- 1Institute of Ecology and Evolution, School of Biological Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
- 2Institute of Immunology and Infection Research, School of Biological Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Parasites rely on exploiting resources from their hosts and vectors for survival and transmission. This includes nutritional resources, which vary in availability between different hosts and changes during infections. For malaria (Plasmodium) parasites, sexual reproduction (sporogony) and subsequent development of oocysts, which produce sporozoites infectious to the vertebrate host, occurs in the mosquito vector. Mosquitoes in the field exhibit diversity in the amount and type of food they acquire, directly impacting the nutrients available for the replication and development of parasites. While the rate of parasite transmission from vector to host is influenced by the nutritional state of mosquitoes, whether this is due to resource limitation mediating parasite development and productivity is poorly understood. We use the rodent model parasite P. chabaudi and the vector Anopheles stephensi to ask how variation in the amount of sugar and blood provided to malaria-infected mosquitoes affects the potential for parasites to transmit from vector to host. We show that parasites in well-resourced mosquitoes reach a larger oocyst size earlier in development, suggesting faster growth, and have a 1.7-fold higher sporozoite burden than parasites whose vectors only receive sugar. However, this increase in productivity is only partly explained by oocyst development, suggesting that resource availability also impacts the ability of sporozoites to reach the salivary glands. This challenges the assumption of a simple relationship between the number or size of oocysts and onward transmission potential. Furthermore, our findings suggest malaria parasites may actively adjust oocyst growth rate to best exploit nutritional resources; while parasites in low-resourced mosquitoes exhibited a reduction in oocyst burden during sporogony, the remaining oocysts developed more rapidly in the later stages of oocyst development, catching up to reach a similar size to those in well-resourced mosquitoes. Understanding the impacts of resource availability for malaria transmission is urgent given that parasites encounter increasingly variable vectors as consequences of climate change and vector control tools.
Introduction
Parasites by definition rely on hosts, exploiting them for food and shelter (Rózsa and Garay, 2023). Many parasite species, including vector-transmitted parasites, have multi-host lifecycles, where different life stages are found in phylogenetically diverse definitive and intermediate host species (Webster et al., 2017). These parasites are exposed to extensive variation in the within-host/vector environmental conditions they experience, and so, adapt to exploit environments which provide different types and amounts of resources. For example, malaria parasites (Plasmodium) exploit nutritional resources in the blood of their vertebrate host, but also must be able to successfully utilise resources present in the gut and haemolymph of their insect vector (Lefevre et al., 2017). In addition, parasites face variation in how well-resourced individual con-specific hosts/vectors are, and in how nutritional resources vary during the course of infections within hosts/vectors. For example, resource availability in mosquito vectors can vary across larval breeding habitats which subsequently affects adult fitness (Takken et al., 2013; Shapiro et al., 2016), and for malaria parasites, the density of red blood cells (RBC) available within the vertebrate host reduces as parasite density increases, and the resulting anaemia leads to an alteration in the RBC age structure as the host recovers (Birget et al., 2017). Other causes of variation between individual hosts/vectors include immune status, infection with other parasites, age, sex and reproductive status, which can also alter the nutritional resources available for parasites to exploit. For example, vectors show age-specific changes in foraging (Alto et al., 2003; Cator et al., 2020), and co-infection of multiple parasite strains causes competition for limited resources within the vertebrate host (Pollitt et al., 2011).
The nutritional resources available within vectors impacts parasite transmission by influencing multiple parameters of vectorial capacity (i.e. the efficiency of vector-borne disease transmission under natural conditions) (Takken et al., 2013; Shapiro et al., 2016; Almire et al., 2021). Adult female mosquitoes rely on both blood and sugar sources for nutrition during their lifespan; blood provides a nutritional boost of proteins and lipids which are necessary for egg production, and sugar sources provide the majority of energy for meeting the mosquito’s metabolic needs, including powering processes such as flight (Foster, 1995). Climatic variation (Gu et al., 2011; Stone et al., 2012), season, and access to vertebrate hosts (which is reduced by bed net use (Killeen et al., 2007)) generate variation in blood and sugar availability, impacting vector behaviour, lifespan and fecundity (Fernandes and Briegel, 2005; Gary and Foster, 2006; Ma and Roitberg, 2008; Lyimo et al., 2012; Dieng et al., 2015; Hagan et al., 2018; Barredo and Degennaro, 2020; Yan et al., 2021; Vantaux et al., 2023). Furthermore, the type of plant sugar and blood meal sources used by mosquitoes determines their longevity, biting behaviour and susceptibility to malaria infection (Hien et al., 2016; Emami et al., 2017; Ebrahimi et al., 2018; Vantaux et al., 2023). Thus, the availability and quality of nutritional resources available to mosquitoes affects vectorial capacity via vector population dynamics, susceptibility to infection, and biting rates. However, whether and how nutritional resources mediate transmission via additional direct effects on parasite development and productivity within vectors is poorly understood.
Malaria parasites rely on nutrients from the vector’s blood and sugar meals throughout sporogony. Sporogony involves gametogenesis and fertilisation within the mosquito midgut, traversal of the mosquito midgut wall to form oocysts, and extensive growth and replication within oocysts to produce tens of thousands of vertebrate-host-infectious sporozoites, which must egress from oocysts and migrate to the salivary glands (Beier, 1998). Glucose is required to power microgamete motility during mating (Talman et al., 2014), and mosquito derived-lipids and amino acids are required for sporozoite production (Atella et al., 2009; Costa et al., 2018; Shaw et al., 2020; Kwon et al., 2021). Thus, reducing the amount of lipids available to oocysts lowers the quantity of sporozoites as well as their ability to infect a vertebrate host (Costa et al., 2018), and feeding already-infected mosquitoes an additional blood meal can speed up oocyst development (Shaw et al., 2020; Kwon et al., 2021). However, the overall impacts of nutritional resources on transmission, and to what extent parasites can optimise their amount and schedule of resource exploitation, are unknown.
Theory for the evolution of life history traits predicts that while natural selection acts to maximise fitness, expression of traits is limited by trade-offs and constraints commonly caused by limited resources available for growth, maintenance and reproduction (Stearns, 1989). Applying life history theory to parasites has revealed sophisticated strategies deployed within the host (Reece et al., 2009; Schneider and Reece, 2021), and could help to understand parasite strategies within the vector (Carrillo-Bustamante et al., 2023). A key concept is that each highly genetically related genotype of single-celled malaria parasites within an infection can be viewed as an organism from the perspective of natural selection (Gardner and Grafen, 2009; Schneider and Reece, 2021), adopting strategies that are collectively beneficial for the genotype. For example, in the vertebrate host, the rodent malaria P. chabaudi plastically alters the sex ratio of sexual transmission stage parasites (gametocytes) (Reece et al., 2008) and the proportion of asexual parasites committing to form gametocytes (Schneider et al., 2018a). Specifically, parasite genotypes adjust these traits during infections, and between different hosts, in manners that maintain fitness across different environmental conditions (Pigliucci, 2005), such as variable degrees of competition with co-infecting genotypes and the availability of red blood cell resources (De Roode et al., 2005; Bell et al., 2006; Birget et al., 2017).
Here, we apply life history theory to explain parasite strategies in the vector, and how they may maximise fitness (i.e. between-host transmission). For example, a common trade-off is offspring quality vs quantity, and parasites may also face this trade-off during sporozoite production, the strength of which will vary dependent on resource availability. For example, under nutrient-limiting conditions, a small number of oocysts could continue growing, to ensure completion of sporogony for a small number of sporozoites rather than producing more lower quality sporozoites or risk not completing sporogony at all (Habtewold et al., 2021). Additionally, the length of time it takes for parasites to complete sporogony (the extrinsic incubation period, EIP) is dependent on mosquito resources (Shaw et al., 2020). If resources are limiting, faster development may occur at the expense of quality and/or quantity of sporozoites, or alternatively may be extended to wait for additional incoming resources (Carrillo-Bustamante et al., 2023). Conversely, excess resources may allow parasites to develop unhindered, producing more high quality sporozoites at a fast rate. Following these scenarios, parasites in medium-resourced mosquitoes should adopt intermediate strategies, constrained to developing slower than in well-resourced mosquitoes, but producing more/better sporozoites than low-resourced mosquitoes. How parasites respond to resource availability will also depend on whether, and how, parasites sense resource supply, and whether vector death is imminent or if the vector will survive long enough to forage for more resources.
While previous studies suggest parasites capitalise on an increase in resource availability by speeding up sporogony (Shaw et al., 2020), it is unknown whether parasite development and productivity are limited in poorly-resourced mosquitoes. By perturbing mosquito nutritional status after infection with P. chabaudi, we investigate how parasites respond to both an increase and decrease in the availability of within-vector resources. We provide mosquitoes with (i) low fructose, representing vectors with limited access to all resources, (ii) high fructose, representing vectors with limited access to blood meals but plentiful resources for their survival, or (iii) high fructose plus an additional blood meal, representing well-fed vectors with access to both types of resources. We hypothesise that if parasites can detect changes in resource availability and/or vector condition, they will adopt different optimal development strategies to maximise transmission, including changes to sporozoite quantity, quality and/or developmental speed (i.e. the EIP). Overall, we demonstrate that parasite development during sporogony is plastic and propose hypotheses for future studies to differentiate whether this is due to constraints or whether parasites are adopting adaptive (fitness-maximising) strategies. We also explore implications for transmission potential because well-resourced mosquitoes are likely to have higher vectorial capacity.
Materials and methods
We performed two experiments to test how nutritional resources garnered by mosquitoes affect malaria parasite development and onward transmission potential. First, we confirmed the extent to which different food treatments perturbed mosquito physiological condition by comparing survival rates and nutritional status in uninfected mosquitoes. Second, we infected mosquitoes with P. chabaudi and subsequently perturbed food treatments to quantify the impact on oocyst development and sporozoite burden.
Vectors, hosts, and parasites
We used the highly tractable Anopheles stephensi-P. chabaudi-lab mouse model system, which closely reflects the within-host behaviours and within-vector dynamics of the most virulent human malaria parasite, P. falciparum, in its most common (An. gambiae complex) vectors (Spence et al., 2012; Schneider and Reece, 2021; Shaw et al., 2022). We housed adult An. stephensi SD500 mosquitoes at 26°C, 70% relative humidity on a 12L: 12D cycle and provided them with ad libitum access to 8% fructose solution following emergence. Three days post-pupation, we transferred adult female mosquitoes to experimental cages. In both experiments, we provided mosquitoes with an initial blood meal at 5-7 days post-pupation. Prior to the initial blood meal, we starved mosquitoes overnight by providing water only. On day 1 post-blood meal (pBM), we removed unfed females from cages, and on day 3 pBM we provided an oviposition site (a small petri dish lined with filter paper, filled with water) in each cage to give mosquitoes the opportunity to lay eggs.
