarine invertebrates (Ctenophora, Cnidaria, Crustacea: Decapoda) in relation to hydrological parameters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 143, 25–36.
Ayoub A., Gjorgiev B., Sansavini G. (2018). Cooling towers performance in a changing climate: Techno-economic modeling and design optimization. Energy 160, 1133–1143. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.080
Bacouillard L., Baux N., Dauvin J. C., Desroy N., Geiger K. J., Gentil F., et al. (2020). Long-term spatio-temporal changes of the muddy fine sand benthic community of the Bay of Seine (eastern English Channel). Mar. Environ. Res. 161, 105062. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.105062
Baldanzi S., McQuaid C. D., Cannicci S., Porri F. (2013). Environmental domains and range-limiting mechanisms: testing the Abundant Centre Hypothesis using Southern African sandhoppers. PloS One 8, e54598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054598
Bamber R. N. (1990). Power station thermal effluents and marine crustaceans. J. thermal Biol. 15 (1), 91–96. doi: 10.1016/0306-4565(90)90054-L
Baram M. S. (1972). The legal and regulatory framework for thermal discharge from nuclear power plants. Envtl. Aff. 2, 505.
Beesley A., Lowe D. M., Pascoe C. K., Widdicombe S. (2008). Effects of CO2-induced seawater acidification on the health of Mytilus edulis. Climate Res. 37 (2-3), 215–225. doi: 10.3354/cr00765
Bensoussan N., Romano J. C., Harmelin J. G., Garrabou J. (2010). High resolution characterization of northwest Mediterranean coastal waters thermal regimes: to better understand responses of benthic communities to climate change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 87, 431–441. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.01.008
Billman E. J., Wagner E. J., Arndt R. E. (2006). Effects of temperature on the survival and growth of age-0 least chub (Iotichthys phlegethontis). Western North Am. Nat. 66, 434–440. doi: 10.3398/1527-0904(2006)66[434:EOTOTS]2.0.CO;2
Bozorgchenani A., Seyfabadi J., Shokri M. R. (2018). Effects of thermal discharge from Neka power plant (southern Caspian Sea) on macrobenthic diversity and abundance. J. Thermal Biol. 75, 13–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.05.002
Breitburg D., Levin L. A., Oschlies A., Grégoire M., Chavez F. P., Conley D. J., et al. (2018). Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science. 359, eaam7240. doi: 10.1126/science.aam7240
Briggs M. A., Albertson L. K., Lujan D. R., Tronstad L. M., Glassic H. C., Guy C. S., et al. (2021). Carcass deposition to suppress invasive lake trout causes differential mortality of two common benthic invertebrates in Yellowstone Lake. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 194, 285–295. doi: 10.1127/fal/2020/1352
Bryan N. J., Moorhead D. L., Crail T. D. (2014). Habitat characteristics of a unionid refuge in the thermal plume of a power plant in western Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 40 (3), 699–704. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2014.05.015
Burton D. T., Richardson L. B., Margrey S. L., Abell P. R. (1976). Effects of low ΔT powerplant temperatures on estuarine invertebrates. J. (Water pollut. Control Federation) 48 (10), 2259–2272. Available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25040024.
Busch D. S., McElhany P. (2016). Estimates of the direct effect of seawater pH on the survival rate of species groups in the California current ecosystem. PloS One 11, e0160669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160669
Cai L., Rao Y., Zhao X., Yang D., Zhou X., Wang D., et al. (2023). Spatial and seasonal distributions of ten species of benthic macrofauna and twelve water environmental factors in a subtidal zone near the Daya Bay nuclear power plant. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1093468
Caputi N., Kangas M., Chandrapavan A., Hart A., Feng M., Marin M., et al. (2019). Factors affecting the recovery of invertebrate stocks from the 2011 Western Australian extreme marine heatwave. Front. Mar. Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00484
Cardoso-Mohedano J. G., Bernardello R., Sanchez-Cabeza J. A., Ruiz-Fernández A. C., Alonso-Rodriguez R., Cruzado A. (2015). Thermal impact from a thermoelectric power plant on a tropical coastal lagoon. Water Air Soil pollut. 226, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11270-014-2202-8
Castro M. M. D., Song T. W., Pinto J. M. (2000). Minimization of operational costs in cooling water systems. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 78, 192–201. doi: 10.1205/026387600527220
ÇETİN Y., Adem A. C. I. R. (2022). Decontamination applications in primary circuit equipment of nuclear power plants. Int. J. Energy Stud. 7, 195–216. doi: 10.58559/ijes.1178889
Chan H. Y., Xu W. Z., Shin P. K. S., Cheung S. G. (2008). Prolonged exposure to low dissolved oxygen affects early development and swimming behaviour in the gastropod Nassarius festivus (Nassariidae). Mar. Biol. 153, 735–743. doi: 10.1007/s00227-007-0850-6
Chatzinikolaou E., Grigoriou P., Keklikoglou K., Faulwetter S., Papageorgiou N. (2017). The combined effects of reduced pH and elevated temperature on the shell density of two gastropod species measured using micro-CT imaging. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 74, 1135–1149. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsw219
Chavan P., Kumar R., Kirubagaran R., Venugopalan V. P. (2017). Comparative toxicological effects of two antifouling biocides on the marine diatom Chaetoceros lorenzianus: Damage and post-exposure recovery. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 144, 97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.001
Cheng I., Ko P. C., Hu S. I., Hu C. P., Wei T. P. (2004). Nearshore macrobenthic communities of two nuclear power plants in northern Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 12, 5. doi: 10.51400/2709-6998.2260
