- 1School of Economics and Management, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China
- 2School of Traffic and Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China
Port construction and operations significantly impact the surrounding environment, creating an urgent need to explore pathways for enhancing port sustainability. Public environmental concern plays a vital role in driving environmental governance and offers new directions for improving port sustainability. Using panel data from 44 coastal ports and their respective cities between 2010 and 2021, this study empirically analyzes the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability and its underlying mechanisms. Additionally, we examine how this impact varies across different city samples. The baseline regression results demonstrate that public environmental concern has a significant positive impact on port sustainability. This finding remains robust after a series of robustness checks and addressing endogeneity issues. Mechanism analysis reveals that public environmental concern can enhance port sustainability by increasing local government environmental investments. Furthermore, the development of digital infrastructure can amplify the positive effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability. Heterogeneity analysis indicates that the positive impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger in cities with lower government environmental regulation intensity, lower pollution emissions, higher education levels, and greater transparency in environmental information disclosure.
1 Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of the global economy and the increasing severity of climate change issues, environmental protection has become a topic of global concern. In 2015, the member states of the United Nations signed the “2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development,” with the 13th Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) being “Climate Action.” This goal mandates necessary actions to mitigate climate change and address its impacts, including raising societal education and awareness about climate change (Leal Filho et al., 2021, 2023). In this context, public environmental awareness and concern have been gradually increasing, becoming a significant force in driving environmental governance. Public environmental concern, which refers to the degree of individual concern about environmental issues, the Earth’s ecosystem, and natural sustainability, not only influences daily lifestyles and consumption choices but also has potential impacts on policy formulation and implementation. Ports, as crucial hubs for global trade and logistics, face significant environmental pressures while promoting economic development. The construction and operation of ports generate wastewater, exhaust gases, and solid waste, and the greenhouse gas emissions from ships docking at ports seriously affect the surrounding environment and even public health (Li et al., 2024). Studies have shown that shipping emissions lead to large-scale ecological disasters related to global warming, acidification, and eutrophication (Jutterström et al., 2021). Additionally, they pose public health issues, such as increased incidences of lung cancer, allergies, asthma, and premature death (Corbett et al., 2007; Ji, 2020). Moreover, the construction and operation of ports, encompassing engineering projects like land reclamation and dredging of shipping channels, can result in the destruction of fish habitats and contamination of water quality, thereby exerting profound impacts on fish assemblages (Barletta et al., 2016). These perturbations contribute to the depletion of fisheries resources, augment the challenges associated with fishing endeavors, and ultimately impinge upon artisanal fishing livelihoods. Therefore, the sustainable development of ports is not only a necessity for economic growth but also a requirement for environmental protection. Port sustainability is crucial for achieving SDG 9 and SDG 11, as enhancing port sustainability can promote industrial innovation and infrastructure upgrades, support the construction of sustainable cities and communities, enhance economic competitiveness, foster inclusive growth, ensure efficient resource utilization, and build a resilient foundation against risks. How to promote port development while reducing its negative environmental impacts has become an urgent issue. Government regulation driven by public environmental concern can encourage enterprises to adopt green technologies and fulfill their environmental, social, and governance commitments. Public environmental concern shapes public environmental awareness and advocates for sustainable consumption through public opinion (Chen et al., 2022), thereby guiding resources towards sustainable industries through market mechanisms and promoting green technology innovation and sustainable development. This provides new directions for the sustainable development of ports.
Public environmental concern refers to the degree of awareness and attention that the public gives to environmental issues and ecological protection. It reflects societal attitudes towards environmental quality, the utilization of natural resources, biodiversity conservation, and climate change. Public environmental concern stems from the broader concept of environmental concern, which is considered to be the extent to which individuals are concerned about environmental issues, the Earth’s ecosystem, and natural sustainability (Fransson and Gärling, 1999; Hartmann and Apaolaza-Ibáñez, 2012). Singh and Bansal (2012) view environmental concern as people’s awareness of environmental and ecological issues and their perceived necessity for actions to address these problems. In other words, environmental concern is related to individuals’ awareness of environmental issues and can be manifested in various ways, such as attitudes, cognition, and personal responses to environmental problems (Weigel and Weigel, 1978). Wiidegren (1998) demonstrated that people’s environmental attitudes gradually form over time, and positive environmental attitudes can help increase environmental concern. Ünal et al. (2018) found that environmental knowledge can enhance individuals’ concern and awareness of environmental issues. Wurzinger and Johansson (2006) also found that tourists with more environmental knowledge showed relatively higher environmental concern for issues related to their travel destinations. Abdul-Muhmin (2007) pointed out that the occurrence of environmental events that threaten nature and disrupt the balance between humans and nature, whether at the regional or international level, seems to positively influence the level of environmental concern. Conversely, Nash et al. (2019) found that people’s perception of global climate change might be limited due to it being beyond their personal perceptual capacity, whereas local environmental phenomena are more easily perceived.
Public environmental concern is considered one of the key factors in encouraging public participation in environmental protection, promoting the formulation of good policies by the government, and improving environmental quality (Li et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2019). Numerous studies have analyzed the drivers of public environmental concern. On the individual level, factors such as age (Gray et al., 2019), gender (Hunter et al., 2004), income (Liu and Mu, 2016), residence location (Fransson and Gärling, 1999), and education level (Marquart-Pyatt, 2007) influence public environmental concern. On the macro level, regional pollution (Hao and Song, 2020), population density (Facchini et al., 2017), and economic development (Franzen and Meyer, 2010; Hao and Song, 2020) also affect public environmental concern.
Dooms et al. (2004) define port sustainability as “commercial strategies and activities that meet the current and future needs of ports and their stakeholders while protecting and sustaining human and natural resources.” In recent decades, there have been prominent initiatives like sustainable ports, eco-ports, and green ports to address the increasing concern over port sustainability (Puig and Darbra, 2019; Wu et al., 2019). In 2013, the World Association for Waterborne Transport Infrastructure (PIANC) Working Group proposed that sustainable ports should be based on “green growth economic strategies,” “living in harmony with nature,” “corporate social responsibility,” and “stakeholder participation”. Similar to eco-ports, the European Sea Ports Organization (ESPO) initiated the Eco Ports project to create ports that coexist with the environment, emphasizing environmental awareness and management improvements (Darbra et al., 2004). Green ports, with sustainability as their primary goal (Paola et al., 2017), focus on monitoring and improving environmental performance by optimizing economic measures to reduce the environmental impact of port operations. Key measures include reducing greenhouse gas emissions within ports, optimizing energy consumption, enhancing water resource management, efficiently handling waste, and adopting environmentally friendly transportation modes and technologies (Alamoush et al., 2020). In 2014, China issued “The Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Transformation and Upgrading of Ports,” which mentioned advancing the green transformation process of ports, strengthening port environmental protection, and actively encouraging ports to carry out ecological protection and restoration projects. The 2019 “Guiding Opinions on Building World-Class Ports” explicitly emphasized establishing a clean and low-carbon port energy system to reduce pollution emissions in port operation areas. The advent of digital innovation has prompted the maritime industry to adopt environmentally sustainable practices to reduce its ecological impact. Utilizing digital technologies can achieve significant time and cost savings in maritime shipping (Fruth and Teuteberg, 2017). This shift focuses on improving energy efficiency, reducing ship emissions, exploring alternative fuel sources, optimizing routes and speeds, and minimizing the environmental footprint of the shipping industry (Jimenez et al., 2022).
Academia generally agrees that evaluating port sustainability should comprehensively consider economic, environmental, and social issues, adopting a holistic view of sustainability (Haddad and Bergek, 2023). Economically, ports are critical nodes in logistics, supply chains, and transportation networks. Approximately 80% of global trade volume and over 70% of trade value are handled by sea, processed by ports worldwide (Cheng et al., 2015). The increase in cargo throughput and trade has significantly boosted the economic benefits derived from ports. Socially, ports face significant pressure from local communities. Port operations cause noise pollution and traffic congestion (Beškovnik and Bajec, 2015). Thus, ports must assume increasing responsibility for their neighboring relations (Shiau and Chuang, 2015). Some scholars view employee safety and security and neighboring relations as indicators for evaluating the social dimension of ports (Kang and Kim, 2017; Lu et al., 2016). Ports have become more socially conscious, demonstrating greater concern for their workforce and its safety (Beškovnik and Bajec, 2015). Environmentally, the impacts of port operations include air pollutants, greenhouse gas emissions, land and soil use, waste, noise, and light issues, water and climate change (Van den Berg and De Langen, 2017). Air pollution caused by ships docked at ports involves not only CO2 emissions but also pollutants such as SO2, NOx, PM10, CO, and VOCs from fuel combustion (Van den Berg and De Langen, 2017). The emissions of SO2, NOx, and PM10 are significant issues locally and regionally, as they contribute to acid rain, photochemical smog, and, more importantly, severe cardiovascular and respiratory problems such as asthma (Spiegler et al., 2012).
Several studies have attempted to establish comprehensive evaluation frameworks to assess port sustainability. Zhou and Xin (2008) used the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to assess the sustainability capacity of various port cities globally, emphasizing the importance of developing soft power. Shao et al. (2009), using the DPSIR model, established an evaluation index system to analyze the ecological construction of coastal ports in China and proposed strategies for building eco-ports. Hou (2010) analyzed the dynamic mechanism of port economic sustainability and established a system dynamics model for port economic sustainability. Wang and Jin (2017) selected five representative ports in the Bohai and Yellow Sea regions of China, using questionnaires to collect data and applying the analytic hierarchy process to analyze the sustainable development performance of these ports and explore the impact of changing evaluation standards on comprehensive scores. Li et al. (2019) constructed a sustainability evaluation model and index system for small ports using energy analysis and analyzed the ecological-economic system characteristics and sustainability of Haiyang Port in Yantai, Shandong Province, China. Zhao et al. (2020) explored coal port sustainability measures based on the triple bottom line of economy, environment, and society, using the case of Huanghua Port, one of China’s largest coal transportation ports, to investigate the integration and optimization role of smart technologies in coal port sustainability. Jaafar et al. (2021) established a concept for a halal-friendly sustainable port based on qualitative data from 38 port stakeholders in southern Malaysia, implementing it to meet sustainable practice goals and drive innovation. Ogara et al. (2023) proposed a framework for evaluating the sustainability of port cities in the WIO region and more broadly applicable to GS countries through a systematic literature review (SLR) to identify themes in existing port city and marine ecosystem sustainability indicator frameworks. Beyene et al. (2024a) used exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to identify key factors related to economic, social, and environmental sustainability and developed a measurement framework to assess the sustainability of dry ports in Ethiopia. Beyene et al. (2024b) emphasized the need to prioritize research linking port sustainability with sustainable development goals, focusing on the relationship between port sustainability, internal sustainability, external cooperation, and port operational quality.