For all uninfected blood meals in the first experiment, and additional blood meals in the second experiment, we used 8-10 week old male and female Per1/2-null (on a C57Bl/6 J background) clock disrupted mice (O’Donnell et al., 2020) housed under standard 12L:12D conditions with ad libitum access to food and drinking water. When housed in 12L:12D conditions, Per1/2-null mice exhibit a wildtype rhythmic phenotype (Bae et al., 2001), and were excess from a breeding colony to ethically reduce the number of mice specifically bred for the present study (Prescott and Lidster, 2017). To infect mosquitoes with malaria in the second experiment during their initial blood meal, we allowed female mosquitoes to blood feed on mice infected with P. chabaudi (genotype ER, passage number A17). Mice were 10 week old C57Bl/6 J male mice given ad libitum access to food and drinking water (supplemented with 0.05% para-aminobenzoic acid to aid parasite development (Jacobs, 1964)). We pre-treated mice with 125mg/kg phenylhydrazine (PHZ) prior to infection to enhance gametocyte production. Three days after PHZ treatment, we infected mice with 1x107 P. chabaudi ring stage parasitised red blood cells by intraperitoneal (IP) injection. Transmissions occurred on day 5 post-infection. On day 4 post-infection, we took blood samples from all mice for quantification of gametocytes by microscopy, selecting those with the highest gametocytemia for transmission feeds. Prior to donating a blood meal, we anaesthetised mice (65mg/kg ketamine hydrochloride and 0.85mg/kg medetomidine in PBS) and placed each mouse on a cage of mosquitoes for 20 minutes.
Experiment 1: resource perturbation in uninfected mosquitoes
To confirm that varying the availability of nutritional resources successfully perturbed mosquito condition, we assessed the impact of four feeding treatments on mosquito nutritional status (lipid, glycogen and total sugars content) and lifespan without the confounding effects of malaria infection (Figure 1A). We first allowed a cage of female mosquitoes (n=1000) to take an initial blood meal 5-7 days post-pupation from four mice, then placed them on ad libitum 8% fructose solution. Three days later (day 3 pBM, to follow a gonotrophic cycle), we randomly transferred n=40 mosquitoes to each of 24 paper pots with mesh lids and oviposition sites. The following day (day 4 pBM), we randomly allocated six pots to each of four treatments, which involved ad libitum access to either: (i) 0.08% fructose (0.08% fruc), (ii) 0.8% fructose (0.8% fruc), (iii) 8% fructose (8% fruc) and (iv) 8% fructose and an additional blood meal on day 4 pBM (8% fruc + bm).
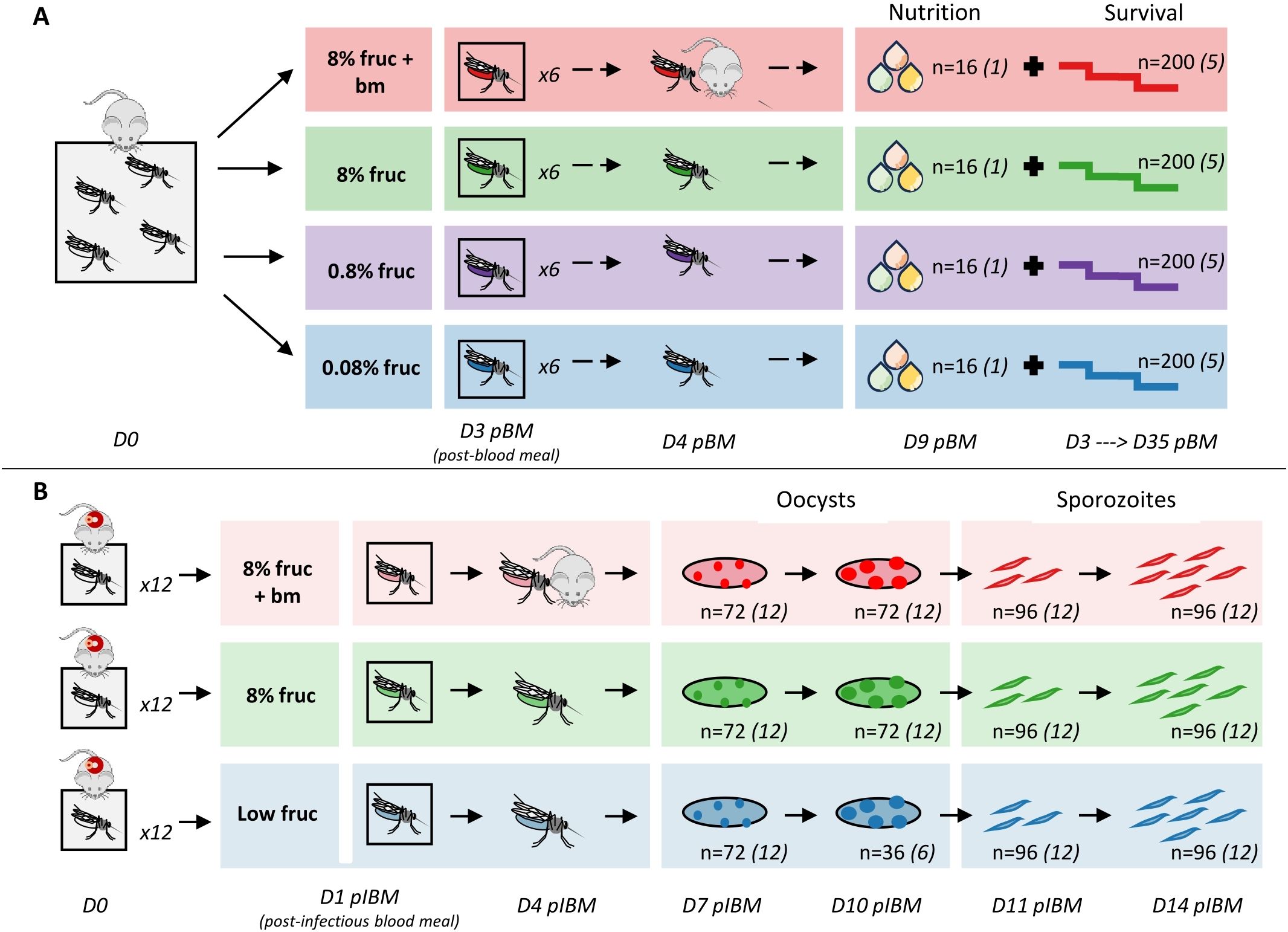
Figure 1. Experimental design and sampling for investigating the effect of resource availability on nutritional status (lipids, glycogen, total sugars) and survival in uninfected mosquitoes (A) and parasite development within infected mosquitoes (B). Sample sizes (n) refer to the total number of individual mosquitoes collected for each sampling point across replicate pots (denoted by number in italics).
From day 4 pBM we tracked mosquito survival by recording daily deaths until day 35 pBM (n=5 pots per treatment group). On day 9 pBM, we collected n=16 mosquitoes from the sixth pot (n=1 pot per treatment group), and froze them at -20°C before undertaking lipid, glycogen and total sugar analyses following modified Van Handel protocols (Van Handel, 1985a, b; Van Handel and Day, 1988). In brief, we removed a wing from each mosquito to quantify body size, and lysed individual mosquitoes in 100µl 2% sodium sulphate and added 750µl of 1:2 chloroform:methanol. We centrifuged samples at 17949xg for 3 minutes; the supernatant was collected for lipid and total sugars analysis, and the precipitate was used for glycogen analysis. We were unable to collect data on lipids and total sugars from two mosquitoes. We conducted lipid analysis following (Meuti et al., 2015) with minor modifications: 250µl supernatant was used, and 80µl of sample was added to 96-well plates and we measured absorbance at 525nm and 490nm on a microplate reader (Varioskan Flash, ThermoFisher Scientific). We carried out glycogen analysis by adding 200µl anthrone reagent to the precipitate, and heating to 90°C for 15 minutes. After cooling at 4°C for 5 minutes, we added 40µl to a 96-well plate containing 40µl anthrone reagent and absorbance was measured at 625nm and 555nm on a microplate reader. Total sugars analysis followed the same protocol to glycogen with minor differences: we heated 125µl of supernatant at 90°C until the solvent evaporated, and then added 200µl anthrone reagent. After heating and cooling as above, we added 80µl to 96-well plates before measuring absorbance at the same wavelengths.
Experiment 2: resource perturbation in infected mosquitoes
To investigate how perturbations of nutritional status of mosquito vectors affect sporogony, we fed all mosquitoes an infected blood meal, and then assessed the impact of three feeding treatments on: (i) oocyst prevalence (the proportion of mosquitoes infected with oocysts), (ii) oocyst burden (the number of oocysts per gut in infected mosquitoes), (iii) oocyst size (a proxy for growth rate), (iv) sporozoite prevalence (the proportion of mosquitoes with detectable sporozoites), and (v) sporozoite burden (the number of sporozoites in individual mosquitoes) (Figure 1B). To infect mosquitoes, we anaesthetised infected mice (n=30) and exposed each mouse to a pot of mosquitoes (n=12 pots per treatment group, n=80 mosquitoes per pot) for 20 min, with the exception of the six mice with the highest gametocyte loads, which were simultaneously exposed to pairs of pots. We took blood samples from mice at the point of transmissions to confirm gametocyte numbers by quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-qPCR) (Schneider et al., 2018a).
Pots of mosquitoes were randomly allocated to treatment groups on day 1 post-infectious blood meal (pIBM): (i) low fructose (low fruc; 0.08% fructose for 6 days, increased to 0.8% fructose thereafter), (ii) 8% fructose (8% fruc) or (iii) 8% fructose plus an additional blood meal on day 4 pIBM (8% fruc + bm). Despite pilot data revealing 0.08% fructose is sufficient for naïve mosquitoes to survive the experimental period, this proved not be the case for infected mosquitoes. Because deaths within the first few days of infection were unexpectedly high in the low fructose group, we ensured enough mosquitoes survived for the duration of data collection by increasing fructose concentration to 0.8% from day 6 pIBM. By perturbing the diets of mosquitoes once infected, we avoided any impacts of altering mosquitoes prior to infection in manners that could confound impacts on parasite development by affecting mosquito uptake of infectious blood and susceptibility.
On days 7 and 10 pIBM, we sampled mosquitoes (n=6 per pot per time point) to determine oocyst prevalence, burden, and size. On day 10, we collected mosquitoes from only 6 pots in the low fructose group due to the low survival described above. To visualise oocysts, we anaesthetised mosquitoes on ice, and dissected midguts in a drop of phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Dissected midguts were stained in 0.25% mercurochrome and photographed at 40x magnification using a light microscope on a single focal plane. Using ImageJ (Schneider et al., 2012), we placed a grid over each midgut photograph and used this to count total oocysts, and measure the area of up to 30 oocysts per gut, starting at the central grid square in the midgut. Measurements were calibrated using a photograph of a micrometer taken at the same magnification. We also used these measurements to calculate a metric we termed oocyst coverage, that accounts for changes in both the number and size of oocysts as a proxy for the total biomass of each infection (oocyst coverage = mean oocyst volume multiplied by burden per mosquito gut). On days 11 and 14 pIBM, we sampled mosquitoes (n=8 per pot) to determine sporozoite prevalence and burden over time. Mosquitoes were anaesthetised on ice, and bisected following Foley et al. (2012). We stored head/thorax samples at -20°C until DNA extraction and quantification by qPCR (Schneider et al., 2018b).
Nucleic acid extraction and quantification of parasites
To quantity gametocyte densities in mice used to infect mosquitoes, we extracted RNA from 10µl blood samples following Schneider et al. (2018a), and used an RT-qPCR assay targeting the sexual stage-specific expressed gene PSOP1 (PCHAS_0620900) (Wargo et al., 2006).