Chou Y., Lin T. Y., Chen C. T. A., Liu L. L. (2004). Effects of Nuclear Power Plant thermal effluent on marine sessile invertebrate communities in southern Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 12 (5), 448–452. doi: 10.51400/2709-6998.2267
Chuang Y. L., Yang H. H., Lin H. J. (2009). Effects of a thermal discharge from a nuclear power plant on phytoplankton and periphyton in subtropical coastal waters. J. Sea Res. 61, 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2009.01.001
Colella M. A., Ruzicka R. R., Kidney J. A., Morrison J. M., Brinkhuis V. B. (2012). Cold-water event of January 2010 results in catastrophic benthic mortality on patch reefs in the Florida Keys. Coral Reefs 31, 621–632. doi: 10.1007/s00338-012-0880-5
Comfort C. M., Vega L. (2011). “Environmental assessment for ocean thermal energy conversion in Hawaii: Available data and a protocol for baseline monitoring,” in OCEANS’11 MTS/IEEE KONA (Kona, Hawaii, USA: IEEE), 1–8. doi: 10.23919/OCEANS
Copping A. E., Freeman M. C., Gorton A. M., Hemery L. G. (2020). Risk retirement-decreasing uncertainty and informing consenting processes for marine renewable energy development. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 8, 172. doi: 10.3390/jmse8030172
Crema R., Pagliai A. B. (1980). The structure of benthic communities in an area of thermal discharge from a coastal power station. Mar. pollut. Bull. 11 (8), 221–224. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(80)90410-5
Crook E. D., Potts D., Rebolledo-Vieyra M., Hernandez L., Paytan A. (2012). Calcifying coral abundance near low-pH springs: implications for future ocean acidification. Coral Reefs 31, 239–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00334344
Dallas L. J., Bean T. P., Turner A., Lyons B. P., Jha A. N. (2016). Exposure to tritiated water at an elevated temperature: Genotoxic and transcriptomic effects in marine mussels (M. galloprovincialis). J. Environ. radioactivity 164, 325–336. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.07.034
Dalpadado P., Roxy M. K., Arrigo K. R., van Dijken G. L., Chierici M., Ostrowski M., et al. (2024). Rapid climate change alters the environment and biological production of the Indian Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 906, 167342. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167342
Deabes E. A. (2020). The impact of thermal power stations on coastline and benthic fauna: Case study of El-Burullus power plant in Egypt. Results Eng. 7, 100128. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2020.100128
Deldicq N., Langlet D., Delaeter C., Beaugrand G., Seuront L., Bouchet V. M. (2021). Effects of temperature on the behaviour and metabolism of an intertidal foraminifera and consequences for benthic ecosystem functioning. Sci. Rep. 11, 4013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83311-z
Dong Z. G., Chen Y. H., Ge H. X., Li X. Y., Wu H. L., Wang C. H., et al. (2018). Response of growth and development of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) to thermal discharge from a nuclear power plant. BMC Ecol. 18 (1), 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12898-018-0191-y
Dong S., Lei Y., Li T., Jian Z. (2020). Response of benthic foraminifera to pH changes: Community structure and morphological transformation studies from a microcosm experiment. Mar. Micropaleontol. 156, 101819. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2019.101819
Egyptian Government. (2009). Protection of Environment (Law No. 9) (Egypt: Ministry of Environment of Egypt).
Ehler C. (2008). Conclusions: benefits, lessons learned, and future challenges of marine spatial planning. Mar. Policy 32, 840–843. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2008.03.014
Ellingsen K., Gray J. S. (2002). Spatial patterns of benthic diversity: is there a latitudinal gradient along the Norwegian continental shelf? J. Anim. Ecol. 71, 373–389. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2656.2002.00606.x
Everall N. C., Johnson M. F., Wilby R. L., Bennett C. J. (2015). Detecting phenology change in the mayfly E phemera danica: responses to spatial and temporal water temperature variations. Ecol. Entomol. 40, 95–105. doi: 10.1111/een.12164
Fabricius K. E., De’ath G., Noonan S., Uthicke S. (2014). Ecological effects of ocean acidification and habitat complexity on reef-associated macroinvertebrate communities. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 281, 20132479. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2479
Falfushynska H. I., Gnatyshyna L. L., Golubev A. P., Stoliar O. B. (2012). Main partitioning criteria for the characterization of the health status in the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea from spontaneously polluted area in western ukraine. Environ. Toxicol. 27 (8), 485–494. doi: 10.1002/tox.20663
Farshchi M., Nasrolahi A., Shokri M. R. (2020). Variability in benthic invertebrate community structure near warm water effluents of a power plant in the southern Caspian Sea. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 40, 101507. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101507
Feugere L., Angell L., Fagents J., Nightingale R., Rowland K., Skinner S., et al. (2021). Behavioural stress propagation in benthic invertebrates caused by acute pH drop-induced metabolites. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.773870
Florin A. B., Mo K., Svensson F., Schagerström E., Kautsky L., Bergström L. (2013). First records of Conrad´ s false mussel, Mytilopsis leucophaeata (Conrad 1831) in the southern Bothnian Sea, Sweden, near a nuclear power plant. BioInvasions Records 2, 303–309. doi: 10.3391/bir.2013.2.4.02
Gall M. L., Holmes S. P., Campbell H., Byrne M. (2021). Effects of marine heatwave conditions across the metamorphic transition to the juvenile sea urchin (Heliocidaris erythrogramma). Mar. pollut. Bull. 163, 111914. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111914