Despite the significant contributions and insights provided by the growing body of literature on port sustainability, several research gaps remain to be addressed. Based on the literature review, we have identified the following research gaps: (1) There is a lack of quantitative assessments of port sustainability, and among the existing quantitative assessments, the development status of the port cities is often overlooked. (2) Current studies primarily focus on the impacts of government policies and technological innovations on port sustainability, with insufficient research on the relationship between public environmental concern and port sustainability.
Unlike previous studies, this research incorporates the development status of cities into the evaluation index system to quantitatively assess port sustainability. It then empirically analyzes the impact and mechanisms of public environmental concern on port sustainability. Based on the aforementioned research gaps, this study sets the following research objectives: (1) To examine 44 coastal ports in China and their respective cities, which exhibit diversity in economic development, industrial layout, and urban planning, making the selection of study subjects more practically significant. (2) To include the development status of the port cities in the evaluation of port sustainability and establish a comprehensive port sustainability evaluation index system. (3) To explore the impact and mechanisms of public environmental concern on port sustainability based on the evaluation of port sustainability. (4) To conduct an in-depth analysis of how the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability varies across different city samples.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
Public environmental concern affects port sustainability in multiple ways. Firstly, as public environmental awareness increases, residents and non-governmental organizations become more attentive and exert pressure on port pollution issues, compelling port managers and operators to adopt environmental measures to reduce harmful emissions and pollutants (Wang and Wheeler, 2005). This pressure not only stems from the demands of local communities but is also driven by international environmental protection organizations, creating a strong bottom-up force that pushes ports to invest more resources in environmental management and technological innovation. Secondly, public expectations for environmental quality influence the policy formulation and enforcement by governments and regulatory agencies (Kathuria, 2007). In response to public demands, governments may introduce stricter environmental regulations and standards, requiring port operators to adhere to green operation practices and conduct regular environmental assessments and monitoring. This policy environment raises the environmental threshold for ports and promotes the development and application of green technologies and clean energy, thereby improving the overall environmental performance of ports. Additionally, public environmental concern impacts the market and business models of ports. An increasing number of customers and partners consider environmental performance a crucial factor when selecting port services (Wu et al., 2022), prioritizing ports with superior environmental records. This market-driven incentive mechanism encourages ports to continuously optimize their environmental management and sustainable development strategies to maintain a competitive edge. Lastly, the role of media coverage and public opinion oversight cannot be overlooked. Media exposure of environmental issues can quickly draw public attention, creating public pressure that forces ports to take immediate measures to address environmental crises and place greater emphasis on sustainable development in their long-term planning.
This paper subsequently delves into the mechanisms through which public environmental concern influences port sustainability, examining the perspectives of governmental environmental investment and digital infrastructure development. In fostering port sustainability, public environmental concern plays a pivotal role by catalyzing local governmental environmental investment. This mechanism underscores not only the profound concern of the populace regarding environmental issues but also demonstrates the immense potential of public engagement in advancing environmental protection and sustainable development. Firstly, public environmental concern is instrumental in promoting sound public policies and environmentally responsible behaviors (Lotspeich and Chen, 1997). During electoral processes, it can directly influence candidates’ policy orientations, urging local governments to prioritize environmental protection in policy formulation. Public demonstrations and advocacy campaigns swiftly capture societal attention, exerting substantial pressure on governments to enforce environmental regulations rigorously (Kathuria, 2007). By highlighting pollution issues in port operations, such as emissions adversely impacting surrounding waters and air quality, public environmental concern effectively amplifies the social repercussions of corporate pollution. This societal pressure diminishes firms’ negotiating prowess with local environmental agencies, compelling them to confront stricter oversight and heightened penalties for violations (Wang and Wheeler, 2005). Concurrently, regulatory bodies intensify penalties for port pollution, further motivating firms to alter their conduct and reduce emissions (Ebenstein, 2012). Secondly, as national and public discourse continues to propel local governments towards green development, establishing and achieving energy and environmental targets have begun to be regarded as benchmarks for evaluating mayoral performance (Zheng et al., 2014). Consequently, local governments must pay greater heed to the demands and expectations of public environmental concern when formulating and implementing environmental policies. To meet these demands, local governments augment investments in environmental protection, encompassing financial, technological, and human resources. These investments not only enhance port environmental performance but also bolster the port’s long-term competitiveness, fostering harmonious economic, social, and environmental development. Lastly, amidst escalating environmental challenges, the populace increasingly leans towards taking action, such as community engagement, resource conservation, opting for eco-friendly products, and advocating for stringent enforcement of environmental regulations (Wu et al., 2022). These actions mirror the populace’s profound concern for environmental issues and underscore the significant role of public engagement in environmental governance. Through these actions, the public continually urges local governments to increase environmental investments, fostering sustainable development in pivotal sectors such as ports.
Digital infrastructure plays a crucial role in enhancing the promotional effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability. Firstly, digital infrastructure significantly enhances the transparency of environmental information. By establishing digital platforms for environmental information disclosure, air quality monitoring networks, and water quality monitoring systems, the public can access detailed data about ports and their surrounding environments in real-time. This increased transparency enables the public to gain a more accurate understanding of the actual environmental impacts of port operations, thereby allowing them to express their environmental concerns more precisely. When the public discovers that port emissions exceed standards or other environmental issues exist, they can utilize digital platforms to rapidly disseminate information, creating public pressure and thus prompting enterprises to adopt green strategies and innovative technologies (Mousavi and Bossink, 2020) to reduce pollution and improve environmental governance performance. Secondly, digital infrastructure enhances the public’s participation capabilities. Through digital platforms such as social media, online forums, and mobile applications, the public can more conveniently engage in environmental discussions and decision-making processes. These platforms not only provide channels for the public to express their opinions and demands but also facilitate communication and cooperation among the public, forming a tighter and more powerful environmental protection network. This, in turn, prompts local governments and enterprises to pay greater attention to environmental protection and sustainable development. Furthermore, digital infrastructure facilitates the analysis and utilization of environmental data. Through advanced technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, vast amounts of environmental data can be deeply mined and analyzed, revealing the complex relationships between port operations and environmental protection. These analytical results not only provide the public with more accurate and comprehensive environmental information but also serve as a basis for local governments and enterprises to formulate more scientific and reasonable environmental policies and decisions.
Based on the above theoretical analysis, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H1: Public environmental concern has a significant positive impact on port sustainability.
H2: Public environmental concern can promote port sustainability by fostering local governmental environmental investment.
H3: Urban digital infrastructure enhances the promotional effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability.
3 Methodology
3.1 Sample
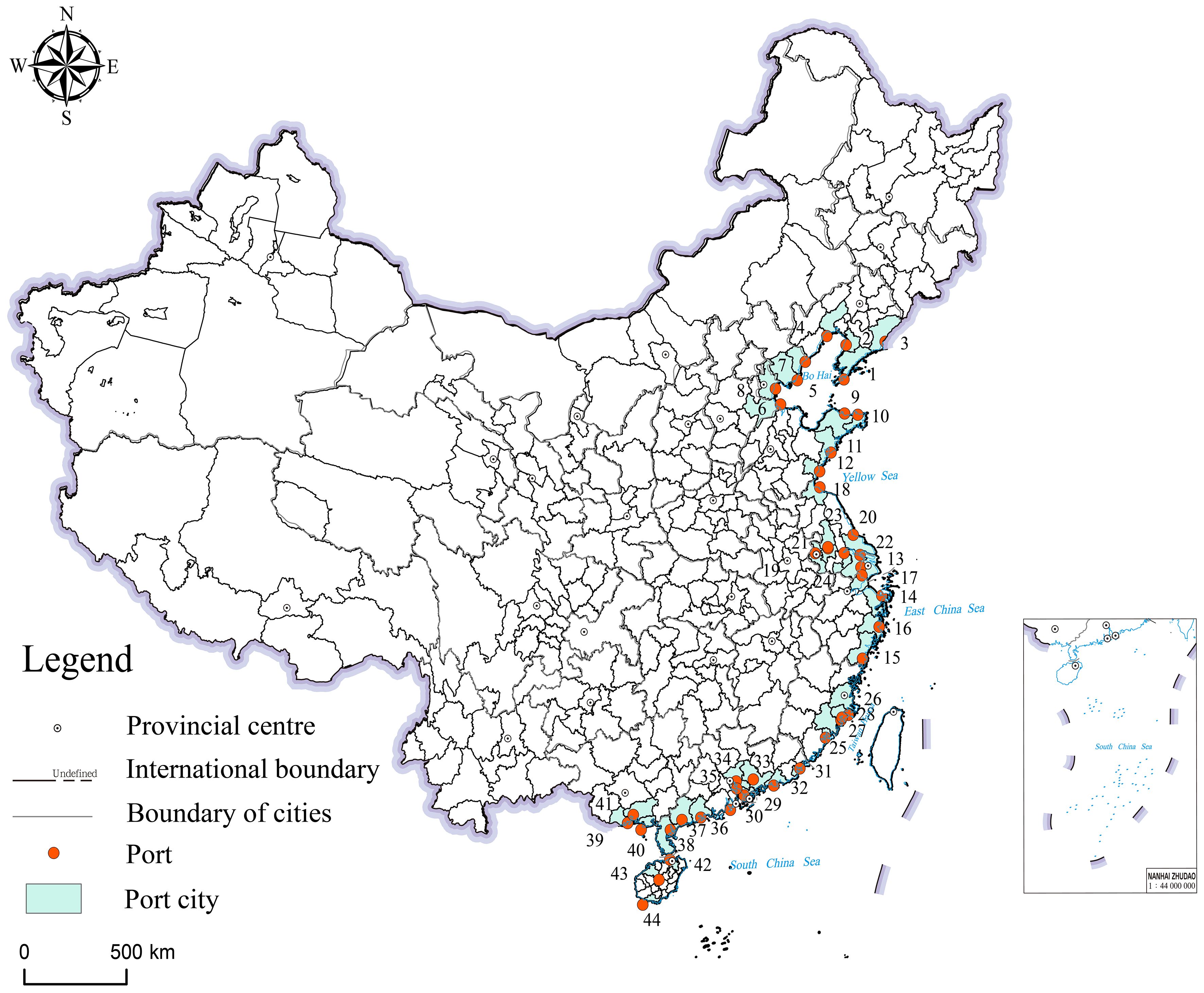
Based on the “National Coastal Port Layout Plan” issued by the Ministry of Transport in 2006 (https://www.gov.cn/ztzl/2007-07/20/content_691642.htm), this study selects 44 ports from five major port clusters along the Chinese coast and their respective municipal administrative regions (see Table 1) as the research objects. The study period covers the years from 2010 to 2021. The geographical distribution of various ports and port cities is depicted in Figure 1. These ports are not only pivotal nodes in China’s maritime transportation network, connecting domestic and international markets through sea routes and facilitating optimal resource allocation and rapid industrial development, but they also play a crucial role within their respective municipal administrative regions. For instance, Shanghai Port, one of China’s largest ports, is located in Shanghai City, one of the most economically developed cities in China. The development of Shanghai Port has driven industrial upgrading and economic growth in surrounding areas. Similarly, Guangzhou Port and Shenzhen Port, important ports in the Pearl River Delta region, have played a vital role in the economic development of Guangdong Province and even the entire South China region. Furthermore, these port cities exhibit diversity in industrial layout and urban planning, with some focusing on heavy industry development and others emphasizing the cultivation of high-tech and service industries. Therefore, by examining these diverse and significant ports and their cities as research subjects, studying the impact of public environmental concern on sustainability can enhance public environmental awareness, promote green port development, strengthen the scientific basis of policy formulation, drive industry-wide environmental transformation, and achieve sustainable development goals. This has a positive effect on achieving a win-win situation for both environmental protection and economic development.
