
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci. , 30 October 2024
Sec. Marine Biogeochemistry
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1462522
This article is part of the Research Topic The Biological Pump: A Hunt For Microbial Key Players Involved in Ocean Carbon and Nutrient Fluxes View all 4 articles
Extracellular polymeric substances, such as transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) composed of acidic polysaccharides, are important particulate organic carbon (POC) components of marine environments that affect particle dynamics and ocean carbon export. However, how polymeric substances interact with and shape bacterial communities associated with marine particles is poorly understood. This study investigated whether the composition of particle-associated bacterial communities differs between sinking and suspended particles, which differ in their polymeric substance contents, in the upper water column of the subtropical, oligotrophic Kuroshio region. Bacterial taxa likely involved in polymer degradation (Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Bacteroidia) were enriched on sinking particles with a lower TEP: POC ratio, indicating that bacterial degradation of polymeric substances promotes particle sinking by removing positively buoyant polymers. By contrast, suspended particles were increasingly enriched for Bdellovibrionota and Desulfobacterota as the TEP: POC ratio increased. These taxa, which include predatory microbes, seem to prefer polymer-rich environments with a high density of potential prey. Planctomycetota were not significantly related to the TEP: POC ratio, indicating their broad niche breadth on particles’ polymeric substance contents. The results suggest that the bacterial niche differentiation associated with the particle polymeric-substance gradient shapes bacterial communities in a subtropical ocean.
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), excreted by phytoplankton and bacteria, abiotically assemble to form stable gel particles that are part of the particulate organic carbon (POC) pool in the oceans (Verdugo et al., 2004; Verdugo, 2012). Gel particle formation links the dissolved and particulate phases of the organic matter and leads to a size continuum of particles in the oceans (Verdugo et al., 2004; Verdugo, 2012). Marine gel particles include transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) consisting of acidic polysaccharides (Passow and Alldredge, 1994) and proteinaceous Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stainable particles (CSP; [Long and Azam, 1996]), which are thought to have different origins and fates (Cisternas-Novoa et al., 2015; Zamanillo et al., 2021). Previous studies have found that TEP influences carbon export through the regulation of particles’ stickiness and buoyancy, thereby affecting the partitioning between suspended and sinking particles in the water column (Mari et al., 2017; Romanelli et al., 2023; Yamada et al., 2024). Little is known about the role of CSP in particle property regulations (Thornton, 2018); however, a recent study has suggested an involvement of CSP in the aggregation of virus-infected diatom cells (Yamada et al., 2018).
Previous studies have found that gel particles are hotspots of bacterial activity (Busch et al., 2017; Grossart et al., 2006). Although particle-associated bacteria typically account for only approximately 1% of the total bacterial abundance in the open ocean, as enumerated by epifluorescence microscopy (Nagata, 2008), they are important for particulate organic matter degradation. They produce various extracellular hydrolytic enzymes that cleave EPS, altering the physicochemical properties of particles and contributing to particle remineralization (Giljan et al., 2022; Grossart et al., 2006; Smith et al., 1992; Wang et al., 2024). Bacterial production and processing of EPS regulate the oceanic biological carbon pump (Nagata et al., 2021; Quigg et al., 2021), mediating carbon transfer from the sunlit layer to depths below the pycnocline (Boyd et al., 2019; Herndl and Reinthaler, 2013). Therefore, investigating bacterium–EPS interactions could enable a more accurate prediction of biological carbon pump variations (Mari et al., 2017; Nguyen et al., 2022; Yamada et al., 2024).
Particle-associated bacterial communities are typically enriched with polymer-degrading taxa, such as Bacteroidia, Gammaproteobacteria, and Planctomycetota (Boeuf et al., 2019; DeLong et al., 1993; Duret et al., 2019; Mestre et al., 2017), indicating that bacteria that are adapted to high-nutrient environments (copiotrophs) interact with EPS. These bacterial communities are distinct from free-living communities, which tend to be dominated by oligotrophic taxa, such as the alphaproteobacterial SAR11 clade (Giovannoni et al., 2014; Morris et al., 2012). The composition of particle-associated bacterial communities varies across particle types, distinguished by particle size (Mestre et al., 2017; Yung et al., 2016) and sinking velocity (sinking vs. suspended particles) (Duret et al., 2019). In the Scotia Sea, Duret et al. (2019) found that the class Gammaproteobacteria and order Rhodobacterales (class Alphaproteobacteria) were enriched on sinking particles, and order Flavobacteriales (class Bacteroidia) on suspended particles. They speculated that the lability of organic matter drove bacterial niche partitioning on particles; however, they did not investigate the organic constituents of sinking and suspended particles. Therefore, the factors responsible for the variability of the composition of particle-associated bacterial communities across particle types are unclear.
Here, the bacterial community compositions of sinking and suspended particles with concomitant measured amounts of EPS (TEP and CSP) relative to particulate organic carbon (POC) were examined. The aim was to evaluate the enrichment patterns of particle-associated bacterial community composition along the EPS gradient of sinking and suspended particles in an oligotrophic, subtropical ocean region. Samples were collected from the mixed layer and the bottom of the euphotic zone of the Kuroshio region, an oligotrophic, subtropical region of the western North Pacific Ocean. In this region, suspended particles tend to have higher TEP: POC and CSP: POC ratios than sinking particles (Yamada et al., 2024). The results suggested that the partitioning of sinking and suspended particles is involved in EPS self-assembly and gel particle aggregation (Verdugo et al., 2004; Verdugo, 2012) accompanied by the aggregation of various other particles, including microbes, organic detritus, mineral dust, and skeletons (Cruz and Neuer, 2019; Richardson and Jackson, 2007), and together with microbial production and the degradation of EPS (Yamada et al., 2024). However, the compositions of the bacterial communities on sinking and suspended particles in the Kuroshio region are unknown. Through differential abundance analysis with bias correction [ANCOM-BC; (Lin and Peddada, 2020)], the present study investigated bacterial taxa enrichment patterns across free-living, suspended particles, and sinking particle fractions. This enabled us to identify the bacterial taxa enriched in particular fractions and those present at equal abundances in multiple fractions. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed to assess the relationship of the particle-associated bacterial community composition with the EPS: POC ratio.
Sampling stations were deployed in the western North Pacific subtropical region (Supplementary Figure S1) during a cruise of R/V Hakuho-maru (KH-20-9) between 10 September and 5 October 2020. Oceanographic and chemical data collected during the cruise have been published elsewhere (Yamada et al., 2024) (Supplementary Table S1). This study uses the published data to interpret microbial community variation in a new context. Although Yamada et al. (2024) deployed thirteen stations during the cruise, this study examined only eight stations due to logistical constraints on microbial data collection.
At each station, the depth profiles of temperature, salinity, chlorophyll-a, and photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) were determined using a conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) system (SBE 911 Plus, Sea-Bird Electronics) equipped with sensors for chlorophyll fluorescence (Chlorophyll fluorometer, Seapoint Sensors Incs.) and PAR (PRR800/810; Biospherical Instruments Inc.).
Samples were collected at the mixed layer (ML; 10 or 40 m depending on the station) and the bottom of the euphotic zone (Z1%; the layer at which PAR is 1% of the sea-surface value) using marine snow catchers [MSCs; (Lampitt et al., 1993)]. The ML was sampled using a small MSC (sampling volume of 100 L; OSIL, Hampshire, UK), and the Z1% a large MSC (sampling volume of 300 L; OSIL, Hampshire, UK). The MSC was lowered to the target depth and closed using a drop-weight messenger. After recovery, the MSC was set on the deck to allow sinking particles to settle into polypropylene containers at the bottom of the MSC. After 2 h, seawater samples for the suspended particle fraction analysis were collected from a faucet in the top section of the MSC. Subsequently, the top section was detached from the bottom section of the MSC, and the bottom containers (containing the seawater sample) were removed for the sinking particle fraction analysis.
Seawater samples (2 L) for the suspended particle fraction analysis were sequentially filtered through 0.8- and 0.2-µm pore-size cellulose acetate filters (47 mm, Advantec Toyo Kaisha, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) under a gentle vacuum (< 150 mmHg). Microbes collected on the 0.8-µm pore-size filters were regarded as having been attached to suspended particles (SS fraction), whereas those collected on the 0.2-µm pore-size filters were regarded as free-living (FL fraction; > 0.2 - 0.8 µm). The samples collected from the bottom containers were filtered through 0.8-µm pore-size cellulose acetate filters; the microbes therein were regarded as having been attached to sinking particles (SK fraction). The filters for prokaryotic community analyses were stored at −80°C until DNA extraction in the onshore laboratory.
For the measurement of POC and particulate organic nitrogen (PON) concentrations, seawater samples (suspended particle: 6.6-18 liters; sinking particle: 0.12 liters) were filtered through pre-combusted (450°C for 4 h) glass fiber filters (GF/F, Whatman, Maidstone, Kent, UK). For the determination of TEP and CSP concentrations, seawater samples (12.5–300 mL) were filtered through 47-mm, 0.4-μm polycarbonate filters (Whatman) under a gentle vacuum (< 150 mmHg). Filters for the determination of TEP were stained with Alcian blue (8GX; Sigma-Aldrich; 0.02% w/v dissolved in 0.06% v/v acetic acid; 0.2-µm pre-filtered) (Passow and Alldredge, 1995), and those for the determination of CSP were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (G-250, SERVA electrophoresis; 0.04% dissolved in 0.2-µm prefiltered seawater; 0.2-µm pre-filtered) (Cisternas-Novoa et al., 2014). Blank filters were prepared by filtering 300 mL of surface seawater through 0.4-μm polycarbonate filters. Sample and blank filters were stored at −20°C until analysis in the onshore laboratory.
For the POC and PON measurements, the filters were fumed overnight with HCl to remove carbonates and dried at 60°C for 24 h. POC and PON concentrations were determined using an elemental analyzer (Carlo-Erba NA-1500, Fisons Instruments, Beverly, MA, USA). TEP and CSP concentrations were determined spectrophotometrically (Cisternas-Novoa et al., 2014; Passow and Alldredge, 1995). The dyes were extracted from filters with 80% sulfuric acid (2 h, room temperature) (TEP) or 50% isopropyl alcohol with 3% sodium dodecyl sulfate (2 h at ca. 37 °C) (CSP). The absorbances of the extracts were measured at 787 nm (TEP) or 615 nm (CSP) using a microplate reader (Multiskan GO; Thermo Scientific). After blank subtraction, TEP and CSP concentrations were determined using xanthan gum (for TEP) or bovine serum albumin (BSA; for CSP) as the standards. The coefficients of determination (R²) of these calibration lines were 0.975 and 0.986, respectively (Supplementary Figure S2). The TEP and CSP concentrations were expressed as micrograms of xanthan gum equivalent per liter (µg Xeq. L−1) and micrograms of BSA equivalent per liter (µg BSAeq. L−1), respectively. For the determination of chlorophyll-a concentrations, seawater samples were filtered through glass fiber filters (GF/F, Whatman, Maidstone, Kent, UK) and extracted with N,N-dimethylformamide. The concentration of chlorophyll-a in the extract was measured using a fluorometer (Welschmeyer, 1994). Concentrations of nutrients (nitrate and phosphate) were determined spectrophotometrically using an autoanalyzer (QuAAtro, Bran+Luebbe) according to Armstrong et al. (1967) (Armstrong et al., 1967). The detection limits of nitrate and phosphate were 0.05 and 0.01 μM, respectively.
Prokaryotic DNA collected on cellulose acetate filters was extracted using the DNeasy PowerSoil Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) (Hirai et al., 2017). The filters were cut into small pieces (< 5 mm2), placed in a 2-mL tube (DNA LoBind® Tubes, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), and lysed in 400 µL of FL Buffer (400 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 60 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, and 1% [wt/v] SDS) at 60°C for 10 min. Lysis was stopped by the addition of 120 µL of 3 M potassium acetate buffer (pH 4.8) and incubation on ice for 5 min. After centrifugation (16,000 x g at room temperature for 5 min), the supernatant was transferred to a 1.5-mL tube. This step was repeated twice. The supernatant was purified according to the DNeasy PowerSoil Kit protocol. First, the supernatant was mixed with a double volume of C4 solution and DNA was purified following the manufacturer’s manual. Then, 50 µL of DNA solution was stored in 1.5-mL tubes at −80°C until small subunit rRNA gene amplification.
Prokaryotic community composition was characterized based on the V4–V5 region of 16S rRNA gene fragments amplified using LA Taq polymerase (TAKARA Bio, Kusatsu, Japan) with the primers 530F and 907R (Supplementary Table S2) (Nunoura et al., 2012). The PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 96°C for 1 min, followed by 25–30 cycles of denaturation at 96°C for 25 s, annealing at 52°C for 4 s, and extension at 72°C for 1 min; and a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The Illumina adaptor sequence and Illumina Multiplexing PCR Primer 2.0 sequence were added to the 5′-ends of the primers. The amplicon libraries were mixed with Illumina PhiX Control ver. 3 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at a 1:1 ratio and sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq Reagent Kit ver. 3 (600 cycles) on the Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The sequence data is publicly available in the UTokyo Repository (https://doi.org/10.15083/0002010027).