Gangur A. N., Marshall D. J. (2020). Facultative feeding in a marine copepod: effects of larval food and temperature on performance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 652, 33–47. doi: 10.3354/meps13470
Gao Y., Xie Z., Qian J., Tu Z., Yang C., Deng Y., et al. (2023). Effects of diel-cycling hypoxia and salinity on lipid metabolism and fatty acid composition of the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Mar. Environ. Res. 191, 106124. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106124
Garcia-Soto C., Cheng L., Caesar L., Schmidtko S., Jewett E. B., Cheripka A., et al. (2021). An overview of ocean climate change indicators: Sea surface temperature, ocean heat content, ocean pH, dissolved oxygen concentration, arctic sea ice extent, thickness and volume, sea level and strength of the AMOC (Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation). Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.642372
Giraud M., Garçon V., de la Broise D., L’Helguen S., Sudre J., Boye M. (2019). Potential effects of deep seawater discharge by an Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion plant on the marine microorganisms in oligotrophic waters. Sci. Total Environ. 693, 133491. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.297
Golmen L. G., Masutani S. M., Ouchi K. (2005). “Ocean thermal energy conversion and the next generation fisheries,” in World Renewable Energy Congress (WREC 2005). Eds. Imbabi M. S., Mitchell C. P. (UK: The World Renewable Energy Congress), 789–795.
Górska B., Grzelak K., Kotwicki L., Hasemann C., Schewe I., Soltwedel T., et al. (2014). Bathymetric variations in vertical distribution patterns of meiofauna in the surface sediments of the deep Arctic Ocean (HAUSGARTEN, Fram strait). Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Papers 91, 36–49. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.05.010
Guimarães L. S. F., de Carvalho-Junior L., Façanha G. L., da Silva Resende N., Neves L. M., Cardoso S. J. (2023). Meta-analysis of the thermal pollution caused by coastal nuclear power plants and its effects on marine biodiversity. Mar. pollut. Bull. 195, 115452. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115452
Hamilton H. J., Gosselin L. A. (2020). Ontogenetic shifts and interspecies variation in tolerance to desiccation and heat at the early benthic phase of six intertidal invertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 634, 15–28. doi: 10.3354/meps13189
Heip C., Craeymeersch J. A. (1995). Benthic community structures in the North Sea. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 49, 313–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02368359
Hillebrand H., Soininen J., Snoeijs P. (2010). Warming leads to higher species turnover in a coastal ecosystem. Global Change Biol. 16, 1181–1193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02045.x
Hoegh-Guldberg O., Poloczanska E. S., Skirving W., Dove S. (2017). Coral reef ecosystems under climate change and ocean acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00158
Hoglund J., Thomas K. (1992). The black goby Gobius niger as a potential paratenic host for the parasitic nematode Anguillicola crassus in a thermal effluent of the Baltic. Dis. OF Aquat. ORGANISMS 13 (3), 175–180. doi: 10.3354/dao013175
Hussain K. J., Mohanty A. K., Satpathy K. K., Prasad M. V. R. (2010). Abundance pattern of wedge clam Donax cuneatus (L.) in different spatial scale in the vicinity of a coastal nuclear power plant. Environ. Monit. Assess. 163, 185–194. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-0826-8
Hwang J. S., Tu Y. Y., Tseng L. C., Fang L. S., Souissi S., Fang T. H., et al. (2004). Taxonomic composition and seasonal distribution of copepod assemblages from waters adjacent to nuclear power plant I and II in northern Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 12 (5), 380–391. doi: 10.51400/2709-6998.2259
Hyvärinen H. S., Sjönberg T., Marjomäki T. J., Taskinen J. (2022). Effect of low dissolved oxygen on the viability of juvenile Margaritifera margaritifera: Hypoxia tolerance ex situ. Aquat. Conserv.: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 32, 1393–1400. doi: 10.1002/aqc.3859
IEA. (2024). IEA world energy balances. Available online at: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-product/world-energy-statistics-and-balances (accessed May 20, 2024).
IMO/FAO/UNESCO/WMO/WHO/IAEA/UN/UNEP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Pollution (GESAMP). (1984). Thermal Discharges in the Marine Environment (No. 24). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations.
Ingels J., Tchesunov A. V., Vanreusel A. (2011). Meiofauna in the Gollum Channels and the Whittard Canyon, Celtic Margin—how local environmental conditions shape nematode structure and function. PloS One 6, e20094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020094
International Finance Corporation (IFC) (2007). Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Facilities (Washington, D.C., USA: World Bank Group).
Islam S. S., Samanta S., Mahato S., Bhattacharya S., Midya S. (2024). “Diversity of meiobenthic fauna in costal environment: As a bioindicator,” in Spatial Modeling of Environmental Pollution and Ecological Risk (Cambridge, UK: Woodhead Publishing), 275–299. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-95282-8.00029-8
Issakhov A., Zhandaulet Y. (2021). Thermal pollution zones on the aquatic environment from the coastal power plant: Numerical study. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 25, 100901. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2021.100901
Jansujwicz J. S., Johnson T. R. (2015). Understanding and informing permitting decisions for tidal energy development using an adaptive management framework. Estuar. Coasts 38, 253–265. doi: 10.1007/s12237-013-9678-0
Jawad L. A. (2021). “The effects of thermal pollution on the aquatic life in the southern marshes of Iraq,” in Southern IRAQ’s Marshes: Their Environment and Conservation (Springer International Publishing, Cham). , 559–571.