3.2 Description of variables
3.2.1 Dependent variable
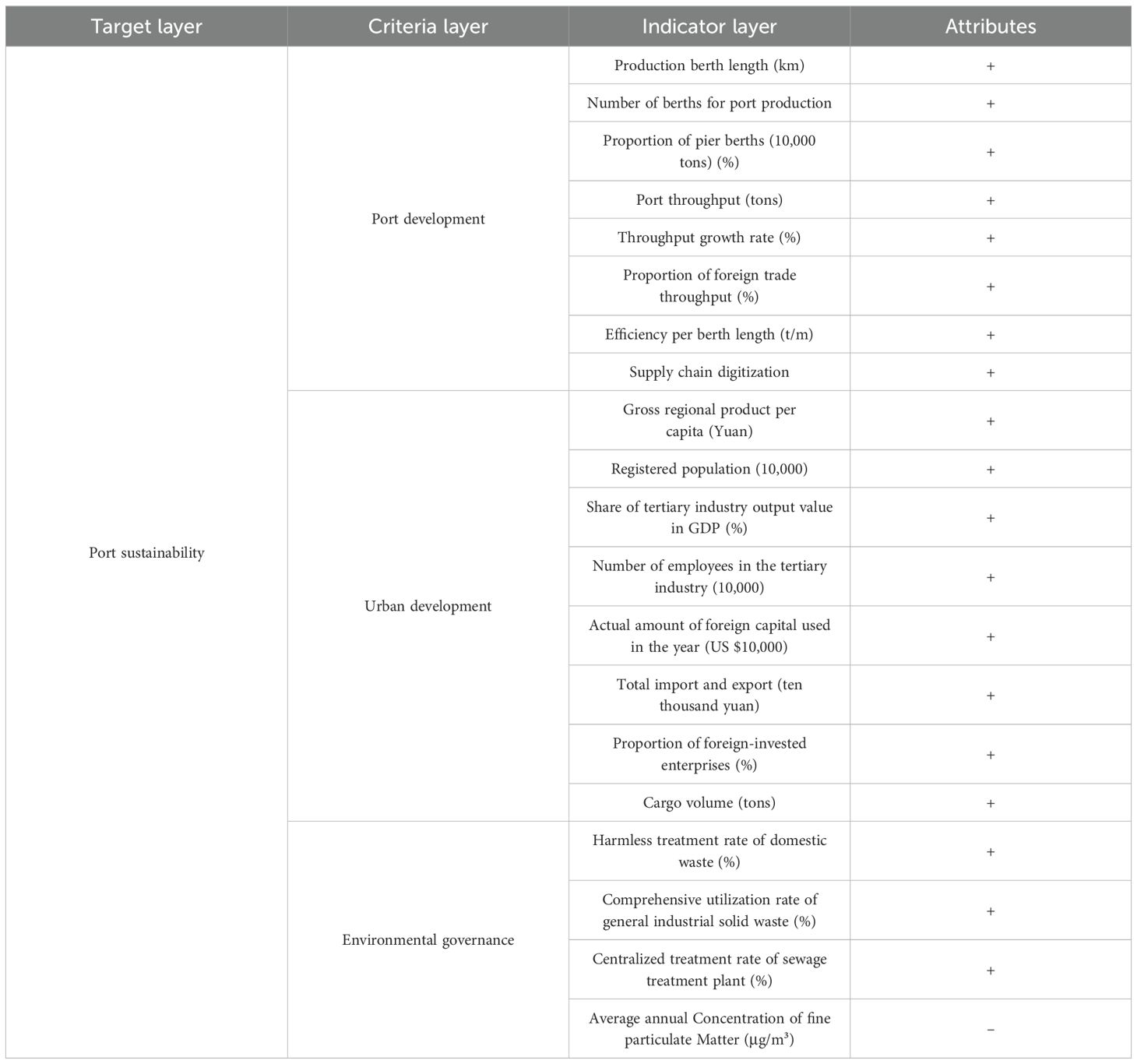
The dependent variable in this study is Port Sustainability (PSD). Referring to relevant studies (Ye and Zhao, 2016; Liu et al., 2023), the indicators for port sustainability are selected based on seven principles: scientificity, feasibility, independence, completeness, conciseness, hierarchy, and dynamism. These indicators cover three main aspects: port development status, urban development status, and environmental governance status.
Excellent geographic location, deep-water channels, and other natural port conditions are crucial factors for port development. The physical infrastructure of a port is a significant indicator of its scale and serves as the foundation for its development. The length, number, and size of port berths are indicators used to measure port scale. Throughput is the most critical metric for assessing port scale and capacity. It reflects the port’s competitiveness and indirectly indicates its revenue and profit scale. The growth level of throughput can reflect the port’s competitiveness and development potential. Foreign trade throughput reflects the degree of foreign trade dependence of the port and its hinterland, making it an essential indicator of port development. There are various metrics for measuring port operational efficiency. Based on data availability and representativeness, this study selects the utilization efficiency of the port coastline, measured by the ratio of port throughput to berth length, to reflect port operational efficiency. The digitalization of the supply chain is an important means to promote port sustainability, helping ports achieve long-term and stable development through improved efficiency and green operations. The above data is used to measure port development status. Data on the port is obtained from the Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China (https://www.mot.gov.cn/), and data on supply chain digitalization pilot cities is sourced from the Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China (http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/).
The development of the cities where ports are located serves as the foundation and support for port development. The economic development level and population size of these cities directly influence the current state and future prospects of port development. Urban development not only promotes trade volume growth but also provides various services to the port industry. The GDP of port cities generally correlates positively with port throughput, and the total import and export volume of the city is closely related to the port’s throughput. The proportion and scale of the tertiary industry in port cities indirectly affect the throughput and revenue capacity of local ports. The outward economic orientation of port cities has a significant impact on ports. Foreign investment injects vitality into the industrial development of port cities and influences the import and export volume of the ports. Hence, the actual utilization of foreign capital in port cities profoundly affects port construction and development. The intermodal transport system in port cities determines the breadth and depth of hinterland cargo sources, which are the foundation for port survival. An efficient intermodal transport system facilitates the continuous transport of goods from a vast direct and indirect hinterland to the port, increasing the port’s business volume and promoting port development. This study selects eight indicators to represent urban development status: per capita GDP of port cities, registered population size, the proportion of tertiary industry output, the number of employees in the tertiary industry, the actual utilization of foreign capital, total import and export volume, the proportion of foreign-invested enterprises, and total freight volume of the city. The relevant data is obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn).
There are various indicators to measure the environmental governance status of cities, covering aspects such as air, water, and noise. This study selects four indicators to evaluate the environmental governance status of port cities: harmless disposal rate of household waste, comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste, centralized treatment rate of sewage treatment plants and annual average concentration of inhalable particulate matter (PM10).These indicators respectively measure the governance of household waste, solid waste, water, and air in port cities. The relevant data is obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn).
To establish a comprehensive evaluation system for port sustainability, the aforementioned indicators were selected, as detailed in Table 2. This study employs the entropy method to measure port sustainability, with the specific measurement process outlined below:
Firstly, the collected indicator data undergo normalization. The processing method for positive indicators is shown in Equation 1, while the method for negative indicators is presented in Equation 2.
Secondly, the information entropy and weights of each indicator are calculated. A larger variation in the value of a particular indicator x implies that it provides more information, thus warranting a higher weight, and vice versa.
Calculation of Information Entropy for Each Indicator:
Calculation of Weights for Each Indicator:
Finally, the comprehensive score for port sustainability is computed using the weighted summation formula:
In Equations 1-6, Xij represents the original value of the jth indicator in the ith year. Zij denotes the normalized indicator value. ej signifies the information entropy value of the indicator. ωj represents the weight of the indicator. PSDi stands for port sustainability.
3.2.2 Independent variable
The independent variable in this study is public environmental concern (PEC). Public environmental concern plays a role in coordinating public environmental behavior, and the rise of social networks has further enhanced the universality of public environmental participation. Public environmental concern can measure the degree of public involvement in environmental issues beyond formal regulations. Therefore, this study uses the Baidu Environmental Pollution Search Index as a proxy variable for public environmental concern. Baidu Search Engine boasts an extensive user base in China, with its search index serving as a reliable indicator of public attention towards specific topics. Environmental pollution, as a prevalent societal concern, can be quantified through search indices. Moreover, Baidu Index employs advanced data processing techniques to ensure the accuracy and reliability of its data. Although search behavior may be influenced by various factors, the overall search index for environmental pollution on Baidu still provides a good reflection of the public’s overall level of concern regarding environmental pollution issues. Consequently, it serves as an effective proxy variable for studying public environmental concerns. The Baidu Index is divided into total search index, PC search index, and mobile search index based on search channels. The total search index is the weighted sum of the PC and mobile search indices. Thus, this study employs the Baidu Environmental Pollution Total Search Index to represent public environmental concern (Liu and Yuan, 2024).
3.2.3 Control variables
To accurately analyze the impact of new productive capacity on port sustainability, avoid omitting variables, and ensure the robustness of empirical results, the following control variables are introduced in the regression model. Economic growth rate (EGR, defined as the growth rate of regional gross domestic product) in regions with rapid economic expansion typically coincides with increased trade activities and cargo transportation demands, which directly propel the development of ports. Government expenditure (GE, represented by general budget expenditures of local governments as a proportion of regional GDP) can be allocated to the construction of port infrastructure and supporting facilities such as transportation, environmental protection, and public services in the vicinity of ports. These investments contribute to enhancing port operational efficiency and service quality. Scientific expenditure (SE, calculated as scientific expenditure as a proportion of general budget expenditures of local governments) supports research and development (R&D) and innovation in port-related technologies, including intelligence, automation, and green technologies. These advancements can improve port operational efficiency, reduce operational costs, and mitigate environmental pollution. Regions with adequate current assets (CA, measured by total current assets as a proportion of regional GDP) facilitate easier access to financing support for enterprises, enabling them to expand production scales and increase trade activities, which indirectly promotes port development. The scale of the transportation industry (STI, indicated by the number of employed individuals in the transportation industry as a proportion of total regional employment) is a crucial support for port development. A larger scale implies a more comprehensive transportation network surrounding the port, facilitating more convenient cargo transportation. An increase in the employment rate (ER, defined as the total number of employed individuals in a region as a proportion of the total regional population) can enhance residents’ income and consumption capacity, thereby stimulating growth in trade activities and cargo transportation demands. The data for these control variables are obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn).
