- 1WorldFish, Jalan Batu Maung, Bayan Lepas, Penang, Malaysia
- 2WorldFish Bangladesh and South Asia, Dhaka, Bangladesh
The hilsa fishery, Bangladesh’s largest single-species fishery, generates over USD 3 billion annually, contributing 12% to annual fish production and supporting 2.5 million people. However, the growing human population and the associated demand for fish protein have led to overfishing of both adult and juvenile hilsa in the gill net fishery. In respons, the Department of Fisheries (DoF) and WorldFish implemented the ECOFISH-BD project (2015–2019), funded by USAID, to promote sustainable management practices. Despite the ecological and economic importance of hilsa shad (Tenualosa ilisha), there is a significant gap in the literature regarding the economic evaluation of conservation initiatives. This study addrress that gap by examining the ECOFISH-BD project and assessing its return on investment (ROI) in terms of ecological and socio-economic outcomes. The research evaluates the historical context influencing hilsa production, assesses the project’s impact on stock recovery, and conducts a cost-benefit analysis to determine the ROI related to hilsa fishery management and community livelihoods. Using the difference-in-difference method, the study measured changes in income and assets, revealing a significant increase of 86.19% in income and 63.99% in overall assets in the intervention group compared to the baseline. Despite these positive outcomes, challenges such as unequal benefit distribution, power imbalances in the hilsa value chain, and the persistence of debt trap remain. While it is difficult to fully isolate the project’s effects from other external factors, the project has played a significant role in the recovery of hilsa stocks and the subsequent increase in catch volumes. Furthermore, the project demonstrates strong economic viability, evidenced by an internal rate of return of 32.8%. This study underscores the profitability and investment potential of small-scale fisheries, challenging common misconceptions and advocating for increased investment and institutional support to maximize long-term socio-economic and ecological benefits.
1 Introduction
Bangladesh is a leading global fish-producing nation, ranking second in the world for freshwater open water fish catches, 14th in marine fish harvesting, and fifth in aquaculture production (FAO, 2024; DoF, 2024). Fish production contributed 2.52 percent to the national GDP (DoF, 2024), 1.39 percent to foreign exchange earnings (BER, 2020), and provided 62.58 percent of the total animal protein consumed in the country (FRSS, 2020). Beyond its economic importance, the fisheries sector is a vital source of employment, with over 17 million individuals, both men and women, depending on it for their livelihoods across the supply chain (BFTI, 2016).
The hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) fishery is the largest single-species fishery in Bangladesh, with an annual landed value exceeding USD 2.5 billion (Sarker et al., 2019). It contributes approximately 12 percent to the country’s annual fish production (Mahmud, 2020), making it a critical component of Bangladesh’s fisheries sector in terms of both economic value and food security. Hilsa primarily inhabits coastal waters but migrate upstream to spawn in coastal rivers (Rahman and Naevdal, 2000; Bladon et al., 2019; Merayo et al., 2020). The average annual global share of hilsa has largely shifted to Bangladesh, which now accounts for 86.7%. India follows with 8.0%, while Myanmar contributes 4.0%. The remaining share comes from countries such as Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, and Kuwait (Rahman et al., 2018). This high catch rate in Bangladesh is due to the country’s ideal geographic and ecological conditions, including vast river systems like the Padma, Meghna, and Jamuna, and the nutrient-rich coastal waters of the Bay of Bengal. Hilsa prefer this region because of the presence of sub-surface oxygen, relatively low salinity, strong tidal action, high turbidity, heavy siltation, and abundant plankton growth (Pillay and Rosa, 1963; Rahman et al., 2017; Hossain et al., 2019). However, the hilsa shad fishery plays a crucial role in providing livelihoods for millions across several countries. In Bangladesh, around half a million people directly depend on the hilsa fishery, most of whom are poor (Islam et al., 2016) and an additional 2.5 million are indirectly involved in supply-chain activities such as processing, transportation, and marketing (Sarker et al., 2019). In the West Bengal region, about 0.46 million fishers are involved in the hilsa shad fishing (Dutta et al., 2021), whereas approximately 1.6 million fishers in Myanmar depend on this fishery (Bladon, 2017).
Hilsa holds deep cultural and religious significance in South Asia, particularly among Bengali-speaking populations, symbolized by the saying “mache bhate Bengali” (“fish and rice make the Bengali”) (Mohammed et al., 2016). This fish occupies a prominent position within the rich biodiversity of the Ganges River system and is celebrated through various dishes and ceremonial festivals. Beyond its economic importance, hilsa is socially, culturally, and religiously significant in Bangladesh and people in several Indian states, as well as among diaspora communities worldwide (Mohammed and Wahab, 2013).
Numerous studies have concluded that a growing human population, poverty, and the corresponding demand for fish protein have driven the overfishing of both adult and juvenile (jatka) hilsa in the gill net fishery (Dewhurst-Richman et al., 2016; Rahman et al., 2013). Until the 1970s, hilsa was abundantly available in the 100 rivers of Bangladesh. However, over the next 30 years, the population gradually declined, reaching a low point in 2002 with catches of only 199,032 tons (Mahmud, 2020). This decline resulted from several factors: the closure of fish migratory routes, river siltation, overfishing, indiscriminate harvesting of broodstocks and juveniles, the use of fishing nets with very small mesh sizes, mechanization of fishing, increasing numbers of fishers, pollution, and climatic variability (Wahab et al., 2019).
In efforts to reverse the declining trend, the Government of Bangladesh initiated the Hilsa Fishery Management Action Plan (HFMAP) in 2005 (Mohammed and Wahab, 2013). This plan included several management measures such as the establishment of five sanctuaries, enforcement of the ban on hilsa and jatka (juvenile hilsa) fishing during certain periods and the provision of compensation to affected fishers (Nahiduzzaman et al., 2018). While the government of Bangladesh initiated the HFMAP to protect, conserve, and sustainably manage hilsa populations, several international agencies also became involved in supporting these efforts. These agencies aimed not only at conserving hilsa but also at enhancing the livelihood resilience of the fishing communities reliant on this vital resource (Hossain et al., 2018). Among these initiatives, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) funded the Enhanced Coastal Fisheries in Bangladesh (ECOFISH-BD) project to tackle various challenges, including the lack of a co-management system, insufficient stakeholder engagement, particularly with local communities, illegal fishing largely driven by the poverty of hilsa fishers, limited awareness regarding hilsa conservation, and a weak connection between scientific research and policy development. However, this project (2014-2019) was a collaborative effort between the Bangladesh Department of Fisheries (DoF) and WorldFish, a CGIAR research organization. This initiative focused on research-driven hilsa fisheries management, conservation practices, and building resilience among small-scale artisanal fishers, particularly those dependent on hilsa. The project’s holistic approach combined scientific research, community engagement, and policy advocacy to safeguard hilsa populations while simultaneously improving the livelihoods of coastal fishing communities (van Brakel et al., 2018).
A collaborative, science-based “co-management” was initiated by supporting the Department of Fisheries (DoF) and local communities. This approach involved both government stakeholders and small-scale fishing communities, with a special focus on engaging women of the fishing households in the project initiatives (Islam et al., 2020). The initiative aimed to diversify the livelihoods of 20,800 coastal small- scale artisanal fishing households, and improve access to resources and technologies, thereby achieving a balance between livelihood improvement and conservation efforts (Wahab et al., 2020).
The scientific literature on hilsa shad has its roots in the early 1900s, when researchers began documenting its biological characteristics and ecological importance. These investigations have provided valuable insights into the species’ life cycle, migration patterns, and habitat requirements, establishing a strong foundation for understanding its economic significance. In recent years, there has been a notable surge of interest in the management of hilsa shad fisheries, particularly in the Bay of Bengal and neighboring regions. Despite the growing focus on conservation and fisheries management, there remains a notable gap in the scientific literature regarding the economic evaluation of these initiatives, particularly for short-term projects that aim to supplement ongoing management and conservation efforts by governments. This lack of economic analysis constrains the ability to fully understand the financial and social gains of conserving such a vital species. Research on the return on investment (ROI) of such conservation initiatives is scarce, which hinders the ability to measure the true impact and justify the costs involved. Without a clear understanding of the economic returns—whether through increased fish stocks, improved market stability, or reduced poverty—it becomes challenging to assess the overall effectiveness of these interventions. Such knowledge is critical for shaping future policy decisions and for ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Moreover, the long-term economic benefits of hilsa conservation remain underexplored. While projects aimed at conserving hilsa often highlight ecological successes, such as population recovery and biodiversity preservation, there is little focus on quantifying the economic gains these projects bring to communities that depend on the species. For example, increased fish stocks can lead to greater fishing yields, stabilized fish markets, and enhanced food security for millions of people in South Asia. Improved livelihoods, poverty reduction, and community resilience could also be major benefits of these conservation efforts, but they are seldom evaluated in economic terms.The absence of such studies leaves a gap in understanding the full scope of financial and social returns from these conservation initiatives. Without clear data on the ROI, it becomes difficult for stakeholders—including governments, international donors, and conservation organizations—to justify the continued funding of similar projects. This is especially crucial for short-term projects that must demonstrate tangible benefits within a limited timeframe in order to complement and sustain longer-term government efforts.
A relevant case in this context is the evaluation of the ECOFISH BD project, a recently completed initiative focusing on hilsa. Assessing the return on investment (ROI) of this initiative, in terms of both long-term ecological and economic outcomes, could offer valuable insights into how sustainable fisheries management contributes to biodiversity conservation and socio-economic development. By incorporating a historical context, such an evaluation would help demonstrate the project’s broader impact on hilsa recovery and the livelihoods of fishing communities. Such evaluations would not only fill critical gaps in the existing literature but also help inform future policy and investment decisions, ensuring that initiatives like ECOFISH BD deliver tangible, measurable benefits for the communities they aim to serve.
The key question is to what extent the project has contributed to the sustainable management of the hilsa fishery in Bangladesh and whether the investment is justified in terms of value for money, taking into account the historical context. Given limited resources and competing priorities, governments and development partners are keen to understand the effectiveness of such interventions. The seek to assess whether their investments are yielding tangible benefits for both the environment, in this case, hilsa fishery management, and the communities that are reliant on this resource for their livelihoods. This evaluation entails analyzing factors such as the ecological impact of project measures, the socio-economic well-being of fishing communities, and the overall resilience of the hilsa fishery ecosystem. Insights gained from this evaluation enable policymakers and stakeholders to identify intervention effectiveness, and areas for improvement, and guide future decisions to ensure the fishery’s long-term viability of the hilsa fishery. Moreover, assessing the project’s impact on local livelihoods provides evidence for future interventions aimed at enhancing both environmental sustainability and socio-economic resilience. Therefore, the objectives of this study are the following: a) to analyze the historical context influencing hilsa, Tenualosa ilisha (Teleostei: Dorosomatidae) production in Bangladesh, b) to evaluate the contribution of project activities toward the recovery of hilsa stock, and c) to conduct a cost-benefit analysis to determine the project’s return on investment in hilsa fishery management and community livelihoods.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area and sampling method
The study was conducted in six districts of the Meghna River Basin in southern Bangladesh: Bhola, Chandpur, Laxmipur, Barishal, Jhalokati, and Pirojpur. A purposive sampling approach was used to select 12 unions (two from each district) and 24 villages within these unions. These areas are predominantly inhabited by fishing households who rely on fishing as their primary livelihood and are significantly impacted by government-imposed fishing bans at various times throughout the year. The sampling covered 1,200 households: 600 beneficiaries (treatment) and 600 control households (i.e. households outside the area of influence of the project). The two groups were sampled in a panel through a baseline (May 2016) and an end-line (October 2019). Fifty households were sampled in each selected village. The overall sampling was structured as a two-stage cluster sampling based on a sample frame generated by a separate household listing exercise. In the first stage, a sample cluster was selected independently with probability proportional to the cluster’s population in each stratum. The strata were the six districts in Bangladesh encompassing the program area (Figure 1). The second stage involved the use of systematic random sampling at the village level to select a set number of households (50 in each village) to be included in the evaluation. To reduce the heterogeneity within and between groups (treatment and control), which is likely to result from the relatively large geographical area covered by the program, the sampling effort focused on the central region of intervention. The control villages were then selected in the same districts as the treatment villages to optimize the comparability between the two groups, though in different unions (the lowest tier of administrative hierarchy in Bangladesh), to reduce the risk of the spillover effect.