Jebakumar J. P. P., Nandhagopal G., Babu B. R., Ragumaran S., Ravichandran V. (2018). Impact of coastal power plant cooling system on planktonic diversity of a polluted creek system. Mar. pollut. Bull. 133, 378–391. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.018.05.053
Jebure H. A., Meshjel M. H. (2019). Impact of Wasit power plant effluents on biodiversity of benthic fauna in Tigris river, province Wasit/Iraq. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 50 (3), 960–971.
Jenner H. A., Taylor C. J. L., Van Donk M., Khalanski M. (1997). Chlorination by-products in chlorinated cooling water of some European coastal power stations. Mar. Environ. Res. 43, 279–293. doi: 10.1016/S0141-1136(96)00091-8
Jia Y., Nihous G. C., Richards K. J. (2012). Effects of ocean thermal energy conversion systems on near and far field seawater properties—A case study for Hawaii. J. Renewable Sustain. Energy 4 (6), 063104. doi: 10.1063/1.4766820
Jones S. J., Lima F. P., Wethey D. S. (2010). Rising environmental temperatures and biogeography: poleward range contraction of the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis L., in the western Atlantic. J. Biogeogr. 37, 2243–2259. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02386.x
Jouhara H., Khordehgah N., Almahmoud S., Delpech B., Chauhan A., Tassou S. A. (2018). Waste heat recovery technologies and applications. Thermal Sci. Eng. Prog. 6, 268–289. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.017
Kalimuthu K., Hamli H., Engan M. T., Rasidi J. B., Rabullah M., Ismail J., et al. (2022). Diversity of fish and macrobenthos at the coastal area of Tanjung Kidurong Power Plant (TKPP), Sarawak, Malaysia. Egyptian J. Aquat. Biol. Fisheries 26 (1), 585–607. doi: 10.21608/EJABF.2022.226426
Kang H., Chen X., Deng W., Wang X., Cui H., Liu X., et al. (2021). Skeletal growth response of porites coral to long-term ocean warming and acidification in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.: Biogeosci. 126, e2021JG006423. doi: 10.1029/2021JG006423
Kastendiek J., Schroeter S. C., Dixon J. (1981). The effect of the seawater cooling system of a nuclear generating station on the growth of mussels in experimental populations. Mar. pollut. Bull. 12 (12), 402–407. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(81)90155-7
Keshavmurthy S., HSU C. M., KUO C. Y., MENG P. J., WANG J. T., Chen C. A. (2012). Symbiont communities and host genetic structure of the brain coral Platygyra verweyi, at the outlet of a nuclear power plant and adjacent areas. Mol. Ecol. 21, 4393–4407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05704.x
Kim J. H., Jeong S. Y., Kim P. J., Dahms H. U., Han K. N. (2017). Bio-effect-monitoring of long-term thermal wastes on the oyster, Crassostrea gigas, using heat shock proteins. Mar. pollut. Bull. 119, 359–364. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.04.035
Kimmerer W., Weaver M. J. (2013). Vulnerability of estuaries to climate change. (Oxford, UK: CRC Press), 277–289. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-384703-4.00438-X
Kolar H. R., McKeown E. P., Purcell M. E., Gaughan P. J., Westbrook A. G., Barry M. G., et al. (2013). “The design and deployment of a real-time wide spectrum acoustic monitoring system for the ocean energy industry,” in 2013 MTS/IEEE OCEANS-Bergen (Bergen, Norway: IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS-Bergen.2013.6608126
Kolehmainen S. E., Martin F. D., Schroeder P. B. (1974). Thermal studies on tropical marine ecosystems in Puerto Rico (No. CONF-740820-1; SM-187/14) (Mayaguez: Puerto Rico Nuclear Center).
Krepski T., Pilecka-Rapacz M., Czerniawski R., Domagała J. (2014). Analysis of benthic macroinvertebrate communities from the lower sections of large river in relation to different environmental factors. Open Life Sci. 9, 1037–1047. doi: 10.2478/s11535-014-0346-6
Kroeker K. J., Kordas R. L., Crim R. N., Hendriks I. E., Ramajo L., Singh G. S., et al. (2013). Impacts of ocean acidification on marine organisms: quantifying sensitivities and interaction with warming. Global Change Biol. 19, 1884–1896. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12179
Kroeker K. J., Kordas R. L., Crim R. N., Singh G. G. (2010). Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol. Lett. 13, 1419–1434. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01518.x
Kroeker K. J., Micheli F., Gambi M. C., Martz T. R. (2011). Divergent ecosystem responses within a benthic marine community to ocean acidification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 14515–14520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107789108
Kumar A., Sharma R. (2020). Mitigation of thermal pollution from industrial discharges. Environ. Manage. 65, 123–136.