3.3 Baseline model
To empirically examine the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability, we have constructed an empirical benchmark model, namely the two-way fixed effects panel data model. The two-way fixed effects panel data model is a statistical method used for analyzing panel data. This model accounts for both individual fixed effects and time fixed effects by incorporating individual and time dummy variables, enabling the control of unobservable heterogeneity and thus providing more accurate estimates of the impact of independent variables on dependent variables. Such models are widely applied in fields such as economics and sociology for assessing policy effects, studying industry trends, and other purposes, aiding in the provision of more reliable conclusions and decision-making foundations. The specific form of the benchmark model is presented in Equation 7:
Where k represents the city, i represents the year; the dependent variable PSD represents port sustainability; PEC represents public environmental concern; Control represents a series of city-level control variables, and the purpose of adding control variables is to mitigate the interference of endogeneity such as omitted variables; α and β are the regression coefficients of the corresponding variables; μk represents the city fixed effects, υi represents the year fixed effects; ϵik represents the random disturbance term.
4 Empirical analysis
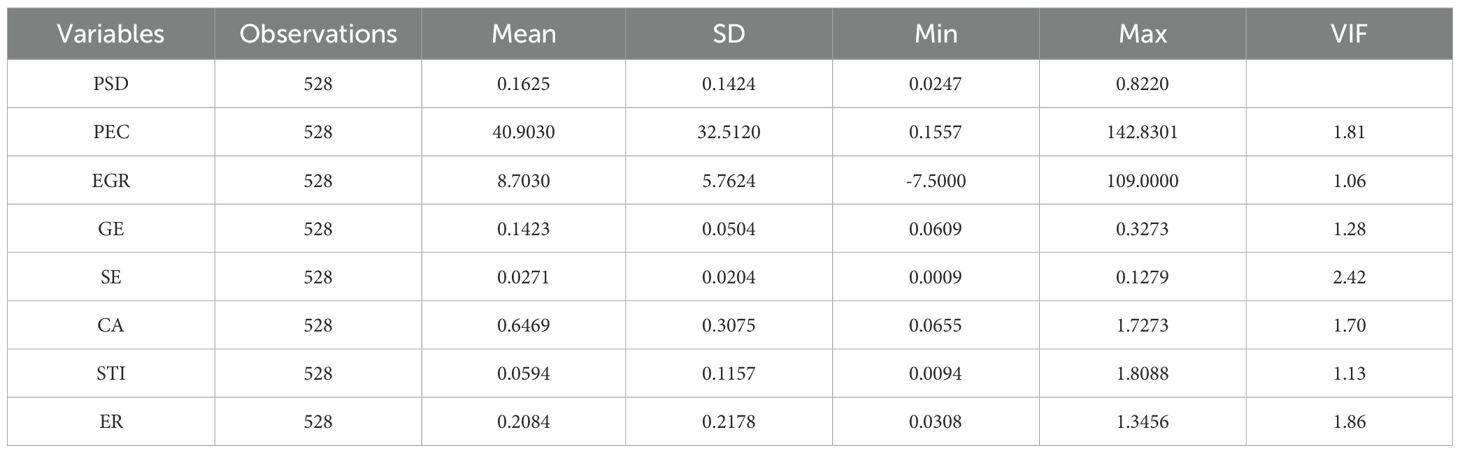
To ensure the consistency and validity of the model estimation, we analyzed the multicollinearity of all variables before testing hypotheses. The variance inflation factors (VIF) for all variables are smaller than 10, thus indicating that the multicollinearity is not the main concern of the study. Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics and correlations.
4.1 Baseline regression
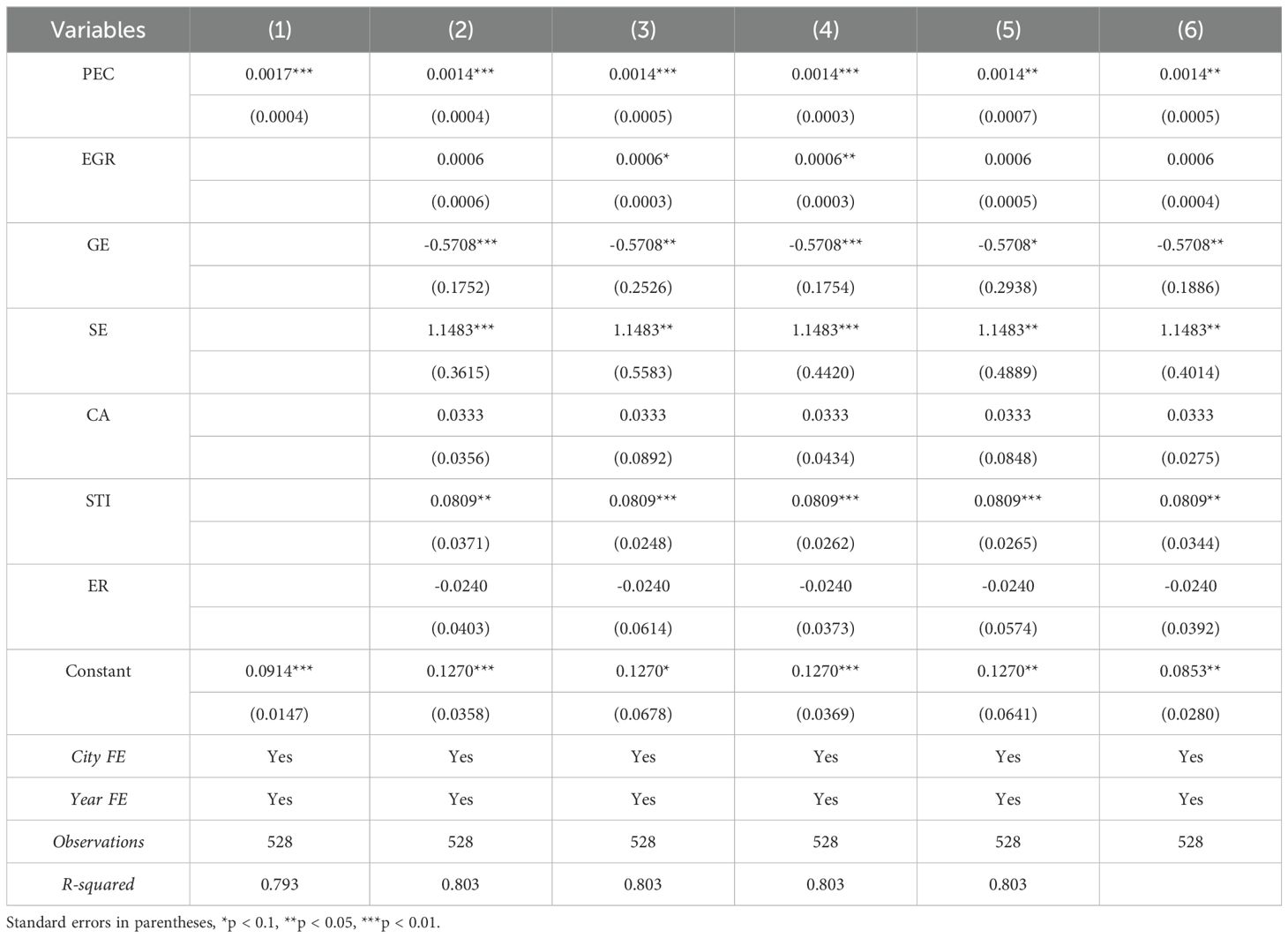
To identify the causal relationship between public environmental concern and port sustainability, this paper conducts an empirical test on the baseline model specified in Equation 1. The regression results are presented in Table 4. In Table 4, column (1) regresses the key independent variable and the dependent variable while controlling for city and year; column (2) includes control variables in the regression; column (3) clusters standard errors at the city level; column (4) clusters standard errors at the city-year level; column (5) uses robust standard errors with city and year double clustering; column (6) employs Driscoll-Kraay standard errors (Driscoll and Kraay, 1998). The results show that the estimated coefficients for PEC are all significantly positive, indicating that, ceteris paribus, an increase in public environmental concern significantly promotes port sustainability. Hypothesis 1 is verified.
4.2 Instrumental variable regression
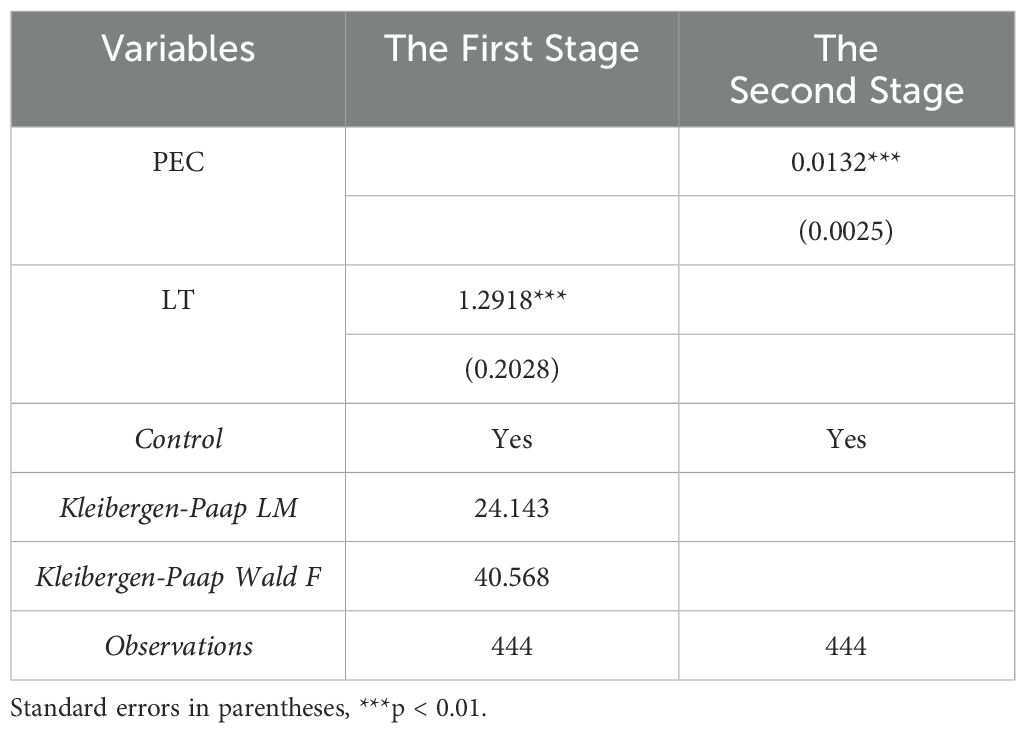
Considering potential endogeneity issues such as omitted variables, reverse causality, and measurement errors, we adopt the instrumental variable method and use the two-stage least squares (2SLS) approach for endogeneity testing. Specifically, this paper uses the number of landline telephones per 100 people (LT) as the instrumental variable. (1) In terms of relevance, historically, regions with higher fixed telephone penetration rates often experienced higher levels of economic development and social informatization. These regions are more likely to develop environmental awareness and concern during the modernization process. Therefore, the current public environmental concern is relatively higher in these regions. From this perspective, using the number of landline telephones per capita as an instrumental variable for public environmental concern meets the relevance requirement. (2) In terms of exogeneity, the number of landline telephones per 100 people in 1984 is historical data, making it unlikely to directly affect current port sustainability. Thus, this variable satisfies the exogeneity condition. Additionally, given that this variable is cross-sectional data and cannot be directly applied as an instrumental variable in the model, this paper uses the interaction term between this variable and time dummy variables as the instrumental variable for policy variables. Table 5 reports the estimation results of the instrumental variable regression. Column (1) presents the first-stage estimation results of the instrumental variable regression, showing that the instrumental variable LT is highly positively correlated with public environmental concern. The Kleibergen-Paap LM and Kleibergen-Paap Wald F tests also confirm that the chosen instrumental variable does not suffer from under-identification or weak identification issues, indicating that the instrumental variable is valid. Column (2) shows the second-stage results of the instrumental variable regression, where the coefficient for PEC is positive and significant at the 1% level. These results further validate that the chosen instrumental variable meets the exogeneity condition. The instrumental variable regression results indicate that after addressing potential endogeneity issues, the conclusions drawn from the baseline regression still hold.