To quantify sporozoite burden and prevalence, we extracted DNA from mosquito head/thorax samples following the CTAB-based phenol-chloroform extraction method from Chen et al. (2010) with minor modifications as described in Schneider et al (2018b). We eluted extracted DNA in 30μl of water, and froze at -20°C until use. A qPCR targeting a region of the 18S rRNA gene (Bell et al., 2009) was used to quantify salivary gland sporozoites. Quantification of parasite genomes was determined by comparing threshold cycle (Ct) against a standard curve, generated from DNA extracted from microscopy-quantified blood stage parasites of P. chabaudi genotype ER.
Statistical analysis
We used R v. 4.1.3 for data analysis. We analysed nutritional content (lipid, glycogen, total sugars) of mosquitoes using linear models with feeding treatment as a main effect. We corrected for body size by dividing nutritional content by wing length, and then multiplying by the mean wing length across all mosquitoes. To estimate how feeding treatment affected survival in uninfected mosquitoes, we used Kaplan-Meier curves (survminer (Kassambara et al., 2021)) and a cox proportional hazards model with mosquito pot as a cluster to account for non-independent measures within mosquito pots (coxme (Therneau, 2022)). We confirmed that pots of mosquitoes across feeding treatments were provided with similar gametocytemias using a linear model (feeding treatment: F2, 33 = 0.56, p = 0.58).
For all subsequent models investigating parasite metrics, we included mouse as a random effect to account for pots fed simultaneously on the same mouse, and we added a random effect of mosquito pot or a nested random effect of mosquito identity within mosquito pot to account for non-independent measures within mosquito pots and mosquito guts respectively. We tested the impact of feeding treatment, day pIBM and their interaction on oocyst and sporozoite prevalences, using binomial generalised linear mixed models (glmm). We used linear mixed models (lmm) to investigate how feeding treatment, day pIBM and their interaction affected (i) oocyst burden of infected mosquitoes, (ii) oocyst coverage, (iii) oocyst diameter, (iv) oocyst size variation within a gut (coefficient of variation: standard deviation of oocyst diameter per gut divided by mean oocyst diameter per gut), and (v) sporozoite burden. We also used a lmm to investigate how feeding treatment affected the correlation between oocyst diameter and oocyst burden on day 7 pIBM. Similar lmms were used to test for correlations between sporozoite burden on day 14 pIBM and pooled means per pot for (i) oocyst diameter, (ii) square root oocyst coverage, and (iii) square root oocyst burden on day 10 pIBM, and whether these varied by feeding treatment.
We minimised all models using likelihood ratio tests, and corrected Akaike information criterion (AICc) for non-nested models, and tested for conformation to model assumptions using DHARMa (Hartig, 2022), or easystats (Makowski et al., 2020) for models with nested random effects. Nutrition, sporozoite burden, oocyst burden and oocyst coverage data were all square-root transformed to meet assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variance. We present predicted means from the best fitting minimised models (predict() function, lme4 (Bates et al., 2015)), and estimated SEMs from parametric bootstrapping (bootMer function). We used model predictions to fit linear regression curves. We conducted post hoc pairwise comparisons using the Tukey method with the emmeans package (Lenth, 2023) for minimised models containing a significant effect.
Results
Resources affect mosquito nutrition and survival
We used uninfected mosquitoes to verify that varying the concentration of fructose in sugar meals and an additional blood meal affected lipid (F3, 58 = 43.9, p < 0.001), glycogen (F3, 60 = 10.7, p < 0.001) and total sugars (F3, 58 = 91.8, p < 0.001) content (Figure 2). Mosquitoes fed 8% fructose contained 357 ± 61.8µg lipids each, which was approx. 10-fold higher than mosquitoes fed 0.08% fructose (38.6 ± 7.80µg), but 1.7-fold lower than when an additional blood was given (594 ± 65.6µg) (Figure 2A, Table 1). Similarly, for total sugars, mosquitoes on the lowest fructose diets contained 44.1 ± 15.7µg each, 20-fold lower than those fed on 8% fructose (896 ± 56.5µg). However, an additional blood meal only slightly increased total sugar content to 1065 ± 132µg compared to 8% fructose (Figure 2B, Table 1). In contrast, glycogen stores were similar across mosquitoes fed 0.8% or more fructose (204-262µg), but were approximately 2.7-fold lower in mosquitoes fed 0.08% fructose (85.5 ± 9.81µg) (Figure 2C, Table 1).
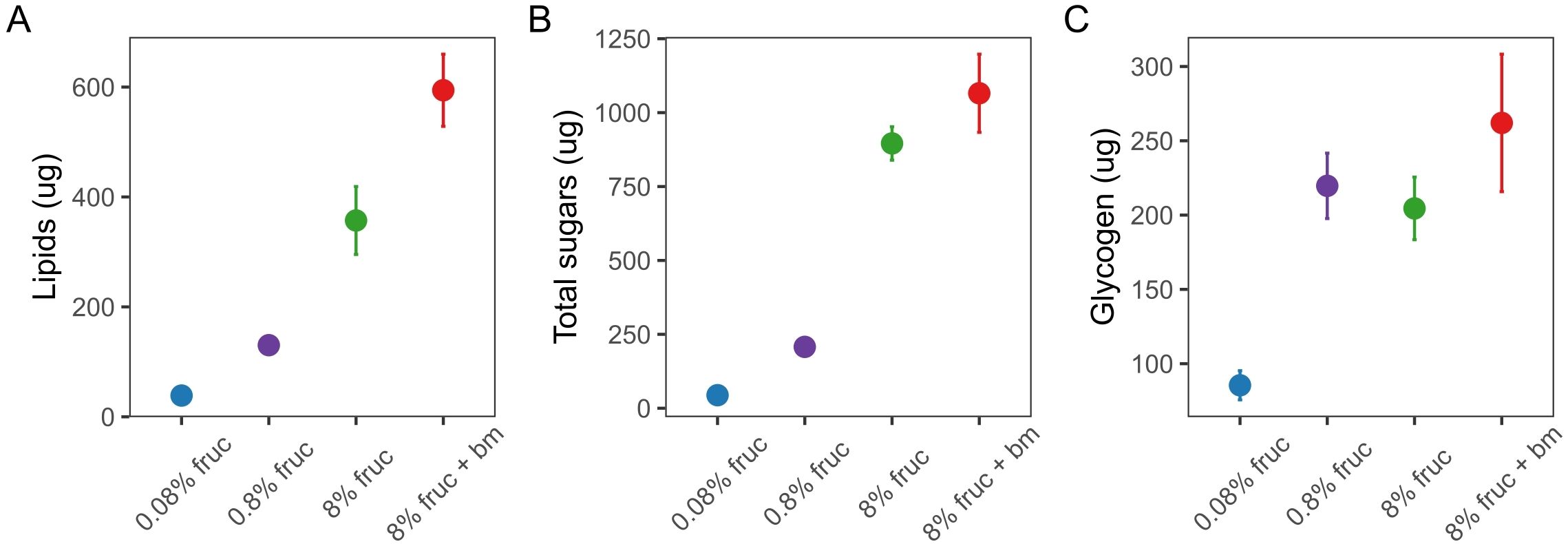
Figure 2. The body-size adjusted concentration (µg) per mosquito of lipids (A), total free sugars (B) and glycogen (C) in individually assayed mosquitoes under differing feeding treatments at d9 post-uninfected blood meal (pBM). Data presented are mean ± SEM.
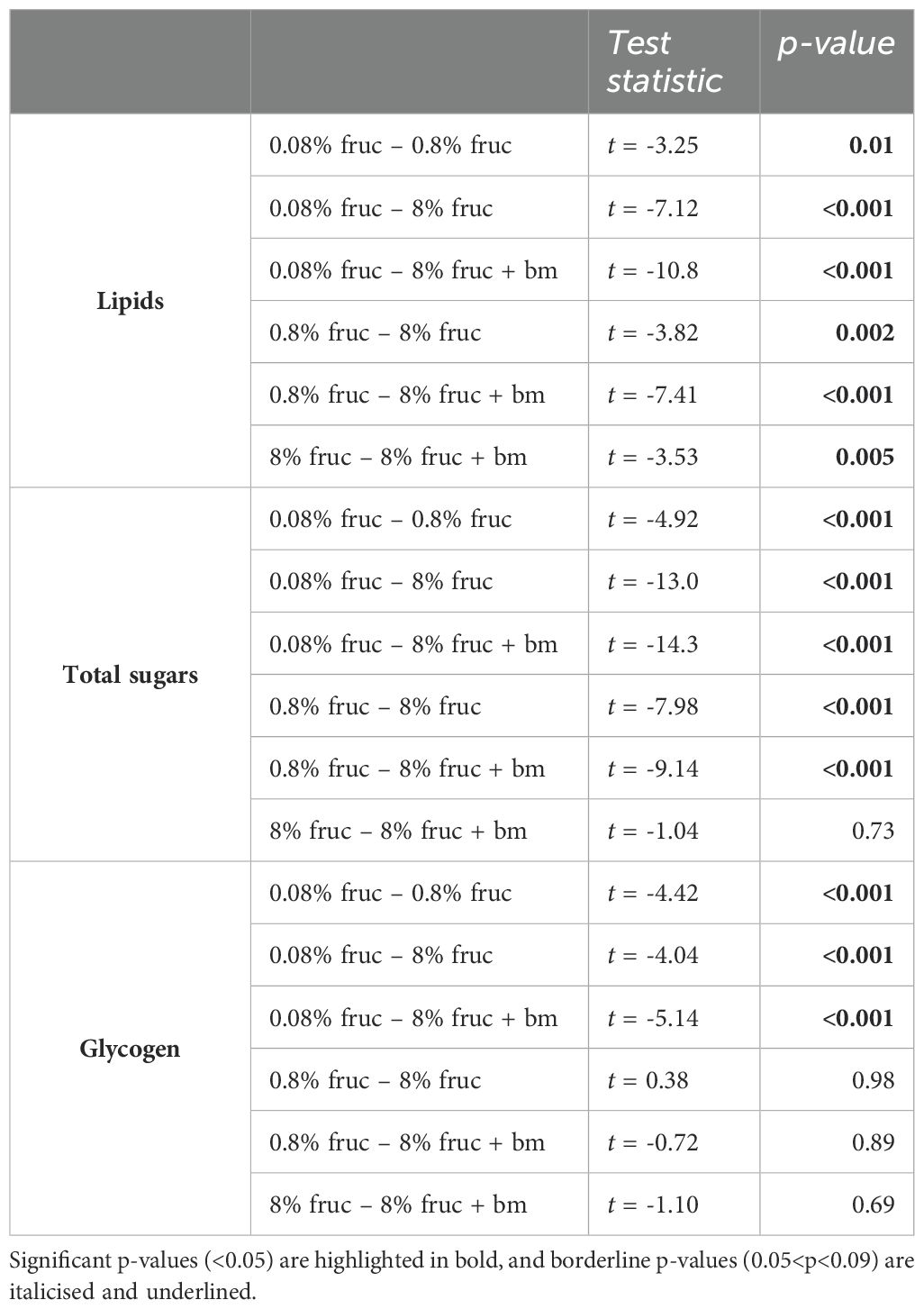
Table 1. Post hoc pairwise comparisons for nutritional content of mosquitoes provided with different feeding treatments.
