- 1School of Marine Technology and Geomatics, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang, China
- 2College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Nanjing, China
Sea ice thickness (SIT) is a critical and sensitive parameter in the climate system, with its dynamic changes profoundly influencing global climate models, navigational routes, and the potential for Arctic resource development. Given the widespread application of current satellite remote sensing technology in monitoring SIT, significant uncertainties remain. This study first underscores the importance of in-situ observations as a direct measurement method for SIT. However, the limitations of in-situ data in terms of acquisition cost, spatiotemporal coverage continuity, and distribution uniformity significantly hinder the effective evaluation of multi-source SIT products. To address this, the study innovatively introduces the Triple Collocation (TC) method, which effectively mitigates the impact of errors from individual data sources on the overall evaluation results through a mutual validation mechanism among multiple satellite data sources. This allows for a scientific assessment of multi-source SIT products even in the context of scarce in-situ observations. The findings indicate that the TC method not only successfully resolves the challenges of multi-source data evaluation but also facilitates data integration among these products, significantly enhancing the overall accuracy and spatiotemporal consistency of SIT data.
1 Introduction
Sea ice is one of the most sensitive environmental factors in the climate system. Acting as an insulator for heat, moisture, and material exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere, it tightly links global atmospheric circulation, oceanic water cycles, and the balance of temperature, salinity, and heat through complex physical feedback processes (Walsh, 1983; Johannessen et al., 2020; Spreen et al., 2020).The study of sea ice and its variations is therefore of significant relevance to current global climate research.
Beyond its climatic impact, the melting of Arctic sea ice has profound implications for human society, such as the opening of navigational routes, the development of natural resources, and the enhancement of strategic positioning. The rapid melting of Arctic sea ice allows for seasonal navigation in much of the Arctic Ocean, presenting opportunities for new shipping routes (Stroeve and Notz, 2015; Theocharis et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021). Additionally, the melting sea ice exposes rich natural resources previously covered by extensive ice sheets, making resource extraction feasible. This, coupled with the opening of new shipping lanes, introduces new dynamics in economic trade among energy-demanding nations (Wang et al., 2023). The central location of the Arctic shipping routes will further underscore its strategic importance, enhancing its allure and significantly elevating its strategic position in international politics.
Accurately grasping the variability of sea ice is crucial for studying global climate change and ensuring the regular operation of Arctic shipping routes and resource development (Kim et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021b). Sea ice concentration and sea ice thickness (SIT) are two critical parameters representing the horizontal and vertical characteristics of sea ice variation, respectively. Since 1979, satellite remote sensing technology has been widely used to estimate sea ice concentration and thickness. However, compared to sea ice concentration retrievals, satellite remote sensing products for SIT still exhibit significant retrieval errors (Zheng et al., 2021). Errors in altimetric satellite products, such as those from CryoSat-2 (CS2), originate from measurement inaccuracies in sea ice freeboard height and the conversion bias between freeboard height and thickness (Alexandrov et al., 2010; Laxon et al., 2013). Microwave satellite products, like those from the Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission, face limitations due to the penetration depth of microwaves, leading to uncertainties in SIT retrieval (Ricker et al., 2017). Optical satellite products, such as those from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Polar Pathfinder (APP-x), are constrained by observational errors related to weather conditions and the accuracy of input auxiliary variables. Numerical model products, like the Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling Assimilation System (PIOMAS), encounter spatial errors during the data assimilation process (Gregory et al., 2021). Due to the distinct sources of error in different SIT products, these errors vary across different spatial and temporal scales, leading to a degradation in the quality of outcomes based on these SIT products.
Currently, most researchers rely on in-situ data to evaluate and validate existing satellite remote sensing data for SIT. Kwok and Cunningham (2015) utilized in-situ datasets from Upward-Looking Sonar (ULS), submarine draft measurements, electromagnetic induction sounding systems, and Operation IceBridge (OIB) SIT data to assess CS2 data in terms of mean values, standard deviations, and correlations, finding more significant discrepancies between CS2 and OIB data (Kwok and Cunningham, 2015). Kaleschke et al. (2015) analyzed the differences between SMOS and CS2 due to their fundamental differences in radiometric and altimetric measurement principles, highlighting the higher uncertainty of SMOS in thick ice and CS2’s higher uncertainty in thin ice due to its reliance on accurate freeboard measurements (Kaleschke et al., 2015). Feng et al. (2021) validated CS2 SIT data using OIB and ULS data, revealing an average difference of approximately 0.165 m between CS2 and OIB data in March 2015, and differences ranging from 0.11 to 0.12 m between CS2 and ULS data from November 2010 to March 2018 (Feng et al., 2021). Traditional evaluation methods rely on comparing satellite retrievals with in-situ observations, commonly using metrics such as mean values, root mean square error, and correlation to assess temporal and spatial variations in sea ice data.
In-situ observations are the most direct method for measuring SIT, providing highly accurate results and reliable evaluations of SIT products. However, obtaining in-situ observations in the Arctic region faces three primary challenges: 1) high costs; 2) difficulty in acquiring continuous temporal and spatial data, hindering the evaluation of spatiotemporal variations in different sea ice data products; and 3) highly uneven distribution of existing in-situ data, leading to insufficient representativeness and challenges in comprehensively evaluating the performance of wide-area polar SIT data products. Consequently, current research primarily focuses on comparing the characteristics of different SIT data, with in-situ data serving mainly as a reference and not directly used for SIT evaluation and integration.
To fully utilize SIT remote sensing data and improve its accuracy and spatiotemporal resolution, researchers have explored various multi-source data fusion methods, achieving some success. Ricker et al. (2017) employed weighted mean (WM) and optimal interpolation (OI) methods to integrate weekly SMOS and CS2 SIT data, forming weekly CS2SMOS data. In the Barents Sea, the OI method reduced the root mean square error of CS2SMOS thickness data by approximately 0.7 m compared to CS2 data, but the fusion effect of CS2SMOS was inferior to the original data in the mixed ice of the Beaufort Sea (Ricker et al., 2017). Wang et al. (2020) extended Ricker et al. (2017)’s work by developing an optimal multi-sensor data fusion method, combining daily SMOS and weekly CS2SMOS data to generate new daily CS2SMOS SIT data, reducing observational uncertainties, providing better spatial coverage for coastal regions, and improving the accuracy of thin ice observations at the edges (Wang et al., 2020). However, significant errors persisted in areas such as the Davis Strait, Baffin Bay, and the southern coast of Greenland.
The Triple Collocation (TC) method has proven effective in estimating random errors in satellite products in the absence of reliable in-situ observation data (Stoffelen, 1998; McColl et al., 2014). TC estimates the error values and correlation coefficients of SIT time series using three independent datasets linearly related to the true value, without requiring extensive, high-density in-situ data. This method is particularly important for validating SIT in regions lacking observational data and has been widely used to validate satellite products, such as sea surface wind (Stoffelen, 1998), soil moisture (Yilmaz and Crow, 2014) and terrestrial snow depth (Qiao et al., 2022). However, there are few studies on validating SIT using TC, and more importantly, TC demonstrates the potential to integrate multiple datasets from different sources, thereby improving accuracy and reducing uncertainty (Yilmaz et al., 2012; Gruber et al., 2017).
The objective of this study is to explore the effectiveness of the TC method in evaluating SIT data, enabling evaluation in regions without observational data. Furthermore, based on the evaluation results, this study aims to design a multi-source SIT data fusion method to enhance the accuracy and spatiotemporal resolution of sea ice data. The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 introduces the data sources used in this study; Section 3 describes the evaluation and fusion methods for product data with limited in-situ observations; Section 4 analyzes the evaluation and fusion results; Section 5 discusses the effective spatial resolution of the fused products; and Section 6 summarizes the findings of this study.
2 Data presentation
2.1 Product data
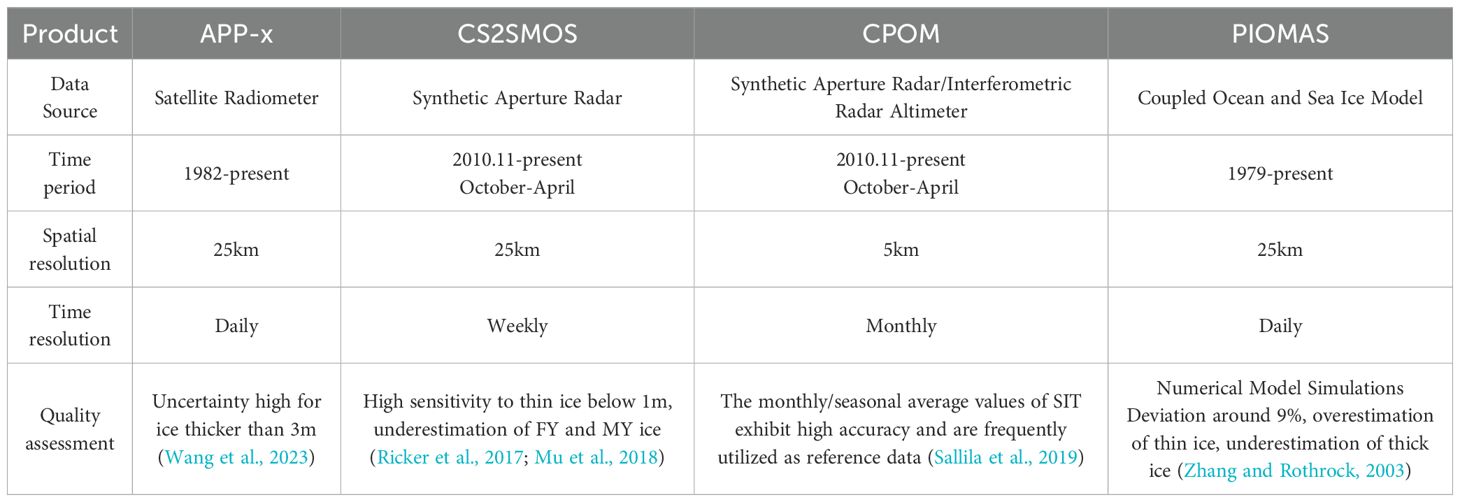
2.1.1 APP-x
The APP-x extended product, developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), provides estimates of SIT alongside 18 other geophysical variables in climate data records (Key et al., 2016). These estimates have been available for the Arctic and Antarctic Oceans since 1982, with data provided twice daily.