Lamadrid-Rose Y., Boehlert G. W. (1988). Effects of cold shock on egg, larval, and juvenile stages of tropical fishes: Potential impacts of ocean thermal energy conversion. Mar. Environ. Res. 25, 175–193. doi: 10.1016/0141-1136(88)90002-5
Lan W. R., Huang X. G., Lin L. X., Li S. X., Liu F. J. (2020). Thermal discharge influences the bioaccumulation and bioavailability of metals in oysters: Implications of ocean warming. Environ. pollut. 259. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113821
Lardicci C., Rossi F., Maltagliati F. (1999). Detection of thermal pollution: variability of benthic communities at two different spatial scales in an area influenced by a coastal power station. Mar. pollut. Bull. 38 (4), 296–303. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00149-0
Li Z., Xing Y., Liu Z., Chen X., Jiang X., Xie Z., et al. (2020). Seasonal changes in metacommunity assembly mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrates in a subtropical river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 729, 139046. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139046
Lin J., Zou X. Q., Huang F. M. (2018). Effects of the thermal discharge from an offshore power plant on plankton and macrobenthic communities in subtropical China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 131, 106–114.
Loi T., Wilson B. J. (1979). Macroinfaunal structure and effects of thermal discharges in a mesohaline habitat of Chesapeake Bay, near a Nuclear Power Plant. Mar. Biol. 55 (1), 3–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00391711
Liu C. C. (2018). Ocean thermal energy conversion and open ocean mariculture: The prospect of Mainland-Taiwan collaborative research and development. Sustain. Environ. Res. 28, 267–273. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2018.06.002
Liu H., Li J., Wang H., Huang H., Xie F., Song X. (2023). High-temperature thermal discharge inhibits plankton community metabolism in a partly eutrophicated bay in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 9, 1016074. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1016074
LLC, Honolulu Seawater Air Conditioning (2014). Final environmental impact statement for the proposed Honolulu Seawater Air Conditioning project, Honolulu, Hawai’i. Ed. Engineers USA Co (Honolulu, HI: Cardno TEC, Inc.), 834.
Macias D., Hong S., Yang K. M., Kim J., Kim J. H. (2024). Variability of marine epifauna assemblages in response to the microhabitat type and thermal stress. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 71. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2024.103392
Mariu A., Chatha A. M. M., Naz S., Khan M. F., Safdar W., Ashraf I. (2023). Effect of temperature, pH, salinity and dissolved oxygen on fishes. J. Zool. Syst. 1, 1–12. doi: 10.56946/jzs.v1i2.198
Martin J., Planque B. (2006). Variability in the onset of hatching of Maja brachydactyla Bals(Brachyura: Majidae) in the English Channel in relation to sea temperature. Invertebrate Reprod. Dev. 49 (3), 143–150. doi: 10.1080/07924259.2006.9652205
Martínez M. L., Vázquez G., Pérez-Maqueo O., Silva R., Moreno-Casasola P., Mendoza-González G., et al. (2021). A systemic view of potential environmental impacts of ocean energy production. Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev. 149, 111332. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111332
Masilamoni J. G., Nandakumar K., Jesudoss K. S., Azariah J., Satapathy K. K., Nair K. V. K. (2002). Influence of temperature on the physiological responses of the bivalve Brachidontes striatulus and its significance in fouling control. Mar. Environ. Res. 53, 51–63. doi: 10.1016/S0141-1136(01)00109-X
Masutani S. M., Takahashi P. K. (2001). Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC). Oceanography 22, 625. doi: 10.1006/rwos.2001.0031
Mazik K., Hitchman N., Quintino V., Taylor C. J., Butterfield J., Elliott M. (2013). Sublethal effects of a chlorinated and heated effluent on the physiology of the mussel, Mytilus edulis L.: A reduction in fitness for survival? Mar. pollut. Bull. 77, 123–131. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.10.020
McClure R., Acker T., Dawson J. (2010). “Environmental assessment and monitoring of ocean energy sites—A rapid, proven, and economical approach,” in OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE (Piscataway, New Jersey, USA: IEEE), 1–5. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS.2010.5664110
McIntyre A. D. (1969). Ecology of marine meiobenthos. Biol. Rev. 44, 245–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1969.tb00828.x
Michie L. E., Thiem J. D., Boys C. A., Mitrovic S. M. (2020). The effects of cold shock on freshwater fish larvae and early-stage juveniles: implications for river management. Conserv. Physiol. 8, coaa092. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coaa092
Moher D., Shamseer L., Clarke M., Ghersi D., Liberati A., Petticrew M. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Møller B., Dahl-Madsen K. I. (1983). Biological Monitoring of Thermal Effects of Cooling Water Discharges from Danish Power Plants. Water Sci. Technol. 15 (10), 89–99. doi: 10.2166/wst.1983.0058
Murugesan P., Muniasamy M., Muthuvelu S., Vijayalakshmi S., Balasubramanian T. (2011). Utility of benthic diversity in assessing the health of an ecosystem. Indian J. Geo Marine Sci. 40, 783–793.
Muthukumar C., Balasubramaniyan S., Garlapati D., Bharathi M. D., Kumar B. C., James R. A., et al. (2022). Impact of untreated sewage and thermal effluent discharges on the air-sea CO2 fluxes in a highly urbanized tropical coastal region. Mar. pollut. Bull. 175, 113166. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113166
Myers E. P., Hoss D. E., Matsumoto W. M., Peters D. S., Seki M. P., Uchida R. N., et al. (1986). The potential impact of ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) on fisheries. (U.S. Department of Commerce: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration).