Mosquito survival was also affected by feeding treatment. Compared to mosquitoes fed 8% fructose, an additional blood meal increased lifespan (HR: 0.41, 95% CI 20.6-44.8, z = -6.17, p < 0.001), whereas those given 0.08% fructose had the fastest mortality rate (HR: 30.4, 95% CI 0.70-1.36, z = 17.2, p < 0.001), with a median survival of 11 days (95% CI 11-12). However, there was no difference between groups given intermediate levels (0.8% and 8%) of fructose (HR: 0.98, 95% CI 0.32-0.55, z = -0.135, p = 0.892), which had median survivals of 32 (95% CI 30-34) and 33 (95% CI 31-34) days respectively (Figure 3). Note, too few mosquitoes died within the 35 day monitoring window to accurately predict median survival for mosquitoes given an additional blood meal.
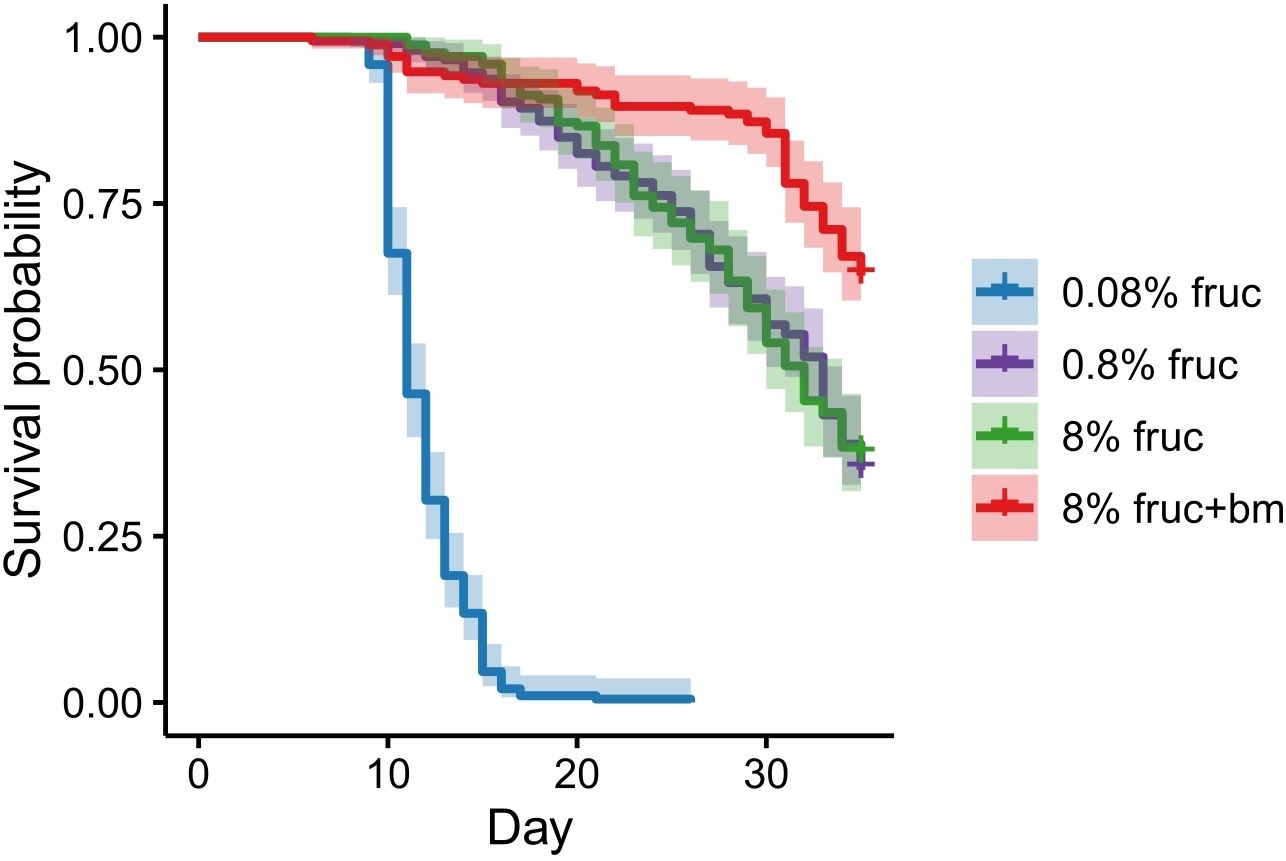
Figure 3. Mosquito survival in response to differing feeding treatments imposed following an initial meal of uninfected blood. Data presented are Kaplan-Meier curves ± 95% confidence intervals.
Resources affect parasite development within mosquitoes
First, we verified the assumption of our experimental design, that infection prevalence did not differ according to treatment group, ensuring that subsequent comparisons of parasite performance across treatment groups was not confounded by contributions of unequal proportions of infected mosquitoes. Overall oocyst prevalence was high, at 92 ± 2%, and did not vary between treatments (χ22 = 1.03, p = 0.60). While oocyst prevalence increased slightly between day 7 and 10 pIBM, from 89 ± 3% to 96 ± 1% (χ21 = 5.79, p = 0.016), this did not differ across treatments (χ22 = 0.36, p = 0.84) (Figure 4A) and is most likely due to oocysts becoming easier to identify as they grow.
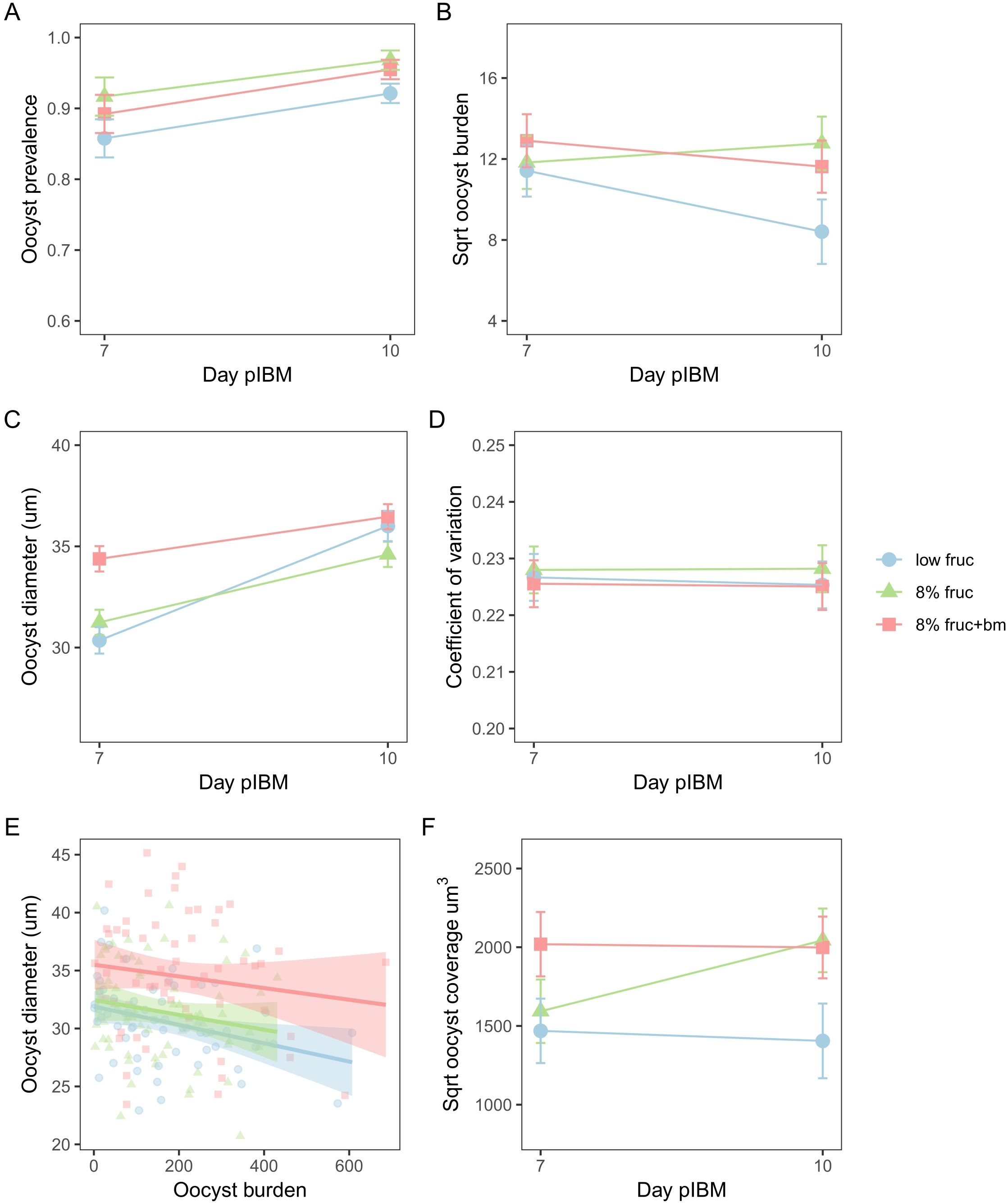
Figure 4. Oocyst development metrics from day 7 to day 10 post-infectious blood meal (pIBM) for mosquitoes subjected to different feeding treatments. Data presented are oocyst prevalence, defined as the proportion of infected mosquitoes (A), oocyst burden (B), oocyst diameter (C), and oocyst size variation as measured by the coefficient of variation (D), the correlation between oocyst burden and oocyst size on day 7 pIBM only (E) and oocyst coverage over time (F). To account for multiple measures per mosquito pot and per mosquito, data presented are predicted means ± SEM from the minimised models for (A–D) and (F), and data points are minimised linear model predictions for individual mosquitoes, with lines and shading denoting best fit linear model estimates ± 95% confidence intervals for (E).
Second, we examined parasite development in terms of oocyst burdens, growth rate, and coverage. We find that oocyst burden varied between feeding treatments in manners that depended on day pIBM (χ22 = 8.11, p = 0.017). Specifically, burden dropped between day 7 and 10 pIBM by 1.8-fold in mosquitoes on the low fructose diet (sqrt burden: 11.4 ± 1.3 to 8.4 ± 1.6), but only marginally (by 1.2-fold) in mosquitoes given an additional blood meal (sqrt burden: 12.9 ± 1.3 to 11.6 ± 1.3). In contrast, oocyst burden increased marginally (by 1.2-fold) in mosquitoes fed on 8% fructose (sqrt burden: 11.8 ± 1.3 to 12.8 ± 1.3) (Figure 4B, Table 2).