SIT estimates are derived from AVHRR satellite radiometer measurements using a one-dimensional thermodynamic model based on the surface energy balance equation (Key et al., 2016). Ice thickness is calculated using solar radiation, surface heat flux, surface albedo, and transmittance, with surface fluxes determined by variables such as surface skin and air temperature, surface pressure, relative humidity, ice temperature, wind speed, cloud cover, and snow depth. Therefore, the Optimal Thermodynamic Ice Model (OTIM) relies on inputs such as cloud cover, surface skin temperature, surface broadband radiation flux, and surface shortwave radiation flux, the latter two obtained during daytime retrievals. APP-x product sea ice concentration data are sourced from Nimbus-7 Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) special sensor microwave imager (SSM/I) data, processed using the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) team algorithm (Key et al., 2016). Sea ice type is derived from AVHRR direct reflectance measurements.
2.1.2 PIOMAS
The PIOMAS couples the Parallel Ocean Program (POP) with the Thickness and Enthalpy Distribution (TED) sea ice model, using Generalized Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates (GOCC). PIOMAS incorporates reanalysis data from National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCEP/NCAR), including 2 m surface temperature, 10 m near-surface wind fields, precipitation, evaporation, specific humidity, and longwave/shortwave radiation. It employs physical processes such as surface heat, salinity (or freshwater), and dynamics as boundary conditions at the sea surface. The model also integrates satellite data based on the principles of viscous-plastic rheology and variations in ice thickness. PIOMAS has simulated numerous sea ice and ocean parameters, including SIT, since January 1979.
2.1.3 CS2SMOS
The CS2 product is from the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI), version 1.2 (Ricker et al., 2014; Hendricks et al., 2016), and SMOS thickness data are from Hamburg University, version 3.1 (Tian-Kunze et al., 2014).
CryoSat-2, equipped with a Ku-band synthetic aperture radar interferometric radar altimeter (SIRAL), measures the height difference between the snow/ice surface and the sea surface. Using the hydrostatic equilibrium assumption, this height difference is used to derive SIT. The CS2L1b radar waveform data, retracked using the Threshold First Maximum Retracker Algorithm (TFMRA) waveform retracking method with a 50% threshold, are used to estimate the surface elevation of sea ice and leads. Unlike Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling (CPOM), CS2 uses the DTU15 global mean sea surface height model to calculate sea surface height anomalies. Sea ice concentration and type are derived from Ocean and Sea Ice Satellite Application Facility (OSI-SAF) products, with areas having sea ice concentration greater than 70% identified as sea ice regions. Snow thickness and density data are obtained from MW99 data (Warren et al., 1999).
SMOS, equipped with the Microwave Imaging Radiometer using Aperture Synthesis (MIRAS), uses L-band (1.4 GHz) information to estimate SIT. The thickness retrieval is based on the thermodynamic equilibrium equation, where the heat flux entering the snow-ice system equals the atmospheric heat flux, including sensible heat flux, latent heat flux, longwave radiation, shortwave radiation, and conductive heat flux. The conductive heat flux-thickness relationship is used to estimate thickness.
The CS2SMOS product, developed by the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) and Hamburg University, merges CS2 and SMOS thickness estimates, providing weekly SIT data on the EASE2.0 grid with a resolution of 25 km (https://smos-diss.eo.esa.int), from November 2010 to the present. This study uses data from November 2010 to April 2021.
2.1.4 CPOM
The CPOM is an independent organization dedicated to providing polar observation and simulation data. It was the first to publicly offer Arctic SIT products based on CS2 radar altimeter data, providing near-real-time (NRT) thickness products with observation cycles of 28 days, 14 days, and 2 days.
CPOM uses CS2L1b data to retrieve Arctic SIT. The stack standard deviation (SSD) and pulse peakiness are used to differentiate radar waveforms from leads and sea ice. The surface height of sea ice is determined by setting the retracking point at 70% of the leading edge of the ice radar waveform, using the Gaussian-fitting waveform retracking algorithm proposed by Giles et al. (2007). The retrieval of Arctic SIT also requires auxiliary data, such as mean sea surface height, sea ice concentration, sea ice type, and snow thickness. The global mean sea surface height is derived from the University College London 2013(UCL13) model to calculate sea surface height anomalies and ice freeboard height. Daily polar grid sea ice concentration products from the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) are used to identify areas with sea ice concentration greater than 75%, and sea ice type data are obtained from OSI-SAF products. Snow thickness and density over sea ice are based on climatological data provided by Warren et al. (1999), and modified according to the method described by Laxon et al. (2013) (MW99). In MW99, the snow thickness on first-year ice is set to 50% of the climatological data, and snow density is a monthly constant based on each ice type.
Based on the above, a summary of the characteristics of the four SIT products is shown in Table 1.
2.2 In-situ data
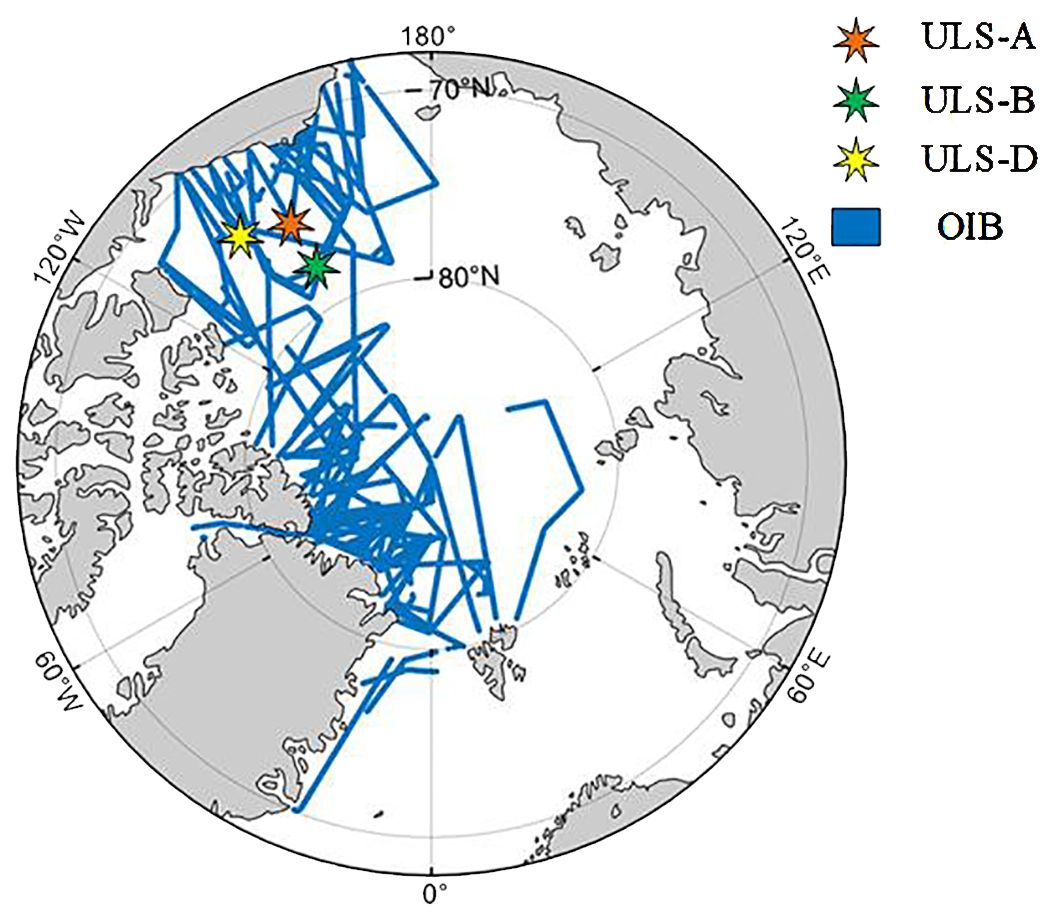
2.2.1 OIB
The OIB was initiated in 2009 to bridge the observational gap between the conclusion of the ICESat mission in 2009 and the commencement of the ICESat-2 mission in 2018. OIB collects elevation measurements of sea ice and land ice. Compared to ULS, IceBridge provides a broader spatial measurement range of SIT, although the observation period is shorter, primarily concentrated in a few days during March and April from 2010 to 2019. This study utilizes eight years of publicly available IceBridge data from 2012 to 2019, sourced from the National Snow and Ice Data Center (https://nsidc.org/data/nsidc-0708/versions/1).
2.2.2 ULS
The ULS devices are deployed as part of the Beaufort Gyre Exploration Project (BGEP) in the Beaufort Sea (https://www2.whoi.edu/site/beaufortgyre/). ULS data are obtained using devices that emit sonar signals from the seabed upward, measuring the distance to the ice bottom to determine sea ice draft, which is then converted to overall SIT using empirical models. The instruments are typically positioned at depths of 50 m and 85 m, providing distance measurements to the ice bottom every 2 seconds, with a footprint diameter of approximately 2 meters (Krishfield and Proshutinsky, 2006). Ice draft is calculated by subtracting the corrected distance (accounting for instrument tilt, sound speed, and seawater density variations) from the depth measured by pressure sensors (Melling et al., 1995). The accuracy of sonar-determined draft measurements is controlled within 0.05 to 0.10 m (Kwok and Cunningham, 2015), and the draft is converted to thickness by multiplying by a coefficient of 1.1, based on the average density ratio of seawater to sea ice (Nguyen et al., 2011). Four buoys have been deployed, with buoys A, B, and D providing continuous observations since 2010. This study uses ULS data from these three buoys for the winter half-years from 2011 to 2021. ULS provides long-term continuous observations but only covers a few fixed points.
The spatial resolution of ULS and OIB sampling points is also illustrated in Figure 1.