Nayak A., Equbal J., Rout S. S., Dash B., Thiruchitrambalam G., Bhadury P., et al. (2022). Macrobenthic community of an anthropogenically influenced mangrove associated estuary on the East coast of India: An approach for ecological assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1008912
Nicastro A., Bishop M. J. (2013). Weak and habitat-dependent effects of nutrient pollution on macrofaunal communities of southeast Australian estuaries. PloS One 8, e65706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065706
O’Carroll J. P. J., Kennedy R. M., Savidge G. (2017). Identifying relevant scales of variability for monitoring epifaunal reef communities at a tidal energy extraction site. Ecol. Indic. 73, 388–397. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.005
O’Hagan A. M. (2020). Supplement. Marine Spatial Planning and Marine Renewable Energy (Richland, WA (United States: Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL). doi: 10.2172/1633205
Oh J. H., Kug J. S., An S. I., Jin F. F., McPhaden M. J., Shin J. (2024). Emergent climate change patterns originating from deep ocean warming in climate mitigation scenarios. Nat. Climate Change 14, 260–266. doi: 10.1038/s41558-024-01928-0
Oshimi R., Tabeta S., Mizuno K. (2021). Water quality modeling in subtropical shallow waters to predict environmental impacts of ocean thermal energy conversion. J. Mar. Sci. Technol., 335–347. doi: 10.1007/s00773-021-00837-7
Osman A. I., Chen L., Yang M., Msigwa G., Farghali M., Fawzy S., et al. (2023). Cost, environmental impact, and resilience of renewable energy under a changing climate: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 21, 741–764. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01532-8
Padhi R. K., Subramanian S., Mohanty A. K., Satpathy K. K. (2019). Monitoring chlorine residual and trihalomethanes in the chlorinated seawater effluent of a nuclear power plant. Environ. Monit. Assess. 191, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7611-0
Pan S. Y., Snyder S. W., Packman A. I., Lin Y. J., Chiang P. C. (2018). Cooling water use in thermoelectric power generation and its associated challenges for addressing water-energy nexus. Water Energy Nexus 1, 26–41. doi: 10.1016/j.wen.2018.04.002
Pelc R., Fujita R. M. (2002). Renewable energy from the ocean. Mar. Policy 26, 471–479. doi: 10.1016/S0308-597X(02)00045-3
Przeslawski R., Ahyong S., Byrne M., Woerheide G., Hutchings P. A. T. (2008). Beyond corals and fish: the effects of climate change on noncoral benthic invertebrates of tropical reefs. Global Change Biol. 14, 2773–2795. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01693.x
Pusceddu A., Gambi C., Corinaldesi C., Scopa M., Danovaro R. (2014). Relationships between meiofaunal biodiversity and prokaryotic heterotrophic production in different tropical habitats and oceanic regions. PloS One 9, e91056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091056
Qiao L., Ren C., Sun X., Li T., Gui F., Zhao A. (2023). Benthic foraminiferal community structure and diversity in intertidal zone near China resources wenzhou power plant. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 21, (4), 3177–3192. doi: 10.15666/aeer/2104_31773192
Rajagopal S., Venugopalan V. P., van der Velde G., Jenner H. A. (2003). Comparative chlorine and temperature tolerance of the oyster Crassostrea madrasensis: Implications for cooling system fouling. Biofouling 19, 115–124. doi: 10.1080/0892701021000028497
Rao Y., Cai L., Chen X., Zhou X., Fu S., Huang H. (2021). Responses of functional traits of macrobenthic communities to human activities in Daya Bay (A subtropical semi-enclosed bay), China. Front. Environ. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.766580
Raptis C. E., van Vliet M. T., Pfister S. (2016). Global thermal pollution of rivers from thermoelectric power plants. Environ. Res. Lett. 11 (10), 104011. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/10/104011
R Core Team. (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Available online at: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed July 06, 2023).