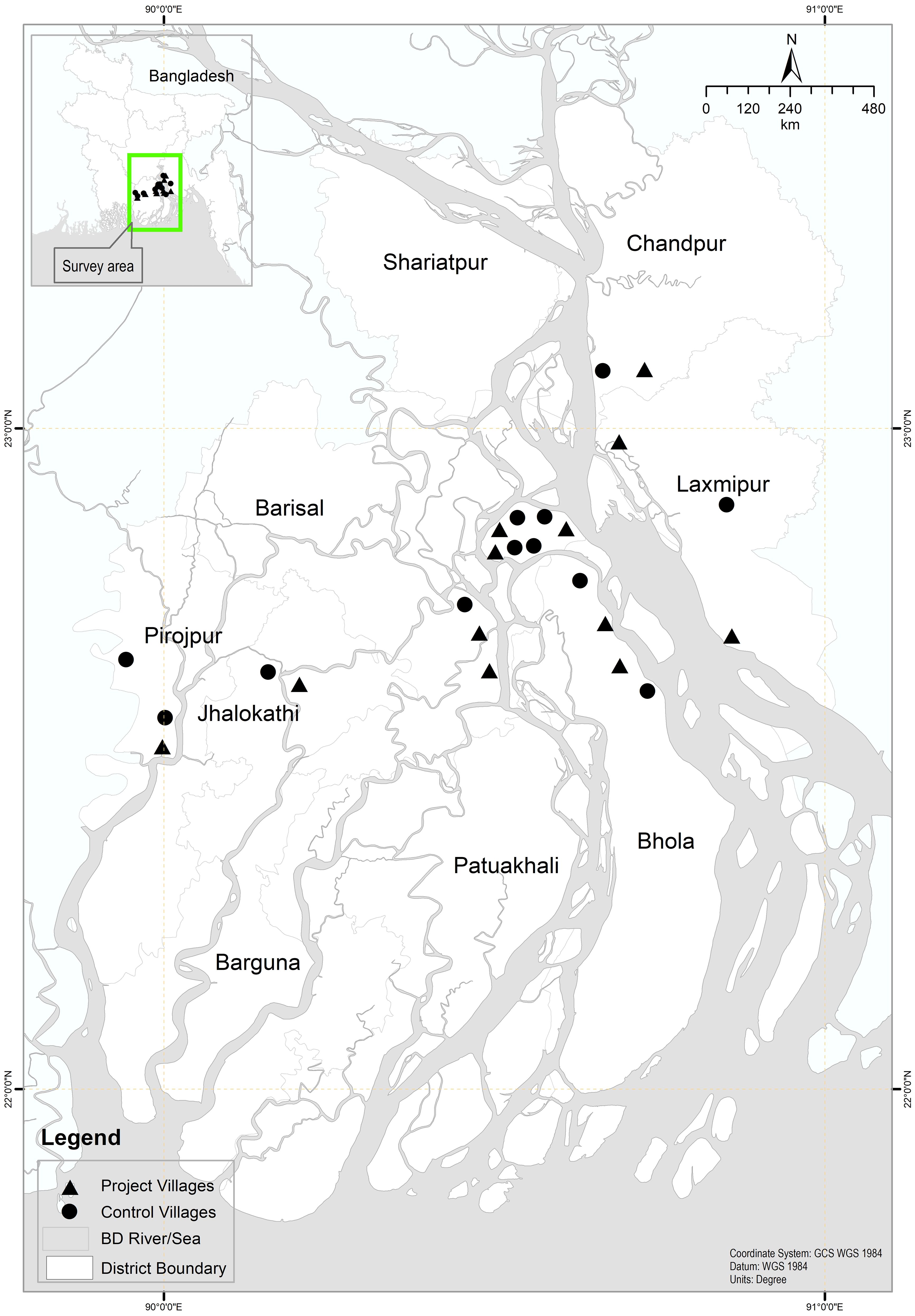
Figure 1. Map showing the fishing villages in six coastal districts of Bangladesh where sampling was conducted. Triangles represent project-intervened villages, while circles denote control villages.
To ensure the comparability, a t-test of socioeconomic and demographic characteristics between the treatment and control groups was conducted. As a result, we did not observe a statistically distinguishable difference between the two groups. For example, the t-test results for some of the socioeconomic characteristics were age (t = -0.899, p = 0.37), literacy level (F = 0.013, p = 0.91), household size (t = -1.892, p = 0.06), livelihood diversification (t = -1.269, p = 0.20), assets (t = -1.495, p = 0.13), and savings (t = -1.508, p = 0.13). We were therefore able to conclude that the control and treatment groups were statistically comparable.
2.2 Key informant interviews
For this study, key informant interviews were utilized as the primary method of data collection. A total of 20 interviews were conducted with a diverse group of participants, including representatives from conservation organizations and key stakeholders involved in resource management. The informants were selected based on their expertise in hilsa management initiatives, with several participants playing key roles in policy development, offering valuable perspectives on the challenges and opportunities in hilsa management. Additionally, interviews were conducted with members of the ECOFISH-BD science team and representatives of hilsa fisher communities from the village of Uttar Bogula in Chandpur District. Uttar Bogula fishing village was selected for key informant interviews (KII) due to its representative characteristics and historical significance in hilsa fishing in Bangladesh. This remote area offers insights into the challenges faced by fishing communities, particularly regarding illegal hilsa fishing. As one of three model villages in the ECOFISH project, Uttar Bogula participates in initiatives that promote sustainable fishing practices and community development, reflecting a positive shift in awareness of hilsa conservation.
The objective of these interviews was to qualitatively assess the “contribution” of the ECOFISH-BD project to institution-building and policy reform. Through these conversations, insights were gathered on the project’s effectiveness in fostering institutional frameworks, enhancing governance structures, and implementing policy changes that support sustainable hilsa fishery management. For instance, informants highlighted successful collaborations between local communities and government agencies that led to the establishment of co-management committees, improving stakeholder engagement in decision-making processes. Additionally, participants shared examples of capacity-building initiatives that empowered fishers with knowledge of alternate income generating activities, sustainable practices and legal regulations. This qualitative assessment offers a detailed understanding of the project’s impact on both the social and ecological dimensions of hilsa fishery management. This information was also used to interpret the overall results of the study, offering a comprehensive understanding of the project’s impact on both social and ecological dimensions of hilsa fishery management.
2.3 Frame of reference
This frame of reference is structured following the framework of Bladon et al., 2018. This study delineates the timeline as pre- and post-2016 to elucidate the institutional framework within which ECOFISH-BD operated and the project’s potential role in instigating policy changes, either directly or indirectly. The frame of reference was established by defining baseline conditions and comparing them to the post-intervention scenario.
2.4 Impact evaluation
A wide range of techniques is available for conducting impact evaluations, encompassing both qualitative (process tracing) and quantitative (experimental and quasi-experimental) approaches. The choice of technique depends on the specific context, particularly the availability of counterfactuals and data. In this study, the difference-in-difference (DiD) technique was employed. This quantitative approach is particularly suitable for assessing the impact of interventions by comparing the changes in outcomes over time between a treatment group and a control group. According to Khandker et al., 2010, “an impact evaluation is essentially a problem of missing data, because one cannot observe the outcomes of program participants had they been beneficiaries. Without information of the counterfactual, the next best alternative is to compare outcomes of the treated with a comparison group that has not been treated.”
Baseline and endline surveys were conducted as part of the Monitoring and Evaluation plan of the project, collecting household panel data before and after the intervention. This approach facilitated structuring the evaluation framework using a difference-in-difference (DiD) design, which compares treatment and control groups at baseline and endline to assess the program’s impact (Figure 2).
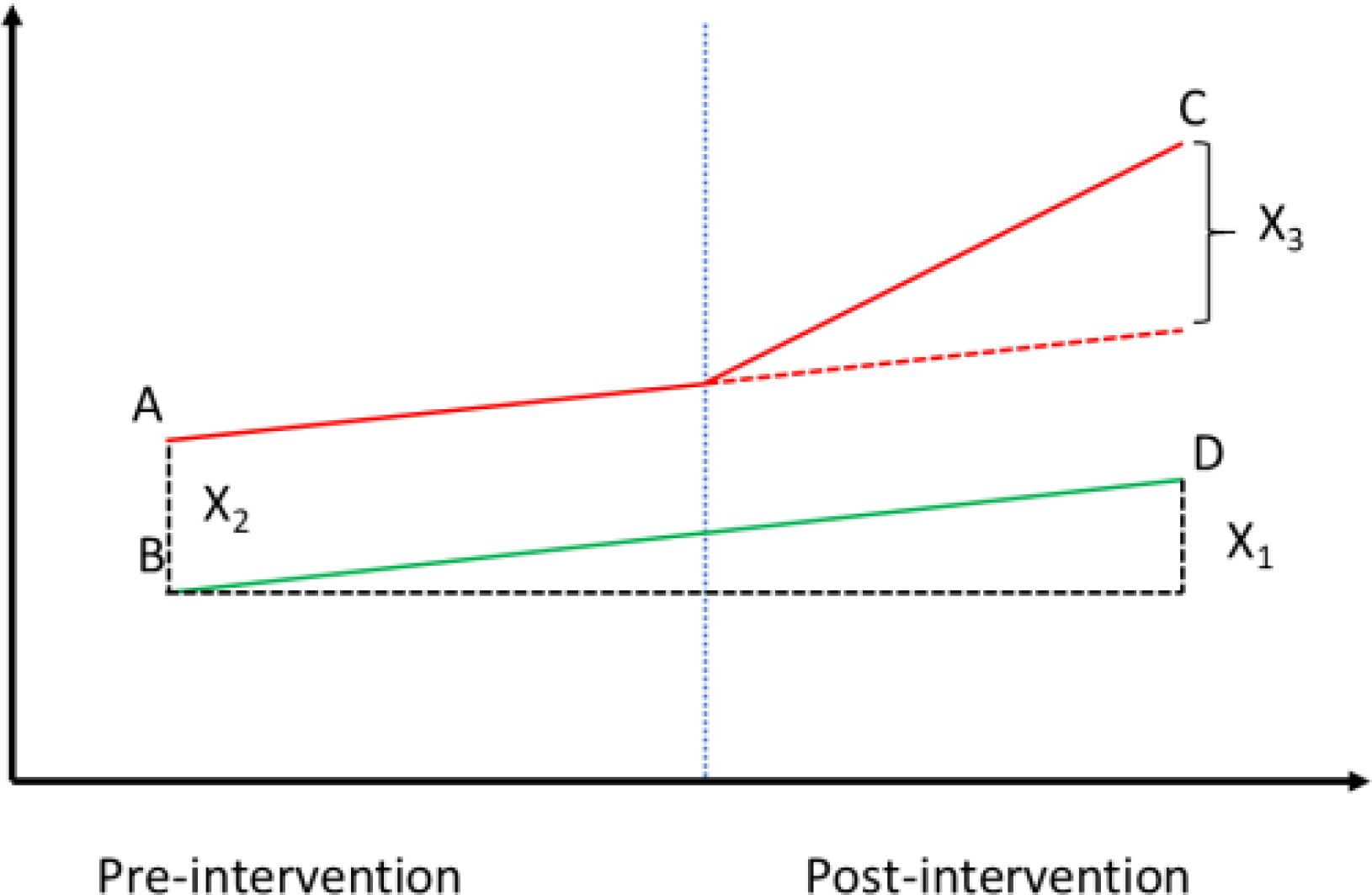
Figure 2. Diagrammatic depiction of the Difference-in-Differences (DID) method; Note: X2 represents the initial difference between two groups (a treatment group and a control group) before the intervention takes place, X1 captures the time trend in the control group, reflecting changes over time that would have occurred even without the intervention, and X3 indicates the difference in changes between the two groups over time, which can be attributed to the intervention.
As demonstrated by Ravallion (2008) and others, the DiD estimate can be calculated using a regression framework. Specifically, the estimating equation can be specified using a two-period OLS model. This can be mathematically depicted as follows:
Where D is the average treatment effect, is the outcome of the intervention group, and is outcome of control group. The difference is then considered as an additional social and ecological outcome over time period T attributable to the project. It can be shown that this interaction represents the DiD estimate of the impact of the project on the outcome D assuming that the unobserved heterogeneity in the model is time invariant and uncorrelated with the treatment over time (Ravallion, 2008).
DiD is usually implemented as an interaction term between time T and treatment group dummy variables in a regression model and can be represented as follows:
2.5 Economic evaluation
An economic evaluation of a sustainable development project involves analyzing its objectives and achieved results to assess “additionality,” determining if the intervention led to additional benefits. To examine additionality, an assessment was conducted on the extent to which the project has resulted in measurable improvements in both social and ecological dimensions. This entailed evaluating enhancements in community well-being, economic stability, and improvements in fish stocks and fish size.