Forward and reverse sequences were merged using PEAR ver. 0.9.8 (Zhang et al., 2014). The primer and adaptor sequences at the two ends of merged sequences were removed using Cutadapt ver. 3.4 (Martin, 2011) and sequence reads with a quality score < 30 were trimmed. After denoising and removing chimeras, the sequences were clustered into an amplicon sequence variant (ASV) with 99% sequence identity using the DADA2 plugin (Callahan et al., 2016) in QIIME 2 (Bolyen et al., 2019). A representative sequence of each ASV was classified using blastn and the SILVA 138 database (Yilmaz et al., 2014). Sequence read count data without reads classified as chloroplasts and eukaryotes were used in the statistical analyses.
The alpha diversity of bacterial communities was characterized using the Hill numbers as the effective number of species. Hill numbers of order q = 0, 1, and 2 were converted from the number of ASVs, and Shannon’s and Simpson’s indices (Chao et al., 2014). Shannon’s and Simpson’s indices were calculated from the sequence read count data rarefied according to the minimum library using the “diversity” function in R package “vegan” (Oksanen et al., 2022). To evaluate the effects of the sampling layer and fraction on the effective numbers of species, a two-way analysis of variance (two-way ANOVA) was performed using JMP Pro (MA, USA). To investigate the differences (beta-diversity) in bacterial community composition among the sampling layers, fractions, and water masses using standard distance-based statistical procedures and visualization, Permutational analysis of multivariate dispersion (PERMDISP) (Anderson, 2006) and Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) (Anderson, 2001) were performed on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix calculated from Hellinger-transformed data. The differences in bacterial community compositions based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix were visualized via non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS). PERMDISP and PERMANOVA were performed using the “betadisper” and “adonis2” functions in R package “vegan” (Oksanen et al., 2022). All analyses can be found at https://github.com/Akiko-Ebihara/EPS-PAbacteria2020.
To investigate the enrichment pattern of bacterial taxa in the three microhabitat fractions (SK, SS, and FL fractions), differential abundance analysis was performed using ANCOM-BC [(Lin and Peddada, 2020); https://github.com/FrederickHuangLin/ANCOM-BC] after prevalence filtering to remove ASVs that occurred in < 10% of the samples (Faust, 2021). A two-step procedure was used to divide bacterial ASVs into microhabitat categories based on their enrichment patterns (Figure 1). In the first step, the ASVs were divided into Category FL (ASVs more enriched in the FL than the particle [PA; including SK and SS] fractions), Category PA (ASVs more enriched in the PA than the FL fraction and present in > 10% of the samples of the PA fraction), and Category FL/PA (ASVs present in equal abundances in the PA and FL fractions). In the second step, the ASVs of Category PA were divided into Category SK (ASVs more enriched in the SK than the SS fraction), Category SS (ASVs more enriched in the SS than the SK fraction), and Category SK/SS (ASVs present in equal abundances in the SK and SS fractions). The significance of enrichment was evaluated by calculating the log fold change, based on the p-value adjusted for the false discovery rate using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure [false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05; FDR, adjusted p-value].
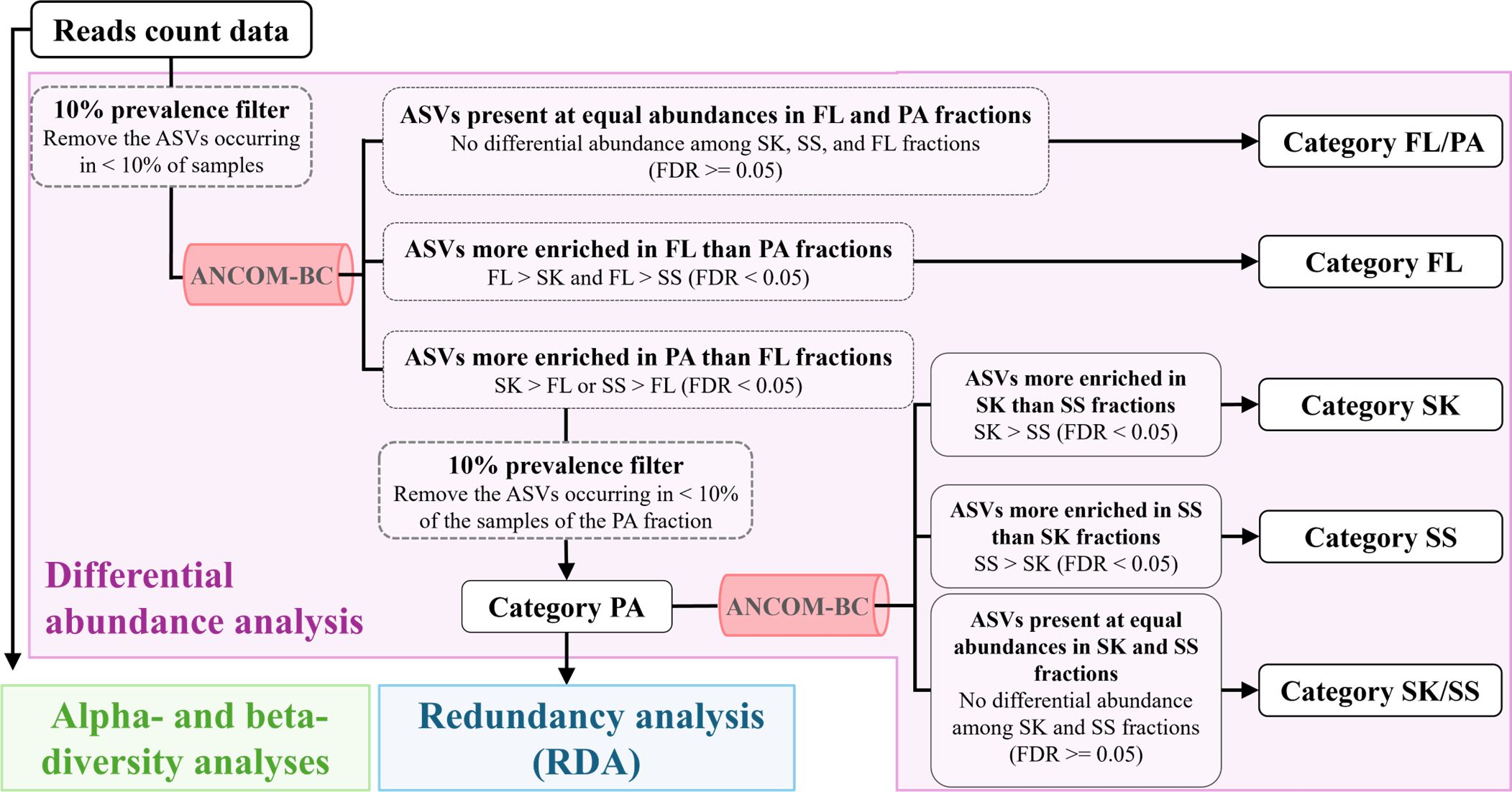
Figure 1. Division of amplicon sequence variants into microhabitat categories. Differential abundance analysis is shown in purple. FL, free-living fraction; PA, particle-associated fraction (including SK and SS); SK, sinking-particle fraction; SS, suspended-particle fraction.
To investigate the relationships among particle-associated bacterial community composition (Category PA), environmental variables, and particle biochemical properties, RDA combined with compositional data analysis was performed to circumvent the problem of spurious correlations resulting from a constant-sum constraint of the relative-abundance data (Gloor et al., 2017). Zeros in the relative-abundance data of the Category PA community in the SK and SS fractions were replaced by the multiplicative simple replacement algorithm, which preserves the relative multivariate structure of the data using the “multRep” function in R package “ZCompositions” (Palarea-Albaladejo and Martín-Fernández, 2015). Subsequently, the data were centered-log-ratio (CLR) transformed (Aitchison, 1983; Gloor et al., 2017) using the “clr” function in R package “compositions” (van den Boogaart and Tolosana-Delgado, 2008). The RDA was performed using “rda” functions in R package “vegan” (Oksanen et al., 2022) with the CLR-transformed Category PA data as a response variable and the environmental variables as the explanatory variables. The environmental variables were centered and standardized using the “decostand” function. Collinearity was avoided by removing a highly correlated explanatory variable (|r| > 0.8 and FDR < 0.05, where r is Pearson’s correlation coefficient and FDR is the p-value adjusted using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure). Important explanatory variables were selected using the “rda” and the “ordiR2step” functions in R package “vegan” (Oksanen et al., 2022). The distributions of ASVs and samples on the RDA ordinations were represented by type I-scaled RDA scores, which reflected their distances. The correlations of explanatory variables with the RDA axes were represented by correlation-scaled RDA scores (type II scaling). To examine differences in bacterial distribution across microhabitat categories along the RDA ordinations, t-tests were performed using JMP Pro (MA, USA). To investigate the distribution patterns of taxa along the RDA ordinations, the one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed using JMP Pro (MA, USA).
The sampling area was characterized by high temperature (26-29°C), low chlorophyll-a concentration (0.08-0.77 µg L-1), and low nutrient concentrations (nitrate concentration, < 0.02-0.81 µM) in the ML (Table 1; Supplementary Table S3). The ML and Z1% samples consisted of Kuroshio surface water and shelf water from the East China Sea, respectively (Supplementary Figure S3). The TEP: POC and CSP: POC ratios of the sinking particles in the ML were 0.68 ± 0.36 and 0.20 ± 0.09 (mean ± standard deviation), respectively (Table 2; Supplementary Table S4). These were approximately threefold lower than the corresponding ratios of the suspended particles (Table 2; Supplementary Table S4). The POC: PON ratio was lower in the suspended particles (mean ± standard deviation, 10.6 ± 1.9) than sinking particles (16.6 ± 9.2) (Table 2; Supplementary Table S4).
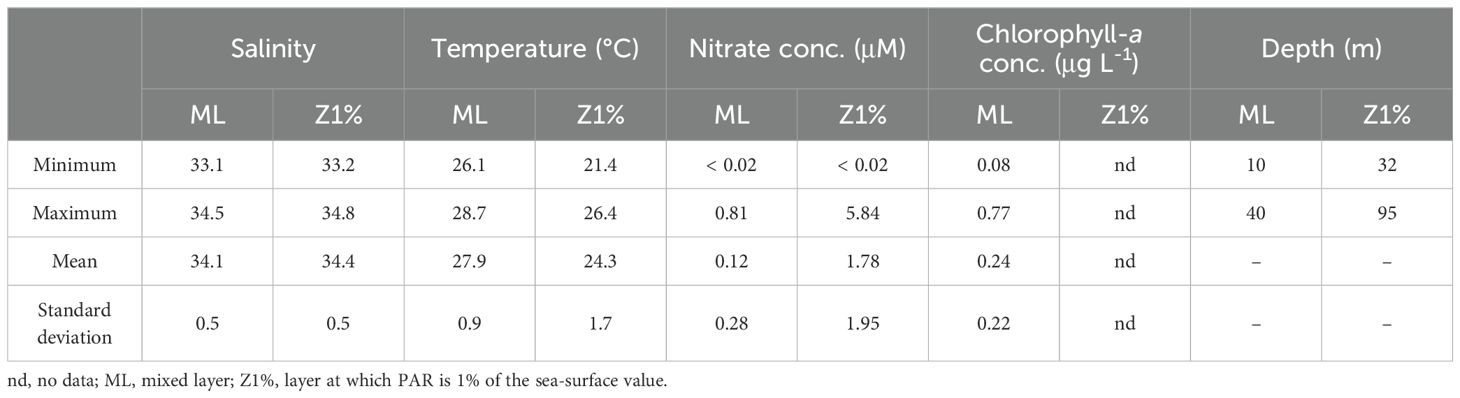
Table 1. Summary of environmental variables (salinity, temperature, nitrate and chlorophyll-a concentrations, and depth) for the data collected at the eight stations shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
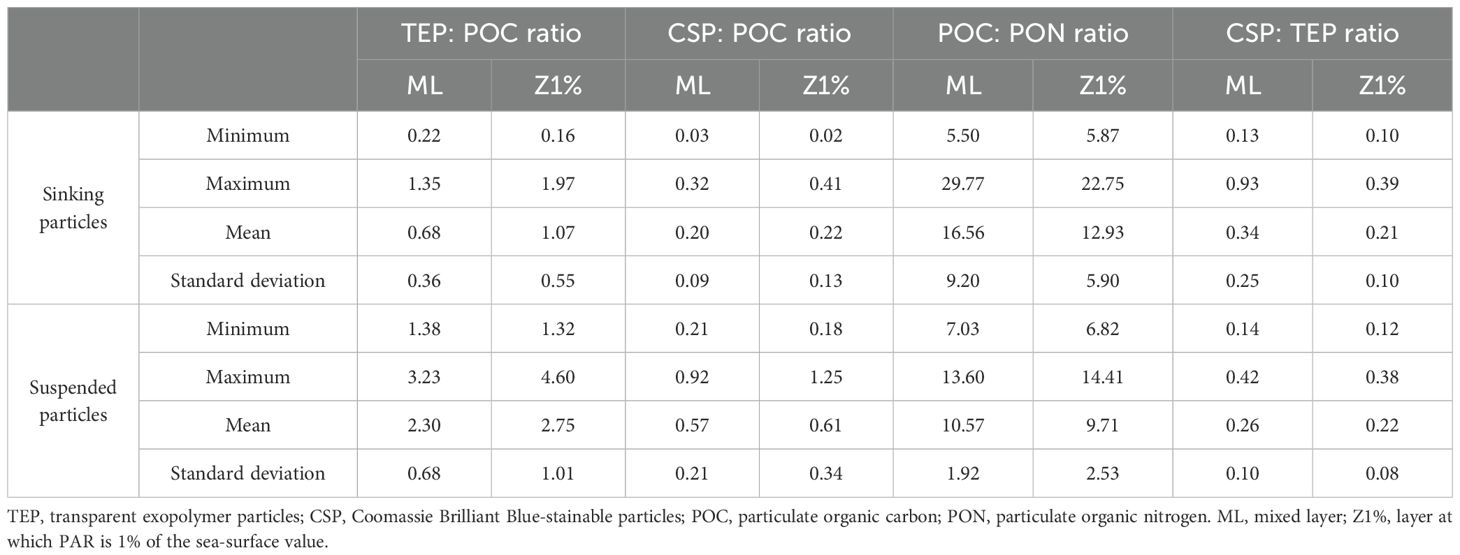
Table 2. Summary of particle property variables [the ratios of TEP: POC (μg Xeq.:μg C), CSP: POC (μg BSAeq.:μg C), POC: PON (mol:mol), and CSP: TEP (μg BSAeq. : μg Xeq.)] in suspended and sinking particles collected at the eight stations shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
Alphaproteobacteria and Cyanobacteria were the most abundant taxa, together accounting for 26.2–77.6% of the total reads irrespective of the fraction (Figure 2; Supplementary Table S5). Approximately half of alphaproteobacterial reads were affiliated with the SAR11 clade (Figure 2; Supplementary Table S5). Prochlorococcus accounted for most of the Cyanobacteria (Supplementary Table S6). Other abundant taxa (mean relative abundance > 5% in at least one of the three fractions) were Gammaproteobacteria, Bacteroidia, and Planctomycetota (Figure 2; Supplementary Table S5). These taxa tended to be more abundant in the particle (SK and SS) fractions than in the FL fraction (Figure 2).
