
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 22 November 2024
Sec. Marine Fisheries, Aquaculture and Living Resources
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1434633
This article is part of the Research TopicChallenges in Fishery Assessment MethodologiesView all 12 articles
The changes in fish community structure hold profound implications for our under-standing of the stability and sustainability of marine ecosystems. To uncover the evolving trends in the fish community structure of the Wailingding marine ranching area, this study analyzed fishery resource survey data collected in April 2020 and March 2023, employed methods such as the relative importance index, Bray–Curtis clustering, similarity percentage (SIMPER) analysis, biomass spectrum, ABC curves, and redundancy analysis to analyze the interannual changes and stability characteristics of fish community structure in spring. The results indicate that 26 and 62 fish species were captured in spring 2020 and 2023, respectively, with Thrissa kammalensis and Leiognathus ruconius merging as the dominant species in each year. In 2020, warm water, upper-middle fish species predominated, followed by a shift to warm water, demersal, and benthic species in 2023. Cluster analysis revealed distinct spatial patterns, with fish communities in both years divisible into three discernible groups. SIMPER analysis identified T. kammalensis in 2020 and L. ruconius in 2023 as the main typical species of the fish communities, with Pampus argenteus and Dasyatis zugei as the primary discriminating species between communities, respectively. The slopes of the standard biomass spectra for both year were less than -1, indicating a decline in the overall biomass of the fish community, particularly among larger-bodied species. ABC curve analysis indicated that the fish community in spring 2020 was in a state of moderate disturbance (W=0.225), while in spring 2023, it was in a state of severe disturbance (W=-0.145). The primary environmental factors influencing fish community distribution in both springs were water temperature, depth, and salinity. In summary, the Wailingding marine ranching area has experienced a transition in dominant fish species towards smaller forage fish species, typified by L. ruconius. The level of disturbance experienced by fish communities is progressively intensifying, leading to a decline in the structural stability. Concurrently, there has been an increase in the biomass of reef-associated and reef-dependent fish species.
The marine environment, referred to as the “blue pantry” for obtaining high-end food and premium protein (Hu et al., 2022), offers a vast quantity of high-quality protein through fishing and marine aquaculture. Within the extensive and intricate marine ecosystem, structural changes in marine fish communities have become a focal point of research (Cheikh et al., 2023). The changes in fish community structure hold profound implications for our understanding of the stability and sustainability of marine ecosystems. In recent years, significant alterations in the structure of marine fish resource communities have been observed (Chen et al., 2023), primarily attributed to intensified climate change, the spread of over-fishing, and severe habitat degradation. These changes manifest clearly in declining fishery resource densities, reduced levels of population structure heterogeneity, and diminished species richness, as well as a trend towards smaller and younger fish populations (Hong et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Consequently, these developments have garnered widespread attention.
Quantitative methods used to assess community structure stability include ABC curves and biomass spectra (Dang et al., 2021; Guan et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023). Among these, ABC curves (abundance–biomass comparison curves) determine the expected response of biological communities to disturbances by analyzing the impact of external disturbances on the community (Fang et al., 2023). Wijeyaratne and Bellanthudawa (2018) utilized ABC curves to predict the level of environmental pressure in the Diya Bay wetland system. Liu et al. (2021) employed ABC curves to discover seasonal variations in the response to external disturbances of the aquatic animal community in the waters of Zhanjiang Port. The biomass size spectrum (BSS), derived from the particle size spectrum proposed by Sheldon et al. in 1972, reflects the individual composition and stability of aquatic ecosystem communities. Magnussen (2002) utilized the biomass spectrum to discover that, in the Faroe Islands’ shallow coastal areas, species dominance shifted from large-bodied fish species to smaller-bodied ones. Wang et al. (2022) employed biomass spectrum analysis to examine the characteristics of and interannual variations in the fish community structure of the southern coastal waters of Zhejiang Province during the spring season. Xu et al. (2020) utilized the biomass size spectrum method to determine the disturbance status of fish community populations in different years in various marine areas of Daya Bay.
Due to its rich biodiversity and diverse hydrological characteristics, the Wailing-ding area in Zhuhai has become a significant habitat for many important marine and estuarine fish species. It serves not only as a breeding and nursery ground for various economically valuable fish species but also acts as a vital migration pathway for migratory fish species. Additionally, it is an integral component of the important fishing grounds in the South China Sea (Augspurger et al., 2017). However, in recent years, with the rapid economic growth of surrounding cities, issues such as eutrophication and environmental pollution in the Pearl River Estuary have become increasingly prominent. Concurrently, intensive fishing activities have led to a severe decline in fishery resources (Liu et al., 2023), resulting in significant impacts on the structure of fish communities. As a result, the fish community structure in the Wailingding area has undergone changes, such as a de-crease in resource abundance and fish catches showing trends towards younger and smaller individuals (Huang et al., 2022).
As apex consumers in aquatic ecosystems, fish play a crucial role in estuarine ecosystems. According to the trophic cascade effect, changes in their community structure can have multifaceted impacts on the structure and functioning of aquatic ecosystems, thereby playing a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem health and stability (Cong et al., 2021).
To address the decline in fishery resources, the Zhuhai municipal government has devised strategies to establish marine ranching in the Wailingding area. Through systematic improvement of the ecological environment and scientific resource enhancement measures, their aim is to promote the increase in and sustainable utilization of fishery resources.
Currently, research on the nearshore fish community structure in the Wailingding area of Zhuhai primarily focuses on distribution patterns and seasonal variations (Yan et al., 2015; Mo et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2023), with a lack of comprehensive studies on trends in interannual variations. This study utilizes bottom trawl survey data on fishery resources, collected during the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023 in the Wailingding marine ranching area, Zhuhai. Through the application of cluster analysis, similarity analysis, biomass spectra, ABC curves, and redundancy analysis, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the fish com-munity structure, disturbance status, and their relationship with environmental factors in this region. The aim is to identify these short-term changes and to lay the groundwork for future research that can track longer-term trends in the fish community structure of the Wailingding marine ranching area and provide data support for the conservation of fishery resources and the establishment of marine ranching in this area.
The data used in this study were obtained from the bottom trawl surveys con-ducted by the South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences in the Wailingding marine ranching area, Zhuhai, in April 2020 and March 2023. The surveys comprised 12 sampling stations (Figure 1). A nearshore single-vessel bottom trawl fishing vessel was used for the survey, with an average mouth width of 24 m and a mesh size of 3 cm at the cod end. Standardized processing of the fishing data was conducted based on the trawl time (1 h) and trawl speed (3 knots). The survey and sample preservation were carried out following the Marine Survey Specifications (GB/T 12763-2007), and species identification was based on the Fisheries of the South China Sea and Marine Fishes of China publications (Chen and Zhang, 2015). Water environ-mental data, including the surface water temperature, bottom water temperature, salinity, and pH, were collected using a multi-parameter water quality analyzer (YSI 6900). Depth measurements were taken at each station using a depth sounder. The ecological types of fish were classified according to Marine Fishes of China and the differences in fish community structure were tested using one-way analysis of similarities (ANOSIM).
Using the index of relative importance (IRI) proposed by Pinkas et al. (1971), the importance of species within the community was determined. The calculation formula (Equation 1) is as follows:
where N represents the percentage of individuals of a certain species relative to the total number of individuals, W represents the percentage of biomass of a certain species relative to the total biomass, and F represents the percentage of occurrences of a certain species relative to the total number of sampling stations.
In this study, dominant species are defined as those with an IRI ≥ 1000, important species have an IRI between 1000 and 100, common species have an IRI between 100 and 10, and rare species have an IRI < 10 (Guo et al., 2020). Additionally, fish species can be classified into warm water, warm-temperate water, and cold water species based on their temperature preference (Zhang and Huang, 2009).
Using Primer 6.0 software, fish community structure analysis was conducted. Standardized biomass data of fish were square-root transformed, followed by calculation of Bray–Curtis similarity coefficients to construct a similarity matrix. Hierarchical cluster analysis (CLUSTER) was employed to cluster the fish communities, and SIMPER analysis was performed based on the clustering results to determine the average contribution rates of different fish species to intra-group similarity and inter-group dissimilarity. Fish species with an average contribution rate of intra-group similarity greater than 4% were identified as typical species, while those with an average contribution rate of inter-group dissimilarity greater than 4% were identified as discriminant species (Wang et al., 2022). The stress coefficient (stress) was used to assess the quality of NMDS two-dimensional plots. Typically, when 0.1 ≤ stress < 0.2, an NMDS two-dimensional plot can be used with some interpretative significance; when 0.05 ≤ stress < 0.1, the sorting effect is generally reliable and considered a good sorting; and when stress < 0.05, it indicates good representativeness (Xia et al., 2016).