Cost-effectiveness was determined by comparing project costs to benefits generated, utilizing return on investment (ROI) and cost-benefit analysis (CBA). ROI measures financial return relative to project costs, while CBA assesses economic, social, and environmental benefits against expenditures. While impact evaluation focuses on the contribution that is attributable to an intervention, a CBA focuses on whether the net benefits outweigh the costs of the project. Therefore, a CBA is often seen as complementary to impact evaluation.
The costs and benefits of the project are identified and expressed in monetary terms, then aggregated to estimate net benefit. Direct and indirect social benefits accruing to hilsa fisher communities are elicited in terms of both income and asset change using impact evaluation techniques. Some benefits, however, are intangible and not reflected in conventional markets, known as non-consumptive benefits. Estimates from Mohammed et al., 2016, employing the contingent valuation method (CVM), are used to consider both consumptive and non-consumptive benefits in the cost-benefit analysis (CBA).
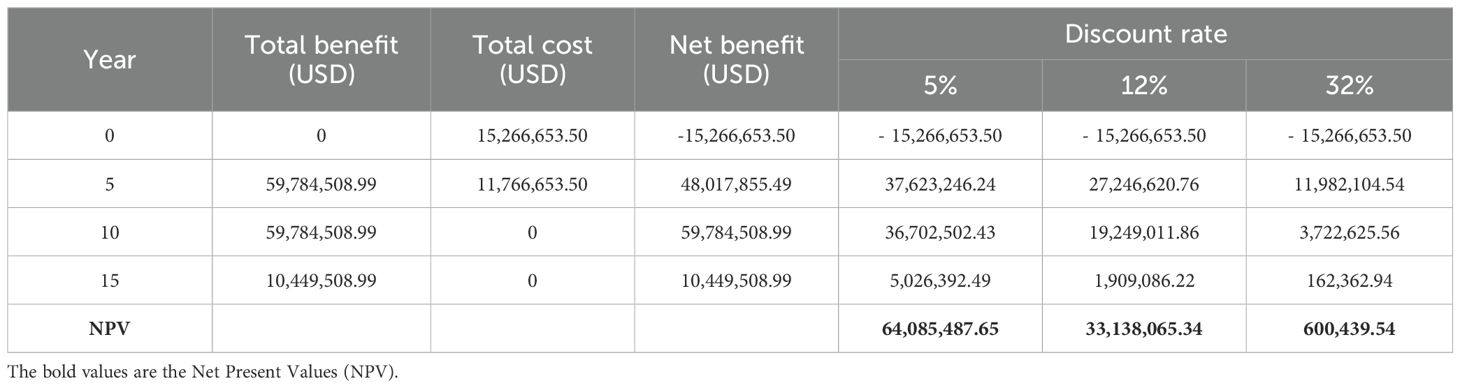
Net present value (NPV) is a crucial metric for capturing the time value of money in project appraisals aimed at enhancing societal benefits. Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) employs a social discount rate to reflect the social rate of time preference, which measures the rate at which society values present benefits over future ones (Babulo et al., 2012). The choice of social discount rate significantly impacts decision-making, particularly when comparing projects (Moore et al., 2013a; Moore et al., 2013b). Thomas and Chindarkar (2019) highlighted that a high social discount rate diminishes the weight of future benefits and costs, favoring projects with immediate benefits. Conversely, a low discount rate enhances the valuation of future benefits and costs, a common practice in environmental projects where benefits often accrue in the long term. For this study, a discount rate of 5 percent was utilized, representing the interest rate charged to commercial banks and financial institutions by the central bank of Bangladesh. Additionally, a 12 percent “real social discount rate” was applied. Net benefits were categorized into direct and indirect benefits. Direct net benefits, derived from the impact evaluation analysis, pertain to those accrued by households in intervention villages compared to control villages.
Direct costs incurred by the project, such as staff, operations, general overhead, deliveries, and other costs, are considered. These costs are obtained from the project’s financial documents and aggregated accordingly. Indirect costs, such as opportunity costs incurred by intervention communities to participate in project activities, are not included due to a lack of data. The time value of money is considered to present net benefits in their current value. The net present value is estimated using a specific equation below.
Where NPV is net present value, NBt is net benefit at time t, and i is interest rate.
3 Results
3.1 Institutional milestones of hilsa fisheries management in Bangladesh
The study examined the institutional factors influencing the success and effectiveness of interventions in natural resource management, with a special focus on the management and conservation of artisanal hilsa fisheries in Bangladesh. The findings indicated that social and ecological changes within the fisheries sector occur within specific institutional contexts, highlighting the need for both retrospective and prospective assessments of policy, legal, and institutional context during impact evaluations. The timeline of key institutional milestones in post-independence Bangladesh was developed to provide insights into the historical contexts and significant events that shape the dynamics of the socio-ecological system (Figure 3). By analyzing these contexts and events, it became possible to identify the primary drivers influencing the interactions between social and ecological factors. This analytical approach is particularly relevant for understanding the foundational strategies of the ECOFISH initiative in managing hilsa fisheries.
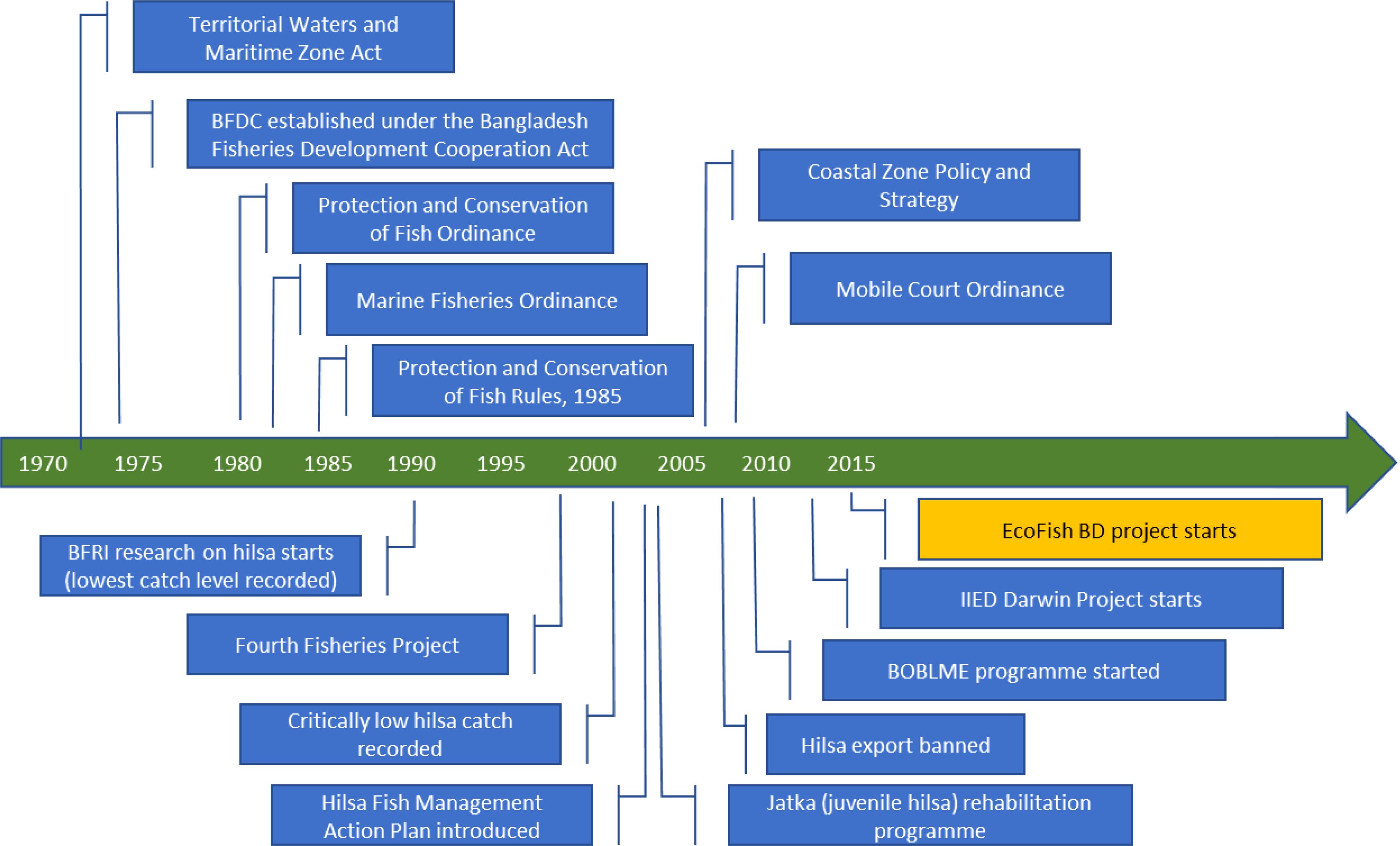
Figure 3. Timeline of key institutional milestones in post-independence Bangladesh (adapted from Bladon et al., 2018).
In post-independence Bangladesh, several factors triggered the development of institutional frameworks for fisheries management. These factors include the need for sustainable management of fisheries resources, observations of critically low catch levels—leading to the establishment of the Bangladesh Fisheries Research Institute and a jatka (juvenile hilsa) rehabilitation program—the dire socioeconomic conditions, which prompted initiatives like the vulnerable group feeding program in the 1970s, and the goals of augmenting food security. While evaluating the effectiveness of these institutional milestones is beyond the scope of this study, it is believed that they may have contributed to the sustainable management of the hilsa fishery in Bangladesh. These institutional frameworks have also facilitated the operation of ECOFISH-BD, enabling it to pursue its objective of enhancing the resilience of the hilsa fishery in the Lower Meghna region.
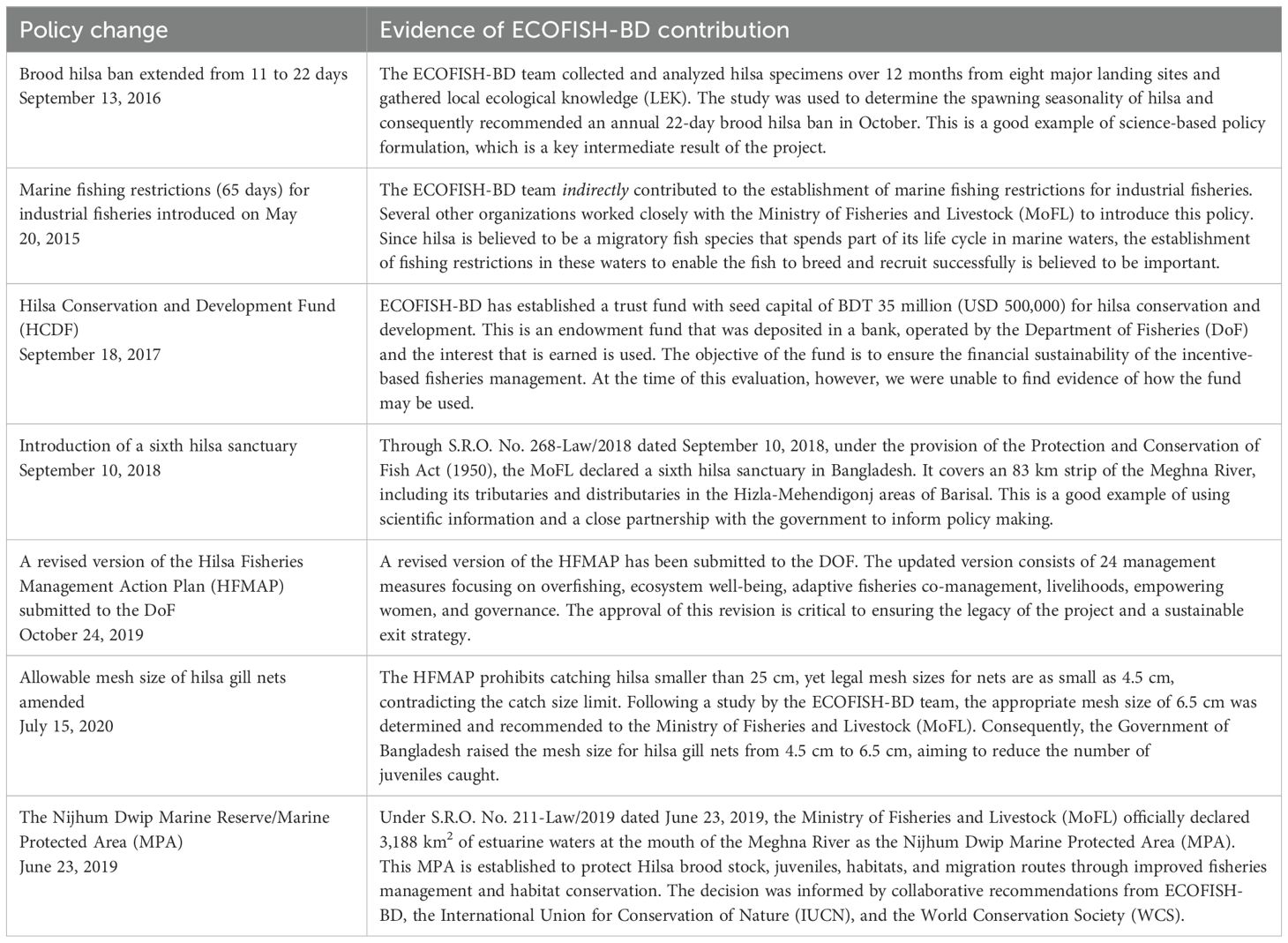
3.2 Policy reforms
ECOFISH-BD has directly or indirectly played a catalytic role in introducing policy and institutional reforms for the conservation and management of the hilsa fishery in Bangladesh (Table 1). This has been achieved by generating scientific evidence and through meaningful partnerships and structured engagement with local authorities, particularly the DoF. The question remains whether these authorities will continue to effectively implement the policy changes, after the project has ended. As such, to ensure a sustainable exit strategy, the project must ensure that these systems are officially recognized by the government and continue to be supported.