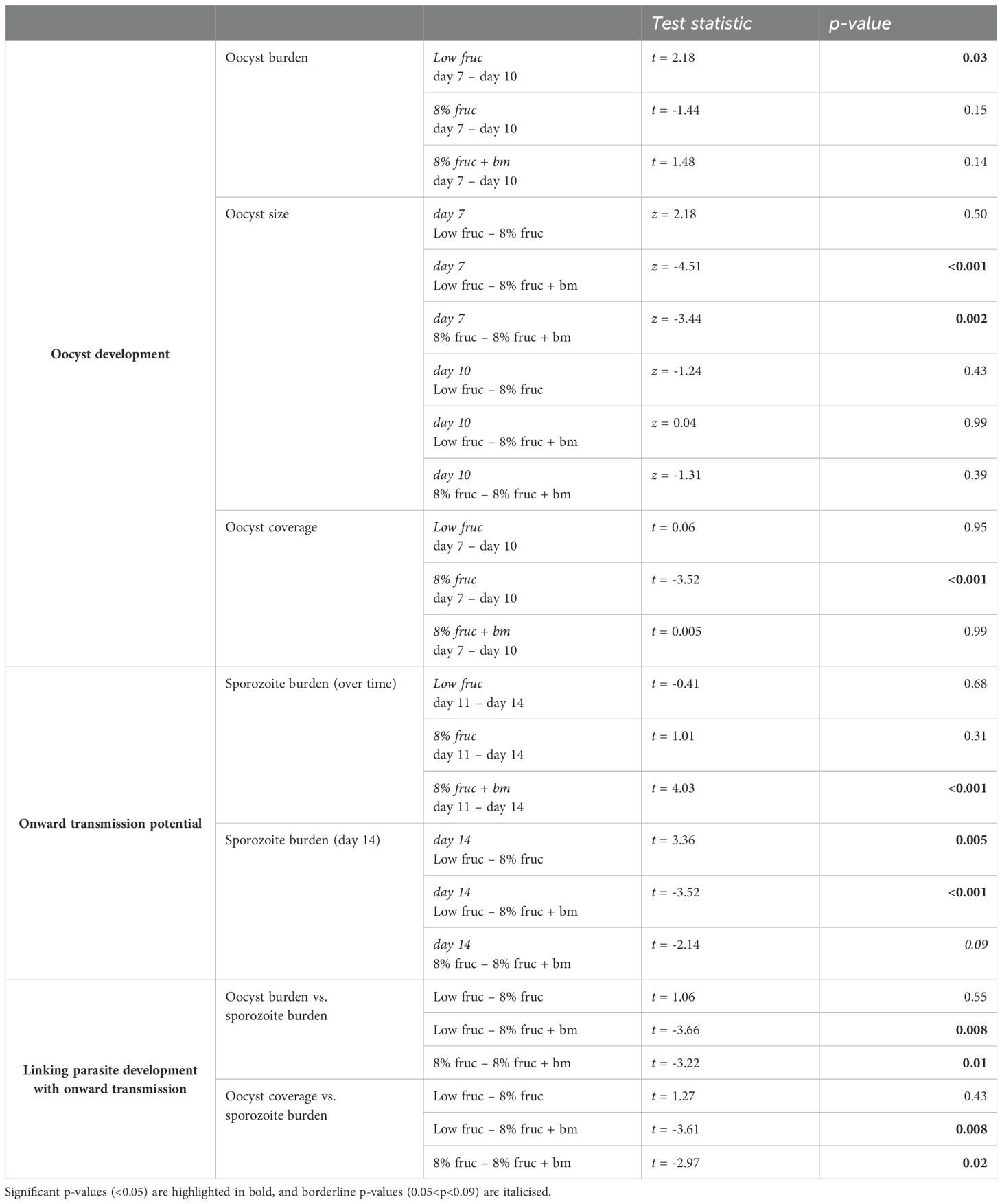
Table 2. Post hoc pairwise comparisons for oocyst development and onward transmission potential across mosquito feeding treatments over time.
Oocyst diameter, which reflects growth rate, also differed across feeding treatments in manners that depended on day pIBM (χ22 = 58.2, p < 0.001). Oocysts were larger on day 7 in mosquitoes provided with an additional blood meal (34.4 ± 0.63µm) compared to those on fructose only diets (8% fruc: 31.2 ± 0.62µm, low fruc: 30.4 ± 0.65µm). From day 7 to day 10, oocysts in mosquitoes provided with an additional blood meal increased in size the least (by 6%). Oocysts in mosquitoes fed on 8% fructose grew at a similar rate to those provided an additional blood meal, increasing by 10% to reach a marginally smaller size on day 10 (8% fruc: 34.6 ± 0.62µm, 8% fruc: + bm 36.5 ± 0.62µm). In contrast, despite being small on day 7, oocysts grew at the fastest rate in the low fructose group, increasing by 16%, and reached a similar size to those in the additional blood meal group by day 10 (low fruc: 36.0 ± 0.75µm) (Figure 4C, Table 2). Oocysts within a midgut had similar size variation regardless of feeding treatment (interaction: χ22 = 1.44, p = 0.49, feeding treatment: χ22 = 0.75, p = 0.69) and day pIBM (χ21 = 1.13, p = 0.29) (Figure 4D).
Finally, we find that oocyst burden negatively correlated with oocyst size on day 7, where diameter was reduced by 0.006 ± 0.003µm per additional oocyst (burden: χ21 = 5.85, p = 0.016) equally across all treatments (χ22 = 0.26, p = 0.88) (Figure 4E); a small difference in oocyst diameter is likely to be biologically significant because oocysts are spheres, causing small changes in diameter to result in large changes in volume. To account for this trade-off, we explored how patterns in total infection biomass, termed oocyst coverage (oocyst burden multiplied by mean oocyst volume per mosquito gut) differed over time. We find that oocyst coverage differed across feeding treatment in manners dependent on day pIBM (χ22 = 7.57, p = 0.022). Coverage was approximately 1.8-fold higher in mosquitoes given an additional blood meal compared to those on a low fructose diet and stayed constant in these groups from day 7 to day 10. In contrast, oocyst coverage increased 1.4-fold in mosquitoes on 8% fructose diets, reaching a similar level to the coverage in mosquitoes provided with an additional blood meal by day 10 (sqrt oocyst coverage for 8% fruc: 2043 ± 202µm3, 8% fruc + bm: 2000 ± 196µm3) (Figure 4F, Table 2).
Resources shape onwards transmission potential
To test whether the developmental impacts of feeding treatments on parasites affects their onwards transmission potential, we compared the prevalence and the burden of sporozoites within mosquito salivary glands over time. Sporozoite prevalence was very high (98 ± 5%) across all feeding treatments (interaction: χ22 = 2.07, p = 0.36, feeding treatment: χ22 = 3.18, p = 0.20), and stayed consistent over time (χ21 = 0.16, p = 0.69) (Figure 5A). In contrast, sporozoite burden differed across feeding treatments in day pIBM-dependent manners (χ22 = 9.61, p = 0.0082). Sporozoite burden was consistently higher in mosquitoes provided with an additional blood meal, despite a 1.6-fold reduction from day 11 to 14 pIBM (sqrt burden: 427 ± 25 to 334 ± 24) in this group. In contrast, for groups provided with only fructose, sporozoite burden stayed consistent from day 11 to 14 pIBM. By day 14 pIBM, compared to mosquitoes fed an additional blood meal, those provided with 8% fructose had approximately 1.7-fold fewer sporozoites (day 14 sqrt burden: 255 ± 25), and sporozoite burden was 5.6-fold lower in mosquitoes fed on a low fructose diet (day 14 sqrt burden: 140 ± 27) (Figure 5B, Table 2).
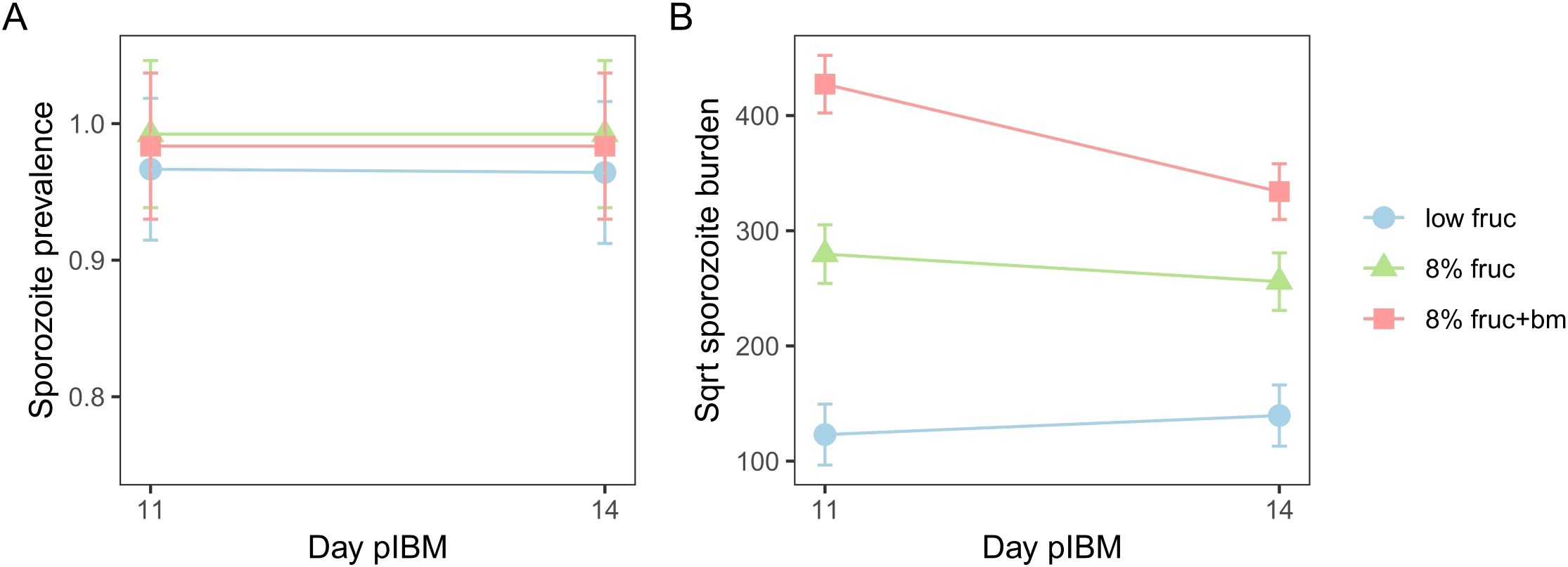
Figure 5. The impact of mosquito feeding treatments on sporozoite prevalence (A) and sporozoite burden (B) between day 11 and day 14 post-infectious blood meal (pIBM). Data presented are predicted means ± SEM from minimised linear models.
Linking parasite development and transmission potential
Finally, we explored whether the patterns we observe in the burdens and growth of oocysts can explain treatment group differences in sporozoite burden. We tested for correlations between oocyst metrics on day 10 and sporozoite burden on day 14, asking to what extent higher sporozoite burdens could be due to more productive oocysts in well-resourced mosquitoes. We find a positive correlation between oocyst and sporozoite burdens (χ21 = 13.1, p < 0.001), with the same slope across all feeding treatments (χ22 = 3.40, p = 0.18), and that oocyst productivity increased as access to resources increased (χ22 = 16.8, p < 0.001). Specifically, oocysts in mosquitoes provided an additional blood meal produced the most sporozoites, approximately 2.9-fold and 2-fold more than mosquitoes on the low fructose and 8% fructose diets, respectively (Figure 6A, Table 2). The relationships observed between oocyst and sporozoite burdens across feeding treatments are mirrored by oocyst coverage and sporozoite burden (oocyst coverage: χ21 = 13.3, p < 0.001; treatment: χ22 = 15.6, p < 0.001; oocyst coverage by treatment: χ22 = 3.84, p = 0.15) (Figure 6B, Table 2). In contrast, we find that oocyst size did not correlate with sporozoite burden (χ21 = 0.009, p = 0.93) within any feeding treatments (χ22 = 3.80, p = 0.15) (Figure 6C).