Ridall A., Ingels J. (2021). Suitability of free-living marine nematodes as bioindicators: status and future considerations. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.685327
Riera R., Núñez J., Martín D. (2011). Effects of thermal pollution on the soft-bottoms surrounding a power station in the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Oceanology 51, 1040–1046. doi: 10.1134/S0001437011060142
Saraswat R., Nigam R., Pachkhande S. (2011). Difference in optimum temperature for growth and reproduction in benthic foraminifer Rosalina globularis: Implications for paleoclimatic studies. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 405, 105–110. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2011.05.026
Sarkar S. K., Bhattacharya A., Giri S., Bhattacharya B., Sarkar D., Nayak D. C., et al. (2005). Spatiotemporal variation in benthic polychaetes (Annelida) and relationships with environmental variables in a tropical estuary. Wetlands Ecol. Manage. 13, 55–67. doi: 10.1007/s11273-003-5067-y
Sasikumar N., Azariah J., Nair K. V. K. (1993). Changes in the composition of a tropical marine fouling community at a power plant discharge. Biofouling 6, 221–234. doi: 10.1080/08927019309386225
Schiel D. R., Steinbeck J. R., Foster M. S. (2004). Ten years of induced ocean warming causes comprehensive changes in marine benthic communities. Ecology 85, 1833–1839. doi: 10.1890/03-3107
Schratzberger M., Danovaro R., Ingels J., Montagna P. A., Rohal Lupher M., Semprucci F., et al. (2023). “Hidden players—Meiofauna mediate ecosystem effects of anthropogenic disturbances in the ocean,” in New Horizons in Meiobenthos Research: Profiles, Patterns and Potentials (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 175–255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21622-0_7
Schratzberger M., Ingels J. (2018). Meiofauna matters: the roles of meiofauna in benthic ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 502, 12–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2017.01.007
Schroeter S. C., Dixon J. D., Kastendiek J., Smith R. O., Bence J. R. (1993). Detecting the ecological effects of environmental impacts: a case study of kelp forest invertebrates. Ecol. Appl. 3 (2), 331–350. doi: 10.2307/1941836
Simard M. A., Paquet A., Jutras C., Robitaille Y., Blier P. U., Courtois R., et al. (2012). North American range extension of the invasive Asian Clam in a St. Lawrence River power station thermal plume. Aquat. Invasions 7 (2). doi: 10.3391/ai.2012.7.1.009
Singh D. P., Saraswat R., Nigam R. (2021). Untangling the effect of organic matter and dissolved oxygen on living benthic foraminifera in the southeastern Arabian Sea. Mar. pollut. Bull. 172, 112883. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112883
Sivaperumal P., Khot M., Chakraborty S. K., Pawase A., Jaiswar A. K. (2022). Diversity of intertidal macrobenthic fauna around Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg districts of Maharashtra, west coast of India. Indian J. Geo.-Mar. Sci. (IJMS) 51 (01), 56–66. doi: 10.56042/ijms.v51i01.65900
Smith K. E., Burrows M. T., Hobday A. J., King N. G., Moore P. J., Sen Gupta A., et al. (2023). Biological impacts of marine heatwaves. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 15, 119–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-032122-121437
Snelgrove P. V. (1998). The biodiversity of macrofaunal organisms in marine sediments. Biodivers. Conserv. 7, 1123–1132. doi: 10.1023/A:1008867313340
Snoeijs P. J. M. (1989). Effects of increasing water temperatures and flow rates of epilithic fauna in a cooling-water discharge basin. J. Appl. Ecol. 26 (3), 935–956. doi: 10.2307/2403703
Steinbeck J. R., Schiel D. R., Foster M. S. (2005). Detecting long-term change in complex communities: A case study from the rocky intertidal zone. Ecol. Appl. 15 (5), 1813–1832. doi: 10.1890/04-1046
Sun X., Li Z., Ding X., Ji G., Wang L., Gao X., et al. (2022). Effects of algal blooms on phytoplankton composition and hypoxia in coastal waters of the northern Yellow Sea, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.897418
Suresh K., Ahamed M. S., Durairaj G., Nair K. V. K. (1993). Impact of power plant heated effluent on the abundance of sedentary organisms, off Kalpakkam, East coast of India. Hydrobiologia 268, 109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00006881
Suresh K., Durairaj G., Nair K. V. K. (1996). Harpacticoid copepod distribution on a sandy shore in the vicinity of a power plant discharge, at Kalpakkam, along the east coast of India. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 25, 307–311.
Taylor C. J. (2006). The effects of biological fouling control at coastal and estuarine power stations. Mar. pollut. Bull. 53, 30–48. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.01.004
Teixeira T. P., Neves L. M., Araújo F. G. (2009). Effects of a nuclear power plant thermal discharge on habitat complexity and fish community structure in Ilha Grande Bay, Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 68 (4), 188–195. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.06.004
Teixeira T. P., Neves L. M., Araújo F. G. (2012). Thermal impact of a nuclear power plant in a coastal area in Southeastern Brazil: effects of heating and physical structure on benthic cover and fish communities. Hydrobiologia 684, 161–175. doi: 10.1007/s10750-011-0980-1
Thieltges D. W., Strasser M., van Beusekom J. E., Reise K. (2004). Too cold to prosper—winter mortality prevents population increase of the introduced American slipper limpet Crepidula fornicata in northern Europe. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 311, 375–391. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.05.018
Titelboim D., Almogi-Labin A., Herut B., Kucera M., Schmidt C., Hyams-Kaphzan O., et al. (2016). Selective responses of benthic foraminifera to thermal pollution. Mar. pollut. Bull. 105, 324–336. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.002
Urban-Malinga B. (2014). Meiobenthos in marine coastal sediments. Geol. Society London Special Publications 388, 59–78. doi: 10.1144/SP388.9
Vaquer-Sunyer R., Duarte C. M. (2008). Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 15452–15457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803833105