3.3 Impact evaluation
3.3.1 Income change
The treatment group experienced a substantial increase in overall income, from a mean baseline value of BDT 70,443 to BDT 131,159 at endline (86.19%), reflecting a statistically significant difference (t = 11.39, p < 0.001). Conversely, the control group’s income remained relatively stable, with a slight increase (52.66%) from BDT 68,970 to BDT 105,290, but not statistically significant (t = 1.16, p = 0.243). Income from hilsa (river) fishing followed a similar trend, with a substantial rise (74.27%) in the treatment group (baseline: BDT 67,950; endline: BDT 118,419) compared to a modest increase (52.77%) in the control group (baseline: BDT 67,249; endline: BDT 102,733), both statistically significant (t = 7.15, p < 0.001) (Table 2).
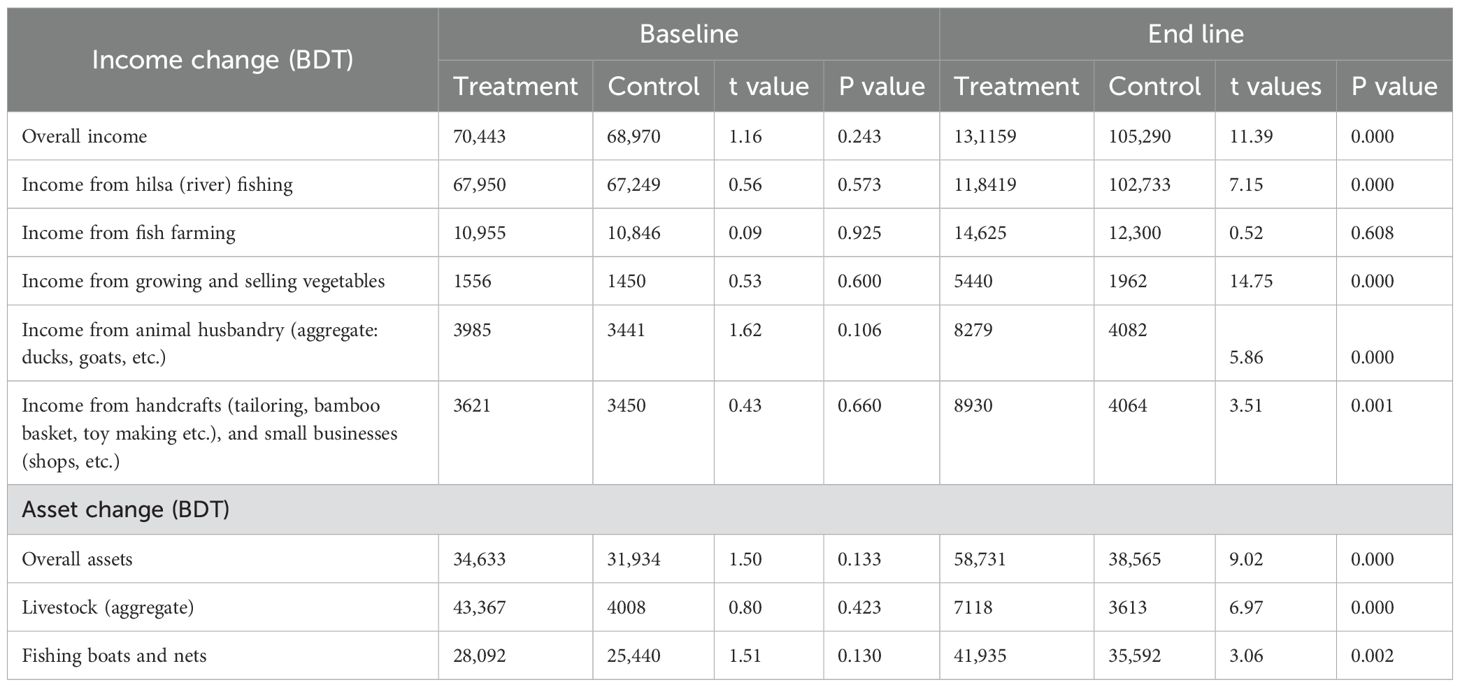
Table 2. Statistical summary of the income changes observed in both the control and treatment groups.
Furthermore, income from diversified livelihood activities also exhibited significant differences. Notably, income from growing and selling vegetables saw a significant increase (249.61%) in the treatment group (baseline: BDT 1,556; endline: BDT 5,440) compared to a smaller rise (35.31%) in the control group (baseline: BDT 1,450; endline: BDT 1,962), which was statistically significant (t = 14.75, p < 0.001). Similar trends were observed in income from animal husbandry, handcrafts, and small businesses, with the treatment group experiencing considerable growth compared to the control group, all demonstrating statistical significance (p < 0.05).
The regression analysis revealed several noteworthy findings about the intervention’s impact on different income sources among households. Overall, the intervention had a significant positive effect on aggregate income (β = 24,397.43, p < 0.001), representing a 22.40 percent increase with an average of BDT 24,397.43 (USD 290) in annual income. Specifically, significant positive effects were observed for income increased by 12.20 percent from river fishing (β = 14,985.07, p < 0.001) and income increased by 114 percent from handcrafts (β = 4,695.03, p < 0.001) compared to the control households. However, the effect on income from fish farming (β = 2,216.61, p > 0.05) and small-scale agriculture (β = 3,372.37, p > 0.05) was not statistically significant.
Additionally, the coefficient of determination (R²) for each income source provides insights into the proportion of variance explained by the regression model. For instance, the R² value for aggregate income (R² = 0.4034) indicates that approximately 40.34 percent of the variability in overall income can be accounted for by the independent variables included in the regression model. Similarly, R² values for other income sources ranged from 0.0675 to 0.3446, suggesting moderate to high explanatory power for these specific income categories.
Certain households within the intervention groups benefitted from support in small-scale agriculture, which included provisions of vegetable seeds and training in farming techniques. Likewise, selected households in the intervention group received training in livestock management and animal husbandry. Additionally, a subset of households underwent comprehensive training in crafts and received necessary inputs. These interventions led to modest yet statistically significant increases in annual income from these activities, amounting to BDT 3,372, BDT 3,654, and BDT 4,695, respectively (Table 3).
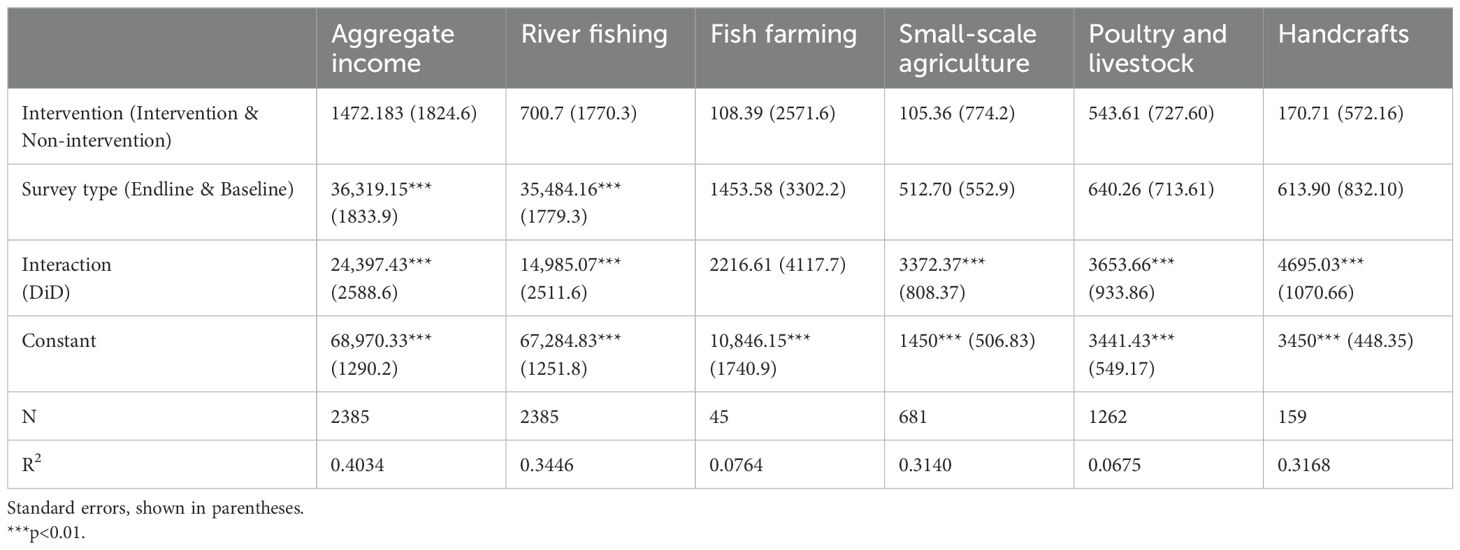
Table 3. Regression results for different sources of income using the DiD model, comparing the treatment group to the control group over time.
3.3.2 Asset building
Regarding asset changes, the treatment group exhibited a significant increase in overall assets, including livestock and fishing boats and nets, from baseline to endline assessments. Specifically, livestock assets surged substantially (63.99%) in the treatment group (baseline: BDT 43,367; endline: BDT 71,118) compared to the control group (baseline: BDT 4,008; endline: BDT 3,613), demonstrating statistical significance (t = 6.97, p < 0.000). Similarly, the treatment group experienced a significant increase (49.28%) in fishing boats and nets assets (baseline: BDT 28,092; endline: BDT 41,935) compared to the control group (baseline: BDT 25,440; endline: BDT 35,592), indicating statistical significance (t = 3.06, p = 0.002) (Table 2).
The regression analysis results for aggregate assets, livestock, and fishing boats and nets indicate several significant findings. In the intervention group, the aggregate asset value showed a statistically significant increase, with an estimated coefficient of 2698.97 (p < 0.001) (Table 4). Livestock holdings also demonstrated a significant positive effect, with an estimated coefficient of 359.23 (p < 0.001). Similarly, fishing boats and nets in the intervention group exhibited a substantial increase, supported by a coefficient estimate of 2651.45 (p < 0.001). Conversely, the survey type variable showed a significant positive effect on aggregate assets, with an estimated coefficient of 6630.55 (p < 0.001), indicating a considerable increase in assets associated with the survey type. However, it had a negative impact on livestock holdings, as indicated by a coefficient of -394.73 (p < 0.001). Interestingly, the interaction term i.e. DiD had a significant positive effect on aggregate assetsand livestock by 43.84 and 60.42 percent increased with an estimated coefficient of 17467.04 (p < 0.001) and 3145.83 (p < 0.001) respectively, suggesting that specific interventions and survey types may have influenced these outcomes. The constants for all variables were statistically significant, indicating their baseline values. The R-squared values for the regression models were relatively low, suggesting that the independent variables accounted for a small proportion of the variance in the dependent variables.