Biomass size spectrum analysis was employed to investigate the relationship between fish biomass and mean body mass in the Wailingding area of Zhuhai. Firstly, the average individual mass of each species was calculated for each season. Subsequently, the average individual mass was divided into several intervals of 10 g each, and the total biomass for each interval was computed. Then, the natural logarithm of the ratio of the average individual body mass to the interval width was used as the x-axis, while the natural logarithm of the total biomass for each interval was used as the y-axis. The standardized biomass spectrum was obtained through linear regression of the values of Gi (Magnussen, 2002). The calculation formula (Equation 2) is as follows:
where ni represents the catch quantity of the i-th interval, t stands for the interval, and Ti denotes the upper limit value of the i-th interval.
When the slope of the spectrum line is -1, it indicates a stable state of the biological community, meaning that biomass is evenly distributed with increasing body mass. When the slope is greater than -1, biomass increases with increasing body mass, and when the slope is less than -1, biomass decreases with increasing body mass (Macpherson et al., 2002). The catch quantity of the group with the minimum average individual mass often affects the slope of the standardized biomass spectrum. The smaller the catch quantity of the minimum individual mass, the flatter the regression line will be and vice versa.
The ABC curve method involves comparing biomass dominance curves with abundance dominance curves on the same axis to analyze the characteristics of communities under different disturbance conditions (Wu et al., 2020). Based on the theories of r-selection and k -selection in biological evolution, ABC curves reflect the response of communities under different disturbance conditions (Dang et al., 2021). Under undisturbed conditions, the community is dominated by k-selected species (large-bodied species with slow growth and late maturation), leading to a biomass dominance curve higher than the abundance dominance curve. Under moderate disturbance, the number of k-selected species gradually decreases, while the number of r-selected species (small-bodied species with fast growth and early maturation) increases. This results in the biomass and abundance dominance curves intersecting. Under severe disturbance, the community is dominated by r-selected species, leading to an abundance dominance curve higher than the biomass dominance curve (Yemane et al., 2005). In this study, the ABC curve uses the total species data from the survey sites as samples. The W value represents the relative relationship between biomass and abundance. When the biomass dominance curve is above the abundance dominance curve, W is positive; otherwise, W is negative. The ABC curve was plotted using Primer 6.0, and the calculation formula (Equation 3) is as follows:
where Ai and Bi represent the cumulative percentages of abundance and biomass, respectively, corresponding to species number i in the ABC curve, while S denotes the total number of species.
A selection of five environmental factors—surface water temperature, bottom water temperature, salinity, water depth, and pH—were chosen as explanatory variables. Standardized abundance was utilized as the response variable for redundancy analysis (RDA) sorting. Monte Carlo permutation tests were conducted using CANOCO 5 software to identify environmental variables significantly impacting the fish community. The resulting ordination plots were depicted using a species–environmental factor biplot. In the RDA ordination plot, environmental factors are represented by line segments with arrows. The length of these lines indicates the strength of the relationship between the distribution of fish communities and species and the corresponding environmental factor, with longer lines indicating stronger correlations and vice versa. The cosine of the angle between the species and environmental factor arrows reflects their correlation, where a smaller angle signifies a stronger correlation (Braak, 1989). Before conducting RDA analysis, trend correspondence analysis diagnostics were performed. If the maximum gradient length in the results is less than 3, RDA analysis is chosen. If it exceeds 4, canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) is chosen. If it falls between 3 and 4, both analysis methods are acceptable. In this study, trend correspondence analysis was applied to fish biomass data from two spring seasons. The results indicated that the maximum values of the first four axes were all less than 3, thus RDA analysis was selected.
In spring 2020, a total of 26 fish species were collected, belonging to 1 class, 5 orders, 13 families, and 19 genera, all of the class Actinopterygii. Among them, there were 12 species of Clupeiformes, accounting for 46.15% of the total species. In spring 2023, a total of 62 fish species were collected, belonging to 2 classes, 12 orders, 36 families, and 48 genera. Except for Raja hollandi, Dasyatis akajei, Dasyatis bennetti, and Dasyatis zugei, that belong to the class Chondrichthyes, they all belonged to the class Actinopterygii. Among them, there were 34 species of Perciformes, accounting for 54.84% of the total species (Table 1).
In both spring of 2020 and 2023, eight of the same fish species were captured (Figure 2). The ANOSIM analysis results indicate a significant difference in species com-position between spring 2020 and 2023 (P=0.001) (Figure 2).
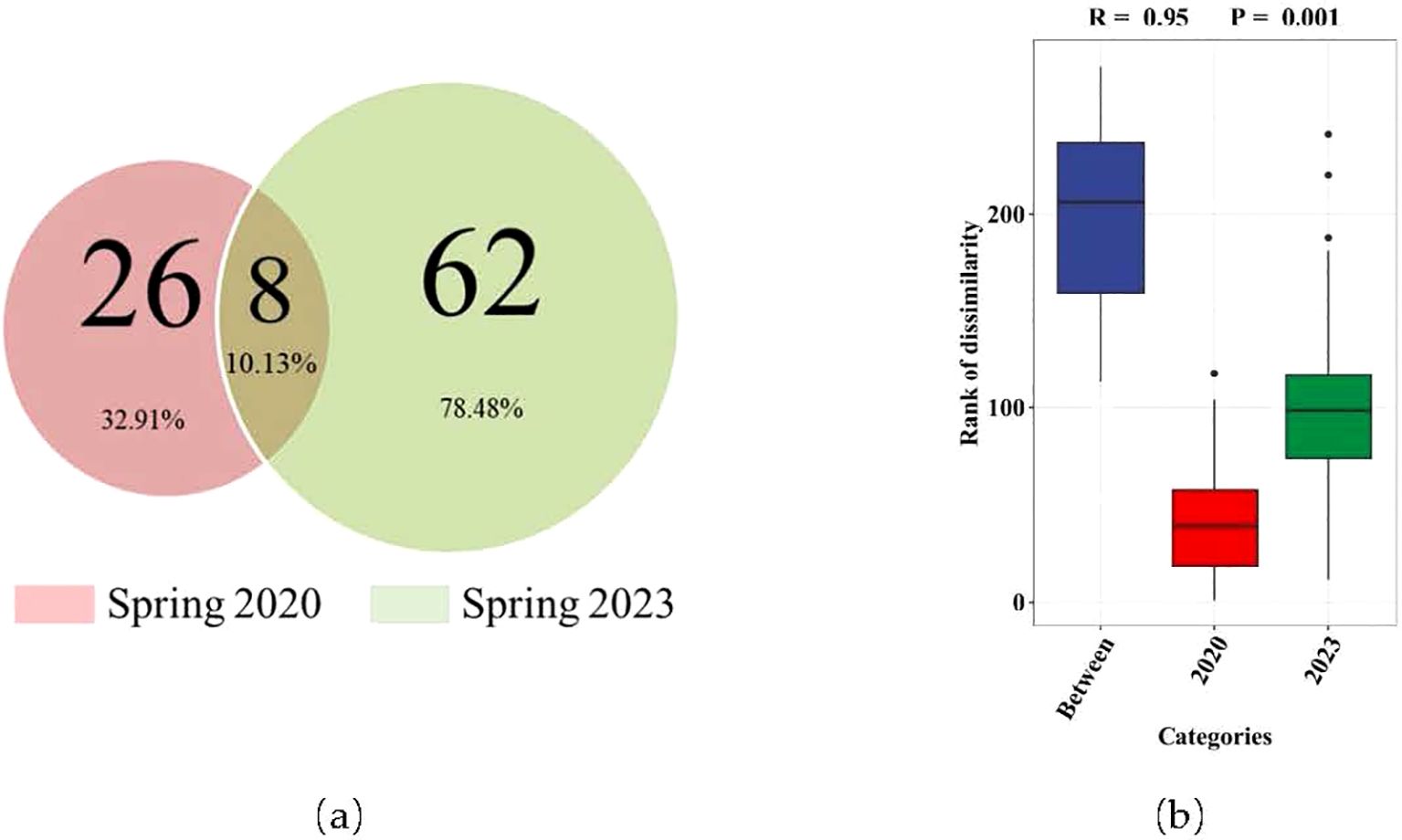
Figure 2. The diversity of fish species (A) and differences in composition between spring 2020 and 2023 (B).