3 Research methodology and design
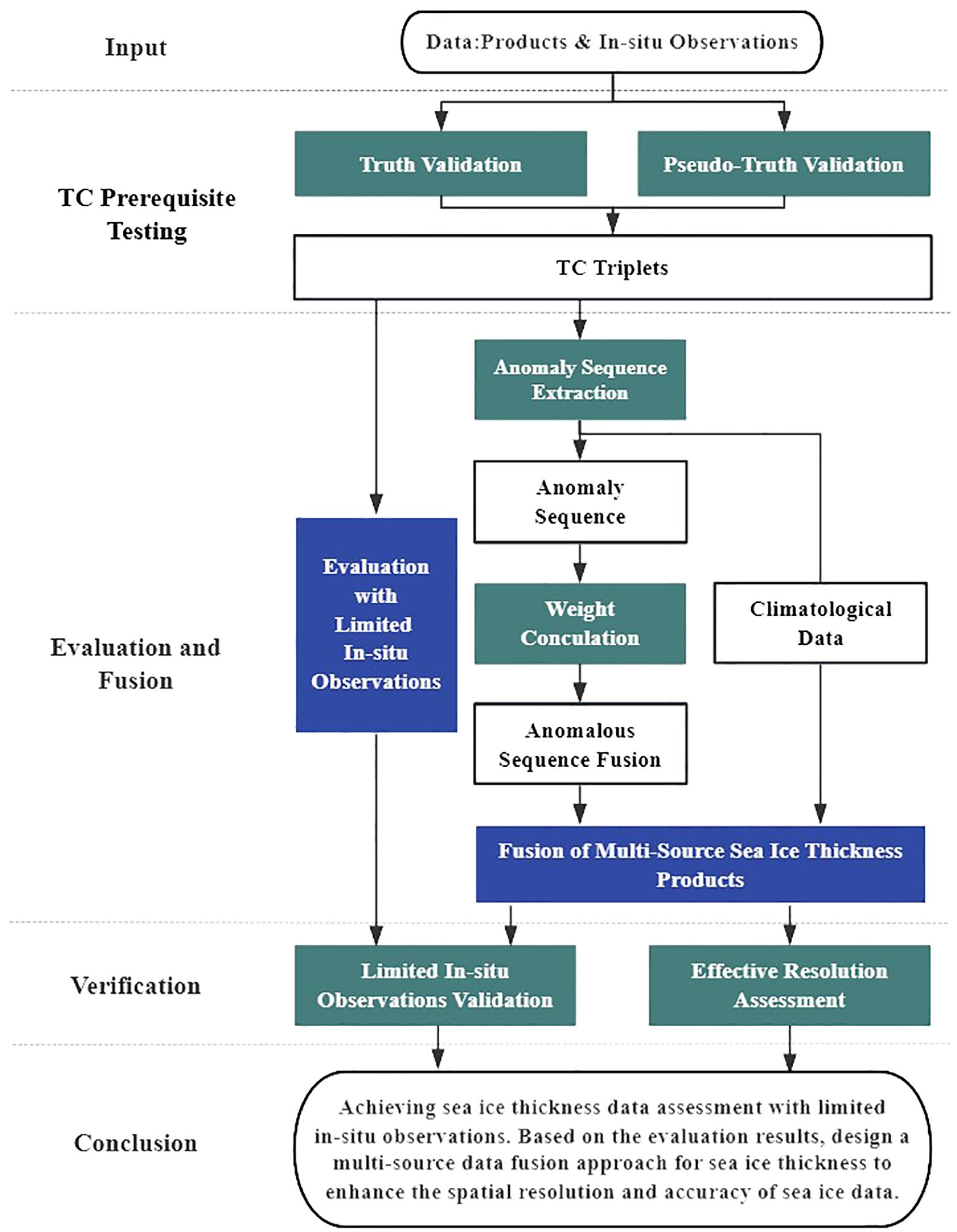
This study presents a novel framework tailored for the evaluation and integration of SIT data with limited in-situ observations. The methodology is divided into two main phases:
First, we analyze the uncertainty of SIT data. By utilizing limited in-situ observations and pseudo-truth methods, we establish that the assumptions of the TC method (a non-truth-based data evaluation approach) are satisfied. Subsequently, we identify suitable triplets for the evaluation of SIT data without requiring in-situ observations. Secondly, we propose a multi-source SIT data integration scheme with in-situ observations. This scheme is based on the fusion weights determined from the SIT anomaly datasets, aiming to enhance the accuracy and spatiotemporal resolution of SIT products.
The detailed experimental design process is illustrated in Figure 2.
3.1 Prerequisite testing for the TC algorithm
The application of the TC algorithm necessitates the fulfillment of three foundational assumptions: 1) all three datasets in the triplet are linearly related to an unknown reference dataset; 2) the errors in each dataset are mutually uncorrelated; and 3) the errors in each dataset are uncorrelated with the unknown reference dataset. Among these, violation of assumption 2) is regarded as the primary source impacting the effectiveness of TC estimation methods. However, many newly developed global gridded products often involve the overlapping use of common inputs and/or processing methods, which inevitably increases the possibility of correlated errors among different products (Chen et al., 2021b). For instance, both the CS2SMOS and CPOM SIT products include data from the CS2 radar altimeter and use the same mean sea level height standard, DTU15 MSS. Therefore, the application of the TC algorithm only requires low error correlation among each dataset. Since the quality of TC-based fusion results also depends on the composition of TC triplet members (Koster et al., 2021), careful consideration should be given to the selection of triplet members to minimize violations of the fundamental assumptions when error correlations exist between parent datasets (Chen et al., 2021b).
To validate assumption 2), this study assumes a linear relationship between the true SIT value and the product datasets of SIT, which can be expressed as:
where represents the unknown true SIT value; represents the product datasets of SIT; represents random errors, represents the bias coefficient of the product data relative to the true value, and represents the bias intercept relative to the true value.
The Mann-Whitney U test method is employed to assess the significance of the linear relationship between the and the , with a significance level of . The value from the test results determines whether the linear relationship is significant. If significance is observed, assumption 1) is also validated.
By performing linear fits of SIT datasets with the true data from ULS and OIB, the random errors can be extracted, and covariance calculations can be used to test the correlation of product errors. Given the limited spatial coverage of the OIB and ULS in-situ data, which are mostly distributed in the Western Hemisphere of the Arctic, a pseudo-truth validation method is also used. This involves using each of the four product datasets as reference data to test the error correlations between products, thereby addressing the limitations of the spatial and temporal resolution of in-situ observation data and overcoming the representativeness issue of in-situ observation data. Suitable triplet data for product data fusion are filtered based on the correlation test results.
For assumption 3), if the unknown reference dataset is the true value, the mutual uncorrelation between product errors and the true value holds. When the unknown reference dataset is a certain product dataset, assumption 3) can be decomposed into the mutual uncorrelation between product errors and the true value, and the mutual uncorrelation between the errors of different product datasets. The former holds, and the latter reverts to the test for assumption 2). In conclusion, if assumption 2) holds, all three prerequisites for the TC algorithm are satisfied.
3.2 Evaluation of sea ice thickness data with limited in-situ observations using the TC algorithm
The insufficient spatiotemporal resolution of in-situ datasets impacts the accuracy of TC algorithm assumptions and the evaluation based on these in-situ datasets. This study leverages the TC algorithm to assess product data quality with limited in-situ observations. The covariance between any two of the three SIT products is expressed as follows, according to the covariance calculation formula and (Equation 1):
where represents the covariance, and denotes the variance of the true SIT.
The TC method assumes that the errors in SIT products are independent of the true SIT errors, i.e., , and that the random errors of the three products are uncorrelated, i.e., when . Under these assumptions, (Equation 2) simplifies to:
Where is the variance of the random error in the dataset.
The root mean square error of each SIT product can be estimated as follows:
The correlation coefficients (R) between the different datasets and the true values are calculated using the following formulas:
where represents the correlation coefficient between the dataset and the true values.
Thus, the TC algorithm enables the evaluation of SIT product data quality with limited in-situ observations.
3.3 Data fusion method
Influenced by the TC algorithm, this section performs fusion processing on the SIT anomaly datasets, superimposing climatological mean data to achieve the integration of SIT product data.
3.3.1 Construction of outlier time series
SIT products derived from various methods may exhibit systematic differences, i.e., different dynamic ranges and climatologies. These differences are influenced by the characteristics of varying spatial and temporal scales and different forcing datasets during processing. It is noteworthy that the TC algorithm is most robust for anomalous error representation because the climatology of geophysical products comprises limited degrees of freedom, and the climatological errors of different products may be interrelated, potentially violating the TC assumption (Draper et al., 2013). Therefore, before applying the TC method, this study converts the selected four SIT products into zero-mean anomaly datasets (Chen et al., 2017). Here we choose the anomaly calculation against the long-term seasonality (also often termed as the climatology) following common practice of previous (Dorigo et al., 2010; Peng et al., 2021), which is calculated as the average of the same day of the year (DOY) for their overlapping period (Liu et al., 2012). The mean values of the same day during the overlapping period of the products from 2011 to 2021 winter halves are calculated, as shown in (Equation 10).
Where ANO refers to SIT anomalies; YR refers to the years 2011-2021; DOY refers to a specific day of the year; ORI refers to the original time series data of SIT; N represents the number of valid years for SIT values.
3.3.2 TC fusion algorithm
The TC method assumes three error-independent datasets, all linearly related to the unknown true value in the error model (McColl et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2017, 2021a). The error model of TC can be expressed as follows:
where represents SIT anomaly dataset, denotes the unknown reference SIT anomaly dataset, represents the random error of the SIT anomaly dataset, and and represent the least squares intercept and slope of the SIT anomaly dataset, respectively. For convenience, in the following, will directly represent the anomaly datasets of the SIT products in the triplet.