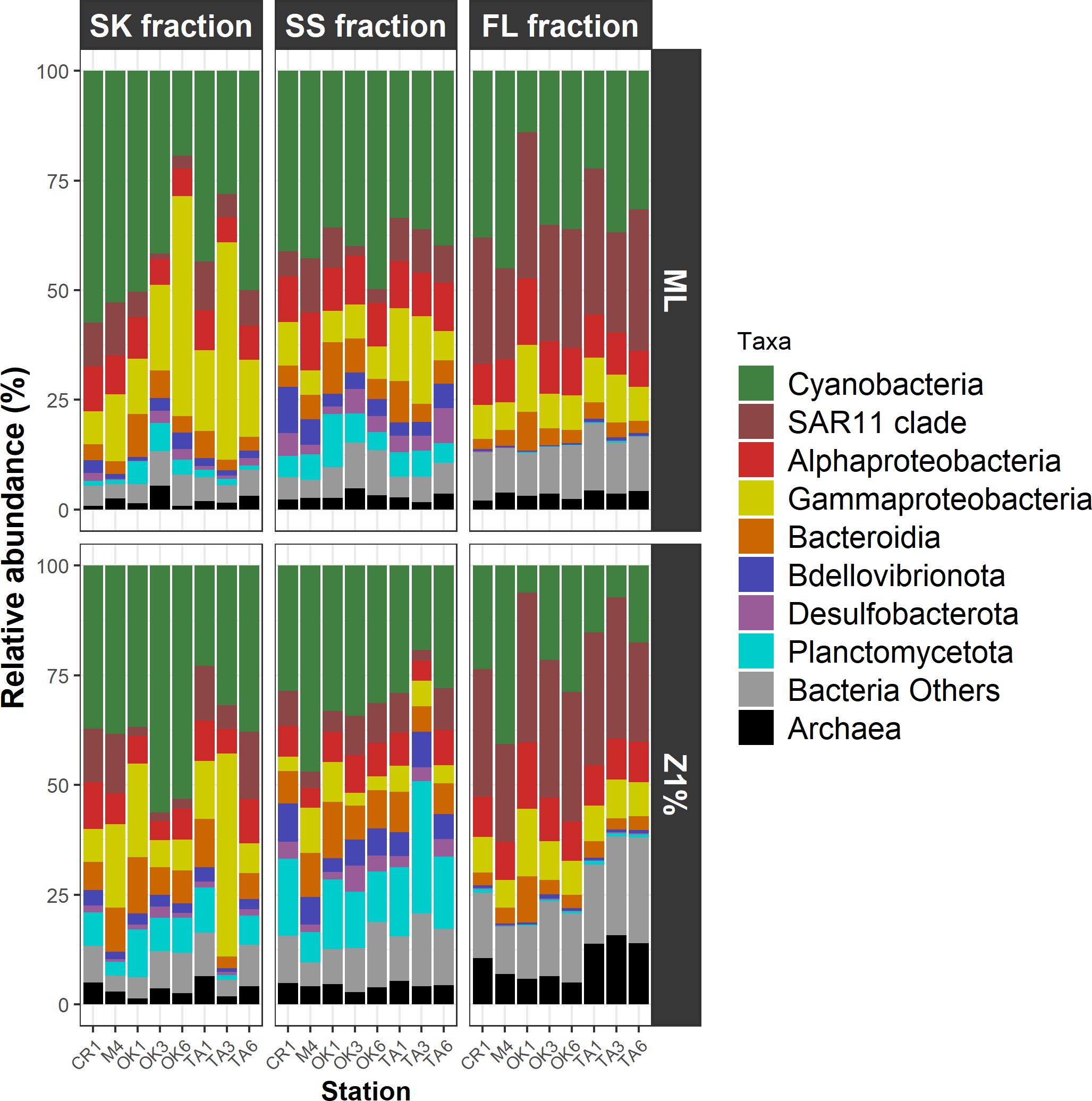
Figure 2. Taxonomic compositions of prokaryotic communities. Amplicon sequence variants are summarized according to phylum and class. FL, free-living fraction; SK, sinking-particle fraction; SS, suspended-particle fraction. ML, mixed layer; Z1%, layer at which PAR is 1% of the sea-surface value.
NMDS plots based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilatory matrix (Figure 3; Supplementary Figure S4) revealed some visually evident clustering patterns, such as the distinction between the FL and other fractions (SK and SS). However, differences in community centroid positions among the sampling layers, fractions, and water masses could not be evaluated due to heterogeneous dispersion (PERMDISP: p = 0.033, 0.003, and 0.009 for the layers, fractions, and water masses, respectively) (Supplementary Table S7). The Hill numbers, a measure of the effective number of species, were higher at the Z1% than in the ML (two-way ANOVA: p < 0.0001, p < 0.0001, and p = 0.0004 for the sampling layer factor for Hill numbers of order q = 0, 1, and 2, respectively) (Supplementary Figure S5; Supplementary Table S8), and higher in the FL and SS fractions than in the SK fraction [Tukey HSD: p = 0.033 and 0.036 for the pairs of SK and SS fractions (q = 1) and SK and FL fractions (q = 2), respectively] (Supplementary Table S9).
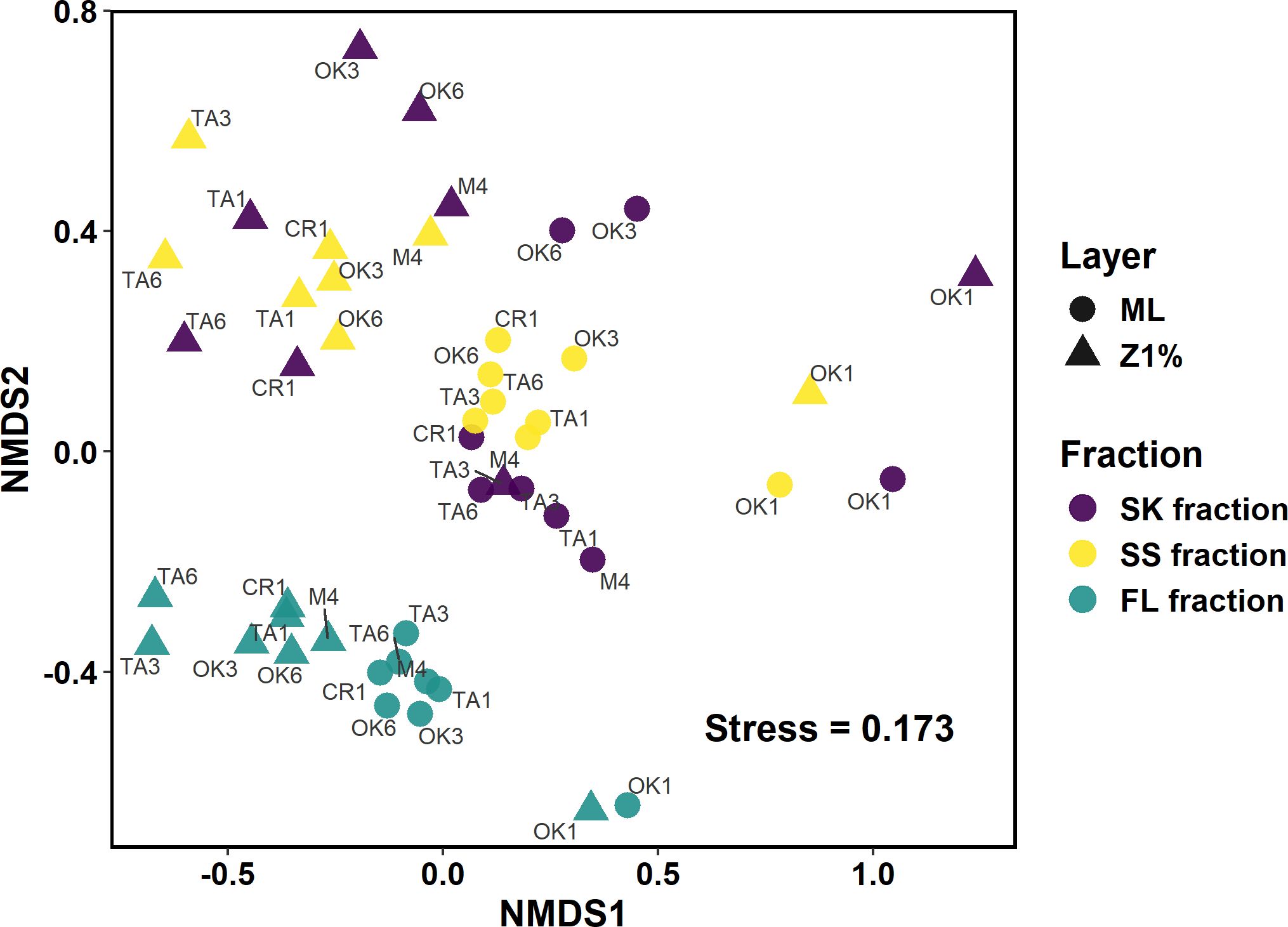
Figure 3. Non-metric multidimensional scaling ordinations representing the Bray–Curtis dissimilarities among samples. Symbol color and shape indicate the sampling fractions and layers, respectively. Names of sampling stations are shown. FL, free-living fraction; SK, sinking particle fraction; SS, suspended-particle fraction. ML, mixed layer; Z1%, layer at which PAR is 1% of the sea-surface value.
ANCOM-BC revealed patterns of taxonomic enrichment across microhabitat categories. Most of the ASVs present in equal abundances in the FL and PA fractions (Category FL/PA), which accounted for 14.4%–60.9% of total reads (Figure 4; Supplementary Table S10), were Cyanobacteria (Supplementary Table S11). Alphaproteobacteria, including the SAR11 and SAR116 clades, was the dominant class enriched in the FL relative to the PA fraction (Category FL) (Supplementary Table S12). The communities enriched in the SK fraction (Category SK) included members of Alphaproteobacteria (Rhodobacteraceae), Gammaproteobacteria (Oceanospirillales, Cellvibrionales, and Alteromonadales), and Bacteroidia (Flavobacteriaceae, Saprospiraceae, and Cyclobacteriaceae) (Table 3; Supplementary Table S13). The community enriched in the SS fraction (Category SS) consisted mainly of Bdellovibrionota (OM27 clade) and Desulfobacterota (Table 4; Supplementary Table S14). The community classified as Category SK/SS shared taxa with those of Categories SK and SS; uniquely, it also included Planctomycetota (OM190, Phycisphaerae, and Planctomycetes) (Table 5; Supplementary Table S15).