In spring 2020, 23 species of warm water fish, 3 species of warm-temperate water fish, and no cold water fish were caught in the study area. In terms of vertical distribution, there were 17 species in the upper-middle layer, 8 species in the near-bottom layer, and 1 species in the bottom layer. Regarding feeding habits, there were 15 herbivorous species, 8 carnivorous species, and 3 omnivorous species (Table 2). In spring 2023, 53 species of warm water fish, 9 species of warm-temperate water fish, and no cold water fish were caught. The vertical distribution consisted of 4 species in the up-per-middle layer, 24 species in the near-bottom layer, and 34 species in the bottom layer. In terms of feeding habits, there were 8 herbivorous species, 23 carnivorous species, and 31 omnivorous species.
In terms of temperature preference, both in 2020 and 2023, warm water species dominated, accounting for 88.46% and 85.48% of the total fish species, respectively. Regarding vertical distribution, in 2020, the majority of fish species were found in the upper-middle and near-bottom layers, while in 2023, they were mainly distributed in the near-bottom and bottom layers. In terms of feeding habits, herbivorous species dominated in 2020, whereas omnivorous and carnivorous species were predominant in 2023.
Based on the cluster analysis of fish biomass and survey sites during the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023, the fish communities were clustered into three groups at a similarity level of 54% in 2020. Group A comprised one survey site, Group B comprised two survey sites, and Group C comprised nine survey sites. The non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) results for 2020 showed a stress value of 0.16, indicating a suitable fit (Figure 3A). Similarly, in 2023, the fish communities were clustered into three groups at a similarity level of 37%, with Group A comprising one survey site, Group B comprising two survey sites, and Group C comprising nine survey sites. The stress value for 2023 was 0.12, also indicating a suitable fit (Figure 3B).
Based on the SIMPER results (Table 3), in the spring of 2020, the average similarity percentage within Group B was 58.63%, there were eight typical species, such as Thrissa kammalensis, which contributed 94.03% to the average similarity; within Group C, the average similarity percentage was 62.68%, there were five typical species, such as T. kammalensis, which contributed 89.13% to the average similarity. The average dissimilarity percentage between Groups A and B, A and C, and B and C were 57.33%, 50.31% and 48.27%, respectively. There were five main discriminating species, such as Pampus argenteus, which contributed 70.07%, 65.71% and 55.32% to the dissimilarity between groups, respectively.
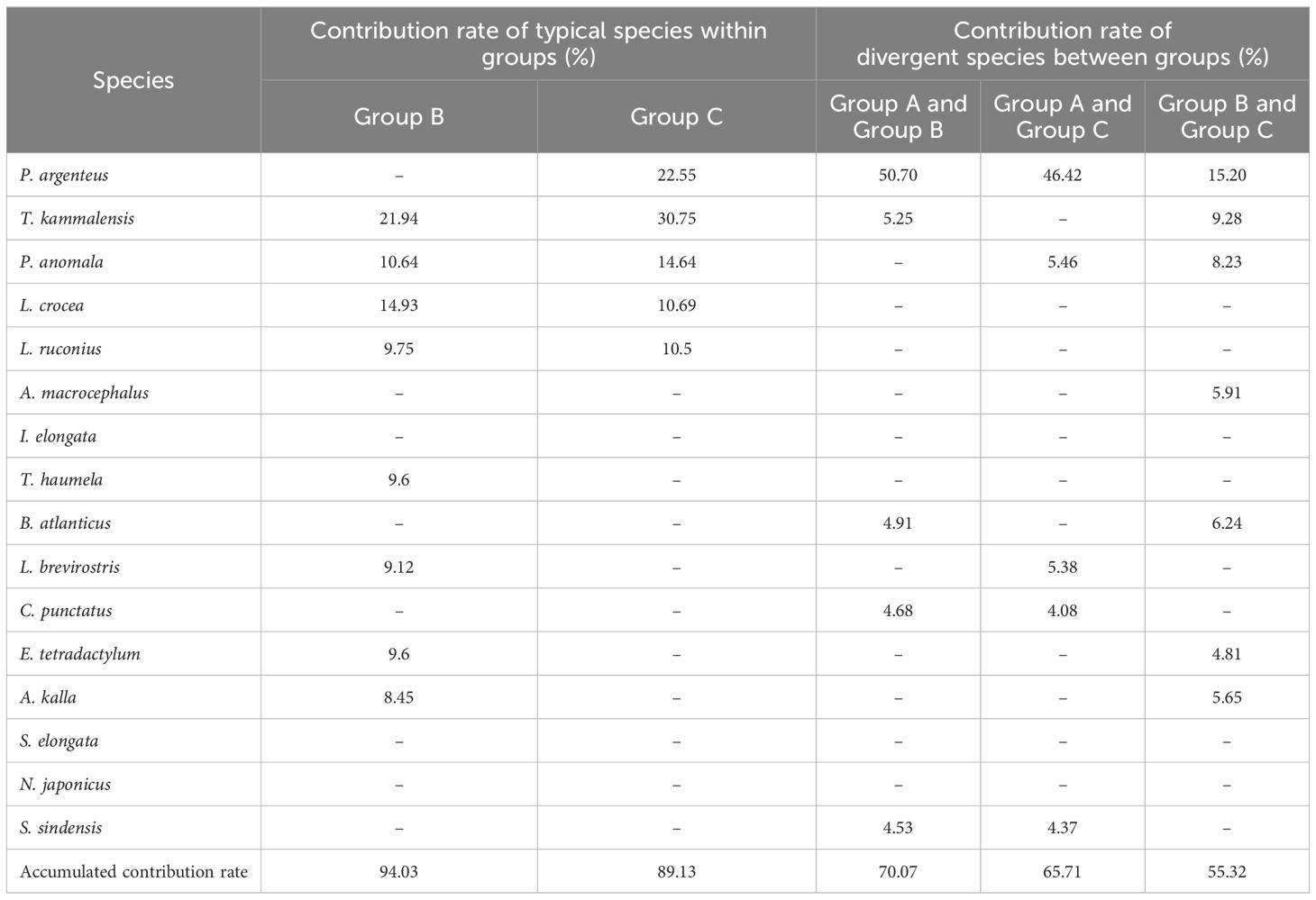
Table 3. Species contributing above 4% of accumulative similarity within a group and dissimilarity be-tween groups in spring 2020.
Based on the SIMPER results (Table 4), in the spring of 2023, the average similarity percentage within Group B was 44.93%, there were five typical species, such as Drepane punctata, which contributed 93.65% to the average similarity; within Group C, the average similarity percentage was 42.33%, there were five typical species, such as D. zugei, which contributed 78.37% to the average similarity. The average dissimilarity percentage between Groups A and B, A and C, and B and C were 90.01%, 84.14% and 64.00%, respectively. There were twelve main discriminating species, such as D. zugei, which contributed 66.25%, 55.32% and 51.99% to the dissimilarity between groups, respectively.