To eliminate systematic differences in multiple SIT anomaly datasets (Draper et al., 2013), this section uses recalibrated error variance to estimate the merging weights of SIT anomalies. For recalibration, an arbitrary anomaly dataset is selected as the reference dataset. Here, anomaly dataset X is chosen, and the other two datasets are recalibrated to this reference product (Gruber et al., 2016), as calculated by:
where , , refer to the recalibrated SIT anomaly datasets; and are the multiplicative scaling parameters for Y and Z, respectively; denotes the covariance of the time series of anomaly datasets X and Y. The error variance of the recalibrated SIT anomaly datasets is calculated as follows:
where denotes the error variance of the recalibrated anomaly dataset , and indicates the time average. The fusion weights of SIT anomalies are determined by the error variances of the recalibrated SIT anomaly datasets (Dong et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2021), as follows:
The least squares-based fusion calculation formula for SIT anomaly datasets is:
The fused anomaly datasets is added to the climatological mean subtracted in (Equation 10) to obtain the multi-source fused SIT dataset.
4 Results analysis
4.1 TC premise test results and analysis
In this study, in-situ observation validation utilized ULS and OIB in-situ observation data as reference true value datasets. The SIT data from four different products were resampled to achieve spatial and temporal consistency with the in-situ data, facilitating product error correlation verification. Spatially, when the in-situ data was ULS, the product data were resampled to three fixed points (A, B, D). When the in-situ data was OIB, the product data and OIB data were both resampled to the EASE2 grid of NSIDC (Dong et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2023; Jinghui Jiang et al., 2023). Temporally, the ULS data covered the years 2010-2021, while the OIB data covered March to April of 2010-2019. For pseudo -truth validation, the product data were used as reference values. The temporal and spatial scales of other product data were matched using the resampling method to calculate the error covariance between pairs of product datasets, thereby verifying the correlation of product errors. This validation required traversing all product data and calculating all error covariance results, enabling correlation testing without true values and compensating for the limitations of correlation tests with limited in-situ observations. Initially, the reference data and product data were linearly fitted to obtain error sequences, and the covariance between product errors was calculated to verify error correlation between products. As an example of true value validation, the linear fitting results are shown in Figure 3.
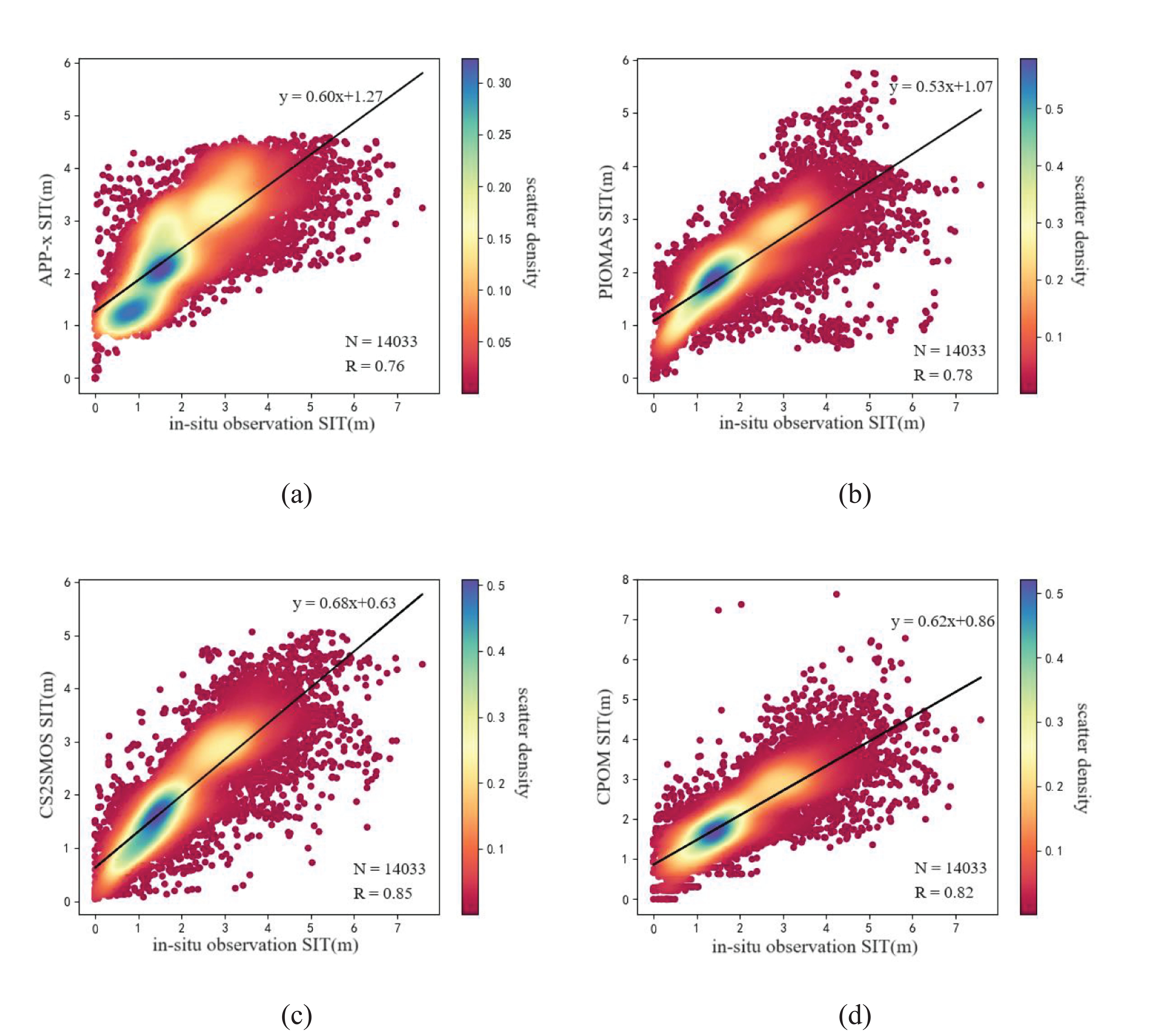
Figure 3. Linear regression results between the truth and product data (truth: ULS and OIB in-situ observations) (A) APP-x; (B) PIOMAS; (C) CS2SMOS; (D) CPOM.
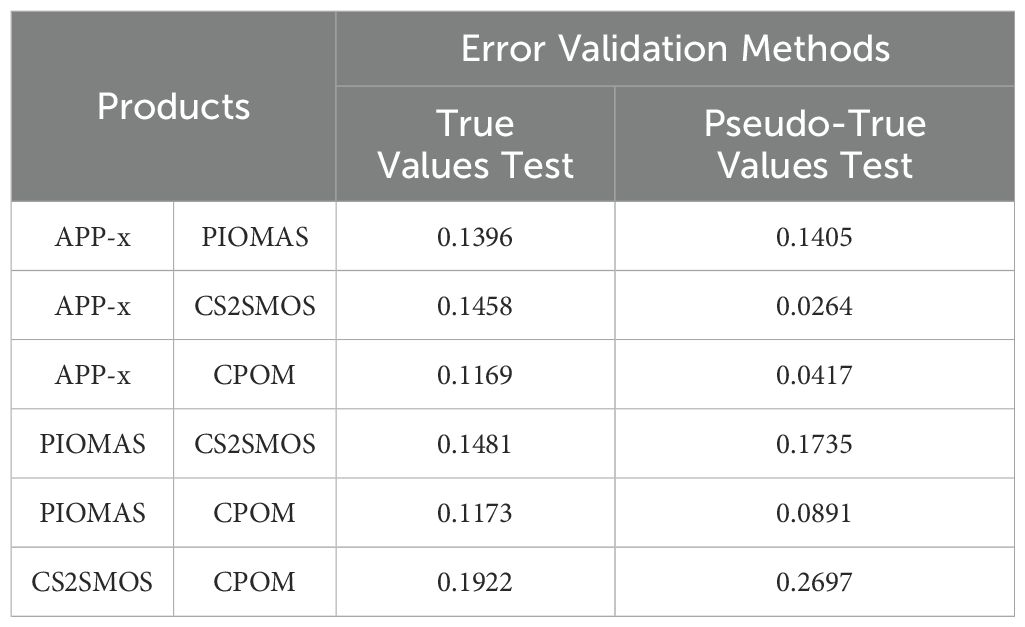
Based on the Mann-Whitney U test, all results indicated p < 0.001, demonstrating a significant relationship for the aforementioned linear fitting results. This confirms the linear relationship between the true values and the product data. Using the same method, the significance of the fit between the reference data from the pseudo-true value test method and the product data was tested, and all results showed p < 0.001, indicating a valid linear relationship. Consequently, the error after the product’s linear fitting was calculated, and the covariance of errors between each pair of product data was computed. For the pseudo-true value method, the covariance of errors for each pair of products was calculated twice and then averaged. The results of the true value and pseudo-true value tests are presented in Table 2.
The table indicates that when using the true value as a reference for linear fitting, the error covariances between the products are all below 0.2, except for the error covariance between CS2SMOS and CPOM. For all other data pairs, the error covariances are below 0.15. When using OIB and ULS as true values, the results of the correlation test for product errors fall within the acceptable range of the study. The results of the error correlation tests for the four types of products using both true and pseudo-true values are generally consistent. Compared to other product datasets, the error covariance between CS2SMOS and CPOM is relatively larger, likely due to different product members in the triplet. Therefore, in this section, two TC triplets were constructed: Triplet (A) consisting of APP-x, PIOMAS, and CS2SMOS; and Triplet (B) consisting of APP-x, PIOMAS, and CPOM. These triplets will be used for the evaluation and integration of multi-source SIT data products in the following sections.