4.3 Robustness test
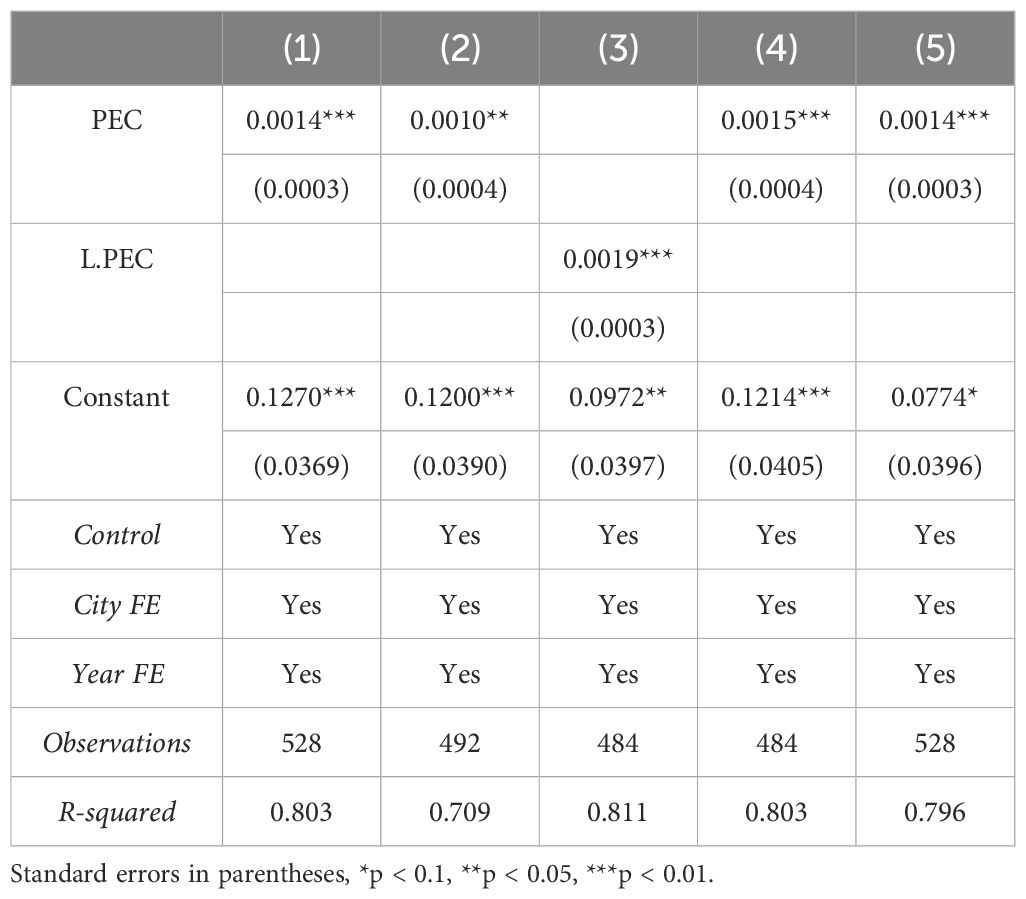
To ensure the reliability of the research results, this paper conducts robustness checks from the following five aspects: First, control for the time trend of city administrative levels. Considering that some cities in the sample are provincial capitals or sub-provincial cities, which may receive more resources and policy support due to their administrative level, leading to differentiated impacts on port sustainability over time. To alleviate estimation bias, this paper controls for the interaction terms of the dummy variables of city administrative levels and time trends in the baseline regression model. If a city is a provincial capital or sub-provincial city, the value is 1; otherwise, it is 0. Second, exclude certain samples. To mitigate possible omitted variable bias and selection bias, we exclude the samples of Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, as these megacities differ significantly from other cities in terms of economic development levels and preferential policies. The regression is then re-estimated after removing these cities from the sample. Third, consider the potential lagged effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability. This paper lags public environmental concern by one period to examine the impact of changes in public environmental concern on port sustainability in the following period. Fourth, besides controlling for the endogeneity bias of the key independent variable, we are also concerned about the potential endogeneity of other control variables. To test the robustness and eliminate this concern, all other control variables are lagged by one period and the regression is re-estimated. Fifth, considering the possibility of measurement anomalies in public environmental concern and port sustainability data, which may lead to discrepancies between estimated values and actual situations, we apply a 1% winsorization to the selected variable data and re-estimate the regression. The regression results are shown in columns (1) to (5) of Table 6. The results indicate that the coefficients for public environmental concern are all significantly positive, further validating the reliability of the baseline regression results.
5 Mechanism analysis
5.1 Government environmental input mechanism
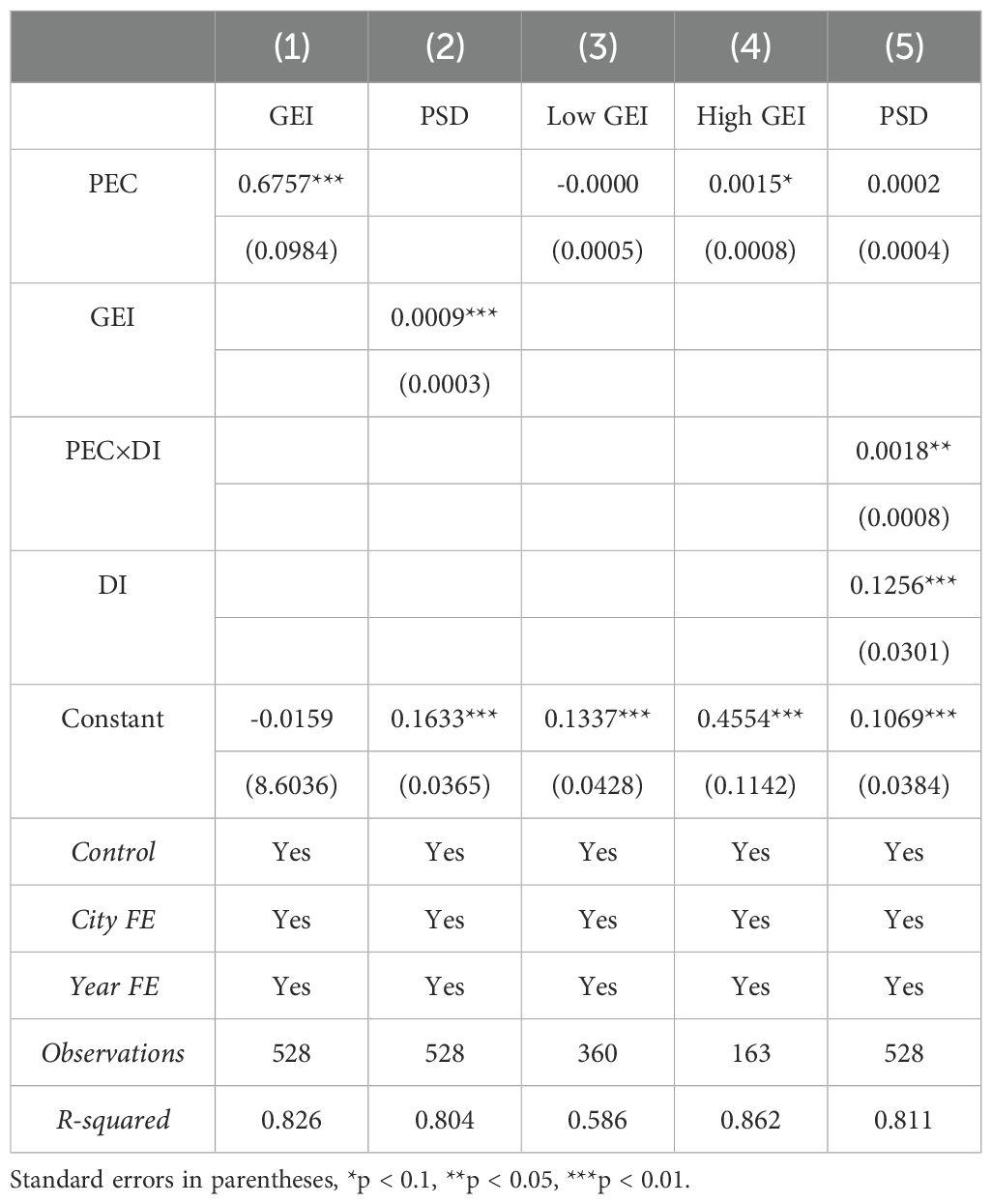
To test whether public environmental concern can promote port sustainability by increasing local government environmental investment, this paper follows the approach of Yu et al. (2023). We use the ratio of the output value of the secondary industry in each city to the output value of the secondary industry in its province as a weight and multiply it by the provincial environmental pollution investment to serve as a proxy variable for local government environmental investment (GEI). First, this paper examines the impact of public environmental concern on government environmental investment. Then, it tests the impact of government environmental investment on port sustainability. Using the 2016 city-year average of government environmental investment as the dividing standard, the sample is divided into high and low groups for group regression. The regression results are shown in columns (1) to (4) of Table 7. The results indicate that the increase in public environmental concern significantly promotes the increase in government environmental investment, and the increase in government environmental investment significantly enhances port sustainability. The group regression results show that the positive effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger in cities with higher government environmental investment compared to those with lower government environmental investment. This demonstrates that public environmental concern can enhance port sustainability by increasing local government environmental investment. Public environmental concern influences government environmental investment behavior, prompting governments to take measures to improve the existing environmental conditions. As government environmental investment increases, the enthusiasm of various social entities to participate in social construction and production will rise, leading to the long-term development of port sustainability. Hypothesis 2 is verified.