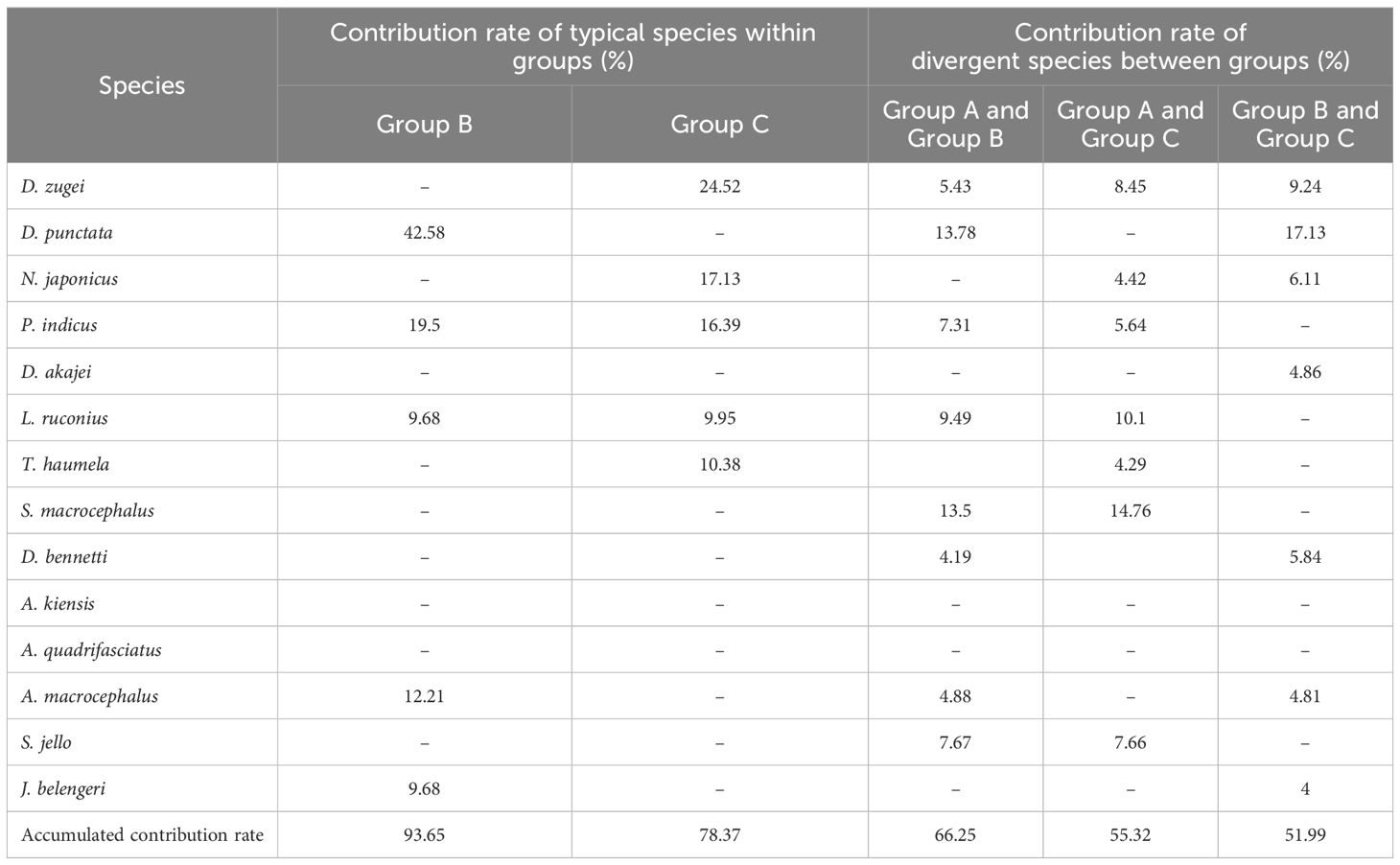
Table 4. Species contributing above 4% of accumulative similarity within a group and dissimilarity be-tween groups in spring 2023.
Based on the index of relative importance, in the spring of 2020, 4 dominant species, 5 important species, 11 common species, and 6 rare species were caught during the survey (Table 5). Among them, the highest index of relative importance was observed for T. kammalensis (IRI=5657.9), followed by P. argenteus (IRI=5587.5) (Figure 4). In the spring of 2023, 5 dominant species, 7 important species, 14 common species, and 36 rare species were caught during the survey. Leiognathus ruconius had the highest index of relative importance (IRI=5866.1), followed by Trichiurus haumela (IRI=2187.8).
Figure 5 shows the regression analysis of the standardized biomass spectrum. The linear regression equation for the standardized biomass spectrum in spring 2020 is y=-3.512x+32.554(R2 = 0.4125); the linear regression equation for the standardized bio-mass spectrum in spring 2023 is y=-1.1616x+22.107(R2 = 0.2446).
Figure 6 illustrates the variation in the biomass-to-average-individual-mass ratio. In spring 2020, fish species with an average individual mass of less than 10 g accounted for 5.04% of the total biomass, while those with masses between 10 g and 20 g ac-counted for 24.96%. Fish with masses between 20 g and 50 g contributed 11.29% to the total biomass, whereas those between 50 g and 80 g represented 56.86%, with P. argenteus contributing a significant proportion of 46.58%. Fish with masses above 80 g contributed only 1.87% to the total biomass. In spring 2023, fish species with an average individual mass of less than 10 g accounted for 14.79% of the total biomass, showing an increase compared with 2020. Those with masses between 10 g and 20 g contributed 4.26%, representing a decrease from 2020. Species with masses between 20 g and 50 g contributed 1.09%, also showing a decrease from 2020. Fish with masses be-tween 50 g and 80 g contributed 23.86% to the total biomass, indicating a significant decrease from 2020. Fish with masses above 80 g contributed 56.00% to the total bio-mass, showing a substantial increase from 2020.
In the spring of 2020, the numerical dominance curve and the biomass dominance curve of the fish community intersected, with a W statistic value of 0.025 (Figure 7), indicating a moderate level of disturbance. The top five species by biomass percentage were P. argenteus, T. kammalensis, Psenopsis anomala, Larimichthys crocea, and L. ruconius, while the top five species by numerical percentage were T. kammalensis, L. ruconius, P. argenteus, Bregmaceros atlanticus, and L. crocea. Among these six species, only P. argenteus and P. anomala had biomass percentages higher than their numerical percentages, with P. anomala having a biomass percentage 32.21% higher than its numerical percentage.
In the spring of 2023, the numerical dominance curve of the fish community was above the biomass dominance curve, with a W statistic value of -0.145 (Figure 7), indicating a state of severe disturbance. The top five species by biomass percentage were D. zugei, D. punctata, Nemipteras japonicus, Platycephalus indicus, and D. akajei, while the top five species by numerical percentage were L. ruconius, T. haumela, Apogon kiensis, Apogon quadrifasciatus, and P. indicus. Among these nine species, L. ruconius, T. haumela, A. kiensis, and A. quadrifasciatus had numerical percentages higher than their biomass percentages, with L. ruconius having a numerical percentage 44.51% higher than its biomass percentage. Overall, the stability of the fish community in the Wailingding marine ranching area in Zhuhai has not been without disturbance, with an increasing proportion of small-bodied fish species dominating the community structure.
The biomass matrices of fish communities during the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023 were subjected to detrended correspondence analysis (DCA). The results indicated that the maximum gradient lengths of both survey periods were less than 3, warranting the adoption of redundancy analysis (RDA) in conjunction with Monte Carlo permutation tests. This analytical approach aimed to investigate the relationship between the fish community structure and environmental factors, thereby identifying the environmental variables that significantly influence the community structure.
Based on the results of RDA (Figure 8), the five environmental factors explained 44.7% of the variation in fish community composition in the study area during the spring of 2020. The first and second axes of ordination contributed 43.45% and 0.76%, respectively, to the explained species–environment relationships. However, the five environmental factors did not significantly influence the structure of and variation in the fish communities (P > 0.05). Notably, surface water temperature (SST), bottom water temperature (SDT), and salinity (sal.) exerted considerable influence on the distribution of fish communities, collectively explaining 44% of the species–environment relationships.