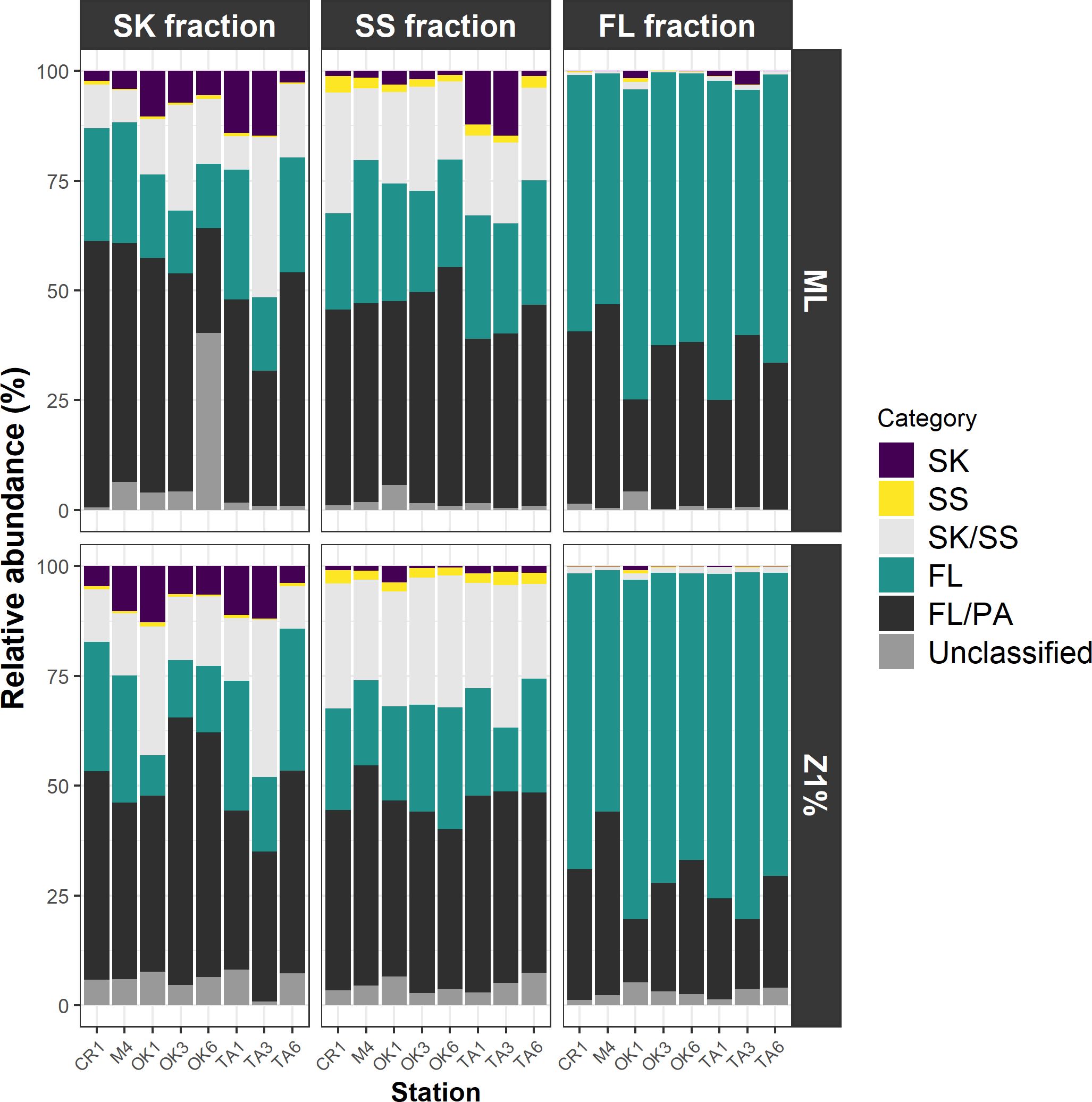
Figure 4. Contributions of the communities in each microhabitat category. Those labeled unclassified are amplicon sequence variants for which differential abundance analysis was not performed because of their infrequency. FL, free-living fraction; SK, sinking-particle fraction; SS, suspended-particle fraction. ML, mixed layer; Z1%, layer at which PAR is 1% of the sea-surface value.
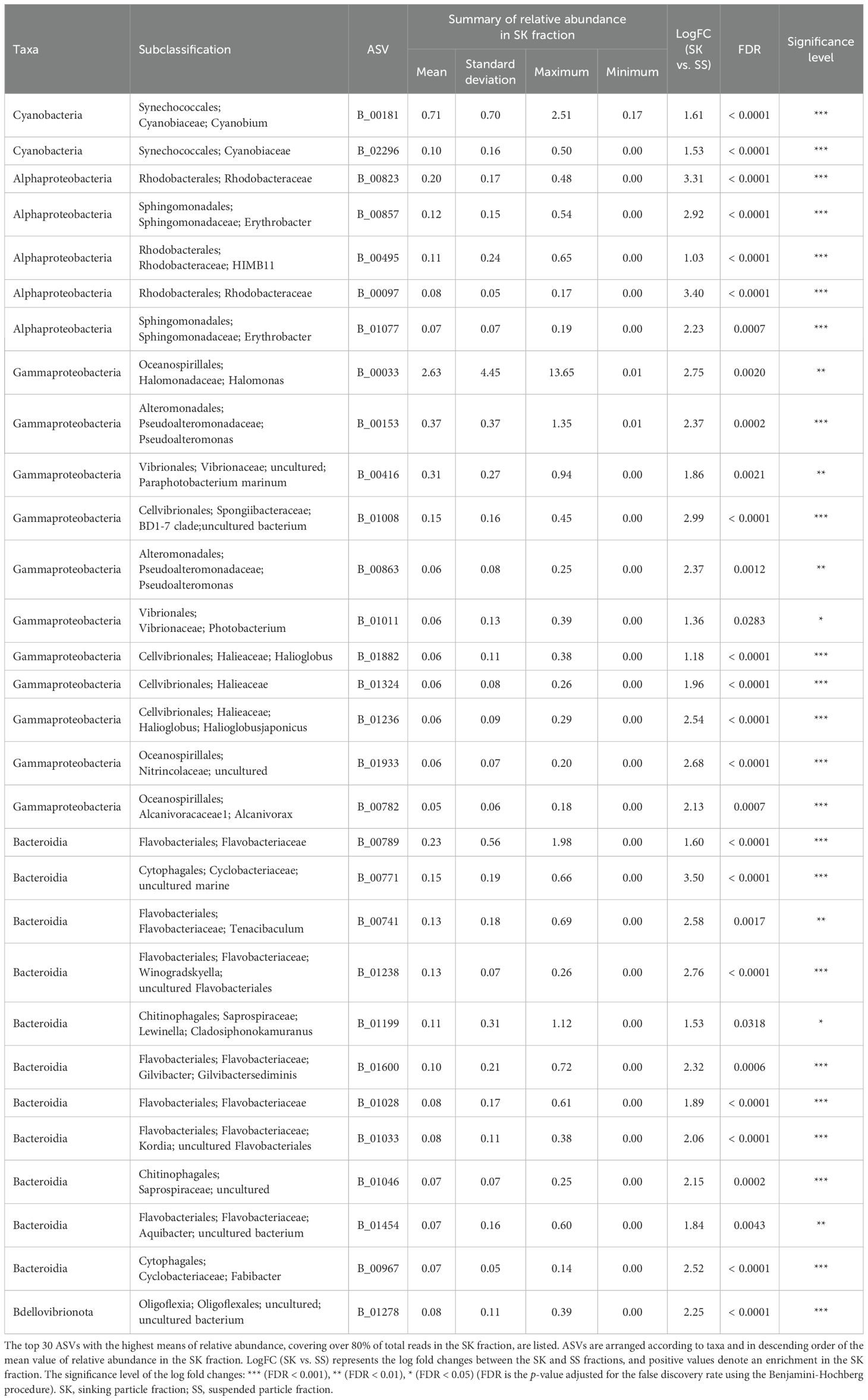
Table 3. Relative abundance in the SK fraction of the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) classified as Category SK.
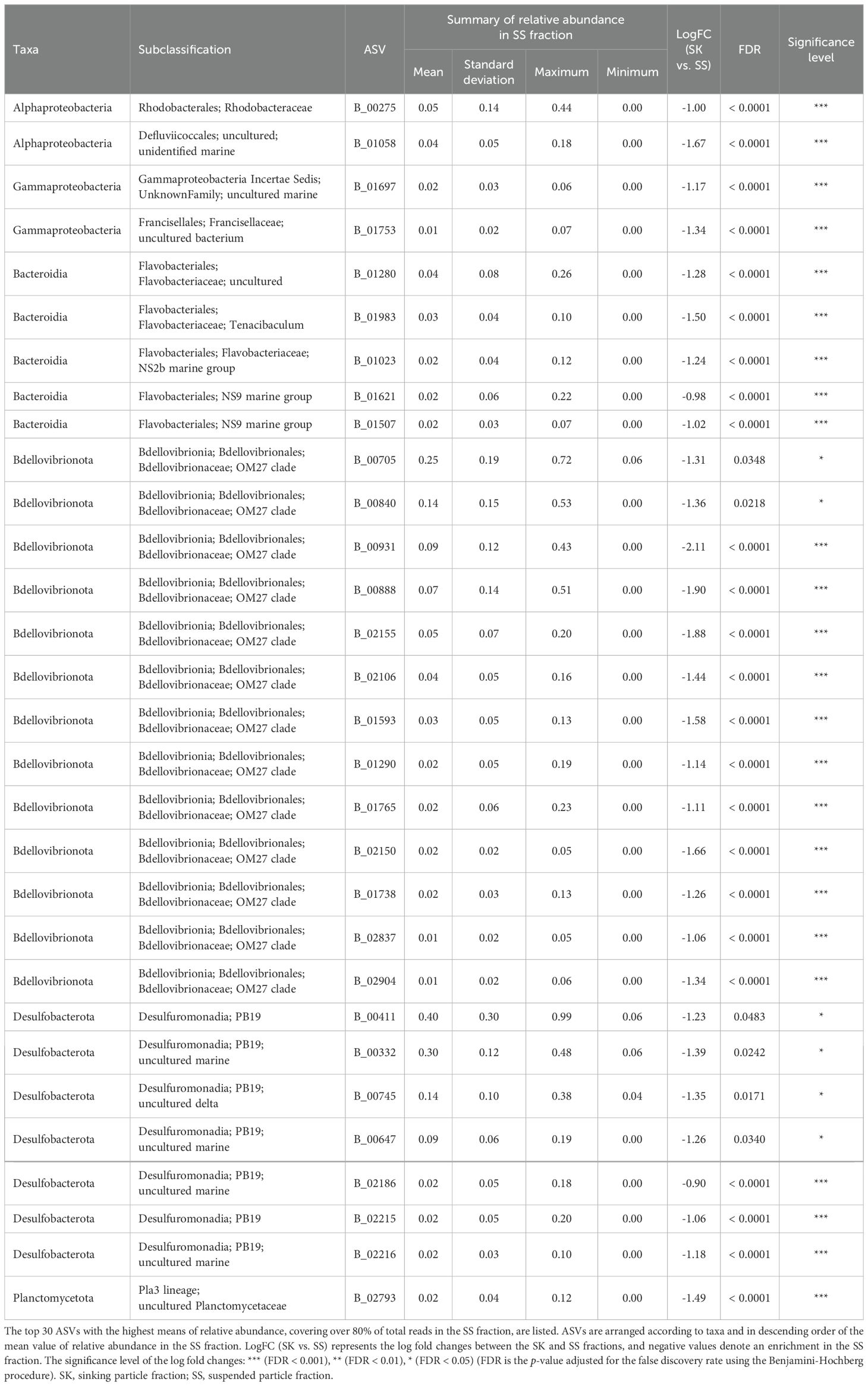
Table 4. Relative abundance in the SS fraction of the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) classified as Category SS.