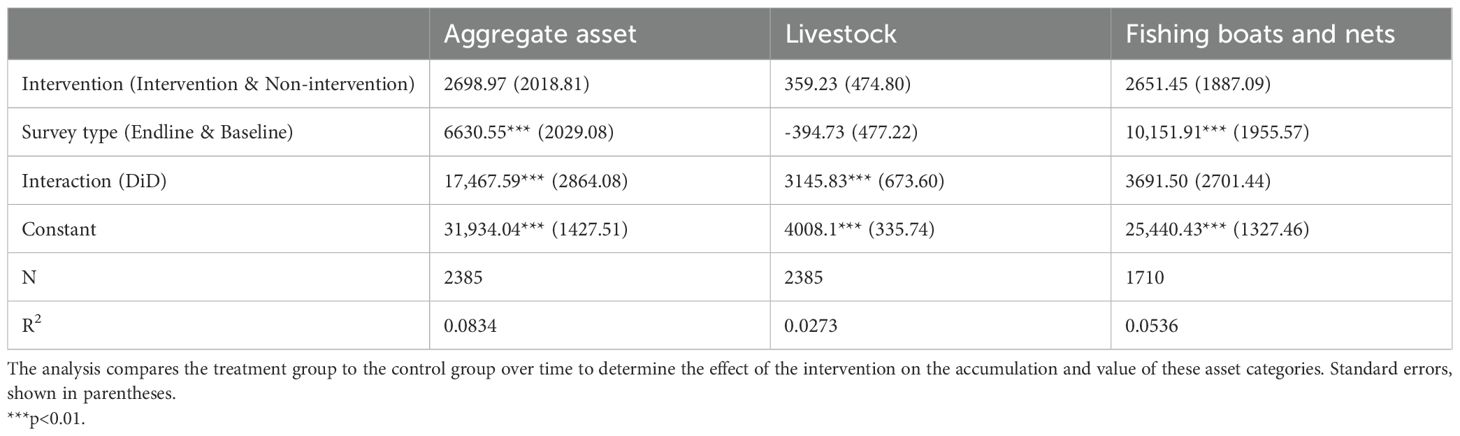
Table 4. Regression results for changes in assets, livestock, and fishing boats & nets using the DiD model.
3.3.3 Socioeconomic characteristics and changes in household income
The table (Table 5) presents the results of the regression analysis examining the changes in overall income and income from fishing as dependent variables, with various explanatory variables such as the location of the household (inside or outside the hilsa sanctuary area), age, household size, educational level, fisher ID cardholder, boat and fishing gear ownership, number of sources of income, and land ownership. Sanctuary type showed a statistically significant positive effect on the change in overall income (coefficient = 5890.47, p < 0.05) and income from fishing (coefficient = 6553.95, p < 0.05). Additionally, having a Fisher ID card was associated with a significant increase in both overall income (coefficient = 8441.17, p < 0.05) and income from fishing (coefficient = 11,494.50, p < 0.01). Possessing a fishing boat also had a significant positive impact on both overall income (coefficient = 27,393.09, p < 0.001) and income from fishing (coefficient = 25,952.11, p < 0.001). Conversely, the number of sources of income had a significant negative effect on both overall income (coefficient = -5993.85, p < 0.05) and income from fishing (coefficient = -10600, p < 0.05). Homestead land ownership was positively associated with changes in both overall income (coefficient = 883.20, p < 0.001) and income from fishing (coefficient = 692.32, p < 0.01). However, other variables such as age, household size, education level, possession of a fishing net, and ownership of cropland did not show statistically significant associations with changes in either overall income or income from fishing. The constant terms were also significant for overall income (coefficient = 41,255.75, p < 0.001) but not for income from fishing.
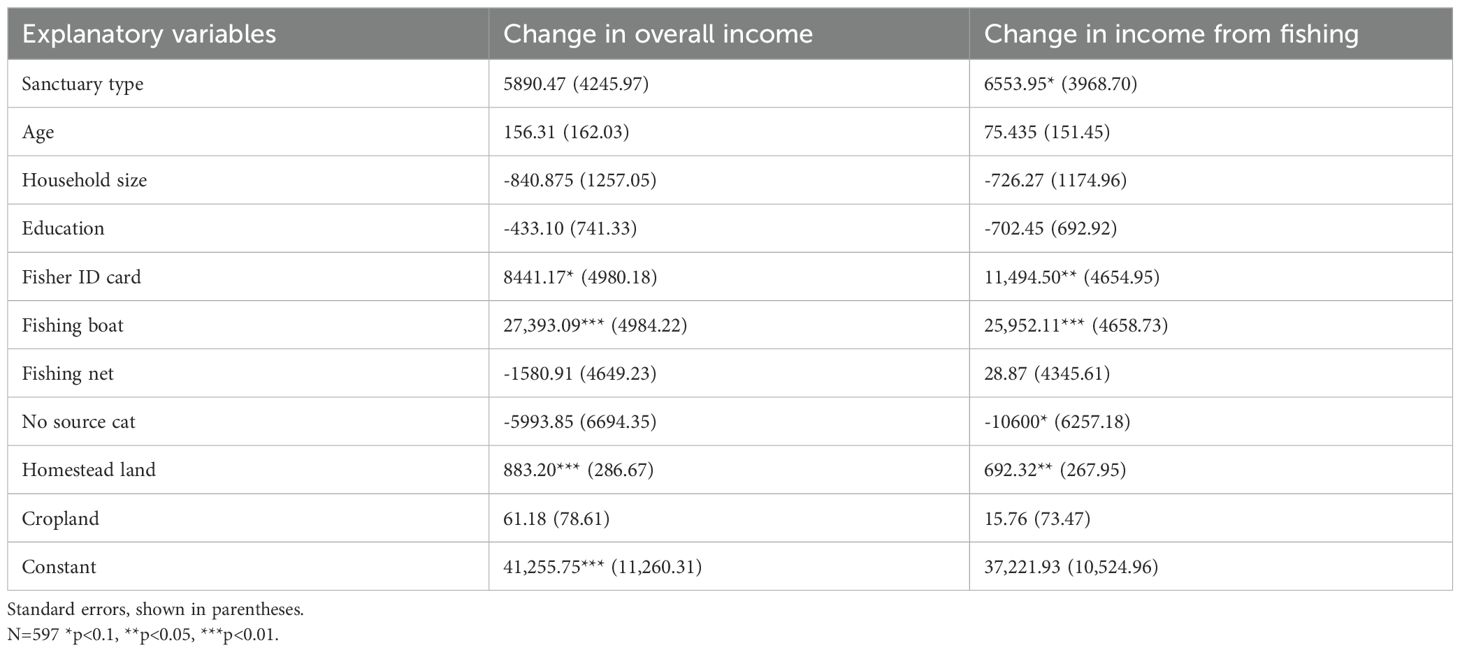
Table 5. Regression results for changes in both overall income and fishing income are influenced by various socioeconomic characteristics of fishers.
3.4 Economic evaluation
Economic evaluations are crucial for sustainable development projects as they demonstrate the cost-effectiveness of an intervention. Thomas and Chindarkar (2019) emphasized that decision-makers dealing with “competing alternatives” must determine whether it is economically feasible to invest public funds (taxpayers’ or aid money) in a specific sustainable development project. While impact evaluation primarily assesses the extent to which individuals benefit from an intervention compared to a scenario without intervention, economic evaluation delves deeper by also examining the costs incurred to implement the project and quantifying the monetary benefits gained by beneficiaries.
3.4.1 Consumptive and non-consumptive benefits
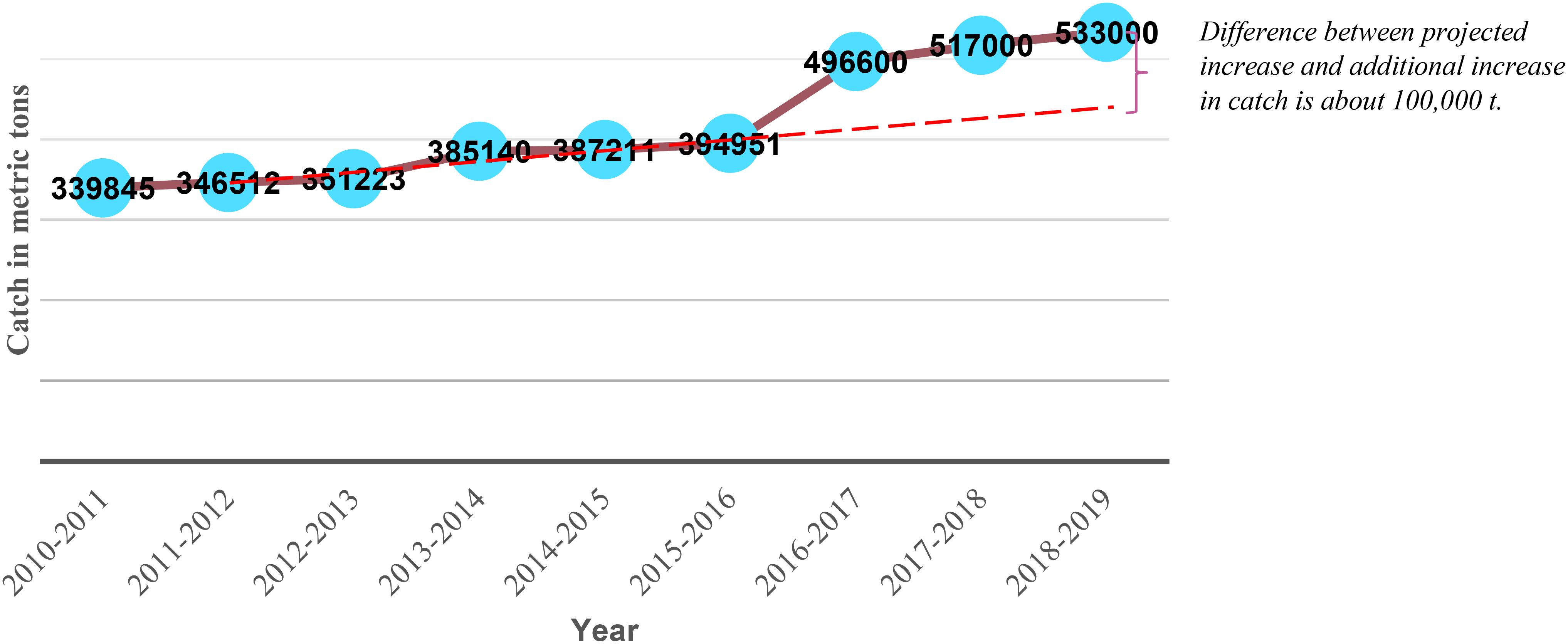
The hilsa catch has notably recovered since 2015, with the recorded catch in 2019 reaching 533,000 metric tons (FRSS, 2020), marking a 37 percent increase from the 2015 level (Figure 4). The estimated overall catch value in 2019 amounted to USD 3386.12 million (at USD 6.35 per kg of hilsa). To analyze the recovery, a comparison was made between the actual and projected hilsa landings in terms of volume. A predictive regression model was employed to generate an ex-ante projection using data points from 2001 to 2015. The projected catch level is depicted by the dotted line in Figure 4. The analysis revealed a difference of approximately 100,000 metric tons between actual and projected catch levels post-2015. Translating this difference into monetary terms, considering the average retail price of hilsa at USD 6.35 per kg of hilsa during the study period, the value of the “additional hilsa catch” is estimated to be around USD 635.29 million.