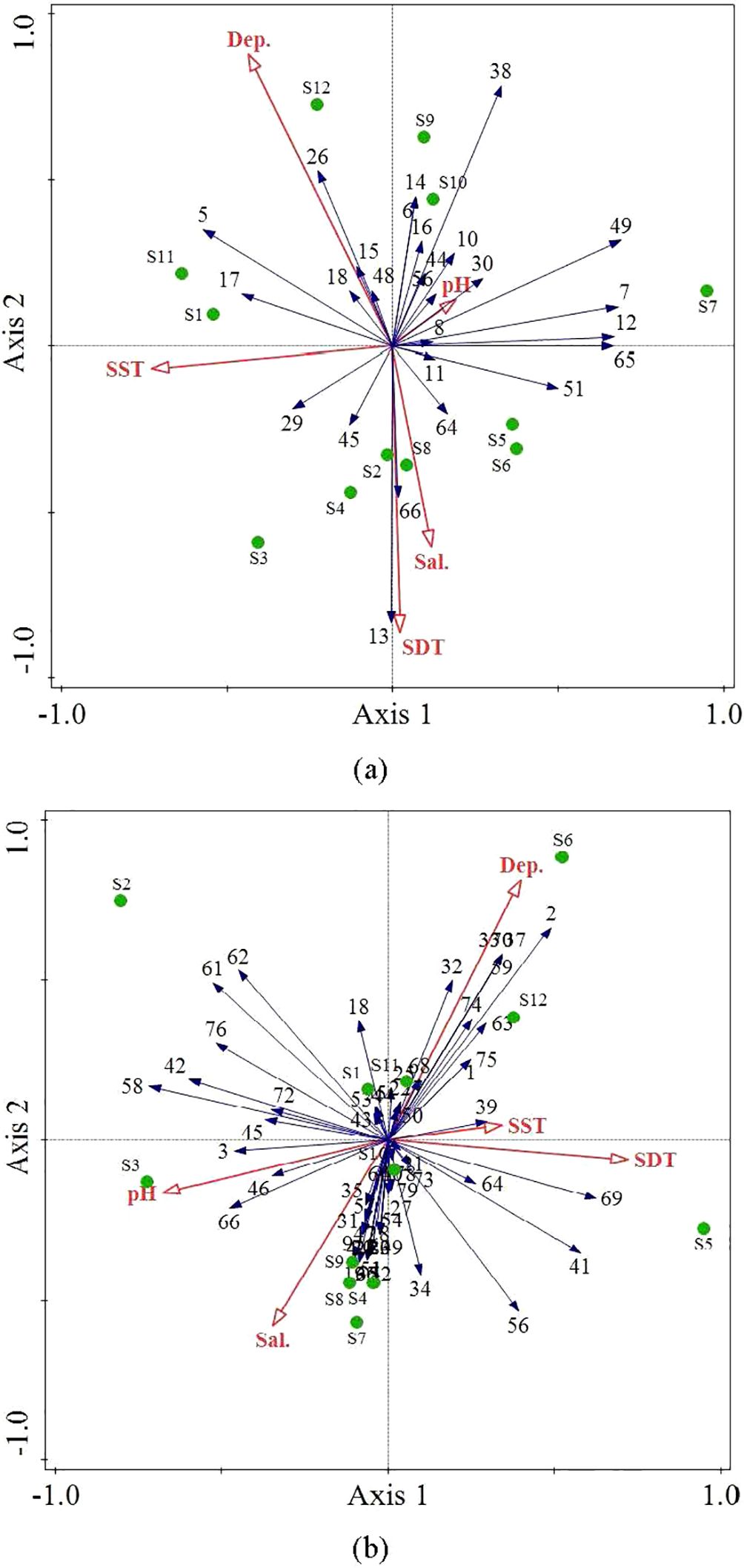
Figure 8. Redundancy analysis of fish species and environmental factors in the Wailingding marine ranching area in Zhuhai in the spring of 2020 (A) and 2023 (B).
In spring 2023, the five environmental factors collectively explained 44.5% of the relationship between fish and environmental variables in the study area. The first and second axes of ordination contributed 18.61% and 12.61%, respectively, to the explained species–environment relationships. However, these five environmental factors did not significantly influence the structure of and variation in fish communities (P > 0.05). Notably, the depth (depth), surface water temperature (SST), and bottom water temperature (SDT) had a considerable impact on the distribution of fish communities, collectively explaining 31.4% of the species–environment relationships.
The coastal waters near Zhuhai represent an area of brackish water influenced by the combined effects of the Pearl River runoff and the South China Sea’s shelf water (Song et al., 2023). The strong interaction between estuarine tidal currents and river runoff typically exerts an influence on the behavior and migration of fish species, making it an important habitat for a variety of euryhaline and eurythermal fish species for habitation, growth, and reproduction (Dai et al., 2019). This study found that in the spring seasons of both 2020 and 2023, warm water fish species predominated, followed by warm-temperate-water species, with no significant variation observed in the proportions of fish species according to their thermal preferences. The prevalence of warm water species in the coastal waters of Zhuhai is attributed to the influence of coastal currents and the South China Sea’s warm currents (Huang et al., 2023). Additionally, due to the subtropical marine characteristics of the Pearl River Estuary’s coastal waters, warm water species have a competitive advantage in this region (Su et al., 2020), which is consistent with previous investigations (Li et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2022). However, the number of species surveyed in the spring of 2020 (26 species) was significantly lower, accounting for only 41.94% of the species surveyed in the spring of 2023 (62 species). This phenomenon is primarily associated with the establishment of marine ranching. The Wailingding marine ranching area in Zhuhai deployed artificial reefs in August 2021, July 2022, and December 2022, which significantly contributed to the recovery of fishery resources within the effective impact range (Feng et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2022a). The establishment of marine ranching based on artificial reefs and focused on resource restoration plays a vital role in the conservation and enhancement of fishery resources (Wang et al., 2019).
According to the clustering results, there have been significant interannual variations in the composition of fish communities. In comparison to 2020, the main dominant typical species in the 2023 community had transitioned from P. argenteus to D. zugei; the species D. punctata and Sparus macrocephalus had significantly increased their contribution to inter-group dissimilarity, replacing P. argenteus as the primary discriminant species among the fish community groups. This shift not only indicates temporal variations in the composition of fish communities in the Wailingding marine ranching area but also reflects a succession phenomenon in the fish community structure. This succession involves a decline in the functional roles of traditional fish species such as P. argenteus, T. kammalensis, P. anomala, and L. crocea within the community, while species such as D. punctata, N. japonicus, and P. indicus are experiencing an increase in their community status; L. ruconius, with its increasingly high catch numbers, has gradually replaced T. kammalensis in the community and become an important bait species in the ecosystem (Yan et al., 2011). The dominant position of L. ruconius in the community structure changes has gradually become apparent. Jiang (Jiang et al., 2022) used analysis methods such as eDNA metabarcoding and bottom trawling surveys to reveal that L. ruconius is one of the dominant species in the vicinity of the Pearl River Estuary, maintaining nutritional interactions with numerous other fish species. Overall, the fish community structure in the Wailingding marine ranching area appears to be dynamic, primarily dominated by generalist and small-to-medium-sized fish species. The succession of species reflects its adaptation to external disturbances and internal interspecies interactions. However, the significant increase in the abundance of forage fish in the water column indicates a weakening of top-down control in the food web, posing a potential threat to the stability of the community structure, and fishing strategies need to be adjusted to protect species that make significant contributions to ecosystem function and fishery yield. To protect the ecological balance and support sustainable fisheries, we propose implementing size-selective fishing regulations that target larger, predatory fish species while conserving smaller, reef-associated and demersal species. This strategy aims to reduce top-down pressure on smaller fish populations, allowing their numbers to recover and maintain the overall health of the ecosystem.
Since 1986, significant fluctuations in dominant species have been observed in the nearshore waters of the Pearl River Estuary, as depicted in Table 6. The dominant fish species have transitioned from economically valuable species such as Coilia grayii, Arius sinensis, N. japonicus, and Collichthys lucidus to economically less valuable species such as Leiognathus brevirostris, Odontamblyopus rubicundus, L. ruconius, T. kammalensis, and D. zugei. Notably, T. kammalensis and L. ruconius have become prominent in the community structure. The total power of fishing vessels in the northeastern part of the South China Sea increased from 74,700 kW in 1965 to 831,900 kW in 2017, a 10.14-fold increase (Yuan et al., 2022b). This shift in dominant species reflects the dynamic adaptability of fish communities in response to fishing pressure and environmental changes. Studies by Jin et al. and others have found that, under a high-intensity fishing pressure, dominant populations of larger individuals with higher trophic levels in fish communities in Laizhou Bay are gradually being replaced by smaller individuals with lower trophic levels (Jin and Deng, 2000). L. ruconius occupies a very dominant position in the community. Zhen et al. (2014) believes that species with r-selection traits, such as early maturity, rapid growth, and strong plasticity in feeding habits, can gradually become dominant under high-intensity fishing pressure.
This study also found significant fluctuations in the IRI values of the dominant species between years. The IRI value of the dominant fish species, P. anomala, decreased significantly from 1249 in 2020 to 39.1 in 2023, while the IRI value of L. ruconius increased significantly (2591.6 → 5866.1), becoming the main dominant species. This indirectly indicates a significant increase in the proportion of small bait fish in the waters near Waillingding area. The reasons for this trend may include the lower sensitivity of small fish to fishing and other disturbances, as well as a reduction in higher-trophic-level organisms in the area, leading to reduced predation pressure on small individuals (Solé and Montoya, 2001). Consequently, L. ruconius, a small bait fish, is able to gradually emerge as a dominant species in the community structure. Additionally, Yu et al. (2016) found evidence of a feeding relationship between P. argenteus and L. ruconius, suggesting a competitive interaction between these two species.