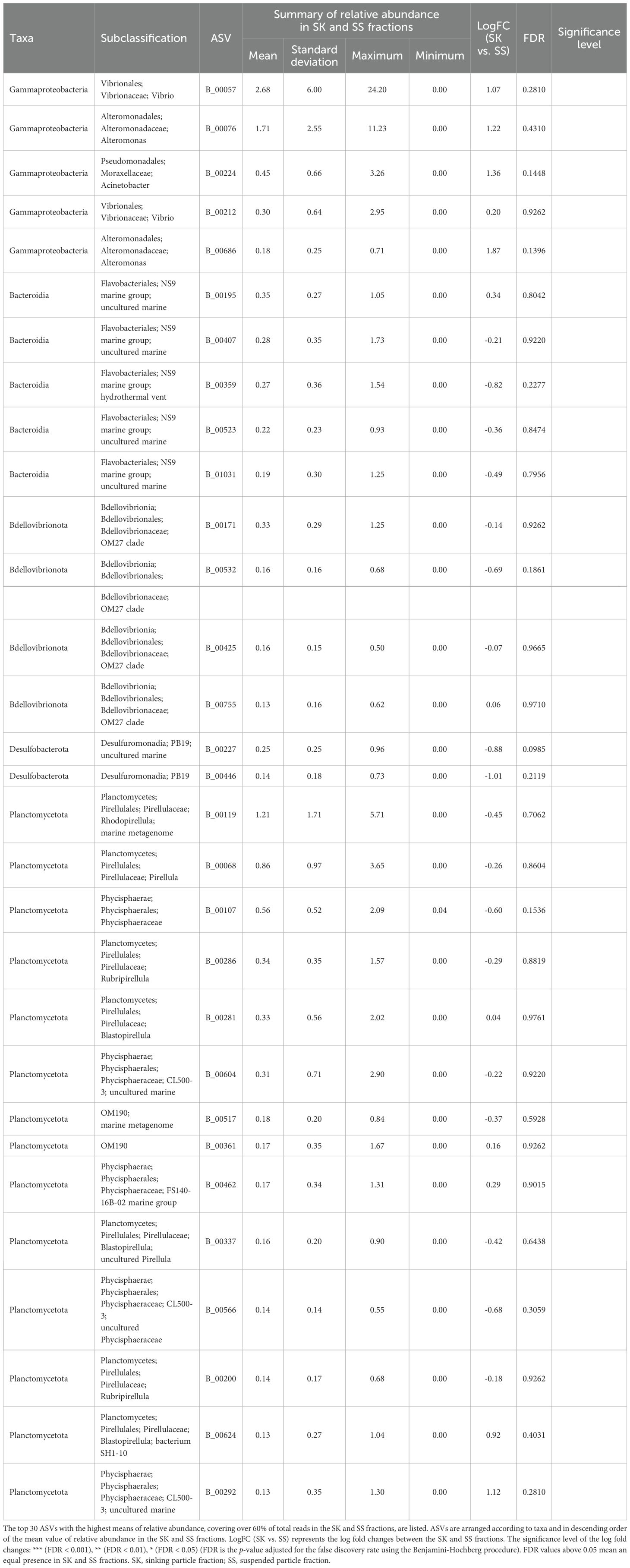
Table 5. Relative abundance in the SK and SS fractions of the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) classified as Category SK/SS.
Particle properties related to the EPS gradient of particles (TEP: POC, CSP: POC, and CSP: TEP ratios) and oceanographic parameters (depth, temperature, and nitrate concentration) were considered explanatory variables in the first RDA model. Nitrate concentrations below the detection limit of 0.02 µM were replaced by zero. Because the TEP: POC ratio was strongly positively correlated with the CSP: POC ratio (r = 0.81 and FDR < 0.001), the CSP: POC ratio was excluded from the analysis (Supplementary Table S16). The final RDA model included four variables (depth, temperature, nitrate concentration, and TEP: POC ratio) as significant explanatory variables for the variability in particle-associated bacterial community composition. These explanatory variables explained 26.5% of the variation in the bacterial communities associated with sinking and suspended particles (Table 6; Figure 5). The RDA ordinations indicated that the first axis was negatively correlated with the TEP: POC ratio, and the second axis was correlated with depth and depth-related parameters (temperature and nitrate concentration) (Figure 5). In this model, the variation of community structure explained by the first and second axes was 13.0% and 12.5%, respectively (Figure 5). On the first axis, the ASVs enriched in the SS fraction (Figure 5; Category SS) were separated from those enriched in the SK fraction (Category SK) (Supplementary Table S17). The ASVs present at equal abundances in the SK and SS fractions (Category SK/SS) were distributed along the first axis (Figure 5). On the second axis, bacterial communities were separated by sampling layer (ML vs. Z1%) (Figure 5).
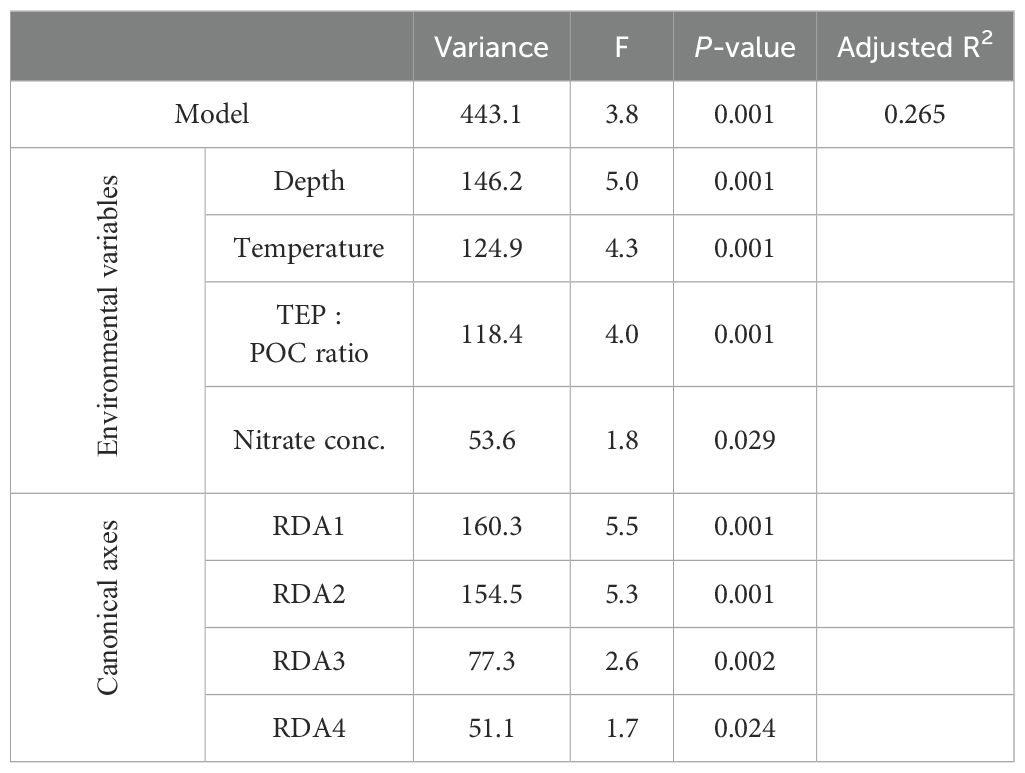
Table 6. Statistical summary of the redundancy analysis (RDA) model, explanatory variables (depth, temperature, TEP: POC ratio, and nitrate concentration), and canonical axes.
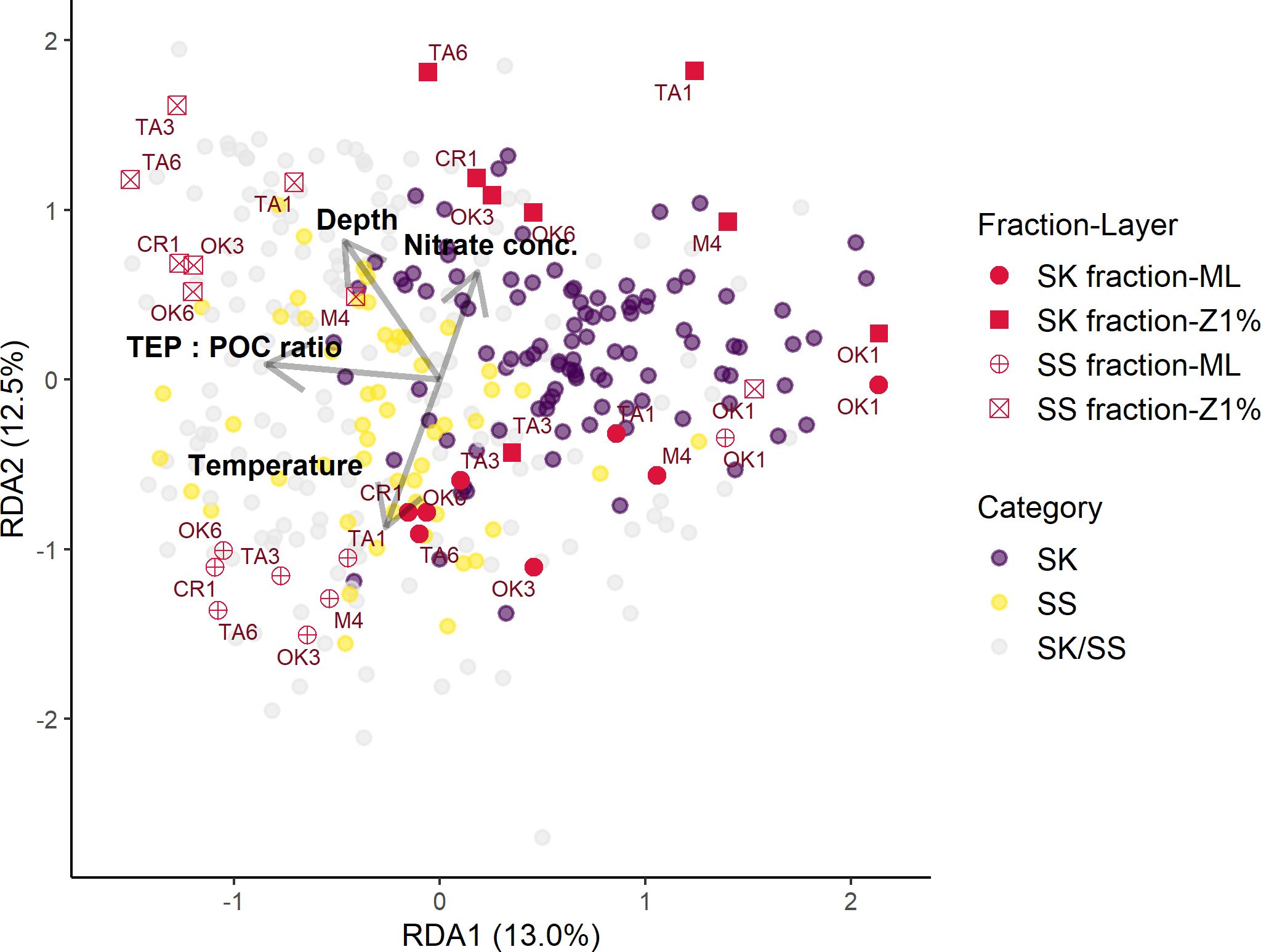
Figure 5. Scores and correlations of amplicon sequence variants (ASVs; purple, yellow, and gray dots), samples (red symbols), and explanatory variables (gray arrows) on the redundancy analysis axes in the model. Dot color corresponds to ASV category. Arrow length is the strength of the influence on community variation. Symbol shape corresponds to sampling fraction and layer; the names of sampling stations are shown. SK, sinking-particle fraction; SS, suspended-particle fraction. ML, mixed layer; Z1%, layer at which PAR is 1% of the sea-surface value. TEP, transparent exopolymer particles; POC, particulate organic carbon.
The distribution patterns of ASVs on the RDA ordinations differed among taxa (Figure 6). The mean RDA first scores of Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Bacteroidia were 0.60, 0.42, and 0.39, respectively (Table 7). These values positively and significantly differed from zero (the one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test: p < 0.05) (Figure 7; Table 7), indicating that they were negatively correlated with the TEP: POC ratio. By contrast, the mean RDA first scores of Bdellovibrionota (−0.35) and Desulfobacterota (−0.65) were negatively and significantly different from zero (Figure 7; Table 7), indicating that they were positively correlated with the TEP: POC ratio. There was no significant relationship between the RDA first score and Planctomycetota (mean RDA first score, 0.06) (Table 7). The mean RDA second score of Desulfobacterota (−0.34) and Planctomycetota (0.36) was significantly different from zero, indicating that they were correlated with sampling depth (Table 8).