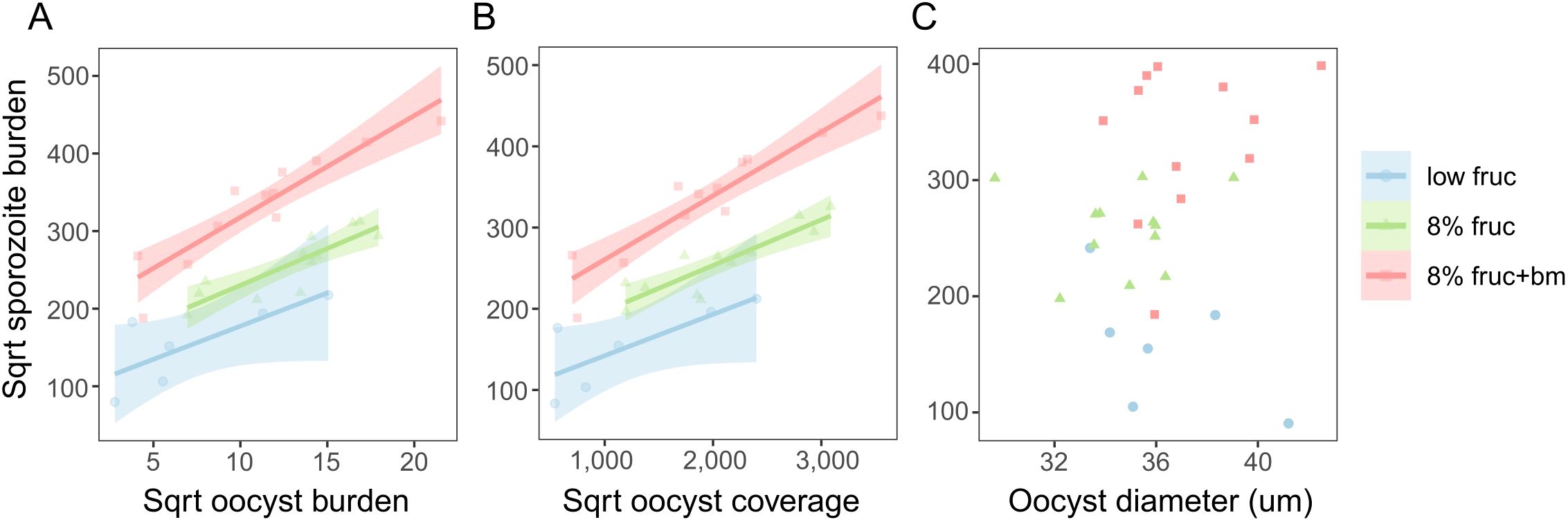
Figure 6. Correlations between sporozoite burden on day 14 pIBM and oocyst burden (A), overall oocyst coverage (B) and oocyst size (C) on day 10 pIBM for the differing mosquito feeding treatments. Data points are minimised linear model predictions per pot, taking into account multiple measures per pot of mosquitoes. Lines and shading denote best fit linear model estimates ± 95% confidence intervals.
Discussion
Here we examine how variation in resource availability within the mosquito affects components of vectorial capacity and the development of malaria parasites. Our feeding treatments perturbed mosquito nutritional status and survival. We show that resource availability influences mosquito survival in line with previous studies (Ebrahimi et al., 2018; Chisulumi et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2023); mosquitoes receiving the lowest fructose concentration contained less lipids and total sugars, and over 50% did not live long enough for sporogony to complete (10-14 days). While mosquitoes on intermediate fructose diets did live long enough for sporogony completion, mosquitoes receiving an additional blood meal had higher lipid stores than mosquitoes on fructose-only diets, and the longest lifespan (Figures 2, 3). We also find that oocyst development follows different trajectories dependent on resource availability. Despite a trade-off between oocyst number and size in all treatments (Figure 4), parasites developing in mosquitoes with an additional blood meal had more productive oocysts; they reached a larger size earlier in development, and more sporozoites reached the salivary glands despite having a similar oocyst burden and final size to those in mosquitoes fed 8% fructose (Figures 4, 5). When mosquitoes receive only sugar resources, oocyst development is affected in complex ways but the overall impact on sporozoite density correlates with the amount of sugar provided. In very poorly resourced mosquitoes, oocyst burden dropped during development, but oocysts grew more quickly between days 7-10 pIBM than those in mosquitoes on 8% fructose and in mosquitoes provided with an additional blood meal (Figure 4). The different responses of parasites in the best (i.e. consistent oocyst burden and large size by day 7) and the least (i.e. loss of oocysts coupled with catch-up growth) resourced mosquitoes resulted in total parasite biomass in the gut (oocyst coverage) remaining consistent over time for these groups, while coverage increased when mosquitoes had plentiful sugar without an additional blood meal (Figure 4). Oocyst productivity increased with resources; more sporozoites consistently reached the salivary glands in mosquitoes provided an additional blood meal (Figure 6). However, this was not explained by differences in oocyst size because both the best and least resourced mosquitoes had oocysts of the same size by the end of development (Figure 4).
In addition to the vector living long enough, transmission requires successful development of the parasite within the vector. Like previous studies using P. falciparum, we show that an additional blood meal increases P. chabaudi oocyst size earlier in sporogony (Shaw et al., 2020; Habtewold et al., 2021; Kwon et al., 2021). This suggests parasites can utilise additional resources provided by a blood meal to develop more rapidly. Specifically, malaria parasites require lipids for generating membranes for subdivision into sporozoites (Shaw et al., 2020), so additional lipids from the blood meal may alleviate a resource constraint that prevents parasites from replicating within oocysts. Surprisingly, we also find that later in development, oocyst size increases most rapidly in mosquitoes on the lowest fructose diet. These parasites are likely to be resource limited and we suggest that the corresponding reduction in oocyst burden in this group alleviates resource constraints and allows surviving oocysts to rapidly reach maturity. The mechanism underpinning the reduction in oocyst numbers is unknown; some oocysts could starve and subsequently be degraded, and/or late-stage immune responses of mosquitoes could target developing oocysts (Gupta et al., 2009; Smith et al., 2015), both of which coincidently benefit surviving parasites. However, poorly-resourced mosquitoes are unlikely to be able to invest more in immune function than those given an additional blood meal because mosquitoes in a poor nutritional state have downregulated immune pathways (Yan et al., 2023), a reduced melanisation response (Koella and Sørensen, 2002), and increased susceptibility to pathogens likely via a reduction in immune investment (Muturi et al., 2011). Alternatively, malaria parasites have evolved sophisticated strategies during other life stages to optimise survival and transmission in the face of variable resource supply (Schneider and Reece, 2021), and previous studies suggest that parasites undergo programmed cell death at the ookinete stage to regulate infection intensity (Pollitt et al., 2010; Reece et al., 2011). While ‘suicidal’ apoptosis has not yet been observed in oocysts (Kakani et al., 2016), it may be beneficial to reduce oocyst number, trading off quantity for quality, to reduce competition for limited resources and ensure that the remaining oocysts are successful. Testing whether parasites in poorly-resourced mosquitoes display markers of cell death or are labelled by mosquito immune markers could disentangle whether the reduction in oocysts is due to a parasite adaptive suicide response to resource limitation, killing by mosquito immune responses and/or oocysts simply starving and degrading due to lack of resources available (i.e. resource constraints). Further work should also consider the impact of resource availability across a range of starting oocyst densities, and how these interact to modulate development (Pollitt et al., 2013).
In addition to potentially modulating oocyst density, our finding that oocysts follow different size trajectories suggest that parasites may plastically alter oocyst growth rate in response to resource variation. For example, oocyst coverage changed (increased) over time only when mosquitoes received an intermediate resource supply (8% fructose), remaining static in the other groups. Perhaps a lack of resources from blood is a constraint that forces oocysts to develop slowly, or they reach a size where they adaptively stop and wait for richer resources, only committing to complete development as best as possible if a blood meal is not acquired. Even though oocyst size and coverage in mosquitoes fed 8% fructose eventually caught up with those in mosquitoes receiving an additional blood meal, they produced fewer sporozoites, as also observed for P. falciparum (Kanatani et al., 2024) and P. berghei (Shiau et al., 2024). Our findings that lipid levels varied more across feeding treatments than total sugars and glycogen suggests lipids are an important resource during oocyst development. Restricted lipid trafficking in mosquitoes results in smaller, less productive oocysts which produce less infectious and less virulent sporozoites (Costa et al., 2018), and is consistent with the hypothesis that parasites are constrained, even when sugar is plentiful. However, other studies show that parasites become dormant under sugar-only conditions but can rapidly exploit an additional blood meal even later in development than in our study (Habtewold et al., 2021). A rapid response to a change in resource availability may also explain why oocysts in very poorly-resourced mosquitoes increased in size the fastest following a reduction in their number. Investigating the quality and quantity of sporozoites from mosquitoes under different feeding regimes would help elucidate whether parasites adjust their development in beneficial ways in response to resources or are simply directly constrained by resource availability.
Mosquitoes harbouring higher numbers of sporozoites in their salivary glands are more likely to infect a vertebrate host (Aleshnick et al., 2020; Kanatani et al., 2024), and high density infections may lead to faster within-vector development (Andolina et al., 2024). Therefore, resource availability may underpin a significant amount of heterogeneity in malaria transmission, through additive impacts on parasite development and mosquito behaviour/survival. Accounting for this variability in epidemiological models of vector-borne diseases may improve predictions of transmission and the impacts of vector control tools (Cator et al., 2020). For example, vector control tools which disrupt mosquito metabolism (e.g. insecticides (Ingham et al., 2021)) or mosquito foraging (e.g. bed nets (Killeen et al., 2007)) may interrupt transmission by reducing resources available to parasites, and subsequently sporozoite burden.
Our resource perturbations also uncover that oocyst metrics can only partly explain patterns in sporozoite burden, highlighting that traditionally used parameters (such as oocyst burden) are not the best predictor of transmission potential. Instead, sporozoite burden may be more appropriate, especially given that it correlates with infectivity to a vertebrate host (Aleshnick et al., 2020; Kanatani et al., 2024). Studies that test for trade-offs between oocyst metrics, the quantity of sporozoites and their quality (i.e. ability to reach the salivary glands), oocyst rupture success and/or the number of sporozoites per oocyst, are needed to understand what underpins how different developmental trajectories determine transmission potential. For example, lipid deprivation reduces sporozoite metabolic activity and infectivity to a vertebrate host (Costa et al., 2018), suggesting that parasites deprived of resources from multiple blood meals may produce fewer and less infective sporozoites. We also found that lipid stores differed across our feeding treatments, providing further support that lipid levels can drive differences in sporozoite burden. Furthermore, future studies should consider whether the failure of some oocysts in the gut to rupture (Andolina et al., 2024) could be a parasite strategy. For example, entering reversible dormancy during nutrient-limiting conditions (Habtewold et al., 2021) could help spread out sporozoite egress to reduce the immune shock to the vector, manage the demands made by sporozoites during migration to the salivary glands, and prevent crowding in the salivary glands. Performing sporozoite motility assays (e.g (Beyer et al., 2021)), investigating patterns of oocyst rupture (Andolina et al., 2024) and the effects of mosquito immunity on sporozoites (Hillyer et al., 2007), and isolating oocysts (Siden-Kiamos et al., 2020) to investigate per oocyst productivity could begin to tease apart how resource availability influences transmission potential.