The biomass spectrum reveals the biomass distribution patterns of all members of an ecosystem (Russo et al., 2024). Our research findings indicate that, in the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023, the trend and degree of change in fish biomass with average body mass are roughly similar. However, the slope of the spectra lines is less than -1 in both cases, indicating that in recent years, the biomass of fish communities in this area has decreased, with an increase in average body mass. Research has shown that fishing is an important factor influencing the slope of these spectra lines (Zwanenburg, 2000). Fishing mortality leads to a decrease in the slope of the fish biomass spectrum, indicating a reduction in the abundance of large-bodied fish (Blanchard et al., 2009). From the biomass spectrum distribution (Figure 7), it can be observed that the proportion of biomass of small fish below 10 g increased significantly from 5.04% in 2020 to 14.79% in 2023, primarily due to the increased biomass of L. ruconius. The average individual mass of medium-sized fish, represented by P. anomala, decreased compared with 2020, resulting in a decrease in this species’ proportion in the total biomass from 8.84% in 2020 to 0.18%. This indicates a decrease in the number of large individuals of P. anomala and an increase in small individuals, showing a clear trend towards miniaturization. The biomass proportion of large fish species such as S. macrocephalus, D. punctata, Epinephelus akaara, Epinephelus awoara, and N. japonicus has increased compared with 2020. The increase in biomass is primarily attributed to reef-associated and demersal fish species. However, it is observed that the resource enhancement effect is currently limited to reef-associated and demersal fish species. These specific groups may be attributed to the protective and conservation effects of artificial reefs in the marine ranching area of Wailingding Island. The optimization of fish community structure through artificial reef deployment is a long-term process (Chen et al., 2013), and it will take longer to fully demonstrate the overall conservation effect on marine fishery resources in the area.
The ABC curve of the fish communities can reflect the relative abundance of medium-to-large-sized fish and small-sized fish, as well as the variation in size composition within the community. The dominance of certain species within the community determines the position of the biomass dominance curve and the numerical dominance curve to some extent (Li et al., 2017). From the ABC curve results of this study, it can be observed that, in the spring of 2020, the biomass dominance curve and the numerical dominance curve of fish communities intersected. Only P. argenteus and T. kammalensis dominated the biomass, with biomass proportions as high as 46.51% and 22.43%, respectively. Meanwhile, T. kammalensis and L. ruconius ranked first and second in numerical dominance, accounting for 34.15% and 22.47% of the total, respectively. Although the community is in a state of moderate disturbance, it is already approaching a state of severe disturbance. In the spring of 2023, the numerical dominance curve was completely above the biomass dominance curve, with the highest biomass proportion being 17.94% for D. zugei, while L. ruconius exhibited a remarkably high numerical dominance of 51.34%. The predominance of numbers of small-sized forage fish indicates a state of severe disturbance within the community. The increasing dominance of small-sized forage fish species, represented by L. ruconius, in the community, coupled with the declining resource level of P. argenteus—which was previously dominant in the biomass curve—can be attributed to several factors. On the one hand, the dominant fish species, exemplified by L. ruconius, have exhibited adaptive changes under the pressure of overfishing. These adaptations include an early maturation age, a shortened maturation period, and a trend towards smaller sizes. This shift in size and dietary habits has been corroborated by previous studies (Su et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2023). On the other hand, the reduction in mid-to-upper-trophic-level predators has also provided favorable conditions for the development of small-sized fish species (Zhang et al., 2021). This further confirms the declining trend of predator resources in the fish community structure of the Zhuhai Outer Wailingding Sea, leading to a decrease in trophic cascade effects and an overall decline in community stability.
Through the analysis of changes between years, although a conservation effect of artificial reef construction on fishery resources is gradually being achieved, the fish community in the Wailingding marine ranching area in Zhuhai currently lacks spatial continuity in terms of cluster sites and species composition. Therefore, the stability of the spatial pattern of fish communities in this area is low, posing significant challenges to the sustainable development of fishery resources in the region. This is especially critical given the multiple pressures of global climate change, environmental pollution, and human fishing activities. Methods for maintaining the stability of the fishery community structure and accelerating the recovery and growth of fishery resources in this area deserve attention from fishery researchers and managers. However, short-term survey results may have certain biases, and the data obtained from this survey may not fully reflect the mechanisms of change in the biological community structure of this marine area. Therefore, regular and standardized monitoring and surveys are particularly important.
There is a close relationship between fish community and environmental factors, and changes in habitat conditions can lead to heterogenization of community structure (Proto et al., 2018). In this study, the main physicochemical factors affecting the distribution of fish communities in the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023 were surface water temperature, bottom water temperature, water depth, and salinity, with surface water temperature having a particularly significant influence. This is consistent with the view that water temperature is the most important hydrological factor controlling fish growth and resource density (Gibson, 1994). The surface water temperature ranged from 20.2°C to 23.5°C, and the bottom water temperature ranged from 20.3°C to 23.0°C during the two surveys in the spring seasons. These temperatures fall within the suitable range for warm water fish species to survive (Fang et al., 2000). The results also indicate that warm water species dominate the composition of the community, with over 85% of the fish species being warm water species in both the spring seasons of 2020 and 2023, further confirming the influence of water temperature on fish distribution.
Water depth and salinity are also critical factors influencing fish distribution, as confirmed by multiple studies. Water depth can indirectly affect fish distribution by influencing the distribution of prey organisms, dissolved oxygen levels, and light availability (Wang et al., 2010; Pinault et al., 2014). Areas with high chlorophyll-a concentrations tend to have correspondingly high numbers of phytoplankton. Phytoplankton serve as primary producers and prey for zooplankton and other organisms, thereby providing abundant food for consumers that feed on planktonic organisms (Feng et al., 2024). Tang et al. (2022) conducted research on the Wan Shan Archipelago in the Pearl River Estuary, where Wailingding Island is located, and demonstrated a close correlation between the distribution of pelagic organisms and phytoplankton communities. Hu et al. (2018) found that the distribution of most fish species is positively correlated with water depth, a feature that can also be observed in the ordination diagram of this study (Figures 3, 4). The surveyed area in this study is located in a brackish water convergence zone with a wide range of salinity, providing a favorable habitat for fish species of different ecological types. Tian et al. (2023) investigated the distribution characteristics of the eggs of Stolephorus commersonnii in the Pearl River Estuary. They classified the Pearl River Estuary into three types (river water, brackish water, and high-salinity water) using the K-means dynamic clustering method based on the bottom temperature and salinity of the station table, and their results indicated a close relationship between the quantity and distribution of fish eggs and water masses.
Additionally, the spatial heterogeneity of habitat environments also has significant implications for the stability of community structure and ecological functionality. Complex and varied habitat environments can provide a richer variety and abundance of fish species. In addition to the unique topography of islands and reefs, the establishment of marine ranching and associated infrastructure has altered the topography of surrounding areas, increasing the heterogeneity of habitats for nekton and thereby influencing the structure of biological communities (Han et al., 2019). In this study, the surveyed habitats included island reefs, artificial reefs, and seaweed beds. On the one hand, the presence of rocky reefs and artificial reefs increased habitat complexity, attracting reef-associated fish species and crustaceans. On the other hand, seaweed beds provided excellent food sources and spawning environments, playing a crucial role as breeding habitats for many fish species. Future research should employ long-term monitoring to assess the impact of artificial reefs on fishery resources and determine their long-term conservation effectiveness. This requires longer-term monitoring and a broader sampling approach to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms underlying changes in fish community structure.