5.2 Digital infrastructure regulatory mechanism
To verify whether the construction of urban digital infrastructure can enhance the positive effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability, this paper selects the following data: the ratio of postal business volume to GDP, the ratio of telecommunications business volume to GDP, the “Broadband China” policy, the ratio of international internet users to the total population, the ratio of year-end mobile phone users to the total population, the proportion of employees in information transmission, computer services, and software industries to the total number of employees, the “Smart City” policy, and the “E-commerce” policy. We then use the entropy method to calculate the comprehensive score, which serves as a proxy variable for the level of digital infrastructure construction (DI) in each city. Next, we add the interaction term PEC×DI to the baseline model for regression. The results are reported in column (5) of Table 7. The results show that the coefficient of PEC×DI is significantly positive, indicating that in cities with higher levels of digital infrastructure construction, the positive effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability is greater. This suggests that the construction of digital infrastructure can strengthen the positive impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability. Hypothesis 3 is verified.
6 Heterogeneity analysis
Due to differences in the economic, social, and environmental conditions, economic foundation, and industry types of cities, the external validity of the baseline regression results may vary across different types of cities. Therefore, this paper conducts heterogeneity tests from four aspects: government environmental regulation, pollution emissions, education level, and environmental information disclosure.
6.1 Heterogeneity of government environmental regulation
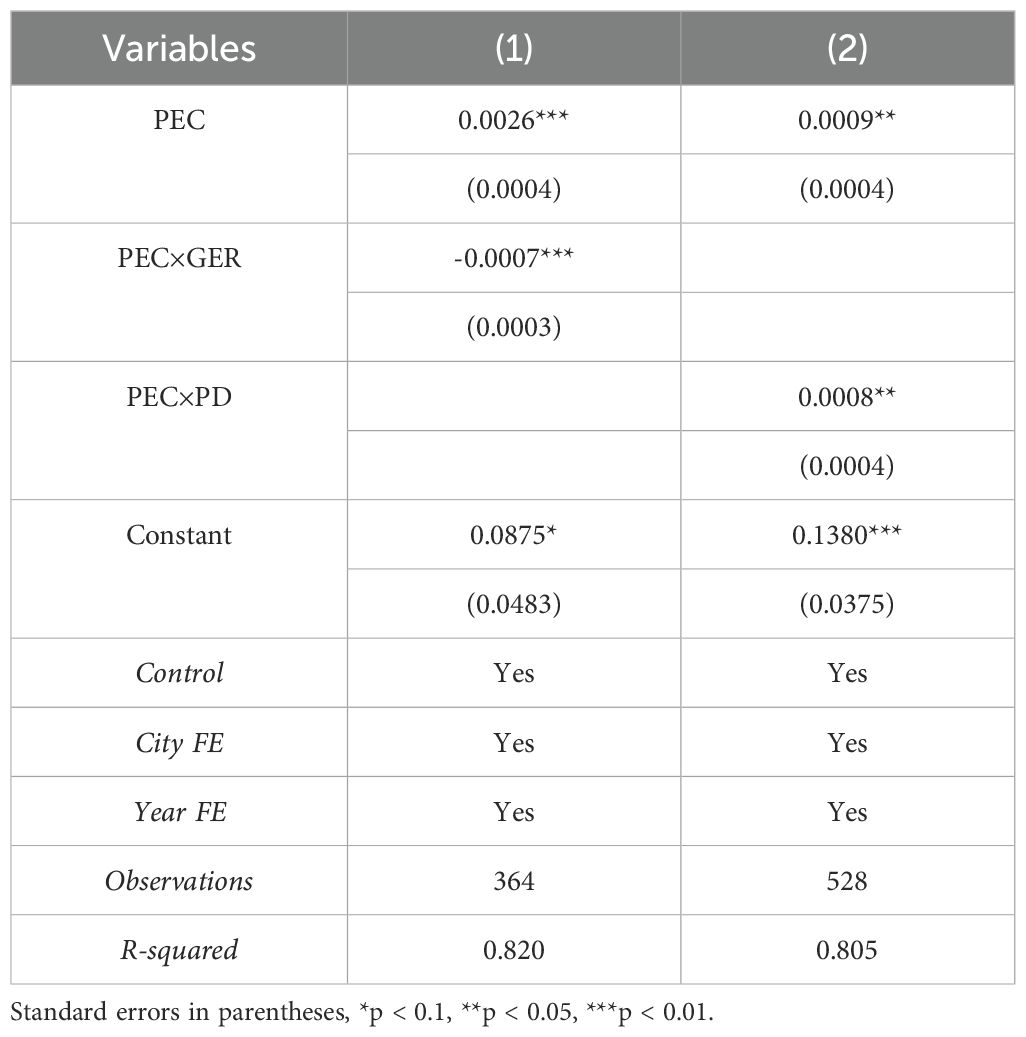
In government work reports, a higher frequency of environmental terms indirectly reflects a higher degree of government attention to environmental protection, thereby increasing the intensity of environmental regulation. Referring to the approach of Chen et al. (2018), this paper processes the text of government work reports using word segmentation to count the frequency of environment-related terms and calculates their proportion relative to the total word frequency of the entire report to measure the intensity of government environmental regulation. We construct a dummy variable for government environmental regulation (GER), where GER equals 1 if the intensity of government environmental regulation is above the mean, and 0 otherwise. The specific environment-related terms include: “environmental protection,” “pollution control,” “energy consumption,” “emission reduction,” “sewage discharge,” “ecology,” “green,” “low carbon,” “air,” “chemical oxygen demand,” “sulfur dioxide,” “carbon dioxide,” “PM10,” and “PM2.5,” totaling 14 terms. Next, we add the interaction term PEC×GER to the baseline model for regression. The results are reported in column (1) of Table 8. The results show that the coefficient of PEC×GER is -0.0007 and significant, while the coefficient of PEC is 0.0026 and significant. This indicates that in cities with relatively weaker government environmental regulation, the positive impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger compared to cities with stronger government environmental regulation.
6.2 Heterogeneity of pollution emissions
To examine whether the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability differs in cities with varying pollution emission levels, this paper uses per capita industrial wastewater discharge as a proxy variable for pollution emission levels. We construct a dummy variable for city pollution emission levels (PD), where PD equals 1 if the city’s pollution emission levels are above the mean, and 0 otherwise. Next, we add the interaction term PEC×PD to the baseline model for regression. The results are reported in column (2) of Table 8. The results show that the coefficient of PEC×PD is 0.0008 and significant, while the coefficient of PEC is 0.0009 and significant. This indicates that in cities with lower pollution emission levels, the positive impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger compared to cities with higher pollution emission levels.
6.3 Heterogeneity of urban education level
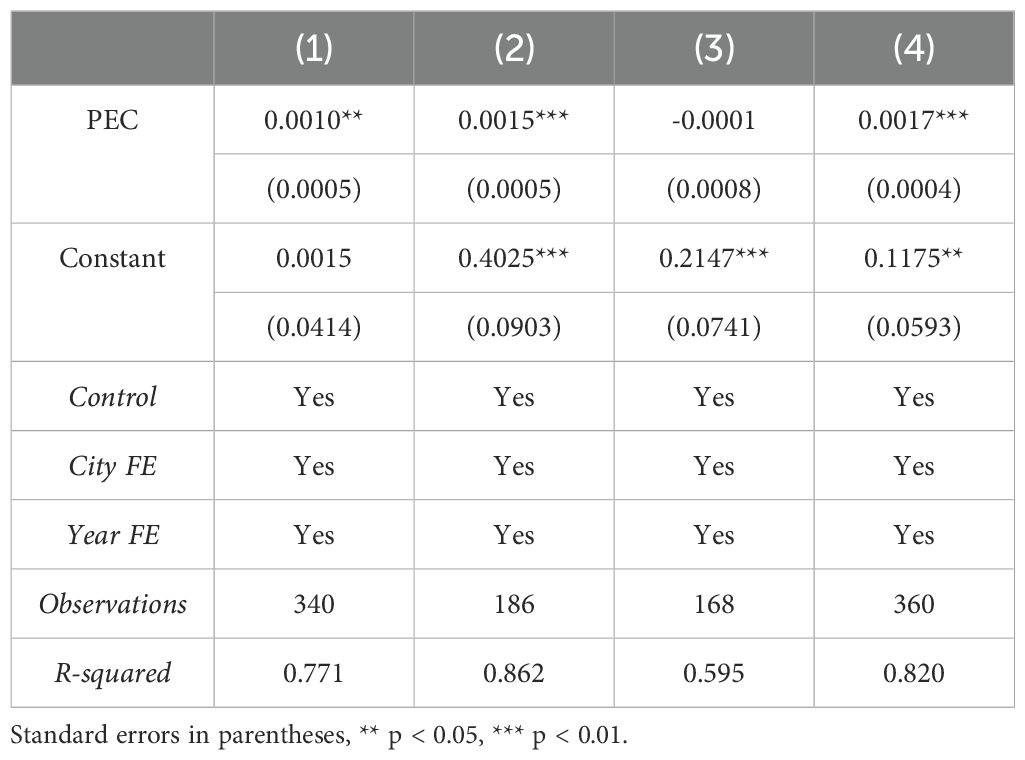
Due to differences in economic development and educational resources, there is significant variability in education levels across cities in China. To examine whether the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability differs in cities with varying education levels, this paper uses the annual city average number of full-time teachers in regular higher education institutions per capita as the basis for classification. The study sample is divided into low education level and high education level groups, and separate regressions are conducted for each group. The regression results are shown in columns (1) and (2) of Table 9. The results indicate that in the sample of cities with lower education levels, the coefficient of public environmental concern is 0.0010 and significant, while in the sample of cities with higher education levels, the coefficient of public environmental concern is 0.0015 and significant. This suggests that the positive impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger in cities with higher education levels. The reason is that, compared to cities with lower education levels, cities with higher education levels have a populace with stronger environmental awareness and higher sensitivity to environmental information, leading to a stronger incentive effect on port sustainability.
6.4 Heterogeneity of environmental information disclosure
After the implementation of the “Measures for Environmental Information Disclosure (Trial)”, local governments are required to disclose information on major pollutant emissions. This paper categorizes the 113 evaluated cities into an environmental information disclosure group, while the remaining cities are categorized into a non-disclosure group, and separate regressions are conducted for each group. The regression results are shown in columns (3) and (4) of Table 9. The results indicate that in the sample of cities with environmental information disclosure, the coefficient of public environmental concern is 0.0017 and significant, whereas in the non-disclosure group, the coefficient is negative and not significant. This suggests that when environmental information is disclosed, the incentive effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger.