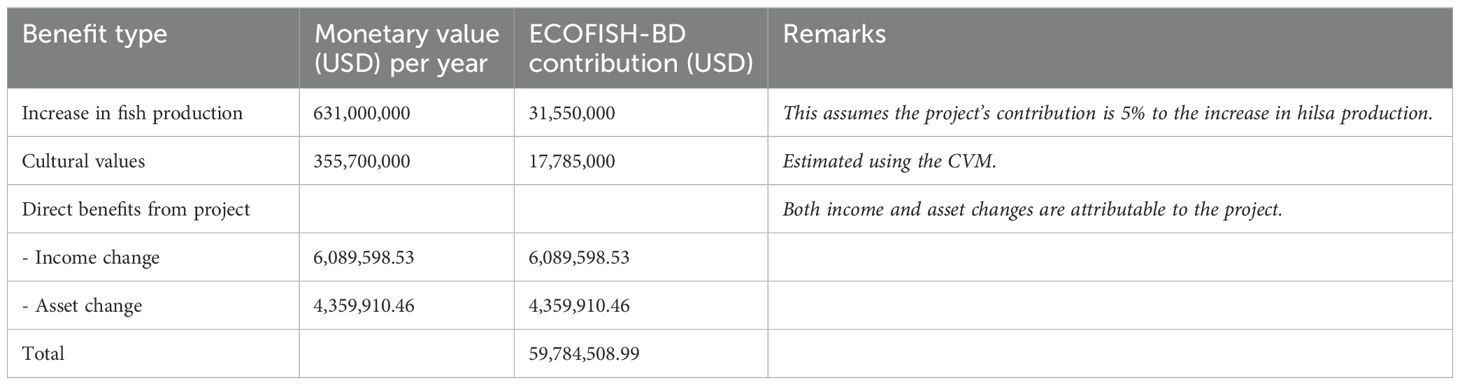
The CVM allows for the estimation of non-market goods and services, such as cultural values, by creating a hypothetical market scenario to uncover their hidden or implicit demand. The study determined that the willingness to pay for improved hilsa management to sustain its cultural services was BDT 63.71 per month per household. Adjusting for inflation (i = 5.5 percent), this amounts to BDT 67.21 in 2020. Given the reverence for hilsa as part of the national identity and the lack of evidence for “distance decay” of these values, household-level estimates were extrapolated. This analysis revealed that the non-consumptive value of hilsa is approximately USD 355.7 million.
The Difference-in-Differences (DiD) analysis for both income and asset changes between households in intervention and control areas revealed significant findings. Households in intervention areas experienced an annual income increase of USD 292.77. Additionally, these households were able to increase the annual value of their assets by up to USD 209.61 per household. When these figures are multiplied by the number of beneficiaries (20,800 households), it results in an aggregate income increase of USD 6.1 million and an aggregate asset increase of USD 4.4 million.
3.4.1.1 Level and type of contribution expected
A critical question in assessing the effectiveness of ECOFISHBD is whether the observed increases in hilsa catch and stock recovery since 2015 can be directly attributed to the project’s interventions. While the question is straightforward, answering it proves complex due to the absence of a counterfactual, making it difficult to isolate the impact of the interventions from other influencing factors. For instance, in addition to the project, multiple factors may have contributed to the increase in hilsa abundance, including government incentives for hilsa fishers to comply with regulations, enhanced enforcement mechanisms, changes in the biophysical characteristics of hilsa habitat, and other unexplained natural phenomena. Given the absence of a counterfactual and the necessary data to determine the causal impact of the intervention, it is more pragmatic to focus on the project’s contribution to the observed outcomes. This approach involves examining whether the project played a significant role in influencing or supporting the positive change in hilsa stock recovery. Table 6 outlines the key questions typically addressed in both “attribution” and “contribution” analyses, helping to differentiate between direct causal effects and contributions to broader, multi-faceted outcomes. Our analysis suggests that while it is not possible to definitively attribute the stock recovery to ECOFISH-BD alone, the project has made substantial contributions by facilitating policy reforms, and promoting sustainable fishing practices through scientific research, community, and stakeholder engagement.
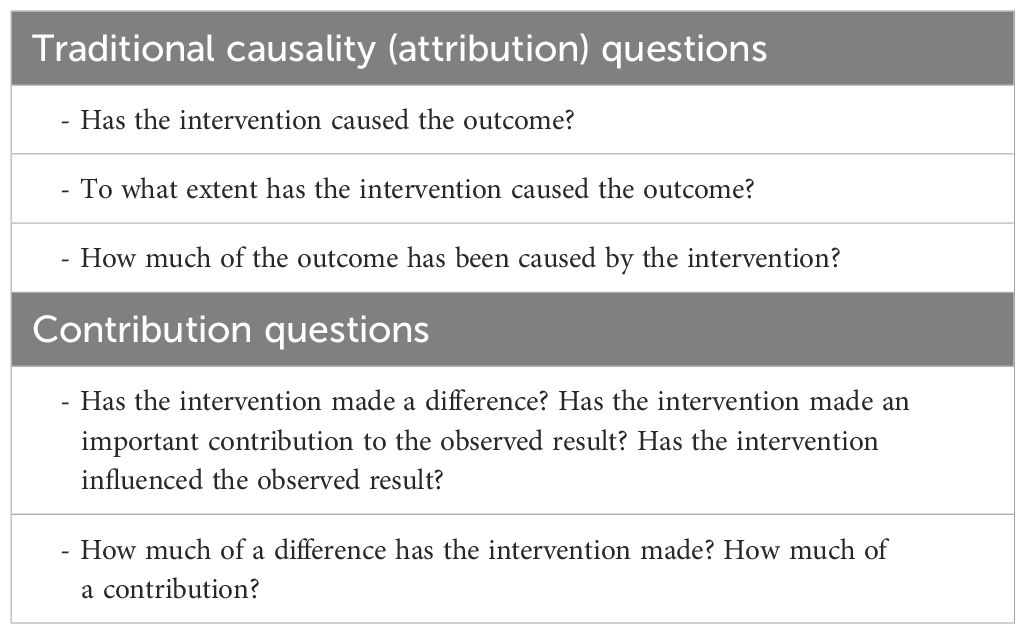
Table 6. Types of cause-effect questions (adapted from Mayne, 2008).
As shown in Table 7, there is substantial evidence suggesting that ECOFISH-BD has significantly contributed to the increased hilsa production in Bangladesh, despite challenges in objectively quantifying the exact level of contribution. Based on interviews with key stakeholders and using very conservative estimates, it is estimated that the project may have contributed between 2 and 8 percent to the observed increase in fish production. This estimate is derived from the difference between projected and actual or reported hilsa catch during the project’s implementation. The monetary value of the project’s contribution to increased hilsa production is similarly estimated to range between USD 12.6 million and USD 50.5 million, reflecting the economic benefits associated with the additional fish production (Table 7).
3.4.2 Net present value and internal rate of return
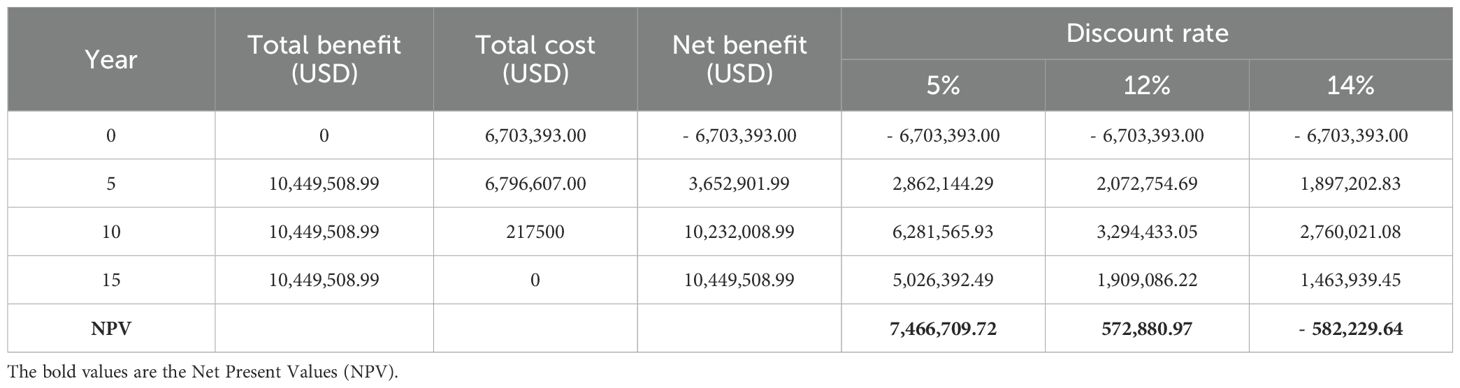
The NPV analysis of direct benefits of the project, presented in Table 8, was conducted using discount rates of 5, 12, and 14 percent. The results demonstrate that the project remains profitable at both 5 and 12 percent discount rates. However, at discount rates exceeding 13 percent, the NPV becomes negative, indicating that the present value of costs surpasses the present value of revenues. This suggests that the profitability of the project is sensitive to higher discount rates, and sustained economic benefits may diminish if future cost increases or reduced revenues are factored into the analysis. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining economic efficiency at moderate discount rates to ensure the continued viability of similar conservation and management projects.
Table 9 aggregates both the direct and indirect net benefits of the project. The monetary values of the project’s estimated contribution to increased fish production (at a 5 percent discount rate) and the non-consumptive value of hilsa to the target population. Unlike Table 8, which only considers the costs of household benefits, Table 9 includes the overall project expenditure, totaling USD 13.5 million. Additionally, the analysis factos in an additional USD 10 million that will be invetsted over the next five years, as well as in-kind contributions from the Government of Bangladesh. These in-kind contributions, including staff costs, office space, and other resources, are valued at BDT 150 million (approximately USD 1.8 million). The Government of Bangladesh is expected to maintain this level of support through 2024, which has been incorporated into the total project cost. The results indicate a significant return on investment, with the project generating significant benefits across all reasonable social discount rates. Notably, the internal rate of return (IRR), the discount rate at which net present value (NPV) equals zero, is calculated to be 32.8 percent.
4 Discussion
The development and establishment of institutional frameworks for managing and conserving fisheries resources in Bangladesh, particularly the hilsa fishery, have played a crucial role in addressing both ecological and socio-economic challenges. The historical context and significant policy milestones underscore the dynamic interaction between social-ecological systems and institutional responses (Sarker et al., 2019; Bladon et al., 2018). Over time, the Bangladesh fisheries authority has implemented a range of measures to conserve and manage artisanal hilsa fishing. Given that hilsa is a migratory fish, effective management and conservation necessitate both inland and marine fishery legislation. Alongside fishery-related legislation, non-fishery policies have also influenced hilsa conservation, emphasizing the necessity of a comprehensive approach (Islam et al., 2016). For instance, the introduction of the vulnerable group feeding program in the 1970s aimed to alleviate dire socioeconomic conditions, thereby indirectly supporting the fisheries sector (Rubaba and Yoonyoung, 2016). However, challenges remain despite policy reforms. Prior to 1995, access rights to fisheries were often awarded through competitive bidding, favoring individuals with financial resources and influence. Although the shift away from competitive bids toward open-access fishing marked a policy change (Pomery et al., 2016), it failed to significantly alter the existing power dynamics. Even with these policy reforms, financially privileged individuals continue to reap disproportionate benefits from access to fisheries resources rights (Porras et al., 2017). These disparities iunderscores the persistent socio-economic inequalities within the fisheries sector, which must be addressed to ensure equitable resource management. Nevertheless, these institutional advancements have laid the groundwork for more sustainable fisheries management and initiatives like the ECOFISH-BD project. Focused on enhancing the resilience of the hilsa fishery in the Lower Meghna region, ECOFISH-BD serves as a prime example of how both historical and contemporary institutional frameworks can effectively support sustainable development goals. Through strategic partnerships and scientific research, particularly in collaboration with the Department of Fisheries (DoF), the ECOFISH-BD project has been pivotal in driving policy and institutional reforms to conserve and manage Bangladesh’s hilsa fishery. Notable achievements include extending the brood hilsa ban from 11 to 22 days, establishing the Hilsa Conservation and Development Fund (HCDF), and designating a sixth hilsa sanctuary and a Marine Protected Area (MPA) (Wahab et al., 2020). However, the long-term success of these reforms relies heavily on ongoing government support and robust enforcement mechanisms. Thus, while ECOFISH-BD has been influential in organizing critical reforms, sustained commitment and collaboration remain imperative for effectively navigating the complex fisheries management and ensuring the continuing conservation of hilsa populations in Bangladesh.
This study evaluated the impact of a USAID-funded intiative to enhance the conservation and sustainable management of the hilsa fishery in Bangladesh, with a particular focus on improving the livelihoods of low-income fishing communities dependent on this fishery. The study indicated a statistically significant increase in income and assets among households in the intervention group when compared to the control group. This increase holds significant importance for rural households in Bangladesh in contributing to the achievement of the SDG goal to eradicate poverty (Haque et al., 2022). Apart from fish farming, all alternative income-generating activities provided statistically significant benefits to recipient households, including small-scale agriculture, poultry and animal husbandry, and handicrafts. These findings highlight the importance of tailored interventions in improving household livelihoods. This is significant because the majority of hilsa fishers are poor (Islam et al., 2017), and due to limited opportunities for alternative income-generating activities (AIGA), low-income fishers may prioritize immediate economic needs over biodiversity concerns, potentially resulting in non-compliance (van Brakel et al., 2018; Islam et al., 2020).