Overall, our study highlights that the best-resourced mosquitoes are likely to have a higher vectorial capacity than those with reduced access to resources, and that parasites can efficiently utilise additional resources available to them. Our results also suggest that parasites may adjust their development to suit their resource supply when facing limited conditions. While not directly investigated here, the nutritional status of mosquitoes can impact other components of vectorial capacity; for example, starved mosquitoes are more likely to host seek compared to well-resourced mosquitoes (Gary and Foster, 2001; Stone et al., 2012). These effects are likely to synergise with the impacts of resources on parasite activities to generate complex consequences for transmission. Beyond malaria, many other vector-borne parasites (e.g. dengue virus, zika virus, Leishmania parasites) utilise resources from their vector (Serafim et al., 2018; Armstrong et al., 2020; Brackney et al., 2021), for replication/development (Herd et al., 2021). Vector-borne parasites/pathogens experience significant variation in resource availability within their vectors (due to a variety of factors, including age (Carrillo-Bustamante et al., 2023), climate (Barr et al., 2023) and insecticide resistance mechanisms (Rivero et al., 2011; Tchouakui et al., 2020; Ingham et al., 2021)). Thus, understanding the extent to which parasites are constrained and/or can adaptively adjust their development in response to vector condition is crucial for predicting disease transmission patterns, and parasites’ evolutionary potential in the face of changes to their vectors (Oke et al., 2022).
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: Edinburgh DataShare repository [https://doi.org/10.7488/ds/7822].
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the University of Edinburgh, and complied with UK Home Office regulations (Animals Scientific Procedures Act 1986; SI 2012/3039; PPL PP8390310). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CO: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AO’D: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. PS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work was funded by the Wellcome Trust (202769/Z/16/Z), the Royal Society (URF\R\180020 and RGF\EA\181046), and the University of Edinburgh’s School of Biological Sciences.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ronnie Mooney for technical assistance and Gregor Doyle for help with data collection and processing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aleshnick M., Ganusov V. V., Nasir G., Yenokyan G., Sinnis P. (2020). Experimental determination of the force of malaria infection reveals a non-linear relationship to mosquito sporozoite loads. PloS Pathog. 16, e1008181. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008181
Almire F., Terhzaz S., Terry S., McFarlane M., Gestuveo R. J., Szemiel A. M., et al. (2021). Sugar feeding protects against arboviral infection by enhancing gut immunity in the mosquito vector Aedes aEgypti. PloS Pathog. 17, 1–26. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009870
Alto B. W., Lounibos’ L. P., Juliano S. A. (2003). Age-dependent bloodfeeding of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus on artificial and living hosts. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 19, 347–352.
Andolina C., Graumans W., Guelbeogo M., van Gemert G.-J., Ramjith J., Harouna S., et al. (2024). Quantification of sporozoite expelling by Anopheles mosquitoes infected with laboratory and natural P. falciparum infections. eLife 12, RP90989. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90989.3
Armstrong P. M., Ehrlich H. Y., Magalhaes T., Miller M. R., Conway P. J., Bransfield A., et al. (2020). Successive blood meals enhance virus dissemination within mosquitoes and increase transmission potential. Nat. Microbiol. 5, 239–247. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0619-y
Atella G. C., Bittencourt-Cunha P. R., Nunes R. D., Shahabuddin M., Silva-Neto M. A. C. (2009). The major insect lipoprotein is a lipid source to mosquito stages of malaria parasite. Acta Tropica 109, 159–162. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.10.004
Bae K., Jin X., Maywood E. S., Hastings M. H., Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R. (2001). Differential functions of mPer1, mPer2, and mPer3 in the SCN circadian clock. Neuron 30, 525–536. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00302-6
Barr J. S., Estevez-Lao T. Y., Khalif M., Saksena S., Yarlagadda S., Farah O., et al. (2023). Temperature and age, individually and interactively, shape the size, weight, and body composition of adult female mosquitoes. J. Insect Physiol. 148, 104525. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2023.104525
Barredo E., Degennaro M. (2020). Not just from blood: mosquito nutrient acquisition from nectar sources. Trends Parasitol. 36, 473–484. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.02.003
Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67, 1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Beier J. C. (1998). Malaria parasite development in mosquitoes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 43, 519–543. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.43.1.519
Bell A. S., Blanford S., Jenkins N., Thomas M. B., Read A. F. (2009). Real-time quantitative PCR for analysis of candidate fungal biopesticides against malaria: Technique validation and first applications. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 100, 160–168. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2009.01.006
Bell A. S., de Roode J. C., Sim D., Read A. F. (2006). Within-host competition in genetically diverse malaria infections: Parasite virulence and competitive success. Evolution 60, 1358. doi: 10.1554/05-611.1
Beyer K., Kracht S., Kehrer J., Singer M., Klug D., Frischknecht F. (2021). Limited Plasmodium sporozoite gliding motility in the absence of TRAP family adhesins. Malaria J. 20, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03960-3
Birget P. L. G., Repton C., O’Donnell A. J., Schneider P., Reece S. E. (2017). Phenotypic plasticity in reproductive effort: Malaria parasites respond to resource availability. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 284, 20171229. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1229
Brackney D. E., LaReau J. C., Smith R. C. (2021). Frequency matters : How successive feeding episodes by blood-feeding insect vectors influences disease transmission. PloS Pathog. 17, e1009590. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009590
Carrillo-Bustamante P., Levashina E. A., Costa G. (2023). Evolutionary modelling indicates that mosquito metabolism shapes the life-history strategies of Plasmodium parasites. Nat. Commun. 14, 8139. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43810-1
Cator L. J., Johnson L. R., Mordecai E. A., El Moustaid F., Smallwood T. R. C., LaDeau S. L., et al. (2020). The role of vector trait variation in vector-borne disease dynamics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.00189
Chen H., Rangasamy M., Tan S. Y., Wang H., Siegfried B. D. (2010). Evaluation of five methods for total DNA extraction from western corn rootworm beetles. PloS One 5, e11963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011963
Chisulumi P. S., Nampelah B., Yohana R., Philbert A., Kweka E. J. (2022). Diet and Oviposition Deprivation Effects on Survivorship, Gonotrophic Dissociation, and Mortality of Anopheles Gambiae s.s. J. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 6313773. doi: 10.1155/2022/6313773
Costa G., Gildenhard M., Eldering M., Lindquist R. L., Hauser A. E., Sauerwein R., et al. (2018). Non-competitive resource exploitation within mosquito shapes within-host malaria infectivity and virulence. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05893-z
De Roode J. C., Pansini R., Cheesman S. J., Helinski M. E. H., Huijben S., Wargo A. R., et al. (2005). Virulence and competitive ability in genetically diverse malaria infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 7624–7628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500078102
Dieng H., Hui O. S., Hassan A. A., Abang F., Ghani I. A., Satho T., et al. (2015). Changes in the biting activity of a dengue vector relative to larval and adult nutritional histories: Implications for preventive measures. J. Asia-Pacific Entomol. 18, 507–513. doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2015.06.006
Ebrahimi B., Jackson B. T., Guseman J. L., Przybylowicz C. M., Stone C. M., Foster W. A. (2018). Alteration of plant species assemblages can decrease the transmission potential of malaria mosquitoes. J. Appl. Ecol. 55, 841–851. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.13001
Emami S. N., Ranford-Cartwright L. C., Ferguson H. M. (2017). The transmission potential of malaria-infected mosquitoes (An.Gambiae-Keele, An.arabiensis-Ifakara) is altered by the vertebrate blood type they consume during parasite development. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–9. doi: 10.1038/srep40520
Fernandes L., Briegel H. (2005). Reproductive physiology of Anopheles Gambiae and Anopheles atroparvus. J. Vector Ecol. 30, 11–26.
Foley D. H., Harrison G., Murphy J. R., Dowler M., Rueda L. M., Wilkerson R. C. (2012). Mosquito bisection as a variable in estimates of PCR-derived malaria sporozoite rates. Malaria J. 11, 145. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-145
Foster W. A. (1995). Mosquito sugar feeding and reproductive energetics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 40, 443–474. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.40.010195.002303
Gardner A., Grafen A. (2009). Capturing the superorganism: A formal theory of group adaptation. J. Evol. Biol. 22, 659–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01681.x
Gary R. E., Foster W. A. (2001). Effects of available sugar on the reproductive fitness and vectorial capacity of the malaria vector Anopheles Gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 38, 22–28. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585-38.1.22
Gary R. E., Foster W. A. (2006). Diel timing and frequency of sugar feeding in the mosquito Anopheles Gambiae, depending on sex, gonotrophic state and resource availability. Med. Vet. Entomol. 20, 308–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2915.2006.00638.x
Gu W., Müller G., Schlein Y., Novak R. J., Beier J. C. (2011). Natural plant sugar sources of Anopheles mosquitoes strongly impact malaria transmission potential. PloS One 6, e15996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015996
Gupta L., Molina-Cruz A., Kumar S., Rodrigues J., Dixit R., Zamora R. E., et al. (2009). The STAT Pathway Mediates Late-Phase Immunity against Plasmodium in the Mosquito Anopheles Gambiae. Cell Host Microbe 5, 498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.04.003
Habtewold T., Sharma A. A., Wyer C. A. S., Masters E. K. G., Windbichler N., Christophides G. K. (2021). Plasmodium oocysts respond with dormancy to crowding and nutritional stress. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81574-0
Hagan R. W., Didion E. M., Rosselot A. E., Holmes C. J., Siler S. C., Rosendale A. J., et al. (2018). Dehydration prompts increased activity and blood feeding by mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24893-z
Hartig F. (2022). DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level / Mixed) Regression Models. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=DHARMa. (Accessed August 16, 2024).
Herd C. S., Grant D. G., Lin J., Franz A. W. E. (2021). Starvation at the larval stage increases the vector competence of Aedes aEgypti females for Zika virus. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 15, 1–20. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010003
Hien D. F., d. S., Dabiré K. R., Roche B., Diabaté A., Yerbanga R. S., et al. (2016). Plant-mediated effects on mosquito capacity to transmit human malaria. PloS Pathog. 12, 1–17. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005773
Hillyer J. F., Barreau C., Vernick K. D. (2007). Efficiency of salivary gland invasion by malaria sporozoites is controlled by rapid sporozoite destruction in the mosquito haemocoel. Int. J. Parasitol. 37, 673–681. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.12.007
Ingham V. A., Tennessen J. A., Lucas E. R., Elg S., Yates H. C., Carson J., et al. (2021). Integration of whole genome sequencing and transcriptomics reveals a complex picture of the reestablishment of insecticide resistance in the major malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii. PloS Genet. 17, e1009970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009970
Jacobs R. L. (1964). Role of p-aminobenzoic acid in Plasmodium berghei infection in the mouse. Exp. Parasitol. 15, 213–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(64)90017-7
Kakani P., Suman S., Gupta L., Kumar S. (2016). Ambivalent outcomes of cell apoptosis: A barrier or blessing in malaria progression. Front. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00302
Kanatani S., Stiffler D., Bousema T., Yenokyan G., Sinnis P. (2024). Revisiting the Plasmodium sporozoite inoculum and elucidating the efficiency with which malaria parasites progress through the mosquito. Nat. Commun. 15, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44962-4
Kassambara A., Kosinski M., Biecek P. (2021). survminer: Drawing Survival Curves using “ggplot2”. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=survminer. (Accessed August 16, 2024).