Vargas C. A., Aguilera V. M., Martín V. S., Manríquez P. H., Navarro J. M., Duarte C., et al. (2011). Temperature effects on oxygen thresholds for hypoxia in marine benthic organisms. Global Change Biol. 17 (5), 1788–1797. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02343.x
Venugopalan V. P., Rajagopal S., Jenner H. A. (2011). Operational and environmental issues relating to industrial cooling water systems: an overview. Operational Environ. Consequences Large Ind. Cooling Water Syst., 1–12. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-1698-21
Viotti S., Sangil C., Hernández C. A., Hernández J. C. (2019). Effects of long-term exposure to reduced pH conditions on the shell and survival of an intertidal gastropod. Mar. Environ. Res. 152, 104789. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.104789
Viviani D. A., Bjorkman K. M., Karl D. M., Church M. J. (2011). Plankton metabolism in surface waters of the tropical and subtropical Pacific Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 62 (1), 1–12. doi: 10.3354/ame01451
Wang Y. S., Lou Z. P., Sun C. C., Sun S. (2008). Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar. pollut. Bull. 56, 1871–1879. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.07.017
Wang Y. S., Sun C. C., Lou Z. P., Wang H. L., Mitchell B. G., Wu M. L., et al. (2011). Identification of water quality and benthos characteristics in Daya Bay, China, from 2001 to 2004. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 40, 82–95. doi: 10.2478/s13545-011-0009-4
Warwick R. M., Clarke K. R. (1993). Increased variability as a symptom of stress in marine communities. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 172, 215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(93)90098-9
Wasti A., Ray P., Wi S., Folch C., Ubierna M., Karki P. (2022). Climate change and the hydropower sector: A global review. Wiley Interdiscip. Reviews: Climate Change 13, e757. doi: 10.1002/wcc.757
West A., Penk M. R., Larney R., Piggott J. J. (2021). Response of macroinvertebrates to industrial warm discharges: the River Shannon case study (Ireland). Inland Waters 11, 381–395. doi: 10.1080/20442041.2021.1904761
Williams B. K. (2011). Adaptive management of natural resources—framework and issues. J. Environ. Manage. 92, 1346–1353. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.10.041
Williamson B. J., Fraser S., Blondel P., Bell P. S., Waggitt J. J., Scott B. E. (2017). Multisensor acoustic tracking of fish and seabird behavior around tidal turbine structures in Scotland. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 42, 948–965. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2016.2637179
Wither A., Bamber R., Colclough S., Dyer K., Elliott M., Holmes P., et al. (2012). Setting new thermal standards for transitional and coastal (TraC) waters. Mar. pollut. Bull. 64, 1564–1579. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.05.019
Wong C. K., Hwang J. S., Chen Q. C. (1998). Taxonomic composition and grazing impact of calanoid copepods in coastal waters near nuclear power plants in northern Taiwan. ZOOLOGICAL Stud. 37 (4), 330–339.
Xu D., Wang H., Han D., Chen A., Niu Y. (2021). Phytoplankton community structural reshaping as response to the thermal effect of cooling water discharged from power plant. Environ. pollut. 285, 117517. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117517
Yang Y., Yi Y., Zhou Y., Wang X., Zhang S., Yang Z. (2020). Spatio-temporal variations of benthic macroinvertebrates and the driving environmental variables in a shallow lake. Ecol. Indic. 110, 105948. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105948
Yanygina L. V. (2015). Spatial distribution of Gmelinoides fasciatus Steb. thermally polluted Water (Belovo Reservoir Southwest Siberia). Int. J. Environ. Res. 9 (3), 877–884.
Ying R., Cao Y., Yin F., Guo J., Huang J., Wang Y., et al. (2020). Trophic structure and functional diversity reveal pelagic-benthic coupling dynamic in the coastal ecosystem of Daya Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 113, 106241. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106241
Yuan L. L. (2004). Assigning macroinvertebrate tolerance classifications using generalised additive models. Freshw. Biol. 49, 662–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01206.x
Zeng C., Rotllant G., Giménez L., Romano N. (2020). Effects of environmental conditions on larval growth and development. Dev. Biol. Larval Ecol. Natural History Crustacea 7, 195–222.
Zeppilli D., Bongiorni L., Cattaneo A., Danovaro R., Santos R. S. (2013). Meiofauna assemblages of the Condor Seamount (North-East Atlantic Ocean) and adjacent deep-sea sediments. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanogr. 98, 87–100. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.08.009
Zeppilli D., Sarrazin J., Leduc D., Arbizu P. M., Fontaneto D., Fontanier C., et al. (2015). Is the meiofauna a good indicator for climate change and anthropogenic impacts? Mar. Biodivers. 45, 505–535. doi: 10.1007/s12526-015-0359-z
Zimina L. M., Zimin V. L., Khayrutdinova J. (1993). Some results of the long-time ecological monitoring of the Leningrad NPP cooling water body (Koporskaya bay, gulf of Finland). Hydrological. Chem. Biol. Processes Transformation Transport Contaminants Aquat. Environments Proc. HYDROCHEMISTRY, 137–146.
Keywords: thermal emission, cold emission, ocean thermal energy conversion, benthos, mitigation actions
Citation: Leng Q, Mohamat-Yusuff F, Mohamed KN, Zainordin NS and Hassan MZ (2024) Impacts of thermal and cold discharge from power plants on marine benthos and its mitigation measures: a systematic review. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1465289. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1465289
Received: 16 July 2024; Accepted: 19 November 2024;
Published: 20 December 2024.
Edited by:
Yen-Chiang Chang, Dalian Maritime University, ChinaReviewed by:
M. Rafiuddin Ahmed, University of the South Pacific, FijiPeriyadan K. Krishnakumar, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2024 Leng, Mohamat-Yusuff, Mohamed, Zainordin and Hassan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ferdaus Mohamat-Yusuff, ZmVyZGl1c0B1cG0uZWR1Lm15
 Qingxue Leng
Qingxue Leng Ferdaus Mohamat-Yusuff
Ferdaus Mohamat-Yusuff Khairul Nizam Mohamed
Khairul Nizam Mohamed Nazatul Syadia Zainordin1
Nazatul Syadia Zainordin1 Mohd Zafri Hassan
Mohd Zafri Hassan