6.5 Discussion on heterogeneity analysis results
In cities with relatively weaker government environmental regulations, public environmental concern exhibits a stronger promotive effect on port sustainability. Several plausible reasons underpin this phenomenon. Firstly, when governmental environmental regulations are lax, enterprises face lesser pressure to enhance their environmental performance, lacking the impetus for proactive environmental improvements (Chang et al., 2021). Consequently, public environmental concern emerges as a crucial external force driving enterprises to adopt eco-friendly practices. The heightened attention to environmental issues and the public’s resistance to polluting behaviors create formidable societal pressure, compelling enterprises to prioritize environmental concerns, thereby fostering more sustainable development strategies within ports. Secondly, cities with weaker environmental regulations often lack stringent environmental regulations and monitoring mechanisms, rendering corporate environmental behavior more reliant on intrinsic morality and responsibility. An elevated level of environmental concern can stimulate the public’s environmental awareness and sense of responsibility (Yoon et al., 2021), encouraging more active participation in environmental initiatives, thereby fostering a conducive environmental atmosphere that positively influences enterprises to emphasize environmental issues and enhance ports’ environmental performance. Lastly, in cities with weaker environmental regulations, ports often possess greater potential for improvement in environmental aspects. As environmental concern increases, ports can more readily achieve significant enhancements in environmental performance through measures such as improved environmental technologies and optimized operational practices.
In cities with lower pollution emissions, public environmental concern exhibits a more potent promotive effect on port sustainability. This may be attributed to several factors. Firstly, a low-pollution environment per se indicates that these cities have achieved certain successes in environmental protection, leading to heightened public expectations and demands for environmental protection. Consequently, as environmental concern intensifies, the public becomes more sensitive to the environmental performance of key sectors such as ports, thereby pushing ports to adopt stricter and more effective environmental measures to maintain and enhance environmental quality. Secondly, cities with lower pollution emissions tend to possess more developed environmental infrastructure and regulatory systems (Lu et al., 2024), providing favorable conditions for ports to achieve sustainable development. Lastly, an increase in public environmental concern enhances public environmental awareness and participation, fostering broader environmental consensus and action. In cities with lower pollution emissions, such consensus and action may be more easily formed and sustained, urging key sectors such as ports to make greater efforts in environmental protection, thereby realizing sustainable development.
In city samples with higher education levels, public environmental concern demonstrates a stronger promotive effect on port sustainability. On one hand, the enhancement of education levels significantly bolsters the public’s cognition and understanding of environmental issues (Beata and Bartkus, 2023). Well-educated citizens are more adept at acquiring, comprehending, and analyzing environmental information, thereby forming a more comprehensive and profound understanding of environmental problems. This heightened cognition prompts them to pay closer attention to ports’ environmental performance, maintaining a high degree of vigilance regarding environmental risks and impacts associated with port operations, and consequently exerting potent oversight on port sustainability. On the other hand, the public with higher education levels often possesses stronger environmental awareness and a sense of responsibility (Harring et al., 2020). They are more inclined to view environmental protection as a social responsibility and moral obligation, actively participating in environmental initiatives, and urging ports to adopt more environmentally friendly and sustainable development strategies through social opinion and consumer choices. This active participation not only elevates ports’ environmental performance but also fosters an overall societal atmosphere conducive to environmental protection.
In city samples with environmental information disclosure, public environmental concern exhibits a more potent promotive effect on port sustainability. Firstly, environmental information disclosure enhances the public’s right to know and to supervise. When cities implement environmental information disclosure policies, the public can readily access ports’ environmental data, operational status, and other pertinent information, thereby forming a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of environmental issues (Pan et al., 2022). This transparency prompts the public to pay closer attention to ports’ environmental performance, maintaining a high degree of vigilance regarding environmental risks and impacts associated with port operations, and consequently exerting potent oversight on port sustainability. Secondly, environmental information disclosure fosters communication and interaction between the public and ports. By accessing environmental information, the public can more directly understand ports’ environmental efforts and achievements, thereby enhancing trust and support for ports. Simultaneously, the public can engage in closer interactions with ports by providing feedback, suggestions, and other inputs, jointly driving continuous improvement and optimization of ports’ environmental performance. Lastly, environmental information disclosure stimulates the public’s environmental awareness and a sense of responsibility. When the public can clearly see ports’ environmental performance, they are more likely to form a consensus on environmental protection, viewing it as a social responsibility and moral obligation. This consensus and sense of responsibility prompt the public to more actively engage in environmental initiatives, urging ports to adopt more environmentally friendly and sustainable development strategies through social opinion and consumer choices.
7 Conclusion
In this paper, our research sample comprises 44 coastal ports and their respective cities in China from 2010 to 2021. We integrate the development status of port cities into port sustainability assessments and establish a comprehensive port sustainability evaluation index system to assess the sustainability of each port. Subsequently, we empirically analyze the impact and mechanism of public environmental concern on port sustainability, and delve into the manifestation of this impact across different city samples. The primary conclusions drawn are as follows:
First of all, within the sample selected for our study, public environmental concern has a significant positive impact on port sustainability. After a series of robustness checks and addressing endogeneity issues, the results remain robust.
Secondly, Public environmental concern can promote port sustainability by increasing local government environmental investment, while the construction of digital infrastructure can further enhance this positive effect.
Finally, in cities with lower government environmental regulation intensity, lower pollution emission levels, higher education levels, and transparent environmental information disclosure, the promotion effect of public environmental concern on port sustainability is stronger.
Despite significant advancements in exploring the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability, the present study is not devoid of limitations and simplifications. The specific limitations of this research are manifested in the following aspects: Firstly, the utilization of Baidu Search Index as a proxy for public environmental concern may possess inherent constraints, potentially failing to comprehensively and accurately reflect the genuine attitudes and attention of the public. Furthermore, in constructing the indicator system for port sustainability, due to data availability issues, we may have omitted certain factors that have significant yet difficult-to-quantify impacts on port sustainability. Secondly, although the control variables selected in this paper cover multiple dimensions, they may still fail to fully capture all potential impacts of public environmental concern on port sustainability. Thirdly, while the research subjects in this paper possess a certain degree of representativeness, they may not fully represent the situations of all ports and cities. Differences in geographical location, economic development levels, and industrial structures among various ports and cities may lead to heterogeneity in the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability. The simplifications in this study encompass the following two aspects: Firstly, to facilitate analysis and extract key information and trends, a simplified panel regression model was employed. Such simplification may fail to capture potential nonlinear relationships or more complex interaction effects. Secondly, in the analysis of the mechanism of action, we neglected other possible intermediary variables or pathways, which to some extent limits our exploration of more complex mechanisms.
In future research, the impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability development can be further explored from the following perspectives: One important perspective is the diversity of China’s coastal ports, which include large comprehensive ports, specialized ports, and small local ports. Different types of ports have significant differences in functional positioning, economic contribution, and environmental impact. Future research can refine the analysis of public environmental concern on the sustainability of different types of ports, examining its performance and mechanisms in various port contexts. Another perspective is the complex interactions between public environmental concern and socioeconomic factors. Public environmental concern does not exist in isolation; it interacts with factors such as economic development level, industrial structure, social culture, and policy regulations. Future studies can adopt a systemic approach to examine these interactive effects. A third perspective involves utilizing dynamic models and prospective analysis methods to study the temporal changes in the impact of public environmental concern. By constructing dynamic system models, researchers can analyze the interactions among public environmental concern, government policies, corporate behavior, and environmental quality, and predict the long-term impact of public environmental concern on port sustainability development. This dynamic analysis will help in formulating more scientific and sustainable port development strategies.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn).
Author contributions
JS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZF: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JN: Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XR: Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. General Project of the National Social Science Foundation, grant/award number: 21BJY223; General Project of the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation, grant/award number: CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0046; and Major Project of Chongqing Social Science Planning “Construction of Western Land-Sea New Passage”, grant/award number: 2023ZDLH06. Chongqing Graduate Research Innovation Project (CYS240513).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdul-Muhmin A. G. (2007). Explaining consumers’ willingness to be environmentally friendly. Int. J. Consumer Stud. 31, 237–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-6431.2006.00528.x
Alamoush A. S., Ballini F., Ölçer A. I. (2020). Ports’ technical and operational measures to reduce greenhouse gas emission and improve energy efficiency: A review. Mar. pollut. Bull. 160, 111508. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111508
Barletta M., Cysneiros F. J. A., Lima A. R. A. (2016). Effects of dredging operations on the demersal fish fauna of a South American tropical–subtropical transition estuary. J. Fish Biol. 89, 890–920. doi: 10.1111/jfb.12999
Beata S., Bartkus P.-R. M. C. (2023). The role of education in the economics of sustainable development. Proc. Comput. Sci. 225, 4177–4186. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.10.414
Beškovnik B., Bajec P. (2015). Application of environmental and social sustainable measures by port of Koper: the basis for the regional approach. Problemy Ekorozwoju 10, 99–106.
Beyene Z. T., Nadeem S. P., Jaleta M. E. (2024a). Developing a measurement framework for Ethiopian dry port sustainability: an empirical study. Sustainability 16, 3878. doi: 10.3390/su16093878
Beyene Z. T., Nadeem S. P., Jaleta M. E., Kreie A. (2024b). Research trends in dry port sustainability: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 16, 263. doi: 10.3390/su16010263
Chang K.-C., Wang D., Lu Y., Chang W., Ren G., Liu L., et al. (2021). Environmental regulation, promotion pressure of officials, and enterprise environmental protection investment. Front. Public Health 9. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.724351
Chen Z., Kahn M. E., Liu Y., Wang Z. (2018). The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Economics Manage. 88, 468–485. doi: 10.1016/j.jeem.2018.01.010
Chen L., Li W., Yuan K., Zhang X. (2022). Can informal environmental regulation promote industrial structure upgrading? Evidence from China. Appl. Economics 54, 2161–2180. doi: 10.1080/00036846.2021.1985073
Cheng T. C. E., Zanjirani Farahani R., Lai K., Sarkis J. (2015). Sustainability in maritime supply chains: Challenges and opportunities for theory and practice. Transportation Res. Part E: Logistics Transportation Rev. 78, 1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2015.03.007
Corbett J. J., Winebrake J. J., Green E. H., Kasibhatla P., Eyring V., Lauer A. (2007). Mortality from ship emissions: A global assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 8512–8518. doi: 10.1021/es071686z
Darbra R. M., Ronza A., Casal J., Stojanovic T. A., Wooldridge C. (2004). The Self Diagnosis Method: A new methodology to assess environmental management in sea ports. Mar. pollut. Bull. 48, 420–428. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.10.023
Dooms M., Macharis C., Verbeke A. (2004). Proactive stakeholder management in the port planning process: empirical evidence from the Port of Brussels. European Regional Science Association. Available online at: https://EconPapers.repec.org/RePEc:wiw:wiwrsa:ersa04p271
Driscoll J. C., Kraay A. C. (1998). Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev. Economics Stat 80, 549–560. doi: 10.1162/003465398557825
Ebenstein A. (2012). The consequences of industrialization: evidence from water pollution and digestive cancers in China. Rev. Economics Stat 94, 186–201. doi: 10.1162/REST_a_00150
Facchini F., Gaeta G. L., Michallet B. (2017). Who cares about the environment? An empirical analysis of the evolution of political parties’ environmental concern in European countries, (1970-2008). Land Use Policy 64, 200–211. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.02.017
Fransson N., Gärling T. (1999). Environmental concern: Conceptual definitions, measurement methods, and research findings. J. Environ. Psychol. 19, 369–382. doi: 10.1006/jevp.1999.0141
Franzen A., Meyer R. (2010). Environmental attitudes in cross-national perspective: A multilevel analysis of the ISSP 1993 and 2000. Eur. Sociological Rev. 26, 219–234. doi: 10.1093/esr/jcp018
Fruth M., Teuteberg F. (2017). Digitization in maritime logistics—What is there and what is missing? Cogent Business Manage. 4, 1411066. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2017.1411066
Gray S. G., Raimi K. T., Wilson R., Árvai J. (2019). Will Millennials save the world? The effect of age and generational differences on environmental concern. J. Environ. Manage. 242, 394–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.071
Haddad C. R., Bergek A. (2023). Towards an integrated framework for evaluating transformative innovation policy. Res. Policy 52, 104676. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2022.104676
Hao F., Song L. (2020). Environmental concern in China: A multilevel analysis. Chin. Sociological Rev. 52, 1–26. doi: 10.1080/21620555.2019.1654367
Harring N., Jagers S. C., Matti S. (2020). Higher education, norm development, and environmental protection. Higher Educ. 79, 291–305. doi: 10.1007/s10734-019-00410-7
Hartmann P., Apaolaza-Ibáñez V. (2012). Consumer attitude and purchase intention toward green energy brands: The roles of psychological benefits and environmental concern. J. Business Res. 65, 1254–1263. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.11.001
Hou J. (2010). Sustainable development of port economics based onsystem dynamics. Syst. Engineering-Theory Pract. 30, 56–61.