4.2 Evaluation and analysis of sea ice thickness based on the TC algorithm with limited in-situ observations
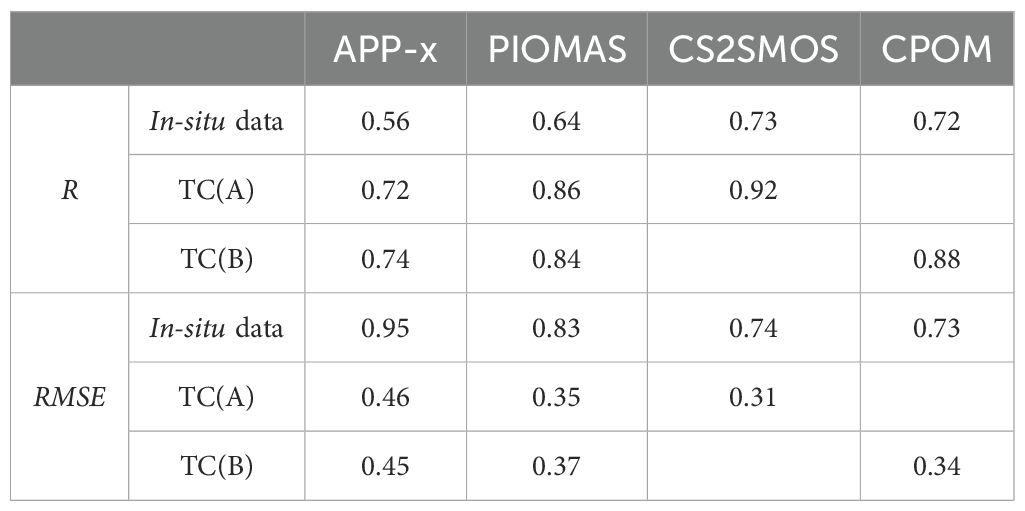
Using the TC algorithm to evaluate SIT data with limited in-situ observations, we validated the results by comparing them against in-situ data and product data using two indicators: correlation and root mean square error (RMSE). This approach tests the reliability of SIT data evaluations derived from the TC algorithm with limited in-situ observations. Initially, we conducted an assessment using OIB in-situ data and TC method product results, as presented in Table 3.
Table 3 presents the R and RMSE values for different SIT products, evaluated using two methods. The results indicate that, compared to evaluations based on in-situ datasets, the TC method generally yields higher correlation values with the true values. However, both methods consistently show that CS2SMOS has the highest correlation, followed by CPOM and PIOMAS, with APP-x having the lowest correlation. This suggests that while the TC method’s correlation values differ, the ranking of the correlations between different products is consistent with the evaluation based on in-situ datasets. The comparison of RMSE values calculated by both methods also reveals that APP-x has the highest RMSE, while CS2SMOS has the lowest. Additionally, the TC analysis results for the two triplets show that the R and RMSE values for the same product with the true values are similar across different triplets, indicating the robustness of the TC method. Although the TC method does not provide unique error results under different combination conditions, this does not affect the relative comparison between different products.
The ULS data, which is a long-term time series at fixed points, offers more accurate correlation evaluation results. By utilizing ULS in-situ datasets to assess the correlation of the TC fusion results, the findings are presented in Tables 4, 5.
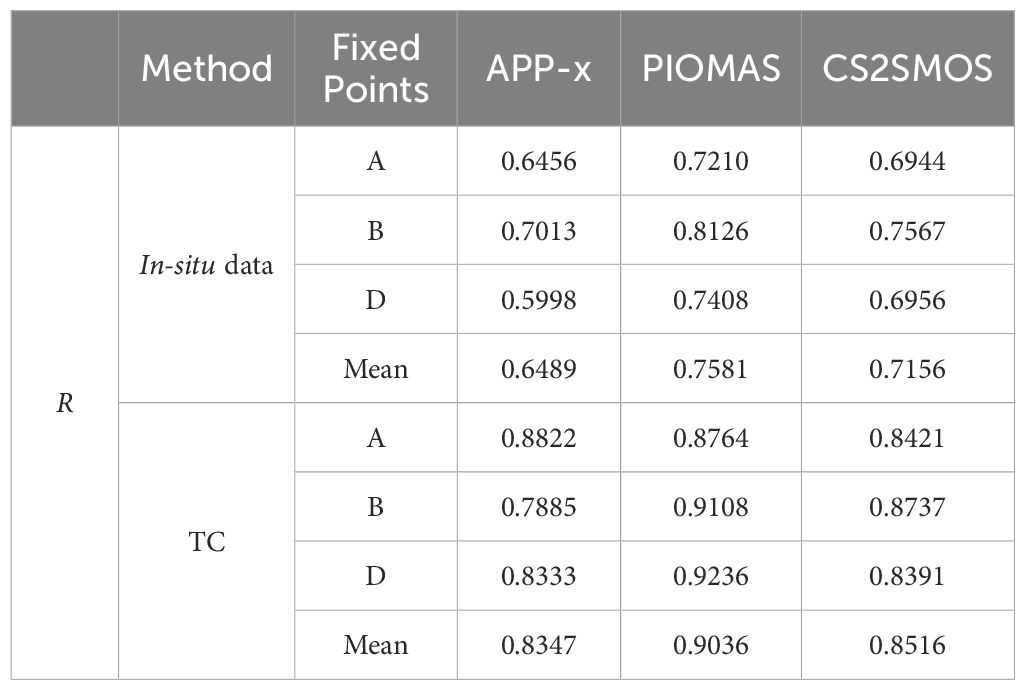
Table 4. Comparison of observed ULS data with evaluation product results from the TC method (Triplets A).
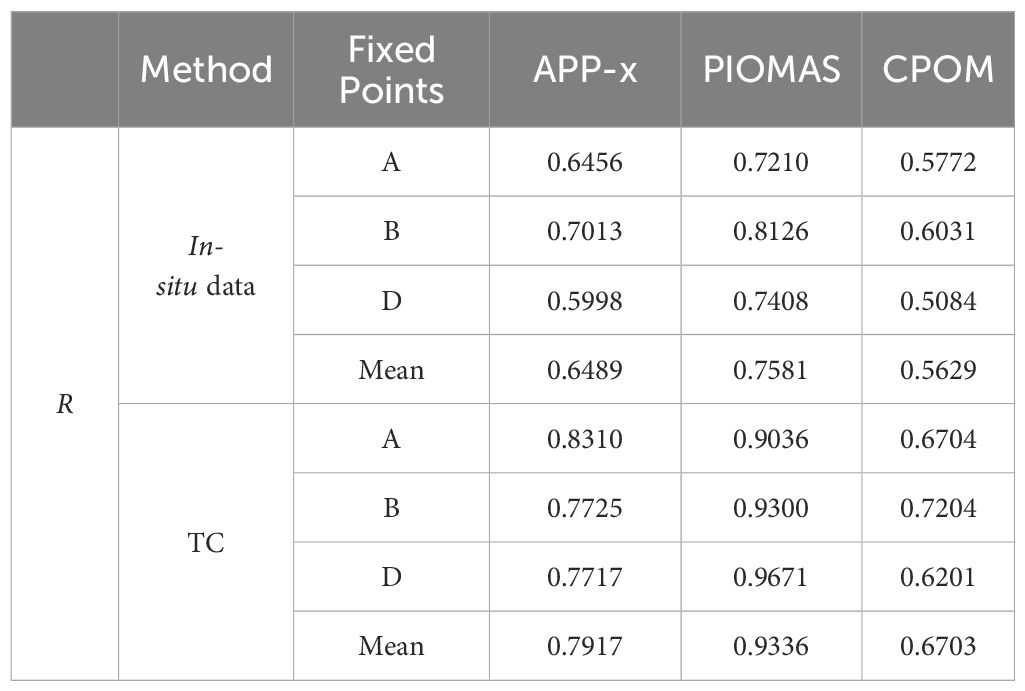
Table 5. Comparison of observed ULS data with evaluation product results from the TC method (Triplets B).
From Tables 4, 5, it can be observed that, compared to the evaluation based on the true values, the correlation results obtained by the TC method are generally higher. However, both methods indicate that PIOMAS has the highest correlation, followed by APP-x, with CPOM having the lowest correlation. This suggests that while the TC method yields different correlation values, the ranking of the correlations among different products remains consistent with the results of the evaluation based on actual measurements. It can also be found that the conclusions derived from comparing product evaluations with OIB as the in-situ observations to TC-based product correlations with limited in-situ observations still hold when using ULS as the in-situ observations for comparison. In summary, TC-based product evaluation with limited in-situ observations can effectively compare the relative quality of product data, providing a reliable reference for selecting appropriate product data in different scenarios.
4.3 Results and analysis of sea ice thickness data fusion
In this study, when fusing the triplet (A) TC, we selected the climatological and corresponding SIT anomaly datasets of each product in triplet (A) - APP-x, PIOMAS, and CS2SMOS. These datasets were combined to obtain three fused SIT datasets, referred to as Fused-A1, Fused-A2, and Fused-A3 in the subsequent discussion. Similarly, for the fusion of triplet (B) TC, we selected the climatological and corresponding SIT anomaly datasets of each product in triplet (B) - APP-x, PIOMAS, and CPOM. These datasets were combined to obtain three fused SIT datasets, referred to as Fused-B1, Fused-B2, and Fused-B3. The accuracy of the three parent products in triplet (A) - APP-x, PIOMAS, and CS2SMOS, along with the three fused products Fused-A1, Fused-A2, and Fused-A3, was assessed using R, RMSE, and mean absolute error (MAE) with respect to ULS observed data. The results are presented in Table 6. Similarly, accuracy evaluations for the parent and fused products in triplet (B) were conducted, with results shown in Table 7.
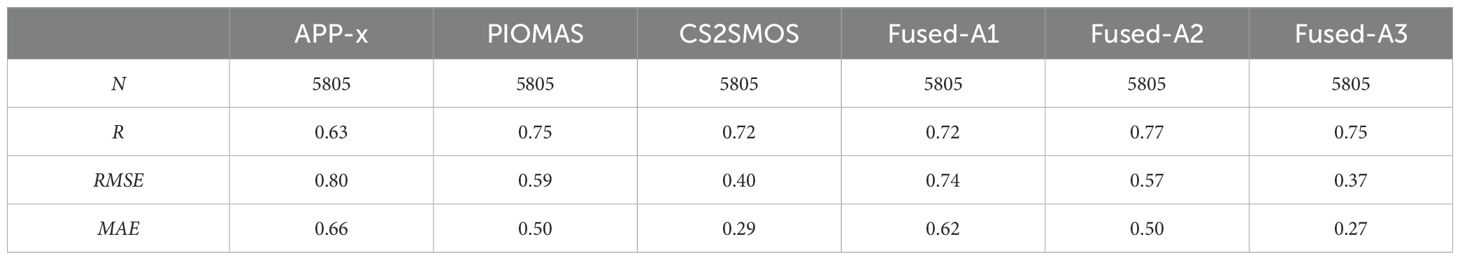
Table 6. Accuracy evaluation results of SIT parent products and fusion products for triplets (A) based on ULS.