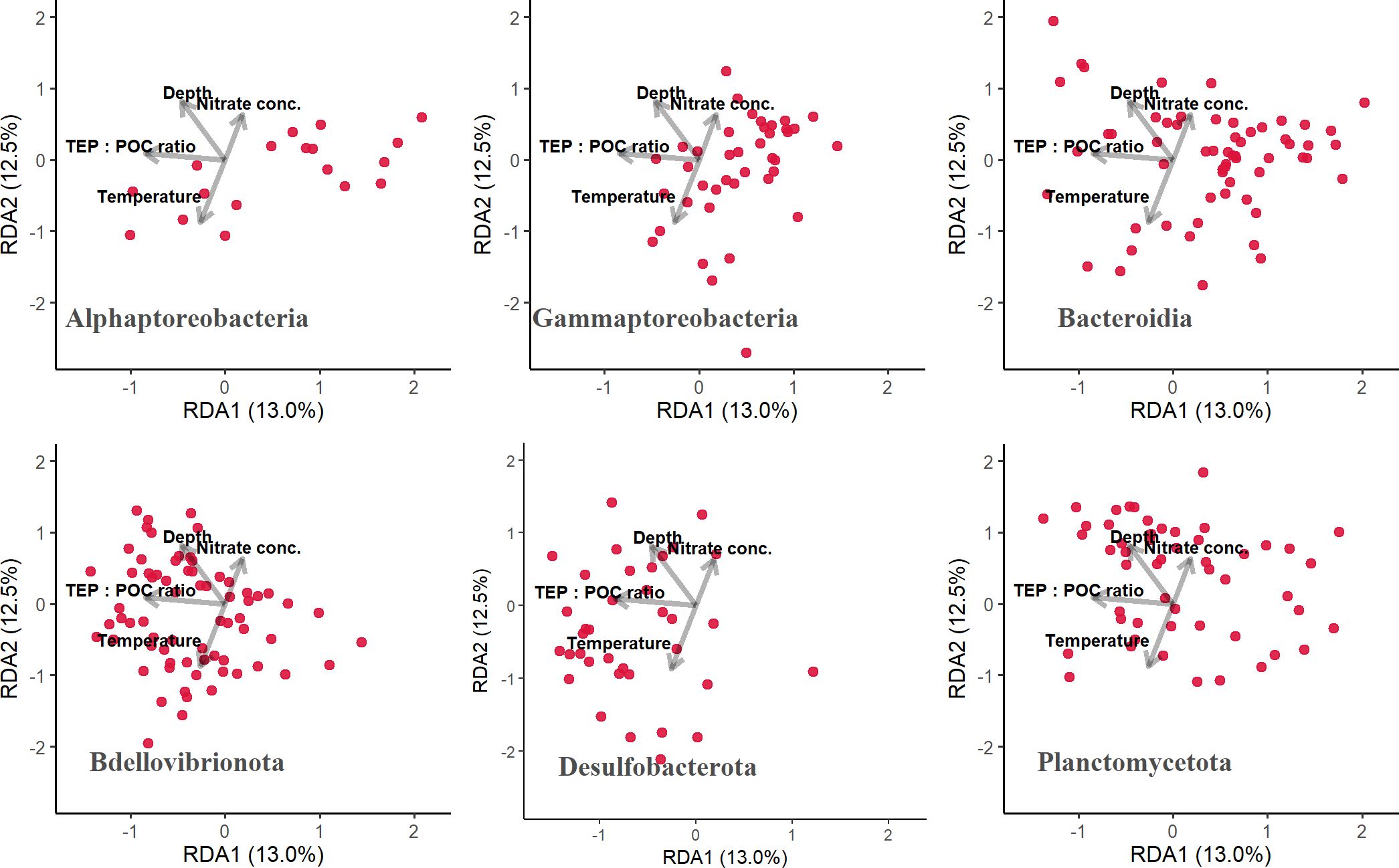
Figure 6. Distribution patterns of amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) belonging to each taxon on the redundancy analysis ordinations. Each plot was drawn separately for each taxon, and dots represent ASVs. TEP, transparent exopolymer particles; POC, particulate organic carbon.
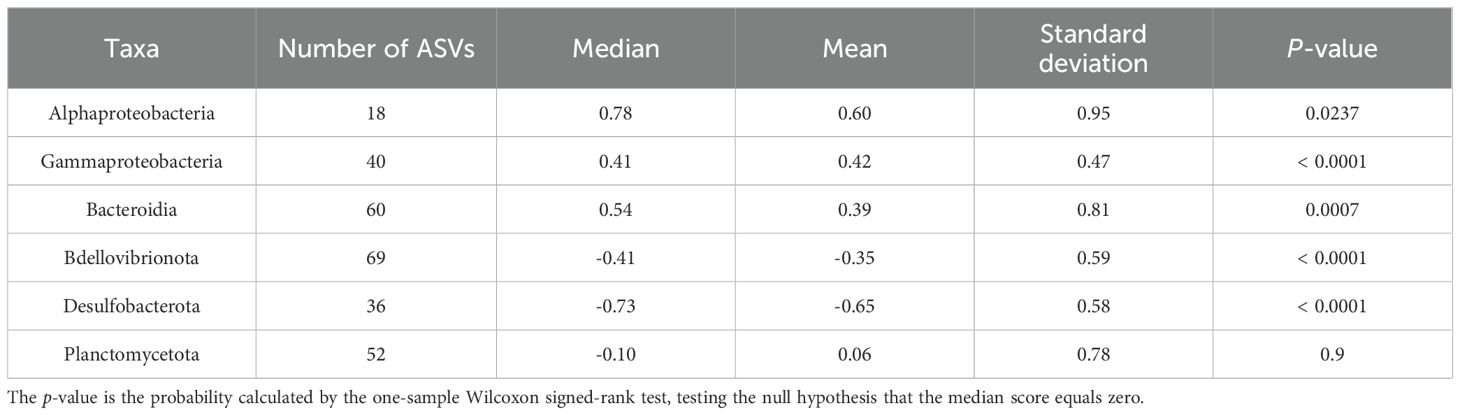
Table 7. Statistical summary of the RDA first score of amplicon sequence variants for individual taxa.
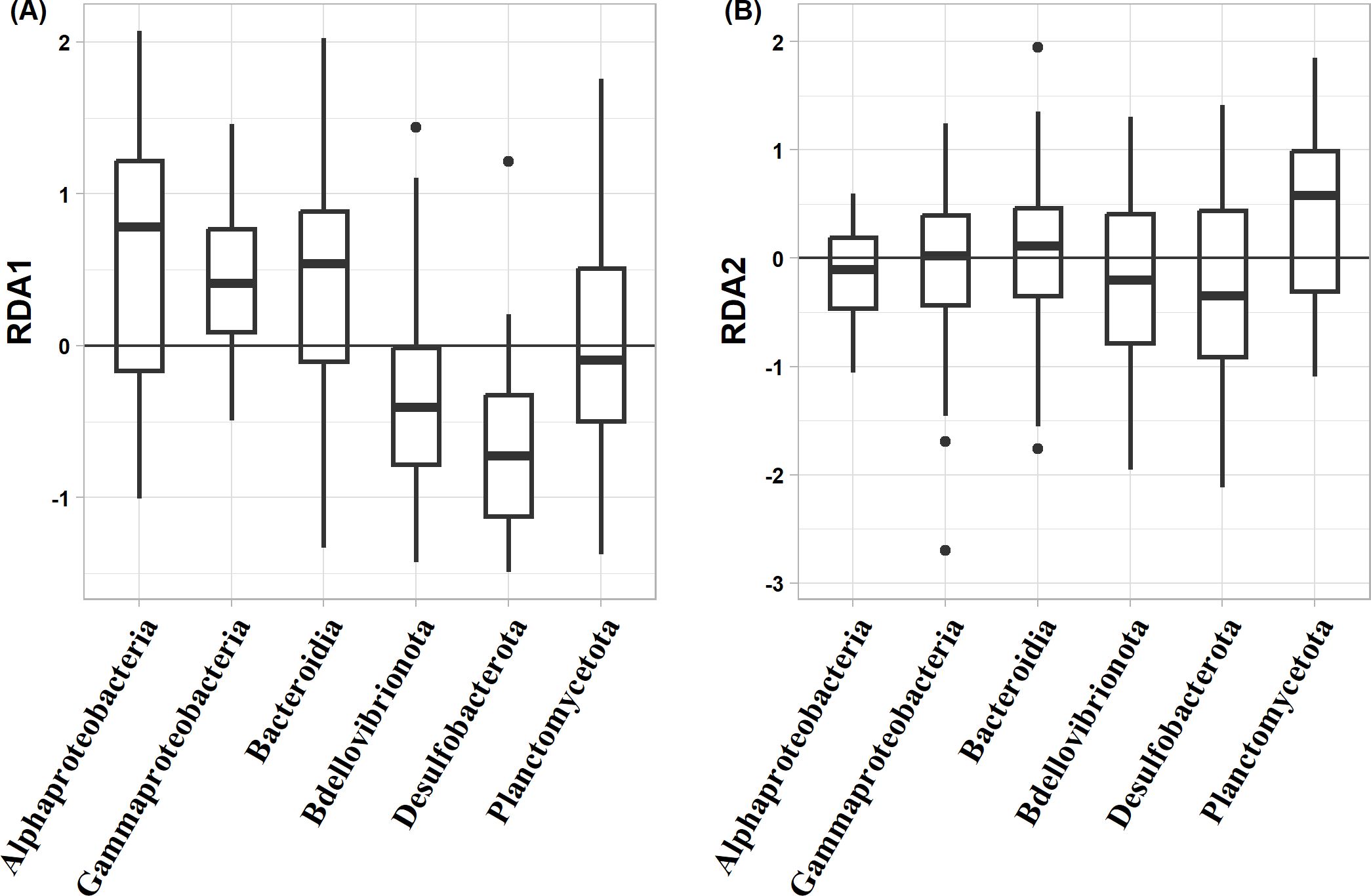
Figure 7. Box-whisker plots of redundancy analysis (RDA) (A) first scores and (B) second scores among taxa. A score of zero indicates that the amplicon sequence variant is neither positively nor negatively related to the RDA axes. Lines in boxes are medians. Box boundaries indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles. Error bars above and below boxes indicate the 5th and 95th percentiles.
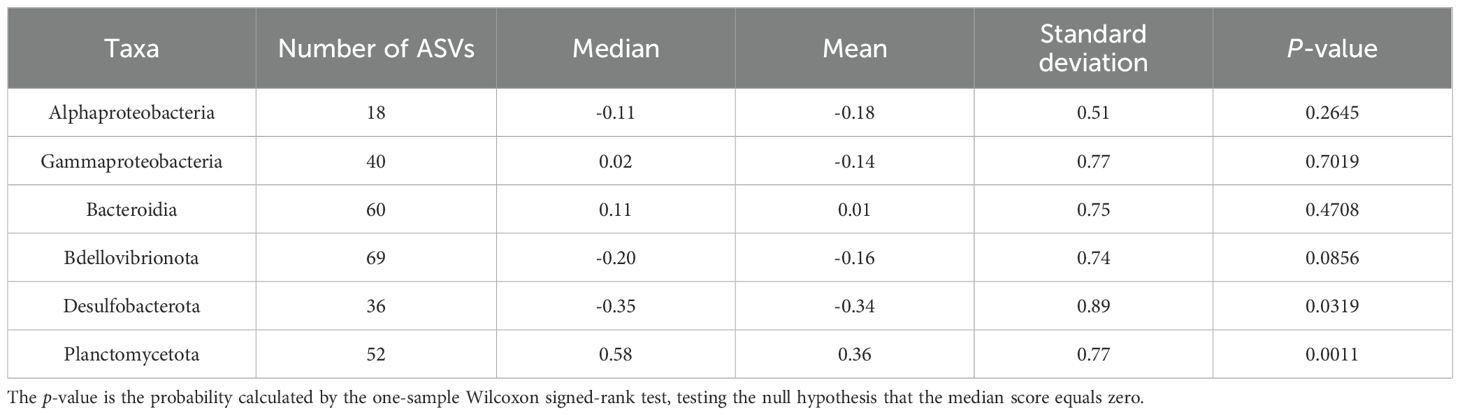
Table 8. Statistical summary of the RDA second score of amplicon sequence variants for individual taxa.
This study identified bacterial taxa enriched in particles collected in the euphotic zone of an oligotrophic, subtropical Kuroshio region. The RDA model, in which the particle TEP: POC ratio was a significant explanatory variable, explained the variability of the composition of particle-associated bacterial communities on sinking and suspended particles.
Cyanobacteria (Prochlorococcus) and the alphaproteobacterial SAR11 and SAR116 clades dominated the communities classified as Categories FL/PA and FL, in agreement with reports that these taxa are abundant in subtropical oceans (Morris et al., 2002; Partensky et al., 1999). They undergo metabolic streamlining to reduce their nutrient requirement in an oligotrophic ocean (Dupont et al., 2012; Giovannoni et al., 2005; Roda-Garcia et al., 2021). Additionally, their small size facilitates nutrient uptake in oligotrophic environments (Giovannoni et al., 2005). Although these taxa are free-living (Morris et al., 2011; Tripp et al., 2008), Prochlorococcus accounted for a substantial proportion of total reads in not only the FL fraction but also the SK and SS fractions. This likely reflects their ready incorporation into aggregates, which is facilitated by polymer production (Cruz and Neuer, 2019). The dispersal of Prochlorococcus across free-living and particle microhabitats shows the connection between microhabitats, facilitating the homogenization of community assembly across the free-living and particle phases in the Kuroshio region.
The bacterial taxa enriched on particles were divided into three categories: those enriched on sinking (Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Bacteroidia) or suspended (Bdellovibrionota and Desulfobacterota) particles, and those equally abundant on sinking and suspended particles (Planctomycetota). The distinct enrichment of taxa between the sinking and suspended particles suggests niche differentiation between the two particle types (Duret et al., 2019). RDA indicated that the TEP: POC ratio explained the community variability between the sinking and suspended particles. Because of the strong positive correlation between the TEP: POC and CSP: POC ratios, the TEP: POC ratio has potential as an indicator of EPS (TEP and CSP) richness in particles collected in the Kuroshio region.