Sustaining the income gains beyond the project duration will require reinvesting a portion of the earnings into asset building. Asset accumulation empowers low-income individuals and families to save, gradually build wealth, and use these savings when needed (Sherraden, 2007). Therefore, strengthening asset building within fisher communities and devising a sustainable exit strategy to ensure long-term impact are critical to the project’s success. Overall asset accumulation, including livestock and fishing boats and nets, was assessed as key indicators of the project’s asset-building objectives. The analysis of household survey data from both the control and intervention groups revealed a statistically significant difference in asset building between the two groups. This difference is primarily attributed to two factors. First, some beneficiary households in intervention villages were able to reinvest some of their savings into building an asset base. Second, some households in intervention villages received input support, such as cattle, goats, checken, seeds, and seedlings for small-scale farming, as well as business literacy training, which may have contributed to their ability to manage their finances and enhance their investment behavior.
Contrary to the initial assumption that increased income would directly results in higher ownership of fishing boats and gear, our analysis reveals that the asset value of fishing boats and gear in the intervention villages is not statistically different from that of the control group. While this does not entirely eliminate the possibility of a moderate increase in boat and gear ownership across both groups, it suggests that income gains were not predominantly reinvested in fishing related assests. Instead, it highlights the potential role of income diversification in stabilizing fishing efforts. By providing alternative sources of income beyond fishing, the project may contribute to supporting more sustainable fisheries management practices.
While there has been a reported increase in hilsa catch compared to 2015 levels (Khan et al., 2020), potentially benefiting households both within and outside sanctuary areas, the statistically significant difference in fishing income between intervention and control areas requires further investigation. One potential explanation is that households in intervention areas may have benefited from co-management practices (Islam et al., 2020), which could have improved their bargaining power in negotiating fish prices. However, this explanation remains inconclusive, as an in-depth analysis of local power dynamics and profitability along the hilsa supply chain is beyond the scope of this study.
It is widely recognized that impact evaluations of development projects need to look beyond cumulative benefits and loses (Gertler et al., 2011). While assessing overall impact is valuable for determining whether a project has achieved its objectives, it is equaly important to examine how these benefits are distributed. One key question arises- Who gets what and why? Specially, in terms of income and asset-building benefits, who benefitted more than others? Did low-income and vulnerable groups gain disproportionately more than the non-poor, or was the distribution uneven? Although the concept of distributive justice has been central to philosophy and the social sciences (Olsaretti, 2018), there is no consensus on what constitutes a fair, equitable or just distribution (Merayo et al., 2019). While defining terms like “pro-poor” or “inclusive” may appear straightforward, assessing whether and to what extent an initiative truly embodies these qualities is challenging in practice. How can we determine if the benefit distribution mechanism we adopt is genuinely inclusive? According to Mohammed, 2011, a pro-poor approach should include systematically favoring low-income and marginalized groups within society. This consideration is particularly important in the context of hilsa fishery in Bangladesh, where power imbalances are prominent. Ensuring that the most vulnerable communities benefit more requires intentional design and careful evaluation of the distribution mechanisms used to ensure equity in outcomes.
Interviews with project implementers indicated that the poorest sections of the target population were specifically targeted. However, as noted by Uraguchi and Mohammed (2016), many development projects are susceptible to both “inclusion” and “exclusion” errors, where either unintended groups receive benefits or intended groups are left out. Therefore, it is important to examine how benefits are distributed among different socioeconomic groups. To address this, a regression analysis was conducted, with overall income and income from fishing regressed against the socioeconomic characteristics of respondents. This analysis aimed to provide a clearer understanding of how the benefits were allocated and to identify any disparities in benefit distribution among different socioeconomic groups.
In Model I (overall income change), households with a fisher ID card, boat, and land experienced a statistically significant positive income change compared to those without these assets. A similar trend emerged in Model II (change in income from fishing). These findings suggest that households with a fisher ID card, which were likely targeted, benefited more from the intervention. However, the disproportionate benefits observed among landowners raise concerns about equity and fairness, indicating that the project may not have adequately reached landless households, who are often among the poorest. To enhance inclusivity in future interventions, addressing these equity concerns is important and ensure that landless households are not left behind. This approach aligns with the broader principle that development interventions should focus on disadvantaged groups to tackle systemic inequalities (FAO, 2022). By doing so, future projects can better promote equitable outcomes and ensure that the most vulnerable populations receive the support they need.
The hilsa catch has shown a remarkable recovery since 2015. While catch level serves as a crucial metric, it alone does not reliably indicate stock recovery as higher catches might merely reflect increased fishing effort or input. Therefore, it is essential to consider the catch-per-unit-effort (CPUE) as an indicator, which provides deeper insight into stock recovery patterns. A recent study by Karim et al., 2019 utilized time series downstream catch-effort data from the Bay of Bengal, sourced from the Department of Fisheries (DOF). The study employed surplus production models (SPMs) to estimate key parameters such as Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY) and CPUE. The findings indicated that the F ratio (F/FMSY) across all SPMs was less than 1, while the B ratio (B/BMSY) was greater than 1. These indicators strongly suggest that hilsa stock is recovering, accompanied by a surge in hilsa catch within Bangladesh. Moreover, a noticeable shift from smaller to larger size groups of hilsa indicates an improvement in the fishery’s status. Over the five-year project period, the average size of individual hilsa has significantly increased from 535 grams in 2015 to 915 grams in 2019, representing a substantial growth of 400 grams (Rahman et al., 2020). This notable increase in size indicates the positive impact of targeted conservation and management strategies on the sustainability and productivity of the hilsa fishery. Hilsa, being a crucial fish species in Bangladesh, not only serves as a staple food source but also holds significant cultural and religious importance (Mohammed and Wahab, 2013). As highlighted by Mohammed et al., 2016, hilsa possesses both consumptive and non-consumptive values. These values are considered during the calculation of “gains” within the project intervention areas.
A key question that remains whether the observed increases in hilsa catch and stock recovery since 2015 can be attributed to ECOFISH-BD. While this is straightforward to pose, providing a definite answer is far more complex. Without a clear counterfactual, it is challenging to isolate the specific impact of ECOFISH-BD from other potential contributing factors. Alongside ECOFISH-BD, a range of other plausible factors may have contributed to the recovery of the hilsa population, including government efforts to incentivize hilsa fishers to comply with fishing regulations, improved enforcement, and changes in the biophysical characteristics of hilsa habitats or other unexplained natural phenomena. However, despite these potential influences, it is important to recognize that ECOFISH-BD, since its inception in 2014, has operated at a scale capable of impacting the entire hilsa fishery. Given the scope and magnitude of its interventions, including community-based co-management, habitat protection, and livelihood diversification—it is plausible to attribute at least part of the observed increase in hilsa catch and stock recovery to the efforts of the ECOFISH-BD project (Dutton et al., 2018).
In the absence of a clear counterfactual and the necessary data to determine the causal impact of the intervention, the focus can shift to contribution analysis. This approach aims to understand whether the project contributed to or influenced the observed outcomes. By assessing the extent to which ECOFISH-BD may have impacted the observed increases in hilsa catch and overall stock recovery, it becomes possible to contextualize the project’s role within the broader landscape of other influencing factors. Contribution analysis, while not providing definite causal proof, allows for a reasoned evaluation of the project’s influence on the outcomes (Mayne, 2008). However, there was an increase in hilsa landing and productivity between 2015 and 2019—a surplus catch of about 100,000 t. While it is difficult to objectively measure the contribution of ECOFISH-BD to this overall increase in fish landing, using conservative estimates we found that the monetary estimation of the project’s contribution could be between USD 12.6 million and USD 50.5 million. These findings align with previous studies indicating strong economic returns from investments in fisheries management and conservation efforts (Sumaila et al., 2012; Sala et al., 2016). The project demonstrates continued economic viability, with an internal rate of return (IRR) of 32.8 percent, far exceeding conventional thresholds for project sustainability, and remains robust under both 5 and 12 percent discount rates. This high IRR underscores the significant economic benefits of the project, particularly for households in intervention areas, supporting the case for sustained investment in conservation and fisheries management initiatives. These results echo prior research that highlights the economic value of sustainable fisheries management (Anderson et al., 2018) and the role of institutional support in enhancing long-term socio-economic and ecological gains (Fitzgerald et al., 2020). These findings highlight the importance of sustainable investment in small-scale fisheries and the role of institutional support in maximizing long-term socio-economic and ecological benefits.
5 Conclusion
The analysis indicates a significant return on investment across all reasonable social discount rates, with an internal rate of return as high as 32.8 percent. This demonstrates that ECOFISH-BD is a highly profitable and economically viable investment. This initiative holds the potential to deliver substantial benefits to target communities and the nation, even under higher discount rates. However, to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of the project, several key concerns must be addressed.
First, for the project to achieve lasting conservation outcomes, the sustainability of its impacts must be monitored and maintained. Second, the study highlights important distributional and equity issues, particularly the disproportionate economic benefits accruing to landowners compared to landless households. Moving forward, future project design should incorporate a systematic approach to support those most disadvantaged, ensuring that no one is left behind. Finally, the persistence of local power structures continue to pose challenges, perpetuating financial exclusion. The reliance of fishers on rich intermediaries for credit limits their ability to maximize the benefits from fishing activities. Although there is no evidence of significant changes in these power dynamics, future initiatives should focus on promoting financial inclusion and reducing long-term debt burdens to empower fishers and challenge these rigid power structures. Moreover, the study reveals that the non-monetary values of small-scale fisheries are often inadequately captured in national economic accounts, limiting their consideration in policy decisions.
Contrary to the misconception that small-scale fisheries are unprofitable and not a viable investment, this study demonstrates that the small-scale hilsa fishery in Bangladesh is indeed profitable and investible. Employing up to three million people, the hilsa fishery serves as a critical source of livelihood and income, despite facing challenges such as poor infrastructure, limited access to financial services, pollution, river diversion, and competition with industrial fleets. The failure of markets and national accounting systems to recognize the non-monetary and social values associated with artisanal and small-scale fisheries further complicates policy and decision-making processes.
This research addresses a significant knowledge gap regarding the value of small-scale fisheries and is poised to shift perceptions among policymakers and development partners. The findings underscore the urgent need for increased investment in this sector, highlighting its potential to deliver both socio-economic and ecological benefits. Moving forward, a targeted approach that fosters financial inclusion, addresses equity concerns, and supports sustainable management practices will be crucial for ensuring the long-term viability and success of small-scale fisheries. By prioritizing these aspects, future interventions can create a more equitable framework that benefits marginalized groups, ultimately enhancing the sustainability of fisheries resources in Bangladesh and beyond.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because the manuscript presents a re-analysis of data utilizing the established dataset sourced from the monitoring and evaluation framework of the Enhanced Coastal Fisheries in Bangladesh (ECOFISH-BD) project. Within the framework of the ECOFISH-BD Project, comprehensive baseline (2016) and endline (2019) data were systematically collected to fulfill the program’s monitoring and evaluation objectives, as outlined in the Monitoring and Evaluation Plan. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
EM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. AH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MN: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is part of the CGIAR Research Program on Fish Agri-Food Systems (FISH), supported by Windows 1 & 2 grants from the CGIAR Fund to WorldFish for the Global FISH CRP.
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere appreciation to the members of fishing households, academics, government officials, development professionals, and the project team for their valuable contributions. We also thank the reviewers for their insightful feedback and suggestions, which have significantly strengthened this manuscript. The Open Access fees for this article were funded by the Asia–Africa BlueTech Superhighway (AABS) Project of WorldFish, supported by UK International Development under the Blue Planet Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anderson J. L., Asche F., Garlock T. (2018). Globalization and commoditization: The transformation of the seafood market. J. Commodity Markets 12, 2–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomm.2017.12.004
Babulo B. B., Muys B., Haregeweyn N., Descheemaeker K., Deckers J., Poesen J., et al. (2012). Cost-benefit analysis of soil and water conservation measure: The case of exclosures in northern Ethiopia. For. Policy Econ. 15, 27–36. doi: 10.1016/j.forpol.2011.09.008
Bangladesh Economic Review (BER) (2020). Finance Division, Ministry of Finance, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. Available online at: www.mof.gov.bd (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Bangladesh Foreign Trade Institute (BFTI) (2016). Study on sector based need assessment of business promotion council- fisheries products (Kawran Bazar, Dhaka: BFTRI).
Bladon A. (2017). Carrots and sticks: incentives to conserve hilsa fish in Myanmar (International Institute for Enviornment and Development). Available at: https://www.iied.org/carrots-sticks-incentivesconserve-hilsa-fish-Myanmar (Accessed March 15, 2020).