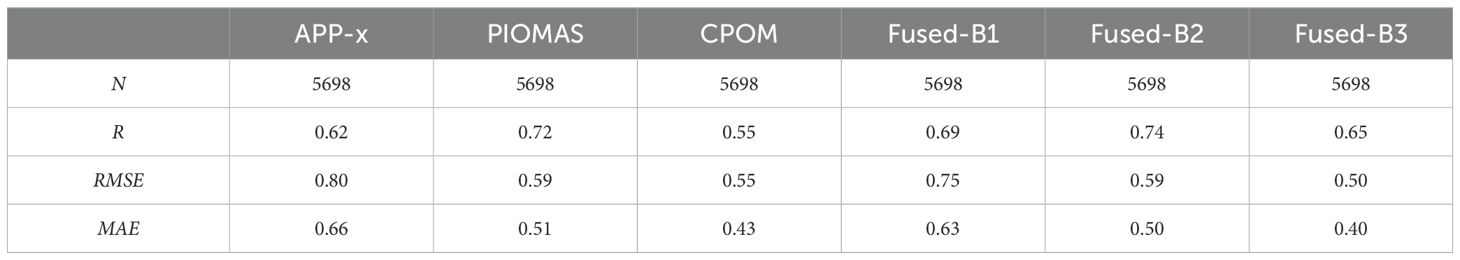
Table 7. Accuracy evaluation results of SIT parent products and fusion products for triplets (B) based on ULS.
Upon analyzing the table, we compare the climatology products with the corresponding fused products and find that the precision assessment results of the fused products are superior to those of the original climatology products. The precision assessment result of the fused product Fused-A3, derived from the CS2SMOS climatology data and triplet (A) anomaly fusion, is superior to the original CS2SMOS product. Comparing the fusion results with the product data reveals that the fusion results have achieved precision improvements over their corresponding climatology mean products. Among triplet (A), the fusion result Fused-A3 based on CS2SMOS climatology data exhibits the highest precision. In triplet (B), the fusion results Fused-B2 and Fused-B3, based on PIOMAS and CPOM respectively, demonstrate higher precision compared to the fusion product Fused-B1 based on APP-x climatology data. The evaluation results of the merged product based on OIB observations are consistent with those based on ULS observations.
In terms of spatial distribution, all OIB data from 2012 to 2019 were temporally and spatially matched with the fused products. Subsequently, the spatial distribution map of the differences between the observed OIB data and the fused products was plotted, as shown in Figure 4.
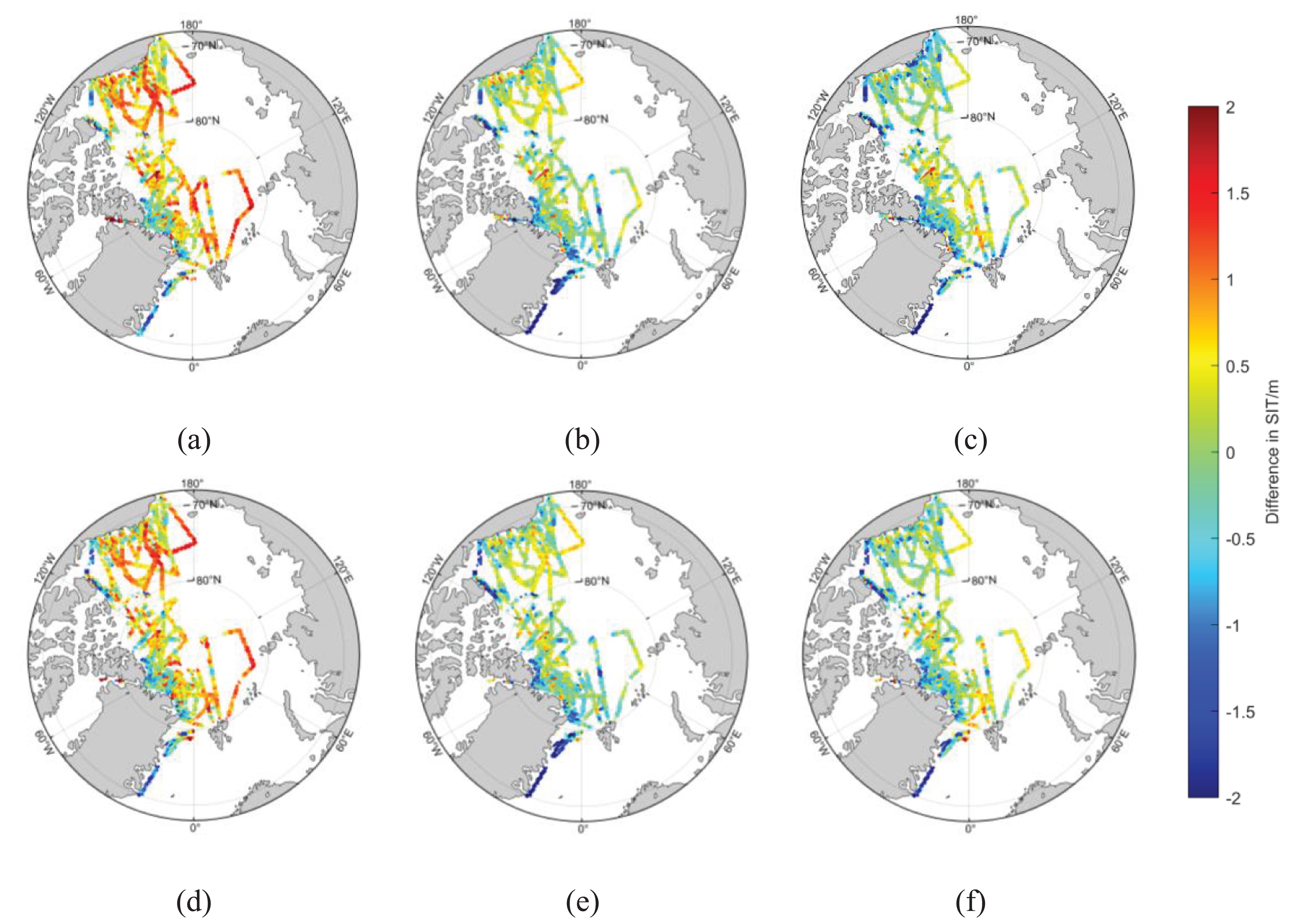
Figure 4. Spatial Differences Between OIB and SIT Fusion Products from 2012 to 2019 (A) Fused-A1, (B) Fused-A2, (C) Fused-A3, (D) Fused-B1, (E) Fused-B2, (F) Fused-B3.
Figure 4 illustrates that within the Triplet (A) fusion results, Fused-A1 exhibits the largest discrepancies compared to the in-situ data among the various fusion products. In the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas, Fused-A3 shows smaller discrepancies relative to Fused-A2 when compared to the in-situ data. In other regions, the discrepancy results of Fused-A3 and Fused-A2 are close to the in-situ data.
For the Triplet (B) fusion results, Fused-B1 demonstrates the largest discrepancies relative to the in-situ data compared to other fusion products. In the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas, Fused-B3 presents smaller discrepancies compared to Fused-B2 when compared to the in-situ data. In the central Arctic region, Fused-B2 shows smaller discrepancies than Fused-B3 compared to the in-situ data. In other regions, the discrepancy results of Fused-A3 and Fused-A2 are similar to the in-situ data.
In summary, the TC algorithm enhances the accuracy of the original climate-related products. The highest accuracy fusion product shows an improvement in precision over all parent products. Selecting high-quality parent products before performing data fusion with the TC algorithm is crucial for achieving high-accuracy fusion products.
5 Discussion
The integration of product thickness data affects not only the precision of the product itself but also the spatial resolution. In this study, the spatial resolution of the CPOM SIT product data in the determined triplet (B) is 5 km. Therefore, the spatial resolution analysis will be exemplified using the integration results of triplet (B). Firstly, the APP-x and PIOMAS SIT product data in the TC triplet (B) are resampled onto the CPOM product grid. The resampled SIT data from the three sources are then integrated to form TC, and the effective spatial resolution of the integrated product is measured using the wavenumber spectrum method. Given that the precision of the integrated product Fused-B1, based on APP-x climatological data, is lower than that of Fused-B2 and Fused-B3, and considering that Fused-B3 is based on CPOM climatological data where the daily data is generated by replicating monthly data, this study opts for Fused-B2, which is based on PIOMAS climatological data. The effective spatial resolution of Fused-B2 will be discussed using the wavenumber spectrum method.
A wavenumber spectrum is a power spectrum plotted with wavenumber on the horizontal axis. The simplest and most intuitive wavenumber spectrum represents the wavenumber and spectral energy (i.e., the square of the amplitude in Fourier space) obtained via Fourier transform. Previous studies have computed meridional, zonal, and isotropic spectra based on this principle. In this section, the meridional spectrum is calculated by obtaining the wavenumber spectrum from the sequence data along each longitude line in the region and then averaging them (Wang et al., 2019). Following the methods used in previous studies to calculate wavenumber spectra for other oceanic parameters, the sequence data is first detrended, and a Blackman-Harris window is applied to prevent spectral energy leakage. The Burg method (MATLAB built-in function) is then used to estimate the wavenumber spectrum (Nardelli et al., 2016). Using November 21, 2017, as an example, the meridional spectra for CPOM, PIOMAS, and the integrated product Fused-B2 are computed for a sea area with complete SIT data and within the latitude range [78°N-80°N, 343°E-355°E]. The results are shown in Figure 5.