The fish community structure in the spring of 2023 in the Wailingding marine ranching area in Zhuhai exhibited certain changes compared with 2020. These changes are primarily manifested in the following aspects: (1) a significant change in species composition over the three-year period, with an increase in species richness observed in 2023; (2) the dominant species gradually shifted towards smaller bait fish species, represented by L. ruconius, leading to a reduction in the trophic levels within the food web; (3) initial indication of increasing disturbance levels affecting the fish community, further long-term monitoring is necessary to confirm these preliminary findings and to develop effective conservation strategies. (4) there was an increase in the biomass of reef-associated and demersal fish species, these specific groups may be attributed to the protective and conservation effects of artificial reefs.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
HY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology. PC: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS, China (2023TD06、2021SD02) and Guangdong Key Areas R&D Program Projects (2020B1111030002).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Augspurger J. M., Warburton M., Closs G. P. (2017). Life-history plasticity in amphidromous and catadromous fishes: a continuum of strategies. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 27, 177–192. doi: 10.1007/s11160-016-9463-9
Blanchard J. L., Jennings S., Law R., Castle M. D., McCloghrie P., Rochet M. J., et al. (2009). How does abundance scale with body size in coupled size-structured food webs? J. Anim. Ecol. 78, 270–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01466.x
Braak C. J. F. T. (1989). Canoco—an extension of Decorana to analyze species-environment relationships. Hydrobiologia 184, 169–170. doi: 10.1007/BF02392953
Cheikh S., Cungen Y., Ousmane N., Hamet D., Ngor N. (2023). Community structure of fish in Nanji islands national nature reserve and its relationship with environmental variation. J. Water Res. Protect. 15, 377–392. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2023.158022
Chen D. G., Zhang M. Z. (2015). Marine Fishes in Chinese Sea (Qingdao, China: China Ocean University Press).
Chen H. J., Feng C., Yang P. R., Xu J. T., Zhang Q. H., Xu J. H., et al. (2023). Current situation and prospect of the research on the culture of thamnaconus modestus. J. Jiangsu Ocean University: Natural Sci. Edit. 2, 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-8248.2023.02.004
Chen P. M., Yuan H. R., Jia X. P., Qin C., Cai W. G., Yu J., et al. (2013). Changes in fishery resources of Yangmeikeng artificial reef area in Daya Bay. South China Fish. Sci. 9, 100–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2013.05.016
Cong T. T., Tong C. F., Zhao C. J., Chen Z. T., He Z. F., Liu M. Y. (2021). Community composition and distribution characteristics of the fish assemblages in the rivers of Chongming Island in summer. J. Acta Ecol. Sinica. 41, 2067–2076. doi: 10.5846/stxb202002240321
Dai X. J., Yang Z. J., Tian S. Q., Gao C. X., Dai L. B. (2019). Taxonomic diversity of fish species in the off southern Zhejiang, East China Sea. J. Haiyang Xuebao 41, 43–51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253–4193.2019.08.005
Dang Y. C., Dai X. J., Wu F. (2021). Seasonal variations in fish community structure in the Dianshan lake. J. Fish. Sci. 40, 361–368. doi: 10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.19290
Fang S. M., Yang S. Y., Zhang C. M. (2000). Selective water temperature and its seasonal variation for main species fished by light-seine from the southern Taiwan Straits. J. J. Fish. China 24, 370–375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0615.2000.04.015
Fang D. D., Yang H. L., Zhang H., Wu J. M., Wei Q. W. (2023). Interannual variation of fish community structure in Shishou section of Yangtze river. J. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 32, 2338–2347. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj202311009
Feng X., Dai X. J., Fan J. T., Chen P. M. (2023). Seasonal variation of fishery resources in Wailingding marine ranching and adjacent waters. J. South China Fish. Sci. 19, 32–38. doi: 10.12131/20220308
Feng X., Dai X. J., Yuan H. R., Cheng Z. Z., Chen P. M. (2024). Relationship between community structure of nekton and environmental factors in Wailingding marine ranching area. J. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 33, 186–201. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20230304115
Feng X., Fan J. T., Sun X., Hong J. Z., Chen P. M. (2021). The stock enhancement effect evaluation of artificial reef in Wailingding, Zhuhai. J. J. South. Agric. 52, 3228–3236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2021.12.005
Gibson R. N. (1994). Impact of habitat quality and quantity on the recruitment of juvenile flatfishes. J. Netherlands J. Sea Res. 32, 191–206. doi: 10.1007/s10641-004-0090-2
Guan Y., Song P. Q., Wang L. M., Zhang H. S., Li H., Li Y., et al. (2023). Differences in community structure of nekton in the coastal waters of Dongshan bay between generations. J. Period. Ocean Univ. China. 53, 31–42. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20210402
Guo P. J., Jiang X. Q., Yu. C. G., Deng X. Y., Zhang P., Xu Y. J. (2020). Analysis of the fish community structure in the spring and autumn of the Zhoushan coastal fishing grounds. J. Prog. Fish. Sci. 41, 1–11. doi: 10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20190311001
Han X. D., Zhang S. Y., Wang Z. H., Wang K., Lin J., Deng M. X., et al. (2019). Fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the Ma’an Archipelago and its eastern waters. J. J. Fish. China 43, 1483–1496. doi: 10.11964/jfc.20180211197
Hong Z. Z., Zhang C., Tian P. Y. J., Ye Z. J., Liu Q. (2020). Interannual variation in biological characteristics of sand lance (Am-modytes personatus) in the Yellow Sea. J. J. Fish. Sci. China. 27, 701–708. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2020.19261
Hu Y. J., Liang J., Xu H. X., Fang P. E., Guo A., Zhao R., et al. (2022). Construction status, problems and future prospects of marine ranching in ecological conservation type in Zhejiang province. J. J. Zhejiang Ocean University: Natural Sci. 5, 373–381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2022.05.001
Hu C. L., Zhang H. L., Zhang Y. Z., Pan G. L., Xu K. D., Bi Y. X., et al. (2018). Fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the Nature Reserve of Trichiurus japonicus. J. J. Fish. China 42, 694–703. doi: 10.11964/jfc.20170410787
Huang H. L., Feng C., Li L. Z., Rao X., Chen S., Yang J. L. (2022). The development status and prospect of contemporary marine fisheries. J. J. Fish. Sci. China. 29, 938–949. doi: 10.12264/JFSC2021-0386
Huang C. H., Liu X. J., Guo H. Q., Hou P., Chen W. (2023). Analysis of seasonal variation characteristics of circulation in pearl river estuary. J. Pearl River 44, 48–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2023.07.007
Jiang P. W., Li M., Zhang S., Chen Z. Z., Xu S. N. (2022). Investigating the fish diversity in Pearl River estuary based on environmental DNA matebarcoding and bottom trawling. J. Acta Hydrobiol. Sci. 46, 1701–1711. doi: 10.7541/2022.2021.0265
Jin X. S., Deng J. Y. (2000). Variations in community structure of fishery resources and biodiversity in the L aizhou Bay, Shandong. J. Biodivers. Sci. 8, 65–72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2000.01.009
Li Y. Z., Chen G. B., Sun D. R. (2000). Analysis of the composition of fishes in the Pearl River estuarine waters. J. J. Fish. China 24, 312–317. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0615.2000.04.004
Li B. X., Li A. X., Dong J. Y., Lv S. L., Wang X. F. (2023). Intertidal macrozoobenthic community structure and its disturbed state in Zhanjiang Bay. J. South China Fish. Sci. 19, 12–20. doi: 10.12131/20220199
Li Z. Y., Wu Q., Shan X. J., Wang X. L., Jin X. S. (2017). Interannual variations in fish community structure in the Bohai Sea J. J. Fish. Sci. China 24, 403–413. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2017.16154
Li K. Z., Yin J. Q., Huang L. M., Huang Z. R., Lin Q., Xiong L. L. (2012). Seasonal variations of bottom nekton in the Lingding Bay of Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Ecol. Sci. 31, 1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2012.01.001
Li H. T., Zou K. S., Zhang S., Cao Y. T., Lu Z. C., Chen Z. Z., et al. (2022). Species composition of fishes in the Pearl River estuary based onenvironmental DNA metabarcoding. J. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 31, 1423–1433. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20210603476
Liu W. Y., Huang J. Q., Dai G. X., Liu G. Q., Lei X. T., Zhou Y. D., et al. (2023). RDA analysis between fish community structure and environmental factors in the Lingdingyang Estuary. J. Fish. Inf. Strat. 38, 32–41. doi: 10.13233/j.cnki.fishis.2023.01.005
Liu Q., Wang X. F., Lv S. L., Lin K., Zhang J. (2021). Analysis of nekton community structure and diversity in Zhanjiang harbour waters. J. J. Guangdong Ocean Univers. 41, 101–110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2021.02.014
Macpherson E., Gordoa A., Garcia-rubies A. (2002). Biomass size spectra in littoral fishes in protected and unprotected areas in the NW Mediterranean. J. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 55, 777–788. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2001.0939
Magnussen E. (2002). Demersal fish assemblages of Faroe Bank: species composition, distribution, biomass spectrum and diversity. J. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 238, 211–225. doi: 10.3354/meps238211
Mo W. J., He Y., Wang J. P., He Z. J., Yang Y. (2022). Distribution and habitat characteristics of fishes in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 28, 1622–1628. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2021.05048
Pinault M., Bissery C., Gassiole G., Magalon H., Quod J. P., Galzin R. (2014). Fish community structure in relation to environmental variation in coastal volcanic habitats. J. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 460, 62–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.06.005
Pinkas L., Oliphant M. S., Iverson L. K. (1971). Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. J. Fish Bull. 152, 1–105.