Bladon A. J., Mohammed E. Y., Ali L., Milner-Gulland E. J. (2018). Developing a frame of reference for fisheries management and conservation interventions. FISHERIES Res. 208, 296–308. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2018.08.010
Bladon A., Myint K. T., Ei T., Khine M., Aye P. T., Thwe T. L., et al. (2019). Spawning seasonality of hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) in Myanmar’s Ayeyarwady Delta (London: IIED: International Institute for Environment and Development Working Paper). Available at: http://pubs.iied.org/16661IIED (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Dewhurst-Richman N., Mohammed E. Y., Ali M. L., Hassan K., Wahab M. A., Ahmed Z. F., et al. (2016). Balancing carrots and sticks: incentives for sustainable hilsa fishery management in Bangladesh (London: International Institute for Environment and Development). Available at: http://pubs.iied.org/16619IIED (Accessed March 15, 2020).
DoF (2024). National Fish Week Compendium (In Bengali) Vol. 160 (Bangladesh: Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock).
Dutta S., Al-Abri I., Paul S. (2021). Bio-economic trends of Hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) fishery: perspectives of transboundary management between India and Bangladesh. Mar. Policy 128, 104483. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104483
Dutton I. M., Hossain M. S., Kabir H. (2018). Midterm performance evaluation report of USAID/Bangladesh Enhanced Coastal Fisheries (ECOFISH) project (Vienna, VA 22182, USA: Accelerating Capacity for Monitoring and Evaluation (ACME) activity held by International Business and Technical Consultants, Inc. (IBTCI).
FAO (2022). Strengthening coherence between social protection and fisheries policies – Framework for analysis and action (Rome: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 671/1). doi: 10.4060/cc2411en. (Accessed February 23, 2024).
FAO (2024). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024 – Blue Transformation in action (Rome). doi: 10.4060/cd0683en. (Accessed September 18, 2024).
Fisheries Resources Survey System (FRSS) (2020). Fisheries statistical report of Bangladesh Vol. 32 (Bangladesh: Department of Fisheries), 1–57.
Fitzgerald M. L., Newbold S. J., Kling D. A. (2020). Catalyzing fisheries conservation investment. Front. Ecol. Environ. doi: 10.1002/fee.2147
Gertler P. J., Martinez S., Premand P., Rawlings L. B., Vermeersch C. M. J. (2011). Impact Evaluation in Practice (Washington DC: The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank 1818 H Street NW), 20433.
Haque A. B. M. M., Nahiduzzaman M., Saha S. M. (2022). Can adaptive co-management reduce poverty and inequality in the coastal fishing community? An impact evaluation in the riverine system in Bangladesh. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci. 56. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2022.102721
Hossain M. A. R., Das I., Genevier L., Hazra S., Rahman M., Barange M., et al. (2019). Biology and fisheries of hilsa shad in bay of bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 651 (2), 1720–1734. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.034
Hossain M. S., Sharifuzzaman S. M., Rouf M. A., Pomeroy R. S., Hossain M. D., Chowdhury S. R., et al. (2018). Tropical hilsa shad (Tenualosa ilisha): Biology, fishery and management. Fish Fish 20 (1), 44–65. doi: 10.1111/faf.12323
Islam M., Mohammed E. Y., Ali L. (2016). Economic incentives for sustainable hilsa fishing in Bangladesh: an analysis of the legal and institutional framework. Mar. Policy 68, 8–22. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2016.02.005
Islam M., Nahiduzzaman M., Wahab M. A. (2020). Fisheries co-management in hilsa shad sanctuaries of Bangladesh: Early experiences and implementation challenges. Mar. Policy 117, 103955. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.103955
Islam M. M., Shamsuzzaman M. M., Mozumder M. M. H., Xiangmin X., Ming Y., Jewel M. A. S. (2017). Exploitation and conservation of coastal and marine fisheries in bangladesh: do the fishery laws matter? Mar. Pol. 76, 143–151. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2016.11.026
Karim E., Liu Q., Ming S., Barman P., Hasan S., Hoq E. (2019). Assessing recent gradual upsurge of marine captured hilsa stock (Tenualosa ilisha) in Bangladesh. Aquaculture Fisheries 4, 156–165. doi: 10.1016/j.aaf.2019.02.005
Khan M., Wahab M. A., Haque A. B. M. M., Nahiduzzaman M., Phillips M. J. (2020). Value chain impact of the increased hilsa shad (Tenualosa ilisha) harvest in Bangladesh. Int. Food Agribusiness Manage. Rev. 23, 355–268. doi: 10.22434/IFAMR2019.0201
Khandker S., Koolwal G. B., Samad H. A. (2010). Handbook on Impact Evaluation: Quantitative Methods and Practices (Washington, DC: World Bank).
Mahmud Y. (Ed.) (2020). Hilsa Fisheries Research and Development in Bangladesh (Bangladesh: Bangladesh Fisheries Research Institute), 309 p.
Mayne J. (2008). Contribution analysis: An approach to exploring cause and effect. ILAC Brief 16, 4. https://hdl.handle.net/10568/70124.
Merayo E., Myint K. T., Ei T., Khine M., Aye P. T., Thwe T. L., et al. (2020). Migratory patterns of Hilsa shad in the Myanmar Ayeyarwady delta: lessons for fisheries management (London: IIED: International Institute for Environment and Development Working Paper). Available at: http://pubs.iied.org/16665IIED (Accessed April 12, 2024).
Merayo E., Porras E., Harper S., Steele P., Mohammed E. Y. (2019). Subsidy reform and distributive justice in fisheries (London: IIED: International Institute for Environment and Development working paper).
Mohammed E. Y. (2011). Pro-poor benefit distribution in REDD+: who gets what and why does it matter? REDD working papers (London: IIED).
Mohammed E. Y., Ali L., Ali S., Hussein B., Wahab M. A., Sage N. (2016). Hilsa’s non-consumptive value in Bangladesh: Estimating the non-consumptive value of the hilsa fishery in Bangladesh using the contingent valuation method (London: International Institute for Environment and Developmen). Available at: http://pubs.iied.org/16626IIED (Accessed March 15, 2020).
Mohammed E. Y., Wahab M. A. (2013). Direct economic incentives for sustainable fisheries management: the case of hilsa conservation in Bangladesh (London: International Institute for Environment and Development).
Moore M., Boardman A., Vining A. (2013a). The choice of the social discount rate and the opportunity cost of public funds. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 4, 401–409. doi: 10.1515/jbca-2012-0008
Moore M. A., Boardman A. E., Vining A. K. (2013b). More Appropriate Discounting: The rate of Social Time Preference and the value of the Social Discount Rate. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 4, 1–16. doi: 10.1515/jbca-2012-0008
Nahiduzzaman M., Islam M. M., Wahab M. A. (2018). “Impacts of fishing bans for conservation on hilsa fishers livelihoods: Challenges and opportunities,” in Conserving ilish, securing livelihoods: Bangladesh-India perspectives. Eds. Nishat B., Mandal S., Pangare G. (International Water Association, London).
Olsaretti S. (Ed.) (2018). The Oxford handbook of distributive justice (Oxford: Oxford University Press).
Pomery R., Thompson P., Courtney C. A. (2016). Marine Tenure and Smallscale Fisheries: Learning from the Bangladesh Experience and Recommendation for the Hilsa Fishery (Washington, DC: USAID Tenure and Global Climate Change Program).
Porras I., Mohammed E. Y., Ali L., Ali M. S., Hossain M. B. (2017). Power and profits in Bangladesh’s hilsa fishery: a value chain analysis. Mar. Policy 84, 60–68. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2017.06.031
Rahman M., Naevdal G. (2000). Population genetic studies of hilsa shad, Tenualosa ilisha (Hamilton), in Bangladesh waters: Evidence for the existence of separate gene pools. Fish. Manage. Ecol. 7, 401–411. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2400.2000.00211.x
Rahman M. A., Pramanik M. M. H., Flura, Ahmed T., Hasan M. M., Khan M. H., et al. (2017). Impact assessment of twenty-two days fishing ban in the major spawning grounds of Tenualosa ilisha (Hamilton, 1822) on its spawning success in bangladesh. J. Aquac Res. Dev. 8, 489. doi: 10.4172/2155-9546.1000489
Rahman M. A., Rahman B. M. S., Hasan S. J., Flura T., Hasan M. M., Khan M. H., et al. (2013). Impact of eleven days fishing ban in the major spawning grounds of Hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) (Hamilton) on its breeding success. Bangladesh Res. Publications J. 9, 116–122.
Rahman M. J., Wahab M. A., Amin S. M. N., Nahiduzzaman M., Romano N. (2018). Catch trend and stock assessment of hilsa, Tenualosa ilisha, using digital image measured length-frequency data. Mar. Coast. Fisheries: Dynamics Management Ecosystem Sci. 10, 386–401. doi: 10.1002/mcf2.2018.10.issue-4
Rahman M. J., Wahab M. A., Nahiduzzaman M., Haque A. B. M. M., Cohen P. (2020). Hilsa fishery management in bangladesh. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 414, 012018. https://fish.cgiar.org/publications/hilsa-fishery-management-bangladesh.
Ravallion M. (2008). “Evaluating anti-poverty programs,” in Handbook of Development Economics, vol. 4 . Ed. Ravallion M. (Amsterdam: Elsevier).
Rubaba A., Yoonyoung C. (2016). Vulnerable Group Feeding: Bangladesh - Program Brief (English) (Washington, D.C: World Bank Group). Available at: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/461531552967731486/Vulnerable-Group-Feeding-Bangladesh-Program-Brief (Accessed June 10, 2020).
Sala E., Costello C., Parme J. D. B., Fiorese M., Heal, Kelleher K., et al. (2016). Fish banks: an economic model to scale marine conservation. Mar. Policy 73, 154–161. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2016.07.032
Sarker M. N., Naseri M., Uddin M. S., Das N., Humayun M. (2019). On the management of single fish species of hilsa shad (Tenualosa ilisha) resources of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Zool. 47, 173–183. doi: 10.3329/bjz.v47i1.42055
Sherraden M. (2007). “Can the poor save?,” in Saving and Asset Building in Individual Development Accounts (Routledge, New York).
Sumaila U. R., Cheung W., Dyck A., Gueye K., Huang L., Lam V., et al. (2012). Benefits of rebuilding global marine fisheries outweigh costs. PloS One 7, e40542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040542
Thomas V., Chindarkar N. (2019). Economic Evaluation of Sustainable Development (Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan).
Uraguchi Z. B., Mohammed E. Y. (2016). “Harnessing market forces for financial inclusion in marine and coastal conservation: Lessons from market systems development approach,” in Marine Transboundary Conservation and Protected Areas. Ed. Mackelworth P.. United Kingdom: Routledge.
van Brakel M. L., Nahiduzzaman M., Haque A. M., Mustafa M. G., Rahman M. J., Wahab M. A. (2018). Reimagining large-scale open-water fisheries governance through adaptive co-management in hilsa shad sanctuaries. Ecol. Soc. 23, 26. doi: 10.5751/ES-09917-230126
Wahab M. A., Beveridge M. C. M., Phillips M. J. (Eds.) (2019). Hilsa: Status of fishery and potential for aquaculture Vol. 2019-16 (Penang, Malaysia: WorldFish. Proceedings), 196p.
Wahab M. A., Rahman M. J., Haque A. M., Nahiduzzaman M. (2020). USAID Enhanced Coastal Fisheries in Bangladesh Project (ECOFISH): Completion Report,(2014-2019) (WorldFish). Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/4543 (Accessed September 25, 2021).
Keywords: hilsa fishery, economic evaluation, co-management, small-scale fisheries, livelihoods, conservation
Citation: Mohammed EY, Haque ABMM and Nahiduzzaman M (2025) Impact evaluation of hilsa fishery restoration in Bangladesh: money well spent? Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1437783. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1437783
Received: 24 May 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Reniel Cabral, James Cook University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Hadayet Ullah, University of Adelaide, AustraliaMohammad Mojibul Hoque Mozumder, University of Helsinki, Finland
Copyright © 2025 Mohammed, Haque and Nahiduzzaman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Md. Nahiduzzaman, TS5OYWhpZHV6emFtYW5AY2dpYXIub3Jn; bmFoaWR6bUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†ORCID: Md. Nahiduzzaman, orcid.org/0000-0002-5152-992X
 Essam Yassin Mohammed
Essam Yassin Mohammed A. B. M. Mahfuzul Haque
A. B. M. Mahfuzul Haque Md. Nahiduzzaman
Md. Nahiduzzaman