The bacterial taxa enriched on sinking particles, including Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Bacteroidia, are found during phytoplankton blooms (Francis et al., 2021; Kruger et al., 2019; Pontiller et al., 2022; Sidhu et al., 2023; Teeling et al., 2012). Alphaproteobacteria often dominate bacterial communities on marine particles (Boeuf et al., 2019; Milici et al., 2017). Studies have found that Rhodobacteraceae (class Alphaproteobacteria), which are known to be primary colonizers of surfaces (Dang and Lovell, 2016; Elifantz et al., 2013), were enriched on sinking particles in the Scotia Sea (Duret et al., 2019) and the North Atlantic Ocean (Baumas et al., 2021). Gammaproteobacteria and Bacteroidia are frequently present in marine particle-associated bacterial communities (Boeuf et al., 2019; Ganesh et al., 2014; Reintjes et al., 2023). The genomes of Bacteroidia encode genes that produce enzymes capable of hydrolyzing polysaccharides and proteins (Bennke et al., 2016; Cottrell et al., 2005; Kruger et al., 2019), as well as genes involved in the uptake of high-molecular-weight molecules using TonB-dependent transporters (Kruger et al., 2019; Tang et al., 2012), facilitating the efficient use of polymeric substances. By contrast, metagenomic analyses of Gammaproteobacteria from North Sea spring blooms revealed a range of potential lifestyles, including the exploitation of small organic molecules such as amino acids, oligopeptides, sugar monomers, and oligosaccharides (Francis et al., 2021). This suggests that Gammaproteobacteria scavenge the low-molecular-weight organic compounds released by bacteria during polymer hydrolysis. On this basis, these taxa are believed to be able to adapt to polymer-rich particle environments (Reintjes et al., 2023; Sidhu et al., 2023; Teeling et al., 2012). Importantly, RDA revealed a negative correlation between the occurrence of these taxa and the TEP: POC ratio. Specifically, the TEP: POC ratio decreased with the increasing abundance of these polymer-degrading taxa on particles. The interpretation and the biogeochemical implications of this are as follows. These taxa rapidly colonize and proliferate on particles rich in EPS. By exploiting EPS (e.g., polysaccharides and proteins), they alter the microhabitat from EPS-rich to EPS-depleted, ultimately increasing particle density by removing positively buoyant EPS components and promoting particle sinking (Mari et al., 2017; Yamada et al., 2024). This process, akin to bacterial ‘gardening’, enhances carbon export by converting suspended into sinking particles.
The bacterial taxa enriched on suspended particles included Bdellovibrionota and Desulfobacterota. RDA revealed that these taxa were positively correlated with the TEP: POC ratio, suggesting that their abundance is elevated on EPS-rich particles. Bdellovibrionota and Desulfobacterota (previously classified as Deltaproteobacteria [Waite et al., 2020]), include predatory taxa and are found in particles and sediments in oceanic environments (Dang and Lovell, 2016; Liau et al., 2022; Sockett, 2009). Duret et al. (2019) reported that Desulfobacterota were enriched on suspended particles in the upper mesopelagic layer of the Scotia Sea (Duret et al., 2019). Despite their ubiquity on marine particles, the ecology, predatory activity, and functions in ocean biogeochemical cycles of these taxa are unknown. A study of the ecology of predatory bacteria, using Bdellovibrionota as a model, showed that they predate gram-negative bacteria in biofilms, thereby altering biofilm surface structure and colonization by other bacteria (Wucher et al., 2021). Given that marine aggregates, in which bacterial densities are two- to three-fold higher than surrounding seawater (Alldredge and Silver, 1988), are active sites for predation by protist grazers (Caron et al., 1982) and viruses (Riemann and Grossart, 2008), bacterial predators may modulate community and particle dynamics. Further studies are needed to investigate this possibility.
Planctomycetota, including Planctomycetes, were equally present on sinking and suspended particles. Planctomycetes are found on particles in subtropical and tropical oceans (DeLong et al., 2006; Ganesh et al., 2014) and can degrade polymers; their draft genome encodes a larger number of sulfatases (which cleave sulfate esters of polysaccharides) than freshwater Planctomycetes (Glockner et al., 2003; Woebken et al., 2007). The wide distribution of Planctomycetota along the RDA first axis implies a broad niche breadth for the particles’ polymeric substance contents in the Kuroshio region.
It is increasingly evident that polymeric substances control ocean carbon export via the partitioning of sinking and suspended particles (Engel et al., 2020; Mari et al., 2017; Yamada et al., 2024). Polymeric substances not only serve as nutritional substrates for bacteria but also provide three-dimensional structures harboring bacterial communities. The degradation and transformation of polymers by particle-associated bacterial communities can affect multiple particle properties, including size, density, shape, and porosity, thereby contributing to the regulation of carbon export (Mari et al., 2017; Romanelli et al., 2023; Yamada et al., 2024). Therefore, insight into the interactions between bacterial communities and polymeric substances on marine particles could be applied to improve ocean biogeochemical models (Maerz et al., 2020; Nguyen et al., 2022).
As well as the particle EPS: POC ratio, the depth and depth-related parameters (temperature and nitrate concentration), represented by the RDA second axis, significantly explained particle-associated community variability. Taxonomically, Desulfobacterota was negatively correlated with the second axis (i.e., more enriched in the shallower layer), whereas Planctomycetota was positively correlated with the second axis (i.e., more enriched in the deeper layer), suggesting depth-dependent niche partitioning. The results align with reports that microbial communities exhibit depth-dependent patterns in stratified water columns in subtropical oceans (DeLong et al., 2006; Stephens et al., 2024; Treusch et al., 2009), which are influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, light, and nutrient availability (Fuhrman et al., 2006; Van Mooy et al., 2004). However, there is little information on the environmental factors that control depth-dependent variability in particle-associated bacterial communities (Stephens et al., 2024). Further studies of this issue that consider particle dynamics (aggregation and sinking) in the upper water column are warranted.
This study analyzed the bacterial community compositions of sinking and suspended particles collected in the euphotic zone of a subtropical ocean. The most important finding is that the enrichment pattern of bacterial taxa differed between sinking and suspended particles, which was explained in part by the particles’ polymeric substance contents. This indicates niche differentiation among bacterial taxa attaching to particles and the effects of certain taxa on polymer dynamics, which in turn would further affect community composition. The next step is to investigate the effects of the bacterium–polymeric substance interactions of individual taxa on particle dynamics.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
AE: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. HF: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TY: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TM: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TN: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP19H05667 and World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI), MEXT, Japan, and JST FOREST Program Grant Number JPMJFR2070.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1462522/full#supplementary-material
Aitchison J. (1983). Principal component analysis of compositional data. Biometrika 70, 57–65. doi: 10.1093/biomet/70.1.57
Alldredge A. L., Silver M. W. (1988). Characteristics, dynamics and significance of marine snow. Prog. Oceanography 20, 41–82. doi: 10.1016/0079-6611(88)90053-5
Anderson M. J. (2001). A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 26, 32–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.pp.x
Anderson M. J. (2006). Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 62, 245–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2005.00440.x
Armstrong F., Stearns C., Strickland J. (1967). The measurement of upwelling and subsequent biological process by means of the Technicon Autoanalyzer® and associated equipment. Deep Sea Res. Oceanographic Abstracts 14 (3), 381–389. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(67)90082-4
Baumas C. M. J., Le Moigne F. A. C., Garel M., Bhairy N., Guasco S., Riou V., et al. (2021). Mesopelagic microbial carbon production correlates with diversity across different marine particle fractions. ISME J. 15, 1695–1708. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00880-z
Bennke C. M., Kruger K., Kappelmann L., Huang S., Gobet A., Schuler M., et al. (2016). Polysaccharide utilisation loci of Bacteroidetes from two contrasting open ocean sites in the North Atlantic. Environ. Microbiol. 18, 4456–4470. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13429
Boeuf D., Edwards B. R., Eppley J. M., Hu S. K., Poff K. E., Romano A. E., et al. (2019). Biological composition and microbial dynamics of sinking particulate organic matter at abyssal depths in the oligotrophic open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 11824–11832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903080116
Bolyen E., Rideout J. R., Dillon M. R., Bokulich N. A., Abnet C. C., Al-Ghalith G. A., et al. (2019). Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 852–857. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Boyd P. W., Claustre H., Levy M., Siegel D. A., Weber T. (2019). Multi-faceted particle pumps drive carbon sequestration in the ocean. Nature 568, 327–335. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1098-2
Busch K., Endres S., Iversen M. H., Michels J., Nöthig E.-M., Engel A. (2017). Bacterial colonization and vertical distribution of marine gel particles (TEP and CSP) in the arctic fram strait. Front. Mar. Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00166
Callahan B. J., McMurdie P. J., Rosen M. J., Han A. W., Johnson A. J., Holmes S. P. (2016). DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 13, 581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869
Caron D. A., Davis P. G., Madin L. P., Sieburth J. M. (1982). Heterotrophic bacteria and bacterivorous protozoa in oceanic macroaggregates. Science 218, 795–797. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4574.795
Chao A., Gotelli N. J., Hsieh T. C., Sander E. L., Ma K. H., Colwell R. K., et al. (2014). Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: a framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 84, 45–67. doi: 10.1890/13-0133.1
Cisternas-Novoa C., Lee C., Engel A. (2014). A semi-quantitative spectrophotometric, dye-binding assay for determination of Coomassie Blue stainable particles. Limnology Oceanography: Methods 12, 604–616. doi: 10.4319/lom.2014.12.604
Cisternas-Novoa C., Lee C., Engel A. (2015). Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and Coomassie stainable particles (CSP): Differences between their origin and vertical distributions in the ocean. Mar. Chem. 175, 56–71. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.03.009
Cottrell M. T., Yu L., Kirchman D. L. (2005). Sequence and expression analyses of Cytophaga-like hydrolases in a Western arctic metagenomic library and the Sargasso Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 8506–8513. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8506-8513.2005
Cruz B. N., Neuer S. (2019). Heterotrophic bacteria enhance the aggregation of the marine picocyanobacteria prochlorococcus and synechococcus. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01864
Dang H., Lovell C. R. (2016). Microbial surface colonization and biofilm development in marine environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80, 91–138. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00037-15
DeLong E. F., Franks D. G., Alldredge A. L. (1993). Phylogenetic diversity of aggregate-attached vs free-living marine bacterial assemblages. Limnology Oceanography 38, 924–934. doi: 10.4319/lo.1993.38.5.0924
DeLong E. F., Preston C. M., Mincer T., Rich V., Hallam S. J., Frigaard N. U., et al. (2006). Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean’s interior. Science 311, 496–503. doi: 10.1126/science.1120250
Dupont C. L., Rusch D. B., Yooseph S., Lombardo M. J., Richter R. A., Valas R., et al. (2012). Genomic insights to SAR86, an abundant and uncultivated marine bacterial lineage. ISME J. 6, 1186–1199. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.189
Duret M. T., Lampitt R. S., Lam P. (2019). Prokaryotic niche partitioning between suspended and sinking marine particles. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 11, 386–400. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12692
Elifantz H., Horn G., Ayon M., Cohen Y., Minz D. (2013). Rhodobacteraceae are the key members of the microbial community of the initial biofilm formed in Eastern Mediterranean coastal seawater. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 85, 348–357. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12122
Engel A., Endres S., Galgani L., Schartau M. (2020). Marvelous marine microgels: on the distribution and impact of gel-like particles in the oceanic water-column. Front. Mar. Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00405
Faust K. (2021). Open challenges for microbial network construction and analysis. ISME J. 15, 3111–3118. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01027-4
Francis B., Urich T., Mikolasch A., Teeling H., Amann R. (2021). North Sea spring bloom-associated Gammaproteobacteria fill diverse heterotrophic niches. Environ. Microbiome 16, 15. doi: 10.1186/s40793-021-00385-y
Fuhrman J. A., Hewson I., Schwalbach M. S., Steele J. A., Brown M. V., Naeem S. (2006). Annually reoccurring bacterial communities are predictable from ocean conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 13104–13109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602399103
Ganesh S., Parris D. J., DeLong E. F., Stewart F. J. (2014). Metagenomic analysis of size-fractionated picoplankton in a marine oxygen minimum zone. ISME J. 8, 187–211. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.144
Giljan G., Arnosti C., Kirstein I. V., Amann R., Fuchs B. M. (2022). Strong seasonal differences of bacterial polysaccharide utilization in the North Sea over an annual cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 24, 2333–2347. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15997
Giovannoni S. J., Cameron Thrash J., Temperton B. (2014). Implications of streamlining theory for microbial ecology. ISME J. 8, 1553–1565. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.60