Killeen G. F., Smith T. A., Ferguson H. M., Mshinda H., Abdulla S., Lengeler C., et al. (2007). Preventing childhood malaria in Africa by protecting adults from mosquitoes with insecticide-treated nets. PloS Med. 4, 1246–1258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040229
Koella J. C., Sørensen F. L. (2002). Effect of adult nutrition on the melanization immune response of the malaria vector Anopheles stephensi. Med. Vet. Entomol. 16, 316–320. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2915.2002.00381.x
Kwon H., Simões M. L., Reynolds R. A., Dimopoulos G., Smith R. C. (2021). Additional feeding reveals differences in immune recognition and growth of plasmodium parasites in the mosquito host. mSphere 6, 1–14. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00136-21
Lefevre T., Ohm J., Dabiré K. R., Cohuet A., Choisy M., Thomas M. B., et al. (2017). Transmission traits of malaria parasites within the mosquito: Genetic variation, phenotypic plasticity, and consequences for control. Evol. Appl. 11, 456–469. doi: 10.1111/eva.12571
Lenth R. V. (2023). emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=emmeans. (Accessed August 16, 2024).
Lyimo I. N., Keegan S. P., Ranford-Cartwright L. C., Ferguson H. M. (2012). The impact of uniform and mixed species blood meals on the fitness of the mosquito vector Anopheles Gambiae s.s: Does a specialist pay for diversifying its host species diet? J. Evol. Biol. 25, 452–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02442.x
Ma B. O., Roitberg B. D. (2008). The role of resource availability and state-dependence in the foraging strategy of blood-feeding mosquitoes. Evol. Ecol. Res. 10, 1111–1130.
Makowski D., Ben-Shachar M., Lüdecke D. (2020). The {easystats} collection of R packages. Available online at: https://easystats.github.io/easystats/. (Accessed August 16, 2024).
Meuti M. E., Short C. A., Denlinger D. L. (2015). Mom Matters : Diapause Characteristics of Culex pipiens – Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera : Culicidae) Hybrid Mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 52, 131–137. doi: 10.1093/jme/tju016
Muturi E. J., Kim C. H., Alto B. W., Berenbaum M. R., Schuler M. A. (2011). Larval environmental stress alters Aedes aEgypti competence for Sindbis virus. Trop. Med. Int. Health 16, 955–964. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2011.02796.x
O’Donnell A. J., Prior K. F., Reece S. E. (2020). Host circadian clocks do not set the schedule for the within-host replication of malaria parasites. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 287, 20200347. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2020.0347
Oke C. E., Ingham V. A., Walling C. A., Reece S. E. (2022). Vector control: agents of selection on malaria parasites? Trends Parasitol. 38, 890-903. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2022.07.006
Pigliucci M. (2005). Evolution of phenotypic plasticity: Where are we going now? Trends Ecol. Evol. 20, 481–486. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2005.06.001
Pollitt L. C., Churcher T. S., Dawes E. J., Khan S. M., Sajid M., Basáñez M. G., et al. (2013). Costs of crowding for the transmission of malaria parasites. Evol. Appl. 6, 617–629. doi: 10.1111/eva.12048
Pollitt L. C., Colegrave N., Khan S. M., Sajid M., Reece S. E. (2010). Investigating the evolution of apoptosis in malaria parasites: The importance of ecology. Parasites Vectors 3, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-105
Pollitt L. C., Mideo N., Drew D. R., Schneider P., Colegrave N., Reece S. E. (2011). Competition and the evolution of reproductive restraint in malaria parasites. Am. Nat. 177, 358–367. doi: 10.1086/658175
Prescott M. J., Lidster K. (2017). Improving quality of science through better animal welfare: The NC3Rs strategy. Lab. Anim. 46, 152–156. doi: 10.1038/laban.1217
Reece S. E., Drew D. R., Gardner A. (2008). Sex ratio adjustment and kin discrimination in malaria parasites. Nature 453, 609–614. doi: 10.1038/nature06954
Reece S. E., Pollitt L. C., Colegrave N., Gardner A. (2011). The meaning of death: Evolution and ecology of apoptosis in protozoan parasites. PloS Pathog. 7, 1–9. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002320
Reece S. E., Ramiro R. S., Nussey D. H. (2009). Plastic parasites: Sophisticated strategies for survival and reproduction? Evol. Appl. 2, 11–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2008.00060.x
Rivero A., Magaud A., Nicot A., Vézilier J. (2011). Energetic cost of insecticide resistance in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 48, 694–700. doi: 10.1603/ME10121
Rózsa L., Garay J. (2023). Definitions of parasitism, considering its potentially opposing effects at different levels of hierarchical organization. Parasitology 150, 761–768. doi: 10.1017/S0031182023000598
Schneider P., Greischar M. A., Birget P. L. G., Repton C., Mideo N., Reece S. E. (2018a). Adaptive plasticity in the gametocyte conversion rate of malaria parasites. PloS Pathog. 14, e1007371. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007371
Schneider C. A., Rasband W. S., Eliceiri K. W. (2012). NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089
Schneider P., Reece S. E. (2021). The private life of malaria parasites: Strategies for sexual reproduction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 244, 111375. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2021.111375
Schneider P., Rund S. S. C., Smith N. L., Prior K. F., O’Donnell A. J., Reece S. E. (2018b). Adaptive periodicity in the infectivity of malaria gametocytes to mosquitoes. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 285, 20181876. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.1876
Serafim T. D., Coutinho-Abreu I. V., Oliveira F., Meneses C., Kamhawi S., Valenzuela J. G. (2018). Sequential blood meals promote Leishmania replication and reverse metacyclogenesis augmenting vector infectivity. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 548–555. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0125-7
Shapiro L. L. M., Murdock C. C., Jacobs G. R., Thomas R. J., Thomas M. B. (2016). Larval food quantity affects the capacity of adult mosquitoes to transmit human malaria. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 283, 20160298. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.0298
Shaw W. R., Holmdahl I., Itoe M., Werling K., Marquette M., Paton D., et al. (2020). Multiple blood feeding in mosquitoes shortens the Plasmodium falciparum incubation period and increases malaria transmission potential. PloS Pathog. 16, e1009131. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.24.991356
Shaw W. R., Marcenac P., Catteruccia F. (2022). Plasmodium development in Anopheles: a tale of shared resources. Trends Parasitol. 38, 124–135. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.08.009
Shiau J. C., Garcia-diaz N., Kyle D. E., Pathak A. K. (2024). The influence of oviposition status on measures of transmission potential in malaria-infected mosquitoes depends on sugar availability. Parasites Vectors 17, 236. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06317-2
Siden-Kiamos I., Spanos L., Currà C. (2020). A method for purification of Plasmodium oocysts from mosquito midguts. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–6. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64121-1
Smith R. C., Barillas-Mury C., Jacobs-Lorena M. (2015). Hemocyte differentiation mediates the mosquito late-phase immune response against Plasmodium in Anopheles Gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 112, E3412–E3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420078112
Spence P. J., Jarra W., Lévy P., Nahrendorf W., Langhorne J. (2012). Mosquito transmission of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium chabaudi. Malaria J. 11, 407. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-407
Stearns S. C. (1989). Trade-offs in life-history evolution. Funct. Ecol. 3, 259–268. doi: 10.2307/2389364
Stone C. M., Jackson B. T., Foster W. A. (2012). Effects of plant-community composition on the vectorial capacity and fitness of the malaria mosquito Anopheles Gambiae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hygiene 87, 727–736. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0123
Takken W., Smallegange R. C., Vigneau A. J., Johnston V., Brown M., Mordue-Luntz A. J., et al. (2013). Larval nutrition differentially affects adult fitness and Plasmodium development in the malaria vectors Anopheles Gambiae and Anopheles stephensi. Parasites Vectors 6, 345. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-345
Talman A. M., Prieto J. H., Marques S., Ubaida-Mohien C., Lawniczak M., Wass M. N., et al. (2014). Proteomic analysis of the Plasmodium male gamete reveals the key role for glycolysis in flagellar motility. Malaria J. 13, 315. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-315
Tchouakui M., Riveron Miranda J., Mugenzi L. M. J., Djonabaye D., Wondji M. J., Tchoupo M., et al. (2020). Cytochrome P450 metabolic resistance (CYP6P9a) to pyrethroids imposes a fitness cost in the major African malaria vector Anopheles funestus. Heredity 124, 621–632. doi: 10.1038/s41437-020-0304-1
Therneau T. M. (2022). coxme: Mixed Effects Cox Models. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=coxme. (Accessed August 16, 2024).
Van Handel E. (1985a). Rapid determination of glycogen and sugars in mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1, 299–301.
Van Handel E. (1985b). Rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1, 302–304.
Van Handel E., Day J. F. (1988). Assay of lipids, glycogen and sugars in individual mosquitoes: correlations with wing length in field-collected Aedes vexans. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 4, 549–550.
Vantaux A., Moiroux N., Dabiré K. R., Cohuet A., Lefèvre T. (2023). Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission. Peer Community J. 3, e54. doi: 10.24072/pcjournal.288
Wargo A. R., Randle N., Chan B. H. K., Thompson J., Read A. F., Babiker H. A. (2006). Plasmodium chabaudi: Reverse transcription PCR for the detection and quantification of transmission stage malaria parasites. Exp. Parasitol. 112, 13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2005.08.013
Webster J. P., Borlase A., Rudge J. W. (2017). Who acquires infection from whom and how? Disentangling multi-host and multimode transmission dynamics in the ‘elimination’ era. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 372, 20160091. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0091
Yan J., Kibech R., Stone C. M. (2021). Differential effects of larval and adult nutrition on female survival, fecundity, and size of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aEgypti. Front. Zool. 18, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12983-021-00395-z
Keywords: plasmodium, anopheles, sporogony, parasite fitness, life history, nutrition
Citation: Oke CE, O’Donnell AJ, Schneider P and Reece SE (2024) Plasticity in malaria parasite development: mosquito resources influence vector-to-host transmission potential. Front. Malar. 2:1481816. doi: 10.3389/fmala.2024.1481816
Received: 16 August 2024; Accepted: 14 October 2024;
Published: 01 November 2024.
Edited by:
Jayme A. Souza-Neto, Kansas State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Bianca Burini, University of Florida, United StatesThiago Luiz Alves E Silva, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2024 Oke, O’Donnell, Schneider and Reece. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Catherine E. Oke, Y2F0aGVyaW5lLm9rZUBlZC5hYy51aw==
 Catherine E. Oke
Catherine E. Oke Aidan J. O’Donnell
Aidan J. O’Donnell Petra Schneider1
Petra Schneider1 Sarah E. Reece
Sarah E. Reece