Hunter L. M., Hatch A., Johnson A. (2004). Cross-national gender variation in environmental behaviors*. Soc. Sci. Q. 85, 677–694. doi: 10.1111/j.0038-4941.2004.00239.x
Jaafar H. S., Abd Aziz M. L., Ahmad M. R., Faisol N. (2021). Creating innovation in achieving sustainability: halal-friendly sustainable port. Sustainability 13, 13339. doi: 10.3390/su132313339
Ji J. S. (2020). The IMO 2020 sulphur cap: a step forward for planetary health? Lancet Planetary Health 4, e46–e47. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30002-4
Jimenez V. J., Kim H., Munim Z. H. (2022). A review of ship energy efficiency research and directions towards emission reduction in the maritime industry. J. Cleaner Production 366, 132888. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132888
Jutterström S., Moldan F., Moldanová J., Karl M., Matthias V., Posch M. (2021). The impact of nitrogen and sulfur emissions from shipping on the exceedance of critical loads in the Baltic Sea region. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 21, 15827–15845. doi: 10.5194/acp-21-15827-2021
Kang D., Kim S. (2017). Conceptual model development of sustainability practices: the case of port operations for collaboration and governance. Sustainability 9, 2333. doi: 10.3390/su9122333
Kathuria V. (2007). Informal regulation of pollution in a developing country: Evidence from India. Ecol. Economics 63, 403–417. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.11.013
Leal Filho W., Aina Y. A., Dinis M. A. P., Purcell W., Nagy G. J. (2023). Climate change: Why higher education matters? Sci. Total Environ. 892, 164819. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164819
Leal Filho W., Sima M., Sharifi A., Luetz J. M., Salvia A. L., Mifsud M., et al. (2021). Handling climate change education at universities: an overview. Environ. Sci. Europe 33, 109. doi: 10.1186/s12302-021-00552-5
Li W., Angel R., Kim S.-W., Jiménez-Moreno E., Proszkowiec-Weglarz M., Plumstead P. W. (2018). Impacts of age and calcium on Phytase efficacy in broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 238, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2018.01.021
Li F., Fan M., Li R. (2019). Sustainable development of small local port based on anemergy analysis: A case of Haiyang port. Mar. Environ. Sci. 38, 712–719. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2019.05.010
Li X., Zhao Y., Cariou P., Sun Z. (2024). The impact of port congestion on shipping emissions in Chinese ports. Transportation Res. Part D: Transport Environ. 128, 104091. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2024.104091
Liu X., Ji X., Zhang D., Yang J., Wang Y. (2019). How public environmental concern affects the sustainable development of Chinese cities: An empirical study using extended DEA models. J. Environ. Manage. 251, 109619. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109619
Liu X., Mu R. (2016). Public environmental concern in China: Determinants and variations. Global Environ. Change 37, 116–127. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.01.008
Liu J., Qi Y., Lyu W. (2023). Port resilience in the post-COVID-19 era. Ocean Coast. Manage. 238, 106565. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2023.106565
Liu X., Yuan Q. (2024). Do public environmental concerns promote the development of green finance? Empirical evidence from 284 cities in China. Auditing Economic Res. 39, 107–116.
Lotspeich R., Chen A. (1997). Environmental protection in the people’s republic of China. J. Contemp. China 6, 33–59. doi: 10.1080/10670569708724264
Lu C.-S., Shang K.-C., Lin C.-C. (2016). Examining sustainability performance at ports: port managers’ perspectives on developing sustainable supply chains. Maritime Policy Manage. 43, 909–927. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2016.1199918
Lu H., Xiao C., Jiao L., Du X., Huang A. (2024). Spatial-temporal evolution analysis of the impact of smart transportation policies on urban carbon emissions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 101, 105177. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2024.105177
Marquart-Pyatt S. T. (2007). Concern for the environment among general publics: A cross-national study. Soc. Natural Resour. 20, 883–898. doi: 10.1080/08941920701460341
Mousavi S., Bossink B. (2020). Corporate-NGO partnership for environmentally sustainable innovation: Lessons from a cross-sector collaboration in aviation biofuels. Environ. Innovation Societal Transitions 34, 80–95. doi: 10.1016/j.eist.2019.12.005
Nash N., Capstick S., Whitmarsh L., Chaudhary I., Manandhar R. (2019). Perceptions of local environmental issues and the relevance of climate change in Nepal’s terai: perspectives from two communities. Front. Sociology 4. doi: 10.3389/fsoc.2019.00060
Ogara D. A. E., Morishita J., Davies P. J., Mbui M., Gamoyo M., Njoroge N., et al. (2023). An indicator-based approach to assess sustainability of port-cities and marine management in the Global South. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1052128
Pan D., Fan W., Kong F. (2022). Dose environmental information disclosure raise public environmental concern? generalized propensity score evidence from china. J. Cleaner Production 379, 134640. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134640
Paola B., Logoteam d., Rijeka H. (2017). Contribution to the implementation of “Green Port” concept in Croatian seaports. Scientific J Maritime Res 31, 1. doi: 10.31217/p.31.1.3
Puig M., Darbra R. M. (2019). “Chapter 31 - the role of ports in a global economy, issues of relevance and environmental initiatives,” in World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed. Ed. Sheppard C. (Academic Press, Sustainability at Work eJournal), 593–611. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-805052-1.00034-6
Shao C., Ju M., He Y., Sun X. (2009). Study on index system of eco-ports based on DPSIR model. Mar. Environ. Sci. 28, 333–337.
Shiau T.-A., Chuang C.-C. (2015). Social construction of port sustainability indicators: a case study of Keelung Port. Maritime Policy Manage. 42, 26–42. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2013.863436
Singh A., Bansal M. (2012). Green Marketing: A Study of Consumer Attitude & Environmental Concern. Sustainability at Work eJournal. Available online at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:167757004.
Spiegler V. L. M., Naim M. M., Wikner J. (2012). A control engineering approach to the assessment of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Production Res. 50, 6162–6187. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2012.710764
Ünal A. B., Steg L., Gorsira M. (2018). Values versus environmental knowledge as triggers of a process of activation of personal norms for eco-driving. Environ. Behav. 50, 1092–1118. doi: 10.1177/0013916517728991
Van den Berg R., De Langen P. W. (2017). Environmental sustainability in container transport: the attitudes of shippers and forwarders. Int. J. Logistics Res. Appl. 20, 146–162. doi: 10.1080/13675567.2016.1164838
Wang L., Jin M. (2017). Port Sustainability ranking study – Taking the five ports around the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea as examples. Jianghuai Forum 3, 68–73. doi: 10.16064/j.cnki.cn34-1003/g0.2017.03.011
Wang H., Wheeler D. (2005). Financial incentives and endogenous enforcement in China’s pollution levy system. J. Environ. Economics Manage. 49, 174–196. doi: 10.1016/j.jeem.2004.02.004
Weigel R., Weigel J. (1978). Environmental concern: the development of a measure. Environ. Behav. 10, 3–15. doi: 10.1177/0013916578101001
Wiidegren Ö. (1998). The new environmental paradigm and personal norms. Environ. Behav. 30, 75–100. doi: 10.1177/0013916598301004
Wu L., Yang M., Sun K. (2022). Impact of public environmental attention on environmental governance of enterprises and local governments. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 32, 1–14. doi: 10.12062/cpre.20210625
Wu X., Zhang L., Dong Y. (2019). Towards sustainability in Xiamen Harbor, China. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 27, 100552. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100552
Wurzinger S., Johansson M. (2006). Environmental concern and knowledge of ecotourism among three groups of Swedish tourists. J. Travel Res. 45, 217–226. doi: 10.1177/0047287506291602
Ye X., Zhao Y. (2016). Evaluation of the sustainable development level of port based on the clustering methodology. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 25, 17–24. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj2016Z1003
Yoon A., Jeong D., Chon J. (2021). The impact of the risk perception of ocean microplastics on tourists’ pro-environmental behavior intention. Sci. Total Environ. 774, 144782. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144782
Yu K., Li Z., Yang S., Zhong J. (2023). Impact and difference of heterogeneous environmental regulations on the high-quality development of the Yangtze River economic belt. Economic Geogr. 43, 34–43. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.10.004
Zhao D., Wang T., Han H. (2020). Approach towards sustainable and smart coal port development: the case of Huanghua Port in China. Sustainability 12, 3924. doi: 10.3390/su12093924
Zheng S., Kahn M. E., Sun W., Luo D. (2014). Incentives for China’s urban mayors to mitigate pollution externalities: The role of the central government and public environmentalism. Regional Sci. Urban Economics 47, 61–71. doi: 10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2013.09.003
Keywords: port sustainability, public environmental concern, environmental governance, government environmental investments, digital infrastructure
Citation: Shen J, Ren X, Feng Z and Nie J (2025) The impact of public environmental concerns on port sustainability: evidence from 44 port cities in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1454242. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1454242
Received: 25 June 2024; Accepted: 10 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Mario Barletta, Federal University of Pernambuco, BrazilReviewed by:
Bogusz Wiśnicki, Maritime University of Szczecin, PolandEster Santos, Federal University of Pernambuco, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Ren, Feng and Nie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaohong Ren, cmVueGg4MTRAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Jia Shen
Jia Shen Xiaohong Ren1*
Xiaohong Ren1*