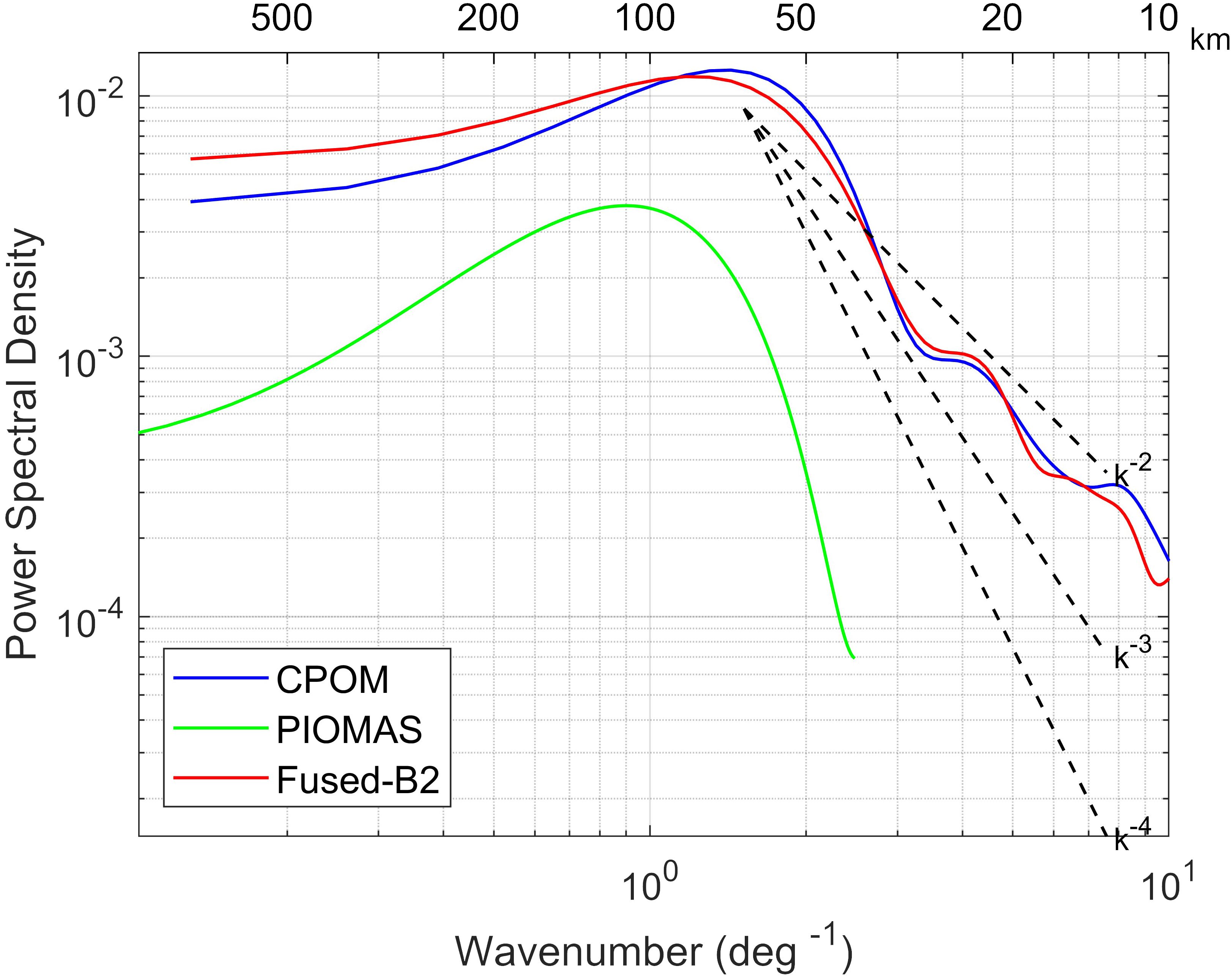
Figure 5. Zonal Wavenumber Spectra of Three SIT Products within [78°N-80°N, 343°E-355°E] on November 21, 2017.
The CPOM dataset, characterized by a spatial resolution of 5 km, demonstrates energy attenuation patterns consistent with the Fused-B2 fusion product. Previous research indicates that the ideal spectral slope derived from quasi-geostrophic turbulence theory is approximately -2, and the wavenumber spectral slope for passive tracers moving along isopycnal lines is also around -2 (Callies and Ferrari, 2013). Despite sea ice not being a strict passive tracer, its thickness is closely linked to seawater temperature and salinity, with corresponding spectral slopes reported to fall between -3 and -2 (Castro et al., 2017; Yi and Wang, 2024). Consequently, this study contends that a plausible spectral slope for SIT should also be within the -3 to -2 range. Considering the Nyquist folding frequency, both the Fused-B2 fusion product and CPOM achieve a spatial resolution of 5 km, while PIOMAS is incapable of resolving mesoscale variations below 25 km.
6 Conclusion
For the first time, this study establishes a comprehensive system for the evaluation and fusion of SIT data in scenarios with limited in-situ observations. The TC algorithm is incorporated into the processing of four types of SIT products: CS2SMOS, APP-x, PIOMAS, and CPOM. This approach allows for the assessment of uncertainties in SIT data and achieves quality evaluation and data fusion with limited in-situ observations. This study combines true value testing and pseudo-true value testing to verify the prerequisites for applying the TC algorithm, selecting product data triplets suitable for TC fusion. Based on the characteristics of the TC algorithm, a large-scale, long-term product data ranking was achieved without in-situ observations. The results indicate that the CS2SMOS product data exhibit the highest quality among the four types of product data used in this study. Anomalous time series were extracted from the product data, and data fusion was performed using the TC algorithm. The experiments demonstrated that the fusion results showed improved accuracy compared to the original climatological product data. The optimal fusion data results, Fused-A3 and Fused-B2, exhibited superior accuracy compared to all parent product data.
In addition to evaluating the accuracy of the fusion results, this study also investigates the spatial resolution of the fusion results. Taking the triplet (B), which includes the CPOM product with a spatial resolution of 5 km, and its fusion product Fused-B2 as examples, the effective spatial resolution was discussed using wavenumber spectrum analysis results. The findings reveal that the effective spatial resolution of the fusion product can reach 5 km. Compared to the parent product CPOM, the temporal resolution is improved; compared to the parent products APP-x and PIOMAS, the spatial resolution is enhanced. This addresses the limitation where satellite observations cannot simultaneously achieve high temporal resolution, spatial resolution, and spatial coverage in SIT products.
Future research will focus on the following areas: deepening error analysis by conducting more thorough quantitative analyses of the errors in different types of remote sensing data and clarifying their spatiotemporal distribution characteristics. Optimizing fusion algorithms by integrating machine learning or deep learning techniques to further improve the spatiotemporal resolution and accuracy of the fused data. Enhancing application validation by applying the fused SIT data to practical scenarios such as Arctic navigation planning and natural resource development to verify their effectiveness and utility.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
TL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BW: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. KL: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RS: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by XC, grant number “No. 62073332”, and the APC was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alexandrov V., Sandven S., Wahlin J., Johannessen O. M. (2010). The relation between sea ice thickness and freeboard in the Arctic. Cryosphere 4, 373–380. doi: 10.5194/tc-4-373-2010
Callies J., Ferrari R. (2013). Interpreting energy and tracer spectra of upper-ocean turbulence in the submesoscale range (1–200 km). J. Phys. Oceanography 43, 2456–2474. doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-13-063.1
Castro S. L., Emery W. J., Wick G. A., Tandy W. (2017). Submesoscale sea surface temperature variability from UAV and satellite measurements. Remote Sens. 9, 1089–1108. doi: 10.3390/rs9111089
Chen F., Crow W. T., Ciabatta L., Filippucci P., Panegrossi G., Marra A. C., et al. (2021a). Enhanced large-scale validation of satellite-based land rainfall products. J. Hydrometeorology 22, 245–257. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-20-0056.1
Chen F., Crow W. T., Colliander A., Cosh M. H., Jackson T. J., Bindlish R., et al. (2017). Application of triple collocation in ground-based validation of soil moisture active/passive (SMAP) level 2 data products. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 10, 489–502. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2569998
Chen J.-L., Kang S.-C., Guo J.-M., Xu M., Zhang Z.-M. (2021b). Variation of sea ice and perspectives of the Northwest Passage in the Arctic Ocean. Adv. Climate Change Res. 12, 447–455. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2021.02.002
Dong J., Lei F., Wei L. (2020). Triple collocation based multi-source precipitation merging. Front. Water 2, 1041–1066. doi: 10.3389/frwa.2020.00001
Dong Z., Shi L., Lin M., Zeng T. (2022). A suitable retrieval algorithm of arctic snow depths with AMSR-2 and its application to sea ice thicknesses of cryosat-2 data. Remote Sens. 14. doi: 10.3390/rs14041041
Dorigo W. A., Scipal K., Parinussa R. M., Liu Y. Y., Wagner W., de Jeu R. A. M., et al. (2010). Error characterisation of global active and passive microwave soil moisture datasets. Hydrology Earth System Sci. 14, 2605–2616. doi: 10.5194/hess-14-2605-2010
Draper C., Reichle R., Jeu R., Naeimi V., Parinussa R., Wagner W. (2013). Estimating root mean square errors in remotely sensed soil moisture over continental scale domains. Remote Sens. Environ. 137, 288–298. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.06.013
Feng X., Zhang S., Li J., Geng T., Xuan Y., Li F. (2021). Arctic sea ice thickness variations from CryoSat-2 satellite altimetry data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 64, 7011–7029. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9777-9
Giles K. A., Laxon S. W., Wingham D. J., Wallis D., Krabill W. B., Leuschen C., et al. (2007). Combined airborne laser and radar altimeter measurements over the Fram Strait in May 2002. Remote Sens. Environ. 111, 182–194. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.02.037
Gregory W., Lawrence I. R., Tsamados M. (2021). A Bayesian approach towards daily pan-Arctic sea ice freeboard estimates from combined CryoSat-2 and Sentinel-3 satellite observations. Cryosphere 15, 2857–2871. doi: 10.5194/tc-15-2857-2021
Gruber A., Dorigo W. A., Crow W., Wagner W. (2017). Triple collocation-based merging of satellite soil moisture retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55, 6780–6792. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2734070
Gruber A., Su C.-H., Zwieback S., Crow W., Dorigo W., Wagner W. (2016). Recent advances in (soil moisture) triple collocation analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 45, 200–211. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2015.09.002
Hendricks S., Ricker R., Helm V. (2016). User guide – AWI cryoSat-2 sea ice thickness data product (v1.2). (AWI Organization). Available at: http://epic.awi.de/41242/.