Giovannoni S. J., Tripp H. J., Givan S., Podar M., Vergin K. L., Baptista D., et al. (2005). Genome streamlining in a cosmopolitan oceanic bacterium. Science 309, 1242–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.1114057
Glockner F. O., Kube M., Bauer M., Teeling H., Lombardot T., Ludwig W., et al. (2003). Complete genome sequence of the marine planctomycete Pirellula sp. strain 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 8298–8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1431443100
Gloor G. B., Macklaim J. M., Pawlowsky-Glahn V., Egozcue J. J. (2017). Microbiome datasets are compositional: and this is not optional. Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02224
Grossart H. P., Czub G., Simon M. (2006). Algae-bacteria interactions and their effects on aggregation and organic matter flux in the sea. Environ. Microbiol. 8, 1074–1084. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.00999.x
Herndl G. J., Reinthaler T. (2013). Microbial control of the dark end of the biological pump. Nat. Geosci 6, 718–724. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1921
Hirai M., Nishi S., Tsuda M., Sunamura M., Takaki Y., Nunoura T. (2017). Library construction from subnanogram DNA for pelagic sea water and deep-sea sediments. Microbes Environments 32, 336–343. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME17132
Kruger K., Chafee M., Ben Francis T., Glavina Del Rio T., Becher D., Schweder T., et al. (2019). In marine Bacteroidetes the bulk of glycan degradation during algae blooms is mediated by few clades using a restricted set of genes. ISME J. 13, 2800–2816. doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0476-y
Lampitt R. S., Wishner K. F., Turley C. M., Angel M. V. (1993). Marine snow studies in the northeast atlantic-ocean - distribution, composition and role as a food source for migrating plankton. Mar. Biol. 116, 689–702. doi: 10.1007/Bf00355486
Liau P., Kim C., Saxton M. A., Malkin S. Y. (2022). Microbial succession in a marine sediment: Inferring interspecific microbial interactions with marine cable bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 24, 6348–6364. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16230
Lin H., Peddada S. D. (2020). Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 11, 3514. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17041-7
Long R. A., Azam F. (1996). Abundant protein-containing particles in the sea. Aquat. Microbial Ecol. 10, 213–221. doi: 10.3354/ame010213
Maerz J., Six K. D., Stemmler I., Ahmerkamp S., Ilyina T. (2020). Microstructure and composition of marine aggregates as co-determinants for vertical particulate organic carbon transfer in the global ocean. Biogeosciences 17, 1765–1803. doi: 10.5194/bg-17-1765-2020
Mari X., Passow U., Migon C., Burd A. B., Legendre L. (2017). Transparent exopolymer particles: Effects on carbon cycling in the ocean. Prog. Oceanography 151, 13–37. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2016.11.002
Martin M. (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 17 (1), 10–12. doi: 10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Mestre M., Borrull E., Sala M., Gasol J. M. (2017). Patterns of bacterial diversity in the marine planktonic particulate matter continuum. ISME J. 11, 999–1010. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.166
Milici M., Vital M., Tomasch J., Badewien T. H., Giebel H.-A., Plumeier I., et al. (2017). Diversity and community composition of particle-associated and free-living bacteria in mesopelagic and bathypelagic Southern Ocean water masses: Evidence of dispersal limitation in the Bransfield Strait. Limnology Oceanography 62, 1080–1095. doi: 10.1002/lno.10487
Morris J. J., Johnson Z. I., Szul M. J., Keller M., Zinser E. R. (2011). Dependence of the cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus on hydrogen peroxide scavenging microbes for growth at the ocean’s surface. PloS One 6, e16805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016805
Morris J. J., Lenski R. E., Zinser E. R. (2012). The Black Queen Hypothesis: evolution of dependencies through adaptive gene loss. mBio 3 (2), 10–1128. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00036-12
Morris R. M., Rappé M. S., Connon S. A., Vergin K. L., Siebold W. A., Carlson C. A., et al. (2002). SAR11 clade dominates ocean surface bacterioplankton communities. Nature 420, 806–810. doi: 10.1038/nature01240
Nagata T. (2008). Organic matter-bacteria interactions in seawater. Microbial Ecol. oceans 2, 207–241. doi: 10.1002/9780470281840.ch7
Nagata T., Yamada Y., Fukuda H. (2021). Transparent exopolymer particles in deep oceans: synthesis and future challenges. Gels 7 (3), 75. doi: 10.3390/gels7030075
Nguyen T. T. H., Zakem E. J., Ebrahimi A., Schwartzman J., Caglar T., Amarnath K., et al. (2022). Microbes contribute to setting the ocean carbon flux by altering the fate of sinking particulates. Nat. Commun. 13, 1657. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29297-2
Nunoura T., Takaki Y., Kazama H., Hirai M., Ashi J., Imachi H., et al. (2012). Microbial diversity in deep-sea methane seep sediments presented by SSU rRNA gene tag sequencing. Microbes Environments 27, 382–390. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.me12032
Oksanen J., Simpson G., Blanchet F., Kindt R., Legendre P., Minchin P., et al. (2022). Vegan: Community Ecology Package (R Package Version 2.6-2). doi: 10.32614/CRAN.package.vegan
Palarea-Albaladejo J., Martín-Fernández J. A. (2015). zCompositions — R package for multivariate imputation of left-censored data under a compositional approach. Chemometrics Intelligent Lab. Syst. 143, 85–96. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.02.019
Partensky F., Hess W. R., Vaulot D. (1999). Prochlorococcus, a marine photosynthetic prokaryote of global significance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63, 106–127. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.1.106-127.1999
Passow U., Alldredge A. (1994). Distribution, size and bacterial colonization of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 185–198. doi: 10.3354/meps113185
Passow U., Alldredge A. (1995). A dye-binding assay for the spectrophotometric measurement of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP). Limnology Oceanography 40, 1326–1335. doi: 10.4319/lo.1995.40.7.1326
Pontiller B., Martinez-Garcia S., Joglar V., Amnebrink D., Perez-Martinez C., Gonzalez J. M., et al. (2022). Rapid bacterioplankton transcription cascades regulate organic matter utilization during phytoplankton bloom progression in a coastal upwelling system. ISME J. 16, 2360–2372. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01273-0
Quigg A., Santschi P. H., Xu C., Ziervogel K., Kamalanathan M., Chin W.-C., et al. (2021). Aggregation and degradation of dispersants and oil by microbial exopolymers (ADDOMEx): toward a synthesis of processes and pathways of marine oil snow formation in determining the fate of hydrocarbons. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.642160
Reintjes G., Heins A., Wang C., Amann R. (2023). Abundance and composition of particles and their attached microbiomes along an Atlantic Meridional Transect. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1051510
Richardson T. L., Jackson G. A. (2007). Small phytoplankton and carbon export from the surface ocean. Science 315, 838–840. doi: 10.1126/science.1133471
Riemann L., Grossart H. P. (2008). Elevated lytic phage production as a consequence of particle colonization by a marine Flavobacterium (Cellulophaga sp.). Microbial Ecol. 56, 505–512. doi: 10.1007/s00248-008-9369-8
Roda-Garcia J. J., Haro-Moreno J. M., Huschet L. A., Rodriguez-Valera F., Lopez-Perez M. (2021). Phylogenomics of SAR116 clade reveals two subclades with different evolutionary trajectories and an important role in the ocean sulfur cycle. mSystems 6, e0094421. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00944-21
Romanelli E., Sweet J., Giering S. L. C., Siegel D. A., Passow U. (2023). The importance of transparent exopolymer particles over ballast in determining both sinking and suspension of small particles during late summer in the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Elem Sci. Anth 11. doi: 10.1525/elementa.2022.00122
Sidhu C., Kirstein I. V., Meunier C. L., Rick J., Fofonova V., Wiltshire K. H., et al. (2023). Dissolved storage glycans shaped the community composition of abundant bacterioplankton clades during a North Sea spring phytoplankton bloom. Microbiome 11, 77. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01517-x
Smith D. C., Simon M., Alldredge A. L., Azam F. (1992). Intense hydrolytic enzyme-activity on marine aggregates and implications for rapid particle dissolution. Nature 359, 139–142. doi: 10.1038/359139a0
Sockett R. E. (2009). Predatory lifestyle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Annual. Rev. Microbiol. 63, 523–539. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073346
Stephens B. M., Durkin C. A., Sharpe G., Nguyen T. T. H., Albers J., Estapa M. L., et al. (2024). Direct observations of microbial community succession on sinking marine particles. ISME J. 18. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wrad010
Tang K., Jiao N., Liu K., Zhang Y., Li S. (2012). Distribution and functions of TonB-dependent transporters in marine bacteria and environments: implications for dissolved organic matter utilization. PloS One 7, e41204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041204
Teeling H., Fuchs B. M., Becher D., Klockow C., Gardebrecht A., Bennke C. M., et al. (2012). Substrate-controlled succession of marine bacterioplankton populations induced by a phytoplankton bloom. Science 336, 608–611. doi: 10.1126/science.1218344
Thornton D. C. O. (2018). Coomassie stainable particles (CSP): protein containing exopolymer particles in the ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00206
Treusch A. H., Vergin K. L., Finlay L. A., Donatz M. G., Burton R. M., Carlson C. A., et al. (2009). Seasonality and vertical structure of microbial communities in an ocean gyre. ISME J. 3, 1148–1163. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.60
Tripp H. J., Kitner J. B., Schwalbach M. S., Dacey J. W., Wilhelm L. J., Giovannoni S. J. (2008). SAR11 marine bacteria require exogenous reduced sulphur for growth. Nature 452, 741–744. doi: 10.1038/nature06776
van den Boogaart K. G., Tolosana-Delgado R. (2008). compositions”: A unified R package to analyze compositional data. Comput. Geosciences 34, 320–338. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2006.11.017
Van Mooy B. A. S., Devol A. H., Keil R. G. (2004). Relationship between bacterial community structure, light, and carbon cycling in the eastern subarctic North Pacific. Limnology Oceanography 49, 1056–1062. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.4.1056
Verdugo P. (2012). Marine microgels. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 4, 375–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142759
Verdugo P., Alldredge A. L., Azam F., Kirchman D. L., Passow U., Santschi P. H. (2004). The oceanic gel phase: a bridge in the DOM–POM continuum. Mar. Chem. 92, 67–85. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.06.017
Waite D. W., ChuvoChina M., Pelikan C., Parks D. H., Yilmaz P., Wagner M., et al. (2020). Proposal to reclassify the proteobacterial classes Deltaproteobacteria and Oligoflexia, and the phylum Thermodesulfobacteria into four phyla reflecting major functional capabilities. Int. J. Systematic Evolutionary Microbiol. 70, 5972–6016. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004213
Wang F. Q., Bartosik D., Sidhu C., Siebers R., Lu D. C., Trautwein-Schult A., et al. (2024). Particle-attached bacteria act as gatekeepers in the decomposition of complex phytoplankton polysaccharides. Microbiome 12, 32. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01757-5
Welschmeyer N. A. (1994). Fluorometric analysis of chlorophyll a in the presence of chlorophyll b and pheopigments. Limnology Oceanography 39, 1985–1992. doi: 10.4319/lo.1994.39.8.1985
Woebken D., Teeling H., Wecker P., Dumitriu A., Kostadinov I., DeLong E. F., et al. (2007). Fosmids of novel marine Planctomycetes from the Namibian and Oregon coast upwelling systems and their cross-comparison with planctomycete genomes. ISME J. 1, 419–435. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.63
Wucher B. R., Elsayed M., Adelman J. S., Kadouri D. E., Nadell C. D. (2021). Bacterial predation transforms the landscape and community assembly of biofilms. Curr. Biol. 31, 2643–2651.e2643. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.03.036
Yamada Y., Ebihara A., Fukuda H., Otosaka S., Mitarai S., Nagata T. (2024). Functions of extracellular polymeric substances in partitioning suspended and sinking particles in the upper oceans of two open ocean systems. Limnology Oceanography. 69 (5), 1101–1114. doi: 10.1002/lno.12554
Yamada Y., Tomaru Y., Fukuda H., Nagata T. (2018). Aggregate formation during the viral lysis of a marine diatom. Front. Mar. Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00167
Yilmaz P., Parfrey L. W., Yarza P., Gerken J., Pruesse E., Quast C., et al. (2014). The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D643–D648. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1209
Yung C. M., Ward C. S., Davis K. M., Johnson Z. I., Hunt D. E. (2016). Insensitivity of diverse and temporally variable particle-associated microbial communities to bulk seawater environmental parameters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 3431–3437. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00395-16
Zamanillo M., Ortega-Retuerta E., Cisternas-Novoa C., Marrasé C., Pelejero C., Pascual J., et al. (2021). Uncoupled seasonal variability of transparent exopolymer and Coomassie stainable particles in coastal Mediterranean waters. Elementa: Sci. Anthropocene 9. doi: 10.1525/elementa.2020.00165
Keywords: particle dynamics, bacterial community composition, niche differentiation, ocean carbon export, transparent exopolymer particles, differential abundance analysis
Citation: Ebihara A, Fukuda H, Yamada Y, Yokokawa T, Miki T and Nagata T (2024) Structuring of particle-associated bacterial communities along the extracellular polymeric substance gradient of sinking and suspended particles in an oligotrophic, subtropical region of the western North Pacific Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1462522. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1462522
Received: 10 July 2024; Accepted: 25 September 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Kelly Robert Redeker, University of York, United KingdomReviewed by:
Quentin Devresse, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres (HZ), GermanyCopyright © 2024 Ebihara, Fukuda, Yamada, Yokokawa, Miki and Nagata. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Akiko Ebihara, ZWJpaGFyYS1hQGFvcmkudS10b2t5by5hYy5qcA==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.