Proto T. J., Pinto-da-Rocha R., Da Rocha P. L. B., Andersen A. (2018). Regional distribution patterns can predict the local habitat specialization of arachnids in heterogeneous landscapes of the Atlantic Forest. J. Diversity Distrib. 24, 375–386. doi: 10.1111/ddi.12685
Russo L., Bellardini D., Steinberg D. K., Congestri R., Lomas M. W., Alelio D. (2024). Long-term oscillations in the normalized biomass-size spectrum reveal the impact of oligotrophication on zooplankton trophic structure in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. J. Mar. Environ. Res. 193, 106295. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106295
Solé R. V., Montoya M. (2001). Complexity and fragility in ecological networks. J. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 268, 2039–2045. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1767
Song X. Y., Lin Y. J., Zhang L. K., Xiang C. H., Huang Y. D., Zhen C. Y. (2023). Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso-and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. J. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 42, 136–148. doi: 10.11978/2022137
Su L., Chen Z. Z., Zhang K., Xu Y. W., Qiu Y. S. (2021). Establishment of quality status evaluation system of fishery resources in Beibu gulf based on bottom trawl survey data. J. Guangdong Ocean Uncivil. 1, 10–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2021.01.002
Su X. Y., Zhong Y., Li Y., Tan M. T., Huang Y. D., Liu S., et al. (2020). Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of phytoplankton in waters around typical islands in the Pearl River Estuary. J. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 39, 30–42. doi: 10.11978/2020008
Tang G. L., Liu Y., Wu P., Sun D. R., Xiao Y. Y., Wang T., et al. (2022). Community structure of fishery resources and its relationship to environmental factors in the Wanshan Islands Sea of the Pearl River Estuary in spring. J. Fish. Sci. China. 29, 1198–1209 doi: 10.12264/JFSC2021-0545
Tian F. G., He W., Huang B. B., Lou Q. S., Hu H. N., Deng W. (2023). Spatial distribution of eggs of Stolephorus commersonnii in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Chin. J. Ecol. 42, 694–701. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202303.018
Wang Y. F., Hu Q. W., Yu J., Chen P. M., Shu L. M. (2019). Effect assessment of fishery resources proliferation in Zhelin Bay marine ranching in eastern Guangdong. J. South China Fish. Sci. 15, 12–19. doi: 10.12131/20180143
Wang X. H., Qiu Y. S., Du F. Y., Lin Z. J., Sun D. R., Huang S. L. (2010). Fish community pattern and its relation to environmental factors in the Beibu Gulf. J. J. Fish. China 34, 1579–1586. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2010.06827
Wang T., Shi J., Yu Y. F., Zhao J. F., Xiao Y. Y., Liu Y., et al. (2023). Research progress and conservation suggestions of coral reef fishes in the Xisha Islands. J. Chin. J. Ecol. 42, 1755–1763. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202306.023
Wang Y., Zhao J., Gao C. X., Wang S. C., Ye S. (2022). Structure and interannual variation of fish communities in the offshore waters of southern Zhejiang province in spring. J. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sinica. 53, 1455–1466. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20220300080
Wijeyaratne W. M. D. N., Bellanthudawa B. K. A. (2018). Abundance-Biomass Comparison approach to assess the environmental stressors in Diyawannawa wetland in monsoonal and non-monsoonal seasons. J. Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 23, 135–149. doi: 10.4038/sljas.v23i2.7555
Wu Q., Li C., Gao T. Y., Li W., Zhang W. J., Wang J. J., et al. (2020). Community structure and spatio-temporal variation of fish in Liuxi river reserve. J. Fish. Sci. 39, 234–244. doi: 10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2020.02.011
Xia L. J., Yu C. G., Cai H. C., Zhen J., Chen W. D., Wu E. W., et al. (2016). Community structure and diversity of shrimp in Nanji Islands marine conservation area. J. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 38, 73–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.02.007
Xu S. N., Guo J. Z., Fan J. T., Xu Y. W., Su L., Li C. H. (2020). Annual variation in fish biomass size spectrum in Daya Bay,South China Sea in summer. J. South China Fish. Sci. 16, 28–38. doi: 10.12131/20200016
Yan L., Tan Y. G., Yang L., Lian X. P., Yang B. Z., Zhang P., et al. (2015). The resources community structure of stow-net fishery in the Pearl River Estuary coastal waters of the South China Sea. J. J. Biol. 32, 52–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2015.05.052
Yan Y. R., Yang H. C., Lu H. S., Li R. W. (2011). Feeding ecology of dorab wolf-herring, Chirocentrus dorab from the Beibu Gulf. J. Acta Ecol. Sin. 31, 654–665.
Yang L., Zhang X. F., Tan Y. G., Zhang P. (2008). Analysis of the catch composition of small shrimp-beam-trawl net in shallow waters of Pearl River Estuary, China. J. South China Fish. Sci. 4, 70–77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2008.06.010
Ye Y. H. (1995). Dynamic analysis of fishery resources in Pearl River Estuary. J. Fish. Sci. Technol. 4, 4–7.
Yemane D., Field J. G., Leslie R. W. (2005). Exploring the effects of fishing on fish assemblages using Abundance Biomass Comparison (ABC) curves. J. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 62, 374–379. doi: 10.1016/j.icesjms.2005.01.009
Yu J., Zhao M., Chen P. M., Zhang Y. P. (2016). Food habits of 8 species of economical fishes in the Pearl River estuary shallow waters. J. J. South. Agric. 47, 483–488. doi: 10.3969/:issn.2095-1191.2016.03.483
Yuan H. R., Chen P., Li X. G. (2022a). Taxonomic diversity and eco-exergy changes in fishery resources associated with artificial reefs over 14 years in Daya Bay, China. J. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1054933
Yuan H. R., Chen P. M., Yu J., Li X. G. (2022b). Assessment of quality of fishery resources in the northeastern south China sea. J. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 930. doi: 10.3390/jmse10070930
Yuan H. R., Lin Z. J., Chen Y. X., Chen P. M. (2023). Eco-dynamic analysis of the community structure of nekton in the northern south China sea. J. fishes 8, 578. doi: 10.3390/fishes8120578
Zhan H. G. (1998). Study on fish community structure in the Zhujiang estuary and adjacent waters. J. Haiyang Xuebao 20, 91–97.
Zhang Y. Z., Huang L. M. A. (2009). study on fish species diversity and community structure in eastern waters of Xiamen. J. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 28, 66–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.02.011
Zhang H. S., Song P. Q., Li Y., Liu S. G., Wang X. H., Zhen J. S., et al. (2021). Diversity and community structure of nekton in the central and southern East China Sea in autumn. J. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 40, 575–586. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.04.003
Zhen Y. J., Li J. S., Zhang Q. Y., Hong W. S. (2014). Research progresses of resource biology of important marine pelagic food fishes in China. J. J. Fish. China 38, 149–160. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2014.48799
Keywords: fish community, cluster analysis, biomass spectrum, ABC curve, redundancy analysis
Citation: Yuan H, Chen P, Chen Y and Zhang S (2024) Structure and interannual variation of fish communities in the Wailingding marine ranching area of Zhuhai in spring. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1434633. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1434633
Received: 18 May 2024; Accepted: 04 November 2024;
Published: 22 November 2024.
Edited by:
Pablo Presa, University of Vigo, SpainReviewed by:
Qiang Xu, Hainan University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Yuan, Chen, Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shouyu Zhang, c3l6aGFuZ0BzaG91LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.