Jiang M., Zhong W., Xu K., Jia Y. (2023). Estimation of arctic sea ice thickness from chinese HY-2B radar altimetry data. Remote Sens. 15, 1180–1206. doi: 10.3390/rs15051180
Jinghui Jiang Q. S., Liu S., Wan J. (2023). Estimation of Arctic sea ice thickness from CryoSat-2 altimetry data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 44, 2145–2167. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2023.2195575
Johannessen O., Bobylev L., Shalina E., Sandven S. (2020). Sea ice in the arctic past, present and future: past, present and future. (Berlin, Germany: Springer). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-21301-5
Kaleschke L., Tian-Kunze X., Maaß N., Ricker R., Hendricks S., Drusch M. (2015). “Improved retrieval of sea ice thickness from SMOS and CryoSat-2,” in 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. (IGARSS), 5232–5235. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7327014
Key J., Wang X., Liu Y., Dworak R., Letterly A. (2016). The AVHRR polar pathfinder climate data records. Remote Sens. 8, 167–186. doi: 10.3390/rs8030167
Kim J.-M., Sohn B.-J., Lee S.-M., Tonboe R. T., Kang E.-J., Kim H.-C. (2020). Differences between ICESat and cryoSat-2 sea ice thicknesses over the arctic: consequences for analyzing the ice volume trend. J. Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 125, e2020JD033103. doi: 10.1029/2020JD033103
Koster R. D., Liu Q., Reichle R. H., Huffman G. J. (2021). Improved estimates of pentad precipitation through the merging of independent precipitation data sets. Water Resour. Res. 57, e2021WR030330. doi: 10.1029/2021WR030330
Krishfield R. A., Proshutinsky A. (2006). BGOS ULS data processing procedure. Available online at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:130370100 (Accessed April 30, 2024).
Kwok R., Cunningham G. F. (2015). Variability of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume from CryoSat-2. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A: Mathematical Phys. Eng. Sci. 373, 20140157. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0157
Laxon S. W., Giles K. A., Ridout A. L., Wingham D. J., Willatt R., Cullen R., et al. (2013). CryoSat-2 estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume. Geophysical Res. Lett. 40, 732–737. doi: 10.1002/grl.50193
Liu Y. Y., Dorigo W. A., Parinussa R. M., de Jeu R. A. M., Wagner W., McCabe M. F., et al. (2012). Trend-preserving blending of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 123, 280–297. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.03.014
McColl K. A., Vogelzang J., Konings A. G., Entekhabi D., Piles M., Stoffelen A. (2014). Extended triple collocation: Estimating errors and correlation coefficients with respect to an unknown target. Geophysical Res. Lett. 41, 6229–6236. doi: 10.1002/2014GL061322
Melling H., Johnston P. H., Riedel D. A. (1995). Measurements of the underside topography of sea ice by moored subsea sonar. J. Atmospheric Oceanic Technol. 12, 589–602. doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(1995)012<0589:MOTUTO>2.0.CO;2
Mu L., Losch M., Yang Q., Ricker R., Losa S. N., Nerger L. (2018). Arctic-wide sea ice thickness estimates from combining satellite remote sensing data and a dynamic ice-ocean model with data assimilation during the cryoSat-2 period. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans 123, 7763–7780. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014316
Nardelli B. B., Droghei R., Santoleri R. (2016). Multi-dimensional interpolation of SMOS sea surface salinity with surface temperature and in situ salinity data. Remote Sens. Environ. 180, 392–402. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.052
Nguyen A. T., Menemenlis D., Kwok R. (2011). Arctic ice-ocean simulation with optimized model parameters: Approach and assessment. J. Geophysical Res. 116, 25–43. Available at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:129842766.
Peng J., Tanguy M., Robinson E. L., Pinnington E., Evans J., Ellis R., et al. (2021). Estimation and evaluation of high-resolution soil moisture from merged model and Earth observation data in the Great Britain. Remote Sens. Environ. 264, 112610. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112610
Qiao D., Li Z., Zeng J., Liang S., McColl K. A., Bi H., et al. (2022). Uncertainty characterization of ground-based, satellite, and reanalysis snow depth products using extended triple collocation. Water Resour. Res. 58, e2021WR030895. doi: 10.1029/2021WR030895
Ricker R., Hendricks S., Helm V., Skourup H., Davidson M. (2014). Sensitivity of CryoSat-2 Arctic sea-ice freeboard and thickness on radar-waveform interpretation. Cryosphere 8, 1607–1622. doi: 10.5194/tc-8-1607-2014
Ricker R., Hendricks S., Kaleschke L., Tian-Kunze X., King J., Haas C. (2017). A weekly Arctic sea-ice thickness data record from merged CryoSat-2 and SMOS satellite data. Cryosphere 11, 1607–1623. doi: 10.5194/tc-11-1607-2017
Sallila H., Farrell S. L., McCurry J., Rinne E. (2019). Assessment of contemporary satellite sea ice thickness products for Arctic sea ice. Cryosphere 13, 1187–1213. doi: 10.5194/tc-13-1187-2019
Spreen G., de Steur L., Divine D., Gerland S., Hansen E., Kwok R. (2020). Arctic sea ice volume export through fram strait from 1992 to 2014. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans 125, e2019JC016039. doi: 10.1029/2019JC016039
Stoffelen A. (1998). Toward the true near-surface wind speed: Error modeling and calibration using triple collocation. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans 103, 7755–7766. doi: 10.1029/97JC03180
Stroeve J., Notz D. (2015). Insights on past and future sea-ice evolution from combining observations and models. Global Planetary Change 135, 119–132. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.10.011
Theocharis D., Rodrigues V. S., Pettit S., Haider J. (2019). Feasibility of the Northern Sea Route: The role of distance, fuel prices, ice breaking fees and ship size for the product tanker market. Transportation Res. Part E: Logistics Transportation Rev. 129, 111–135. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2019.07.003
Tian-Kunze X., Kaleschke L., Maaß N., Mäkynen M., Serra N., Drusch M., et al. (2014). SMOS-derived thin sea ice thickness: algorithm baseline, product specifications and initial verification. Cryosphere 8, 997–1018. doi: 10.5194/tc-8-997-2014
Walsh J. E. (1983). The role of sea ice in climatic variability: Theories and evidence 1. Atmosphere-Ocean 21, 229–242. doi: 10.1080/07055900.1983.9649166
Wang K., Lavergne T., Dinessen F. (2020). Multi-sensor data merging of sea ice concentration andthickness. Adv. Polar Sci. 31 (1), 1–13.
Wang S., Qiao F.-L., Dai D., Zhou X. (2019). Anisotropy of the sea surface height wavenumber spectrum from altimeter observations. Sci. Rep. 9, 15896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52328-w
Wang Y., Liu K., Zhang R., Qian L., Shan Y. (2021). Feasibility of the Northeast Passage: The role of vessel speed, route planning, and icebreaking assistance determined by sea-ice conditions for the container shipping market during 2020–2030. Transportation Res. Part E: Logistics Transportation Rev. 149, 102235. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2021.102235
Wang Y., Zhang R., Liu K., Fu D., Zhu Y. (2023). Framework for economic potential analysis of marine transportation: A case study for route choice between the suez canal route and the northern sea route. Transportation Res. Rec. 2677, 1–16. doi: 10.1177/03611981221144286
Warren S. G., Rigor I., Untersteiner N., Radionov V. F., Bryazgin N. N., Aleksandrov Y. I., et al. (1999). Snow depth on arctic sea ice. J. Climate 12, 1814–1829. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<1814:sdoasi>2.0.co;2
Yi D. L., Wang P. (2024). Global wavenumber spectra of sea surface salinity in the mesoscale range using satellite observations. Remote Sens. 16, 1753–1765. doi: 10.3390/rs16101753
Yilmaz M., Crow W. (2014). Evaluation of assumptions in soil moisture triple collocation analysis. J. Hydrometeorology 15, 1293–1302. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-13-0158.1
Yilmaz M. T., Crow W. T., Anderson M. C., Hain C. (2012). An objective methodology for merging satellite- and model-based soil moisture products. Water Resour. Res. 48, 11502–11547. doi: 10.1029/2011WR011682
Zhang J., Rothrock D. A. (2003). Modeling global sea ice with a thickness and enthalpy distribution model in generalized curvilinear coordinates. Monthly Weather Rev. 131, 845–861. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2003)131<0845:MGSIWA>2.0.CO;2
Zheng F., Sun Y., Yang Q., Longjiang M. U. (2021). Evaluation of arctic sea-ice cover and thickness simulated by MITgcm. Adv. In Atmospheric Sci. 38, 20. doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-9223-6
Keywords: sea ice thickness, limited in-situ observations, triple collocation, multi-source data evaluation, multi-source data fusion
Citation: Li T, Wang Y, Wang B, Liu K, Chen X and Sun R (2024) Evaluation and fusion of multi-source sea ice thickness products with limited in-situ observations. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1464391. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1464391
Received: 14 July 2024; Accepted: 02 October 2024;
Published: 25 October 2024.
Edited by:
Sabrina Speich, École Normale Supérieure, FranceReviewed by:
Mukesh Gupta, Université du Québec à Rimouski, CanadaRichard Arthur Allard, Naval Research Laboratory, United States
Lujun Zhang, Nanjing University, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Wang, Wang, Liu, Chen and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yangjun Wang, d2FuZ3lhbmdqdW4xOEBudWR0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Tongtong Li
Tongtong Li Yangjun Wang
Yangjun Wang Bin Wang1
Bin Wang1 Rui Sun
Rui Sun